Cell surface coating with hydrogel sheath through on-cell surface enzymatic cross-linking
-
1
Osaka University, Materials Engineering Science, Japan
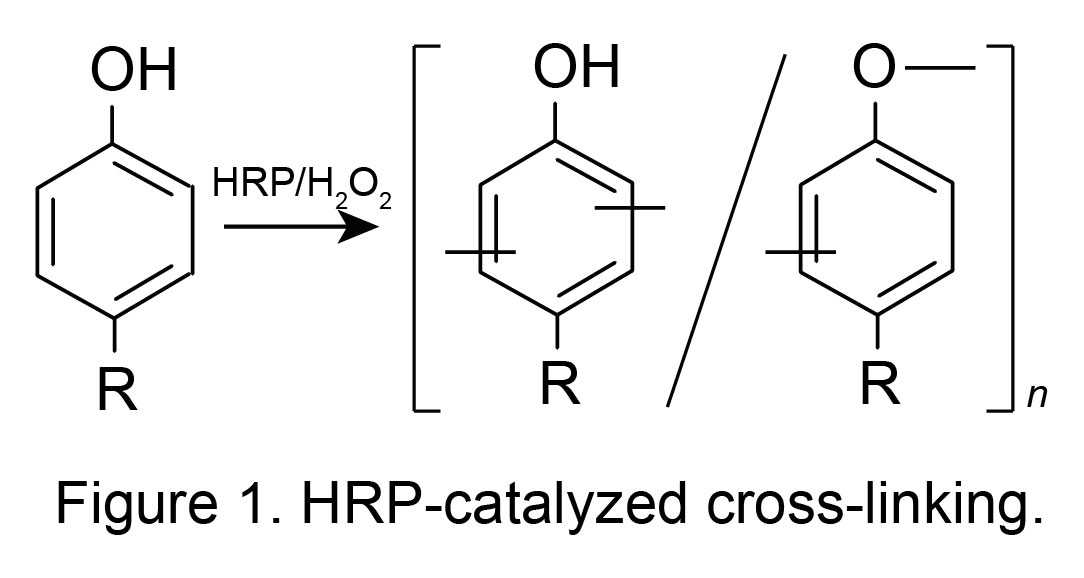
Cell surface engineering such as immobilization of molecules and coating with a thin polymeric sheath in a biocompatible fashion but without genetic or metabolic-based methodologies attracts attention in the field of biology, biomedical and biomaterials. The technology enables to give new functionalities to improve usefulness of individual cells in these fields. In this study, hydrogel sheaths were fabricated on the surfaces of individual mammalian cells through the cross-linking of polymer molecules catalyzed by horseradish peroxidase (HRP) in aqueous solution (Figure 1).
For confining the progress of the cross-linking only on the cell surface, HRP was anchored to cell membrane by soaking the cells in the solution containing the HRP conjugated with a biocompatible anchor molecule for cell membrane (BAM) (Figure 2).
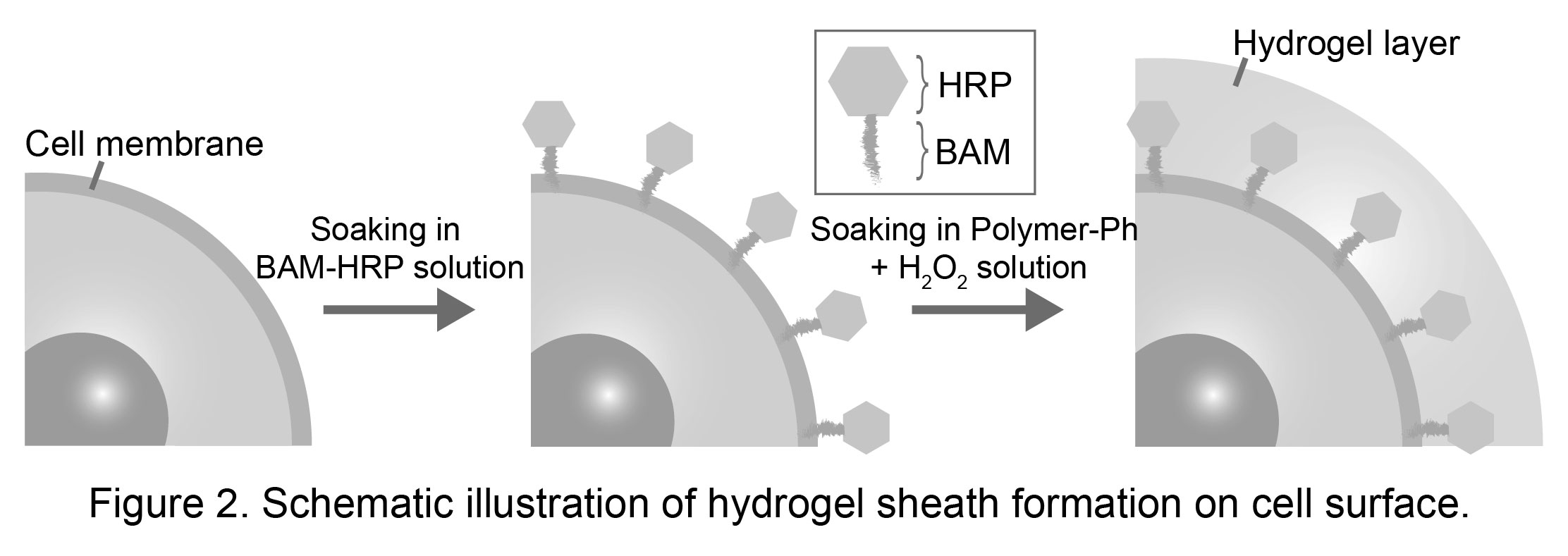
The hydrogel sheath of about 1 micrometer thickness was obtained by soaking the cells with the anchored HRP in aqueous solution containing polymers possessing phenolic hydroxyl (Ph) moieties and H2O2 for 10 min. The hydrogel sheaths could be made from a variety of polymers possessing Ph moieties, e.g., derivatives of polysaccharide, protein and synthetic polymer. Cytocompatibility of the on-cell surface enzymatic hydrogel sheath formation was confirmed from the viability of the enclosed cells (> 90%) and subsequent normal growth after removal of the hydrogel sheath[1],[2].
References:
[1] Sakai S AND Taya M, ACS Macro Lett. 3: 975 (2014)
[2] Sakai S et al, Biomaterials 53: 494(2015)
Keywords:
enzyme,
biomacromolecule
Conference:
10th World Biomaterials Congress, Montréal, Canada, 17 May - 22 May, 2016.
Presentation Type:
Poster
Topic:
Layer-by-layer deposition techniques
Citation:
Sakai
S,
Hotta
T and
Taya
M
(2016). Cell surface coating with hydrogel sheath through on-cell surface enzymatic cross-linking.
Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol.
Conference Abstract:
10th World Biomaterials Congress.
doi: 10.3389/conf.FBIOE.2016.01.00707
Copyright:
The abstracts in this collection have not been subject to any Frontiers peer review or checks, and are not endorsed by Frontiers.
They are made available through the Frontiers publishing platform as a service to conference organizers and presenters.
The copyright in the individual abstracts is owned by the author of each abstract or his/her employer unless otherwise stated.
Each abstract, as well as the collection of abstracts, are published under a Creative Commons CC-BY 4.0 (attribution) licence (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/) and may thus be reproduced, translated, adapted and be the subject of derivative works provided the authors and Frontiers are attributed.
For Frontiers’ terms and conditions please see https://www.frontiersin.org/legal/terms-and-conditions.
Received:
27 Mar 2016;
Published Online:
30 Mar 2016.