Abstract
We analyze several generic proximal splitting algorithms well suited for large-scale convex nonsmooth optimization. We derive sublinear and linear convergence results with new rates on the function value suboptimality or distance to the solution, as well as new accelerated versions, using varying stepsizes. In addition, we propose distributed variants of these algorithms, which can be accelerated as well. While most existing results are ergodic, our nonergodic results significantly broaden our understanding of primal–dual optimization algorithms.
1 Introduction
We propose new algorithms for the generic convex optimization problem:where M ≥ 1 is typically the number of parallel computing nodes in a distributed setting; the are linear operators; and are real Hilbert spaces (all spaces are supposed of finite dimension); R and Hm are proper, closed, convex functions with values in , the proximity operators of which are easy to compute; and the Fm are convex -smooth functions; that is ∇Fm is -Lipschitz continuous, for some .
This template problem covers most convex optimization problems met in signal and image processing, operations research, control, machine learning, and many other fields, and our goal is to propose new generic distributed algorithms able to deal with nonsmooth functions using their proximity operators, with acceleration in presence of strong convexity.
1.1 Contributions
Our contributions are the following:
(1) New algorithms: We propose the first distributed algorithms to solve (Eq. 1) in whole generality, with proved convergence to an exact solution, and having the full splitting, or decoupling, property: ∇Fm, , Km and are applied at the m-th node, and the proximity operator of R is applied at the master node connected to all others. No other more complicated operation, like an inner loop or a linear system to solve, is involved.
(2) Unified framework: The foundation of our distributed algorithms consists in two general principles, applied in a cascade, which are new contributions in themselves and could be used in other contexts:
(a) We show that problem (Eq. 1) with M = 1, i.e. the minimization of F + R + H◦K, can be reformulated as the minimization of in a different space, with preserved smoothness and strong convexity properties. Hence, the linear operator disappears and the Davis–Yin algorithm (Davis and Yin, 2017) can be applied to this new problem. Through this lens, we recover many algorithms as particular cases of this unified framework, like the PD3O, Chambolle–Pock, Loris–Verhoeven algorithms.
(b) We design a non-straightforward lifting technique, so that the problem (Eq. 1), with any M, is reformulated as the minimization of in some product space.
(3) New convergence analysis and acceleration: Even when M = 1, we improve upon the state of the art in two ways:
(a) For constant stepsizes, we recover existing algorithms, but we provide new, more precise, results about their convergence speed, see Theorem 1 and Theorem 5.
(b) With a particular strategy of varying stepsizes, we exhibit new algorithms, which are accelerated versions of them. We prove O(1/k2) convergence rate on the last iterate, see Theorem 3 and Theorem 4, whereas current results in the literature are ergodic, e.g. Chambolle and Pock (2016b).
1.2 Related Work
Many estimation problems in a wide range of scientific fields can be formulated as large-scale convex optimization problems (Palomar and Eldar, 2009; Sra et al., 2011; Bach et al., 2012; Bubeck, 2015; Polson et al., 2015; Chambolle and Pock, 2016a; Glowinski et al., 2016; Stathopoulos et al., 2016; Condat, 2017a; Condat et al., 2019b). Proximal splitting algorithms (Combettes and Pesquet, 2010; Boţ et al., 2014; Parikh and Boyd, 2014; Komodakis and Pesquet, 2015; Beck, 2017; Condat et al., 2019a) are particularly well suited to solve them; they consist of simple, easy to compute, steps that can deal with the terms in the objective function separately.
These algorithms are generally designed as sequential ones, for M = 1, and then they can be extended by lifting in product space to parallel versions, well suited to minimize F + R + ∑mHm ○ Km, see for instance Condat et al., 2019a, Section 8. However, it is not straightforward to adapt lifting to the case of a finite-sum , with each function Fm handled by a different node, which is of primary importance in machine learning. This generalization is one of our contributions.





There is a vast literature on distributed optimization to minimize , with a focus on strategies based on (block-)coordinate or randomized activation, as well as replacing the gradients by cheaper stochastic estimates (Cevher et al., 2014; Richtárik and Takáč, 2014; Gorbunov et al., 2020; Salim et al., 2020). Replacing the full gradient by a stochastic oracle in the accelerated algorithms with varying stepsizes we propose is not straightforward; we leave this direction for future research. In any case, the generalized setting, with the smooth functions Fm at the nodes supplemented or replaced by nonsmooth functions Hm, possibly composed with linear operators, seems to have received little attention. We want to make up for that. Decentralized optimization over networks is an active research topic (Latafat et al., 2019; Alghunaim et al., 2021). In this paper, we focus on the centralized client–server model, with one master node connected to several client nodes, working in parallel. We leave the study of decentralized algorithms for future work.
When M = 1 and K = I, where I denotes the identity, Davis and Yin (2017) proposed an efficient algorithm, along with an extensive study of its convergence rates and possible accelerations. But the ability to handle a nontrivial K is behind the success of the Chambolle and Pock (2011) or \Condat (2013), Vũ (2013): they are well suited for regularized inverse problems in imaging (Chambolle and Pock, 2016a), for instance with the total variation and its variants (Bredies et al., 2010; Condat, 2014, 2017b; Duran et al., 2016); other examples are computer vision problems (Cremers et al., 2011), overlapping group norms for sparse estimation in data science (Bach et al., 2012), and trend filtering on graphs (Wang et al., 2016). Another prominent case is when H is an indicator function, so that the problem becomes: minimize F(x) + R(x) subject to Kx = b. If K is a gossip matrix like the minus graph Laplacian, decentralized optimization over a network can be tackled (Shi et al., 2015; Scaman et al., 2017; Salim et al., 2021).
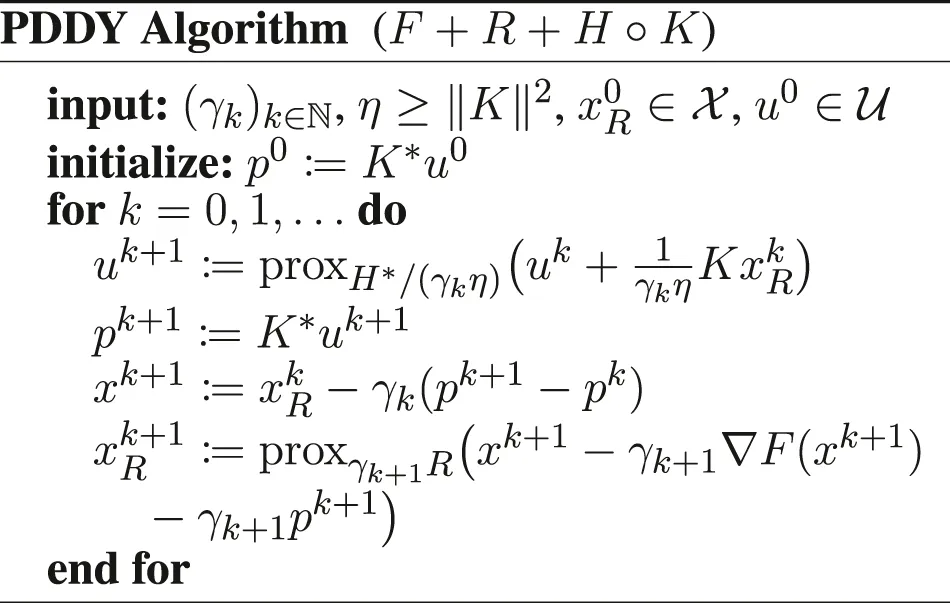
When M = 1 and K is arbitrary, there exist algorithms to solve (Eq. 1) in full generality, for example, the Combettes and Pesquet (2012), Condat, (2013), Vũ (2013), PD3O (Yan, 2018) and PDDY (Salim et al., 2020) algorithms. However, their convergence rates and possible accelerations are little understood. Our main contribution is to derive new convergence rates and accelerated versions of the PD3O and PDDY algorithms, and their particular cases, including Chambolle and Pock (2011) and Loris and Verhoeven (2011) algorithms. In order to do this, we show that these two algorithms can be viewed as instances of the Davis–Yin algorithm. This reformulation technique is inspired by the recent one of O’Connor and Vandenberghe (O’Connor and Vandenberghe, 2020); it makes it possible to split the composition H°K and to derive algorithms, which call the operators proxH, K, K* separately. This technique is fundamentally different from the one in Salim et al. (2020), showing that the PD3O and PDDY algorithms are primal–dual instances of the operator version of Davis–Yin splitting to solve monotone inclusions. Notably, we can derive convergence rates with respect to the objective function and accelerations, which is not possible with the primal–dual reformulation of Salim et al. (2020). On the other hand, the latter encompasses the Condat–Vũ algorithm (Condat, 2013; Vũ, 2013), which is not the case of our approach. So, these are complementary interpretations.
1.3 Organization of the paper
In Section 2, we propose new nonstationary versions (i.e. with varying stepsizes) of several algorithms for optimization problems made of three terms, and we analyze their convergence rates. The derivation details are pushed to the end of the paper in Section 5 for ease of reading. In Section 3, we further propose distributed algorithms, which can minimize the sum of an arbitrary number of terms. Again, the derivation details are deferred to Section 6. Numerical experiments illustrating the good match between our theoretical results and practical performance are shown in Section 4.
2 Minimization of 3 Functions With a Linear Operator
Let us focus on the problem (Eq. 1) when M = 1:where is a linear operator, and are real Hilbert spaces, R and H are proper, closed, convex functions, and F is a convex and LF-smooth function. We will see in Section 3 that using an adequate lifting technique, (2) can be extended to (1) and, accordingly, parallel or distributed versions of the sequential algorithms to solve (Eq. 2) will be derived. That is why we first study the case M = 1. For any function G, we denote by μG ≥ 0 some constant such that G is μG-strongly convex; that is, G − (μG/2)‖ ⋅‖2 is convex.
The dual problem to (Eq. 2) iswhere K* is the adjoint operator of K and G* is the convex conjugate of a function G (Bauschke and Combettes, 2017); we recall the Moreau identity: (Bauschke and Combettes, 2017). We suppose that the following holds:
Assumption 1 There exists such that 0 ∈ ∇F(x*) + ∂R(x*) + K*∂H(Kx*), which implies that x*is a solution to (Eq. 2); see for instanceCombettes and Pesquet, 2012, Proposition 4.3 for sufficient conditions on the functions for this property to hold.
2.1 Deriving the Nonstationary PD3O and PDDY Algorithms
The main difficulty in (Eq. 2) is the presence of the linear operator K. Indeed, if K = I, the Davis–Yin algorithm (Davis and Yin, 2017) is well suited to minimize F + R + H. Note that there is a minor mistake in the way Algorithm 3 in Davis and Yin (2017) is initialized. This is corrected here. Thus, the Davis–Yin algorithm is as follows:
Let be a sequence of stepsizes. Let and . For k = 0, 1, … iterate
To make this algorithm applicable to
K≠
I, we reformulate the problem (
Eq. 2) as follows:
(1) We choose a value η ≥‖K‖2; we recommend to set η = ‖K‖2 in practice. Then there exists a real Hilbert space and a linear operator such that KK* + CC* = ηI. C is not unique, for instance, we can set . We actually don’t need to exhibit C, its existence is sufficient here and there will be no call to C in the algorithms.
(2) Now, the problem (Eq. 2) can be rewritten as:
where
,
, where
if
w= 0, +
∞otherwise}, and
. Indeed, we introduce the variable
w, but also the constraint that
w= 0. Since
,
,
, the equivalence between (2) and (5) follows.
We have , . Most importantly, for every γ > 0, we have (O’Connor and Vandenberghe, 2020):
Note that in O’Connor and Vandenberghe (2020), the authors use , whereas we add . This difference is essential, so that is LF-smooth and μF-strongly convex. Also, is μR-strongly convex.
Then, we can apply the Davis–Yin algorithm (4) to solve the problem (Eq. 5). We set F, R, H in (Eq. 4) as , , , respectively. The details of the substitutions yielding the algorithms are deferred to Section 5 for the convenience of reading; most notably, whenever CC* appears, it is replaced by ηI − KK*. The obtained algorithms turns out to be a nonstationary version of the PD3O algorithm (Yan, 2018), shown above. On the other hand, if we exchange the two functions and set F, R, H in (Eq. 4) as , , , we obtain a different algorithm. It turns out to be a nonstationary version of the PDDY algorithm proposed recently (Salim et al., 2020), shown above too. With constant stepsizes γk ≡ γ ∈ (0, 2/LF), for both the PD3O and PDDY algorithms, xk and uk converge to some solutions x* and u* of (Eq. 2) and (Eq. 3), respectively; this result was known for η > ‖K‖2 (Yan, 2018; Salim et al., 2020) and shown for η = ‖K‖2 for the PD3O algorithm in O’Connor and Vandenberghe (2020), but convergence with η = ‖K‖2 for the PDDY algorithm, as stated in Theorem 2, is new.
Particular cases of the PD3O and PDDY algorithms, which are shown above, are the following:
(1) If K = I and η = 1, the PD3O algorithm reverts to the Davis–Yin algorithm (Eq. 4); the PDDY algorithm too, but with H and R exchanged in (Eq. 4).
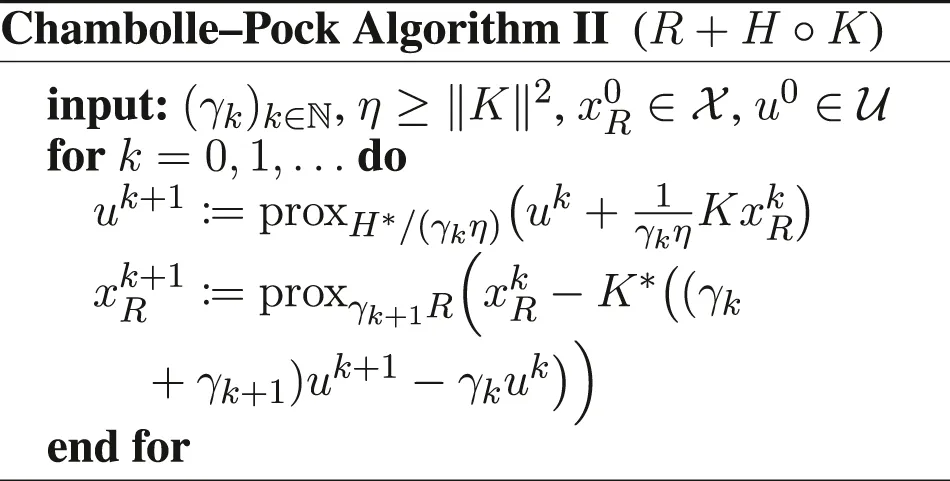
(2) If F = 0, the PD3O and PDDY algorithms revert to the forms I and II (Condat et al., 2019a) of the Chambolle–Pock algorithm, a.k.a. Primal–Dual Hybrid Gradient algorithm (Chambolle and Pock, 2011), respectively.
(3) If R = 0, the PD3O and PDDY algorithms revert to the Loris–Verhoeven algorithm (Loris and Verhoeven, 2011), also discovered independently as the PDFP2O (Chen et al., 2013) and PAPC (Drori et al., 2015) algorithms; see also Combettes et al. (2014); Condat et al. (2019a) for an analysis as a primal–dual forward–backward algorithm.
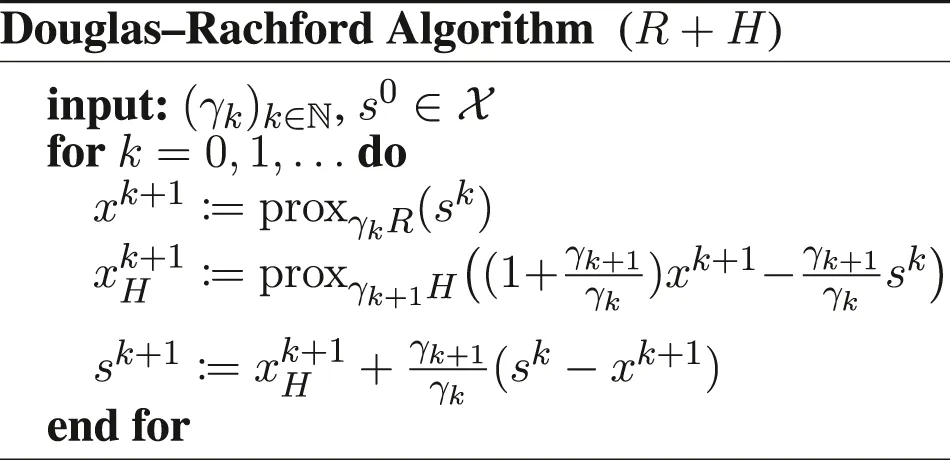
(4) If F = 0 in the Davis–Yin algorithm or K = I and η = 1 in the Chambolle–Pock algorithm, we obtain the Douglas–Rachford algorihm; it is equivalent to the ADMM, see the discussion in Condat et al. (2019a).
(5) If H = 0, the PD3O and PDDY algorithms revert to the forward–backward algorithm, a.k.a. proximal gradient descent. The Loris–Verhoeven algorithm with K = I and η = 1, too.
2.2 Convergence Analysis
We first give convergence rates for the PD3O algorithm with constant stepsizes.
(convergence rate of the PD3O algorithm). In the PD3O algorithm, suppose that γk ≡ γ ∈ (0, 2/LF) and η ≥‖K‖2. Then xkand ukconverge to some solutions x*and u*of (2) and (3), respectively. In addition, suppose that H is continuous on an open ball centered at Kx*. Then the following hold:
Define the weighted ergodic iterate , for every k ≥ 1. Then
Furthermore, if H is L-smooth for some L > 0, we have a faster decay for the best iterate so far:
ProofThe convergence of xk follows from Davis and Yin, 2017, Theorem 2.1 and the convergence of uk follows from the one of the variable in the notations of Davis and Yin (2017). (i) follows from Davis and Yin, 2017, Theorem 3.1, using the following facts; first, in this theorem, the function corresponding to is supposed to be Lipschitz-continuous on a certain ball, but since the rate is asymptotic and Kxk → Kx*, it is sufficient to consider the property around Kx*; second, it is well known that if a convex real-valued function is continuous on a convex open set, it is Lipschitz-continuous on every compact subset of this set (Unknown author, 1972); third, if H is continuous, is continuous too. (ii) follows from Davis and Yin (2017), Theorem 3.2 and (iii) follows from Theorem D.5 in the preprint of Davis and Yin (2017).□ Theorem 1 applies to the particular cases of the PD3O algorithm, like the Loris–Verhoeven, Chambolle–Pock, Douglas–Rachford algorithms. Our results are new even for them.
Remark 1 We can note that the forward–backward algorithm x k+1 = proxγR(xk − γ∇F(xk)), which is a particular case of the PD3O algorithm when H = 0, is monotonic. So, the best iterate so far is the last iterate. Hence,Theorem 1 (iii) yields Ψ(xk) − Ψ(x*) = o(1/k) for the forward–backward algorithm.For the PDDY algorithm, we cannot derive a similar theorem, since is not continuous around (x*, 0). Still, we can establish convergence of the variables:
(convergence of the PDDY algorithm). In the PDDY algorithm, suppose that γk ≡ γ ∈ (0, 2/LF) and η ≥‖K‖2. Then xkandboth converge to some solution x*of (Eq. 2), and ukconverges to some solution u*of (Eq. 3).
ProofThe convergence of xk and to the same solution x* of (Eq. 2) follows from Davis and Yin, 2017, Theorem 2.1. The convergence of the variable , in the notations of Davis and Yin (2017), implies in our setting, according to (6), that K*uk and C*uk both converge to some elements. But since ηuk = KK*uk + CC*uk, uk converges to some element . Finally, we have x* = proxγR(x* − γ∇F(x*) − γK*u*), so that 0 ∈ ∂R(x*) + ∇F(x*) + K*u*, and , so that Kx* ∈ (∂H)−1(u*). Hence, u* is a solution to (Eq. 3).□We now give accelerated convergence results using varying stepsizes, when F or R is strongly convex; that is, μF + μR > 0. In that case, we denote by x* the unique solution to (Eq. 2).
(convergence rate of the accelerated PD3O algorithm). Suppose that μF + μR > 0. Let κ ∈ (0, 1) and γ0 ∈ (0, 2(1 − κ)/LF). Set γ1 = γ0and
Suppose that η ≥‖K‖2. Then in the PD3O algorithm, there exists c0 > 0 (whose expression is given inSection 5) such that, for every k ≥ 1,
ProofThis result follows from Davis and Yin, 2017, Theorem 3.3, stated for convenience as Lemma 1 in Section 5.□Note that with the stepsize rule in (Eq. 7), we have k γk → 1/(μFκ + μR) as k → + ∞, so that γk = O(1/k) and γk+1/γk → 1. Also, when F = 0, LF can be taken arbitrarily small, so that we can choose any γ0 > 0. Theorem 3 is new for the PD3O and Loris–Verhoeven algorithms, but has been derived in O’Connor and Vandenberghe (2020) for the Chambolle–Pock algorithm. For the forward–backward algorithm, strong convexity yields linear convergence with constant stepsizes, so this nonstationary version does not seem interesting.Concerning the PDDY algorithm, is not necessarily strongly convex, even if H is. So, we only consider the case where F is strongly convex. As a consequence of Lemma 1, we get:
(convergence rate of the accelerated PDDY algorithm). Suppose that μF > 0. Let κ ∈ (0, 1) and γ0 ∈ (0, 2(1 − κ)/LF). Set γ1 = γ0and
Suppose that η ≥‖K‖2. Then in the PDDY algorithm, there exists c0 > 0 (whose expression is given inSection 5) such that, for every k ≥ 1,
Moreover, if η > ‖K‖2, as well.
Finally, we consider the case where, in addition to strong convexity of F or R, H is smooth; in that case, the algorithms with constant stepsizes converge linearly; that is, as a consequence of Lemma 2, we have:
(linear convergence of the PD3O and PDDY algorithms). Suppose that μF + μR > 0 and that H is LH-smooth, for some LH > 0. Let x*and u*be the unique solutions to (2) and (3), respectively. Suppose that γk ≡ γ ∈ (0, 2/LF) and η ≥‖K‖2. Then the PD3O algorithm converges linearly: there exists ρ ∈ (0, 1] such that, for every,
The PDDY algorithm converges linearly too: there exists ρ ∈ (0, 1] such that, for every,
Linear convergence of the other variables in the algorithms can be derived as well, see Proposition 1. Lower bounds for ρ can be derived from Theorem D.6 in the preprint version of Davis and Yin (2017). We don’t provide them, since they are not tight, as noticed in Remark D.2 of the same preprint. For instance, for the PDDY or Loris–Verhoeven algorithms with μF > 0,
If H = 0, by setting LH = 0, we get ρ = γμF(2 − γLF). But then the PDDY algorithm reverts to the forward–backward algorithm, for which it is known that whenever γ ≤ 2/(LF + μF), which corresponds to the larger value ρ = γμF(2 − γμF).
We emphasize that linear convergence comes for free with the algorithms, if the conditions are met, without any modification. That is, there is no need to know μF, μR, LH, since the conditions on the two parameters γ and η do not depend on these values. For the particular case of the Chambolle–Pock algorithm, as pointed out in O’Connor and Vandenberghe (2020), this is in contrast to existing linear convergence results (Chambolle and Pock, 2016a), derived for a modified version of the algorithm, which depends on these values.
3 Distributed Proximal Algorithms
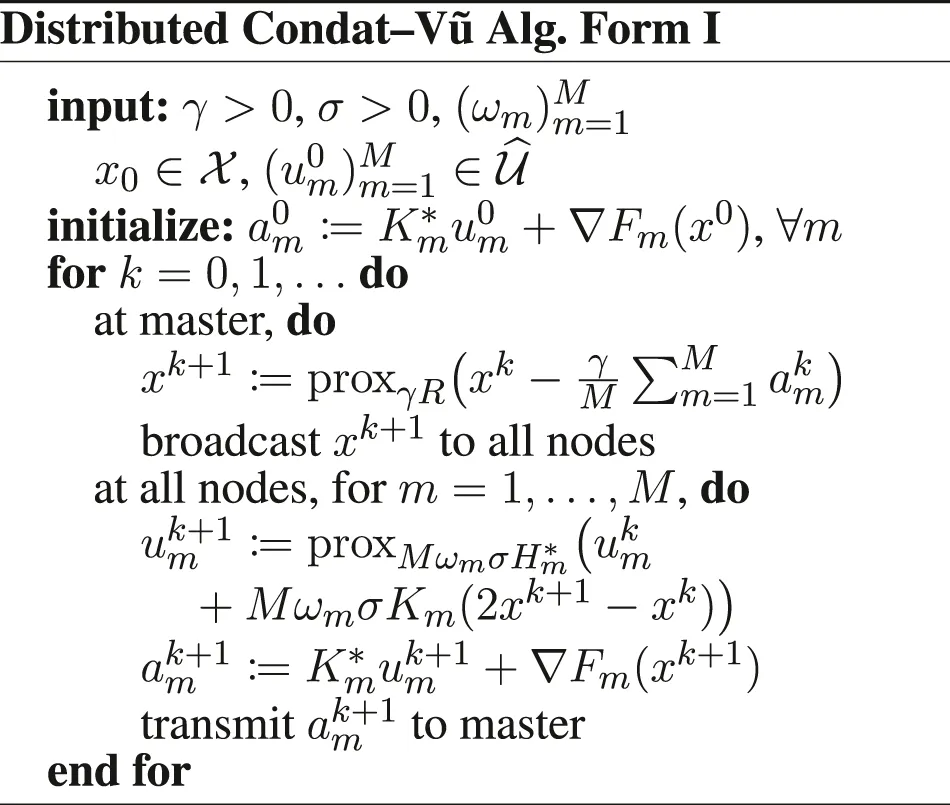
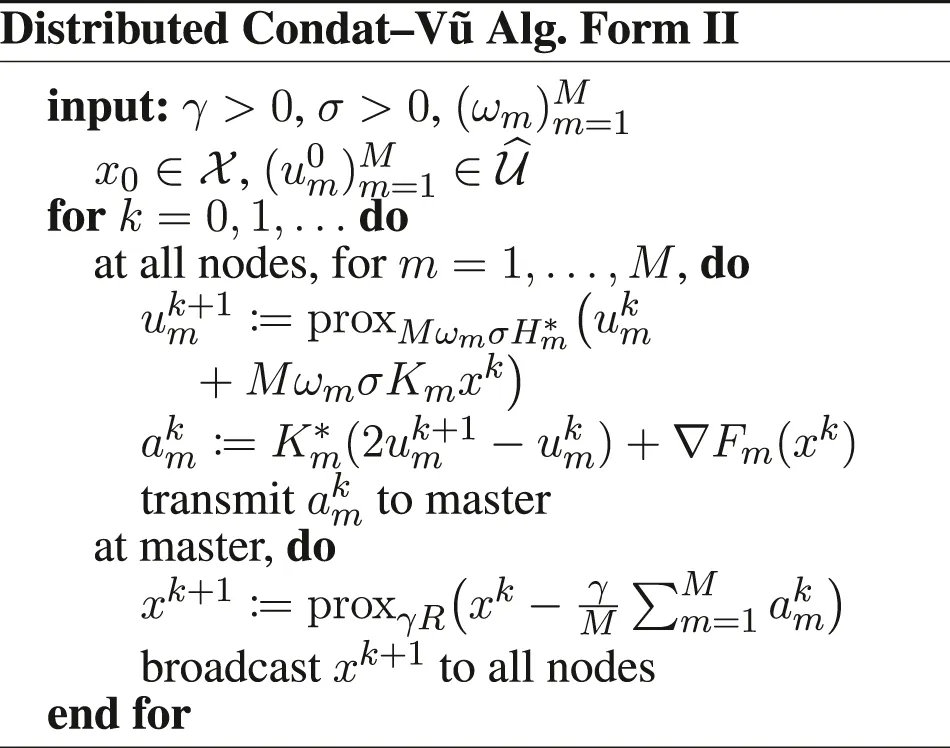
We now focus on the more general problem (Eq. 1) and we derive distributed versions of the PD3O and PDDY algorithms to solve it. For this, we develop a lifting technique: we recast the minimization of as the minimization ofas follows. Let be a sequence of positive weights, whose sum is 1; they can be used to mitigate different ‖Km‖, by setting ωm ∝ 1/‖Km‖2, or different , by setting , as a rule of thumb.
We introduce the Hilbert space (M times), endowed with the inner productand the Hilbert space , endowed with the inner product
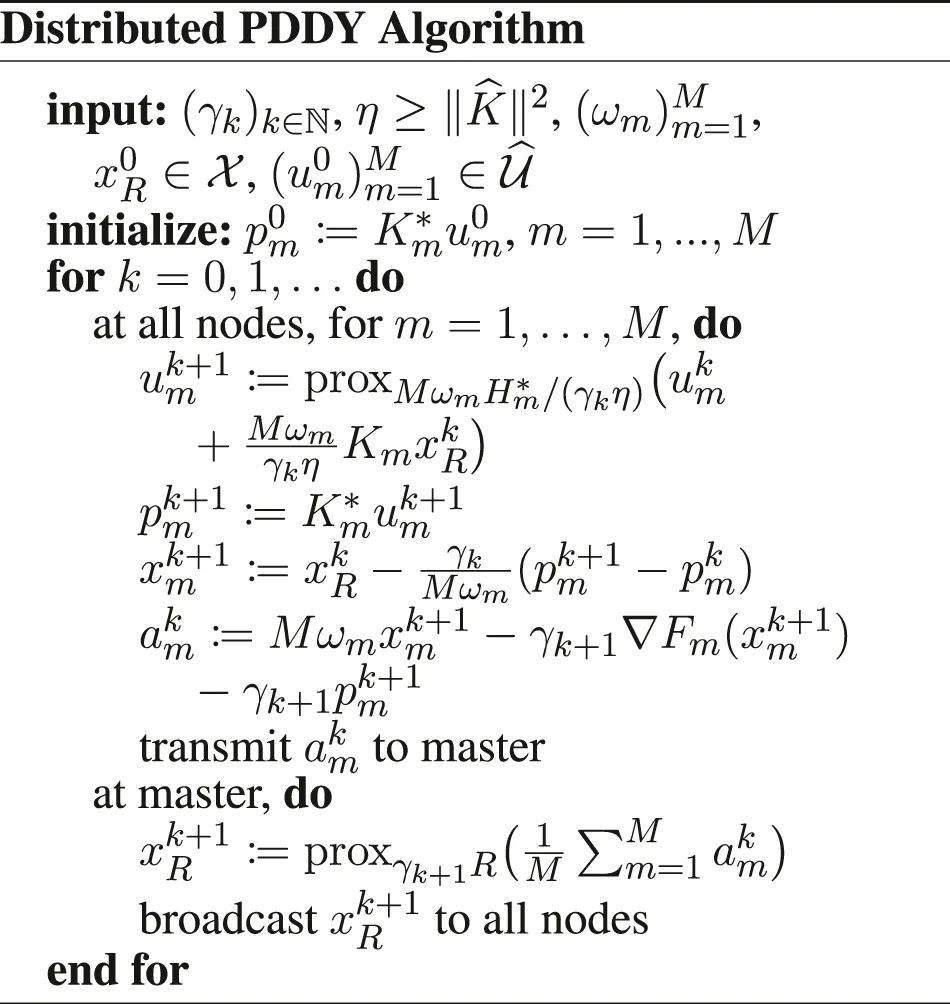
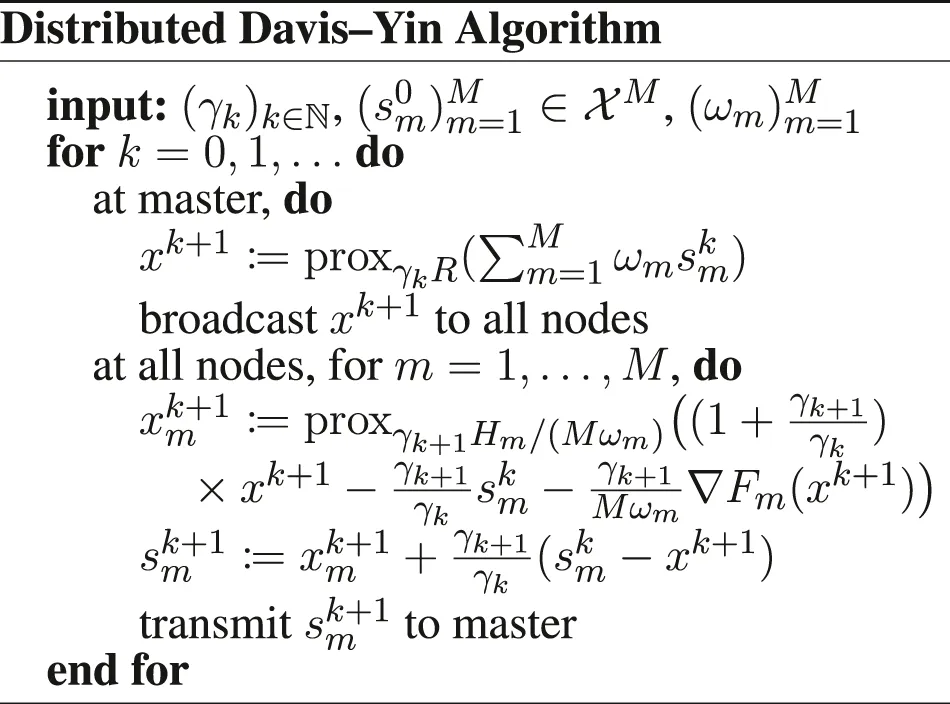
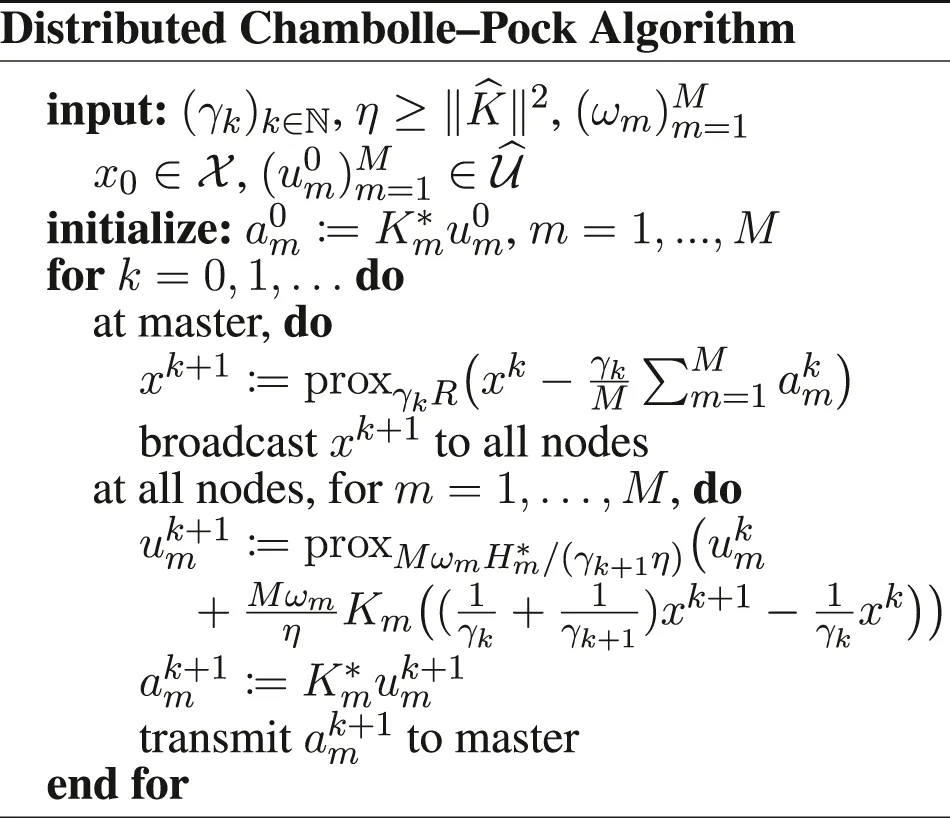
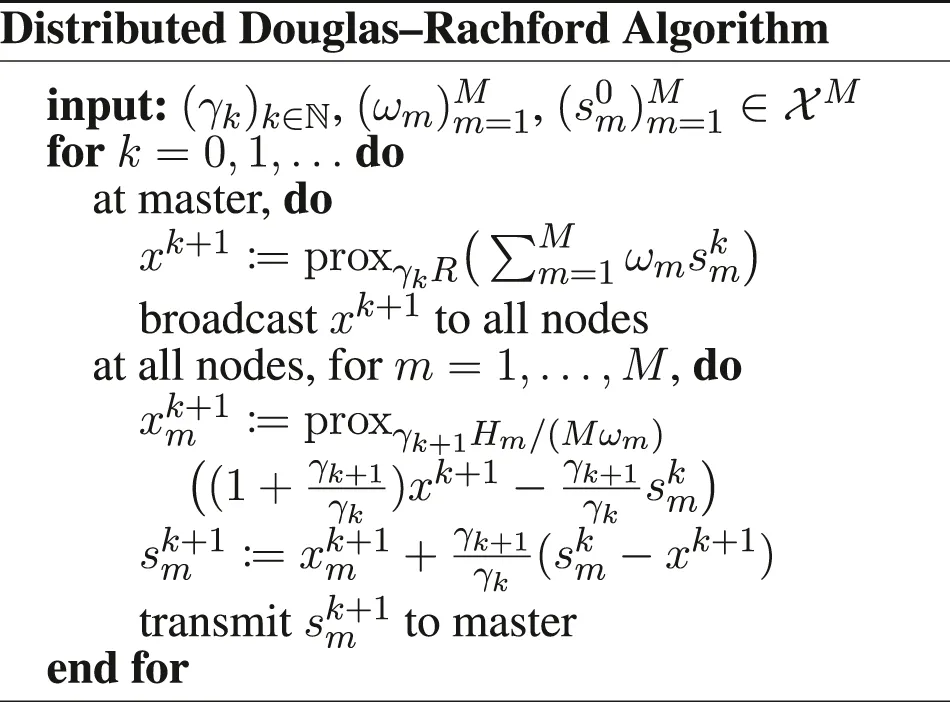
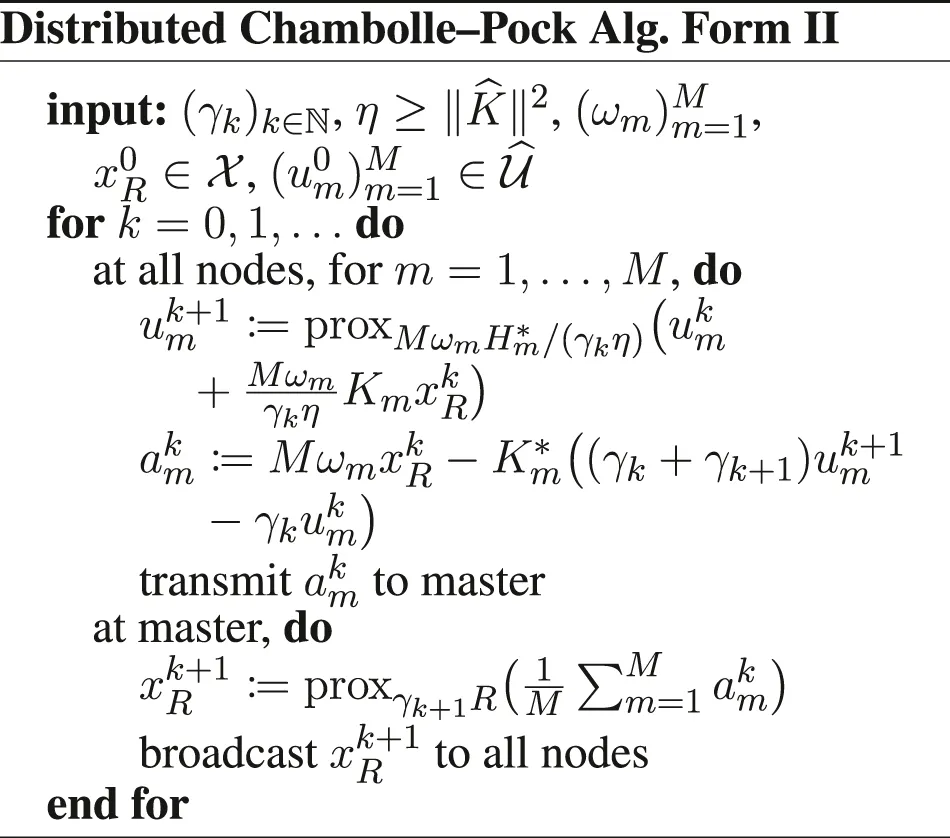
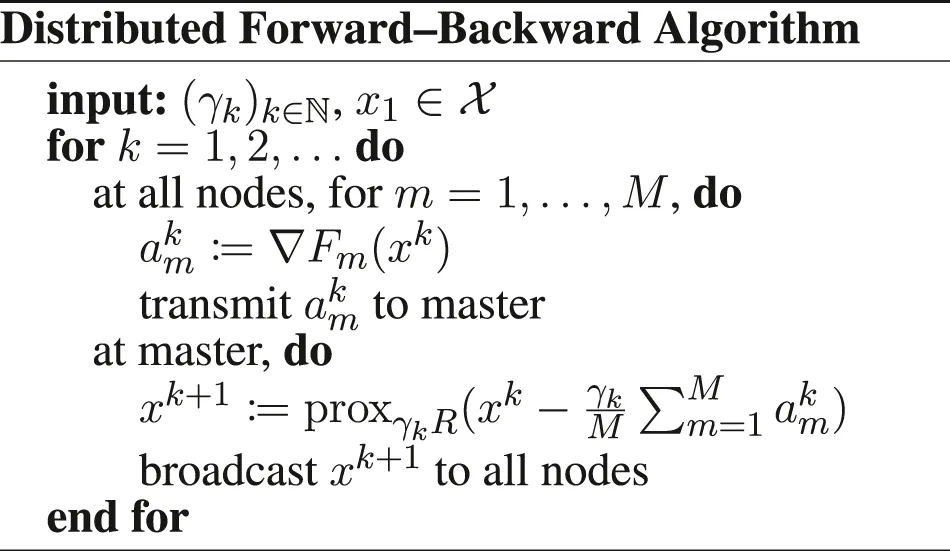
Furthermore, we introduce , and the functions if x1 = ⋯ = xM, + ∞ otherwise, , , and . We have to be careful when defining the gradient and proximity operators, because of the weighted metrics; see in Section 6 for details. Doing these substitutions in the PD3O and PDDY algorithms, we obtain the new Distributed PD3O and Distributed PDDY algorithms, shown above. Their particular cases, also shown above, are the distributed
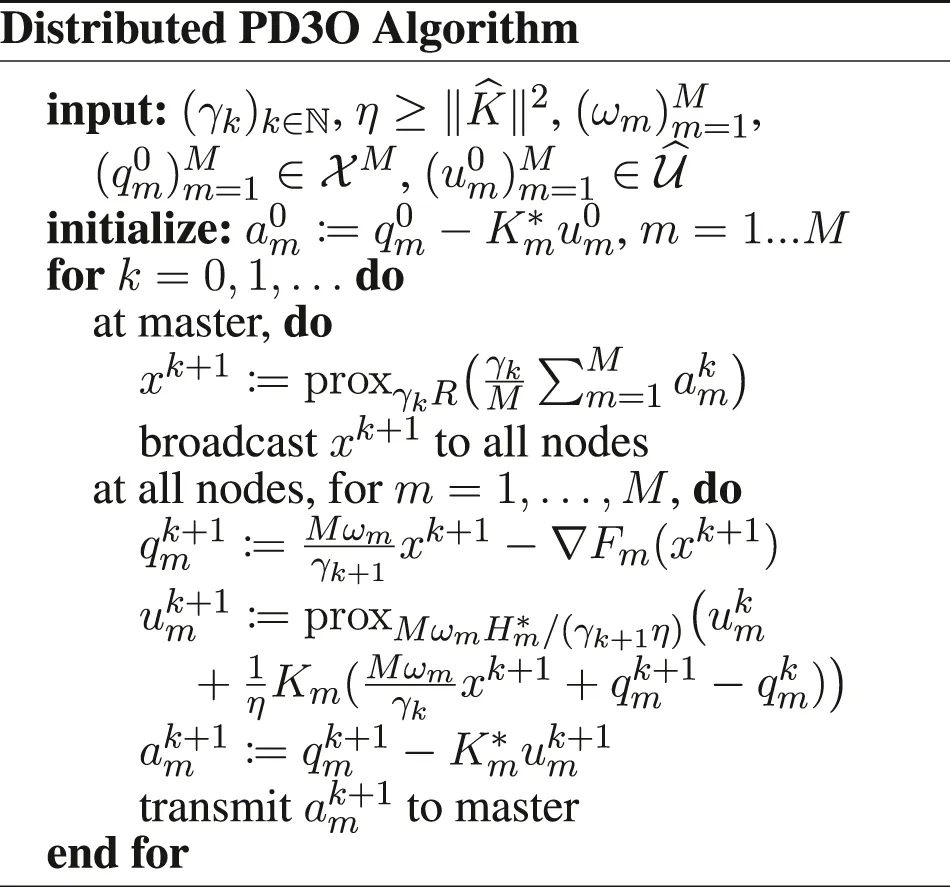
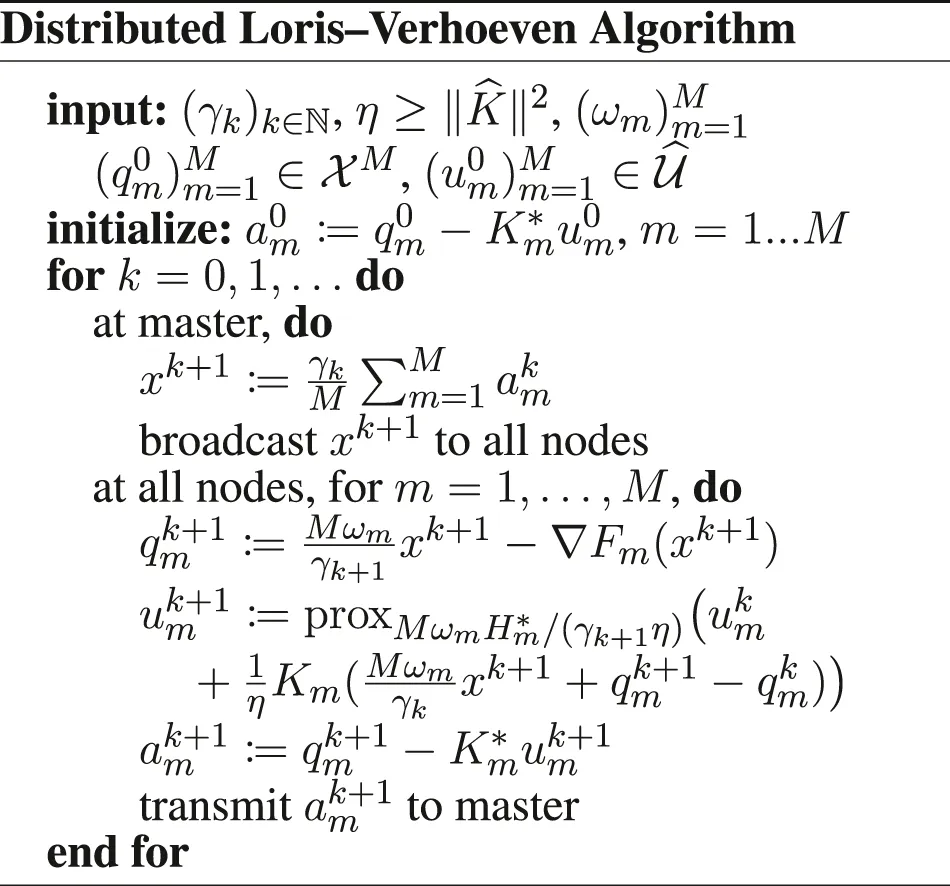
Davis–Yin algorithm when Km ≡ I and η = 1, the distributed Loris–Verhoeven algorithm when R = 0, the distributed Chambolle–Pock algorithm when Fm ≡ 0, the distributed Douglas–Rachford algorithm when Fm ≡ 0, Km ≡ I and η = 1, the (classical) distributed forward–backward algorithm when Hm ≡ 0.
We can easily translate Theorems 1–5 to these distributed algorithms; the corresponding theorems are given in Section 6. In a nutshell, we obtain the same convergence results and rates with any number of nodes M ≥ 1 as in the non-distributed setting, for any and , where and are detailed in Section 6. Hence, to our knowledge, we are the first to propose distributed proximal splitting methods with guaranteed, possibly accelerated, convergence, to minimize an arbitrary sum of smooth or nonsmooth functions, possibly composed with linear operators.
4 Experiments
4.1 Image Deblurring Regularized With Total Variation
We first consider the non-distributed problem (Eq. 2), for the imaging inverse problem of deblurring, which consists in restoring an image y corrupted by blur and noise (Chambolle and Pock, 2016a). So, we setwhere the linear operator A corresponds to a 2-D convolution with a lowpass filter, with LF = 1. The filter is approximately Gaussian and chosen so that F is μF-strongly convex with μF = 0.01. y is obtained by applying A to the classical 256 × 256 Shepp–Logan phantom image, with additive Gaussian noise. R = ı0 enforces nonnegativity of the pixel values. H°K corresponds to the classical ‘isotropic’ total variation (TV) (Chambolle and Pock, 2016a; Condat, 2017b), with H = 0.6 times the l1,2 norm and K the concatenation of vertical and horizontal finite differences.
We compare the nonaccelerated, i.e. with constant γk, and accelerated versions, with decaying γk, of the PD3O, PDDY and Condat–Vũ algorithms. We initialize the dual variables at zero and the estimate of the solution as y. We set γ0 = 1.7, κ = 0.15, η = 8 ≥‖K‖2 (except for the accelerated Condat–Vũ algorithm proposed in Chambolle and Pock (2016b), for which η = 16 and γ = 0.5).
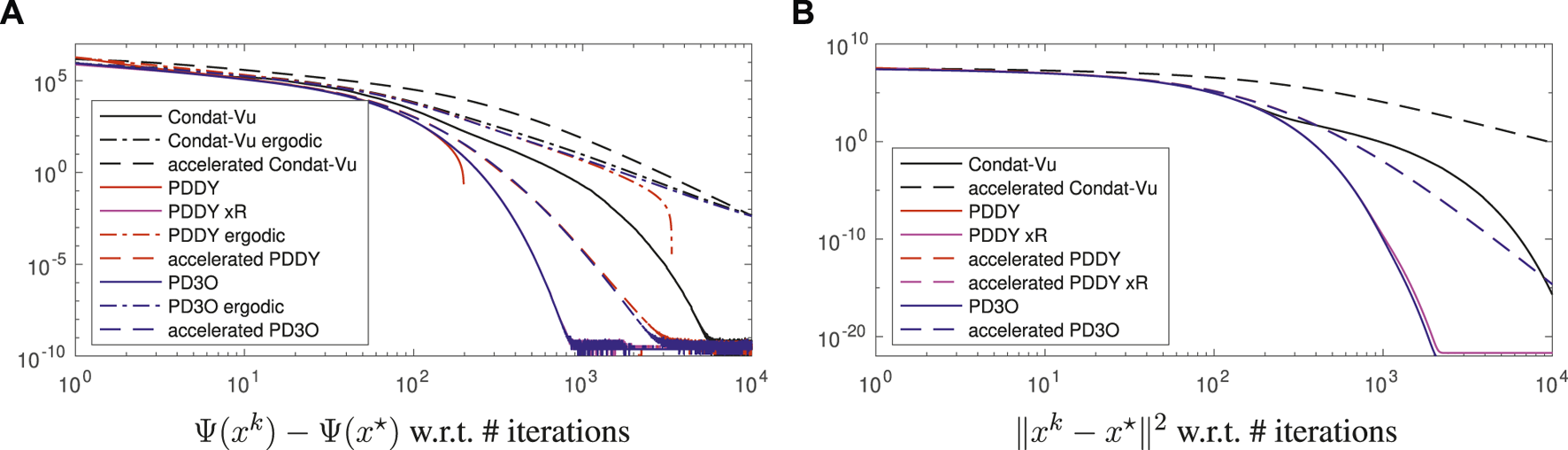
The results are illustrated in Figure 1 (implementation in Matlab). We observe that the PD3O and PDDY algorithms have almost identical variables: the pink, red, blue curves are superimposed; we know that both algorithms are identical and revert to the Loris–Verhoeven algorithm when R = 0. Here R ≠ 0 but the nonnegativity constraint does not change the solution significantly, which explains the similarity of the two algorithms.
FIGURE 1
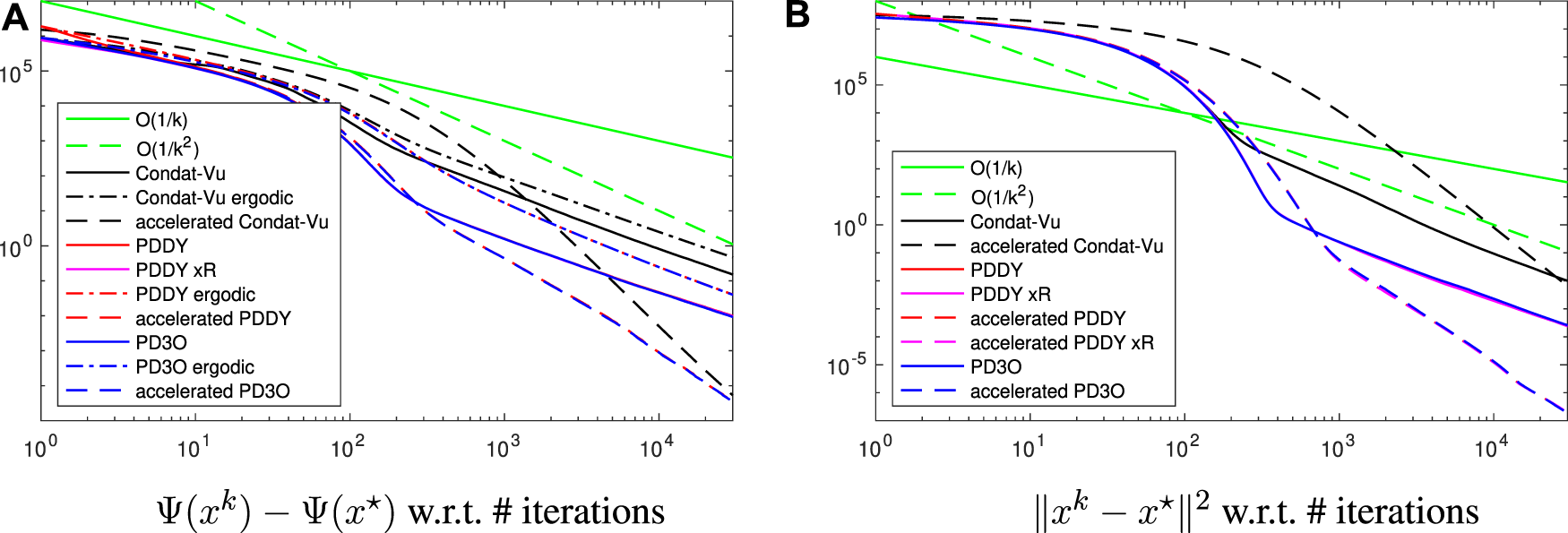
Convergence error, in log-log scale, for the experiment of image deblurring regularized with the total variation, see Section 4.1 for details.
Note that xk in the PDDY algorithm is not feasible with respect to nonnegativity, and the red curve actually shows F(xk) + H(Kxk) − Ψ(x*). In the nonaccelerated case, Ψ(xk) decays faster than O(1/k) but slower than O(1/k2), which is coherent with Theorem 1. The same holds for .
The accelerated versions improve the convergence speed significantly: Ψ(xk) and ‖xk − x*‖2 decay even faster than O(1/k2), in line with Theorem 3 and Theorem 4. In all cases, the Condat–Vũ algorithm is outperformed. Also, there is no interest in considering the ergodic iterate instead of the last iterate, since the former converges at the same asymptotic rate as the latter, but slower.
4.2 Image Deblurring Regularized With Huber-TV
We consider the same deblurring experiment as before, but we make H smooth by taking the Huber function instead of the l1 norm in the total variation; that is, λ|⋅| in the latter is replaced byfor some ν > 0 and λ > 0 (set here as 0.1 and 0.6, respectively). We can also write h without branching as . It is known that h is Lh-smooth with Lh = λ/ν. For any γ > 0 and , we have . Except for H, everything is unchanged.
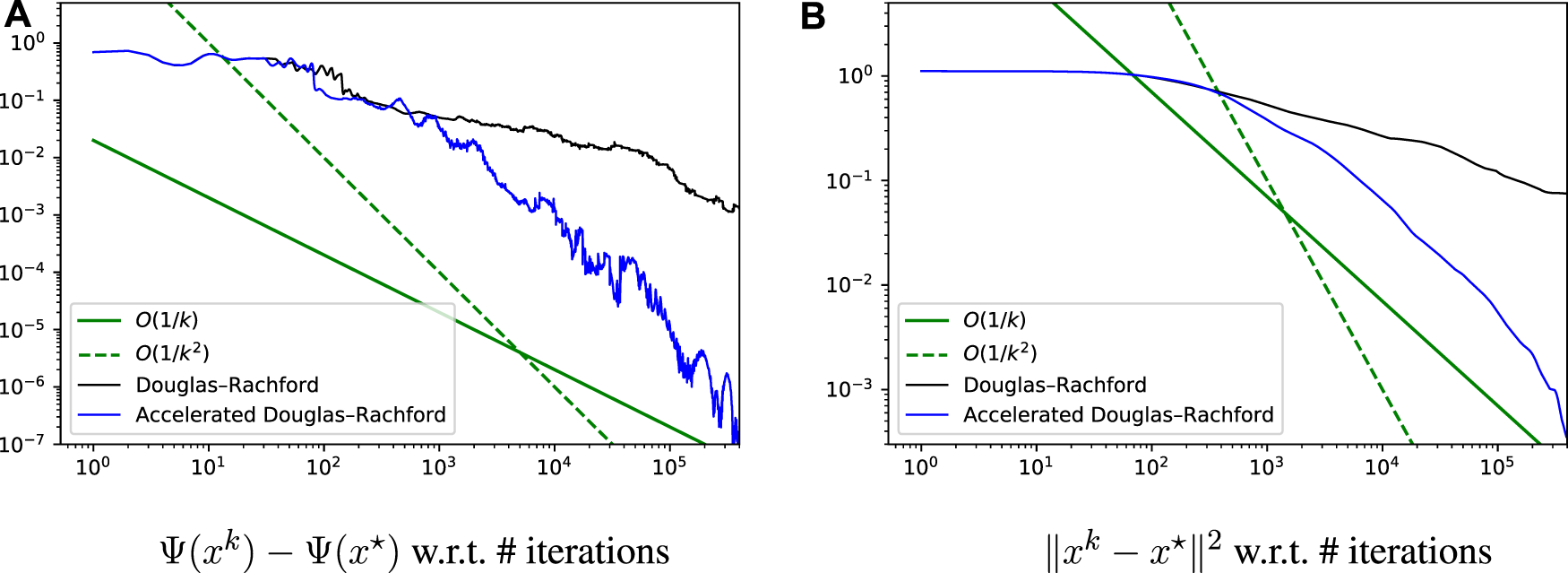
The results are illustrated in Figure 2. Again, the PD3O and PDDY algorithms behave very similarly; they converge linearly, as proved in Theorem 5, and achieve machine precision in finite time. xk in the PDDY algorithm is not feasible and F(xk) + H(Kxk) − Ψ(x*) (red curve) takes negative values (not shown in log scale); so, is the variable to study in this setting. We tested the ‘accelerated’ versions of the algorithms with decaying γk, but in this scenario, they are much slower and not suitable. Again, the Condat–Vũ algorithm is outperformed and the ergodic sequences converge much slower. Interestingly, the image x* is visually the same with TV and with Huber-TV.
FIGURE 2
Convergence error, in log-log scale, for the experiment of image deblurring regularized with the smooth Huber-total-variation, so that linear convergence occurs, see Section 4.2 for details.
4.3 SVM With Hinge Loss
Here we consider Problem (Eq. 1) in the special case with , for some d ≥ 1, Fm ≡ 0, and Km ≡ I; that is, the problem of minimizing
In particular, to train a binary classifier, we consider the classical SVM problem with hinge loss, which has the form (Eq. 9) with , for some α > 0, and , with data samples and bm ∈ { − 1, 1}.
For any γ > 0 we have proxγR(x) = x/(1 + γα). We could view the dot product as a linear operator Km, but it is more interesting to integrate it in the function Hm. Indeed, as is perhaps not well known, the proximity operator of Hm has a closed form: for any γ > 0,where . Thus, we use the Distributed Douglas–Rachford algorithm, a particular case of the distributed PD3O and PDDY algorithms. Since R is α-strongly convex, we also use the accelerated version of the algorithm with varying stepsizes, like in Theorem 3. We can note that in the context of Federated learning (Konečný et al., 2016; Malinovsky et al., 2020), where each m corresponds to the smart phone or computer of a different user with its own data (am, bm) stored locally, the problem is solved in a collaborative way but with preserved privacy, without the users sharing their data.
The method was implemented in Python on a single machine and tested on the dataset ‘australian’ from the LibSVM base (Chang and Lin, 2011), with d = 15 and M = 680. We set ωm ≡ 1/M, α = 0.1, γ0 = 0.1, and we used zero vectors for the initialization. The results are shown in Figure 3. Despite the oscillations, we observe that both the objective suboptimality and the squared distance to the solution converge sublinearly, with rates looking like and O(1/k2) for the nonaccelerated and accelerated algorithms, respectively, as guaranteed by Theorem 1 and Theorem 3. The proposed accelerated version of the distributed Douglas–Rachford algorithm yields a significant speedup.
FIGURE 3
Convergence error, in log-log scale, for the SVM binary classification experiment with hinge loss, see Section 4.3 for details.
5 Derivation of the Algorithms
In this section, we give the details of the derivation of the PD3O and PPDY algorithms, and their particular cases, to solve:with same notations and assumptions as above. Let η ≥‖K‖2, let be a real Hilbert space and be a linear operator, such that KK* + CC* = ηI. We set Q : (x, w)↦Kx + Cw. We have QQ* = ηI. Let be a sequence of positive stepsizes.
5.1 The Davis–Yin Algorithm
In this section, we state the results on the Davis–Yin algorithm, which we be needed to analyze the PD3O and PPDY algorithms.
The Davis–Yin algorithm to minimize the sum of 3 convex functions over a real Hilbert space (assuming that there exists a solution z* such that ) is (Davis and Yin, 2017):
Let , . For k = 0, 1, … iterate:
Equivalently, introducing the variable : let . For k = 0, 1, … iterate:
Equivalently: let . For k = 0, 1, … iterate:
In our notations, Theorem 3.3 of Davis and Yin (2017) translates into Lemma 1 as follows; we assume that is -smooth and -strongly convex and that G is μG-strongly convex, for some , , μG ≥ 0.
Lemma 1(accelerated Davis–Yin algorithm). Suppose that. Let z*be the unique minimizer of; that is,. Letbe such thatand. Let κ ∈ (0, 1) and. Set γ1 = γ0and Then, for every k ≥ 1,where Note that .Linear convergence occurs in the following conditions, according to Theorem D.6 in the preprint version of Davis and Yin (2017), which translates into Lemma 2 as follows. We assume that is -smooth and -strongly convex, G is μG-strongly convex, and J is μJ-strongly convex, for some , , μG ≥ 0, μJ ≥ 0. We consider constant stepsizes γk ≡ γ, for some .
Lemma 2(linear convergence of the Davis–Yin algorithm). Suppose thatand that G is LG-smooth, for some LG > 0, or J is LJ-smooth, for some LJ > 0. Let z*be the unique minimizer of; that is,. The dual problem of minimizingoveris strongly convex too; letbe its unique solution. We haveand. Set. Then, the Davis–Yin algorithm (Eq. 11) converges linearly: there exists ρ ∈ (0, 1] such that, for every,Loose lower bounds for ρ are given in Davis and Yin, 2017, Theorem D.6.We have the following corollary of Lemma 2:
Proposition 1(linear convergence of the other variables in the Davis–Yin algorithm). In the same conditions and notations as inLemma 2, we have, for every, Also, in the form (Eq. 12) of the algorithm,and, in the form (Eq. 10) of the algorithm,
ProofLet . By nonexpansiveness of the proximity operator, in view of the first line in (Eq. 11), we have , so that (Eq. 14) follows from (Eq. 13). In addition, in view of the second line in (Eq. 11), we haveand, by nonexpansiveness of I − proxγG and ,Using the same arguments, in view of the second line in (Eq. 12),Finally, as visible in the first line of (Eq. 16), since , and using the Moreau identity, we have , so that
5.2 The PD3O Algorithm
We set , , , , as defined in Section 2. Doing the substitutions in (Eq. 12), we get the algorithm:
Let and . For k = 0, 1, … iterate:
We can remove the variable rw and the algorithm becomes: Let and . For k = 0, 1, … iterate:
After replacing CC* by ηI − KK*, the iteration becomes:
We can change the variables, so that only one call to ∇F and K* appears, which yields the algorithm: Let and . For k = 0, 1, … iterate:
When γk ≡ γ is constant, we recover the PD3O algorithm (Yan, 2018).
To derive Theorem 3 from Lemma 1, we simply have to notice that the variable in the latter corresponds to the pair (xk+1, 0). Also, in the conditions of Theorem 3, let u* be any solution of (Eq. 3); that is, u* ∈ ∂H(Kx*) and 0 ∈ ∂R(x*) + ∇F(x*) + K*u*. Then the constant c0 is
If K = I and η = 1, the PD3O algorithm reverts to the Davis–Yin algorithm, as given in (Eq. 4). In the conditions of Theorem 3, let u* be any solution of (Eq. 3); that is, u* ∈ ∂H(x*) and 0 ∈ ∂R(x*) + ∇F(x*) + u*. Then the constant c0 is
5.3 The PDDY Algorithm
The PDDY algorithm is obtained like the PD3O algorithm from the David–Yin algorithm, but after swapping the roles of and .
To obtain the PDDY algorithm, starting from (Eq. 10), let us first write the Davis–Yin algorithm as: Let and . For k = 0, 1, … iterate:
Equivalently: Let . For k = 0, 1, … iterate:
We set , , , , as defined in Section 2. Doing the substitutions in (Eq. 16), we get the algorithm: Let , . For k = 0, 1, … iterate:
We can remove the variable rw and rename rx as s:
The algorithm becomes: Let , . For k = 0, 1, … iterate:
Equivalently: Let , . For k = 0, 1, … iterate:
We can write the algorithm with only one call of K* per iteration by introducing an additional variable p: Let , . Set p0 = K*u0. For k = 0, 1, … iterate:
When γk ≡ γ is constant, we recover the PDDY algorithm (Salim et al., 2020).
Let us now derive Theorem 4 from Lemma 1. The variable in the latter corresponds to the pair , so that becomes
Therefore, in the conditions of Theorem 4, let u* be any solution of (Eq. 3); that is, u* ∈ ∂H(Kx*) and 0 ∈ ∂R(x*) + ∇F(x*) + K*u*. Then the constant c0 is
The last statement in Theorem 4 is obtained as follows. First, for every k ≥ 1, , so that . Second, from (Eq. 17), ‖xk+1 − x*‖2 = O(1/k2) and . So, assuming that η > ‖K‖2, ‖γk(uk − uk+1)‖2 = O(1/k2). Hence, .
If K = I and η = 1, the PDDY algorithm reverts to the Davis–Yin algorithm, as given in (Eq. 4), but with R and H exchanged. In the conditions of Theorem 4, let u* be any solution of (Eq. 3); that is, u* ∈ ∂H(x*) and 0 ∈ ∂R(x*) + ∇F(x*) + u*. Then the constant c0 is
This is the same value as in (Eq. 15), corresponding to the Davis–Yin algorithm, viewed as the PD3O algorithm, with R and H exchanged. Indeed, u* is defined differently in both cases; that is, with the exchange, u* ∈ ∂R(x*) in (Eq. 15).
5.4 R = 0: The Loris–Verhoeven Algorithm
If R = 0, the PD3O algorithm becomes: Let and . For k = 0, 1, … iterate:whereas the PDDY algorithm becomes: Let , . Set p0 = K*u0. For k = 0, 1, … iterate:
Equivalently,or:which is equivalent to (18). So, when R = 0, both the PD3O and PPDY revert to an algorithm which, for γk ≡ γ, is the Loris–Verhoeven algorithm (Loris and Verhoeven, 2011; Combettes et al., 2014; Condat et al., 2019a).
Let u* be any solution of (Eq. 3); that is, u* ∈ ∂H(Kx*) and 0 ∈ ∇F(x*) + K*u*. In the conditions of Theorem 3, c0 is:
On the other hand, in Theorem 4,
It is not clear how these two values compare to each other. They are both valid, in any case.
5.5 F = 0: The Chambolle–Pock and Douglas–Rachford Algorithms
If F = 0, the PD3O algorithms reverts to: Let and . For k = 0, 1, … iterate:
For γk ≡ γ, this is the form I (Condat et al., 2019a) of the Chambolle–Pock algorithm (Chambolle and Pock, 2011).
In the conditions of Theorem 3, let u* be any solution of (Eq. 3); that is, u* ∈ ∂H(Kx*) and 0 ∈ ∂R(x*) + K*u*. Then the constant c0 is
On the other hand, if F = 0, the PDDY algorithm reverts to: Let , . Set p0 = K*u0. For k = 0, 1, … iterate:which can be simplified as: Let , . For k = 0, 1, … iterate:knowing that we can retrieve the variable xk as .
For γk ≡ γ, this is the form II (Condat et al., 2019a) of the Chambolle–Pock algorithm (Chambolle and Pock, 2011).
Note that with constant stepsizes, the Chambolle–Pock form II can be viewed as the form I applied to the dual problem. This interpretation does not hold with varying stepsizes as in Theorem 3: the stepsize playing the role of γk would be 1/(γkη), which tends to + ∞ instead of 0, so that the theorem does not apply.
Note, also, that Theorem 4 does not apply, since F = 0 is not strongly convex. Finally, if the accelerated Chambolle–Pock algorithm form I is applied to the dual problem, our results do not guarantee convergence of the primal variable xk to a solution. So, we cannot derive an accelerated Chambolle–Pock algorithm form II.
If K = I, and η = 1, the Chambolle-Pock algorithm form I becomes the Douglas–Rachford algorithm: Let and . For k = 0, 1, … iterate:
We can rewrite the algorithm using only the meta-variable sk = xk − γkuk: Let . For k = 0, 1, … iterate:
Using the Moreau identity, we obtain: Let . For k = 0, 1, … iterate:and for γk ≡ γ, we recognize the classical form of the Douglas–Rachford algorithm (Combettes and Pesquet, 2010).
In the conditions of Theorem 3, let u* be any solution of (Eq. 3); that is, u* ∈ ∂H(x*) and 0 ∈ ∂R(x*) + u*. Then the constant c0 is
On the other hand, if K = I, and η = 1, the Chambolle-Pock algorithm form II becomes: Let , . For k = 0, 1, … iterate:
Using the Moreau identity, we obtain: Let , . For k = 0, 1, … iterate:
Introducing the meta-variable , we obtain: Let . For k = 0, 1, … iterate:
Thus, we recover exactly the Douglas–Rachford algorithm (Eq. 19), with R and H exchanged.
6 Derivation of the Distributed Algorithms
6.1 The Distributed PD3O Algorithm and its Particular Cases
Let us adopt the notations of Section 3 and precise the different operators. The gradient of in is
We define the linear subspace . is -smooth, with . But since is applied to an element of in the algorithms, we can weaken the condition on to be: for every and ,
That is, is such that, for every ,
Notably,satisfies the condition.
The adjoint operator of is
Thus,
But if F1 = ⋯ = FM, we can restrict the norm to andwhich is .
For any ζ > 0, we have , where and . We also have , , and , .
By doing all these substitutions in the PD3O algorithm, we obtain the distributed PD3O algorithm, and all its particular cases, shown above. Theorem 1 becomes Theorem 6 as follows. The objective function is .
(convergence rate of the Distributed PD3O Algorithm). In the Distributed PD3O Algorithm, suppose that, wheresatisfies (20); if Fm ≡ 0, we can choose any γ > 0. Also, suppose that, whereis defined in (21) or (22). Then xkconverges to some solution x*of (1). Also,converges to some element, for every m = 1, … , M. In addition, suppose that every Hmis continuous on an open ball centered at Kmx*. Then the following hold:
Define the weighted ergodic iterate , for every k ≥ 1. Then
Furthermore, if every H m is L m -smooth for some L m > 0, we have a faster decay for the best iterate so far:
The theorem applies to the particular cases of the Distributed PD3O Algorithm, like the distributed Loris–Verhoeven, Chambolle–Pock, Douglas–Rachford algorithms. We can note that the distributed forward–backward algorithm is monotonic, so Theorem 6 (iii) (with Hm ≡ 0) yields Ψ(xk) − Ψ(x*) = o(1/k) for this algorithm.
We now give accelerated convergence results using varying stepsizes, in presence of strong convexity. For this, we have to define the strong convexity constants and . Like for the smoothness constant, we can restrict their definition to . So, becomes the strong convexity constant of the average function . That is, is such that the functionis convex. It is much weaker to require than to ask all Fm to be strongly convex. Similarly, we have , the strong convexity constant of R. Thus, since the Accelerated Distributed PD3O Algorithm can be viewed as the accelerated PD3O algorithm applied to the minimization of , we have all the ingredients to invoke Theorem 3, which is transposed as:
(Accelerated Distributed PD3O Algorithm). Suppose that. Let x*be the unique solution to (1). Let κ ∈ (0, 1) and. Set γ1 = γ0and
Suppose that , where is defined in (21) or (22). Then in the Distributed PD3O Algorithm, there existssuch that, for every k ≥ 1,
As for Theorem 5, its counterpart in the distributed setting is:
(linear convergence of the Distributed PD3O Algorithm). Suppose thatand that every Hmis Lm-smooth, for some Lm > 0. Let x*be the unique solution to (1). We suppose thatand, whereis defined in (21) or (22). Then the Distributed PD3O Algorithm converges linearly: there exists ρ ∈ (0, 1] andsuch that, for every,
We can remark that the Distributed Davis–Yin algorithm (with ωm = 1/M and γk ≡ γ) has been proposed in an unpublished paper by Ryu and Yin (Ryu and Yin, 2017), where it is named Proximal-Proximal-Gradient Method. Their results are similar to ours in Theorem 6 and Theorem 8 for this algorithm, but their condition γ < 3/(2L), with , is worse than ours. Also, our accelerated version with varying stepsizes in Theorem 7 is new.
6.2 The Distributed PDDY Algorithm
The Distributed PDDY Algorithm, shown above, is derived the same way as the Distributed PD3O Algorithm. However, the smoothness constant cannot be defined only on , so that we haveand
Moreover,except if Fm ≡ 0, in which case the Distributed PDDY Algorithm becomes the Distributed Chambolle–Pock Algorithm Form II, for which we can set
We can note that when Km ≡ I, the Distributed PDDY Algorithm reverts to a form of distributed Davis–Yin algorithm, which is different from the Distributed Davis–Yin Algorithm obtained from the PD3O algorithm, shown above. Similarly, when R = 0, we obtain a different algorithm than the Distributed Loris–Verhoeven Algorithm shown above. When Fm ≡ 0, the Distributed PDDY Algorithm reverts to the Distributed Chambolle–Pock Algorithm Form II, which is still different from the Distributed Douglas–Rachford Algorithm when Km ≡ I.
The counterpart of Theorem 2 is:
(convergence of the Distributed PDDY Algorithm). In the Distributed PDDY Algorithm, suppose that γk ≡ γ ∈ (0, 2/LF) and, whereis defined in (23) or (24). Then allas well asconverge to the same solution x*of (1), and everyconverges to some element.
The counterpart of Theorem 4 is:
(Accelerated Distributed PDDY Algorithm). Suppose that. Let x*be the unique solution to (1). Let κ ∈ (0, 1) and. Set γ1 = γ0and
Suppose that , where is defined in (23) or (24). Then in the Distributed PDDY Algorithm, there existssuch that, for every k ≥ 1,
Consequently, for every m = 1, … , M,
Moreover, if , as well.
The counterpart of Theorem 5 is:
(linear convergence of the Distributed PDDY Algorithm). Suppose thatand that every Hmis Lm-smooth, for some Lm > 0. Let x*be the unique solution to (1). Suppose thatand, whereis defined in (23) or (24). Then the Distributed PDDY Algorithm converges linearly: there exists ρ ∈ (0, 1] andsuch that, for every,
6.3 The Distributed Condat–Vũ Algorithm
We can apply our product-space technique to other algorithms; in particular, we can derive distributed versions, shown below, of the Condat–Vũ algorithm (Condat, 2013; Vũ, 2013; Condat et al., 2019a), which is a well known algorithm for the problem (Eq. 2).
The smoothness constant is the same as for the Distributed PD3O Algorithm; we can set .
Moreover, the norm of is smaller for the Condat–Vũ algorithm: we have , whatever the functions Fm. This is because the gradient descent step is completely decoupled from the dual variables in the Condat–Vũ algorithm.
The price to pay is a stronger condition on the parameters for convergence:
(convergence of the Distributed Condat–Vũ Algorithm). Suppose that the parameters γ > 0 and σ > 0 are such that
Then x k converges to a solution x * of (1). Also,converges to some element, for every m = 1, … , M.
When Fm ≡ 0, the two forms of the Distributed Condat–Vũ Algorithm revert to the two forms of the Distributed Chambolle–Pock Algorithm, respectively. In that case, with constant stepsizes γk ≡ γ, the convergence condition is , which is the same as above with σ = 1/(ηγ).
Statements
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: LibSVM, https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/∼cjlin/libsvm/.
Author contributions
GM wrote the code and generated the results for the SVM experiment in Section 4.3. PR contributed to the paper writing and to the project management. LC did all the rest.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Alghunaim S. A. Ryu E. K. Yuan K. Sayed A. H. (2021). Decentralized Proximal Gradient Algorithms with Linear Convergence Rates. IEEE Trans. Automat. Contr.66, 2787–2794. 10.1109/tac.2020.3009363
2
Bach F. Jenatton R. Mairal J. Obozinski G. (2012). Optimization with Sparsity-Inducing Penalties. Found. Trends Mach. Learn.4, 1–106. 10.1561/2200000015
3
Bauschke H. H. Combettes P. L. (2017). Convex Analysis and Monotone Operator Theory in Hilbert Spaces. 2nd edn. New York: Springer.
4
Beck A. (2017). “First-Order Methods in Optimization,” in MOS-SIAM Series on Optimization (SIAM).
5
Boţ R. I. Csetnek E. R. Hendrich C. (2014). “Recent Developments on Primal–Dual Splitting Methods with Applications to Convex Minimization,” in Mathematics without Boundaries: Surveys in Interdisciplinary Research. Editors PardalosP. M.RassiasT. M. (New York: Springer), 57–99.
6
Bredies K. Kunisch K. Pock T. (2010). Total Generalized Variation. SIAM J. Imaging Sci.3, 492–526. 10.1137/090769521
7
Bubeck S. (2015). Convex Optimization: Algorithms and Complexity. FNT Machine Learn.8, 231–357. 10.1561/2200000050
8
Cevher V. Becker S. Schmidt M. (2014). Convex Optimization for Big Data: Scalable, Randomized, and Parallel Algorithms for Big Data Analytics. IEEE Signal. Process. Mag.31, 32–43. 10.1109/msp.2014.2329397
9
Chambolle A. Pock T. (2011). A First-Order Primal-Dual Algorithm for Convex Problems with Applications to Imaging. J. Math. Imaging Vis.40, 120–145. 10.1007/s10851-010-0251-1
10
Chambolle A. Pock T. (2016a). An Introduction to Continuous Optimization for Imaging. Acta Numerica25, 161–319. 10.1017/s096249291600009x
11
Chambolle A. Pock T. (2016b). On the Ergodic Convergence Rates of a First-Order Primal-Dual Algorithm. Math. Program159, 253–287. 10.1007/s10107-015-0957-3
12
Chang C.-C. Lin C.-J. (2011). LibSVM: A Library for Support Vector Machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol.2, 27. 10.1145/1961189.1961199
13
Chen P. Huang J. Zhang X. (2013). A Primal–Dual Fixed point Algorithm for Convex Separable Minimization with Applications to Image Restoration. Inverse Probl.29, 025011. 10.1088/0266-5611/29/2/025011
14
Combettes P. L. Condat L. Pesquet J.-C. Vũ B. C. (2014). “A Forward–Backward View of Some Primal–Dual Optimization Methods in Image Recovery,” in Proc. Of IEEE ICIP (Paris, France: IEEE), 4141–4145.
15
Combettes P. L. Pesquet J.-C. (2012). Primal-Dual Splitting Algorithm for Solving Inclusions with Mixtures of Composite, Lipschitzian, and Parallel-Sum Type Monotone Operators. Set-valued Anal.20, 307–330. 10.1007/s11228-011-0191-y
16
Combettes P. L. Pesquet J.-C. (2010). “Proximal Splitting Methods in Signal Processing,” in Fixed-Point Algorithms for Inverse Problems in Science and Engineering. Editors BauschkeH. H.BurachikR.CombettesP. L.ElserV.LukeD. R.WolkowiczH. (New York: Springer-Verlag), 185–212.
17
Condat L. (2017a). “A Convex Approach to K-Means Clustering and Image Segmentation,” in Proc. Of EMMCVPR. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Editors PelilloM.HancockE. (Venice, Italy: Springer, 2018), Vol. 10746, 220–234.
18
Condat L. (2014). A Generic Proximal Algorithm for Convex Optimization—Application to Total Variation Minimization. IEEE Signal. Process. Lett.21(8), 985–989. 10.1109/LSP.2014.2322123
19
Condat L. (2013). A Primal-Dual Splitting Method for Convex Optimization Involving Lipschitzian, Proximable and Linear Composite Terms. J. Optim. Theor. Appl.158, 460–479. 10.1007/s10957-012-0245-9
20
Condat L. (2017b). Discrete Total Variation: New Definition and Minimization. SIAM J. Imaging Sci.10, 1258–1290. 10.1137/16m1075247
21
Condat L. Kitahara D. Contreras A. Hirabayashi A. (2019a). Proximal Splitting Algorithms: A Tour of Recent Advances, with New Twists. Preprint arXiv:1912.00137.
22
Condat L. Kitahara D. Hirabayashi A. (2019b). “A Convex Lifting Approach to Image Phase Unwrapping,” in Proc. Of IEEE ICASSP (Brighton, UK: IEEE), 1852–1856. 10.1109/icassp.2019.8682258
23
Cremers D. Pock T. Kolev K. Chambolle A. (2011). “Convex Relaxation Techniques for Segmentation, Stereo and Multiview Reconstruction,” in Markov Random Fields for Vision and Image Processing (Cambridge: MIT Press).
24
Davis D. Yin W. (2017). A Three-Operator Splitting Scheme and its Optimization Applications. Set-valued Anal.25, 829–858. 10.1007/s11228-017-0421-z
25
Drori Y. Sabach S. Teboulle M. (2015). A Simple Algorithm for a Class of Nonsmooth Convex-Concave Saddle-point Problems. Operations Res. Lett.43, 209–214. 10.1016/j.orl.2015.02.001
26
Duran J. Moeller M. Sbert C. Cremers D. (2016). Collaborative Total Variation: A General Framework for Vectorial TV Models. SIAM J. Imaging Sci.9, 116–151. 10.1137/15m102873x
27
Gorbunov E. Hanzely F. Richtárik P. (2020). A Unified Theory of SGD: Variance Reduction, Sampling, Quantization and Coordinate Descent. Proc. Int. Conf. Artif. Intell. Stat. (Aistats), PMLR108, 680–690.
28
Komodakis N. Pesquet J.-C. (2015). Playing with Duality: An Overview of Recent Primal?dual Approaches for Solving Large-Scale Optimization Problems. IEEE Signal. Process. Mag.32, 31–54. 10.1109/msp.2014.2377273
29
Konečný J. McMahan H. B. Yu F. X. Richtárik P. Suresh A. T. Bacon D. (2016). “Federated Learning: Strategies for Improving Communication Efficiency,” NIPS Private Multi-Party Machine Learn. Workshop. Paper arXiv:1610.05492.
30
Latafat P. Freris N. M. Patrinos P. (2019). A New Randomized Block-Coordinate Primal-Dual Proximal Algorithm for Distributed Optimization. IEEE Trans. Automat. Contr.64, 4050–4065. 10.1109/tac.2019.2906924
31
Loris I. Verhoeven C. (2011). On a Generalization of the Iterative Soft-Thresholding Algorithm for the Case of Non-separable Penalty. Inverse Probl.27, 125007. 10.1088/0266-5611/27/12/125007
32
Malinovsky G. Kovalev D. Gasanov E. Condat L. Richtárik P. (2020). “From Local SGD to Local Fixed point Methods for Federated Learning,” in Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, 119, 6692–6701.
33
O’Connor D. Vandenberghe L. (2020). On the Equivalence of the Primal-Dual Hybrid Gradient Method and Douglas–Rachford Splitting. Math. Program179, 85–108. 10.1007/s10107-018-1321-1
34
D. P. Palomar Y. C. Eldar (Editors) (2009). Convex Optimization in Signal Processing and Communications (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press).
35
Parikh N. Boyd S. (2014). Proximal Algorithms. FNT in Optimization1, 127–239. 10.1561/2400000003
36
Polson N. G. Scott J. G. Willard B. T. (2015). Proximal Algorithms in Statistics and Machine Learning. Statist. Sci.30, 559–581. 10.1214/15-sts530
37
R. Glowinski S. J. Osher W. Yin (Editors) (2016). Splitting Methods in Communication, Imaging, Science, and Engineering (New York: Springer International Publishing).
38
Richtárik P. Takáč M. (2014). Iteration Complexity of Randomized Block-Coordinate Descent Methods for Minimizing a Composite Function. Math. Program144, 1–38. 10.1007/s10107-012-0614-z
39
Ryu E. K. Yin W. (2017). Proximal-proximal-gradient Method. Preprint arXiv:1708.06908.
40
Salim A. Condat L. Kovalev D. Richtárik P. (2021). An Optimal Algorithm for Strongly Convex Minimization under Affine Constraints. Preprint arXiv:2102.11079.
41
Salim A. Condat L. Mishchenko K. Richtárik P. (2020). Dualize, Split, Randomize: Fast Nonsmooth Optimization Algorithms. Preprint arXiv:2004.02635.
42
Scaman K. Bach F. Bubeck S. Lee Y. T. Massoulié L. (2017). Optimal Algorithms for Smooth and Strongly Convex Distributed Optimization in Networks. Proc. 34th Int. Conf. Machine Learn. (Icml)70, 3027–3036.
43
Shi W. Ling Q. Wu G. Yin W. (2015). EXTRA: An Exact First-Order Algorithm for Decentralized Consensus Optimization. SIAM J. Optim.25, 944–966. 10.1137/14096668x
44
Sra S. Nowozin S. Wright S. J. (2011). Optimization for Machine Learning. Cambridge: The MIT Press.
45
Stathopoulos G. Shukla H. Szucs A. Pu Y. Jones C. N. (2016). Sensor Fault Diagnosis. FnT Syst. Control.3, 249–362. 10.1561/2600000008
46
Unknown author (1972). Every Convex Function Is Locally Lipschitz. The Am. Math. Monthly79, 1121–1124.
47
Vũ B. C. (2013). A Splitting Algorithm for Dual Monotone Inclusions Involving Cocoercive Operators. Adv. Comput. Math.38, 667–681. 10.1007/s10444-011-9254-8
48
Wang Y.-X. Sharpnack J. Smola A. Tibshirani R. (2016). Trend Filtering on Graphs. J. Machine Learn. Res.17, 1–41.
49
Yan M. (2018). A New Primal-Dual Algorithm for Minimizing the Sum of Three Functions with a Linear Operator. J. Sci. Comput.76, 1698–1717. 10.1007/s10915-018-0680-3
Summary
Keywords
convex nonsmooth optimization, proximal algorithm, splitting, convergence rate, distributed optimization
Citation
Condat L, Malinovsky G and Richtárik P (2022) Distributed Proximal Splitting Algorithms with Rates and Acceleration. Front. Sig. Proc. 1:776825. doi: 10.3389/frsip.2021.776825
Received
14 September 2021
Accepted
20 October 2021
Published
25 January 2022
Volume
1 - 2021
Edited by
Hadi Zayyani, Qom University of Technology, Iran
Reviewed by
Junfeng Yang, Nanjing University, China
Olivier Fercoq, Télécom ParisTech, France
Updates
Copyright
© 2022 Condat, Malinovsky and Richtárik.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Laurent Condat, laurent.condat@kaust.edu.sa
This article was submitted to Signal Processing for Communications, a section of the journal Frontiers in Signal Processing
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.