- 1Cinvestav Tamaulipas, Center for Research and Advanced Studies, Ciudad Victoria, Mexico
- 2School of Engineering, National Autonomous University of Mexico, Coyoacan, Mexico
- 3Computer Science Department, National Institute of Astrophysics, Optics and Electronics, Tonantzintla, Mexico
Since the rise of the Internet, several IT services and applications have become widely accessible, making cloud computing a vital solution for its deployment for corporate and personal use. Additionally, the Internet of Things (IoT) has accelerated large-scale data generation, e.g., for monitoring applications in medical and industrial environments. Cloud computing and IoT are seamlessly integrated: IoT devices generate data later stored and accessed in the cloud, enabling efficient data use across multiple applications and processing models. Consequently, cloud services are increasingly being used for outsourcing the high processing and storage requirements demanded by IoT applications. While this integration offers significant advantages, it also presents major data security challenges, particularly concerning the confidentiality and access control of outsourced sensitive data. It is especially relevant because cloud service providers are typically assumed to be honest but curious and, hence, untrustworthy. In this context, Ciphertext-Policy Attribute-Based Encryption (CP-ABE) can successfully enforce complex access control over outsourced data. It is achieved by encrypting it using fine-grained access policies and delegating access control to decryption keys dependent on end-user attributes. Although CP-ABE offers several advantages, its wide adoption and efficient deployment in practical applications is still hindered by some issues. One of the major concerns involves the strong dependency on a centralized trusted authority setting and managing CP-ABE’s access control policies and attribute sets. This dependency represents a single point of failure that threatens the system’s continuous operation. In this paper, we eliminate CP-ABE’s dependency on a single trusted authority by adopting a decentralization strategy relying on blockchain’s main features. Therefore, we propose a blockchain-based approach to distribute among multiple peers the users’ secret keys generation and management tasks performed by the trusted authority, solving CP-ABE’s centralization problem. By combining blockchain, CP-ABE, and Elliptic Curve Integrated Encryption Scheme (ECIES), we ensure the confidentiality of CP-ABE critical components regardless of their heterogeneous privacy requirements. We evaluated our proposal considering a case study in the eHealth domain, whose results confirm its deployment feasibility in practical applications, where confidentiality and access control hold while resiliency and the system’s continuous operation are achieved.
1 Introduction
Attribute-Based Encryption (ABE) (Sahai and Waters, 2005) is a cryptographic technique that enables many-to-many encryption and provides flexible data access management. Due to its characteristics, it simplifies secure data sharing with multiple users, even in untrusted environments. ABE can be classified into two families: Ciphertext-Policy Attribute-Based Encryption (CP-ABE) (Bethencourt et al., 2007) and Key-Policy Attribute-Based Encryption (KP-ABE) (Goyal et al., 2006). Given its features, CP-ABE is considered more suitable for enforcing access control in cloud storage scenarios. The key components of CP-ABE include access control policies used for data encryption and attribute sets that further describe the users’ access capabilities. On the one hand, attributes describe users’ characteristics or responsibilities within the context in which the CP-ABE system is deployed. These attributes can be shared by multiple users, highlighting one of the main advantages of any CP-ABE scheme: the capability to facilitate data sharing among a large number of users (Alston, 2017; Sahai and Waters, 2005). On the other hand, access control policies are defined over subsets of attributes to encrypt the owner’s data, and only the users whose attributes satisfy a particular policy can decrypt the data. In other words, CP-ABE policies establish a fine-grained data access control mechanism while ensuring the confidentiality of sensitive information (Kumar et al., 2018). Therefore, these core components are tightly related and eliminate the need for traditional public or private keys. In a cloud context, this prevents redundant encryption, simplifies key management, and addresses key distribution challenges.
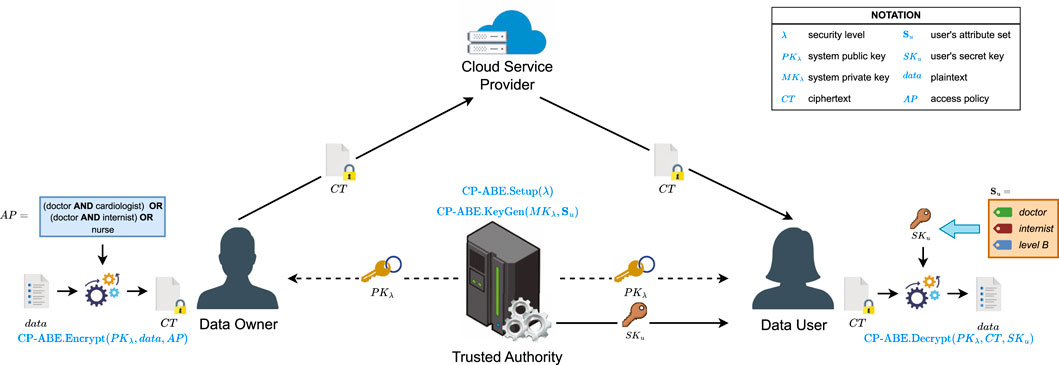
Figure 1 shows a typical CP-ABE system model consisting of four main entities, each performing different tasks according to its role. Data owners (DO) possess sensitive data that needs to be outsourced to a cloud service provider (CSP) but whose confidentiality must also be preserved. Therefore, the DO must encrypt the data before outsourcing it to the cloud. The CSP is responsible for storing the encrypted data and ensuring it is only accessible to authorized users. Aided by the CSP, data users (DU) can perform query operations on the owner’s encrypted data. In order to decrypt any encrypted data, the DU must possess their user secret key to execute the decryption algorithm and retrieve the plaintext. Finally, a trusted authority (TA) is responsible for running the system initialization algorithm and the key generation algorithm based on each user’s attribute set. The TA also handles the distribution of the system’s public key and the corresponding user secret keys through secure communication channels while keeping the system’s master key private. A basic CP-ABE system model consists of four main algorithms (Bethencourt et al., 2007):
As mentioned above, the security components of CP-ABE are managed by a centralized trusted authority. These include those required for generating system keys, managing the attribute universe, and granting access to end users based on the attributes they possess. In this sense, the TA is responsible for performing the operations required to set up and handle the essential components of any CP-ABE scheme. However, this approach creates a strong dependency on the trusted authority, resulting in a single point of failure if the TA suddenly fails or gets compromised, putting the entire solution at risk. Therefore, it is essential to reduce reliance on a single trusted authority by distributing its tasks between multiple entities to ensure the system’s continuous operation while achieving resilient and efficient CP-ABE practical implementations. By incorporating multiple authorities sharing responsibility for CP-ABE’s critical operations, fine-grained access control and user attribute management are still ensured, even if one of these authorities fails. Any CP-ABE scheme is generally easily adaptable to multiple application domains, and several works in the literature have introduced multi-authority CP-ABE constructions aiming to achieve or enhance CP-ABE decentralization. Although different approaches have been proposed to achieve decentralization, they often result in increased complexity or fall short of achieving full decentralization.
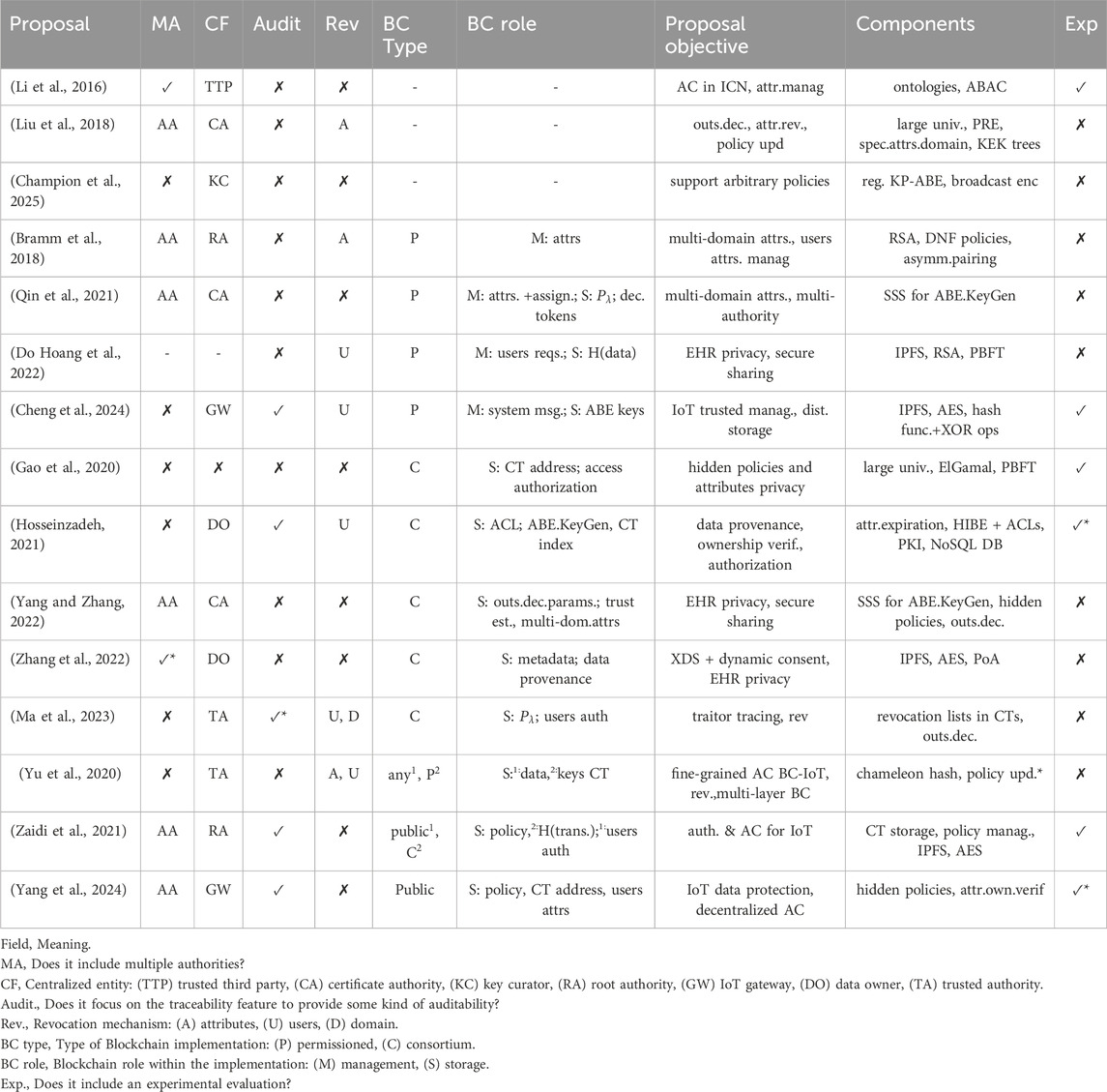
One of the first approaches to addressing ABE decentralization includes a trusted central authority in the system model (Chase, 2007; Bramm et al., 2018; Liu et al., 2016; Liu et al., 2018). This central entity coordinates other authorities, each possessing and managing its specific attribute domain. Initially, the central authority sets up the system and generates global identifiers and secret keys for the dependent authorities. In this way, any entity assuming the role of authority can accomplish its tasks without the central authority’s involvement. The tasks of the dependent authorities include managing users’ attributes and secret keys but relying on the parameters defined during the system setup. However, the possibility of having single points of failure is not completely eliminated because, without the central authority, no entity is responsible for managing the remaining authorities. Alternative approaches eliminate the central authority (Chase and Chow, 2009; Lewko and Waters, 2011) or rely on the application of a distributed coordination protocol (Ziegler et al., 2020) between trusted authorities, particularly for the generation of users’ secret keys. It implies distributing the attributes and users’ secret keys management tasks previously performed by a central authority. However, this approach leads to increased computational and communication costs, especially when attributes are collectively managed by all authorities or when each attribute has its singular secret key. This setup can also pose challenges for data users who have multiple attribute keys.
Blockchain integration into ABE schemes has been recently explored due to blockchain’s inherent capability to decentralize processes by eliminating intermediaries and distributing tasks among multiple peers. For instance, proposals like (Qin et al., 2021; Bramm et al., 2018; Yang and Zhang, 2022) employ blockchain to manage user attributes across multiple attribute domains within the system. This approach also ensures a reliable record of users’ activities, thus easing the monitoring of their behavior and identifying potential data misuse. Meanwhile, in (Yang and Zhang, 2022; Do Hoang et al., 2022; Hosseinzadeh, 2021; Zhang et al., 2022), blockchain is mainly used to establish data provenance by storing all interactions between system users and patients’ electronic health records in the ledger, with the records’ privacy and secure sharing ensured through ABE. However, the main goal of these proposals is not to decentralize the trusted authority’s tasks within ABE implementations. Instead, they aim to provide deployments where multiple attribute authorities issue and manage attributes across domains or maintain a record of the actions carried out within the system to track data provenance–similar to an event log.
As stated before, several works in the literature attempt to address ABE decentralization issues by incorporating different approaches into their solutions. Nonetheless, existing works focus on only a few tasks or do not provide fully decentralized solutions. Based on the analysis of the existing literature in the state of the art, we can summarize the main challenges observed in current CP-ABE decentralization approaches as follows:
1. Centralization. Using a central authority to set up and manage dependent authorities undermines true decentralization.
2. Unfeasibility. The increased computational and communication costs associated with collective attribute management make existing approaches impractical.
3. Different scope. Although blockchain is incorporated into CP-ABE solutions, the decentralization of the trusted authority’s essential tasks is not addressed.
In this sense, the motivation of our work focuses on decentralizing the tasks performed by CP-ABE’s trusted authority, aiming to eliminate its reliance on a centralized entity. We first identified the CP-ABE operations suitable for decentralization based on their characteristics, expected outcomes, and the specific entities responsible for their execution. Based on those results, we defined the users’ secret keys generation and management as the tasks eligible for decentralization. Hence, we developed a strategy to distribute these tasks among multiple entities, leveraging the characteristics of blockchain technology. In this paper, we present a blockchain-based approach to decentralize the tasks performed by CP-ABE’s trusted authority. The key contributions of our work are outlined as follows:
In this way, we address a significant issue in CP-ABE where dependency on a single (centralized) trusted authority leads to single points of failure and interruption in the scheme’s operations if that entity fails or is breached. Moreover, given the characteristics of blockchain, scalability, and transparency are ensured since every transaction recorded in the ledger is first validated by the network peers and then easily accessible to them, thereby increasing trust within the system.
The remainder of this paper is structured as follows: Section 2 provides background information on blockchain and consensus mechanisms. Section 3 presents a brief discussion of related works in the state of the art. Section 4 details our proposal for decentralizing the trusted authority’s tasks in ABE constructions by incorporating blockchain. Section 5 describes the prototype implementation and the validation for our proposal. Finally, Section 6 presents the conclusions drawn from this work and outlines potential directions for future research.
2 Background
Decentralizing information systems involves eliminating single points of failure by distributing computing resources and information management across multiple entities or servers. This approach enhances flexibility in accessing resources and resilience against potential failures. Typically, decentralization is achieved through distributed systems, where resources collaborate to reach a common goal while providing users with an interface similar to that of a centralized system. This design ensures transparent resource sharing and data processing for users, making it impossible for them to identify how these resources are and the complexity of their management (Tanenbaum and Van Renesse, 1985; Qin et al., 2021).
2.1 Blockchain
Blockchain has emerged as a disruptive technology well suited to address decentralization issues with no intermediaries required. To achieve that goal, it involves mechanisms, algorithms, and other technologies, such as distributed storage, consensus protocols, and the application of cryptographic algorithms (Storublevtcev, 2019; Zhai et al., 2019). Nowadays, blockchain technology is increasingly used for decoupling traditionally centralized processes or tasks (Díaz et al., 2025; Dávila et al., 2023; Wu et al., 2025). In this context, incorporating blockchain into CP-ABE schemes can be particularly useful for accomplishing the CP-ABE trusted authority decentralization by distributing its tasks among multiple peers. Blockchain background dates back to the early 1990s (Haber and Stornetta, 1991), but its formal definition emerged after the release of Bitcoin (Nakamoto, 2008). It remains a relatively new technology for which, additionally, new proposals continue emerging under different application scenarios. It consists of a consensus-driven ledger where data is stored in a database replicated in multiple peer-to-peer (P2P) nodes, ensuring transparency throughout the network (Storublevtcev, 2019; Yaga et al., 2018; Jayavarma et al., 2025). In this ledger, cryptographically signed transactions are grouped and recorded consecutively into blocks containing relevant data about the set of transactions.
Besides, each block includes two hash values: the first one being the digital fingerprint of the current block’s content and the other representing the fingerprint of the preceding block, thereby ensuring the immutability of stored transactions (Wüst and Gervais, 2018; Yaga et al., 2018; Jayavarma et al., 2025). Thus, transaction integrity depends on the chaining of blocks through their hash values. Any deliberate or accidental alteration in a block would require changing its hash value and those of all subsequent blocks. New blocks must be verified before being added to the ledger, and blockchain peers must collectively agree on the validity of the transactions. Since no centralized authorities are involved, trust among unknown nodes is established through cryptographic evidence provided by digital signatures and the hash values stored within the blocks. In order to achieve this, a consensus algorithm helps peers coordinate and agree on a shared network transaction history and its validity within a decentralized environment (Retamal et al., 2017).
Depending on who can participate in the network, blockchains can be divided into two major types: permissionless and permissioned. Permissionless blockchains are completely open since no central authority regulates access or sets roles, allowing any peer to join and equally participate in the network anonymously. Since data is publicly available to everyone, the peers can propose or validate blocks and query ledger transactions, simplifying collective transaction maintenance. The key features of permissionless blockchains include high transparency and decentralization, as well as anonymity and the existence of incentives for encouraging honest participation within the network (Retamal et al., 2017; Pastorino, 2022). Conversely, permissioned blockchains involve a certificate authority that verifies the identities of potential network participants, regulating who can join the network, perform validation tasks, or access the ledger. Consequently, these networks are considered partially centralized because a select group of trusted peers proposes and validates transactions while others only use the blockchain as a service. Therefore, access to the ledger is restricted to authorized, identifiable entities, allowing it to process a higher number of transactions per second if compared to permissionless approaches (Yaga et al., 2018; Wüst and Gervais, 2018).
2.2 Consensus algorithms
Consensus algorithms are essential components of a blockchain network for defining the rules and criteria that network peers must follow to reach agreements regarding the network status and transaction validity. Such protocols help nodes to make decisions in a distributed environment where no central authority exists by establishing the criteria and steps to follow in case of node failure or inconsistencies in the agreement (Zhai et al., 2019; Ongaro and Ousterhout, 2014). In this way, it guarantees data integrity and consistency across the network by establishing a common transaction history (Kaur et al., 2021). Although there are different consensus protocols employed in blockchain, each one has strengths and weaknesses, aiming to balance efficiency and security. Proof-of-Work (PoW) appears with Bitcoin and is well-known for its strong security but also because of its substantial energy consumption. In PoW, blockchain nodes compete to solve a cryptographic puzzle that involves finding a number that produces a hash value below a predefined target once concatenated with the block’s data. This process demands significant computational power and delays block acceptance, originating temporary forks in the blockchain. In such cases, the blockchain branch with the longest block sequence is considered valid, while blocks on the shorter branch are discarded. (Kaur et al., 2021; Ismail and Materwala, 2019). Proof-of-Stake (PoS) offers a more energy-efficient solution compared to PoW. It leverages the cryptocurrencies or tokens held by network peers to determine their influence in block proposal and validation, assigning more influence to those with a higher stake. Instead of solving complex mathematical problems, block proposers are selected for generating the next block once defined the number of tokens each node is willing to invest, thus achieving better scalability than PoW (Kaur et al., 2021; Xiao et al., 2020).
Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) derives from PoS and arises to narrow down the consensus group size and the volume of exchanged messages between the delegates. In other words, in DPoS, a small set of peers is elected as validators or delegates through a voting process, whose influence is determined by their stake. However, unlike PoW and PoS, delegates proportionally distribute the earned rewards among their respective voters (Kaur et al., 2021; Ismail and Materwala, 2019). Pure Proof-of-Stake (PPoS) is also a PoS variant where Verifiable Random Functions (VRFs) (Micali et al., 1999) are employed for the random selection of potential block proposers and committees’ members. These members vote on a block in a private and non-interactive way, whose voting influence is defined by their online stake. However, it is ensured that all network peers can participate in the consensus for a certain number of rounds, given the pseudo-random nature of the VRFs and a parameter indicating how many times a user has been chosen. For a block to be written to the blockchain, block proposals are first filtered in a soft-vote step, and once a block is selected, it moves to a certify-vote step to confirm its validity and write it to the ledger (Gilad et al., 2017; Algorand consensus, 2024). Proof-of-Authority (PoA) is a reputation-based protocol where a specific group of peers considered trustworthy exclusively validate and append blocks to the ledger. Validator peers are selected based on their identity verification before their incorporation into the network, and considering they stake their reputation instead of tokens, their authority is gradually built as they participate in the network. Therefore, PoA achieves high performance by relying on a limited number of block validators, implying less message exchange (De Angelis et al., 2018; Ismail and Materwala, 2019).
3 Related work
In (Do Hoang et al., 2022), blockchain serves as an enabler for the decentralized storage of sensitive healthcare data. Meanwhile, data owners set the attributes that potential users must possess as a tuple of a label and an identification phrase to access their data. Data owners are also responsible for keeping secret the decryption keys and sharing them with data users once they become authorized. In (Gao et al., 2020), a blockchain-based solution is proposed, where confidentiality for attributes and access control policies is also guaranteed through homomorphic encryption and enhanced hidden policies, respectively. In that proposal, the data owner has two tasks: encrypting the sensitive data to send its address to the blockchain and generating access transactions to deliver the corresponding decryption keys to the users. Conversely, to access the plaintext, data users must locally verify the policy’s satisfiability to generate a proof of access that must be validated in the blockchain. As can be noticed, although both proposals deploy a blockchain network, they focus on building trust for access control management rather than decentralizing the system tasks.
In (Hosseinzadeh, 2021), authors explore the integration of ABE and blockchain in computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems to enhance sensitive medical data security. Their focus is primarily on patients’ privacy and unauthorized access or tampering prevention. ABE and Hierarchical Identity-Based Encryption (HIBE) are used to ensure sensitive data confidentiality and fine-grained access control at different levels according to the organizational hierarchy. Meanwhile, blockchain is intended to reduce the computational overhead related to the users’ secret keys generation by distributing this task among the network peers. Besides, any interaction with patients’ health records is registered in the blockchain ledger, thus providing a mechanism for managing access control and establishing data provenance while ensuring data integrity and confidentiality. However, even though some level of decentralization is achieved when generating the users’ secret keys, data owners remain as central figures responsible for defining the access permissions for a list of requestors over their medical records.
In (Yang and Zhang, 2022), the authors focus on enhancing digital healthcare systems by developing a proposal for secure Cross-Enterprise Document Sharing (XDS) while preserving patients’ confidentiality. That work proposes integrating a multi-authority ABE scheme with blockchain and verifiable outsourced decryption to allow the authorities interoperability and reduce the computational overhead on the users’ side, respectively. Blockchain enables the attribute authorities to collectively manage the system users’ attributes through a secret sharing scheme, thus generating a key pair for each attribute. Blockchain also stores public parameters that allow the results’ correctness verification. In (Zhang et al., 2022), an XDS framework relying on ABE and consortium blockchain–a kind of permissioned blockchain with shared governance–is presented. In that work, patients act as individual attribute authorities, leaving them the attributes issuance, keys management, and system initialization. Therefore, the blockchain is not used to decentralize ABE tasks but for registering the medical records metadata, allowing its retrieval from a document repository. Only three attributes are considered in the system domain in order to achieve constant ciphertexts and reduce the algorithms’ execution times. This approach alleviates some burden to the attribute authorities but limits the potential of ABE. However, it also uses AES for wrapping ABE ciphertexts, leading to a key distribution problem which solution or implementation is not discussed.
In (Ma et al., 2023), a lightweight setting of a blockchain-based solution for IoT smart factories is proposed, where hidden access policies are used, and users’ behavior is constantly monitored to identify malicious users and revoke them. It is noticeable that the role of blockchain within the system is performing users’ authentication and storing ciphertexts’ indexes and public keys. Similar to (Do Hoang et al., 2022), blockchain is employed as a decentralized storage facilitator. Hence, it is not concerned about decentralizing essential tasks, such as those performed by the trusted authority. The role of the trusted authority remains in that proposal and adds a domain manager, who is responsible for the encryption tasks within the smart factory. In (Yu et al., 2020), a blockchain solution for an IoT scenario is proposed, which integrates the chameleon hash function, aiming to guarantee the integrity of the data stored in the ledger despite its update. That work aims to achieve fine-grained and updatable access control by deploying a multi-layer redactable blockchain, where sensitive data storage is separated from access control management. Similar to (Ma et al., 2023), the centralized trusted authority is maintained, as the primary goal of the proposal is to enable revocation and ledger updates while preserving immutability, rather than to decentralize tasks.
In (Cheng et al., 2024), the authors address the challenges associated with IoT devices’ trusted management by proposing a framework designed to enhance the trustworthiness of IoT interactions. That framework utilizes hash functions and XOR operations to enable lightweight authentication and incorporates an edge-based decentralized environment for data storage. It also integrates blockchain for behavior traceability over the messages exchanged between IoT devices and employs CP-ABE to ensure confidentiality and fine-grained access control. Although the system’s public key and users’ secret keys from CP-ABE are stored and distributed through the blockchain, that work’s main goal does not focus on CP-ABE decentralization. Instead, they propose to replace CP-ABE’s trusted authority with an IoT gateway, i.e., another centralized entity.
In (Yang et al., 2024), an optimized CP-ABE scheme based on (Cheung and Newport, 2007) is presented to ensure reliable and traceable access control for IoT data while supporting a large attribute universe. By incorporating blockchain, the authors aim to provide a decentralized system where policies and attributes are stored in the ledger while maintaining its privacy. At this point, it is important to note that the presence of an Attribute Management Node (AMN) is assumed in the blockchain network, which is responsible for generating users’ secret keys. Therefore, data users can obtain their secret keys from the blockchain after completing a challenge-response mechanism to verify the attribute sets’ ownership. Despite this, it remains unclear who is responsible for assigning and delivering attribute sets to users or for storing these attributes in the blockchain ledger.
Conversely, a consensus-oriented multi-authority solution based on (Müller et al., 2008) and built over asymmetric pairings is presented in (Bramm et al., 2018). By using blockchain, the authors aim to address the revocation and user key management problems in distributed environments. Each trusted authority within the system defines an attribute domain and assigns the appropriate attributes to each user. As a result, every user can have several attribute sets, which are stored in wallets according to the domains where they are registered. A trusted authority can hold exclusiveness over any attribute, but it can also grant permission to other authorities to include such an attribute in their domain. In this way, any authority can manage user attributes, either from their particular domain or from the users’ wallets holding their multiple identities. These operations are performed via transactions on the blockchain, allowing monitoring of the access rights status in the system. However, such a proposal requires a central authority that generates, assigns, and protects the trusted authorities’ secret keys. Therefore, in addition to requiring a fully trustworthy authority, this approach fails to guarantee a high level of decentralization.
In (Gao et al., 2020), a construction incorporating blockchain technology is presented to guarantee distributed and trusted access control management, where fully hidden access control policies are processed as transactions. Such a proposal removes the trusted authority from the system model, leaving the key generation and transaction validation processes to be performed by data owners and data users through smart contracts. Although that approach aims to eliminate single points of failure, it requires that every access request to a data owner’s information results in a transaction between the involved users. In addition, the ElGamal cryptographic algorithm is employed to generate access proofs for potential users, which involves comparing the user’s set of attributes against the data’s associated policy. These two aspects lead to computational and communication overheads since data owners must always be aware of potential users’ requests.
In (Champion et al., 2025), a registered KP-ABE scheme is introduced, capable of supporting arbitrary circuit policies based on the
Based on the review presented above, it is evident that most of the previous works adopt different approaches, depending on their main goals, which often do not focus on decentralizing ABE trusted authority. Some works propose incorporating multiple authorities, whether attribute or trusted authorities, but still maintain a central entity to coordinate these authorities. In (Bramm et al., 2018), a root authority is responsible for creating the AAs keys, while in (Yu et al., 2020), the figure of a TA remains, although keys are stored in a key chain. In (Qin et al., 2021), the same certificate authority that allows peers to participate in the blockchain also initializes the system and issues keys for AAs and DUs. Meanwhile, in (Liu et al., 2018), a central authority sets up public parameters and generates identifiers for DUs and AAs. In addition to system initialization and the generation of attribute authorities’ keys, such approaches involve other operations performed by the central entities. For instance, they execute a special setup for each attribute authority and data user (Qin et al., 2021), manage requests from AAs and DUs (Liu et al., 2018), and even generate the users’ secret keys, despite the deployment of a blockchain-based solution (Ma et al., 2023).
Moreover, some works in the literature fail to specify who assigns the attribute sets to data users or how this process is carried out. Additionally, they often divide the users’ secret keys into multiple sub-keys. Some proposals, such as (Hosseinzadeh, 2021), state that users request their attributes from the blockchain, which then forwards the request to an attribute data store. However, it is not clear who sets up this data store and who designates attributes to data users. In (Qin et al., 2021; Yang and Zhang, 2022), attribute authorities collaborate to generate a key for each attribute a user possesses, yet the process of assigning attributes to users is not detailed. Furthermore, in (Yang and Zhang, 2022), part of the secret key is generated by data users themselves. Similarly, in (Ma et al., 2023), the trusted authority is responsible for generating users’ secret keys, but the assignment of attribute sets remains unclear. Table 1 provides a comparative summary of the existing proposals in the literature discussed above, highlighting the key features of each proposal as well as the specific objectives each aims to achieve.
Based on the summary in Table 1 and the literature review, it is clear that decentralizing tasks of the trusted authority within CP-ABE schemes remains an open problem. Many works fail to effectively achieve the necessary decentralization for practical CP-ABE schemes and, in some cases, introduce additional components and operations that negatively impact the scheme’s overall efficiency.
Therefore, in applications involving multiple users and attributes, these approaches are unlikely to achieve scalability or ensure the system’s continuous operation. Furthermore, many proposals that integrate ABE and blockchain do not prioritize decentralizing the tasks of the trusted authority (TA). Instead, these works primarily focus on providing mechanisms for granting authorization, ensuring data provenance, securely sharing assets, or managing revocation, among other objectives. In contrast, this work highlights the importance of reducing CP-ABE schemes’ strong dependency on a trusted authority. Our proposal seeks to enhance the practicality and usability of CP-ABE constructions by delegating the TA’s tasks–such as public key and parameter distribution, as well as users’ secret keys generation and management–to the blockchain network. By adopting a consensus-driven approach, these tasks are executed in a manner similar to that of a single-authority scheme, without introducing additional operations to the core algorithms of CP-ABE.
4 Decentralization of CP-ABE trusted authority’s tasks
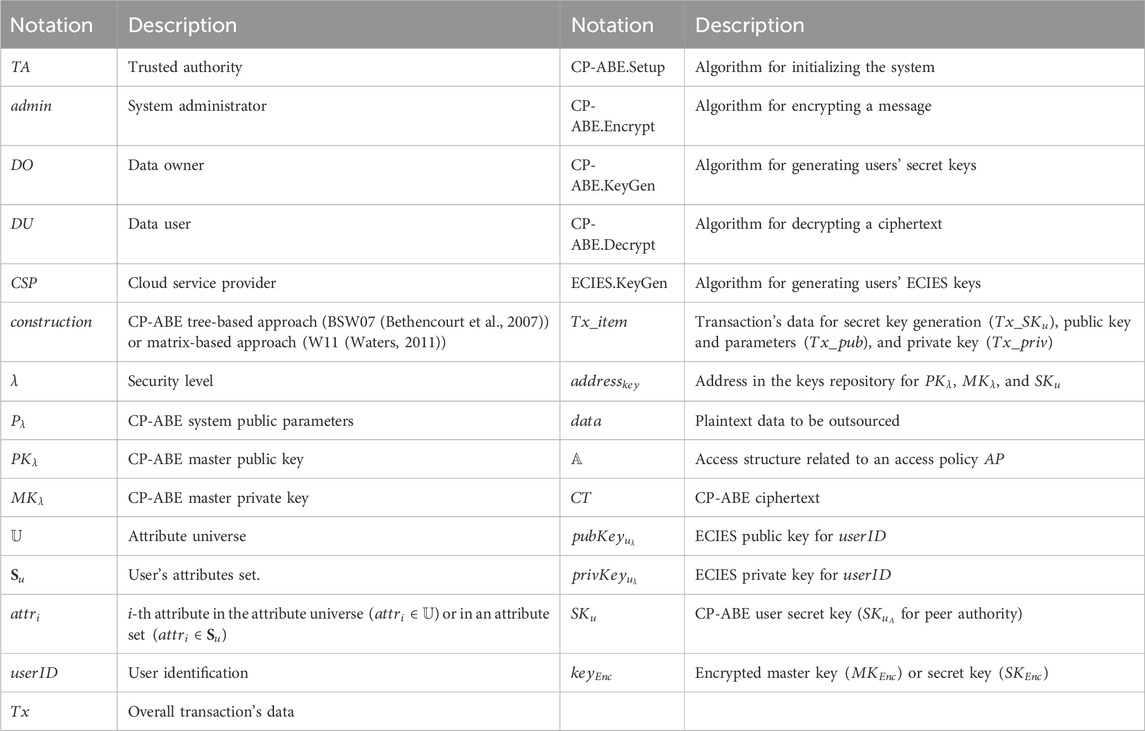
There are several tasks performed by trusted entities in CP-ABE schemes in order to manage either the attributes (attribute authority) or the system and users’ keys (trusted authority). Based on both authorities’ characteristics, it is worth noting that a single trusted attribute authority could perform such tasks. However, the existence of single points of failure within this approach remains unsolved, causing the entire solution to collapse if this entity crashes. Several proposals have attempted to tackle the decentralization issue in CP-ABE schemes by incorporating multiple authorities into their solutions. Sometimes these authorities are managed by a central trusted authority and work together through a distributed coordination protocol. Nonetheless, such approaches often do not consider completely decentralized solutions or focus only on the decentralization of certain tasks performed by the trusted authority. From a thorough review, we first identified (1) all the operations carried out by the CP-ABE trusted authority, related either to attributes or keys, and (2) whether they are part of CP-ABE core algorithms and the order in which they must be performed to achieve the intended result. Then, we analyzed its eligibility for decentralization based on its characteristics and expected outcomes, additionally defining the most suitable approach to follow. The notation and acronyms used in the rest of this work are shown in Table 2.
As stated in Section 1, of the four entities considered in the basic CP-ABE system model, the trusted authority is the one responsible for initializing the system by executing the CP-ABE.Setup algorithm and generating the users’ secret keys with the CP-ABE.KeyGen algorithm. Nevertheless, it typically remains out of the works’ scope how the system and users’ keys are managed and delivered to the intended recipients, as well as the attribute definition and management. For the system keys generation, the CP-ABE.Setup algorithm receives as input a security parameter and initializes the system, creating its public and private keys. From this key pair, only the public key must be shared with data owners and data users, while the private key remains only accessible to trusted entities. At this point, it is important to notice that any public parameter related to the system initialization, such as the public key, could be available to any user within the system. The CP-ABE.KeyGen algorithm receives as input the system’s private key and a set of attributes describing the user’s access capabilities. It outputs the user’s secret key
Within any CP-ABE scheme, the definition and management of an attribute universe that describes the application domain and the possible attributes the system users may possess is essential. These tasks must be done by a trusted entity, e.g., a system administrator aware of the application domain, while the trusted authority stores and manages all the relevant information regarding those attributes. The attribute universe must be publicly available to system users since it serves as a core element for proper access policies definition and access rights management. Conversely, as input for the users’ secret key generation algorithm, data users’ privacy must be guaranteed, and their corresponding attribute set must not be disclosed because it represents users’ specific access rights. The blockchain-based solution proposed in this paper contributes to decentralizing the trusted authority’s tasks. Our proposal focuses on distributing the public key and parameters to the system users, attribute universe management, as well as users’ secret keys generation and management among the peers comprising the blockchain network. The confidentiality of the system’s critical components is also guaranteed by relying on CP-ABE itself to encrypt the system master key and the Elliptic Curve Integrated Encryption Scheme (ECIES) to encrypt the users’ secret keys before delivering them to the intended recipients. By combining these strategies, we aim to appropriately decentralize the two tasks a TA generally executes as part of a CP-ABE system while preserving privacy and confidentiality where needed.
4.1 General solution architecture and system model
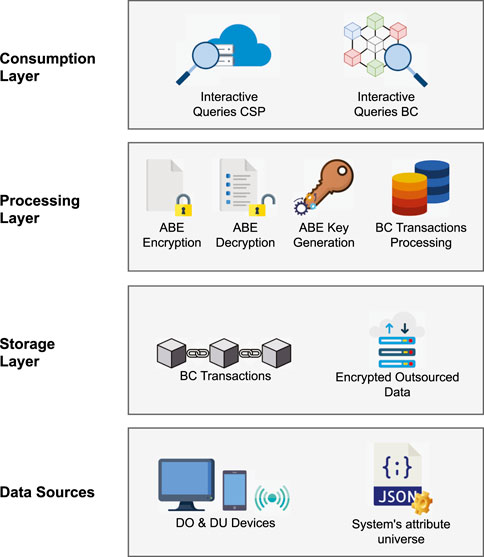
Figure 2 depicts the architecture considered in our proposal, consisting of three layers and the system’s data sources at the bottom of the stack. In this context, owners’ and users’ devices generate sensitive data while the system’s attribute universe is defined based on the application domain characteristics. Both serve as the data sources that must be handled at the storage layer. This layer comprises the cloud service provider storing the encrypted outsourced data and the blockchain ledger storing the data related to the transactions performed as part of the decentralization mechanism proposed. Meanwhile, the processing layer includes all the operations involved in integrating the blockchain network into the CP-ABE scheme–i.e., the CP-ABE core algorithms execution and the blockchain transactions processing. Lastly, the consumption layer handles interactive queries submitted to both the cloud service provider and the blockchain network, providing end users with an interface to access the stored data upon request.
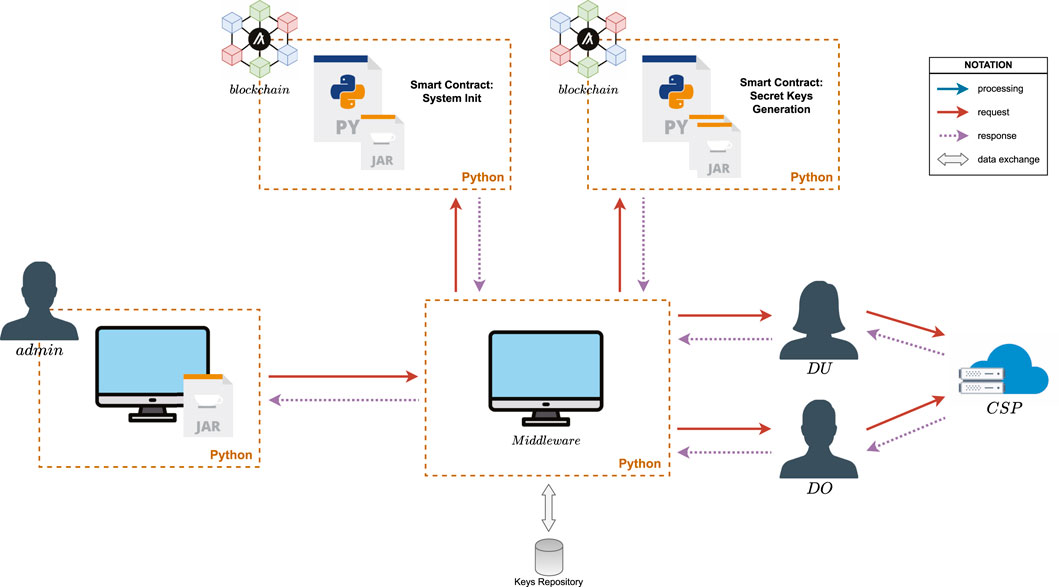
Figure 3 shows the proposed system model incorporating a permissionless blockchain to decentralize the aforementioned tasks. In our proposal, the trusted authority TA is replaced by the peers comprising the blockchain network, whereas data owners DO, data users DU, and the cloud service provider CSP continue to perform the same tasks as in the traditional CP-ABE system model (Figure 1). We also consider the existence of a system administrator admin, who performs the CP-ABE system initialization. This one-time task consists of executing the CP-ABE.Setup algorithm to generate the system’s key pair
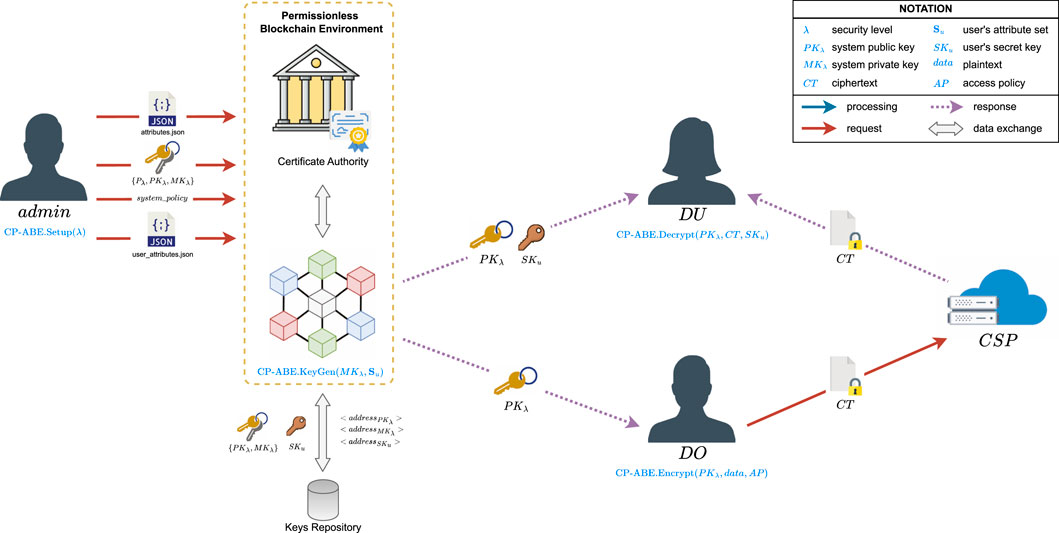
Figure 3. General view of the proposed decentralization approach for the TA’s tasks in CP-ABE systems.
4.2 Algorithms details
As mentioned before, CP-ABE’s keys and attributes can be categorized into public and private data. Public data includes the system’s public key and the attribute universe, while sensitive data involves the system’s master key and the users’ attribute sets and secret keys. Whereas the attribute universe is meant to be available to every user in the system, individual users’ attribute sets are intended to remain private, only known by the users described by such attribute sets. The same happens with the users’ secret keys and system keys. The former is generated from each user’s private attribute set and must be securely stored, either by the users themselves or encrypted and saved in the blockchain ledger. In the case of the system keys, there is a public component comprising the system’s public parameters and the public key, as well as a private component related to the master key. On the one hand, the public parameters and public key must be accessible to any user, allowing them to perform encryption and decryption tasks, i.e., to execute CP-ABE.Encrypt and CP-ABE.Decrypt algorithms, respectively. On the other hand, the system master key must remain only accessible to those entities in charge of generating the users’ secret keys, thus avoiding its use by malicious users for creating apocryphal secret keys.
Based on the heterogeneous privacy requirements of attributes and keys within CP-ABE schemes, we propose a permissionless blockchain solution that also integrates CP-ABE and ECIES. In this way, privacy and confidentiality of the system’s critical components are guaranteed, even if such data is stored in the blockchain ledger and is publicly accessible to any peer participating in the network. In our solution, public data is made available as plaintext on the blockchain ledger to enable system users to perform encryption and decryption operations over outsourced data. Meanwhile, sensitive data is first encrypted and then stored in the keys repository, with only their addresses stored in the public ledger. As a result, even in the case of a peer failure or a successful internal or external attack on the blockchain network, sensitive data cannot be directly accessed or read without the corresponding key.
It is worth mentioning that our proposal relies on the four basic algorithms defined in (Bethencourt et al., 2007) where system keys are generated independently from the attributes universe. Additionally, our proposal considers three possible security levels (128-, 192-, and 256-bit), according to the recommendations of international standards, such as the NIST SP800-57 report and the ECRYPT-CSA D5.4 project (Giry, 2020).
4.2.1 System initialization
In the state of the art, a CP-ABE scheme’s initialization typically involves executing the CP-ABE.Setup algorithm to generate the system’s public and master keys. Although the attribute universe is an essential component, it is assumed that setting the attribute universe occurs eventually before data encryption and the users’ secret keys generation. In our proposal, we consider that system initialization involves defining the attribute universe and generating the system’s key pair. These main tasks also comprise setting the appropriate access control policy for encrypting the system’s master key in order to ensure its confidentiality.
The system initialization begins with the admin defining the attribute universe
Once the system policy and the attribute universe are defined, including its domain and control attributes, the system keys must be generated. Even though the system setup is a core algorithm in any CP-ABE scheme, it is a one-time task not eligible for decentralization, as it is executed only during system initialization. Therefore, as displayed in Figure 3, the admin is also responsible for executing the CP-ABE.Setup algorithm to generate the system’s public parameters
As stated before, the public data–i.e.,
4.2.2 Users’ secret keys: Generation and management
Users’ secret keys generation and management involve two main tasks: assigning the attribute sets to data users and generating the corresponding keys based on those sets. As in the case of CP-ABE system initialization, attributes’ assignment is assumed to happen eventually before the secret keys generation. Existing works in the literature lack specifying who is responsible for assigning attribute sets to data users or how it is accomplished. Occasionally, this assignment is referred to as carried out by an attribute authority. However, it is not specified whether that entity is the same as the trusted authority, whether they collaborate, or what process is followed. In our proposal, we consider this two-step process to be performed collaboratively by the system administrator and the blockchain.
Secret keys generation and management begin on the admin’s side, who must create an ECIES key pair for a given user, where
On the blockchain’s side, the admin’s request for creating a user’s secret key triggers the retrieval and decryption of CP-ABE’s
Upon retrieval and decryption of the system’s master key and having the attribute set
The user’s secret key, as another sensitive item and due to the storage constraints of the blockchain ledger, must be stored as an encrypted asset in the keys repository. In this sense, the blockchain peer encrypts
5 Implementation and evaluation results
In this section, we present the evaluation of our proposal to demonstrate its feasibility and effectiveness in reducing CP-ABE schemes’ dependency on a trusted authority. First, we describe the experimental settings and characteristics of the prototype deployed on the Algorand blockchain. Then, we present the results of our proposal evaluation by analyzing the interactions between the system entities and the outputs they produce when executing the operations defined in the protocol described in Section 4. Finally, we discuss the compliance of our proposal with the security guarantees provided by CP-ABE and blockchain, highlighting how our approach leverages blockchain features to decentralize the tasks performed by the CP-ABE’s trusted authority without modifying the underlying scheme.
5.1 Experimental settings
As a proof of concept and for validation purposes, a prototype of the proposed solution was implemented in the testnet of the Algorand blockchain, a permissionless framework where transactions’ validity can be confirmed within approximately 1 minute. This network uses the Pure Proof-of-Stake (PPoS) Byzantine agreement protocol to reach consensus. At each block round, a block proposer and a set of voting committees are randomly chosen from the pool of all token holders based on their account’s stake in the network (Gilad et al., 2017). Figure 4 shows the architecture of the prototype developed in Python3, using algosdk for the communication between the application and the Algorand environment, and the eciespy library for implementing the ECIES operations. It also employs executable JAR files built from the Java-based FABECS application (Hinojosa-Cabello et al., 2022; Hinojosa-Cabello, 2020), an approach for secure storage and retrieval developed over Type-III pairings and compliant with both tree-based and matrix-based access structures. Such JAR files encapsulate the functionality of the four CP-ABE core algorithms, allowing the easy execution of the users’ secret key generation, data encryption, and decryption operations within the blockchain network, as well as the system initialization on the admin’s side.
5.2 Implementation results and proposal validation
In this section, we consider a privacy-preserving case study in the eHealth domain for our proposal evaluation following the operations workflow given in the model depicted in Figure 5. Through this model, we describe how the entities involved in the system model presented in Figure 3 interact through messages, the operations they perform, and the outputs each state produces. By analyzing the entities’ behavior and providing a comprehensive exploration of all possible states of the system, we verify the correctness and security of our protocol. Based on the description given in Section 4.2, our decentralization proposal is deployed in the healthcare domain within a single organization–thus, in the context of a single attribute domain–with the following characteristics:
1. The system begins with ten users, three holding the role of data owner, four only as data users, and three as both data owners and data users.
2. The keys managed within the system can provide a security level equal to or greater than 128-bit since the deployment is done over the asymmetric setting.
3. The system can be deployed with both tree-based (BSW07) (Bethencourt et al., 2007) and matrix-based (W11) (Waters, 2011) CP-ABE schemes.
4. There are three main attributes in the attribute universe, each with three possible values, resulting in a total of nine different attributes.
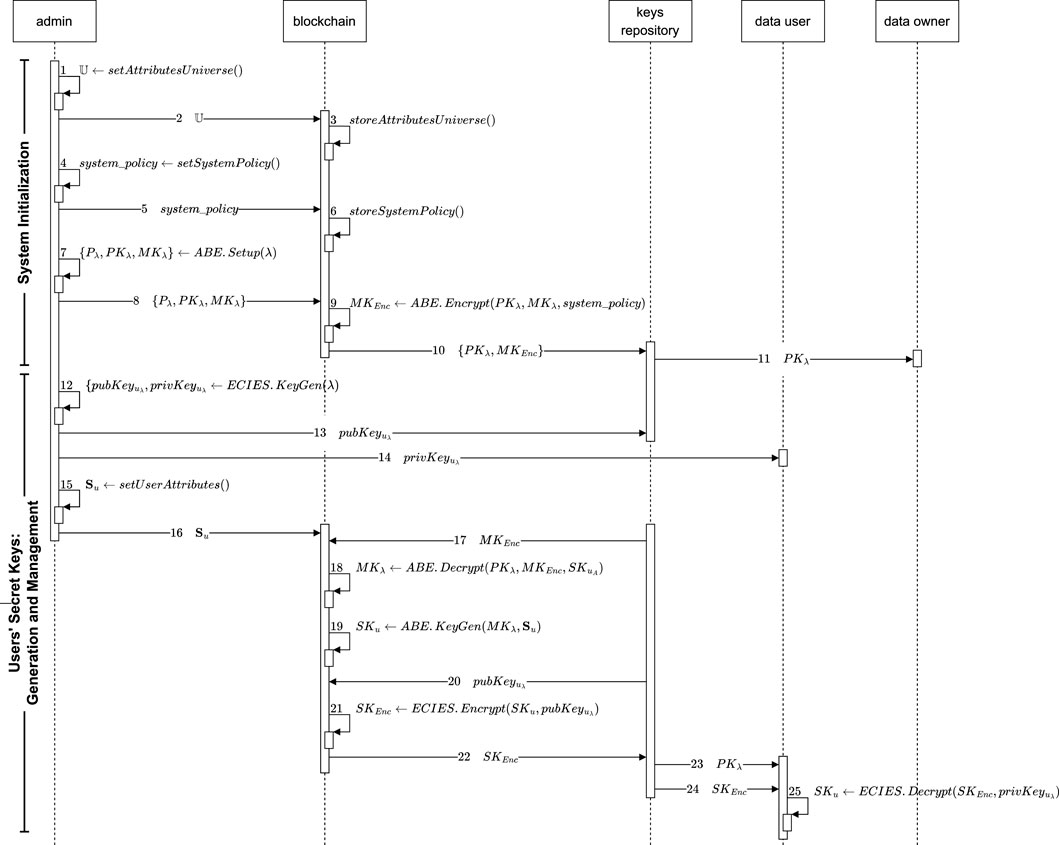
Figure 5. Operations workflow for the decentralization of the tasks performed by the trusted authority in CP-ABE schemes.
Since the system setup and the attribute universe definition are independent, there is no strict order to perform these operations. In our case, we consider that the attribute universe definition is first done because the attributes required in this specific scenario are well-known. Then, the system access policy is set, considering the system role of data owner as a control attribute, which also implies a high level of trustworthiness. Finally, the CP-ABE setup is performed in order to generate the system’s public and private keys that later allow the users’ secret keys generation, as well as the encryption and decryption tasks. This process is shown in Figure 5 in the ‘System Initialization’ phase (operations 1–11). The attributes in the universe

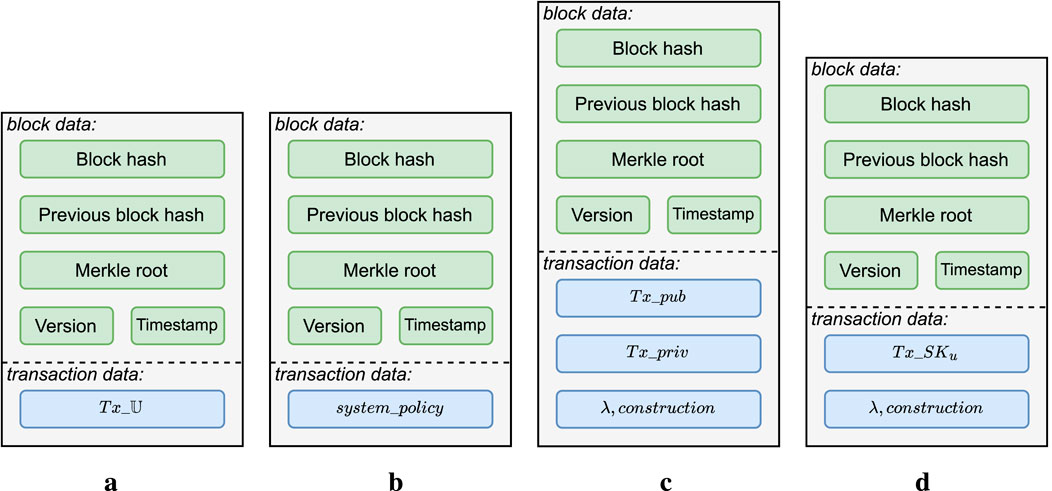
Figure 6. Blocks structure for the different transactions stored in the blockchain. (a) Attributes universe. (b) System policy. (c) System keys and parameters. (d) Users’ secret keys.
Listing 1. Attributes universe structure.
The admin sets the control attributes that must be granted to the blockchain peers and allow the definition of the access control policy
Hence, by assigning the aforementioned values for the control attributes, the generic policy shown in Equation 1 is transformed into the system policy shown in Equation 2. As another component that does not require encryption, the system policy is the following item to be stored in the blockchain. Therefore, once sent to the network by the admin and added to the ledger,
It is worth noting that, in practical applications, not necessarily every data owner will have associated a high degree of trustworthiness. In fact, data owners’ trust level can be decreased, either automatically or by the admin, due to misbehavior or as a consequence of a revocation process. However, the revocation issue is out of the scope of this paper. Moreover, although each blockchain peer can access the
Depending on the application domain needs and the sensitivity of the data stored within the system, one or more security levels can be configured. For our case study, we considered both tree- and matrix-based CP-ABE deployments for
After that, the admin is now able to securely store the system keys and parameters in the keys repository and the blockchain ledger, respectively (see Figure 5, operations 8–11). It is important to recall that public data must be distributed among the system users upon request, while the master key must remain private, only available to the block proposers. Thus, admin sends to the blockchain the request containing
First, the master key is encrypted by means of the CP-ABE. Encrypt algorithm, which receives as input the system’s public and private keys and the access policy previously defined to output the encrypted system private key
As depicted in Figure 5, operations 12–25 from the ‘Users’ Secret Keys: Generation and Management’ phase are executed to generate and deliver a user’s secret key. The system administrator first creates an ECIES key pair by executing the ECIES.KeyGen
Listing 2. Attribute set for
Having the decrypted key and the user’s attribute set, the block proposer executes the CP-ABE.KeyGen algorithm to output the user’s secret key
5.3 Threat model
Despite its advantages, CP-ABE faces adoption challenges mainly due to its reliance on a centralized trusted authority, which raises several risks (Liu et al., 2024; Xie et al., 2023). By combining blockchain, CP-ABE, and ECIES into a single solution, our decentralization approach eliminates the dependency on a single trusted authority. Our work is compliant with the recommended security levels (Giry, 2020) and guarantees the security services provided by CP-ABE and blockchain, including confidentiality, fine-grained access control, collusion resistance, integrity, and immutability. Since we are not modifying CP-ABE algorithms, we assume in our implementation that the definitions and security properties given in works (Bethencourt et al., 2007; Waters, 2011) hold. However, replacing a centralized trusted authority with a blockchain-based decentralized architecture introduces new considerations and potential threats that may arise from misconfigurations or an improper, weak off-chain implementation. Under this assumption, we identify the following relevant threat vectors:
1. Collusion attacks. On CP-ABE, multiple users attempt to decrypt ciphertexts that they are not individually authorized to access. On the blockchain, malicious participants try to manipulate the consensus or misuse smart contracts.
2. Attribute and key leakage. Sensitive attributes or keys may be unintentionally exposed by the system administrator or trusted authorities due to insecure transmission, storage, or weak authentication mechanisms.
3. Attribute and key forgery. An attacker may attempt to manipulate or forge attribute assignments or keys to gain unauthorized access either to the application domain ciphertexts or the cryptographic material stored at the keys repository.
4. Sybil attacks. A malicious party creates multiple fake peers to gain influence over the blockchain consensus or manipulate smart contract execution.
The CP-ABE threat model focuses on ensuring data confidentiality and collusion-resistance while relying on a fully trusted authority responsible for generating and distributing the system’s parameters and keys. It assumes the existence of adversarial entities, such as unauthorized or colluding users and external attackers, who may attempt to decrypt data without satisfying the underlying access policies. On the one hand, unauthorized users are system users who, without possessing the required attributes, attempt to decrypt a given ciphertext either individually or by colluding with other users. Colluding users also try to access ciphertexts by combining their attributes or secret keys to overcome access restrictions. On the other hand, external attackers may intercept encrypted data and then attempt to gain unauthorized access. However, by definition, CP-ABE schemes are collusion-resistant and ensure that only users whose attribute sets satisfy the access policy embedded in the ciphertext can successfully decrypt the data. In this sense, even if unauthorized users obtain the ciphertext, they cannot decrypt it to extract the plaintext or infer any meaningful information from it.
In our proposal, we leverage blockchain features and security guarantees to replace the centralized trusted entity with multiple trusted peers. In this way, the users’ secret keys generation and management tasks, as well as the system’s parameters and keys distribution, are performed by multiple blockchain peers. Although attributes and keys have heterogeneous privacy requirements, only public keys and parameters are stored in plaintext, while sensitive data is encrypted before being stored in the blockchain ledger and the keys repository to reduce the risk of data leakage. Hence, it is ensured that such data cannot be accessed by unauthorized users or without possessing the appropriate decryption key. Additional mitigation strategies to prevent attribute and key leakage would include relying on secure communication channels for data transmission, robust authentication methods for accessing the repository, and enabling audit logs to verify compliance with secure storage and communication protocols. Moreover, attribute and key forgery are mitigated, as only the admin can assign attributes to users, and all key-related operations are executed within a smart contract-controlled environment and recorded on-chain.
By distributing the users’ secret keys generation and management tasks among the blockchain peers, we eliminate the reliance on a centralized trusted entity or off-chain synchronization between authorities. Therefore, we assume a secure, permissionless environment with a built-in Byzantine fault-tolerant consensus protocol resilient to a bounded number of faulty or adversarial nodes for our proposal deployment. In this sense, blockchain peers are assumed to be valid participants within the network that follow the consensus protocol correctly to vote and agree on a single block finalization per round, thus ensuring robustness against Sybil or collusion attacks and forking.

Figure 7. Setup algorithm execution for BSW07 and W11 schemes’ constructions. (a) Tree-based system setup. (b) Matrix-based system setup. Outputs of the CP-ABE.
5.4 Discussion
To assess the computational overhead of our blockchain-based decentralization approach, we conducted a series of experiments over the operations comprising both the system initialization and users’ secret keys generation tasks. All the experiments were executed at least 35 times to get more reliable results, according to the Central Limit Theorem (CLT) (Montgomery, 2013). It is worth noting that our proposal aims to decentralize the trusted authority’s tasks while preserving the privacy and confidentiality of CP-ABE’s critical components–namely, the system master key and the users’ secret keys. As stated in Section 5.1, the prototype deployed on the Algorand blockchain testnet employs executable JAR files built from the FABECS application (Hinojosa-Cabello et al., 2022; Hinojosa-Cabello, 2020), which encapsulate the functionality of CP-ABE core algorithms. Recent advances in computing discrete logarithms have led to revised key size recommendations, reducing the security level of the BN256 curve from 128-bit to 100-bit. To ensure at least
Figure 8 presents the response times for system initialization, with Figures 8a,c illustrating the centralized approach, and Figures 8b,d showing the decentralized approach. As expected, the centralized setting achieves better performance, remaining below 4 ms, regardless of the security level or construction evaluated, as it only involves executing the CP-ABE.Setup algorithm. In contrast, the decentralized setting involves executing not only this algorithm but also the CP-ABE.Encrypt algorithm to encrypt the system master key, along with blockchain-related operations to store the attribute universe and system policy on the ledger and the system key pair in the keys repository. Although
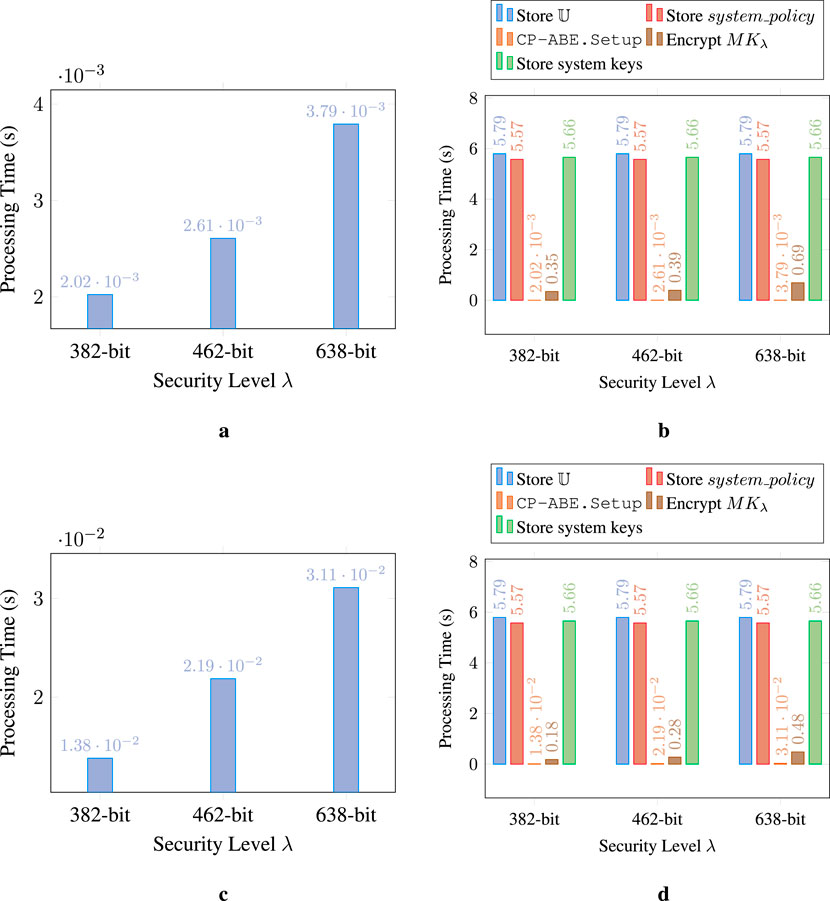
Figure 8. Performance evaluation of the system initialization. (a) Centralized W11: CP-ABE.Setup (Hinojosa-Cabello, 2020). (b) Decentralized W11: System initialization. (c) Centralized BSW07: CP-ABE.Setup (Hinojosa-Cabello, 2020). (d) Decentralized BSW07: System initialization.
For the users’ secret keys generation, Figures 9a,c depict the response times of the centralized approach, while Figures 9b,d represent those of the decentralized approach. Similarly to system initialization, the centralized setting performs better than its counterpart, as it only involves executing one algorithm (CP-ABE.KeyGen) that is slightly affected when increasing the security level. At this point, it is worth mentioning that we tested a fixed configuration of 10 attributes in the user attribute set, i.e.,
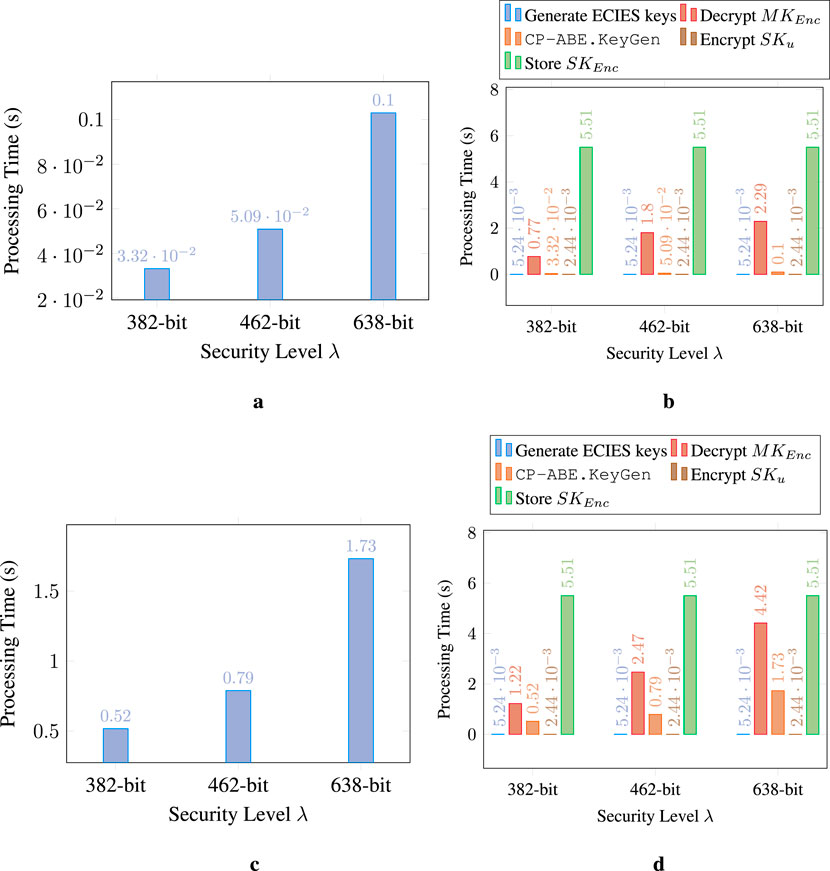
Figure 9. Performance evaluation of the secret keys generation. (a) Centralized W11: CP-ABE.KeyGen (Hinojosa-Cabello, 2020). (b) Decentralized W11: Secure users’ secret keys generation. (c) Centralized BSW07: CP-ABE.KeyGen (Hinojosa-Cabello, 2020). (d) Decentralized BSW07: Secure users’ secret keys generation.
Regarding the blockchain storage costs, our proposal is constrained by the limitations imposed by the blockchain network used to implement the solution described in Section 4. Specifically, in the case of our implementation, the Algorand network allows a maximum storage capacity of 1 KB per transaction and 5 MB per block (Algorand, 2025). For transactions, its size limit includes the transaction header, signature, and any additional information included in the transaction. For blocks, on average, a new block is created in the Algorand network every 4.5 s, and the amount of transactions it contains depends on the size of the individual transactions. It is important to recall that, in our proposal, only the keys’ addresses, the attribute universe, and the system policy are actually stored in the blockchain ledger. Both the system keys and the users’ secret keys are stored in the keys repository, either encrypted or in plaintext, based on their privacy requirements.
On Algorand, the standard transaction fee is 0.001 ALGO, regardless of transaction complexity. Considering ALGO currently trading at approximately USD 0.17, this represents a cost around USD 0.00017 per transaction. If the system were migrated to a different blockchain, this cost could vary significantly, as other platforms may charge higher or dynamic fees based on network congestion, transaction size, or priority. When it comes to communication costs, they depend on the number of peers and the network’s capacity, as well as the messages exchanged for achieving consensus and propagating transactions and blocks. Since Algorand’s protocol is optimized for fast transaction propagation, the propagation cost is assumed to be low, which enables achieving high throughput and scalability (Gilad et al., 2017). As stated before, transaction latency is around 4.5 s until a new block is created. Although PPoS requires exchanging information between committee members to reach a consensus, it relies on the efficient use of Verifiable Random Functions (VRF) and a gossip protocol, reducing the overall communication between peers. Therefore, it entails a very low communication overhead compared to other consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS).
The results of the performance evaluation confirm that our blockchain-based decentralization approach is suitable for its integration into CP-ABE deployments to replace the centralized trusted authority. By incorporating Algorand, we provide a lightweight, cost-effective alternative in terms of communication and transaction costs. While processing blockchain transactions represents the primary source of overhead, their computational cost remains bounded and predictable, making the approach feasible to use in practical applications. Therefore, although it introduces additional latency when compared with the centralized setting, it delivers significant advantages by eliminating the single point of failure associated with CP-ABE’s traditional trusted authority. Moreover, by integrating CP-ABE and ECIES, the confidentiality of CP-ABE critical components is preserved by encrypting sensitive data before being recorded on the blockchain ledger. In this way, the risk of information leakage due to blockchain’s transparency feature is mitigated, thus achieving a secure, auditable, and decentralized strategy for distributing the users’ secret keys generation and management tasks.
As stated in Section 4.1, in our approach, the system administrator is assumed to be part of the broader system apart from the CP-ABE scheme, handling foundational tasks such as general system maintenance. However, we also leverage their domain knowledge to define an attribute universe suited to the deployment environment and to assign attribute sets to users, extending their responsibilities beyond basic user enrollment. Additionally, the administrator is responsible for initializing the CP-ABE system, a one-time task that generates CP-ABE public and private keys. Once the system initialization is complete and the users are assigned their corresponding attribute sets, the system operates independently since the admin role is limited to these setup and assignment tasks. Hence, although the admin might be considered a potential single point of failure, their involvement in the system operation is limited to well-defined foundational activities rather than ongoing encryption or decryption operations.
Our approach achieves full decentralization by leveraging blockchain features to distribute the trusted authority’s tasks among multiple entities. Unlike federated or partially decentralized CP-ABE schemes, our decentralization strategy removes the need for a central trusted authority or explicit inter-authority coordination (Chase, 2007; Bramm et al., 2018; Liu et al., 2016; Liu et al., 2018; Chase and Chow, 2009; Lewko and Waters, 2011; Ziegler et al., 2020). Existing solutions typically rely on a central entity to coordinate subordinate authorities or manage attributes collectively, leading to increased overhead without eliminating single points of failure. Our solution distributes the users’ secret key generation and management across multiple blockchain peers, making the system resilient to node failure, as no single authority is critical for continuous operation. Moreover, inter-authority coordination, task validation, and synchronization are achieved inherently through the blockchain’s consensus mechanism and the execution of smart contracts. This design also ensures the auditability of all key management actions since attribute assignment and key issuance are recorded in the blockchain ledger. By addressing the limitations faced by federated or partially decentralized CP-ABE schemes, our blockchain-based approach ensures uninterrupted system operation while preserving the privacy and confidentiality of CP-ABE’s critical components.
As outlined in Section 4.2, our proposal requires an external repository for storing essential cryptographic materials: the CP-ABE public key and users’ ECIES public keys in plaintext, and the CP-ABE master key and users’ secret keys in encrypted form. This repository ensures access to the necessary keys for performing ABE operations, compensating the limitations of blockchain–namely, handling large volumes of sensitive data on-chain. Even though encryption mitigates the exposure of sensitive keys, by considering external storage, it is assumed that it remains persistently available and protected against unauthorized access. Although relying on external repositories has its limitations, it provides a practical and well-balanced solution aligned with current best practices in cryptographic systems. To further mitigate this dependency, alternatives such as storing keys on the client side or on-demand reconstruction could be explored, but they also present their own challenges.
6 Conclusion
The centralized approach of CP-ABE systems, where generally a trusted authority is responsible for distributing the system public key, generating and managing the users’ secret keys, poses substantial challenges for ensuring the system’s continuity if that entity fails. Most of the existing approaches to decentralize the trusted authority’s tasks often introduce additional complexity that results counterproductive given the significant computational or communication costs involved. This paper discussed a novel approach for decentralizing the tasks of the trusted authority in CP-ABE systems without compromising the privacy and confidentiality of the implied components in the process, such as the users’ attributes and their private decryption keys. We detailed a permissionless blockchain-based approach that includes CP-ABE and ECIES to effectively decentralize the trusted authority’s tasks. With a software prototype, our approach was validated for a correct integration and execution of the overall operations workflow, using as a case study an application scenario in the eHealth domain. Moreover, we conducted a series of experiments to evaluate the computational overhead of the proposed approach. The performance results demonstrate its suitability for real-world deployment into existing CP-ABE schemes. By leveraging the Algorand blockchain, our approach offers a lightweight and cost-effective solution with minimal communication and transaction costs.
Future work includes enhancing user privacy by integrating a mechanism to securely retrieve the user’s secret key address from the blockchain ledger, e.g., zero-knowledge proofs, thereby preventing impersonation attacks. Additionally, it could be explored the integration of our approach into other blockchain networks to promote interoperability and increase flexibility. However, it is important to notice the current technological limitations of existing blockchain solutions, which could constrain our approach integration or lead to substantial changes in its adaption to the requirements of the blockchain environment.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
MH-C: Software, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Conceptualization, Investigation. RA-P: Methodology, Investigation, Writing – review and editing, Supervision, Conceptualization. MM-S: Supervision, Methodology, Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing. JG-H: Writing – review and editing, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was done as part of a research internship at the School of Engineering from the National Autonomous University of Mexico. It was partially supported by the project UNAM-PAPIIT TA101723 and by the Algorand Centres of Excellence programme managed by the Algorand Foundation. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions, or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the Algorand Foundation.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Algorand (2025). Algorand parameter tables. Available online at: https://developer.algorand.org/docs/get-details/parameter_tables/ (Accessed January, 2025).
Alston, A. (2017). “Attribute-based encryption for attribute-based authentication, authorization, storage, and transmission in distributed storage systems,”. Cornell University. doi:10.48550/arXiv.1705.06002
Barbulescu, R., and Duquesne, S. (2019). Updating key size estimations for pairings. J. Cryptol. 32, 1298–1336. doi:10.1007/s00145-018-9280-5
Bethencourt, J., Sahai, A., and Waters, B. (2007). “Ciphertext-policy attribute-based encryption,” in 2007 IEEE symposium on security and privacy (SP ’07), 321–334. doi:10.1109/SP.2007.11
Bramm, G., Gall, M., and Schütte, J. (2018). Blockchain-based distributed attribute based encryption.
Champion, J., Hsieh, Y. C., and Wu, D. J. (2025). Registered ABE and adaptively-secure broadcast encryption from succinct LWE. In Advances in Cryptology -- CRYPTO 2025. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Y., Tauman Kalai, S. F., Kamara. (eds), 16002. Springer, Cham. doi:10.1007/978-3-032-01881-6_1
Chase, M. (2007). “Multi-authority attribute based encryption,” in Theory of cryptography conference. Springer, 515–534.
Chase, M., and Chow, S. S. (2009). “Improving privacy and security in multi-authority attribute-based encryption,” in Proceedings of the 16th ACM conference on computer and communications security, 121–130.
Cheng, G., Wang, Y., Deng, S., Xiang, Z., Yan, X., Zhao, P., et al. (2024). A lightweight authentication-driven trusted management framework for iot collaboration. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 17, 747–760. doi:10.1109/TSC.2023.3349305
Cheung, L., and Newport, C. (2007). “Provably secure ciphertext policy Abe,” in Proceedings of the 14th ACM conference on computer and communications security. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, 456–465. doi:10.1145/1315245.1315302
Dávila, R., Aldeco-Pérez, R., and Bárcenas, E. (2023). “On the formal verification of smart contracts,” in 2023 11th international conference in software engineering research and innovation (CONISOFT), 18–24. doi:10.1109/CONISOFT58849.2023.00013
De Angelis, S., Aniello, L., Baldoni, R., Lombardi, F., Margheri, A., and Sassone, V. (2018). Pbft vs proof-of-authority: applying the cap theorem to permissioned blockchain.
Díaz, F., Menchaca, C., and Weidener, L. (2025). Exploring the decentralized science ecosystem: insights on organizational structures, technologies, and funding. Front. Blockchain 8, 1524222. doi:10.3389/fbloc.2025.1524222
Do Hoang, H., Duy, P. T., Tien, N. T., and Pham, V. H. (2022). “A blockchain-based approach and attribute-based encryption for healthcare record data exchange,” in 2022 RIVF international conference on computing and communication technologies (RIVF). IEEE, 65–70.
Gao, S., Piao, G., Zhu, J., Ma, X., and Ma, J. (2020). Trustaccess: a trustworthy secure ciphertext-policy and attribute hiding access control scheme based on blockchain. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 69, 5784–5798. doi:10.1109/tvt.2020.2967099
Gilad, Y., Hemo, R., Micali, S., Vlachos, G., and Zeldovich, N. (2017). “Algorand: scaling byzantine agreements for cryptocurrencies,” in Proceedings of the 26th symposium on operating systems principles, 51–68.
Giry, D. (2020). NIST recommendation for key management. Available online at: https://www.keylength.com/en/4/ (Accessed January, 2025).
Goyal, V., Pandey, O., Sahai, A., and Waters, B. (2006). “Attribute-based encryption for fine-grained access control of encrypted data,” in Proceedings of the 13th ACM conference on computer and communications security, 89–98.
Hinojosa-Cabello, M. B. (2020). An attribute-based encryption scheme for storage, sharing and retrieval of digital documents in the cloud. Master’s thesis, Cinvestav. Available online at: https://repositorio.cinvestav.mx/handle/cinvestav/3178.
Hinojosa-Cabello, M. B., Morales-Sandoval, M., and Marin-Castro, H. M. (2022). “Novel constructions for ciphertext-policy attribute-based searchable encryption,” in 2022 IEEE Mexican international conference on computer science (ENC), 1–8. doi:10.1109/ENC56672.2022.9882941
Hosseinzadeh, K. S. (2021). Towards secure and intelligent diagnosis: deep learning and blockchain technology for computer-aided diagnosis systems. Saskatoon, SK: University of Saskatchewan.
Ismail, L., and Materwala, H. (2019). A review of blockchain architecture and consensus protocols: use cases, challenges, and solutions. Symmetry 11, 1198. doi:10.3390/sym11101198
Jayavarma, A., Parakkat Kesava Panikker, P., and Nair, M. G. (2025). Revolutionizing the energy sector: exploring diversified blockchain platforms for a sustainable future. Front. Blockchain 8, 1544770. doi:10.3389/fbloc.2025.1544770
Kaur, S., Chaturvedi, S., Sharma, A., and Kar, J. (2021). A research survey on applications of consensus protocols in blockchain. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2021, 1–22. doi:10.1155/2021/6693731
Kumar, P. P., Kumar, P. S., and Alphonse, P. (2018). Attribute based encryption in cloud computing: a survey, gap analysis, and future directions. Netw. Comput. Appl. 108, 37–52. doi:10.1016/j.jnca.2018.02.009
Lewko, A., and Waters, B. (2011). “Decentralizing attribute-based encryption,” in Annual international conference on the theory and applications of cryptographic techniques. Springer, 568–588.
Li, B., Huang, D., Wang, Z., and Zhu, Y. (2016). Attribute-based access control for icn naming scheme. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secure Comput. 15, 194–206. doi:10.1109/tdsc.2016.2550437
Liu, Z., Jiang, Z. L., Wang, X., Yiu, S. M., Zhang, C., and Zhao, X. (2016). Dynamic attribute-based access control in cloud storage systems. IEEE Trustcom/BigDataSE/ISPA (IEEE), 129–137. doi:10.1109/trustcom.2016.0055
Liu, Z., Jiang, Z. L., Wang, X., and Yiu, S. M. (2018). Practical attribute-based encryption: outsourcing decryption, attribute revocation and policy updating. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 108, 112–123. doi:10.1016/j.jnca.2018.01.016
Liu, X., Wei, Z., Li, G., and Chen, J. (2024). An enhanced traceable access control scheme based on multi-authority cp-abe for cloud-assisted e-health system. Comput. Netw. 254, 110766. doi:10.1016/j.comnet.2024.110766
Ma, R., Zhang, L., Wu, Q., Mu, Y., and Rezaeibagha, F. (2023). Be-trdss: blockchain-Enabled secure and efficient traceable-revocable data-sharing scheme in industrial internet of things. IEEE Trans. Industrial Inf. 19, 10821–10830. doi:10.1109/tii.2023.3241618
Menezes, A., Sarkar, P., and Singh, S. (2016). Challenges with assessing the impact of NFS advances on the security of pairing-based cryptography. IACR Cryptol. ePrint Arch. 2016, 1102. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-61273-7_5
Micali, S., Rabin, M., and Vadhan, S. (1999). “Verifiable random functions,” in 40th annual symposium on foundations of computer science (cat. No. 99CB37039). IEEE, 120–130.
Montgomery, D. (2013). Applied statistics and probability for engineers. 6th. edn. Incorporated: John Wiley and Sons.
Müller, S., Katzenbeisser, S., and Eckert, C. (2008). “Distributed attribute-based encryption,” in International conference on information security and cryptology. Springer, 20–36.
Ongaro, D., and Ousterhout, J. (2014). “In search of an understandable consensus algorithm,” in USENIX annual technical conference (USENIX ATC 14), 305–319.
Qin, X., Huang, Y., Yang, Z., and Li, X. (2021). A blockchain-based access control scheme with multiple attribute authorities for secure cloud data sharing. J. Syst. Archit. 112, 101854. doi:10.1016/j.sysarc.2020.101854
Retamal, C. D., Roig, J. B., and Tapia, J. L. M. (2017). La blockchain: fundamentos, aplicaciones y relacion con otras tecnologias disruptivas. Econ. Ind. 405, 33–40.
Sahai, A., and Waters, B. (2005). “Fuzzy identity-based encryption,”, 2005. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 457–473. doi:10.1007/11426639_27
Storublevtcev, N. (2019). “Cryptography in blockchain,” in 19th international conference, Saint Petersburg, Russia, July 1–4, 2019, proceedings, part II 19. Springer, 495–508. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-24296-1_39
Tanenbaum, A. S., and Van Renesse, R. (1985). Distributed operating systems. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 17, 419–470. doi:10.1145/6041.6074
Waters, B. (2011). “Ciphertext-policy attribute-based encryption: an expressive, efficient, and provably secure realization,” in Public key cryptography – PKC 2011. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 53–70.
Wu, G., Zhou, J., and Fu, X. (2025). Improved blockchain-based ecdsa batch verification scheme. Front. Blockchain 8, 1495984. doi:10.3389/fbloc.2025.1495984
Wüst, K., and Gervais, A. (2018). Do you need a blockchain? 2018 crypto valley conference on blockchain technology (CVCBT). IEEE, 45–54.
Xiao, Y., Zhang, N., Lou, W., and Hou, Y. T. (2020). A survey of distributed consensus protocols for blockchain networks. IEEE Commun. Surv. & Tutorials 22, 1432–1465. doi:10.1109/comst.2020.2969706
Xie, B., Zhou, Y. P., Yi, X. Y., and Wang, C. Y. (2023). An improved multi-authority attribute access control scheme base on blockchain and elliptic curve for efficient and secure data sharing. Electronics 12, 1691. doi:10.3390/electronics12071691
Yaga, D., Mell, P., Roby, N., and Scarfone, K. (2018). Blockchain technology overview. Tech. Rep. doi:10.6028/NIST.IR.8202
Yang, X., and Zhang, C. (2022). Blockchain-based multiple authorities attribute-based encryption for ehr access control scheme. Appl. Sci. 12, 10812. doi:10.3390/app122110812
Yang, Z., Chen, X., He, Y., Liu, L., Che, Y., Wang, X., et al. (2024). An attribute-based access control scheme using blockchain technology for iot data protection. High-Confidence Comput. 4, 100199. doi:10.1016/j.hcc.2024.100199
Yu, G., Zha, X., Wang, X., Ni, W., Yu, K., Yu, P., et al. (2020). Enabling attribute revocation for fine-grained access control in blockchain-iot systems. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 67, 1213–1230. doi:10.1109/tem.2020.2966643
Zaidi, S. Y. A., Shah, M. A., Khattak, H. A., Maple, C., Rauf, H. T., El-Sherbeeny, A. M., et al. (2021). An attribute-based access control for iot using blockchain and smart contracts. Sustainability 13, 10556. doi:10.3390/su131910556
Zhai, S., Yang, Y., Li, J., Qiu, C., and Zhao, J. (2019). “Research on the application of cryptography on the blockchain,”, 1168. Bristol, United Kingdom: IOP Publishing. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/1168/3/032077
Zhang, L., Kan, H., and Huang, H. (2022). “Patient-centered cross-enterprise document sharing and dynamic consent framework using consortium blockchain and ciphertext-policy attribute-based encryption,” in Proceedings of the 19th ACM international conference on computing frontiers, 58–66.
Keywords: decentralization, ciphertext-policy attribute-based encryption, trusted authority, blockchain, privacy, confidentiality
Citation: Hinojosa-Cabello MB, Aldeco-Perez R, Morales-Sandoval M and Garcia-Hernandez JJ (2025) Blockchain-based decentralization approach for Ciphertext-Policy Attribute-Based Encryption schemes. Front. Blockchain 8:1622270. doi: 10.3389/fbloc.2025.1622270
Received: 07 May 2025; Accepted: 01 September 2025;
Published: 07 October 2025.
Edited by:
Brijesh Kumar Chaurasia, Pranveer Singh Institute of Technology PSIT, IndiaReviewed by:
Muath Obaidat, The City University of New York, United StatesNidhi Ranjan, University of Mumbai, India
Copyright © 2025 Hinojosa-Cabello, Aldeco-Perez, Morales-Sandoval and Garcia-Hernandez. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rocio Aldeco-Perez, cmFsZGVjb0B1bmFtLm14
 Melissa Brigitthe Hinojosa-Cabello
Melissa Brigitthe Hinojosa-Cabello Rocio Aldeco-Perez
Rocio Aldeco-Perez Miguel Morales-Sandoval
Miguel Morales-Sandoval Jose Juan Garcia-Hernandez
Jose Juan Garcia-Hernandez