- 1Mayo Clinic Alix School of Medicine, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, United States
- 2Department of Radiology, Division of Vascular and Interventional Radiology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, United States
Background: The aim of this systematic review was to determine the patency and complications related to percutaneous metallic biliary stent placement for malignant biliary obstruction in the current literature.
Methods: This review was performed using the Preferred Reporting Items of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines. EMBASE and PubMed were queried yielding 891 articles, 18 of which were included in the final analysis. The Newcastle-Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale was used to appraise article quality. Patient demographics, technical success rate, and procedure outcomes were recorded. Complications were classified as “major” if they resulted in blood transfusion or additional invasive procedures or were reported as such in the literature. Complications that did not meet these criteria were classified as “minor”.
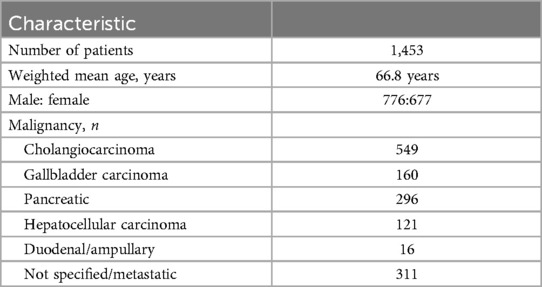
Results: A total of 1,453 patients (677 female; weighted age 66.8 years) underwent biliary stent placement. The weighted technical success rate was 97.7%. The incidence of stent occlusion was 13.5% with 6.6% of patients requiring further intervention to maintain patency. There were 277 (19.1%) complications, of which 87 were classified as major. The most common complications were pancreatitis (93, 6.4%), cholangitis (69, 4.8%), and bleeding (64, 4.4%). In cases of bleeding, 4.7% of patients needed a blood transfusion and 15.6% required a procedure to treat bleeding. There were 6 (0.4%) procedure-related deaths.
Conclusion: In conclusion, percutaneous metallic stent placement for malignant biliary obstruction has a high technical success rate and relatively low rate of occlusion. Although nearly one in five procedures resulted in a complication, most cases were minor.
Introduction
Unresectable malignant biliary obstruction is a common consequence of pancreatic adenocarcinoma, cholangiocarcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma and gallbladder carcinoma (1). This condition may lead to jaundice, pruritus, and cholangitis, significantly increasing morbidity and compounding the burdens associated with cancer progression. Tumor invasion and metastatic spread frequently preclude curative resection and limit treatment options for patients with biliary obstruction.
Stent placement is a widely accepted treatment for unresectable malignant biliary obstruction, offering symptom palliation and improved quality of life (2, 3). The percutaneous approach to stent placement has demonstrated safety and efficacy. Bare metal stents may be preferred over covered stents due to operator experience, cost, and potentially lower rates of stent migration (4). However, several complications can occur during stent placement including hemorrhage, bile leakage, and pancreatitis (5). Additionally, these stents can occlude and necessitate secondary interventions for biliary diversion or stent recanalization.
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the outcomes of percutaneously placed uncovered metallic biliary stents for the treatment of malignant biliary obstruction in the current literature with particular focus on stent patency and complications.
Methods
Search strategy
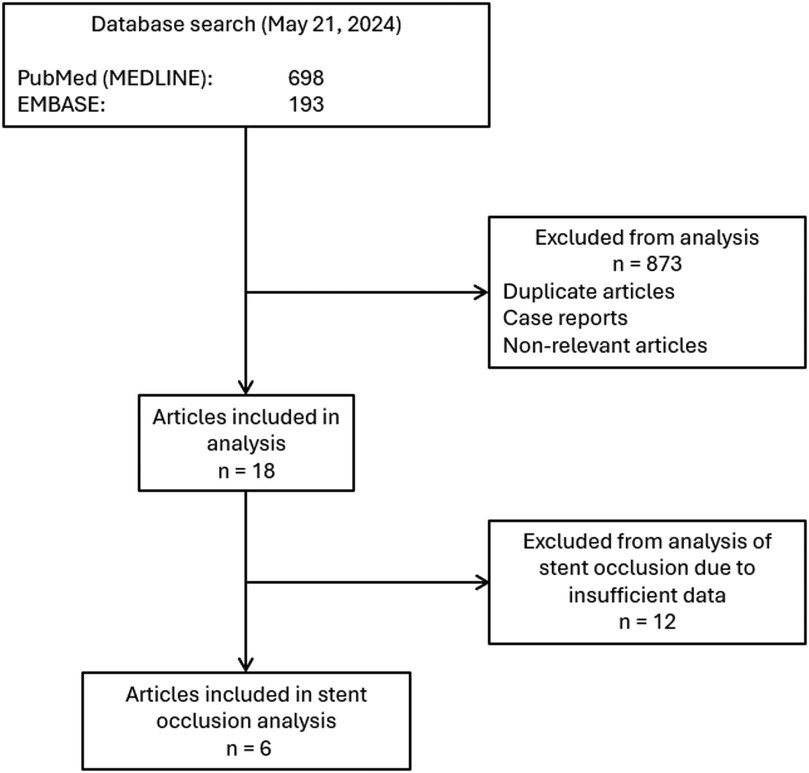
This systematic review was conducted following the Preferred Reporting Items of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines (6). Institutional review board (IRB) approval was precluded by the study design. Articles published on or before May 2024 were identified using the terms: “percutaneous” AND [biliary OR “bile duct” (MeSH)] AND [stent or “stents” (MeSH)], AND “placement”. This query yielded 193 articles in EMBASE and 698 articles in PubMed. A total of 891 article abstracts were reviewed. Duplicate articles, case reports, and nonrelevant articles were excluded. The final analysis included 18 articles published from 2002 to 2022 (7–24). A summary of the search strategy is shown in Figure 1.
Quality assessment
The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for cohort studies was used to appraise article quality (25). Two independent reviewers assessed each article to evaluate the selection methods, comparability, and outcome robustness of the study. These three metrics were used to calculate a numeric total that correlates with the level of evidence (good, fair, or poor). Discrepancies between the reviewers were resolved by consensus.
Data extraction and outcome measures
Raw data extraction was performed on articles that met the inclusion criteria. Patient demographics, technical success rate, procedure outcomes regarding patency rates and number of re-interventions, and complications were recorded. Weighted means were performed where possible. Complications recorded included bleeding, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, cholangitis, other infection, peritonitis/bile leak, pneumonia, and pneumothorax. Complications were classified as “major” if they resulted in blood transfusion, required additional invasive procedures (e.g., arterial embolization), or were reported as such by the authors of a given study. Complications that did not meet these criteria were classified as “minor” in accordance with the Society of Interventional Radiology (SIR) guidelines (26). The average duration of stent patency was collected when available (6 of 18 studies), providing an additional metric for determining the efficacy of stent placement.
Results
According to NOS criteria, 16 of the 18 articles were rated as “poor” due to lack of a comparison group within the study. Two other articles that compared covered and uncovered stents with matched cohorts based on age and sex received a “fair” quality rating (15, 19).
A total of 1,453 patients (677 female) underwent biliary stent placement. The weighted mean patient age was 66.8 years. Two studies were excluded from age analysis due to incomplete demographic data (27, 28). Table 1 summarizes patient characteristics. The weighted technical success rate of percutaneous metallic biliary stent placement was 97.7%. Hilar lesions were treated in 845 patients and ampullary lesions treated in 451 patients. Lesion location could not be determined from 3 studies (19, 20, 24).
Patency outcomes
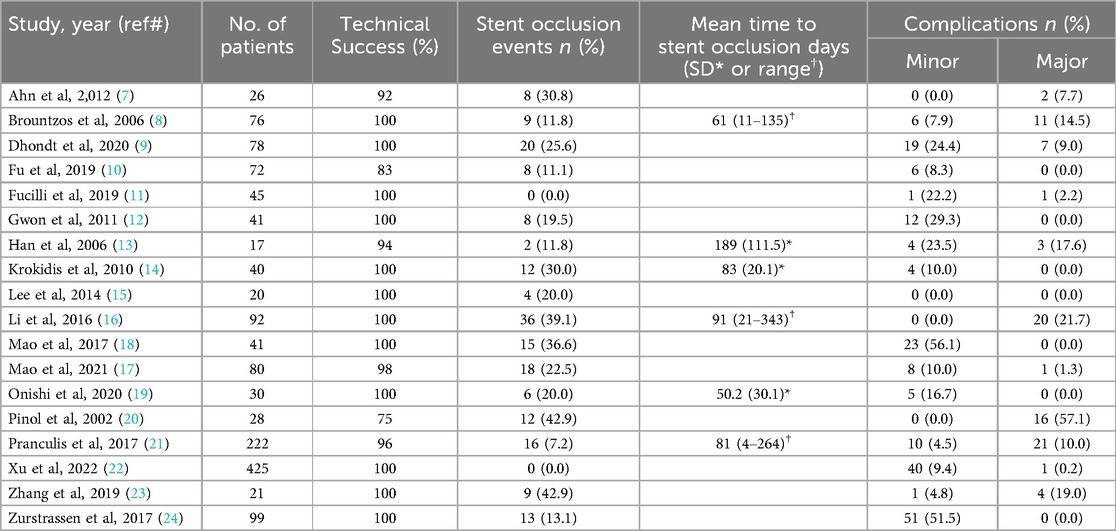
The mean stent primary patency duration ranged from 114.7 ± 15.1 days to 413 ± 63.0 days (7, 8, 13–15, 21). In the 6 articles that contained data on stent occlusion, the weighted mean time to occlusion was 83.9 days, ranging from raw means of 50.2 days to 189 days (8, 13, 14, 16, 19, 21). In total, 196 (13.5%) patients developed stent occlusion. Furthermore, 6.6% of patients required another procedure to recanalize their stent. Post-stent biliary drains were placed in 3.9% of cases for biliary diversion.
Safety outcomes
There were 277 complications (19.1% of patients), of which 87 (6.0%) were classified as major. The most common complications were pancreatitis (93, 6.4%), cholangitis (69, 4.8%), and bleeding (64, 4.4%). Additional complications included other infection, peritonitis/bile leak, pneumonia, cholecystitis, and pneumothorax (27 [1.9%], 9 [0.6%], 9 [0.6%], 4 [0.3%], and 2 [0.1%], respectively).
Among the 64 cases of bleeding complication, 3 (4.7%) patients needed a blood transfusion and 10 (15.6%) patients underwent a procedure such as transarterial embolization to control the bleeding. There were 6 procedure-related deaths (0.4%) associated with stent placement. Patency data and complication rates from each study are summarized in Table 2.
Discussion
Percutaneous metallic biliary stent placement is a common palliative therapy for malignant biliary obstruction. However, much the existing literature on this procedure is limited to small retrospective studies. This systematic review consolidates the current data to better characterize stent placement outcomes. The analysis revealed that percutaneous uncovered metallic biliary stent placement has a high technical success rate, low stent occlusion rate, and a procedure-related mortality rate of less than 1%. While most complications were minor, the overall complication rate of approximately 19.1% is noteworthy.
The technical success rate of percutaneous biliary stent placement surpasses that of the endoscopic approach. A study in 2009 by Paik et al. comparing these methods in patients with advanced hilar cholangiocarcinoma reported a technical success rate of 92.7% in the percutaneous group vs. 77.3% in the endoscopic group (29). Similarly, a randomized clinical trial by Pinol et al. reported a technical success rate of 75% for percutaneous placement compared to 58% for endoscopic placement. This study also found higher therapeutic success rates in the percutaneous group (71% vs. 61%) (20). Additionally, percutaneous approaches are often preferred when initial endoscopic attempts are unsuccessful (30, 31).
The rate of stent occlusion among the analyzed studies was low at 13.5% with a weighted mean time to occlusion of 83.9 days. Uncovered stents were the focus of this review. The literature presents mixed findings regarding potential superior patency of covered stents. Some studies report no significant difference in patency or complication rates between covered and uncovered stents (4, 15, 19). For example, a randomized multicenter trial of 400 patients with malignant biliary distal biliary obstruction found no significant differences between covered and uncovered metallic stents placed endoscopically (p = 0.30) (32). Conversely, a randomized trial of 80 patients comparing percutaneously placed stents for pancreatic cancer reported a mean patency of 166 days vs. 234 days for uncovered and covered stents (p < 0.01), respectively (14). Overall, this systematic review highlights that palliative percutaneous biliary stenting for unresectable malignancies helped the majority of patients achieve internal bile drainage without needing secondary procedures to maintain patency or adding morbidity to end of life care.
The total complication rate among the articles reviewed was 19.1% with nearly one third of these events considered to be “major”. The most common complication was pancreatitis, accounting for 33.6% of the 277 complications, though the severity of these cases remains unclear due to inconsistent reporting across studies. While limited literature directly compares percutaneous and endoscopic biliary metallic stent placement, available data suggest endoscopic techniques have similar or higher complication rates. For example, a retrospective study of 4,623 patients with endoscopically placed biliary stents for malignant biliary obstruction reported an adverse event rate of 15.7%, with pancreatitis being the most frequent complication (4.7%) (33). Ho et al. reported an 18% complication rate with endoscopically placed partially covered biliary metal stents (34). A 2023 study by Paik et al. found a combined adverse event rate of 32% for metallic and plastic stents that were placed endoscopically for malignant biliary obstruction (35). Additionally, in a prospective study on malignant hilar obstruction, De Palma et al. reported early complications in 8.2% of patients and late complications in 22.9% of patients with endoscopically placed metallic stents (36). Further comparative studies are needed to clarify the outcome differences between percutaneous and endoscopic metallic stent placement for malignant obstruction.
This study has several limitations primarily due to its retrospective nature and the overall quality of the included articles, most of which received a “poor” rating based on NOS criteria. The heterogeneity of the data precluded meta-analysis, and there was inconsistent reporting of complication severity, repeat interventions, and stent patency duration. Patient follow-up was not standardized. Additionally, this systematic review focused on uncovered stents due to their widespread use and to avoid confounding factors related to stent design, which may obscure conclusions on patency and complications.
Percutaneous uncovered metallic stent placement for malignant biliary obstruction has a high technical success rate and very low procedure-related mortality. The need for secondary interventions to maintain stent patency or achieve biliary diversion was low. However, while most complications were minor, the overall complication rate was 19.1%, underscoring the importance of careful patient selection to optimize palliative care for those with unresectable biliary malignancies.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
JB: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CR: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MJ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MA: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RF: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ET: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Lorenz JM. Management of malignant biliary obstruction. Semin Intervent Radiol. (2016) 33(4):259–67. doi: 10.1055/s-0036-1592330
2. Abraham NS, Barkun JS, Barkun AN. Palliation of malignant biliary obstruction: a prospective trial examining impact on quality of life. Gastrointest Endosc. (2002) 56(6):835–41. doi: 10.1067/mge.2002.129868
3. Lee TH, Moon JH, Park SH. Biliary stenting for hilar malignant biliary obstruction. Dig Endosc. (2020) 32(2):275–86. doi: 10.1111/den.13549
4. Chen MY, Lin JW, Zhu HP, Zhang B, Jiang GY, Yan PJ, et al. Covered stents versus uncovered stents for unresectable malignant biliary strictures: a meta-analysis. Biomed Res Int. (2016) 2016:6408067. doi: 10.1155/2016/6408067
5. Song J, Deng J, Wen F. Risk factors associated with acute pancreatitis after percutaneous biliary intervention: we do not know nearly enough. Gastroenterol Res Pract. (2023) 2023:9563074. doi: 10.1155/2023/9563074
6. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Br Med J. (2009) 339:b2535. doi: 10.1136/bmj.b2535
7. Ahn SJ, Bae JI, Han TS, Won JH, Kim JD, Kwack KS, et al. Percutaneous biliary drainage using open cell stents for malignant biliary hilar obstruction. Korean J Radiol. (2012) 13(6):795–802. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2012.13.6.795
8. Brountzos EN, Ptochis N, Panagiotou I, Malagari K, Tzavara C, Kelekis D. A survival analysis of patients with malignant biliary strictures treated by percutaneous metallic stenting. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. (2007) 30(1):66–73. doi: 10.1007/s00270-005-0379-3
9. Dhondt E, Vanlangenhove P, De Man M, Huyck L, Defreyne L. No advantage of expanded polytetrafluoroethylene and fluorinated ethylene propylene-covered stents over uncovered nitinol stents for percutaneous palliation of malignant infrahilar biliary obstruction: results of a single-center prospective randomized trial. J Vasc Interv Radiol. (2020) 31(1):82–92. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2019.07.013
10. Fu YF, Zhou WJ, Shi YB, Cao W, Cao C. Percutaneous stenting for malignant hilar biliary obstruction: a randomized controlled trial of unilateral versus bilateral stenting. Abdom Radiol (NY). (2019) 44(8):2900–8. doi: 10.1007/s00261-019-02010-6
11. Fucilli F, Licinio R, Lorusso D, Giorgio P, Caruso ML. One stage percutaneous transhepatic biliary stenting for malignant jaundice: a safe, quick and economical option of treatment. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2019) 23(17):7684–93. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201909_18892
12. Gwon DI, Ko GY, Sung KB, Yoon HK, Shin JH, Hyoung Kim J, et al. Percutaneous biliary metallic stent placement in patients with unilobar portal vein occlusion caused by advanced hilar malignancy: outcome of unilateral versus bilateral stenting. AJR Am J Roentgenol. (2011) 197(4):795–801. doi: 10.2214/AJR.11.6424
13. Han YH, Kim MY, Kim SY, Kim YH, Hwang YJ, Seo JW, et al. Percutaneous insertion of zilver stent in malignant biliary obstruction. Abdom Imaging. (2006) 31(4):433–8. doi: 10.1007/s00261-005-8017-8
14. Krokidis M, Fanelli F, Orgera G, Tsetis D, Mouzas I, Bezzi M, et al. Percutaneous palliation of pancreatic head cancer: randomized comparison of ePTFE/FEP-covered versus uncovered nitinol biliary stents. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. (2011) 34(2):352–61. doi: 10.1007/s00270-010-9880-4
15. Lee SJ, Kim MD, Lee MS, Kim IJ, Park SI, Won JY, et al. Comparison of the efficacy of covered versus uncovered metallic stents in treating inoperable malignant common bile duct obstruction: a randomized trial. J Vasc Interv Radiol. (2014) 25(12):1912–20. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2014.05.021
16. Li M, Li K, Qi X, Wu W, Zheng L, He C, et al. Percutaneous transhepatic biliary stent implantation for obstructive jaundice of perihilar cholangiocarcinoma: a prospective study on predictors of stent patency and survival in 92 patients. J Vasc Interv Radiol. (2016) 27(7):1047–55.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2016.02.035
17. Mao X, Wen F, Liang H, Sun W, Lu Z. A preliminary single-center investigation of percutaneous biliary stenting in malignant hilar biliary obstruction: what impacts the clinical success and the long-term outcomes? Support Care Cancer. (2021) 29(11):6781–92. doi: 10.1007/s00520-021-06271-0
18. Mao XN, Lu ZM, Wen F, Liang HY, Guo QY. Bare-metal stents across the vater’s ampulla is a safe method for patients with lower bile duct obstruction. Medicine (Baltimore). (2017) 96(45):e7475. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007475
19. Onishi Y, Yoshioka T, Arai Y, Inaba Y, Saito H, Aramaki T, et al. Randomized controlled study to compare uncovered stent versus covered stent as percutaneous endoprosthesis for malignant biliary obstruction (JIVROSG-0207). Am J Clin Oncol. (2020) 43(11):784–7. doi: 10.1097/COC.0000000000000750
20. Pinol V, Castells A, Bordas JM, Real MI, Llach J, Montana X, et al. Percutaneous self-expanding metal stents versus endoscopic polyethylene endoprostheses for treating malignant biliary obstruction: randomized clinical trial. Radiology. (2002) 225(1):27–34. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2243011517
21. Pranculis A, Kievisas M, Kievisiene L, Vaicius A, Vanagas T, Kaupas RS, et al. Percutaneous transhepatic biliary stenting with uncovered self-expandable metallic stents in patients with malignant biliary obstruction - efficacy and survival analysis. Pol J Radiol. (2017) 82:431–40. doi: 10.12659/PJR.901785
22. Xu C, Xu GX, Liu S, Shi HB, Zhou WZ. Acute pancreatitis after percutaneous metallic stent insertion for malignant biliary obstruction: a retrospective 2-center study. Turk J Gastroenterol. (2023) 34(9):961–7. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2023.22442
23. Zhang JX, Liu J, Wang B, Liu S, Zu QQ, Shi HB. Retrospective comparison of different percutaneous approaches to manage occluded primary uncovered self-expandable metal stents in patients with unresectable malignant hilar biliary obstruction. Scand J Gastroenterol. (2019) 54(11):1397–402. doi: 10.1080/00365521.2019.1683602
24. Zurstrassen CE, Bitencourt AGV, Guimaraes MD, Cavalcante A, Tyng CJ, Amoedo MK, et al. Percutaneous stent placement for the treatment of malignant biliary obstruction: nitinol versus elgiloy stents. Radiol Bras. (2017) 50(2):97–102. doi: 10.1590/0100-3984.2015.0183
25. Wells G, Shea B, O'Connell D, Robertson J, Peterson J, Welch V, et al. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomised Studies in Meta-analyses. Ottawa, ON: University of Ottawa (2013).
26. Sacks D, McClenny TE, Cardella JF, Lewis CA. Society of interventional radiology clinical practice guidelines. J Vasc Interv Radiol. (2003) 14(9 Pt 2):S199–202. doi: 10.1097/01.rvi.0000094584.83406.3e
27. Al Nakshabandi A, Ali FS, Albustami I, Hwang H, Qiao W, Johnston NC, et al. Biliary drainage in hilar and perihilar cholangiocarcinoma: 25-year experience at a tertiary cancer center. Gastrointest Endosc. (2024) 99(6):938–49.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2023.12.006
28. Pappas P, Leonardou P, Kurkuni A, Alexopoulos T, Tzortzis G. Percutaneous insertion of metallic endoprostheses in the biliary tree in 66 patients: relief of the obstruction. Abdom Imaging. (2003) 28(5):678–83. doi: 10.1007/s00261-003-0004-3
29. Paik WH, Park YS, Hwang JH, Lee SH, Yoon CJ, Kang SG, et al. Palliative treatment with self-expandable metallic stents in patients with advanced type III or IV hilar cholangiocarcinoma: a percutaneous versus endoscopic approach. Gastrointest Endosc. (2009) 69(1):55–62. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2008.04.005
30. Levy MJ, Baron TH, Gostout CJ, Petersen BT, Farnell MB. Palliation of malignant extrahepatic biliary obstruction with plastic versus expandable metal stents: an evidence-based approach. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2004) 2(4):273–85. doi: 10.1016/s1542-3565(04)00055-2
31. Jang SI, Hwang JH, Lee KH, Yu JS, Kim HW, Yoon CJ, et al. Percutaneous biliary approach as a successful rescue procedure after failed endoscopic therapy for drainage in advanced hilar tumors. J Gastroen Hepatol. (2017) 32(4):932–8. doi: 10.1111/jgh.13602
32. Kullman E, Frozanpor F, Soderlund C, Linder S, Sandstrom P, Lindhoff-Larsson A, et al. Covered versus uncovered self-expandable nitinol stents in the palliative treatment of malignant distal biliary obstruction: results from a randomized, multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc. (2010) 72(5):915–23. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2010.07.036
33. Lubbe J, Sandblom G, Arnelo U, Jonas E, Enochsson L. Endoscopic stenting for malignant biliary obstruction: results of a nationwide experience. Clin Endosc. (2021) 54(5):713–21. doi: 10.5946/ce.2021.016
34. Ho H, Mahajan A, Gosain S, Jain A, Brock A, Rehan ME, et al. Management of complications associated with partially covered biliary metal stents. Dig Dis Sci. (2010) 55(2):516–22. doi: 10.1007/s10620-009-0756-x
35. Paik WH, Jung MK, Kim DU, Song TJ, Yang MJ, Choi YH, et al. Side-by-side placement of fully covered metal stents versus conventional 7F plastic stents in malignant hilar biliary obstruction: prospective randomized controlled trial. Dig Endosc. (2024) 36(4):473–80. doi: 10.1111/den.14669
Keywords: bile duct, biliary stent, malignant biliary obstruction, complications, outcomes
Citation: Bock J, Reisenauer CJ, Jundt MC, Augustine MR, Frimpong RG and Takahashi EA (2025) Complications of percutaneously placed uncovered metallic biliary stents for malignant obstruction: a systematic review. Front. Radiol. 5:1639323. doi: 10.3389/fradi.2025.1639323
Received: 1 June 2025; Accepted: 22 July 2025;
Published: 5 August 2025.
Edited by:
Michele Pinon, Ospedale Pediatrico Regina Margherita, ItalyReviewed by:
Kiran Maddu, Emory University, United StatesJiazhao Song, University Hospital Erlangen, Germany
Copyright: © 2025 Bock, Reisenauer, Jundt, Augustine, Frimpong and Takahashi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Edwin A. Takahashi, VGFrYWhhc2hpLmVkd2luQG1heW8uZWR1
 Jonathan Bock
Jonathan Bock Christopher J. Reisenauer
Christopher J. Reisenauer Michael C. Jundt2
Michael C. Jundt2 Edwin A. Takahashi
Edwin A. Takahashi