- 1Yuxi Normal University, Yuxi, China
- 2Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming, China
- 3Honghe University, Honghe, China
Introduction: Nucleus segmentation plays an essential role in digital pathology,particularly in cancer diagnosis and the evaluation of treatment efficacy. Accurate nucleus segmentation provides critical guidance for pathologists. However, due to the wide variability instructure, color, and morphology of nuclei in histopathological images, automated segmentation remains highly challenging. Previous neural networks employing wavelet-guided, boundary-aware attention mechanisms have demonstrated certain advantages in delineating nuclear boundaries. However, their feature fusion strategies have been suboptimal, limiting overall segmentation accuracy.
Methods: In this study, we propose a novel architecture—the Multi-Scale Wavelet Fusion Attention Network (MSWAFFNet)—which incorporates an Attention Feature Fusion (AFF) mechanism to effectively integrate high-frequency features extracted via 2D Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) from different Unet scales. This approach enhances boundary perception and improves segmentation performance. To address the variation across datasets, we apply a series of preprocessing steps to normalize the color distribution and statistical characteristics, thereby ensuring training consistency.
Results and Discussion: The proposed method is evaluated on three public histopathology datasets (DSB, TNBC, CoNIC), achieving Dice coefficients of 91.33%, 80.56%, and 91.03%, respectively—demonstrating superior segmentation performance across diverse scenarios.
1 Introduction
In recent years, deep learning has achieved remarkable success and significantly enhanced medical imaging performance. Beyond improving image quality, deep learning has also enabled novel capabilities such as image classification, segmentation, and cross-modality image translation. Numerous studies have leveraged automated approaches to assist in diagnosis and address specific challenges across various medical imaging modalities. The rapid advancement of image processing techniques based on convolutional neural networks (CNNs) has revolutionized both medical diagnostics and treatment planning. From identifying complex patterns in clinical images to accurately segmenting lesion areas, neural network–based methods have become indispensable tools in modern healthcare. Histopathology, as a critical component of medical diagnostics, has also benefited substantially from deep learning advancements. Nevertheless, existing models still require further optimization to improve generalization and ensure robust performance across diverse clinical scenarios.
Nucleus segmentation in histopathological images is a crucial step in the analysis of microscope-acquired data. The quality of these images and the effectiveness of their processing significantly impact medical decision-making, enabling earlier diagnoses and potentially reducing the cost of subsequent treatments (Krupinski, 2000; Galić et al., 2023). Due to the inherent complexity of this task, automating the segmentation process remains challenging. In this context, deep learning frameworks have gained increasing popularity (Xu et al., 2023). However, nucleus segmentation must address several difficulties, including variations in image quality across different microscopes, diverse staining protocols, blurred cell boundaries, intensity heterogeneity across cancer subtypes, and the close proximity or overlapping of nuclei in histopathological images (Mouelhi et al., 2018). Among deep learning–based segmentation approaches, U-Net architectures remain the most widely adopted (Al Qurri and Almekkawy, 2023). For instance, U-Net achieves high accuracy on classical benchmark datasets (Castro et al., 2024), but its performance degrades considerably on more complex or varied datasets (Azad et al., 2024). To improve performance, a Fast U-Net (FU-Net) was proposed in (Olimov et al., 2021), which redesigned the encoder of the traditional U-Net by introducing bottleneck convolutional layers into both encoder and decoder branches, improving computational efficiency and segmentation accuracy. Nevertheless, accurate nucleus segmentation remains difficult, particularly in separating clustered or overlapping nuclei in microscopic images (Gehlot et al., 2020). One major limitation of U-Net–based networks arises from the downsampling process, where operations such as max or average pooling often violate the Nyquist sampling theorem. This can result in the loss of high-frequency detail and distortion of structural information in the low-frequency domain (Wang et al., 2024). To preserve image details, several studies have explored using Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) as a replacement for traditional pooling layers (Williams and Li, 2018). More recent architectural advancements include HanNet (H et al., 2021), a hybrid attention nested U-Net incorporating dense connections for improved feature representation. In (Vahadane et al., 2021), a dual-encoder attention U-Net was proposed, introducing a secondary encoder to better capture attention-relevant features. A multitask U-Net variant was introduced in (Zhao et al., 2021), where a context encoding layer was applied after each encoder and its output was fused with decoder features using attention mechanisms. Another enhancement was proposed in (Lal et al., 2021), where residual blocks were added to extract high-level semantic features, coupled with attention mechanisms to improve decoding. Building upon these developments, Imtiaz et al. (2023) proposed a boundary-aware, wavelet-guided network that combines encoder and decoder information via attention while generating explicit boundary cues. This approach helped preserve fine structural details and small nuclei, and the incorporation of wavelet features led to improved segmentation performance over prior methods.
While feature fusion is widely adopted in deep learning–based segmentation models, it is not universally suitable across all scenarios (Dai et al., 2021). Simple fusion strategies such as direct addition or concatenation often lack adaptability to spatial variation and semantic heterogeneity, particularly in histopathological images where nuclei are densely packed or overlapping. These fixed strategies may dilute critical high-frequency boundary information or amplify irrelevant noise, ultimately compromising segmentation accuracy. Previous studies such as (Li et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2022) have focused on soft feature selection within single layers, leaving cross-layer fusion—especially via skip connections—largely unaddressed. This limitation also extends to U-Net variants that incorporate discrete wavelet feature extraction (Imtiaz et al., 2023). Moreover, in attention-based modules, the success of feature fusion heavily relies on accurately learning fusion weights across multi-scale representations. Although wavelet transforms help preserve high-frequency boundary features, the subsequent fusion and utilization of these features remain suboptimal in many existing frameworks.
To address the limitations of existing segmentation methods, we propose a novel architecture called the Multi-Scale Wavelet Attention Feature Fusion Network (MSWAFFNet). Prior to feeding data into the network, we apply a comprehensive preprocessing pipeline designed to mitigate data diversity issues and normalize color distribution across different image modalities. In contrast to traditional skip connection strategies and conventional feature aggregation units, our approach performs separate fusion of wavelet-based features and boundary-aware features at multiple scales. This design enhances the model’s ability to capture fine-grained structural information. To validate the effectiveness and generalizability of our method, we conducted extensive experiments on three publicly available datasets. These datasets encompass a large number of histopathological images from various organs and disease types, thereby ensuring a robust assessment of cross-dataset generalization performance.
2 Materials and methods
In this section, the proposed method is described in detail, including the preprocessing steps, the overall network architecture, the boundary wavelet attention module, and the feature fusion module. The model proposed in this paper uses U-Net as the backbone network and incorporates a boundary wavelet-aware attention module and a multi-scale attention fusion module to extract and integrate boundary information into the U-Net through an attention mechanism. The overall structure is shown in Figure 1.
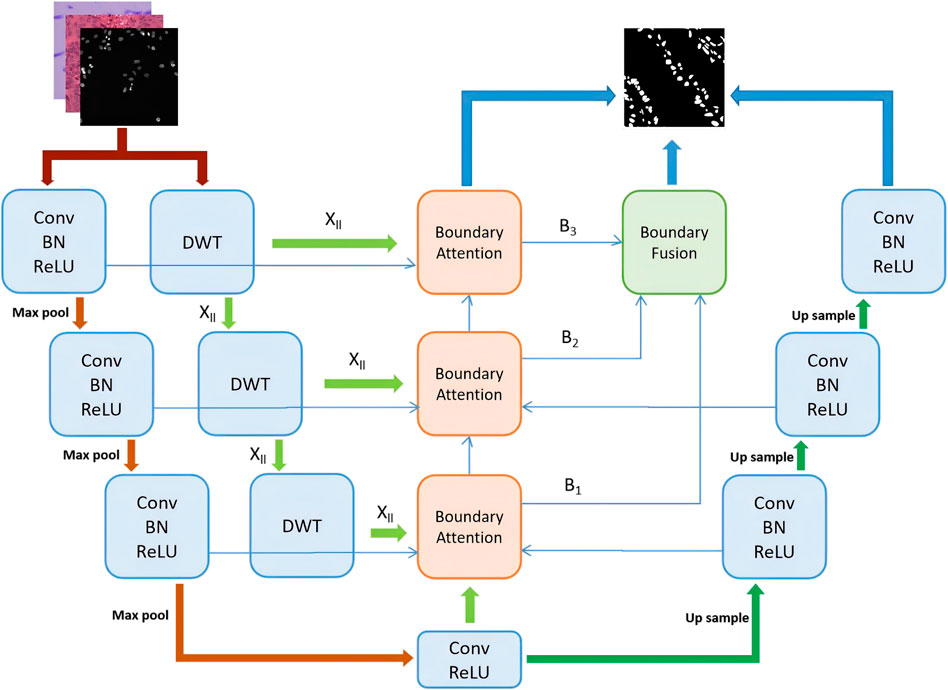
Figure 1. The structure of MSWAFFNet. The basic U-Net includes three downsampling layers and three upsampling layers. In each downsampling step, DWT is used to extract wavelet boundary information, which is then fused into boundary information through a fusion module. Subsequently, all different wavelet boundary information is upsampled and fused through an attention fusion mechanism. Finally, the ultimate output is obtained by combining all the outputs.
2.1 Preprocessing
Since we use several very different datasets, it is necessary to normalize them using appropriate methods. Effective preprocessing can significantly improve the prediction results. Due to the differences between the datasets, it is essential to process them to have similar characteristics for training.
In the experiments, three main preprocessing steps were primarily used. First, basic image augmentation techniques were employed to increase the amount of training data for the supervised deep neural network (Maharana et al., 2022). The most common forms of augmentation include flipping, rotation, adding noise, and random cropping. By representing a broader range of potential data points, the augmented data narrows the gap between the training set, validation set, and any upcoming test sets, thereby enhancing the performance of the neural network.
The second preprocessing step is color intensity level transformation, which can make datasets from different sources more uniform, providing users with a comparable view of data from different studies or modalities (Nan et al., 2022). By transforming the intensity levels to a similar visual appearance, it reduces the side effects that might be introduced by different modalities in the model.
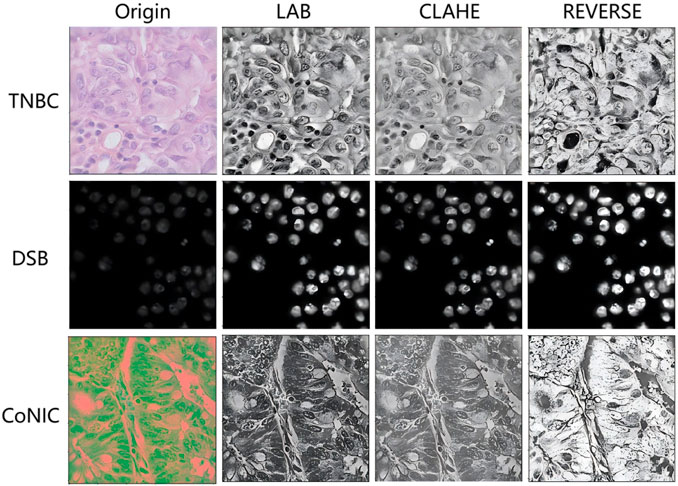
Finally, a combination of contrast enhancement and color inversion techniques was used (Reza, 2004) to produce the final images for the training set to be fed into the network. Contrast enhancement increases the contrast between the darkest and brightest regions of the image, thereby enhancing visibility and the ability to see fine details. On the other hand, color inversion describes the reversal of brightness values in the color transitions within the image. In Figure 2, we provide an example of the effect of image preprocessing, where different images are transformed into more consistent black-and-white images, thus reducing the difficulty of model training.
2.1.1 Intensity level transformation
One of the key issues in the nucleus segmentation task is the generalization performance of the model to different image modalities. Due to their variations in visual appearance and intensity levels, it is challenging to train a universal model that performs equally well on both modalities. Therefore, we adopted color intensity transformation to normalize the datasets first, thereby reducing the difficulty of training the network. To achieve this, we used the LAB color space transformation scheme (Gonzales and Wintz, 1987). The LAB color space, defined by the International Commission on Illumination, represents colors as three values: L for perceived lightness, and A and B for the four unique colors in human vision: red, green, blue, and yellow. Converting all three-channel images to the LAB color space helps preserve the original structure and maintains similar brightness and color statistical levels by leveraging the uniformity of data characteristics.
2.1.2 Contrast enhancement and inversion
Typically, nuclei in cellular space have small regions that may be overlooked by algorithms. Therefore, contrast enhancement is a crucial step to improve the visibility of small nucleus regions. In this method, Contrast-Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization (CLAHE) is applied to enhance the contrast of histopathological images (Reza, 2004). By limiting the contrast, it provides better equalization and reduces the problem of noise amplification. Generally, in both modalities, brightfield images are primarily used in clinical settings. Thus, a color inversion operation is performed on all images to shift the intensity levels of fluorescence histopathological images, as their overall intensity levels are much higher than those of brightfield histopathological images. The inversion process
2.2 Boundary wavelet-aware attention
Boundary Wavelet-Aware Attention (BWA) is divided into two parts: Wavelet Guided Attention Unit (WGAU) and Boundary Aware Unit (BAU), as shown in Figure 3. This mechanism first extracts image information at different frequencies using Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT). The 2D-DWT uses Multi-Resolution Analysis (MRA) to transform a 2D signal into a series of wavelet coefficients at various scales and orientations (Mallat, 1989). Each level of decomposition receives a set of coefficients as a result of applying MRA to the rows and columns of the 2D signal. The low-pass filtered signal is subtracted from the original signal, leaving only the high-pass filtered signal to produce the wavelet coefficient
where
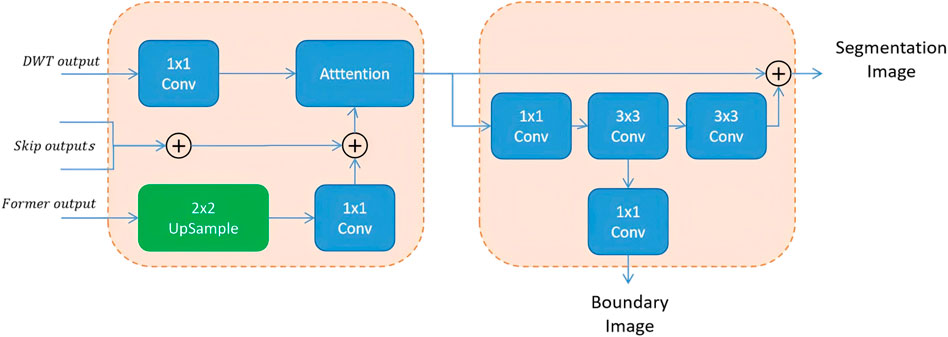
The second part, BAU, adds a side branch to the output that has been processed through summation and attention mechanisms, to additionally output a boundary information map. Since aggregation modules are added at different levels of the U-Net, each level outputs a boundary map at a different scale. Therefore, upsampling is used to fuse these maps and obtain the final boundary-aware map.
However, when the BAU block fuses the multi-scale boundary-aware maps, it uses a very simple summation method. Although this simple attention-based approach can achieve improved perception of multi-scale features and better results after feature fusion, it still has several drawbacks.
2.3 Multi-Scale Boundary Fusion Module
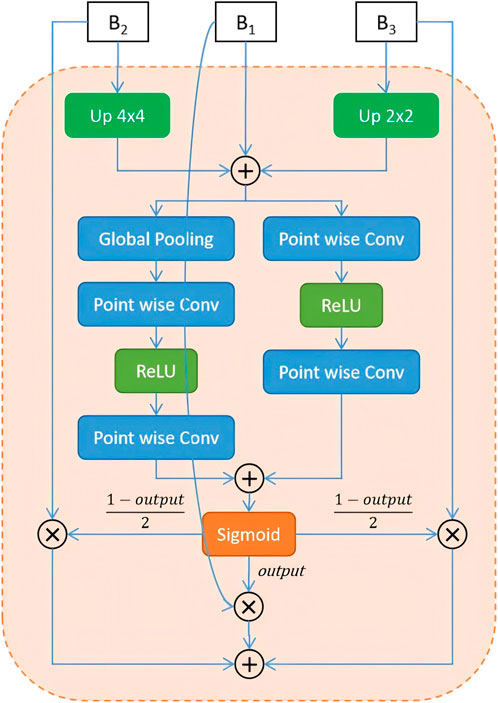
To address the limitations of traditional fusion strategies—such as direct addition or concatenation—which often fail to adaptively integrate multi-scale features, Dai et al. (2021) proposed the Attention Feature Fusion (AFF) mechanism. AFF has since shown strong performance in various vision tasks by extending attention-based fusion from same-level to cross-level scenarios, including both short and long skip connections (Fu et al., 2022). Motivated by these advances and the need to better preserve boundary information, we adopt and further enhance the AFF framework in our model. Specifically, after extracting high-frequency boundary cues through the Boundary-Aware Wavelet (BAW) module, we apply AFF to adaptively fuse multi-scale features rather than relying on fixed operations such as addition or concatenation. In our implementation, global channel attention is obtained via global average pooling, while local channel attention is captured using point-wise convolutions. These two attention maps are then combined to generate adaptive fusion weights that guide the integration of boundary-aware and wavelet-enhanced features. This design enables our model to better emphasize discriminative regions, particularly around cell contours. The complete structure of the AFF-based boundary fusion module is shown in Figure 4.
3 Results and discussion
In this section, we introduce the datasets used in the experiments and their sources, and then present the experimental setup conditions and results.
3.1 Dataset
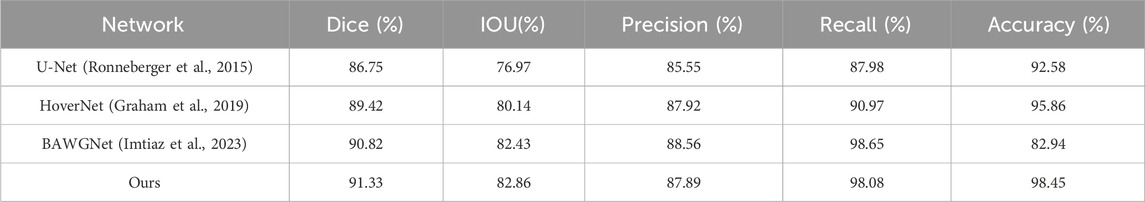
To validate the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm, three public available datasets were used. The first is the Data Science Bowl (DSB-2018) dataset, released by Kaggle for competition purposes (Caicedo et al., 2019). This dataset contains over 37,000 manually annotated nuclei from more than 30 experiments across different samples, cell lines, microscopy instruments, imaging conditions, operators, research facilities and staining protocols. The annotations were manually made by a team of expert biologists. It is one of the earlier and well-annotated datasets with a significant amount of data, and many networks have been tested on this dataset, often achieving good results. The training set of this dataset includes 670 images, with 546 being fluorescence and the rest brightfield. The test set contains 65 images.
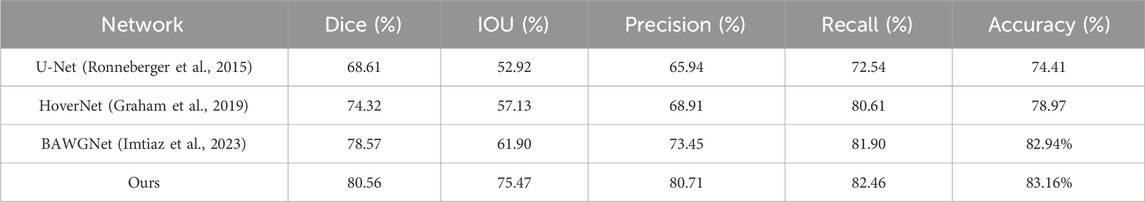
The second dataset is the Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) dataset (Naylor et al., 2018), which consists of 50 images with a total of 4022 annotated cells, including normal epithelial and myoepithelial breast cells, invasive cancer cells, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, adipocytes, macrophages, and inflammatory cells. The image size is 500
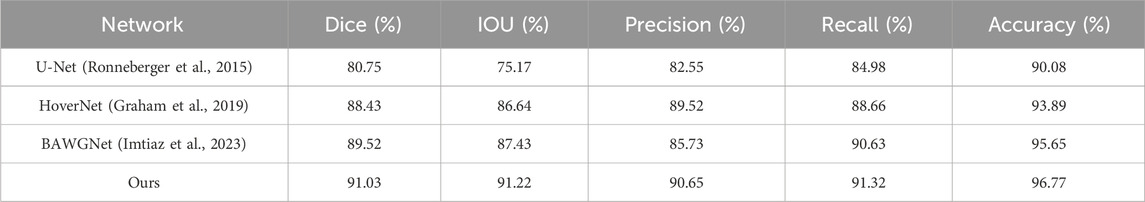
The third dataset is the CoNIC(Lizard dataset) dataset (Graham et al., 2021), which comes from the CoNIC challenge. It includes histological image regions of colon tissue from 6 different dataset sources, with complete segmentation annotations for different types of nuclei. They provided 4,981 patches of size 256
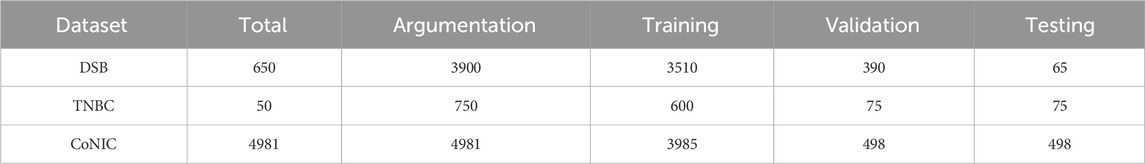
For all datasets, we divided the datasets into training, validation, and testing sets in an 8:1:1 ratio. The DSB dataset provided additional test data, which is also evaluated. Data augmentation techniques, such as rotation, flipping, translation, and cropping, were applied to all datasets. The data used for each dataset is listed in Table 1.
3.2 Experimental setup
For the DSB dataset, where the image sizes are not uniform, all images were first resized to 256
To enable our proposed model to perform the nucleus segmentation task more effectively, different hyperparameters were selected based on empirical analysis. Our model was implemented in TensorFlow 2.15 (Pyhton 3.9) on a Windows system with an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4090 GPU. And the core code can be obtained from https://gitee.com/hu_yang_sheng/mswaffnet.git. To reduce the network’s loss, a learning rate of 0.01 was chosen, along with an SGD optimizer with weight decay values of
Where the TP, TN, FP, and FN represent true positive, true negative, false positive, and false negative predictions, respectively. We trained and tested our model on the three datasets and compared it with state-of-the-art segmentation networks.
3.3 Segmentation and analysis
3.3.1 Ablation study
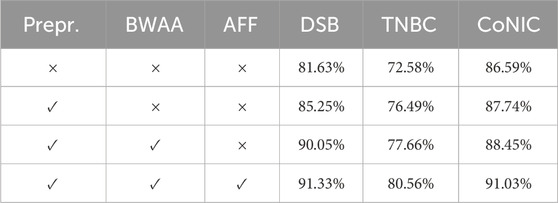
In proposed network, the traditional U-Net architecture is used as the backbone network. Additionally, two modules were incorporated, and their individual and combined performances were compared. In Table 2, we evaluate using the Dice metric. After analyzing the table, it was found that there is an improvement across all three datasets. The preprocessing steps allow for the reduction of intensity variations between cell subtypes and enable the model to distinguish between nucleus and non-nucleus features. When using Boundary Wavelet-Aware Attention, the attention mechanism guides spatial features from the frequency domain information of DWT, which helps in effectively representing features by combining spatial and frequency level information, providing feature maps with fine-scale details. Secondly, the wavelet boundary information is fused using AFF.
3.3.2 Quantitative analysis
To demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method, comparative analyses for the TNBC, DSB, and CoNIC datasets are presented in Tables 3–5, respectively. Compared to existing networks, our network exhibits better performance in the nucleus segmentation task. The robustness and effectiveness of the proposed network are confirmed by high scores in other metrics that can verify the accuracy of nucleus region determination. The proposed network’s capability is enhanced by the additional wavelet domain information provided by wavelet, which is fused using the attention mechanism in attention fusion. Furthermore, with the help of the boundary-aware unit, it can effectively capture small nucleus regions, thereby improving precision and recall. We report the mean and 95% confidence interval of Dice scores based on 5 independent runs. In addition, paired t-tests between our method and baselines show statistically significant improvements (p < 0.01).
Quantitative analysis alone does not always determine the effectiveness and superiority of a method. Figure 5 shows the segmentation performance of different networks, including our proposed network, in some challenging cases. It is evident from the segmentation performance of other networks that all of them struggle with these issues. On the other hand, our proposed method, through its effective utilization of spatial and frequency level information along with boundary information, significantly addresses these challenges and demonstrates its performance notably in the challenging nucleus segmentation task.
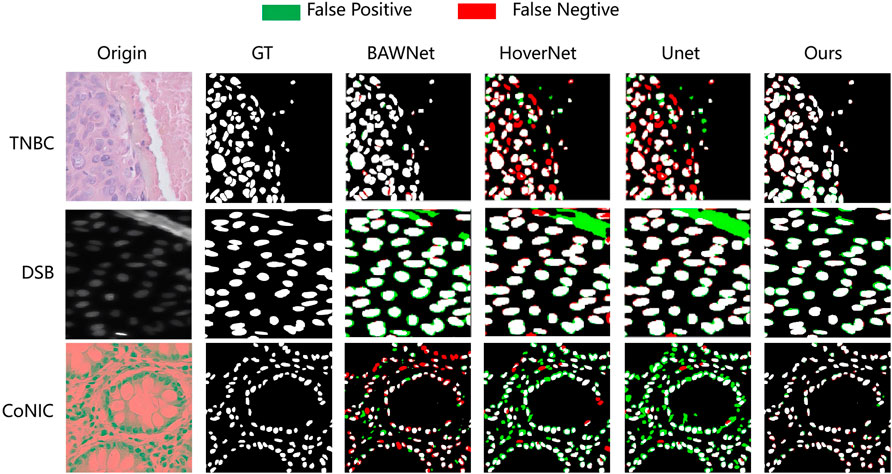
Figure 5. The proposed network visually compares the nucleus segmentation performance of each network in three datasets.
3.3.3 Limitations and future work
Although our model demonstrates superior performance compared to previous methods across the evaluated datasets, it is important to note that these datasets were carefully curated and annotated by expert pathologists. In real-world clinical scenarios, issues such as noise contamination, low-contrast images, and out-of-focus artifacts may still occur. While such conditions may be excluded during model development, they represent inevitable challenges for clinical deployment. Although we employed preprocessing techniques to normalize image appearance—primarily to address differences between fluorescence and H&E stained images—these methods were not specifically designed to handle more complex visual degradations. Another emerging trend is the widespread application of large-scale models (Hörst et al., 2024). Recent studies have begun to explore the use of such models in histopathological image analysis, showing promising progress. In our future work, we plan to build upon these advances and further improve the performance of large models in this domain. And for clinical work, we plan to actively collaborate with hospitals and further investigate advanced preprocessing strategies to enhance the model’s robustness and practicality in real-world clinical environments. In the future, we plan to strengthen collaboration with hospitals, and our follow-up work will focus on two main directions:
1. Refining and improving model performance using real clinical data. Data from different hospitals often exhibit domain-specific variations, which may differ significantly from public datasets. Incorporating such data will help enhance the robustness and generalizability of the model.
2. Engineering integration into real-world clinical workflows. We aim to design a practical deployment pipeline that allows the model to be embedded into pathologists’ routine diagnostic processes, making it easier for clinicians to evaluate and validate the quality of the segmentation results in real time.
4 Conclusion
Accurate nucleus segmentation can provide valuable reference information for pathologists. Although this challenging task has been addressed through various techniques, neural networks based on wavelet-guided boundary-aware attention have shown certain advantages in identifying nucleus boundaries, but their feature fusion performance has not been ideal, limiting the accuracy of segmentation. In this study, we propose a Multi-Scale Wavelet Fusion Attention Network that effectively fuses high-frequency 2D Discrete Wavelet Transform features using an Attention Feature Fusion mechanism to achieve more precise identification of nucleus regions. Additionally, considering the differences between different datasets, we ensured the consistency of training data by transforming them to have similar color statistics. Through experiments conducted on three publicly available pathological datasets, the main performance metrics demonstrate the superiority of our method in accurately segmenting nuclei in cellular microscopic images compared to existing architectures.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The manuscript presents research on animals that do not require ethical approval for their study.
Author contributions
JZ: Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. YH: Validation, Writing – review and editing. ZA: Project administration, Validation, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Project of Ding Zhiming Academician Expert Workstation (No: 202305AF150036). And sponsored by the Opening Foundation of Yunnan Key Laboratory of Smart City in Cyberspace Security (No. 202105AG070010).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Al Qurri, A., and Almekkawy, M. (2023). Improved UNet with attention for medical image segmentation. Sensors 23, 8589. doi:10.3390/s23208589
Azad, R., Aghdam, E. K., Rauland, A., Jia, Y., Avval, A. H., Bozorgpour, A., et al. (2024). Medical image segmentation review: the success of U-Net. IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis Mach. Intell. 46, 10076–10095. doi:10.1109/tpami.2024.3435571
Caicedo, J. C., Goodman, A., Karhohs, K. W., Cimini, B. A., Ackerman, J., Haghighi, M., et al. (2019). Nucleus segmentation across imaging experiments: the 2018 data science bowl. Nat. methods 16, 1247–1253. doi:10.1038/s41592-019-0612-7
Castro, S., Pereira, V., and Silva, R. (2024). Improved segmentation of cellular nuclei using UNET architectures for enhanced pathology imaging. Electronics 13, 3335. doi:10.3390/electronics13163335
Dai, Y., Gieseke, F., Oehmcke, S., Wu, Y., and Barnard, K. (2021). “Attentional feature fusion,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF winter conference on applications of computer vision, 3560–3569.
Fu, B., Zhang, M., He, J., Cao, Y., Guo, Y., and Wang, R. (2022). StoHisNet: a hybrid multi-classification model with CNN and transformer for gastric pathology images. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 221, 106924. doi:10.1016/j.cmpb.2022.106924
Galić, I., Habijan, M., Leventić, H., and Romić, K. (2023). Machine learning empowering personalized medicine: a comprehensive review of medical image analysis methods. Electronics 12, 4411. doi:10.3390/electronics12214411
Gehlot, S., Gupta, A., and Gupta, R. (2020). “Ednfc-net: convolutional neural network with nested feature concatenation for nuclei-instance segmentation,” in ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP), 1389–1393.
Gonzales, R. C., and Wintz, P. (1987). Digital image processing; addison-wesley longman publishing Co., Inc.
Graham, S., Vu, Q. D., Raza, S. E. A., Azam, A., Tsang, Y. W., Kwak, J. T., et al. (2019). Hover-net: simultaneous segmentation and classification of nuclei in multi-tissue histology images. Med. image Anal. 58, 101563. doi:10.1016/j.media.2019.101563
Graham, S., Jahanifar, M., Vu, Q. D., Hadjigeorghiou, G., Leech, T., Snead, D., et al. (2021). CoNIC: colon nuclei identification and counting challenge 2022. arXiv Prepr. arXiv:2111.14485. doi:10.48550/arXiv.2111.14485
He, H., Zhang, C., Chen, J., Geng, R., Chen, L., Liang, Y., et al. (2021). A hybrid-attention nested UNet for nuclear segmentation in histopathological images. Front. Mol. Biosci. 8, 614174. doi:10.3389/fmolb.2021.614174
Hörst, F., Rempe, M., Heine, L., Seibold, C., Keyl, J., Baldini, G., et al. (2024). CellViT: vision transformers for precise cell segmentation and classification. Med. Image Anal. 94, 103143. doi:10.1016/j.media.2024.103143
Imtiaz, T., Fattah, S. A., and Kung, S.-Y. (2023). BAWGNet: boundary aware wavelet guided network for the nuclei segmentation in histopathology images. Comput. Biol. Med. 165, 107378. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.107378
Kha, Q.-H., Tran, T.-O., Nguyen, V.-N., Than, K., and Le, N. Q. K. (2022). An interpretable deep learning model for classifying adaptor protein complexes from sequence information. Methods 207, 90–96. doi:10.1016/j.ymeth.2022.09.007
Krupinski, E. A. (2000). The importance of perception research in medical imaging. Radiat. Med. 18, 329–334.
Lal, S., Das, D., Alabhya, K., Kanfade, A., Kumar, A., and Kini, J. (2021). NucleiSegNet: robust deep learning architecture for the nuclei segmentation of liver cancer histopathology images. Comput. Biol. Med. 128, 104075. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.104075
Li, X., Wang, W., Hu, X., and Yang, J. (2019). “Selective kernel networks,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 510–519.
Maharana, K., Mondal, S., and Nemade, B. (2022). A review: data pre-processing and data augmentation techniques. Glob. Transitions Proc. 3, 91–99. doi:10.1016/j.gltp.2022.04.020
Mallat, S. G. (1989). A theory for multiresolution signal decomposition: the wavelet representation. IEEE Trans. pattern analysis Mach. Intell. 11, 674–693. doi:10.1109/34.192463
Mouelhi, A., Rmili, H., Ali, J. B., Sayadi, M., Doghri, R., and Mrad, K. (2018). Fast unsupervised nuclear segmentation and classification scheme for automatic allred cancer scoring in immunohistochemical breast tissue images. Comput. methods programs Biomed. 165, 37–51. doi:10.1016/j.cmpb.2018.08.005
Nan, Y., Del Ser, Y., Walsh, S., Schönlieb, C., Roberts, M., Selby, I., et al. (2022). Data harmonisation for information fusion in digital healthcare: a state-of-the-art systematic review, meta-analysis and future research directions. Inf. Fusion 82, 99–122. doi:10.1016/j.inffus.2022.01.001
Naylor, P., Laé, M., Reyal, F., and Walter, T. (2018). Segmentation of nuclei in histopathology images by deep regression of the distance map. IEEE Trans. Med. imaging 38, 448–459. doi:10.1109/TMI.2018.2865709
Reza, A. M. (2004). Realization of the contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE) for real-time image enhancement. J. VLSI signal Process. Syst. signal, image video Technol. 38, 35–44. doi:10.1023/b:vlsi.0000028532.53893.82
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., and Brox, T. (2015). “U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation,” in Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18Th international conference, Munich, Germany, October 5-9, 2015, proceedings, part III, 18, 234–241. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Vahadane, A., Atheeth, B., and Majumdar, S. (2021). “Dual encoder attention u-net for nuclei segmentation,” in 2021 43rd annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society (EMBC), 3205–3208.
Williams, T., and Li, R. (2018). “Wavelet pooling for convolutional neural networks,” in International conference on learning representations.
Xu, H., Xu, Q., Cong, F., Kang, J., Han, C., Liu, Z., et al. (2023). Vision transformers for computational histopathology. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 17, 63–79. doi:10.1109/rbme.2023.3297604
Zhang, H., Wu, C., Zhang, Z., Zhu, Y., Lin, H., Zhang, Z., et al. (2022). “Resnest: split-attention networks,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2736–2746.
Zhao, J., He, Y.-J., Zhao, S.-Q., Huang, J.-J., and Zuo, W.-M. (2021). AL-Net: Attention learning network based on multi-task learning for cervical nucleus segmentation. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inf. 26, 2693–2702. doi:10.1109/jbhi.2021.3136568
Keywords: deep learning, image segmentation, nucleus segmentation, attention fusion, discrete wavelet transform
Citation: Zhang J, Hu Y and An Z (2025) MSWAFFNet: improved segmentation of nucleus using feature fusion of multi scale wavelet attention. Front. Signal Process. 5:1527975. doi: 10.3389/frsip.2025.1527975
Received: 14 November 2024; Accepted: 14 October 2025;
Published: 07 November 2025.
Edited by:
Frederic Dufaux, L2S, Université Paris-Saclay, CNRS, CentraleSupélec, FranceReviewed by:
Nguyen Quoc Khanh Le, Taipei Medical University, TaiwanGiovanni Scribano, University of Ferrara, Italy
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Hu and An. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhenzhou An, YW5AeXhudS5lZHUuY24=
 Jun Zhang1
Jun Zhang1 Yangsheng Hu
Yangsheng Hu