- 1Department of Entomology, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, United States
- 2Department of Animal Science, McGill University, Ste. Anne de Bellevue, QC, Canada
- 3Department of Biology, Baylor University, Waco, TX, United States
Introduction: Females of the Northern house mosquito, Culex pipiens, enter an overwintering dormancy, or diapause, in response to short day lengths and low environmental temperatures that is characterized by small egg follicles and high starvation resistance. During diapause, Culex pipiens Major Royal Jelly Protein 1 ortholog (CpMRJP1) is upregulated in females of Cx. pipiens. This protein is highly abundant in royal jelly, a substance produced by honey bees (Apis mellifera), that is fed to future queens throughout larval development and induces the queen phenotype (e.g., high reproductive activity and longer lifespan). However, the role of CpMRJP1 in Cx. pipiens is unknown.
Methods: We first conducted a phylogenetic analysis to determine how the sequence of CpMRJP1 compares with other species. We then investigated how supplementing the diets of both diapausing and nondiapausing females of Cx. pipiens with royal jelly affects egg follicle length, fat content, protein content, starvation resistance, and metabolic profile.
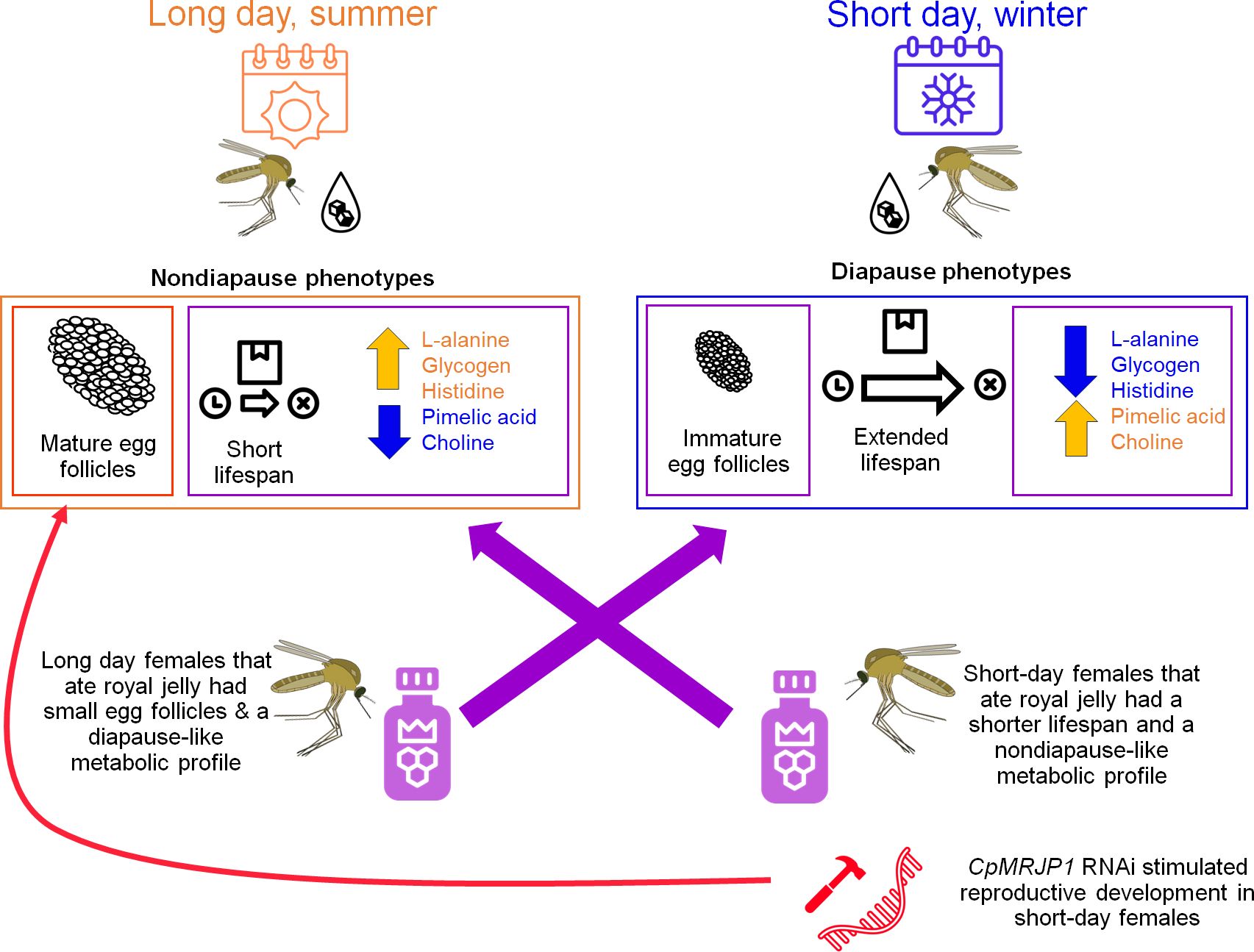
Results: We found that feeding royal jelly to females reared in long-day, diapause-averting conditions significantly reduced the egg follicle lengths and switched their metabolic profiles to be similar to diapausing females. In contrast, feeding royal jelly to females reared in short-day, diapause-inducing conditions significantly reduced lifespan and switched their metabolic profile to be similar nondiapausing mosquitoes. Moreover, RNAi directed against CpMRJPI significantly increased egg follicle length of short-day reared females, suggesting that these females averted diapause.
Discussion: Taken together, our data show that consuming royal jelly reverses several key seasonal phenotypes of Cx. pipiens and that these responses are likely mediated in part by CpMRJP1.
1 Introduction
Females of the Northern house mosquito, Culex pipiens, enter diapause in response to short daylengths and low environmental temperatures that act as harbingers of the approaching winter (1). Diapause allows mosquitoes to survive unfavorable winter conditions (2, 3), and it involves a unique suite of behavioral, hormonal and metabolic changes (4–6). In Cx. pipiens, exposure to short days as eggs, larvae, pupae and early adults causes adult females to enter an adult reproductive diapause (7). Diapause in females of Cx. pipiens is characterized by reproductive arrest, resulting in a decrease in the size of egg follicles as females divert energy away from reproduction (8). Adult mosquitoes that enter diapause feed on sugar-rich plant nectar, causing an increase in whole-body fat content (5, 9). Several genes that regulate metabolism are differentially expressed between diapausing and nondiapausing female mosquitoes; specifically, Robich and Denlinger (5) found that a gene associated with lipid accumulation, fatty acid synthase, was upregulated in diapausing females of Cx. pipiens, while two genes that encode enzymes related to digesting a blood meal, trypsin and chymotrypsin-like proteins, were down-regulated. Although many of the genes involved in generating diapause phenotypes have been well-characterized, it is still unclear what genes and proteins regulate diapause and initiate largescale metabolic and behavioral changes. However, insulin signaling and the Forkhead Transcription Factor, FOXO, have been implicated in regulating diapause responses in Cx. pipiens and several other insect species [reviewed in (10, 11)].
Royal jelly is produced by worker honey bees (Apis mellifera), and is a rich source of amino acids, lipids, vitamins, and other nutrients (12). Specifically, Nagai and Inoue (13) found that royal jelly consists of water (50–60%), proteins (18%), carbohydrates (15%), lipids (3–6%) as well as smaller amounts of water-soluble vitamin B and related components including vitamin B1, vitamin B2, vitamin B6, biotin, acetylcholine, pantothenic acid, inositol, and nicotinic acid. Worker bees and drones feed on royal jelly for the first 3 and 5 days of larval life respectively, after which they feed on beebread (a type of fermented pollen) and honey. However, future queen bees consume royal jelly exclusively, and this induces female larvae to follow the queen developmental trajectory that is characterized by high reproductive outputs and a longer lifespan (14, 15). One protein in royal jelly, referred to as Major Royal Jelly Protein 1 (AmMRJP1), produces strong antibacterial activity and is the most abundant glycoprotein within royal jelly, constituting over 50% of total protein content (16, 17). Surprisingly, the gene encoding the ortholog of AmMRJP1 in Cx. pipiens (CpMRJP1) is upregulated by FOXO and is more abundantly expressed in whole bodies of diapausing females of Cx. pipiens (18). The tissue specificity of CpMRJP1 transcription and translation as well as the function of CpMRJP1 in diapausing mosquitoes has not been characterized. However, the upregulation of CpMRJP1 in diapausing mosquitoes is surprising because these females are not reproductively active but do live substantially longer than nondiapausing females, especially in the absence of food (8).
Although it is unclear how increasing the abundance of AmMRJP1 or its orthologs impacts animals, several studies demonstrate that consuming royal jelly affects the physiology of invertebrates and mammals, including humans. Integrating royal jelly into human diets can improve reproductive health, combat neurodegenerative disorders, slow aging, and promote wound-healing (19). In rats, proteins in royal jelly can also function as antioxidants, protecting the testes of males against oxidative stress (20). Additionally, supplementing the diets of male rams with royal jelly increases sperm motility and viability (21). Similarly, royal jelly positively impacts fertility as well as semen quality and quantity in male rabbits (22). Introducing royal jelly into the diet of Drosophila melanogaster (L.) extends adult lifespan in males and females, possibly by increasing antioxidant activity, and stimulates feeding behavior and fecundity in females (23). Royal jelly also extends adult lifespan in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans (Maupas) (24), suggesting that royal jelly may promote longevity across a wide range of invertebrates. Moreover, Fischman et al. (25) demonstrate that consuming royal jelly enhances the likelihood that alfalfa leaf cutting bees will enter diapause. While several studies have examined the role of royal jelly in animals, little is known about how consuming royal jelly might influence the seasonal responses and metabolic profile of mosquitoes, and to what extent these changes are induced by MRJP1.
Although metabolomic studies to uncover the differences between diapausing and nondiapausing Cx. pipiens have not been completed, previous research has examined metabolic differences between diapasuing and nondiapausing Asian tiger mosquitoes, Aedes albopictus (Skuse), flesh flies Sarcophaga crassipalpis (Macquart), and parasitic wasps, Nasonia vitripennis (Walker) (26–28). Not surprisingly, metabolomic studies demonstrate that diapausing mosquitoes, flesh flies, and parasitic wasps upregulate metabolites that act as cryoprotectants (26–28). In diapausing N. vitripennis the abundance of members of the glycolysis pathway are more abundant, reflecting an overall perturbation of the metabolic pathways in diapause (28). In Ae. albopictus, the monoamine neurohormones dopamine and octopamine, as well as phosphocholine and oleoyl glycine were more abundant in nondiapausing eggs compared to diapausing eggs (26). One objective of this study is to identify specific metabolites that are differentially abundant between diapausing and nondiapausing Cx. pipiens and how consuming diets that include royal jelly influences the overall metabolome of long and short-day reared mosquitoes.
Females of Cx. pipiens (L.) transmit pathogens that cause St. Louis encephalitis (29), West Nile virus (30), and canine heartworm (31) that infect millions of humans and animals each year (32). Female mosquitoes transmit these pathogens when they take a bloodmeal from a human or animal host (33). However, disease transmission is not equally distributed across time (34), in large part because diapausing mosquitoes no longer ingest blood (6) and, as a result, no longer transmit diseases (34). Therefore, uncovering molecular regulators of diapause in mosquitoes and other blood-feeding arthropods may offer novel opportunities to control these disease vectors and thereby improve human and animal health.
We first conducted phylogenetic analyses to determine how the sequence of CpMRJP1 compared to that in other insects. To characterize how consuming royal jelly affects seasonal phenotypes in mosquitoes, we measured the abundance of CpMRJP1 mRNA transcripts, reproductive development, lifespan, overall fat and protein content, as well as the metabolic profile of long and short-day reared females of Cx. pipiens that had consumed sugar water only (control) and those that consumed diets that included royal jelly. We also assessed which, if any, of the physiological impacts of royal jelly on seasonal responses were mediated by CpMRJP1 by using RNA interference (RNAi) to knock down this transcript in mosquitoes reared in long-day, diapause-averting and short day, diapause-inducing conditions. We hypothesized that mosquitoes that consumed diets including royal jelly would enter a diapause-like state regardless of environmental conditions, characterized by small egg follicles and increased longevity. Accordingly, we hypothesized that long and short-day reared mosquitoes that consumed royal jelly, and therefore had higher levels of AmMRJP1 within their guts, would exhibit a metabolic profile that was similar to that of diapausing mosquitoes that consumed sugar water. In contrast, we hypothesized that knocking down CpMRJP1 with RNAi would prevent mosquitoes reared in short-day, diapause-inducing conditions from entering diapause and would decrease longevity.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Sequence alignment and phylogenetic analyses
The amino acid sequence of Culex quinquefasciatus MRJP1 (CPIJ008700) was extracted from Vectorbase (https://vectorbase.org/vectorbase/app/) and fed into NCBI blastp search (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi) to identify the potential evolutionary origin of this protein. Amino acid sequences from the top dipteran matches were extracted and used for comparison and determination of phylogenetic relationships among dipteran species. As Drapeau et al. (14) indicate that MRJP1 is closely-related to the yellow gene in insects, the amino acid sequences of yellow from Culex quinquefasiatus, extracted from Vectorbase, and yellow and its associated paralogs in Drosophila melanogaster, extracted from FlyBase, were used for the phylogenetic analysis. The following amino acid sequences were used to make the phylogenetic tree: MRJP1 from Cx. quinquefasciatus (XP_001850268.2), MRJP1 from Apis mellifera (NP_001011579.1), MRJP1 from Aedes aegypti (XP_021693794.1), MRJP1-like from Sabethes cyaneus (XP_053682299.1), MRJP1-like isoform X2 from Anopheles funestus (XP_049285312.1), yellow from Cx. quinquefasiatus (CQUJHB005397), yellow from D. melanogaster (FBgn0004034), yellow-like from Ae. albopictus (XP_019534039.2), yellow-like from Anopheles maculipalpis (XP_050069861.1), yellow-like from An. merus (XP_041787038.1), yellow-like from An. nili (XP_053679995.1), yellow-like isoform X1 from An. funestus (XP_049285311.1), yellow-like from An. moucheti (XP_052891110.1), yellow-like from An. marshallii (XP_053669181.1), yellow-like from An. stephensi (XP_035901855.1), yellow-like from An. cruzii (XP_052868860.1), yellow-like from An. aquasalis (XP_050087457.1). The following paralogs from D. melanogaster were also included: yellow-b (FBgn0032601), yellow-c (FBgn0041713), yellow-d (FBgn0041712), yellow-d2 (FBgn0034856), yellow-e (FBgn0041711), yellow-e2 (FBgn0038151), yellow-e3 (FBgn0038150), yellow-f (FBgn0041710), yellow-f2 (FBgn0038105), yellow-g (FBgn0041709), yellow-g2 (FBgn0035328), yellow-h (FBgn0039896).
Sequence alignment was performed using Clustal Omega (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/jdispatcher/msa/clustalo) and phylogenetic analyses were conducted using the maximum likelihood method in MEGA 11 software, with bootstrap values calculated from 500 trees (35). To characterize the protein composition and domains, we conducted an InterProScan search (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/search/sequence/).
2.2 Mosquito rearing
A colony of Culex pipiens established in June 2013 from Columbus, Ohio (Buckeye strain) was used in this experiment. From the time that they were first instar larvae and until the adults were collected for analyses, mosquitoes were reared at 18°C and exposed to either long-day, diapause-averting conditions (photoperiod of Light: Dark 16:8 hr) or short-day, diapause-inducing conditions (photoperiod of L:D 8:16 hr). Larvae were reared in plastic containers filled with reverse osmosis water and were fed a diet of ground fish food (Tetramin Tropical Fish Flakes) according to the procedure described by Meuti et al. (36). To optimize our metabolomic procedure and allow us to acquire spectra from single mosquitoes, we conducted a preliminary experiment where mosquito pupae were transferred to cages that contained sugar water only. For all subsequent experiments, pupae from both the long and short-day photoperiods were randomly and equally divided into two cages, one that contained sugar water only (control) and one that contained 2 g of Royal Jelly (Starkish) that was dissolved in 1.5 mL of 10% sucrose solution (experimental treatment). Adult mosquitoes consumed their prescribed dietary treatments ad libitum (4 treatments total; n≅150 adults/treatment). One week after peak adult emergence, mosquitoes were euthanized and collected for experimental analyses.
2.3 Measuring the abundance of MRJP1 mRNA
Quantitative real time PCR (qRT-PCR) was used to assess how the abundance of CpMRJP1 was affected by supplementing the diet of adult mosquitoes with royal jelly. The procedure for qRT-PCR was based on (37). We designed primers for CpMRJP1 (CPIJ008700-RA) using Primer3 (Forward: TGAACGATCGTCTGCTGTTC; Reverse: TCCTCCCACATGGTATCGTT; (38). A standard curve verified that the primers met the MIQE guidelines (39). RNA was isolated from female mosquitoes (n=5 females/biological replicate; 5 biological replicates/rearing condition and feeding treatment) one week following adult emergence using TRIzol according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Complementary DNA (cDNA) was synthesized using the SuperScript III kit (Invitrogen), following the manufacturer’s instructions. All qRT-PCR reactions were done in triplicate on a 96-well plate using a CFX Connect qRT-PCR machine (BioRad). Each well contained a 10 μL reaction, consisting of 5 μL of iTaq Universal SybrGreen Supermix (BioRad), 400 nM of forward and reverse primers for either CpMRJP1 or our reference gene (Ribosomal Protein 19; RpL19; 39), 3.2 μL of molecular grade water, and 1 μL of cDNA. qRT-PCR reactions were completed through an initial denaturation at 94°C for 2 min, followed by 40 cycles at 94°C for 15 sec and 60°C for 1 min. A melt curve was run after each qRT-PCR reaction to ensure that only a single PCR product was produced. The abundance of CpMRJP1 transcripts was normalized to the abundance of RpL19 using the 2-ΔCT method as previously described (40). We ran a model to ensure that the abundance of RpL19 mRNA did not differ significantly among dietary treatments (p = 0.778) and therefore was a suitable reference gene for this study.
2.4 Assessing diapause status
To assess the diapause status of long and short day-reared females that had consumed sugar water (control) or diets that included royal jelly, we used two common markers of diapause: egg follicle length and fat content. One-week after adult emergence, we randomly euthanized 20 female mosquitoes from each dietary and rearing treatment and dissected their ovaries and egg follicles in a 0.9% saline solution (NaCl). The length of 10 egg follicles/female were measured at 200 times magnification using an inverted microscope (Nikon; n = 20 females/treatment). We also randomly selected eight, one-week-old females from the same cohorts and dietary treatments and measured the fat content in each female mosquito using a Vanillin lipid assay (41) that was modified to allow us to measure samples using a plate reader (42). The data were normalized by dividing the measured lipid content by the lean mass of the whole-body mosquito (lean mass = μg mosquito wet mass - μg of lipid).
2.5 Measuring protein content
As royal jelly is protein-rich, we also wanted to determine whether supplementing the diet with royal jelly affected the whole-body protein content of female mosquitoes. The protein content within eight, randomly selected individual female mosquitoes from the same cohort and dietary treatments as the lipid and egg follicle treatments was measured using a Bradford Assay kit (BioRad) following the manufacturer’s instructions (43). In brief, each female mosquito was weighed and then homogenized in 200 μL of a 10% ethanol solution. Samples were added in triplicate to a 96-well plate, and 250 μL of Quick Start Bradford 1X Dye Reagent (BioRad) was added to each well. The absorbance of each sample was measured using a FLUOStar Omega Microplate Reader. Measurements were normalized by dividing the protein content by the wet mass of each female mosquito (44).
2.6 Evaluating longevity in the absence of food
In the field, diapausing females are able to survive for 3–6 months in without access to food (45). Therefore, we wanted to determine how dietary conditions affected the lifespan of female mosquitoes in the absence of food. Long and short-day reared mosquito pupae were placed in cages with access to sugar water or royal jelly (4 treatments total). One week after peak adult emergence, all male mosquitoes as well as the royal jelly or sugar-water food sources were removed from each cage. The remaining females (n = 70 – 75 females/treatment) were counted and allowed constant access to water. Every week thereafter we counted and removed dead females from the cage until no female mosquitoes remained.
2.7 Performing metabolomic analyses
The experimental protocol for all metabolomic analyses employed tissue extraction followed by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) analysis and was based on the procedure described in Wu et al. (46). One mosquito was weighed and placed in a 2 mL microtube with approximately 750 mg of ceramic beads. For our initial experiment, 3 short-day reared, diapausing and 3 long-day reared, nondiapausing mosquitoes that had consumed sugar water only were used. For our second experiment, 10 independent female mosquitoes from each photoperiodic and dietary treatment, and from the same cohort as the egg follicle, fat content, and protein measurement experiments were randomly selected (n = 40 total). Mosquito samples were homogenized in 400 µL cold methanol and 85 µL water, and the homogenate was transferred to a separate tube without beads. Next, 400 µL chloroform and 200 µL water were added to the homogenate, which was then vortexed and centrifuged (2,000 rcf for 5 min at 4°C). The aqueous (methanol) layer was isolated and collected in a new 1.5 mL microtube before being dried in an evaporator. Deuterium oxide (heavy water), trimethylsilylpropanoic acid (TSP), and boric acid were added to the evaporated extracts and vortexed. The pH of the samples was manually adjusted to 7.4 and then transferred to 5 mm NMR tubes.
The metabolites in each mosquito sample were measured using NMR spectroscopy following the procedure detailed in (47). 1D 1H NOESY spectra were obtained for the aqueous extracts. In addition, one 1H-13C HSQC spectrum of a pooled sample was acquired for the four separate dietary and photoperiodic conditions according to (48). Avance III HD 800 and Ascend 850 MHz spectrometers, each with an inverse cryoprobe and z-gradients (Bruker BioSpin, Billerica, MA), were utilized to obtain NMR measurements, and resulting NMR spectra were analyzed as described in Newell et al. (47) and (49). Topspin 3.6.1 and AMIX 3.9.15 software (Bruker BioSpin, Billerica, MA) were used for preprocessing. The untargeted approach of spectral binning was chosen, where each spectrum is divided into small sections, or bins, which are subsequently analyzed. It should be noted that this approach provides broad coverage across various classes of metabolites, as compared to a targeted approach where only a predefined subset of metabolites of interest is quantified. In the initial experiment to optimize the protocol, 1D NMR spectra were binned with a bin width of 0.005 ppm. In contrast, for the second experiment that evaluated the effects of consuming diets that included royal jelly, the bin width was lowered to 0.003 ppm because these measurements were taken using a higher-frequency instrument (850MHz). Spectra were binned using the R package mrbin [Version 1.5.0; (50)}. Signals that showed large inter-spectra chemical shift differences were manually added to broader bins. Noise signals were automatically removed, and data was scaled using PQN (probabilistic quotient normalization) to correct for differences in sample mass and extraction efficacies. Each bin was then scaled to unit variance. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) models were generated to visualize metabolic data and screen for outliers regarding data quality. Signals of interest were identified using public databases and identifications were validated using the acquired HSQC spectrum and measurements of pure samples.
2.8 Assessing the effect of knocking down MRP1 with RNAi
RNA interference (RNAi) was used to knock down CpMRJP1 mRNA to evaluate how this protein affects the diapause status of female mosquitoes. The procedure for RNA interference was based on the protocol detailed in (37). Double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) specific to CpMRJP1 and Beta-galactosidase from E. coli (β-gal; control) were synthesized using the Promega T7 RNAi Express Kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions. We selected β-gal dsRNA as a control because mosquitoes do not consume lactose and hence genes encoding β-gal proteins are absent from their genomes, and because we have previously used β-gal dsRNA as a control in RNAi experiments (37, 40). We designed primers to synthesize a 230 bp fragment of CpMRJP1 (CPIJ008700-RA) in Cx. pipiens using Primer3 (Forward: CACCGCCAAACCGAACAAAT; Reverse: TGAGCAGCCCAAAGTACAGG; 37), which served as the template to create dsRNA. On the day of adult emergence, 3 μg of either β-gal or CpMRJP1 dsRNA was injected into the thorax of long and short day-reared mosquitoes. Following injection, females were placed into small plastic containers (4.62 x 6.75 x 7.19 inches) where they consumed 10% sucrose solution ad libitium. To confirm gene knockdown, RNA was isolated using Trizol according to the manufacturer’s instructions from 3 biological replicates each containing 5 whole-body, female mosquitoes that were euthanized two days after dsRNA injection. cDNA was synthesized and qRT-PCR was conducted as described above (section 2.3), except that we used CpMRJP1 qRT-PCR primers that were previously designed by Sim et al. (18), and that after normalizing CpMRJP1 expression to the RpL19 reference gene, CpMRJP1 expression was again normalized to its expression in β-gal-dsRNA injected mosquitoes from the same photoperiodic condition (40).
To determine how CpMRJP1 dsRNA affected seasonal phenotypes, the egg follicle lengths (n = 20) and fat content (n = 8) of randomly selected females were measured ten days following dsRNA injection as described above (section 2.4). After feeding on sugar water for one week, the lifespan of β-gal or dsMRJP1 dsRNA-injected females (n = 37 – 49 females/treatment) in the absence of food was also measured as described above (section 2.5).
2.9 Data analysis
All data analyses were conducted in R version 3.3.3 (51). Two-way ANOVAs and Tukey’s post-hoc tests were used to determine whether dietary treatment and/or photoperiod significantly affected CpMRJP1 mRNA abundance, egg follicle length, lipid content, and protein content in female mosquitoes. Student’s T-tests were used to determine whether injecting CpMRJP1 dsRNA effectively reduced CpMRJP1 mRNA abundance, while two-way ANOVAs were used to determine whether dsRNA injection and photoperiod significantly affected the egg follicle length or fat content. A value of alpha < 0.05 was applied to discern statistical significance.
To determine how supplementing the diet with royal jelly and knocking down CpMRJP1 with RNAi affected the longevity of female mosquitoes in the absence of food, we used Cox-proportional hazards models (survival package) that included the effects of diet and photoperiod. Hazard ratios were obtained from these models as an estimate of the ratio between the risk of dying between photoperiodic and dietary treatments, where negative hazard ratios (HR) indicate a protective effect. Kaplan Meier survival curves were also plotted and used to provide the median survival time or the time at which 50% of the population was still alive as defined by (52, 53), and log-rank tests were used to determine significant differences between treatments.
For analysis of NMR metabolomics data, for each spectral bin, a general linear model (GLM) was created to account for the effect of diet (sugar water or royal jelly), photoperiod (long or short day-rearing conditions), and the interaction term between diet and photoperiod. To correct resulting p-values multiple testing, we used a False Discovery Rate (FDR) of 5% (54). Signals that were significant in the GLM analysis were tested for pairwise group differences using Tukey’s Honest Significant Difference (HSD) test. An Artificial Neural Network (ANN) was generated using R packages keras (version 2.11.1) and tensorflow (version 2.11.0). A dense network was generated with one input neuron per NMR bin (N=1823), 200 hidden neurons with ReLU activation function, and 2 output neurons, representing “short day” and “long day” rearing conditions. The ANN was trained on the data from the “sugar water” group using leave-one-out cross validation. Samples from the “royal jelly” group were then predicted using the trained ANN.
Pathway enrichment analysis was performed by downloading KEGG pathway maps of Culex pipiens pallens with KEGG code cpii (55) using the R package KEGGREST (version 1.36.3). Fisher’s Exact Test was used to assess the number of matching metabolites per pathway. A pathway uniqueness score u was calculated as follows: For each pathway, each observed metabolite was assigned the inverse of the number of pathways in which this metabolite occurs organism-wide, then the maximum value was chosen as the pathway uniqueness score. Therefore, higher values of u indicate pathways with more metabolites that uniquely occur in that respective pathway, and we further investigated pathways with u≥0.2.
3 Results
3.1 Phylogenetic analysis of Culex pipiens MRJP1
To identify the evolutionary relationships of Cx. pipiens MRJP1 with MRJP/yellow homologues in other insects, we conducted a phylogenetic analysis using amino acid sequences of MRJP/yellow proteins from dipteran species. First, we conducted a BLAST search using the protein sequence of Cx. quinquefasciatus MRJP1 (CPIJ008700) and extracted the amino acid sequences of the top hits from dipteran species. We also obtained the protein sequences of Yellow in Cx. quinquefasciatus and D. melanogaster, as well as 13 Yellow-like proteins in D. melanogaster from Vectorbase (56). Multiple sequence alignment was performed to compare sequence identity between species. The sequence identity between Cx. quinquefasciatus MRJP1 and Yellow from D. melanogaster was found to be 23.41%, while it was 21.39% with Yellow from Cx. quinquefasciatus. This result is consistent with the high identity of 20–30% shared between MRJP and Yellow paralogs in D. melanogaster, suggesting a common evolutionary origin (57). Additionally, we performed a sequence identity comparison between MRJP1 proteins from Cx. quinquefasciatus and Apis mellifera to gain insights into the evolutionary and functional aspects of this protein. Our findings unveil that MRJP1 in these species share 129 identical amino acid residues, corresponding to a percent identity of 26.88%. Through alignment of the amino acid sequences between Yellow and MRJP1 in Cx. quinquefasciatus, D. melanogaster, and Apis mellifera, we identified a consensus conserved MRJP domain in all four sequences, indicating the preservation of the MRJP domain throughout insect evolution (Figure 1A).
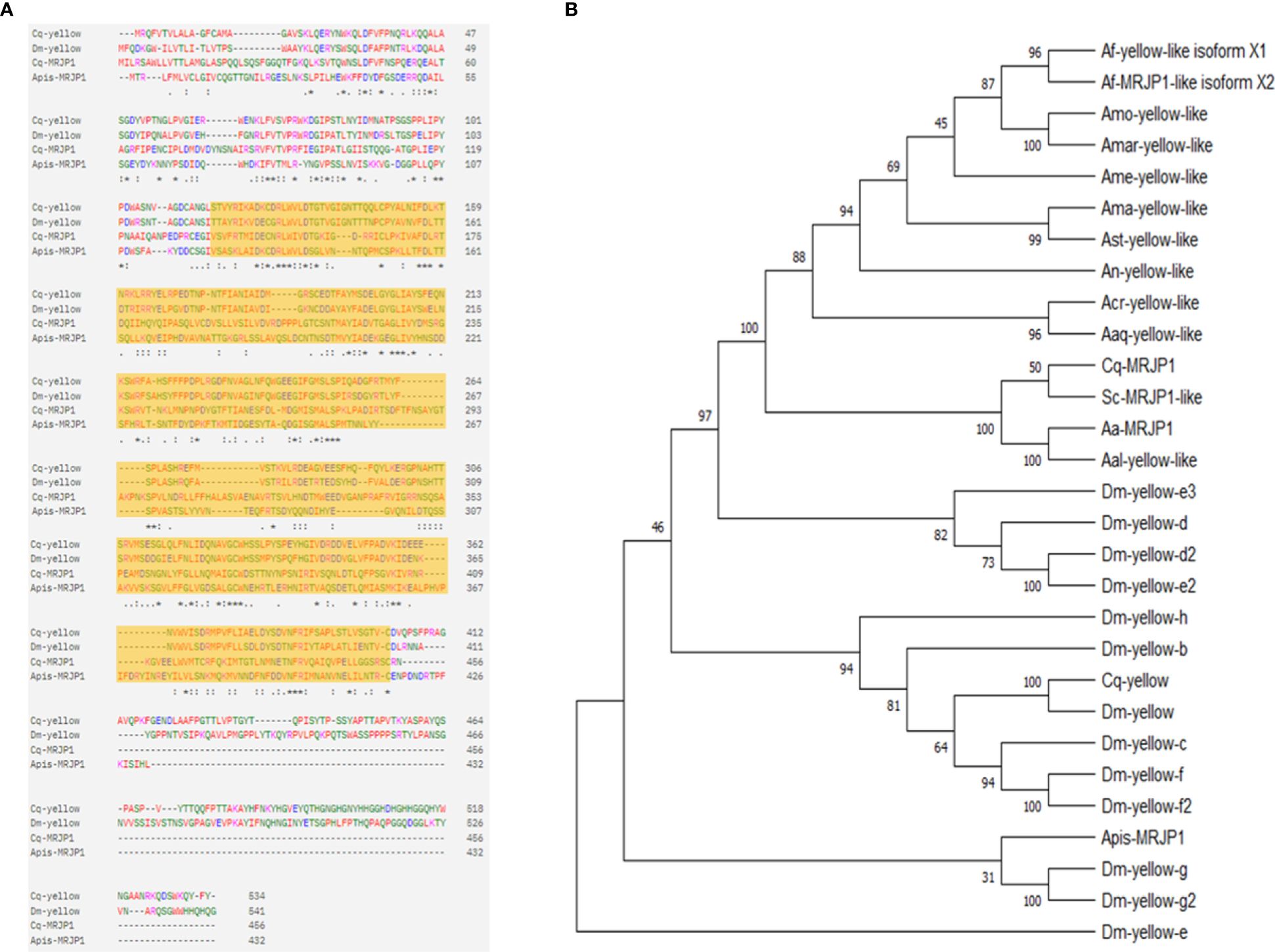
Figure 1 Phylogenetic analysis and sequence alignment of MRJP/Yellow family proteins’ sequences in insect species. (A) Sequence alignment on the amino acid sequences of Yellow and MRJP1 proteins from Culex quinquefasciatus, Drosophila melanogaster, and Apis mellifera. The highlighted region indicates the conserved MRJP domain present in all four sequences; the . : or * indicate amino acid residues that are conserved across 2, 3 or 4 sequences. (B) The phylogenetic tree was generated using MEGA v.11 maximum likelihood estimation with bootstrap analysis. The bootstrap consensus tree inferred from 500 replicates is taken to represent the evolutionary history of the taxa analyzed (Felsenstein, 1985). The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test 500 replicates are shown next to the branches. Apis, Apis mellifera; Aal, Aedes albopictus; Ast, Anopheles stephensi; An, Anopheles nili; Acr, Anopheles cruzii; Aa, Aedes aegypti; Amo, Anopheles moucheti; Amar, Anopheles marshallii; Sc, Sabethes cyaneus; Aaq, Anopheles aquasalis; Af-yellow, Anopheles funestus; Ame, Anopheles merus; Cq, Culex quinquefasciatus; Ama, Anopheles maculipalpis; Af, Anopheles funestus; Dm, Drosophila melanogaster.
We also conducted a functional analysis of Cx. quinquefasciatus MRJP1 using InterProScan and found that it belongs to the Royal jelly/protein yellow family in the InterPro database and the MRJP family in the Pfam database. This result is consistent with previous findings indicating that all Yellow proteins have a conserved MRJP domain (58). Subsequently, we used these sequences to create a phylogenetic tree to discover evolutionary relationships (Figure 1B). The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated H3 clustered together in 500 bootstrap replicates is shown adjacent to the branches. The tree was drawn to scale, with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic tree. In the resulting phylogenetic tree, Yellow proteins in Cx. quinquefasciatus and D. melanogaster were found to be closely related and clustered together with all other Yellow paralogs in D. melanogaster. As expected, Cx. quinquefasciatus MRJP1 closely clustered with MRJP/Yellow-like proteins from other dipteran species identified in the BLAST top matches. However, MRJP1 was found to be farther away from Yellow from Cx. quinquefasciatus and D. melanogaster and other Yellow paralogs from D. melanogaster as well as MRJP1 in A. meliferra (Figure 1B). The distant relationship between Yellow of Cx. quinquefasciatus and D. melanogaster and MRJP1 in Cx. quinquefasciatus revealed by our phylogenetic analysis suggests that MRJP1 likely has different functions and targets than Yellow in D. melanogaster.
3.2 Measuring MRJP1 mRNA abundance in response to rearing and dietary conditions
The relative abundance of MRJP1 mRNA did not change significantly in response to dietary treatment or photoperiodic conditions (Figure 2A). A two-way ANOVA revealed that there was not a statistically significant interaction between the effects of diet and photoperiod on the abundance of CpMRJP1 mRNA (F1,16 = 0.589, p = 0.458). Simple main effects analysis showed that diet did not have a statistically significant effect on CpMRJP1 abundance (F1,16 = 0.025, p = 0.876). Contrary to previous experiments (18), there was no significant difference in the abundance of MRJP1 transcripts between females reared in long day or short-day conditions (F1,16 = 2.67, p = 0.122), likely due to high levels of variation in CpMRJP1 transcript abundance in the short-day reared females.
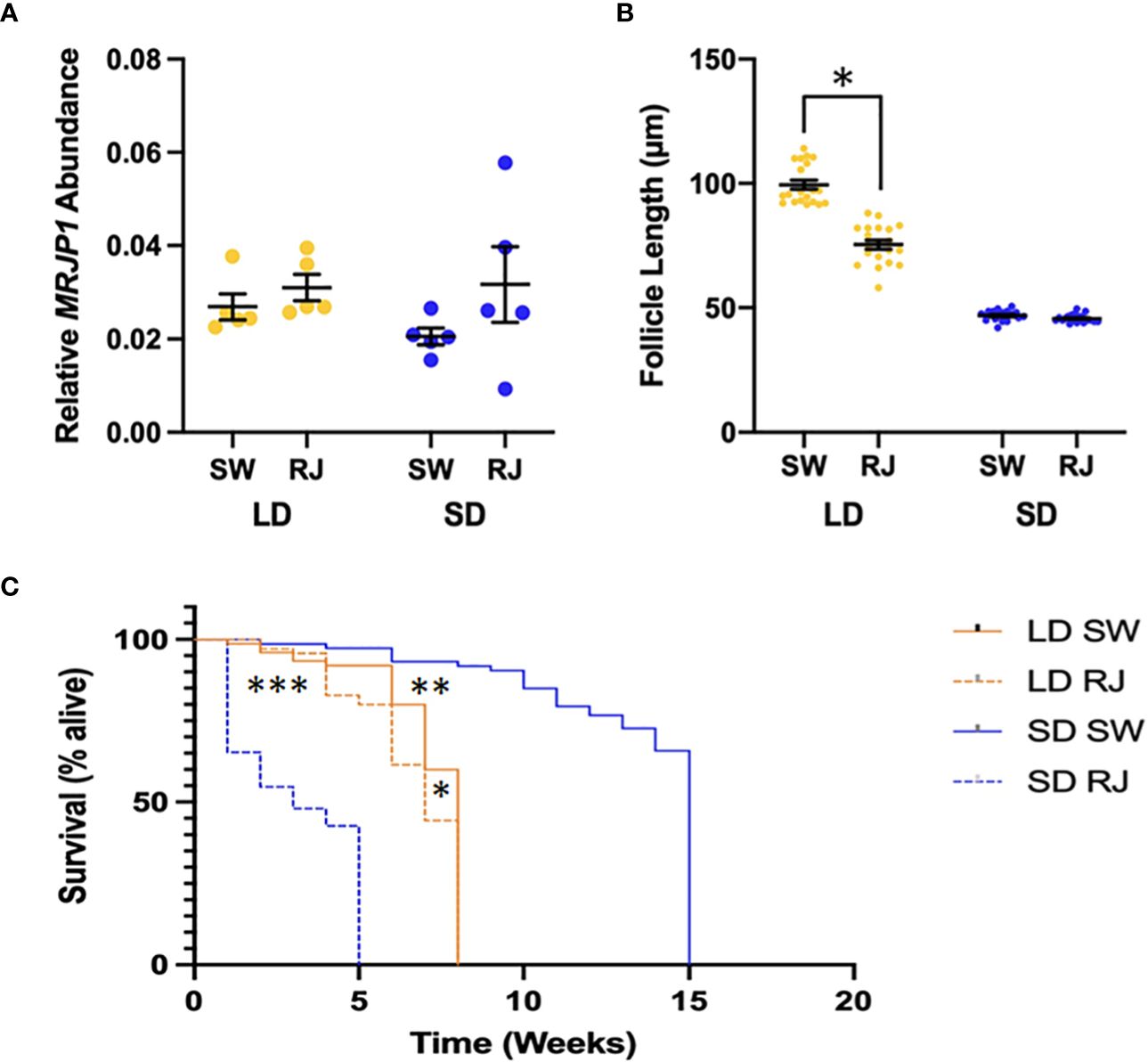
Figure 2 Phenotypic effects of consuming royal jelly (RJ) in mosquitoes. (A) Consuming RJ did not have any significant effect on relative MRJP1 mRNA abundance in long day (LD) or short day (SD) reared mosquitoes. (B) Consuming RJ significantly decreases egg follicle length in long day (LD) mosquitoes. Significant difference denoted by * (Tukey’s post-hoc test; p < 0.001). (C) The lifespan of female mosquitoes was significantly different between long day (LD) and short day (SD) mosquitoes. The consumption of royal jelly (RJ) by mosquitoes in both rearing conditions led to a significant decrease in lifespan. Significant differences denoted by *** (SD RJ to SD SW; p < 0.001), ** (LD SW to SD SW; p < 0.001) and * (LD RJ to LD SW; p = 0.03).
3.3 Assessing the effects of royal jelly on mosquito diapause status and lifespan
Egg follicle length can be used to determine diapause status of female mosquitoes of Cx. pipiens (5,8), such that an average egg follicle length of less than 75 μm indicates diapause, follicle lengths between 75 and 90 μm indicates an intermediate state, and follicles greater than 90 μm indicates nondiapause (42). We used a two-way ANOVA to evaluate the effects of both photoperiod and diet on egg follicle size. Our model revealed that both photoperiod (F1,76 = 1008.2, p < 0.001) and diet (F1,76 = 95.32, p < 0.001) independently affected egg follicle length. Moreover, there was a significant interaction between photoperiod and diet on egg follicle length (F1,76 = 78.4; p < 0.001). As expected, one week after adult emergence all long-day reared females that consumed sugar water (controls) were in a clear nondiapause state (Figure 2B; average egg follicle length of 99.5 ± 1.8 μm). However, 50% of long-day reared females that consumed diets including royal jelly had egg follicles that were characteristic of being in diapause, while the remaining females were in an intermediate state, and none of the long day-reared females that had consumed diets including royal jelly had egg follicle lengths that were large enough to be considered in a nondiapause state (Figure 2B). Therefore, consuming royal jelly caused a significant decrease in the overall average egg follicle length in long-day reared females (average egg follicle length of 75.4 ± 1.8 μm; Tukey’s post-hoc test, p < 0.001, 95% CI = [19.3, 28.9]). Females reared in short-day conditions had significantly smaller egg follicles compared to those reared in long-day conditions (Tukey’s post-hoc test, p < 0.001, 95% CI = [-43.7, -38.5]). All females reared in short-day conditions were in a clear diapause state (Figure 1B), regardless of whether they consumed sugar water only (46.9 ± 0.4 μm) or diets that included royal jelly (45.7 ± 0.3 μm); therefore dietary treatment did not effect the egg follicle length of dietary treatment did not significantly impact egg follicle length of short day-reared females (Tukey’s post-hoc test, p = 0.92).
We also used a two-way ANOVA to assess whether dietary treatment and/or photoperiod affected the fat content of female mosquitoes (Supplementary Figure S2A), as previous studies demonstrate that diapausing females accumulate significantly higher levels of fat than nondiapausing mosquitoes (37, 42). Our analyses revealed that neither photoperiod (F1,28 = 0.378, p = 0.54) nor diet (F1,28 = 0.567, p = 0.458) affected fat content. However, there was a slight but non-significant interaction between photoperiod and diet (F1,28 = 3.91, p = 0.058). Short day-reared females that consumed sugar water had higher levels of lipid relative to those that consumed royal jelly, although this result was not statistically significant (SD RJ = 22.19 ± 2.46% lipid; SD SW = 29.48 ± 4.75% lipid; Tukey’s HSD, p = 0.822).
A two-way ANOVA of the effects of photoperiod and diet on protein content revealed that photoperiod (F1,25 = 4.97, p = 0.035) but not diet (F1,25 = 0.03, p = 0.865) significantly affected the protein levels within female mosquitoes. Our analyses also revealed that there was no significant interaction between photoperiod and diet on protein content (F1,25 = 0.03, p = 0.576). Females reared in long-day conditions had roughly the same amount of protein whether they consumed sugar water or diets that included royal jelly (Supplementary Figure S2B; average protein content LD RJ = 12.16 ± 0.76 μg/mg; LD SW = 12.60 ± 1.41 μg/mg; Tukey’s HSD, p = 0.99). Dietary treatment did not significantly affect the protein content of short-day reared females (SD RJ = 10.22 ± 0.98 μg/mg; SD SW = 9.33 ± 1.32 μg/mg; Tukey’s HSD; p = 0.95). However, females reared in short-day conditions contained significantly less protein than long-day reared females (Tukey’s HSD, p = 0.034, 95% CI = [-5.04, -0.200]).
As diapausing females can survive for prolonged periods without without food (reviewed in 11), we also assessed the starvation resistance of mosquitoes reared in different photoperiodic conditions that consumed either sugar water or diets including royal jelly for seven days prior to food removal (Figure 2C). Our Cox proportional hazards model revealed that photoperiod significantly impacted survival time in the absence of food, such that short-day reared females were significantly less likely to die relative to long-day reared females (Supplementary Table S1; z = -8.427; p < 0.001). Although consuming diets that include royal jelly did not significantly impact survival time relative to feeding on sugar water (Supplementary Table S1; z = 1.48; p = 0.138), there was a strong interaction between photoperiod and diet, such that under short-day conditions, consuming diets that included royal jelly significantly increased the risk of death (z = 12.3; p < 0.001). The median survival time of long-day reared females that consumed sugar water was eight weeks of age, while the median survival time of sugar-fed, short-day reared mosquitoes was 15 weeks (Figure 2C), and the risk of dying was significantly lower for short-day reared females (Tukey’s HSD, z = 8.47, p < 0.001). However, the opposite was observed with female mosquitoes that consumed diets including royal jelly; the median survival time of long-day reared mosquitoes that consumed royal jelly was 7 weeks while the median survival time of short-day reared, royal jelly-fed mosquitoes was 3 weeks, showing that under short-day conditions consuming diets that include royal jelly significantly increased the risk of dying (Tukey’s HSD, z = 10.58; p < 0.001). Under long-day conditions, consuming royal jelly did not affect the risk of dying (Tukey’s HSD, z = 1.482; p = 0.4486), whereas under short-day conditions, consuming diets that included royal jelly reduced the median survival time by 12 weeks and significantly increased the risk of death (Tukey’s HSD, z = 13.27; p < 0.001).
3.4 Characterizing the effects of royal jelly on the metabolomic profile of long and short day-reared mosquitoes
Preliminary data collected during initial optimization of the metabolomics protocol suggests that there are largescale differences in the metabolic profile of diapausing and nondiapausing Cx. pipiens (Supplementary Figure S2A). A Principal Component Analysis (PCA) reveals partial group separations for both the photoperiodic conditions and consuming royal jelly, indicating that both factors affect the metabolism of female mosquitoes (Supplementary Figure S2B). It should be noted that PCA does not search for differences between groups of interest, but it rather separates samples according to signals of largest variance. Frequently in metabolomics studies, confounding factors obscure PCA group separations by adding to the overall variance of the dataset. Therefore, additional analyses were performed to find differential signals. General linear models (GLM) revealed that 168 out of 1823 spectral signals significantly changed in response to at least one of the following: photoperiod, diet, or their interaction (Supplementary Table S1). Figure 3A shows a heatmap of all signals that significantly changed. Notably, nondiapausing mosquitoes that consumed sugar water exhibit strong metabolic differences compared to diapausing mosquitoes that also consumed sugar water (Supplementary Table S1; Figure 3A). Visual inspection revealed that mosquitoes reared under long-day, diapause-averting conditions switch to a “diapause-like” metabolic profile after consuming royal jelly. In contrast, females reared under short-day, diapause-inducing conditions switched to a “nondiapause-like” metabolic state after consuming royal jelly (Supplementary Table S2; Figure 3A). To confirm these qualitative observations, an artificial neural network (ANN) was trained on the sugar water group to predict long-day or short-day rearing conditions. Using leave-one out cross validation of each SW sample (Supplementary Table S2) reveals that the ANN correctly predicted most short-day (“diapause”) and long-day (“nondiapause”) samples in the sugar water group. However, when using the ANN to predict the photoperiod of mosquitoes that had consumed royal jelly (Supplementary Table S3), most short-day samples were predicted as being long-day, and most long-day samples were predicted to be short-day. The ANN results thus confirm that consuming royal jelly switches the metabolic profile of long-day reared females to be “diapause-like” and short-day reared females to be “nondiapause-like.”
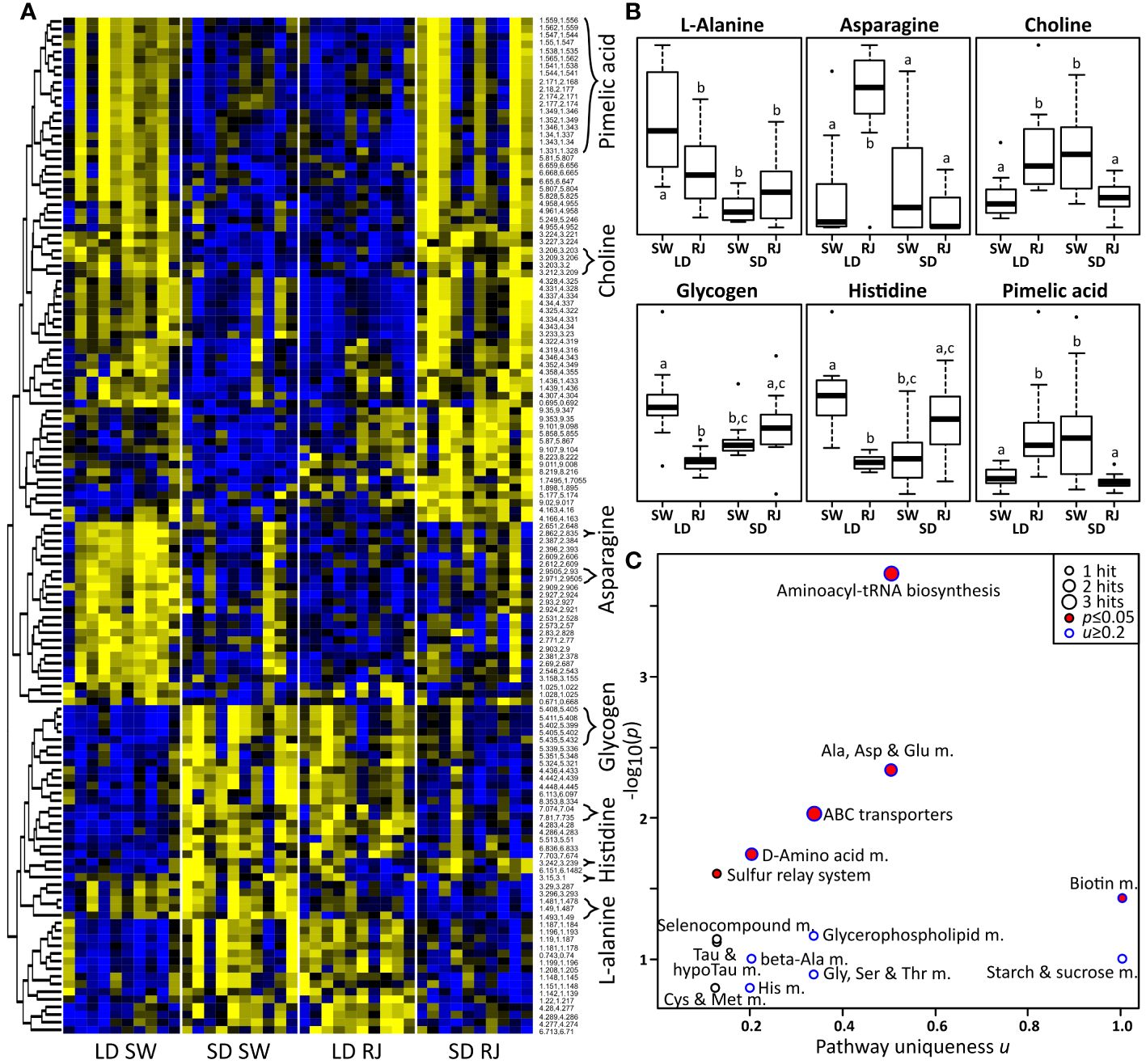
Figure 3 Consuming royal jelly reverses seasonal differences in the mosquito metabolome. (A) Heat map of NMR signals that were significantly different between treatment groups. Signals that were unambiguously identified are labeled with the respective metabolite name. Yellow represents metabolites that were highly abundant, while blue represents metabolites that were less abundant. (B) Boxplots of significantly altered metabolites (arbitrary units). Different superscript letters indicate differences with p ≤ 0.05. (C) Pathway enrichment analysis plot. RJ, royal jelly; SW, sugar water; SD, short-day, diapause-inducing conditions; LD, long-day, diapause-averting conditions; m., metabolism; Tau, taurine.
Among the significant signals (Supplementary Table S2), six metabolites could be unambiguously identified using existing information in NMR databases (Supplementary Table S3; Figure 3B). Short day-reared, diapausing mosquitoes that consumed sugar water and long day-reared mosquitoes that consumed royal jelly had significantly higher levels of pimelic acid, asparagine, and choline; but significantly lower levels of L-alanine, histidine, and glycogen, compared to long-day mosquitoes that consumed sugar water (Figure 3B; see Supplementary Table S3 for GLM coefficients and Tukey’s HSD p-values). Identical trends are seen in mosquitoes reared in short-day, diapause-inducing conditions that consumed sugar water (significant in all except asparagine). In contrast, short day-reared mosquitoes that consumed royal jelly showed opposite metabolic trends when compared to short-day, sugar-fed controls; however, this difference was only significant for choline and pimelic acid.
Metabolic pathway enrichment results indicate that several pathways were affected by photoperiod and diet. When plotting the negative decadic logarithm of the p-value versus the uniqueness score u, pathways of interest are expected to be found toward the top (p ≤ 0.05) or the right (u ≥ 0.2) in the resulting scatterplot (Figure 3C). Pathways of high interest were found to be Alanine, Aspartate and Glutamate Metabolism (p = 0.0044, u = 0.5), Biotin Metabolism (p = 0.036, u = 0.5), Starch and Sucrose metabolism (u = 1.0), Glycerohospholipid metabolism (u = 0.33), and Histidine Metabolism (u = 0.33). Some pathways such as Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis, ABC transporters, Sulfur relay system, and D-amino acid metabolism were significant. However, these significant differences were caused by repetitive metabolic reactions in these pathways and/or non-specific reactions, therefore we chose to treat these results as statistical artifacts and do not further discuss them.
3.5 Effects of CpMRJP1 dsRNA on mosquito diapause status and survival
A knockdown confirmation analysis was performed to determine if CpMRJP1 dsRNA significantly reduced the abundance of CpMRJP1 mRNA transcripts (Figure 4A). We found that MRJP1 dsRNA significantly reduced the abundance of CpMRJP1 transcripts in both long-day (71% reduction in transcript abundance relative to β-gal dsRNA-injected controls; T = 4.75; p = 0.009) and short-day reared females (74% reduction in transcript abundance relative to β-gal dsRNA-injected controls; T = 7.40, p = 0.0018).
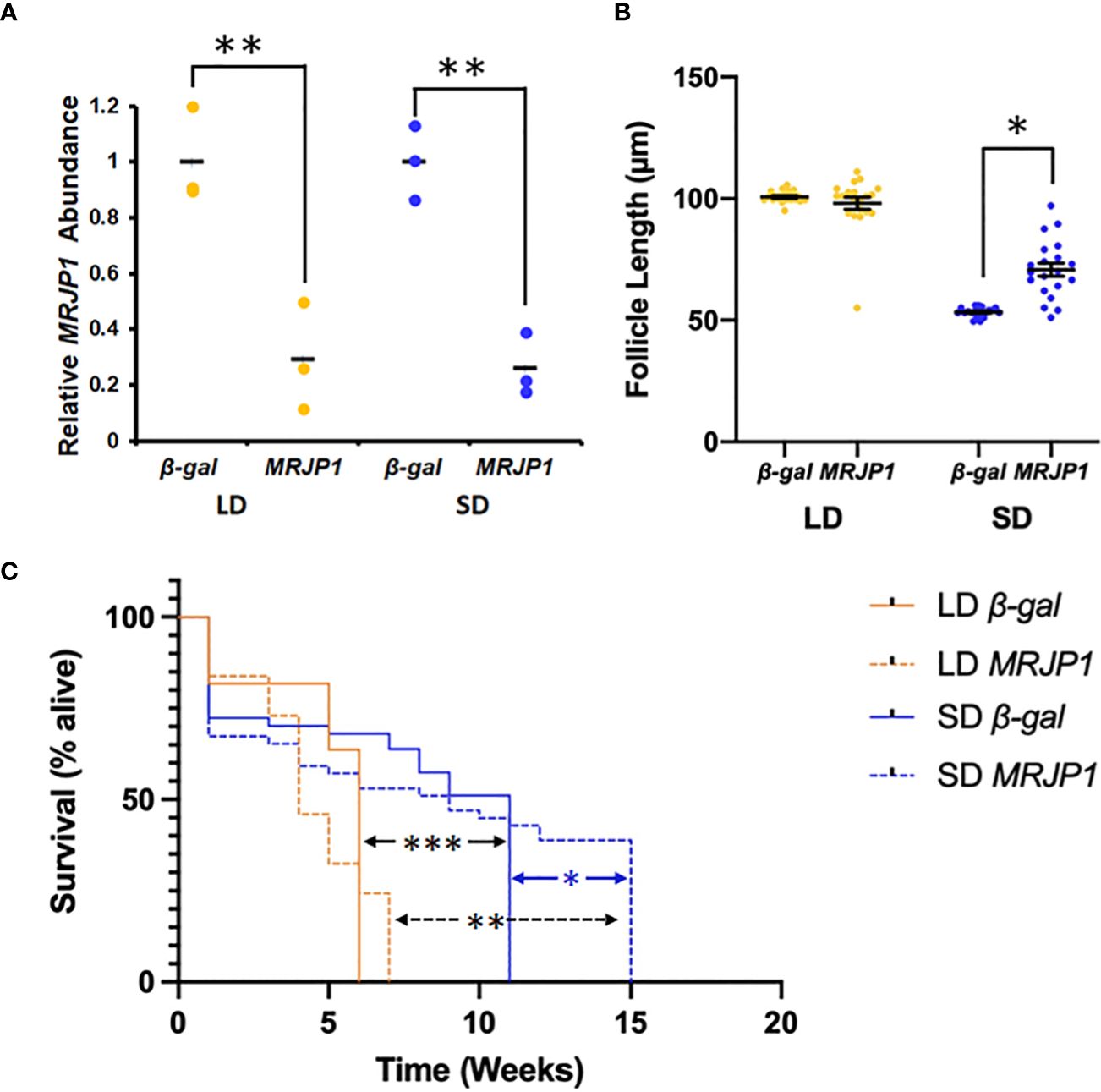
Figure 4 dsRNA against MRJP1 affects seasonal phenotypes in mosquitoes. (A) Treatment with dsRNA for MRJP1 significantly reduced the abundance of relative CpMRJP1 mRNA abundance relative to β-gal dsRNA-injected controls in long day (LD) or short day (SD) mosquitoes. Significant difference denoted by * (p < 0.01). (B) dsRNA against MRJP1 caused a significant increase in egg follicle length in short day (SD) mosquitoes. Significant difference denoted by * (p < 0.001). (C) dsRNA against MRJP1 significantly affected the lifespan of (SD) conditions. Significant differences denoted by *** (LD β-gal to SD β-gal; p < 0.001), ** (LD MRJP1 to SD MRJP1; p < 0.001) and * (SD β-gal to SD MRJP1; p = 0.0187).
Knocking down CpMRJP1 dsRNA significantly affected egg follicle length in short-day reared females (Figure 4B). A two-way ANOVA was used to determine how photoperiod and dsRNA injection affected egg follicle length, and revealed that both photoperiod (F1, 76 = 394; p < 0.001) and dsRNA treatment (F1, 76 = 15.4; p = 0.0019) had significant effects. Moreover, there was a significant interaction between photoperiod and dsRNA treatment (F1, 76 = 28.3; p <0.001). All females reared in long-day conditions that were injected β-gal and CpMRJP1 dsRNA were in a clear nondiapause state, such that the average egg follicle length of β-gal dsRNA-injected (100.7 ± 0.5 μm) and CpMRJPI dsRNA-injected mosquitoes (98.1 ± 2.5 μm) were not significantly different (Figure 3B; Tukey’s HSD; p = 0.76). Females reared in short-day conditions that were injected with β-gal dsRNA were in a clear diapause state, with an average egg follicle length of 53.3 ± 0.4 μm. However, the average egg follicle length of females reared in short-day conditions that were injected with CpMRJP1 dsRNA was 70.7 ± 2.7 μm, and females were found to be in a mixture of diapause (70%), intermediate (25%), and nondiapause (5%) states. Overall, knocking down CpMRJP1 significantly increased egg follicle length in short-day reared females (Tukey’s HSD; p < 0.001; 95% [CI = 10.4, 24.4]).
We also used a two-way ANOVA to determine whether photoperiod and knocking down CpMRJP1 affected fat content (Supplementary Figure S3B). Our analyses revealed that dsRNA injection did not affect fat content (F1, 26 = 2.28, p = 0.143). However, photoperiod had a significant impact on fat content (F1, 26 = 4.47; p = 0.045), such that β-gal and MRJP1 dsRNA-injected, short-day reared females had higher levels of fat than dsRNA-injected long-day reared females. This was largely driven by a non-significant trend where females reared in long-day conditions and injected with β-gal dsRNA had slightly less fat (6.45 ± 0.78%) than long day-reared mosquitoes injected with CpMRJP1 dsRNA (10.97 ± 0.40%; Tukey’s HSD, p = 0.181), and short-day reared mosquitoes injected with β-gal dsRNA (Tukey’s HSD, p = 0.092) or CpMRJP1 dsRNA (Tukey’s HSD, p = 0.072). Our 2-way ANOVA also confirmed that that there was not a significant interaction between photoperiod and dsRNA injection (F1, 26 = 2.12, p = 0.157).
We also investigated how injection with MRJP1 dsRNA affected the lifespan of long and short day-reared females relative to β-gal dsRNA-injected controls in the absence of food (Figure 4C). A Cox proportional hazards model revealed that short photoperiods had a protective effect on female lifespan in the absence of food (Supplementary Table S1; HR = -1.31 ± 0.209; z = -6.28, p < 0.001), while knocking down CpMRJP1 had a slight, but non-significant protective effect (HR = -0.307 ± 0.167; z = -1.83; p = 0.0668). The median survival time of long-day reared, β-gal dsRNA-injected females was six weeks while the median survival time of short-day reared, β-gal dsRNA-injected females was eleven weeks (Tukey’s HSD, z = -6.28, p < 0.001). The median survival time of long-day reared, CpMRJP1 dsRNA-injected females was four weeks, while the median survival time of short-day reared, CpMRJP1 dsRNA-injected females was nine weeks (Tukey’s HSD, z = -1.314, p < 0.001). While knocking down CpMRJP1 did not significantly affect the likelihood of dying in females reared in long-day conditions relative to β-gal injected controls (Tukey’s HSD, z = -1.833, p = 0.258), dsRNA against CpMRJP1 significantly extended the total lifespan in short-day conditions (Figure 4C; all β-gal-injected females were dead at 11 weeks; all MRJP1-dsRNA injected females were dead at 15 weeks; Log Rank Test of survival differences: X21 = 5.9, p = 0.02).
4 Discussion
Our phylogenetic analyses show that CpMRJP1 forms a unique clade with MRJP’s in the paddled-beauty mosquito, Sabethes cyaneus, and Ae. aegypti (Figure 1B). Additionally, our results demonstrate that ingesting royal jelly reverses some, but not all, of the phenotypes associated with diapause in female mosquitoes. Specifically, female mosquitoes reared in long-day, diapause-averting conditions that consumed a diet including royal jelly enter a diapause-like state with small egg follicles (Figure 2B). In contrast, consuming a diet that includes royal jelly significantly reduced the lifespan of females reared in short-day, diapause-inducing conditions (Figure 2C). While consuming a diet containing royal jelly does not cause significant differences in fat content within long or short day-reared mosquitoes (Supplementary Figure S1A), it alters the metabolic profile of mosquitoes (Figure 3; Supplementary Figure S2; Supplementary Table S1). Specifically, long-day reared mosquitoes that consumed a diet containing royal jelly were metabolically similar to diapausing controls, and there were no significant differences in the relative abundance of 5/6 metabolites we identified between these two groups (Figure 3B; Supplementary Table S2). In contrast, short-day reared mosquitoes that consumed a diet containing royal jelly were metabolically similar to nondiapausing controls as there were no significant difference in any of the identified metabolites between long-day reared females that consumed sugar and short-day reared females that consumed diets with royal jelly (Figure 3B; Supplementary Table S2). As royal jelly is a complex mixture containing several proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and vitamins, it is currently not clear how royal jelly might be mediating these effects. However, it is likely that some of the traits we observed are induced through the action of MRJP1. This is because knocking down CpMRJP1 significantly increased the egg follicle lengths of short-day reared females (Figure 4B) and allowed them to live significantly longer than β-gal dsRNA-injected controls in the absence of food (Figure 4C).
Transcripts encoding CpMRJP1, an ortholog of MRJP1 in Apis mellifera that is the most abundant protein in royal jelly, were upregulated in diapausing females (18). Another study demonstrated that consuming royal jelly increased the likelihood that alfalfa leaf cutting bees would enter diapause (25). Therefore, we hypothesized that consuming diets that include royal jelly, and thereby artificially increasing the levels of AmMRJP1 within mosquitoes, would induce diapause phenotypes in long-day reared mosquitoes. Although our current study did not show any significant differences in CpMRJP1 mRNA abundance between diapausing and nondiapausing, sugar-fed mosquitoes (Figure 2A), we found that long day-reared females that consumed diets containing royal jelly had significantly smaller egg follicles (Figure 2B). This indicates that feeding female mosquitoes royal jelly in conditions that typically prevent diapause causes them to arrest reproductive development. However, in contrast to our results, consuming royal jelly promotes reproductive development in honey bee queens (15) and fruit flies (23). As other species also become more virile and fecund upon consuming royal jelly (22, 23), there must be a separate, unique pathway through which royal jelly acts in Cx. pipiens to confer reproductive arrest. We believe these effects are mediated through CpMRJP1 because knocking down this transcript stimulated reproductive development in mosquitoes reared in short day, diapause-inducing conditions (Figure 4B).
Reproductive arrest is not the only indicator of diapause, as diapausing females of Cx. pipiens also display an increase in fat content (37, 42, 59). We observed a trend where long-day reared females that consumed royal jelly had slightly higher fat content than females that consumed sucrose solution (Supplementary Figure S1A). However, due to high variation within our samples, the fat content was not significantly different between rearing conditions or food source. Typically, the increase in fat content is a consequence of the feeding habits of female mosquitoes; short-day reared females gorge on nectar that is rich in sugar (5, 6, 9) which they then convert into lipids (9). In contrast, nondiapausing mosquitoes do not accumulate substantial levels of fat (9, 37, 42). These differences are not likely not driven by lipid deposition into egg follicles as other researchers found that female mosquitoes of Ae. aegypti only deposit lipids into their egg follicles several hours after blood-feeding (60), and none of the mosquitoes in our study were given access to vertebrate blood. Although it is unclear why we did not observe significant increases in the fat content of diapausing females relative to nondiapausing sugar-fed controls, the absence of an effect of consuming diets that include royal jelly could be the result of nutritional differences in royal jelly (14), and/or because female mosquitoes in the royal jelly treatment may not have consumed as much food as the sugar-fed, control mosquitoes. Unfortunately, we did not measure how much food the mosquitoes consumed in our experiments. However, we conducted follow-up experiments demonstrating that long and short-day reared mosquitoes die within six days of adult emergence if they are provided access to only water. All our phenotypic measurements were collected from females that were seven-days old, indicating that they must have consumed at least some of their respective diets.
As royal jelly contains a high proportion of protein (13, 14), we chose to examine whether protein content changed between females that consumed diets that included royal jelly relative to those who fed on only sucrose (Supplementary Figure S1B). Consuming diets containing royal jelly did not affect the protein content of long or short-day reared mosquitoes, possibly because females in the royal jelly treatment may not have consumed as much food as those in the sucrose treatment as discussed above. However, we did find that females reared in long-day conditions have significantly greater protein content than those reared in short-day conditions. Early in diapause, females of Cx. pipiens produce fewer proteins than they do upon diapause termination (61). Furthermore, diapausing female mosquitoes are relatively inactive and take refuge in protected shelters (62), so they would not require as much protein to power their flight muscles.
In addition to determining how supplementing the diet of mosquitoes with royal jelly would affect seasonal phenotypes, we used RNAi to elucidate the functional role of CpMRJP1 in diapausing females of Cx. pipiens. We were able to successfully knock-down the relative abundance of CpMRJP1 transcripts in both long and short-day reared Cx. pipiens (Figure 4A). However, knocking down CpMRJP1 only induced phenotypic effects in short-day reared females, where it significantly increased the egg follicle length of 7-day old mosquitoes such that approximately 30% of the females sampled were categorized as being in an intermediate or nondiapause state (Figure 4B). Therefore, knocking down CpMRJP1 causes short-day reared females to avert diapause, and again suggests that the gene encoding CpMRJP1 plays a critical role in arresting egg follicle development during diapause induction in females of Cx. pipiens.
Knocking down CpMRJP1 did not lead to a significant change in fat content of females reared in short-day conditions (Supplementary Figure S3B), although, we observed a trend in which the long day-reared females that were injected with CpMRJP1 dsRNA had a slight, but non-significant, higher level of fat compared to β-gal dsRNA-injected controls. This is surprising, seeing as CpMRJP1 mRNA is upregulated in diapausing mosquitoes that acquire high levels of fat (18), but we found that the fat content slightly increased when CpMRJP1 was knocked down with RNAi. Overall, the female mosquitoes that were injected with CpMRJP1 or β-gal dsRNA had lower levels of fat (Supplementary Figure S3B) than the female mosquitoes that were not injected and allowed to consume sugar water in the initial dietary experiment (Supplementary Figure S1A). Therefore, we conclude that injecting mosquitoes likely caused some minor injuries that impaired their ability to consume the sucrose source that was within their cage. These results, combined with the effects of consuming royal jelly, suggest that CpMRJP1 may not be directly involved in accumulating fat during diapause and rather that this protein regulates reproductive development and/or starvation resistance.
Consuming diets that contained royal jelly for one week prior to food removal significantly reduced the median survival time in the absence of food for both long and short-day reared mosquitoes, relative to mosquitoes that consumed 10% sucrose for one week before food removal (Figure 2C). The decrease in survival was most dramatic and pronounced in mosquitoes reared in short-day, diapause-inducing conditions where consuming diets that included royal jelly reduced the median lifespan by 12 weeks. This is a surprising result, seeing as royal jelly increases the lifespan of honey bees and fruit flies (14, 23). Additionally, in short-day conditions, knocking down MRJP1 with RNAi increased lifespan (Figure 4C). Although CpMRJP1 dsRNA-injected mosquitoes initially died sooner and had a lower median survival time than β-gal dsRNA injected controls, knocking down CpMRJP1 in short day-reared mosquitoes extended their lifespan by four weeks. Taken together, our data suggest that a factor within royal jelly, possibly MRJP1, may reduce the starvation resistance of diapausing mosquitoes.
We found six metabolites that were significantly differentially abundant between diapausing and nondiapausing mosquitoes as well as those that had consumed royal jelly (Figure 3B). It is obvious that consuming royal jelly caused largescale changes in whole mosquito metabolomes that partially reversed the seasonal phenotypes of the mosquitoes (Figure 3A), and these results were further supported by artificial neural network predictions. In addition, mosquitoes reared in short-day, diapause-inducing conditions that consumed diets that included royal jelly had a metabolic profile that was similar to nondiapausing mosquitoes, such that both long-day reared, sugar-fed controls and short-day reared, royal jelly-fed mosquitoes had significantly lower levels of asparagine, choline, and pimelic acid as well as higher levels of glycogen, and histidine (Figure 3B). These metabolic results are consistent with the phenotypes we observed, where ingesting diets that contained royal jelly both induced diapause phenotypes in long-day reared mosquitoes (e.g., reduced egg follicle length) and caused short-day reared females to exhibit nondiapause phenotypes (e.g., reduced starvation tolerance).
A pathway enrichment analysis (Figure 3C) revealed several metabolic pathways that were affected by day length and/or royal jelly consumption. One of the affected pathways is the biotin metabolism pathway, with its metabolite pimelic acid being upregulated during diapause and in long day-reared mosquitoes that consumed royal jelly (Figure 3B). Pimelic acid is a precursor of biotin (vitamin B7) that can be made during fatty acid synthesis, specifically, it has been linked to the FabF enzyme in the bacteria Bacilus subtilis (63). While FabF is also part of fatty acid synthesis in Cx. pipiens, and fatty acid synthesis is upregulated in diapause (5), no pimelic acid synthesis has been previously reported for this organism, and further experiments would be required to investigate this possibility. Pimelic acid is also a metabolite in mosquito microbiomes (64). Therefore, microbial contributions may explain the observed change. Supplementing the diets of honey bee with pimelic acid has been shown to decrease stress responses and increasing survival times (65). Decreased levels of pimelic acid could thus partially explain the decreased life expectancy of short day-reared mosquitoes that consumed royal jelly. The observed increase in pimelic acid in diapause-inducing conditions also indicates a potential microbial contribution to mosquito diapause.
Our analyses also show that the starch and sucrose metabolism pathway was similarly affected (Figure 3C), with glycogen being less abundant in diapause and in long-day reared mosquitoes that consumed diets that included royal jelly (Figure 2B). A previous study reports metabolic flux of dietary glucose toward glycogen in diapausing Cx. pipiens (66). However, that study did not analyze glycogen in nondiapausing animals and thus cannot be directly compared to our data. In accordance with our results, Zhou and Meisfeld (67) found that glycogen decreases during the first weeks of diapause in Cx. pipiens as compared to nondiapausing mosquitoes, with a simultaneous increase in body fat. Our findings suggest that consuming diets that contain royal jelly significantly reduced the diapause-associated catabolism of glycogen in short-day reared mosquitoes.
The alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism (AAGM) pathway was also significantly affected. One metabolite in this pathway, L-alanine, was less abundant in diapausing mosquitoes and females reared in long-day conditions that consumed royal jelly (Figure 3B). Alanine can, via pyruvate and the glycolysis/gluconeogenesis pathway, feed into starch and sucrose metabolism. Therefore, our finding that the abundance of L-alanine decreased diapausing mosquitoes is consistent with the observed drop in glycogen as discussed above. Alanine is also downregulated in diapausing N. vitripennis (28), but is more abundant in diapausing flesh flies, where it likely functions as a cryoprotectant (27). We also found that asparagine, another metabolite of the AAGM pathway, was significantly upregulated in long-day reared mosquitoes that consumed royal jelly (Figure 3B). Asparagine was upregulated in diapausing pupae of the moth Antheraea pernyi (68) but was less abundant in diapausing larvae of the parasitoid N. vitripennis (28). Together with the downregulation of L-alanine, these results suggest that L-aspartate is preferably converted into L-asparagine rather than L-alanine in diapausing Cx. pipiens to meet their differing metabolic needs.
Glycerophospholipid metabolism also changed across photoperiods and dietary treatments (Figure 3C), such that choline was upregulated in diapausing mosquitoes and in long-day reared mosquitoes that consumed diets including royal jelly (Figure 3B). As choline is a precursor of phosphatidylcholine, the observed differences suggest that there are differences in phospholipid synthesis during diapause. This could indicate that diapausing insects are catabolizing phospholipids to generate precursors for triglycerides, which would be consistent with previous studies that have shown that triglyceride stores increase during diapause in Cx. pipiens (5, 9) and other insects (reviewed in 69). However, this finding could also indicate that diapausing insects are synthesizing more and/or different phospholipids. Previous studies have demonstrated that diapausing insects increase the concentration of unsaturated fatty acids within cell membranes to increase membrane fluidity and enhance cold tolerance (69–71). Future studies are necessary to distinguish whether phospholipid catabolism and/or anabolism are occurring within diapausing Cx. pipiens.
Both photoperiod and diet affected histidine metabolism (Figure 3C), such that histidine was significantly downregulated in diapausing Cx. pipiens and long-day reared mosquitoes that consumed diets containing royal jelly (Figure 3B). Although histidine is upregulated in diapausing N. vitripennis (28), histidine is less abundant in diapause-destined larvae of the cotton bollworm, Heliocoverpa armigera (72). In pre-diapausing H. armigera, down-regulating histidine likely leads to lower levels of its byproduct histamine, an inhibitory neurotransmitter, that may alter the photoperiodic responses necessary for diapause induction (72).
Notably, royal jelly contains multiple proteins, lipids, vitamins, and carbohydrates (13), and any of these components could have directly or indirectly altered mosquito reproductive development, starvation resistance and metabolic profiles. Our RNAi experiments support the findings of our feeding experiments; specifically, consuming royal jelly (thereby artificially increasing the abundance of AmMRJP1 within mosquitoes) decreased egg follicle length in long-day reared mosquitoes, whereas knocking down CpMRJP1 increased egg follicle length short-day reared females. Taken together, this suggests that higher levels of MRJP1 promotes reproductive arrest. However, at this time we still do not know precisely where and when CpMRJP1 is being expressed or how it might be mediating these effects. It is also unclear if consuming AmMRJP1 on its own or other components in royal jelly promotes the metabolomic switch that we observed. Therefore, future studies are necessary to characterize the mechanism by which MRJP1 promotes reproductive arrest in Cx. pipiens and to delineate the effects of MRJP1 from other components in royal jelly.
5 Conclusions
This study demonstrates that consuming diets that include royal jelly has opposing effects on phenotypes associated with diapause in Cx. pipiens. In long-day reared mosquitoes, these include suppressing reproductive development and causing the metabolomic profile to resemble that of diapausing females. In contrast, in short-day reared females, consuming diets that include royal jelly reduces starvation resistance and shifts the metabolomic profile to be more similar to long-day reared mosquitoes. As royal jelly is a complex mixture of multiple proteins, sugars, lipids, vitamins and other substances (13), it is currently unclear how consuming royal jelly switches seasonal phenotypes in Cx. pipiens; but we can conclude that this effect on diapause was mediated at least in part by MRJP1. This is because knocking down CpMRJP1 caused females that were reared in short-day, diapause-inducing conditions to avert diapause and develop significantly larger egg follicles and to live significantly longer than β-gal dsRNA injected controls. As diapausing females of Cx. pipiens do not bite humans and other animals (6), they do not transmit debilitating diseases (62). Future work should investigate whether it would be possible to develop control measures that use royal jelly to induce diapause in female mosquitoes during the long days of summer to reduce disease transmission. Additionally, future work should be done to elucidate whether AmMRJP1 alone or other components of royal jelly induce reproductive arrest, cause largescale metabolic shifts and alter mosquito starvation resistance. Such studies will not only uncover the underpinnings of the interesting results we observed in this study, but may also lead to exciting insights on the molecular regulation of seasonal responses in other insects and animals.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Ethics statement
The manuscript presents research on animals that do not require ethical approval for their study.
Author contributions
OB: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AA: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. MK: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. XW: Investigation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. CS: Investigation, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. MM: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by state and federal funds appropriated to The Ohio State University, College of Food, Agricultural, and Environmental Sciences, Ohio Agricultural Research and Development Center through an Undergraduate SEEDS Grant (2020-061) awarded to OB, as well as an NSF Grant (IOS 1944324) awarded to MM, MK, and CS. MK was also supported by the Foods for Health Discovery Theme. MM was also supported by the USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture, Hatch Multi-State project NE 1943. This work was partly supported by the National Institutes of Health under grant number R15AI139861 awarded to CS.
Acknowledgments
We thank Lydia Fyie for assistance with survival and other data analyses, and Derek Huck for providing guidance and protocols on protein measurement and mosquito metabolomics, and additional members of the Meuti and Klein laboratories for their input and support in the design and execution of the experiments as well as critical feedback and edits on the manuscript. We also thank the CCIC NMR facility for their support.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/finsc.2024.1358619/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Eldridge BF. The effect of temperature and photoperiod on blood-feeding and ovarian development in mosquitoes of the Culex pipiens complex. Am J Trop Med Hygiene. (1968) 17:133–40. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1968.17.133
2. Denlinger DL, Armbruster PA. Chapter eleven - molecular physiology of mosquito diapause. In: Raikhel AS, editor. Advances in insect physiology. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Academic Press (2016). p. 329–61.
3. Denlinger DL, Armbruster PA. Mosquito diapause. Annu Rev Entomol. (2014) 59:73–93. doi: 10.1146/annurev-ento-011613-162023
4. Mitchell CJ, Briegel H. Fate of the blood meal in force-fed, diapausing Culex pipiens (Diptera: Culicidae). J Med Entomol. (1989) 26:332–41. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/26.4.332
5. Robich RM, Denlinger DL. Diapause in the mosquito Culex pipiens evokes a metabolic switch from blood feeding to sugar gluttony. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States Am. (2005) 102:15912–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0507958102
6. Bowen MF, Davis EE, Haggart DA. A behavioural and sensory analysis of host-seeking behaviour in the diapausing mosquito Culex pipiens. J Insect Physiol. (1988) 34:805–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-1910(88)90155-2
7. Sanburg LL, Larsen JR. Effect of photoperiod and temperature on ovarian development in Culex pipiens pipiens. J Insect Physiol. (1973) 19:1173–90. doi: 10.1016/0022-1910(73)90202-3
8. Spielman A, Wong J. Environmental control of ovarian diapause in Culex pipiens. Ann Entomol Soc America. (1973) 66:905–7. doi: 10.1093/aesa/66.4.905
9. Sim C, Denlinger DL. Transcription profiling and regulation of fat metabolism genes in diapausing adults of the mosquito Culex pipiens. Physiol Genomics. (2009) 39:202–9. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00095.2009
10. Sim C, Denlinger D. Insulin signaling and the regulation of insect diapause. Front Physiol. (2013) 4. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2013.00189
11. Hahn DA, Denlinger DL. Energetics of insect diapause. Annu Rev Entomol. (2011) 56:103–21. doi: 10.1146/annurev-ento-112408-085436
12. Colhoun EH, Smith MV. Neurohormonal properties of royal jelly. Nature. (1960) 188:854–5. doi: 10.1038/188854a0
13. Nagai T, Inoue R. Preparation and the functional properties of water extract and alkaline extract of royal jelly. Food Chem. (2004) 84:181–6. doi: 10.1016/S0308-8146(03)00198-5
14. Drapeau MD, Albert S, Kucharski R, Prusko C, Maleszka R. Evolution of the Yellow/Major Royal Jelly Protein family and the emergence of social behavior in honey bees. Genome Res. (2006) 16:1385–94. doi: 10.1101/gr.5012006
15. Page RE, Peng CYS. Aging and development in social insects with emphasis on the honey bee, Apis mellifera L. Exp Gerontol. (2001) 36:695–711. doi: 10.1016/S0531-5565(00)00236-9
16. Fontana R, Mendes MA, De Souza BM, Konno K, César LMM, Malaspina O, et al. Jelleines: A family of antimicrobial peptides from the Royal Jelly of honeybees (Apis mellifera). Peptides. (2004) 25:919–28. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2004.03.016
17. Ohashi K, Natori S, Kubo T. Change in the mode of gene expression of the hypopharyngeal gland cells with an age-dependent role change of the worker honeybee Apis mellifera L. Eur J Biochem. (1997) 249:797–802. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1997.t01-1-00797.x
18. Sim C, Kang DS, Kim S, Bai X, Denlinger DL. Identification of FOXO targets that generate diverse features of the diapause phenotype in the mosquito Culex pipiens. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States America. (2015) 112:3811–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1502751112
19. Pasupuleti VR, Sammugam L, Ramesh N, Gan SH. Honey, propolis, and royal jelly: A comprehensive review of their biological actions and health benefits. In: Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity, vol. 2017. London, United Kingdom: Hindawi Limited (2017). doi: 10.1155/2017/1259510
20. Asadi N, Kheradmand A, Gholami M, Saidi SH, Mirhadi SA. Effect of royal jelly on testicular antioxidant enzymes activity, MDA level and spermatogenesis in rat experimental Varicocele model. Tissue Cell. (2019) 57:70–7. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2019.02.005
21. Amini S, Masoumi R, Rostami B, Shahir MH, Taghilou P, Arslan HO. Effects of supplementation of Tris-egg yolk extender with royal jelly on chilled and frozen-thawed ram semen characteristics. Cryobiology. (2019) 88:75–80. doi: 10.1016/j.cryobiol.2019.03.008
22. El-Hanoun AM, Elkomy AE, Fares WA, Shahien EH. Impact of royal jelly to improve reproductive performance of male rabbits under hot summer conditions. World Rabbit Sci. (2014) 22:241–8. doi: 10.4995/wrs.2014.1677
23. Xin XX, Chen Y, Chen D, Xiao F, Parnell LD, Zhao J, et al. Supplementation with major royal-jelly proteins increases lifespan, feeding, and fecundity in Drosophila. J Agric Food Chem. (2016) 64:5803–12. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b00514
24. Honda Y, Fujita Y, Maruyama H, Araki Y, Ichihara K, Sato A, et al. Lifespan-extending effects of royal jelly and its related substances on the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. PloS One. (2011) 6:1–10. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023527
25. Fischman BJ, Pitts-Singer TL, Robinson GE. Nutritional regulation of phenotypic plasticity in a solitary bee (Hymenoptera: Megachilidae). Environ Entomol. (2017) 46:1070–9. doi: 10.1093/ee/nvx119
26. Batz ZA, Armbruster PA. Diapause-associated changes in the lipid and metabolite profiles of the Asian tiger mosquito, Aedes albopictus. J Exp Biol. (2018) 221:jeb189480. doi: 10.1242/jeb.189480
27. Michaud MR, Denlinger DL. Shifts in the carbohydrate, polyol, and amino acid pools during rapid cold-hardening and diapause-associated cold-hardening in flesh flies (Sarcophaga crassipalpis): A metabolomic comparison. J Comp Physiol B: Biochem System Environ Physiol. (2007) 177:753–63. doi: 10.1007/s00360-007-0172-5
28. Li Y, Zhang L, Chen H, Koštál V, Simek P, Moos M, et al. Shifts in metabolomic profiles of the parasitoid Nasonia vitripennis associated with elevated cold tolerance induced by the parasitoid’s diapause, host diapause and host diet augmented with proline. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. (2015) 63:34–46. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2015.05.012
29. Bailey CL, Eldridge BF, Hayes DE, Watts DM, Tammariello RF, Dalrymple JM. Isolation of St. Louis encephalitis virus from overwintering Culex pipiens mosquitoes. Science. (1978) 199:1346 LP – 1349. doi: 10.1126/science.628843
30. Hamer GL, Kitron UD, Brawn JD, Loss SR, Ruiz MO, Goldberg TL, et al. Culex pipiens (Diptera: Culicidae): A bridge vector of west nile virus to humans. J Med Entomol. (2008) 45:125–8. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/45.1.125
31. Cancrini G, Scaramozzino P, Gabrielli S, Di PM, Toma L, Romi R. Aedes albopictus and Culex pipiens Implicated as Natural Vectors of Dirofilaria repens in Central Italy. J Med Entomol. (2007) 44:1064–6. doi: 10.1603/0022-2585(2007)44[1064:AAACPI]2.0.CO;2
32. Farajollahi A, Fonseca DM, Kramer LD, Marm Kilpatrick A. “Bird biting” mosquitoes and human disease: A review of the role of Culex pipiens complex mosquitoes in epidemiology. Infect Genet Evol. (2011) 11:1577–85. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2011.08.013
33. Brugman VA, Hernández-Triana LM, Medlock JM, Fooks AR, Carpenter S, Johnson N. The role of Culex pipiens L. (Diptera: Culicidae) in virus transmission in Europe. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2018) 15:389. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15020389
34. Hay SI, Myers MF, Burke DS, Vaughn DW, Endy T, Ananda N, et al. Etiology of interepidemic periods of mosquito-borne disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States Am. (2000) 97:9335–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.16.9335
35. Felsenstein J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution. (1985) 39:783–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.1985.tb00420.x
36. Meuti ME, Siperstein A, Wolkoff M. Rearing and maintaining a Culex colony in the laboratory. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. (2023) 2023:108080. doi: 10.1101/pdb.prot108080
37. Meuti ME, Stone M, Ikeno T, Denlinger DL. Functional circadian clock genes are essential for the overwintering diapause of the Northern house mosquito, Culex pipiens. J Exp Biol. (2015) 218:412–22. doi: 10.1242/jeb.113233
38. Rozen S, Skaletsky H. Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. In: Misener S, Krawetz SA, editors. Bioinformatics methods and protocols. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ (1999). p. 365–86.
39. Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans J, Huggett J, Kubista M, et al. The MIQE guidelines: Minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem. (2009) 55:611–22. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2008.112797
40. Chang V, Meuti ME. Circadian transcription factors differentially regulate features of the adult overwintering diapause in the Northern house mosquito, Culex pipiens. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. (2020) 121:103365. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2020.103365
41. Van Handel E. Rapid determination of total lipids in mosquitoes. J Am Mosq Control Assoc. (1985) 1:302–4.
42. Meuti ME, Short CA, Denlinger DL. Mom matters: Diapause characteristics of Culex pipiens-Culex quinquefasciatus (Diptera: Culicidae) hybrid mosquitoes. J Med Entomol. (2015) 52:131–7. doi: 10.1093/jme/tju016
43. Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochem. (1976) 72:248–54. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999
44. Huck DT, Klein MS, Meuti ME. Determining the effects of nutrition on the reproductive physiology of male mosquitoes. J Insect Physiol. (2021) 129:104191. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2021.104191
45. Ciota AT, Drummond CL, Drobnack J, Ruby MA, Kramer LD, Ebel GD. Emergence of Culex pipiens from overwintering hibernacula. J Am Mosq Control Assoc. (2011) 27:21–9. doi: 10.2987/8756-971X-27.1.21
46. Wu H, Southam AD, Hines A, Viant MR. High-throughput tissue extraction protocol for NMR- and MS-based metabolomics. Analytical Biochem. (2008) 372:204–12. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2007.10.002
47. Newell C, Sabouny R, DustinS H, TE S, Khan A, MS K, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells shift mitochondrial dynamics and enhance oxidative phosphorylation in recipient cells. Front Physiol. (2018) 9. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01572
48. Gronwald W, Klein MS, Kaspar H, Fagerer SR, Nürnberger N, Dettmer K, et al. Urinary metabolite quantification employing 2D NMR spectroscopy. Analytical Chem. (2008) 80:9288–97. doi: 10.1021/ac801627c
49. Klein MS, Dorn C, Saugspier M, Hellerbrand C, Oefner PJ, Gronwald W. Discrimination of steatosis and NASH in mice using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Metabolomics. (2011) 7:237–46. doi: 10.1007/s11306-010-0243-6
50. Klein MS. Affine transformation of negative values for NMR metabolomics using the mrbin R package. J Proteome Res. (2021) 20:1397–404. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.0c00684
51. R Core Team. The R foundation. Vienna, Austria: The R Project for Statistical Computing (2017). Available at: https://www.r-project.org.
52. Therneau TM. A package for survival analysis in R (2020). Available online at: https://cran.r-project.org/package=survival.
53. Therneau TM, Grambsch PM. Modeling survival data: extending the Cox model. New York: Springer (2000).
54. Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Society: Ser B (Methodological). (1995) 57:289–300. doi: 10.1111/j.2517-6161.1995.tb02031.x
55. Peng C, Qian Z, Xinyu Z, Qianqian L, Maoqing G, Zhong Z, et al. A Draft Genome Assembly of Culex pipiens pallens (Diptera: Culicidae) Using PacBio Sequencing. Genome Biol Evol. (2021) 13:evab005. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evab005
56. Drapeau MD. The family of yellow-related Drosophila melanogaster proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2001) 281:611–3. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.4391
57. Buttstedt A, Moritz RFA, Erler S. Origin and function of the major royal jelly proteins of the honeybee (Apis mellifera) as members of the yellow gene family. Biol Rev. (2014) 89:255–69. doi: 10.1111/brv.12052
58. Ferguson LC, Green J, Surridge A, Jiggins CD. Evolution of the insect yellow gene family. Mol Biol Evol. (2011) 28:257–72. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msq192
59. Sim C, Denlinger DL. Insulin signaling and FOXO regulate the overwintering diapause of the mosquito Culex pipiens. Proc Natl Acad Sci. (2008) 105:6777–81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0802067105
60. Sun J, Hiraoka T, Dittmer NT, Cho KH, Raikhel AS. Lipophorin as a yolk protein precursor in the mosquito, Aedes aegypti. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. (2000) 30:1161–71. doi: 10.1016/S0965-1748(00)00093-X
61. Zhang C, Wei D, Shi G, Huang X, Cheng P, Liu G, et al. Understanding the regulation of overwintering diapause molecular mechanisms in Culex pipiens pallens through comparative proteomics. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:1–12. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42961-w
62. Eldridge BF. Diapause and related phenomena in Culex mosquitoes: their relation to arbovirus disease ecology. In: Harris KF, editor. Current topics in vector research, vol. 4 . Springer New York, New York, NY (1987). p. 1–28.
63. Manandhar M, Cronan JE. Pimelic acid, the first precursor of the Bacillus subtilis biotin synthesis pathway, exists as the free acid and is assembled by fatty acid synthesis. Mol Microbiol. (2017) 104:595–607. doi: 10.1111/mmi.13648
64. Sonenshine DE, Stewart PE. Microbiomes of blood-feeding arthropods: genes coding for essential nutrients and relation to vector fitness and pathogenic infections. A Rev Microorg. (2021) 9:2433. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9122433
65. Jorand JP, Bounias M, Chauvin R. The “survival hormones”: Azelaic and pimelic acids, suppress the stress elicited by isolation conditions on the steroids and phospholipids of adult worker honeybees. Hormone Metab Res. (1989) 21:553–7. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1009286
66. King B, Li S, Liu C, Kim SJ, Sim C. Suppression of glycogen synthase expression reduces glycogen and lipid storage during mosquito overwintering diapause. J Insect Physiol. (2020) 120:103971. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2019.103971
67. Zhou G, Miesfeld RL. Energy metabolism during diapause in Culex pipiens mosquitoes. J Insect Physiol. (2009) 55:40–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2008.10.002
68. Mansingh A. Changes in the free amino acids of the haemolymph of Antheraea pernyi during induction and termination of diapause. J Insect Physiol. (1967) 13:1645–55. doi: 10.1016/0022-1910(67)90160-6
69. Michaud MR, Denlinger DL. Oleic acid is elevated in cell membranes during rapid cold-hardening and pupal diapause in the flesh fly, Sarcophaga crassipalpis. J Insect Physiol. (2006) 52:1073–82. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2006.07.005
70. Khani A, Moharramipour S, Barzegar M, Naderi-Manesh H. Comparison of fatty acid composition in total lipid of diapause and non-diapause larvae of Cydia pomonella (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Insect Sci. (2007) 14:125–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7917.2007.00134.x
71. Reynolds J, Poelchau MF, Rahman Z, Armbruster PA, Denlinger DL. Transcript profiling reveals mechanisms for lipid conservation during diapause in the mosquito, Aedes albopictus. J Insect Physiol. (2012) 58:966–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2012.04.013
Keywords: reproductive diapause, major royal jelly protein 1 (MRJP1), metabolomics, NMR spectroscopy, machine learning, qRT-PCR, RNA interference (RNAi)
Citation: Bianco OE, Abdi A, Klein MS, Wei X, Sim C and Meuti ME (2024) Consuming royal jelly alters several phenotypes associated with overwintering dormancy in mosquitoes. Front. Insect Sci. 4:1358619. doi: 10.3389/finsc.2024.1358619
Received: 20 December 2023; Accepted: 14 May 2024;
Published: 07 June 2024.
Edited by:
Nicholas Teets, University of Kentucky, United StatesReviewed by:
Geoffrey Michael Attardo, University of California, Davis, United StatesChao Chen, University of Florida, United States
Copyright © 2024 Bianco, Abdi, Klein, Wei, Sim and Meuti. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Megan E. Meuti, meuti.1@osu.edu
 Olivia E. Bianco1
Olivia E. Bianco1 Matthias S. Klein
Matthias S. Klein Xueyan Wei
Xueyan Wei Cheolho Sim
Cheolho Sim Megan E. Meuti
Megan E. Meuti