- Department of Oncology Science, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, OK, United States
Glioblastoma (GBM), a highly aggressive and malignant form of primary adult brain cancer, poses significant therapeutic challenges. Despite our improved understanding of the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying tumorigenesis and the evolution of GBM, targeted molecular therapies have failed to improve patient survival outcomes. The failure of standard treatments and targeted therapies is mainly attributed to the acquisition of phenotypic plasticity of tumor cells and GBM stem-like cells. Epigenetic modifications and their mediators have emerged as crucial regulators of phenotypic plasticity, influencing tumor heterogeneity, therapy resistance and disease progression. Here, we summarize and provide insights into epigenetic regulation of GBM plasticity and specifically, focus on the roles played by DNA- and histone modifiers and non-coding RNAs in driving phenotypic plasticity and resistance. We also delve into their dynamics in response to standard therapies and the challenges for targeting them to overcome phenotypic plasticity and resistance in GBM.
Introduction
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the deadliest and most common primary adult brain tumor with a median survival of 14–15 months post-diagnosis. Tumors are highly refractory to standard treatments of surgical resection, fractionated radiation and chemotherapy with temozolomide (TMZ) (Wu et al., 2021). This results in near universal recurrence of GBM in all patients, indicating the critical need for better therapeutic strategies. The aggressive behavior and treatment resistance of GBM is primarily attributed to the presence of a small subset of tumor cells with stem-like properties, the GBM stem-like cells (GSCs). GSCs can self-renew and differentiate into multiple lineages by reactivating developmental transcriptional programs and signaling pathways. GSCs exhibit metabolic adaptability, increased tumorigenic properties, enhanced DNA repair capacity and chemo-radiation resistance compared to non-stem cancer cells (Prager et al., 2020). Furthermore, GSCs also exhibit cellular and lineage flexibility, transdifferentiating into different cell types, particularly, endothelial-like cells (EC) and pericyte-like cells (PC), the two major cellular components of the blood vessels (Ricci-Vitiani et al., 2010; Cheng et al., 2013). These GSC-derived EC and PC integrate into the vasculature, aid in the maintenance of blood-tumor-barrier and tumor growth (Cheng et al., 2013; Zhou et al., 2017).
Although standard chemo-radiation therapy can eliminate proliferating tumor cells, the therapeutic stress can reprogram the non-stem tumor cells to acquire a multipotent status. This multipotent status allows tumor cells to dedifferentiate and acquire stem-like characteristics, become GSC-like giving rise to therapy-resistant clonal populations that contribute to tumor recurrence (Bhat et al., 2020). Radiation therapy has been shown to promote the transition of GSCs from a proneural-(PN) to a mesenchymal (MES)-like state (PMT) similar to epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in other cancers (Minata et al., 2019; Shibue and Weinberg, 2017). These radiation-induced MES-like GSCs display increased capacity for invasion, therapeutic resistance, and poor prognosis (Minata et al., 2019). Furthermore, a recent study demonstrated that radiation therapy induces the transdifferentiation of GSCs into both EC-like and PC-like cells and these transdifferentiated cells provide a trophic niche to support tumor recurrence (Muthukrishnan et al., 2022). TMZ chemotherapy has also been reported to promote GSC transdifferentiation in ECs (Baisiwala et al., 2019). These studies support the prevailing notion that sandard chemo-radiation therapy acts as a double-edged sword in that they eliminate proliferating tumor cells but induce plasticity in surviving tumor cells and GSCs leading to therapeutic resistance and recurrence.
The mechanisms contributing to GSC plasticity include cell-intrinsic and extrinsic factors, their localization to hypoxic, invasive or perivascular niches and interactions with the stromal cells in the tumor microenvironment (TME) (Uribe et al., 2022). For instance, the hypoxic niche, characterized by low oxygen levels and overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs), promotes GSC maintenance, chemoresistance, and proneural to mesenchymal-like transition (PMT) (Bar et al., 2010; Joseph et al., 2015). Specifically, HIF-1α promotes glucose uptake and the conversion of pyruvate to lactate, which contributes to the acidic pH (Lu et al., 2002). This altered environment not only supports the metabolic needs of the tumor but also induces PMT in GBM cells, allowing them to adapt and resist therapy (Joseph et al., 2015; Shen et al., 2015). While the hypoxic niche is abundant in MES-like GSC, the invasive niche is enriched with PN-GSCs. Radiation treatment induces the phenotypic transition of the invasive PN-GSCs to MES-like state (Minata et al., 2019). The perivascular niche also regulates GSC response to chemo-radiation therapy via activation of signaling pathways such as NOTCH1 (Guichet et al., 2014). Moreover, the tumor-associated macrophages/microglia (TAM) and reactive astrocytes also promote stemness and PMT of GSC and tumor cells by secreting proinflammatory cytokines like CCL20 and IL-6/8, and activating NF-κB and YAP/TAZ signaling, which in turn induce the expression of mesenchymal proteins and contribute to tumor recurrence (Henrik Heiland et al., 2019; Chen and Hambardzumyan, 2021).
A growing body of evidence has implicated a key role for epigenetic alterations and reorganization of the chromatin structure as a major driver of phenotypic plasticity in GBM. Particularly, hypoxia and radiation are reported to alter DNA methylation and histone modifications allowing GSCs to dynamically shift between phenotypic states (Uribe et al., 2022). Since epigenetic modifications drive the phenotypic adaptability and lineage plasticity of GSC and these alterations are reversible, in principle, the proteins and enzymes of the epigenetic machinery are deemed as promising therapeutic targets to prevent GBM recurrence. This review will focus primarily on the epigenetic regulators associated with phenotypic plasticity and therapeutic resistance in GBM. First, we will provide an overview of the recent findings from single-cell studies examining GSC plasticity, followed by a comprehensive discussion of the epigenetic mechanisms of DNA methylation, histone modifications and non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) involved in regulating phenotypic plasticity and treatment resistance in GBM.
Single-cell studies of cellular states and plasticity in GBM
Advances in single-cell sequencing technologies over the last decade have enabled a deeper underst anding of the inter- and intra-tumor heterogeneity of GBM, the complexity and diversity of cell populations that contribute to tumor evolution and therapeutic resistance. Patel et al., conducted the first single-cell RNA sequencing study in primary GBM tumors to investigate intra-tumoral heterogeneity and revealed the existence of multiple molecular subtypes and cellular states within an individual tumor. They noted that these cellular states are associated with diverse transcriptional programs related to oncogenic signaling, stemness, immune response and hypoxia (Patel et al., 2014). Subsequently, the study by Darmanis et al., examined intra- and inter-tumoral heterogeneity by isolating tumor cells from the core and peripheral regions of primary GBM tumors. This study reported significant genomic and transcriptomic diversity within the tumor core, whereas they found a more uniform gene signature in infiltrating tumor cells across patient tumors (Darmanis et al., 2017). A landmark study by Neftel et al., using a large cohort of patient tumors showed that tumor cells exist in four major cellular states: neural progenitor (NPC), oligodendrocyte progenitor (OPC) cell-, astrocytic (AC)- and mesenchymal (MES)- like states and that these cellular states are influenced by specific genomic alterations (Neftel et al., 2019). Other studies utilizing patient-derived orthotopic xenograft (PDOX) and in vitro models also demonstrated that GSCs exhibit plasticity and their heterogeneity arises from reversible state transitions and is influenced by the hypoxic environment (Dirkse et al., 2019). Another study utilizing a combination of single-cell RNA- and ATAC-sequencing of primary GBM tumors demonstrated that GSC heterogeneity exists along a single axis of variation and follows a continuum of PN to MES states (Wang et al., 2019). Furthermore, recent studies comparing GBM tumor cells with normal human fetal and adult brain cells revealed that GBM tumorigenesis recapitulates human brain development. These studies showed that the majority of cycling cells are derived from glial-progenitor-like cells and there is an invasive population of GSC with an outer radial glia-like phenotype observed during normal human brain development (Bhaduri et al., 2020; Couturier et al., 2020). Figure 1 provides an overview of the cellular states observed in GBM tumors in response to therapy and by the tumor microenvironment.
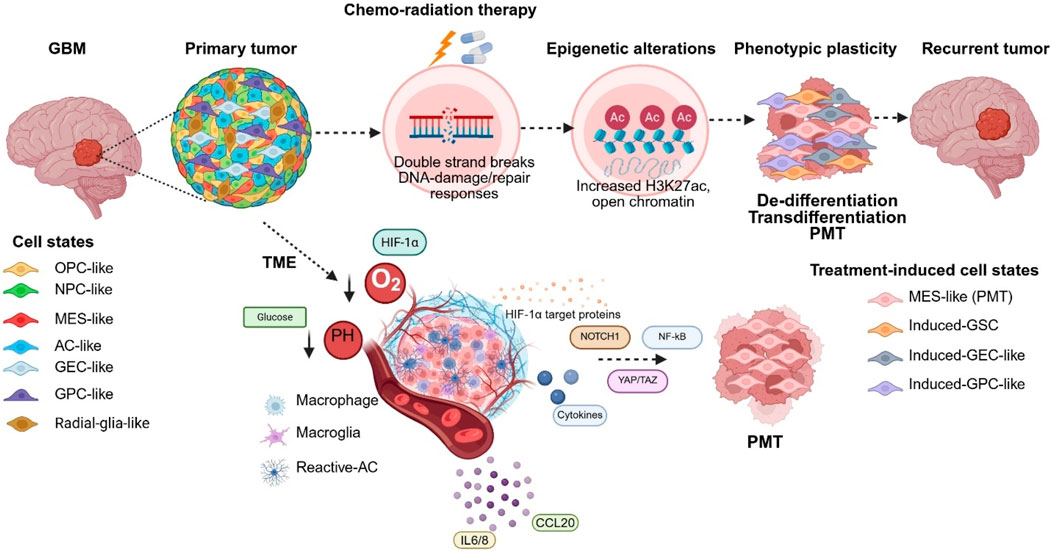
Figure 1. Cellular states and phenotypic plasticity of GSC. Proneural to Mesenchymal transition (PMT) is mediated by chemical cues such as hypoxia, acidic pH, chemo-radiation therapy and interactions with tumor-associated macrophages/microglia, reactive astrocytes. Radiation therapy also promotes phenotypic plasticity by promoting PMT, de-differentiation of tumor cells to GSC-like states and transdifferentiation of GSC into vascular-like cells. (OPC-Oligodendrocyte-progenitor cell, NPC- Neural Progenitor Cell, MES-Mesenchymal, AC-Astrocyte, GEC- GBM-derived Endothelial Cell, GPC-GBM-derived Pericytes).
There are also an increasing number of studies exploring the epigenetic landscape of GBM given the strong evidence of a developmental regulation of GSC. Guilhamon et al., performed single-cell ATAC-sequencing of primary GBM tumors to map the chromatin accessibility of GSC and identified that GSC exist in three states: reactive, constructive and invasive. These cell states possess unique transcriptional signatures and were found in varying proportions within tumors (Guilhamon et al., 2021). Another study by Lu et al., compared the epigenetic landscape of murine and human GSC cultures and found that they aligned along the PN-MES axis and proposed that epigenetic control of GSC is dictated by their developmental origin (Lu et al., 2022). More recent studies have begun to explore the spatial heterogeneity of GBM identifying novel cell types. Jain et al., combined single-cell RNA sequencing and spatial transcriptomics to elegantly demonstrate for the first time the presence of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) within GBM, which were thought to be absent due to the lack of brain fibroblasts. They demonstrated that CAFs have pro-tumoral effects on GSC but not non-stem tumor cells and promote tumor growth (Jain et al., 2023). In summary, these single-cell transcriptomic and epigenomic studies have illustrated the complexity of cellular states and plasticity of GSC that contributes to treatment resistance and recurrence in GBM.
Epigenetic mechanisms of GBM plasticity and resistance
The ability of GSC and tumor cells to adapt to diverse microenvironments and persist in the face of treatment requires them to undergo reversible transitions between various cellular states. This transition between different cellular states termed “phenotypic plasticity” is driven by the dynamic restructuring of the transcriptional programs unique to each cell state. Epigenetic modifications play a crucial role in this process as they are reversible events that do not modify the DNA and allow the GSCs to rapidly and efficiently turn on or turn off genes. DNA- and histone methylation is one of the most well-studied epigenetic mechanisms in GBM (J Dabrowski and Wojtas, 2019). However, recent studies have indicated that other histone modifications as well as non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) play key roles in regulating GBM plasticity and resistance (Azab, 2023; Yin et al., 2013). For instance, radiation-induced transdifferentiation of GSCs is driven by increased histone acetylation in vascular gene regions. Blocking the histone acetyltransferase (HAT) activity of P300 reversed these epigenetic changes, prevented transdifferentiation, sensitized tumors to radiation and reduced tumor growth (Muthukrishnan et al., 2022). Another example is the repressive methylation of miRNA-148a by DNA methyltransferases, which contributes to GSC maintenance and PMT (Li et al., 2019a). In addition, the H3K27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) on promoters of Nanog and PAX6 promotes GSC enrichment and endothelial differentiation, whereas active H3K27ac on the promoters of WNT5A and DLX5 enhances GSC differentiation between proliferative and slow-cycling states (Liau et al., 2017).
DNA methylation
In GBM, DNA methylation is strongly associated with predicting response to chemotherapy efficacy (Hegi et al., 2005). Early studies determined that methylation of the O(6)-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) gene promoter as a valuable prognostic biomarker for responsiveness to TMZ therapy (Zhao et al., 2018).
Methylation involves the transfer of a methyl group from S-adenosyl-L-methionine to the C5 position of cytosine residues in the DNA, resulting in the formation of 5-methylcytosine (5mC) (Okano et al., 1998). This process is catalyzed by enzymes called DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) and include DNMT1, DNMT2 and DNMT3 (DNMT3a and DNMT3b). DNMT1 is involved in methylation maintenance and extension including non-CpG sites, while DNMT2 targets tRNA and DNMT3a and DNMT3b function as de novo methyltransferases that methylate CpG (Zhang and Xu, 2017). Several DNMTs including DNMT1 and DNMT3b are highly expressed in GBM and their dysregulation is associated with aberrant cell cycle progression and maintenance of genomic stability (Rajendran et al., 2011). Cheray et al., demonstrated that disruption of specific interactions of DNMT1 with histone modifying enzymes can either suppress or enhance tumorigenesis in a murine GBM model (Cheray et al., 2013). In another study, they showed that inhibition of the DNMT1 interaction with CpG binding protein 1 (CFP1), a member of histone methyltransferase complex, increased sensitivity to TMZ chemotherapy (Cheray et al., 2014). Moreover, DNMT1 and DNMT3b have been shown to be activated by reprogramming transcription factors, OCT4 and SOX2, which leads to global changes in DNA methylation and downregulation of miRNAs that inhibits GBM stemness and tumor-propagating potential (Lopez-Bertoni et al., 2015).
In addition to DNMTs, demethylases such as ten-eleven translocation (TET) dioxygenases (TET1, TET2 and TET3) catalyze the oxidation of 5-methyl deoxycytosine (5-mdC) to 5-hydroxymethyl-2′deoxycytidine (5-hmdC), 5-formly-2′deoxycytidine (5-fdC) and 5-carboxyl-2′deoxycytidine (5-cadC) at promoters and enhancers in a replication-independent manner leading to transcriptional reactivation (Ito et al., 2010; Ito et al., 2011). TET2 overexpression has been shown to regulate neural differentiation and inhibit GBM tumor growth (García et al., 2018), while epigenetic repression of TET3 promotes GBM tumorigenesis (Carella et al., 2020). Furthermore, repression of TET2 by SOX2 and loss of 5hmdC and 5mdC levels is associated increased malignancy and GSC stemness (Lopez-Bertoni et al., 2022). Recent bulk- and single-cell multiomic studies examining global DNA methylation patterns in longitudinal patient samples identified that methylation patterns can be predictive of immune cell infiltration, the extent of necrosis and also patient survival (Klughammer et al., 2018). In addition, DNA methylation was reported to be elevated in aggressive tumors and tightly linked with transcriptional disruption and altered by hypoxia and radiation-stress responses (Johnson et al., 2021). Targeting DNA methylation and DNMTs with small molecule inhibitors such as 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine, Decitabine and Phthalimido-alkanamide have shown potent anti-tumoral effects and sensitized GBM cells to chemo-radiation therapy in animal models, making it an attractive strategy to overcome therapeutic resistance (Kratzsch et al., 2018; Yamashita et al., 2019; Wee et al., 2019; Gallitto et al., 2020).
Histone modifiers
Post-translational modifications (PTMs) of histones can influence chromatin structure, gene expression and the transcriptional landscape of cells (Kumari et al., 2023). Several histone PTMs have been identified and include acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, ubiquitination, lactylation, sumoylation, neddylation, citrullination, ADP-ribosylation, crotonylation, etc. Of these modifications, histone methylation and acetylation are well-characterized in GBM (McCornack et al., 2023). Other histone modifications like ubiquitination, sumoylation, lactylation and phosphorylation are less well-studied. However, these modifications are frequently found in GBM cells and have been linked to poor survival, tumorigenesis and resistance to TMZ (Cheng et al., 2020; Zhou et al., 2019; Wu et al., 2014; Pacaud et al., 2015; Tao et al., 2013).
Histone acetyltransferases and histone deactylases
Acetylation of histones is mediated by the action of lysine/histone acetyltransferases (KATs/HATs) that catalyze the addition of acetyl groups to N-terminal domain lysine residues, whereas the removal of acetyl groups is catalyzed by histone deactyleases (HDACs). HATs are divided into subgroups based on the their structure and sequence homology and include the Gcn5-related N-acetyltransferase (GNAT)-, MYST- and p300/CBP families as well as nuclear receptor coactivators (SRC-1, ACTR, TIF2), TAFII250 and TFIIIC (Sterner and Berger, 2000). Compared to other histone modifying enzymes, HATs are less well-studied in GBM. Nevertheless, they have been shown to play important roles in regulating GBM plasticity and resistance. Bhat K et al., revealed that radiation induced de-differentiation of tumor cells to GSC-like state is driven by alterations in histone acetylation and methylation, and extensive chromatin remodeling in promoters of Yamanaka factors SOX2, OCT4 and NANOG (Bhat et al., 2020). Muthukrishnan et al., also showed that radiation treatment increases H3K27 acetylation and chromatin accessiblity in specific vascular gene regions to promote GSC transdifferentiation to vascular-like cell states (Muthukrishnan et al., 2022). In another study, Mladek et al., identified that the RBBP4/P300 complex regulates transcription of DNA repair genes via histone acteylation and sensitizes GBM cells to TMZ chemotherapy (Mladek et al., 2022).
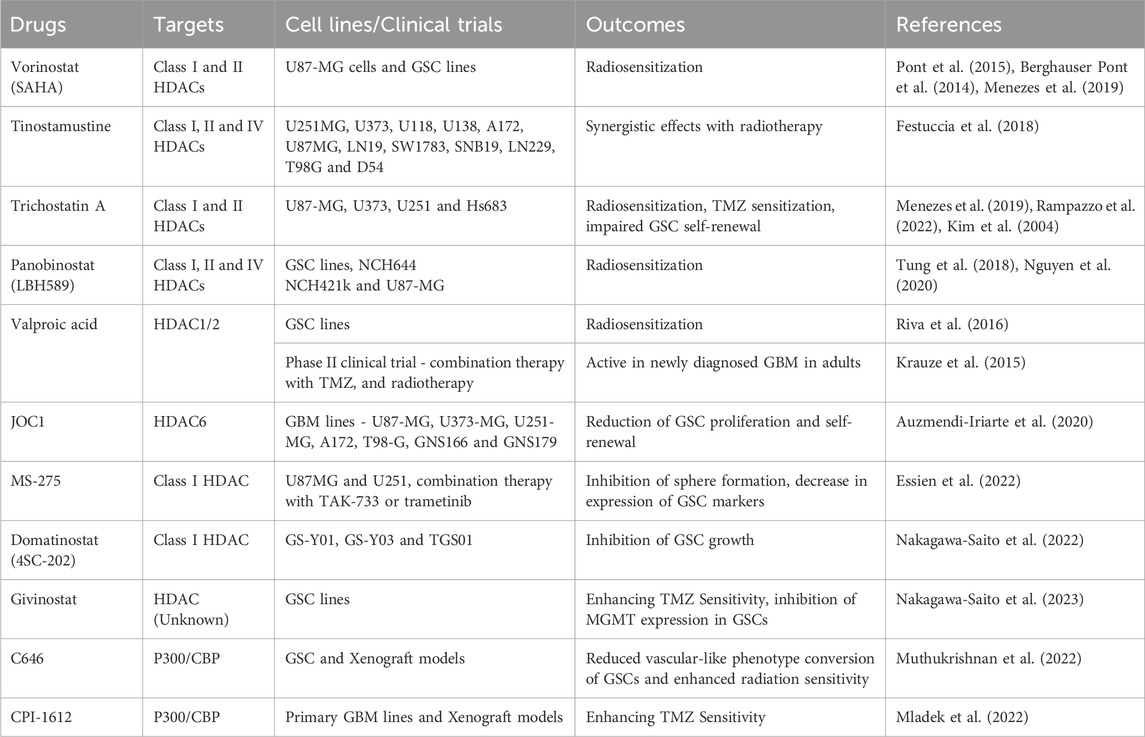
While HATs are less well-studied but play a crucial role in promoting plasticity, HDACs have been extensively investigated in GBM resistance. They are grouped into four main classes. Class I HDACs (HDAC1, 2, 3 and 8) have been implicated in GBM, while classes II (HDAC4, 5, 6, 7, 9 and 10) and IV (HDAC11) are over-expressed in low-grade astrocytoma (Lucio-Eterovic et al., 2008). Class III HDACs comprise the sirtuin (SIRT) family of proteins and have been shown to be aberrantly expressed in different GBM cell lines (Kunadis and Piperi, 2022). HDACs 1, 2, 3, 6 and 8 are all associated with TMZ resistance (Yang et al., 2020; Hanisch et al., 2022). SIRT1 was also shown to enhance TMZ resistance in both human GBM lines and xenograft models (Li et al., 2019b). While the investigation of HAT inhibitors is challenging due to their dual roles as both oncogenes and tumor suppressors and lack of substrate selectivity, several HDAC inhibitors (HDACis) have been widely investigated in GBM. HDACis sensitize GBM to radio-chemotherapy and have also been tested in combination with immunotherapies. However, clinical trials using various HDACis have yielded mixed results, with some showing only modest benefits and others displaying disappointing results due to unanticipated toxicity (Everix et al., 2023). Table 1 outlines HAT and HDAC inhibitors investigated in pre-clinical models of GBM as well as in clinical trials.
Histone methyltransferases and histone demethylases
Histone methyltransferases (HMTs) such as lysine methyltransferase (KMTs) and arginine methyltransferase (PRMTs) catalyze the addition of methyl groups on lysine and arginine residues on histones, particularly on H3 and H4 (Greer and Shi, 2012). Histone demethylases (HDMs), which remove methyl groups on histones, are categorized into two groups: the amino oxidase homolog lysine demethylases (KDMs) and the JmjC domain-containing histone demethylases (D’Oto et al., 2016). G9a, a histone methyltransferase is highly expressed in GBM cells and sensitizes tumors to chemo-radiation treatment (Ciechomska et al., 2018). Of the PRMTs, PRMT2 expression was eleveated in GBM and shown to be essential for GSC renewal and GBM tumorigenesis through methylation of H3R8me2a and activation of oncogenic transcriptional programs (Dong et al., 2018). PRMT6 promotes tumorigenicity and radiation response in GSC through methylation of regulator of chromatin condensation 1 (RCC1) signaling (Huang et al., 2021). The SET domain and mariner transposase fusion gene (SEMTAR), an HMT responsible for H3K36 methylation, contributes to radiation resistance by recruiting Ku80 DNA damage repair protein, facilitating the nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) repair pathway. This recruitment enhances DNA repair, enabling survival of residual GBM cells after radiation (Kaur et al., 2020).
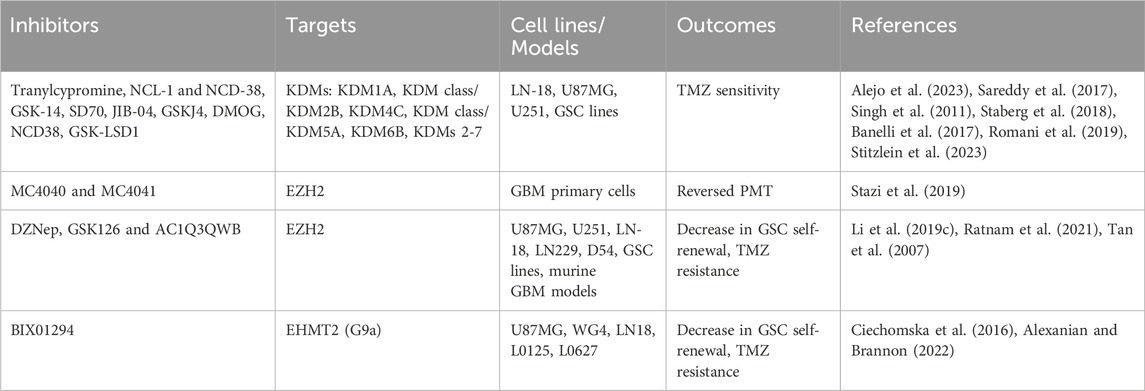
Histone demthylases are overexpressed in GBM and influence tumorigenicity and chemotherapy resistance. KDM5A and KDM6B are implicated in mediating TMZ resistance (Romani et al., 2019). Inhibition of KDM4C and KDM7A activity in GSCs induces DNA damage and disrupts the stem cell-like chromatin state, leading to GSC differentiation into a more differentiated, non-proliferative state. This differentiation is linked to a loss of self-renewal capacity, enhancing GSC response to DNA-damaging therapies (Mallm et al., 2020). Furthemore, Lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1/KDM1A) promotes self-renewal of GSC and TMZ resistance (Alejo et al., 2023). EZH2 (Enhancer of Zeste homolog 2), a catalytic subunit of the PRC2 complex and a H3K27 methyltransferase, has been extensively investigated in GBM and plays a key role in promoting GSC stemness and TMZ resistance (Sharma et al., 2017; Yu et al., 2023). Inhibitors targeting EZH2 including UNC1999, GSK343, GSK126, tazemetostat and CPI-1205 have shown potent effects in blocking PMT in GBM (Yu et al., 2017; Grinshtein et al., 2016). A summary of HMTs and HDMs inhibitors evaluated in GBM are presented in Table 2.
BET proteins
Bromodomain and Extraterminal Domain (BET) proteins recognize lysine-acetylated histones and function as epigenetic readers that regulate transcription (Belkina and Denis, 2012). These proteins including BRD2, BRD3, BRD4 and BRDT have emerged as promising anticancer targets in a broad spectrum of human malignancies including GBM. Among BET proteins, BRD4 was shown to be critical regulator of GSC stemness and tumorigenicity via regulation of NOTCH1 promoter (Tao et al., 2020). Inhibition of BET proteins sensitizes GBM cells to TMZ by reducing the MGMT expression (Tancredi et al., 2022). Several BET inhibitors, such as JQ1 and ZBC260 have been shown to reduce GSC stemness and PMT and improving TMZ sensitivity (Colardo et al., 2023; Duan et al., 2023). Furthermore, OTX015 (MK-8628), a novel inhibitor targeting BRD2/3/4 was reported to exhibit significant anti-tumor effects in combination with TMZ in orthotopic xenograft models (Berenguer-Daizé et al., 2016). However, it is worth noting that while BET proteins are attractive therapeutic targets for combinatiorial therapies in GBM, the lack of selective inhibitors targeting individual members of the BET family has slowed their development in clinical trials.
Other histone PTMs
The understudied modifications such as ubiquitination, sumoylation, phosphorylation, palmitoylation, succinylation and lactylation are being increasingly recognized as critical regulators of GBM resistance and progression. Abnormal histone ubiquitination patterns have been found to be associated with poor prognosis and enhanced survival in GBM (Jeusset and McManus, 2019). For example, BMI1-mediated ubiquitination of histone H2A at lysine 119 (H2AK119ub1) leads to transcriptional repression of tumor suppressor genes and contributes to the self-renewal and proliferation of GSCs (Kong et al., 2018). Several deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) such as USP1, USP3, USP4 and USP22, are also implicated in GBM. USP1 is overexpressed in GSCs and has been shown to enhance the radiosensitivity of GBM cells (Kong et al., 2018). Phosphorylation of histone H3 at sites such as H3T6 and H3S10 are associated with increased DNA damage repair capacity and resistance to TMZ and radiation therapy (Pacaud et al., 2015). Inhibition of histone phosphorylation using enzastaurin has been shown to increase GBM sensitivity to chemo-radiation therapy (Pacaud et al., 2015). Histone lactylation, facilitated by lactyltransferases, involves the transfer of lactate from lactyl-CoA to histones (Lu et al., 2024). Specifically, histone H3K9 lactylation (H3K9la) drives TMZ resistance in GBM by activating LUC7L2, which reduces MLH1 expression and impairs mismatch repair. Targeting lactylation with stiripentol, an LDHA/B inhibitor, was shown to restore TMZ sensitivity in resistant GBM cells (Yue et al., 2024). Together, these studies underscore the importance of investigating less common histone PTMs in mediating GBM plasticity and resistance, which can open new avenues for therapeutic targeting.
Non-coding RNAs
Approximately 70% of the genome can generate non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), which include long-ncRNAs (lncRNA), miRNAs and circRNAs and regulate the translation of messenger RNAs to functional proteins. All ncRNAs, especially miRNAs and lncRNAs are dysregulated in GBM and play key roles in driving plasticity and resistance (Shahzad et al., 2021). While there are still gaps in understanding how miRNAs interact with lncRNAs, these ncRNAs may serve as predictive or prognostic biomarkers and novel therapeutic targets for improving GBM outcomes (Mousavi et al., 2022). Here, we will mainly focus on miRNAs and lncRNAs implicated in GBM resistance (Figure 2).
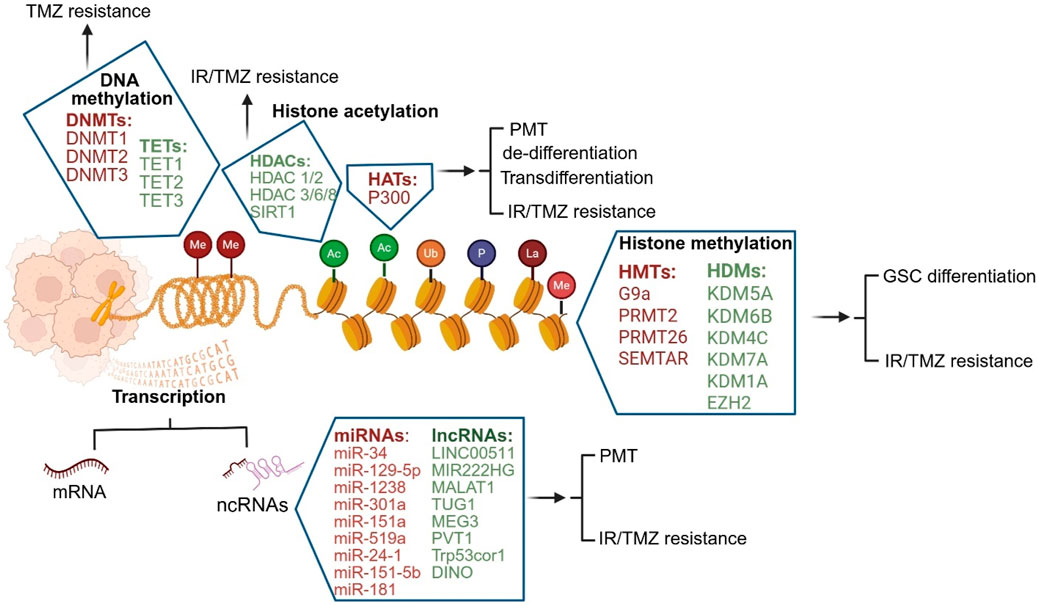
Figure 2. Epigenetic mechanisms mediating GBM plasticity and resistance. DNA methylation, histone modifications such as methylation, acetylation, ubiquitination, phosphorylation, and lactylation, as well as non-coding RNAs are the most well-characterized epigenetic mechanisms in GBM (DNMT- DNA methyltransferases, TET- Ten-eleven translocation, HDAC- Histone deacetylases, HAT- Histone acetyltransferases, HDM- Histone demethylases, HMT- Histone methyltransferases, ncRNA-non-coding RNA, miRNA-micro-RNA, siRNA-small interference RNA, piRNA- Piwi-interacting RNA).
miRNAs
miRNAs are small ncRNAs that typically consist of 20–22 nucleotides. They act as both tumor suppressors and onco-miRNAs and are highly dysregulated in GBM. miRNAs are predominantly involved in mediating chemo-radiation resistance and PMT. MiR-34 enhances GSC self-renewal, and therapeutic resistance by targeting EGFR signaling (Yin et al., 2013). MiR-129-5p promotes TMZ resistance by targeting DNMT3a (Gu et al., 2018). Moreover, miRNAs such as miR-1238 promotes resistance to TMZ via targeting CAV1/EGFR pathway, while miR-301a promotes resistance through regulating BTG1 (Yin et al., 2019; Xiao et al., 2021), while others, like miR-151a and miR-519a, enhance chemosensitivity by targeting STAT3/Bcl2 signaling pathway (Zeng et al., 2018; Li et al., 2018). Several other miRNAs are implicated in modulating the radiation-response of GBM. Overexpression of miR-24-1 and miR-151-5b, following radiation, reduces the expression of the tumor suppressor PDCD4, promoting resistance (Chao et al., 2013; Mukherjee et al., 2022; Sufianov et al., 2022). Additionally, miR-181a sensitizes GBM cells to radiation by targeting Bcl-2, while miR-301a, secreted in exosomes by hypoxic cells, activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling to enhance radiation resistance (Chen et al., 2010; Yue et al., 2019).
Long-non coding RNAs
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are a diverse group of RNA molecules typically longer than 200 nucleotides. They constitute over 80% of total non-coding RNAs and play crucial roles in regulation of gene expression, chromatin remodeling and cell signaling (Zhang et al., 2019). In the context of GBM, lncRNAs are key epigenetic regulators that influence tumor biology, including plasticity and resistance (Doghish et al., 2025). Several lncRNAs have been shown to directly affect the malignant characteristics of GSCs (Stackhouse et al., 2020; de Oliveira et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2023). For example, LINC00511 and MIR222HG induce PMT, which is associated with increased tumor aggressiveness, therapeutic resistance and worse prognosis for patients (Fan et al., 2023; Azam et al., 2020). MALAT1 regulates the PI3K/Akt pathway and promotes TMZ resistance (Cai et al., 2018). Other lncRNAs, such as TUG1 and MEG3, contribute to drug resistance by regulating drug efflux pumps and metabolic pathways that help GBM cells evade treatment (Luo et al., 2021). PVT1, Trp53cor1, TUG1 and DINO activate the p53-dependent DNA repair pathways to enhance GBM survival after radiation (Aryankalayil et al., 2018). Targeting these miRNAs and lncRNAs represent a promising approach to combat GBM resistance.
Challenges and opportunities in targeting epigenetic modifiers in GBM
Although fractionated radiation and TMZ chemotherapy continue to be the standard of care for GBM, the benefits are short-lived as tumors invariably develop resistance. Since epigenetic modifiers play a crucial role in the acquisition of phenotypic plasticity and resistance, a better understanding of their functions and mechanisms is vital to develop effective therapeutic modalities for GBM. Future investigations should focus on determining the underlying molecular mechanisms by which DNA methylation, histone modifications and ncRNAs influence GSC plasticity and resistance; as well as how their dynamics are altered by environmental stressors.
Targeting epigenetic modifiers with small molecule inhibitors remains a key challenge for GBM. There are several barriers that need to be addressed including: a) the inability of the inhibitors to cross the blood-brain-barrier and penetrate the tumors, b) lack of selectivity to target tumor cells, while sparing normal cells, c) lack of substrate specificity and off-target effects and d) unanticipated cytotoxicity. It is also imperative that more research is needed to develop rational pre-clinical models and drug delivery strategies to tackle these challenges. PROTACs (Proteolysis Targeting Chimeras) technology has emerged as a powerful strategy for drug delivery selectively targeting histone modifier enzymes. By harnessing the ubiquitin-proteasome system, PROTACs induce the selective degradation of these enzymes, allowing for the modulation of epigenetic regulation with high specificity (Rutherford and McManus, 2024; Alhasan et al., 2024). For instance, SPP-ARV-825 nanosystem combines the BRD4-degrading PROTAC ARV-825 with a micelle designed to cross the blood-brain barrier. This system effectively reduces tumor cell proliferation, induces apoptosis and inhibits tumor-associated macrophage polarization in GBM (Yang et al., 2022). The PROTAC-like inhibitor J22352 targets HDAC6 for degradation and significantly inhibited GBM progression by enhancing autophagic cell death and activating anti-tumor immunity (Liu et al., 2019). Moreover, nucleotide- and RNAi-based approaches such as antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), locked nucleic acids (LNAs), peptide nucleic acids (PNAs), morpholino oligonucleotides (MO), miRNA mimics and antagomirs, short interfering RNAs (siRNAs) and short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs) are also an alternative and viable therapeutic strategy. Nanoparticles (NPs) have emerged as a promising approach to deliver chemotherapeutics and RNAi molecules as they increase their lifespan in circulation and improve their cellular uptake and endosomal escape. Several types of NPs have been tested for systemic delivery of RNAi-based molecules and chemotherapeutics including liposomes, polymeric NPs, micelles, dendrimers, artificial DNA nanostructures, silica NPs, nanotubes, metal NPs and quantum dots enabling drug delivery to the brain (Lopez-Bertoni et al., 2018). These novel and emerging approaches have the potential to overcome the limitations associated with delivery, target specificity and safety and need to be further validated in pre-clinical models for their anti-tumor efficacy prior to clinical translation.
Conclusions and future directions
Our review has highlighted the functional significance of epigenetic modifications in driving GBM plasticity and resistance. By elucidating the epigenetic landscape of GBM, we can potentially identify novel biomarkers, improve patient stratification and design rational and personalized treatment strategies for better clinical outcomes. In order for pre-clinical findings to translate into successful clinical trials, chemotherapeutics will need to be tested on humanized animal models and patient-derived organoid models that more closely mimic patient tumors. Moreover, leveraging multi-omics technologies including single-cell and spatial transcriptomics, epigenomics, proteomics and metabolomics combined with histology and functional imaging can potentially reveal how GBM tumors evolve across space and time, their adaptation to different environments and therapeutic insults, unravel novel cellular and molecular interactions and identify novel mechanisms driving plasticity, resistance and recurrence.
Author contributions
FA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. SK: Writing – review and editing. SM: Conceptualization, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the Department of Oncological Science, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
GBM, Glioblastoma; TMZ, Temozolomide; GSCs, GBM stem-like cells; EC, Endothelial-like cells; PC, Pericyte-like cells; PN, Proneural; MES, Mesenchymal; PMT, Proneural to mesenchymal transition; EMT, Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; TME, Tumor microenvironment; ncRNAs, Non-coding RNAs; NPC, Neural progenitor-like cells; OPC, Oligodendrocyte progenitor-like cells; AC, Astrocyte-like cells; PDOX, Patient-derived orthotopic xenograft; ATAC, Assay for Transposase-Accessible Chromatin; CAFs, Cancer-associated fibroblasts; 5mC, 5-methylcytosine; DNMTs, DNA methyltransferases; CFP1, CpG binding protein 1; TET, Ten-eleven translocation; 5-mdC, 5-methyl deoxycytosine; 5-hmdC, 5-hydroxymethyl-2′deoxycytidine; 5-fdC, 5-formly-2′deoxycytidine; 5-cadC, 5-carboxyl-2′deoxycytidine; PRC2, Polycomb repressive complex protein 2; DNMTis, DNA methyltransferase inhibitors; PTMs, Post-translational modifications; HDACs, Histone deacetylases; HATs, Histone acetyltransferases; KATs, Lysine/histone acetyltransferases; GNAT, Gcn5-related N-acetyltransferase; TAFII250, TATA-binding protein-associated factor 250; TFIIIC, Transcription factor IIIC; HIF2A, Hypoxia-inducible factor 2A; HDACis, Histone deacetylase inhibitors; HMTs, Histone methyltransferases; KMTs, Lysine methyltransferases; PRMTs, Arginine methyltransferases; HDMs, Histone demethylases; KDMs, Lysine demethylases; EZH2, Enhancer of zeste homolog 2; BET, Bromodomain and extraterminal domain; MGMT, O-6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase; NHEJ, non-homologous end joining; lncRNA, Long non-coding RNA; miRNAs, MicroRNAs; TCGA, The Cancer Genome Atlas; MMPs, Matrix metalloproteinases; ASOs, Antisense oligonucleotides; LNAs, Locked nucleic acids; PNAs, Peptide nucleic acids; MO, Morpholino oligonucleotide; siRNAs, Short interfering RNAs; shRNAs, Short hairpin RNAs; NPs, Nanoparticles.
References
Alejo, S., Palacios, B., Venkata, P. P., He, Y., Li, W., Johnson, J., et al. (2023). Lysine-specific histone demethylase 1A (KDM1A/LSD1) inhibition attenuates DNA double-strand break repair and augments the efficacy of temozolomide in glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 25, 1249–1261. doi:10.1093/neuonc/noad018
Alexanian, A. R., and Brannon, A. (2022). Unique combinations of epigenetic modifiers synergistically impair the viability of the U87 glioblastoma cell line while exhibiting minor or moderate effects on normal stem cell growth. Med. Oncol. 39, 86. doi:10.1007/s12032-022-01683-2
Alhasan, B. A., Morozov, A. V., Guzhova, I. V., and Margulis, B. A. (2024). The ubiquitin-proteasome system in the regulation of tumor dormancy and recurrence. Biochimica Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Rev. Cancer 1879, 189119. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2024.189119
Aryankalayil, M. J., Chopra, S., Levin, J., Eke, I., Makinde, A., Das, S., et al. (2018). Radiation-induced long noncoding RNAs in a mouse model after whole-body irradiation. Radiat. Res. 189, 251–263. doi:10.1667/rr14891.1
Auzmendi-Iriarte, J., Saenz-Antoñanzas, A., Mikelez-Alonso, I., Carrasco-Garcia, E., Tellaetxe-Abete, M., Lawrie, C. H., et al. (2020). Characterization of a new small-molecule inhibitor of HDAC6 in glioblastoma. Cell Death Dis. 11, 417. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-2586-x
Azab, M. A. (2023). The potential role of histone modifications in glioblastoma therapy: review article. J. Mol. Pathology 4 (4), 196–212. doi:10.3390/jmp4040018
Azam, Z., To, S-S. T., and Tannous, B. A. (2020). Mesenchymal transformation: the rosetta stone of glioblastoma pathogenesis and therapy resistance. Adv. Sci. 7, 2002015. doi:10.1002/advs.202002015
Baisiwala, S., Auffinger, B., Caragher, S. P., Shireman, J. M., Ahsan, R., Lee, G., et al. (2019). Chemotherapeutic stress induces transdifferentiation of glioblastoma cells to endothelial cells and promotes vascular mimicry. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 1–14. doi:10.1155/2019/6107456
Banelli, B., Daga, A., Forlani, A., Allemanni, G., Marubbi, D., Pistillo, M. P., et al. (2017). Small molecules targeting histone demethylase genes (KDMs) inhibit growth of temozolomide-resistant glioblastoma cells. Oncotarget 8, 34896–34910. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.16820
Bar, E. E., Lin, A., Mahairaki, V., Matsui, W., and Eberhart, C. G. (2010). Hypoxia increases the expression of stem-cell markers and promotes clonogenicity in glioblastoma neurospheres. Am. J. Pathol. 177, 1491–1502. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2010.091021
Belkina, A. C., and Denis, G. V. (2012). BET domain co-regulators in obesity, inflammation and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 12, 465–477. doi:10.1038/nrc3256
Berenguer-Daizé, C., Astorgues-Xerri, L., Odore, E., Cayol, M., Cvitkovic, E., Noel, K., et al. (2016). OTX015 (MK-8628), a novel BET inhibitor, displays in vitro and in vivo antitumor effects alone and in combination with conventional therapies in glioblastoma models. Int. J. Cancer 139, 2047–2055. doi:10.1002/ijc.30256
Berghauser Pont, L. M., Spoor, J. K., Venkatesan, S., Swagemakers, S., Kloezeman, J. J., Dirven, C. M., et al. (2014). The Bcl-2 inhibitor Obatoclax overcomes resistance to histone deacetylase inhibitors SAHA and LBH589 as radiosensitizers in patient-derived glioblastoma stem-like cells. Genes Cancer 5, 445–459. doi:10.18632/genesandcancer.42
Bhaduri, A., Di Lullo, E., Jung, D., Müller, S., Crouch, E. E., Espinosa, C. S., et al. (2020). Outer radial glia-like cancer stem cells contribute to heterogeneity of glioblastoma. Cell stem Cell 26, 48–63.e6. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2019.11.015
Bhat, K., Saki, M., Vlashi, E., Cheng, F., Duhachek-Muggy, S., Alli, C., et al. (2020). The dopamine receptor antagonist trifluoperazine prevents phenotype conversion and improves survival in mouse models of glioblastoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 117, 11085–11096. doi:10.1073/pnas.1920154117
Cai, T., Liu, Y., and Xiao, J. (2018). Long noncoding RNA MALAT 1 knockdown reverses chemoresistance to temozolomide via promoting micro RNA-101 in glioblastoma. Cancer Med. 7, 1404–1415. doi:10.1002/cam4.1384
Carella, A., Tejedor, J. R., García, M. G., Urdinguio, R. G., Bayón, G. F., Sierra, M., et al. (2020). Epigenetic downregulation of TET3 reduces genome-wide 5hmC levels and promotes glioblastoma tumorigenesis. Int. J. Cancer 146, 373–387. doi:10.1002/ijc.32520
Chao, T-F., Xiong, H.-H., Liu, W., Chen, Y., and Zhang, J-X. (2013). MiR-21 mediates the radiation resistance of glioblastoma cells by regulating PDCD4 and hMSH2. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Med. Sci. 33, 525–529. doi:10.1007/s11596-013-1153-4
Chen, G., Zhu, W., Shi, D., Lv, L., Zhang, C., Liu, P., et al. (2010). MicroRNA-181a sensitizes human malignant glioma U87MG cells to radiation by targeting Bcl-2. Oncol. Rep. 23, 997–1003. doi:10.3892/or_00000725
Chen, Z., and Hambardzumyan, D. (2021). Macrophage-tumor cell intertwine drives the transition into a mesenchymal-like cellular state of glioblastoma. Cancer Cell 39, 743–745. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2021.05.003
Cheng, C. D., Dong, Y. F., Niu, W. X., and Niu, C. S. (2020). HAUSP promoted the growth of glioma cells in vitro and in vivo via stabilizing NANOG. Pathology - Res. Pract. 216, 152883. doi:10.1016/j.prp.2020.152883
Cheng, L., Huang, Z., Zhou, W., Wu, Q., Donnola, S., Liu, J. K., et al. (2013). Glioblastoma stem cells generate vascular pericytes to support vessel function and tumor growth. Cell 153, 139–152. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.02.021
Cheray, M., Nadaradjane, A., Bonnet, P., Routier, S., Vallette, F. M., and Cartron, P. F. (2014). Specific inhibition of DNMT1/CFP1 reduces cancer phenotypes and enhances chemotherapy effectiveness. Epigenomics 6, 267–275. doi:10.2217/epi.14.18
Cheray, M., Pacaud, R., Nadaradjane, A., Vallette, F. M., and Cartron, P. F. (2013). Specific inhibition of one DNMT1-including complex influences tumor initiation and progression. Clin. Epigenetics 5, 9. doi:10.1186/1868-7083-5-9
Ciechomska, I. A., Marciniak, M. P., Jackl, J., and Kaminska, B. (2018). Pre-treatment or post-treatment of human glioma cells with BIX01294, the inhibitor of histone methyltransferase G9a, sensitizes cells to temozolomide. Front. Pharmacol. 9, 1271. doi:10.3389/fphar.2018.01271
Ciechomska, I. A., Przanowski, P., Jackl, J., Wojtas, B., and Kaminska, B. (2016). BIX01294, an inhibitor of histone methyltransferase, induces autophagy-dependent differentiation of glioma stem-like cells. Sci. Rep. 6, 38723. doi:10.1038/srep38723
Colardo, M., Gargano, D., Russo, M., Petraroia, M., Pensabene, D., D’Alessandro, G., et al. (2023). Bromodomain and extraterminal domain (BET) protein inhibition hinders glioblastoma progression by inducing autophagy-dependent differentiation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (8), 7017. doi:10.3390/ijms24087017
Couturier, C. P., Ayyadhury, S., Le, P. U., Nadaf, J., Monlong, J., Riva, G., et al. (2020). Single-cell RNA-seq reveals that glioblastoma recapitulates a normal neurodevelopmental hierarchy. Nat. Commun. 11, 3406. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-17186-5
Darmanis, S., Sloan, S. A., Croote, D., Mignardi, M., Chernikova, S., Samghababi, P., et al. (2017). Single-cell RNA-seq analysis of infiltrating neoplastic cells at the migrating front of human glioblastoma. Cell Rep. 21, 1399–1410. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2017.10.030
de Oliveira, J. C., Oliveira, L. C., Mathias, C., Pedroso, G. A., Lemos, D. S., Salviano-Silva, A., et al. (2019). Long non-coding RNAs in cancer: another layer of complexity. J. Gene Med. 21, e3065. doi:10.1002/jgm.3065
Dirkse, A., Golebiewska, A., Buder, T., Nazarov, P. V., Muller, A., Poovathingal, S., et al. (2019). Stem cell-associated heterogeneity in Glioblastoma results from intrinsic tumor plasticity shaped by the microenvironment. Nat. Commun. 10, 1787. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-09853-z
Doghish, A. S., Mahmoud, A., Abd-Elmawla, M. A., Zaki, M. B., Aborehab, N. M., Hatawsh, A., et al. (2025). Innovative perspectives on glioblastoma: the emerging role of long non-coding RNAs. Funct. and Integr. Genomics 25, 43. doi:10.1007/s10142-025-01557-6
Dong, F., Li, Q., Yang, C., Huo, D., Wang, X., Ai, C., et al. (2018). PRMT2 links histone H3R8 asymmetric dimethylation to oncogenic activation and tumorigenesis of glioblastoma. Nat. Commun. 9, 4552. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-06968-7
D’Oto, A., Tian, Q. W., Davidoff, A. M., and Yang, J. (2016). Histone demethylases and their roles in cancer epigenetics. J. Med. Oncol. Ther. 1, 34–40.
Duan, W., Yu, M., and Chen, J. (2023). BRD4: new hope in the battle against glioblastoma. Pharmacol. Res. 191, 106767. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2023.106767
Essien, E. I., Hofer, T. P., Atkinson, M. J., and Anastasov, N. (2022). Combining HDAC and MEK inhibitors with radiation against glioblastoma-derived spheres. Cells 11 (5), 775. doi:10.3390/cells11050775
Everix, L., Seane, E. N., Ebenhan, T., Goethals, I., and Bolcaen, J. (2023). Introducing HDAC-targeting radiopharmaceuticals for glioblastoma imaging and therapy. Pharmaceuticals 16, 227. doi:10.3390/ph16020227
Fan, Y., Gao, Z., Xu, J., Wang, H., Guo, Q., Li, B., et al. (2023). SPI1-mediated MIR222HG transcription promotes proneural-to-mesenchymal transition of glioma stem cells and immunosuppressive polarization of macrophages. Theranostics 13, 3310–3329. doi:10.7150/thno.82590
Festuccia, C., Mancini, A., Colapietro, A., Gravina, G. L., Vitale, F., Marampon, F., et al. (2018). The first-in-class alkylating deacetylase inhibitor molecule tinostamustine shows antitumor effects and is synergistic with radiotherapy in preclinical models of glioblastoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 11, 32. doi:10.1186/s13045-018-0576-6
Gallitto, M., Cheng He, R., Inocencio, J. F., Wang, H., Zhang, Y., Deikus, G., et al. (2020). Epigenetic preconditioning with decitabine sensitizes glioblastoma to temozolomide via induction of MLH1. J. Neurooncol 147, 557–566. doi:10.1007/s11060-020-03461-4
García, M. G., Carella, A., Urdinguio, R. G., Bayón, G. F., Lopez, V., Tejedor, J. R., et al. (2018). Epigenetic dysregulation of TET2 in human glioblastoma. Oncotarget 9, 25922–25934. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.25406
Greer, E. L., and Shi, Y. (2012). Histone methylation: a dynamic mark in health, disease and inheritance. Nat. Rev. Genet. 13, 343–357. doi:10.1038/nrg3173
Grinshtein, N., Rioseco, C. C., Marcellus, R., Uehling, D., Aman, A., Lun, X., et al. (2016). Small molecule epigenetic screen identifies novel EZH2 and HDAC inhibitors that target glioblastoma brain tumor-initiating cells. Oncotarget 7, 59360–59376. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.10661
Gu, X., Gong, H., Shen, L., and Gu, Q. (2018). MicroRNA-129-5p inhibits human glioma cell proliferation and induces cell cycle arrest by directly targeting DNMT3A. Am. J. Transl. Res. 10, 2834–2847.
Guichet, P.-O., Guelfi, S., Teigell, M., Hoppe, L., Bakalara, N., Bauchet, L., et al. (2014). Notch1 stimulation induces a vascularization switch with pericyte-like cell differentiation of glioblastoma stem cells. Stem Cells 33, 21–34. doi:10.1002/stem.1767
Guilhamon, P., Chesnelong, C., Kushida, M. M., Nikolic, A., Singhal, D., MacLeod, G., et al. (2021). Single-cell chromatin accessibility profiling of glioblastoma identifies an invasive cancer stem cell population associated with lower survival. eLife 10, e64090. doi:10.7554/eLife.64090
Hanisch, D., Krumm, A., Diehl, T., Stork, C. M., Dejung, M., Butter, F., et al. (2022). Class I HDAC overexpression promotes temozolomide resistance in glioma cells by regulating RAD18 expression. Cell Death Dis. 13, 293. doi:10.1038/s41419-022-04751-7
Hegi, M. E., Diserens, A.-C., Gorlia, T., Hamou, M.-F., de Tribolet, N., Weller, M., et al. (2005). MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 352, 997–1003. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa043331
Henrik Heiland, D., Ravi, V. M., Behringer, S. P., Frenking, J. H., Wurm, J., Joseph, K., et al. (2019). Tumor-associated reactive astrocytes aid the evolution of immunosuppressive environment in glioblastoma. Nat. Commun. 10, 2541. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-10493-6
Huang, T., Yang, Y., Song, X., Wan, X., Wu, B., Sastry, N., et al. (2021). PRMT6 methylation of RCC1 regulates mitosis, tumorigenicity, and radiation response of glioblastoma stem cells. Mol. Cell 81, 1276–1291.e9. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2021.01.015
Ito, S., D’Alessio, A. C., Taranova, O. V., Hong, K., Sowers, L. C., and Zhang, Y. (2010). Role of Tet proteins in 5mC to 5hmC conversion, ES-cell self-renewal and inner cell mass specification. Nature 466, 1129–1133. doi:10.1038/nature09303
Ito, S., Shen, L., Dai, Q., Wu, S. C., Collins, L. B., Swenberg, J. A., et al. (2011). Tet proteins can convert 5-methylcytosine to 5-formylcytosine and 5-carboxylcytosine. Science 333, 1300–1303. doi:10.1126/science.1210597
Jain, S., Rick, J. W., Joshi, R. S., Beniwal, A., Spatz, J., Gill, S., et al. (2023). Single-cell RNA sequencing and spatial transcriptomics reveal cancer-associated fibroblasts in glioblastoma with protumoral effects. J. Clin. Invest. 133, e147087. doi:10.1172/jci147087
J Dabrowski, M., and Wojtas, B. (2019). Global DNA methylation patterns in human gliomas and their interplay with other epigenetic modifications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 3478. doi:10.3390/ijms20143478
Jeusset, L. M., and McManus, K. J. (2019). Developing targeted therapies that exploit aberrant histone ubiquitination in cancer. Cells 8 (2), 165. doi:10.3390/cells8020165
Johnson, K. C., Anderson, K. J., Courtois, E. T., Gujar, A. D., Barthel, F. P., Varn, F. S., et al. (2021). Single-cell multimodal glioma analyses identify epigenetic regulators of cellular plasticity and environmental stress response. Nat. Genet. 53, 1456–1468. doi:10.1038/s41588-021-00926-8
Joseph, J. V., Conroy, S., Pavlov, K., Sontakke, P., Tomar, T., Eggens-Meijer, E., et al. (2015). Hypoxia enhances migration and invasion in glioblastoma by promoting a mesenchymal shift mediated by the HIF1α–ZEB1 axis. Cancer Lett. 359, 107–116. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2015.01.010
Kaur, E., Nair, J., Ghorai, A., Mishra, S. V., Achareker, A., Ketkar, M., et al. (2020). Inhibition of SETMAR–H3K36me2–NHEJ repair axis in residual disease cells prevents glioblastoma recurrence. Neuro-Oncology 22, 1785–1796. doi:10.1093/neuonc/noaa128
Kim, J. H., Shin, J. H., and Kim, I. H. (2004). Susceptibility and radiosensitization of human glioblastoma cells to trichostatin A, a histone deacetylase inhibitor. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 59, 1174–1180. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.03.001
Klughammer, J., Kiesel, B., Roetzer, T., Fortelny, N., Nemc, A., Nenning, K. H., et al. (2018). The DNA methylation landscape of glioblastoma disease progression shows extensive heterogeneity in time and space. Nat. Med. 24, 1611–1624. doi:10.1038/s41591-018-0156-x
Kong, Y., Ai, C., Dong, F., Xia, X., Zhao, X., Yang, C., et al. (2018). Targeting of BMI-1 with PTC-209 inhibits glioblastoma development. Cell Cycle 17, 1199–1211. doi:10.1080/15384101.2018.1469872
Kratzsch, T., Kuhn, S. A., Joedicke, A., Hanisch, U. K., Vajkoczy, P., Hoffmann, J., et al. (2018). Treatment with 5-azacitidine delay growth of glioblastoma xenografts: a potential new treatment approach for glioblastomas. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 144, 809–819. doi:10.1007/s00432-018-2600-1
Krauze, A. V., Myrehaug, S. D., Chang, M. G., Holdford, D. J., Smith, S., Shih, J., et al. (2015). A phase 2 study of concurrent radiation therapy, temozolomide, and the histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid for patients with glioblastoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 92, 986–992. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.04.038
Kumari, S., Gupta, R., Ambasta, R. K., and Kumar, P. (2023). Emerging trends in post-translational modification: shedding light on Glioblastoma multiforme. Biochimica Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Rev. Cancer 1878, 188999. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2023.188999
Kunadis, E., and Piperi, C. (2022). Exploring the multi-faceted role of sirtuins in glioblastoma pathogenesis and targeting options. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 12889. doi:10.3390/ijms232112889
Li, H., Chen, L., Li, J-J., Zhou, Q., Huang, A., Liu, W-W., et al. (2018). miR-519a enhances chemosensitivity and promotes autophagy in glioblastoma by targeting STAT3/Bcl2 signaling pathway. J. Hematol. Oncol. 11, 70. doi:10.1186/s13045-018-0618-0
Li, Y., Chen, F., Chu, J., Wu, C., Li, Y., Li, H., et al. (2019a). miR-148-3p inhibits growth of glioblastoma targeting DNA methyltransferase-1 (DNMT1). Oncol. Res. 27, 911–921. doi:10.3727/096504019x15516966905337
Li, Y., Chen, X., Cui, Y., Wei, Q., Chen, S., and Wang, X. (2019b). Effects of SIRT1 silencing on viability, invasion and metastasis of human glioma cell lines. Oncol. Lett. 17, 3701–3708. doi:10.3892/ol.2019.10063
Li, Y., Ren, Y., Wang, Y., Tan, Y., Wang, Q., Cai, J., et al. (2019c). A compound AC1Q3QWB selectively disrupts HOTAIR-mediated recruitment of PRC2 and enhances cancer therapy of DZNep. Theranostics 9, 4608–4623. doi:10.7150/thno.35188
Liau, B. B., Sievers, C., Donohue, L. K., Gillespie, S. M., Flavahan, W. A., Miller, T. E., et al. (2017). Adaptive chromatin remodeling drives glioblastoma stem cell plasticity and drug tolerance. Cell stem Cell 20, 233–246. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2016.11.003
Liu, J. R., Yu, C. W., Hung, P. Y., Hsin, L. W., and Chern, J. W. (2019). High-selective HDAC6 inhibitor promotes HDAC6 degradation following autophagy modulation and enhanced antitumor immunity in glioblastoma. Biochem. Pharmacol. 163, 458–471. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2019.03.023
Lopez-Bertoni, H., Johnson, A., Rui, Y., Lal, B., Sall, S., Malloy, M., et al. (2022). Sox2 induces glioblastoma cell stemness and tumor propagation by repressing TET2 and deregulating 5hmC and 5mC DNA modifications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 7, 37. doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00857-0
Lopez-Bertoni, H., Kozielski, K. L., Rui, Y., Lal, B., Vaughan, H., Wilson, D. R., et al. (2018). Bioreducible polymeric Nanoparticles containing multiplexed cancer stem cell regulating miRNAs inhibit glioblastoma growth and prolong survival. Nano Lett. 18, 4086–4094. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b00390
Lopez-Bertoni, H., Lal, B., Li, A., Caplan, M., Guerrero-Cázares, H., Eberhart, C. G., et al. (2015). DNMT-dependent suppression of microRNA regulates the induction of GBM tumor-propagating phenotype by Oct4 and Sox2. Oncogene 34, 3994–4004. doi:10.1038/onc.2014.334
Lu, H., Forbes, R. A., and Verma, A. (2002). Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 activation by aerobic glycolysis implicates the warburg effect in carcinogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 23111–23115. doi:10.1074/jbc.M202487200
Lu, X., Maturi, N. P., Jarvius, M., Yildirim, I., Dang, Y., Zhao, L., et al. (2022). Cell-lineage controlled epigenetic regulation in glioblastoma stem cells determines functionally distinct subgroups and predicts patient survival. Nat. Commun. 13, 2236. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-29912-2
Lu, Z., Zheng, X., Shi, M., Yin, Y., Liang, Y., Zou, Z., et al. (2024). Lactylation: the emerging frontier in post-translational modification. Front. Genet. 15, 1423213. doi:10.3389/fgene.2024.1423213
Lucio-Eterovic, A. K., Cortez, M. A., Valera, E. T., Motta, F. J., Queiroz, R. G., Machado, H. R., et al. (2008). Differential expression of 12 histone deacetylase (HDAC) genes in astrocytomas and normal brain tissue: class II and IV are hypoexpressed in glioblastomas. BMC cancer 8, 243. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-8-243
Luo, Q., Zhang, F., Li, W., Wang, F., Wu, L., and Huang, B. (2021). Overexpression of lncRNA MEG3 inhibits proliferation and invasion of glioblastoma U251 cells in vitro by suppressing HIF1α expression. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 41, 141–145. doi:10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2021.01.21
Mallm, J. P., Windisch, P., Biran, A., Gal, Z., Schumacher, S., Glass, R., et al. (2020). Glioblastoma initiating cells are sensitive to histone demethylase inhibition due to epigenetic deregulation. Int. J. Cancer 146, 1281–1292. doi:10.1002/ijc.32649
McCornack, C., Woodiwiss, T., Hardi, A., Yano, H., and Kim, A. H. (2023). The function of histone methylation and acetylation regulators in GBM pathophysiology. Front. Oncol. 13, 1144184. doi:10.3389/fonc.2023.1144184
Menezes, A., Dos Reis, G. H., Oliveira-Nunes, M. C., Mariath, F., Cabanel, M., Pontes, B., et al. (2019). Live cell imaging supports a key role for histone deacetylase as a molecular target during glioblastoma malignancy downgrade through tumor competence modulation. J. Oncol. 2019, 1–16. doi:10.1155/2019/9043675
Minata, M., Audia, A., Shi, J., Lu, S., Bernstock, J., Pavlyukov, M. S., et al. (2019). Phenotypic plasticity of invasive edge glioma stem-like cells in response to ionizing radiation. Cell Rep. 26, 1893–1905.e7. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2019.01.076
Mladek, A. C., Yan, H., Tian, S., Decker, P. A., Burgenske, D. M., Bakken, K., et al. (2022). RBBP4-p300 axis modulates expression of genes essential for cell survival and is a potential target for therapy in glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 24, 1261–1272. doi:10.1093/neuonc/noac051
Mousavi, S. M., Derakhshan, M., Baharloii, F., Dashti, F., Mirazimi, S. M. A., Mahjoubin-Tehran, M., et al. (2022). Non-coding RNAs and glioblastoma: insight into their roles in metastasis. Mol. Ther. - Oncolytics 24, 262–287. doi:10.1016/j.omto.2021.12.015
Mukherjee, S., Shelar, B., and Krishna, S. (2022). Versatile role of miR-24/24-1*/24-2* expression in cancer and other human diseases. Am. J. Transl. Res. 14, 20–54.
Muthukrishnan, S. D., Kawaguchi, R., Nair, P., Prasad, R., Qin, Y., Johnson, M., et al. (2022). P300 promotes tumor recurrence by regulating radiation-induced conversion of glioma stem cells to vascular-like cells. Nat. Commun. 13, 6202. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-33943-0
Nakagawa-Saito, Y., Mitobe, Y., Togashi, K., Suzuki, S., Sugai, A., Kitanaka, C., et al. (2023). Givinostat inhibition of sp1-dependent MGMT expression sensitizes glioma stem cells to temozolomide. Anticancer Res. 43, 1131–1138. doi:10.21873/anticanres.16258
Nakagawa-Saito, Y., Saitoh, S., Mitobe, Y., Sugai, A., Togashi, K., Suzuki, S., et al. (2022). HDAC class I inhibitor domatinostat preferentially targets glioma stem cells over their differentiated progeny. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (15), 8084. doi:10.3390/ijms23158084
Neftel, C., Laffy, J., Filbin, M. G., Hara, T., Shore, M. E., Rahme, G. J., et al. (2019). An integrative model of cellular states, plasticity, and genetics for glioblastoma. Cell 178, 835–849.e21. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2019.06.024
Nguyen, T. T. T., Zhang, Y., Shang, E., Shu, C., Torrini, C., Zhao, J., et al. (2020). HDAC inhibitors elicit metabolic reprogramming by targeting super-enhancers in glioblastoma models. J. Clin. Invest. 130, 3699–3716. doi:10.1172/jci129049
Okano, M., Xie, S., and Li, E. (1998). Cloning and characterization of a family of novel mammalian DNA (cytosine-5) methyltransferases. Nat. Genet. 19, 219–220. doi:10.1038/890
Pacaud, R., Cheray, M., Nadaradjane, A., Vallette, F. M., and Cartron, P. F. (2015). Histone H3 phosphorylation in GBM: a new rational to guide the use of kinase inhibitors in anti-GBM therapy. Theranostics 5, 12–22. doi:10.7150/thno.8799
Patel, A. P., Tirosh, I., Trombetta, J. J., Shalek, A. K., Gillespie, S. M., Wakimoto, H., et al. (2014). Single-cell RNA-seq highlights intratumoral heterogeneity in primary glioblastoma. Science 344, 1396–1401. doi:10.1126/science.1254257
Pont, L. M., Naipal, K., Kloezeman, J. J., Venkatesan, S., van den Bent, M., van Gent, D. C., et al. (2015). DNA damage response and anti-apoptotic proteins predict radiosensitization efficacy of HDAC inhibitors SAHA and LBH589 in patient-derived glioblastoma cells. Cancer Lett. 356, 525–535. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2014.09.049
Prager, B. C., Bhargava, S., Mahadev, V., Hubert, C. G., and Rich, J. N. (2020). Glioblastoma stem cells: driving resilience through chaos. Trends Cancer 6, 223–235. doi:10.1016/j.trecan.2020.01.009
Rajendran, G., Shanmuganandam, K., Bendre, A., Mujumdar, D., Goel, A., and Shiras, A. (2011). Epigenetic regulation of DNA methyltransferases: DNMT1 and DNMT3B in gliomas. J. Neurooncol 104, 483–494. doi:10.1007/s11060-010-0520-2
Rampazzo, E., Manfreda, L., Bresolin, S., Cani, A., Mariotto, E., Bortolozzi, R., et al. (2022). Histone deacetylase inhibitors impair glioblastoma cell motility and proliferation. Cancers (Basel) 14, 1897. doi:10.3390/cancers14081897
Ratnam, N. M., Sonnemann, H. M., Frederico, S. C., Chen, H., Hutchinson, M-K. N. D., Dowdy, T., et al. (2021). Reversing epigenetic gene silencing to overcome immune evasion in CNS malignancies. Front. Oncol. 11, 719091. doi:10.3389/fonc.2021.719091
Ricci-Vitiani, L., Pallini, R., Biffoni, M., Todaro, M., Invernici, G., Cenci, T., et al. (2010). Tumour vascularization via endothelial differentiation of glioblastoma stem-like cells. Nature 468, 824–828. doi:10.1038/nature09557
Riva, G., Butta, V., Cilibrasi, C., Baronchelli, S., Redaelli, S., Dalprà, L., et al. (2016). Epigenetic targeting of glioma stem cells: short-term and long-term treatments with valproic acid modulate DNA methylation and differentiation behavior, but not temozolomide sensitivity. Oncol. Rep. 35, 2811–2824. doi:10.3892/or.2016.4665
Romani, M., Daga, A., Forlani, A., Pistillo, M. P., and Banelli, B. (2019). Targeting of histone demethylases KDM5A and KDM6B inhibits the proliferation of temozolomide-resistant glioblastoma cells. Cancers (Basel) 11, 878. doi:10.3390/cancers11060878
Rutherford, K. A., and McManus, K. J. (2024). PROTACs: current and future potential as a precision medicine strategy to combat cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 23, 454–463. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.Mct-23-0747
Sareddy, G. R., Viswanadhapalli, S., Surapaneni, P., Suzuki, T., Brenner, A., and Vadlamudi, R. K. (2017). Novel KDM1A inhibitors induce differentiation and apoptosis of glioma stem cells via unfolded protein response pathway. Oncogene 36, 2423–2434. doi:10.1038/onc.2016.395
Shahzad, U., Krumholtz, S., Rutka, J. T., and Das, S. (2021). Noncoding RNAs in glioblastoma: emerging biological concepts and potential therapeutic implications. Cancers (Basel) 13, 1555. doi:10.3390/cancers13071555
Sharma, V., Malgulwar, P. B., Purkait, S., Patil, V., Pathak, P., Agrawal, R., et al. (2017). Genome-wide ChIP-seq analysis of EZH2-mediated H3K27me3 target gene profile highlights differences between low- and high-grade astrocytic tumors. Carcinogenesis 38, 152–161. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgw126
Shen, H., Hau, E., Joshi, S., Dilda, P. J., and McDonald, K. L. (2015). Sensitization of glioblastoma cells to irradiation by modulating the glucose metabolism. Mol. Cancer Ther. 14, 1794–1804. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.mct-15-0247
Shibue, T., and Weinberg, R. A. (2017). EMT, CSCs, and drug resistance: the mechanistic link and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 14, 611–629. doi:10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.44
Singh, M. M., Manton, C. A., Bhat, K. P., Tsai, W. W., Aldape, K., Barton, M. C., et al. (2011). Inhibition of LSD1 sensitizes glioblastoma cells to histone deacetylase inhibitors. Neuro-Oncology 13, 894–903. doi:10.1093/neuonc/nor049
Staberg, M., Rasmussen, R. D., Michaelsen, S. R., Pedersen, H., Jensen, K. E., Villingshøj, M., et al. (2018). Targeting glioma stem-like cell survival and chemoresistance through inhibition of lysine-specific histone demethylase KDM2B. Mol. Oncol. 12, 406–420. doi:10.1002/1878-0261.12174
Stackhouse, C. T., Gillespie, G. Y., and Willey, C. D. (2020). Exploring the roles of lncRNAs in GBM pathophysiology and their therapeutic potential. Cells 9, 2369. doi:10.3390/cells9112369
Stazi, G., Taglieri, L., Nicolai, A., Romanelli, A., Fioravanti, R., Morrone, S., et al. (2019). RETRACTED ARTICLE: dissecting the role of novel EZH2 inhibitors in primary glioblastoma cell cultures: effects on proliferation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, migration, and on the pro-inflammatory phenotype. Clin. Epigenetics 11, 173. doi:10.1186/s13148-019-0763-5
Sterner, D. E., and Berger, S. L. (2000). Acetylation of histones and transcription-related factors. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 64, 435–459. doi:10.1128/mmbr.64.2.435-459.2000
Stitzlein, L. M., Gangadharan, A., Walsh, L. M., Nam, D., Espejo, A. B., Singh, M. M., et al. (2023). Comparison of pharmacological inhibitors of lysine-specific demethylase 1 in glioblastoma stem cells reveals inhibitor-specific efficacy profiles. Front. Neurol. 14, 1112207. doi:10.3389/fneur.2023.1112207
Sufianov, A., Begliarzade, S., Ilyasova, T., Liang, Y., and Beylerli, O. (2022). MicroRNAs as prognostic markers and therapeutic targets in gliomas. Non-coding RNA Res. 7, 171–177. doi:10.1016/j.ncrna.2022.07.001
Tan, J., Yang, X., Zhuang, L., Jiang, X., Chen, W., Lee, P. L., et al. (2007). Pharmacologic disruption of Polycomb-repressive complex 2-mediated gene repression selectively induces apoptosis in cancer cells. Genes Dev. 21, 1050–1063. doi:10.1101/gad.1524107
Tancredi, A., Gusyatiner, O., Bady, P., Buri, M. C., Lomazzi, R., Chiesi, D., et al. (2022). BET protein inhibition sensitizes glioblastoma cells to temozolomide treatment by attenuating MGMT expression. Cell Death Dis. 13, 1037. doi:10.1038/s41419-022-05497-y
Tao, B. B., He, H., Shi, X. H., Wang, C. L., Li, W. Q., Li, B., et al. (2013). Up-regulation of USP2a and FASN in gliomas correlates strongly with glioma grade. J. Clin. Neurosci. 20, 717–720. doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2012.03.050
Tao, Z., Li, X., Wang, H., Chen, G., Feng, Z., Wu, Y., et al. (2020). BRD4 regulates self-renewal ability and tumorigenicity of glioma-initiating cells by enrichment in the Notch1 promoter region. Clin. Transl. Med. 10, e181. doi:10.1002/ctm2.181
Tung, B., Ma, D., Wang, S., Oyinlade, O., Laterra, J., Ying, M., et al. (2018). Krüppel-like factor 9 and histone deacetylase inhibitors synergistically induce cell death in glioblastoma stem-like cells. BMC cancer 18, 1025. doi:10.1186/s12885-018-4874-8
Uribe, D., Niechi, I., Rackov, G., Erices, J. I., San Martín, R., and Quezada, C. (2022). Adapt to persist: glioblastoma microenvironment and epigenetic regulation on cell plasticity. Biol. (Basel) 11, 313. doi:10.3390/biology11020313
Wang, L., Babikir, H., Müller, S., Yagnik, G., Shamardani, K., Catalan, F., et al. (2019). The phenotypes of proliferating glioblastoma cells reside on a single Axis of variation. Cancer Discov. 9, 1708–1719. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.cd-19-0329
Wang, Y., Fu, Y., Lu, Y., Chen, S., Zhang, J., Liu, B., et al. (2023). Unravelling the complexity of lncRNAs in autophagy to improve potential cancer therapy. Biochimica Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Rev. Cancer 1878, 188932. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2023.188932
Wee, C. W., Kim, J. H., Kim, H. J., Kang, H. C., Suh, S. Y., Shin, B. S., et al. (2019). Radiosensitization of glioblastoma cells by a novel DNA methyltransferase-inhibiting phthalimido-alkanamide derivative. Anticancer Res. 39, 759–769. doi:10.21873/anticanres.13173
Wu, H. C., Lin, Y. C., Liu, C. H., Chung, H. C., Wang, Y. T., Lin, Y. W., et al. (2014). USP11 regulates PML stability to control Notch-induced malignancy in brain tumours. Nat. Commun. 5, 3214. doi:10.1038/ncomms4214
Wu, W., Klockow, J. L., Zhang, M., Lafortune, F., Chang, E., Jin, L., et al. (2021). Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM): an overview of current therapies and mechanisms of resistance. Pharmacol. Res. 171, 105780. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105780
Xiao, F., Zhang, S. M., and Wang, Y. P. (2021). MiR-301a is interrelated with poor prognosis and contributes to temozolomide resistance in human glioma. Pharmazie 76, 34–37. doi:10.1691/ph.2021.0814
Yamashita, A. S., da Costa Rosa, M., Borodovsky, A., Festuccia, W. T., Chan, T., and Riggins, G. J. (2019). Demethylation and epigenetic modification with 5-azacytidine reduces IDH1 mutant glioma growth in combination with temozolomide. Neuro-Oncology 21, 189–200. doi:10.1093/neuonc/noy146
Yang, T., Hu, Y., Miao, J., Chen, J., Liu, J., Cheng, Y., et al. (2022). A BRD4 PROTAC nanodrug for glioma therapy via the intervention of tumor cells proliferation, apoptosis and M2 macrophages polarization. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 12, 2658–2671. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2022.02.009
Yang, W. B., Hsu, C. C., Hsu, T. I., Liou, J. P., Chang, K. Y., Chen, P. Y., et al. (2020). Increased activation of HDAC1/2/6 and Sp1 underlies therapeutic resistance and tumor growth in glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 22, 1439–1451. doi:10.1093/neuonc/noaa103
Yin, D., Ogawa, S., Kawamata, N., Leiter, A., Ham, M., Li, D., et al. (2013). miR-34a functions as a tumor suppressor modulating EGFR in glioblastoma multiforme. Oncogene 32, 1155–1163. doi:10.1038/onc.2012.132
Yin, J., Zeng, A., Zhang, Z., Shi, Z., Yan, W., and You, Y. (2019). Exosomal transfer of miR-1238 contributes to temozolomide-resistance in glioblastoma. EBioMedicine 42, 238–251. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.03.016
Yu, T., Wang, Y., Hu, Q., Wu, W., Wu, Y., Wei, W., et al. (2017). The EZH2 inhibitor GSK343 suppresses cancer stem-like phenotypes and reverses mesenchymal transition in glioma cells. Oncotarget 8, 98348–98359. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.21311
Yu, T., Zhou, F., Tian, W., Xu, R., Wang, B., Zeng, A., et al. (2023). EZH2 interacts with HP1BP3 to epigenetically activate WNT7B that promotes temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma. Oncogene 42, 461–470. doi:10.1038/s41388-022-02570-w
Yue, Q., Wang, Z., Shen, Y., Lan, Y., Zhong, X., Luo, X., et al. (2024). Histone H3K9 lactylation confers temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma via LUC7L2-mediated MLH1 intron retention. Adv. Sci. 11, 2309290. doi:10.1002/advs.202309290
Yue, X., Lan, F., and Xia, T. (2019). Hypoxic glioma cell-secreted exosomal miR-301a activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling and promotes radiation resistance by targeting TCEAL7. Mol. Ther. 27, 1939–1949. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.07.011
Zeng, A., Wei, Z., Yan, W., Yin, J., Huang, X., Zhou, X., et al. (2018). Exosomal transfer of miR-151a enhances chemosensitivity to temozolomide in drug-resistant glioblastoma. Cancer Lett. 436, 10–21. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2018.08.004
Zhang, W., and Xu, J. (2017). DNA methyltransferases and their roles in tumorigenesis. Biomark. Res. 5, 1. doi:10.1186/s40364-017-0081-z
Zhang, X., Wang, W., Zhu, W., Dong, J., Cheng, Y., Yin, Z., et al. (2019). Mechanisms and functions of long non-coding RNAs at multiple regulatory levels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 5573. doi:10.3390/ijms20225573
Zhao, Y-H., Wang, Z.-F., Cao, C-J., Weng, H., Xu, C-S., Li, K., et al. (2018). The clinical significance of O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase promoter methylation status in adult patients with glioblastoma: a meta-analysis. Front. Neurol. 9, 127. doi:10.3389/fneur.2018.00127
Zhou, W., Chen, C., Shi, Y., Wu, Q., Gimple, R. C., Fang, X., et al. (2017). Targeting glioma stem cell-derived pericytes disrupts the blood-tumor barrier and improves chemotherapeutic efficacy. Cell stem Cell 21, 591–603.e4. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2017.10.002
Keywords: GBM, epigenetic, DNA methylation, histone modifications, non-coding RNAs, GBM stem-like cells, phenotypic plasticity, therapeutic resistance
Citation: Amirmahani F, Kumar S and Muthukrishnan SD (2025) Epigenetic mechanisms of plasticity and resistance in glioblastoma: therapeutic targets and implications. Front. Epigenet. Epigenom. 3:1519449. doi: 10.3389/freae.2025.1519449
Received: 29 October 2024; Accepted: 06 May 2025;
Published: 16 May 2025.
Edited by:
Renhong Huang, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, ChinaReviewed by:
Alfredo Garcia Venzor, National Institute of Genomic Medicine (INMEGEN), MexicoHina Sultana, University of North Carolina System, United States
Copyright © 2025 Amirmahani, Kumar and Muthukrishnan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sree Deepthi Muthukrishnan, c3JlZWRlZXB0aGktbXV0aHVrcmlzaG5hbkBvdWhzYy5lZHU=
 Farzaneh Amirmahani
Farzaneh Amirmahani Saurav Kumar
Saurav Kumar Sree Deepthi Muthukrishnan
Sree Deepthi Muthukrishnan