- 1Department of Anatomical Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Public Health, and Nursing, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
- 2Division of Hematology and Medical Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Public Health and Nursing, Universitas Gadjah Mada/Dr. Sardjito General Hospital, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
- 3Universitas Gadjah Mada Academic Hospital, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Introduction: T-cell lymphoma contributes to malignancy worldwide, and the prognosis of this cancer is related to CD30 expression. Some T-cell lymphomas, including extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma (ENKTCL), an aggressive lymphoma, have been commonly associated with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection. EBV can be detected using Epstein-Barr-encoded RNA (EBER) in situ hybridization (ISH). In addition, hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection also has a role in the occurrence of non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL). A nonstructural protein of the HCV, NS3, may be involved in lymphoma development. Furthermore, the Epstein-Barr virus has also long been associated with CD30. However, the relationship between CD30 and NS3 was unknown. This research aims to study the relationship between CD30, NS3, and EBER in T-cell lymphoma.
Methods: Data and paraffin blocks were collected from NHL T-cell patients, and 30 samples were chosen for the study after meeting the criteria. The paraffin block was stained with CD30, NS3, and EBER immunohistochemistry and read by two pathologists.
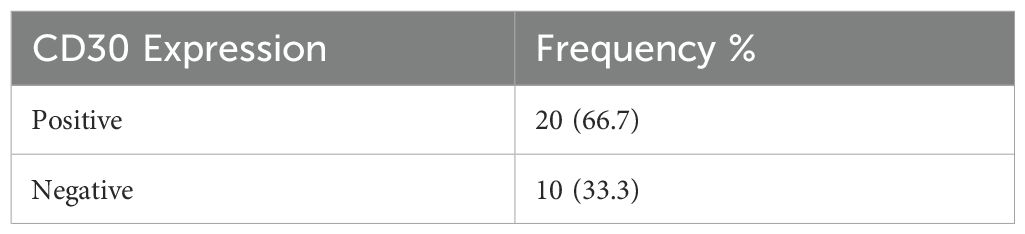
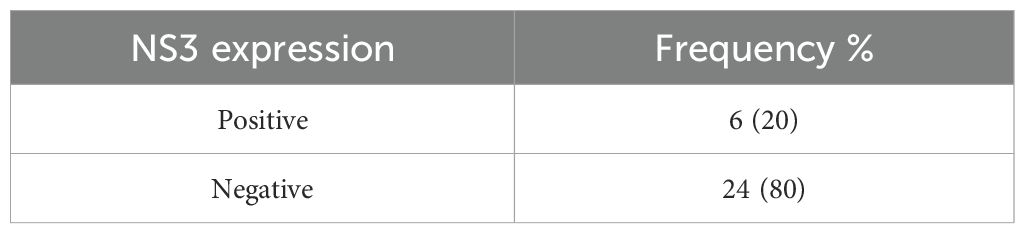
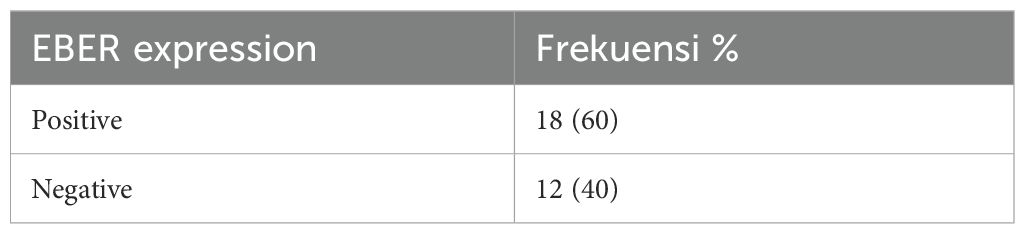
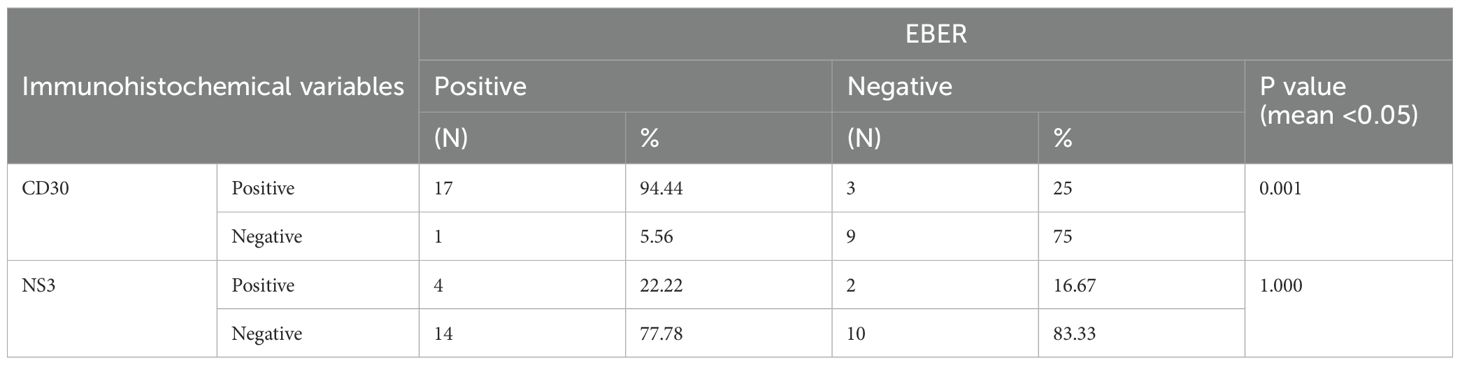
Results: From 30 cases, the dominant subtype expressing CD30 was Extranodal Natural Killer T-cell Lymphoma (ENKTCL) (84.62%). In total, 20 (66.7%) samples expressed CD30, 6 (20%) expressed NS3, and 18 (60%) samples expressed EBER. There is no significant relationship between NS3 and EBER. Meanwhile, CD30 expression correlated statistically with EBER (P = 0.001).
Discussion: CD30 expression in T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma was not significantly associated with clinicopathology data in this study. CD30, NS3, and EBER were expressed in T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. There exists a relationship between CD30 and EBER, but this study revealed no relationship between NS3 and EBER expression.
Introduction
Global data for 2020 estimate that there will be 544,352 new cases of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), where the mortality rate is predicted to be 47.7% (1). Non-Hodgkin lymphoma T-cell lymphocytes comprise 10% of all NHL cases (2).
In the context of histopathology diagnosis of lymph node lesions, CD30 is a marker that can be found in both reactive and neoplastic lymphoid tissue. CD30, a transmembrane glycoprotein, is known to be uniformly expressed in Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) and anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) (3). CD30 expression in normal lymph nodes is a reactive phenomenon, often associated with immune responses. In healthy individuals, CD30 is usually expressed by T and B immunoblasts in the parafollicular region and the peripheral edge of germinal centers (4). Strong expression in specific morphological contexts suggests the diagnosis of lymphoma, particularly ALCL, HL, and some subset T-cell lymphomas (5, 6). Research shows that patients who are CD30 positive have a better prognosis compared to patients who are CD30 negative in NHL and Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (ALCL) (7–9).
CD30 has also been reported in a subset of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) and EBV-positive nodal T-cell and NK-cell lymphoma cases, indicating its potential role in various lymphoma subtypes (4, 10). CD30 expression has been associated with distinct clinicopathologic features in systemic Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase negative (ALK−) ALCLs, emphasizing the heterogeneity of these neoplasms (11). CD30 expression has been a key feature in T-cell NHL, with studies showing its presence in extranodal peripheral T-cell lymphomas (PTCLs) (12).
Furthermore, the expression of CD30 has been linked to survival outcomes in posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders, highlighting its prognostic value in diverse lymphoma subtypes (13). CD30 has emerged as a potential therapeutic target for diagnosing and treating T-cell NHL. Studies have shown that CD30-targeting therapies, such as Brentuximab Vedotin, have demonstrated efficacy in patients with high CD30-expressing non-Hodgkin lymphomas (14). The selective and dense expression of CD30 on lymphomatous cells makes it an attractive target for drug-conjugated antibody-directed treatment, particularly in refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma and ALCL (15).
The marker of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection has been investigated in the context of CD30 expression in various lymphoma subtypes. Studies have shown that EBER was not associated with CD30 expression in certain lymphomas, indicating the complex interplay between viral markers and lymphoma pathogenesis (16). Additionally, the presence of EBER-positive nonneoplastic cells has been reported in specific lymphoma cases, suggesting a potential role of EBV in the tumor microenvironment (17).
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection also plays a significant role in malignancies, especially hepatocellular carcinoma and lymphoma. With the advent of new treatments for HCV infection, there is hope to reduce the incidence of various malignant diseases caused by complications of viral infections (18). In addition, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), which infects more than 90% of the world’s adult population, is also associated with various malignancies. EBV can cause chronic disease in immunocompetent patients and various opportunistic diseases in immunocompromised patients. A rare group of EBV-associated T/NK-cell lymphoproliferative diseases (EBV-T/NK-LPDs) has also been identified (19). There is limited data on investigating the clinicopathological features of T-cell NHL in Indonesia regarding CD30 expression, NS3 expression, and EBER expression. Thus, research on these aspects aims to provide more data to understand the role of these molecules in T-cell NHL.
Methods
This research is a non-experimental retrospective observational-analytic study with a cross-sectional approach conducted at the Department of Anatomical Pathology/Dr. Sardjito General Hospital Yogyakarta from January 2016 to December 2021. The local ethics committee has approved this study, Ref No.: KE/FK/0444/EC/2021. The research subjects were 30 T-cell non-Hodgkin Lymphoma cases selected using purposive sampling. The dependent variables included CD30, NS3, and EBER expression, while the independent variables included clinicopathological characteristics. The study procedures included clinical data collection, re-examining hematoxylin-eosin-stained slides, immunohistochemical examination of CD30 and NS3, and EBER in situ hybridization.
Samples stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) were evaluated microscopically and subdivided into different morphological variants. According to standard antibody-specific protocols, immunohistochemical staining was performed on 4-μm formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue sections. Antigen retrieval was performed using the Starr Trek detection kit (Biocare Medical, Pacheco, CA). Samples were stained using monoclonal anti-CD30 antibodies (mouse monoclonal antibody MoAb CD30 cell marque Ber-H2) to identify CD30 immunoreactivity. Lymph node tissues stained with the CD30 antibody in Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) cases were used as positive controls. We used IHC to detect the HCV nonstructural 3 (NS3) protein using the anti-hepatitis C virus NS3 protein antibody (rabbit polyclonal antibody; GeneTex, Irvine, CA). EBER was assessed by CISH using ZytoFast probes (ZytoVision).
Each biomarker, CD30 and NS3, was scored based on the the percentage of positive membrane neoplastic cells. EBER expression was evaluated based on nuclear brown signals within the cells. Based on previous literature (20, 21), a cut-off value of 5% was used for all markers. Two pathologists, blinded to clinical data, reviewed all slides independently to ensure consistency in interpretation.
The X2 tests or Fisher’s exact test assessed associations between biomarker expression (CD30, NS3, and EBER) and clinicopathological variables. Variables with a p-value <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
Clinical characteristics of study subjects
This study analyzed 30 FFPE samples from T-cell non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL) patients at the Department of Anatomical Pathology/Dr. Sardjito General Hospital Yogyakarta, between January 2016 and December 2021, selected from an initial pool of 59 diagnosed cases. The cohort comprised 66.7% males and 33.3% females, with an average age of 50 years. Age distribution showed 73.3% were under 60 years, 16.7% were over 60 years, and 10% were under 18 years. Eighty-three percent (83.3%) of subjects were in early Ann Arbor stages (I-II), while 16.7% were in advanced stages (III-IV). Nodal involvement in this study included various regions such as cervical, inguinal, axillary, mediastinal, and submandibular lymph nodes. Extranodal involvement was predominantly single (83.3%), with 56.7% of cases affecting nasal organs. Other extra nodal tissues involved in this study are the scalp, parotid, axilla, lumbar, antebrachial, and crural regions. Reviewed by two pathologists, the cases were categorized as NHL T cells, NOS (53.3%), Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma (40%), and Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma (6.7%).
Association between positive CD30 expression and clinicopathological characteristics
This study used an immunohistochemical examination method to determine CD30 expression. The representative expression of CD30 is shown in Figures 1, 2. CD30 expression criteria were calculated based on the percentage of positivity with a 5% cut-off (20, 22). Staining with CD30 primary antibody in HL cases in lymph node tissue was used as a positive control. The results of this study from a total of 30 subjects examined showed 20 (66.7%) samples with positive CD30 and 10 (33.3%) samples with negative CD30 expression (Table 1).

Figure 2. CD30 positive expression highlighted by brown color in the membrane and cytoplasm of tumor cells (400x Magnification).
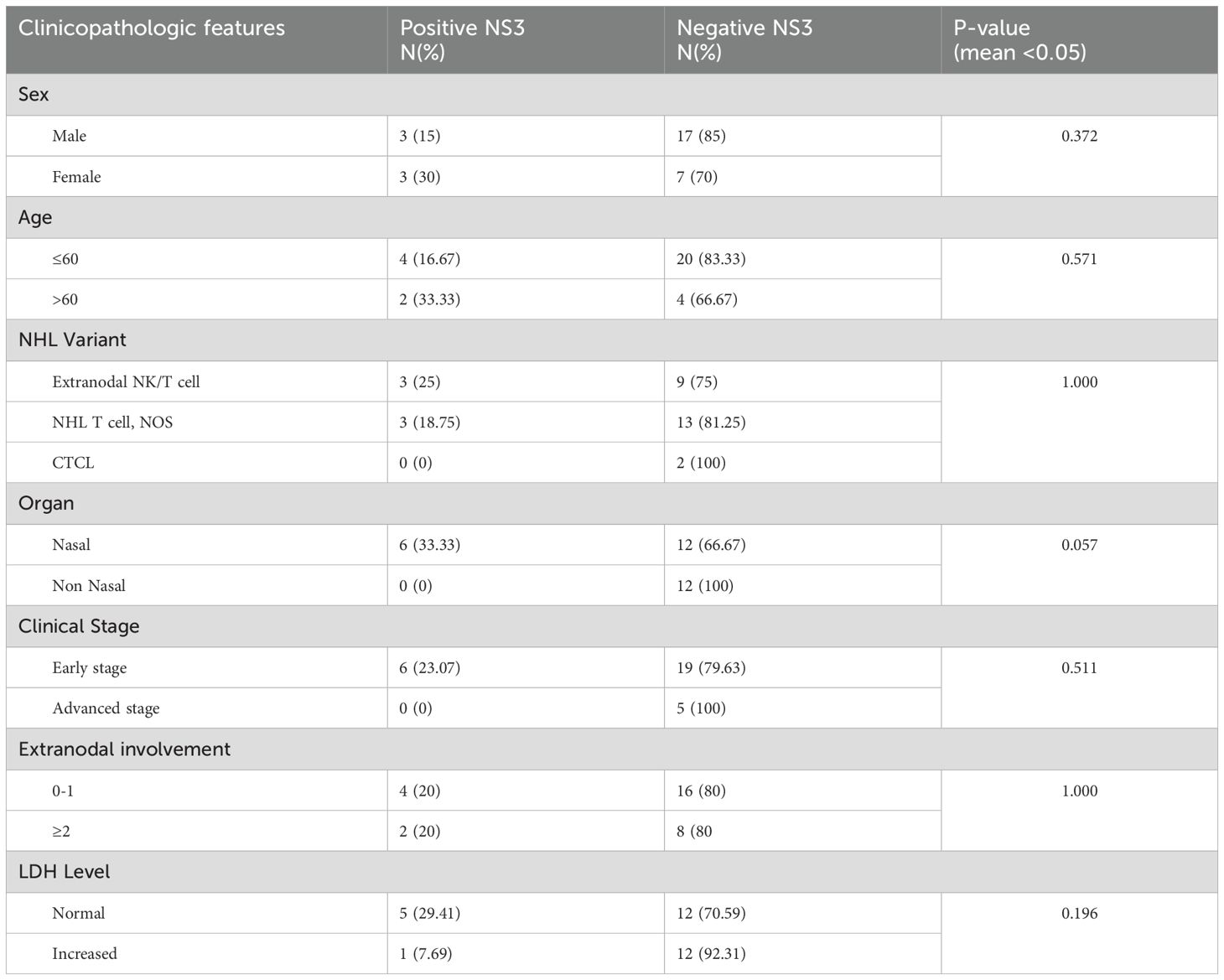
Based on the CD30 expression examination results, there were 20 patients with positive CD30 expression. Clinicopathological characteristics with positive CD30 include male gender, namely, 14 (70%) participants with an average age of 48 years (≤ 60). Positive CD30 expression based on T-cell NHL morphology was highest in extranodal NK/T cell variants, namely 11 (84.62%). Then, for positive CD30 expression based on the location of the lesion, the most positive expression in the nasal area was 13 (72.22%). For the stage, 17 (68%) cases were in the early stage (I-II), and 3 (40%) cases were in the advanced stage (III). For extranodal involvement of values 0-1, there were 13 cases (65%), and elevated serum LDH occurred in 9 (69.23%) cases (Table 2). There was no association between CD30 and clinicopathological characteristics in this study.
Association between positive NS3 expression and clinicopathological characteristics
The immunohistochemical method was used to determine the expression of NS3. The negative and positive NS3 expressions in the cytoplasm of tumor cells are presented in Figures 3A-G. The criteria for NS3 expression used in this study are the same as several previous studies, namely a 5% cut-off (23). NS3 of hepatitis C cases in liver biopsy was used as a positive control. In 30 subjects examined, there were 24 (80%) negative-stained samples and 6 (20%) positive-stained samples (Table 3).

Figure 3. (A) Negative NS3 Expression (400x Magnification). (B–G) NS3 positive expression in the cytoplasm of tumor cells showed by brown color. (400x Magnification).
Based on the NS3 expression examination results, six patients had positive NS3 expression. Clinicopathologic characteristics were as follows: positive NS3 appeared equal according to gender, namely 3 (15% in men and 30% in women) participants, and negative NS3 numbers were higher in men, namely 17 patients compared to 7 patients for women. The average age was 53 years (≤ 60). Positive NS3 expression based on NHL T cell morphology was most prevalent in extranodal NK/T and NHL T cell, NOS variants, namely three (25% in extranodal NK/T cell) and three (18.75% in NHL T cell, NOS) respectively. Then, for positive NS3 expression based on the location of the lesion, the most common location was the nasal area, showing up in 6 (33.33%) patients. For stage, six (23,07%) cases were at an early stage, and no positive cases were at an advanced stage (III). For extranodal involvement, 0–1 showed there were four cases (20%), and elevated serum LDH occurred in one (7.69%) case (Table 4). There was no association between NS3 and clinicopathological characteristics in this study.
Association between positive EBER expression and clinicopathological characteristics
The RNA-encoded in situ hybridization method was used to determine EBER expression, which is shown in Figures 4, 5. The EBER expression criteria used in this study are the same as those used in several previous studies, using a 5% cut-off (21, 24). Staining with EBER primary antibodies uses tonsils as a positive control. In 30 samples examined, 18 (60%) samples were positive, and 12 (40%) were negative (Table 5).
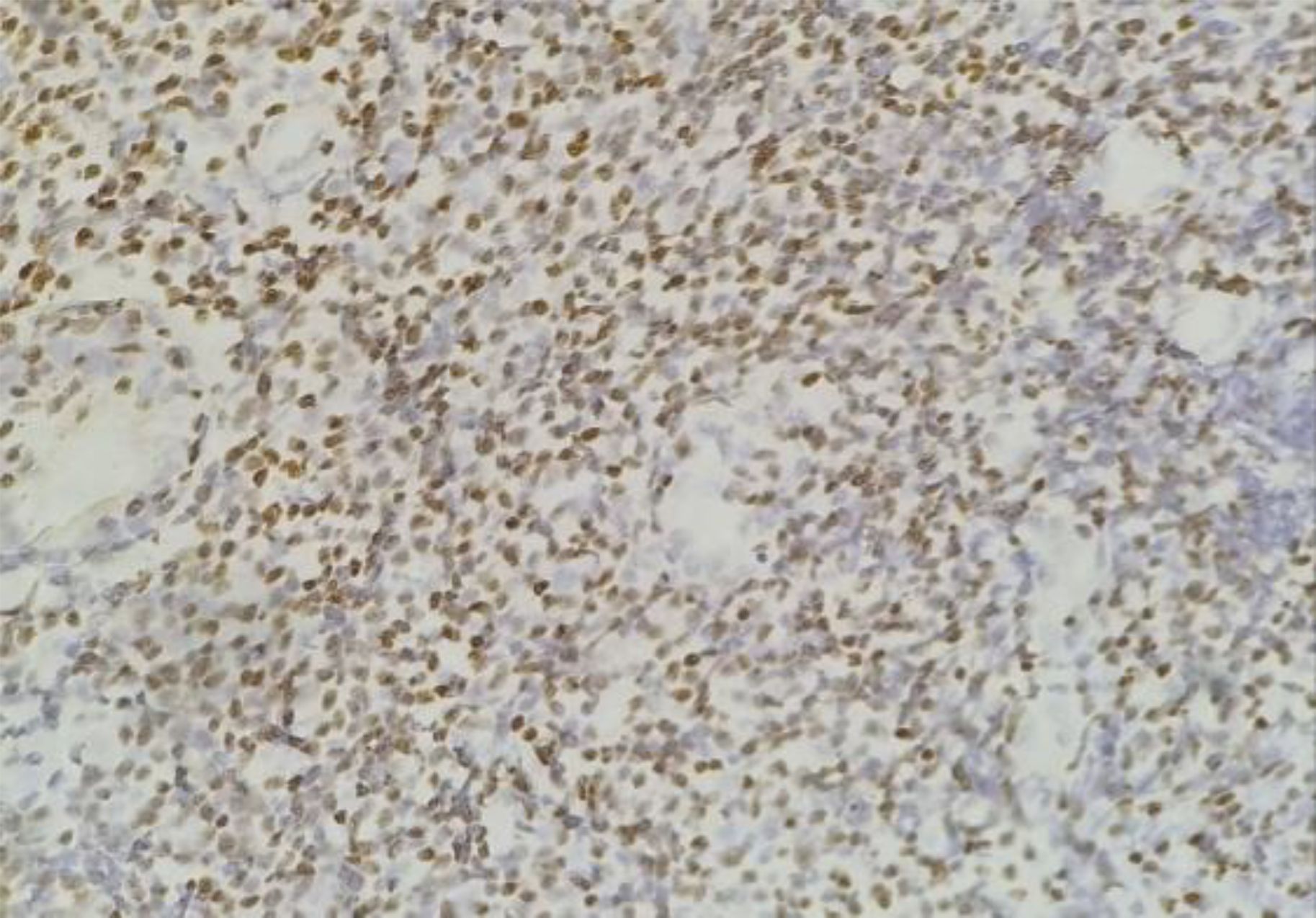
Figure 5. EBER positive expression in the nuclei of tumor cells showed by brown color (400x magnification).
Based on the EBER expression examination results, 18 patients showed positive EBER expression. Clinicopathologic characteristics with positive EBER included male gender in 12 cases (60%). The average age was 38 years (≤ 60). Positive EBER expression based on T-cell NHL morphology was most common in extranodal NK/T cell variants, namely, 10 cases (76.92%). Then, the location of the lesions showed highest prominence in the nasal area, 12 (66.67%) cases were found. For stage, 15 (60%) cases were at an early stage, and 3 (60%) positive cases were at an advanced stage (III). For extranodal involvement, 0-1 accounted for 11 cases (55%), and elevated serum LDH occurred in 8 (61.54%) cases (Table 6). There was no association between EBER and clinicopathological characteristics in this study.
Relationship between EBER, CD30, and NS3
In T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), there is a relationship between EBER and CD30 expression (P= 0.001). However, there is no significant relationship between EBER and NS3 expression and CD30 and NS3 (Tables 7, 8).
Discussion
Results showed that T-cell NHL in Yogyakarta predominantly affected male patients (66.7%, n=20) with an average age of 50 years. Most patients (83.3%, n=25) were diagnosed at early Ann Arbor clinical stages (I-II), with 82.8% (n=25) having less than one extranodal involvement, primarily in the nasal region (56.67%, n=17). Morphological variants included T-cell NHL not otherwise specified (NOS) (53.3%, n=16), Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma (ENKTCL) (41.4%, n=12), and Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (6.3%, n=2). These findings align with several international studies, with an average age of 52 years for T-cell NHL, with a male predominance of approximately 80%, 64.6% of patients at Ann Arbor stage I/II (25), and 65-72% with extranodal involvement (25). However, some variations exist in other studies: a median age of 65 years in the UK, a median age of 54 years in India, with Peripheral T-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified (PTCL, NOS), lymphoblastic lymphoma, and anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL) as the most common variants (26, 27). In Europe, T/NK-cell lymphoma cases were most frequent in adult male patients with an average age of 65 years, with Peripheral T-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified (PTCL-NOS), Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL), and Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL) as the predominant morphological variants (28).
CD30 expression is a significant lymphoma marker and an activation molecule in B and T cells, primarily controlling and stimulating memory cells for apoptosis induction (29). This study found that 66.7% (n=20) of 30 T-cell NHL subjects showed positive CD30 expression. Regarding anatomical location, CD30 expression was most common in the nasal region, which aligns with previous findings of CD30-positive T-cell lymphoproliferation in head and neck mucosal sites (30) and increased CD30 expression in paranasal sinus mucosa, especially in allergic groups (31). The study’s limitations in establishing significant relationships may be due to the rarity of this lymphoma type.
This study reported positive NS3 expression in 20.7% (n=6) of T-cell NHL patients, distributed among ENKTCL and T-cell NHL not otherwise specified (NOS) subtypes. Epidemiological studies have shown an increased risk of NHL in HCV-infected patients, primarily in high-prevalence areas (23). HCV prevalence varies globally, with the highest rates (>10%) being seen in Egypt, Central Africa, Mongolia, and Bolivia, while the Asian continent, particularly China and India, accounts for the most significant number of HCV-infected individuals (32). Hepatitis C diagnosis typically involves serologic testing for anti-HCV antibodies and HCV RNA detection in serum. However, RT-PCR detection of HCV RNA in liver biopsy specimens could rapidly diagnose at least 60% of anti-HCV antibody-positive but serum HCV RNA-negative patients (33). Methods such as in situ hybridization (ISH), immunohistochemistry, and in situ PCR can complement virus detection in hepatitis C diagnosis, addressing the challenges in localizing HCV products in infected tissues (34). These findings underscore the complexity of HCV detection and its relationship with lymphoma, particularly in non-endemic areas like Indonesia.
This study found positive EBER results in 60% (n=18) of cases, primarily distributed in Extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma (ENKTCL) and T-cell NHL, NOS subtypes, as per WHO 5th edition classification. Previous research has elucidated how EBV contributes to lymphomagenesis: EBV latent membrane protein (LMP-1) activates the NF-kB and PI3K/Akt pathways, upregulating survivin and inhibiting apoptosis. JAK/STAT activation regulates EZH2, leading to DNA methylation and gene transcription, promoting cell proliferation. Both pathways upregulate PD-L1 expression, enabling immune evasion. Genetic alterations, including chromosome 6q deletion and mutations in P53, ECSIT, and DDX3X, also contribute to ENKTCL oncogenesis (35, 36). This study demonstrated high EBER expression in ENKTCL and AITL, supporting previous findings despite certain statistical limitations (37, 38).
This study observed cases with positive CD30 expression also showing positive NS3 expression, although these were not statistically significant. The tendency for NS3-positive cases to exhibit CD30 positivity aligns with the theory that HCV-related chronic hepatitis patients have increased CD30 expression, correlating with disease activity and severity. This supports the hypothesis that the immune response maintains chronic HCV infection, and the correlation between HCV NS3 and CD30 expression could indicate disease severity (39). While no statistically significant relationship was found between CD30 and NS3 expression in T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) patients, this finding is novel as previous studies have not addressed this relationship in NHL. Related research has shown CD30 to be a marker for liver cirrhosis surveillance in chronic HCV-infected transplant recipients (40), and a decrease in serum CD30 (sCD30) levels has been associated with successful HCV treatment (41). These findings suggest avenues for further investigation into the role of CD30 and NS3 in T-cell NHL and HCV-related pathologies.
In this study, 17 cases (94.44%) were positive for both CD30 and EBER. There is a relationship between CD30 and EBER, and it was statistically significant. Previous studies have demonstrated an association between CD30 and EBER. Type II latency pattern of EBV infection has been observed in ENKTCL patients, where tumor cells express EBERs, EBV nuclear antigen-1 (EBNA-1), latent membrane protein (LMP)-1, and LMP-2. LMP-1 is the most critical EBV element involved in cell proliferation. It induces TNF-α-induced expression of B-cell lymphoma (Bcl-2) and protein-3 to inhibit apoptosis. LMP-1 also regulates c-Myc, interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-10 to accelerate cell proliferation. LMP-1 has also been shown to regulate CD30; thus, LMP-1 expression may be associated with high levels of CD30 expression in patients with ENKTCL (42). In addition, a previous study in India also reported that CD30-overexpressing PTCL and ALCL were predominantly EBER-positive (43). A previous study demonstrated that LMP1 regulated CD30 through BCR/NF-κB signaling. CD30 could protect against mitochondrial dysfunction through increasing BNIP3 expression to affect cell survival in EBV+DLBCL (Wei Ting 11). A meta-analysis of 10 retrospective studies showed that extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma (ENKTL)-expressed CD30 is significantly associated with a more favorable prognosis (44).
An earlier study revealed that CD30 expression in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) was associated with a more favorable prognosis, including a higher 5-year overall survival rate. However, when CD30 is co-expressed with EBER (CD30+/EBER+), clinical outcomes become poorer, suggesting that Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection may contradict the favorable effects of CD30 expression (8). Our study revealed a relationship between CD30 and EBV EBER in T-cell NHL. This result may add data for further research on whether CD30 and EBV EBER positivity impact clinical condition in T-cell NHL.
In this study, there were four cases positive for NS3 and also EBER. Statistically, there was no significant relationship between them. The four cases consisted of one patient with NHL T-cell lymphoma and three patients diagnosed with ENKTCL. Interestingly, all these patients were also positive for CD30. It is consistent with the theory that patients with HCV-related chronic hepatitis will have increased CD30 expression, which correlates with disease activity and severity (39). In the medical records of these four patients, HIV serologic testing was also performed, but the results were negative. The possibility of both simultaneously causing lymphoma is still controversial (45). This is due to monoclonal B-cell expansion and no intraclonal variation. EBV and HCV stimulate B cells by binding to the same surface protein complex. This study was conducted on DLBCL patients. It was also stated that EBV accelerates the course of the disease. In another study, it was also stated that, in immunocompromised patients, EBV more often causes lymphoma compared to HCV, which is more associated with liver malignancies (46).
In summary, the present study revealed that CD30 expression in T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma was not significantly associated with clinicopathology data. CD30, NS3, and EBER were expressed in T-cell non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. There is a relationship between CD30 and EBER, but this study revealed no relationship between NS3 and EBER expression in T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Faculty of Medicine, Public Health and Nursing, UGM-Sardjito Hospital. Ref. No: KE/FK/0444/EC/2021. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants\’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
RJ: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LS: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. IF: Investigation, Writing – original draft. MH: Resources, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Funding acquisition. NA: Funding acquisition, Validation, Conceptualization, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Investigation, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by Hibah DAMAS Penelitian 2021, Faculty of Medicine, Public Health, and Nursing, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta, Indonesia. (Grant No: 248/UN1/FKKMK/PPKE/PT/2021).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Luo J, Craver A, Bahl K, Stepniak L, Moore K, King J, et al. Etiology of non-Hodgkin lymphoma: A review from epidemiologic studies. J Natl Cancer Center. (2022) 2:226–34. doi: 10.1016/j.jncc.2022.08.003
2. Rizvi MA, Evens AM, Tallman MS, Nelson BP, and Rosen ST. T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. (2006) 107(4):1255–64. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-03-1306
3. Kim SJ, Yoon DH, Kim JS, Kang HJ, Lee HW, Eom H-S, et al. Efficacy of brentuximab vedotin in relapsed or refractory high-CD30–expressing non-Hodgkin lymphomas: results of a multicenter, open-labeled phase II trial. Cancer Res Treat. (2020) 52:374–87. doi: 10.4143/crt.2019.198
4. Hu S, Xu-Monette ZY, Balasubramanyam A, Manyam GC, Visco C, Tzankov A, et al. CD30 expression defines a novel subgroup of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with favorable prognosis and distinct gene expression signature: a report from the International DLBCL Rituximab-CHOP Consortium Program Study. Blood. (2013) 121(14):2715–24. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-10-461848
5. Wadsworth PA, Miranda RN, Bhakta P, Bhargava P, Weaver D, Dong J, et al. Primary splenic diffuse large B-cell lymphoma presenting as A splenic abscess. EJHaem. (2023) 4:226–31. doi: 10.1002/jha2.642
6. Wu R and Lim MS. Updates in pathobiological aspects of anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1241532. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1241532
7. Karube K, Kakimoto Y, Tonozuka Y, and Ohshima K. The expression of CD30 and its clinico-pathologic significance in peripheral T-cell lymphomas. Expert Rev Hematol. (2021) 14:777–87. doi: 10.1080/17474086.2021.1955344
8. Li P, Jiang L, Zhang X, Liu J, and Wang H. CD30 expression is a novel prognostic indicator in extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. BMC Cancer. (2014) 14:890. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-890
9. Reynelda Santoso M, Suci Hardianti M, Indrawati I, and Anggorowati N. CD30 expression and its correlation with clinicopathologic features in Indonesian diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Asian Pacific J Cancer Biol. (2020) 5:107–13. doi: 10.31557/apjcb.2020.5.3.107-113
10. Yu F, Wang J, Ke Z, Zhang Y, Xu L, Zhang H, et al. EBV-positive nodal T-cell and NK-cell lymphoma. Am J Surg Pathol. (2024) 48:406–16. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000002184
11. Wang J, Zhong L, Lin W, Zhang W, Xi Y, Liu Y, et al. JAK/STAT3 signaling activation related to distinct clinicopathologic features in systemic ALK– anaplastic large cell lymphomas. Am J Surg Pathol. (2023) 47:55–64. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000001995
12. Tian Z, Tian J, and Liao J. NK/T-cell lymphoma with rash and peripheral neuropathy as the first manifestation: A case report and literature review. Diagn Pathol. (2023) 18:2. doi: 10.1186/s13000-023-01286-z
13. Kinch A, Amini R-M, Hollander P, Molin D, Sundström C, and Enblad G. CD30 expression and survival in posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders. Acta Oncol (Madr). (2020) 59:673–80. doi: 10.1080/0284186X.2020.1731924
14. Saleh K, Michot J-M, and Ribrag V. Updates in the treatment of peripheral T-cell lymphomas. J Exp Pharmacol Volume. (2021) 13:577–91. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S262344
15. Al-Khreisat MJ, Hussain FA, Abdelfattah AM, Almotiri A, Al-Sanabra OM, and Johan MF. The role of NOTCH1, GATA3, and c-MYC in T cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Cancers (Basel). (2022) 14:2799. doi: 10.3390/cancers14112799
16. Baptista MJ, Tapia G, Muñoz-Marmol A, Muncunill J, Garcia O, Montoto S, et al. Genetic and phenotypic characterisation of HIV-Associated aggressive B-Cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas, which do not occur specifically in this population: diagnostic and prognostic implications. Histopathology. (2022) 81:826–40. doi: 10.1111/his.14798
17. Yin Y, Liu H, Luo M, Yu G, Yin W, and Li P. Primary extranodal soft tissue lennert lymphoma (Lymphoepithelioid variant pf peripheral T-cell lymphoma, unspecified): A case report and review of the literature. Diagn Pathol. (2023) 18:12. doi: 10.1186/s13000-023-01297-w
18. Khaled H, Abu-Taleb F, and Haggag R. Hepatitis C virus and non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas: A minireview. J Adv Res. (2017) 8:131–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2016.11.005
19. Wong Y, Meehan MT, Burrows SR, Doolan DL, and Miles JJ. Estimating the global burden of Epstein–Barr virus-related cancers. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2022) 148:31–46. doi: 10.1007/s00432-021-03824-y
20. Kim WY, Nam SJ, Kim S, Kim TM, Heo DS, Kim C-W, et al. Prognostic implications of CD30 expression in extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma according to treatment modalities. Leuk Lymphoma. (2015) 56:1778–86. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2014.974048
21. Ziarkiewicz M, Wołosz D, Dzieciątkowski T, Wilczek E, Dwilewicz-Trojaczek J, Jędrzejczak WW, et al. Epstein–Barr virus-positive diffuse large B cell lymphoma in the experience of a tertiary medical center in Poland. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). (2016) 64:159–69. doi: 10.1007/s00005-015-0341-2
22. Lee WJ, Moon IJ, Shin HJ, Won CH, Chang SE, Choi JH, et al. CD30-positive cutaneous extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma: clinicopathological features and survival outcomes. Int J Dermatol. (2019) 58:688–96. doi: 10.1111/ijd.14362
23. Couronné L, Bachy E, Roulland S, Nadel B, Davi F, Armand M, et al. From hepatitis C virus infection to B-cell lymphoma. Ann Oncol. (2018) 29:92–100. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx635
24. Hwang J, Suh CH, Won Kim K, Kim HS, Armand P, Huang RY, et al. The incidence of Epstein-Barr virus-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13:1785. doi: 10.3390/cancers13081785
25. Nijland ML, Koens L, Pals ST, Berge IJM, Bemelman FJ, and Kersten MJ. Clinicopathological characteristics of T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma arising in patients with immunodeficiencies: A single-center case series of 25 patients and A review of the literature. Haematologica. (2018) 103:486–96. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2017.169987
26. Pileri SA, Tabanelli V, Fiori S, Calleri A, Melle F, Motta G, et al. Peripheral T-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified: clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and future treatment. Cancers (Basel). (2021) 13:4535. doi: 10.3390/cancers13184535
27. Smith A, Crouch S, Lax S, Li J, Painter D, Howell D, et al. Lymphoma incidence, survival and prevalence 2004–2014: sub-type analyses from the UK’s Haematological Malignancy Research Network. Br J Cancer. (2015) 112:1575–84. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.94
28. Phan A, Veldman R, and Lechowicz MJ. T-cell lymphoma epidemiology: the known and unknown. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. (2016) 11:492–503. doi: 10.1007/s11899-016-0353-y
29. Muta H and Podack ER. CD30: from basic research to cancer therapy. Immunol Res. (2013) 57:151–8. doi: 10.1007/s12026-013-8464-1
30. Sciallis AP, Law ME, Inwards DJ, McClure RF, Macon WR, Kurtin PJ, et al. Mucosal CD30-positive T-cell lymphoproliferations of the head and neck show A clinicopathologic spectrum similar to cutaneous CD30-positive T-cell lymphoproliferative disorders. Modern Pathol. (2012) 25:983–92. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2012.38
31. Suzuki H, Goto S, Ikeda K, Oshima T, Furukawa M, and Takasaka T. IL-12 receptor β2 and CD30 expression in paranasal sinus mucosa of patients with chronic sinusitis. Eur Respir J. (1999) 13:1008. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-3003.1999.13e13.x
32. Vannata B, Arcaini L, and Zucca E. Hepatitis C virus-associated B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas: what do we know? Ther Adv Hematol. (2016) 7:94–107. doi: 10.1177/2040620715623924
33. Qian X, Guerrero RB, Plummer TB, Alves VF, and Lloyd RV. Detection of hepatitis C virus RNA in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections with digoxigenin-labeled cRNA probes. Diagn Mol Pathol. (2004) 13:9–14. doi: 10.1097/00019606-200403000-00002
34. Austria A and Wu GY. Occult hepatitis C virus infection: A review. J Clin Transl Hepatol. (2018) 6:1–6. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2017.00053
35. Cai Q, Cai J, Fang Y, and Young KH. Epstein-Barr virus-positive natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Front Oncol. (2019) 9:386. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00386
36. Gru AA, Haverkos BH, Freud AG, Hastings J, Nowacki NB, Barrionuevo C, et al. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in T cell and NK cell lymphomas: time for a reassessment. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. (2015) 10:456–67. doi: 10.1007/s11899-015-0292-z
37. Donzel M, Bonjour M, Combes J-D, Broussais F, Sesques P, Traverse-Glehen A, et al. Lymphomas associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection in 2020: results from A large, unselected case series in France. EClinicalMedicine. (2022) 54:101674. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101674
38. Haverkos BM, Pan Z, Gru AA, Freud AG, Rabinovitch R, Xu-Welliver M, et al. Extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma, nasal type (ENKTL-NT): an update on epidemiology, clinical presentation, and natural history in North American and European cases. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. (2016) 11:514–27. doi: 10.1007/s11899-016-0355-9
39. Foschi FG, Gramenzi A, Castelli E, Cursaro C, Pagani S, Margotti M, et al. Soluble CD30 serum level in HCV-positive chronic active hepatitis: A surrogate marker of disease activity? Cytokine. (2000) 12:815–8. doi: 10.1006/cyto.1999.0653
40. Bharat A, Narayanan K, Golocheikine A, Steward N, Crippin J, Lisker-Melman M, et al. Elevated soluble CD30 characterizes patients with hepatitis C virus-induced liver allograft cirrhosis. Transplantation. (2007) 84:1704–7. doi: 10.1097/01.tp.0000295973.31877.7b
41. Yang S, Fu L, Chang C, Yeh H, Chen G, and Kao J. Changes of soluble CD26 and CD30 levels correlate with response to interferon plus ribavirin therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2006) 21:1789–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2006.04677.x
42. Cao M. Nuclear factor kB represses the expression of latent membrane protein 1 in Epstein-Barr virus transformed cells. World J Virol. (2014) 3:22. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v3.i4.22
43. Amandeep K, Robin S, Ramica S, and Sunil K. Peptic ulcer: A review on etiology and pathogenesis. Irjp. (2012) 2012:3.
44. Chen Z, Guan P, Shan T, Ye Y, Gao L, Wang Z, et al. CD30 expression and survival in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget. (2018) 9:16547–56. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.24044
45. Libra M, Gloghini A, De Re V, Rupolo M, Navolanic P, Gasparotto D, et al. Aggressive forms of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in two patients bearing coinfection of Epstein-Barr and hepatitis C viruses. Int J Oncol. (2005) 26(4):945–50. doi: 10.3892/ijo.26.4.945
Keywords: T-cell, NHL, CD30, NS3, EBER
Citation: Juwita RA, Saputra LA, Fiilasari I, Hardianti MS and Anggorowati N (2025) CD30 associates with EBER-EBV but not HCV-NS3 in T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Front. Virol. 5:1583648. doi: 10.3389/fviro.2025.1583648
Received: 26 February 2025; Accepted: 13 May 2025;
Published: 04 June 2025.
Edited by:
Fabio Bagnoli, GlaxoSmithKline, ItalyReviewed by:
Naoyuki Kondo, Kansai Medical University, JapanDaniel Stern Cardinale, Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey, United States
Copyright © 2025 Juwita, Saputra, Fiilasari, Hardianti and Anggorowati. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Nungki Anggorowati, bnVuZ2tpQHVnbS5hYy5pZA==; bnVuZ2tpYXdAZ21haWwuY29t
†Present address: Rizki Amalia Juwita, Ulin General Hospital, Banjarmasin, South Kalimantan, Indonesia
Lili Ananta Saputra, Department of Anatomic Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Kristen Duta Wacana, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Ika Fiilasari, Dr. Moewardi Hospital, Surakarta, Central Java, Indonesia
‡ORCID: Nungki Anggorowati, orcid.org/0000-0002-3268-5492
 Rizki Amalia Juwita1†
Rizki Amalia Juwita1† Mardiah Suci Hardianti
Mardiah Suci Hardianti Nungki Anggorowati
Nungki Anggorowati