- 1Department of Urology, Taizhou Central Hospital (Taizhou University Hospital), Taizhou, Zhejiang, China
- 2Department of Urology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
- 3Department of Urology, The First People’s Hospital of Pinghu, Pinghu, Zhejiang, China
Background: Chronic prostatitis type IIIb/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS) poses significant therapeutic challenges. This study aimed to investigate and compare the clinical efficacy and safety of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) versus tamsulosin for treating CP/CPPS.
Methods: In this randomized controlled trial, 65 patients with CP/CPPS were allocated to two groups. Group A (n = 35) received LIPUS treatment twice weekly, while Group B (n = 30) received tamsulosin sustained-release capsules (0.2 mg, once nightly). The treatment duration was four weeks for all patients. Outcomes were assessed using the National Institutes of Health Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI), Self-Rating Anxiety Scale (SAS), and International Index of Erectile Function-5 (IIEF-5) at baseline and 4 weeks post-intervention.
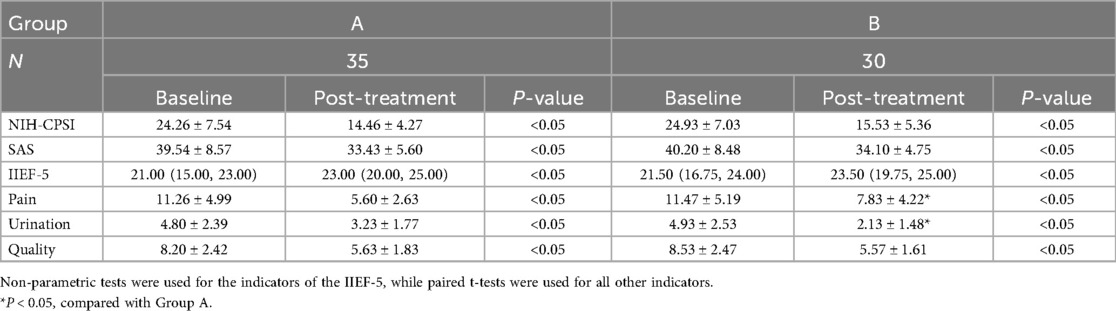
Results: After 4 weeks, both groups showed significant improvements in all NIH-CPSI domains (pain, urinary, quality of life), SAS, and IIEF-5 scores compared to baseline (all P < 0.05). Group A demonstrated significantly greater improvement in pain symptoms than Group B (P < 0.05), whereas Group B showed superior improvement in urinary symptoms compared to Group A (P < 0.05). No statistically significant differences were found between the groups for the remaining symptom domains (P > 0.05).
Conclusion: Both LIPUS and tamsulosin significantly alleviated CP/CPPS-related symptoms with a favorable safety profile. LIPUS was more effective for pain relief, while tamsulosin was superior for urinary symptoms. Combination therapy may represent a promising approach for managing CP/CPPS.
Introduction
Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS) is a frequently encountered urological condition marked by persistent discomfort in the pelvic region, manifestations of lower urinary tract dysfunction (LUTS), and impairments in sexual function.This condition poses significant clinical challenges due to its high incidence, recalcitrant nature, and frequent recurrence (1). Epidemiological data indicate that CP/CPPS affects an estimated 6%–33% of the male population in China (2). Multifactorial pathogenesis involving subclinical pathogen colonization,neurogenic inflammation, and pelvic floor myofascial dysfunction (3).
Conventional management of CP/CPPS primarily involves pharmacotherapy (tailored to symptomatology and history) supplemented by general measures such as lifestyle modifications. However, suboptimal treatment outcomes and high relapse rates persist as major therapeutic challenges in urological practice (4). Emerging physical modalities, including extracorporeal shockwave therapy and therapeutic ultrasound, have gained increasing attention as potential treatments in recent years (5).
Current first-line pharmacotherapy employs α1-adrenoceptor antagonists (e.g., tamsulosin) to reduce functional urethral resistance by 40%–60% through selective α1a-subtype inhibition. However, >50% of patients experience recurrence within 1 year (6). Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) represents a non-invasive, safe form of microenergy therapy defined by its low acoustic intensity and pulsed emission profile. While LIPUS application for treating mild-to-moderate erectile dysfunction (ED) is maturing-supported by multicenter Chinese clinical trials demonstrating efficacy in improving erectile function and reversing pathological changes in the corpus cavernosum (7), its utility for CP/CPPS requires rigorous validation.
Chronic prostatic inflammation constitutes a key pathological feature of CP/CPPS. Preclinical studies have established LIPUS's anti-inflammatory potential, evidenced by its inhibition of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced phosphorylation of key protein kinases (ERK, p38 MAPK, Akt) and attenuation of TLR4 signal transduction in target cells (8). This mechanistic insight provides a sound rationale for exploring LIPUS in CP/CPPS. Consequently, this randomized controlled trial seeks to evaluate and contrast the therapeutic effectiveness and safety of LIPUS in comparison with tamsulosin sustained-release capsules among individuals diagnosed with CP/CPPS, primarily aiming to alleviate and manage symptoms associated with this condition.
Materials and methods
Study population
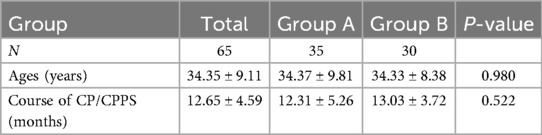
A total of 65 patients with NIH Category III CP/CPPS were consecutively enrolled from the Department of Urology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine and Pinghu First People's Hospital between January 2022 and December 2024, aged 18–56 years.
Selection criteria
Inclusion criteria required: (i) diagnosis of CP/CPPS per NIH classification with persistent clinical symptoms for >3 months, (ii) absence of concurrent therapies (e.g., antibiotics, extracorporeal shockwave treatment) during the intervention period, (iii) provision of written informed consent.
Exclusion criteria required: (i) documented hypersensitivity to tamsulosin sustained-release or renal impairment, (ii) confounding urological conditions: benign prostatic hyperplasia, active urinary tract infections, neurogenic bladder, or urolithiasis, (iii) perineal anatomical abnormalities or prior pelvic surgery/radiotherapy, (iv) diagnosed coagulopathies or thrombotic disorders.
Study protocol
According to the inclusion criteria, 65 patients with CP/CPPS were recruited from outpatient clinics and randomly allocated to two groups: Group A received LIPUS (twice weekly for four weeks), while Group B was administered tamsulosin hydrochloride (0.2 mg sustained-release capsules orally once daily at bedtime for four weeks). All patients documented NIH-CPSI scores, SAS scores, IIEF-5 scores, and recorded adverse events before and after the 4-week intervention.
LIPUS therapy application
Transperineal LIPUS therapy was delivered using a Y-shaped (circular) probe (WBL-ED device, Beijing WBL Medical Equipment Co). The initial treatment session employed an intensity of 300 mW/cm² and escalated to 360 mW/cm² (sessions 2–8) to mitigate treatment adaptation. Patients were positioned supine with hips abducted and flexed. The probe was oriented perpendicular to the perineal body midpoint (2 cm anterior to anus, 1 cm posterior to scrotum) with ultrasound gel.Each session lasted approximately 20 min, administered twice weekly (with 1–2-day intervals) over four weeks, totaling eight sessions.
Statistical analysis
GraphPad Prism software (Version 10.0.2) was used for all statistical analyses. Data normality was evaluated using the Shapiro–Wilk test. Continuous variables conforming to normal distribution were reported as mean ± SD. Pre-post changes within each group were examined with paired t-tests. A two-sided P < 0.05 indicated statistical significance. All continuous variables not following a normal distribution were presented as median (25th percentile, 75th percentile). Where normality or homogeneity of variance assumptions were violated, non-parametric tests (Wilcoxon signed-rank for intragroup) were implemented at P < 0.05.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Boards (IRB) of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine (approval no. 20220367) and The First People's Hospital of Pinghu (approval no. 2023088). Written informed consent was obtained from all participants prior to enrollment. The trial was registered with the Chinese National Medical Research Registration Filing Information System (registration number: MR-33-25-055872).
Results
Patients' information
A total of 65 patients were enrolled, The mean age of the patients was 34.36 ± 9.04 years (range: 18–56 years), The mean disease duration was 12.64 ± 4.56 months (range: 3–26 months).No statistically significant differences in baseline characteristics (including age, disease duration) were observed between the intervention and control groups (P > 0.05), confirming cohort comparability at enrollment (Table 1).
NIH-CPSI scores
No significant intergroup difference in baseline NIH-CPSI scores was observed before intervention. After 4 weeks of treatment, both groups exhibited statistically significant improvements in all NIH-CPSI domains (pain, urinary, and quality of life (QoL); P < 0.05). Notably, Group A demonstrated significantly greater improvement in pain domains than Group B, whereas Group B showed superior amelioration in urinary domains compared to Group A (Table 2).
IIEF-5 scores
After 4 weeks of treatment, both groups exhibited statistically significant increases in IIEF-5 scores from baseline (P < 0.05). No significant intergroup difference in IIEF-5 scores improvement was observed (P > 0.05) (Table 2).
SAS scores
Post-treatment SAS scores showed significant reductions from baseline in both groups (P < 0.05). The magnitude of SAS score reduction was comparable between groups, with no statistical significance (P > 0.05) (Table 2).
Safety
Two adverse events (AEs) occurred in Group A, transient perineal pain during initial treatment in two cases, both self-resolved without intervention, One AE of mild dizziness occurred in Group B and resolved after rest, None of the three adverse events interrupted the treatment course.
Discussion
CP/CPPS poses a significant clinical challenge in urology, attributable to its complex pathophysiology and the limited efficacy of existing therapies that primarily target symptom alleviation and quality-of-life enhancement (4, 9). Among pharmacotherapeutic options, antibiotic use remains contentious, with contemporary guidelines predominantly contraindicating their administration in non-inflammatory CP/CPPS (1, 10). In contrast, α-adrenergic receptor antagonists, such as tamsulosin, constitute a cornerstone for managing LUTS (11). Concurrently, LIPUS has emerged as a promising modality within “microenergy medicine”.LIPUS is characterized by minimal thermal effects and reliance on non-thermal bioeffects—acoustic cavitation, acoustic streaming, and enhanced mass transfer—to drive mechanotransduction-mediated biological responses (12). These bioeffects collectively suppress inflammation through inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced phosphorylation of ERK/p38/Akt kinases and TLR4 signaling, concomitantly regulating matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) activity, promoting stem cell differentiation, and stimulating neurovascular regeneration (8, 13–15). Nevertheless, clinical validation is constrained, as evidenced by Li et al.'s randomized trial involving 60 patients with comorbid ED and CP/CPPS (16). Against this backdrop of unmet clinical needs and evolving therapeutic concepts, we conducted the present randomized controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy of LIPUS vs. the standard pharmacologic agent, tamsulosin.
This randomized controlled trial enrolled 65 patients with CP/CPPS. Both four-week therapeutic regimens—LIPUS and tamsulosin sustained-release—significantly improved pain, urinary, QoL, SAS scores and IIEF-5 scores compared to baseline (all P < 0.05).The key finding of this study is the distinct therapeutic profile of each intervention: while both modalities significantly improved overall symptoms, tamsulosin demonstrated superior efficacy in alleviating urinary symptoms (P < 0.05), whereas LIPUS was significantly more effective in reducing pelvic pain (P < 0.05). This differential effect suggests that these treatments may target distinct pathophysiological pathways underlying CP/CPPS.
The superior improvement in urinary symptoms observed with tamsulosin aligns with established clinical practice and pharmacological principles (11). As a selective α1-adrenergic receptor antagonist, tamsulosin primarily acts by relaxing smooth muscle in the prostate and bladder neck, thereby reducing dynamic obstruction and improving urinary flow (6). Our findings thus reinforce the role of alpha-blockers as a cornerstone for managing LUTS in CP/CPPS patients, consistent with current guideline recommendations (1, 11).
Within urology, LIPUS has demonstrated therapeutic efficacy for ED as evidenced by reversal of cavernosal pathology in multicenter randomized trials (7). In our study, we demonstrated that LIPUS treatment resulted in significant pain relief, which aligns with previous mechanistic studies indicating that LIPUS may alleviate inflammation and reduce pain by downregulating inflammatory mediators such as COX-2 and IL-1β (6, 16, 17).
Both therapies yielded comparable improvements in QoL, anxiety (SAS), and ED (IIEF-5). This suggests that benefits in these secondary domains may be contingent upon the alleviation of core symptoms, namely pain and urinary disturbances (18, 19). The strong comorbidity between pain, anxiety, and sexual health in CP/CPPS has been substantiated by recent epidemiological studies (20, 21). Consequently, our results reinforce the validity of the biopsychosocial model and the UPOINT phenotyping system, which advocate for a multidimensional assessment and tailored management strategy (22). The incorporation of SAS and IIEF-5 scales in our trial aligns with this modern, patient-centered approach, allowing for a comprehensive evaluation of treatment efficacy beyond core urological symptoms.
This prospective dual-center clinical trial investigated LIPUS therapy for CP/CPPS. Despite its randomized controlled design, limitations include prolonged intervention durations, modest cohort size (n = 65), and inadequate longitudinal monitoring (>6 months), which may introduce selection bias and limit generalizability. Consequently, validation via large-scale, multi-center randomized trials is imperative. The data suggest the potential for the combination of LIPUS and tamsulosin sustained-release to offer improved management of CP/CPPS symptoms (pain and urinary). Furthermore, optimization of LIPUS treatment protocols—specifically energy intensity, session duration, and therapeutic scheduling—may potentiate LIPUS-mediated anti-inflammatory and neuromodulatory effects, thereby enhancing symptom management and quality-of-life improvement. However, rigorously designed randomized controlled trials are warranted to validate the long-term efficacy and safety of this combined approach.
Conclusion
LIPUS and tamsulosin sustained-release capsules exhibit significant clinical efficacy in ameliorating CP/CPPS-related symptoms, with both interventions demonstrating favorable safety profiles. LIPUS was more effective for pain relief, while tamsulosin showed greater benefit for LUTS.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by This study was approved by the Institutional Review Boards (IRB) of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine (approval no. 20220367) and The First People's Hospital of Pinghu (approval no. 2023088). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
JH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. ZL: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. SZ: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. BL: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. KL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Zhejiang Medical Science and Technology Plan Project (Grant Number: 2024XY173).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/frph.2025.1714803/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Borgert BJ, Wallen EM, Pham MN. Prostatitis: a review. JAMA. (2025) 334(11):1003–13. doi: 10.1001/jama.2025.11499
2. Mi H, Chen K, Mo ZN. Epidemiological characteristics of chronic prostatitis in China. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. (2012) 18(7):579–82.22994040
3. Khan FU, Ihsan AU, Khan HU, Jana R, Wazir J, Khongorzul P, et al. Comprehensive overview of prostatitis. Biomed Pharmacother. (2017) 94:1064–76. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.08.016
4. Lai HH, Pontari MA, Argoff CE, Bresler L, Breyer BN, Chou R, et al. Male chronic pelvic pain: aUA guideline: part II treatment of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. J Urol. (2025) 214(2):127–37. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000004565
5. Kim KS, Choi YS, Bae WJ, Cho HJ, Ha U-S, Hong S-H, et al. Clinical efficacy of multi-focal low-intensity extracorporeal shockwave therapy in the treatment of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: prospective-randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled study. World J Mens Health. (2022) 40(4):678–85. doi: 10.5534/wjmh.210078
6. Akinaga J, García-Sáinz JA, Pupo AS. Updates in the function and regulation of α1 -adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. (2019) 176(14):2343–57. doi: 10.1111/bph.14617
7. Cui W, Li H, Guan R, Li M, Yang B, Xu Z, et al. Efficacy and safety of novel low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) in treating mild to moderate erectile dysfunction: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, sham-controlled clinical study. Transl Androl Urol. (2019) 8(4):307–19. doi: 10.21037/tau.2019.07.03
8. Lin G, Reed-Maldonado AB, Lin M, Xin Z, Lue TF. Effects and mechanisms of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound for chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Int J Mol Sci. (2016) 17(7):1057. doi: 10.3390/ijms17071057
9. Magistro G, Wagenlehner FM, Grabe M, Weidner W, Stief CG, Nickel JC. Contemporary management of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Eur Urol. (2016) 69(2):286–97. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2015.08.061
10. Rees J, Abrahams M, Doble A, Cooper A. Prostatitis expert reference group (PERG). diagnosis and treatment of chronic bacterial prostatitis and chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: a consensus guideline. BJU Int. (2015) 116(4):509–25. doi: 10.1111/bju.13101
11. Deng W, Du X, Zhou W, Mei X, Tian Y, Chen L, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis: α-adrenergic receptor blockers in chronic prostatitis. Ann Palliat Med. (2021) 10(9):9870–8. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-2160
12. Xin Z, Lin G, Lei H, Lue TF, Guo Y. Clinical applications of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound and its potential role in urology. Transl Androl Urol. (2016) 5(2):255–66. doi: 10.21037/tau.2016.02.04
13. Nakamura T, Fujihara S, Yamamoto-Nagata K, Katsura T, Inubushi T, Tanaka E. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound reduces the inflammatory activity of synovitis. Ann Biomed Eng. (2011) 39(12):2964–71. doi: 10.1007/s10439-011-0408-0
14. Ye K, Li Z, Yin Y, Zhou J, Li D, Gan Y, et al. LIPUS-SCs-Exo promotes peripheral nerve regeneration in cavernous nerve crush injury-induced ED rats via PI3K/akt/FoxO signaling pathway. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2023) 29(11):3239–58. doi: 10.1111/cns.14256
15. Piotrzkowska D, Siwak M, Adamkiewicz J, Dziki L, Majsterek I. The therapeutic potential of pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMF) and low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) in peripheral nerve regeneration: a comprehensive review. Int J Mol Sci. (2025) 26(19):9311. doi: 10.3390/ijms26199311
16. Li Z, Li D, Zu X, Xiang B, Wang G, Tang Z. Evaluation of efficacy and safety of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound in patients with concurrent erectile dysfunction and chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: a prospective, randomized controlled study. BMC Urol. (2024) 24(1):232. doi: 10.1186/s12894-024-01630-5
17. Iwabuchi Y, Tanimoto K, Tanne Y, Inubushi T, Kamiya T, Kunimatsu R, et al. Effects of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in mandibular condylar chondrocytes. J Oral Facial Pain Headache. (2014) 28(3):261–8. doi: 10.11607/ofph.1156
18. Song G, Wang M, Chen B, Long G, Li H, Li R, et al. Lower urinary tract symptoms and sexual dysfunction in male: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Med (Lausanne). (2021) 8:653510. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.653510
19. Gao J, Gao P, Hao Z, Zhou Z, Liu J, Li H, et al. Comparison of national institutes of health-chronic prostatitis symptom Index with international Index of erectile function 5 in men with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: a large cross-sectional study in China. Biomed Res Int. (2015) 2015:560239. doi: 10.1155/2015/560239
20. Ma C, Cai Z, Xiong J, Li H. History of prostatitis is an independent risk factor for erectile dysfunction: a cross-sectional study. Biomed Res Int. (2020) 2020:8964673. doi: 10.1155/2020/8964673
21. Li ASW, Van Niekerk L, Wong ALY, Matthewson M, Garry M. Psychological management of patients with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS): a systematic review. Scand J Pain. (2022) 23(1):25–39. doi: 10.1515/sjpain-2022-0049
Keywords: low-intensity pulsed ultrasound, tamsulosin sustained-release, chronic prostatitis type IIIb/chronic pelvic pain syndrome, efficacy, safety
Citation: Huang J, Liao Z, Zhao S, Lv B and Liang K (2025) Evaluation of a low-intensity pulsed ultrasound for chronic prostatitis type IIIb/chronic pelvic pain syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Front. Reprod. Health 7:1714803. doi: 10.3389/frph.2025.1714803
Received: 28 September 2025; Revised: 7 November 2025;
Accepted: 20 November 2025;
Published: 4 December 2025.
Edited by:
Linlin Sun, Peking University, ChinaReviewed by:
Kamil Nurimanov, State Institution “Academician O.F. Vozianov Institute of Urology of NAMS of Ukraine”, UkraineMustafa Küçükyangöz, TC Saglik Bakanligi Bolu Izzet Baysal Devlet Hastanesi, Türkiye
Copyright: © 2025 Huang, Liao, Zhao, Lv and Liang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bodong Lv, bGJkMTY4QHpqdS5lZHUuY24=; Ke Liang, bGlhbmdrZTc3MTExNkAxNjMuY29t
 Jiahao Huang
Jiahao Huang Zedong Liao2
Zedong Liao2 Shankun Zhao
Shankun Zhao Bodong Lv
Bodong Lv Ke Liang
Ke Liang