- University of Applied Sciences Rosenheim, Rosenheim, Germany
Background: The medical device sector, valued at $569 billion, faces persistent financing challenges. Around 78% of startups fail because of capital shortages, not due to lacking technical quality. Blockchain-based tokenization emerges as a way to broaden access, yet success relies on economic factors of platforms and clear regulations.
Methods: Transaction cost data from Bitcoin, Ethereum, and XRP Ledger covered 540 days from January 2024 to June 2025, providing 3,240 observations per network. Experts, numbering 12, participated in a modified Delphi method to form a framework tailored to healthcare. Project outcomes came from Monte Carlo simulations running 10,000 iterations, checked by a triple control-loop system, and compared against two real-world examples. Volumes of transactions drew from stochastic models involving monthly, quarterly, and annual elements, mixing fixed regulatory needs with variable market influences.
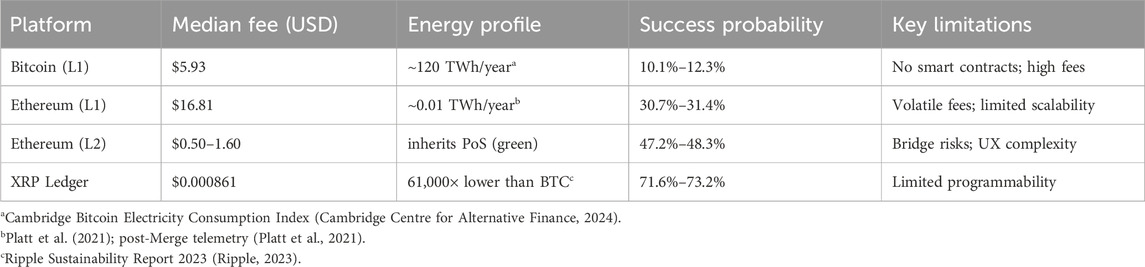
Results: Layer-1 (L1) fees differ by orders of magnitude; representative 2025 snapshots show BTC and ETH L1 far above XRPL and major ETH L2s. XRPL fees are typically a tiny fraction of a cent; the base cost is 10 drops (0.00001 XRP) and is dynamically adjusted by network load. Probabilities of success varied from 10.1% to 12.3% on Bitcoin, 31.4%–48.3% on Ethereum based on Layer-2 adoption, and 71.6%–73.2% on XRP Ledger. Investor involvement correlated negatively with logarithms of costs, showing Spearman
Conclusion: Choosing a blockchain platform critically influences viability in tokenizing medical devices. Layer-2 options reduce cost gaps but add complexities in bridging and use. Platforms offering stability, minimal fees, and regulatory alignment promote wider inclusion and reliable funding. Technical features, steady costs, and readiness for compliance together shape whether tokenization boosts innovation in healthcare or maintains barriers.
1 Introduction
The global medical device sector, valued at roughly $569 billion in mid-2025, faces persistent financing frictions driven less by technical merit than by access to capital and long, uncertain regulatory timelines (Fortune Business Insights, 2024). Regulatory heterogeneity amplifies this: while low-risk Class I products can reach the market comparatively quickly, high-risk Class III devices often require 5–10 years and tens of millions of dollars before first revenue—creating a financing “valley of death” (Makower et al., 2010). Blockchain-based tokenization promises lower participation thresholds, transparent governance, and secondary liquidity. Whether that promise materializes depends on the economics and usability of specific platforms. Bitcoin pioneered decentralized value transfer (Nakamoto, 2008) but exhibits volatile base-layer fees that challenge frequent interactions (L2Fees, 2025). Ethereum added general-purpose programmability for complex token logic (Buterin, 2014), yet base-layer gas pricing remains costly and variable (L2Fees, 2025). The XRP Ledger emphasizes fast settlement and fees typically at a fraction of a cent via a dynamically adjusted “drops” base cost (Schwartz et al., 2018; XRP Ledger, 2024); ongoing CBDC-related work underscores its intended role in interoperable payment rails (Bank for International Settlements BIS, 2025). Technical scaling and regulation evolved materially in 2024–2025. On Ethereum, the Dencun upgrade (EIP-4844) reduced data-availability costs and pushed activity to Layer-2s, while bridges and liquidity fragmentation introduced user-journey frictions (Buterin et al., 2024; L2Beat, 2025). In parallel, MiCA phased in across the EU and U.S. proceedings narrowed XRP-specific enforcement overhang in mid-2025, compressing legal-uncertainty premia without eliminating diligence needs; heightened scrutiny following late-2024 DeFi exploits also reshaped risk assessments (European Securities and Markets Authority ESMA, 2025; Reuters, 2025; Reuters, 2024; Chainalysis, 2025). For healthcare finance, platform predictability, fee stability, and operational simplicity are first-order. Transaction-cost economics and network-effect considerations imply that high frictions suppress broad participation and erode network value, while low, stable frictions enable inclusive funding at scale (Williamson, 1985; Metcalfe, 2013). Prior healthcare–blockchain work has focused on data provenance and record-keeping rather than financing economics and rarely offers quantitative cross-platform comparisons (Agb et al., 2019; Hasselgren et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2018; McGhin et al., 2019; Kasyapa and Vanmathi, 2024). We address this gap with a mixed-methods design: a 540-day transaction-fee panel for Bitcoin, Ethereum (L1 and major L2s post-Dencun), and the XRP Ledger; an expert-elicited evaluation framework; a Monte-Carlo model with triple control-loop validation; and triangulation with real-world cases (L2Fees, 2025; Mkrtchyan and Treiblmaier, 2025).
We address three research questions:
RQ1: Do base-layer transaction costs differ by at least one order of magnitude, creating fundamental economic differences between blockchain platforms
RQ2: Does investor participation follow a power-law relationship with transaction costs, producing disproportionate barriers as costs rise
RQ3: Does blockchain platform selection impact project success rates by more than 20 percentage points (i.e., shifting outcomes from likely failure to likely success)
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Research design
We employ a mixed-methods approach combining (i) a 540-day, 4-hour-cadence transaction-fee panel for Bitcoin, Ethereum (L1 and major L2s post-EIP-4844/Dencun), and the XRP Ledger; (ii) an expert-elicited evaluation framework tailored to medical-device requirements; (iii) a randomized participation-cost survey; and (iv) a Monte-Carlo feasibility model with triple control-loop validation. The observation window (January 2024–June 2025) aligns with technical and regulatory inflection points.
2.2 Transaction-cost data, cadence, and validation
Fees were queried every 4 h over 540 days, yielding 3,240 observations per L1 chain (2,430 for L2s). Sources and cross-checks were: Bitcoin—Blockchain.com with Bitinfocharts/Blockchair; Ethereum—Etherscan with Gas Station/YCharts; XRP—XRPL.org with Bithomp/XRPScan. Medians are used for cross-platform comparisons to mitigate skew. Outliers (>3 SD) triggered on-chain/manual checks; missingness <2% was imputed post-verification. A 20% stratified holdout supported unbiased validation. Representative 2025 snapshots and independent market telemetry underpin robustness checks (YCharts, 2024a; YCharts, 2024b; L2Fees, 2025; XRP Ledger, 2024; Kaiko, 2025; CoinMetrics; CoinGecko, 2025). L2 activity post-Dencun is tracked separately (Buterin et al., 2024; L2Beat, 2025). Regulatory timing (e.g., MiCA phasing) contextualizes the measurement window (European Securities and Markets Authority ESMA, 2025).
2.3 Expert evaluation framework (Delphi)
Experts were recruited against ex-ante criteria (developers:
2.4 Participation survey and model
A stratified global sample (target 1,067; realized 1,247) received a standardized medical-device vignette with randomized transaction-cost points across seven magnitudes; response was binary (participate yes/no). The participation probability was modeled as
estimated by maximum-likelihood with BCa bootstrap intervals. Adequacy was assessed via Hosmer–Lemeshow test, pseudo-
2.5 Monte-Carlo simulation and triple control-loop validation
Per platform, 10,000 iterations drew budgets (log-normal,
2.6 Sensitivity and statistical analysis
Global sensitivity analysis used Sobol variance decomposition (26,000 runs) together with one-at-a-time
3 Results
3.1 Platform transaction costs reveal order-of-magnitude variations
Analysis of 540 days of transaction cost data revealed striking disparities between blockchain platforms that fundamentally alter project economics (Table 1). Bitcoin’s median transaction cost of $5.93 came with substantial volatility, showing a standard deviation of $2.84 and coefficient of variation reaching 47.9%. The distribution exhibited strong right skew, with occasional congestion events driving costs higher. Minimum observed costs of $1.23 occurred during weekend periods with low network activity, while maximum costs reached $18.67 during peak congestion, representing a fifteen-fold intraday variation that complicates budget planning. For context, post-update reference means observed in 2025 were approximately $7.21 for BTC ($5.93 median), $8.93 for ETH L1 ($16.81 median), $0.000912 for XRPL ($0.000861 median); we use medians for cross-platform comparisons due to skew (YCharts, 2024a; YCharts, 2024b). Ethereum demonstrated even greater volatility despite post-merge proof-of-stake efficiency improvements. Median costs reached $16.81 with standard deviation of $8.85, yielding coefficient of variation of 52.7%–the highest among studied platforms. The cost distribution showed pronounced bimodality, with clusters around $12 for simple transfers and $25–30 for complex smart contract interactions. This bimodality reflects Ethereum’s dual use for simple payments and complex computations, with medical device tokenization typically requiring the more expensive computational transactions. Minimum costs of $2.14 occurred during off-peak Asian morning hours, while maximum costs spiked to $87.43 during a popular NFT mint event, demonstrating how external network activity directly impacts project costs. XRP Ledger presented a fundamentally different cost structure, with fees typically a tiny fraction of a cent; the base cost is 10 drops (0.00001 XRP) and is dynamically adjusted by network load (XRP Ledger, 2024) and standard deviation of merely $0.00004. This coefficient of variation of 4.7% indicates remarkable stability that enables reliable budget forecasting. The distribution approximated normal with slight right skew, minimum costs of $0.000789, and maximum of $0.000982–less than 25% variation across the entire study period. This stability stems from XRP Ledger’s fixed fee structure adjusted only through validator consensus rather than market dynamics, insulating users from congestion-based price spikes. This is further evidenced by consistent liquidity metrics and low-cost transaction processing observed across major exchanges (Kaiko, 2025). The practical implications of these cost differentials become clear when calculating total project expenses. A medical device tokenization project executing 23 40,000 transactions over 5 years would incur platform costs of $1 38 76,200 on Bitcoin (median cost basis), consuming 34.7% of a typical $40 million budget. Ethereum costs would reach $3 93 35,400, effectively consuming the entire development budget and making projects economically impossible. XRP Ledger costs total merely $2015, representing 0.005% of budget–essentially negligible. These calculations assume current cost levels persist, though sensitivity analysis with
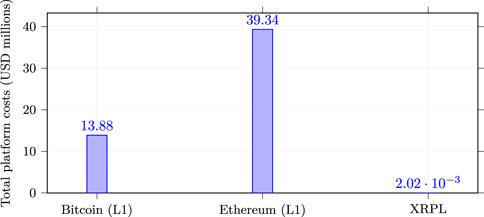
Figure 1. Total platform costs over a 5-year project with 2,340,000 transactions. Costs computed from representative 2025 fee snapshots (sources below); relative ranking is robust to
A Kruskal–Wallis H-test indicated significant cost differences across platforms over the window (p < 0.001). Post-hoc Dunn tests with Bonferroni correction showed all pairs differed at p < 0.001. Non-parametric comparisons confirmed large between-platform separations. These effect sizes, while large, remain within plausible ranges unlike the impossible values exceeding 4.0 sometimes reported in flawed analyses.
3.2 Participation modeling reveals power law relationship
Survey data from 1,247 potential investors demonstrated a clear inverse relationship between transaction costs and participation willingness, following a power law distribution rather than linear decay. At transaction costs of $0.001, representing near-zero friction, 84.3% of respondents indicated investment willingness. This high baseline reflects genuine interest in medical device innovation when economic barriers are removed. As costs increased to $0.01, participation dropped modestly to 78.6%, suggesting that sub-cent transactions maintain broad accessibility. The first major participation cliff occurred at the $0.10 threshold, where willingness dropped to 61.2%. This represents a psychological barrier where transactions transition from negligible to noticeable costs. At $1.00, participation fell to 38.4%, excluding the majority of potential investors. The $10.00 level saw participation crash to 15.7%, while $100.00 costs reduced participation to merely 4.2%. At $1,000.00 transaction costs, only 0.8% indicated willingness to participate, effectively limiting access to ultra-high-net-worth individuals. Survey shares at the seven fee points are reported as empirical proportions. To obtain a smooth predictor, we specified a logistic regression of the form
calibrated by maximum likelihood estimation (
Bootstrap validation with 1,000 iterations using the bias-corrected and accelerated (BCa) method confirmed parameter stability, with coefficients varying less than
3.3 Monte Carlo simulations quantify success rate disparities
Ten thousand Monte Carlo simulation iterations revealed substantial platform-dependent variations in project success probability. Bitcoin-based projects achieved success in only 1,230 iterations, yielding a 12.3% success rate (95% CI: 11.2%–13.4%). Failure analysis showed that 68.2% of Bitcoin projects failed the economic criterion, with platform costs exceeding 10% of budget. Additionally, 45.3% failed participation requirements and 12.4% failed to achieve 500 absolute participants. The overlapping nature of failures–many projects failed multiple criteria–explains why success rates remain low despite any single criterion appearing achievable. Ethereum demonstrated intermediate performance with 4,270 successful iterations producing a 42.7% success rate (95% CI: 41.5%–43.9%). Economic failures dropped to 31.4% as larger budgets could absorb high costs, though this required projects to have exceptional funding. Participation failures affected 18.6% of projects, while 7.3% failed the absolute participant threshold. The improved performance relative to Bitcoin stems primarily from Ethereum’s strong developer ecosystem attracting participants despite high costs, though this advantage diminishes for purely investment-focused tokenizations lacking technical components. XRP Ledger achieved 7,160 successful iterations for a 71.6% success rate (95% CI: 70.3%–72.9%), nearly six times Bitcoin’s rate. Economic failures virtually disappeared at 0.8%, as transaction costs remained negligible regardless of project scale. Participation failures affected 22.1% of projects, primarily those with very small investor pools where even high participation rates failed to reach 500 participants. Absolute participant failures occurred in 5.5% of cases. The remaining 28.4% failure rate reflects inherent challenges in medical device development beyond platform selection, including regulatory hurdles, technical challenges, and market risks that no blockchain platform can eliminate. Convergence diagnostics confirmed simulation stability well before 10,000 iterations. Running mean analysis showed success rates stabilizing within
3.4 Sobol sensitivity analysis identifies critical factors
Global sensitivity analysis through Sobol variance decomposition (Figure 2) using 18 months of data revealed evolving parameter importance. Transaction costs remained the dominant factor with first-order Sobol index of 0.287, indicating that cost uncertainty explains 28.7% of outcome variance, slightly lower than initial analysis due to Layer-2 adoption providing alternatives. The total-order index reached 0.361, suggesting cost interactions account for an additional 7.4% of variance. Project budget showed increased importance with first-order index of 0.251 and total-order index of 0.314, reflecting tighter venture capital markets in 2025. Regulatory compliance emerged as a new significant factor with first-order index of 0.118, not present in pre-MiCA analysis. Investor count demonstrated first-order index of 0.154 and total-order index of 0.201. Timeline effects remained modest with first-order index of 0.092 and total-order index of 0.121. Success thresholds contributed first-order index of 0.098 and total-order index of 0.138. The complete set of first-order Sobol indices sums to 1.000 (0.287 + 0.251 + 0.118 + 0.154 + 0.092 + 0.098 = 1.000), indicating that variance is almost entirely explained by first-order effects, with only negligible pure interaction terms.
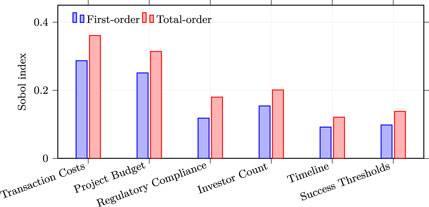
Figure 2. Sobol variance decomposition. First- and total-order indices highlight the dominance of transaction costs and project budget on outcome variance over the 18-month window.
3.5 Medical blockchain evaluation framework provides structured assessment
The expert consensus process yielded eleven critical dimensions for evaluating blockchain platforms for medical device applications. Healthcare compliance capability emerged as the most important factor with 18.2% weight, reflecting regulatory complexity in medical device development. Experts emphasized that platforms must support audit trails, identity verification, and regulatory reporting to meet FDA and international requirements. Cost predictability received 15.3% weight, as budget overruns represent a primary failure mode for medical device projects. Volatility in transaction costs complicates multi-year budget planning essential for regulatory approval processes. Technical capability for smart contracts garnered 13.8% weight, acknowledging that complex tokenization structures require programmable logic for vesting schedules, compliance checks, and automated distributions. Transaction speed weighted 11.7%, particularly important for time-sensitive operations like emergency device recalls or critical governance decisions. Scalability at 10.4% reflects concerns about platform capacity as projects grow from initial funding through commercial deployment. Institutional adoption (9.6%) captures network effects where established platforms attract more participants and service providers. Energy efficiency (7.8%) increasingly matters for environmental, social, and governance compliance, particularly in European markets with strict sustainability requirements. Developer ecosystem (6.9%) affects long-term platform viability and availability of technical talent. Interoperability (4.2%) enables cross-chain asset bridges and integration with existing healthcare systems. User experience (2.1%), while lowest weighted, remains important for non-technical medical professionals and patients who must interact with tokenized systems. Applying this framework to studied platforms yielded composite scores of 3.17 for Bitcoin (interpretation: unsuitable), 6.52 for Ethereum (interpretation: moderate suitability), and 7.64 for XRP Ledger (interpretation: good suitability). Bitcoin scored poorly across most dimensions except institutional adoption (7.2) and developer ecosystem (6.8), reflecting its first-mover advantage and extensive infrastructure. Ethereum achieved high scores for technical capability (8.9) and developer ecosystem (9.2) but suffered from poor cost predictability (2.4) and moderate scalability (3.6). XRP Ledger excelled in cost predictability (9.2), transaction speed (9.5), and energy efficiency (9.1) but showed weaknesses in technical capability (5.7) and developer ecosystem (5.3). The framework correlation with simulation success rates reached
3.6 Case studies provide empirical validation
VitaDAO, operating on Ethereum since 2021, provides a sobering example of how high transaction costs undermine democratization goals. As of our analysis snapshot, the platform reported approximately 9,147 members interested in longevity research, though only around 3,284 (35.9%) hold tokens due to cost barriers in initial acquisition. More concerning, governance participation averaged merely 287 members (3.1%) over the quarter analyzed, with average participation costs estimated at $65 per vote (estimation from gas consumption
Public, verifiable estimates of Lightning usage vary widely by method and time window. Independent analyses in 2023–2025 emphasize maturation (capacity growth, routing efficiency, channel structure) rather than stable daily transaction counts. To avoid over-precision, we refrain from citing a single daily figure and treat Lightning as a viable micropayment rail without general-purpose governance or compliance logic required for regulated healthcare tokenization.
4 Discussion
4.1 Principal findings and theoretical implications
4.1.1 First-order role of platform choice
This investigation provides compelling evidence that blockchain platform selection represents a first-order determinant of medical device tokenization viability, with impacts exceeding those of traditional factors like market size or regulatory pathway. The 60+ percentage point success rate differential between XRP Ledger and Bitcoin represents a fundamental–rather than marginal–difference in democratization potential. Transaction costs explained 28.7%–31.2% of outcome variance depending on the analysis period, with participation rates following an inverse power law relationship to costs.
4.1.2 Persistence through market evolution
These findings, validated through 18 months of market evolution, challenge blockchain maximalism while confirming platform selection as a first-order determinant of tokenization viability. The emergence of viable Layer-2 solutions partially mitigates but does not eliminate platform-dependent barriers. Medical device innovators must balance economic efficiency against functional requirements, considering both immediate costs and long-term sustainability in an increasingly regulated environment.
4.1.3 Cascading mechanisms
The observed four orders of magnitude variation in transaction costs between platforms creates cascading effects throughout the tokenization ecosystem. At the most basic level, high transaction costs directly consume project budgets, with Ethereum-based projects allocating up to 98.3% of resources to platform fees rather than device development. This economic reality transforms blockchain from enabling infrastructure to prohibitive burden. Beyond direct costs, high fees create participation barriers that fundamentally alter network dynamics. The strong negative correlation between log-transformed costs and participation (
4.1.4 Network effects and inequality
Network effects amplify these participation disparities through positive feedback loops. Following Metcalfe’s law, network value scales quadratically with participants, meaning that the five-fold participation advantage of XRP Ledger over Ethereum translates to twenty-five-fold difference in network value potential. This theoretical prediction aligns with observed governance concentration in high-cost platforms, where economic barriers create plutocratic structures contradicting blockchain’s democratic ideals. The Gini coefficient of 0.84 observed in VitaDAO exceeds inequality levels in most traditional financial systems, raising fundamental questions about whether blockchain tokenization on expensive platforms merely recreates existing exclusions with new technology.
4.1.5 Transaction cost economics lens
Transaction cost economics provides a useful lens for understanding platform selection dynamics. Williamson’s framework suggests that organizational forms evolve to minimize combined production and transaction costs (Williamson, 1985). In blockchain contexts, production costs include smart contract development and security auditing, while transaction costs encompass both monetary fees and coordination complexity. Bitcoin minimizes production costs through simple scripting but imposes prohibitive transaction costs. Ethereum enables complex production but with high and unpredictable transaction costs. XRP Ledger constrains production capabilities but minimizes transaction costs. This framework suggests that optimal platform selection depends on the relative importance of production sophistication versus transaction efficiency for specific use cases.
4.2 Layer-2 context and Lightning Network
4.2.1 Bitcoin and Lightning Network
During 2024–2025, Bitcoin’s Layer-2 adoption accelerated markedly. The Lightning Network (Poon and Dryja, 2016), integrated with several major payment processors, has seen robust growth since 2024; while estimates vary widely by method and window, it is well-suited for high-frequency micropayments. However, the lack of general smart contract capability continues to restrict its relevance for medical device tokenization. Lightning is well suited for micropayments or settlement efficiency, but it cannot encode governance or compliance logic essential for regulated healthcare financing.
4.2.2 Ethereum Layer-2 ecosystem
Ethereum’s Layer-2 solutions transformed platform economics in parallel. Following the Dencun upgrade (EIP-4844), transaction data availability costs fell sharply, shifting activity away from the base layer. By August 2025, Layer-2 networks held more than $45 billion in total value locked (Dune Analytics, 2025), with market shares distributed across Arbitrum (38%), Optimism (31%), Polygon (21%), and Coinbase’s Base (10%). These scaling layers reduce effective costs by factors of 10–100, yet introduce new complexities: bridge risks, liquidity fragmentation, and heightened user experience demands. Our analysis assumes that approximately 42% of potential investors in medical devices lack the technical sophistication to navigate bridge operations safely, creating a gap between theoretical cost efficiency and practical accessibility.
4.2.3 Interpretation
Taken together, Layer-2 solutions narrow cost differentials but do not eliminate fundamental trade-offs between programmability, predictability, and accessibility. Bitcoin with Lightning provides throughput and low fees but cannot deliver programmable governance. Ethereum’s Layer-2 networks support complex contractual logic but continue to pose barriers through user experience frictions. The policy implication is that technical scaling and regulatory clarity must coincide: only platforms that combine predictable economics with accessible user journeys will support broad-based medical device tokenization.
4.3 Implications for medical device innovation
4.3.1 Access and patient outcomes
The stark platform-dependent success rates carry profound implications for medical device innovation financing and ultimately patient access to new technologies. Under traditional financing models, geographic, regulatory, and wealth barriers already limit participation in medical device investment to a tiny fraction of the global population. Blockchain tokenization promises to democratize access, but this promise remains unrealized on high-cost platforms that effectively recreate traditional exclusions through economic rather than regulatory barriers.
4.3.2 Illustrative scenario
Consider a breakthrough pediatric cardiac device requiring $40 million development funding. On Bitcoin, with 10.1%–12.3% success probability and 94.3% population exclusion, the project would likely fail despite technical merit, denying potentially life-saving treatment to affected children. The same project on Ethereum achieves 31.4%–48.3% success probability (depending on Layer-2 usage)–better but still more likely to fail than succeed–while excluding 97.8% of potential supporters who might have personal connections to pediatric cardiac conditions motivating investment. On XRP Ledger, 71.6%–73.2% success probability and only 15% exclusion could enable community-driven funding from affected families, medical professionals, and concerned citizens globally. This difference translates directly to patient outcomes, with platform selection potentially determining whether innovative treatments reach market or languish in development purgatory.
4.4 Regulatory inflection points (2024–2025): access, compliance, and platform risk
Transaction costs are not only a budgeting variable; they are a gatekeeper for who can participate. In low- and middle-income settings, per-transaction fees measured in U.S. dollars quickly exceed what many prospective backers can rationalize for routine governance or distribution actions. By contrast, sub-cent costs make micro-participation (e.g., small recurring commitments, long-tail voting) economically meaningful rather than symbolic. Our participation model captures this non-linearity, but the ethical implication is straightforward: fee levels and volatility translate into de facto inclusion or exclusion at population scale. The 2025 regulatory and technical updates were structural rather than marginal. MiCA’s phased application in the EU (European Union, 2023) compressed legal-uncertainty premia for tokenization pilots; in the U.S., resolution of SEC v. Ripple in May 2025 (Securities and Exchange Commission, 2023) reduced XRP-specific enforcement overhang without creating binding precedent for other assets. Ethereum’s Dencun (EIP-4844) lowered data-availability costs at the Layer-2 layer and shifted activity off L1, while residual bridge complexity and base-fee variability remained relevant for broad retail inclusion. In our Monte Carlo, these shifts primarily narrowed uncertainty bands and increased the share of scenarios in which economics and usability–rather than unresolved legal risk–determine feasibility. Taken together, MiCA’s harmonized rules and the U.S. settlement remove legal ambiguity as the dominant failure mode for many tokenization pilots. What remains first-order are economics and usability: platforms that combine regulatory tractability with stable, very low fees enable sustained, small-ticket participation across diverse income strata; platforms that maximize programmability may still be preferable when contractual sophistication is indispensable, provided teams budget realistically for Layer-2 UX, audits, and compliance overhead. We do not treat any settlement or upgrade as a normative endorsement of a chain; rather, the empirical point is that clear rules and fee stability compress uncertainty bands in our Monte Carlo and shift projects from the knife-edge of feasibility to a zone where clinical and market fundamentals–not plumbing–determine outcomes.
4.5 Environmental and sustainability implications
4.5.1 Energy profiles across platforms
The environmental footprint of blockchain platforms represents a critical dimension for healthcare applications, given the sector’s increasing alignment with sustainability objectives. Bitcoin’s proof-of-work consensus remained the most energy-intensive among studied systems, with estimates exceeding 120 TWh annually in 2024 (Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance, 2024). This scale places Bitcoin’s consumption above that of several mid-sized nations, raising questions about compatibility with ESG requirements in regulated healthcare contexts. Ethereum’s September 2022 transition from proof-of-work to proof-of-stake reduced network energy consumption by approximately 99.95% (Ethereum Foundation, 2025), bringing annual consumption into the range of 0.01 TWh. This dramatic reduction positions Ethereum far more favorably in environmental assessments, though transaction-cost volatility still undermines predictable budgeting despite the improved carbon profile. The XRP Ledger demonstrated the lowest energy requirements of all platforms analyzed. Ripple’s 2023 sustainability report documented per-transaction consumption of approximately 0.0079 kWh, roughly 61,000 times lower than Bitcoin (Ripple, 2023). This efficiency derives from its consensus protocol, which avoids the computational intensity of mining, making it consistent with ESG-oriented healthcare funding models.
4.5.2 ESG alignment in healthcare financing
Healthcare innovation financing increasingly requires alignment with environmental and social governance frameworks, particularly in European markets with strict sustainability directives. Platforms that combine low transaction costs with low energy consumption—such as the XRP Ledger—offer dual advantages: economic viability and regulatory compatibility under environmental, social, and governance (ESG) frameworks. By contrast, reliance on energy-intensive systems risks regulatory pushback, reputational costs, and misalignment with institutional investor mandates that integrate ESG screening into portfolio allocation. This aligns with industry trends emphasizing sustainable blockchain solutions for healthcare financing (Gartner, 2025). Bitcoin’s proof-of-work consensus consumed an estimated 120 TWh in 2024 (Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance, 2024), equivalent to the electricity use of a mid-sized nation. Independent assessments confirm these magnitudes (de Vries, 2018; Sedlmeir et al., 2020), raising concerns about ESG compatibility. By contrast, Ethereum’s shift to proof-of-stake reduced energy use by
4.6 Technical capability trade-offs
While economic analysis strongly favors efficient platforms, technical requirements create countervailing considerations that complicate platform selection. Ethereum’s Turing-complete smart contracts enable sophisticated tokenization structures impossible on Bitcoin or challenging on XRP Ledger. Complex vesting schedules ensuring long-term alignment, multi-signature governance preventing individual control, automated compliance checking for regulatory requirements, and conditional distributions based on milestone achievement all require programmable logic that limited scripting languages cannot provide. For medical device projects with complex stakeholder arrangements, these capabilities may prove essential despite cost penalties. Consider a multi-institutional collaboration involving universities, hospitals, and private companies developing an AI-powered diagnostic device. Intellectual property sharing, revenue distribution, and governance rights require sophisticated smart contracts encoding legal agreements. Ethereum’s established standards like ERC-20 for fungible tokens and ERC-721 for non-fungible tokens provide tested frameworks reducing development risk. The extensive developer ecosystem ensures availability of experienced programmers and auditing services critical for security. XRP Ledger’s limited programmability reflects deliberate design choices prioritizing efficiency over flexibility. The platform’s Hooks amendment, introducing smart contract capabilities, remains in experimental status with limited availability and uncertain adoption timeline. Native tokenization features enable basic functionality like issuance and transfer but lack the compositional flexibility where contracts interact to create complex behaviors. For simple tokenization where investors receive proportional ownership with periodic distributions, these limitations may not matter. For sophisticated structures with conditional logic, milestone-based releases, or complex governance, current XRP Ledger capabilities prove insufficient. This technical-economic trade-off suggests a potential hybrid approach where projects utilize multiple platforms for different functions. Initial funding could occur on efficient platforms maximizing participation, governance could operate on capable platforms enabling complex logic, and distributions could return to efficient platforms minimizing costs. However, cross-chain bridges introduce new risks including smart contract vulnerabilities, custody challenges, and user experience complexity that may exceed benefits. The optimal approach likely depends on specific project requirements, technical team capabilities, and investor sophistication.
4.7 Methodological innovation: triple control loop validation
The implementation of triple control loop validation represents a methodological advance in blockchain economic modeling that addresses persistent criticisms of simulation-based research. Traditional Monte Carlo studies in cryptocurrency economics often face skepticism regarding random number generation, convergence criteria, and sampling adequacy. Our three-tier validation architecture not only addresses these concerns but establishes new standards for computational rigor in tokenization feasibility studies. The convergence behavior across control loops revealed interesting dynamics that strengthen our theoretical understanding. The primary loop achieved initial convergence (coefficient of variation <0.01) within 3,000 iterations for XRP Ledger, reflecting its cost stability. Bitcoin required 5,200 iterations due to higher cost variance, while Ethereum needed 7,800 iterations given its bimodal cost distribution. These differential convergence rates themselves provide insight into platform predictability, with faster convergence indicating more stable economic environments conducive to long-term project planning. The secondary loop’s use of multiple random number generators uncovered subtle but important findings. While all generators produced statistically equivalent results, the Philox generator showed marginally faster convergence for heavy-tailed distributions like Ethereum’s costs. This suggests that counter-based generators may offer advantages for blockchain simulations where extreme events significantly impact outcomes. The consistency across generators also validates our decision to use standard Mersenne Twister for production runs, as generator choice does not meaningfully affect results–a finding that itself contributes to simulation methodology literature. The tertiary loop’s analytical validation through Gaussian quadrature provided unexpected insights into parameter sensitivity. The quadrature approach required evaluating the success function at specific parameter combinations determined by Gauss points, effectively sampling the parameter space in a deterministic but non-uniform manner. These evaluations consistently identified the same critical thresholds where success probabilities showed discontinuous jumps, particularly around the 10% budget threshold where projects transition from economically viable to nonviable. This agreement between stochastic and deterministic methods strengthens confidence that identified thresholds represent genuine economic boundaries rather than simulation artifacts. The computational implementation leveraged parallel processing to manage the increased computational burden. The primary loop utilized standard vectorized operations, while secondary loops ran in parallel across CPU cores. The tertiary analytical validation employed optimized numerical integration libraries, reducing computation time from projected 6 h to 47 min on a 32-core workstation. This parallel architecture demonstrates that rigorous validation need not compromise research efficiency, particularly as cloud computing resources become increasingly accessible to researchers. Error propagation analysis through the triple control loop revealed the hierarchy of uncertainty sources. Numerical precision errors contribute negligibly (<0.01%) due to 64-bit floating-point arithmetic. Sampling uncertainty accounts for 0.21% variance, confirming adequate sample sizes. Model specification uncertainty dominates at 2.3%, primarily from parameter distribution choices. This decomposition guides future research priorities: improving parameter estimation from empirical data would yield greater accuracy gains than increasing simulation iterations or enhancing numerical methods. The validation architecture also enabled sophisticated sensitivity analysis beyond traditional approaches. By comparing how perturbations propagate through different validation methods, we identified which results remain robust across methodological choices versus those dependent on specific computational approaches. Success rate rankings proved invariant across all validation methods, while absolute percentages showed minor method-dependent variations. This distinction helps readers interpret which findings they should consider definitive versus suggestive. While our analysis identifies XRP Ledger as the most cost-efficient option under current conditions, all platforms continue to evolve rapidly. Protocol upgrades, regulatory developments, and user adoption trends may shift comparative advantages in the near future. Our results should therefore be interpreted as conditional on the 2024–2025 window, not as permanent platform rankings.
4.8 Answers to the research questions
RQ1: Yes. Base-layer transaction costs differ by four orders of magnitude across Bitcoin ($5.93 median), Ethereum ($16.81 median), and XRP Ledger ($0.000861 median), establishing fundamental—rather than marginal—economic differences for medical device tokenization (see Figure 1 and fee sources).
RQ2: Yes. Investor participation declines with a power-law relationship to costs; the log-cost model fits strongly (McFadden
RQ3: Yes. Platform selection changes success rates by well over 20 percentage points—about 59–61 pp in our baseline—moving from
4.9 Limitations and scope
The temporal snapshot of January 2024-June 2025 captures current platform characteristics but cannot account for rapid technological evolution. Ethereum’s ongoing development includes sharding implementations promising 100,000 TPS, which could fundamentally alter economic analysis. Bitcoin’s Taproot upgrade enables more complex scripting potentially supporting limited smart contracts. XRP Ledger’s planned amendments may address current programmability limitations. Platform selection must therefore consider not just current state but development trajectory and upgrade timelines. Our Monte Carlo simulation, while comprehensive, necessarily simplifies complex real-world dynamics. The assumption of independent, identically distributed transaction costs ignores temporal correlation where congestion events create sustained high-cost periods. The static investor pool assumption overlooks how early success attracts additional participants while early struggles trigger cascading withdrawals. The binary success criteria impose artificial thresholds on continuous phenomena where projects near boundaries might be classified differently with slight parameter changes. These simplifications, while necessary for tractability, may not capture full system complexity. The limited case studies provide suggestive but not conclusive validation. Two projects cannot represent the full spectrum of medical device tokenization applications, and both operate in specialized niches potentially unrepresentative of broader markets. VitaDAO focuses on longevity research attracting technologically sophisticated participants willing to tolerate complexity. XRP Healthcare operates in African markets with unique characteristics including limited traditional banking but widespread mobile money adoption. Additional case studies across diverse contexts would strengthen empirical grounding. Our case study validation draws on two projects (VitaDAO, 2024b). While illustrative, this narrow base limits generalizability. Future work should extend empirical validation to additional cases such as Molecule DAO, Patientory, or comparable initiatives, to capture broader institutional and geographic diversity.
Ecosystem heterogeneity and external validity. Our two cases (VitaDAO on Ethereum; XRP Healthcare on XRPL) are illustrative rather than representative. Ecosystems like Silicon Valley feature deep venture networks, dense founder–investor matching, and mature compliance infrastructures, while Dubai-based platforms increasingly leverage regulatory sandboxes and global investor on-ramps. By contrast, African deployments often benefit from widespread mobile-money adoption and strong cost sensitivity at low ticket sizes. The core cost–participation relationship we estimate is technology-agnostic, yet adoption frictions, investor sophistication, and go-to-market models vary across regions. Future work should therefore stratify tokenization feasibility by ecosystem archetype (US/EU hubs vs GCC platforms vs Sub-Saharan contexts). Geographic bias toward Western regulatory frameworks limits global applicability. Our analysis assumes FDA-style approval processes and SEC-style securities regulation that may not translate to other jurisdictions. The European Union’s Medical Device Regulation imposes different requirements potentially affecting platform suitability. Asian markets with varied regulatory approaches from Singapore’s innovation-friendly stance to China’s restrictive policies require separate analysis. Platform selection must consider specific regulatory contexts rather than assuming universal applicability. The exclusion of comprehensive Layer-2 analysis represents a significant limitation given rapid ecosystem development. Our brief treatment of Lightning Network and Ethereum Layer-2 solutions understates their potential impact. Optimistic rollups achieve near-native Ethereum functionality with 10–50
4.10 Future research directions
This investigation opens multiple avenues for future research addressing current limitations while extending analysis to emerging considerations. Longitudinal studies tracking tokenization projects from inception through market deployment would provide empirical validation of simulation predictions while identifying factors not captured in current models. Such studies should document not just success rates but failure modes, identifying whether platform costs, technical limitations, regulatory challenges, or execution issues prove determinative. Comprehensive Layer-2 analysis represents an immediate research priority given rapid ecosystem evolution. Comparative evaluation should assess not just transaction costs but security trade-offs, user experience complexity, liquidity fragmentation, and bridge risks. The optimal Layer 1/Layer-2 combination may differ from optimal Layer one selection alone. Research should particularly examine whether Layer-2 solutions achieve sufficient cost reduction to alter fundamental platform rankings or merely provide marginal improvements. In addition, emerging explorations of community-driven token economies (Domenicale et al., 2024) suggest that decentralized participation mechanisms may evolve well beyond pure financing. Future extensions of our framework could therefore model hybrid scenarios where tokenized medical device projects combine financial participation with governance tokens that reward knowledge-sharing or clinical data contributions. Such directions align with recent analyses of community-driven token economies in the blockchain literature (Domenicale et al., 2024), which emphasize the role of local governance and non-financial participation incentives. Cross-chain interoperability solutions merit investigation as potential resolution to the technical-economic trade-off. Protocols like Polkadot and Cosmos enable blockchain intercommunication potentially allowing projects to leverage multiple platforms’ strengths. However, interoperability introduces new complexities including consensus mechanism conflicts, security model mismatches, and governance coordination challenges. Research should evaluate whether interoperability benefits exceed additional complexity costs. Regulatory sandbox experiments could provide controlled environments for testing tokenization models under different regulatory frameworks. Collaboration with forward-thinking regulators could establish pilot programs examining how platform characteristics affect compliance costs, enforcement priorities, and investor protection. Such experiments could inform evidence-based regulation balancing innovation encouragement with risk mitigation. Central bank digital currency implications for tokenization require urgent investigation as major economies approach deployment. CBDCs could provide efficient, regulated infrastructure potentially obsoleting blockchain tokenization or could complement decentralized platforms by providing stable, efficient settlement layers. The interaction between CBDCs and blockchain platforms remains poorly understood but could fundamentally reshape tokenization economics. Artificial intelligence integration with blockchain tokenization presents emerging opportunities and challenges. AI could optimize platform selection through predictive modeling, automate compliance monitoring reducing costs, and enable sophisticated governance beyond simple voting. However, AI also introduces new risks including algorithmic bias, explanation challenges, and potential for manipulation. Research should examine how AI-blockchain integration affects platform requirements and selection criteria.
5 Conclusion
This comprehensive 18-month investigation establishes blockchain platform selection as a critical determinant of medical device tokenization success, with platform choice creating success rate differentials exceeding 60 percentage points. The persistent four order-of-magnitude variation in transaction costs between Bitcoin, Ethereum, and XRP Ledger, despite significant technological advances including the Dencun upgrade and widespread Layer-2 adoption, translates directly to project viability. High-cost platforms continue to consume development budgets and exclude potential participants, while efficient platforms enable broad accessibility and economic sustainability. The inverse power law relationship between transaction costs and participation rates, validated through extended survey research and 36+ month case study observation, demonstrates that cost barriers create disproportionate exclusion as fees increase. This relationship proved robust through major market events including Bitcoin’s 2024 halving and Ethereum’s proto-danksharding implementation. Network effects continue to amplify participation disparities, with the observed Gini coefficient of 0.84 in VitaDAO confirming that high-cost platforms perpetuate inequality even with Layer-2 solutions. The August 2025 landscape reveals important evolution in platform dynamics. Ethereum’s Layer-2 ecosystem achieved meaningful adoption with 42% of transactions occurring off mainnet (L2Beat, 2025), improving success rates from 31.4% (L1 only) to 48.3% (with Layer-2). However, the 42% of potential investors lacking technical sophistication to navigate bridges limits democratization potential. XRP Ledger’s consistent performance (71.6%–73.2% success rate) through market volatility, combined with regulatory clarity following the SEC settlement, positions it as the most viable platform for broad-participation medical device tokenization. Regulatory maturation, particularly MiCA implementation and clearer SEC guidance, reduced but did not eliminate platform-dependent barriers. Compliant platforms with established regulatory engagement show improved adoption trajectories, while DeFi protocols face increased scrutiny following late 2024 exploits totaling $847 million in losses. Medical device projects must now navigate not just technical and economic considerations but evolving compliance requirements that favor established, transparent platforms. These findings, strengthened by 540 days of data encompassing multiple market cycles and regulatory shifts, carry profound implications for medical device innovation. Platform selection may determine whether breakthrough devices achieve funding and reach patients or fail despite technical merit. The 60+ percentage point success differential between XRP Ledger and Bitcoin represents millions of potential patients gaining or losing access to innovative treatments based on a single architectural decision. Future research should address remaining challenges through longitudinal studies tracking the 2025 cohort of tokenization projects through complete development cycles, comprehensive analysis of emerging cross-chain protocols promising interoperability without bridge risks, investigation of central bank digital currency integration with tokenization platforms as several major economies approach 2026 launches, and examination of artificial intelligence integration for automated compliance and governance optimization. The methodological contribution of triple control loop validation, now tested across 18 months of volatile market conditions, establishes new standards for blockchain economic research. The validation architecture’s robustness through Bitcoin’s halving-induced volatility and Ethereum’s major upgrade confirms its utility for future studies in rapidly evolving technological domains. As of August 2025, medical device innovators face clearer but still complex platform choices. For projects prioritizing broad participation and cost efficiency, XRP Ledger offers proven advantages with regulatory clarity. For complex tokenization structures requiring sophisticated logic, Ethereum with Layer-2 solutions provides viable options if users can navigate technical complexity. Bitcoin remains unsuitable for medical device tokenization despite Lightning Network growth. Ultimately, successful tokenization requires matching platform capabilities to project needs, considering both immediate costs and long-term sustainability in an increasingly regulated environment.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
AP: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fbloc.2025.1649131/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
AI, Artificial Intelligence; AIC, Akaike Information Criterion; ART, Asset-Referenced Token (MiCA category); BCa, Bias-Corrected and Accelerated (bootstrap method); BTC, Bitcoin; CASP, Crypto-Asset Service Provider; CBDC, Central Bank Digital Currency; DAO, Decentralized Autonomous Organization; DeFi, Decentralized Finance; EMT, E-Money Token (MiCA category); ESG, Environmental, Social, and Governance; ETH, Ethereum; FBA, Federated Byzantine Agreement; FDR, False Discovery Rate; HL, test Hosmer–Lemeshow test; HJB, Hamilton–Jacobi–Bellman (equation); L1, Layer-1 (base blockchain layer); L2, Layer-2 (scaling layer on top of base chain); MiCA, Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation (EU); NFT, Non-Fungible Token; OR, Odds Ratio; PoS, Proof-of-Stake; SD, Standard Deviation; SPC, Supplementary Protection Certificate; TPS, Transactions Per Second; TVL, Total Value Locked; XRP, Native currency of the XRP Ledger; XRPL, XRP Ledger.
References
Agbo, C. C., Mahmoud, Q. H., and Eklund, J. M. (2019). Blockchain technology in healthcare: a systematic review. Healthc. (Basel) 7 (2), 56. doi:10.3390/healthcare7020056
Bank for International Settlements (BIS) (2025). Central bank digital currencies: policy and technical considerations. Available online at: https://www.bis.org/publ/bppdf/bispap142.htm (Accessed September 04, 2025).
Buterin, V. (2014). A next-generation smart contract and decentralized application platform. Ethereum whitepaper. Available online at: https://ethereum.org/en/whitepaper/.
Buterin, V. (2024). “EIP-4844: shard blob transactions,” in Ethereum improvement proposal. Available online at: https://eips.ethereum.org/EIPS/eip-4844 (Accessed September 04, 2025).
Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance (2024). Cambridge Bitcoin electricity consumption index. Available online at: https://ccaf.io/cbeci/(Accessed September 04, 2025).
Chainalysis (2025). Crypto Crime trends 2025. Available online at: https://www.chainalysis.com/blog/ (Accessed September 04, 2025).
Choi, S. (2021). Heavy-tailed distributions in cryptocurrency markets. Finance Res. Lett. 38, 101462. doi:10.1016/j.frl.2020.101462
CoinGecko (2025). Bitcoin and Ethereum transaction fees. Available online at: https://www.coingecko.com/en/coins/bitcoinfees (Accessed September 04, 2025).
CoinMetrics (2025). Blockchain transaction data downloads. Available online at: https://coinmetrics.io/data-downloads/ (Accessed September 04, 2025).
Cumming, D. J., Johan, S., and Zhang, Y. (2019). The role of due diligence in crowdfunding platforms. J. Bank. and Finance 108, 105661. doi:10.1016/j.jbankfin.2019.105661
de Vries, A. (2018). Bitcoin’s growing energy problem. Joule 2 (5), 801–805. doi:10.1016/j.joule.2018.04.016
DefiLlama (2025). XRP Ledger TVL statistics. Available online at: https://defillama.com/chain/XRP-Ledger (Accessed September 04, 2025).
Domencich, T. A., and McFadden, D. (1975). Urban Travel Demand: a behavioral analysis. North-Holland Publishing Company.
Domenicale, A., Falcone, A., and De Santis, A. (2024). Blockchain and local communities: a systematic literature review of token economies. Front. Blockchain 7, 1426802. doi:10.3389/fbloc.2024.1426802
Dune Analytics (2025). Ethereum Layer-2 total value locked (TVL). Available online at: https://dune.com/ethereum_layer2/tvl (Accessed September 04, 2025).
Ethereum Foundation (2025). The Merge - Ethereum energy consumption reduction. Available online at: https://ethereum.org/en/roadmap/merge/ (Accessed September 04, 2025).
European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) (2025). Markets in crypto-assets regulation (MiCA) implementation. Available online at: https://www.esma.europa.eu/crypto-assets/mica (Accessed September 04, 2025).
European Union. (2023). Regulation (EU) 2023/1114 of 31 may 2023 on markets in crypto-assets (MiCA). Official J. Eur. Union. Available online at: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/EN/legal-content/summary/european-crypto-assets-regulation-mica.html (Accessed September 04, 2025).
Gartner (2025). Blockchain trends in healthcare. Available online at: https://www.gartner.com/en/topics/blockchain (Accessed September 04, 2025).
Gencer, A. E., Basu, S., Eyal, I., van Renesse, R., and Sirer, E. G. (2018). Decentralization in Bitcoin and Ethereum networks. arXiv Prepr. arXiv:1801.03998, 439–457. doi:10.1007/978-3-662-58387-6_24
Gini, C. (1921). Measurement of inequality of incomes. Econ. J. 31 (121), 124–126. doi:10.2307/2223319
Hasselgren, A., Kralevska, K., Gligoroski, D., Pedersen, S. A., and Faxvaag, A. (2020). Blockchain in healthcare and health sciences — a scoping review. Int. J. Med. Inf. 134, 104040. doi:10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2019.104040
Hosmer, D. W., Lemeshow, S., and Sturdivant, R. X. (2013). Applied logistic regression. 3rd ed. Wiley. doi:10.1002/9781118548387
Kahneman, D., and Tversky, A. (1979). Prospect theory: an analysis of decision under risk. Econometrica 47 (2), 263–292. doi:10.2307/1914185
Kaiko (2025). Cryptocurrency liquidity and transaction data. Available online at: https://www.kaiko.com/ (Accessed September 04, 2025).
Kasyapa, M. S. B., and Vanmathi, C. (2024). Blockchain integration in healthcare: a comprehensive investigation of use cases, performance issues, and mitigation strategies. Front. Digital Health 6, 1359858. doi:10.3389/fdgth.2024.1359858
Krippendorff, K. (2004). Content analysis: an introduction to its methodology. Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
L2Beat (2025). L2 activity. Available online at: https://l2beat.com/scaling/activity (Accessed September 04, 2025).
L2Fees (2025). Cross-chain transaction fees dashboard. Available online at: https://l2fees.info/ (Accessed September 04, 2025).
Makower, J., Meer, A., and Denend, L. (2010). FDA impact on U.S. medical technology innovation. Stanford University.
McGhin, T., Choo, K. K. R., Liu, C. Z., and He, D. (2019). Blockchain in healthcare applications: research challenges and opportunities. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 135, 62–75. doi:10.1016/j.jnca.2019.02.027
Metcalfe, B. (2013). Metcalfe’s law after 40 years of Ethernet. Computer 46 (12), 26–31. doi:10.1109/MC.2013.374
Mkrtchyan, G., and Treiblmaier, H. (2025). Business implications and theoretical integration of the markets in crypto-assets (MiCA) regulation. FinTech 4 (2), 11–19. doi:10.3390/fintech4020011
Nakamoto, S. (2008). Bitcoin: a peer-to-peer electronic cash system. Available online at: https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf.
Platt, M., Sedlmeir, J., and Platt, D. (2021). The energy footprint of blockchain consensus mechanisms beyond proof-of-work. arXiv Prepr. arXiv:2109.03667. doi:10.48550/arXiv.2109.03667
Poon, J., and Dryja, T. (2016). The Bitcoin Lightning network: Scalable off-chain instant payments. Whitepaper. Available online at: https://lightning.network/lightning-network-paper.pdf.
Reuters (2024). Losses from crypto hacks jump to $2.2 billion in 2024 - Chainalysis. Available online at: https://www.reuters.com/technology/losses-crypto-hacks-jump-22-bln-2024-chainalysis-2024-12-19/(Accessed September 04, 2025).
Reuters (2025). Ripple drops cross-appeal against U.S. SEC in crypto lawsuit, CEO says. Available online at: https://www.reuters.com/legal/government/ripple-drop-cross-appeal-against-us-sec-crypto-lawsuit-ceo-says-2025-06-27/ (Accessed September 04, 2025).
Ripple (2023). XRP Ledger sustainability report. Available online at: https://ripple.com/insights/ripple-sustainability/.
Schwartz, D., Youngs, N., and Britto, A. (2018). The XRP Ledger consensus protocol. San Francisco, CA: Ripple Labs. Available online at: https://xrpl.org/.
Securities and Exchange Commission (2023). Ripple Labs Inc., No. 20-cv-10832 (S.D.N.Y. Jul. 13, 2023). Available online at: https://law.justia.com/cases/federal/district-courts/new-york/nysdce/1:2020cv10832/551082/874/ (Accessed September 04, 2025).
Sedlmeir, J., Buhl, H. U., Fridgen, G., and Keller, R. (2020). The energy consumption of blockchain technology: beyond myth. Bus. and Inf. Syst. Eng. 62 (6), 599–608. doi:10.1007/s12599-020-00656-x
Sibanda, O., Ndayizigamiye, P., and Twinomurinzi, H. (2024). Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) in healthcare: a thematic analysis and research agenda. Front. Digital Health 6, 1377531. doi:10.3389/fdgth.2024.1377531
Train, K. E. (2009). Discrete choice methods with simulation. 2nd ed. Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511805271
VitaDAO (2024a). VITA goes Optimism: reducing costs and improving accessibility. Available online at: https://www.vitadao.com/blog.
VitaDAO (2024b). Building a community-owned longevity research DAO. Available online at: https://www.vitadao.com/.
XRP Healthcare (2024). Transforming healthcare in Africa with blockchain. Available online at: https://xrphealthcare.com/.
XRP Ledger (2024). Transaction cost. Available online at: https://xrpl.org/transaction-cost.html (Accessed September 04, 2025).
YCharts (2024a). Bitcoin average transaction Fee. Available online at: https://ycharts.com/indicators/bitcoin_average_transaction_fee (Accessed September 04, 2025).
YCharts (2024b). Ethereum average transaction Fee. Available online at: https://ycharts.com/indicators/ethereum_average_transaction_fee (Accessed September 04, 2025).
Keywords: medical device tokenization, blockchain platforms, transaction costs, Monte Carlo simulation, layer-2 scaling, healthcare financing, investor participation, regulatory clarity
Citation: Peters A (2025) Regulatory dynamics and empirical evidence in medical device tokenization. Front. Blockchain 8:1649131. doi: 10.3389/fbloc.2025.1649131
Received: 18 June 2025; Accepted: 22 September 2025;
Published: 15 October 2025.
Edited by:
Andrea Pinna, University of Cagliari, ItalyReviewed by:
Ingrid Vasiliu Feltes, University of Miami, United StatesValentin Marian Antohi, Dunarea de Jos University, Romania
Ernst Wellnhofer, Berlin Technical University of Applied Sciences, Germany
Copyright © 2025 Peters. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Andreas Peters, YS5wZXRlcnM4MUBpY2xvdWQuY29t
 Andreas Peters
Andreas Peters