- 1Laboratory of Epigenetics, Istituti Clinici Scientifici Maugeri IRCCS, Pavia, Italy
- 2Department of Translational Medicine and Surgery, Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Rome, Italy
- 3Institute for Systems Analysis and Computer Science, National Research Council (CNR) – IASI, Rome, Italy
- 4Fondazione “Policlinico Universitario A. Gemelli IRCCS”, Rome, Italy
- 5Molecular Cardiology Laboratory, IRCCS Policlinico San Donato, Milan, Italy
Breast cancer (BC) remains a leading cause of cancer-related morbidity and mortality worldwide. Its marked heterogeneity - encompassing molecular subtypes, histological characteristics, and variable therapeutic responses - continues to pose persistent clinical challenges Although advances in surgery, hormone therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapies have significantly improved patient outcomes, issues such as therapeutic resistance and disease relapse are still common, underscoring the need for novel molecular targets. Within this context, non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) have emerged as pivotal regulators of breast cancer biology and hold promise as diagnostics and therapeutic agents. These non-protein-coding RNA molecules include diverse subclasses, such as long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), circular RNAs (circRNAs), and small non-coding RNAs (sncRNAs), each characterized by distinct structural features and biological functions. Mounting evidence implicates ncRNAs in key oncogenic processes - such as tumor initiation, progression, metastasis, immune evasion, and treatment resistance - often in a subtype-specific manner. Importantly, ncRNA expression profiles differ significantly across BC subtypes, and their stability in body fluids underscores their potential utility in liquid biopsy-based diagnostics. This review provides an integrated overview of the multifaceted roles of ncRNAs in BC, emphasizing their mechanisms of action, contributions to tumor heterogeneity, and translational potential as both biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Understanding ncRNAs complexity and context-specific functions may pave the way toward more precise, personalized interventions for BC patients.
1 Introduction
Breast cancer (BC) is one of the most common malignancies worldwide, responsible for 670,000 deaths reported globally and 2.3 million diagnoses. This tumor may interest both women and men, but the incidence is massively tilted for the female gender, representing 99% of the whole cases, against 0.5%–1% of the male group. Breast cancer is a type of tumor with different outcomes and presentations; it is a very heterogeneous disease in which both environmental and genetic factors are involved (World Health Organization - www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/breast-cancer). Human breasts are paired mammary glands that develop in females during puberty under the influence of various pubertal hormones; it has an inner structure made of epithelial components consisting of lobules and ducts (distributed throughout the fibrous and the adipose tissues), leading out to the nipple (1).
Most breast cancers are adenocarcinomas, and they can be invasive or non-invasive, according to their tendency to be circumscribed in the lobules and/or in the ducts (i.e., lobular carcinoma in situ and ductal carcinoma in situ) or to metastasize and “invade” other organs or tissues (i.e., Paget’s disease, Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC), medullary carcinoma, inflammatory breast cancer, mucinous carcinoma, tubular carcinoma, phyllodes tumor and infiltrating lobular/ductal carcinoma) (2–10). The possibility of developing breast cancer can be increased by various genetic or non-genetic factors, like the presence of mutations in breast cancer susceptibility one and two genes (BRCA1 and BRCA2), smoke, obesity, or prolonged exposure to estrogen and progesterone hormones (11–13). Based on molecular and histological evidence, breast cancer comprises several histological and biological/molecular subtypes with distinct behaviors and responses to therapy: Luminal A, Luminal B, HER2 positive, and TNBC (Figure 1). Luminal A breast cancers are positive for the estrogen receptor (ER) and/or for the progesterone receptor (PR) but not for the Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2); luminal B are ER+ and/or PR+ and HER2+/−, with a general higher proliferation rate; HER2 breast cancers are only HER2+, while TNBCs are ER-, PR- and HER2-. This last subtype represents the most aggressive form of the tumor, a feature determined by its ability to metastasize and by the lack of targeted treatment strategies. In fact, according to the molecular characteristics of each BC type, different approaches are adopted to reduce/suppress the tumor (14).
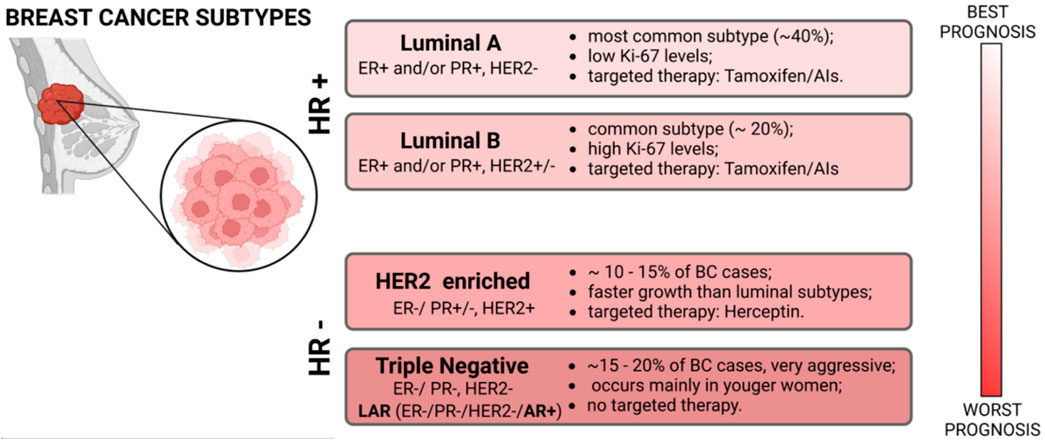
Figure 1. Scheme of the main molecular classification of Breast Cancer subtypes with their principal markers, histological grade, therapeutic approaches, and prognosis.
In luminal-like breast cancers, the standard procedure is represented by an endocrine therapy (15–17), while in HER2+ BCs an anti-HER2 humanized monoclonal antibody currently represents the most effective treatment (18). These compounds can be used alone or in combination with other procedures like surgery, radiotherapy, or chemotherapy, but a consistent portion of patients develop a resistance to the deputed drug (15). For triple-negative breast cancers there is no standardized treatment regimen and chemotherapy still represents the primary systemic treatment, but the efficacy of conventional post-operative adjuvant chemo-radiotherapy is poor (19). One exception is represented by a specific TNBC subtype named “LAR” (Luminal AR+) characterized by an enrichment in androgen response, fatty acid metabolism, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Interestingly, the LAR-subtype is closely related to the L2 (ER + luminal BC) hormone-responsive cells, and its cell lines were uniquely sensitive to the AR antagonist Bicalutamide; therefore, the next-generation AR antagonist Enzalutamide is currently being evaluated in AR-positive (AR+) TNBC in combination with Paclitaxel (20).
In this very heterogeneous and partially uncovered context, a pivotal role could be represented by epigenetics: understanding the intricate interplay of the epigenetic modifiers could be critical for unraveling the complexities of BC progression and developing targeted therapeutic interventions (21, 22). Non-coding RNAs are essential components of the complex epigenetic regulation machinery (Figure 2), and they play crucial roles in the post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. Indeed, the dysregulation of their functions can result in unfavorable outcomes across various disease pathways (23).
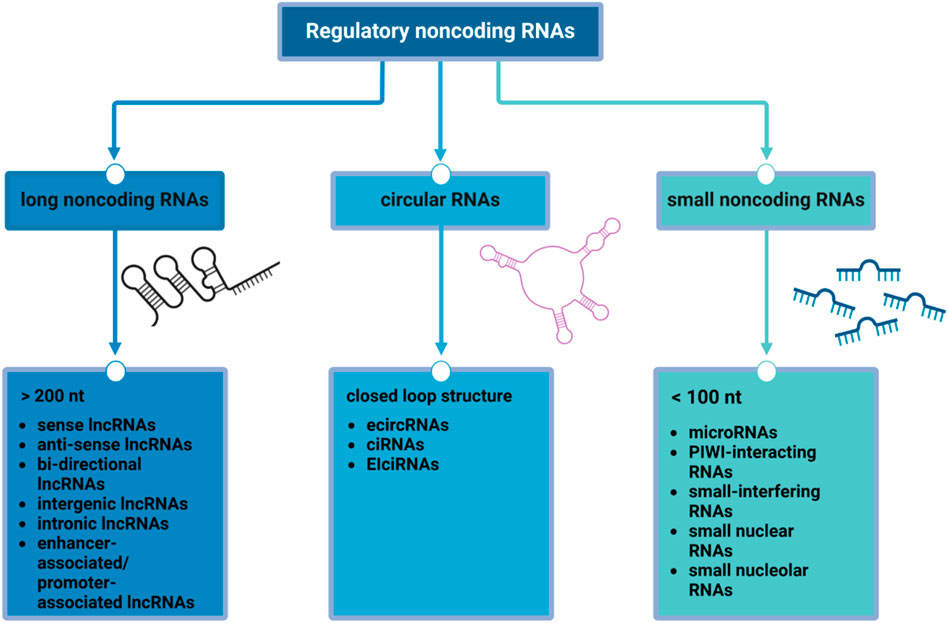
Figure 2. Regulatory non-coding RNAs. The scheme shows the main classes of non-coding RNAs according to their size and structure: long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), mainly involved in protein synthesis and epigenetic modifications and post-transcriptional processing; circular RNAs (circRNAs), acting as competing endogenous RNA, miRNA sponge, and regulators of alternative splicing and parental gene expression; small non-coding RNAs (sncRNAs), whose functions includes RNA silencing, RNA splicing, maturation and modifications, regulation of transposon activity and chromatin state and gametogenesis.
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are RNA sequences that do not translate into proteins and can be generally categorized into three main classes (24): long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), small non-coding RNAs (sncRNAs) and circular RNAs (circRNAs). CircRNAs are a class of endogenous non-coding RNA, characterized by their covalently closed-loop structures without a 5′cap or a 3′poly(A) tail (25), while sncRNAs and lncRNAs are regulatory RNAs that differ in size (26).
2 Selection criteria and methodology
This review article aims to highlight the roles of non-coding RNAs in a very heterogeneous disease such as breast cancer. Over the years, many therapeutic approaches have been established and employed for BC, although they are inadequate or outdone in severe conditions. Given the avenue of new technologies and the growing body of research showing non-coding RNA involvement in BC tumorigenesis, progression, and invasion, this review aims to draw researchers’ and clinicians’ attention to the ncRNA’s potential use as biomarkers and therapeutic targets, examining their mechanisms and regulatory functions. We curated relevant studies primarily through a PubMed search using keywords tailored to each section of this manuscript, for example, “Epigenetics and Breast Cancer”, “non-coding RNAs in cancer”, “small non-coding RNAs and Breast Cancer”, “long non-coding RNAs and Breast Cancer” and “circRNAs and Breast Cancer”, deepening the research by focusing on peer-reviewed articles published in English, with a preference for those published during the last decade (2015–2025). Additional references were included based on cross-referencing and input from expert contributors to ensure thematic completeness and scientific accuracy.
We carefully evaluated the information extracted from these studies to ensure an accurate representation of the original research findings. The articles mentioned in this review were chosen prioritizing our purpose to give the reader an overview of every non-coding element in relationship with BC by following the same path: biogenesis, general biological role, eventual implication in tumorigenesis, invasiveness and migration and drug resistance, with a final focus on the consequent possible application as biomarkers or target for new advanced treatment. While every effort was made to include the most pertinent evidence, due to the volume of research in this area and the limitations inherent to a narrative format, we could not include every relevant article, and we apologize to the authors whose work could not be incorporated into this review.
This manuscript offers an overview of current knowledge in this field; despite the richness of the literature available, our work emerges as a comprehensive and didactic paper of particular interest for those who approach to the field for the first time and need a brief overlook to the theme. At the same time, the constant progress of the research highlights the need for adjourned reports of the state of the art.
3 Long non-coding RNAs
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are transcripts longer than 200 nucleotides that are not translated into proteins and exhibit limited evolutionary conservation (27). Classification of lncRNAs is often based on their genomic positioning relative to protein-coding genes. Sense lncRNAs are transcribed from the strand as adjacent/overlapping protein-coding genes, while anti-sense lncRNAs are generated from the opposite strand. Bidirectional lncRNAs originate from the protein-coding gene’s promoter but are transcribed in the opposite direction. Intergenic lncRNAs are generated from regions between protein-coding sequences, and intronic lncRNAs are transcribed within the introns of coding genes (28). In addition, lncRNAs situated between two encoding protein genes can be classified into two main groups: enhancer-associated (elncRNA), which often regulate the expression of nearby genes on the same chromosome, and promoter-associated lncRNAs, which regulate chromosomal status and epigenetic inheritance (29–32).
The functional roles of lncRNAs are closely linked to their subcellular localization (Figure 3): in the nucleus, they participate in the modulation of epigenetic regulators and influence transcriptional programs through chromatin remodelling/interactions, and through the spatial organization of the nuclear compartment via scaffolding (33). Within the chromatin, lncRNAs can act as molecular scaffolds or guides for proteins, facilitating or inhibiting their recruitment and activity at specific genomic loci (34). In the cytoplasm, lncRNAs can regulate mRNA post-transcriptional processes, affecting mRNA stability and translation and modulating signaling pathways. Importantly, in the cytoplasm, they also act as miRNA “sponges”: they can bind miRNAs, thus reducing their availability to interact with target mRNAs, thereby indirectly regulating gene expression (35).
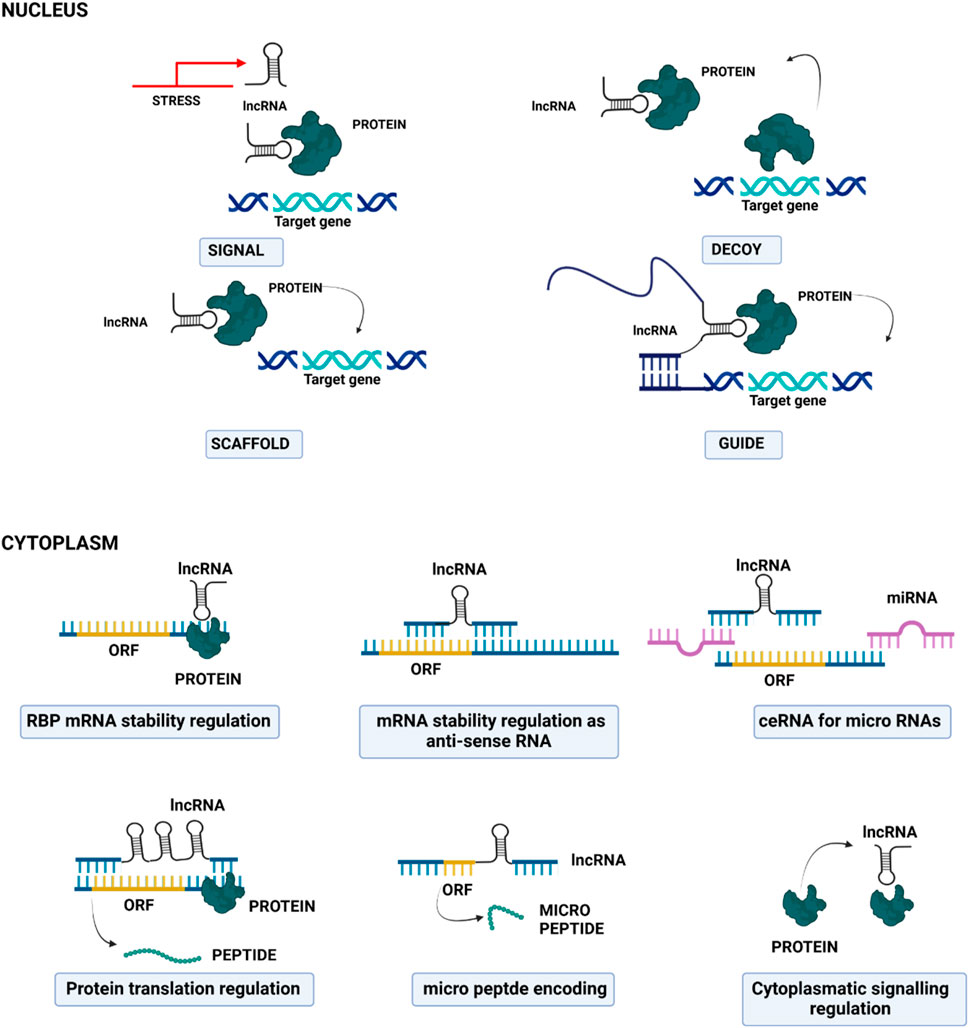
Figure 3. Cartoon depicting the principal molecular mechanisms of action of long non-coding RNAs in the nucleus (upper part) and in the cytoplasm (lower part).
Furthermore, lncRNAs can be also transported into mitochondria, where they are implicated in the regulation of mitochondrial metabolism, apoptosis, and in their crosstalk with the nuclei (36). LncRNAs can also be packaged into exosomes, which are then released into the extracellular environment; next, exosome-localized lncRNAs can reach recipient cells, where they contribute to epigenetic regulation, cell-type reprogramming, and genomic instability (37).
Due to their extensive gene regulatory capabilities, lncRNAs influence a wide range of physiological processes, including cell differentiation, growth, and responses to diverse stresses and stimuli. Moreover, they play key roles in the nervous, cardiovascular, hematopoietic and immune systems and their associated pathologies. The involvement of lncRNAs in oncogenesis, specifically in cancer initiation and progression, is increasingly recognized. LncRNA exert their effects on cancer cell proliferation and survival, often by modulating key oncogenic or tumor-suppressive transcription factors, such as p53 (38–40).
In breast cancer, a growing body of evidence highlights the aberrant expression of specific lncRNAs across different BC subtypes, with strong correlations with tumor initiation, progression, and clinical outcomes (Table 1). Furthermore, lncRNAs are particularly attractive as therapeutic targets due to several advantageous properties: high tissue-specificity, regulation of specific elements of key cellular networks, limited toxic effects associated with their targeting, the often fast-turnover and their low expression levels, which could facilitate quicker effects with lower doses (41–43).
LncRNAs can intervene in the regulation of breast cancer stem cells (BCSCs) related pathways; examples are the lncRNA LINC01133 (which induces Kruppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) gene) (44, 45) and the long intergenic non-coding RNA 00511 (LINC00511) which functions as a miR-185-3p “sponge”, indirectly activating (via the E2F1 protein targeting) the transcription of Nanog, a promoter of regeneration and prolonged proliferative potential of stem-like cancer cells, able to mediate oncogenic reprogramming. Thus, the LINC00511/miR-185-3p/E2F1/Nanog axis may also have therapeutic potential, by regulating breast cancer stemness and tumorigenesis (46). Another important example is represented by LINC00617, which can also impact on the BCSCs self-renewal capacity through the activation of SOX2 transcription mediated by hnRNP-K recruiting (47). Several long non-coding RNAs can also regulate breast cancer stem cells through epigenetic modifications, like the repression of the tumor suppressor long non-coding RNA (TSLNRs) EPB41L4A-AS2 through the enrichment of H3K27me3 (48).
A long non-coding RNA that actively intervenes in the development and maintenance of BC is HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) that inhibits miR-7 expression, leading to increased SETDB1 expression in BCSCs, inducing the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT).
HOTAIR can additionally foster H3K27 acetylation and E-cadherin promoter methylation, this mechanism inhibits E-cadherin production furtherly promoting EMT (49).
Non-coding RNAs are also implied in breast cancer metastatic progression; as depicted in Figure 3, they can act by different mechanisms, such as the degradation or silencing of specific mRNAs, the target of enzymes and microprocessor subunits involved in miRNA biogenesis, and the sponging of miRNAs, thus altering the expression of several genes and modulating different cell signaling pathways. Metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) has been correlated with an increased tumor size and stage, and a consequent poor prognosis in human patients: it undergoes tight transcriptional control in tumor cells by several transcription factors, both positively and negatively (50). For example, hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) upregulates MALAT1 with the mediation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) (51); the induced lncRNA then acts as a miRNA sponge of miR-3064-5p, a mechanism that promotes tumor growth and migration in breast cancer cells (52).
Conversely, the depletion of MALAT1 triggers the arrest of the cell cycle followed by a reduced cellular proliferation rate. It activates p53 – a tumor suppressor that participates in apoptosis and senescence processes–and its target genes (53).
According to several studies, this long non-coding could be essential in developing and metastasizing TNBC and HER2-positive BC because the presence of metastatic lymph nodes is correlated with MALAT1 expression in breast cancer patients. In addition, MYC and its downstream immune regulatory genes (CD47 and PD-L1) are related to metastasis and relapse in these subtypes of BCs and are positively regulated by MALAT1 (54). Huang and colleagues demonstrated that the knockdown of MALAT1 in MCF-7 cells reduced EGF expression, suggesting that it might initiate angiogenesis in BC, through modification of miR-145 (55). According to multiple lines of evidence, MALAT1 is also implicated in regulating signaling pathways associated with cancer progression, such as the Wnt signalling (56), but it is still uncertain how it affects these pathways.
Another important example of the contribution of the lncRNAs in breast cancer metastasis formation is represented by neuroblastoma-associated transcript 1 (NBAT1) (57), and by the aforementioned HOTAIR. The former induces BC cells invasiveness by reducing H3K27me3 levels, while the latter induces migration and invasion by recruiting the polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) which leads to the variation of H3K27 methylation levels and global gene expression alterations (58).
LncRNAs can often interfere in protein translation; it was in fact shown that abnormally expressed lncRNAs can be also related to multidrug resistance in breast cancer. In endocrine therapies, the resistance to Tamoxifen can be mediated by the induction of an autophagy mechanism; this mechanism can be triggered by long non-coding RNAs–such as H19 – acting on key mediators of the process (59). In HER2+ BCs, an augmented expression of the lncRNA AFAP1-AS1 can induce resistance to Trastuzumab by binding to AUF1, thus promoting ERBB2 translation (60). Furthermore, several lncRNAs can also be involved positively or negatively in the resistance to Doxorubicin/Adriamycin: lncRNA BORG, for example, can activate the NF-kB signaling decreasing the genomic damage, whilst LINC00668 targets staphylococcal nuclease domain-containing 1 (SND1) and improves the resistance to DOX (61).
An altered immune response in the tumor microenvironment can also markedly affect cancer occurrence and development. In this context, lncRNAs can regulate the function of immune cells impacting the antigen presentation ability of dendritic cells (DCs): for instance, the lncRNA XIST (62) down-modulation in M1-type macrophages (M1) leads to the transformation in anti-inflammatory M2 macrophage (M2) to promote tumor cell proliferation and migration. Recent studies have shown that lncRNAs can intervene in immunosuppression and may be a potential target for cancer immunotherapy, but the mechanism of tumor immune escape is highly complex and needs to be extensively investigated (62). Undoubtedly, they are promising predictive biomarkers and therapeutic targets for breast cancer immunotherapy, although further research is still required.
All these correlations make long non-coding RNAs good candidates as biomarkers for tumor diagnosis and prognosis and for predicting disease progression, but also as therapeutic targets in the shape of small molecule inhibitors, siRNAs, antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), and CRISPR-Cas9. Vaidya and Collogues, for instance, studied the Differentiation Antagonizing Non-Coding RNA (DANCR), which is a non-coding RNA involved in the regulation of different oncogenic mechanisms and undruggable by conventional molecules; it was demonstrated that the delivery of siRNA against DANCR and its subsequent inhibition epigenetically represses the expression of cancer-driven pathways, such as Wnt signaling, EMT, and phosphorylation of several kinases: siDANCR-NP effectively inhibits migration and invasion of cancer cells in vitro and tumor growth in vivo (63). A small molecular inhibitor, AC1Q3QWB, has been implemented in breast cancer-rived xenografts, resulting in efficient disruption of PRC2 recruitment by HOTAIR without notable off-target effects (64).
On the other hand, these compounds are not easy to design, and although lncRNAs are opening a new door for clinical diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer, there are still many difficulties that must be faced and overcome.
4 Circular RNAs
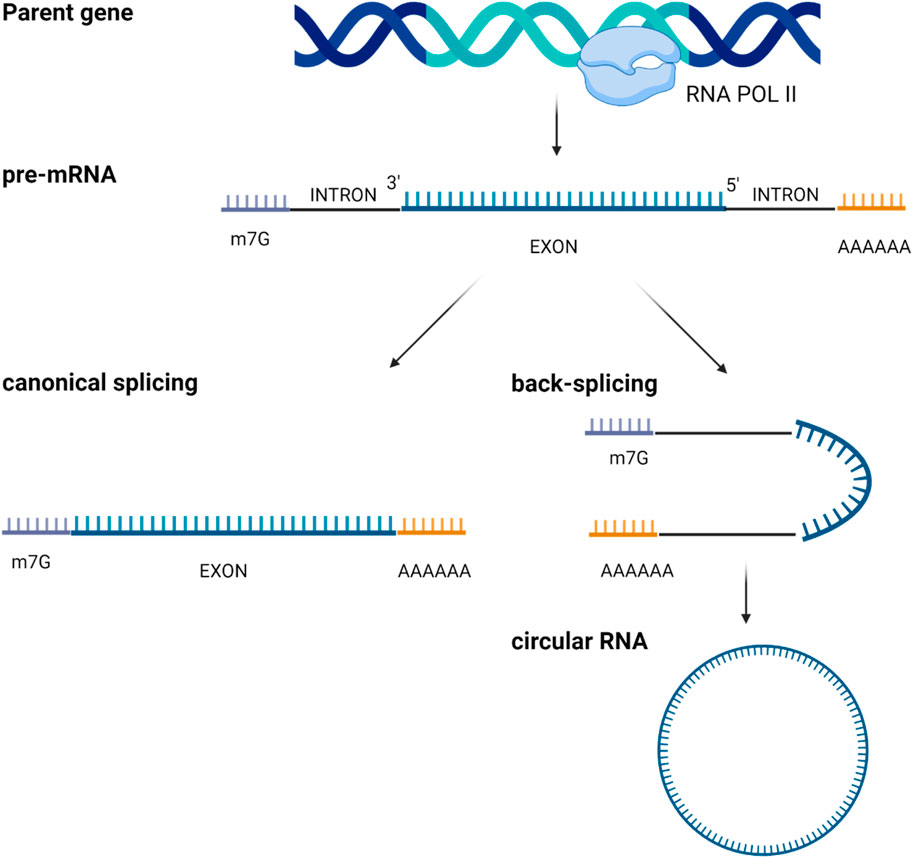
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) represent a subclass of single-stranded RNAs derived from precursor mRNAs or lncRNAs and characterized by a covalently closed loop structure. CircRNAs are generated by a process known as “RNA back-splicing” in which the 3′-end of an exon is joined to the 5′-end of the same or an upstream exon, via a 3′, 5′-phosphodiester bond. This event creates a closed circular structure containing a characteristic back-splicing junction (Figure 4).
CircRNAs are broadly categorized based on their composition. Most of them are composed only by exonic sequences and are referred to as exonic circRNAs (ecircRNAs). Less frequently, circRNAs may be formed entirely from intronic regions (IcirRNAs) or may contain both exonic and intronic sequences (EIciRNAs). EcircRNAs are mostly localized in the cytoplasm, although the precise mechanism governing their nuclear export remains insufficiently understood (65); interestingly, some ecircRNAs are found within the nucleus where they increase the nuclear retention of specific proteins or recruit proteins to chromatin (66). Conversely, most intron-containing circRNAs are retained in the nucleus, where they may regulate their parental gene expression (67).
Recent investigations have extended our understanding of circRNA biology by identifying a subset of circRNAs localized in mitochondria, extending the complexity of the mitochondrial transcriptome (68–70). However, the presence and functional relevance of circRNAs in other organelles and subcellular compartments remain largely unexplored and warrant further study.
The unique structure of these RNAs makes them more resistant to exonucleases than their linear counterparts, providing them with a longer half-life; in fact, circRNAs are often stable and accumulate in most cell types, with an especially high abundance in neural tissues. These features make circRNAs attractive candidates as diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
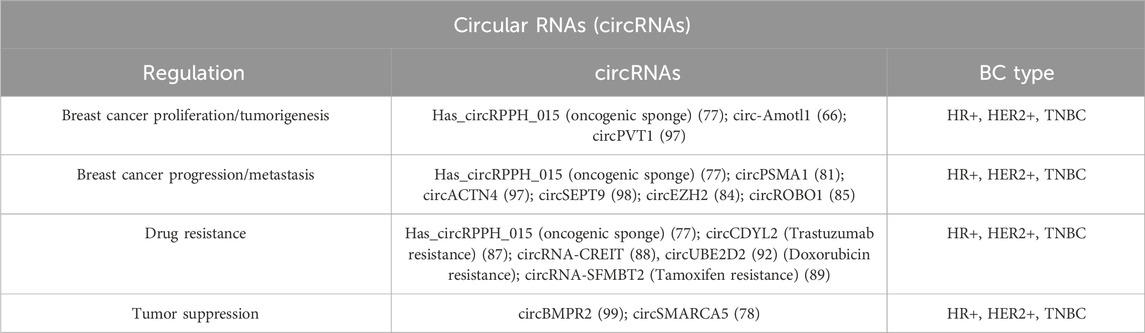
A growing body of research has documented the distinct expression profiles and functional significance of circRNAs in a range of pathological conditions, including cancer (70–72), cardiovascular disease (73), neurological disorder (74), and autoimmune disease (75). Despite these advancements, the mechanisms underlying the abnormal landscape of circRNAs and how circRNAs exert their physiopathological roles remain poorly understood. Table 2 summarizes key circular RNAs involved in the BC pathological processes.
Of note, one of the main features of circular RNAs is that they can act as miRNA “sponges,” or competitive inhibitors. By circRNAs interaction/sequestration, miRNAs are prevented from binding to their mRNA targets, inhibiting miRNA-mediated gene silencing and protecting target mRNAs from degradation (76). Some circRNAs can be classified as oncogenic sponges, as they facilitate multiple malignant behaviors, including tumor proliferation, distance metastatization, and drug resistance. An example is Has_circRPPH_015, which is upregulated in BC tissues. At the same time, its knockdown restrains aggressive behaviors of BC cell line MCF-7: in fact, this circRNA can bind to miR-326 and negatively regulates ELK; on the contrary, an elevated expression of miR-326 inhibits cell proliferation, colony formation, and cell invasion in this BC line (77).
CircRNAs bind often to transcription factors promoters, regulating their expression. At the same time, they can also function as scaffold in the modulation of protein-protein interactions, or even have translational potential.
CircRNAs participate both positively and negatively in breast cancer development and progress, acting as either oncogenes or tumor suppressors and their aberrant expression can be associated with tumoral cell proliferation, apoptosis, autophagy, invasion, migration, and treatment resistance.
A differential expression of circRNAs has been recently associated with diverse breast tumor status, drawing attention to the possibility to outline a circRNA “signature” in different tumor biopsies or cell lines. Cancer cells can in fact release these ncRNAs in urine, plasma, and saliva, opening the possibility of using circular RNAs as potential biomarkers in diagnosis and prognosis, as for the case of circSMARCA5, Hsa_circ_0104824 that were shown to be decreased in BC patients’ blood compared to controls (78, 79). In other studies, circPSMA1 appeared upregulated in serum/plasma of BC patients compared with those of healthy controls (80–82). More specifically, the overexpression of circPSMA1 promoted TNBC cell proliferation, migration, and metastasis both in vitro and in vivo (81), together with another circRNA - circ-Amotl1 - which is involved in tumorigenesis, enhancing the stability of c-MYC and the expression of its targets (66). CircPVT1 can work through both ceRNA and protein scaffolding mechanisms: it sponges miR-181a-2-3p to modulate ESR1 mRNA stability and downstream estrogen/ERα-target genes, while it represses type I IFNs and ISGs by binding MAVS to disturb RIGI–MAVS complex formation. This dual function contributes to ERα-positive BC development (83). CircRNAs are thus becoming more clinically relevant in breast cancer diagnosis, particularly for their early detection and stratification into different subtypes; which ameliorates the disease prognosis; however, they have been poorly explored in HER2-related BC subtypes, and more investigations are needed.
Beyond tumorigenesis, these non-coding RNAs also play a role in progression and metastasis: in a recent work, Peng and colleagues showed that an overexpression of circEZH2 impacted on the vitality and the invasion of breast cancer cells, while its knockdown led to the opposite effects (84). The same molecular mechanism is furtherly used by circROBO1, another important actor in the migration and invasiveness of BC cancer cell, especially in liver metastasis (85).
Resistance to treatments represents still a challenging issue in breast cancer therapy and survival; in this scenario, a more personalized approach could represent a significant improvement and circRNAs might be promising predictive biomarkers, according to their ability to regulate BC cell sensibility to drugs/treatments (86). For example, the circular RNA circCDYL2 confers Trastuzumab resistance in BC patients by stabilizing GRB7 and preventing its ubiquitination degradation; this enhances its interaction with FAK, which thus sustains the activities of downstream AKT and ERK1/2 (87). A recent work demonstrated that circRNA-CREIT is aberrantly downregulated in Doxorubicin-resistant TNBC cells: the RNA binding protein DHX9 is responsible for its reduction by interacting with the flanking inverted repeat Alu (IRAlu) sequences and inhibiting back-splicing. Mechanistically, circRNA-CREIT acts as a scaffold for proteins interaction, affecting the PKR/eIF2α signaling axis - related to stress granules (SGs) assembly - and the RACK1/MTK1 apoptosis signaling pathway. Further investigations revealed that a combination of the SG inhibitor ISRIB and Doxorubicin synergistically inhibits TNBC tumor growth. Besides, circRNA-CREIT could be packaged into exosomes and disseminate Doxorubicin sensitivity among TNBC cells (88).
In hormone therapies, Zheng and colleagues observed that circRNA-SFMBT2 appeared to be directly related to cell proliferation and Tamoxifen resistance in vitro (89), whereas circ_0025202 has been reported as a potential predictive biomarker of BC resistance to Tamoxifen (90), but more research is needed to confirm the data.
In the end, circular RNAs can be potential biomarkers also in chemotherapy resistance, as well as radiotherapy and immunotherapy resistance. The inhibition of cirCDR1as, for example, increases the sensitivity to 5-fluorouracil and Cisplatin of initially resistant BC cells, while an augmented expression of circSMARCA5 improves the chemosensitivity to Cisplatin of BC cells and tumors (78). CircKDM4C is strongly associated with Doxorubicin resistance cells both in vivo and in vitro being a potential biomarker for a Doxorubicin response prediction (91). Similarly, circUBE2D2 is involved in Doxorubicin resistance in TNBC cells, acting at the cellular level as a sponge of miR-512-3p, resulting in the upregulation of CDCA3 expression (92). Several studies have also investigated the role of circRNAs in ADM-resistance (93) and the resistance to taxanes (94, 95). Lastly, a recent work by Li and colleagues reported that the circular HER2 RNA (circHER2) encodes for a novel protein–HER2-103 – that is expressed in a marked percentage of TNBC cases, with a worse overall prognosis than circ-HER2/HER2–103 negative patients; in their work, HER2-103 enhanced both homo and hetero dimerization of EGFR/HER3, AKT phosphorylation and malignant phenotypes.
Furthermore, Pertuzumab, an antibody employed in HER2+ tumor treatment, could represent a potential antagonist due to the congruence of the amino acid sequence of HER2-103 and HER2 CR1 domain. This antibody in fact decreased the in vivo tumorigenicity only of the triple-negative tumoral cells expressing the circ-HER2/HER2–103 (96). Altogether, these studies show that circRNAs may predict responsiveness to chemo-, radio-, immuno-, and hormone-therapies, and further clinical investigations are encouraged for validation.
5 Small non-coding RNAs
Small non-coding RNAs (sncRNAs) are a class of highly abundant ncRNAs that are typically <100 nucleotides (nt) long, transcribed from noncoding genomic regions with the ability to regulate various aspects of gene expression during normal animal physiology and development. sncRNAs control gene expression by regulating chromatin architecture, transcription, RNA splicing, editing, translation, and turnover. They are further divided into different subtypes: micro RNAs (miRNAs), PIWI-interacting RNAs (piRNAs), small-interfering RNAs (siRNAs), small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) and small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) (100).
5.1 MicroRNAs
MicroRNAs constitute a subgroup of abundant endogenous small noncoding RNAs made by single-stranded RNAs of approximately 19–24 nt length (26). Almost 2,500 putative miRNAs are currently identified in the human genome, but the number is increasing rapidly due to the development of high-throughput sequencing technologies. Approximately 50% of miRNAs are located in chromosomal regions prone to structural changes, making them crucial regulators of gene expression and promising candidates for biomarker development (101).
In general, micro RNAs target messenger RNAs that contain stretches of a complementary sequence to decrease their expression, although many miRNAs can also act on other non-coding RNAs (102); it is also known that one single miRNA can have more than one target and that one single gene can be modulated by more than one miRNA (103). A large body of works revealed the important role of miRNAs in many biological functions such as development, cell differentiation, embryogenesis, metabolism, organogenesis, and apoptosis (104). Furthermore, it has recently been proposed that circulating miRNAs could potentially contribute to intercellular communication and be introduced as targets of therapeutics for the treatment of different diseases (105).
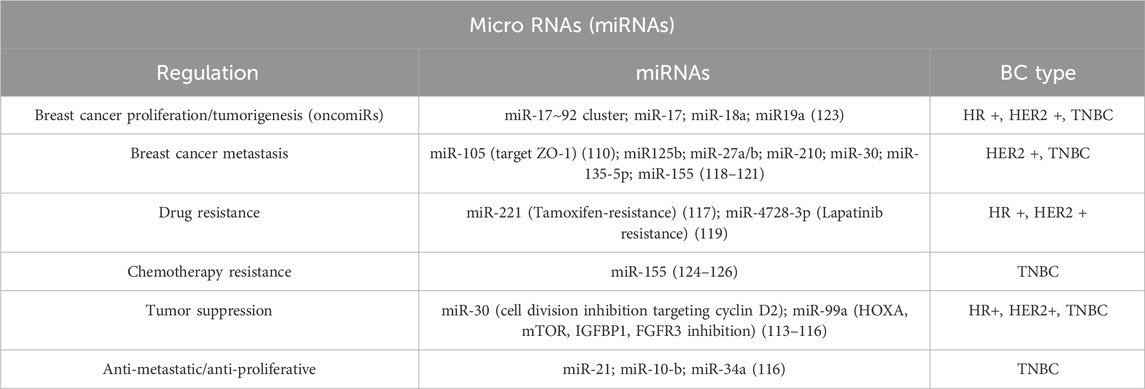
MicroRNAs can also be localized extracellularly (such as in plasma/serum, urine, saliva, and seminal fluid), conserving more stability than cellular miRNAs (106–108). Some extracellular miRNAs are just products of cellular activities. However, many researches highlighted the importance of these miRNAs in different regulation processes and multiple studies have demonstrated that extracellular miRNAs can exert biological functions in recipient cells to regulate their activity, thereby acting as intercellular signaling molecules. miR-105 is in fact expressed and secreted by metastatic breast cancer cells, in a potent regulator of migration through the target of ZO-1 (109, 110). MicroRNA expression patterns are frequently dysregulated in cancer, and great differences may be observed between normal and cancerous tissues and between localized and aggressive forms of cancer, depending on the type and stage of the disease (Table 3). It has been shown that certain microRNAs can induce oncogenesis, while others are involved in regulating gene targets associated with metastasis; they can either enhance or suppress the cancer phenotype by targeting tumor suppressor genes or oncogenes. Oncogenic miRNAs are often referred to as oncomiRs and are overexpressed in cancer cells, while tumor-suppressor miRNAs are usually downregulated, suggesting a significant role in cancer progression and representing potential targets for therapeutic intervention (23, 111).
In breast cancer, miRNA expression patterns also vary among the different subtypes. Luminal A and luminal B are very similar, but they differ in a more prominent dysregulation of subtype B compared to the A, which shows an abnormal regulation of 657 miRNAs against only 67 of the counterparts (112–116). Luminal A manifests a strong reduction in miR-1290, together with a downregulation of miR-29a, miR-181a, and miR-652 and enrichment of miR-30c-5p, miR-30b-5p, and miR-99a/let7c/miR-125b cluster (113). Notably, in luminal A there is an evident presence of miRNAs associated with tumor suppression coherently with the low proliferation grade of this BCs subtype: miR-30 for instance, inhibits cell division through cyclin D2 targeting, or miR-99a which reduces tumor growth by inhibiting proteins such as mTOR signaling (112). Conversant enrichment of miR-182-5p, miR-200b-3p, miR-15b-3p, miR-149-5p, miR-193b-3p and miR-342-3p defines, on the contrary, luminal B signature (112–116). In luminal-like breast cancers, microRNAs can also have a role in treatment responses: Tamoxifen resistance is an important issue in treating this neoplasia, reducing the success of therapy and resulting in either recurrence or metastatic or advanced-stage disease. It has been noticed that miR-221 can provoke resistance to Tamoxifen by altering the cell cycle and evading apoptosis. It also regulates some signaling pathways like the Cip/Kip family (p21, p27, and p57), ERα, and phosphatase and PTEN. These regulations can lead to an increased proliferation and survival of BC cells and a decrease in apoptosis (117).
Numerous microRNAs are also associated with HER2+ breast cancer, in particular miR-125b (connected to metastasis and worst patient outcomes) is reported to be upregulated, while miR-181d and miR-195-5p are downregulated (118). miR-4728-3p is encoded within a HER2 intron, and its mRNA targets include downstream targets of HER2 signal transduction and the estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1). This microRNA is strongly related to HER2+ BC subtype and when its expression is particularly increased, the efficacy of HER2 inhibitor Lapatinib is minimized (119).
Of note, microRNAs are expressed in a context-dependent manner, lying upon an evolving transcriptome, thus identifying changes in their landscape before and after eventual treatments could be helpful in the development of improved therapies, especially in cancers, when there is a shift in the abundance of relative target mRNAs during tumor progression (116).
In the end, TNBCs have also been seen in correlation with miRNA expression profile; in particular, miR-27a/b, miR-210, and miR-30 are associated with worse survival and miR-155 and miR-493 are conversely associated with better outcomes (120, 121). Some micro RNAs associated with TNBCs are also reported to be associated with metabolic processes. For example, miR-210 is involved in glucose uptake, lactate production, and extracellular acidification rate (120, 121). Generally, there is an increase in the expression of miR-135b, a non-coding RNA that regulates the expression of ER, AR, and hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha subunit inhibitor (HIF1AN), probably participating in the typical loss of hormone receptor of TNBCs. Several studies also highlighted the upregulation of miR-135-5p, which regulates migration processes in BC, with the functional differences among different subtypes arising from context-specific signaling networks (122).
Most of the triple-negative breast cancer molecular subtype data of miRNA associations is on BL1 and BL2, but it is very likely that there are specific correlations with other molecular subtypes even if they remain not completely clear yet. Basal-like triple-negative breast cancers manifest a signature of overexpression of the miR-17∼92 (iR-17, miR-18a, miR-19a, miR-20a, miR-19b-1, and miR-92a-1) and miR-106b-25 clusters; the proto-oncogene cMYC regulates the former to modulate the critical transcription factor E2F1, resulting in cancer proliferation. This miRNA cluster is often referred to as oncomiR-1, and it can also inhibit the inositol polyphosphate-4-phosphatase type II B (INPP4B) and associates with the BL1TNBC subtype. BL1 and BL2 show a difference in the expression of the miR17∼92 cluster, miR-17, miR-18a, and miR-19a, which is lower in the latter (123).
MicroRNAs could also be perfect candidates for a new class of non-invasive biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic evaluation of cancer. Circulating miRNAs present in serum and plasma are highly stable and tissue-specific, as their collection in whole blood is undoubtedly a non-invasive and reproducible technique. Circulating levels of miRNAs are known to return to baseline levels after tumor removal, which justifies the potential usefulness of circulating miRNAs as biomarkers of cancer treatment efficacy. One of the most representative examples is miR-155, whose levels are significantly increased in breast cancers (likely contributing to cancer metastasis and chemotherapy resistance), and restored after therapy; while the mechanisms is not completely determined yet, these observations suggest that miR-155 could represent a valid biomarker also for the tumoral stage identification (124–126). The high relevance of these small non-codings in breast cancer suggests that they have therapeutic potential that could be achieved via oncogenic miRNAs suppression/silencing or through the enrichment of tumor suppressive ones. In the first case, it is possible to eliminate the oncogenic miRNAs by delivering an oligomer complementary (referred to as antagomir), which binds to the mature miRNA, resulting in inhibition and degradation of the target. The counterpart is represented by an enrichment in tumor-suppressive miRNAs, reached through the delivery of miRNA mimics (double-stranded RNA sequences with the same sequence as the miRNA) in cells. In this context, there are three molecules primarily studied: miR-21, miR-10-b, and miR-34a that have shown a profound preclinical therapeutic potential, with both anti-metastatic and anti-proliferative properties (116).
Indeed, further analysis of the role of specific miRNAs and novel agents for manipulating tumor-specific miRNAs is required.
5.2 PIWI-interacting RNAs
PIWI-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) are a class of small non-coding RNAs with a length of generally 26–31 nt that interact with members of the PIWI family of proteins specifically expressed in germ cells to form a silencing complex named piRISC. PiRNAs originate from intergenic repetitive elements in the genome called piRNA clusters (approximately 186 in the whole human genome); in mammals, these clusters are dispersed within the chromosomes comparatively randomly, but synthetically preserved (127).
PIWI is widely expressed in various tumors, including seminomas, prostate, breast, gastrointestinal, ovarian, and endometrial cancer, and could act as an oncogene (12, 128). Since this evidence, researchers have started to assume a possible role of piRNAs in cancer and/or oncogenesis. In recent years, growing data supports the link between piRNAs and tumors: their abnormal expression is associated with various cancers and may play a pro-cancer or anti-cancer role in initiation, progression, and metastasis (Table 4). For example, an aberrant upregulation of piR-651 has a crucial function in carcinogenesis in different types of cancers, like colon, lung, gastric and breast (129). In fact, this piRNA pathway plays a role in the balance between self-renewal and cell division and the perturbance of this symmetry may strongly impact tumor progression. PiR-651 overexpression significantly promotes cell proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells by markedly reducing cell apoptosis and arrested cells in the G2/M phase by regulating the cell cycle.
Additionally, piR-651 contributes to the methylation level modulation of PTEN promoter, and its consequent downregulation is also directly related to Tamoxifen resistance (130, 131); this highlights the potential role of this PIWI-interacting RNA as a potential diagnostic indicator and therapeutic target in the management of breast cancer (131).
BC promotion and progression has been found in association with several piRNAs, such as piR-4987 – which is associated with lymph node positivity and poorer outcomes (132) – and piRNA-021285, which mediates the methylation of some related oncogenes in the tissues, representing a potential regulator of invasive BC (133). Recent studies also highlighted that the PIWIL2 protein works in combination with piR-932 influencing the biological behavior of BCSCs through the methylation of Latexin (LXN) gene (134), coding for a tumor suppressor protein which reduces the risk of old stem cells transforming into cancer stem cells (135).
Although piRNA regulation of human CSCs remains unclear, the upregulation of piR-823 was identified in tested luminal breast cancer cells, resulting as a potential oncogenic regulator of cell proliferation and colony formation. Its upregulation increases the expression of DNMTs, promoting DNA methylation of APC gene, activating Wnt signaling and inducing cancer cell stemness; this contributes to tumorigenesis, thus representing a promising target for treatment (136, 137).
On the other hand, piRNAs can also have a tumor suppressive effect: piR-36712 inhibits SEPW1 expression, consequently increasing wild-type P53, P21, and E-cadherin levels; at the same time, it decreases SLUG levels, with a significant reduction in proliferation, migration, and invasion. Interestingly, piRNA-36712 has also a synergistic anticancer effect combined with chemotherapeutic agents (Paclitaxel and Doxorubicin) for BC cells (138).
Noteworthy, piR-2158 contributes to the inhibition of mammary gland tumorigenesis via regulating cancer stem cells and tumor angiogenesis (139, 140), it competes with FOSL1 resulting in the inhibition of IL-11 (141, 142), a key regulator of cancer cell stemness and tumoral growth (143). A recent study by Wu and colleagues detected a novel PIWI-interacting RNA that could have a protective role in BC (144): piR-YBX1, whose overexpression significantly inhibited the proliferation, migration, and invasion ability of TNBC cells both in vivo and in vitro. When upregulated, piR-YBX1 binds YBX1 mRNA leading to its degradation and markedly lowering its expression at both transcript and protein levels (145–147). YBX1 has a well-known oncogenic activity, and some ncRNAs can interact with it influencing directly cancer progression (148–150). There are other possible oncogenes degraded by piR-YBX1, but more evidence is required to confirm this thesis.
Interestingly, YBX1 can influence TNBC cancer development by regulating the MAPK signaling pathway via binding RAF1; this mechanism has a pivotal role in reverting the effects of piR-YBX1 overexpression. It becomes important then to state that the effect of agopiR-YBX1 on the inhibition of distant metastasis is still not proven (144). There are many interrogatives regarding piRNA biology and mechanisms, especially in the modulation of various diseases, but recent innovations in RNA sequencing methods, such as piRNA single-cell RNA-seq and spatial RNA-seq are promising tools for a rapid development of the field of piRNAs in tumors. In fact, these ncRNAs could be potential biomarkers in cancer diagnosis and treatment, but simultaneously, multiple independent, large-scale and prospective cohorts are needed to validate their effectiveness (151).
5.3 Small nuclear RNAs
Small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs located in the Cajal bodies (CBs) and splicing speckles in the nucleus (152); they are present in all eukaryotic cells and account approximately for about 1% of total mammalian cellular RNA (153). These highly abundant nuclear RNAs form the core of ribonucleoprotein particles, called snRNPs, which function by splicing introns from primary genomic transcripts and play important roles in gene expression (154). Each snRNP comprises post-transcriptionally modified uridylic acid-rich small nuclear RNA and a cortege of associated proteins (155, 156). Based on their function and intra-nuclear localization, mammalian snRNPs can be classified into three major classes: major and minor spliceosomal snRNPs (respectively, U1, U2, U4, U5, U6 and U11, U12, U4atac and U6atac) that function in the removal of pre-mRNA introns and are predominantly nucleoplasmic; and a third group composed by the small Cajal body RNPs (scaRNPs), that accumulate in CBs and direct the site-specific 2′-O-ribose methylation and pseudo-uridylation of the RNA polymerase (Pol)-II-transcribed spliceosomal snRNAs. Recent data suggest that they could fill additional roles in gene expression regulation: U1 and U2 have been implicated in transcriptional regulation, with U1 enhancing the first phosphodiester bond formation during the beginning of transcription and with U2 interacting with a component of the pre-initiation complex Transcription Factor II H (TFIIH) (157, 158). Furthermore, a potential RNA degradation can be caused by the polyadenylation inhibition derived from the U1 bond to the 5′ splice site-like sequence in the 3′UTR of some mRNAs.
Some studies have shown that the abundance of snRNA can be regulated under some cell stress conditions (159); U6atac relies on both RNA polymerases II and III and its levels rise as a stress-respond increased by activating the p38MAPK pathway. The kinase stabilizes U6atac, promoting the expression of numerous minor intron-containing genes that are otherwise repressed consequently to a low U6atac availability. This mechanism can also influence the expression of key genes (as PTEN) and modulates cytokine production (160).
In cancer, aberrant mRNA splicing is frequent. Nevertheless, there has been minimal analysis of snRNAs as “basal factors” required for catalyzing the process. U1 is one of the most abundant ncRNAs in human cells and plays an important role in splicing pre-mRNAs, aberrancies in this process are considered a primary cause of human disease (161). Dvinge and colleagues depicted that, although U1, U2, U4, U5, and U6 snRNA are present in equal stoichiometry within the spliceosome, their relative levels vary during development across tissues and across cancer samples, especially in the context of BCs. This suggests that snRNA levels play important roles in establishing tissue-specific and developmental stage-specific splicing programs (162). In the same manuscript, scientists pointed out how snRNAs dysregulation can shape the global transcriptome of breast cancer and contribute to tumorigenesis itself: U1 and U5A were abundantly found in HER2+ BC subtype, whereas the two clusters of triple-negative analyzed samples showed a higher relative presence of U6 and comparatively low levels of U2 and U5A. Undoubtedly, further work is required to determine their effective contribution to the definition and/or regulation of each subtype (162). A recent work by Caggiano and colleagues evidenced that the inhibition of U2 snRNP induces persistent DNA damage in triple-negative breast cancer cells and organoids; this inhibition downregulates genes involved in DNA damage response (DDR), whose structure is characterized by numerous small exons and that are expressed at high levels in TNBC (163). DDR genes comprising many exon-intron junctions are probably more likely to be affected by splicing inhibition because of the numerous splicing reactions required to process them. For instance, BRCA1/2 and ATRIP are among the most affected genes. This window of vulnerability in TNBC cells could be exploited therapeutically (163).
U1 snRNA exerts a significant impact also on migration and invasion in breast cancer cell lines, activating proto-oncogenes and downregulating ORF-disruptive splicing changes in tumor suppressors (like ATM). U1 inhibition results in premature transcription termination and mRNA shortening; conversely, U1 over-expression negates these effects and significantly decreases cell line ability to migrate and spread (164), presenting a suitable target for inhibiting BC invasion. U1 can also silence the polyadenylation signals (PAS) activity, leading to shortened mRNA 3-UTR regions and therefore shortened mRNA isoforms, typical of certain cell types but also present in various cancers, including BC (165).
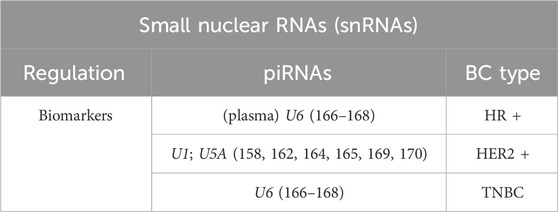
Thanks to their location in the nucleus, snRNAs can be detected through liquid biopsy and potentially be used for early non-invasive cancer detection (Table 5). An example is represented by the persistence of elevated levels of U6 in the plasma of ER+ and ER-breast cancer patients, both active and inactive, but not in healthy cases; this evidence hence indicates an increased polymerase III activity in breast tumors, regardless of the disease progression (166, 167).
5.4 Small nucleolar RNAs
Small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) are non-coding RNAs ranging from 60 to 300 bp, primarily located in the nucleoli of eukaryotic cells, and generally derived from intronic sequences. They are categorized into C/D box snoRNAs, H/ACA box snoRNAs and scaRNAs (small Cajal RNAs). The first two modify ribosomal RNA (rRNA) through 2′-O-methylation and pseudouridylation, respectively, while scaRNAs localize in the Cajal bodies (171). These snoRNAs associate with specific proteins to form RNPs. C/D snoRNAs possess conserved C and D motifs (located at the 5′ and 3′, respectively), forming “kink-turn” structures recognized by binding proteins (172). H/ACA snoRNAs include H and ACA motifs and feature “pseudouridylation pockets” targeting uridines in rRNA (173). Some snoRNAs, lacking an apparent complementarity with rRNAs at known modified positions, are called “orphan snoRNAs,” and may play broader roles beyond canonical rRNA modifications (174).
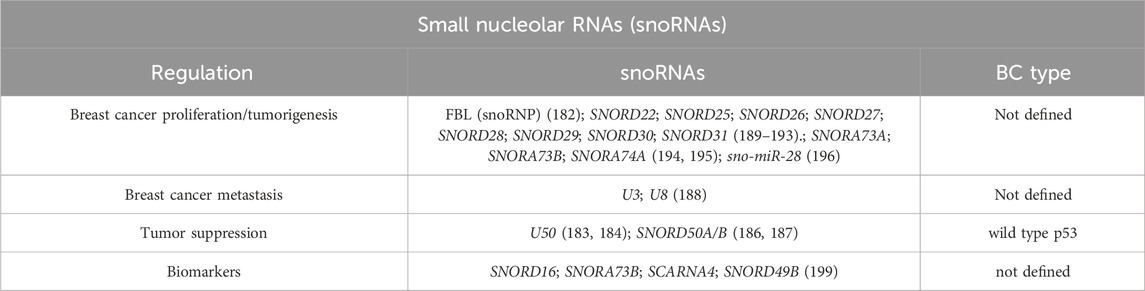
In recent years, there has been increasing interest, and several studies have confirmed that snoRNAs are involved in processes like alternative splicing, ac4C modifications, and even miRNA-like activity, positioning snoRNAs as regulators of cellular function (174–178). A 2016 work by Krishnan and colleagues reported over 40 snoRNAs differentially expressed in breast cancer tissue, of which 13 can have prognostic significance (179). Besides, functional studies suggest that snoRNAs can be up- or downregulated in BC, acting as oncogenes or tumor suppressors (180). For example, the snoRNA host gene ZFAS1 is downregulated in breast cancer, and it might control cellular homeostasis, proliferation and differentiation (181). Elevated snoRNAs and fibrillarin (FBL, an enzymatic snoRNP) expression has been linked to impaired p53 activation and increased tumorigenicity (182), while snoRNA U50, usually downregulated in prostate and breast cancer, has a significant correlation with tumor grade (183). It mediates the methylation of C2848 in 28 S rRNA, acting as a potential tumor-suppressor gene (184, 185).
Other small nucleolar RNAs, such as SNORD50A and SNORD50B (SNORD50A/B), negatively regulate KRAS oncoproteins and modulate p53 signaling through GMPS interaction (186, 187). Conversely, small nucleolar RNAs can also be involved in BC development and metastasis, U3 and U8 (upregulated in BC tissues) are essential for pre-rRNA processing reactions, leading to the synthesis of the small and large ribosomal subunits. Their depletion triggers p53-mediated anti-tumor stress responses. Tumors derived from U3-knockdown cells displayed markedly lower metabolic volume and activity than tumors derived from aggressive control cancer cells; this indicates distinctive tumor growth properties that may reflect non-conventional regulatory functions of U3 in mRNA metabolism (188). The overexpression of small nucleolar RNA host genes (SNHGs) like SNHG1 and SNGH3 influences proliferation, migration, and EMT through regulation of miRNAs (like miR-186-5p, miR-154-3p, miR-330-5p and miR-384) and key oncogenic pathways (such as Notch signaling) (189–193).
SNORA73A, SNORA73B, and SNORA74A are also bound to PARP-1 to activate its catalytic activity and mediate ADPRylation of DDX21, promoting cell proliferation in BC (194). In addition, SNORA71A also promotes the binding of G3BP1-ROCK2 and increases the expression of ROCK2, promoting the EMT process (195).
SnoRNA-derived fragments (sno-miRNAs or sdRNAs) such as sdRNA-93 and sno-miR-28, exhibit microRNA-like behavior, promoting cancer cell invasion and affecting genes like Pipox and TAF9B, which stabilizes p53 in physiological conditions. A brief explanation of this process is that the interaction between p53, NHG1, sno-miR-28, and TAF9B results in a signaling cascade, which significantly affects p53 and modifies its downstream gene network (196–198).
All these various implications highlight the potential diagnostic value of these non-coding RNAs (Table 6). Multiple studies have highlighted that snoRNAs are also detectable in body fluids like blood, plasma and urine, suggesting their utility as non-invasive cancer biomarkers. For instance, a very recent study identified four snoRNAs–SNORD16, SNORA73B, SCARNA4, and SNORD49B–that are significantly increased in the plasma of breast cancer patients, especially in early-stage patients, representing an interesting diagnostic potential. Nevertheless, how snoRNAs facilitate BC cells acquiring cancer hallmarks and contribute to therapeutic sensitivity or resistance is unknown. Besides, the cell signaling pathways, molecular mechanisms, and their regulation are unclear and require detailed investigation (199).
6 Conclusion
As thoroughly discussed, non-coding RNAs represent a vast resource in the comprehension and treatment of breast cancer; they act at different levels and with different mechanisms both in the development and in the inhibition of these tumors. All the direct and indirect correlations described in this manuscript suggest non-coding RNAs as perfect candidates as biomarkers for diagnosing tumors, judging patient prognosis, and predicting disease progression. Moreover, multiple studies have proved that many of these ncRNAs are stably expressed in BC patients’ blood, plasma, urine, and other body fluids even at early stages, providing evidence for a novel class of non-invasive biomarkers for BC.
Among them, an emerging and promising diagnostic tool is represented by circRNAs. Their unique structure, as mentioned above, provides them with stability and specificity, making them interesting candidates for therapeutic strategies. Furthermore, many studies show circRNAs ability to regulate BC cell sensibility to treatment, predicting responsiveness to chemo-, radio-, immuno-, and hormone-therapies, highlighting their potential to overcome the resistance issue. All these various implications highlight the potential diagnostic value of these non-coding RNAs.
Furthermore, with the continuous discovery of ncRNAs structural information and regulatory functions, small molecule inhibitors against ncRNAs have been developed with broad prospects for clinical diagnosis and treatment of tumors. RNA interference (RNAi) can be harnessed to inhibit the expression of cognate mRNA by exogenous RNA-based molecules that can be synthetically designed against any target RNA. The new anti-tumor drugs against ncRNAs have become a new promising trend in cancer treatment. At present, the research of new molecules targeting ncRNAs has made some progress.
a. small (or short) interfering RNAs, siRNAs, which target transcripts via RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), downregulating mRNA levels;
b. miRNAs sponges, molecules designed as decoys that specifically target microRNA seed families;
c. antisense oligonucleotides (e.g., ASOs or LNA Gapmers) that hybridize with their target RNA, blocking the formation of its secondary structure and mediating degradation by the RNAse-H;
d. aptamers, nucleic acid-based structures that act similarly to antibodies and interfere with the RNA tertiary structure, through which they associate with their interactors;
e. CRISPR-Cas9 technology, which may be exploited for targeted repression via guide RNAs but can also restore expression of dormant ncRNAs with tumor suppressor properties;
f. indirect modulators of lncRNAs are also a new direction in drug development.
There are many examples of RNAi, such as siRNAs, that can target all kinds of proteins, including traditionally undruggable proteins, and there is also evidence that these molecules could be superior to antibodies or small molecule inhibitors when inhibiting the same pathway, demonstrating a high therapeutic potential (200).
Although ncRNAs are opening a new door for clinical diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer and these nucleic acid-based approaches have great potential for clinical application, their limitations should be considered, and further investigations are needed to.
• increase their stability,
• avoid rapid degradation,
• evaluate off-target effects due to possible sequence pairing,
• implement an efficient delivery system for tissue recognition and intercellular localization
• overcame immune barriers.
In this perspective, several strategies are under investigation to efficiently deliver these molecules against BC-related ncRNA targets, such as synthetic ionizable lipids (LNP), including ASOs targeting MALAT1 and HOTAIR lncRNAs (201) or ZIF-90 (202) nanoparticles enveloping dual antisense oligonucleotide targeting miR-21/miR-155 to treat TNBC and inhibit metastasis.
Undoubtedly, research improvements in this field will provide more action strategies in the understanding of BC cancer biology, in its correct diagnosis, and in the development of personalized, targeted therapies that may also be helpful in the more aggressive forms of the disease, opening new avenues for precision medicine in a heterogeneous disease such as breast cancer.
Author contributions
VB: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. SD: Investigation, Writing – review and editing. AA: Investigation, Writing – review and editing. MG: Investigation, Writing – review and editing. SNe: Investigation, Writing – review and editing. LC: Investigation, Writing – review and editing. VP: Investigation, Writing – review and editing. SN: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. AF: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. FM: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. CG: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. SA: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The study was supported by the Italian Ministry of University and Research and EU funding within the MUR PNRR “National Center for Gene Therapy and Drugs based on RNA Technology” (Project no. CN00000041 CN3 RNA) and by the Italian National Research Council (CNR),cHJvZ2V0dGlAY25yLml0(IMMUNAGE) to AF; Next-Generation UE – PNRR M6C2 – Investimento 2.1 Valorizzazione e potenziamento della ricerca biomedica del SSN (PNRR-POC-2023–12376976 to CG. This work was also supported by AIRC under IG 2019-ID 22858 project to SN and by Ricerca Corrente funding from Italian Ministry of Health to IRCCS Policlinico San Donato (#1.07.128; #1.07.125; #1.07.127; # 1.07.129) to FM. FM is also supported by the Italian Ministry of Health (POS-T4 CAL. HUB.RIA T4-AN-09), and by the European Union (Next-Generation EU-NRRP M6C2 Inv. 2.1 PNRR-MAD 2022–12375790 and PNRR-MCNT2-2023-12377983, and Romania’s PNRR-III-C9-2022-I8, CF 186/24.11.2022, contr. 760062/23.05.2023).
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Christian Steinkuhler and Gianluca Fossati from Italfarmaco S. p.A. for their kind advice and Spadotto, V. (2025) https://BioRender.com/u88m942 for the graphical abstract created in BioRender. All figures were created in https://BioRender.com.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Bazira, PJ, Ellis, H, and Mahadevan, V. Anatomy and physiology of the breast. Surgery (Oxford) (2022) 40:79–83. doi:10.1016/j.mpsur.2021.11.015
2. Landskron, G, De la Fuente, M, Thuwajit, P, Thuwajit, C, and Hermoso, MA. Chronic inflammation and cytokines in the tumor microenvironment. J Immunol Res (2014) 2014:1–19. doi:10.1155/2014/149185
3. Nakhlis, F, and Morrow, M. Ductal carcinoma in situ. Surg Clin North America (2003) 83:821–39. doi:10.1016/S0039-6109(03)00072-0
4. Chuba, PJ, Hamre, MR, Yap, J, Severson, RK, Lucas, D, Shamsa, F, et al. Bilateral risk for subsequent breast cancer after lobular carcinoma-in-situ: analysis of surveillance, epidemiology, and end results data. J Clin Oncol (2005) 23:5534–41. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.04.038
5. Errichetti, E, Avellini, C, Pegolo, E, and De Francesco, V. Dermoscopy as a supportive instrument in the early recognition of erosive adenomatosis of the nipple and mammary Paget’s disease. Ann Dermatol (2017) 29:365. doi:10.5021/ad.2017.29.3.365
6. Foulkes, WD, Smith, IE, and Reis-Filho, JS. Triple-negative breast cancer. New Engl J Med (2010) 363:1938–48. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1001389
7. Priya, VSL, and Prasaad, PR. Tubulo-lobular carcinoma: a rare mixed invasive carcinoma of. Int J Res Med Sci (2017) 5:2818. doi:10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20172496
8. Sera, T, Kashiwagi, S, Takashima, T, Asano, Y, Goto, W, Iimori, N, et al. Multiple metastatic malignant phyllodes tumor of the breast with tonsillar metastasis: a case report. BMC Res Notes (2017) 10:55. doi:10.1186/s13104-017-2375-5
9. Cariati, M, Bennett-Britton, TM, Pinder, SE, and Purushotham, AD. “Inflammatory” breast cancer. Surg Oncol (2005) 14:133–43. doi:10.1016/j.suronc.2005.07.004
10. Inoue, M, Nakagomi, H, Nakada, H, Furuya, K, Ikegame, K, Watanabe, H, et al. Specific sites of metastases in invasive lobular carcinoma: a retrospective cohort study of metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer (2017) 24:667–72. doi:10.1007/s12282-017-0753-4
11. Ban, KA, and Godellas, CV. Epidemiology of breast cancer. Surg Oncol Clin North America (2014) 23:409–22. doi:10.1016/j.soc.2014.03.011
12. Kamińska, M, Ciszewski, T, Łopacka-Szatan, K, Miotła, P, and Starosławska, E. Breast cancer risk factors. Menopausal Rev (2015) 3:196–202. doi:10.5114/pm.2015.54346
13. Antoniou, A, Pharoah, PDP, Narod, S, Risch, HA, Eyfjord, JE, Hopper, JL, et al. Average risks of breast and ovarian cancer associated with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations detected in case series unselected for family history: a combined analysis of 22 studies. Am J Hum Genet (2003) 72:1117–30. doi:10.1086/375033
14. Harbeck, N, and Gnant, M. Breast cancer. The Lancet (2017) 389:1134–50. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31891-8
15. Peng, J, Sengupta, S, and Jordan, VC. Potential of selective estrogen receptor modulators as treatments and preventives of breast cancer. Anti-Cancer Agents Med Chem (2009) 9:481–99. doi:10.2174/187152009788451833
16. Mauri, D, Pavlidis, N, Polyzos, NP, and Ioannidis, JPA. Survival with aromatase inhibitors and inactivators versus standard hormonal therapy in advanced breast cancer: meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst (2006) 98:1285–91. doi:10.1093/jnci/djj357
17. Nigro, O, Marrazzo, C, Gallerani, E, Bascialla, L, Gueli, R, Grigioni, E, et al. Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors plus aromatase inhibitor in first-line treatment hormone-receptor-positive/HER2-negative advanced breast cancer women with or without visceral disease: time to turn page? Anticancer Drugs (2020) 31:528–32. doi:10.1097/CAD.0000000000000904
18. Schwartzberg, LS, Franco, SX, Florance, A, O’Rourke, L, Maltzman, J, and Johnston, S. Lapatinib plus letrozole as first-line therapy for HER-2+ hormone receptor–positive metastatic breast cancer. The Oncologist (2010) 15:122–9. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2009-0240
19. Nagini, S. Breast cancer: current molecular therapeutic targets and new players. Anti-Cancer Agents Med Chem (2017) 17:152–63. doi:10.2174/1871520616666160502122724
20. Lehmann, BD, Colaprico, A, Silva, TC, Chen, J, An, H, Ban, Y, et al. Multi-omics analysis identifies therapeutic vulnerabilities in triple-negative breast cancer subtypes. Nat Commun (2021) 12:6276. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-26502-6
21. Zamperla, MG, Illi, B, Barbi, V, Cencioni, C, Santoni, D, Gagliardi, S, et al. HDAC6 inhibition disrupts HDAC6-P300 interaction reshaping the cancer chromatin landscape. Clin Epigenetics (2024) 16:109. doi:10.1186/s13148-024-01725-8
22. Atlante, S, Visintin, A, Marini, E, Savoia, M, Dianzani, C, Giorgis, M, et al. α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase inhibition counteracts breast cancer-associated lung metastasis. Cell Death Dis (2018) 9:756. doi:10.1038/s41419-018-0802-8
23. Trnkova, L, Buocikova, V, Mego, M, Cumova, A, Burikova, M, Bohac, M, et al. Epigenetic deregulation in breast cancer microenvironment: implications for tumor progression and therapeutic strategies. Biomed and Pharmacother (2024) 174:116559. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116559
24. Shi, J, Zhou, T, and Chen, Q. Exploring the expanding universe of small RNAs. Nat Cell Biol (2022) 24:415–23. doi:10.1038/s41556-022-00880-5
25. Ju, J, Song, Y, Chen, X, Wang, T, Liu, C, and Wang, K. CircRNA is a potential target for cardiovascular diseases treatment. Mol Cell Biochem (2022) 477:417–30. doi:10.1007/s11010-021-04286-z
26. Wei, J-W, Huang, K, Yang, C, and Kang, C-S. Non-coding RNAs as regulators in epigenetics. Oncol Rep (2017) 37:3–9. doi:10.3892/or.2016.5236
27. Derrien, T, Johnson, R, Bussotti, G, Tanzer, A, Djebali, S, Tilgner, H, et al. The GENCODE v7 catalog of human long noncoding RNAs: analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression. Genome Res (2012) 22:1775–89. doi:10.1101/gr.132159.111
28. Ma, L, Bajic, VB, and Zhang, Z. On the classification of long non-coding RNAs. RNA Biol (2013) 10:924–33. doi:10.4161/rna.24604
29. Cabili, MN, Trapnell, C, Goff, L, Koziol, M, Tazon-Vega, B, Regev, A, et al. Integrative annotation of human large intergenic noncoding RNAs reveals global properties and specific subclasses. Genes Dev (2011) 25:1915–27. doi:10.1101/gad.17446611
30. Ingolia, NT, Lareau, LF, and Weissman, JS. Ribosome profiling of mouse embryonic stem cells reveals the complexity and dynamics of Mammalian proteomes. Cell (2011) 147:789–802. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.10.002
31. Marques, AC, Hughes, J, Graham, B, Kowalczyk, MS, Higgs, DR, and Ponting, CP. Chromatin signatures at transcriptional start sites separate two equally populated yet distinct classes of intergenic long noncoding RNAs. Genome Biol (2013) 14:131. doi:10.1186/gb-2013-14-11-r131
32. Wang, KC, and Chang, HY. Molecular mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell (2011) 43:904–14. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2011.08.018
33. Herman, AB, Tsitsipatis, D, and Gorospe, M. Integrated lncRNA function upon genomic and epigenomic regulation. Mol Cell (2022) 82:2252–66. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2022.05.027
34. Saldaña-Meyer, R, Rodriguez-Hernaez, J, Escobar, T, Nishana, M, Jácome-López, K, Nora, EP, et al. RNA interactions are essential for CTCF-Mediated genome organization. Mol Cell (2019) 76:412–22.e5. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2019.08.015
35. Cesana, M, Cacchiarelli, D, Legnini, I, Santini, T, Sthandier, O, Chinappi, M, et al. A long noncoding RNA controls muscle differentiation by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. Cell (2011) 147:358–69. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.09.028
36. Zhao, Y, Sun, L, Wang, RR, Hu, J-F, and Cui, J. The effects of mitochondria-associated long noncoding RNAs in cancer mitochondria: new players in an old arena. Crit Rev Oncology/Hematology (2018) 131:76–82. doi:10.1016/j.critrevonc.2018.08.005
37. Fatima, F, and Nawaz, M. Vesiculated long non-coding RNAs: offshore packages deciphering trans-regulation between cells, cancer progression and resistance to therapies. Noncoding RNA (2017) 3:10. doi:10.3390/ncrna3010010
38. Kim, T, Jeon, Y-J, Cui, R, Lee, J-H, Peng, Y, Kim, S-H, et al. Role of MYC-Regulated long noncoding RNAs in cell cycle regulation and tumorigenesis. J Natl Cancer Inst (2015) 107:dju505. doi:10.1093/jnci/dju505
39. Sánchez, Y, Segura, V, Marín-Béjar, O, Athie, A, Marchese, FP, González, J, et al. Genome-wide analysis of the human p53 transcriptional network unveils a lncRNA tumour suppressor signature. Nat Commun (2014) 5:5812. doi:10.1038/ncomms6812
40. Trimarchi, T, Bilal, E, Ntziachristos, P, Fabbri, G, Dalla-Favera, R, Tsirigos, A, et al. Genome-wide mapping and characterization of notch-regulated long noncoding RNAs in acute leukemia. Cell (2014) 158:593–606. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2014.05.049
41. Statello, L, Guo, C-J, Chen, L-L, and Huarte, M. Author correction: gene regulation by long non-coding RNAs and its biological functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol (2021) 22:159. doi:10.1038/s41580-021-00330-4
42. Lee, J-S, and Mendell, JT. Antisense-mediated transcript knockdown triggers premature transcription termination. Mol Cell (2020) 77:1044–54.e3. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2019.12.011
43. Lai, F, Damle, SS, Ling, KK, and Rigo, F. Directed RNase H cleavage of nascent transcripts causes transcription termination. Mol Cell (2020) 77:1032–43.e4. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2019.12.029
44. Tu, Z, Schmöllerl, J, Cuiffo, BG, and Karnoub, AE. Microenvironmental regulation of long noncoding RNA LINC01133 promotes cancer stem cell-like phenotypic traits in triple-negative breast cancers. Stem Cells (2019) 37:1281–92. doi:10.1002/stem.3055
45. Yu, F, Li, J, Chen, H, Fu, J, Ray, S, Huang, S, et al. Kruppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) is required for maintenance of breast cancer stem cells and for cell migration and invasion. Oncogene (2011) 30:2161–72. doi:10.1038/onc.2010.591
46. Lu, G, Li, Y, Ma, Y, Lu, J, Chen, Y, Jiang, Q, et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC00511 contributes to breast cancer tumourigenesis and stemness by inducing the miR-185-3p/E2F1/Nanog axis. J Exp and Clin Cancer Res (2018) 37:289. doi:10.1186/s13046-018-0945-6
47. Li, H, Zhu, L, Xu, L, Qin, K, Liu, C, Yu, Y, et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC00617 exhibits oncogenic activity in breast cancer. Mol Carcinog (2017) 56:3–17. doi:10.1002/mc.22338
48. Pang, B, Wang, Q, Ning, S, Wu, J, Zhang, X, Chen, Y, et al. Landscape of tumor suppressor long noncoding RNAs in breast cancer. J Exp and Clin Cancer Res (2019) 38:79. doi:10.1186/s13046-019-1096-0
49. Song, Y, Wang, R, Li, L-W, Liu, X, Wang, Y-F, Wang, Q-X, et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR mediates the switching of histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation to methylation to promote epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer. Int J Oncol (2019) 54:77–86. doi:10.3892/ijo.2018.4625
50. Arun, G, and Spector, DL. MALAT1 long non-coding RNA and breast cancer. RNA Biol (2019) 16:860–3. doi:10.1080/15476286.2019.1592072
51. Sallé-Lefort, S, Miard, S, Nolin, M-A, Boivin, L, Paré, MÈ, Debigaré, R, et al. Hypoxia upregulates Malat1 expression through a CaMKK/AMPK/HIF-1α axis. Int J Oncol (2016) 49:1731–6. doi:10.3892/ijo.2016.3630
52. Shih, C-H, Chuang, L-L, Tsai, M-H, Chen, L-H, Chuang, EY, Lu, T-P, et al. Hypoxia-induced MALAT1 promotes the proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells by sponging miR-3064-5p. Front Oncol (2021) 11:658151. doi:10.3389/fonc.2021.658151
53. Song, J, Cui, Q, and Gao, J. Roles of lncRNAs related to the p53 network in breast cancer progression. Front Oncol (2024) 14:1453807. doi:10.3389/fonc.2024.1453807
54. Xiping, Z, Bo, C, Shifeng, Y, Feijiang, Y, Hongjian, Y, Qihui, C, et al. Roles of MALAT1 in development and migration of triple negative and Her-2 positive breast cancer. Oncotarget (2018) 9(9):2255–67. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.23370
55. Huang, X, Xia, Y, He, G, Zheng, L, Cai, Y, Yin, Y, et al. MALAT1 promotes angiogenesis of breast cancer. Oncol Rep (2018) 40:2683–9. doi:10.3892/or.2018.6705
56. Ji, Q, Liu, X, Fu, X, Zhang, L, Sui, H, Zhou, L, et al. Resveratrol inhibits invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells via MALAT1 mediated Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway. PLoS One (2013) 8:e78700. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0078700
57. Hu, P, Chu, J, Wu, Y, Sun, L, Lv, X, Zhu, Y, et al. NBAT1 suppresses breast cancer metastasis by regulating DKK1 via PRC2. Oncotarget (2015) 6:32410–25. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.5609
58. Gupta, RA, Shah, N, Wang, KC, Kim, J, Horlings, HM, Wong, DJ, et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer metastasis. Nature (2010) 464:1071–6. doi:10.1038/nature08975
59. Sun, D-E, and Ye, S-Y. Emerging roles of long noncoding RNA regulator of reprogramming in cancer treatment. Cancer Manag Res (2020) 12:6103–12. doi:10.2147/CMAR.S253042
60. Jin, H, Du, W, Huang, W, Yan, J, Tang, Q, Chen, Y, et al. LncRNA and breast cancer: progress from identifying mechanisms to challenges and opportunities of clinical treatment. Mol Ther - Nucleic Acids (2021) 25:613–37. doi:10.1016/j.omtn.2021.08.005
61. Gooding, AJ, Zhang, B, Gunawardane, L, Beard, A, Valadkhan, S, and Schiemann, WP. The lncRNA BORG facilitates the survival and chemoresistance of triple-negative breast cancers. Oncogene (2019) 38:2020–41. doi:10.1038/s41388-018-0586-4
62. Zhao, Y, Yu, Z, Ma, R, Zhang, Y, Zhao, L, Yan, Y, et al. LncRNA-Xist/miR-101-3p/KLF6/C/EBPα axis promotes TAM polarization to regulate cancer cell proliferation and migration. Mol Ther - Nucleic Acids (2021) 23:536–51. doi:10.1016/j.omtn.2020.12.005
63. Vaidya, AM, Sun, Z, Ayat, N, Schilb, A, Liu, X, Jiang, H, et al. Systemic delivery of tumor-targeting siRNA nanoparticles against an oncogenic lncRNA facilitates effective triple-negative breast cancer therapy. Bioconjug Chem (2019) 30:907–19. doi:10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.9b00028
64. Li, Y, Ren, Y, Wang, Y, Tan, Y, Wang, Q, Cai, J, et al. A compound AC1q3qWB selectively disrupts HOTAIR-Mediated recruitment of PRC2 and enhances cancer therapy of DzNEP. Theranostics (2019) 9:4608–23. doi:10.7150/thno.35188
65. Salzman, J, Gawad, C, Wang, PL, Lacayo, N, and Brown, PO. Circular RNAs are the predominant transcript isoform from hundreds of human genes in diverse cell types. PLoS One (2012) 7:e30733. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0030733
66. Yang, Q, Du, WW, Wu, N, Yang, W, Awan, FM, Fang, L, et al. A circular RNA promotes tumorigenesis by inducing c-myc nuclear translocation. Cell Death Differ (2017) 24:1609–20. doi:10.1038/cdd.2017.86
67. Zhang, Y, Zhang, XO, Chen, T, Xiang, JF, Yin, QF, Xing, YH, et al. Circular intronic long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell (2013) 51:792–806. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2013.08.017
68. Liu, X, Wang, X, Li, J, Hu, S, Deng, Y, Yin, H, et al. Identification of mecciRNAs and their roles in the mitochondrial entry of proteins. Sci China Life Sci (2020) 63:1429–49. doi:10.1007/s11427-020-1631-9
69. Wu, Z, Sun, H, Wang, C, Liu, W, Liu, M, Zhu, Y, et al. Mitochondrial Genome-derived circRNA mc-COX2 functions as an oncogene in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Mol Ther - Nucleic Acids (2020) 20:801–11. doi:10.1016/j.omtn.2020.04.017
70. Zhao, Q, Liu, J, Deng, H, Ma, R, Liao, JY, Liang, H, et al. Targeting mitochondria-located circRNA SCAR alleviates NASH via reducing mROS output. Cell (2020) 183:76–93.e22. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.009
71. Li, J, Sun, D, Pu, W, Wang, J, and Peng, Y. Circular RNAs in cancer: biogenesis, function, and clinical significance. Trends Cancer (2020) 6:319–36. doi:10.1016/j.trecan.2020.01.012
72. Ju, H, Zhao, Q, Wang, F, Lan, P, Wang, Z, Zuo, Z, et al. A circRNA signature predicts postoperative recurrence in stage II/III colon cancer. EMBO Mol Med (2019) 11:e10168. doi:10.15252/emmm.201810168
73. Aufiero, S, Reckman, YJ, Pinto, YM, and Creemers, EE. Circular RNAs open a new chapter in cardiovascular biology. Nat Rev Cardiol (2019) 16:503–14. doi:10.1038/s41569-019-0185-2
74. Mehta, SL, Dempsey, RJ, and Vemuganti, R. Role of circular RNAs in brain development and CNS diseases. Prog Neurobiol (2020) 186:101746. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2020.101746
75. Zhou, Z, Sun, B, Huang, S, and Zhao, L. Roles of circular RNAs in immune regulation and autoimmune diseases. Cell Death Dis (2019) 10:503. doi:10.1038/s41419-019-1744-5
76. Zheng, Q, Bao, C, Guo, W, Li, S, Chen, J, Chen, B, et al. Circular RNA profiling reveals an abundant circHIPK3 that regulates cell growth by sponging multiple miRNAs. Nat Commun (2016) 7:11215. doi:10.1038/ncomms11215
77. Zhao, C, Li, L, Li, Z, Xu, J, Yang, Q, Shi, P, et al. A novel circular RNA hsa_circRPPH1_015 exerts an oncogenic role in breast cancer by impairing miRNA-326-mediated ELK1 inhibition. Front Oncol (2020) 10:906. doi:10.3389/fonc.2020.00906
78. Xu, X, Zhang, J, Tian, Y, Gao, Y, Dong, X, Chen, W, et al. CircRNA inhibits DNA damage repair by interacting with host gene. Mol Cancer (2020) 19:128. doi:10.1186/s12943-020-01246-x
79. Li, X, Ma, F, Wu, L, Zhang, X, Tian, J, Li, J, et al. Identification of Hsa_circ_0104824 as a potential biomarker for breast cancer. Technol Cancer Res Treat (2020) 19:1–10. doi:10.1177/1533033820960745
80. Li, Z, Chen, Z, Hu, G, Zhang, Y, Feng, Y, Jiang, Y, et al. Profiling and integrated analysis of differentially expressed circRNAs as novel biomarkers for breast cancer. J Cell Physiol (2020) 235:7945–59. doi:10.1002/jcp.29449
81. Yang, SJ, Wang, DD, Zhong, Sl., Chen, Wq., Wang, Fl., Zhang, J, et al. Tumor-derived exosomal circPSMA1 facilitates the tumorigenesis, metastasis, and migration in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) through miR-637/Akt1/β-catenin (cyclin D1) axis. Cell Death Dis (2021) 12:420. doi:10.1038/s41419-021-03680-1
82. Yang, SJ, Wang, DD, Zhou, SY, Zhang, Q, Wang, JY, Zhong, SL, et al. Identification of circRNA-miRNA networks for exploring an underlying prognosis strategy for breast cancer. Epigenomics (2020) 12:101–25. doi:10.2217/epi-2019-0058
83. Yi, J, Wang, L, Hu, G, Zhang, Y, Du, J, Ding, J, et al. CircPVT1 promotes ER-positive breast tumorigenesis and drug resistance by targeting ESR1 and MAVS. EMBO J (2023) 42:e112408. doi:10.15252/embj.2022112408
84. Liu, P, Wang, Z, Ou, X, Wu, P, Zhang, Y, Wu, S, et al. The FUS/circEZH2/KLF5/feedback loop contributes to CXCR4-induced liver metastasis of breast cancer by enhancing epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Mol Cancer (2022) 21:198. doi:10.1186/s12943-022-01653-2
85. Wang, Z, Yang, L, Wu, P, Li, X, Tang, Y, Ou, X, et al. The circROBO1/KLF5/FUS feedback loop regulates the liver metastasis of breast cancer by inhibiting the selective autophagy of afadin. Mol Cancer (2022) 21:29. doi:10.1186/s12943-022-01498-9
86. De Palma, FDE, Salvatore, F, Pol, JG, Kroemer, G, and Maiuri, MC. Circular RNAs as potential biomarkers in breast cancer. Biomedicines (2022) 10:725. doi:10.3390/biomedicines10030725
87. Ling, Y, Liang, G, Lin, Q, Fang, X, Luo, Q, Cen, Y, et al. CircCDYL2 promotes trastuzumab resistance via sustaining HER2 downstream signaling in breast cancer. Mol Cancer (2022) 21:8. doi:10.1186/s12943-021-01476-7
88. Wang, X, Chen, T, Li, C, Li, W, Zhou, X, Li, Y, et al. CircRNA-CREIT inhibits stress granule assembly and overcomes doxorubicin resistance in TNBC by destabilizing PKR. J Hematol Oncol (2022) 15:122. doi:10.1186/s13045-022-01345-w
89. Li, Z, Li, Y, Han, D, Wang, X, Li, C, Chen, T, et al. CircRNA-SFMBT2 orchestrates ERα activation to drive tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells. Cell Death Dis (2023) 14:482. doi:10.1038/s41419-023-06006-5
90. Sang, Y, Chen, B, Song, X, Li, Y, Liang, Y, Han, D, et al. CircRNA_0025202 regulates tamoxifen sensitivity and tumor progression via regulating the miR-182-5p/FOXO3a axis in breast cancer. Mol Ther (2019) 27:1638–52. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.05.011
91. Liang, Y, Song, X, Li, Y, Su, P, Han, D, Ma, T, et al. CircKDM4C suppresses tumor progression and attenuates doxorubicin resistance by regulating miR-548p/PBLD axis in breast cancer. Oncogene (2019) 38:6850–66. doi:10.1038/s41388-019-0926-z
92. Dou, D, Ren, X, Han, M, Xu, X, Ge, X, Gu, Y, et al. CircUBE2D2 (hsa_circ_0005728) promotes cell proliferation, metastasis and chemoresistance in triple-negative breast cancer by regulating miR-512-3p/CDCA3 axis. Cancer Cell Int (2020) 20:454. doi:10.1186/s12935-020-01547-7
93. Gao, D, Zhang, X, Liu, B, Meng, D, Fang, K, Guo, Z, et al. Screening circular RNA related to chemotherapeutic resistance in breast cancer. Epigenomics (2017) 9:1175–88. doi:10.2217/epi-2017-0055
94. Huang, P, Li, F, Mo, Z, Geng, C, Wen, F, Zhang, C, et al. A comprehensive RNA study to identify circRNA and miRNA biomarkers for docetaxel resistance in breast cancer. Front Oncol (2021) 11:669270. doi:10.3389/fonc.2021.669270
95. Ma, J, Fang, L, Yang, Q, Hibberd, S, Du, WW, Wu, N, et al. Posttranscriptional regulation of AKT by circular RNA angiomotin-like 1 mediates chemoresistance against paclitaxel in breast cancer cells. Aging (2019) 11:11369–81. doi:10.18632/aging.102535
96. Li, J, Ma, M, Yang, X, Zhang, M, Luo, J, Zhou, H, et al. Circular HER2 RNA positive triple negative breast cancer is sensitive to pertuzumab. Mol Cancer (2020) 19:142. doi:10.1186/s12943-020-01259-6
97. Wang, X, Xing, L, Yang, R, Chen, H, Wang, M, Jiang, R, et al. The circACTN4 interacts with FUBP1 to promote tumorigenesis and progression of breast cancer by regulating the expression of proto-oncogene MYC. Mol Cancer (2021) 20:91. doi:10.1186/s12943-021-01383-x
98. Zheng, X, Huang, M, Xing, L, Yang, R, Wang, X, Jiang, R, et al. The circRNA circSEPT9 mediated by E2F1 and EIF4A3 facilitates the carcinogenesis and development of triple-negative breast cancer. Mol Cancer (2020) 19:73. doi:10.1186/s12943-020-01183-9
99. Liang, Y, Song, X, Li, Y, Ma, T, Su, P, Guo, R, et al. Targeting the circBMPR2/miR-553/USP4 axis as a potent therapeutic approach for breast cancer. Mol Ther - Nucleic Acids (2019) 17:347–61. doi:10.1016/j.omtn.2019.05.005
100. Leung, YY, Kuksa, PP, Amlie-Wolf, A, Valladares, O, Ungar, LH, Kannan, S, et al. DASHR: database of small human noncoding RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res (2016) 44:D216–D222. doi:10.1093/nar/gkv1188
101. Lu, TX, and Rothenberg, ME. MicroRNA. J Allergy Clin Immunol (2018) 141:1202–7. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2017.08.034
102. Zhang, P. Overview of micro-RNA. In: MicroRNA: from bench to bedside. Elsevier (2022). p. 3–15. doi:10.1016/B978-0-323-89774-7.00015-7
103. Bartel, DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell (2004) 116:281–97. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00045-5
104. Ha, M, and Kim, VN. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol (2014) 15:509–24. doi:10.1038/nrm3838
105. Turchinovich, A, Tonevitsky, AG, and Burwinkel, B. Extracellular miRNA: a collision of two paradigms. Trends Biochem Sci (2016) 41:883–92. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2016.08.004
106. Weber, JA, Baxter, DH, Zhang, S, Huang, DY, How Huang, K, Jen Lee, M, et al. The microRNA spectrum in 12 body fluids. Clin Chem (2010) 56:1733–41. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2010.147405
107. Gallo, A, Tandon, M, Alevizos, I, and Illei, GG. The majority of microRNAs detectable in serum and saliva is concentrated in exosomes. PLoS One (2012) 7:e30679. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0030679
108. Arroyo, JD, Chevillet, JR, Kroh, EM, Ruf, IK, Pritchard, CC, Gibson, DF, et al. Argonaute2 complexes carry a population of circulating microRNAs independent of vesicles in human plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci (2011) 108:5003–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.1019055108
109. Chen, X, Ba, Y, Ma, L, Cai, X, Yin, Y, Wang, K, et al. Characterization of microRNAs in serum: a novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res (2008) 18:997–1006. doi:10.1038/cr.2008.282
110. Zhou, W, Fong, MY, Min, Y, Somlo, G, Liu, L, Palomares, MR, et al. Cancer-secreted miR-105 destroys vascular endothelial barriers to promote metastasis. Cancer Cell (2014) 25:501–15. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2014.03.007
111. Muñoz, JP, Pérez-Moreno, P, Pérez, Y, and Calaf, GM. The role of microRNAs in breast cancer and the challenges of their clinical application. Diagnostics (2023) 13:3072. doi:10.3390/diagnostics13193072
112. Long, X, Shi, Y, Ye, P, Guo, J, Zhou, Q, and Tang, Y. MicroRNA-99a suppresses breast cancer progression by targeting FGFR3. Front Oncol (2020) 9:1473. doi:10.3389/fonc.2019.01473
113. McDermott, AM, Miller, N, Wall, D, Martyn, LM, Ball, G, Sweeney, KJ, et al. Identification and validation of oncologic miRNA biomarkers for luminal A-like breast cancer. PLoS One (2014) 9:e87032. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0087032
114. Wang, X, Li, Y, Qi, W, Zhang, N, Sun, M, Huo, Q, et al. MicroRNA-99a inhibits tumor aggressive phenotypes through regulating HOXA1 in breast cancer cells. Oncotarget (2015) 6:32737–47. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.5355
115. Hu, Y, Zhu, Q, and Tang, L. MiR-99a antitumor activity in human breast cancer cells through targeting of mTOR expression. PLoS One (2014) 9:e92099. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0092099
116. Arun, RP, Cahill, HF, and Marcato, P. Breast cancer subtype-specific miRNAs: networks, impacts, and the potential for intervention. Biomedicines (2022) 10:651. doi:10.3390/biomedicines10030651
117. Amiruddin, A, Massi, MN, Islam, AA, Patellongi, I, Pratama, MY, Sutandyo, N, et al. MicroRNA-221 and tamoxifen resistance in luminal-subtype breast cancer patients: a case-control study. Ann Med Surg (2012) (2022) 73:103092. doi:10.1016/j.amsu.2021.103092
118. Tashkandi, H, Shah, N, Patel, Y, and Chen, H. Identification of new miRNA biomarkers associated with HER2-positive breast cancers. Oncoscience (2015) 2:924–9. doi:10.18632/oncoscience.275
119. Floros, KV, Lochmann, TL, Hu, B, Monterrubio, C, Hughes, MT, Wells, JD, et al. Coamplification of miR-4728 protects HER2-amplified breast cancers from targeted therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA (2018) 115:E2594–E2603. doi:10.1073/pnas.1717820115
120. Lü, L, Mao, X, Shi, P, He, B, Xu, K, Zhang, S, et al. MicroRNAs in the prognosis of triple-negative breast cancer. Medicine (2017) 96:e7085. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000007085
121. Du, Y, Wei, N, Ma, R, Jiang, S, and Song, D. A miR-210-3p regulon that controls the warburg effect by modulating HIF-1α and p53 activity in triple-negative breast cancer. Cell Death Dis (2020) 11:731. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-02952-6
122. Hua, K, Jin, J, Zhao, J, Song, J, Song, H, Li, D, et al. MiR-135b, upregulated in breast cancer, promotes cell growth and disrupts the cell cycle by regulating LATS2. Int J Oncol (2016) 48:1997–2006. doi:10.3892/ijo.2016.3405
123. De Rinaldis, E, Gazinska, P, Mera, A, Modrusan, Z, Fedorowicz, GM, Burford, B, et al. Integrated genomic analysis of triple-negative breast cancers reveals novel microRNAs associated with clinical and molecular phenotypes and sheds light on the pathways they control. BMC Genomics (2013) 14:643. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-14-643
124. Pasculli, B, Barbano, R, Fontana, A, Biagini, T, Di Viesti, MP, Rendina, M, et al. Hsa-miR-155-5p up-regulation in breast cancer and its relevance for treatment with poly[ADP-ribose] polymerase 1 (PARP-1) inhibitors. Front Oncol (2020) 10:1415. doi:10.3389/fonc.2020.01415
125. Li, Y, Zhang, L, Dong, Z, Xu, H, Yan, L, Wang, W, et al. MicroRNA-155-5p promotes tumor progression and contributes to paclitaxel resistance via TP53INP1 in human breast cancer. Pathol - Res Pract (2021) 220:153405. doi:10.1016/j.prp.2021.153405
126. Garrido-Palacios, A, Rojas Carvajal, AM, Núñez-Negrillo, AM, Cortés-Martín, J, Sánchez-García, JC, and Aguilar-Cordero, MJ. MicroRNA dysregulation in early breast cancer diagnosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Mol Sci (2023) 24:8270. doi:10.3390/ijms24098270
127. Shirzad, H. PiRNA biogenesis and their role in human cancers and other diseases: a narrative review. Iranian J Public Health (2021) 50:2486–94. doi:10.18502/ijph.v50i12.7930
128. Liu, X, Sun, Y, Guo, J, Ma, H, Li, J, Dong, B, et al. Expression of hiwi gene in human gastric cancer was associated with proliferation of cancer cells. Int J Cancer (2006) 118:1922–9. doi:10.1002/ijc.21575
129. Cheng, J, Guo, JM, Xiao, BX, Miao, Y, Jiang, Z, Zhou, H, et al. PiRNA, the new non-coding RNA, is aberrantly expressed in human cancer cells. Clinica Chim Acta (2011) 412:1621–5. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2011.05.015
130. Phuong, NTT, Kim, SK, Lim, SC, Kim, HS, Kim, TH, Lee, KY, et al. Role of PTEN promoter methylation in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat (2011) 130:73–83. doi:10.1007/s10549-010-1304-2
131. Liu, T, Wang, J, Sun, L, Li, M, He, X, Jiang, J, et al. Piwi-interacting RNA-651 promotes cell proliferation and migration and inhibits apoptosis in breast cancer by facilitating DNMT1-mediated PTEN promoter methylation. Cell Cycle (2021) 20:1603–16. doi:10.1080/15384101.2021.1956090
132. Huang, G, Hu, H, Xue, X, Shen, S, Gao, E, Guo, G, et al. Altered expression of piRNAs and their relation with clinicopathologic features of breast cancer. Clin Translational Oncol (2013) 15:563–8. doi:10.1007/s12094-012-0966-0
133. Fu, A, Jacobs, DI, Hoffman, AE, Zheng, T, and Zhu, Y. PIWI-Interacting RNA 021285 is involved in breast tumorigenesis possibly by remodeling the cancer epigenome. Carcinogenesis (2015) 36:1094–102. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgv105
134. Zhang, H, Ren, Y, Xu, H, Pang, D, Duan, C, and Liu, C. The expression of stem cell protein Piwil2 and piR-932 in breast cancer. Surg Oncol (2013) 22:217–23. doi:10.1016/j.suronc.2013.07.001
135. Liang, Y, and Van Zant, G. Aging stem cells, latexin, and longevity. Exp Cel Res (2008) 314:1962–72. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2008.01.032
136. Öner, Ç, Turgut Coşan, D, and Çolak, E. Estrogen and androgen hormone levels modulate the expression of piwi interacting RNA in prostate and breast cancer. PLoS One (2016) 11:e0159044. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0159044
137. Ding, X, Li, Y, Lü, J, Zhao, Q, Guo, Y, Lu, Z, et al. PiRNA-823 is involved in cancer stem cell regulation through altering DNA methylation in association with luminal breast cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol (2021) 9:641052. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.641052
138. Tan, L, Mai, D, Zhang, B, Jiang, X, Zhang, J, Bai, R, et al. PIWI-interacting RNA-36712 restrains breast cancer progression and chemoresistance by interaction with SEPW1 pseudogene SEPW1P RNA. Mol Cancer (2019) 18:9. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-0940-3
139. Bakiri, L, MacHo-Maschler, S, Custic, I, Niemiec, J, Guío-Carrión, A, Hasenfuss, SC, et al. Fra-1/AP-1 induces EMT in mammary epithelial cells by modulating Zeb1/2 and TGFβ expression. Cell Death Differ (2015) 22:336–50. doi:10.1038/cdd.2014.157
140. Feldker, N, Ferrazzi, F, Schuhwerk, H, Widholz, SA, Guenther, K, Frisch, I, et al. Genome-wide cooperation of EMT transcription factor ZEB 1 with YAP and AP-1 in breast cancer. EMBO J (2020) 39:e103209. doi:10.15252/embj.2019103209
141. Moon, EJ, Mello, SS, Li, CG, Chi, JT, Thakkar, K, Kirkland, JG, et al. The HIF target MAFF promotes tumor invasion and metastasis through IL11 and STAT3 signaling. Nat Commun (2021) 12:4308. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-24631-6
142. Nishina, T, Komazawa-Sakon, S, Yanaka, S, Piao, X, Zheng, DM, Piao, JH, et al. Interleukin-11 links oxidative stress and compensatory proliferation. Sci Signal (2012) 5:ra5. doi:10.1126/scisignal.2002056
143. Zhao, Q, Qian, L, Guo, Y, Lü, J, Li, D, Xie, H, et al. IL11 signaling mediates piR-2158 suppression of cell stemness and angiogenesis in breast cancer. Theranostics (2023) 13:2337–49. doi:10.7150/thno.82538
144. Wu, L, Huang, S, Tian, W, Liu, P, Xie, Y, Qiu, Y, et al. PIWI-interacting RNA-YBX1 inhibits proliferation and metastasis by the MAPK signaling pathway via YBX1 in triple-negative breast cancer. Cell Death Discov (2024) 10:7. doi:10.1038/s41420-023-01771-w
145. Prabhu, L, Hartley, AV, Martin, M, Warsame, F, Sun, E, and Lu, T. Role of post-translational modification of the Y box binding protein 1 in human cancers. Genes and Dis (2015) 2:240–6. doi:10.1016/j.gendis.2015.05.001
146. Zhang, H, Yu, H, Ren, D, Sun, Y, Guo, F, Cai, H, et al. CBX3 regulated by YBX1 promotes smoking-induced pancreatic cancer progression via inhibiting SMURF2 expression. Int J Biol Sci (2022) 18:3484–97. doi:10.7150/ijbs.68995
147. Wang, JZ, Zhu, H, You, P, Liu, H, Wang, WK, Fan, X, et al. Upregulated YB-1 protein promotes glioblastoma growth through a YB-1/CCT4/mLST8/mTOR pathway. J Clin Invest (2022) 132:e146536. doi:10.1172/JCI146536
148. Deng, X, Xiong, W, Jiang, X, Zhang, S, Li, Z, Zhou, Y, et al. LncRNA LINC00472 regulates cell stiffness and inhibits the migration and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma by binding to YBX1. Cell Death Dis (2020) 11:945. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-03147-9
149. Xu, J, Ji, L, Liang, Y, Wan, Z, Zheng, W, Song, X, et al. CircRNA-SORE mediates sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma by stabilizing YBX1. Signal Transduction Targeted Ther (2020) 5:298. doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00375-5
150. Zheng, S, Yang, L, Zou, Y, Liang, JY, Liu, P, Gao, G, et al. Long non-coding RNA HUMT hypomethylation promotes lymphangiogenesis and metastasis via activating FOXK1 transcription in triple-negative breast cancer. J Hematol Oncol (2020) 13:17. doi:10.1186/s13045-020-00852-y
151. Zhou, J, Xie, H, Liu, J, Huang, R, Xiang, Y, Tian, D, et al. PIWI-Interacting RNAs: critical roles and therapeutic targets in cancer. Cancer Lett (2023) 562:216189. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216189
152. Galganski, L, Urbanek, MO, and Krzyzosiak, WJ. Nuclear speckles: molecular organization, biological function and role in disease. Nucleic Acids Res (2017) 45:10350–68. doi:10.1093/nar/gkx759
153. Reddy, R, and Busch, H. Small nuclear RNAs: RNA sequences, structure, and modifications. In: Structure and function of major and minor small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer (1988). p. 1–37. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-73020-7_1
154. Valadkhan, S, and Gunawardane, LS. Role of small nuclear RNAs in eukaryotic gene expression. Essays Biochem (2013) 54:79–90. doi:10.1042/BSE0540079
155. Lambowitz, AM, and Zimmerly, S. Group II introns: mobile ribozymes that invade DNA. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Biol (2011) 3:a003616–19. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a003616
156. Will, CL, and Lührmann, R. Splicing of a rare class of introns by the U12-dependent spliceosome. Biol Chem (2005) 386:713–24. doi:10.1515/BC.2005.084
157. McKay, SL, and Johnson, TL. An investigation of a role for U2 snRNP spliceosomal components in regulating transcription. PLoS One (2011) 6:e16077. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0016077
158. Kwek, KY, Murphy, S, Furger, A, Thomas, B, O'Gorman, W, Kimura, H, et al. U1 snRNA associates with tfiih and regulates transcriptional initiation. Nat Struct Biol (2002) 9:800–5. doi:10.1038/nsb862
159. Xiao, L, Wang, J, Ju, S, Cui, M, and Jing, R. Disorders and roles of tsRNA, snoRNA, snRNA and piRNA in cancer. J Med Genet (2022) 59:623–31. doi:10.1136/jmedgenet-2021-108327
160. Younis, I, Dittmar, K, Wang, W, Foley, SW, Berg, MG, Hu, KY, et al. Minor introns are embedded molecular switches regulated by highly unstable U6atac snRNA. Elife (2013) 2:e00780. doi:10.7554/eLife.00780
161. Faustino, NA, and Cooper, TA. Pre-mRNA splicing and human disease. Genes Dev (2003) 17:419–37. doi:10.1101/gad.1048803
162. Dvinge, H, Guenthoer, J, Porter, PL, and Bradley, RK. RNA components of the spliceosome regulate tissue and cancer-specific alternative splicing. Genome Res (2019) 29:1591–604. doi:10.1101/gr.246678.118
163. Caggiano, C, Petrera, V, Ferri, M, Pieraccioli, M, Cesari, E, Di Leone, A, et al. Transient splicing inhibition causes persistent DNA damage and chemotherapy vulnerability in triple-negative breast cancer. Cell Rep (2024) 43:114751. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114751
164. Oh, JM, Venters, CC, Di, C, Pinto, AM, Wan, L, Younis, I, et al. U1 snRNP regulates cancer cell migration and invasion in vitro. Nat Commun (2020) 11:1. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-13993-7
165. Oh, JM, Di, C, Venters, CC, Guo, J, Arai, C, So, BR, et al. U1 snRNP telescripting regulates a size-function-stratified human genome. Nat Struct Mol Biol (2017) 24:993–9. doi:10.1038/nsmb.3473
166. Appaiah, HN, Goswami, CP, Mina, LA, Badve, S, Sledge, GW, Liu, Y, et al. Persistent upregulation of U6:SNORD44 small RNA ratio in the serum of breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res (2011) 13:R86. doi:10.1186/bcr2943
167. Záveský, L, Jandáková, E, Weinberger, V, Minář, L, Hanzíková, V, Dušková, D, et al. Small non-coding RNA profiling in breast cancer: Plasma U6 snRNA, miR-451a and miR-548b-5p as novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers. Mol Biol Rep (2022) 49:1955–71. doi:10.1007/s11033-021-07010-8
168. Pendleton, KE, Chen, B, Liu, K, Hunter, OV, Xie, Y, Tu, BP, et al. The U6 snRNA m 6 A methyltransferase METTL16 regulates SAM synthetase intron retention. Cell (2017) 169:824–35.e14. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.003
169. Buratti, E, and Baralle, D. Novel roles of U1 snRNP in alternative splicing regulation. RNA Biol (2010) 7:412–9. doi:10.4161/rna.7.4.12153
170. Cheng, Z, Sun, Y, Niu, X, Shang, Y, Ruan, J, Chen, Z, et al. Gene expression profiling reveals U1 snRNA regulates cancer gene expression. Oncotarget (2017) 8:112867–74. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.22842
171. Bratkovič, T, and Rogelj, B. The many faces of small nucleolar RNAs. Biochim Biophys Acta (Bba) - Gene Regul Mech (2014) 1839:438–43. doi:10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.04.009
172. Kiss-László, Z, Henry, Y, Bachellerie, J-P, Caizergues-Ferrer, M, and Kiss, T. Site-specific ribose methylation of preribosomal RNA: a novel function for small nucleolar RNAs. Cell (1996) 85:1077–88. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81308-2
173. Bortolin, M-L, Ganot, P, and Kiss, TS. Elements essential for accumulation and function of small nucleolar RNAs directing site-specific pseudouridylation of ribosomal RNAs. EMBO J (1999) 18:457–69. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.2.457
174. Kishore, S, and Stamm, S. The snoRNA HBII-52 regulates alternative splicing of the serotonin receptor 2C. Science (2006) 311:230–2. doi:10.1126/science.1118265
175. Ender, C, Krek, A, Friedländer, MR, Beitzinger, M, Weinmann, L, Chen, W, et al. A human snoRNA with microRNA-like functions. Mol Cell (2008) 32:519–28. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2008.10.017
176. Falaleeva, M, Pages, A, Matuszek, Z, Hidmi, S, Agranat-Tamir, L, Korotkov, K, et al. Dual function of C/D box small nucleolar RNAs in rRNA modification and alternative pre-mRNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2016) 113:E1625–E1634. doi:10.1073/pnas.1519292113
177. Cavaillé, J, Buiting, K, Kiefmann, M, Lalande, M, Brannan, CI, Horsthemke, B, et al. Identification of brain-specific and imprinted small nucleolar RNA genes exhibiting an unusual genomic organization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2000) 97:14311–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.250426397
178. Jin, G, Xu, M, Zou, M, and Duan, S. The processing, gene regulation, biological functions, and clinical relevance of N4-Acetylcytidine on RNA: a systematic review. Mol Ther - Nucleic Acids (2020) 20:13–24. doi:10.1016/j.omtn.2020.01.037
179. Krishnan, P, Ghosh, S, Wang, B, Heyns, M, Graham, K, Mackey, JR, et al. Profiling of small nucleolar RNAs by next generation sequencing: potential new players for breast cancer prognosis. PLoS One (2016) 11:e0162622. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0162622
180. Dsouza, VL, Adiga, D, Sriharikrishnaa, S, Suresh, PS, Chatterjee, A, and Kabekkodu, SP. Small nucleolar RNA and its potential role in breast cancer – a comprehensive review. Biochim Biophys Acta (Bba) - Rev Cancer (2021) 1875:188501. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188501
181. Askarian-Amiri, ME, Crawford, J, French, JD, Smart, CE, Smith, MA, Clark, MB, et al. SNORD-Host RNA Zfas1 is a regulator of mammary development and a potential marker for breast cancer. RNA (2011) 17:878–91. doi:10.1261/rna.2528811
182. Su, H, Xu, T, Ganapathy, S, Shadfan, M, Long, M, Huang, THM, et al. Elevated snoRNA biogenesis is essential in breast cancer. Oncogene (2014) 33:1348–58. doi:10.1038/onc.2013.89
183. Dong, XY, Guo, P, Boyd, J, Sun, X, Li, Q, Zhou, W, et al. Implication of snoRNA U50 in human breast cancer. J Genet Genomics (2009) 36:447–54. doi:10.1016/S1673-8527(08)60134-4
184. Pacilli, A, Ceccarelli, C, Treré, D, and Montanaro, L. SnoRNA U50 levels are regulated by cell proliferation and rRNA transcription. Int J Mol Sci (2013) 14:14923–35. doi:10.3390/ijms140714923
185. Li, JN, Loh, ZJ, Chen, HW, Lee, IY, Tsai, JH, and Chen, PS. SnoRNA U50A mediates everolimus resistance in breast cancer through mTOR downregulation. Translational Oncol (2024) 48:102062. doi:10.1016/j.tranon.2024.102062
186. Siprashvili, Z, Webster, DE, Johnston, D, Shenoy, RM, Ungewickell, AJ, Bhaduri, A, et al. The noncoding RNAs SNORD50A and SNORD50B bind K-Ras and are recurrently deleted in human cancer. Nat Genet (2015) 48:53–8. doi:10.1038/ng.3452
187. Su, X, Feng, C, Wang, S, Shi, L, Gu, Q, Zhang, H, et al. The noncoding RNAs SNORD50A and SNORD50B-mediated TRIM21-GMPS interaction promotes the growth of p53 wild-type breast cancers by degrading p53. Cell Death Differ (2021) 28:2450–64. doi:10.1038/s41418-021-00762-7
188. Langhendries, J-L, Nicolas, E, Doumont, G, Goldman, S, and Lafontaine, DLJ. The human box C/D snoRNAs U3 and U8 are required for pre-rRNA processing and tumorigenesis. Oncotarget (2016) 7:59519–34. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.11148
189. Zimta, AA, Tigu, AB, Braicu, C, Stefan, C, Ionescu, C, and Berindan-Neagoe, I. An emerging class of long non-coding RNA with oncogenic role arises from the snoRNA host genes. Front Oncol (2020) 10:389. doi:10.3389/fonc.2020.00389
190. Xiong, X, Feng, Y, Li, L, Yao, J, Zhou, M, Zhao, P, et al. Long non–coding RNA SNHG1 promotes breast cancer progression by regulation of LMO4. Oncol Rep (2020) 43:1503–15. doi:10.3892/or.2020.7530
191. Wan, Q, Tang, M, Sun, S-L, Hu, J, Sun, Z-J, Fang, Y-T, et al. SNHG3 promotes migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells through the miR-186-5p/ZEB1 axis. Am J Transl Res (2021) 13:585–600.
192. Li, Y, Zhao, Z, Liu, W, and Li, X. SNHG3 functions as miRNA sponge to promote breast cancer cells growth through the metabolic reprogramming. Appl Biochem Biotechnol (2020) 191:1084–99. doi:10.1007/s12010-020-03244-7
193. Ma, Q, Qi, X, Lin, X, Li, L, Chen, L, and Hu, W. LncRNA SNHG3 promotes cell proliferation and invasion through the miR-384/hepatoma-derived growth factor axis in breast cancer. Hum Cel (2020) 33:232–42. doi:10.1007/s13577-019-00287-9
194. Kim, DS, Camacho, CV, Nagari, A, Malladi, VS, Challa, S, and Kraus, WL. Activation of PARP-1 by snoRNAs controls ribosome biogenesis and cell growth via the RNA helicase DDX21. Mol Cell (2019) 75:1270–85.e14. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2019.06.020
195. Hu, T, Lu, C, Xia, Y, Wu, L, Song, J, Chen, C, et al. Small nucleolar RNA SNORA71A promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition by maintaining ROCK2 mRNA stability in breast cancer. Mol Oncol (2022) 16:1947–65. doi:10.1002/1878-0261.13186
196. Yu, F, Bracken, CP, Pillman, KA, Lawrence, DM, Goodall, GJ, Callen, DF, et al. P53 represses the oncogenic Sno-MiR-28 derived from a SnoRNA. PLoS One (2015) 10:e0129190. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0129190
197. Patterson, DG, Roberts, JT, King, VM, Houserova, D, Barnhill, EC, Crucello, A, et al. Human snoRNA-93 is processed into a microRNA-like RNA that promotes breast cancer cell invasion. NPJ Breast Cancer (2017) 3:25. doi:10.1038/S41523-017-0032-8
198. Kim, MJ, Jung, WH, and Koo, JS. Expression of sarcosine metabolism-related proteins in estrogen receptor negative breast cancer according to the androgen receptor and HER-2 status. Int J Clin Exp Pathol (2015) 8:7967–77.
199. Li, X, Zhao, X, Xie, L, Song, X, and Song, X. Identification of four snoRNAs (SNORD16, SNORA73B, SCARNA4, and SNORD49B) as novel non-invasive biomarkers for diagnosis of breast cancer. Cancer Cell Int (2024) 24:55. doi:10.1186/s12935-024-03237-0
200. Ngamcherdtrakul, W, and Yantasee, W. SiRNA therapeutics for breast cancer: recent efforts in targeting metastasis, drug resistance, and immune evasion. Translational Res (2019) 214:105–20. doi:10.1016/j.trsl.2019.08.005
201. Sarkar, S, Moitra, P, Bera, S, and Bhattacharya, S. Antisense oligonucleotide embedded context responsive nanoparticles derived from synthetic ionizable lipids for lncRNA targeted therapy of breast cancer. ACS Appl Mater Inter (2024) 16:45871–87. doi:10.1021/acsami.4c04893
Keywords: breast cancer, epigenetics, non-coding RNAs, long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), circular RNAs (circRNAs), small non-coding RNAs (sncRNAs), hormone therapy
Citation: Barbi V, De Martino S, Aiello A, Gottardi Zamperla M, Negri S, Cis L, Pecci V, Nanni S, Farsetti A, Martelli F, Gaetano C and Atlante S (2025) Non-coding RNAs as novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets in breast cancer. Oncol. Rev. 19:1621144. doi: 10.3389/or.2025.1621144
Received: 30 April 2025; Accepted: 18 August 2025;
Published: 29 August 2025.
Edited by:
Deepa Kushwaha, Rare Genomics Institute, United StatesReviewed by:
Nejat Dalay, Istanbul University, TürkiyeMihir Khambete, Yale University, United States
Copyright © 2025 Barbi, De Martino, Aiello, Gottardi Zamperla, Negri, Cis, Pecci, Nanni, Farsetti, Martelli, Gaetano and Atlante. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Antonella Farsetti, YW50b25lbGxhLmZhcnNldHRpQGNuci5pdA==; Carlo Gaetano, Y2FybG8uZ2FldGFub0BpY3NtYXVnZXJpLml0
 Veronica Barbi
Veronica Barbi Sara De Martino3
Sara De Martino3 Simona Nanni
Simona Nanni Antonella Farsetti
Antonella Farsetti Fabio Martelli
Fabio Martelli Carlo Gaetano
Carlo Gaetano Sandra Atlante
Sandra Atlante