- 1Neuroscience and Behavior Program, University of Massachusetts, Amherst, MA, USA
- 2Commonwealth Honors College, University of Massachusetts, Amherst, MA, USA
- 3Department of Psychological and Brain Sciences, University of Massachusetts, Amherst, MA, USA
Individuals with a history of traumatic brain injury (TBI) often report sleep disturbances, which may be caused by changes in sleep architecture or reduced sleep quality (greater time awake after sleep onset, poorer sleep efficiency, and sleep stage proportion alterations). Sleep is beneficial for memory formation, and herein we examine whether altered sleep physiology following TBI has deleterious effects on sleep-dependent declarative memory consolidation. Participants learned a list of word pairs in the morning or evening, and recall was assessed 12-h later, following an interval awake or with overnight sleep. Young adult participants (18–22 years) were assigned to one of four experimental groups: TBI Sleep (n = 14), TBI Wake (n = 12), non-TBI Sleep (n = 15), non-TBI Wake (n = 15). Each TBI participant was >1 year post-injury. Sleep physiology was measured with polysomnography. Memory consolidation was assessed by comparing change in word-pair recall over 12-h intersession intervals. The TBI group spent a significantly greater proportion of the night in SWS than the non-TBI group at the expense of NREM1. The TBI group also had marginally lower EEG delta power during SWS in the central region. Intersession changes in recall were greater for intervals with sleep than without sleep in both groups. However, despite abnormal sleep stage proportions for individuals with a TBI history, there was no difference in the intersession change in recall following sleep for the TBI and non-TBI groups. In both Sleep groups combined, there was a positive correlation between Intersession Change and the proportion of the night in NREM2 + SWS. Overall, sleep composition is altered following TBI but such deficits do not yield insufficiencies in sleep-dependent memory consolidation.
Introduction
Over 1.7 million incidences of traumatic brain injury (TBI), ranging from mild concussions to severe head trauma, are recorded each year through emergency department visits, hospitalizations, and deaths (Coronado et al., 2011). Notably, even a single, mild TBI may have long-term psychological and physiological consequences [Armed Forces Health Surveillance Center (AFHSC), 2013; Bhalerao et al., 2013], as TBI encompasses both a primary mechanical insult and also a prolonged secondary injury. Secondary injury may be sustained through lactic acid accumulation from local glycolysis, edema, breakdown of the blood brain barrier, excessive neurotransmitter release, lipase activity, protease activity, and apoptosis (Werner and Engelhard, 2007). This assortment of physiological and chemical abnormalities may create adverse, long-lasting symptoms, including short-term memory deficits (Dean and Sterr, 2013) and an increase in subjectively disturbed sleep [Pillar et al., 2003; Verma et al., 2007; Orff et al., 2009; Armed Forces Health Surveillance Center (AFHSC), 2013; Bhalerao et al., 2013].
Subjective sleep complaints are likely rooted in physiological changes in sleep. Objective measures of sleep reveal decreased sleep efficiency (time asleep/time in bed) and increased wake after sleep onset time (WASO) following TBI (Kaufman et al., 2001; Parcell et al., 2008; Shekleton et al., 2010). An increased need for sleep, evidenced by self-reported and objectively measured hypersomnia (Baumann et al., 2007; Kempf et al., 2010; Sommerauer et al., 2013; Imbach et al., 2015) has also been found in post-TBI individuals. Additionally, overnight sleep recordings after chronic TBI show alterations in sleep architecture. Reports of sleep architecture vary, however, suggesting either lower percentage of sleep in non-rapid eye movement stage 2 (NREM2) and REM (Parcell et al., 2008; Schreiber et al., 2008) or a higher percentage of Slow Wave Sleep (SWS; Parcell et al., 2008; Shekleton et al., 2010; Sommerauer et al., 2013) when compared to those without a history of TBI. Finally, alterations in spectral power, a measure of synaptic strength and synchronization, have also been found following injury (Khoury et al., 2013).
Atypical sleep architecture may exacerbate long-term cognitive deficits caused by injury, as sleep is beneficial for the formation of new memories. Specifically, sleep rich in NREM2 and SWS facilitates declarative memory consolidation, which is the stabilization and transfer of memory traces from short-term to long-term memory (Plihal and Born, 1997; Stickgold, 2005; Diekelmann and Born, 2010; Wilson et al., 2012). For instance, it has been suggested that, during NREM2, declarative memory traces are reactivated and redistributed from the hippocampus to neocortex (Kempf et al., 2010), and this transfer is enhanced through increased cortical synchronization that occurs during SWS (Sirota et al., 2003; Takashima et al., 2006). Moreover, specific traits of NREM2 (e.g., sleep spindles or sigma power; Clemens et al., 2005; Genzel et al., 2009; Holz et al., 2012; Ruch et al., 2012) and SWS (e.g., %SWS and delta power; Holz et al., 2012) have been linked with declarative memory performance following a sleep bout (Marshall et al., 2006), particularly early in the night (Plihal and Born, 1997; Genzel et al., 2009). Combined NREM measures (e.g., spindle density across both stages and total %NREM; Plihal and Born, 1997; Clemens et al., 2005; Holz et al., 2012) have also been linked with overnight consolidation. The latter studies align with recent notions that sleep stages may act sequentially or in concordance to have beneficial declarative memory consolidation effects (Mazzoni et al., 1999; Ficca et al., 2000; Clemens et al., 2005; Göder et al., 2007; Ruch et al., 2012).
Despite well-established sleep deficits following brain injury, to our knowledge, sleep-dependent memory consolidation has never been examined in individuals with a history of TBI. Given that both NREM2 and SWS stages have reportedly been affected by TBI, we sought to examine whether these changes in sleep impair sleep-dependent consolidation. To this end, we utilized a word-pair learning task and investigated memory following intervals containing overnight sleep or spent fully awake. We used polysomnography, a system that objectively quantifies sleep quality and architecture, to examine sleep physiology in those with a history of mild TBI (i.e., having suffered from a concussion) compared to controls without a history of TBI. We hypothesized that TBI subjects would have impaired sleep, in measures of sleep stage duration and fragmentation (i.e., lower sleep efficiency and greater WASO) compared to those without a history of TBI. Moreover, we posited that poorer sleep quality would hinder sleep-dependent memory consolidation when compared to those without a history of TBI.
Methods
Participants
Participants were 58 healthy young adult participants (18–22 years). Subjects were recruited through an online recruitment system (SONA) or by word-of-mouth and were compensated with extra credit for a Psychology course or monetary payment. To be eligible, participants were required to habitually sleep more than 6 h per night and have less than 3 naps per week. Participants were excluded if they typically consumed more than 14 cups of coffee or alcohol per week, had a neurological disorder (other than a history of TBI in the TBI group), were taking anti-psychotic or anti-seizure medications, or were taking sleep-affecting medications. Importantly, to specifically examine the chronic effects of TBI (as opposed to transient, acute effects), participants in the TBI group had a history of TBI with injury at least 1 year prior to participation in the study.
Participants were assigned to one of four groups: TBI Wake, TBI Sleep, non-TBI Wake, or non-TBI Sleep. Participants were first assigned to a group based on TBI history and then semi-randomly assigned to a Sleep or Wake group, with careful balance of numbers of TBI incidents and severity of TBIs across the TBI Sleep and TBI Wake groups.
Word-Pair Learning Task
The word-pair task has been utilized to examine declarative memory consolidation in previous studies in our lab (Wilson et al., 2012). Stimuli were 40 semantically-unrelated word pairs consisting of single-syllable nouns. The task had three phases: Encoding, Immediate Recall, and Delayed Recall. During Encoding, word pairs appeared on a computer monitor for 5 s with a 100 ms inter-stimuli interval. Participants passively viewed the pairs and were instructed to use a mnemonic strategy to help remember the pairs. Specifically, participants were told to think of associations between the pairs and to picture this association in their mind (e.g., if “aunt-zoo” was presented, they could imagine their aunt on display at a zoo). This instruction was designed to facilitate hippocampal-dependent contextual learning (Toki et al., 2014). Subsequently, participants practiced recalling the pairs with feedback. The first word from each pair was presented individually in a random order. The first and last two pairs of the encoded list were removed to eliminate primacy and recency effects (leaving a total of 36 pairs). If the participant’s response was incorrect, the correct response was displayed on the computer monitor for 750 ms. If the response was correct, the next stimuli appeared on the screen. Recall practice continued until participants reached 65% proficiency or the full list of words had appeared five times.
The Immediate Recall phase began following the Encoding phase. Participants were presented with one word from the encoded pairs and were instructed to recall the corresponding word in the pair. There was no feedback for correct or incorrect responses. In Session 2, which occurred after a 12-h break, participants completed the Delayed Recall phase, which was identical to the Immediate Recall phase.
Procedure
Procedures were approved by the Institutional Review Board at the University of Massachusetts, Amherst. Before the study commenced, each participant provided written informed consent. Participants then underwent one of two in-lab sessions. For those in the Wake group, session 1 took place in the morning and session 2 took place in the evening, following 12 h awake. For the Sleep group, session 1 took place in the evening and session 2 took place the next morning, following 12 h containing an overnight sleep interval.
In the first session, after completing the consent process and the Stanford Sleepiness Scale (SSS), Morningness-Eveningness Questionnaire (MEQ), Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS), Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), forward digit span test, and TBI questionnaire (all described below), participants performed the Encoding and Immediate Recall phases. Participants returned 12 h later to complete the Delayed Recall phase. Subsequently, participants in the Wake group were instructed not to nap. Participants in the Sleep group were equipped with polysomngraphy electrodes in their home, 1 h prior to their typical bedtime. Twelve hours after session 1, session 2 took place in the lab. Subjects completed the SSS followed by the Delayed Recall phase of the word-pair task.
Questionnaires
During Session 1, participants completed an in-house questionnaire that recorded self-reported number of TBIs, cause of TBI(s), presence of post-concussive syndrome, and symptoms present after the injury. To assess the participant’s sleepiness level, or tendency to fall asleep during certain everyday activities, the ESS was completed (Johns, 1994). The PSQI was administered to assess the participant’s habitual sleep quality and sleep disturbances during the past month of sleep (Buysse et al., 1989). The MEQ was used to determine the participant’s chronotype, or preference for performing tasks and activities during the morning hours or evening hours (Horne and Ostberg, 1976). The SSS was used to determine the participant’s level of sleepiness at the time of the session (Hoddes et al., 1973). Lastly, the participants in the Sleep group were given a sleep survey to gather subjective information about the participant’s sleep during the night prior.
We used the Forward Digit Span task (FDS) from the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale IV to assess possible working memory deficits in the TBI group (Dean and Sterr, 2013). The FDS requires a series of digits to be read to the subject, who is then asked to verbally repeat the digits in the same order. This task begins with a series of 2 digits and increases in length by a single digit per trial up to a series of 10 digits (Wechsler, 2008). Due to late adoption of this measure, the FDS was performed by 18 participants in the TBI group and 24 in the non-TBI group.
Polysomnography
Polysomnography was recorded with the Aura PSG ambulatory system (Grass Technologies). An electrode montage was applied in the participants’ home approximately 1 h before their typical bedtime. The montage included 2 EOG leads (right and left ocular canthus), two chin EMG leads, and six cortical EEG leads (F3, F4, C3, C4, O1, O2) with each electrode referenced to Cz. Data analysis was conducted according to the revised AASM manual (Silber et al., 2007).
Data Analysis
Word-Pair Learning and Consolidation
Word pair data were individually reviewed for total number of correct word pair responses, allowing for misspelling. Recall accuracy was measured as percentage of the total number of word pairs (of 36 possible). The change in performance between Immediate and Delayed Recall was assessed using an Intersession Change score. Intersession Change in recall was calculated by subtracting the Immediate Recall accuracy from the Delayed Recall accuracy and normalizing to baseline accuracy.
Intersession Change was compared across groups using t-tests to determine whether there was a difference between Sleep and Wake group performance. T-tests were also used to compare sleep staging and spectral power between TBI Sleep and non-TBI Sleep groups. Circadian effects at time of encoding were tested using a 2 × 2 ANOVA, with between-subject variables condition (Sleep vs. Wake) and group (TBI vs. non-TBI). Similarly, ANOVA tests were used to compare subjective sleep scores (SSS, ESS, PSQI, MEQ), cognitive performance on the FDS, and Intersession Change. Finally, Pearson’s correlations were performed to investigate relationships between sleep factors (e.g., WASO and %SWS) with Intersession Change to determine whether specific qualities of sleep are related to memory performance. Given the large number of statistical analyses, alpha was set to 0.01.
Polysomnography
EEG, EMG, and EOG data were scored using the American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM) Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events (Silber et al., 2007), identifying periods of wake and sleep stages NREM1, NREM2, SWS, and REM. Two trained sleep researchers scored all polysomnograms. Inconsistencies were discussed between scorers until consensus was reached. Total sleep across the night and percent in each sleep stage was calculated and compared across TBI and non-TBI groups. A combined %NREM2 and %SWS composite (%NREM) was created to address sleep stage interaction effects (Clemens et al., 2005; Göder et al., 2007). Pearson’s R coefficients were used to assess correlations between percent total sleep time spent in each sleep stage and intersession change in recall.
The spectral power density (μV2/Hz) in the sigma (12–15 Hz) and delta (0.5–4 Hz) range was quantified using BrainAnalyzer 2.0 Software (BrainVision, Berlin, Germany). Delta was examined during SWS, and sigma was examined in both NREM2 and over a combined NREM2 and SWS measure (Clemens et al., 2005; Holz et al., 2012). EEG data was first segmented into stages and filtered to 0.3–25 Hz. Raw data inspection was performed to eliminate artifacts, and data were again segmented into 4 s sections. Semi-automatic artifact rejection was performed on individual channels. Fast-Fourier transformation was performed with a Hanning window with 10% overlap. Analyses with delta and sigma utilize relative power (Khoury et al., 2013) in which power in the given spectrum was divided by time in the sleep stage measured (i.e., delta power divided by minutes in SWS; sigma power divided by minutes in NREM2 and NREM2/SWS combined).
Results
Group Descriptions
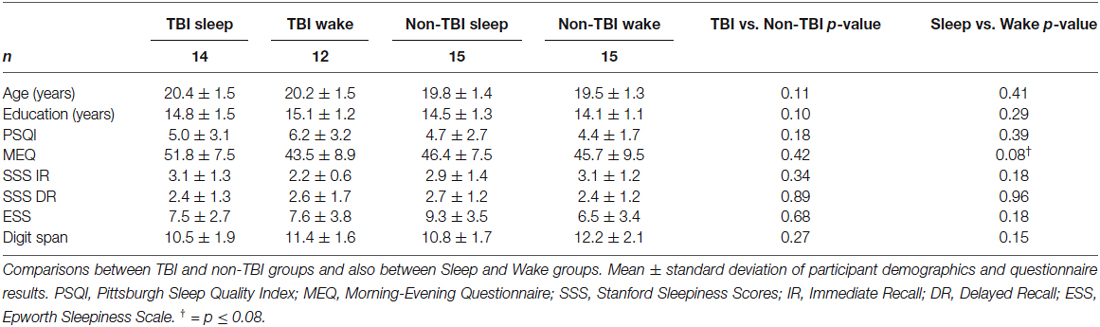
One TBI Sleep participant, 1 TBI Wake participant, and 1 non-TBI Wake participant were excluded for falling above or below 3 standard deviations of the mean in terms of Intersession Change in recall. The final sample included 56 participants across the four groups (Table 1). We confirmed all Wake participants slept >5 h the night before the experiment and all Sleep participants slept >5 h the night of the experiment. No Wake participants reported napping during the 12-h interval between session 1 and 2. No participants reported using alcohol or sleep medications during the study. There were no significant differences in age, gender ratio, or years of education between groups (Table 1).
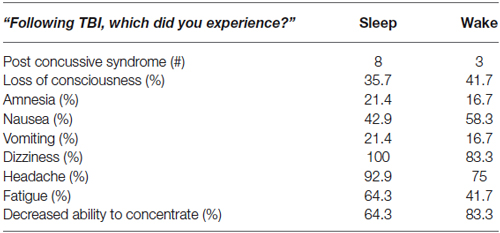
There were no significant differences between TBI Sleep and Wake groups for TBI history or symptoms. Among the 26 TBI participants, there were 34 diagnosed concussions (19 in the Sleep group and 15 in the Wake group; six participants had more than one diagnosed TBI), 11 of which were accompanied by post-concussive syndrome. The average time since most recent concussion was 4.35 ± 3.14 years. The most common symptoms in both groups were dizziness, headache, decreased ability to concentrate, and fatigue (Table 2). Interestingly, only 2 TBI Wake participants and no TBI Sleep participants reported (TBI questionnaire) having sleep disturbances since the time of TBI.
Groups also did not differ in terms of habitual sleep or sleepiness or chronotype. As shown in Table 1, no significant differences were observed in PSQI, SSS at Immediate Recall, SSS at Delayed Recall, ESS, or MEQ scores. Importantly, no significant differences were found for FDS scores, indicating that TBI condition did not affect short-term memory and attention.
Word Pair Learning Task
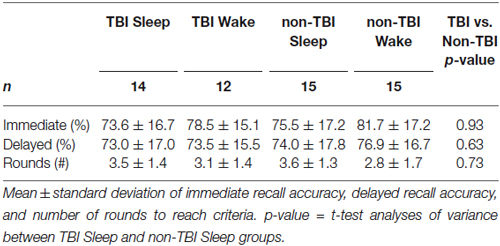
There were no significant differences in baseline performance across all groups as measured by Immediate Recall accuracy, F(3,52) = 0.655; p = 0.58, or by number of rounds to reach criteria, F(3,52) = 1.51, p = 0.22, indicating circadian effects and time-of-day did not affect performance (Table 3). Moreover, there was no significant difference in Immediate Recall for TBI and non-TBI groups, t(52) = −1.38, p = 0.187, or for the number of rounds to reach criteria, t(52) = 0.345, p = 0.63, suggesting that the history of TBI did not impair word-pair learning.
We examined whether performance improvements were greater following sleep compared to wake, as predicted by our previous work (Wilson et al., 2012). There was a significant main effect of condition (Sleep vs. Wake) with greater reduction in recall in the Wake groups, F(1,51) = 9.30; p = 0.004 (Figure 1). The main effect of group (TBI vs. non-TBI) was not significant, F(2,51) = 0.421; p = 0.658, and there was no interaction between the Sleep/Wake condition and TBI/non-TBI status, F(1,51) = 0.006; p = 0.939. These results indicate both Sleep groups significantly outperformed the Wake groups, and there were no differences in sleep-dependent consolidation between the TBI and non-TBI groups.
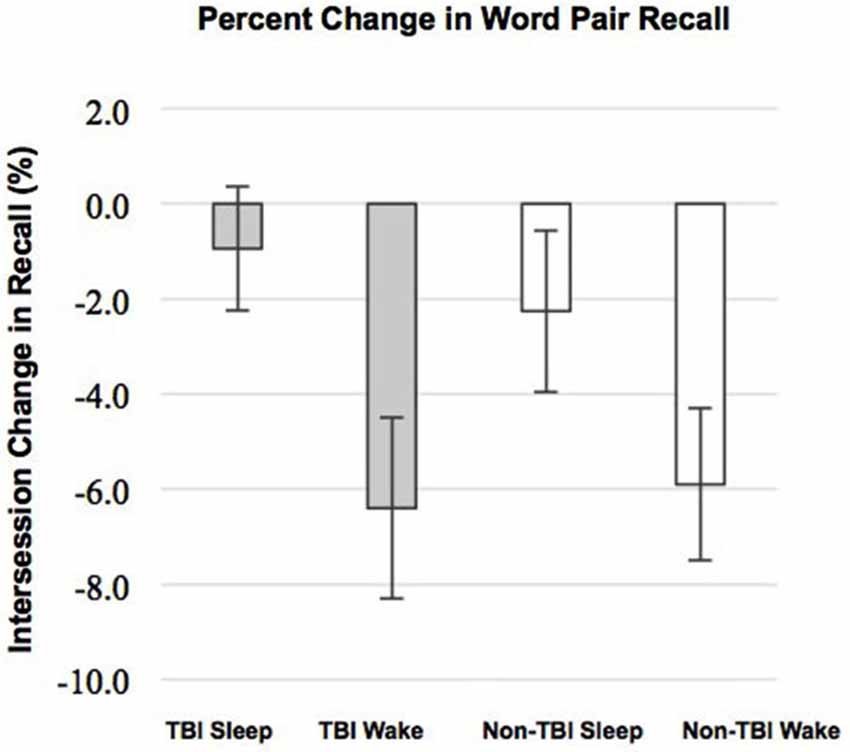
Figure 1. Differences in Intersession Change between Sleep and Wake groups. Error bars represent standard error of the mean.
Sleep Assessments
Due to equipment malfunction and operation errors, five sleep reports were unusable. The following results are based on polysomnography recorded in 11 participants in the TBI Sleep and 13 participants in the non-TBI Sleep group.
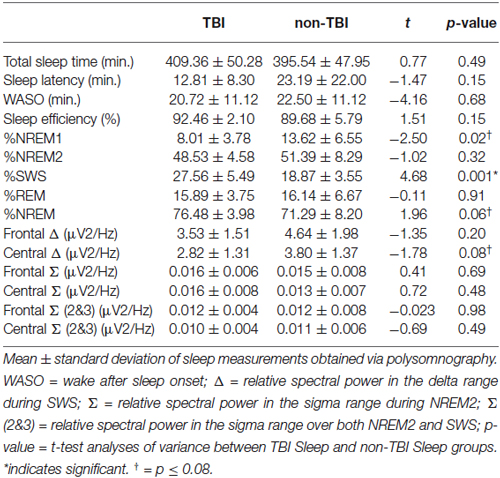
Contrary to our predictions, as shown in Table 4, there were no differences in sleep efficiency or WASO between the TBI and non-TBI Sleep groups. However, a two-tailed t-test showed a significant difference in %SWS between groups, where the TBI Sleep group had greater %SWS than the non-TBI Sleep group, t(22) = 4.675, p = < 0.001, Table 4. This excess of SWS was at the expense of %NREM1, as an additional t-test revealed TBI participants had significantly less %NREM1 compared to non-TBI Sleep participants, t(22) = −2.502, p = 0.02 (Figure 2), yet not when correcting for multiple comparisons. There were no differences between groups in total sleep time, sleep latency, %NREM2 or %REM. The TBI Sleep group spent more time, albeit not significantly more, in %NREM than did the non-TBI Sleep group, t(22) = 1.96, p = 0.06, likely as a result of increased %SWS.
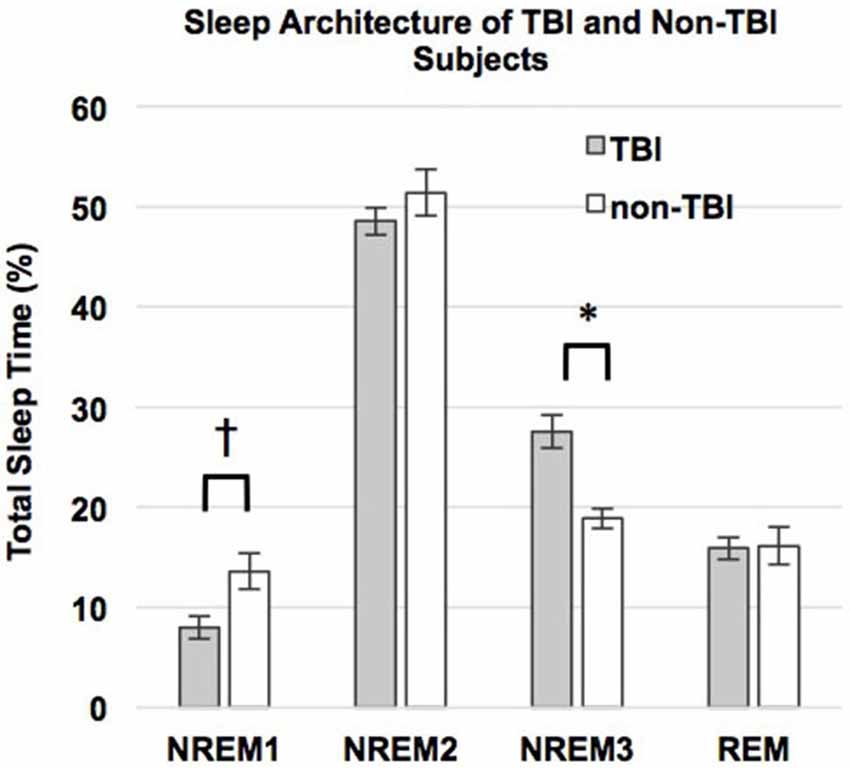
Figure 2. Percent total sleep time spent in each stage of sleep. Error bars represent standard error of the mean. † = p ≤ 0.08.
Spectral power in the relative sigma (12–15 Hz) and relative delta (0.5–4 Hz) bands was compared between TBI and non-TBI Sleep groups using two-tailed t-tests. No differences were found in sigma power, or a combined NREM2/SWS sigma measure at any frontal or central locations. However, the central delta band differed near-significantly between the groups, t(22) = −1.78, p = 0.08, such that that TBI group had lower relative delta power, as has been previously found (Khoury et al., 2013).
Sleep and Memory Performance
We used correlations to assess the relationship between sleep parameters and Intersession Change, a measure of memory consolidation. Given that there were no differences in the Intersession Change between the TBI and non-TBI groups, we initially considered these groups combined, and then analyzed the both the non-TBI and TBI groups separately. Counter to previous work (Holz et al., 2012), there was no significant correlation between Intersession Change and %SWS, %NREM2, delta power, sigma power in NREM2 or sigma power combined over NREM2 and SWS in any of the groups (Table 5). There was, however, a significant positive correlation between total %NREM and Intersession Change in the combined group (see Figure 3, r = 0.516; p = 0.01) and a near-significant positive correlation with Intersession Change (r = 0.56; p = 0.05) in the non-TBI group.
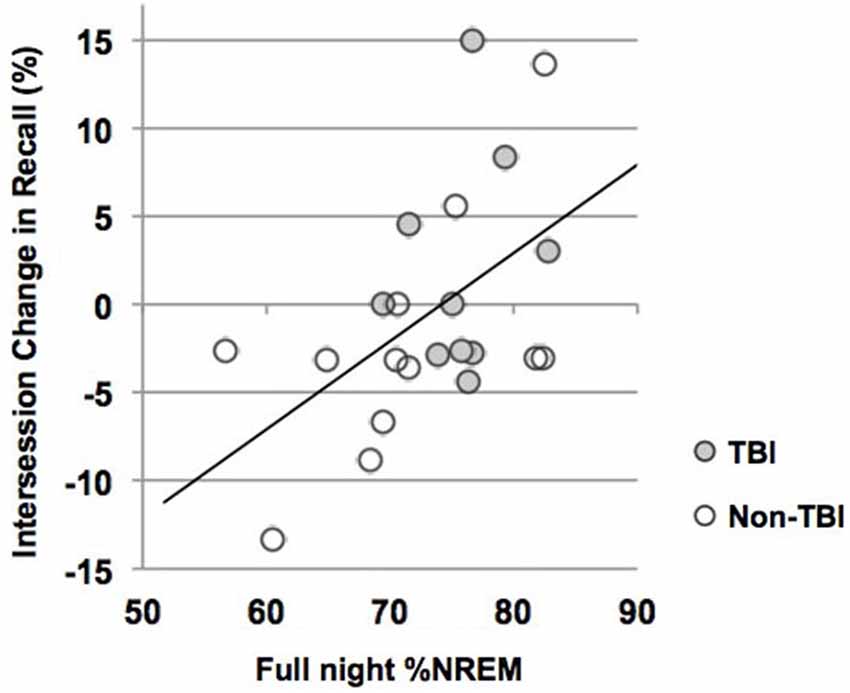
Figure 3. Intersession Change and percent of the night in NREM (%NREM2 + %SWS). Line represents line of best fit for combined groups.
Given that NREM during the first half of the night is particularly beneficial for memory consolidation (Plihal and Born, 1997) we performed a post hoc correlation between %NREM and Intersession Change in each half of the night, including all participants (values not reported). Consistent with prior reports, %NREM in the first half of the night was nearly positively correlated with Intersession Change (r = 0.437; p = 0.04) but this relationship was not present for half two (r = 0.228; p = 0.19).
Discussion
This study investigated whether young adults with a history of TBI have decreased sleep quality and architecture and whether this affects sleep-dependent declarative memory consolidation. Contrary to our predictions, TBI subjects did not have increased WASO or decreased sleep efficiency. However, we report an increase in %SWS sleep, at the expense of %NREM1 sleep, in individuals who have experienced a TBI. This study is also the first to show preserved declarative sleep-dependent memory consolidation in those with a history of TBI. Interestingly, sleep-dependent memory consolidation was exhibited despite atypical sleep architecture.
As has been previously reported, after performing a declarative word-pair learning task, those who slept had a significantly greater Intersession Change than those who remained awake for an equivalent period of time, a hallmark of sleep-dependent memory consolidation. We do not believe this difference in recall is due to circadian effects, as there were no differences between learning at Immediate Recall for those who learned in the morning (Wake groups) and those who learned in the evening (Sleep groups).
Moreover, a significant correlation between %NREM and Intersession Change support an active role of sleep in memory consolidation (Holz et al., 2012; Wilson et al., 2012). We did not find a correlation between %SWS, %NREM2, or spindles and Intersession Change as reported in previous studies (Clemens et al., 2005; Genzel et al., 2009; Holz et al., 2012; Ruch et al., 2012). However, the association between Intersession Change and %NREM is consistent with hypotheses that sleep stages may interact or act sequentially (Mazzoni et al., 1999; Ficca et al., 2000; Clemens et al., 2005; Göder et al., 2007; Ruch et al., 2012). For example, recent studies using experimental sleep stage manipulations have found enhancing both NREM2 and SWS boosts declarative sleep-dependent consolidation (Mednick et al., 2013), whereas enhancing only SWS does not (Feld et al., 2013). It has therefore been suggested that the shared components of NREM2 and SWS (e.g., sleep spindles, slow oscillations) underlie consolidation in concert (Ackermann and Rasch, 2014). Thus, it may be that both NREM2 and SWS are important for declarative sleep-dependent memory consolidation. Of note, given that a large-scale investigation recently found no correlation between sleep staging and sleep-dependent consolidation of declarative memory traces (Ackermann et al., 2014), the relationship between %NREM and memory enhancement in the current study should be interpreted with caution.
Despite prior studies showing that short-term memory is affected in those who have suffered from a TBI (Dean and Sterr, 2013), we did not see deficits in sleep-dependent memory consolidation for those with and without a history of TBI. It has been posited that SWS facilitates restoration following brain injury (Gao et al., 2010; Sommerauer et al., 2013), and it may be that the normal-to-increased amount of SWS, which is a stage that is beneficial for cortical communication and plasticity, conserved both short-term memory and sleep-dependent consolidation in this sample.
Previous studies found decreased sleep efficiency and increased WASO in those with TBI (Kaufman et al., 2001; Parcell et al., 2008; Shekleton et al., 2010), yet we did not find a difference in these measures between groups in the present study. Differing sample demographics may account for these discrepancies in findings. Kaufman et al. (2001) studied younger individuals (10–16.5 years), who have considerably different sleep characteristics and needs than our young adult sample. Participants in the young adult age range are often sleep deprived and may therefore have a higher homeostatic sleep drive than younger adults (Hershner and Chervin, 2014). An increased homeostatic drive may minimize awakenings, which ultimately increases sleep efficiency. Additionally, Parcell et al. (2008) investigated individuals with a history of moderate to severe brain injury, whereas our sample had only mild TBI. It may be that poorer sleep quality accompanies more severe brain injury, and that sleep efficiency remains intact following a mild brain injury in young adults. Finally, because none of the TBI Sleep individuals reported sleep issues following injury, it may be that, by chance, our sample did not include subjects with poor sleep quality.
An increased %SWS was previously found in those with a history of TBI (Parcell et al., 2008; Shekleton et al., 2010; Sommerauer et al., 2013). Consistent with these findings, our non-TBI sample had %SWS in the normal range (~20%), and the TBI group had an unusually high %SWS compared to previous reports (Ohayon et al., 2004), with some exceeding 30%. Additionally, the TBI group had notably lower normalized delta power during SWS. There are multiple hypotheses that attempt to explain increased SWS post-TBI. First, following a series of investigations that found increased sleep need after both acute and chronic TBI, it was posited that SWS and its neuroplastic processes (e.g., axonal sprouting, synaptic remodeling) act as a recovery mechanism that aid in healing (Baumann et al., 2007; Kempf et al., 2010; Sommerauer et al., 2013). This hypothesis is supported by investigations in which SWS accelerates healing following a stroke (Gao et al., 2010). Paralleling this hypothesis, Parcell et al. (2008) suggested TBI may trigger a compensatory mechanism that occurs in response to brain injury, and this mechanism may increase %SWS. This hypothesis is supported by the increased neuronal reorganization, synaptic potentiation and neural proliferation seen following brain injury (Kernie et al., 2001; Nudo, 2011). Strengthening of neurons in response to injury may contribute to the synchronicity required for initiation and maintenance of %SWS. Finally, it has been suggested that the trauma itself increases SWS, as most brain injuries have a widespread affect on multiple brain circuits (Sommerauer et al., 2013). Given the current results, we posit that increased %NREM may be necessary to compensate for marginally lower delta power in the central sites.
At the expense of increased %SWS, the TBI individuals exhibited decreased %NREM1. Of note, %NREM1 found in the current sample is higher than that reported previously in young adults (15–20% vs. 2–5%: Ohayon et al., 2004). However, a closer examination of previous work shows that whereas %NREM1 is low when nocturnal sleep follows an adaptation night (Martin et al., 1997; Fischer et al., 2002), nights without an adaptation period often have NREM1 in a range of 14–23% (Crowley et al., 2002; Baran et al., 2012).
It is important to address the potential limitations of this study. Our sample included subjects who suffered from a concussion at least 1 year prior to enrollment, as we sought to include only those with long-term consequences of TBI. However, we did not require neurological records to verify TBI presence and severity. It is therefore possible that the TBI group included participants who did not suffer from a concussion as reported. Likewise, the non-TBI group may have included individuals who have indeed suffered from a concussion. However, given that we provided equal compensation for participants in both groups, it is doubtful that participants would deliberately falsely report their TBI history.
This sample lacked sleep efficiency and WASO deficits, as have been shown previously. They also lacked cognitive impairment, indicated by Digit Span scores and also unimpaired Immediate Recall performance. It may be, then, that our sample included an atypical population that is not representative of others with acute TBI. The heterogeneity of our sample (e.g., time since TBI, site of injury, etc.) may account for a lack of overlap with previous reports. However, given that differences observed in %SWS and relative delta power are consistent with prior work (Parcell et al., 2008; Shekleton et al., 2010; Khoury et al., 2013), it is unlikely that our sample was dissimilar from others. These results, in fact, highlight the severity of mild TBI, as our heterogeneous group in the chronic TBI stage exhibits characteristics that have been found in more homogenous groups with acute injury. Nonetheless, future work would benefit from neurological exams characterizing the TBI and identifying a more uniform group.
Author Contributions
JM collected data, performed data analysis, wrote the manuscript; KMM collected data, performed data analysis; OSH collected data, performed data analysis; RMCS designed the study, wrote the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
Ackermann, S., Hartmann, F., Papassotiropoulos, A., de Quervain, D. J., and Rasch, B. (2014). No associations between interindividual differences in sleep parameters and episodic memory consolidation. Sleep [Epub ahead of print].
Ackermann, S., and Rasch, B. (2014). Differential effects of non-REM and REM sleep on memory consolidation? Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 14:430. doi: 10.1007/s11910-013-0430-8
Armed Forces Health Surveillance Center (AFHSC). (2013). Incident Diagnoses of Common Symptoms (“sequelae”) following Traumatic Brain Injury, Active Component, U.S. Armed Forces, 2000–2012. Medical Surveillance Monthly Report. 20, Silver Spring, MD: Defense and Veterans Brain Injury Center Silver Spring, 9–13.
Baran, B., Pace-Schott, E. F., Ericson, C., and Spencer, R. M. (2012). Processing of emotional reactivity and emotional memory over sleep. J. Neurosci. 32, 1035–1042. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2532-11.2012
Baumann, C. R., Werth, E., Stocker, R., Ludwig, S., and Bassetti, C. L. (2007). Sleep-wake disturbances 6 months after traumatic brain injury: a prospective study. Brain 130, 1873–1883. doi: 10.1093/brain/awm109
Bhalerao, S. U., Geurtjens, C., Thomas, G. R., Kitamura, C. R., Zhou, C., and Marlborough, M. (2013). Understanding the neuropsychiatric consequences associated with significant traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 27, 767–774. doi: 10.3109/02699052.2013.793396
Buysse, D. J., Reynolds, C. F. 3rd, Monk, T. H., Berman, S. R., and Kupfer, D. J. (1989). The Pittsburgh sleep quality index: a new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res. 28, 193–213. doi: 10.1016/0165-1781(89)90047-4
Clemens, Z., Fabó, D., and Halász, P. (2005). Overnight verbal memory retention correlates with the number of sleep spindles. Neuroscience 132, 529–535. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.01.011
Coronado, V. G., Xu, L., Basavaraju, S. V., McGuire, L. C., Wald, M. M., Faul, M. D., et al. (2011). Surveillance for traumatic brain injury-related deaths—United States, 1997–2007. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 60, 1–32.
Crowley, K., Trinder, J., Kim, Y., Carrington, M., and Colrain, I. M. (2002). The effects of normal aging on sleep spindle and K-complex production. Clin. Neurophysiol. 113, 1615–1622. doi: 10.1016/s1388-2457(02)00237-7
Dean, P. J., and Sterr, A. (2013). Long-term effects of mild traumatic brain injury on cognitive performance. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 7:30. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2013.00030
Diekelmann, S., and Born, J. (2010). The memory function of sleep. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 11, 114–126. doi: 10.1038/nrn2762
Feld, G. B., Wilhelm, I., Ma, Y., Groch, S., Binkofski, F., Mölle, M., et al. (2013). Slow wave sleep induced by GABA agonist tiagabine fails to benefit memory consolidation. Sleep 36, 1317–1326. doi: 10.5665/sleep.2954
Ficca, G., Lombardo, P., Rossi, L., and Salzarulo, P. (2000). Morning recall of verbal material depends on prior sleep organization. Behav. Brain Res. 112, 159–163. doi: 10.1016/s0166-4328(00)00177-7
Fischer, S., Hallschmid, M., Elsner, A. L., and Born, J. (2002). Sleep forms memory for finger skills. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 99, 11987–11991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.182178199
Gao, B., Cam, E., Jaeger, H., Zunzunegui, C., Sarnthein, J., and Bassetti, C. L. (2010). Sleep disruption aggravates focal cerebral ischemia in the rat. Sleep 33, 879–887.
Genzel, L., Dresler, M., Wehrle, R., Grözinger, M., and Steiger, A. (2009). Slow wave sleep and REM sleep awakenings do not affect sleep dependent memory consolidation. Sleep 32, 302–310.
Göder, R., Scharffetter, F., Aldenhoff, J. B., and Fritzer, G. (2007). Visual declarative memory is associated with non-rapid eye movement sleep and sleep cycles in patients with chronic non-restorative sleep. Sleep Med. 8, 503–508. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2006.11.014
Hershner, S. D., and Chervin, R. D. (2014). Causes and consequences of sleepiness among college students. Nat. Sci. Sleep 6, 73–84. doi: 10.2147/NSS.s62907
Hoddes, E., Zarcone, V., Smythe, H., Phillips, R., and Dement, W. C. (1973). Quantification of sleepiness: a new approach. Psychophysiology 10, 431–436. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.1973.tb00801.x
Holz, J., Piosczyk, H., Feige, B., Spiegelhalder, K., Baglioni, C., Riemann, D., et al. (2012). EEG Σ and slow-wave activity during NREM sleep correlate with overnight declarative and procedural memory consolidation. J. Sleep Res. 21, 612–619. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2869.2012.01017.x
Horne, J. A., and Ostberg, O. (1976). A self-assessment questionnaire to determine morningness-eveningness in human circadian rhythms. Int. J. Chronobiol. 4, 97–110.
Imbach, L. L., Valko, P. O., Li, T., Maric, A., Symeonidou, E. R., Stover, J. F., et al. (2015). Increased sleep need and daytime sleepiness 6 months after traumatic brain injury: a prospective controlled clinical trial. Brain 138, 726–735. doi: 10.1093/brain/awu391
Johns, M. W. (1994). Sleepiness in different situations measured by the Epworth sleepiness scale. Sleep 17, 703–710.
Kaufman, Y., Tzischinsky, O., Epstein, R., Etzioni, A., Lavie, P., and Pillar, G. (2001). Long-term sleep disturbances in adolescents after minor head injury. Pediatr. Neurol. 24, 129–134. doi: 10.1016/s0887-8994(00)00254-x
Kempf, J., Werth, E., Kaiser, P. R., Bassetti, C. L., and Baumann, C. R. (2010). Sleep-wake disturbances 3 years after traumatic brain injury. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 81, 1402–1405. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.2009.201913
Kernie, S. G., Erwin, M., and Parada, L. F. (2001). Brain remodeling due to neuronal and astrocytic proliferation after controlled cortical injury in mice. J. Neurosci. Res. 66, 317–326. doi: 10.1002/jnr.10013
Khoury, S., Chouchou, F., Amzica, F., Giguère, J. F., Denis, R., Rouleau, G. A., et al. (2013). Rapid EEG activity during sleep dominates in mild traumatic brain injury patients with acute pain. J. Neurotrauma 30, 633–641. doi: 10.1089/neu.2012.2519
Marshall, L., Helgadóttir, H., Mölle, M., and Born, J. (2006). Boosting slow oscillations during sleep potentiates memory. Nature 444, 610–613. doi: 10.1038/nature05278
Martin, S. E., Wraith, P. K., Deary, I. J., and Douglas, N. J. (1997). The effect of nonvisible sleep fragmentation on daytime function. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 155, 1596–1601. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.155.5.9154863
Mazzoni, G., Gori, S., Formicola, G., Gneri, C., Massetani, R., Murri, L., et al. (1999). Word recall correlates with sleep cycles in elderly subjects. J. Sleep Res. 8, 185–188. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2869.1999.00154.x
Mednick, S. C., McDevitt, E. A., Walsh, J. K., Wamsley, E., Paulus, M., Kanady, J. C., et al. (2013). The critical role of sleep spindles in hippocampal-dependent memory: a pharmacology study. J. Neurosci. 33, 4494–4504. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3127-12.2013
Nudo, R. J. (2011). Neural bases of recovery after brain injury. J. Commun. Disord. 44, 515–520. doi: 10.1016/j.jcomdis.2011.04.004
Ohayon, M. M., Carskadon, M. A., Guilleminault, C., and Vitiello, M. V. (2004). Meta-analysis of quantitative sleep parameters from childhood to old age in healthy individuals: developing normative sleep values across the human lifespan. Sleep 27, 1255–1274.
Orff, H. J., Ayalon, L., and Drummond, S. P. (2009). Traumatic brain injury and sleep disturbance: a review of current research. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 24, 155–165. doi: 10.1097/HTR.0b013e3181a0b281
Parcell, D. L., Ponsford, J. L., Redman, J. R., and Rajaratnam, S. M. (2008). Poor sleep quality and changes in objectively recorded sleep after traumatic brain injury: a preliminary study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 89, 843–850. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2007.09.057
Pillar, G., Averbooch, E., Katz, N., Peled, N., Kaufman, Y., and Shahar, E. (2003). Prevalence and risk of sleep disturbances in adolescents after minor head injury. Pediatr. Neurol. 29, 131–135. doi: 10.1016/s0887-8994(03)00149-8
Plihal, W., and Born, J. (1997). Effects of early and late nocturnal sleep on declarative and procedural memory. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 9, 534–547. doi: 10.1162/jocn.1997.9.4.534
Ruch, S., Markes, O., Duss, S. B., Oppliger, D., Reber, T. P., Koenig, T., et al. (2012). Sleep stage II contributes to the consolidation of declarative memories. Neuropsychologia 50, 2389–2396. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2012.06.008.
Schreiber, S., Barkai, G., Gur-Hartman, T., Peles, E., Tov, N., Dolberg, O. T., et al. (2008). Long-lasting sleep patterns of adult patients with minor traumatic brain injury (mTBI) and non-mTBI subjects. Sleep Med. 9, 481–487. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2007.04.014
Shekleton, J. A., Parcell, D. L., Redman, J. R., Phipps-Nelson, J., Ponsford, J. L., and Rajaratnam, S. M. W. (2010). Sleep disturbance and melatonin levels following traumatic brain injury. Neurology 74, 1732–1738. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181e0438b
Silber, M. H., Ancoli-Israel, S., Bonnet, M. H., Chokroverty, S., Grigg-Damberger, M. M., Hirshkowitz, M., et al. (2007). The visual scoring of sleep in adults. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 3, 121–131.
Sirota, A., Csicsvari, J., Buhl, D., and Buzsáki, G. (2003). Communication between neocortex and hippocampus during sleep in rodents. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 100, 2065–2069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0437938100
Sommerauer, M., Valko, P. O., Werth, E., and Baumann, C. R. (2013). Excessive sleep need following traumatic brain injury: a case-control study of 36 patients. J. Sleep Res. 22, 634–639. doi: 10.1111/jsr.12068
Stickgold, R. (2005). Sleep-dependent memory consolidation. Nature 437, 1272–1278. doi: 10.1038/nature04286
Takashima, A., Petersson, K. M., Rutters, F., Tendolkar, I., Jensen, O., Zwarts, M. J., et al. (2006). Declarative memory consolidation in humans: a prospective functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 103, 756–761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0507774103
Toki, S., Okamoto, Y., Onoda, K., Matsumoto, T., Yoshimura, S., Kunisato, Y., et al. (2014). Hippocampal activation during associative encoding of word pairs and its relation to symptomatic improvement in depression: a functional and volumetric MRI study. J. Affect. Disord. 152–154, 462–467. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2013.07.021
Verma, A., Anand, V., and Verma, N. P. (2007). Sleep disorders in chronic traumatic brain injury. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 3, 357–362.
Werner, C., and Engelhard, K. (2007). Pathophysiology of traumatic brain injury. Br. J. Anaesth. 99, 4–9. doi: 10.1093/bja/aem131
Keywords: sleep, memory consolidation, TBI, traumatic brain injury, NREM
Citation: Mantua J, Mahan KM, Henry OS and Spencer RMC (2015) Altered sleep composition after traumatic brain injury does not affect declarative sleep-dependent memory consolidation. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 9:328. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2015.00328
Received: 28 April 2015; Accepted: 21 May 2015;
Published online: 05 June 2015.
Edited by:
Richard A. P. Roche, Maynooth University, IrelandReviewed by:
Bjoern Rasch, University of Fribourg, SwitzerlandSimon J. Durrant, University of Lincoln, UK
Copyright © 2015 Mantua, Mahan, Henry and Spencer. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution and reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rebecca M. C. Spencer, Department of Psychological and Brain Sciences, University of Massachusetts, 135 Hicks Way, Tobin 419, Amherst, MA 01003, USA,cnNwZW5jZXJAcHN5Y2gudW1hc3MuZWR1
 Janna Mantua
Janna Mantua Keenan M. Mahan
Keenan M. Mahan Owen S. Henry2
Owen S. Henry2 Rebecca M. C. Spencer
Rebecca M. C. Spencer