- 1Department of Population and Family Health, Jimma University, Jimma, Ethiopia
- 2Department of Health Behavior and Society, Jimma University, Jimma, Ethiopia
Background: The burden of sexually transmitted infections and unintended pregnancy remain a major health problem disproportionately affecting young woman in sub Saharan Africa. While there is a growing interest in promoting dual protection as a means of simultaneously preventing both HIV/STIs and unwanted pregnancy, little is known about patterns and predictors of dual protection use based on theoretical models for designing targeted interventions to promote dual protection for youth. This study aimed to examine predictors of dual protection use based on the information-motivation-behavioral skills model among female university students in Ethiopia.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted with 1,020 female students at Mattu University between April and June 2023. Data were collected using a self-administered questionnaire and analyzed using SPSS version 24. Bivariate and multivariate analyses were conducted using structural equation modeling with AMOS program to examine predictors of dual-protection use.
Results: Of the 1,020 participants, 396 (38.8%) had ever had sexual intercourse, 370 (93.4%) of whom were sexually active in the last 12 months. Of these, only 76 (20.5%) used dual protection at last sex in the past 6 months. Multivariate analysis indicated that dual-protection use was directly and strongly predicted by motivation (β = 0.29, P < 0.001) and behavioral skills (β = 0.27, P < 0.001), whereas it was weakly predicted by information (β = 0.04, P < 0.05), while the information had a strong effect (β = 0.27, p < .001) on behavioral skills to indirectly influence dual protection use.
Conclusion: These findings support the key roles of motivation and behavioral skills in directly predicting dual protection use, while information can also influence behavioral skills to indirectly affect dual protection use, suggesting the importance of incorporating all elements of the IMB model constructs in designing targeted intervention to promote dual protection behaviors for youth.
Introduction
Globally, HIV/AIDS and unwanted pregnancies are major public health problems with young women being disproportionately affected. In 2020, of the estimated 1.5 million people newly infected with HIV worldwide, about 260,000 were adolescent girls and young women aged 15–24 years, of these, around 218, 000 (83%) occurred among adolescent girls and young women in sub-Saharan Africa (1–3). In Ethiopia, although the adult HIV prevalence rate declined to 0.93% in 2019, women remained disproportionately affected compared to men (1.22% vs. 0.64%), and the highest prevalence was observed among unmarried young women (9%) (4–7). In addition, like many other countries in sub Saharan Africa, the rate of unwanted pregnancies among young women in Ethiopia remains high, with about 37% of unwanted pregnancies occurring in young women aged 20–24 years in 2011 (6). Recent data from the Ethiopian demographic and health survey (EDHS) also reported that the proportion of young women who begun childbearing before age 20 was approximately 28% in 2016 (8). The fact that adolescent girls and young women in sub-Saharan Africa are substantially affected by the HIV epidemic is because they face several vulnerabilities that increase their risk of unwanted pregnancy and STIs/HIV. These vulnerabilities are rooted in gender roles/social norms, and their limited access to information, education and resources, all of which prevent them from making essential decisions about their health (1–3). As a result, many young women do not receive adequate education about reproductive health, contraception, and safe sex practices, leaving them uninformed about their prevention options and risks. Furthermore, gender inequalies and social norms also place young women in subordinate positions within relationships, making it difficult for them to negotiate safer sex or condom use because they may fear violence from partners if they attempt to assert their preferences regarding condom use (2, 3).
In response to the HIV epidemic, HIV/AIDS prevention programs emphasize safer sexual practices such as abstinence, mutual monogamy, and condom use as effective strategies for reducing the risk of HIV infections among youth (2, 3). In addition, because young women are at increased risk and vulnerable to STI/HIV infections and unwanted pregnancy from the same unsafe sexual practice while both can be prevented simultanousely by the same safer sexual practice as dual protection, the recent WHO/UNAIDS recommendation on HIV prevention for young women emphasize the need for dual protection: defined as safer sexual behaviors that provide simultaneous protection against both HIV/STI and unwanted pregnancy through either abstinence, consistent condom use, or dual-method use (using condom plus hormonal contraceptive), as complementary strategies to maximize prevention efforts for youth in settings with high HIV burden (2, 8). In this study, Dual protection use is defined as simultaneous protection from pregnancy and STI/HIV infection through (either consistent use of a condom alone, or use of two methods (condom plus other contraceptive methods), Consistent condom use is defined as always using a condom in every sexual acts, and Dual-method use is defined as the simultaneous use of a condom for STI/HIV prevention and hormonal methods for pregnancy prevention at the last sex.
In recognition of the problems and vulnerability of unmarried young women to higher risk STI/HIV infections in Ethiopia, the national adolescents’ reproductive health strategy (2007–2015) has stressed the importance of dual protection for unmarried young women to prevent both HIV/STI and unwanted pregnancies simultaneously (6, 7). However, despite the improvements in the rates of contraceptive methods used among unmarried sexually active young women in Ethiopia to 55% in 2016, only 4% used condoms (6, 7), suggesting that they are not dually protected and thus remain at an increased risk of HIV infection. Nevertheless, little is known about patterns and predictors of dual protection practices among young women in Ethiopia. In addition, despite the ranges of dual protection options, studies on dual-protection to date almost exclusively has focused on dual-method use (using condom for STI/HIV prevention and hormonal contraceptive for pregnancy prevention) measured at a single point in time (e.g., at last intercourse) (9). However, focusing exclusively on dual-method use has important limitations in that it ignores the importance of abstinence and consistent condom use for effective risk reduction approach. Thus, there is a need for understanding patterns and predictors of dual protection use based on theoretical models for designing comprhensive interventions to promote diverse dual protection behaviors among youth at risk of HIVSTI and unintended pregnancy.
Ethical consideration and informed consent to participate
Ethical approval was obtained from the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Jimma University with reference No: JUHI/IRB 329/23, date 20/03/2023, which states that “the research protocol meets the ethical and scientific standards outlined in national and international guidelines” in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. A formal letter of support was obtained from Mattu University to their respective colleges requesting to cooperate with researchers during the study. Informed consent was obtained from all the participants based on “written consent form” prepared for this purpose and to be signed by all the participants before participating. As all university-level students are older than 18 years, they are believed to be capable of providing informed consent. In addition, the law in Ethiopia does not require such a group of young people to be accompanied by parents or guardians to provide consent to their behaviors, stating that “Assent will be sought from a study participant under the age of 18 years old” (NRERG 7th ed: Art 6.15). Before start, the study's objective was explained to the participants and voluntary participation was allowed by explaining their full rights to participate or not, and to withdraw their consent at any stage if they wish without giving any reason or no penalty. Furthermore, the participants were also assured that the questionnaire was anonymous and that their responses were fully confidential.
Theoretical perspectives
Various theoretical models have been used to understand HIV risk behaviors and promote safer sexual behaviors across at-risk populations. Of these, the information-motivation-behavioral skills (IMB) model (10–12) is one that has been widely used to understand and promote HIV prevention behaviors. The IMB model asserts that HIV prevention information, motivation, and behavioral skills are fundamental determinants of HIV preventive behaviors (10–12). The model specifies that information and motivation work through behavioral skills to influence HIV-preventive behaviors. The model also assumes that information and motivation may have a direct effect on HIV-preventive behavior when complicated behavioral skills are not required for practice, such as abstinence, as opposed to using condoms by young women (8–10). According to the IMB model, specification of information, motivation, and behavioral skills content most relevant to a specific behavior (abstinence and condom use) and identification of the IMB model constructs that powerfully influence the practice of a specific behavior is crucial for designing empirically targeted interventions to promote a specific sexual health behavior (10, 11, 13, 14).
The IMB model's constructs are also regarded as highly generalizable approach to understanding and promoting sexual health behavior across populations and behaviors of interest (9–11). However, despite the recommendation for its application to a range of sexual health behaviors, there is limited research using the IMB model for understanding predictors of safer sexual dual protection behaviors, such as dual protection use among young women at risk of STI/HIV and unwanted pregnancy.Thus, this study aimed to utilize the IMB model for examining predictors of dual protection use among female university students in Ethiopia for designing targeted interventions to promote dual protection behaviors for this population. The IMB model was chosen because it specifies measurement and statistical procedures for eliciting information, motivation, and behavioral skills factors that are relevant to a particular behaviors (15–18).
Conceptual framework for the present study
As illustrated in Figure 1, the IMB model for predicting dual protection use posits that an individual's levels of information, motivation, and behavioral skills are determinants of dual protection use. Specifically, possessing specific information about the risks of HIV/pregnancy and the benefits of dual protection, motivation to engage in dual protection (attitudes toward dual protection use and social norms regarding it) and behavioral skills for dual protection (the ability to negotiate with partners and self-efficacy in condom use) will directly predict dual protection use. Furthermore, information and motivation also influence behavioral skills, thereby indirectly affecting dual protection use (see Figure 1).
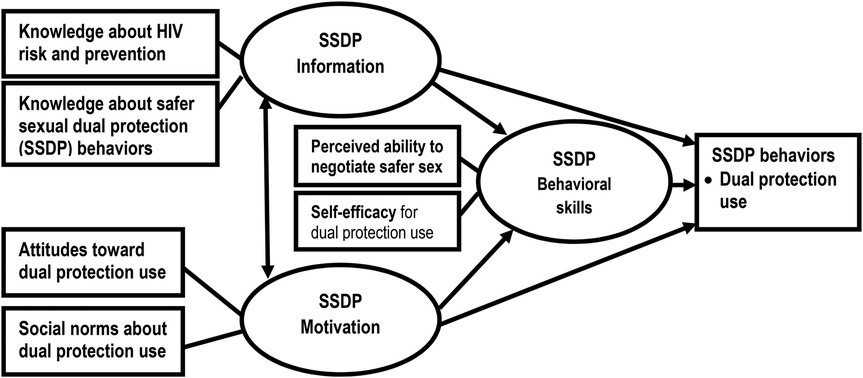
Figure 1. Conceptual framework for the IMB model of the determinants of dual protection use. Source: Adopted from the IMB model of HIV prevention behavior (8–12). Note: Oval represents latent constructs (Information, Motivation and Behavioral skills), Rectangles represent observable variables (Knowledge of HIV risk and safer sexual dual protection behaviors, attitudes and social norms about dual protection use for measuring motivatio and ablity to negociate and self-efficacy). Single-headed arrows represent regression paths, and double-headed arrows represent correlation.
Materials and methods
Study setting, study design and participants
This study was conducted at Mattu University in Ethiopia. Mattu University is a newly established third-generation public university in the country. It has two campuses: the Mattu main campus, located at 551 km southwest of Addis Ababa, and Beddele campus, located at 431 km southwest of Addis Ababa.This study was conducted between April and December 2023.
A cross-sectional survey was used with undergraduate female university students randomly selected from the two campuses of Mattu University. The inclusion criterion includes being unmarried female students and willing to participate and provide informed consent. Whereas married female students, and those who were critically ill were excluded.
Sample size and its determination
To obtain a sufficient number of participants for numerical analysis, the sample size for the study was calculated for different objectives, and the largest size was taken as the final sample size.
Thus, since 1,050 was the largest sample size calculated, it was taken as the final sample size to be used for all objectives, including this study.
Sampling technique
A multistage sampling technique was used to recruit participants from the two campuses of Mattu University. First, three non-health colleges from each campus were selected using stratified sampling. Then, two departments from each college and two classrooms from each department were selected using cluster sampling in which all female students who fulfilled the inclusion criteria were invited to participate in the study.
Measurement
To assess the levels of HIV risk reduction/dual protection information, motivation, behavioral skills, and behaviors, a validated measure of the IMB model of HIV prevention behaviors was was adopted from previous research (8, 10, 13, 14, 19, 20).
A/measures of information
Levels of HIV risk reduction and dual protection information were measured with 12 items, using T/F responses. a) Knowledge about HIV risk and prevention was assessed with 8 items, such as (1) “HIV can be transmitted through sexual intercourse”; 2) “Abstinence is the most effective way of avoiding risk of STI/HIV”; or 3) “Consistent condom use is an effective method of preventing STI/HIV,”. b) Knowledge about safer sexual dual protection behaviors was assessed with four items, such as (1) “Abstinence is the best way to avoid the risk of HIV/STI and pregnancy for unmarried youth”; (2) “Consistent condom use prevents HIV/STI and pregnancy, providing dual protection against both”; and (3) “Dual methods use is options for dual protection against both HIV/STI and pregnancy simultaneously” (8, 10, 13, 14, 19, 20).
B/measures of motivation
Motivation to practice dual protection use was assessed based on attitudes and social norms regarding dual protection, using 5 pionts Likert scale: a) Attitudes toward condom use were assessed with 4 items: (e.g., 1) “condoms do not interfere with sexual enjoyment,” 2) “consistent condom use is effective for preventing HIV/STI and pregnancy”, and 3) “condoms should always be used, even if a woman is using hormonal contraception.” b) Social norms about condom use were assessed with two items: (1) “The belief that condom use may show my partner that I do not love/trust him” and 2) “If I ask my partner to use condoms, he would suspect me that I have another partner and that he would become angry at me” (8, 10, 13, 14, 19, 20).
C/measures of behavioral skills
Behavioral skills for dual protection use were assessed based on perceived ability and Self-efficacy for dual protection, using 5 pionts Likert scale: a) Perceived ability to negotiate with one's partner was assessed with two items: (e.g., 1) “How confident are you in your ability to negotiate with partners to use condoms consistently?” and 2) “How confident are you in using condoms consistently even if you are using hormonal contraception?”). b) Self-efficacy in using condoms was assessed with two items: (e.g., 1) “If your steady partner doesn't want to use a condom, how certain are you that you could convince him to use condoms?”; 2) “If you are already using another method of contraception for pregnancy, how certain are you that you could always use condoms for reducing the risk of HIV?” (8, 10, 13, 14, 19, 20).
D/measures of safer sexual dual protection behaviors
Sexual dual-protection behaviors were assessed using self-reported protection method used.
1) Primary sexual abstinence was assessed by asking “Have you ever had sex to date?” with a response (yes or no).
2) Dual protection use was assessed by asking, “Did you use the dual protection method in your last sex in the past 12 months”?, with a response option (yes/no).
3) Consistent condom use was assessed by asking “How frequently did you use condoms in the past 12 months?” with responses options (1) “always” to (2) “never.”
4) Dual method use was assessed by asking “Did you use condoms plus another contraceptive method in the past 12 months” with responses (yes or no).
Data collection procedure
Data collection was carried out in their classrooms, where students were asked to fill out an anonymous questionnaire prepared in English and then translated into Afaan-Oromoo and Amharic languages, for better understanding of the concepts of each question. The questionnaires were administered by 4 research teams who had a B.Sc degree, but not staff of the same university, and they were trained as supervisors to help students complete the questionnaire, to explain the purpose of the study, clarify questions whenever necessary, and collect the completed questionnaires at the end. A pre-test of the questionnaire was administered to 5% of the sample, with a total of 51 students, but not taking part in the study.
Data analysis
The collected data was cleaned, edited, and analyzed using SPSS version 23. Descriptive statistics were used to summarize the distribution of participants based on their demographic characteristics and the level of HIV risk reduction/dual protection information, motivation, behavioral skills, and behaviors. Bivariate and multivariate analysiswere performed using structural equation modeling (SEM) with AMOS 24 (17, 18) to examine correlates and predictors of dual-protection use. Spearman's correlations were used to examine correlations among the indicators of the IMB model and dual protection use. Estimating the parameters of the measurement model (confirmatory factor analysis) and the structural model (path analysis) was accomplished with a maximum likelihood estimate in AMOS. Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) was used to examine the relationships between the observed variables and latent constructs in the model (i.e., to test the reliability and validity of the measurement model). Path analysis was used to examine the relationships between the latent constructs in the structural model (i.e., the information, motivation and behavioral skills constructs) and identify the predictors of dual protection use.
Results
Descriptive statistics
i/ Sociodemographic characteristics and sexual behaviors of the study participants
As shown in Table 1, of the 1,020 participants, 820 (80.4%) were aged 20–24 years, with a mean age of 20.77 years (SD = 1.146). Regarding ethnicity, 526 (51.6%) were Oromos, followed by Amhara (356; 34.9%). According to religion, 442 (43.3%) were Orthodox, 364 (35.7%) were Protestants, 180 (17.6%) were Muslims, and 34(3.3%) were Waaqeffanna followers. With respect to sexual behaviors, 624 (61.2%) reported never having sexual intercourse, whereas 396 (38.8%) had ever had sexual intercourse. Among sexually active in the past 12 months (n = 370), about 175 (47.3%) used condoms at last sexual encounter, while only 20.5% used dual protection methods in the past year, with 22 (5.9%) using condoms alone, and 54 (14.6%) using two-methods (condom plus hormonal methods) at their last sex (see Table 1).
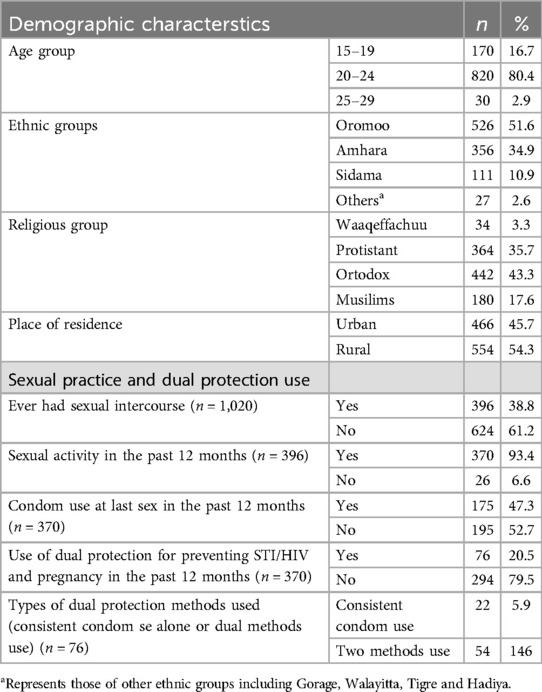
Table 1. Distribution of the participants by demographic characteristics and sexual behaviors (n = 1,020).
ii/ Levels of HIV risk reduction/dual protection information, motivation and behavioral skills among sexually active female university students (n = 396)
As presented in Table 2, among sexually active participants (n = 396), 207 (52.3%) had high knowledge of HIV risk and prevention and 220 (55.6%) had high knowledge of safer sexual dual protection behaviors. Regarding motivation to practice dual protection use among sexually active participants, only fewer than half, 173 (43.7%) had positive attitude toward dual protection use and 157 (39.6%) had supportive norms for dual protection use. With regrad to behavioral skills required for dual protection use, nearly half, 195 (49.2%) had high self-efficacy in negotiating safer sex with partners (see Table 2).
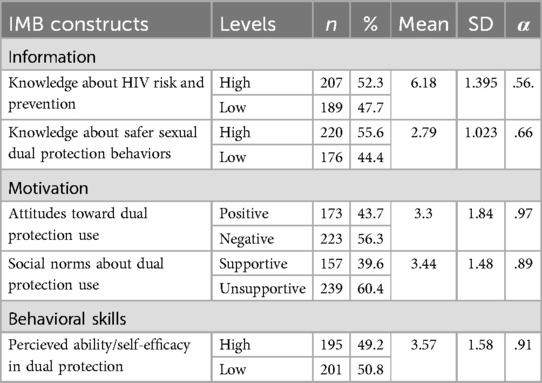
Table 2. Descriptive statistics of the levels of HIV risk reduction/dual protection information, motivation, behavioral skills among sexually active female students (n = 396).
Bivariate correlations analysis among indicators of IMB model and dual protection use
As shown in Table 3, results of Spearman's correlations analysis showed that the informational indicators of knowledge about HIV risk reduction and safer sexual dual protection behaviors were strongly correlated(r = .722, p < .001). In addition, the informational indicators are also correlated with the motivational indicators of attitudes towards dual protection(r = .597, p < .001) and social norms about dual protection use (r = .547, p < .001), and also with the behavioral skill indicators of self-efficacy in using dual protection (r = .508, p < .001).Similarly, the motivational indicators of attitudes toward dual protection use and social norms about dual protection were strongly correlated (r = .910, p < .001), and both are also correlated with the behavioral skill indicators of self-efficacy for dual protection use (r = .637, p < .001) and (r = .565, p < .001) respectively.
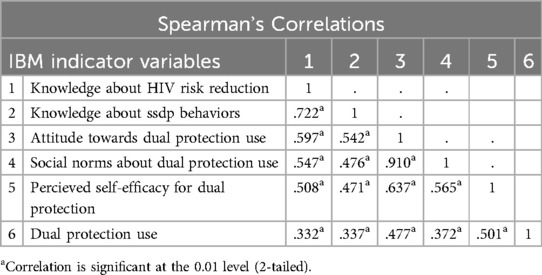
Table 3. Correlational analysis among indicators of IMB model constructs and dual protection use among sexually active female university students (n = 396).
Overall, the bivariate analysis showed that dual protection use was strongly correlated with knowledge about HIV risk reduction (r = .332, p < 0.01), knowledge of safer sexual dual protection behaviors (r = .337, p < 0.01), attitude towards dual protection use (r = .477, p < 0.01), social norms about dual protection use (r = .372, p < 0.01) and perceived self-efficacy for using dual protection (r = .501, p < 0.001) (see Table 3).
Multivariate analysis
The extent to which the data conformed to the theoretical model was assessed using the model's fit indices that revealed the Chi-squared test value (X2 = 11.399, P = .220), comparative fit index (CFI = .99), and root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA = .048), all indicating the model fit was acceptable.
Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA)
As presented in Table 4, the maximum likelihood estimates of the measurement model showed that all the factor loadings for the relationships between the observed variables and latent constructs were strong and statistically significant, suggesting reliability of the model. Specifically, the standardized factor loadings (β = 0.89) for knowledge of HIV risk and prevention and (β = 0.82) for knowledge of safer sexual dual protection behaviors on the information construct suggest their strong and significant relationships. In addition, the standardized factor loadings (β = 1.1) for attitudes toward dual protection use and (β = 0.89) for social norms about dual protection on the motivation construct also suggest strong and significant relationships. Finally, the standardized factor loadings (β = 1.1) for perceived ability to negotiate safer sex and (β = 0.86) for self-efficacy in using dual protection on the behavioral skill construct indicated strong and significant reliability (P < 0.001) (see Table 4).
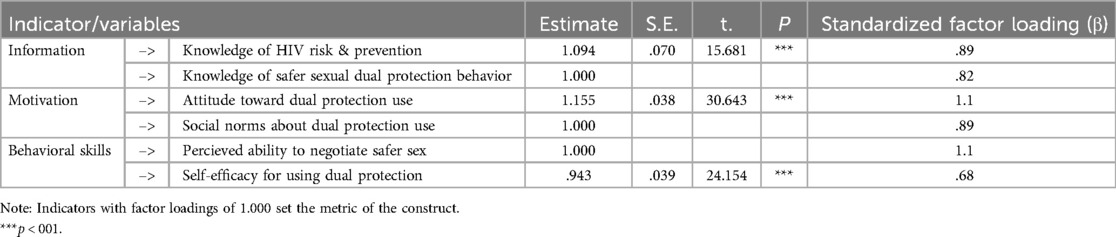
Table 4. Maximum likelihood estimates of the measurement model parameters for the IMB model of dual protection use among sexually active female university students (n = 396).
Path analysis
As shown in Table 5 and Figure 2, the results of path analysis indicated that information (β = 0.27, P < .001) and motivation (β = 0.40, P < .001) were significantly associated with behavioral skills, and that behavioral skills, in turn, were reliably associated with dual protection use (β = 0.27, P < 0.001). In addition, the direct effect of motivation on dual protection use was strong (β = 0.29, P < 0.001), whereas the direct effect of information on dual protection use was moderate (β = 0.04, P < 0.05). Overall, the full model's constructs accounted for approximately 27.4% of the variation in dual-protection use, while the information and motivation constructs explained about 37% of the variation in behavioral skills (see Table 5 and Figure 2).
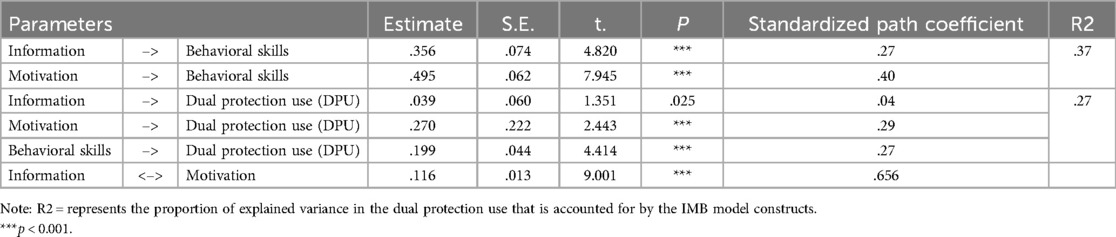
Table 5. Estimates of the structural parameters for the IMB model of dual protection use amongnsexually active female university students (n = 396).
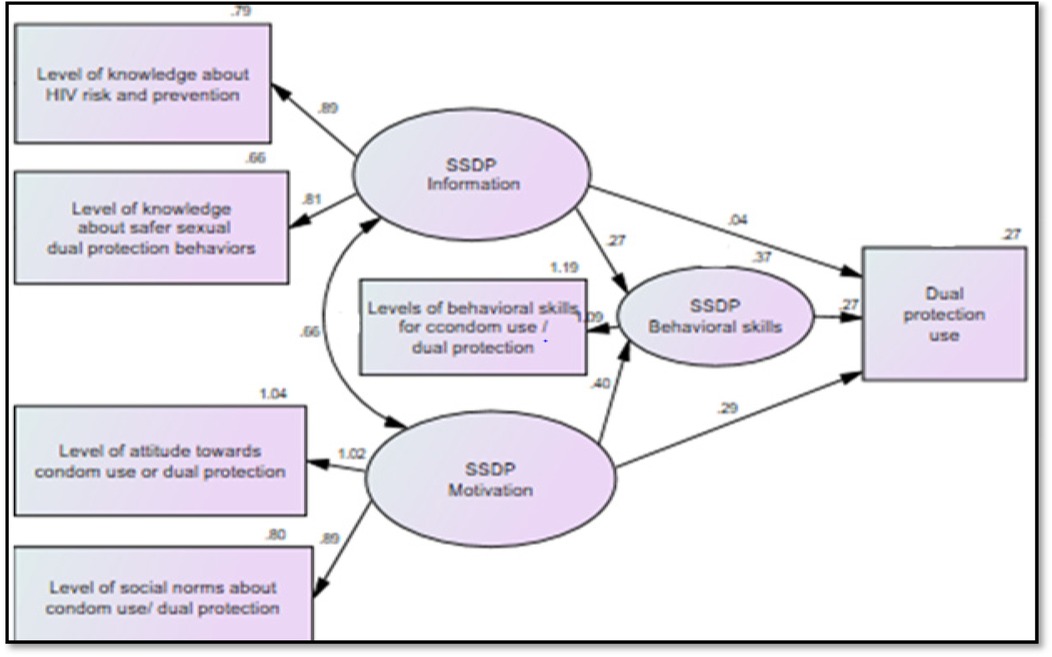
Figure 2. Significant regression paths in the IMB model predictors of dual protection use among sexually active female university students (n = 396). Source: Adopted from the IMB model of HIV prevention behavior (8–12). Note: Oval represents latent constructs, and rectangles represent observable variables. Single-headed arrows represent regression paths, and double-headed arrows represent correlations. Regression coefficients and covariance estimates are standardized.
Discussion
The current study utilized the IMB model for understanding predictors of dual protection use among female university students in Ethiopia. The results showed that significant proportion of female university students were engaged in risky sexual behaviors, such as premarital sex with low use of condom/dual protection that may place them at increase risks for STI/HIV infections. In this study, only 20.5% of sexually active female students have used dual protection methods during intercourse in the past 12 months, with 22 (5.9%) using condoms alone, and 54 (14.6%) using two-methods (condom plus hormonal methods) at their last sex. This finding is in line with those of studies conducted in the United States, where use of dual protection among sexually active adolescents ranged from 14% to 25% (21). Nevertheless, the results of our study are lower than those of studies in Canada, where 30% of sexually active Grade 11 students reported using dual protection at last sex (8). The differences in culture and values might be the cause of these results’ disparity.
In addition, though over two-third of the participants reported to have higher knowledge about HIV risk and prevention, the majority of participants still have a significant knowledge gaps about safer sexual dual protection behaviors, have a negative attitude towards dual protection use, and lower self-efficacy for using dual protection in this study. The findings of this study is consistent with the results of studies conducted among WolaitaSodo University students and Mattu secondary school students in Ethiopia, where many students had unfavorable attitude towards safer sex and inadequate skills for practicing abstinence (17, 22). However, research suggests that knowledge of HIV risk and safer sexual behaviors is crucial to enable people to avoid HIV infection, especially for youth, who are often at greater risk because they may have shorter relationships and thus more partners or may engage in other risky behaviours. In addition, levels of attitudes and skills for practicing safer sex can affect one's practice of sexual behaviors.
Regarding the determinants of dual protection use among sexually active young women, the results of bivariate correlational analysis between indicators of IMB model construct and dual protection use in this study showed that dual protection use is strongly associated with knowledge of safer sexual dual protection behaviors, attitude towards dual protection use, perceived social support for dual protection, and self efficacy to negotiate safer sex with partners. This is consistent with the results of previous studies on the determinants of dual protection use among young women in Canada, which indicated that several factors including social, cultural and psychological factors were correlated with dual methods use (9).
The results from the SEM analysis of IMB model in predicting dual protection use also indicate that information and motivation were independent factors, and each was positively and significantly associated with behavioral skills, and that behavioral skill, in turn, were reliably associated with dual protection use. This finding is consistent with those of previous studies conducted among urban adolescents in the United States (19), among college and university students in the United States (20, 23) and among urban high school youth in the United States (15), among young adults in high HIV burden districts, south Africa (24), among Aferican-American college students in the United States (25), among women in low income housing (26), and underserved minority youth in the United States (27–31) that tested the IMB model's hypothesis that information and motivation are significantly associated with behavioral skills and that behavioral skills, in turn, are associated with HIV-preventive behavior (condom use) (19–21, 23–27). Together, the model constructs accounted for approximately 27.4% of the variance in dual-protection use. In addition, the findings also indicate that information and motivation have reliable effects on behavioral skills, with both constructs explaining about 37% of the variation in behavioral skills. These findings are congruent with the findings of previous studies, in which the model's constructs accounted for one-third to one-half of the variance in condom use) (19–21, 23–27). The results also support the IMB model as a paradigm for explaining and predicting sexual health dual protection of young women.
Limitations
This study has several limitations. First, the study focused only on female university students for the purpose of examining patterns and predictors of dual protection use to simultaneously prevent both STI/HIV and unwanted pregnancy, excluding male students for priority concern. Second, the data based on self-reported sexual behaviors may lead to bias arising from socially desirable responses, because sex remains a sensitive topic in Ethiopian culture. However, the use of self adminstared data collection methods and anounmous questioniiares is intended to reduce such bias.Third, the data from the cross-sectional survey can reveal only the associations between variables at a single point in time; thus, it is recommended that future research should focus on longitudinal studies to test the model.
Conclusions
The current research represents the first attempt to utilize the IMB model for understanding psychological determinants of safer sexual dual protection behaviors among youth in Ethiopia. The findings indicated that a sizable percentage of female university students are engaged in risky sexual practices with low use of dual protection, while the majority of participants lack adequate knowledge of safer sexual dual protection behaviors, favorable attitudes toward dual protection use, and self-efficacy for using dual protection. The results of correlations analysis indicated that predictors of dual protection use were knowledge of safer sexual dual protection behaviors, attitude towards dual protection use and self-efficacy for using dual protection.
These results have significant practical implications, especially for young women at risk of STI/HIV infections even when using hormonal contraception to prevent pregnancy without use of condoms/dual protection in settings with high HIVburdens. By focusing on the application of the IMB model to predict dual protection behavior, this study provides novel insights into the interplay between information, motivation, and behavioral skills in promoting safer sexual dual protection behaviors among youths. These insights will not only advance our theoretical understanding of sexual behavior of youth in high HIV burden settings, but also inform the development of comprhensive interventions that address the diverse needs of young people. Finally, it is recommended that future IMB model test should focus on a search for possible sex differences in the determinants of safer sexual dual protection behaviors between males and females.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by ethical approval was obtained from the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Jimma University, with the committee's reference number:Ref.No.JUHI/IRB 329/23, Date: 20/03/2023 (see attached copy). A formal letter of support was obtained from responsible bodies at Mattu University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
BF: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. GD: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Visualization, Writing – original draft. ZK: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Visualization, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Financial support for this research, which amounts to Eth Birr = 60,000.00, was provided by the Jimma University Institute of Health as a PhD student’s research grant to cover some of the expenses for data collection and analysis. The funders have no competing interests or conflicts of interest concerning manuscript preparation or submission for publication in this journal.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge Jimma University for their financial support and Mattu University for providing this educational opportunity. We acknowledge the data collectors for their support and collaboration throughout the study. Finally, the deepest gratitude was given to the participants. We would also like to acknowledge the AI technologies for providing us a grammar checking assistance in improving language quality of our manuscript writing.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. We would also like to acknowledge the AI technologies for providing us a grammar checking assistance in improving language quality of our manuscript writing.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
AMOS, analysis of moment structure; CCU, consistent condom use; CFA, confirmatory factor analysis; CFI, comparative fit index; DPU, dual protection use; DMU, dual methods use; EDHS, Ethiopian Demographic and Health Survey; FHAPCO, Federal HIV Prevention and Control Office; HIV/AIDS, human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome; IMB, information-motivation-behavioral skills model; RMSEA, root mean square error of approximation; SEM, structural equation modeling; SSDPB, safer sexual dual protection behaviors; SRH, sexual and reproductive health; STIs, sexually transmitted infections; UN, United Nations; UNESCO, United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization; UNAIDS, United Nations Programme of HIV/AIDS; UNFPA, United Nations Fund for Population Activities; USAID, United States Agency for International Development; WHO, World Health Organization.
References
2. Aborode AT, Alexiou A, Ahmad S, Yasir Essar M, Chibueze OS, Al-Zahrani Y, et al. HIV/AIDS epidemic and COVID-19 pandemic in Africa. Front Genet. (2021) 12:670511. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.670511
3. Federal HIV/AIDS Prevention and Control Office (FHAPCO). HIV/AIDS National Strategic Plan for Ethiopia 2021-2025. Addis Ababa: Federal HIV/AIDS Prevention and Control Office (FHAPCO) (2021).
4. CSA I. Ethiopia Demographic and Health Survey: Key Indicators Report. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: Central Statistical Agency (2016).
5. Central Statistical Agency (Ethiopia) and ICF International. Ethiopia Demographic and Health Survey 2011. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia and Calverton, MD, USA: Central Statistical Agency and ICF International (2012).
6. Ethiopia M. Country Progress Report on the HIV Response, 2014. Addis Ababa: Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia (2014).
7. HIV/AIDS JUNPo. Global Report: UNAIDS Report on the Global AIDS Epidemic 2010. Geneva: UNAIDS (2010).
8. Collumbien M, Busza J, Cleland J, Campbell O. Social Science Methods for Research on Sexual and Reproductive Health. Geneva: World Health Organization (WHO) (2012).
9. Berer M. Dual protection: more needed than practised or understood. Reprod Health Matters. (2006) 14(28):162–70. doi: 10.1016/S0968-8080(06)28262-4
10. CSA-Ethiopia I. International. Ethiopia Demographic and Health Survey 2016: Key Indicators Report. Rockville: CSA and ICF (2016).
11. Fisher JD, Fisher WA. Changing AIDS-risk behavior. Psychol Bull. (1992) 111(3):455. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.111.3.455
12. Fisher JD, Fisher WA. Theoretical approaches to individual-level change in HIV risk behavior. In: Peterson JL, DiClemente RJ, editors. Handbook of HIV Prevention. New York, NY: Springer (2000). p. 3–55.
13. Fisher WA, Fisher JD. A general social psychological model for changing AIDS risk behavior. In: Pryor JB, Reeder GD, editors. The Social Psychology of HIV Infection. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc. (1993). p. 127–53.
14. Fisher WA, Fisher JD. Understanding and promoting sexual and reproductive health behavior: theory and method. Annu Rev Sex Res. (1998) 9(1):39–76. doi: 10.1080/10532528.1998.10559926
15. Fisher JD, Fisher WA, Bryan AD, Misovich SJ. Information-motivation-behavioral skills model-based HIV risk behavior change intervention for inner-city high school youth. Health Psychol. (2002) 21(2):177. doi: 10.1037/0278-6133.21.2.177
16. SJ M. A measure of AIDS prevention information, motivation, behavioral skills, and behavior. In: Davis CM, editor. Handbook of Sexuality-Related Measures. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications (1998) p. 328–37.
17. Kline RB. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling. New York, NY: Guilford Publications (2023).
18. Teo T, Knine M. Structural Equation Modeling in Educational Research: Concepts and Applications. Rotterdam: Sense Publishers (2009).
19. Fisher WA, Williams SS, Fisher JD, Malloy TE. Understanding AIDS risk behavior among sexually active urban adolescents: an empirical test of the information–motivation–behavioral skills model. AIDS Behav. (1999) 3:13–23. doi: 10.1023/A:1025411317851
20. Fisher JD, Fisher WA, Williams SS, Malloy TE. Empirical tests of an information-motivation-behavioral skills model of AIDS-preventive behavior with gay men and heterosexual university students. Health Psychol. (1994) 13(3):238. doi: 10.1037/0278-6133.13.3.238
21. Jahanfar S, Nouhjah S. The prevalence of sexual abstinence and its predictors in American university students: a school-based cross-sectional study. J Midwifery Reprod Health. (2021) 9(4):9–15.
22. Obsa AG, Weldihanes B. Knowledge and self-efficacy on HIV/AIDS among undergraduate students of Madda Walabu University, southeast Ethiopia. Glob J Hum Social Sci G Ling Educ. (2017) 17(1):17–20.
23. Fisher JD, Fisher WA, Misovich SJ, Kimble DL, Malloy TE. Changing AIDS risk behavior: effects of an intervention emphasizing AIDS risk reduction information, motivation, and behavioral skills in a college student population. Health Psychol. (1996) 15(2):114. doi: 10.1037/0278-6133.15.2.114
24. Shamu S, Khupakonke S, Farirai T, Slabbert J, Chidarikire T, Guloba G, et al. Knowledge, attitudes and practices of young adults towards HIV prevention: an analysis of baseline data from a community-based HIV prevention intervention study in two high HIV burden districts, South Africa. BMC Public Health. (2020) 20:1–10. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-09356-3
25. Bazargan M, Kelly EM, Stein JA, Husaini BA, Bazargan SH. Correlates of HIV risk-taking behaviors among African-American college students: the effect of HIV knowledge, motivation, and behavioral skills. J Natl Med Assoc. (2000) 92(8):391.10992684
26. Anderson ES, Wagstaff DA, Heckman TG, Winett RA, Roffman RA, Solomon LJ, et al. Information-motivation-behavioral skills (IMB) model: testing direct and mediated treatment effects on condom use among women in low-income housing. Ann Behav Med. (2006) 31(1):70–9. doi: 10.1207/s15324796abm3101_11
27. Bazargan M, Stein JA, Bazargan-Hejazi S, Hindman DW. Using the information-motivation behavioral model to predict sexual behavior among underserved minority youth. J School Health. (2010) 80(6):287–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1746-1561.2010.00503.x
28. Fisher WA, Fisher JD, Harman J. The information-motivation-behavioral skills model: a general social psychological approach to understanding and promoting health behavior. In: Suls J, Wallston KA, editors. Social Psychological Foundations of Health and Illness. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing (2003). p. 82–106. doi: 10.1002/9780470753552.ch4
29. Fisher WA, Fisher JD, Shuper PA. Social psychology and the fight against AIDS: an information–motivation–behavioral skills model for the prediction and promotion of health behavior change. In: Olson J, Zanna M, editors. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology. Vol. 50. Amsterdam: Elsevier (2014). p. 105–93.
30. Akello KO, Ogendi J, Asweto CO. The role of knowledge and attitude on HIV and aids prevention practices among secondary school students: a cross-sectional study of Gwassi south sub-county, Homa bay county, Kenya. medRxiv [Preprint]. (2023). doi: 10.1101/2023.01.10.23284403
Keywords: IMB model, HIV risk reduction, safer sexual dual protection behavior, consistent condom use, dual protection use, female university students
Citation: Feyisa BN, Debelew GT and Koricha ZB (2025) Predictors of dual protection use based on information-motivation-behavior skill model among female university students: a cross-sectional study. Front. Reprod. Health 7:1407854. doi: 10.3389/frph.2025.1407854
Received: 24 April 2024; Accepted: 23 July 2025;
Published: 14 August 2025.
Edited by:
Sarosh Iqbal, Forman Christian College, PakistanReviewed by:
Eustachio Cuscianna, University of Bari Aldo Moro, ItalyHaithem Taha Mohammed Ali, University of Zakho, Iraq
Copyright: © 2025 Feyisa, Debelew and Koricha. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Banti Negero Feyisa, bmFnYXJvX2JAeWFob28uY29t
 Banti Negero Feyisa
Banti Negero Feyisa Gurmesa Tura Debelew1
Gurmesa Tura Debelew1 Zewdie Birhanu Koricha
Zewdie Birhanu Koricha