Alterations of cerebral perfusion and functional connectivity in children with idiopathic generalized epilepsy
- Department of Radiology, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Medical Imaging Center of Guizhou Province, Zunyi, China
A corrigendum on
Alterations of cerebral perfusion and functional connectivity in children with idiopathic generalized epilepsy
by Chen, G., Hu, J., Ran, H., Nie, L., Tang, W., Li, X., Li, Q., He, Y., Liu, J., Song, G., Xu, G., Liu, H., and Zhang, T. (2022). Front. Neurosci. 16:918513. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.918513
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 2 as published. In Figure 2, the annotations of SFG and MOG in the brain region were misplaced. The corrected Figure 2 appears below.
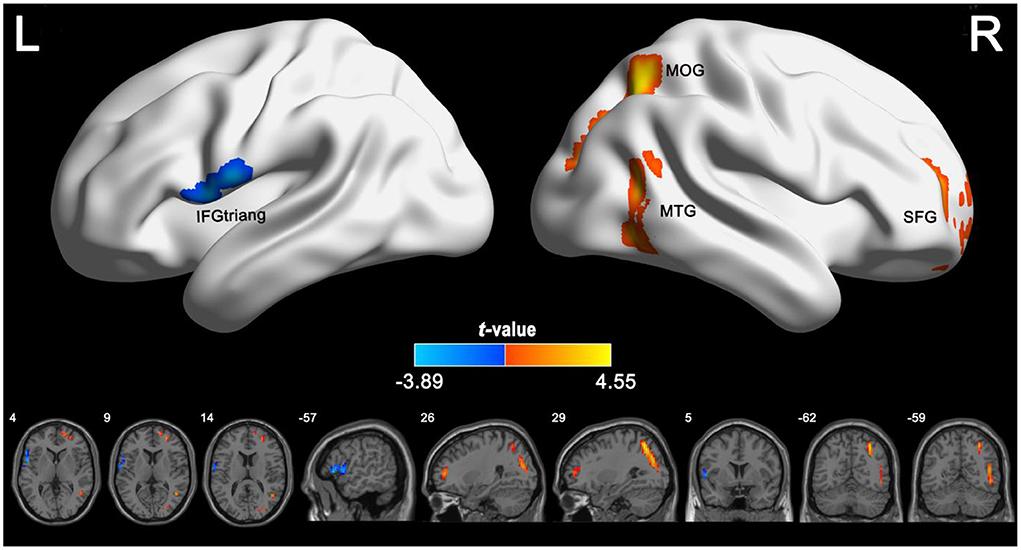
Figure 2. Group differences in CBF between IGE patients and healthy controls. The independent two-sample t test was conducted between the IGE group and the healthy control group. All results were corrected for multiple comparisons (GRF-corrected, P < 0.05). The cold colors denote significantly decreased CBF in the IGE patients. The warm colors denote significantly increased CBF in the IGE patients. CBF, cerebral blood flow; GRF, Gaussian random field; IGE, idiopathic generalized epilepsy.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: idiopathic generalized epilepsy, cerebral blood flow, functional connectivity, arterial spin labeling, resting state fMRI
Citation: Chen G, Hu J, Ran H, Nie L, Tang W, Li X, Li Q, He Y, Liu J, Song G, Xu G, Liu H and Zhang T (2022) Corrigendum: Alterations of cerebral perfusion and functional connectivity in children with idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Front. Neurosci. 16:1011310. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.1011310
Received: 04 August 2022; Accepted: 10 August 2022;
Published: 23 August 2022.
Edited and reviewed by: Ardalan Aarabi, University of Picardie Jules Verne, France
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Hu, Ran, Nie, Tang, Li, Li, He, Liu, Song, Xu, Liu and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tijiang Zhang, tijzhang@163.com; Heng Liu, zmcliuh@163.com
†These authors share first authorship
 Guiqin Chen
Guiqin Chen Jie Hu
Jie Hu Haifeng Ran
Haifeng Ran Lei Nie
Lei Nie Heng Liu
Heng Liu Tijiang Zhang
Tijiang Zhang