- 1Guangzhou Institute of Science and Technology, Guangzhou, China
- 2Guangzhou City Construction College, Guangzhou, China
This study explores the influence on urban sustainable development performance of residents’ resettlement as a result of urban renewal activities, aiming to develop a system dynamics model to simulate the performance of urban sustainable development performance at the perspective of urban renewal. The system dynamics model consists of four subsystems, which are urban economic sector, social service sector, demolition and resettlement sector, and industrial development sector. It was used to simulate the sustainable development performance of Guangzhou city. In the seven scenarios simulated, it is found that increasing the ratio of in-site rehousing and off-site rehousing at the same time can help to promote the sustainable development of the city. The results show that the system dynamics model can effectively simulate the impacts of urban renewal on sustainable development performance, and provides a reference for decision makers to formulate urban sustainable development strategies.
1 Introduction
The United Nations Agenda for Sustainable Development Goals 2030 emphasizes the need to balance goals and indicators in three interconnected dimensions: economic, social, and environmental. Urbanization has shown that the three dimensions have a similar structure: the economic dimension, the demographic dimension, and the spatial dimension (Jiang et al., 2021).
Urbanization in China has progressed to the middle and late stages, and the spatial and qualitative development of cities depends on urban renewal (Zhao and Li, 2019). The basis of urban renewal is the scarcity of land in cities. Due to the increase in land value at the city center, urbanization has extended to the outskirts through converting rural land into urban land for construction, converting it into urban built-up areas. This is a way for urban development to achieve economies of scale. However, a balance between economies of scale and diseconomies of scale is always achieved in urban development. Therefore, There are two main approaches to urban development: urban expansion and urban renewal. Urban renewal means the reuse of underutilized land in urban centers (Zhao and Li, 2019).
The question examined in this paper is how different demolition and resettlement scenarios will affect the sustainable urban development of Guangzhou. This study establishes a system dynamics model for sustainable urban renewal by exposing the interrelationships between demolition and resettlement programs and sustainable urban development, and proposes a demolition and resettlement program that promotes sustainable urban development. In order to fully grasp the complexity of these linkages, this paper takes Guangzhou City as the research area, and by establishing a system dynamics model to study the intrinsic relationship between variables, simulates the sustainable urban development performance of different demolition and resettlement programs, so as to determine appropriate urban renewal management policies and demolition and relocation compensation methods, in order to guide the construction of a sustainable urban development system in Guangzhou and the country as a whole.
The results of the study show that system dynamics modeling is an effective tool for simulating the performance of sustainable urban development and can help decision makers to formulate appropriate strategies for sustainable urban development. In this study of the Guangzhou area, this study finds that increasing the ratio of the use of in-site rehousing and off-site rehousing can increase the performance of urban sustainable development.
Among the many cities in China, taking into account the fact that each city’s development orientation and main objective are not exactly the same, further research on a larger scale may be needed when discussing the generalizability of the model.
This paper is divided into six parts. Chapter 1 introduces the research theme, analysis method and research objectives of this paper. Chapter 2 reviews the previous studies. Chapter 3 describes the research methodology and the context of the study area. Chapter 4 establishes the dynamic model of sustainable urban renewal system. In chapter 5, the model will simulated and analyse the result. Chapter 6 concludes and makes proposals on implementation.
2 Literature review
Many indicators and assessment tools have been developed by previous researchers to assess the performance of sustainable urbanization from different perspectives. These indicators and tools are widely used in academia and practice to assess the level of urban development. However, there are some limitations in using indicators to assess urban sustainability. Since urban development is a complex system containing a variety of variables, indicators do not reflect the systematic interactions among these variables and therefore do not provide normative indicators of future directions of urban development. Uwasu and Yabar, (2011) also believe that existing sustainability indicators and tools may overlook some important features of sustainability, and fail to explicitly address the relationship between the city-building aspects and the socio-economic aspects of urbanization.
Based on the above discussion, there is a need to bring in a methodology to assess a city’s sustainable urban renewal performance by considering the interactions between indicators. Therefore, the objectives of this study are: 1) to develop a sustainable urban renewal evaluation model based on the principle of system dynamics; 2) to demonstrate the application of the sustainable urban renewal model through a case study of Guangzhou, China; and 3) to analyze the simulation results under different scenarios.
An increasing number of scholars are applying system dynamics to urban development. System dynamics is a method created by Prof. Jay Forrester of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) for the systematic study of information feedback in complex systems (Forrester, 1958). Its most important feature is its ability to essentially analyze the internal structure of the system under study. It describes the relations of influence between the elements of the system, and simulates the impact of dynamic changes on the relations of influence between the indicators on the overall behavior of the system (Marzouk and Shimaa 2014). By establishing a complete information feedback system, we studied the linear and nonlinear interactions as well as the inherent large-scale, complex, and dynamic feedback loop structures of systems.
Several studies have been conducted using system dynamics to simulate and evaluate the performance of sustainable urban development. Huang and Chen (1999) developed a dynamic urban system model including six subsystems: land use, population, transportation, water resources, solid waste and wastewater treatment to simulate the performance of sustainable development in the city of Taipei. This model cannot be directly applied to assess other Chinese cities as China has different urban development characteristics. Mavrommati et al. (2013) proposed a system dynamics approach for ecologically sustainable development of urban coastal systems, which focuses on the relationships between the environmental and economic dimensions with no variables for the social dimension. Yu et al. (2022) used Shanghai as the study area to establish a system dynamics model to study the carrying capacity of the city, but the model only revealed the relationship between population, economy and resources, and changes in urban regeneration and land use were not taken into account.
Domestic and foreign scholars have studied the system dynamics of urban sustainable development evaluation. However, the synergistic evolution between research objects within the urban sustainable development system has not been studied from the perspective of urban renewal or housing demolition compensation. Through the system dynamics method, this paper establishes a sustainable urban renewal model.
Existing studies can provide useful references for modeling the performance of urban sustainability in this study. This study will apply system dynamics to simulate the performance of sustainable urban renewal in China. In this paper, commercial buildings are investigated, and the simulation will provide solutions for the government to realize sustainable urban development.
3 Research case and method
3.1 Case
This paper tries to provide policy suggestions to alleviate social conflicts for sustainable urban development. While some authors emphasise the role of environmental governance in sustainable urban development, urban renewal as a high priority task in China over the past decade, policy interventions in urban renewal have had a significant impact on urban development (Zhao and Li, 2018).
Therefore, The model built in this study has two main purposes.
1) To develop Causal Loop Diagrams (CLDs) and Stock-flow Diagrams based on Vensim to describe the logical relationships and interactions between factors comprehensively and systematically, which helps to better demonstrate the changes caused by intra-system changes to the whole system.
2) By simulating and analyzing the SD model, we analyze the impacts of urban renewal activities of various demolition and resettlement types on the sustainable development of the city, and adopt measures that can effectively promote the sustainable development of the city.
In this research, the city of Guangzhou is selected as the study area (Figure 1), which is a thousand-year-old commercial capital with a long history of urban renewal. And the application of the established SD model was demonstrated by a case study of this city. The scale and experience of urban renewal in Guangdong Province is leading in China (Luo, 2020).
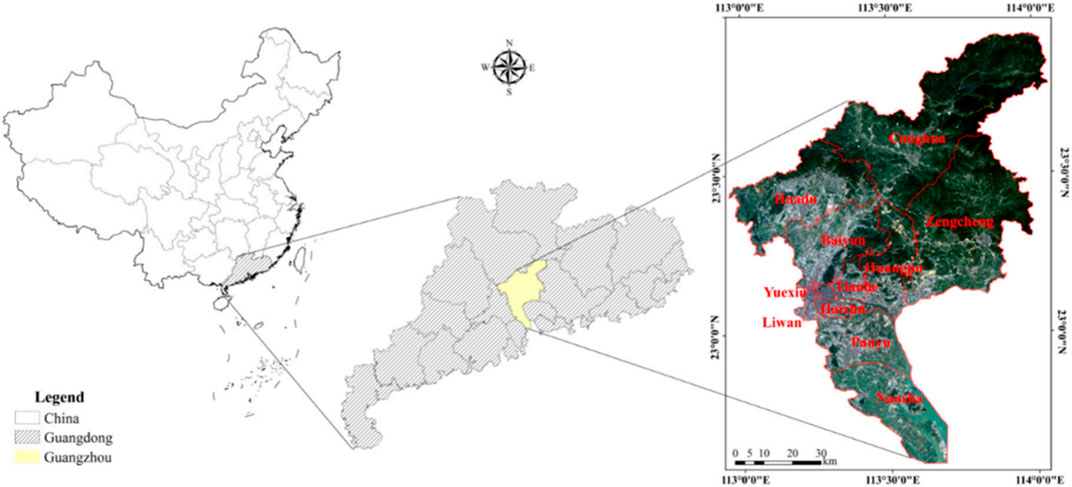
Figure 1. Geographical Location of Guangzhou (Reproduced from Lao et al., 2020, licensed under CC BY 4.0 International).
Guangzhou, Guangdong Province, China, which was chosen for the following reasons. In terms of urban development, Guangzhou is a city with a history of more than 2,200 years, and a large number of historical buildings carrying millennia of culture still remain in the central area of the city. Guangzhou presents housing diversity with Xiguan architecture, which highlights Guangfu culture, and urban villages left behind by rapid urbanisation. In terms of housing development, Guangzhou entered the commercialisation of housing earlier. Also, like other cities, it went through a long period of planned economy prior before housing commercialisation. In economic terms, Guangzhou’s urbanisation rate, GDP and population have been able to maintain good urban data performance over a long period of time without the establishment of a special economic zone.
Urban renewal in Guangzhou, China, is classified as the renewal of old villages, old cities and old factories, and the redevelopment methods are classified as complete reconstruction, micro-renovation and hybrid renovation (Guangzhou Daily, 2021), of which old villages are also known as urban village renovation. Urban villages exist in cities to function as low-cost urban housing and attract people who only need a room to live in, such as low-income people and students. The low rents due to their lack of standardised road planning, safety management and public health standards (Hu, 2014).
Urban villages are mostly renovated by complete reconstruction, which has attracted much attention because of the multiple interests and large amounts of money involved. Complete demolition and reconstruction is an urban renewal activity that involves the re-planning and redevelopment of land. It is also an urban renewal activity that involves the ecological restoration and land reclamation of the area by changing the land use attributes (Guangzhou Daily, 2021). In areas that are included in the annual urban renewal programme, land acquisition and demolition preparations are required. The government adopts “monetary compensation” or “monetary + reserved land” as compensation for land acquisition for village collectives. The developer who acquires the land will compensate the villagers or the village collective by exchanging the property rights with the demolished houses or by monetary compensation.
Before demolishing houses, the demolition compensation or rehousing terms require the consent of the relocation household. There are currently three main types of compensation and resettlement programs, namely, on-site rehousing, off-site rehousing and monetary compensation. These three different programs influence the achievement of sustainable urban development goals through different paths (Liu and Qiao, 2018).
China has continued to issue policies on increasing monetary compensation between 2015 and 2017 in order to meet urban sustainability goals. Between 2013–2017, the proportion of monetary compensation was increased to 60%, following the adoption of state subsidies and measures to give residents whose land was expropriated preferential housing purchase within 1 year. (China Statistics Bureau, 2018).
However, the rise in monetary compensation has led to a number of social problems, such as: soaring house prices and a smaller supply-demand ratio, due to the ineffective use of increased monetary compensation.
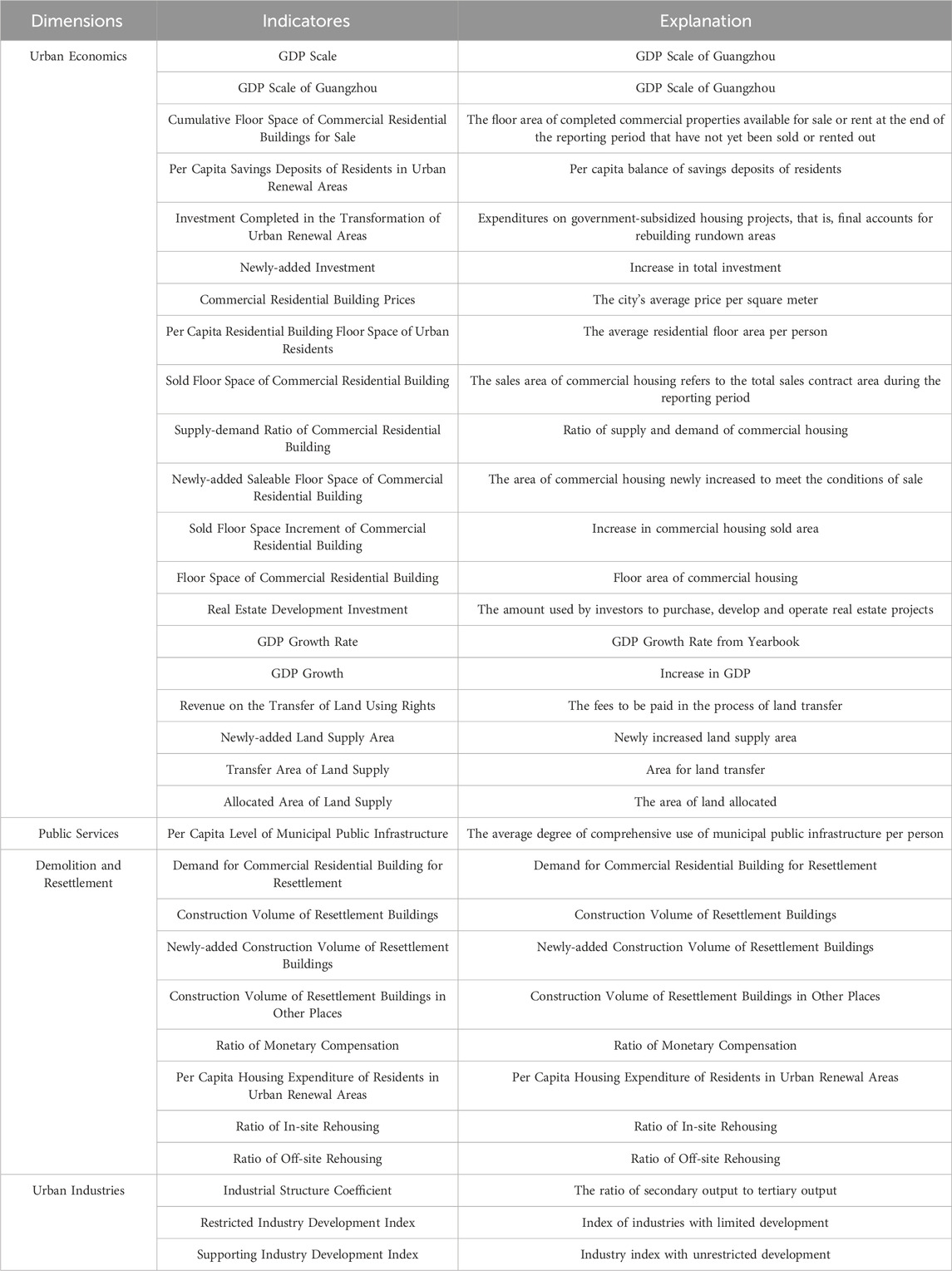
For the purpose of studying the relationship between the three demolition and resettlement programs and urban sustainable development goals, then identifying the methods that can promote sustainable urban development. According to what the United Nations emphasizes in the UN Sustainable Development Goals 2030 Agenda and among the urban sustainable development goals in China, four urban development goals that meet the requirements of the National New Urbanization Plan (2014–2020) are identified as the sustainable development goals for this study. They are the GDP scale, which indicates the economic index of cities. The level of municipal public infrastructure per capita, which indicates the functional service index of cities. The urban industrial structure coefficient, which indicates the urban industry. And the residential floor area per capita, which indicates the urban living environment.
In research methodology, this paper uses causal diagrams and stock-flow diagrams as tools and takes Guangzhou City, Guangdong Province, as the study area. It uses a system dynamics method to study the intrinsic relationship between demolition and resettlement and sustainable urban development. Figure 2 shows the research system framework.
3.2 Methodology
In this study, the system dynamics approach is used to simulate the performance of sustainable urban development. System dynamics has five general steps: articulation of the problem or conceptualization, make causal loop diagram and stock-flow diagram, dynamic hypothesis formulation and validity testing, and then analysis and comparing the results of the different scenarios, the last step is summarizing the suggestion. On the principle of summarizing the research results of scholars and based on the actual situation of Guangzhou’s commercial residential market, this paper analyzes and models four aspects, including housing demolition and compensation, economy, urban public facilities, and industrial development, resulting in the SD model of sustainable urban renewal.
Therefore, in the first step of this study, identifying the key variables of the sustainable urban regeneration model will be based on a review of existing indicators for assessing urban sustainability, such as the Urban Sustainability Index published by McKinsey and Company and Tsinghua University in China (Hua et al., 2016), Zhu et al. (2021), Huang and Cai (2019), Shen et al. (2011), Luo (2019), Zhang, (2015) and Tan et al. (2016), to identify the variables. Also, the availability and accessibility of the data are considered. Finally, 27 variables under the four dimensions were identified (Table 1). Four key variables were included, namely, GDP Scale, Per Capita Residential Building Floor Space of Urban Residents, Per Capita Level of Municipal Public Infrastructure, Industrial Structure Coefficient. And then they are used as the key variables of the SD model. The Technical Line of Research in this Study shows in Fugire 3.2.
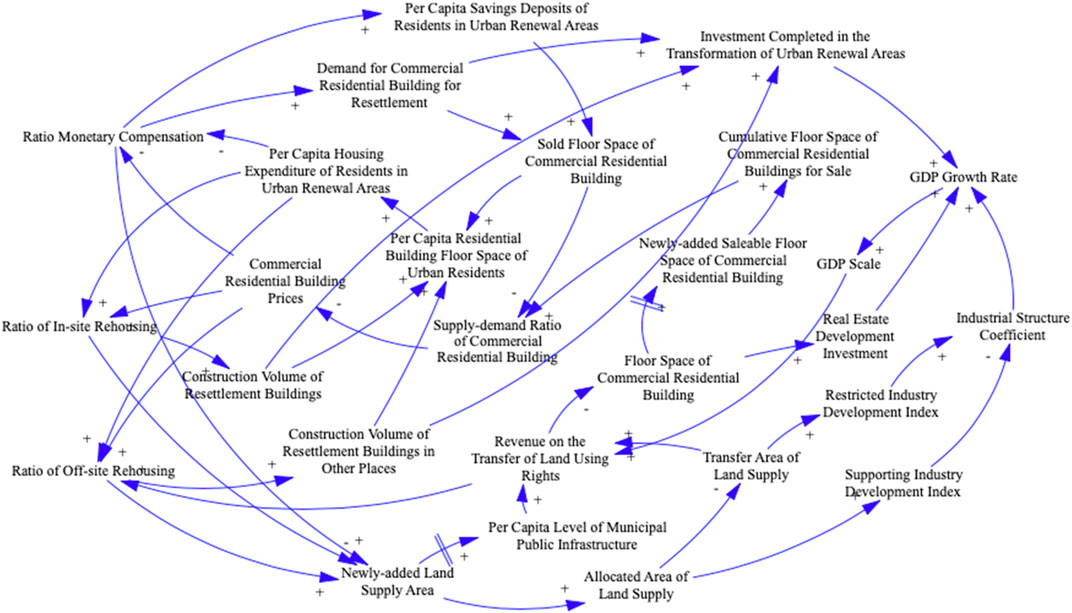
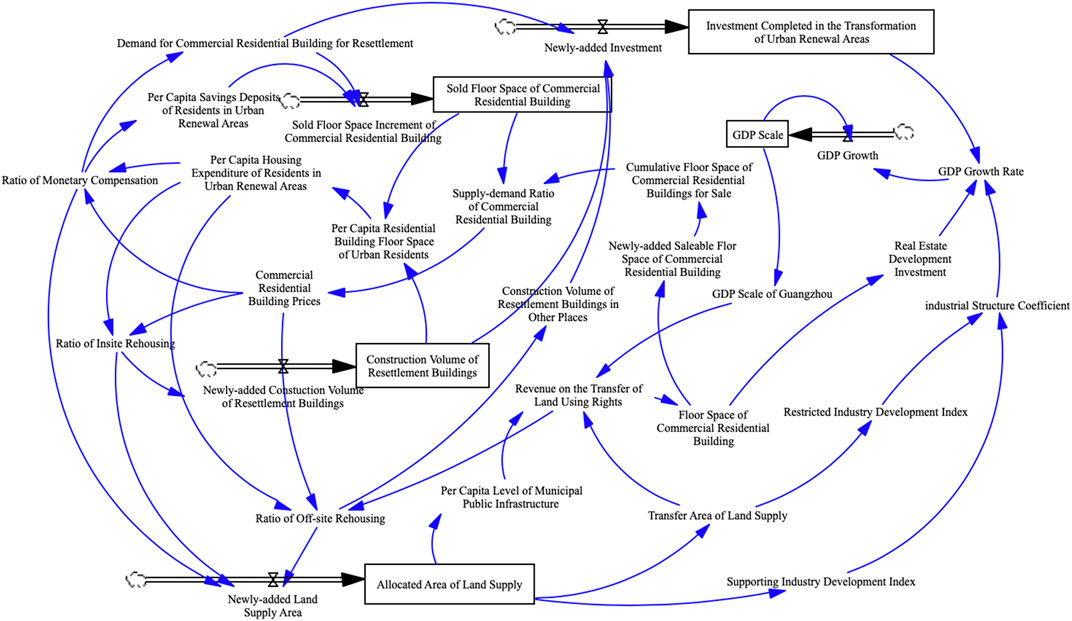
After identifying the key variables, the next step is to make causal loop diagram (Figure 3) and stock-flow diagram (Figure 4). The stock-flow diagram is used to describe the relationship between the variables in the system through the above two flows. In this study, the relationships between variables were analyzed by referring to SD models related to sustainable urbanization such as Shen et al. (2009), Cheng and Liu, (2017), Han et al. (2009), Guan et al. (2011) and Mavrommati et al. (2013).
4 Simulation analysis of the sustainable urban renewal system model: a case study of guangzhou
4.1 Establishment of system boundaries
The boundary of the sustainable urban renewal system is combination of various sub-systems, which involves various links from the allocation and transfer of land to the complete reconstruction of urban villages. In the meantime, integrated reuse of land is a circular economy model (Qin et al., 2013), which transforms the previous fragmented land transfer and reuse into “integration of fragmented land-accumulated land transfer-land reuse”, so as to maximize the use of land resources and to ensure the sustainable development of the stakeholders in urban renewal activities (Long, 2017). In order to study the system of demolition and compensation for urban renewal in China, the sustainable development model of urban renewal is constructed by combining the urban economic subsystem, public service system, demolition and compensation subsystem, and urban industrial subsystem.
4.2 Modeling sustainable urban renewal model
4.2.1 Data sources
This study used datasets on real estate, population, socio-economics, land resources, and industrial development. The main data sources are Guangzhou Statistical Yearbook (2011–2021), Guangdong Statistical Yearbook (2011–2021), China Urban Statistical Yearbook (2009–2022), China Statistical Yearbook (2010–2021), China Statistical Yearbook of Real Estate (2002–2021), public data from the China Statistical Bureau (2015–2022), and the Statistical Bulletin of National Economic and Social Development of Guangzhou Municipality (2015–2022). In the demolition and resettlement subsystem, there is no official information on Demand for Commercial Residential Building for Resettlement, Construction Volume of Resettlement Buildings, Construction Volume of Resettlement Buildings in Other Places, Monetary Compensation, Ratio of In-site Rehousing, and Ratio of Off-site Rehousing are disclosed, so the data are approximated on the basis of news data.
4.2.2 Equations and parameter settings
Based on the stock-flow diagram and the collected data, the equations for the level and auxiliary variables involved were established, as shown in Table 2.
4.2.3 Model checking
First, the SD model needs to be tested for accuracy and feasibility. This can be achieved by obtaining a match between Simulation results (SR) and Historical Data (HD) of the variables in the system. To validate the SD model, the time scope of the variables was set to 5 years, from 2016–2020.
The matching results were obtained through Vensim PLE 5.1 and selected “Sold Floor Space of Commercial Residential Building, Per Capita Savings Deposits of Residents in Urban Renewal Areas, GDP Scale of Guangzhou, Real Estate Development Investment”, a total of four variables were matched to verify the validity of the SD model. The matching results are shown in Table 3. It can be seen that the simulated values of the variables are closer to the actual values and the relative errors are low. This indicates the validity of the SD model. Therefore, the SD model is reliable and can represent the causal feedback relationship between variables, and simulate the performance of sustainable development of the city.
5 Model simulation results and discussion
Guangzhou’s urban renewal activities of complete demolition and reconstruction over the past 10 years have resulted a rapid rise in house prices across the city (Zhang and Dong, 2017), which affects the sustainable development of the economy. Guangdong Province implemented the “Implementation Opinions of the People’s Government of Guangdong Province on Accelerating Shantytown Rehabilitation Work” in 2014 (People’s Government of Guangdong Province, 2014). Guangzhou, as a city with a continuously rising urban population in the country and the largest population in Guangdong Province, requires continuous urban renewal activities to improve the city’s affordability. Therefore, Guangzhou is a good example to study sustainable urban development in cities.
5.1 Simulation scenarios
Scenario analysis is useful for assuming the possible range of the future, and seeking effective strategies and actions on this basis (Kishita et al., 2016). The values of the variables and parameters in the SD model can be adjusted according to different scenarios and the results of the simulation will be different. Subsequently, SD strategies can be developed based on the different simulation results. These development strategies and their impact on the future sustainability performance of the city can be further examined by reusing the SD model.
In this study, seven different development scenarios were assumed for SD model simulation. Seven different development scenarios were assumed for SD model simulation The initial parameters of the model were set as INITIAL TIME = 2016, FINAL TIME = 2030, TIME STEP = 1, Unit for Time: Year.
Current, the proportion of the current compensation method is kept unchanged, and all parameters and variables are kept unchanged.
Scenario one, assuming that the proportion of monetary compensation changes at a rate of increasing by 2% per year, the proportion of in-site rehousing and the proportion of off-site rehousing change at a rate of decreasing by 1% per year, and the amount of in-site rehousing construction and the amount of off-site rehousing construction decrease with the decrease in the proportions. The other variables are held constant in this scenario.
Scenario two, assuming that the proportion of in-site rehousing decreases at a rate of 2% per year, the proportion of off-site rehousing and the proportion of monetary compensation increase at the rate of 1% per year, the amount of in-site rehousing construction decreases with the decrease in the proportion, and the amount of off-site rehousing construction increases with the proportion. In this scenario, other variables are held constant.
Scenario three, assuming that the proportion of off-site rehousing decreases at the rate of 2% per year, the proportion of monetary compensation and the proportion of in-site rehousing increase at the rate of 1% per year, the amount of off-site rehousing construction decreases with the decrease in the proportion, and the amount of in-site rehousing construction increases with the proportion. In this scenario, other variables are held constant.
Scenario four, assumes that the proportion of off-site rehousing increases at a rate of 2% per year, the proportion of monetary compensation and the proportion of in-site rehousing decrease at the rate of 1% per year, the amount of off-site rehousing housing construction increases as the proportion, and the amount of in-site rehousing construction decreases as the proportion decreases. In this scenario, other variables are held constant.
Scenario five, assumes that the proportion of monetary compensation decreases at the rate of 2% per year, the proportion of off-site rehousing and the proportion of in-site rehousing increase at the rate of 1% per year, and the amount of off-site rehousing construction and the amount of on-site rehousing housing construction increase as the proportions increase. Other variables are held constant in this scenario.
Scenario six, assumes that the proportion of in-site rehousing increases at the rate of 2% per year, the proportion of off-site rehousing and the proportion of monetary compensation decrease at the rate of 1% annually, the amount of in-site rehousing construction increases with the proportion, and the amount of off-site rehousing housing construction decreases with the decrease in the proportion. Other variables are held constant in this scenario.
5.2 Simulation results and analyses
The simulation result of the GDP of Guangzhou for 2016–2020 is shown in Figure 5, which shows that the trend of GDP change is the same under the seven scenarios, with Guangzhou’s GDP performance growing the fastest under the environment of Scenario 5. Under the current scenario, GDP grows most slowly.
The simulation results of The Industrial Structure Coefficients are shown in Figure 6, where all seven scenarios exhibit curves with a decreasing trend. The simulation results show that in 2030, the industrial structure coefficient of scenario five curve is the highest, and the industrial structure coefficient developed in the current scenario is the lowest.
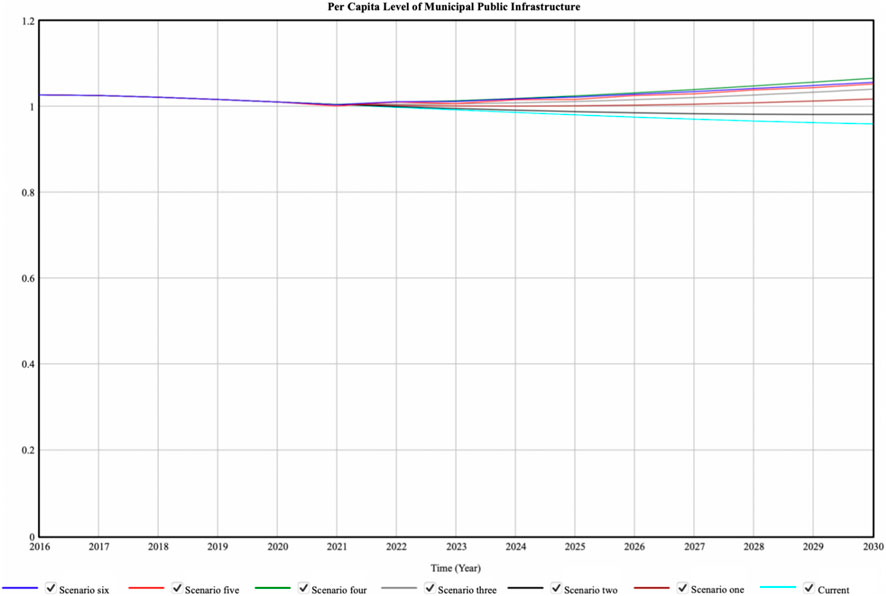
Per Capita Level of Municipal Public Infrastructure has been simulated, the results shown in Figure 7, where the results of the seven scenario simulations are different. In the current scenario, Per Capita Level of Municipal Public Infrastructure has been decreasing and the current one is decreasing the most. The simulation results of the other six scenarios show a decrease and then an increase, and the simulation results of scenario 3.4.5.6 show decrease until 2022 and increase from 2022 onwards. The simulation results for 2021 and 2030 were compared, and the Per Capita Level of Municipal Public Infrastructure for Scenario four was the highest for both.
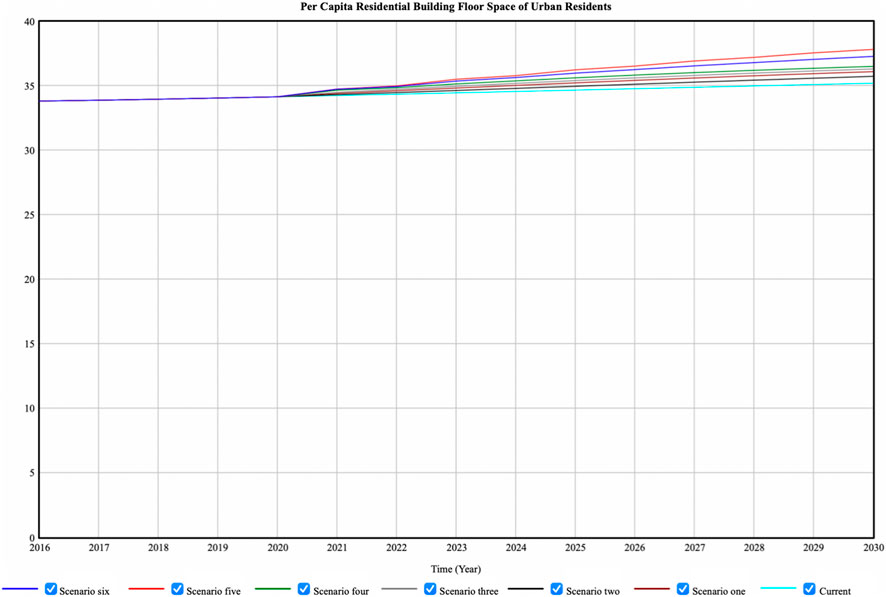
The simulation results of Per Capita Residential Building Floor Space of Urban Residents are shown in Figure 8. The differences between the seven scenarios are small, and all of them show an upward trend. In 2030, the highest one is in scenario 5, and the lowest is in current scenario.
Through comprehensive consideration of the simulation results of the above four important evaluation indicators, it can be concluded that the simulation results of Scenario five are the best.
6 Conclusion
This paper aims to answer the questions from the introduction. It analyzes the demolition and resettlement program for urban renewal system in Guangzhou. Using system dynamics method, it studies the relationship between three demolition and resettlement programs and the sustainable development of the city. It also explores the mixed mode of demolition and resettlement programs that promote the sustainable development of the city. The in-site and off-site rehousing programs are most conducive to the reuse of land resources and sustainable urban development.
On this basis, by modeling a sustainable urban renewal system dynamics model, a comparison of the demolition and resettlement strategies that can be adopted by the local government is concluded by simulation and analysis:
The use of increasing the amount of in-site and off-site rehousing in the same proportion in urban renewal activities can prioritize the promotion of GDP growth, the increase of per capita residential space, the reduction of industrial structure coefficients, and the increase of per capita levels of municipal public infrastructure. Taken together, these four dimensions suggest that the combined strategy can promote sustainable urban development and achieve greater economic and social benefits.
Many cities are still engaged in urban renewal activities. Accurate assessment of the results of sustainable urban renewal is critical to understanding sustainable urban development and supporting the implementation of urban construction. In this paper, a System Dynamics (SD) model, which includes urban economy, social services, demolition and resettlement, and industrial development subsystems, is developed to assist in simulating the performance of sustainable urban renewal. The case study of Guangzhou, China, shows that the SD model is useful in simulating the performance of sustainable urban renewal.
The model has a lot of advantages. First, the method provides a new perspective for assessing sustainable urban renewal performance. Second, by considering the complex and interdependent relationships between variables in the urban development process, the method can improve the accuracy of the assessment results. Third, by analyzing the results in different simulation scenarios, different policies and strategies can be formulated to guide urban development.
What we need to take into account is that different cities have different main tasks in the process of urban development. For other cities in China’s Tier 3.4, where the ratio of supply and demand for commercial housing is higher, the main task is to harmonize the relationship between the ratio of demolition and resettlement and economic growth. It is the further research agenda of this research group to examine the performance of urban renewal in other Chinese cities by using established models of sustainable urban renewal.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
XL: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Validation, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. ZY: Supervision, Resources, Software, Funding acquisition, Writing-original draft, Writing–review and editing. CM: Writing–review and editing, Investigation. JX: Writing–review and editing, Visualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. They acknowledge the financial support from the Guangzhou Institute of Science and Technology Foundation (2023XBZ05, 2023XBZ29, and 2023HGKC17).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Cheng, M., and Liu, C. (2017). Evolutionary game analysis of the behavioral options during demolition process based on system dynamics. Operations Res. Manag. Sci. (2), 35–41. doi:10.12005/orms.2017.0030
China Statistics Bureau (2018). National Bureau of Statistics of China. Available at: https://www.stats.gov.cn/english/InternationalTraining/2018/ (Accessed March 24, 2024).
Department of Fixed Asset Investment Statistics (2021). China statistical Yearbook of real estate. Beijing: China Statistical Publishing House.
Department of Urban socio-economic Survey, National Bureau of Statistics (2022). China urban statistical Yearbook 2022. Beijing: China Statistical Publishing House.
Forrester, J. W. (1958). Industrial dynamics: a major breakthrough for decision makers. Harv. Bus. Rev. 36 (4). doi:10.1007/978-3-642-27922-5_13
Guan, D., Gao, W., Su, W., Li, H., and Hokao, K. (2011). Modeling and Dynamic Assessment of Urban Economy–Resource–environment system with a coupled system dynamics – geographic information system model. Ecol. Indic. 11 (5), 1333–1344. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2011.02.007
Guangdong Survey Team, National Bureau of Statistics and Statistics Bureau of Guangdong Province (2021). Guangdong statistical Yearbook 2021. Beijing: China Statistical Publishing House.
Guangzhou Bureau of Statistics and Guangzhou Survey Team of National Bureau of Statistics (2021). Guangzhou statistical Yearbook 2021. Beijing: China Statistical Publishing House.
Guangzhou Daily (2021). Guangzhou’s urban renewal regulations are open for public comment, Guangzhou urban renewal regulations open for public comment - Guangzhou municipal people’s government portal. Available at: https://www.gz.gov.cn/xw/jrgz/content/post_7368400.html (Accessed March 24, 2024).
Han, J., Hayashi, Y., Cao, X., and Imura, H. (2009). Application of an integrated system dynamics and cellular automata model for Urban Growth Assessment: a case study of Shanghai, China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 91 (3), 133–141. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2008.12.002
Hu, Y. (2014). Cause analysis and countermeasures of environmental health problems in “urban villages” - A case study of dayuan village. Taihe Town, Baiyun Dist. Guangzhou’, Shandong Youth, 81–83. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1004-0927.2014.06.054
Hua, Q., Zhang, Y., Ma, H., Xu, Y., and Zhang, G. (2016). Urban sustainability index 2016. Beijing, Beijing: McKinsey and Co.
Huang, H., and Cai, T. (2019). Mobility characteristics of household’s livelihood capital in urban village demolition and reconstruction: an empirical investigation on two residential resettlements in Wuhan City. Urban Probl. (6), 86–93. doi:10.13239/j.bjsshkxy.cswt.190611
Huang, S. L., and Chen, C. W. (1999). A system dynamics approach to the simulation of urban sustainability. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 34. doi:10.2495/ECO990021
Jiang, H., Sun, Z., Guo, H., Weng, Q., Du, W., Xing, Q., et al. (2021). An assessment of urbanization sustainability in China between 1990 and 2015 using Land Use Efficiency Indicators. npj Urban Sustain. 1 (1), 34. doi:10.1038/s42949-021-00032-y
Kishita, Y., Ohishi, Y., Uwasu, M., Kuroda, M., Takeda, H., and Hara, K. (2016). Evaluating the life cycle CO 2 emissions and costs of thermoelectric generators for passenger automobiles: a scenario analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 126, 607–619. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.02.121
Lao, J., Wang, C., Wang, J., Pan, F., Xi, X., and Liang, L. 2020. Land Use Simulation of Guangzhou Based on Nighttime Light Data and Planning Policies. Remote Sensing 12, 1675. doi:10.3390/rs12101675
Liu, J., Liu, Y., and Wang, X. (2019). An environmental assessment model of construction and demolition waste based on system dynamics: a case study in Guangzhou. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 27 (30), 37237–37259. doi:10.1007/s11356-019-07107-5
Liu, X., and Qiao, Y. (2018). Study on selection of resettlement modes in shantytowns transformation in perspective of urban connotative development: take xi’an as an example. Mod. Urban Res. 9, 91–100. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1009-6000.2018.09.013
Long, C. (2017). Spatial correlation between inter-city producer services agglomeration and intensive land use: based on data from 84 cities. Soc. Sci. Xinjiang (4), 35–44.
Luo, S. (2020). Guangdong leads the country in the scale and experience of urban renewal. Newsclub. Available at: https://www.xxsb.com/content/2020-08/17/content_115048.html.
Luo, Z. (2019). The dilemma and suggestion of sustainable development of rural collective economy under the background of land expropriation and demolition. Econ. Vis. (13), 130–132.
Mavrommati, G., Bithas, K., and Panayiotidis, P. (2013). Operationalizing sustainability in urban coastal systems: a system dynamics analysis. Water Res. 47 (20), 7235–7250. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2013.10.041
National Bureau of Statistics (2022). Statistical communiqué of the People’s Republic of China on the. Stat. Communiqué People’s Repub. China 2021 Natl. Econ. Soc. Dev., Available at: https://www.stats.gov.cn/english/PressRelease/202202/t20220227_1827963.html (Accessed March 24, 2024).
Qin, J., Wang, Y., Tan, W., Cao, R., and Shen, W. (2013). Discussion on land output evaluation during the 11th five-year plan based on the theory of circular economy. Nat. Resour. Econ. China (6), 30–33.
Shen, L.-Y., Jorge Ochoa, J., Shah, M. N., and Zhang, X. (2011). The application of Urban Sustainability Indicators – a comparison between various practices. Habitat Int. 35 (1), 17–29. doi:10.1016/j.habitatint.2010.03.006
Shen, Q., Chen, Q., Tang, B. s., Yeung, S., Hu, Y., and Cheung, G. (2009). A system dynamics model for the sustainable land use planning and development. Habitat Int. 33 (1), 15–25. doi:10.1016/j.habitatint.2008.02.004
State Statistics Bureau (2022a). China urban statistical Yearbook 2022. Beijing: China Statistical Publishing House.
State Statistics Bureau (2022b). National Economy remained stable and saw an increase in the first two months. Available at: https://www.stats.gov.cn/english/(Accessed March 24, 2024).
Tan, Y., Xu, H., and Zhang, X. (2016). Sustainable urbanization in China: a comprehensive literature review. Cities 55, 82–93. doi:10.1016/j.cities.2016.04.002
Uwasu, M., and Yabar, H. (2011). Assessment of sustainable development based on the capital approach. Ecol. Indic. 11 (2), 348–352. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2010.06.002
Xiao, S., Dong, H., Geng, Y., Tian, X., Liu, C., and Li, H. (2020). Policy impacts on municipal solid waste management in Shanghai: A system dynamics model analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 262, 121366. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121366
Zhang, X. (2016). Sustainable urbanization: a bi-dimensional matrix model. J. Clean. Prod. 134, 425–433. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.08.036
Zhang, X., and Dong, J. (2017). Analysis on influencing factors of rising house prices in ordos city and related suggestion— based on microeconomic principles. J. Inn. Mong. Univ. Technology:Natural Sci. Ed. (4), 312–316. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-5167.2017.04.011
Zhao, G., and Li, C. (2018). Research on the reform of spatial planning system from a legislative perspective. Urban Plan. J. (5), 37–49. doi:10.16361/j.upf.201805004
Keywords: urban studies, sustainable cities, urban renewal, causal loop diagrams, dynamics of the system
Citation: Luo X, Yan Z, Ma C and Xie J (2024) Urban sustainable development: inner logic and exploration in Guangzhou. Front. Built Environ. 10:1274589. doi: 10.3389/fbuil.2024.1274589
Received: 09 August 2023; Accepted: 11 April 2024;
Published: 30 May 2024.
Edited by:
Jingkuang Liu, Guangzhou University, ChinaReviewed by:
Shenjun Yao, East China Normal University, ChinaGe Wang, Huazhong Agricultural University, China
Wang Zhenshuang, Dongbei University of Finance and Economics, China
Copyright © 2024 Luo, Yan, Ma and Xie. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zedong Yan, emVkb25nLnlhbkBmb3htYWlsLmNvbQ==
 Xiuming Luo
Xiuming Luo Zedong Yan
Zedong Yan Chong Ma2
Chong Ma2