Dynamic modeling and optimization of an eight bar stamping mechanism based on RBF neural network PID control
- 1School of Intelligent Manufacturing, Anhui Wenda University of Information Engineering, Hefei, China
- 2Faculty of Engineering, Technology and Built Environment, UCSI University, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Introduction: Modern industrial manufacturing often requires the eight-bar stamping mechanism to have high motion accuracy and stability. To meet these stringent requirements, traditional control techniques such as proportional-integral-derivative (PID) control need to be improved.
Methods: In this study, radial basis function neural network is introduced to improve the traditional proportional integral derivative control technique. The improved proportional integral derivative technique is applied to the modeling and optimization of eight kinds of bar stamping mechanisms.
Results: Comparing the improved control technology, the experiment showed that the peak time and adjustment time of the improved technology were 0.516 s and 1.038 s, respectively, which are better than the comparative control technology. In addition, in the comparative analysis of the eight bar stamping mechanism, the proposed architecture scored 9.3 points in operational efficiency, which is significantly greater than the comparative architecture.
Discussion: The results show that the combination of PID control strategy and radial basis function neural network provides a powerful tool for dynamic modeling and optimization of eight-bar stamping mechanism. It not only provides enhanced motion accuracy and stability, but also brings significant practicality to industrial manufacturing. This integration opens up new possibilities for improving the performance of complex mechanical systems to meet the evolving needs of modern manufacturing.
1 Introduction
In modern industrial manufacturing, the eight bar stamping mechanism (8BSM), as an important mechanism, is widely used in various stamping equipment and production lines (Raghavendra and Annigeri, 2021). However, due to its complex dynamic characteristics (DCs) and external interference, improving the motion accuracy and stability of 8BSM has always been a challenge (Desai et al., 2019). Although traditional Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) control technology can achieve certain results in certain situations, it is hard to cater for the wants of contemporary industrial manufacturing for high precision and stability due to its difficult parameter adjustment and susceptibility to external interference (Tian et al., 2020). For example, Wang team and Setiawan team both proposed controllers based on PID control technology, but the PID controllers proposed all have the problem of unstable control effect (Wang and Lu, 2022; Setiawan and Ma’arif, 2021). Therefore, seeking a new control method to improve the effect of 8BSM is of great significance. At present, many studies have been conducted on methods to improve the motion accuracy and stability of the mechanism. For example, Zaidel et al. proposed a neuromorphic algorithm based on nef for inverse kinematics and PID control in order to improve the motion accuracy of the 6-DOF robotic arm (Zaidel et al., 2021). In addition, in order to improve the motion accuracy and stability of the mechanism, Zhang’s team not only proposed a new sampling method based on active Kriging model and adaptive importance sampling, but also proposed a multistage linkage method based on active extreme value Kriging (Zhang et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2023). In recent years, with the continuous development of artificial intelligence technology, artificial intelligence technology has been widely used in various fields. For example, in order to reduce the error of the control system, Barhaghtalab et al. proposed a control method of six-DOF robotic arm based on adaptive fuzzy neural reasoning system (Barhaghtalab et al., 2023). In addition, Chowdhury’s team proposed an entropy-maximized double delay depth deterministic strategy gradient automatic PID tuning method to solve the problem of poor PID tuning method (Chowdhury et al., 2023). In order to improve the computational accuracy and efficiency of reliability evaluation of aero-engine cooling blade system, Li et al. proposed a hierarchical linkage strategy based on multiple integration (Li et al., 2023). As an important neural network, Radial Basis Function (RBF) neural network has the advantages of fast learning speed and high approximation precision, and is widely used in various control systems. For example, Liu team and Feng team will apply RBF neural network to WPT control system and electro-hydraulic servo system control respectively (Liu Y. et al., 2021; Feng et al., 2022). The main motivation of this study is to lift the motion accuracy and stability of 8BSM to meet the requirements of modern industrial manufacturing for high precision and stability. Therefore, this study improves traditional PID technology by introducing RBFNN to overcome the difficulty in adjusting its parameters. The innovation of this study lies in the combination of RBFNN and PID technology, and its application in the dynamic modeling and optimization of 8BSM. This study also provides new ideas and methods for control optimization of similar institutions, and is expected to contribute to the development of industrial manufacturing.
This article is divided into four parts for discussion. The main content of Part 1 is related research on RBFNN, PID control technology, and linkage mechanisms. The main content of Part 2 is the dynamic modeling and optimization process of 8BSM based on RBFNN PID control. Part 3 mainly focuses on the comparison of optimized PID technology and the performance comparison analysis of 8BSM based on optimized PID. Part 4 is a summary of the entire text.
2 Related works
The advancement of neural network technology has made the application fields of RBFNN increasingly widespread. Wang et al. designed an RBFNN processing method combined with adaptive projection learning algorithm to solve the problem of low spatial resolution caused by beam diffraction in THz spectral imaging process. This method can effectively remove noise from non edge images, achieve higher spatial resolution, and effectively recognize targets (Wang et al., 2023). Lu’s team proposed an RBFNN teaching quality evaluation (TQE) method built on genetic algorithm (GA) optimization to solve the low accuracy in current English interpretation TQE. This method could effectively assess the quality of English interpretation, with high accuracy and real-time performance (Lu et al., 2021). In addition, the control technology has also made the application fields of PID technology increasingly broad. Kong et al. established a multi-objective optimization method based on orthogonal experimental design and iSIGHT platform to address the aerodynamic characteristics and handling stability issues of racing tail wings, and developed a hybrid fuzzy PID variable tail wing control system. As the road adhesion coefficient decreased, this system could improve the handling stability of the racing car and suppress body roll, thereby improving the cornering performance and driving safety of the racing car (Kong et al., 2022). Wang et al. proposed a voltage boosting method based on GA and BPNN PID control to solve the problem of low output voltage of photovoltaic panels. This method could effectively improve the dynamic performance and jamproof capacity of the Boost circuit, and achieved optimization through the global optimization of GA and the adaptive adjustment characteristics of BP neural network (Wang et al., 2022).
With the maturity of connecting rod stamping technology, more and more technologies are being applied to connecting rod mechanisms. Liu et al. proposed a novel competitive failure model that considers intermittency to address the failure issue of the contraction mechanism of aircraft linkage doors. This model combined Poisson process, Archard wear model, and failure function to describe the catastrophic and degraded failures of aircraft mechanisms. Practical engineering applications have shown that the new model is effective, and this mechanism has a special degradation process (Liu J. et al., 2021). Zhou’s team proposed a rotating potted vegetable seedling transplanting mechanism based on a linkage mechanism to solve the problems of complex structure and low efficiency of existing transplanting equipment. A software for kinematic analysis and optimization design of the transplanting mechanism was developed through configuration analysis and optimization design. The posture error of the transplanting arm and drilling shovel was relatively small, and the transplanting mechanism of potted vegetable seedlings met the transplanting requirements, with a success rate of 92.4% for seedling retrieval (Zhou et al., 2020). Jomartov et al. constructed a stamping machine tool on the Stephenson II mechanism to address the issue of insufficient accuracy in traditional stamping machines. By adding a three-way connecting rod and a unique connecting rod, the balance of the slider was improved, thereby improving the accuracy of the slider. This stamping machine tool had better characteristics, with less reaction force on the slider guide and a more reasonable force distribution (Jomartov et al., 2022). Li et al. designed a method for preforms on finite element models to address the metal flow problem during non flash forging of powder metallurgy connecting rod preforms. This method could effectively improve the density uniformity of the connecting rod and reduce the generation of cracks. The optimized preform shape improved the overall quality of the connecting rod, providing a new approach for the manufacturing of powder metallurgy connecting rods (Li et al., 2020).
The above related studies indicate that the application fields of RBFNN technology and PID control technology are quite extensive, and there are various methods applied to linkage mechanisms. As a special type of neural network, RBF has many advantages which are suitable for control system modeling. First, RBF has excellent approximation capabilities, second, RBF’s local response characteristics make it excellent when dealing with high-dimensional input data, and in addition, RBF generally learns faster than traditional multi-layer perceptron networks. Compared with other machine learning models, the advantages of RBF are mainly reflected in that RBF is particularly suitable for dealing with nonlinear control problems, RBF shows strong robustness to input noise and parameter perturbation, and RBF has the characteristics of real-time due to its simple structure and fast learning algorithm. Therefore, this research innovatively combines RBF neural network and PID control technology to apply to the dynamic modeling and optimization of eight-link stamping mechanism. The contribution of this study is that the precise modeling of RBF neural network combined with real-time tuning of PID control significantly improves the motion accuracy and stability of the mechanism, and provides an effective new way for the control optimization of similar mechanisms.
3 Dynamic modeling and optimization of 8BSM based on RBFNN and PID control
To complete the demands of modern industrial manufacturing for high precision and stability, this study introduces RBFNN to improve traditional PID control technology and applies it to the dynamic modeling and optimization of 8BSM. It is expected that this method can improve the motion accuracy and stability of 8BSM. This chapter will provide a detailed introduction to the PID control technology that integrates RBFNN and its application in 8BSM.
3.1 PID control technology integrating RBFNN
PID controller has the advantages of simple principle, strong robustness, and wide practicality, making it a mature and widely used control system. Therefore, this study will apply it to the optimization of 8BSM dynamic modeling (Hammoodi et al., 2020; Garai et al., 2023). In a PID control system, the output value depends on the deviation between the system set value and the system output value, the linear weighted combination of deviation integration and deviation differentiation (Phu et al., 2020). The diagram of the PID controller is Figure 1.
In Figure 1,
In addition,
In Eq. 2,
In Eq. 3,
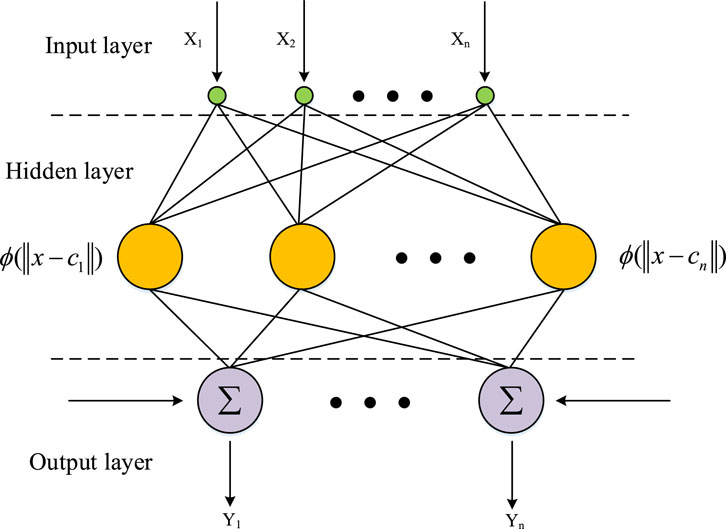
In Figure 2, the three main components of RBFNN are the input, hidden, and output layers. The input layer has several perceptual units. The hidden layer contains several hidden layer nodes, which are generally composed of Gaussian basis functions, and the Gauss function is Eq. 4.
In Eq. 4,
In Eq. 5,
In Eq. 6,
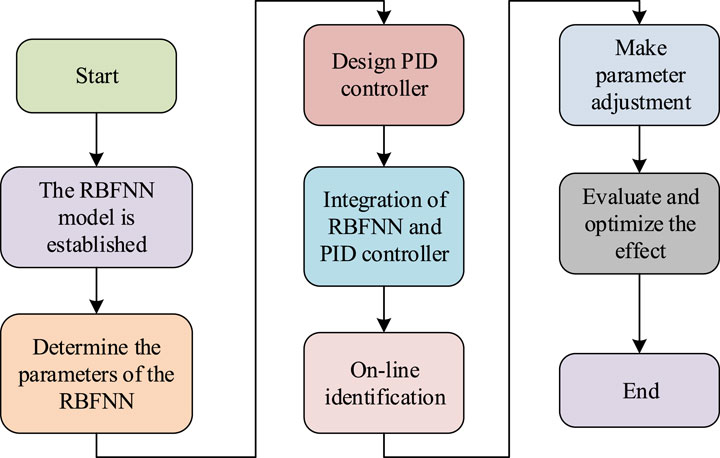
In Figure 3, the PID parameter optimization based on RBFNN first requires constructing an RBFNN model that includes input layer, hidden layer, and output layer to map the system state and output PID control parameters. Determine the network’s parameters through offline training or online adjustment. Next, design a PID controller based on system requirements and integrate it with RBFNN to build a complete control system. The system operation process utilizes RBFNN to identify the DCs of the system online, and adjusts the PID parameters in real-time to optimize the control effect. Finally, the performance indicators of the evaluation system, such as control accuracy, stability, and response speed, are used to measure the optimization effect. The performance indicator evaluation formula is Eq. 7.
In Eq. 7,
3.2 Dynamic optimization of 8BSM based on improved PID technology
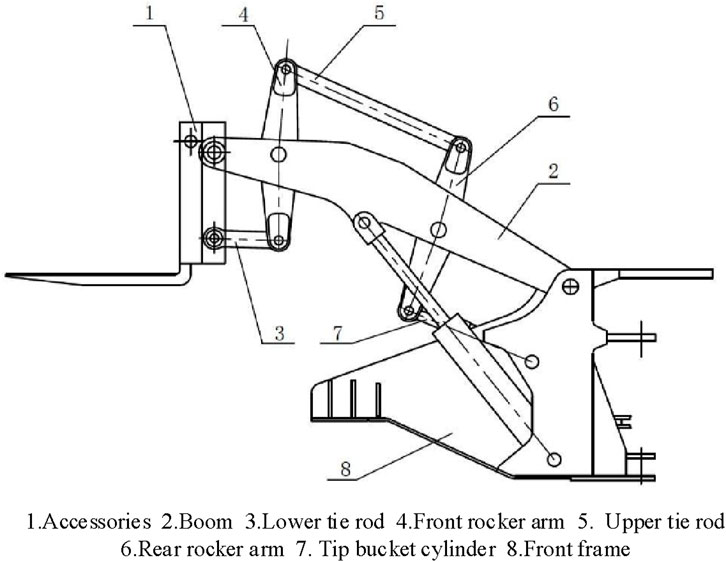
8BSM is a commonly used stamping equipment in industrial manufacturing, with unique design and excellent performance (Choquette et al., 2021). The core part is composed of eight connecting rods, which are connected together in a specific way, enabling the mechanism to achieve efficient and accurate stamping operations. The specific structure of 8BSM is Figure 4.
The advantage of 8BSM lies in its high flexibility and adjustability, and its impulse pressure formula is Eq. 8.
In Eq. 8,
In Eq. 9,
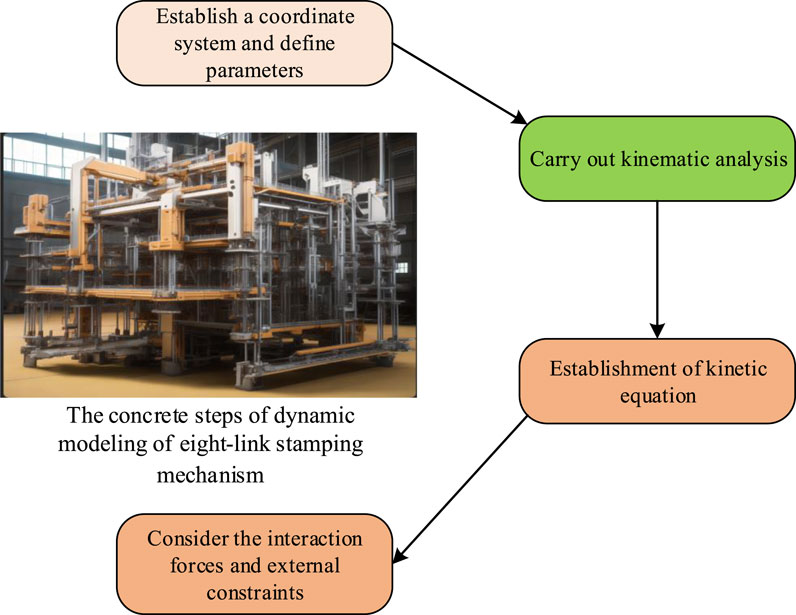
In Figure 5, the dynamic modeling of 8BSM involves multiple steps. Firstly, it is necessary to establish a suitable coordinate system, which should be able to conveniently describe the motion of the mechanism. Next, the relevant parameters of each connecting rod, such as length, angle, mass, and moment of inertia, are defined. These parameters will directly affect the kinematic and DCs of the mechanism. By using the Denavit Hartenberg (D-H) parameter method, the relative position and angle relationship between each connecting rod can be systematically analyzed, and the transformation matrix can be obtained. The formula for the transformation matrix of the connecting rod is Eq. 10.
In Eq. 10,
The establishment of dynamic equations requires considering the effects of multiple forces and constraints. The calculation of kinetic and potential energy of the mechanism is the core part of this process, which involves the mass, moment of inertia, velocity and angular velocity of the connecting rod, as well as the influence of elastic and damping forces. The formula for calculating kinetic energy is Eq. 12.
In Eq. 12,
In Eq. 13,
In Eq. 14,
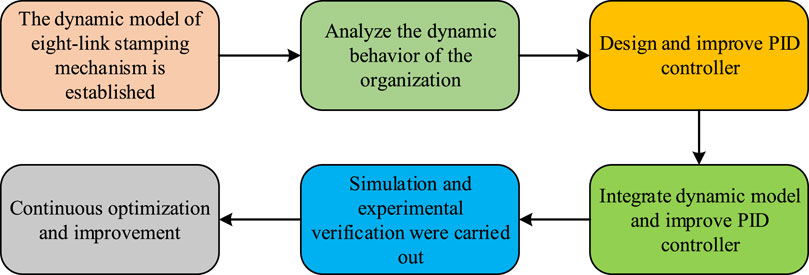
Figure 6. Process of dynamic modeling optimization of eight-link stamping mechanism based on improved PID controller.
In Figure 6, the dynamic model of 8BSM was first established through the application of dynamic principles and methods, and its kinematics, dynamic equations, and impact force were analyzed. Secondly, through in-depth research on dynamic behavior, the changes in its motion trajectory, velocity, acceleration, and impact force under different working conditions were understood. Afterwards, to meet the control requirements, an improved PID controller was designed and a complete control system was constructed by combining the dynamic model. Then, through simulation and experimental verification, the performance of the control system can be evaluated and optimized. Finally, based on actual feedback and application requirements, control parameters will be continuously adjusted, neural network structures will be optimized, and new control strategies will be explored to continuously improve the performance and practicality of the control system. This strategy not only enhances the operational efficiency and product quality of 8BSM, but also provides effective control strategy ideas for similar complex systems.
4 Comparative analysis of improving PID controllers and empirical analysis of optimizing linkage mechanisms
To evaluate the improved PID performance based on RBFNN and the effectiveness of the improved PID controller based on 8BSM, multiple comparative experiments were conducted in this study. This chapter mainly introduces the details and result analysis of various comparative experiments.
4.1 Performance comparison and analysis of improved PID controller based on RBFNN
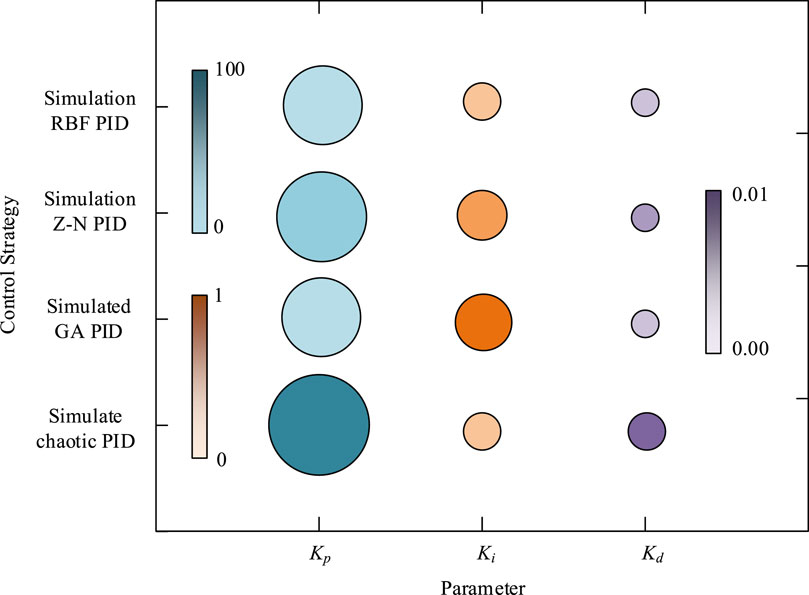
This study utilized RBFNN to optimize the PID parameters (RBF-PID). To analyze the performance of the optimized PID controller using this method, this study compares its performance with PID controllers based on chaos optimization algorithm (Chaotic PID), GA optimization (GA PID), and Z-N formula method (Z-N PID). The specific experimental environment of the comparison test is mainly divided into hardware environment and software environment, in which the hardware environment is divided into three categories: control system hardware, controlled object and auxiliary equipment. The hardware of the control system mainly includes industrial control computer, data acquisition module and power amplifier. The controlled objects mainly include material testing machine, pressure sensor and electric cylinder; Auxiliary equipment mainly includes power supply, signal conditioner and multi-function tester. The software environment mainly includes MATLAB programming software, LabVIEW data acquisition and processing software and Windows10 operating system. The results of comparing the controller parameters of the PID controller obtained by the four methods are shown in Figure 7.
In Figure 7, the Kp, Ki, and Kd values of the PID obtained by Z-N PID, Chaotic PID, and GA PID are 30.21, 0.388, 0.055, 21.45, 0.578, 0.048, 52.36, 0.273, and 0.083, respectively. The three values obtained by RBF-PID are 22.48, 0.271, and 0.045, respectively. After obtaining the parameters of four PID controllers, to calculate the dynamic characteristic indicators of the unit step response under the action of the four PID controllers. The specific data of the dynamic characteristic indicators under Z-N PID, GA-PID, RBF-PID, and Chaotic PID parameters obtained are displayed in Figure 8.
According to Figure 8, the adjustment time, peak time, and rise time of the RBF-PID controller are 0.513 s, 0.478 s, and 0.443 s, respectively. The Chaotic PID controllers are 0.638 s, 0.629 s, and 0.613 s, respectively. The Z-N PID controller is 1.836 s, 0.721 s, and 0.633 s. The GA-PID controller is 1.391 s, 0.811 s, and 0.724 s. The above data indicates that the control performance of the RBF-PID is superior, and the response speed of the target is faster. To further analyze the effectiveness of each PID controller, the control system pressure was adjusted to 10 MPa and 15 MPa respectively. Performing step experiments on a material testing machine with elastic loads under four different PID controller conditions. The step response curves of the four PID controllers are shown in Figure 9.
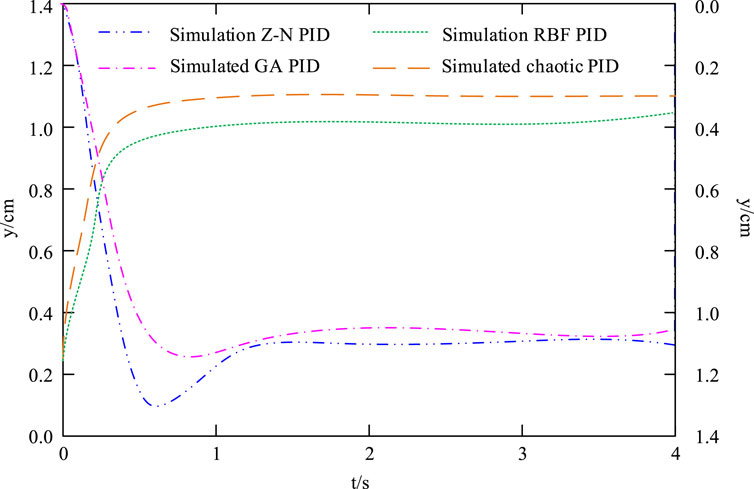
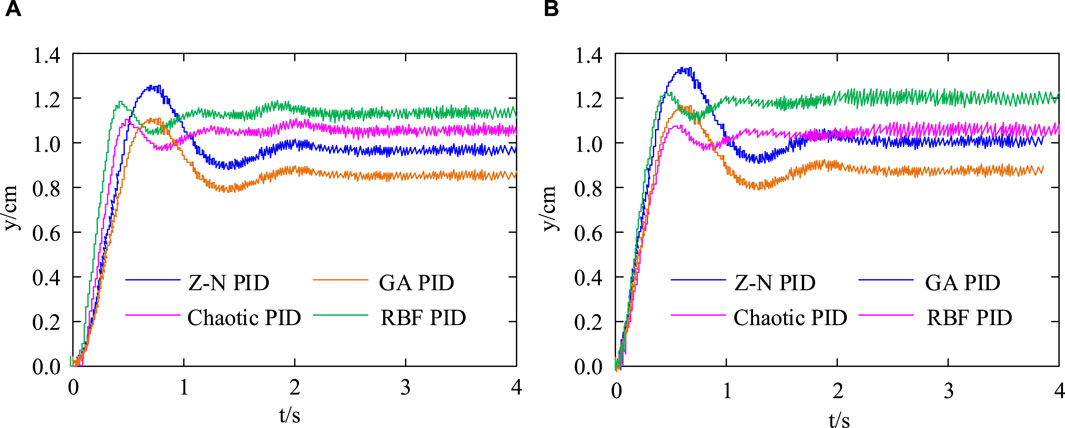
In Figure 9A, when the control system pressure is 10 MPa, the peak times of RBF-PID, Chaotic PID, Z-N PID, and GA PID are 0.516 s, 0.615 s, 0.835 s, and 0.838 s, respectively. The adjustment times for RBF-PID, Chaotic PID, Z-N PID, and GA PID are 1.038 s, 1.121 s, 1.356 s, and 1.384 s, respectively. In Figure 9B, when the control system pressure is 15 MPa, the peak times of RBF-PID, Chaotic PID, Z-N PID, and GA PID are 0.618 s, 0.705 s, 0.758 s, and 0.773 s, respectively. The adjustment times for RBF-PID, Chaotic PID, Z-N PID, and GA PID are 1.113 s, 1.152 s, 1.613 s, and 1.664 s, respectively. The above results indicate that under two different control system pressures, the control effect of Chaotic PID is superior to the three improved PID controllers compared. Afterwards, four types of controllers were used for simulation and experimentation, and the results are shown in Figure 10.
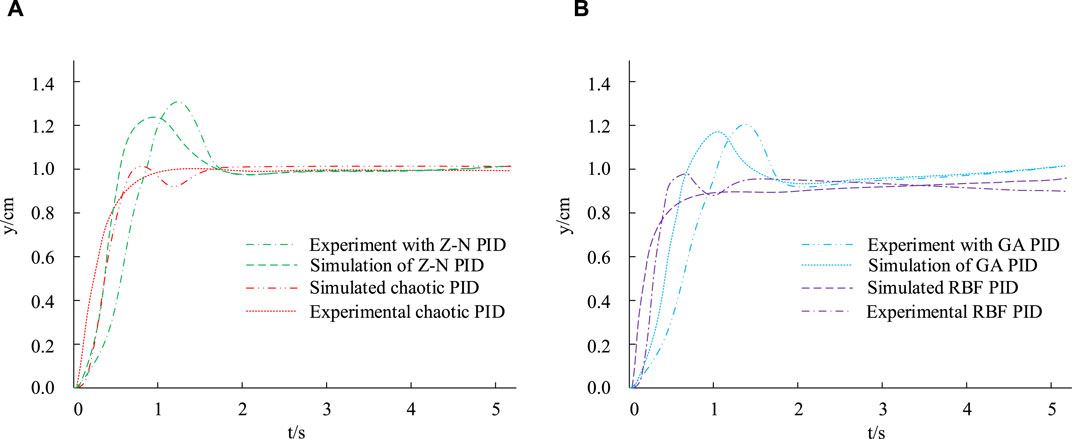
In Figure 10, the simulation and experimental curve trends of the four controllers are basically consistent, and the experimental response time is longer than the simulation response time under the same conditions. In Figure 10A, compared to Z-N PID, Chaotic PID reaches stability earlier. In Figure 10B, compared to GA PID, the RBF-PID controller reaches stability earlier. By comparing Figures 10A, B, RBF-PID has the shortest time to reach stability. The above results indicate that the control effect of RBF-PID controller is better and it is effective.
4.2 Analysis of optimization effect of 8BSM based on improved PID controller
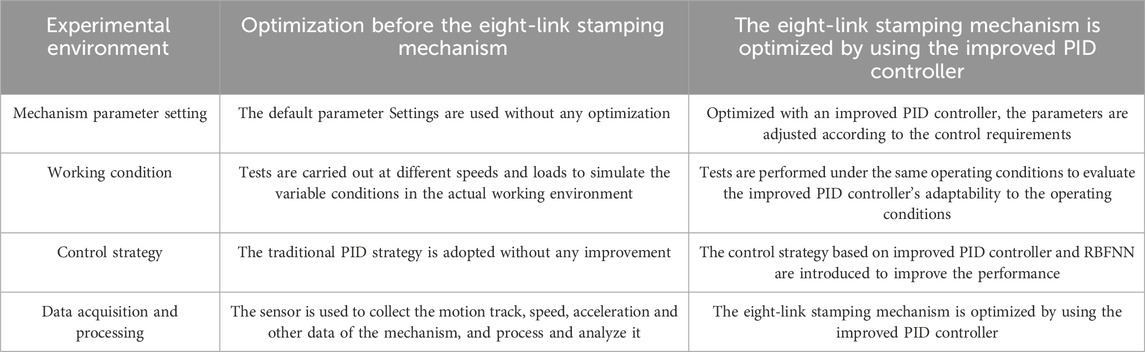
To analyze the actual effect of the proposed dynamic modeling optimization of 8BSM based on improved PID controller, this study will compare the performance of the optimized 8BSM and the pre optimized 8BSM using this method. Table 1 shows the environmental parameters for the comparative experiment.
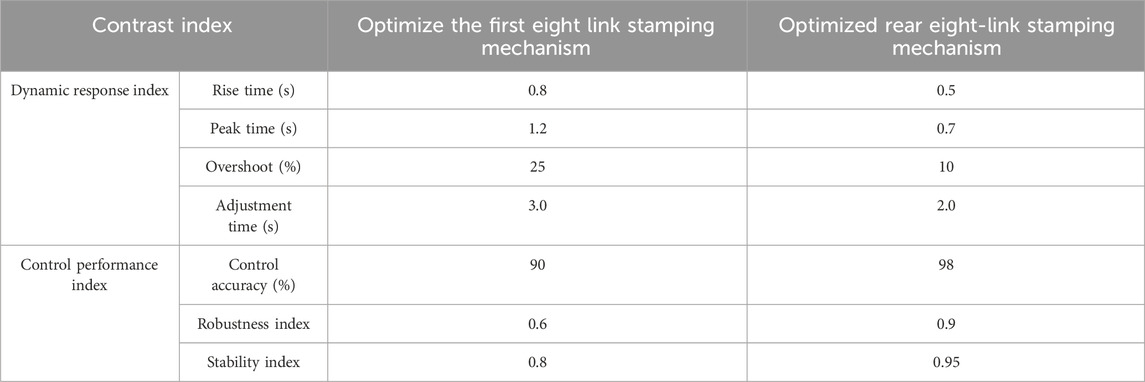
Compare the performance of two types of 8BSM under the conditions of Table 1, and use dynamic response index and control performance index as comparison indicators. The performance comparison results of the two types of 8BSM are shown in Table 2. The rise time, peak time, overshoot rate, and adjustment time of the optimized 8BSM are 0.5 s, 0.7 s, 10%, and 2.0 s, respectively, all better than before optimization. And the control accuracy, robustness, and stability of the optimized 8BSM are significantly better than before optimization. This result indicates that the proposed optimization scheme has a significant optimization effect on 8BSM.
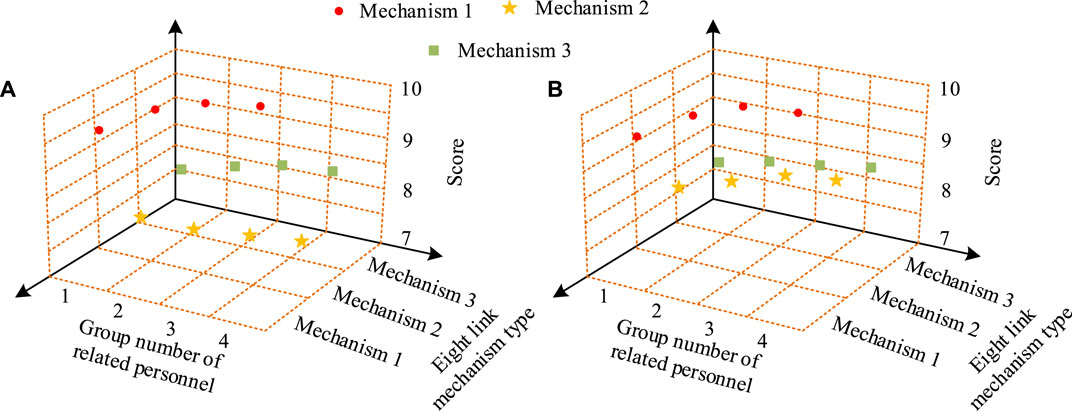
In addition, to further validate the superiority of the designed improved 8BSM, this study selected 40 relevant experts and divided them into four groups to evaluate the proposed improved 8BSM (Mechanism 1), GA-PID optimized 8BSM (Mechanism 2), and Chaotic PID optimized 8BSM (Mechanism 3). The evaluation scores of the three institutions are shown in Figure 11. In Figure 11A, the average operating efficiency score of mechanism 1 is 9.3 points, significantly better than the 7.7 points of mechanism 2 and the 8.1 points of mechanism 3. In Figure 11B, the average product quality score of Institution 1 is 9.2 points, significantly better than the 7.9 points of Institution 2 and the 8.2 points of Institution 3.
5 Conclusion
The complex DCs and external interference of 8BSM make improving its motion accuracy and stability a challenge. To solve this problem, this study adopted a combination of RBFNN and PID control methods, and then applied the improved PID control technology to the optimization of 8BSM. Through comparative analysis of PID control technology based on RBFNN, experimental data proved that the proposed improved PID owned adjustment time, peak time, and rise time of 0.513 s, 0.478 s, and 0.443 s, respectively, which are significantly better than the comparison controller. The empirical analysis of 8BSM showed that the rise time, peak time, overshoot rate, and adjustment time of the optimized 8BSM were 0.5 s, 0.7 s, 10%, and 2.0 s, respectively, which are all better than before optimization. And the control accuracy, robustness, and stability of the optimized 8BSM were significantly better than before optimization. The above results indicate that the proposed eight link dynamic modeling optimization based on improved PID control has a good improvement effect on the eight link system and can be applied in practical production. Although the research has achieved remarkable results in the optimization of the eight-link stamping mechanism, there are still some obvious shortcomings. First of all, the study was mainly carried out under ideal experimental environment, and did not fully consider the complex working conditions and uncertain factors in practical applications, such as temperature change, mechanical wear, etc., which have adverse effects on the control effect. In the future, it is necessary to study how to maintain system stability in complex environment. In addition, the study does not involve other advanced strategies such as fuzzy control and sliding mode control, which may perform better in some scenarios, so a combination of multiple control strategies can be considered in the future. Finally, the research has not yet delved into practical application challenges such as scalability and adaptability to different real-world environments. In practical applications, the size and complexity of the stamping mechanism may vary greatly, and different production environments may also put different requirements on the performance of the control system. Therefore, how to design a control system with good scalability and adaptability to meet the needs of stamping mechanisms in different scales and environments is an important problem to be solved in future research.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
DM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing–original draft. JL: Formal Analysis, Project administration, Resources, Software, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The research is supported by the Anhui Provincial Excellent Youth Talent Support Program titled “Dynamic Simulation and Stability Research of Eight Link Stamping Mechanisms” (No. gxyq2022143) and the Natural Science Research Project of Anhui Provincial Department of Education titled “Research and Optimization of Kinematic Stability of Eight Link Stamping Mechanisms” (No. 2023AH052823); The research in this paper was supported by Anhui Provincial Education Department Natural Science Research Project “Trajectory Planning of The Six-Degree-of-Freedom Industrial Welding Robot Based on Meta-Heuristic Optimization Algorithms” (No. KJ 2021A1192).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Barhaghtalab, M. H., Sepestanaki, M. A., Mobayen, S., Jalilvand, A., Fekih, A., and Meigoli, V. (2023). Design of an adaptive fuzzy-neural inference system-based control approach for robotic manipulators. Appl. Soft Comput. 149, 110970. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2023.110970
Bensafia, Y., Khettab, K., and Idir, A. (2022). A novel fractionalized PID controller using the sub-optimal approximation of FOTF. Algerian J. Signals Syst. 7 (1), 21–26. doi:10.51485/ajss.v7i1.149
Chen, Z. (2022). Research on internet security situation awareness prediction technology based on improved RBF neural network algorithm. J. Comput. Cognitive Eng. 1 (3), 103–108. doi:10.47852/bonviewjcce149145205514
Choquette, J., Gandhi, W., Giroux, O., Stam, N., and Krashinsky, R. (2021). NVIDIA A100 tensor core GPU: performance and innovation. IEEE Micro 41 (2), 29–35. doi:10.1109/mm.2021.3061394
Chowdhury, M. A., Al-Wahaibi, S. S. S., and Lu, Q. (2023). Entropy-maximizing TD3-based reinforcement learning for adaptive PID control of dynamical systems. Comput. Chem. Eng. 178, 108393. doi:10.1016/j.compchemeng.2023.108393
Desai, S. G., Annigeri, A. R., and Timmanagouda, A. (2019). Analysis of a new single degree-of-freedom eight link leg mechanism for walking machine. Mech. Mach. Theory 140 (5), 747–764. doi:10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2019.06.002
Elsisi, M. (2020). New design of robust PID controller based on meta-heuristic algorithms for wind energy conversion system. Wind Energy 23 (2), 391–403. doi:10.1002/we.2439
Elsisi, M. (2021). Optimal design of non-fragile PID controller. Asian J. Control 23 (2), 729–738. doi:10.1002/asjc.2248
Feng, H., Song, Q., Ma, S., Ma, W., Yin, C., Cao, D., et al. (2022). A new adaptive sliding mode controller based on the RBF neural network for an electro-hydraulic servo system. ISA Trans. 129 (5), 472–484. doi:10.1016/j.isatra.2021.12.044
Garai, S., Paul, R. K., Kumar, M., and Choudhury, A. (2023). Intra-annual national statistical accounts based on machine learning algorithm. J. Data Sci. Intelligent Syst. 2 (2), 12–15. doi:10.47852/bonviewjdsis3202870
Ghamari, S. M., Narm, H. G., and Mollaee, H. (2022). Fractional-order fuzzy PID controller design on buck converter with antlion optimization algorithm. IET Control Theory Appl. 16 (3), 340–352. doi:10.1049/cth2.12230
Hammoodi, S. J., Flayyih, K. S., and Hamad, A. R. (2020). Design and implementation speed control system of DC motor based on PID control and matlab simulink. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. 11 (1), 127–134. doi:10.11591/ijpeds.v11.i1.pp127-134
Jomartov, A., Halicioglu, R., and Kuatova, M. (2022). Kinetostatic analysis, manufacturing, and experimental application of a press machine based on Stephenson II mechanism. Proc. Institution Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 236 (8), 1113–1124. doi:10.1177/09544054211062976
Kong, X., Deng, Z., Yu, S., Gao, W., and Wang, B. (2022). Multi-objective optimisation design and fuzzy PID control for racing car variable rear wing system. Int. J. Veh. Saf. 12 (3), 281–306. doi:10.1504/ijvs.2022.10054756
Li, F., Chen, P., Han, J., Deng, L., Yi, J., Liu, Y., et al. (2020). Metal flow behavior of P/M connecting rod preform in flashless forging based on isothermal compression and numerical simulation. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9 (2), 1200–1209. doi:10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.11.047
Li, X. Q., Song, L. K., Choy, Y. S., and Bai, G. C. (2023). Multivariate ensembles-based hierarchical linkage strategy for system reliability evaluation of aeroengine cooling blades. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 138, 108325. doi:10.1016/j.ast.2023.108325
Liu, J., Zhang, Y., Zhuang, X., and Pang, H. (2021b). Competing failure analysis of aircraft connecting-rod-type cabin door retraction mechanism with intermission considered. J. Northwest. Polytech. Univ. 39 (5), 1105–1113. doi:10.1051/jnwpu/20213951105
Liu, Y., Liu, F., Feng, H., Zhang, G., Li, K., Chi, R., et al. (2021a). Frequency tracking control of the WPT system based on fuzzy RBF neural network. Int. J. Intelligent Syst. 37 (7), 3881–3899. doi:10.1002/int.22706
Lu, C., He, B., and Zhang, R. (2021). Evaluation of English interpretation teaching quality based on GA optimized RBF neural network. J. Intelligent Fuzzy Syst. 40 (2), 3185–3192. doi:10.3233/jifs-189357
Phu, N. D., Hung, N. N., Ahmadian, A., and Senu, N. (2020). A new fuzzy PID control system based on fuzzy PID controller and fuzzy control process. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 22 (7), 2163–2187. doi:10.1007/s40815-020-00904-y
Raghavendra, B., and Annigeri, A. R. (2021). Optimal synthesis of planar eight-link walking leg mechanism using genetic algorithm. Mech. Mach. Theory 38 (6), 152–164. doi:10.1504/ijmic.2021.122498
Setiawan, A., and Ma’arif, A. (2021). Stirring system design for automatic coffee maker using OMRON PLC and PID control. Int. J. Robotics Control Syst. 1 (3), 390–401. doi:10.31763/ijrcs.v1i3.457
Tian, J., Zhou, Y., Yang, L., and Hu, S. (2020). Analysis of stick-slip reduction for a new torsional vibration tool based on PID control. Proc. Institution Mech. Eng. Part K J. Multi-body Dyn. 234 (1), 82–94. doi:10.1177/1464419319876397
Wang, H., and Lu, J. (2022). Research on fractional order fuzzy PID control of the pneumatic-hydraulic upper limb rehabilitation training system based on PSO. Int. J. Control Automation Syst. 20 (1), 310–320. doi:10.1007/s12555-020-0847-1
Wang, Q., Xi, H., Deng, F., Cheng, M., and Buja, G. (2022). Design and analysis of genetic algorithm and BP neural network based PID control for boost converter applied in renewable power generations. IET Renew. Power Gener. 16 (7), 1336–1344. doi:10.1049/rpg2.12320
Wang, Q., Zhou, H., and Liu, Q. (2023). Denoising method for terahertz signal using RBF neural network with adaptive projection learning algorithm. Wirel. Netw. 29 (2), 749–759. doi:10.1007/s11276-022-03128-0
Zaidel, Y., Shalumov, A., Volinski, A., Supic, L., and Ezra Tsur, E. (2021). Neuromorphic NEF-based inverse kinematics and PID control. Front. neurorobotics 15, 631159. doi:10.3389/fnbot.2021.631159
Zhang, H., Song, L., and Bai, G. (2023). Active kriging-based adaptive importance sampling for reliability and sensitivity analyses of stator blade regulator. CMES-Computer Model. Eng. Sci. 134 (3), 1871–1897. doi:10.32604/cmes.2022.021880
Zhang, H., Song, L. K., Bai, G. C., and Li, X. Q. (2022). Active extremum Kriging-based multi-level linkage reliability analysis and its application in aeroengine mechanism systems. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 131, 107968. doi:10.1016/j.ast.2022.107968
Keywords: radial basis function, proportional-integrated-derivative, eight bar stamping mechanism, dynamics, modeling
Citation: Ma D and Li J (2024) Dynamic modeling and optimization of an eight bar stamping mechanism based on RBF neural network PID control. Front. Mech. Eng 10:1374491. doi: 10.3389/fmech.2024.1374491
Received: 22 January 2024; Accepted: 20 March 2024;
Published: 12 April 2024.
Edited by:
Kanak Kalita, Vel Tech Dr. RR and Dr. SR Technical University, IndiaReviewed by:
Mehmet Akif Koç, Sakarya University of Applied Sciences, TürkiyeLu-Kai Song, Beihang University, China
Copyright © 2024 Ma and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Juchen Li, qipima1986@163.com
 Dongsheng Ma1
Dongsheng Ma1  Juchen Li
Juchen Li