A mini-review on data science approaches in crop yield and disease detection
- 1Department of Statistics, Computer Science, Application (DISIA), University of Florence, Florence, Italy
- 2Department of Environmental Science and Policy, University of Milan, Milan, Italy
Agriculture constitutes a sector with a considerable environmental impact, a concern that is poised to increase with the projected growth in population, thereby amplifying implications for public health. Effectively mitigating and managing this impact demands the implementation of intelligent technologies and data-driven methodologies collectively called precision agriculture. While certain methodologies enjoy widespread acknowledgement, others, despite their lesser prominence, contribute meaningfully. This mini-review report discusses the prevalent AI technologies within precision agriculture over the preceding five years, with a specific emphasis on crop yield prediction and disease detection domains extensively studied within the current literature. The primary objective is to give a comprehensive overview of AI applications in agriculture, spanning machine learning, deep learning, and statistical methods. This approach aims to address a notable gap wherein existing reviews predominantly focus on singular aspects rather than presenting a unified and inclusive perspective.
1 Introduction
Agriculture plays a central role in the global economy, offering vital income generation and employment opportunities (Phasinam et al., 2022). It holds critical responsibilities in ensuring food quality and safety, preserving the environment, fostering integrated rural development, and maintaining social structure and cohesion in rural areas (Loizou et al., 2019). For instance, in 2022, the European Union’s agricultural sector played a crucial economic role, contributing significantly with a gross value added of 222.3 billion euros. This amount represented about 1.4% of the total gross domestic product (GDP) of Europe. Particularly noteworthy was the relative increase in the estimated agricultural income per annual work unit, reaching a level 44.3% higher than that observed in 2015 (Eurostat, 2023). Furthermore, agriculture remained a crucial employer, with a staggering 8.7 million individuals employed in the agricultural sector across Europe in 2020, affirming its continued prominence within the EU (Eurostat, 2020). These data are projected to further surge in response to the expected increase in the global population, reaching 9.7 billion by 2050 (Pew Research Center, 2019). As evident from the data, the most substantial population increase is expected in Africa, with a projected boost of approximately 92.3% (Pew Research Center, 2019). Following by Latin America and Asia, which are expected to experience population growth by about 21% and 15.23%, respectively (Pew Research Center, 2019). The surge in population in specific regions has led to a notable escalation in food demand. A significant publication by Alexandratos and Bruinsma (2012) underscores the imperative need to increase global agricultural production by 60% to meet this growing food requirement. Developing countries are faced with an even greater challenge, as they would need to enhance agricultural output by 77%, while developed countries should aim for a 24% increase (Malhi et al., 2021). Consequently, the environmental impact of the agricultural sector has amplified, and in the next four decades, the emissions will increase by more than 60% (Fróna et al., 2019). In general, agriculture accounts for more than 11% of the total anthropogenic emission from direct source (Maraseni and Qu, 2016), and this value grows about 3-6% if the storage, transportation, packaging and agricultural input production are included (Tan et al., 2022). Considering direct agricultural emissions, 81% of the global ammonia (NH3) is reached by the agronomic sector (Damme et al., 2021) as a result of the increase in animal feeding operation (Schultz et al., 2019). NH3 has a high impact on the ecosystem leading to the acidification and eutrophication phenomena and also has a key role in the Particulate Matter 2.5 micrometers (PM2.5) generation which is responsible for serious health problems such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder and lung cancer (Lelieveld et al., 2015; Apte et al., 2018). Other emissions from the agricultural sector are methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O) which are greenhouse gases (GHGs) and contribute to climate change. They are produced during the enteric fermentation, manure management, synthetic fertilizer, manure management, synthetic fertilizers, rice cultivation, manure applied to soils and pastures, crop residues, cultivation of organic soils, and burning of crop residues (Han et al., 2019). So it is undeniable that agriculture has a very large influence on climate change, which also has a negative effect on agriculture itself. Indeed, agriculture, being highly susceptible to climate variations, experiences adverse consequences due to significant fluctuations in temperature and rainfall. These variations directly influence crop yields and quality, posing challenges to food production and agricultural sustainability. For instance, extended precipitations could delay production processes due to muddy soils and inaccessible fields for machinery, high temperatures cause the lack of winter chill induces a negative effect on the quality of asparagus and rhubarb and affect flowering time, the increase of CO2 induce the reduction of micro and macronutrients in lettuce, celery (Bisbis et al., 2018).
In order to mitigate the impact of climate change on agriculture and simultaneously reduce agriculture’s contribution to climate change embracing new technologies based on Data Science is required. In fact, data-driven decision-making holds the potential to revolutionize farming practices by enabling more efficient utilization of water, pesticides, and fertilizers, thereby minimizing environmental impacts (Akkem et al., 2023).
2 Data science in agriculture
Nowadays, there are many new technologies based on the Internet of Things (IoT), wireless connection, cloud computing, and block-chain technology that have the potential to revolutionize crop monitoring. An example, is remote sensing technologies, such as satellite-based (Sentinel-3) or Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) systems, utilize spectral images to calculate reflected radiation (Toth and Jóźków, 2016). These images, when subjected to data analysis, provide valuable vegetation indices, including the widely used Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) (Skakun et al., 2018), which assesses crop health based on the Red and Near Infrared reflectance. Beyond general vegetation indices, specific pigment content can be evaluated using remote sensing data. For instance, the Normalized Red Index quantifies chlorophyll levels, while the Normalized Green Index focuses on other pigments, excluding chlorophyll (Qi et al., 1994). In addition to remote sensing, field wireless sensor networks are employed to measure vital weather variables, such as temperature, air humidity, soil moisture, pH and so on (Priya and Yuvaraj, 2019). All these technologies guide agriculture toward a digital revolution, leading to the rise of precision agriculture (PA), which tackles the customization of agricultural practices to fit the unique characteristics of each crop, field, and environmental context. It advocates the adoption of cutting-edge technologies and data-driven approaches to effectively address the inherent heterogeneities within a field (Finger et al., 2019), providing an increase in terms of productivity using less natural resources such as energy and water (Pathan et al., 2020). PA finds broad applicability across various agricultural practices, offering valuable benefits in terms of resource efficiency and enhanced crop management. For instance, in the context of irrigation, PA enables precise water delivery, avoiding wastage and ensuring optimal water utilization. Similarly, in fertilization, PA plays a crucial role in identifying specific areas within the field where nutrients are needed, thereby providing targeted support to plant growth and minimizing resource losses due to over-application. Furthermore, PA’s impact extends to pest control and disease detection, where early warnings through predictive models enable proactive intervention, reducing potential damage and optimizing treatment strategies (Shafi et al., 2019). In Figure 1 are reported the domains where PA techniques are applied.
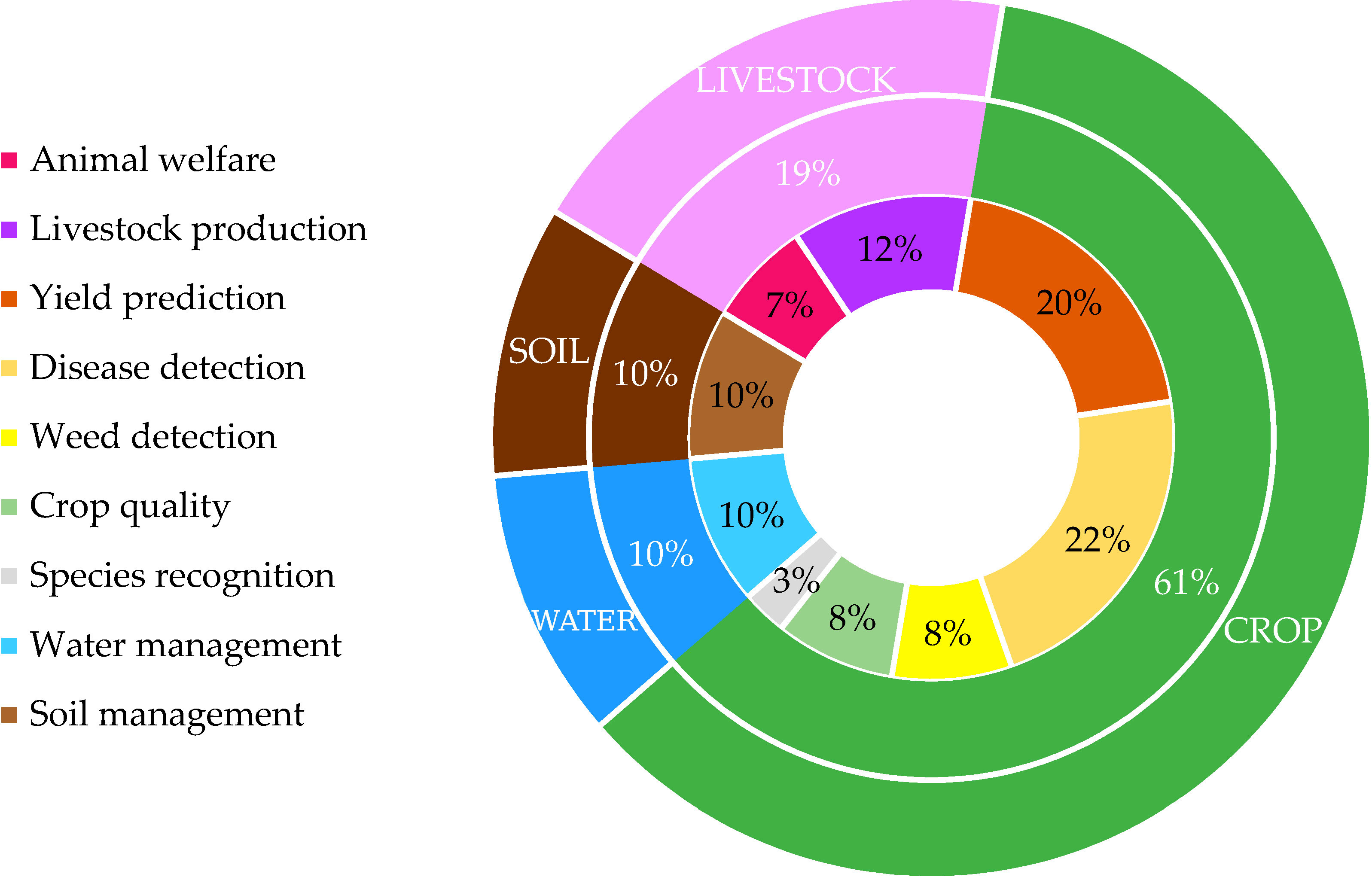
Figure 1 Distribution of the precision agriculture’s publications in for each domain by Liakos et al. (2018).
As evident from the data, the majority of publications in precision agriculture are concentrated in the crop domains (green). Specifically, disease detection (22%) and yield prediction (20%) stand out as the dominant subsections in research. The third most studied domain is livestock production, accounting for 12% of the publications. These new technologies are available in agriculture, paving the way for big data, and making it attractive for advanced data analysis methodologies such as Deep learning (DL) and Machine learning (ML), making them the most used in the recent literature for PA applications (Ayoub Shaikh et al., 2022). Here below are reported recent literatures about ML and DL techniques regarding Yield prediction and Disease detection, since these are the domains in which precision agriculture is most studied, then, another common class of model in PA applications is reviewed.
2.1 Prominent machine and deep learning techniques employed in precision agriculture applications
Crop yield prediction is one of the most important sectors belonging to precision agriculture because accurate model predictions help farmers to optimize crop management, although this task remains quite complex due to the hierarchical nature of crop yield that involves variables ranging from plant genotype to environmental descriptors along time and space. Some of the most recent publications propose semiparametric DL networks to encode nonlinear relationships between variables, for instance, Jeong et al. (2022) developed an early stage prediction of rice yield at pixel scale methodology using as input variables: vegetation indices, transplanting dates, minimum and maximum of temperatures, solar radiation, administrative information, yearly rice maps. The outputs of the remote-sensing integrated crop model (RSCM) (Pistenma et al., 1977) was used to train five different DL models. The model selected was the Long Short-Term Memory combined with 1D-Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), also a comparison between the county-scale model and pixel-scale model was done, county-scale yields lack the significant advantages of satellite images and are less sensitive to spatial variations within each county region, while the pixel-scale crop yield better-representing variations within a region. CNNs are also used for strawberry cultivation to detect and count mature, immature strawberries, and blossoms, through UAV and near-ground digital images in order to predict strawberry yield and perfect harvesting time (Zhou et al., 2021). Another DL technique which finds application in crop yield prediction is deep neural networks which are multilayer feed-forward neural networks very useful with large datasets. Their training commonly involves gradient-based methods, though this can introduce challenges such as converging slowly or getting trapped in local minima due to the initialization of the random weights. To address this issue, a fusion of deep neural networks and genetic algorithms has been explored. This combination aims to address the issue of local minima by identifying a reduced-dimensional subspace of weights. This integration becomes especially relevant when environmental and genotype data are employed for accurate crop yield prediction (Bi and Hu, 2021).
The disease detection is vital to avoid loss of yield and quality of the crop, since pesticides were usually applied uniformly to the whole field, the classification and prediction of the early stage of the disease and finding critical infestation areas, are crucial in order to avoid economic losses and environmental problems, using mainly hourly weather data ranged from two to five years (Fenu and Malloci, 2021). Within this field ML techniques have been introduced for disease management, such as the work by Bhatia et al. (2022). This study conducted a comparative analysis of three ML methods, namely k-Nearest Neighbor (k-NN), Support Vector Machine (SVM), and Na¨ıve Bayes (NB). The aim was to develop an optimized spray prediction model against powdery mildew, by exploiting the tomato powdery mildew dataset (TPMD). This dataset encompasses a range of weather variables like temperature, relative humidity, wind speed, and global radiation, along with leaf wetness data. The findings of this study indicated that SVM exhibited the most favorable classification performance, thus rendering it the most suitable choice for this particular prediction task. Furthermore, a hybrid variant of the SVM was introduced for the detection of powdery mildew. In this approach, SVM worked as a wrapper, enhancing the training set and minimizing the possibility of sample mislabeling. Subsequently, a logistic regression model was applied to the refined training set, leading to a reduction of the classification error (Bhatia et al., 2020). The Random Forest (RF) has been proposed as a machine learning classifier against tomato diseases. A RF uses leaf images of Early Blight, Late Blight, Septoria Leaf spot, Spidermite, Mosaic Virus, Yellow leaf curl virus, to classify the healthy and diseased plant leaves (Govardhan and M B, 2019). RFs have been observed that outperform other supervised ML and DL algorithms such as CNN, SVM and k-NN for the classification of maize plant leaf diseases (Arora et al., 2020).
2.2 Mechanistic-deterministic models in precision agriculture applications
Big data leads to the use of another class of model, namely the mechanistic-deterministic model (MDM), which are not based on statistical relationships between variables, but they model biophysical processes accounting for deterministic relationships between crop growth and environmental, management and genetic factors. MDM are useful to understand complex crop-related phenomena and to optimally manage the agrosystems (Pasquel et al., 2022). These characteristics makes them a widespread tool in the agroenvironmental field, since they can work without massive amounts of data that can be time-consuming and expensive to collect, such as disease observations at level of leaf. Among the many applications developed in this model framework, below a comprehensive selection of models is summarized.
AquaCrop a prominent crop modeling tool by the FAO, predicts crop biomass and yield under diverse water management scenarios. Comprising multiple modules, each simulating aspects of agroecosystems with unique equations, its main components are outlined. The Phenology module identifies plant development stages, while the Climate module includes variables like air temperatures, rainfall, and evapotranspiration demand. The Soil module manages daily water balance, considering soil characteristics. The Canopy module models soil surface coverage, influenced by stress and phenological stage. The Biomass module (Equation 1) calculates plant biomass over time using the formula:
where B signifies final biomass, WP represents water productivity (biomass per cumulative transpiration unit), and Tr denotes daily crop transpiration. The remaining components quantify this equation. Dependencies exist among components, like the influence of carbon dioxide levels on water productivity (Climate), and the connection between green canopy cover and the Soil module. Green canopy cover is affected by air temperatures and evapotranspiration (Climate), creating a web of interdependencies (Raes et al., 2009; Steduto et al., 2009). AquaCrop’s versatility spans various locations and seasons, facilitating its application in a wide range of contexts. Notably, it has been successfully coupled with remote sensing data, specifically green fractional vegetation cover, to estimate maize growth and total above-ground dry biomass in Belgium (Mohamed Sallah et al., 2019). Additionally, its efficacy has been demonstrated in investigating diverse irrigation treatments in Semi-Arid Tropical areas of India (Umesh et al., 2022), as well as exploring varied soil conditions’ impact on maize growth (Shan et al., 2022).
Another famous MDM is the decision support system for agrotechnology transfer (DSSAT) (Jones et al., 2003). It covers a wide range of applications, such as fertilization management (Si et al., 2021), irrigation management (Malik and Dechmi, 2019), impacts of the climate change (Hasan and Rahman, 2020), and so on. One of the main characteristics of DSSAT is that has been developed using a modular approach, where each module has a distinct goal and works independently using different MDM. For instance, the Soil module provides information about soil water, using CERES-Wheat model (Ritchie and Otter, 1985), simulating information about: the daily changes in soil water content due to infiltration of rainfall and irrigation, vertical drainage, unsaturated flow, soil evaporation, and root water uptake processes. The CROPGRO model (Boote et al., 1998) employs input data regarding crop growth, including optimal temperatures for various developmental stages, information on photosynthesis, and nitrogen fixation. It uses this information to simulate parameters such as the emergence day, harvest maturity date, daily senescent plant matter, and other critical elements for determining plant stress, such as the nitrogen stress factor. The modular structure of DSSAT makes easy for user the integration of new modules with different goals e.g. livestock management, also in different programming languages. They are other MDMs whose structure is based on different sub-models, but they achieve the same goal, the optimal agrosystem management (Brown et al., 2014; de Wit et al., 2019). A compartmental model has been proposed for pest management by Savary et al. (2012) which proposed a susceptible-exposed-infectious-removed model (SEIR model) which is composed by four compartments: healthy (H), latent (L), infectious (I), and post-infectious sites (P) epidemics, coupled with other variables such as: crop growth, tissue senescence disease (induced by disease or physiological) and the spatial aggregation of the disease. Those compartments are used to simulate the rice and wheat disease (Savary et al., 2015) over a 120-day duration using a daily time step.
2.3 Statistical methods in precision agriculture application
“Pure” statistical methods remain less prevalent in PA applications; however, they continue to play a significant role in specific sectors of agriculture. For instance, statistical approaches like Mixed Effects Models (MEM) are commonly employed in genome-wide association studies (GWAS) for crop breeding prediction, exemplified by the prominence of studies such as Berhe et al. (2021) use of Mixed Effects Models. In the domain of GWAS, Principal Component Analysis (PCA) is also frequently used due to its ability to reduce data complexity by transforming it into a limited number of Principal Components. These components can subsequently be incorporated as covariates in MEM, often employed to capture population structures (Abdi et al., 2023). PCA’s suitability for various GWAS applications, including genotype-by-environment interaction analysis and trait selection for yield modeling, further underscores its importance (Abdipour et al., 2019; Ahakpaz et al., 2021). In the domain of soil mapping, geostatistical techniques like regression kriging continue to maintain prominence due to their consideration of spatial autocorrelation, a factor not fully embraced by many ML methods (Heuvelink and Webster, 2022). Conversely, within crop yield prediction and disease detection studies, statistical methodologies such as regression models (Chen et al., 2020; Kodaty and Halavath, 2021) and Bayesian networks (Kocian et al., 2020; Singh and Gupta, 2020) have been proposed. In Table 1, the studies cited in the text above are reported, including information about the goal of the study, the variables and the method used.
3 Discussion
The objective of this concise review is to offer a comprehensive overview of the prevailing data science methodologies, highlighting their popularity and significance in the field. Indeed, an extensive portion of the literature is focused on machine learning and deep learning because the black-box/opaque AI methodologies may require less work from experts, albeit at the price of much more computational work because of the big sample size required. On the other hand, mechanistic-deterministic models take the other part of the literature with many applications ranging from fertilization management to disease predictions, but they often neglect the inferential uncertainty, with the risk of falsely over-accurate inferential statements. The MDMs clearly offer significant advantages in agrosystem management, enabling predictions across various scenarios of interest. To achieve this predictive power, a crucial step often involves calibration, which entails identifying optimal, context-specific parameter values (input values) for solving the underlying equations. These parameter values might be initially unknown, necessitating a comparison of observed data with predictions generated by the MDM. This process serves to assess the accuracy of the input values and is called trial-and-error procedure. Conversely, if the input values are sourced from literature or established knowledge, they are considered tuning parameters. However, regardless of the approach taken, both methods fail to quantify the forecast uncertainty inherent in the model (Kennedy and O’Hagan, 2001). In crop modelling with MDMs, the trial-and-error procedure is the most used (Della Nave et al., 2022; Rai et al., 2022; Terán-Chaves et al., 2022; Alvar-Beltrán et al., 2023) where the authors use historical data or build new experiments to achieve their prediction goals. Statistical procedures can be employed in the input value selection phase to facilitate uncertainty quantification in predictions. However, their application within these studies remains circumscribed, in part due to the involved nature of these techniques, but also for the prominent role played by the adopted calibration method on the resulting prediction errors (Gao et al., 2020).
The literature cited in this work highlights the limited number of contributions dealing with statistical methodologies in the PA field, particularly for crop yield prediction and disease detection; future work might consider the quantitative integration of the expert’s degree of belief into the decision-making processes of agriculture (Valleggi et al., 2023, 2024). This starting step also seems helpful in fully harnessing the power of modern structural causal models (Pearl, 2009) and improving decision-making in PA (Stefanini and Valleggi, 2022).
Author contributions
LV: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. FS: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdi H., Alipour H., Bernousi I., Jafarzadeh J., Rodrigues P. C. (2023). Identification of novel putative alleles related to important agronomic traits of wheat using robust strategies in GWAS. Sci. Rep. 13, 9927. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-36134-z
Abdipour M., Younessi-Hmazekhanlu M., Ramazani S. H. R., Hassan Omidi A. (2019). Artificial neural networks and multiple linear regression as potential methods for modeling seed yield of safflower (carthamus tinctorius l.). Ind. Crops Products 127, 185–194. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.10.050
Ahakpaz F., Abdi H., Neyestani E., Hesami A., Mohammadi B., Mahmoudi K. N., et al. (2021). Genotype-by-environment interaction analysis for grain yield of barley genotypes under dryland conditions and the role of monthly rainfall. Agric. Water Manage. 245, 106665. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106665
Akkem Y., Biswas S. K., Varanasi A. (2023). Smart farming using artificial intelligence: A review. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 120, 105899. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2023.105899
Alexandratos N., Bruinsma J. (2012). World agriculture: Towards 2030/2050 (Rome, Italy: FAO). ESA Working Paper No. 12–03.
Alvar-Beltrán J., Saturnin C., Grégoire B., Camacho J. L., Dao A., Migraine J. B., et al. (2023). Using AquaCrop as a decision-support tool for improved irrigation management in the Sahel region. Agric. Water Manage. 287, 108430. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2023.108430
Apte J. S., Brauer M., Cohen A. J., Ezzati M., Pope C. A. I. (2018). Ambient PM2.5 reduces global and regional life expectancy. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 5, 546–551. doi: 10.1021/acs.estlett.8b00360
Arora J., Agrawal U., Sharma P. (2020). Classification of Maize leaf diseases from healthy leaves using Deep Forest. J. Artif. Intell. Syst. 2, 14–26. doi: 10.33969/AIS.2020
Ayoub Shaikh T., Rasool T., Rasheed Lone F. (2022). Towards leveraging the role of machine learning and artificial intelligence in precision agriculture and smart farming. Comput. Electron. Agric. 198, 107119. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2022.107119
Berhe M., Dossa K., You J., Mboup P. A., Diallo I. N., Diouf D., et al. (2021). Genome-wide association study and its applications in the non-model crop Sesamum indicum. BMC Plant Biol. 21, 283. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03046-x
Bhatia A., Chug A., Singh A. P. (2020). “Hybrid svm-lr classifier for powdery mildew disease prediction in tomato plant”, in 2020 7th International Conference on Signal Processing and Integrated Networks (SPIN), Noida, India, 218–223. doi: 10.1109/SPIN48934.2020.9071202
Bhatia A., Chug A., Singh A. P., Singh R. P., Singh D. (2022). A machine learning-based spray prediction model for tomato powdery mildew disease. Indian Phytopathol. 75, 225–230. doi: 10.1007/s42360-021-00430-3
Bi L., Hu G. (2021). A genetic algorithm-assisted deep learning approach for crop yield prediction. Soft Comput. 25, 10617–10628. doi: 10.1007/s00500-021-05995-9
Bisbis M., Gruda N., Blanke M. (2018). Potential impacts of climate change on vegetable production and product quality – A review. J. Cleaner Production 170, 1602–1620. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.09.224
Boote K. J., Jones J. W., Hoogenboom G. (1998). “Simulation of Crop Growth: CROPGRO model”, in Agricultural Systems Modeling and Simulation (New York: CRC Press), 42.
Brischetto C., Bove F., Fedele G., Rossi V. (2021). A weather-driven model for predicting infections of grapevines by Sporangia of Plasmopara viticola. Front. Plant Sci. 12. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.636607
Brown H. E., Huth N. I., Holzworth D. P., Teixeira E. I., Zyskowski R. F., Hargreaves J. N. G., et al. (2014). Plant Modelling Framework: Software for building and running crop models on the APSIM platform. Environ. Model. Softw. 62, 385–398. doi: 10.1016/j.envsoft.2014.09.005
Chen M., Brun F., Raynal M., Makowski D. (2020). Forecasting severe grape downy mildew attacks using machine learning. PloS One 15, e0230254. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0230254
Damme M. V., Clarisse L., Franco B., Sutton M. A., Erisman J. W., Kruit R. W., et al. (2021). Global, regional and national trends of atmospheric ammonia derived from a decadal, (2008–2018) satellite record. Environ. Res. Lett. 16, 055017. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/abd5e0
Della Nave F. N., Ojeda J. J., Irisarri J. G. N., Pembleton K., Oyarzabal M., Oesterheld M. (2022). Calibrating APSIM for forage sorghum using remote sensing and field data under sub-optimal growth conditions. Agric. Syst. 201, 103459. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2022.103459
de Wit A., Boogaard H., Fumagalli D., Janssen S., Knapen R., van Kraalingen D., et al. (2019). 25 years of the WOFOST cropping systems model. Agric. Syst. 168, 154–167. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2018.06.018
Eurostat (2020). Farmers and the agricultural labour force - statistics. Available online at: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Farmers_and_the_agricultural_labour_force_-_statistics (Accessed 2023-08-31).
Eurostat (2023). Performance of the agricultural sector. Available online at: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Performance_of_the_agricultural_sector (Accessed 2023-08-31).
Fenu G., Malloci F. M. (2021). Forecasting plant and crop disease: An explorative study on current algorithms. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 5. doi: 10.3390/bdcc5010002
Finger R., Swinton S. M., El Benni N., Walter A. (2019). Precision farming at the nexus of agricultural production and the environment. Annu. Rev. Resour. Econ. 11, 313–335. doi: 10.1146/annurev-resource-100518-093929
Fróna D., Szenderák J., Harangi-Rákos M. (2019). The challenge of feeding the world. Sustainability 11. doi: 10.3390/su11205816
Gao Y., Wallach D., Liu B., Dingkuhn M., Boote K. J., Singh U., et al. (2020). Comparison of three calibration methods for modeling rice phenology. Agric. For. Meteorol. 280, 107785. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2019.107785
Govardhan M., M B V. (2019). “Diagnosis of tomato plant diseases using random forest”, in 2019 Global Conference for Advancement in Technology (GCAT), Bangalore, India, 1–5. doi: 10.1109/GCAT47503.2019.8978431
Han M., Zhang B., Zhang Y., Guan C. (2019). Agricultural CH4 and N2O emissions of major economies: Consumption-vs. production-based perspectives. J. Cleaner Production 210, 276–286. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.11.018
Hasan M. M., Rahman M. M. (2020). Simulating climate change impacts on T. aman (BR-22) rice yield: a predictive approach using DSSAT model. Water Environ. J. 34, 250–262. doi: 10.1111/wej.12523
Heuvelink G. B., Webster R. (2022). Spatial statistics and soil mapping: A blossoming partnership under pressure. Spatial Stat 50, 100639. doi: 10.1016/j.spasta.2022.100639
Jeong S., Ko J., Yeom J.-M. (2022). Predicting rice yield at pixel scale through synthetic use of crop and deep learning models with satellite data in south and North Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 802, 149726. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149726
Jones J. W., Hoogenboom G., Porter C. H., Boote K. J., Batchelor W. D., Hunt L. A., et al. (2003). The DSSAT cropping system model. Eur. J. Agron. 18, 235–265. doi: 10.1016/S1161-0301(02)00107-7
Kennedy M. C., O’Hagan A. (2001). Bayesian calibration of computer models. J. R. Stat. Society: Ser. B (Statistical Methodol.) 63. doi: 10.1111/1467-9868.00294
Kocian A., Massa D., Cannazzaro S., Incrocci L., Di Lonardo S., Milazzo P., et al. (2020). Dynamic bayesian network for crop growth prediction in greenhouses. Comput. Electron. Agric. 169, 105167. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2019.105167
Kodaty S. C., Halavath B. (2021). “A new approach for paddy leaf blast disease prediction using logistic regression”, in Advances in Information Communication Technology and Computing. Eds. Goar V., Kuri M., Kumar R., Senjyu T. (Springer, Singapore), 533–542. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-5421-6_51
Lelieveld J., Evans J. S., Fnais M., Giannadaki D., Pozzer A. (2015). The contribution of outdoor air pollution sources to premature mortality on a global scale. Nature 525, 367–371. doi: 10.1038/nature15371
Liakos K. G., Busato P., Moshou D., Pearson S., Bochtis D. (2018). Machine learning in agriculture: A review. Sensors 18, 2674. doi: 10.3390/s18082674
Loizou E., Karelakis C., Galanopoulos K., Mattas K. (2019). The role of agriculture as a development tool for a regional economy. Agric. Syst. 173, 482–490. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2019.04.002
Malhi G. S., Kaur M., Kaushik P. (2021). Impact of climate change on agriculture and its mitigation strategies: A review. Sustainability 13, 1318. doi: 10.3390/su13031318
Malik W., Dechmi F. (2019). Dssat modelling for best irrigation management practices assessment under mediterranean conditions. Agric. Water Manage. 216, 27–43. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2019.01.017
Maraseni T. N., Qu J. (2016). An international comparison of agricultural nitrous oxide emissions. J. Cleaner Production 135, 1256–1266. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.07.035
Mohamed Sallah A.-H., Tychon B., Piccard I., Gobin A., Van Hoolst R., Djaby B., et al. (2019). Batch-processing of aquacrop plug-in for rainfed maize using satellite derived fractional vegetation cover data. Agric. Water Manage. 217, 346–355. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2019.03.016
Pasquel D., Roux S., Richetti J., Cammarano D., Tisseyre B., Taylor J. A. (2022). A review of methods to evaluate crop model performance at multiple and changing spatial scales. Precis. Agric. 23, 1489–1513. doi: 10.1007/s11119-022-09885-4
Pathan M., Patel N., Yagnik H., Shah M. (2020). Artificial cognition for applications in smart agriculture: A comprehensive review. Artif. Intell. Agric. 4, 81–95. doi: 10.1016/j.aiia.2020.06.001
Pew Research Center (2019) World’s population is projected to nearly stop growing by the end of the century. Available online at: https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/2019/06/17/worlds-population-is-projected-to-nearly-stop-growing-by-the-end-of-the-ce (Accessed 2023-08-31).
Phasinam K., Kassanuk T., Shabaz M. (2022). Applicability of internet of things in smart farming. J. Food Qual. 2022, e7692922. doi: 10.1155/2022/7692922
Pistenma D. A., Li G. C., Fessenden P., White K., Bagshaw M. A. (1977). Treatment planning for negative pi-meson radiation therapy: simultaneous multi-port irradiation with the Stanford Medical Pion Generator (SMPG). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 3, 315–323. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(77)90270-x
Priya P. K., Yuvaraj N. (2019). An ioT based gradient descent approach for precision crop suggestion using MLP. J. Physics: Conf. Ser. 1362, 12038. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1362/1/012038
Qi J., Chehbouni A., Huete A., Kerr Y., Sorooshian S. (1994). A modified soil adjusted vegetation index. Remote Sens. Environ. 48, 119–126. doi: 10.1016/0034-4257(94)90134-1
Raes D., Steduto P., Hsiao T. C., Fereres E. (2009). AquaCrop—The FAO crop model to simulate yield response to water: II. Main algorithms and software description. Agron. J. 101, 438–447. doi: 10.2134/agronj2008.0140s
Rai T., Kumar S., Nleya T., Sexton P., Hoogenboom G., Rai T., et al. (2022). Simulation of maize and soybean yield using DSSAT under long-term conventional and no-till systems. Soil Res. 60, 520–533. doi: 10.1071/SR21042
Ritchie J., Otter S. (1985). Description and performance of ceres-wheat: a user-oriented wheat yield model. ARS Wheat Yield Project 38, 159–175.
Savary S., Nelson A., Willocquet L., Pangga I., Aunario J. (2012). Modeling and mapping potential epidemics of rice diseases globally. Crop Prot. 34, 6–17. doi: 10.1016/j.cropro.2011.11.009
Savary S., Stetkiewicz S., Brun F., Willocquet L. (2015). Modelling and mapping potential epidemics of wheat diseases—examples on leaf rust and Septoria tritici blotch using EPIWHEAT. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 142, 771–790. doi: 10.1007/s10658-015-0650-7
Schultz A. A., Peppard P., Gangnon R. E., Malecki K. M. (2019). Residential proximity to concentrated animal feeding operations and allergic and respiratory disease. Environ. Int. 130, 104911. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.104911
Shafi U., Mumtaz R., García-Nieto J., Hassan S. A., Zaidi S. A. R., Iqbal N. (2019). Precision agriculture techniques and practices: From considerations to applications. Sensors 19, 3796. doi: 10.3390/s19173796
Shan Y., Li G., Su L., Zhang J., Wang Q., Wu J., et al. (2022). Performance of aquacrop model for maize growth simulation under different soil conditioners in shandong coastal area, China. Agronomy 12. doi: 10.3390/agronomy12071541
Si Z., Zain M., Li S., Liu J., Liang Y., Gao Y., et al. (2021). Optimizing nitrogen application for drip-irrigated winter wheat using the dssat-ceres-wheat model. Agric. Water Manage. 244, 106592. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106592
Singh N., Gupta N. (2020). “Bayesian network for development of expert system in pest management”, in Internet of Things and Analytics for Agriculture, vol. 2 . Eds. Pattnaik P. K., Kumar R., Pal S. (Springer, Singapore), 45–65. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-0663-5_3
Skakun S., Justice C. O., Vermote E., Roger J.-C. (2018). Transitioning from modis to viirs: an analysis of inter-consistency of ndvi data sets for agricultural monitoring. Int. J. Remote Sens. 39, 971–992. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2017.1395970
Steduto P., Hsiao T. C., Raes D., Fereres E. (2009). AquaCrop—The FAO crop model to simulate yield response to water: I. Concepts and underlying principles. Agron. J. 101, 426–437. doi: 10.2134/agronj2008.0139s
Stefanini F. M., Valleggi L. (2022). A bayesian causal model to support decisions on treating of a vineyard. Mathematics 10. doi: 10.3390/math10224326
Tan D., Adedoyin F. F., Alvarado R., Ramzan M., Kayesh M. S., Shah M. I. (2022). The effects of environmental degradation on agriculture: Evidence from European countries. Gondwana Res. 106, 92–104. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2021.12.009
Terán-Chaves C. A., García-Prats A., Polo-Murcia S. M. (2022). Calibration and validation of the FAO aquaCrop water productivity model for perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Water 14, 3933. doi: 10.3390/w14233933
Toth C., Jóźków G. (2016). Remote sensing platforms and sensors: A survey. ISPRS J. Photogrammetry Remote Sens. 115, 22–36. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2015.10.004
Umesh B., Reddy K., Polisgowdar B., Maruthi V., Satishkumar U., Ayyanagoudar M., et al. (2022). Assessment of climate change impact on maize (zea mays l.) through aquacrop model in semi-arid alfisol of southern telangana. Agric. Water Manage. 274, 107950. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2022.107950
Valleggi L., Carella G., Perria R., Mugnai L., Stefanini F. M. (2023). A Bayesian model for control strategy selection against Plasmopara viticola infections. Front. Plant Sci. 14. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1117498
Valleggi L., Scutari M., Stefanini F. M. (2024). Learning Bayesian networks with heterogeneous agronomic data sets via mixed-effect models and hierarchical clustering. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 131, 107867. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2024.107867
Keywords: machine learning, precision agriculture, statistical learning, crop yield, disease detection, sustainability
Citation: Valleggi L and Stefanini FM (2024) A mini-review on data science approaches in crop yield and disease detection. Front. Agron. 6:1352219. doi: 10.3389/fagro.2024.1352219
Received: 07 December 2023; Accepted: 11 March 2024;
Published: 08 April 2024.
Edited by:
Simone Ugo Maria Bregaglio, Council for Agricultural and Economics Research (CREA), ItalyReviewed by:
Alexa Lamm, University of Georgia, United StatesCopyright © 2024 Valleggi and Stefanini. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lorenzo Valleggi, lorenzo.valleggi@unifi.it; Federico Mattia Stefanini, federico.stefanini@unimi.it
 Lorenzo Valleggi
Lorenzo Valleggi Federico Mattia Stefanini
Federico Mattia Stefanini