- 1 The Key Laboratory of Microcosmic Syndrome Differentiation, Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming, China
- 2 Yunnan Key Laboratory of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine for Chronic Disease in Prevention and Treatment, Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming, China
- 3 School of Chinese Medicine, Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming, China
Traditional cancer treatment methods often encounter limitations, such as poor targeting, low bioavailability, and high systemic toxicity. These challenges have led researchers to explore alternative therapeutic strategies. Nickel nanoparticles (NiNPs), owing to their distinctive physicochemical properties and tunable biocompatibility, have attracted considerable attention in cancer therapy and drug delivery applications. These nanomaterials demonstrate excellent magnetic properties, photothermal conversion capabilities, catalytic activity, and potential for multifunctionality and targeted drug delivery via surface modification. This review highlights recent advancements in the use of NiNPs for cancer treatment, emphasizing their advantages as drug carriers that enhance the bioavailability, targeting, and therapeutic efficacy of anticancer agents. Additionally, the synergistic applications of NiNPs in multimodal therapies, including magnetic hyperthermia, photothermal therapy, and chemodynamic therapy, are discussed, as well as their potential as theranostic platforms. Although nickel-based nanodelivery systems show significant promise for clinical translation, issues related to biosafety, degradation metabolism, and long-term toxicity remain and require further investigation to support their clinical application.
1 Introduction
Cancer has become a major global public health concern. Statistical data indicate that approximately 20 million new cancer cases occurred worldwide in 2022, resulting in around 9.7 million deaths (Dolgin, 2021; Filho et al., 2025). Although conventional chemotherapeutic agents exhibit substantial antitumor activity in vitro, typically less than 0.1% of the administered dose reaches the tumor site. Most of the drug is instead distributed to healthy tissues or eliminated by the reticuloendothelial system (Cornen and Vivier, 2018; Niu et al., 2025). This inefficient delivery not only reduces therapeutic efficacy but also increases the risk of toxicity to normal cells. The advancement of nanotechnology has introduced new opportunities to overcome these limitations. Nanocarriers can enhance therapeutic outcomes by improving drug bioavailability, selectivity, and efficacy in target tissues while minimizing toxicity to healthy cells (Haider et al., 2020; Lepeltier et al., 2020). Recent findings suggest that rationally designed nanocarriers can increase drug accumulation in tumors by five-to ten-fold compared to free drugs, thereby enhancing therapeutic effects and reducing systemic toxicity (Haripriyaa and Suthindhiran, 2023; Khizar et al., 2023).
Despite the promise of nanotechnology, existing metallic nanoparticles face limitations that impede clinical translation. For example, gold nanoparticles possess excellent biocompatibility but lack magnetic responsiveness and have limited catalytic activity in chemodynamic therapy (CDT) applications (Nam et al., 2021; Kesharwani et al., 2023; Aggarwal et al., 2025). Silver nanoparticles, although known for their antimicrobial properties, raise concerns regarding long-term toxicity and lack the multifunctionality required for comprehensive cancer treatment (Ferdous and Nemmar, 2020; Takáč et al., 2023). These shortcomings highlight the urgent need for novel nanomaterial platforms. In comparison to other metallic nanoparticles, nickel nanoparticles (NiNPs) offer several distinct advantages. Unlike gold nanoparticles, which primarily rely on photothermal mechanisms, NiNPs function through magnetic targeting, catalytic activity for chemodynamic therapy, and efficient photothermal conversion under NIR-II irradiation (Lei et al., 2019; Roy et al., 2023). The magnetic susceptibility of nickel allows for precise external field manipulation to achieve targeted delivery, a feature absent in precious metals such as gold and silver. In addition, nickel’s unique electronic structure enables Fenton-like catalytic reactions, generating reactive oxygen species (ROS) more effectively than iron-based systems, while offering superior biocompatibility compared to copper-based alternatives (Wu et al., 2022; Dawson et al., 2023). Moreover, compared to precious metals, such as gold and platinum, the cost-effectiveness of nickel renders NiNPs a more economically viable option for large-scale clinical applications, potentially enhancing the accessibility of advanced cancer therapies (Zhou et al., 2023).
NiNPs exhibit exceptional magnetic properties, catalytic activity, photothermal conversion efficiency, and surface modification potential, rendering them promising candidates for drug delivery systems and cancer therapeutics (Ma et al., 2022; Berhe and Gebreslassie, 2023). Their magnetic characteristics enable precise manipulation via external magnetic fields, facilitating targeted delivery to tumor sites and enhancing drug accumulation efficiency at these locations (Bouremana et al., 2022). In addition, their notable catalytic properties promote specific chemical reactions within the tumor microenvironment, generating ROS that induce apoptosis in cancer cells (Shubhra, 2023; Graham et al., 2025). Through strategic surface modification and functionalization, NiNPs can support multiple stimulus-responsive drug release mechanisms, further improving precision in controlled delivery applications (Farzin et al., 2020; Singh et al., 2023). NiNPs offer considerable benefits in precision cancer therapy through multidimensional delivery approaches, including the development of diverse magnetic nanocarriers, surface functionalization strategies, and the application of external magnetic fields for fine-tuned regulation, thereby achieving accurate in vivo drug delivery and controlled release (Peng et al., 2024). Notably, NiNPs can produce multifunctional, synergistic antitumor effects by integrating complementary therapeutic modalities, such as drug delivery, magnetic hyperthermia, photothermal therapy (PTT), and chemodynamic therapy, thus addressing several limitations associated with conventional chemotherapy (Mukherjee et al., 2020).
Although immunotherapy and targeted therapy have revolutionized cancer treatment, persistent challenges remain in addressing drug-resistant tumors, achieving deep penetration of solid tumors, and reducing off-target effects (Fan et al., 2023). NiNPs offer distinctive advantages by enabling the integration of multiple therapeutic modalities within a single platform, thereby supporting personalized treatment strategies tailored to specific tumor characteristics. The magnetic responsiveness of NiNPs facilitates real-time imaging and controlled drug release, aligning with the demands of precision medicine in modern oncology (Alirezaie Alavijeh et al., 2019; Ji et al., 2022). Moreover, unlike persistent metallic nanoparticles, certain nickel-based compounds, such as nickel selenide (NiSe), are biodegradable and can transform into excretable forms in vivo, providing enhanced biosafety. These attributes position NiNPs as next-generation therapeutic agents capable of addressing the shortcomings of current treatments and meeting the evolving needs of cancer therapy.
This review highlights recent developments in nickel-based nanoparticles for cancer treatment, including synthesis methods, targeted delivery techniques, and therapeutic applications. By critically examining the advantages and limitations of NiNPs, this review explores their capacity to overcome the delivery challenges inherent in traditional anticancer therapies and outlines promising directions for future research. It aims to establish a theoretical foundation and technical framework for the development of innovative, effective, and safe nickel nanoparticle platforms to advance precision oncology.
2 Nickel nanoparticles’ characteristics
2.1 Synthesis methods
NiNPs typically exhibit polymorphic and cubic crystalline structures, with particle sizes generally ranging from 10 to 100 nm. The synthesis methods for NiNPs are commonly categorized into three principal approaches: physical, chemical, and biological techniques (Bohra et al., 2024; Gürsoy et al., 2024). Physical synthesis methods utilize a top-down approach, wherein bulk nickel materials are reduced to nanoparticles through mechanical force, thermal energy, or electromagnetic radiation. These techniques offer operational simplicity and scalability for industrial-scale production; however, they often require substantial energy input (Narender et al., 2022; Shahidi et al., 2022). In contrast, chemical synthesis primarily follows bottom-up strategies, constructing nanostructures at the molecular level via chemical reactions—most notably reduction processes. Although these reactions are rapid and cost-effective, they pose risks of chemical contamination that may compromise the purity of the final product (Aali et al., 2021; Kim et al., 2023). Biological synthesis methods provide environmentally friendly alternatives by employing plant extracts, microorganisms, or other biological materials as both reducing and stabilizing agents (Sivagami and Asharani, 2022; Tailor et al., 2023; Alam et al., 2025). These green synthesis approaches offer significant environmental advantages, including reduced toxicity and cost-effectiveness; however, challenges remain regarding reaction yield, batch-to-batch consistency, and colloidal stability, which require further optimization (Jaji et al., 2020; e Silva et al., 2024).
2.2 Magnetic, catalytic, and optical characteristics
NiNPs possess outstanding magnetic properties and are classified as soft magnetic materials, characterized by high magnetic moments and saturation magnetization (Zarenezhad et al., 2022). These properties allow for precise manipulation using external magnetic fields, facilitating targeted drug delivery applications. Furthermore, the intrinsic chemical stability of NiNPs contributes to relatively low toxicity, establishing a reliable foundation for magnetic guidance and magnetic hyperthermia treatments (Vinod and Philip, 2022; Du et al., 2024). In terms of electrical characteristics, NiNPs exhibit excellent conductivity and low resistivity, making them highly suitable for electronic and sensing applications (Chereches and Minea, 2019). NiNPs also demonstrate significant catalytic activity, primarily due to their large specific surface area and unsaturated coordination sites on surface atoms. These active sites promote a range of chemical processes, including redox and electrocatalytic reactions. Notably, NiNPs can mimic enzymatic activity, such as that of peroxidase and catalase, enabling regulation of ROS within the tumor microenvironment and providing a mechanistic basis for CDT (Zhang et al., 2022; Dawson et al., 2023). Regarding optical behavior, NiNPs exhibit notable light absorption in the near-infrared (NIR) region, driven by surface plasmon resonance effects. This property allows NiNPs to efficiently convert absorbed light energy into heat, supporting PTT (Xiong et al., 2022). Importantly, their optical absorption characteristics can be optimized by tuning particle size, morphology, and surface chemistry, thereby enabling compatibility with various laser excitation wavelengths. This adjustability permits precise photothermal control and enhances therapeutic efficacy (Lei et al., 2019; Du et al., 2021a).
2.3 Surface modification and functionalization
Surface modification and functionalization are essential strategies for broadening the application scope of NiNPs and enhancing their biocompatibility. The surface of NiNPs contains numerous active sites, which allow for the attachment of functional molecules through various chemical bonding methods. Common strategies include polymer coating, biomolecule conjugation, and metal shell deposition (Ly et al., 2024). Among these, polymer coating is one of the most widely adopted approaches, employing polymers such as polyethylene glycol (PEG), polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), and polydopamine (PDA) to form protective layers. These coatings prevent nanoparticle aggregation and oxidation, prolong circulation time in the bloodstream, and reduce recognition by the reticuloendothelial system (Shi et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2023).
Biomolecule conjugation improves the targeting ability of NiNPs by attaching recognition ligands, such as antibodies, aptamers, or peptides, to the nanoparticle surface, enabling active targeting of specific cells or tissues. Examples include folate for folate receptor targeting, RGD peptides for integrin targeting, and antibodies for epidermal growth factor receptor targeting, all of which bind selectively to overexpressed receptors on tumor cells (Qin et al., 2023a; Yin et al., 2023). Stimuli-responsive functionalization represents a critical method for designing intelligent nickel-based drug delivery systems. This involves incorporating molecules or polymers that respond to specific stimuli, such as pH, temperature, enzymes, light, or magnetic fields, to enable controlled drug release under defined conditions (Kargozar et al., 2022). Advanced functionalization strategies, such as nickel-substituted hydroxyapatite (Ni-HAp) and RGD-functionalized nanowires, significantly enhance interactions with biological tissues and improve drug delivery efficiency (Kesharwani et al., 2024; Asghar et al., 2025; Lorenzoni et al., 2025).
The excellent physicochemical characteristics and tunable surface chemistry of NiNPs provide a solid foundation for their diverse applications in cancer diagnosis and therapy (Inam et al., 2024). Through surface modification and functionalization strategies, NiNPs have transitioned from basic nanomaterials to clinically relevant therapeutic platforms. Variations in chemical composition and structural design among nickel-based nanomaterials result in substantial differences in their magnetic, optical, and catalytic properties. These property differences directly influence their therapeutic potential and suitability for specific cancer treatment modalities. To assess the functional characteristics and comparative advantages of different nickel-based systems, Table 1 presents a comprehensive analysis of principal nickel-based nanomaterials currently under investigation. The following section will explore how these properties are translated into effective cancer treatment strategies and highlight recent progress in practical applications.
3 Applications of nickel nanoparticles in cancer treatment
3.1 Drug delivery
NiNPs enhance therapeutic efficacy by modulating the tumor microenvironment through multiple mechanisms. These nanoparticles can reprogram tumor-associated macrophages from the pro-tumor M2 phenotype to the anti-tumor M1 phenotype, while simultaneously increasing vascular permeability via controlled generation of ROS, thereby improving drug penetration and accumulation within tumor tissues (Miao et al., 2017; Sang et al., 2021b). Additionally, the catalase-like activity of NiNPs enables the decomposition of endogenous hydrogen peroxide into oxygen, alleviating tumor hypoxia. NiNPs also disrupt the dense extracellular matrix through magnetically driven mechanical forces, further enhancing therapeutic penetration. These regulatory effects on the tumor microenvironment form a strong foundation for diverse therapeutic applications involving NiNPs.
Due to their nanoscale size and surface functionalization, NiNPs can be preferentially taken up by cancer cells, allowing for precise drug delivery to tumor sites. Appropriately engineered NiNPs can achieve targeted delivery of anticancer agents (Du et al., 2021b). For example, Bano et al. developed nickel oxide (NiO) nanoparticles encapsulating doxorubicin (DOX) and functionalized with bovine serum albumin–folic acid (BSA-FA) complexes, which enabled controlled drug release under acidic tumor conditions (pH = 5.5) and red light stimulation (Bano et al., 2016).
Sharma et al. designed magnetic nickel nanowires modified with RGD peptides to enhance tumor cell internalization via integrin receptor-mediated targeting, leading to significantly increased drug accumulation in tumor tissues (Sharma et al., 2015). Further studies demonstrated that lipid-based NINPs with surface-chelated nickel ions enhanced targeting capability, achieving up to 90% internalization in epidermal cancer cells (A431) (Benhabbour et al., 2012). Karaca et al. introduced magnetic nickel nanomachines as drug carriers capable of targeted delivery via wireless control and stimuli-responsive drug release, offering novel insights for precision cancer therapy (Karaca et al., 2021). Additionally, magnetic nickel nanowires functionalized with RGD peptides have shown improved tumor cell uptake through integrin-mediated mechanisms (Qin et al., 2023a). Ramasamy et al. synthesized a magnetic nanocarrier composed of a β-cyclodextrin–folate–dextran polymer coating over nickel–zinc ferrite, which demonstrated efficient drug loading, sustained release, and enhanced cytotoxicity through folate receptor-mediated endocytosis (Ramasamy et al., 2018).
NiNP-based targeted drug delivery systems enable precise drug distribution, significantly reducing exposure to healthy cells while enhancing drug solubility, in vivo stability, and bioavailability, thus minimizing therapeutic side effects (Sanità et al., 2020). This technological advancement is driven by the synergistic use of multidimensional delivery strategies. These include the design of diverse magnetic nanocarriers, surface functionalization (e.g., PEGylation, DOX/PTX conjugation, and folic acid targeting) to enhance stability and specificity, and the precise regulation of nanoparticle migration and biodistribution via external magnetic fields (Sheikh et al., 2021). This integrated drug delivery platform combines targeting efficiency, safety, and therapeutic effectiveness, representing a new paradigm in precision cancer treatment and offering a viable approach to overcome the limitations of traditional chemotherapy.
3.2 Photothermal therapy
PTT is a therapeutic approach that ablates solid tumors through light-induced local hyperthermia generated by photothermal agents (Zhi et al., 2020). It has attracted significant interest in non-invasive cancer treatment due to its high therapeutic efficacy, limited adverse effects on surrounding healthy tissues, and high spatial and temporal resolution, which enables precise treatment control and minimizes damage to normal tissues (Zhang et al., 2021b; Wen et al., 2023). In particular, second near-infrared (NIR-II) lasers have demonstrated superior performance, offering deep tissue penetration, relatively low photon energy, and higher maximum permissible laser exposure limits (Yan et al., 2024; Cui et al., 2025).
The photothermal properties of NiNPs have been extensively investigated for cancer therapy. Upon NIR laser irradiation, aqueous dispersions of NiNPs rapidly elevate in temperature. At the molecular level, this process involves the absorption of photons by conduction electrons in metallic nickel, followed by electron–phonon coupling, which converts photon energy into lattice vibrations, producing heat. The resulting thermal energy initiates multiple cell death pathways, including protein denaturation, DNA damage, and activation of apoptotic cascades (Ahmed et al., 2020). Temperatures above 42°C impair cellular metabolism and induce heat shock protein expression, while those exceeding 50°C cause protein coagulation and immediate necrosis (Paściak et al., 2022; Abbas et al., 2023). This efficient photothermal conversion is attributed to NiNPs’ strong NIR absorption and minimal energy dissipation through radiation. In vivo experiments have confirmed the therapeutic potential of NiNP-based PTT (Xu et al., 2022; Oudjedi and Kirk, 2025). Hu et al. (2021) developed a multifunctional NIR-II-responsive nanoplatform, namely, nickel selenide@polydopamine nanocomposites (NiSe@PDA NCs) for dual-modal imaging-guided PTT. This material exhibited a photothermal conversion efficiency of 48.4% under NIR-II irradiation and served as a T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agent, enabling effective MRI-guided treatment of malignant tumors in both in vitro and in vivo models. Compared to conventional NiNPs, NiSe demonstrates superior photothermal performance due to its modified electronic band structure and enhanced biocompatibility, which also reduces the risk of toxic nickel ion release (Abbas et al., 2023). Zhou et al. (2014) reported that PEG-modified nickel carbide nanocrystals (Ni3C NCs) acted as efficient photothermal agents with strong NIR absorption and photothermal stability, achieving effective tumor cell ablation both in vitro and in vivo. Yao et al. (2022) designed a nickel nanoparticle-doped semiconductor film (Ni–Ti oxide), synthesized via in situ reduction of nickel–titanium layered double hydroxides. This material exhibited stable photothermal effects under NIR irradiation, prolonged stability in physiological environments, and supported both osteogenic differentiation and angiogenesis—features that make it suitable for the combined treatment of bone tumors and deep-seated malignancies.
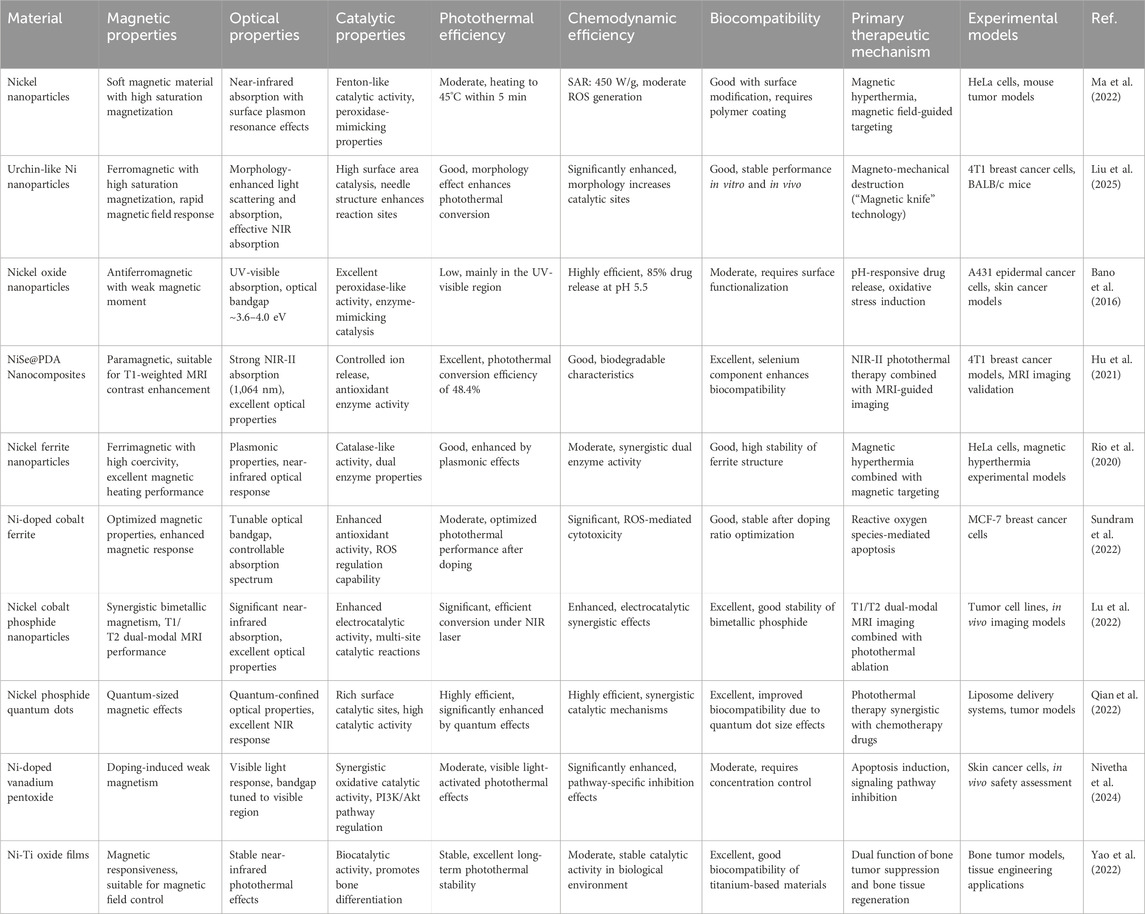
For combination therapy, Wu et al. (2024) developed a liposomal nanoplatform (Ni2P-DOX@Lipo-cRGD), integrating Ni2P quantum dots and DOX into liposomal membranes and cores, respectively (Figure 1). In vivo studies demonstrated that the photothermal properties of Ni2P QDs enabled efficient tumor targeting, high biocompatibility, and complete tumor ablation through synergistic PTT and chemotherapy. In the context of gastric cancer treatment, Song et al. (2023) constructed a multifunctional nanoplatform (NNPIP NPs) that combined PTT with photodynamic therapy (PDT), leading to effective tumor reduction or eradication. These nanoplatforms also served as T1-weighted MRI contrast agents, supporting tumor diagnosis and preoperative staging while reducing toxicity and improving therapeutic selectivity. NiNPs hold substantial promise in PTT due to their excellent photothermal conversion efficiency, adjustable optical properties, and favorable biocompatibility. Through multifunctional integration, which encompasses imaging guidance, chemotherapeutic synergy, and targeted delivery, NiNPs not only enhance the efficacy of PTT but also present innovative treatment strategies for deep-seated and refractory tumors (Han and Choi, 2021; Alamdari et al., 2022).
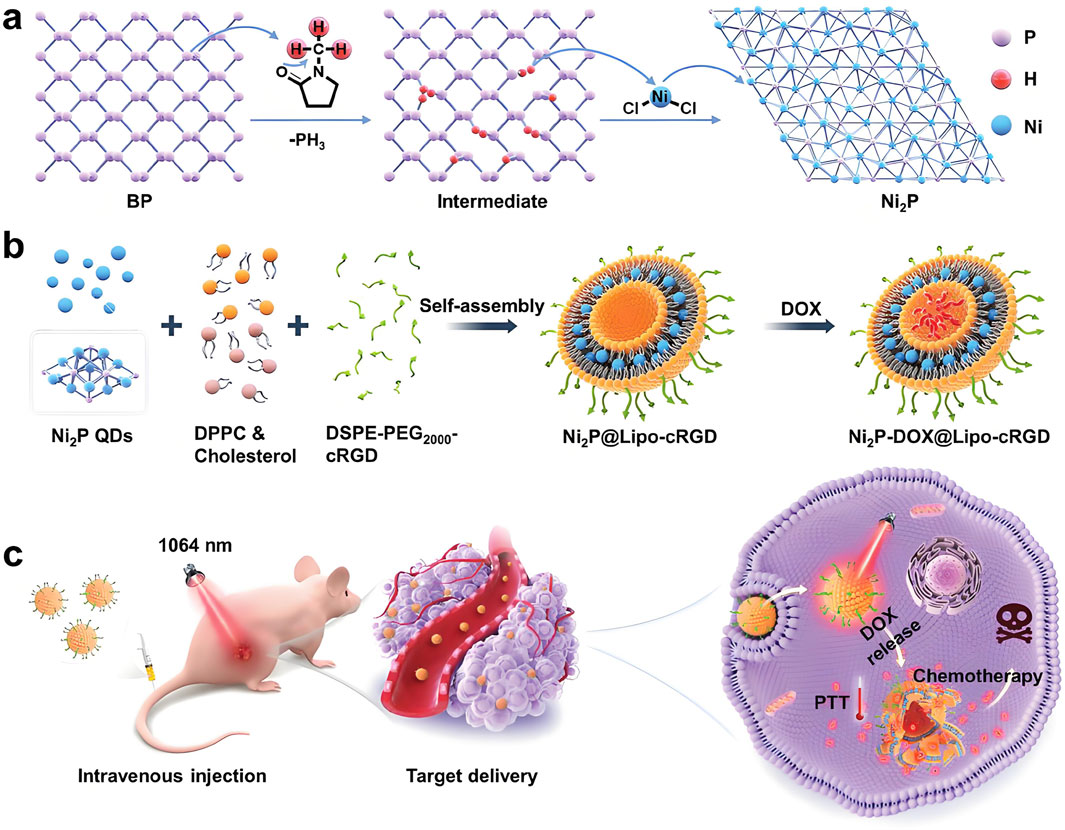
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the development and therapeutic application of a nickel-based nanoplatform. The process includes: (a) topochemical synthesis of Ni2P quantum dots (QDs) from BPQD templates; (b) preparation of Ni2P-DOX@Lipo-cRGD through the incorporation of Ni2P QDs and doxorubicin (DOX) into liposomal structures; and (c) demonstration of the synergistic effects of Ni2P-DOX@Lipo-cRGD in achieving efficient tumor ablation through the combined mechanisms of PTT and chemotherapy. Reproduced with permission from Wu et al. (2024). Copyright (2024) Wiley-VCH GmbH.
3.3 Magnetic hyperthermia therapy
Magnetic hyperthermia is a targeted tumor treatment that selectively destroys cancer cells by generating localized heat within tumor tissues, thereby minimizing harm to adjacent healthy tissues (Vilas-Boas et al., 2020; Yu et al., 2022; Szwed et al., 2024). NiNPs, known for their high magnetic-to-thermal conversion efficiency, generate substantial heat via Néel and Brownian relaxation processes under alternating magnetic fields. Their specific absorption rate (SAR) can reach up to 450 W/g, which is sufficient to elevate tumor temperatures to therapeutic levels and induce cancer cell apoptosis (Ota and Takemura, 2019; Ahghari et al., 2020). The molecular mechanisms underlying magnetic hyperthermia involve two primary relaxation pathways. In Néel relaxation, the magnetic moment of individual nanoparticles flips relative to the crystal lattice in response to the external magnetic field, with the relaxation time determined by the energy barrier (KV/kBT), where K is the magnetic anisotropy constant, V is the particle volume, k_B is the Boltzmann constant, and T is the temperature (Ilg and Kröger, 2020). Brownian relaxation, by contrast, involves the physical rotation of the entire nanoparticle within its surrounding medium, with the relaxation time governed by hydrodynamic volume and fluid viscosity (Ota and Takemura, 2019; Torres et al., 2019). Both mechanisms convert magnetic energy into heat through frictional forces and reorientation of magnetic moments. The heat generated induces a range of cellular stress responses, including mitochondrial dysfunction, elevated ROS, and activation of temperature-sensitive ion channels (Shen et al., 2020). These stressors activate apoptotic signaling cascades involving caspase activation, cytochrome c release, and DNA fragmentation, resulting in targeted cancer cell death while sparing healthy tissue due to the confined nature of thermal induction (Ludwig et al., 2017; Clerc et al., 2018). Unlike photothermal therapies, which are limited by tissue light absorption and scattering, magnetic hyperthermia leverages magnetic fields with high tissue penetration, allowing effective treatment of deep-seated tumors. Additionally, it typically employs low-frequency, low-intensity magnetic fields that are non-harmful to human tissues, offering a safer and minimally invasive option for precision oncology (Sun et al., 2023).
Numerous studies support the therapeutic potential of nickel-based nanomaterials in magnetic hyperthermia. Rio et al. demonstrated that nickel ferrite (NiFe2O4) nanoparticles generate localized heat under alternating magnetic fields and possess both magnetic and plasmonic properties, enabling precise magnetic-guided positioning and synergistic thermal killing of cancer cells (Rio et al., 2020). Hopkins et al. (2017) designed nickel–gold core–shell nanowires (Ni–Au CSNWs) for radiofrequency-mediated thermal therapy. Remote activation of their paramagnetism using radiofrequency irradiation led to effective pancreatic tumor cell death, marked by nuclear shrinkage and fragmentation, thereby validating radiofrequency-induced thermal ablation. In another approach, Cabral et al. (2019) combined the internalization capabilities of boron nitride nanotubes (BNNTs) with the magnetic heating properties of NiFe2O4 nanoparticles to construct a robust hyperthermia platform. Following cellular uptake, this system successfully eradicated a majority of HeLa cancer cells in a single cycle using alternating current (AC) magnetic fields.
In summary, magnetic hyperthermia represents a promising cancer treatment modality enabled by the unique properties of NiNPs. Its advantages, including precise targeting, deep tissue penetration, and low systemic toxicity, make it particularly suitable for managing deep-seated and treatment-resistant tumors.
3.4 Chemodynamic therapy
CDT is an emerging tumor treatment strategy that has attracted considerable attention due to its non-invasive nature and minimal side effects. CDT based on Fenton or Fenton-like reactions generates highly toxic hydroxyl radicals (•OH) in situ within tumor tissues, inducing apoptosis and inhibiting tumor growth (Jia et al., 2022; Mohammed et al., 2022; Gao et al., 2023). At the molecular level, nickel-based nanoparticles catalyze the decomposition of endogenous hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) via Fenton-like reactions (Cao et al., 2022; Lin et al., 2023). This reaction involves the reduction of Ni3+ to Ni2+ in the presence of H2O2, accompanied by the generation of highly reactive •OH radicals. These radicals possess strong oxidative potential and non-selectively attack various biomolecules, including lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids (Koo et al., 2022). Lipid peroxidation disrupts membrane integrity, protein oxidation impairs enzymatic function and structure, and DNA damage leads to base modifications and strand breaks, thus collectively triggering apoptotic cell death pathways (Endale et al., 2023). The selectivity of CDT arises from the elevated H2O2 levels found in the tumor microenvironment relative to normal tissues, ensuring preferential ROS production within cancerous cells (Baghban et al., 2020; Yang et al., 2020; Chu et al., 2023). NiNPs have gained interest in this domain for their antioxidant modulation, Fenton-like catalytic activity, and integration within composite nanomaterials that enhance CDT efficacy, modulate the tumor microenvironment, and improve biosafety (Sang et al., 2021a). Their mechanisms of action include photocatalytic activity, enzyme-mimetic behavior, and biodegradability, offering new opportunities for precision, low-toxicity cancer therapy.
For example, nickel-based nanocomposites can induce apoptosis through catalytic generation of ROS. Nivetha et al. synthesized nickel-doped vanadium pentoxide (Ni@V2O5) nanocomposites, which inhibited skin cancer cell growth by inducing mitochondrial and nuclear damage, enhancing ROS generation, and activating caspase 9/3-mediated apoptotic signaling. Additionally, Ni@V2O5 suppressed the expression of oncoproteins, such as PI3K, Akt, and mTOR, supporting its potential as an anticancer agent (Nivetha et al., 2024). Similarly, Sundram et al. (2022) prepared nickel-doped cobalt ferrite (Ni-CFO) nanoparticles using coriander extract via a precipitation method. Among tested concentrations, 0.8% Ni-CFO exhibited strong magnetic and antioxidant properties. In MCF-7 breast cancer cells, 0.8% Ni-CFO induced apoptosis, inhibited cell adhesion and migration, and downregulated phosphorylated PI3K, Akt, and mTOR.
Moreover, combining CDT with PTT has demonstrated synergistic therapeutic effects, as elevated temperatures not only facilitate thermal ablation but also accelerate Fenton reactions, enhancing ROS production (Zhang et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2021a). Qian et al. (2022) developed PEG-modified sea urchin-like nickel nanoclusters (PUNNCs) for integrated NIR-II photothermal and chemodynamic therapy. The unique morphology of PUNNCs supported efficient photothermal conversion under NIR-II irradiation and enabled the controlled release of Ni2+ ions, thereby boosting CDT performance. Both in vitro and in vivo experiments confirmed the therapeutic efficacy and biosafety of PUNNCs, which effectively suppressed tumor growth and induced cancer cell death (Figure 2). In summary, CDT offers distinct advantages, including high tumor selectivity, minimal side effects, and no need for external energy input (Min et al., 2020). However, challenges remain in optimizing the catalytic efficiency and biocompatibility of nickel-based systems, as well as regulating H2O2 levels within the tumor microenvironment to maximize therapeutic outcomes.
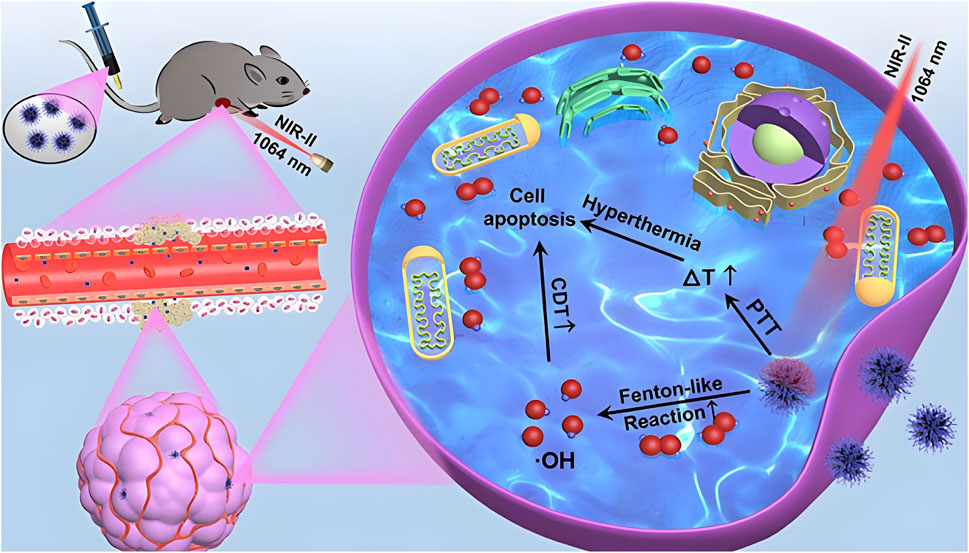
Figure 2. Schematic illustration of 9T-PUNNC nanoparticle-mediated photothermal-enhanced chemodynamic synergistic therapy. The diagram depicts how PEG-modified sea urchin-like nickel nanoclusters (PUNNCs) facilitate dual-mechanism cancer treatment. Under NIR-II irradiation, the structural features of PUNNCs enable excellent photothermal conversion and controlled Ni2+ ion release, enhancing chemodynamic therapy. This synergy results in demonstrated anticancer efficacy and biosafety in both in vitro and in vivo studies. Reproduced with permission from Qian et al. (2022). Copyright (2022) Ivyspring International Publisher.
3.5 Theranostic applications of nickel nanoparticles
NiNPs possess distinctive physicochemical properties that offer substantial potential not only for cancer treatment but also for diagnosis and imaging. Their exceptional magnetic and optical characteristics render them effective contrast agents for MRI and photoacoustic imaging, significantly improving tumor detection sensitivity and resolution compared to conventional imaging materials (Qian et al., 2022; Yu et al., 2017). Notably, their capacity to integrate diagnostic and therapeutic functions enables the realization of theranostic platforms, providing robust technical support for precision oncology.
Recent advancements in nickel nanoparticle-based theranostic systems have demonstrated remarkable multifunctionality. For example, Liu et al. (2018) developed a mesoporous nickel oxide (mNiO) nanoparticle system loaded with artemisinin (ART), capable of integrating T2-weighted MRI and NIR fluorescence imaging. This platform also functions as an efficient drug delivery system with controlled degradation and Ni2+ ion release under acidic tumor conditions. Additionally, it exhibits strong NIR absorption for PTT. Experimental data confirmed that this integrated strategy significantly enhanced antitumor efficacy in hypoxic tumor environments when compared to either free ART or PTT alone, highlighting the potential of natural product-based nanomedicine in cancer therapy. In another study, Lu et al. (2022) designed polyvinylpyrrolidone-coated bimetallic nickel–cobalt phosphide nanoparticles (NiCoP/PVP). Leveraging the complementary magnetic properties of nickel and cobalt, this system enabled dual-mode T1-and T2-weighted MRI, effectively addressing the limitations of single-modality imaging and enhancing diagnostic accuracy. NiCoP/PVP nanoparticles also exhibited strong NIR absorption and efficient photothermal conversion, making them effective agents for tumor photothermal ablation.
Significant progress has also been made in the development of catalytic nickel-based theranostic platforms. Liu et al. (2024) engineered nickel-based single-atom metal clusters (NSAMCs) that overcome several limitations of conventional iron-based agents in ferroptosis therapy. These clusters demonstrated excellent water solubility, colloidal stability, low toxicity, and selective tumor targeting. Their dual-enzyme mimetic activity synergistically induced cancer cell ferroptosis, significantly enhancing therapeutic efficacy. Another innovative approach involved the incorporation of nickel into Fe3O4 crystal lattices to produce carbon-coated nickel ferrite nanocatalysts (NFN@C). This structural modification optimized the electronic configuration of the catalyst, thereby enhancing its efficiency in catalyzing H2O2 into hydroxyl radicals (•OH) within tumor microenvironments. Electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy confirmed increased •OH production following nickel incorporation, indicating improved Fenton reaction efficiency due to electron density modulation. In addition to catalytic activity, NFN@C nanoparticles exhibited excellent NIR-II photothermal conversion capabilities, achieving synergistic effects between PTT and CDT that further improved antitumor outcomes (Zhao et al., 2025) (Figure 3).
Figure 3. Schematic representation of the development and therapeutic mechanism of NFN@C nanocatalysts. The figure includes: (a) synthesis of carbon-coated nickel ferrite nanocatalysts (NFN@C), showing the incorporation of nickel into Fe3O4 crystal lattices; and (b) the mechanism by which NFN@C mediates photothermal-enhanced chemodynamic therapy. Nickel incorporation improves the electronic structure, increasing catalytic efficiency for H2O2 conversion into hydroxyl radicals within tumor microenvironments, while simultaneously enabling efficient photothermal conversion under NIR-II irradiation for synergistic therapeutic benefit. Reproduced with permission from Zhao et al. (2025). Copyright (2025) Wiley-VCH GmbH.
3.6 Emerging applications of nickel nanoparticles
3.6.1 Magneto-mechanical tumor destruction: the “magnetic knife” technology
The “magnetic knife” is an emerging anti-tumor strategy that destroys cancer cells through mechanical forces generated by magnetic nanoparticles under rotating magnetic fields (RMFs). These forces, resembling rotational stirring, physically disrupt tumor cells in a manner comparable to surgical excision (Wei and Wang, 2023; Zhao et al., 2023). Researchers have synthesized urchin-like nickel nanoparticles (UNNPs) via magnetic solvothermal methods, producing structures with high surface area and enhanced interaction with tumor cells. These nanoparticles exhibit high saturation magnetization and strong ferromagnetism, enabling rapid response to external magnetic fields. In both in vitro and in vivo models, UNNPs demonstrated effective tumor suppression and favorable biocompatibility. Their needle-like surface architecture significantly increased contact with cancer cells, resulting in elevated cell necrosis rates under RMF, and effectively inhibited breast cancer growth in mouse models (Qian et al., 2020). Liu et al. further developed a novel synthesis approach for urchin-like magnetic nanoparticles (UMNs) designed to treat triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). These UMNs, prepared through a simplified solvothermal method, mechanically disrupted cell membranes under RMF, leading to increased tumor cell death. In addition, UMNs were loaded with a STAT3 inhibitor (Stattic) and COL10A1 siRNA to form UMNP/St/si complexes. The antitumor activity of this system under RMF was validated both in vitro and in vivo (Liu et al., 2025) (Figure 4). Kim et al. (2016) reported on magnetic nickel–gold-coated nanodisks functionalized with DNA aptamers, which effectively induced ascites cancer cell death under RMFs. This magnetically driven nanomechanical strategy holds strong potential for localized treatment of deep tumors, offering benefits such as simplicity, high efficiency, safety, and low cost (Lopez et al., 2022).
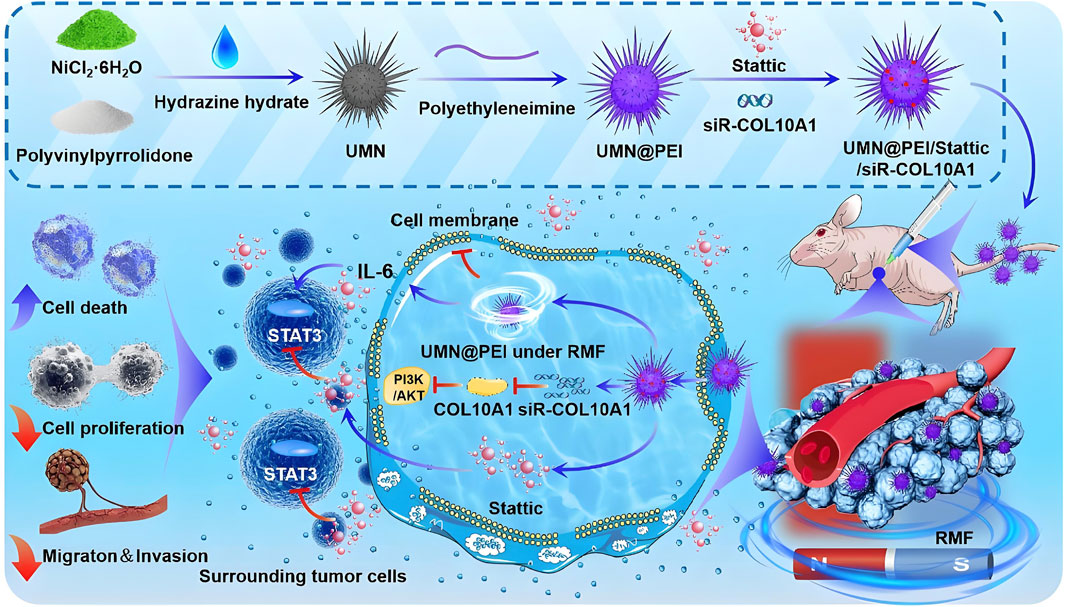
Figure 4. Schematic illustration of rotating magnetic field (RMF)-driven UMNP/St/si therapy for triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). Urchin-like magnetic nanoparticles (UMNPs) are synthesized and loaded with the STAT3 inhibitor (Stattic) and COL10A1 siRNA to form UMNP/St/si complexes. When subjected to RMF, these nanoparticles disrupt cell membranes via magneto-mechanical forces, inhibit IL-6-induced STAT3 pathway activation, and suppress COL10A1 expression to inactivate the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and remodel the extracellular matrix, ultimately reducing tumor growth. Reproduced with permission from Liu et al. (2025). Copyright (2025) Elsevier B.V.
3.6.2 Gene editing technology
Nickel-based platforms offer unique advantages for CRISPR-Cas9 delivery due to their magnetic targeting capabilities and controlled release mechanisms. The magnetic properties of NiNPs enable spatially precise delivery of gene editing components to tumor tissues. Their surface chemistry allows for the co-packaging of multiple CRISPR elements, including guide RNAs, Cas proteins, and donor DNA templates (Hryhorowicz et al., 2019; Rohiwal et al., 2020). Recent studies have shown that NiNPs can be functionalized with pH-responsive polymer coatings that protect the gene editing payload during circulation and facilitate release in acidic tumor environments (Duan et al., 2021). This design enhances tumor-specific accumulation while reducing off-target editing, which is a major limitation in conventional gene therapies. Furthermore, the photothermal properties of NiNPs can be harnessed to trigger localized release through controlled heating, enabling temporal regulation of gene editing activity.
3.6.3 Immunotherapy
Recent advances suggest that NiNPs can be engineered for the precision delivery of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Their magnetic responsiveness enables targeted delivery of immunotherapeutic agents directly to tumor-associated immune cells (Walters et al., 2021). For example, NiNPs coated with anti-PD-L1 or anti-CTLA-4 antibodies can provide localized immune modulation while minimizing systemic immune-related adverse events (Kiaie et al., 2023). Magnetic guidance also facilitates accumulation in tumor-draining lymph nodes, which are key sites for initiating immune responses, thereby enhancing checkpoint blockade therapy effectiveness. Moreover, NiNPs have been employed to support chimeric antigen receptor T cell (CAR-T) therapy by magnetically labeling engineered T cells. This enables real-time tracking of CAR-T cell distribution and activity, improving therapeutic monitoring and potentially optimizing treatment outcomes (Qin et al., 2023b; Pfister et al., 2025).
4 Challenges in nickel nanoparticle applications
To comprehensively evaluate the clinical translation potential of NiNPs, Table 2 presents a comparative analysis of NiNPs and widely studied nanoparticle systems, such as iron oxide, gold, and copper-based platforms, based on key performance parameters. The therapeutic efficacy of NiNPs derives from their ability to convert various forms of energy (photonic, magnetic, and chemical) into localized cytotoxic effects via distinct molecular mechanisms.
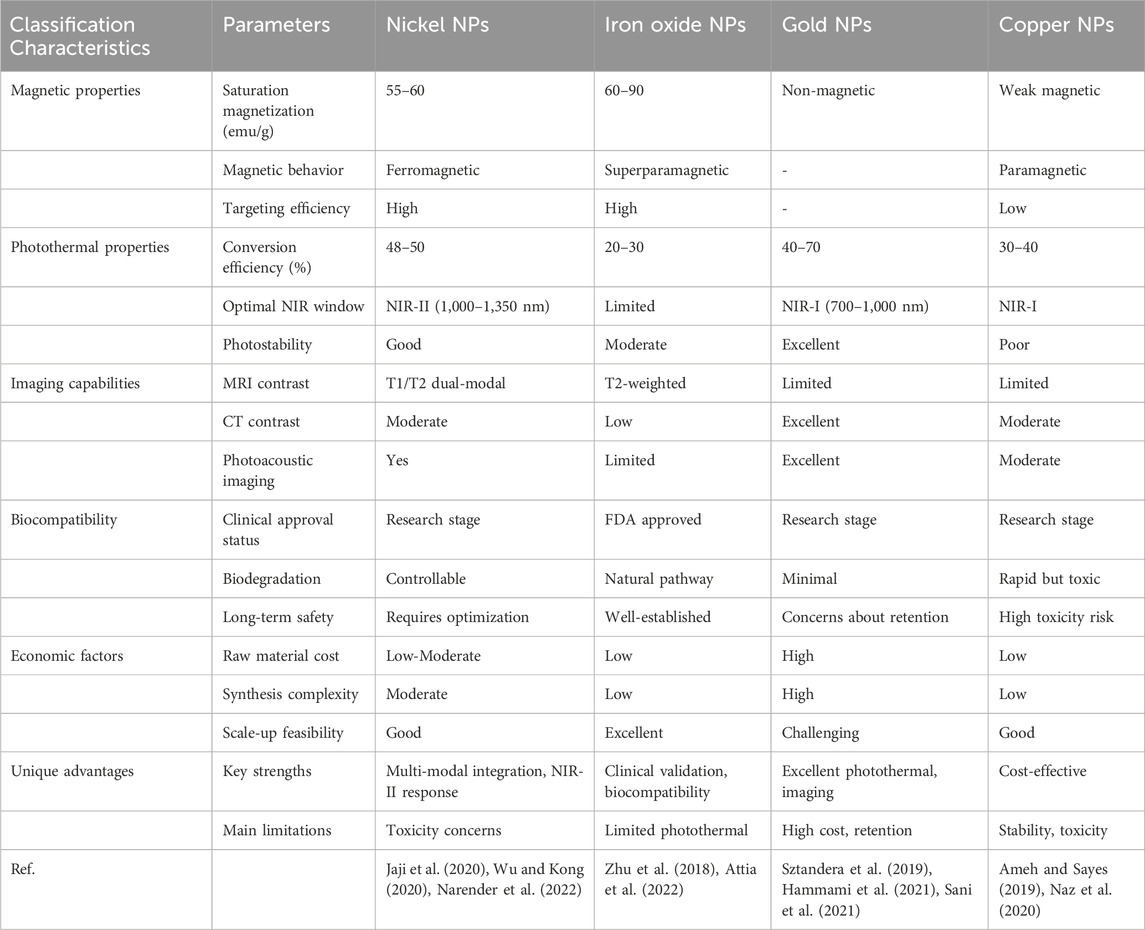
Table 2. Comparative analysis of nickel nanoparticles with established nanoparticle systems for cancer therapy.
Despite these advantages, biosafety concerns represent major barriers to clinical application. Mo et al. (2024) demonstrated that nickel-containing nanoparticles exhibit dose-dependent cytotoxicity, genotoxicity, and carcinogenicity in lung tissues, with IC50 values ranging from 10 to 100 μg/mL in human lung epithelial cells. Ajdari and Ziaee Ghahnavieh (2014) conducted a comprehensive risk assessment showing that nickel-based nanomaterials tend to accumulate in the liver, spleen, and kidneys, with elimination half-lives exceeding 30 days in rodent models. Critical safety concerns include the kinetics of nickel ion release, dose–toxicity relationships, nanoparticle–immune system interactions, and degradation behavior under various physiological conditions.
NiNPs have also been shown to induce oxidative stress and inflammatory responses (Iftikhar et al., 2023). For example, NiO nanoparticles can cause apoptosis, necrosis, and IL-6/IL-8 secretion in lung epithelial cells (BEAS-2B, A549), and long-term exposure has been linked to chronic inflammation. Released nickel ions may interfere with intracellular calcium homeostasis and disrupt mitochondrial function. Although surface modification and delivery optimization can reduce toxicity, a trade-off exists between the thickness of protective coatings and the preservation of therapeutic functionality. Toxicity assessments employ both in vitro and in vivo models. Cell-based assays, including MTT, LDH release, and comet assays, have established dose–response relationships, typically observing cytotoxic effects at concentrations exceeding 50 μg/mL in various cancer cell lines (Mo et al., 2024). In vivo animal studies using rodent models have documented biodistribution patterns characterized by preferential accumulation in reticuloendothelial organs, with tissue nickel concentrations increasing by 10–15-fold relative to baseline following repeated administration (Abudayyak et al., 2020). Pharmacokinetic analyses indicate that surface-modified NiNPs exhibit biphasic elimination: an initial rapid clearance phase (t1/2 = 2–4 h) is followed by a prolonged retention phase (t1/2 = 15–30 days), suggesting a potential risk for long-term tissue accumulation (Di Bucchianico et al., 2018; Vallabani and Karlsson, 2022).
However, long-term risks, such as potential carcinogenicity and chronic organ dysfunction, remain inadequately characterized and require extended follow-up studies to establish definitive causal relationships. Moreover, inconsistencies in experimental protocols, nanoparticle properties, and administration regimens across studies complicate direct comparisons of safety profiles.
5 Summary and future prospects
Considering the potential and current limitations of NiNPs in cancer treatment, future research is likely to focus on the development of degradable NiNPs that retain therapeutic efficacy while enabling complete metabolic clearance, thereby reducing long-term toxicity risks.
Innovative strategies are emerging to address biocompatibility challenges through advanced surface engineering and controllable degradation mechanisms. Recent breakthroughs include the use of biomimetic cell membrane coatings derived from patient-specific cells, which offer immune evasion while maintaining magnetic and photothermal functionality (Jin et al., 2019). These coatings allow NiNPs to avoid immune detection without compromising their therapeutic properties. In addition, self-assembling peptide coatings have been developed to undergo conformational changes in response to tumor-specific enzymes, exposing targeting ligands exclusively within the tumor microenvironment (Liu et al., 2022).
The development of biodegradable NiNPs offers promising solutions to long-term safety concerns. These platforms employ controlled oxidation and complexation reactions to transform persistent nickel structures into excretable forms. One approach involves incorporating nickel into selenide structures that undergo predictable oxidation in biological environments, converting into water-soluble selenate compounds suitable for renal excretion (Menon et al., 2018). Such systems maintain therapeutic performance during treatment while ensuring complete elimination within defined timeframes. Compared to conventional NiNPs, NiSe offers several advantages: (1) reduced cytotoxicity due to a slower nickel ion release rate, which minimizes oxidative stress and cellular interference (Mikhailova, 2023); (2) enhanced biocompatibility attributed to selenium’s natural antioxidant properties; and (3) superior biodegradability via oxidation into water-soluble, physiologically eliminable selenates (Othman et al., 2023; Sowmya et al., 2024). Notably, this degradation process can release therapeutically beneficial selenium ions. Further, NiSe demonstrates improved photothermal and magnetic properties, with composite materials achieving photothermal conversion efficiencies approaching 50% while maintaining high biosafety standards (Abbas et al., 2023). Emerging monitoring technologies are also leveraging the magnetic properties of NiNPs for non-invasive tracking through advanced magnetic particle imaging. This enables clinicians to monitor nanoparticle biodistribution and clearance in real time with high spatial and temporal resolution, supporting adaptive treatment strategies based on patient-specific responses.
Future research will emphasize the design of NiNPs that respond to multiple physiological and biochemical signals in the tumor microenvironment to achieve precise drug release and therapeutic modulation. Exploiting the magnetic properties of NiNPs may also facilitate the development of real-time, non-invasive monitoring systems for in vivo tracking of nanoparticle distribution and degradation, laying the foundation for personalized treatment protocols. Simultaneously, exploring safer, more efficient, and environmentally sustainable synthesis methods will be essential to reduce production costs and enhance product consistency and quality.
In conclusion, while NiNPs hold considerable promise in cancer therapy, their clinical application remains in an exploratory phase. Future work must continue to address concerns related to biocompatibility and toxicity while advancing the design of safe, effective, and clinically translatable nickel-based nanotherapeutics.
Author contributions
FW: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. ST: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. XM: Writing – review and editing. HY: Writing – review and editing. TZ: Writing – review and editing, Visualization. KW: Visualization, Writing – review and editing. JW: Writing – review and editing, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the open Project of Yunnan Clinical Medical Research Center for Geriatric Diseases (Numbers: 2022YJZX-LN18, 2022YJZX-LN20, 2023YJZX-LN08, 2023YJZX-LN10), Open Research Fund Program of Yunnan Key Laboratory of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine for Chronic Disease in Prevention and Treatment (Numbers: YPKLG2024-014).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Aali, H., Baygi, N. J., Mollazadeh, S., and Khaki, J. V. (2021). Improving the physicochemical properties of NaCl-assisted solution combustion synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles by controlling the thermodynamics of the process. Ceram. Int. 47 (14), 19315–19327. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.03.233
Abbas, N., Zhang, J.-M., Nazir, S., Ahsan, M. T., Saleem, S., Ali, U., et al. (2023). A comparative study of structural, vibrational mode, optical and electrical properties of pure nickel selenide (NiSe) and Ce-doped NiSe nanoparticles for electronic device applications. Phys. B Condens. Matter 649, 414471. doi:10.1016/j.physb.2022.414471
Abudayyak, M., Güzel, E., and Özhan, G. (2020). Cytotoxic, genotoxic, and apoptotic effects of nickel oxide nanoparticles in intestinal epithelial cells. Turk J. Pharm. Sci. 17 (4), 446–451. doi:10.4274/tjps.galenos.2019.76376
Aggarwal, R., Sheikh, A., Akhtar, M., Ghazwani, M., Hani, U., Sahebkar, A., et al. (2025). Understanding gold nanoparticles and their attributes in ovarian cancer therapy. Mol. Cancer 24 (1), 88. doi:10.1186/s12943-025-02280-3
Ahghari, M. R., Soltaninejad, V., and Maleki, A. (2020). Synthesis of nickel nanoparticles by a green and convenient method as a magnetic mirror with antibacterial activities. Sci. Rep. 10 (1), 12627. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-69679-4
Ahmed, K., Zaidi, S. F., Mati Ur, R., Rehman, R., and Kondo, T. (2020). Hyperthermia and protein homeostasis: cytoprotection and cell death. J. Therm. Biol. 91, 102615. doi:10.1016/j.jtherbio.2020.102615
Ajdari, M., and Ziaee Ghahnavieh, M. (2014). Histopathology effects of nickel nanoparticles on lungs, liver, and spleen tissues in male mice. Int. Nano Lett. 4 (3), 113. doi:10.1007/s40089-014-0113-8
Alam, M. W., Dhanda, N., Almutairi, H. H., Al-Sowayan, N. S., Mushtaq, S., and Ansari, S. A. (2025). Green ferrites: eco-friendly synthesis to applications in environmental remediation, antimicrobial activity, and catalysis—A comprehensive review. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 39 (2), e7962. doi:10.1002/aoc.7962
Alamdari, S. G., Amini, M., Jalilzadeh, N., Baradaran, B., Mohammadzadeh, R., Mokhtarzadeh, A., et al. (2022). Recent advances in nanoparticle-based photothermal therapy for breast cancer. J. Control. Release 349, 269–303. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.06.050
Alirezaie Alavijeh, A., Barati, M., Barati, M., and Abbasi Dehkordi, H. (2019). The potential of magnetic nanoparticles for diagnosis and treatment of cancer based on body magnetic field and organ-on-the-chip. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 9 (3), 360–373. doi:10.15171/apb.2019.043
Ameh, T., and Sayes, C. M. (2019). The potential exposure and hazards of copper nanoparticles: a review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 71, 103220. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2019.103220
Asghar, M. S., Ghazanfar, U., Rizwan, M., Manan, M. Q., Baig, A., Qaiser, M. A., et al. (2025). Potential molecular interactions and In Vitro hyperthermia, thermal, and magnetic studies of bioactive nickel-doped hydroxyapatite thin films. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 26 (3), 1095. doi:10.3390/ijms26031095
Attia, N. F., El-Monaem, E. M. A., El-Aqapa, H. G., Elashery, S. E. A., Eltaweil, A. S., El Kady, M., et al. (2022). Iron oxide nanoparticles and their pharmaceutical applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 11, 100284. doi:10.1016/j.apsadv.2022.100284
Baghban, R., Roshangar, L., Jahanban-Esfahlan, R., Seidi, K., Ebrahimi-Kalan, A., Jaymand, M., et al. (2020). Tumor microenvironment complexity and therapeutic implications at a glance. Cell Commun. Signal. 18 (1), 59. doi:10.1186/s12964-020-0530-4
Bano, S., Nazir, S., Munir, S., AlAjmi, M. F., Afzal, M., and Mazhar, K. (2016). “Smart” nickel oxide based core-shell nanoparticles for combined chemo and photodynamic cancer therapy. Int. J. Nanomedicine 11, 3159–3166. doi:10.2147/IJN.S106533
Benhabbour, S. R., Luft, J. C., Kim, D., Jain, A., Wadhwa, S., Parrott, M. C., et al. (2012). In vitro and in vivo assessment of targeting lipid-based nanoparticles to the epidermal growth factor-receptor (EGFR) using a novel heptameric ZEGFR domain. J. Control. Release 158 (1), 63–71. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2011.10.013
Berhe, M. G., and Gebreslassie, Y. T. (2023). Biomedical applications of biosynthesized nickel oxide nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomedicine 18, 4229–4251. doi:10.2147/IJN.S410668
Bohra, M., Giaremis, S., Ks, A., Mathioudaki, S., Kioseoglou, J., and Grammatikopoulos, P. (2024). Ferromagnetic-antiferromagnetic coupling in gas-phase synthesized M(Fe, Co, and Ni)-Cr nanoparticles for next-generation magnetic applications. Adv. Sci. 11 (43), e2403708. doi:10.1002/advs.202403708
Bouremana, A., Mouaci, S., Berriah, A., Boutebina, Z., Manseri, A., and Bensouilah, A. (2022). High yield solvothermal synthesis of Ni nanoparticles: structural, microstructural, and magnetic properties. J. Nanoparticle Res. 24 (10), 204. doi:10.1007/s11051-022-05584-3
Cabral, T. C., Ardisson, J. D., de Miranda, M. C., Gomes, D. A., Fernandez-Outon, L. E., Sousa, E. M., et al. (2019). Boron nitride nanotube@NiFe2O4: a highly efficient system for magnetohyperthermia therapy. Nanomedicine 14 (23), 3075–3088. doi:10.2217/nnm-2019-0123
Cao, C., Wang, X., Yang, N., Song, X., and Dong, X. (2022). Recent advances of cancer chemodynamic therapy based on Fenton/Fenton-like chemistry. Chem. Sci. 13 (4), 863–889. doi:10.1039/d1sc05482a
Chereches, E. I., and Minea, A. A. (2019). Electrical conductivity of new nanoparticle enhanced fluids: an experimental study. Nanomater 9 (9), 1228. doi:10.3390/nano9091228
Chu, Z., Yang, J., Zheng, W., Sun, J., Wang, W., and Qian, H. (2023). Recent advances on modulation of H2O2 in tumor microenvironment for enhanced cancer therapeutic efficacy. Coord. Chem. Rev. 481, 215049. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2023.215049
Clerc, P., Jeanjean, P., Hallali, N., Gougeon, M., Pipy, B., Carrey, J., et al. (2018). Targeted magnetic intra-lysosomal hyperthermia produces lysosomal reactive oxygen species and causes Caspase-1 dependent cell death. J. Control. Release 270, 120–134. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.11.050
Cornen, S., and Vivier, E. (2018). Chemotherapy and tumor immunity. Science 362 (6421), 1355–1356. doi:10.1126/science.aav7871
Cui, S., Pan, X., Fan, S., Cao, C., Jiao, Y., Fu, Y., et al. (2025). A novel conjugated polymer synthesized via a noble metal-free catalyst in photothermal therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma mediated by second near-infrared (NIR-II) laser. Mater. Today. Bio 31, 101488. doi:10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101488
Dawson, G. A., Spielvogel, E. H., and Diao, T. (2023). Nickel-catalyzed radical mechanisms: informing cross-coupling for synthesizing non-canonical biomolecules. Accounts Chem. Res. 56 (24), 3640–3653. doi:10.1021/acs.accounts.3c00588
Di Bucchianico, S., Gliga, A. R., Åkerlund, E., Skoglund, S., Wallinder, I. O., Fadeel, B., et al. (2018). Calcium-dependent cyto- and genotoxicity of nickel metal and nickel oxide nanoparticles in human lung cells. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 15 (1), 32. doi:10.1186/s12989-018-0268-y
Dolgin, E. (2021). Cancer’s new normal. Nat. Cancer 2 (12), 1248–1250. doi:10.1038/s43018-021-00304-7
Du, C., Wu, X., He, M., Zhang, Y., Zhang, R., and Dong, C.-M. (2021a). Polymeric photothermal agents for cancer therapy: recent progress and clinical potential. J. Mater. Chem. 9 (6), 1478–1490. doi:10.1039/d0tb02659j
Du, T., Liu, J., Dong, J., Xie, H., Wang, X., Yang, X., et al. (2024). Multifunctional coatings of nickel-titanium implant toward promote osseointegration after operation of bone tumor and clinical application: a review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 12, 1325707. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2024.1325707
Du, Z., Mao, Y., Zhang, P., Hu, J., Fu, J., You, Q., et al. (2021b). TPGS-galactose-modified polydopamine co-delivery nanoparticles of nitric oxide donor and doxorubicin for targeted chemo-photothermal therapy against drug-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13 (30), 35518–35532. doi:10.1021/acsami.1c09610
Duan, L., Ouyang, K., Xu, X., Xu, L., Wen, C., Zhou, X., et al. (2021). Whole transcriptome analysis revealed a stress response to deep underground environment conditions in Chinese hamster V79 lung fibroblast cells. Front. Genet. 12, 698046. doi:10.3389/fgene.2021.698046
Endale, H. T., Tesfaye, W., and Mengstie, T. A. (2023). ROS induced lipid peroxidation and their role in ferroptosis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. Volume, 11–2023. doi:10.3389/fcell.2023.1226044
e Silva, F. A., Salim, V. M. M., and Rodrigues, T. S. (2024). Controlled nickel nanoparticles: a review on how parameters of synthesis can modulate their features and properties. AppliedChem 4 (1), 86–106. doi:10.3390/appliedchem4010007
Fan, D., Cao, Y., Cao, M., Wang, Y., Cao, Y., and Gong, T. (2023). Nanomedicine in cancer therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 8 (1), 293. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01536-y
Farzin, A., Etesami, S. A., Quint, J., Memic, A., and Tamayol, A. (2020). Magnetic nanoparticles in cancer therapy and diagnosis. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 9 (9), e1901058. doi:10.1002/adhm.201901058
Ferdous, Z., and Nemmar, A. (2020). Health impact of silver nanoparticles: a review of the biodistribution and toxicity following various routes of exposure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21 (7), 2375. doi:10.3390/ijms21072375
Filho, A. M., Laversanne, M., Ferlay, J., Colombet, M., Piñeros, M., Znaor, A., et al. (2025). The GLOBOCAN 2022 cancer estimates: data sources, methods, and a snapshot of the cancer burden worldwide. Int. J. Cancer 156 (7), 1336–1346. doi:10.1002/ijc.35278
Gao, H., Cao, Z., Liu, H., Chen, L., Bai, Y., Wu, Q., et al. (2023). Multifunctional nanomedicines-enabled chemodynamic-synergized multimodal tumor therapy via Fenton and Fenton-like reactions. Theranostics 13 (6), 1974–2014. doi:10.7150/thno.80887
Graham, W., Torbett-Dougherty, M., Islam, A., Soleimani, S., Bruce-Tagoe, T. A., and Johnson, J. A. (2025). Magnetic nanoparticles and drug delivery systems for anti-cancer applications: a review. Nanomaterials 15 (4), 285. doi:10.3390/nano15040285
Gürsoy, G., Çiçek, Z., Tekerek, S., Kiray, E., Tanriverdi, A., and Çakmak, E. (2024). Synthesis of NiO nanoparticles from plant extracts via a green synthesis method and antibacterial, antibiofilm and cytotoxicity applications. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 38 (6), e7492. doi:10.1002/aoc.7492
Haider, T., Pandey, V., Banjare, N., Gupta, P. N., and Soni, V. (2020). Drug resistance in cancer: mechanisms and tackling strategies. Pharmacol. Rep. 72 (5), 1125–1151. doi:10.1007/s43440-020-00138-7
Hammami, I., Alabdallah, N. M., jomaa, A. A., and kamoun, M. (2021). Gold nanoparticles: synthesis properties and applications. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 33 (7), 101560. doi:10.1016/j.jksus.2021.101560
Han, H. S., and Choi, K. Y. (2021). Advances in nanomaterial-mediated photothermal cancer therapies: toward clinical applications. Biomedicines 9 (3), 305. doi:10.3390/biomedicines9030305
Haripriyaa, M., and Suthindhiran, K. (2023). Pharmacokinetics of nanoparticles: current knowledge, future directions and its implications in drug delivery. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 9 (1), 113. doi:10.1186/s43094-023-00569-y
Hopkins, X., Gill, W. A., Kringel, R., Wang, G., Hass, J., Acharya, S., et al. (2017). Radio frequency-mediated local thermotherapy for destruction of pancreatic tumors using Ni-Au core-shell nanowires. Nanotechnology 28 (3), 03LT01. doi:10.1088/1361-6528/28/3/03LT01
Hryhorowicz, M., Grześkowiak, B., Mazurkiewicz, N., Śledziński, P., Lipiński, D., and Słomski, R. (2019). Improved delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 system using magnetic nanoparticles into porcine fibroblast. Mol. Biotechnol. 61 (3), 173–180. doi:10.1007/s12033-018-0145-9
Hu, W., Zhen, W., Zhang, M., Wang, W., Jia, X., An, S., et al. (2021). Development of nickel selenide@polydopamine nanocomposites for magnetic resonance imaging guided NIR-II photothermal therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 10 (23), e2101542. doi:10.1002/adhm.202101542
Iftikhar, M., Noureen, A., Jabeen, F., Uzair, M., Rehman, N., Sher, E. K., et al. (2023). Bioinspired engineered nickel nanoparticles with multifunctional attributes for reproductive toxicity. Chemosphere 311 (Pt 1), 136927. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136927
Ilg, P., and Kröger, M. (2020). Dynamics of interacting magnetic nanoparticles: effective behavior from competition between Brownian and Néel relaxation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 22 (39), 22244–22259. doi:10.1039/d0cp04377j
Inam, H., Sprio, S., Tavoni, M., Abbas, Z., Pupilli, F., and Tampieri, A. (2024). Magnetic hydroxyapatite nanoparticles in regenerative medicine and nanomedicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (5), 2809. doi:10.3390/ijms25052809
Jaji, N.-D., Lee, H. L., Hussin, M. H., Akil, H. M., Zakaria, M. R., and Othman, M. B. H. (2020). Advanced nickel nanoparticles technology: from synthesis to applications. Nanotechnol. Rev. 9(1), 1456–1480. doi:10.1515/ntrev-2020-0109
Ji, B., Wei, M., and Yang, B. (2022). Recent advances in nanomedicines for photodynamic therapy (PDT)-driven cancer immunotherapy. Theranostics 12 (1), 434–458. doi:10.7150/thno.67300
Jia, C., Guo, Y., and Wu, F.-G. (2022). Chemodynamic therapy via Fenton and Fenton-like nanomaterials: strategies and recent advances. Small 18 (6), e2103868. doi:10.1002/smll.202103868
Jin, J., Krishnamachary, B., Barnett, J. D., Chatterjee, S., Chang, D., Mironchik, Y., et al. (2019). Human cancer cell membrane-coated biomimetic nanoparticles reduce fibroblast-mediated invasion and metastasis and induce T-cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11 (8), 7850–7861. doi:10.1021/acsami.8b22309
Karaca, G. Y., Kuralay, F., Uygun, E., Ozaltin, K., Demirbuken, S. E., Garipcan, B., et al. (2021). Gold–nickel nanowires as nanomotors for cancer marker biodetection and chemotherapeutic drug delivery. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 4 (4), 3377–3388. doi:10.1021/acsanm.0c03145
Kargozar, S., Mollazadeh, S., Kermani, F., Webster, T. J., Nazarnezhad, S., Hamzehlou, S., et al. (2022). Hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for improved cancer theranostics. J. Funct. Biomaterials 13 (3), 100. doi:10.3390/jfb13030100
Kesharwani, P., Chandra, J., Karim, S., Gupta, G., Karwasra, R., and Sharma, A. (2024). αvβ3 integrin targeting RGD peptide-based nanoparticles as an effective strategy for selective drug delivery to tumor microenvironment. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 96, 105663. doi:10.1016/j.jddst.2024.105663
Kesharwani, P., Ma, R., Sang, L., Fatima, M., Sheikh, A., Abourehab, M. A. S., et al. (2023). Gold nanoparticles and gold nanorods in the landscape of cancer therapy. Mol. Cancer 22 (1), 98. doi:10.1186/s12943-023-01798-8
Khizar, S., Alrushaid, N., Alam Khan, F., Zine, N., Jaffrezic-Renault, N., Errachid, A., et al. (2023). Nanocarriers based novel and effective drug delivery system. Int. J. Pharm. 632, 122570. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.122570
Kiaie, S. H., Salehi-Shadkami, H., Sanaei, M. J., Azizi, M., Shokrollahi Barough, M., Nasr, M. S., et al. (2023). Nano-immunotherapy: overcoming delivery challenge of immune checkpoint therapy. J. Nanobiotechnology 21 (1), 339. doi:10.1186/s12951-023-02083-y
Kim, G., Na, C. W., and Myung, Y. (2023). Facile one-pot synthesis of nickel nanoparticles by hydrothermal method. Materials 16 (1), 76. doi:10.3390/ma16010076
Kim, P. D., Zamay, S. S., Zamay, T. N., Prokopenko, V. S., Kolovskaya, O. S., Zamay, G. S., et al. (2016). The antitumor effect of magnetic nanodisks and DNA aptamer conjugates. Doklady. Biochem. Biophysics 466, 66–69. doi:10.1134/S1607672916010154
Koo, S., Park, O. K., Kim, J., Han, S. I., Yoo, T. Y., Lee, N., et al. (2022). Enhanced chemodynamic therapy by Cu–Fe peroxide nanoparticles: tumor microenvironment-mediated synergistic fenton reaction. ACS Nano 16 (2), 2535–2545. doi:10.1021/acsnano.1c09171
Lei, Z., Zhang, W., Li, B., Guan, G., Huang, X., Peng, X., et al. (2019). A full-spectrum-absorption from nickel sulphide nanoparticles for efficient NIR-II window photothermal therapy. Nanoscale 11 (42), 20161–20170. doi:10.1039/c9nr04005f
Lepeltier, E., Rijo, P., Rizzolio, F., Popovtzer, R., Petrikaite, V., Assaraf, Y. G., et al. (2020). Nanomedicine to target multidrug resistant tumors. Drug Resist. Updat. 52, 100704. doi:10.1016/j.drup.2020.100704
Lin, Y., Zhou, K., Zhang, S., Lu, Y., He, Y., Liu, H., et al. (2023). Carbon-coated magnetite nanoclusters with NIR-II absorbance for imaging-guided photothermal-chemodynamic synergistic therapy. Sci. China Mater. 66 (6), 2492–2503. doi:10.1007/s40843-022-2389-5
Liu, H., Yu, B., Zhou, C., Deng, Z., Wang, H., Zhang, X., et al. (2024). Nickel atom-clusters nanozyme for boosting ferroptosis tumor therapy. Mater. Today. Bio 27, 101137. doi:10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101137
Liu, J., Qiu, X.-R., Tian, Y.-L., Sun, W.-J., Wang, Y.-H., Liu, H., et al. (2025). Urchin-like magnetic nanoparticles loaded with type X collagen siRNA and stattic to treat triple negative breast cancer under rotating magnetic field like an “enchanted micro-scalpel”. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 300, 140318. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.140318
Liu, L., Liu, Y., Ma, L., Mao, F., Jiang, A., Liu, D., et al. (2018). Artemisinin-loaded mesoporous nanoplatform for pH-Responsive radical generation synergistic tumor theranostics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10 (7), 6155–6167. doi:10.1021/acsami.7b18320
Liu, L., Pan, D., Chen, S., Martikainen, M.-V., Kårlund, A., Ke, J., et al. (2022). Systematic design of cell membrane coating to improve tumor targeting of nanoparticles. Nat. Commun. 13 (1), 6181. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-33889-3
Lopez, S., Hallali, N., Lalatonne, Y., Hillion, A., Antunes, J. C., Serhan, N., et al. (2022). Magneto-mechanical destruction of cancer-associated fibroblasts using ultra-small iron oxide nanoparticles and low frequency rotating magnetic fields. Nanoscale Adv. 4 (2), 421–436. doi:10.1039/d1na00474c
Lorenzoni, S., Rodríguez-Nogales, C., and Blanco-Prieto, M. J. (2025). Targeting tumor microenvironment with RGD-functionalized nanoparticles for precision cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 614, 217536. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2025.217536
Lu, Y., Zhang, P., Lin, L., Gao, X., Zhou, Y., Feng, J., et al. (2022). Ultra-small bimetallic phosphides for dual-modal MRI imaging guided photothermal ablation of tumors. Dalton Trans. 51 (11), 4423–4428. doi:10.1039/d1dt03898b
Ludwig, R., Teran, F. J., Teichgraeber, U., and Hilger, I. (2017). Nanoparticle-based hyperthermia distinctly impacts production of ROS, expression of Ki-67, TOP2A, and TPX2, and induction of apoptosis in pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Nanomedicine 12, 1009–1018. doi:10.2147/IJN.S108577
Ly, P.-D., Ly, K.-N., Phan, H.-L., Nguyen, H. H., Duong, V.-A., and Nguyen, H. V. (2024). Recent advances in surface decoration of nanoparticles in drug delivery. Front. Nanotechnol. 6, 1456939. doi:10.3389/fnano.2024.1456939
Ma, C., Zhou, Y., Yan, W., He, W., Liu, Q., Li, Z., et al. (2022). Predominant catalytic performance of nickel nanoparticles embedded into nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dot-based nanosheets for the nitroreduction of halogenated nitrobenzene. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 10 (25), 8162–8171. doi:10.1021/acssuschemeng.2c01345
Menon, S., Ks, S. D., R, S., S, R., and S, V. K. (2018). Selenium nanoparticles: a potent chemotherapeutic agent and an elucidation of its mechanism. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 170, 280–292. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.06.006
Miao, X., Leng, X., and Zhang, Q. (2017). The current state of nanoparticle-induced macrophage polarization and reprogramming research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18 (2), 336. doi:10.3390/ijms18020336
Mikhailova, E. O. (2023). Selenium nanoparticles: green synthesis and biomedical application. Molecules 28 (24), 8125. doi:10.3390/molecules28248125
Min, H., Qi, Y., Zhang, Y., Han, X., Cheng, K., Liu, Y., et al. (2020). A graphdiyne oxide-based iron sponge with photothermally enhanced tumor-specific fenton chemistry. Adv. Mater. 32 (31), e2000038. doi:10.1002/adma.202000038
Mo, Y., Zhang, Y., and Zhang, Q. (2024). The pulmonary effects of nickel-containing nanoparticles: cytotoxicity, genotoxicity, carcinogenicity, and their underlying mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Nano 11 (5), 1817–1846. doi:10.1039/d3en00929g
Mohammed, D. F., Madlool, H. A., Faris, M., Shalan, B. H., Hasan, H. H., Azeez, N. F., et al. (2022). Harnessing inorganic nanomaterials for chemodynamic cancer therapy. Nanomedicine 17 (24), 1891–1906. doi:10.2217/nnm-2022-0187
Mukherjee, S., Liang, L., and Veiseh, O. (2020). Recent advancements of magnetic nanomaterials in cancer therapy. Pharmaceutics 12 (2), 147. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics12020147
Nam, K.-H., Jeong, C. B., Kim, H., Ahn, M., Ahn, S.-J., Hur, H., et al. (2021). Quantitative photothermal characterization with bioprinted 3D complex tissue constructs for early-stage breast cancer therapy using gold nanorods. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 10 (18), e2100636. doi:10.1002/adhm.202100636
Narender, S. S., Varma, V. V. S., Srikar, C. S., Ruchitha, J., Varma, P. A., and Praveen, B. V. S. (2022). Nickel oxide nanoparticles: a brief review of their synthesis, characterization, and applications. Chem. Eng. Technol. 45 (3), 397–409. doi:10.1002/ceat.202100442
Naz, S., Gul, A., and Zia, M. (2020). Toxicity of copper oxide nanoparticles: a review study. IET Nanobiotechnology 14 (1), 1–13. doi:10.1049/iet-nbt.2019.0176
Niu, X., You, Q., Hou, K., Tian, Y., Wei, P., Zhu, Y., et al. (2025). Autophagy in cancer development, immune evasion, and drug resistance. Drug Resist. Updat. 78, 101170. doi:10.1016/j.drup.2024.101170
Nivetha, S., Srivalli, T., Sathya, P. M., Mohan, H., Karthi, N., Muralidharan, K., et al. (2024). Nickel-doped vanadium pentoxide (Ni@V2O5) nanocomposite induces apoptosis targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in skin cancer: an in vitro and in vivo study. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 234, 113763. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2024.113763
Ota, S., and Takemura, Y. (2019). Characterization of Néel and brownian relaxations isolated from complex dynamics influenced by dipole interactions in magnetic nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 123 (47), 28859–28866. doi:10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b06790
Othman, M. S., Aboelnaga, S. M., Habotta, O. A., Moneim, A. E. A., and Hussein, M. M. (2023). The potential therapeutic role of green-synthesized selenium nanoparticles using carvacrol in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Appl. Sci. 13 (12), 7039. doi:10.3390/app13127039
Oudjedi, F., and Kirk, A. G. (2025). Near-infrared nanoparticle-mediated photothermal cancer therapy: a comprehensive review of advances in monitoring and controlling thermal effects for effective cancer treatment. Nano Sel. 6 (3), e202400107. doi:10.1002/nano.202400107
Paściak, A., Marin, R., Abiven, L., Pilch-Wróbel, A., Misiak, M., Xu, W., et al. (2022). Quantitative comparison of the light-to-heat conversion efficiency in nanomaterials suitable for photothermal therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 14 (29), 33555–33566. doi:10.1021/acsami.2c08013
Peng, X., Fang, J., Lou, C., Yang, L., Shan, S., Wang, Z., et al. (2024). Engineered nanoparticles for precise targeted drug delivery and enhanced therapeutic efficacy in cancer immunotherapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 14 (8), 3432–3456. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2024.05.010
Pfister, F., Carnell, L. R., Löffler, L., Boosz, P., Schaft, N., Dörrie, J., et al. (2025). Loading of CAR-T cells with magnetic nanoparticles for controlled targeting suppresses inflammatory cytokine release and switches tumor cell death mechanism. MedComm 6 (1), e70039. doi:10.1002/mco2.70039
Qian, Y., Wang, D., Tian, X., Liu, H., Wang, X., Li, H., et al. (2020). Synthesis of urchin-like nickel nanoparticles with enhanced rotating magnetic field-induced cell necrosis and tumor inhibition. Chem. Eng. J. 400, 125823. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2020.125823
Qian, Y., Zhang, J., Zou, J., Wang, X., Meng, X., Liu, H., et al. (2022). NIR-II responsive PEGylated nickel nanoclusters for photothermal enhanced chemodynamic synergistic oncotherapy. Theranostics 12 (8), 3690–3702. doi:10.7150/thno.70841
Qin, W., Chandra, J., Abourehab, M. A. S., Gupta, N., Chen, Z.-S., Kesharwani, P., et al. (2023a). New opportunities for RGD-engineered metal nanoparticles in cancer. Mol. Cancer 22 (1), 87. doi:10.1186/s12943-023-01784-0
Qin, Y.-T., Li, Y.-P., He, X.-W., Wang, X., Li, W.-Y., and Zhang, Y.-K. (2023b). Biomaterials promote in vivo generation and immunotherapy of CAR-T cells. Front. Immunol. 14, 14–2023. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1165576
Ramasamy, S., Sam David, R. J. R., and Enoch, I. V. M. V. (2018). Folate-molecular encapsulator-tethered biocompatible polymer grafted with magnetic nanoparticles for augmented drug delivery. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 46 (Suppl. 2), 675–682. doi:10.1080/21691401.2018.1468340
Rio, I. S. R., Rodrigues, A. R. O., Rodrigues, C. P., Almeida, B. G., Pires, A., Pereira, A. M., et al. (2020). Development of novel magnetoliposomes containing nickel ferrite nanoparticles covered with gold for applications in thermotherapy. Materials 13 (4), 815. doi:10.3390/ma13040815
Rohiwal, S. S., Dvorakova, N., Klima, J., Vaskovicova, M., Senigl, F., Slouf, M., et al. (2020). Polyethylenimine based magnetic nanoparticles mediated non-viral CRISPR/Cas9 system for genome editing. Sci. Rep. 10 (1), 4619. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-61465-6
Roy, S., Bag, N., Bardhan, S., Hasan, I., and Guo, B. (2023). Recent progress in NIR-II fluorescence imaging-guided drug delivery for cancer theranostics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 197, 114821. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2023.114821
Sang, D., Wang, K., Sun, X., Wang, Y., Lin, H., Jia, R., et al. (2021a). NIR-driven intracellular photocatalytic O2 evolution on Z-scheme Ni3S2/Cu1. 8S@ HA for hypoxic tumor therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13 (8), 9604–9619. doi:10.1021/acsami.0c21284
Sang, Y., Deng, Q., Cao, F., Liu, Z., You, Y., Liu, H., et al. (2021b). Remodeling macrophages by an iron nanotrap for tumor growth suppression. ACS Nano 15 (12), 19298–19309. doi:10.1021/acsnano.1c05392
Sani, A., Cao, C., and Cui, D. (2021). Toxicity of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs): a review. Biochem. Biophysics Rep. 26, 100991. doi:10.1016/j.bbrep.2021.100991
Sanità, G., Carrese, B., and Lamberti, A. (2020). Nanoparticle surface functionalization: how to improve biocompatibility and cellular internalization. Front. Mol. Biosci. 7, 587012. doi:10.3389/fmolb.2020.587012
Shahidi, S., Sanaz, D., Mahmood, G., and Mongkholrattanasit, R. (2022). In situ deposition of magnetic nanoparticles on glass mat using plasma sputtering method. J. Text. Inst. 113(3), 349–359. doi:10.1080/00405000.2021.1880086
Sharma, A., Orlowski, G. M., Zhu, Y., Shore, D., Kim, S. Y., DiVito, M. D., et al. (2015). Inducing cells to disperse nickel nanowires via integrin-mediated responses. Nanotechnology 26 (13), 135102. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/26/13/135102
Sheikh, A., Alhakamy, N. A., Md, S., and Kesharwani, P. (2021). Recent progress of RGD modified liposomes as multistage rocket against cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 803304. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.803304
Shen, J., Rees, T. W., Zhou, Z., Yang, S., Ji, L., and Chao, H. (2020). A mitochondria-targeting magnetothermogenic nanozyme for magnet-induced synergistic cancer therapy. Biomaterials 251, 120079. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120079
Shi, L., Zhang, J., Zhao, M., Tang, S., Cheng, X., Zhang, W., et al. (2021). Effects of polyethylene glycol on the surface of nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery. Nanoscale 13 (24), 10748–10764. doi:10.1039/d1nr02065j
Shubhra, Q. T. H. (2023). Iron oxide nanoparticles in magnetic drug targeting and ferroptosis-based cancer therapy. Med. Rev. 3 (5), 444–447. doi:10.1515/mr-2023-0029
Singh, N., Malik, A., Nohwar, S., Jana, R., and Mondal, P. C. (2023). Covalent surface modification of nickel ferrite nanoparticles for electrochemical supercapacitor performance. New J. Chem. 47 (11), 5308–5315. doi:10.1039/d2nj05566j
Sivagami, M., and Asharani, I. V. (2022). Phyto-mediated Ni/NiO NPs and their catalytic applications-a short review. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 145, 110054. doi:10.1016/j.inoche.2022.110054
Song, P., Jin, S., Cao, Y., Zhang, S., Yin, N., Zhang, H., et al. (2023). Multifunctional biocompatible Ni/Ni-P nanospheres for anti-tumor “neoadjuvant phototherapy” combining photothermal therapy and photodynamic therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 11 (41), 10019–10028. doi:10.1039/d3tb01802d
Sowmya, R., Karthick Raja Namasivayam, S., and Krithika Shree, S. (2024). A critical review on nano-selenium based materials: synthesis, biomedicine applications and biocompatibility assessment. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 34 (7), 3037–3055. doi:10.1007/s10904-023-02959-4
Sun, J., Tong, Y., Jia, Y., Jia, X., Wang, H., Chen, Y., et al. (2023). Effects of extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields on the tumor cell inhibition and the possible mechanism. Sci. Rep. 13 (1), 6989. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-34144-5
Sundram, S., Baskar, S., and Subramanian, A. (2022). Green synthesized nickel doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles exhibit antibacterial activity and induce reactive oxygen species mediated apoptosis in MCF-7 breast cancer cells through inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Environ. Toxicol. 37 (12), 2877–2888. doi:10.1002/tox.23644
Sztandera, K., Gorzkiewicz, M., and Klajnert-Maculewicz, B. (2019). Gold nanoparticles in cancer treatment. Mol. Pharm. 16 (1), 1–23. doi:10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b00810
Szwed, M., and Marczak, A. (2024). Application of nanoparticles for magnetic hyperthermia for cancer treatment-the current state of knowledge. Cancers. 16, (6) 1156. doi:10.3390/cancers16061156
Tailor, G., Chaudhary, J., Jandu, S., Mehta, C., Yadav, M., et al. (2023). A review on green route synthesized nickel nanoparticles: biological and photo-catalytic applications. Results Chem. 6, 101195. doi:10.1016/j.rechem.2023.101195
Takáč, P., Michalková, R., Čižmáriková, M., Bedlovičová, Z., Balážová, Ľ., and Takáčová, G. (2023). The role of silver nanoparticles in the diagnosis and treatment of cancer: are there any perspectives for the future? Life (Basel, Switzerland) 13 (2), 466. doi:10.3390/life13020466
Torres, T. E., Lima, E., Calatayud, M. P., Sanz, B., Ibarra, A., Fernández-Pacheco, R., et al. (2019). The relevance of Brownian relaxation as power absorption mechanism in magnetic hyperthermia. Sci. Rep. 9 (1), 3992. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-40341-y
Vallabani, N. V. S., and Karlsson, H. L. (2022). Primary and secondary genotoxicity of nanoparticles: establishing a co-culture protocol for assessing micronucleus using flow cytometry. Front. Toxicol. 4, 845987. doi:10.3389/ftox.2022.845987
Vilas-Boas, V., Carvalho, F., and Espiña, B. (2020). Magnetic hyperthermia for cancer treatment: main parameters affecting the outcome of in vitro and in vivo studies. Molecules 25 (12), 2874. doi:10.3390/molecules25122874
Vinod, S., and Philip, J. (2022). Thermal and rheological properties of magnetic nanofluids: recent advances and future directions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 307, 102729. doi:10.1016/j.cis.2022.102729
Walters, A. A., Santacana-Font, G., Li, J., Routabi, N., Qin, Y., Claes, N., et al. (2021). Nanoparticle-mediated In Situ molecular reprogramming of immune checkpoint interactions for cancer immunotherapy. ACS Nano 15 (11), 17549–17564. doi:10.1021/acsnano.1c04456
Wang, L., Zhuang, L., He, S., Tian, F., Yang, X., Guan, S., et al. (2021). Nanocarbon framework-supported ultrafine Mo2C@MoOx nanoclusters for photothermal-enhanced tumor-specific tandem catalysis therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13 (50), 59649–59661. doi:10.1021/acsami.1c17085
Wei, Y., and Wang, X. (2023). Biological effects of rotating magnetic field: a review from 1969 to 2021. Prog. Biophysics Mol. Biol. 178, 103–115. doi:10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2022.12.006
Wen, J., Liu, C., Liu, J., Wang, L., Miao, S., Chen, D., et al. (2023). Dextran 40 hybrid biomimetic bismuth-nanoflower designed for NIR II-triggered hypoxic tumor thermoradiotherapy via macrophage escape. Carbohydr. Polym. 310, 120697. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.120697
Wu, L., Jiang, M., Chu, C., Luo, T., Hui, Y., Zhou, W., et al. (2024). Transformation of black phosphorus through lattice reconstruction for NIR-II-Responsive cancer therapy. Adv. Sci. 11 (3), e2305762. doi:10.1002/advs.202305762
Wu, X., Turlik, A., Luan, B., He, F., Qu, J., Houk, K. N., et al. (2022). Nickel-catalyzed enantioselective reductive alkyl-carbamoylation of internal alkenes. Angewandte Chemie 61 (36), e202207536. doi:10.1002/anie.202207536
Wu, Y., and Kong, L. (2020). Advance on toxicity of metal nickel nanoparticles. Environ. Geochem. Health 42 (7), 2277–2286. doi:10.1007/s10653-019-00491-4
Xiong, Z., Lei, H., Yang, J., Liu, Y., Gao, Z., Li, Y., et al. (2022). Deep-ultraviolet plasmon resonance of Ni nanoparticles embedded in BaTiO3 matrix. J. Alloys Compd. 924, 166562. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.166562
Xu, J.-J., Zhang, W.-C., Guo, Y.-W., Chen, X.-Y., and Zhang, Y.-N. (2022). Metal nanoparticles as a promising technology in targeted cancer treatment. Drug Deliv. 29 (1), 664–678. doi:10.1080/10717544.2022.2039804
Yan, D., Zhang, Z., Zhang, J., Li, X., Wu, Q., Gui, Y., et al. (2024). An all-rounder for NIR-II phototheranostics: well-tailored 1064 nm-Excitable molecule for photothermal combating of orthotopic breast cancer. Angewandte Chemie 63 (26), e202401877. doi:10.1002/anie.202401877
Yang, N., Xiao, W., Song, X., Wang, W., and Dong, X. (2020). Recent advances in tumor microenvironment hydrogen peroxide-responsive materials for cancer photodynamic therapy. Nano-Micro Lett. 12 (1), 15. doi:10.1007/s40820-019-0347-0
Yao, M., Hao, X., Shao, H., Wang, D., Li, B., Xing, S., et al. (2022). Metallic nanoparticle-doped oxide semiconductor film for bone tumor suppression and bone regeneration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 14 (42), 47369–47384. doi:10.1021/acsami.2c10672
Yin, L., Li, X., Wang, R., Zeng, Y., Zeng, Z., and Xie, T. (2023). Recent research progress of RGD peptide–modified nanodrug delivery systems in tumor therapy. Int. J. Peptide Res. Ther. 29 (4), 53. doi:10.1007/s10989-023-10523-4
Yu, E. Y., Bishop, M., Zheng, B., Ferguson, R. M., Khandhar, A. P., Kemp, S. J., et al. (2017). Magnetic particle imaging: a novel in vivo imaging platform for cancer detection. Nano lett. 17 (3), 1648–1654. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b04865
Yu, X., Yang, R., Wu, C., Liu, B., and Zhang, W. (2022). The heating efficiency of magnetic nanoparticles under an alternating magnetic field. Sci. Rep. 12 (1), 16055. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-20558-0
Zarenezhad, E., Abdulabbas, H. T., Marzi, M., Ghazy, E., Ekrahi, M., Pezeshki, B., et al. (2022). Nickel nanoparticles: applications and antimicrobial role against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections. Antibiotics 11 (9), 1208. doi:10.3390/antibiotics11091208
Zhang, G., Xie, W., Xu, Z., Si, Y., Li, Q., Qi, X., et al. (2021a). CuO dot-decorated Cu@Gd2O3 core-shell hierarchical structure for Cu(i) self-supplying chemodynamic therapy in combination with MRI-guided photothermal synergistic therapy. Mater. Horizons 8 (3), 1017–1028. doi:10.1039/d0mh01685c
Zhang, Q., Guo, Q., Chen, Q., Zhao, X., Pennycook, S. J., and Chen, H. (2020). Highly efficient 2D NIR-II photothermal agent with fenton catalytic activity for cancer synergistic photothermal-chemodynamic therapy. Adv. Sci. 7 (7), 1902576. doi:10.1002/advs.201902576
Zhang, W., Zhang, H., Li, J., Zou, X., Wang, W., Hu, H., et al. (2023). PVP-capped silver nanoparticles for efficient SERS detection of adenine based on the stabilizing and enrichment roles of PVP. Mikrochim. Acta 191 (1), 1. doi:10.1007/s00604-023-06047-9
Zhang, Y., Zhang, S., Zhang, Z., Ji, L., Zhang, J., Wang, Q., et al. (2021b). Recent progress on NIR-II photothermal therapy. Front. Chem. 9, 728066. doi:10.3389/fchem.2021.728066
Zhang, Z., Shen, C., Sun, K., Jia, X., Ye, J., and Liu, C.-j. (2022). Advances in studies of the structural effects of supported Ni catalysts for CO2 hydrogenation: from nanoparticle to single atom catalyst. J. Mater. Chem. A 10 (11), 5792–5812. doi:10.1039/d1ta09914k
Zhao, C., Rehman, F. U., Shaikh, S., Qazi, R. e.M., Sajid, Z., Mian, A. A., et al. (2023). Metallic nanoscale-knife application in cancer theranostics. Smart Mater. Med. 4, 313–336. doi:10.1016/j.smaim.2022.11.006
Zhao, J., Feng, C., Zheng, F., Qian, Y., Zhang, X., and Wang, H. (2025). Electron density modulation-enhanced magnetic nanocatalysis for anti-tumor therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 35, 2422270. doi:10.1002/adfm.202422270
Zhi, D., Yang, T., O’Hagan, J., Zhang, S., and Donnelly, R. F. (2020). Photothermal therapy. J. Control. Release 325, 52–71. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.06.032
Zhou, P., Jiang, Y., Adeel, M., Shakoor, N., Zhao, W., Liu, Y., et al. (2023). Nickel oxide nanoparticles improve soybean yield and enhance nitrogen assimilation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 57 (19), 7547–7558. doi:10.1021/acs.est.3c00959
Zhou, Z., Wang, J., Liu, W., Yu, C., Kong, B., Sun, Y., et al. (2014). PEGylated nickel carbide nanocrystals as efficient near-infrared laser induced photothermal therapy for treatment of cancer cells in vivo. Nanoscale 6 (21), 12591–12600. doi:10.1039/c4nr03727h
Keywords: nickel nanoparticles, drug delivery, photothermal therapy, magnetic hyperthermia therapy, chemodynamic therapy
Citation: Wang F, Tong S, Ma X, Yang H, Zhang T, Wu K and Wu J (2025) Nickel nanoparticles: a novel platform for cancer-targeted delivery and multimodal therapy. Front. Drug Deliv. 5:1627556. doi: 10.3389/fddev.2025.1627556
Received: 13 May 2025; Accepted: 17 July 2025;
Published: 30 July 2025.
Edited by:
Zi (Sophia) Gu, University of New South Wales, AustraliaReviewed by:
Taskeen Janjua, The University of Queensland, AustraliaMei-Yi Liao, National Pingtung University, Taiwan
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Tong, Ma, Yang, Zhang, Wu and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Junzi Wu, eG5mekB5bnVjbS5lZHUuY24=
† These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Fengyu Wang1,2
†
Fengyu Wang1,2
† Junzi Wu
Junzi Wu