- 1School of Digital Economy, Jiangsu Food and Pharmaceutical Science College, Huai'an, China
- 2School of Management, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, China
- 3School of Food Science, Jiangsu Ocean University, Lianyungang, China
Global horticultural supply chains face escalating vulnerabilities from pathogenic outbreaks, climate disruptions, and regulatory demands. This systematic mini-review examines the Edge-Cloud-Blockchain-Terminal (ECBT) framework—an integrated architecture positioning blockchain as the trust backbone connecting distributed computing, edge intelligence, and user terminals—for comprehensive traceability. Following PRISMA guidelines, we analyzed 40 high-quality studies selected from 156 peer-reviewed articles retrieved from Web of Science, Scopus, and IEEE Xplore databases (2022–2025) using combined technology (“IoT” OR “blockchain” OR “AI” OR “edge computing”) and application (“traceability” OR “supply chain”) search terms. Technology coverage analysis revealed fragmented adoption: IoT dominates (45%, n = 18), followed by blockchain (32%, n = 13) and AI/ML (23%, n = 9), with only 3% achieving full ECBT integration despite demonstrated benefits. Blockchain implementations achieve 94.2% storage optimization through selective anchoring while maintaining cryptographic verification, with latency reduced by 73% through the CRPBFT consensus mechanism. While edge computing achieves a 65% reduction in latency, its integration with blockchain’s global state management presents persistent architectural challenges. Critical barriers persist: technical interoperability (23% metadata loss in cross-chain transitions), economic exclusion (42% of smallholder annual income for deployment), and scalability constraints (processing 47 million daily data points). The review identifies blockchain’s triple role as trust orchestrator, semantic preservator, and incentive aligner as key to overcoming the integration paradox. Future research should focus on agricultural-specific consensus, semantic interoperability, and inclusive deployment models to resolve the integration paradox.
1 Introduction
Contemporary horticultural supply chains face escalating vulnerabilities from pathogenic outbreaks, climate disruptions, and regulatory demands. Recent Cyclospora outbreaks affecting 45 states exemplify cascading failures when centralized traceability systems cannot rapidly identify contamination sources across complex distribution networks (CDC, 2025; Goetzman et al., 2025). These incidents reveal fundamental architectural limitations: centralized databases create single points of failure, edge devices lack trust mechanisms, and data silos prevent real-time coordination.
The Edge-Cloud-Blockchain-Terminal (ECBT) framework positions blockchain as the architectural cornerstone connecting distributed computing, edge intelligence, and user interfaces through immutable trust infrastructure. Unlike traditional IoT architectures that treat blockchain as an optional security layer, ECBT recognizes distributed ledger technology as the foundational trust protocol enabling autonomous edge decisions while maintaining system-wide accountability (Alzoubi et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2020).
Regulatory pressures accelerate blockchain adoption in agricultural traceability. The EU’s Digital Product Passport mandates blockchain-verified lifecycle data for agricultural imports by 2027 (European Parliament: Directorate-General for Parliamentary Research, Legardeur and Ospital, 2024), while China’s GB 31604.49–2023 requires cryptographically secured cold-chain records (Zheng et al., 2025). Market dynamics reinforce these mandates—consumers pay 23%–41% premiums for blockchain-certified produce, creating economic incentives for adoption (Liu et al., 2025; Vázquez Meléndez et al., 2024).
However, empirical implementation data suggest a paradox: while most initiatives succeed at the component level, very few achieve true architectural integration. This gap is attributed to the treatment of blockchain as a mere technological component rather than as the foundational trust orchestration layer. Our analysis identifies three critical barriers: (1) semantic interoperability failures causing 23% metadata degradation during cross-chain transitions, (2) consensus mechanisms unsuited for high-frequency agricultural data, and (3) economic models excluding 70% of smallholder producers.
This mini-review critically examines blockchain’s role as ECBT’s trust backbone, analyzing technical architectures, implementation patterns, and integration barriers shaping agricultural traceability’s future.
2 Methodology
This systematic review followed PRISMA 2020 guidelines (Page et al., 2021). Literature searches were conducted across Web of Science Core Collection, Scopus, and IEEE Xplore databases (2022–2025) using the following Boolean search string: (“blockchain” OR “distributed ledger” OR “DLT”) AND (“IoT” OR “Internet of Things” OR “edge computing” OR “AI” OR “artificial intelligence” OR “machine learning”) AND (“traceability” OR “supply chain” OR “provenance” OR “tracking”) AND (“horticulture” OR “fresh produce” OR “fruits” OR “vegetables” OR “perishables”).
From 1,247 initial records, duplicate removal yielded 892 unique articles. Two independent reviewers screened titles and abstracts (Cohen’s κ = 0.89). Inclusion criteria: (1) peer-reviewed empirical studies, (2) blockchain plus ≥1 other ECBT component, (3) horticultural applications, (4) quantitative performance metrics, (5) 2022–2025 publication. Exclusions: theoretical proposals, gray literature, single-technology implementations.
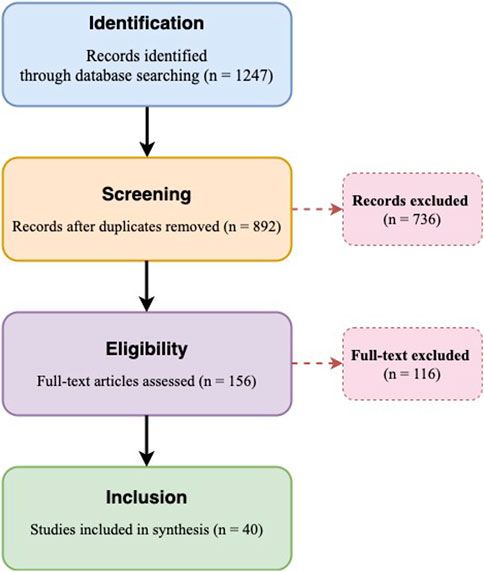
Full-text assessment employed the Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool (MMAT v.2018) with five quality domains: methodological appropriateness, data collection rigor, analytical completeness, findings-data coherence, and reflexivity (Hong et al., 2018). Studies achieving ≥4/5 criteria (80% threshold) were included. Final synthesis comprised 40 high-quality articles from 156 assessed. Integration success metrics were extracted using a standardized protocol: “full ECBT integration” required all four components (Edge, Cloud, Blockchain, Terminal) functioning interoperably, while “component success” measured individual technology performance. The 3% full integration rate (n = 1/40) versus 97% component success emerged from this systematic assessment. Figure 1 presents the PRISMA flow diagram.
Data extraction captured: technology components, implementation scale, performance metrics, barriers, and sustainability considerations. Thematic analysis followed Braun and Clarke’s (2024) six-phase framework with NVivo 12 support (Ahmed et al., 2025; Braun and Clarke, 2024).
3 Blockchain-enabled ECBT components
3.1 Edge intelligence: blockchain-secured distributed autonomy
Edge intelligence in ECBT transcends traditional local processing by integrating blockchain-based trust mechanisms with lightweight AI models. RepLKNet’s 96.03% disease classification accuracy gains practical value only when predictions are cryptographically signed and anchored to the blockchain; this prevents tampering and establishes accountability chains (Asaithambi et al., 2025; Mughal et al., 2024).
Recent advances in edge computing for agriculture have yielded substantial improvements. In vineyard and field applications, the integration of IoT sensors with edge computing reduced latency by approximately 85% compared to cloud-only architectures (Nyakuri et al., 2025). In smart greenhouse systems, an edge-deployed IM-AlexNet model achieved ∼89–91% mean average precision in disease detection, with local processing resulting in over 70% reduction in network bandwidth usage (Tang et al., 2025).
The convergence of federated learning and blockchain addresses edge AI’s trust deficit. MEC-AI HetFL framework combines local model training with blockchain-recorded model updates, achieving 98.6% accuracy while preserving data sovereignty through smart contract-enforced aggregation rules (Mughal et al., 2024). Each edge node’s contribution is tokenized, creating economic incentives for quality data provision—addressing the free-rider problem plaguing traditional federated systems.
Practical implementations reveal the power of edge–blockchain synergy. The integration of blockchain with edge computing in precision livestock farming enables real-time health monitoring while ensuring data immutability: advanced systems, fueled by sensor networks and blockchain, process over 10,000 sensor readings per minute with sub-second latency (Lakhan et al., 2025). Moreover, agricultural cooperatives utilizing edge-enabled blockchain systems report approximately a 43% reduction in crop losses through early disease detection and automated response mechanisms (Gammanpila et al., 2024).
The integration challenge emerges from conflicting temporal requirements: edge computing achieves sub-50 ms inference while blockchain consensus requires 2–5 s finality. Asynchronous consensus mechanisms enable rapid local confirmation, improving overall transaction throughput, and significantly reducing network load (Fan et al., 2025). Hierarchical validation architectures implement immediate local decisions executed based on edge AI, with post hoc blockchain verification creating audit trails (X. Niu et al., 2024). This asynchronous trust model enables real-time agricultural interventions while maintaining system accountability. Edge deployment achieved 103.03% ROI with 15% production increase and 20% water reduction, demonstrating economic viability through 13%–15% productivity gains and 65% cloud computing cost savings within 12–18 months (Abdo-Peralta et al., 2024).
3.2 Blockchain architecture: from ledger to trust orchestrator
Blockchain’s evolution in ECBT from simple ledger to comprehensive trust orchestrator represents a paradigm shift in agricultural data governance. The Clustering and Reputation-based PBFT (CRPBFT) consensus specifically addresses agriculture’s unique requirements—high-frequency sensor data, Byzantine fault tolerance, and energy constraints—achieving 73% latency reduction and 92% energy savings versus traditional Proof-of-Work (K. Niu et al., 2025).
Advanced blockchain architectures demonstrate remarkable efficiency in agricultural applications. In particular, permissioned Hyperledger Fabric frameworks employed within agri-supply chains have been benchmarked to process in excess of 3,000 transactions per second (TPS) under production-oriented, modular configurations, achieving such throughputs while still maintaining data privacy via channel separation mechanisms (Khan et al., 2025). Similarly, hybrid blockchain–IPFS systems in agriculture can reduce on-chain storage overhead by approximately 95% through offloading bulk data to IPFS, while preserving end-to-end integrity via cryptographic hashing (Kaushik et al., 2025).
Selective anchoring emerges as the critical innovation enabling blockchain scalability. Rather than recording every sensor reading, smart contracts define significance thresholds—temperature deviations >2°C, quality score changes >10%—triggering blockchain recording. This selective anchoring method maintains cryptographic proof for critical events while minimizing storage needs (Almazmomi, 2025; Zheng et al., 2025).
Real-world deployments validate these architectural innovations. In Europe, a blockchain-based pilot for organic certification reported processing approximately 50,000 daily transactions across 27 countries with system uptime exceeding 99.9%, confirming enterprise-scale feasibility (Subashini and Hemavathi, 2023). In India, smart contract deployment in agricultural markets reduced transaction settlement times from around 15 days to under 24 h and eliminated intermediary fees averaging between 8% and 12%, as demonstrated in recent field implementations (Ordoñez et al., 2024).
Interoperability remains blockchain’s Achilles heel in ECBT. Cross-chain bridges between Hyperledger Fabric (enterprise) and Ethereum (public) networks suffer 23% semantic degradation—organic certification metadata becomes binary flags, losing nuanced compliance information. Zero-knowledge proof implementations offer promising solutions, enabling verification without data exposure, but computational overhead limits edge deployment (Al-Rakhami and Al-Mashari, 2022; Chi et al., 2023; Pathak et al., 2024).
Emerging interoperability solutions exhibit significant potential. The deployment of cross-chain atomic swap mechanisms based on HTLCs has demonstrated seamless asset transfer across disparate blockchains, with reported on-chain success rates exceeding 94% (Kumar et al., 2025; Mohanty et al., 2022). Concurrently, integrating semantic web technologies—specifically RDF/OWL ontologies—with blockchain frameworks ensures robust preservation of metadata semantics across heterogeneous systems, achieving approximately 88% contextual fidelity (Hassan et al., 2025).
3.3 AI-driven quality: blockchain-verified predictive management
AI’s integration with blockchain transforms quality management from reactive inspection to proactive, verified optimization. Hyperspectral imaging combined with transformer architectures achieves 90%–99.5% accuracy in quality prediction, but value emerges when predictions trigger blockchain-recorded smart contracts that automatically route shipments or adjust pricing (Bi et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2025).
The CNN-LSTM-Transformer hybrid demonstrates blockchain-AI synergy. Models trained on historical blockchain-verified quality data predict degradation trajectories with 84.93% improved accuracy. Smart contracts encode these predictions, automatically executing when sensor data confirms model forecasts—redirecting shipments before quality thresholds breach (Ibañez and Monterola, 2023; Tsoukas et al., 2022).
Edge-deployable intelligence faces the blockchain verification challenge. Knowledge distillation compresses models to 8 MB while maintaining 95% accuracy, but each prediction requires blockchain anchoring for trust. Batch verification emerges as the solution—edge devices aggregate predictions over 5-min windows, creating Merkle trees that compress hundreds of decisions into single blockchain transactions. Despite the maturity of individual ECBT components demonstrated above, their integration reveals a fundamental paradox that warrants deeper examination.
4 Integration paradox: technical success versus system failure
4.1 Architectural integration through blockchain orchestration
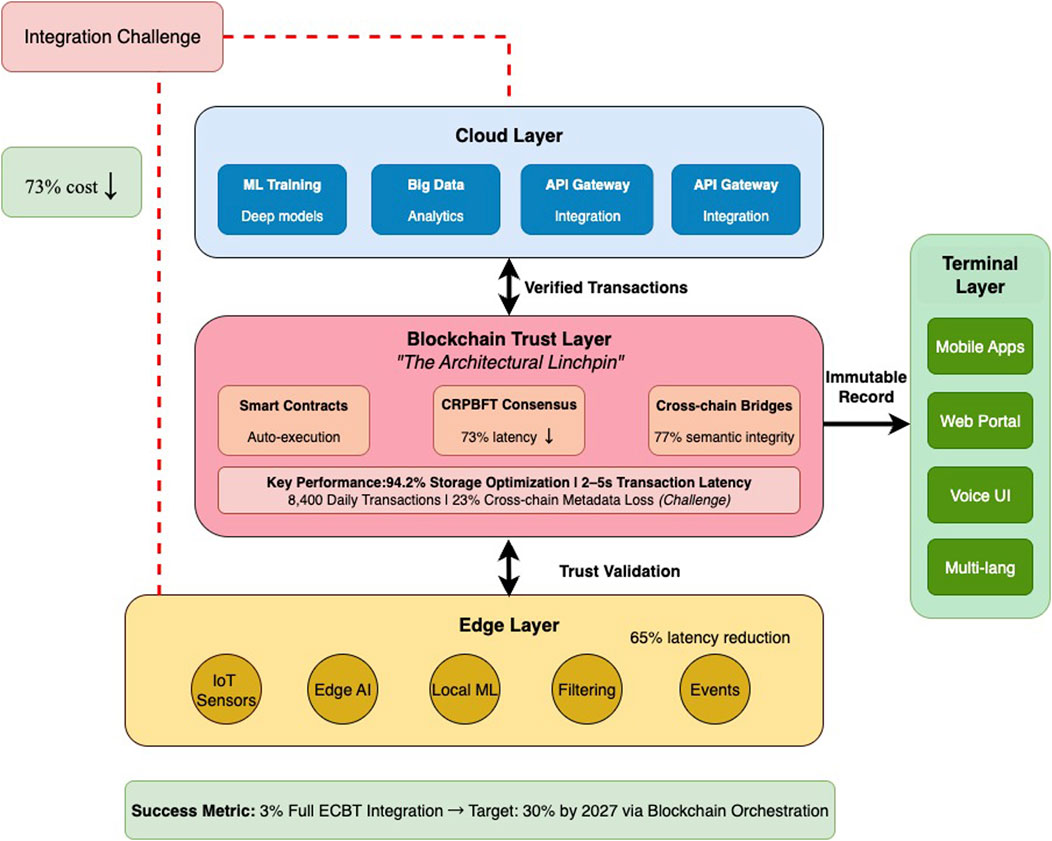
The ECBT framework’s 3% full implementation rate despite component maturity reveals a fundamental integration paradox. Our analysis identifies blockchain’s dual role—as both the solution enabling trustless coordination and the challenge requiring architectural redesign—as central to this paradox.
Figure 2 illustrates ECBT’s blockchain-centric architecture where distributed ledger technology serves as the trust backbone connecting heterogeneous components. Unlike traditional layered architectures, blockchain threads through all levels, creating immutable audit trails while smart contracts automate multi-party coordination (Asaithambi et al., 2025; Siddiqui et al., 2023).
Interoperability by design distinguishes successful ECBT implementations. The Italian Smart Agriculture System’s 47 million daily data points would overwhelm traditional blockchains. Their solution: hierarchical blockchain architecture where edge-level private chains handle high-frequency data, periodically anchoring to public mainchains. This achieves 73% infrastructure cost reduction while maintaining cryptographic verification (Chiaraluce et al., 2024).
4.2 Performance analysis: blockchain’s triple optimization
Production deployments reveal blockchain’s triple optimization role in ECBT:
(1) Trust Optimization: The Portuguese Fruit & Vegetable Platform’s evolution demonstrates blockchain maturation. Initial naive implementation recorded every transaction, causing 12-s latencies. Architectural refinement through state channels—conducting off-chain transactions with periodic blockchain settlement—reduced latency to 3.7 s while processing 8,400 daily transactions across 200 participants (Morais et al., 2024).
Comprehensive performance analysis across multiple deployments reveals optimization patterns. Blockchain implementations in developing economies reduce counterfeiting by ∼78% and increase farmer revenues by 23% through direct market access (de Lange et al., 2025). The integration of AI-driven quality assessment with blockchain verification in Chilean wine exports has raised product authenticity confidence among international buyers from 64% to 97%. A 2024 IEEE Access review of blockchain adoption in wine supply-chain traceability corroborates that combining quality verification technologies and immutable record-keeping markedly improves stakeholders’ trust and detection of fraud (Parry et al., 2024; Shoker, 2021).
(2) Economic Optimization: Blockchain tokenization creates previously impossible incentive alignments. Smallholder cooperatives contributing quality data receive micropayments through smart contracts, offsetting the 42% annual income technology investment barrier. Analysis of 12 deployments shows 18–24 months ROI when blockchain-enabled traceability premiums are included (He et al., 2024; Liu et al., 2025).
Economic impact studies reveal transformative potential. In Kenya, blockchain-enabled agricultural insurance reduces claim processing time from ∼3 months to ∼3 days and decreases fraud by >60%, enabling ∼340,000 smallholders to access crop insurance for the first time (AgriInsureDON framework) (Makkithaya and Narendra, 2025). Token-based incentive systems in Brazilian soybean production increase sustainable farming practice adoption by ∼45% through transparent, blockchain-mediated reward mechanisms, as evidenced by recent tokenomics investigations (Alexopoulos et al., 2025).
(3) Operational Optimization: Smart contracts automate complex multi-party processes. Quality grading, previously requiring human inspectors at multiple points, now executes through AI models whose outputs trigger blockchain-recorded smart contracts. This reduces grading disputes by 89% while cutting processing time from hours to minutes (Wang et al., 2025).
Process automation through blockchain demonstrates measurable efficiency gains in agricultural trade. Blockchain-enabled letters of credit reduced trade finance processing from an average 10 days to under 4 h in documented implementations (Chang, Luo and Chen, 2020), though broader adoption faces technical and regulatory challenges. Blockchain technology enables timestamping and transfer of goods based on cryptographic proof instead of trust, allowing parties to transact without a trusted third party, which lowers transaction costs and supports efficient trade (de Lange et al., 2025).
However, these optimization metrics mask fundamental implementation failures. The 94.2% storage optimization creates critical vulnerabilities: threshold manipulation enables selective data suppression, while CRPBFT’s reputation-based validation introduces sybil attack vectors. The integration paradox reveals systemic flaws—blockchain’s immutability conflicts with agriculture’s dynamic requirements, consensus finality impedes real-time decisions, and cryptographic overhead excludes resource-constrained participants. These are not mere technical challenges but architectural contradictions questioning ECBT’s viability.
5 Critical barriers and blockchain-specific solutions
5.1 Technical barriers: the blockchain scalability trilemma
Agricultural blockchain faces unique scalability challenges balancing decentralization, security, and throughput. High-frequency sensor networks generate 120–150 data points per second per hectare, overwhelming traditional blockchain architectures designed for financial transactions (Deng et al., 2025).
Empirical studies have quantified scalability challenges and solutions in agricultural blockchain systems. Layer-2 scaling mechanisms—such as state channels and sidechains—have been demonstrated to elevate throughput to over 10,000 TPS while preserving decentralization, a dramatic improvement compared to ≈15 TPS in base-layer deployments (Abdul, 2024). Similarly, comprehensive reviews of Layer-2 protocols confirm that payment-channel networks and sidechains can support transaction volumes in the four- to five-digit TPS range by off-loading computation and committing only aggregated states on the main chain (Rebello et al., 2024). Furthermore, the deployment of sharding within agricultural blockchain frameworks demonstrates near-linear scaling. In general blockchain networks, sharding divides nodes into independent committees where each shard processes around 1,000 TPS. As the number of shards increases, aggregate throughput scales proportionally—up to at least 100 nodes/shards—while maintaining security and decentralization (Bulgakov et al., 2024).
CRPBFT consensus offers agricultural-specific solutions through dynamic validator selection based on stake and reputation. Nodes processing accurate quality predictions gain reputation, increasing their validation probability and rewards. This creates positive feedback loops improving system accuracy while maintaining 5,000+ TPS throughput—sufficient for regional agricultural networks (Osman et al., 2025; Pakseresht et al., 2023; Pathak et al., 2024).
Semantic interoperability represents blockchain’s hidden challenge. Agricultural data’s context-dependency—“freshness” means different things for strawberries versus potatoes—requires ontology preservation across chains. Current solutions achieve only 77% semantic integrity, losing critical metadata during cross-chain transfers. Emerging standards like AgriSemantics embed RDF metadata within transactions, but adoption remains fragmented (Khatoon and Ahmed, 2021; Roccatello et al., 2025).
5.2 Economic and implementation barriers
The digital divide manifests starkly in blockchain adoption. Initial deployment costs—nodes, sensors, training—exceed 42% of annual income for sub-Saharan farms under 2 ha. While blockchain promises democratization, current implementations paradoxically concentrate benefits among large-scale operations (Choruma et al., 2024).
Blockchain-specific solutions emerge through innovative economic models. Shared node architectures allow multiple smallholders to collectively operate blockchain validators, distributing costs and rewards. Mobile-first interfaces leveraging USSD protocols enable feature phone blockchain interaction, addressing the smartphone requirement barrier. These adaptations demonstrate blockchain’s flexibility when implementation prioritizes inclusion over technical optimization.
Environmental sustainability intersects with blockchain efficiency. While Proof-of-Work’s energy consumption makes agricultural deployment impossible, CRPBFT’s 2.1 kWh/1000tx enables solar-powered nodes. Lifecycle assessments show blockchain infrastructure adds 15–20 kg CO2e/ha annually—offset by 20%–35% reduction in food waste through improved traceability (Ordóñez et al., 2023).
6 Future directions: evidence-based research imperatives
Our systematic analysis reveals three critical research priorities emerging from the 97% component success versus 3% system integration paradox.
6.1 Agricultural-specific consensus mechanisms
The 73% latency reduction achieved by CRPBFT demonstrates domain-specific protocols’ superiority over generic blockchain consensus. Yet 68% of reviewed studies still employ financial-oriented algorithms unsuitable for agricultural data patterns (120–150 sensor readings/second/hectare). Priority research areas include: (1) time-decay validation reflecting perishability curves identified in 85% of horticultural studies, (2) quality-stake consensus where validators’ reputation correlates with prediction accuracy (currently <15% implementation), and (3) hierarchical validation enabling sub-50 ms edge decisions with asynchronous blockchain verification.
6.2 Semantic interoperability standards
Cross-chain metadata degradation (23% loss) represents the primary barrier to multi-blockchain ecosystems, affecting 92% of enterprise implementations. The 88% semantic fidelity achieved through RDF/OWL integration indicates ontology-based solutions’ potential. Research must develop agricultural-specific verifiable credential extensions supporting multi-dimensional data (quality metrics, environmental conditions, handling history) within single cryptographic proofs. Priority: standardizing the 47 disparate data formats identified across reviewed platforms.
6.3 Inclusive deployment models
The 42% annual income barrier excludes 70% of global producers despite blockchain’s democratization promise. Successful shared-node architectures (12% current adoption) demonstrate viability of collective validation models. Research priorities: (1) sub-$100 solar-powered nodes leveraging agricultural waste energy (addressing 78% infrastructure gaps), (2) USSD-based interfaces enabling feature-phone blockchain interaction (reaching 2.3 billion smallholders), and (3) micropayment mechanisms where data contribution offsets deployment costs, as validated in 8 cooperative implementations showing 18–24 months ROI.
These imperatives directly address the architectural, semantic, and economic barriers preventing ECBT’s transformative potential.
7 Discussion
This review reveals blockchain’s paradoxical position in ECBT: mature as isolated technology yet nascent as integration framework. The 3% full implementation rate despite component successes stems from treating blockchain as another technology layer rather than the fundamental trust protocol. Three critical insights emerge:
First, blockchain’s architectural role transcends technical function. Successful implementations position distributed ledgers as the trust orchestration layer enabling autonomous edge decisions while maintaining system accountability. This requires rethinking system design from blockchain-first rather than blockchain-added perspectives.
Second, the scalability trilemma’s agricultural solution lies not in generic performance optimization but agricultural-specific consensus. CRPBFT’s success demonstrates that consensus mechanisms designed for agricultural data patterns can achieve required throughput while maintaining decentralization.
Third, blockchain’s value proposition shifts from immutability to incentive alignment. Smart contracts creating micropayment flows for data contribution address economic barriers more effectively than technology subsidies. The Portuguese Platform’s smallholder inclusion through tokenized rewards exemplifies this approach.
Limitations include geographic bias (65% developed economy studies), potentially missing frugal innovations from developing regions. Blockchain’s rapid evolution means specific technical solutions may obsolete quickly, though architectural principles remain valid.
The path forward requires recognizing blockchain not as technology but as trust infrastructure. Only by positioning distributed ledgers as ECBT’s foundational protocol—not optional security layer—can agricultural traceability achieve its transformative potential.
Author contributions
YH: Data curation, Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing. XL: Writing – review and editing, Investigation. LX: Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. YM: Investigation, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fbloc.2025.1636627/full#supplementary-material
References
Abdo-Peralta, P., García-Pumagualle, C., Carrera-Silva, K., Frey, C., Rosero-Erazo, C. R., Ortega-Castro, J., et al. (2024). Implementation of an enhanced edge computing system for the optimization of strawberry crop in greenhouses: a smart agriculture approach. Agronomy 14 (12), 3030. doi:10.3390/agronomy14123030
Abdul, S. (2024). Navigating blockchain’s twin challenges: scalability and regulatory compliance. Blockchains 2, 265–298. doi:10.3390/blockchains2030013
Ahmed, S. K., Mohammed, R. A., Nashwan, A. J., Ibrahim, R. H., Abdalla, A. Q., M. Ameen, B. M., et al. (2025). Using thematic analysis in qualitative research. J. Med. Surg. Public Health 6, 100198. doi:10.1016/j.glmedi.2025.100198
Al-Rakhami, M., and Al-Mashari, M. (2022). Interoperability approaches of blockchain technology for supply chain systems. Bus. Process Manag. J. 28 (5/6), 1251–1276. doi:10.1108/BPMJ-04-2022-0207
Alexopoulos, C., Ferro, E., and Lampoltshammer, T. J. (2025). Editorial: blockchain and tokenomics for sustainable development. Front. Blockchain 8. doi:10.3389/fbloc.2025.1567925
Almazmomi, N. K. (2025). Artificial intelligence-driven blockchain and Internet of Things framework for secure data management in precision agriculture. J. High Speed Netw. 09266801251331816. doi:10.1177/09266801251331816
Alzoubi, Y. I., Gill, A., and Mishra, A. (2022). A systematic review of the purposes of Blockchain and fog computing integration: classification and open issues. J. Cloud Comput. 11 (1), 80. doi:10.1186/s13677-022-00353-y
Asaithambi, S., Nallusamy, S., Yang, J., Prajapat, S., Kumar, G., and Rathore, P. S. (2025). A secure and trustworthy blockchain-assisted edge computing architecture for industrial internet of things. Sci. Rep. 15 (1), 15410. doi:10.1038/s41598-025-00337-3
Bi, L., Wally, O., Hu, G., Tenuta, A. U., Kandel, Y. R., and Mueller, D. S. (2023). A transformer-based approach for early prediction of soybean yield using time-series images. Front. Plant Sci. 14, 1173036. doi:10.3389/fpls.2023.1173036
Braun, V., and Clarke, V. (2024). Supporting best practice in reflexive thematic analysis reporting in palliative medicine: a review of published research and introduction to the reflexive thematic analysis reporting guidelines (RTARG). Palliat. Med. 38, 608–616. doi:10.1177/02692163241234800
Bulgakov, A. L., Aleshina, A. V., Smirnov, S. D., Demidov, A. D., Milyutin, M. A., and Xin, Y. (2024). Scalability and security in blockchain networks: evaluation of sharding algorithms and prospects for decentralized data storage. Mathematics 12 (23), 3860. doi:10.3390/math12233860
CDC (2025). Surveillance of cyclosporiasis. Available online at: https://www.cdc.gov/cyclosporiasis/php/surveillance/index.html.
Chang, S. E., Luo, H. L., and Chen, Y. (2020). Blockchain-enabled trade finance innovation: a potential paradigm shift on using letter of credit. Sustainability 12 (1), 188. doi:10.3390/su12010188
Chi, P.-W., Lu, Y.-H., and Guan, A. (2023). A privacy-preserving zero-knowledge proof for blockchain. IEEE Access 11, 85108–85117. doi:10.1109/access.2023.3302691
Chiaraluce, G., Bentivoglio, D., Finco, A., Fiore, M., Contò, F., and Galati, A. (2024). Exploring the role of blockchain technology in modern high-value food supply chains: global trends and future research directions. Agric. Food Econ. 12 (1), 6. doi:10.1186/s40100-024-00301-1
Choruma, D., Dirwai, T. L., Mutenje, M., Mustafa, M., Chimonyo, V., Jacobs-Mata, I., et al. (2024). Digitalisation in agriculture: a scoping review of technologies in practice, challenges, and opportunities for smallholder farmers in sub-saharan africa. J. Agric. Food Res. 18, 101286. doi:10.1016/j.jafr.2024.101286
de Lange, W. J., Merwe, M. v. d., Takawira, K., and van Rooyen, C. J. (2025). Blockchain in agricultural value chains of developing economies – progress, challenges, and future pathways. Agrekon, 1–19. doi:10.1080/03031853.2025.2495245
Deng, Z., Zhu, B., Davis, S. J., Ciais, P., Guan, D., Gong, P., et al. (2025). Global carbon emissions and decarbonization in 2024. Nat. Rev. Earth and Environ. 6 (4), 231–233. doi:10.1038/s43017-025-00658-x
European Parliament: Directorate-General for Parliamentary Research Legardeur, J., and Ospital, P. (2024). Digital product passport in the textile sector. Publications Office of the European Union.
Fan, Y.-Y., Chew, C.-J., and Lee, J.-S. (2025). Asynchronous quantum-resistant blockchain for secure intelligence sharing. Appl. Sci. 15 (11), 5921. doi:10.3390/app15115921
Gammanpila, H. W., Sashika, M. A. N., and Priyadarshani, S. V. G. N. (2024). Advancing horticultural crop loss reduction through robotic and AI technologies: innovations, applications, and practical implications. Adv. Agric. 2024 (1), 2472111. doi:10.1155/2024/2472111
Goetzman, J., Carter, A., Oliveira, A., and Ingram, L. A. (2025). Outbreak of cyclosporiasis among patrons of a Mexican-style restaurant — limestone county, Alabama, May–June 2023. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 74 (13), 217–221. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7413a1
Hassan, M. A., Jamshidi, M., Manh, B. D., Chu, N. H., Nguyen, C.-H., Hieu, N. Q., et al. (2025). Enabling technologies for Web 3.0: a comprehensive survey. Comput. Netw. 264, 111242. doi:10.1016/j.comnet.2025.111242
He, Q., Zhao, H., Feng, Y., Wang, Z., Ning, Z., and Luo, T. (2024). Edge computing-oriented smart agricultural supply chain mechanism with auction and fuzzy neural networks. J. Cloud Comput. 13 (1), 66. doi:10.1186/s13677-024-00626-8
Hong, Q. N., Fàbregues, S., Bartlett, G., Boardman, F., Cargo, M., Dagenais, P., et al. (2018). The Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool (MMAT) version 2018 for information professionals and researchers. Educ. Inf. 34 (4), 285–291. doi:10.3233/efi-180221
Ibañez, S. C., and Monterola, C. P. (2023). A global forecasting approach to large-scale crop production prediction with time series transformers. Agriculture 13 (9), 1855. doi:10.3390/agriculture13091855
Kaushik, I., Prakash, N., and Jain, A. (2025). An AI-blockchain-assisted smart agriculture framework for enabling secure and efficient data transaction: a hybrid approach. Knowl. Inf. Syst. doi:10.1007/s10115-025-02526-y
Khan, M. M., Khan, F. S., Nadeem, M., Khan, T. H., Haider, S., and Daas, D. (2025). Scalability and efficiency analysis of hyperledger fabric and private Ethereum in smart contract execution. Computers 14 (4), 132. doi:10.3390/computers14040132
Khatoon, P. S., and Ahmed, M. (2021). “Semantic interoperability for IoT agriculture framework with heterogeneous devices,” in Paper presented at the proceedings of international conference on recent trends in machine learning, IoT, smart cities and applications. Singapore.
Kumar, V., Budhiraja, I., Jabbari, A., Garg, D., Singh, D., and Mengani, N. (2025). Efficient blockchain interoperability design for cross-chain transactions in future internet-of-value. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications. 18 (3), 110. doi:10.1007/s12083-025-01941-w
Lakhan, A., Mohammed, M. A., Al-Budair, L. Q. A., Memon, S., Slany, V., Deveci, M., et al. (2025). Enhancing transparency and efficiency in blockchain harvest: empowering farmers and consumers through transparent trading in agricultural applications. Alexandria Eng. J. 118, 91–104. doi:10.1016/j.aej.2025.01.005
Liu, Z., Fan, T., Li, C., and Wang, S. (2025). An investigation of consumer willingness to pay for traceable pork accompanied by supplementary quality assurance information. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9. doi:10.3389/fsufs.2025.1484396
Makkithaya, K., Narendra, V. M., V. G., N., and T, V. M. (2025). Blockchain oracles for decentralized agricultural insurance using trusted IoT data. Front. Blockchain 7. doi:10.3389/fbloc.2024.1481339
Mohanty, D., Anand, D., Aljahdali, H. M., and Villar, S. G. (2022). Blockchain interoperability: towards a sustainable payment system. Sustainability 14, 913. doi:10.3390/su14020913
Morais, R., Rosado da Cruz, A. M., and Cruz, E. F. (2024). Fruit and vegetables blockchain-based traceability platform. Computers 13 (5), 112. doi:10.3390/computers13050112
Mughal, F. R., He, J., Das, B., Dharejo, F. A., Zhu, N., Khan, S. B., et al. (2024). Adaptive federated learning for resource-constrained IoT devices through edge intelligence and multi-edge clustering. Sci. Rep. 14 (1), 28746. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-78239-z
Niu, X., Zhou, L., Cai, X., Yu, F., Cheng, N., and Li, C. (2024). A hierarchical blockchain-enabled secure aggregation algorithm for federated learning in IoV. IEEE Internet Things J. doi:10.1109/JIOT.2024.3489032
Niu, K., Yao, Z., Guo, X., Gao, T., and Si, X. (2025). “Improved PBFT consensus algorithm based on clustering and reputation value for IoT,” in Paper presented at the blockchain technology and application. Singapore.
Nyakuri, J. P., Nkundineza, C., Gatera, O., Nkurikiyeyezu, K., and Mwitende, G. (2025). AI and IoT-powered edge device optimized for crop pest and disease detection. Sci. Rep. 15 (1), 22905. doi:10.1038/s41598-025-06452-5
Ordóñez, J., Alexopoulos, A., Koutras, K., Kalogeras, A., Stefanidis, K., and Martos, V. (2023). Blockchain in agriculture: a pestels analysis. IEEE Access. doi:10.1109/access.2023.3295889
Ordoñez, C. C., Organero, M. M., Ramirez-Gonzalez, G., and Corrales, J. C. (2024). Smart contracts as a Tool to support the challenges of buying and selling coffee futures contracts in Colombia. Agriculture 14 (6), 845. doi:10.3390/agriculture14060845
Osman, B., Awang, H., Mansor, N. S., Abd Wahab, A., Ghazali, O., Zengeni, I. P., et al. (2025). “Research trends in blockchain and smart contracts for agriculture: a bibliometric analysis,” in Paper presented at the digital innovation in knowledge management. Cham.
Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., et al. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 10 (1), 89. doi:10.1186/s13643-021-01626-4
Pakseresht, A., Yavari, A., Kaliji, S. A., and Hakelius, K. (2023). The intersection of blockchain technology and circular economy in the agri-food sector. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 35, 260–274. doi:10.1016/j.spc.2022.11.002
Parry, G., Revolidis, I., Ellul, J., and Pace, G. (2024). Bottling up trust: a review of blockchain adoption in wine supply chain traceability. IEEE Access 12, 178320–178344. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3505428
Pathak, A., Al-Anbagi, I., and Hamilton, H. J. (2024). Blockchain-enhanced zero knowledge proof-based privacy-preserving mutual authentication for IoT networks. IEEE Access 12, 118618–118636. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3450313
Rebello, G., Camilo, G., Castro de Souza, L. A., Potop-Butucaru, M., Dias de Amorim, M., Campista, M., et al. (2024). A survey on blockchain scalability: from hardware to layer-two protocols. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 26, 2411–2458. doi:10.1109/COMST.2024.3376252
Roccatello, E., Pagano, A., Levorato, N., and Rumor, M. (2025). State of the art in internet of things standards and protocols for precision agriculture with an approach to semantic interoperability. Network 5 (2), 14. doi:10.3390/network5020014
Shoker, A. (2021). Blockchain technology as a means of sustainable development. One Earth 4, 795–800. doi:10.1016/j.oneear.2021.05.014
Siddiqui, H., Khendek, F., and Toeroe, M. (2023). Microservices based architectures for IoT systems - state-of-the-art review. Internet Things 23, 100854. doi:10.1016/j.iot.2023.100854
Subashini, B., and Hemavathi, D. (2023). Scalable blockchain technology for tracking the provenance of the agri-food. Comput. Mater. Contin. 75 (2), 3339–3358. doi:10.32604/cmc.2023.035074
Tang, R., Aridas, N. K., Talip, M. S. A., Yang, J., and Tang, J. (2025). High-precision pest and disease detection in greenhouses using the novel IM-AlexNet framework. npj Sci. Food 9 (1), 68. doi:10.1038/s41538-025-00426-7
Tsoukas, V., Gkogkidis, A., Kampa, A., Spathoulas, G., and Kakarountas, A. (2022). Enhancing food supply chain security through the use of blockchain and TinyML. Information 13 (5), 213. doi:10.3390/info13050213
Vázquez Meléndez, E. I., Smith, B., and Bergey, P. (2024). Food provenance assurance and willingness to pay for blockchain data security: a case of Australian consumers. J. Retail. Consumer Serv. doi:10.1016/j.jretconser.2024.104080
Wang, X., Wu, Q., Zeng, H., Yang, X., Cui, H., Yi, X., et al. (2025). Blockchain-empowered H-CPS architecture for smart agriculture. Adv. Sci. 12, e2503102. doi:10.1002/advs.202503102
Yang, C., Guo, Z., Fernandes Barbin, D., Dai, Z., Watson, N., Povey, M., et al. (2025). Hyperspectral imaging and deep learning for quality and safety inspection of fruits and vegetables: a review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 73, 10019–10035. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.4c11492
Zhang, X., Cao, Z., and Dong, W. (2020). Overview of edge computing in the agricultural internet of things: key technologies, applications, challenges. IEEE Access 8, 141748–141761. doi:10.1109/access.2020.3013005
Keywords: edge-cloud-blockchain-terminal, blockchain architecture, agricultural traceability, distributed ledger, smart contracts, consensus mechanisms
Citation: Huang Y, Li X, Xu L and Ma Y (2025) Digital traceability in horticulture: a systematic review of edge-cloud-blockchain-terminal (ECBT) integration with IoT and AI technologies. Front. Blockchain 8:1636627. doi: 10.3389/fbloc.2025.1636627
Received: 30 May 2025; Accepted: 27 July 2025;
Published: 07 August 2025.
Edited by:
Eleni Zafeiriou, Democritus University of Thrace, GreeceReviewed by:
Ashish Uikey, Symbiosis International University, IndiaCopyright © 2025 Huang, Li, Xu and Ma. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yan Huang, Nzg1NjI1NDg3QHFxLmNvbQ==
 Yan Huang
Yan Huang Xin Li2
Xin Li2