Introduction: Finding new materials for implantation or injection into human body is most important aim of Biomaterials. Many researchers are looking for its answer in organic compounds found in nature. Chitin, the 2nd most abundant polysaccharide in earth, is one of the organic compounds which have toughness, flexibility, biocompatibility and degradability. Because of its abundance and mechanical properties, biotechnological applications of chitin and chitin derivatives, such as chitosan, are currently an expanding area in biomaterials. However, chitin is not easy to make appropriate shape for tissue engineering because of its insolubility in aqueous solvent. Otherwise, chitosan, which is soluble in acidic aqueous solvent, is used in many biomaterials applications. Chitosan fiber forming properties have been investigated by several researchers. However, the poor tensile strength of chitosan fibers is drawback, especially in the wet state.
To overcome this problem, we introduce heparin, which has negative charge, to dope solution to stabilize chitosan fiber by electrostatic interaction. Heparin is well known as an anticoagulant and for its binding affinity towards various protein (growth factors, Adeno associated virus and so on) . Because of this property, chitosan and heparin complex have not only stability in wet state but also bio-functionality which can deliver heparin-binding protein to target region.
Herein, the morphology and mechanical properties of chitosan fibers obtained by wet-spinning using heparin solution as spinning dope solution are reported for the first time.
Materials and Methods: Chitosan heparin complex fiber was produced by a wet spinning method. Chitosan was dissolved in acidic solution in 1%(w/v) concentration. And heparin (dope solution) was dissolved in DDW in 1%(w/v) concentration. Chitosan solution was injected into a coagulation bath containing heparin solution. Chitosan and heparin complex was spun by physical winding.
Result and Discussion:
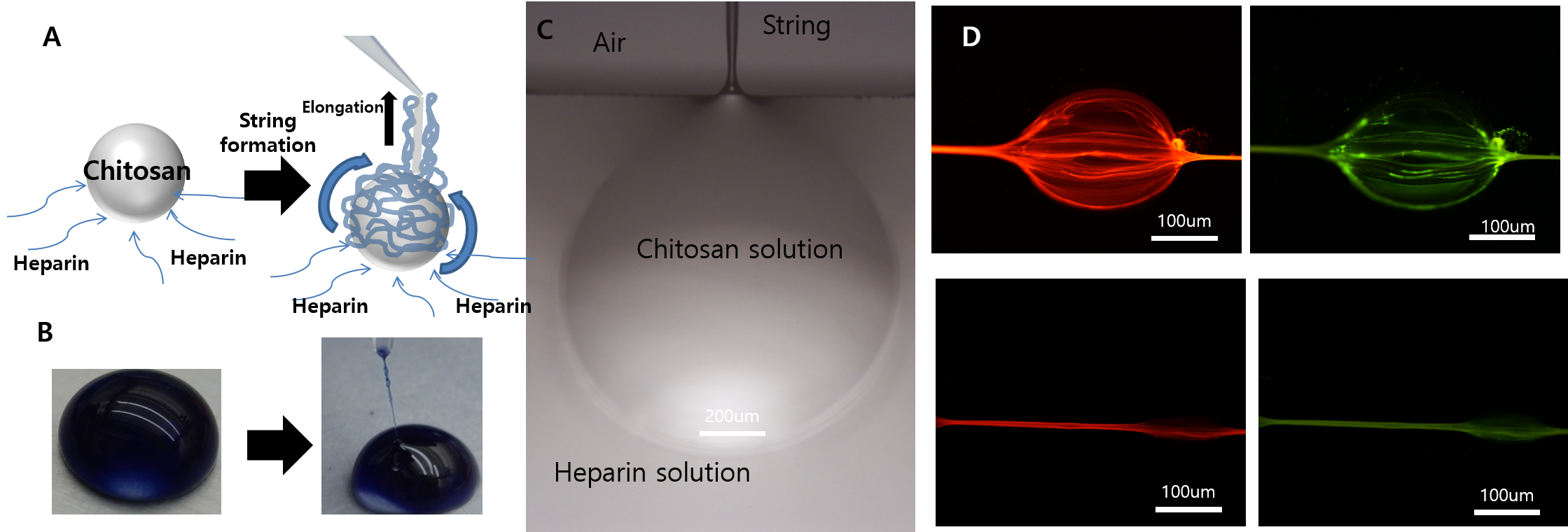
After injecting Chitosan solution into the heparin solution, a 10um-thick chitosan/Heparin complex fiber can be drawn out from the coagulation solution and wound on a reel directly. With regard to tensile test, maximum strain at break and tensile strength of fibers were found to be 11.5±2.4% and 220.3 ± 32.8 MPa, respectively. Drawn from the AAV-GFP solution, the heparin chitosan fiber can bind AAV-GFP and its functionality was confirmed by mouse model
Conclusion: Therefore, this study verified that Heparin solution is a new spinning dope solution for preparing chitosan fibers with strong mechanical properties and multi functionality as a gene delivery carrier.