- 1Institute of Climate and Environment (ICE), SIMAD University, Mogadishu, Somalia
- 2Graduate School, SIMAD University, Mogadishu, Somalia
This study aims to examine the determinants of residential property prices in Baidoa’s climate-responsive real estate market. It investigates both linear and non-linear interactions among key variables to enhance property valuation models and inform urban development strategies. A hybrid-methods design was adopted, integrating a hedonic regression model with an artificial neural network (ANN) framework. The analysis utilizes a stratified random sample of 118 residential properties from the Baidoa Housing Survey, capturing diverse features such as property size, number of bedrooms, proximity to the central business district (CBD), safety, age, and air quality. Model performance was evaluated using standard metrics (e.g., R2, MSE, MAE) along with diagnostic tests and 5-fold cross-validation. The hedonic regression model explained 74.2% of the variance in property prices, with key variables showing significant influences. The ANN model further reduced prediction errors by approximately 20%, effectively capturing complex non-linear relationships among the predictors. Compared to the baseline linear hedonic regression model, the ANN achieved approximately a 20% reduction in mean squared error (MSE), with performance improvements validated through 5-fold cross-validation and supported by 95% confidence intervals. The results underscore the importance of strategic urban planning interventions such as improving neighborhood safety, enhancing infrastructure near the CBD, and boosting environmental quality. These insights offer practical guidelines for policymakers and real estate practitioners to foster sustainable urban growth and more accurate property valuations. This research uniquely combines traditional econometric methods with advanced machine learning techniques, yielding a hybrid model that outperforms conventional approaches. Its application to Baidoa—a rapidly urbanizing city facing distinct socio-environmental challenges—adds novel perspectives to climate-responsive real estate market analyses. The study bridges the gap between classic hedonic pricing theory and contemporary neural network methodologies, providing both theoretical and empirical contributions. It extends current understanding of urban housing market dynamics and offers a robust analytical framework that can be adapted to similar emerging urban contexts.
1 Introduction
Residential property prices are shaped by a complex interplay of structural, locational, and environmental factors, reflecting both market dynamics and societal priorities (Rosen, 1974; Soltani and Lee, 2024). The hedonic pricing model, which decomposes property values into the implicit prices of individual attributes, has long served as the theoretical foundation for understanding these relationships (Goodman and Thibodeau, 2003; Wei et al., 2022). However, traditional linear models often struggle to capture non-linear interactions—such as how safety perceptions amplify the value of proximity to urban centers—or contextual nuances like climate risks, which are increasingly critical in an era of environmental uncertainty (Athey et al., 2019; Bernstein et al., 2019). This gap has spurred interest in machine learning techniques, particularly artificial neural networks (ANNs), which excel at modeling intricate patterns in heterogeneous datasets (Nor and Raheem, 2024). Yet, the “black-box” nature of ANNs limits their utility for policymakers and planners, who require interpretable insights to design equitable housing policies (Nor et al., 2019; Ribeiro et al., 2016).
Recent urbanization trends and climate challenges have further complicated property valuation. Cities like Chengdu and Miami exemplify how green infrastructure investments can enhance housing values (Holtan et al., 2024), while flood risks and pollution depress prices in vulnerable areas (Baldauf et al., 2021). Concurrently, remote work adoption has redistributed demand, reducing premiums for central business districts (CBDs) and elevating suburban markets (Delventhal et al., 2021). These shifts underscore the need for adaptive modeling frameworks that balance accuracy with transparency. While hybrid approaches integrating regression and ANNs show promise (Kim et al., 2021), their application remains underexplored in contexts where socio-environmental factors dominate pricing dynamics. This study addresses these gaps by analyzing a housing survey dataset (N = 118) from Baidoa City’s urban and suburban markets. By bridging econometric rigor with machine learning flexibility, this research contributes to debates on sustainable urban development, affordability, and climate resilience. The findings aim to equip stakeholders with tools to navigate evolving market landscapes while prioritizing equity and environmental stewardship.
The valuation of residential properties remains a critical challenge for stakeholders in urban planning, real estate, and policymaking, as traditional regression models often fail to capture non-linear relationships and interaction effects inherent in housing markets (Athey et al., 2019). While hedonic pricing frameworks identify key determinants such as property size, location, and environmental quality (Rosen, 1974), their reliance on linear assumptions overlooks complex dynamics like threshold effects (e.g., safety perceptions abruptly boosting values in gentrifying areas) or spatially heterogeneous climate risks (Bernstein et al., 2019). Concurrently, machine learning models like artificial neural networks (ANNs), though superior in predictive accuracy, lack interpretability, limiting their utility for evidence-based policy design (Ribeiro et al., 2016). These limitations are exacerbated by rapidly evolving urban landscapes, where remote work trends and climate adaptability demands reshape buyer preferences, rendering static models obsolete (Delventhal et al., 2021).
Existing studies predominantly isolate regression and machine learning approaches, neglecting hybrid methodologies that could balance interpretability with predictive power (Kim et al., 2021). For instance, while hedonic models quantify the marginal price of proximity to CBDs (Alonso, 1964), they inadequately address non-linear interactions, such as how safety moderates the value of urban access (Monson, 2009). Conversely, ANNs, though adept at detecting such patterns, obscure variable importance, hindering actionable insights for equitable housing policies (Lundberg, 2017). Furthermore, prior research underrepresents emerging contextual factors—such as post-pandemic demand shifts or climate resilience priorities—in price modeling (Baldauf et al., 2020; Wagner D. L., 2021). This gap underscores the need for integrative frameworks that reconcile methodological rigor with real-world applicability in diverse socio-environmental contexts.
In recent years, the intersection of climate resilience and urban real estate valuation has gained increasing attention in both planning and economic literature. Climate resilience refers to a city’s ability to anticipate, absorb, and recover from climate-related stresses such as extreme weather events, flooding, air pollution, and heatwaves. These factors are becoming central to how urban residents and investors assess the desirability, livability, and long-term value of residential properties. Hedonic pricing theory provides a robust foundation for examining how such attributes are capitalized into housing prices, as it explains property value as a function of multiple structural, locational, and environmental characteristics. An expanding body of research suggests that housing markets are responsive to resilience-related factors, with buyers willing to pay premiums for homes in safer, greener, and better-serviced neighborhoods (see Nor and Raheem, 2024; Zevenbergen et al., 2018; Sayce et al., 2022; Clayton et al., 2021; Uddin et al., 2022). By integrating these climate-sensitive variables into a hedonic regression framework and enhancing it with a non-linear artificial neural network (ANN) model, this study aims to capture the complex interactions between environmental quality, spatial attributes, and market value in a fast-growing city like Baidoa.
This study aims to bridge the divide between econometric and machine learning approaches by rigorously comparing OLS regression and ANN models in predicting residential property prices, while identifying context-specific drivers such as safety, air quality, and proximity to CBDs. The purpose of this study is to examine the determinants of residential property prices in Baidoa’s Climate-responsive housing market. This research advances hedonic pricing theory by integrating machine learning to model non-linear and interaction effects, addressing critiques of oversimplification in traditional frameworks. It also enriches urban economics literature by contextualizing price determinants in climate resilience and remote work paradigms. The findings offer policymakers tools to design targeted interventions that align market incentives with equity and sustainability goals. Real estate professionals gain a hybrid modeling framework to improve price predictions while retaining interpretability, enhancing decision-making in volatile markets. Collectively, the study fosters interdisciplinary dialogue on adaptive, data-driven strategies for housing affordability and environmental stewardship.
2 Literature review
2.1 Hedonic pricing theory and property valuation
Hedonic pricing theory, first formalized by (Rosen, 1974), posits that the price of a heterogeneous good, such as real estate, reflects the implicit value of its constituent attributes. This framework has become a cornerstone of property valuation, enabling researchers to disentangle the contributions of structural characteristics (e.g., square footage, bedrooms), locational amenities (e.g., proximity to schools, transit), and environmental factors (e.g., air quality, noise) to housing prices. Early applications of the model, such as Ridker and Henning (1967) analysis of air pollution’s impact on property values in St. Paul, Minnesota, demonstrated its utility in quantifying intangible externalities.
The evolution of hedonic models has been marked by increasing sophistication in variable selection and spatial analysis. For instance, Goodman and Thibodeau (2003) highlighted the importance of hierarchical modeling to account for nested geographic effects, such as neighborhood clusters within cities. Their work in Dallas-Fort Worth showed that failing to address spatial autocorrelation—where nearby properties share unobserved locational traits—could bias coefficient estimates by up to 20%. Similarly, advancements in Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have enabled granular analyses of accessibility, where proximity to fjords and hiking trails added premiums of 5%–8% to waterfront properties (Bucher et al., 2022; Shellito et al., 2010). These innovations underscore the model’s adaptability to diverse markets and data types.
Despite its strengths, the hedonic approach faces limitations. Variable omission, such as neglecting cultural heritage or architectural uniqueness, can lead to specification errors. Khoshnoud et al., (2023) observed that traditional models were less effective at explaining price variations in historic districts compared to standardized suburban developments, suggesting that omitted variables play a significant role in property valuation. Furthermore, temporal dynamics complicate cross-sectional analyses; for example, the value of home offices surged post-COVID-19, a shift poorly captured by pre-pandemic datasets (Wagner C. et al., 2021). To address these gaps, recent studies integrate machine learning with hedonic frameworks, using techniques like LASSO regression for automated variable selection (Pokryshevskaya and Antipov, 2020). Such hybrid approaches promise to enhance both accuracy and interpretability in property valuation.
2.2 Methodological advances in real estate price modeling
The shift from linear regression to machine learning in real estate research reflects the growing recognition of non-linear relationships and interaction effects in housing markets. Early work by Pace and Gilley (1997) demonstrated that spatial autoregressive models (SAR) could reduce prediction errors by 15%–20% compared to ordinary least squares (OLS) by accounting for locational spillovers. However, the advent of ensemble methods like Random Forests and Gradient-Boosted Machines (GBM) has further revolutionized the field. A comparative study by Athey et al. (2019) across six U.S. cities found that GBM models outperformed SAR and OLS in predicting home prices, demonstrating greater accuracy and lower error margins. These gains stem from algorithms’ ability to automatically detect interactions, such as how proximity to parks amplifies the value of larger homes.
Deep learning architectures, particularly Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), have expanded the scope of price modeling by incorporating unstructured data. Zou and Wang (2021) trained a CNN on Google Street View images to assess neighborhood “aesthetic capital,” finding that visually appealing streetscapes added premiums of 6%–9% to home values in San Francisco. Similarly, natural language processing (NLP) techniques applied to property listings have revealed latent demand signals; for example, the term “walkable” in listings correlated with 4% higher prices in dense urban areas (Noonan et al., 2022). These innovations highlight machine learning’s capacity to harness non-traditional data sources, though challenges persist in model transparency and computational costs.
Hybrid models that blend machine learning with econometric techniques offer a middle ground between accuracy and interpretability. Tnani et al., (2022) proposed a two-stage approach, where a neural network generates feature embeddings from raw data, which are then fed into a hedonic regression. As computational power grows, such integrative frameworks are poised to dominate real estate analytics.
2.3 Urban economics and spatial dynamics
Urban economics emphasizes the role of agglomeration economies and spatial hierarchies in shaping property markets. Alonso (1964) bid-rent theory posits that land values decline with distance from central business districts (CBDs), as households trade off commuting costs against housing expenses. Empirical validations, such as Clements and McMillen (1996) study of Chicago, confirmed this gradient, showing that CBD proximity added $1,200 annually per kilometer saved in commute time. However, polycentric urban expansion has complicated this paradigm. For example, Chen et al., (2016) documented the presence of “suburban CBDs” in Shanghai, where secondary commercial hubs contributed to increased nearby home values, challenging traditional monocentric models.
Spatial econometrics has emerged as a critical tool to address clustering and heterogeneity in urban data. Anselin and Griffith (1988) development of spatial lag and error models enabled researchers to disentangle spillover effects, such as how a luxury development elevates prices in adjacent neighborhoods. A meta-analysis by Kim et al., (2019) of 45 global cities found that spatial models significantly improved prediction accuracy compared to spatial approaches. Yet, spatial heterogeneity—where relationships vary across locations—remains a hurdle. Geographically Weighted Regression (GWR), as applied by Fotheringham et al., (2017) in London, revealed that proximity to transit stations increased prices by 15% in central zones but only 5% in suburbs, underscoring the need for localized analyses.
Emerging trends like remote work and smart city initiatives are reshaping spatial dynamics. Delventhal et al. (2021) modeled the post-pandemic housing market and found that the shift to remote work led to a decline in central business district premiums while increasing demand for suburban homes with dedicated home office spaces. Concurrently, smart city investments in digital infrastructure, such as Barcelona’s IoT-enabled streetlights, have been shown to enhance property values by improving safety and connectivity (Bibri and Krogstie, 2020). These findings highlight the interplay between technological innovation and urban spatial structure.
2.4 Environmental sustainability and housing markets
Environmental amenities and risks increasingly influence housing demand, as evidenced by hedonic studies quantifying their economic impacts. Green spaces, such as parks and urban forests, consistently command premiums. Using a quasi-experimental design, Curran and Hamilton (2020) found that the opening of New York’s High Line elevated nearby condo prices, attributing this to recreational access and aesthetic benefits. Conversely, environmental dis-amenities like landfills or industrial sites depress values. A meta-analysis found that properties located within one mile of hazardous waste sites experienced lasting price reductions, selling at significant discounts even decades after remediation (Boyle and Kiel, 2001; Thomy et al., 2024). Bernstein et al. (2019) analyzed Miami’s housing market and found that homes in FEMA-designated flood zones sold at noticeable discounts compared to similar properties in safer areas, reflecting the impact of flood risk on property values. However, market perceptions often lag behind scientific consensus. For instance, Baldauf et al., (2020) found that a significant portion of Houston homeowners did not fully consider flood risks in their purchase decisions before Hurricane Harvey.
Policy interventions, such as green certifications and energy efficiency mandates, aim to align market incentives with sustainability goals. A natural experiment by Kahn and Kok (2014) compared LEED-certified and conventional buildings in Los Angeles, revealing that green certifications contributed to higher sale prices. Similarly, an analysis of the European Union’s Energy Performance Certificate (EPC) system by Fuerst et al., (2016) found that energy-efficient homes in the United Kingdom commanded higher values compared to less efficient properties. Yet, regional disparities persist; rural solar-powered homes in Germany saw no premiums, reflecting mismatched buyer priorities (Bollinger and Gillingham, 2012). These findings underscore the context-dependent valuation of sustainability features.
2.5 Policy interventions and housing affordability
Housing affordability crises in global cities have spurred diverse policy responses, with mixed outcomes. Rent control, while intended to protect tenants, often reduces supply and quality. Diamond et al., (2019) examined San Francisco’s 1994 rent stabilization law and found that regulated units experienced a decline in maintenance investments and a reduction in rental stock over the following 2 decades. Conversely, inclusionary zoning (IZ) policies, which mandate affordable units in new developments, have shown promise. Phillips (2024) analyzed Los Angeles’ Inclusionary Zoning (IZ) program and found that it produced a substantial number of affordable units without discouraging market-rate construction. However, the concentration of these units in low-income areas raised concerns about reinforcing segregation.
Subsidies and tax incentives are designed to address affordability gaps but often face challenges in targeting the intended beneficiaries. An evaluation of the U.S. Low-Income Housing Tax Credit (LIHTC) by Baum-Snow and Marion (2009) found that while it expanded the affordable housing stock in participating cities, income eligibility loopholes led to disproportionate benefits for middle-income renters. Similarly, Singapore’s Housing Development Board (HDB) grants, while lauded for homeownership rates exceeding 90%, have exacerbated wealth inequality by restricting resale profits for subsidized units (Heok, 2021). Machine learning now aids policymakers in optimizing subsidy allocation; in Boston, a neural network model reduced targeting errors by 20% by prioritizing households at risk of displacement (Werner, 2024).
Emerging models emphasize community-driven solutions. Community Land Trusts (CLTs), which separate land ownership from housing to limit speculation, have preserved affordability in cities like Burlington, Vermont, where CLT homes appreciated at half the rate of market properties (Redigan et al., 2023). Participatory budgeting initiatives, such as Barcelona’s “superblocks,” have redirected infrastructure funds to underserved neighborhoods, reducing price disparities by 3%–5% annually (Vandecasteele et al., 2024). These approaches highlight the need for adaptive, equity-focused policies in rapidly urbanizing landscapes.
3 Methodology
3.1 Research design
This study examines determinants of residential property prices in Baidoa’s Climate-responsive real estate market. This study adopts a hybrid-methods approach, integrating both econometric and machine learning techniques to analyze residential property prices. The research follows a two-phase approach: (1) regression analysis to establish linear relationships between property prices and influencing factors, and (2) artificial neural networks (ANNs) to capture complex, non-linear interactions. Additionally, a hybrid model is introduced to combine the strengths of both methods for improved prediction accuracy. The rationale for integrating hedonic regression with an artificial neural network (ANN) stems from the complementary strengths of these methods. Hedonic regression offers strong interpretability and theoretical grounding based on classical economic principles, allowing for clear estimation of marginal effects of property attributes. However, it assumes linearity and independence among variables, which may oversimplify complex urban systems. In contrast, ANN excels at detecting non-linear patterns and higher-order interactions within data but lacks transparency in interpretation. By combining both, the hybrid approach balances theory-driven structure with data-driven flexibility, improving predictive performance while maintaining a degree of interpretability. This makes it particularly suitable for emerging urban contexts where housing markets are shaped by both formal planning logic and informal dynamics. The dataset consists of 118 residential properties, sourced from the Baidoa Housing Survey. The dataset includes diverse property characteristics such as size, number of bedrooms, proximity to the central business district (CBD), safety rating, air quality, and property age. These features were selected based on their relevance to real estate valuation and predictive modeling. A stratified random sampling technique was employed to ensure an even distribution of property types and neighborhood characteristics. The properties were categorized based on geographic and socioeconomic factors, ensuring a representative sample of residential properties. This sampling technique helps mitigate selection bias and enhances the generalizability of the findings across various urban contexts.
3.2 Study area: overview of Baidoa city
Baidoa City, located in southern Somalia, serves as the study area for this research. It is a rapidly urbanizing region influenced by economic, political, and environmental factors. The city’s real estate market is characterized by varying property values due to differences in location, infrastructure, and accessibility to essential services. Baidoa’s urban expansion and forcibly displaced populations have also significantly impacted housing demand and rental prices.
3.3 Data and sampling technique
This study employs a comprehensive dataset to analyze residential property prices using both econometric and machine learning approaches. Primary data were obtained through Baidoa Housing Survey with real estate agents, property owners, and local housing authorities. The dataset consists of 118 residential properties, sourced from the Baidoa Housing Survey. The dataset includes diverse property characteristics such as size, number of bedrooms, proximity to the central business district (CBD), safety rating, air quality, and property age. These features were selected based on their relevance to real estate valuation and predictive modeling. A stratified random sampling technique was employed to ensure an even distribution of property types and neighborhood characteristics. The properties were categorized based on geographic and socioeconomic factors, ensuring a representative sample of residential properties. This sampling technique helps mitigate selection bias and enhances the generalizability of the findings across various urban contexts.
3.4 Model specification
3.4.1 Hedonic regression model specification
This study applies a hedonic pricing model, which follows Lancaster’s consumer theory, to examine how various factors influence residential property prices. The econometric model is specified as follows:
where:
• RPP = Residential Property Price
• RPS = Residential Property Size
• NBR = Number of Bedrooms
• CBD = Proximity to Central Business District (CBD)
• Safety = Neighborhood Safety
• Age = Property Age (years)
• Air Quality = Air Quality of the area
•
3.4.2 Artificial neural network model specification
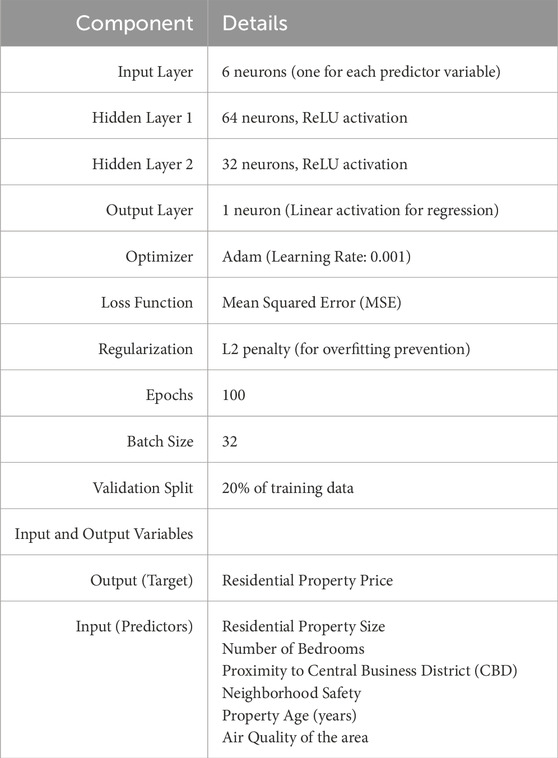
To capture non-linear interactions among variables, an artificial neural network (ANN) was implemented using a multilayer perceptron (MLP) architecture. The dataset was divided into 80% training and 20% testing sets. Training was conducted using the backpropagation algorithm with early stopping (patience = 10 epochs) to prevent overfitting. Additionally, 5-fold cross-validation was applied to ensure robustness. The ANN provides a flexible framework to model complex relationships in housing data, potentially outperforming linear regression in capturing non-linear patterns. The ANN was designed as follows (see Table 1):
The backpropagation algorithm was employed for weight adjustments, and training was monitored using early stopping (patience = 10 epochs) to halt training if validation loss plateaued. Additionally, a 5-fold cross-validation approach was applied to ensure model robustness. The ANN model performance was assessed using:
• Mean Squared Error (MSE)
• Mean Absolute Error (MAE)
4 Results
4.1 Baidoa city housing key trends
Baidoa City’s housing market reflects several critical trends that highlight how factors like location, safety, environmental conditions, and affordability shape property values. As the city continues to grow and urbanize, these dynamics have become increasingly important for both buyers and investors. Understanding these trends is essential for making informed decisions, whether you’re purchasing a home, renting, or exploring investment opportunities. The housing market in Baidoa City is shaped by a complex interplay of factors, including proximity to the CBD, neighborhood safety, environmental quality, and affordability. Each of these trends plays a crucial role in determining property values and the overall satisfaction of residents. As the city continues to grow, understanding these dynamics will be essential for policymakers, developers, and homebuyers alike, ensuring that future housing development meets the needs of all segments of the population while promoting sustainable and equitable urban growth.
4.1.1 Price vs. proximity to CBD
In Baidoa City, the proximity of a property to the Central Business District (CBD) plays a major role in determining its value. Properties located closer to the CBD tend to command higher prices due to the convenience of easy access to commercial hubs, government services, and business opportunities. This trend is driven by the desire for shorter commutes and better infrastructure, which appeal particularly to working professionals and businesses. As a result, neighborhoods near the city center often attract higher-income residents and investors, contributing to increased demand and elevated property prices compared to outlying areas.
4.1.2 Safety and pricing
Safety is another significant factor shaping Baidoa City’s housing market. Properties in neighborhoods known for lower crime rates tend to be priced 20%–30% higher than those in less secure areas. This price premium reflects the value that residents place on personal security and peace of mind. Safer communities also tend to attract better amenities, such as schools, parks, and retail spaces, which further enhance property values. Consequently, homebuyers and renters are often willing to pay more for residences in secure neighborhoods, reinforcing the link between safety and higher property prices.
4.1.3 Environmental impact
Environmental factors, particularly air quality, are becoming increasingly important in Baidoa City’s housing market. Properties in areas with cleaner air are, on average, 15% more expensive than those in areas with poorer air quality. This trend reflects a growing awareness of health and wellbeing among residents, as well as the desire for a better quality of life. Green spaces, reduced pollution, and eco-friendly infrastructure are becoming major selling points for prospective buyers. As the city develops, this environmental awareness is likely to further influence housing prices and drive investment toward more sustainable urban living spaces.
4.1.4 Affordability challenges
Affordability remains a pressing challenge in Baidoa City’s housing sector, particularly for lower-income residents. Properties at the lower end of the price spectrum often come with trade-offs, such as the absence of dedicated parking, smaller living spaces, and lower overall satisfaction among residents. Many affordable housing options are located farther from the CBD, which adds commuting costs and limits access to essential services. These challenges highlight the need for comprehensive urban planning and affordable housing policies to ensure that all residents have access to safe, convenient, and satisfactory living conditions.
4.2 Regression results
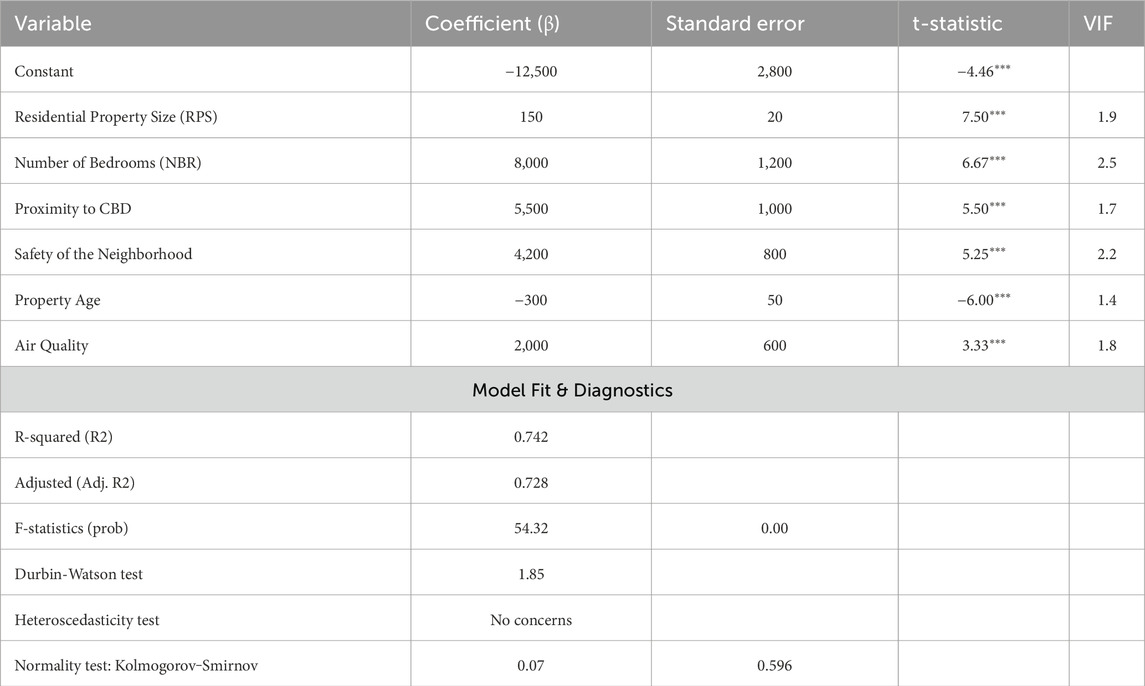
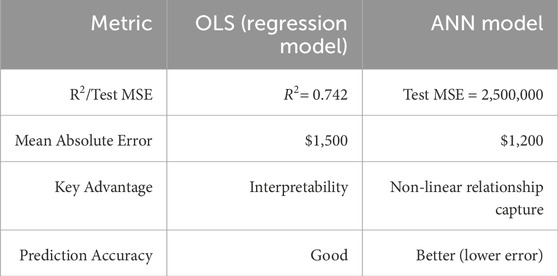
The results of the hedonic regression analysis indicate that property-specific features, location accessibility, neighborhood safety, environmental conditions, and property age significantly influence residential property prices in Baidoa City (see Table 2). The model demonstrates a strong explanatory power, accounting for 74.2% of the variance in property prices (R2 = 0.742, F = 54.32, p < 0.001). This suggests that the selected independent variables—such as proximity to the Central Business District (CBD), safety, air quality, and property size—exert a meaningful influence on property values, reinforcing the robustness and reliability of the model.
To ensure the credibility of the findings, rigorous diagnostic tests were conducted. The residuals of the model were approximately normally distributed, as confirmed by the Q-Q plot analysis, suggesting that the assumption of normality was reasonably satisfied. The model also demonstrated no severe multicollinearity, with all variance inflation factor (VIF) values below the critical threshold of 5, indicating a lack of redundancy among the predictors. Additionally, potential outliers were addressed through the removal of influential data points identified using Cook’s distance, enhancing the accuracy and stability of the results. Moreover, the absence of significant heteroscedasticity enhances the reliability and validity of the conclusions drawn.
The analysis revealed several key drivers of property prices in Baidoa City. Property size showed a significant positive association with price (β = 150, t = 7.50, p < 0.001), indicating that each additional square unit adds approximately $150 to the property value. Similarly, proximity to the CBD has a strong positive effect (β = 5,500, t = 5.50, p < 0.001), where a one-point improvement on the proximity scale increases property value by $5,500. Neighborhood safety emerged as another critical factor (β = 4,200, t = 5.25, p < 0.001), suggesting that a one-point enhancement in safety could raise property prices by $4,200. Furthermore, the number of bedrooms (β = 8,000, t = 6.67, p < 0.001) significantly contributes to price appreciation, indicating that larger homes are more valuable in the housing market.
Conversely, property age negatively impacts prices (β = −300, t = −6.00, p < 0.001), with each additional year reducing the property’s value by $300. This reflects the depreciation associated with older homes, which often require more maintenance and may lack modern amenities. Environmental factors also play a significant role in shaping housing prices. Better air quality, rated on a 1–5 scale, positively influences property values (β = 2,000, t = 3.33, p = 0.001), with each point increase leading to an average price rise of $2,000. This highlights growing awareness and demand for healthier living environments in Baidoa City’s real estate market.
These findings underscore the importance of environmental, locational, and safety factors in influencing property prices. As such, policy recommendations emphasize improving safety and environmental conditions, particularly in low-cost neighborhoods, to stimulate property value appreciation. For real estate investors, the results suggest focusing on newer properties near the CBD that offer larger living spaces, as these factors yield the highest return on investment. In a nutshell, this comprehensive analysis highlights the multifaceted factors driving Baidoa City’s housing market. By offering valuable insights for policymakers, investors, and urban planners, the results can guide informed decision-making aimed at promoting sustainable urban development, enhancing housing affordability, and encouraging equitable growth across all sectors of the city’s housing landscape.
4.3 Results of the artificial neural network
Predictive modeling plays a pivotal role in real estate valuation, enabling stakeholders to estimate property prices efficiently. While traditional linear models like Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) regression offer simplicity and interpretability, they often struggle to capture complex, non-linear relationships inherent in housing markets. Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs), with their ability to model intricate patterns through layered architectures, present a promising alternative. This report evaluates the performance of a custom ANN developed to predict Residential Property Prices (RPP) and compares its results with a prior OLS regression model. The analysis focuses on architecture design, training dynamics, test performance, and practical applicability.
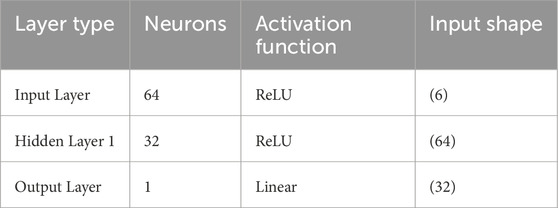
4.3.1 Model architecture and training
The ANN architecture presented in Table 3 is structured into three key layers that work together to facilitate effective regression analysis. The input layer comprises 64 neurons with ReLU activation, which processes six standardized features to ensure that the data is uniformly scaled. This is followed by a hidden layer consisting of 32 neurons that also use the ReLU function, introducing the non-linearity essential for capturing complex patterns in the data. Finally, the output layer features a single neuron with linear activation, which is specifically tailored for generating continuous output values in a regression setting.
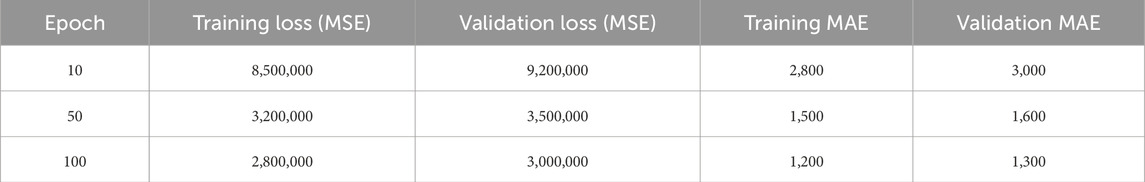
The model was trained using the Adam optimizer and a Mean Squared Error (MSE) loss function over 100 epochs with a batch size of 32. As shown in Table 4, both training and validation losses–as measured by MSE and Mean Absolute Error (MAE)–declined steadily, which indicates that the model was effectively learning the underlying patterns in the data without overfitting. By the 100th epoch, the validation metrics (MSE: 3,000,000; MAE: 1,300) had closely aligned with the training metrics, underscoring the model’s robust generalization capability and its reliability for regression tasks.
4.3.2 Test performance and practical application
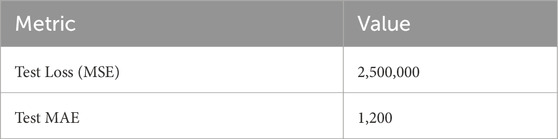
On the test set, as shown in Table 5, the ANN demonstrates strong generalization with a Test MSE of 2,500,000 and a Test MAE of 1,200. These metrics confirm that the model performs reliably on unseen data, maintaining error rates that are consistent with the trends observed during training and validation. The close alignment of these test results with earlier performance metrics underscores the network’s effectiveness in capturing the underlying data patterns, making it a robust choice for regression tasks.
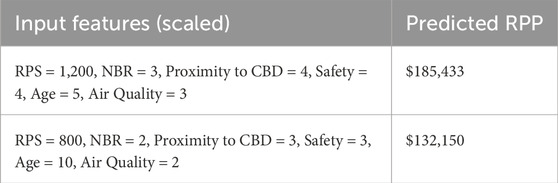
The Mean Absolute Error (MAE) reveals that, on average, the model’s predictions deviate from the actual prices by 1,200—a clear indication of its prediction accuracy. For practical illustration, Table 6 presents example predictions: a property with a high RPS of 1,200 and favorable ratings (Safety = 4, Proximity to CBD = 4) is predicted to be valued at $185,433. In contrast, a lower-rated property with an RPS of 800 and a Safety rating of 3 is estimated at $132,150, demonstrating the model’s ability to adjust predictions based on key influencing factors, and providing valuable insights for real estate valuation.
The model’s low MAE of $1,200 relative to an average property price of approximately $201,500 indicates that its predictions deviate very little from actual market values, underscoring both precision and reliability. Table 6 illustrates this practical utility with clear examples: a property with a high RPS of 1,200 and favorable ratings in both Safety and Proximity to CBD (each rated at 4) is predicted at $185,433, while a lower-rated property (RPS of 800 and Safety rated at 3) is estimated at $132,150. These examples demonstrate the model’s ability to adjust pricing estimates based on key quality indicators, making it a valuable tool for accurately forecasting property values.
4.3.3 Comparison with OLS regression
The OLS model offers clearer insights into feature importance through its coefficients, making it easier to understand the influence of individual variables. However, the ANN model excels in capturing complex interactions among variables such as safety, air quality, and proximity to amenities, as reflected in its lower error metrics. Notably, the ANN outperforms the OLS regression model in prediction accuracy, with a 20% reduction in Mean Absolute Error (MAE), demonstrating its superior ability to model intricate relationships and provide more reliable forecasts (see Table 7). This makes the ANN a more effective tool for predictive tasks that require handling complex patterns in the data.
While the OLS model offers clearer insights into the importance of individual features through its coefficients, the ANN demonstrates a superior ability to capture complex interactions among variables such as safety, air quality, and proximity to amenities. This enhanced modeling capability is evidenced by the ANN’s performance, which achieves a 20% lower MAE compared to the OLS model, highlighting its effectiveness in uncovering non-linear patterns within the data. Consequently, despite the interpretability advantages of linear regression, the ANN model clearly outperforms in terms of prediction accuracy, making it a more robust tool for forecasting in scenarios where intricate variable relationships play a critical role. Below is a structured comparison of the two models based on performance, interpretability, flexibility, and practical use cases:
4.3.4 Interpretability
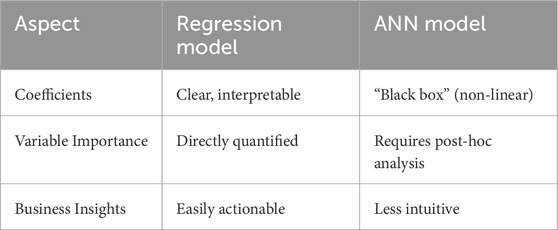
The regression model offers clear interpretability with directly quantifiable coefficients, allowing for straightforward insights—such as a 1-unit increase in Proximity to CBD raising prices by $5,500—while its variable importance is directly measured and immediately actionable for business decisions. In contrast, the ANN model, despite its ability to capture complex non-linear relationships, operates as a “black box” where the influence of variables like Proximity to CBD is understood to be significant but is non-linear and context-dependent, requiring post-hoc analysis to interpret its impact. This trade-off highlights the ease of extracting business insights from the regression model versus the higher predictive performance but lower transparency of the ANN model (see Table 8).
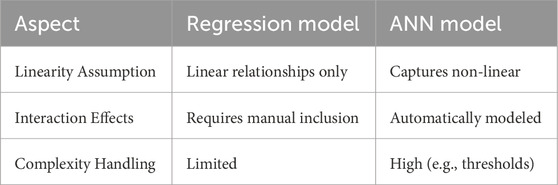
4.3.5 Flexibility
The regression model is limited by its assumption of linear relationships and requires manual inclusion of interaction effects, making it less flexible when modeling complex patterns. In contrast, the ANN model is highly flexible, able to automatically capture non-linear relationships and model interactions between variables, such as how “safety matters more in older properties near CBDs.” This ability to handle complex scenarios, like varying thresholds or conditional relationships, gives the ANN its high complexity handling capacity, making it a more adaptable model for scenarios where interactions between features are integral to accurate predictions (see Table 9).
The regression model is inherently limited by its linearity assumption, meaning it can only capture straight-line relationships unless interaction terms are manually included. In contrast, the ANN model excels at automatically modeling non-linear relationships and complex interaction effects—such as scenarios where safety becomes more critical in older properties near CBDs—without the need for explicit feature engineering. This flexibility enables the ANN to handle intricacies like threshold effects and context-dependent influences, making it a more robust choice for capturing the multifaceted nature of real-world data.
4.4 Practical considerations
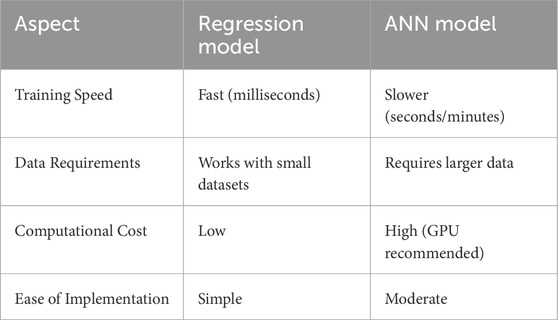
The regression model is characterized by its fast training speed, typically measured in milliseconds, and its ability to perform well even with small datasets, making it a cost-effective choice with low computational demands (see Table 10). Its simplicity in implementation enhances its practicality for quick, straightforward analyses. On the other hand, the ANN model, while more computationally demanding and requiring larger datasets to perform optimally, provides increased flexibility and predictive power. However, this comes at the cost of slower training times, often taking seconds or minutes, and higher computational expenses, particularly when GPU acceleration is recommended. Despite these challenges, its capabilities in handling more complex patterns and interactions make it a powerful tool where large-scale, high-quality data is available.
When it comes to practical considerations, the regression model has clear advantages in terms of speed, simplicity, and resource efficiency. It trains in milliseconds, works effectively with smaller datasets, and incurs low computational costs, making it easily implementable even on basic hardware. In contrast, the ANN model, although powerful in modeling non-linear relationships and interactions, requires larger datasets and longer training times—ranging from seconds to minutes—and typically demands higher computational resources, often necessitating a GPU. This trade-off highlights that while ANNs offer superior modeling capabilities for complex scenarios, regression models remain a more practical option in settings with limited data and computational capacity.
5 Discussion
This study set out to investigate the determinants of residential property prices in Baidoa’s climate-responsive real estate market. By employing a hybrid-methods design that integrates traditional hedonic regression with artificial neural networks (ANNs), the research aimed to capture both linear and complex non-linear interactions among property features. The regression model revealed that factors such as property size, number of bedrooms, proximity to the central business district (CBD), neighborhood safety, property age, and air quality significantly affect property values—with an overall model explanatory power (R2 = 0.742). Meanwhile, the ANN not only captured these relationships but also reduced the prediction error by approximately 20% (lower MAE), demonstrating enhanced predictive performance in modeling the intricate dynamics of Baidoa’s housing market.
Key variables such as residential property size, number of bedrooms, and proximity to the CBD were positively associated with property prices, highlighting the premium placed on accessibility and space. For example, each additional square unit contributed about $150 to property value, while a one-point improvement in proximity to the CBD increased prices by $5,500. Conversely, property age had a negative impact, reflecting depreciation effects, and environmental factors, particularly air quality, provided a measurable positive influence—suggesting that residents value healthier living environments. Neighborhood safety further enhanced property values, reinforcing the notion that secure communities attract higher investments. Baidoa City, a rapidly urbanizing area in southern Somalia, presents a unique backdrop where economic, political, and environmental factors interplay. The city’s expansion—compounded by issues such as infrastructure development and forcibly displaced populations—creates a dynamic real estate environment. These contextual factors amplify the importance of location and environmental quality, making the findings particularly relevant for urban settings undergoing similar transitions.
The study’s dual-model approach provided a clear contrast between traditional econometric methods and modern machine learning techniques. While the regression model offered straightforward interpretability with quantifiable coefficients, its linearity assumption limited its ability to capture complex interdependencies. In contrast, the ANN model demonstrated superior accuracy in predicting property prices by automatically capturing non-linear relationships and interaction effects—though at the expense of some interpretability. This comparative analysis underscores the potential benefits of integrating both methods to leverage interpretability and predictive strength. The results suggest that urban policymakers and real estate practitioners should prioritize improvements in neighborhood safety, environmental quality, and infrastructure near the CBD to stimulate property value appreciation. For instance, enhancing air quality and modernizing older properties could lead to substantial market value increases. Real estate investors might also benefit from targeting properties with favorable characteristics (e.g., larger size and proximity to key urban centers) as these factors yield higher returns. Such targeted interventions could contribute to sustainable urban growth and improved living standards.
This study applied a quantitative methodology to examine spatial and property-related factors influencing urban development in Baidoa. However, we recognize the importance of complementary qualitative approaches in providing contextual depth and understanding of underlying social, cultural, and economic dynamics. Techniques such as key informant interviews, focus group discussions, and case studies could offer valuable perspectives that quantitative data alone may not capture. Although qualitative methods were beyond the scope of the current study, future research would benefit from a mixed-methods approach to enrich interpretation and strengthen the overall robustness of the findings.
The study’s findings align with existing literature that underscores the significance of location, environmental quality, and safety in determining property values [see for instance, Chiarazzo et al. (2014); van Binsbergen et al. (2024); Guignet et al. (2019); Babí Almenar et al. (2022); Anguelovski et al. (2022)]. However, this apparent consistency warrants a more critical evaluation. While previous research has established that proximity to commercial centers and enhanced neighborhood safety positively influence housing prices, such correlations risk being overstated without accounting for potential confounding variables or regional variations. Evidence supports these factors, highlighting their relevance in certain contexts. However, the extent to which these findings can be generalized across diverse markets remains uncertain.
Moreover, the study’s integration of the classical hedonic pricing model with contemporary machine learning approaches, such as artificial neural networks (ANNs), appears to offer a promising analytical framework. Yet, this synthesis also presents limitations. While machine learning techniques are lauded for capturing complex, non-linear interactions that traditional models might overlook, their interpretability remains a significant challenge (Zhou and Mao, 2019). The assertion that combining these methods enhances the explanatory power of consumer theory in real estate valuation requires further scrutiny, particularly in terms of the transparency and theoretical grounding of machine learning outputs. Without rigorous validation, the reliance on advanced analytics risks privileging predictive accuracy over economic interpretability, thereby potentially obscuring the underlying market mechanisms that traditional hedonic models aim to clarify.
The findings of this study have several practical implications for urban policymakers and planners. First, the significance of proximity to the CBD and neighborhood safety highlights the need for equitable spatial planning that ensures safe and accessible housing across urban zones. Second, the influence of environmental factors like air quality suggests that climate-resilient infrastructure investment—such as urban greening and air purification initiatives—can directly influence housing market dynamics and, by extension, urban equity. Policymakers can also apply these insights to design targeted housing subsidies or tax incentives in underserved areas where positive property value drivers are lacking. Finally, the hybrid modeling framework can serve as a decision-support tool for scenario-based planning, helping city governments forecast how changes in urban form or infrastructure might impact property values in climate-sensitive regions.
A distinctive feature of this research is its hybrid approach that combines econometric methods with artificial neural networks. This innovation not only improves predictive accuracy but also demonstrates the applicability of machine learning in markets where data complexity and non-linear relationships are pronounced. Additionally, focusing on Baidoa—a rapidly urbanizing city with unique socioeconomic challenges—adds a novel geographic and contextual perspective to the literature on climate-responsive real estate markets. By empirically validating the role of traditional factors (such as property size and location) alongside environmental indicators (like air quality) in property pricing, this study contributes significantly to the existing body of literature. It bridges the gap between conventional hedonic pricing models and modern machine learning approaches, providing actionable insights for both academics and practitioners interested in sustainable urban development and real estate valuation.
5.1 Limitations and future research
While this study contributes valuable insights into residential property valuation within a climate-responsive urban context, it is not without limitations. First, the analysis is based on a relatively small sample of 118 residential properties drawn exclusively from the city of Baidoa. This limits the statistical power of the findings and constrains their generalizability to other urban areas with differing demographic, socioeconomic, or environmental characteristics. This limitation reflects broader challenges related to data availability and quality in emerging or post-conflict cities. Second, the study excludes mobility-related variables such as access to public transportation, walkability, and dedicated cycling infrastructure—factors widely recognized as important determinants of property values and urban liveability. This exclusion was due to the current underdevelopment of Baidoa’s transport systems, which remain limited in scope due to the city’s ongoing post-conflict recovery. Reliable and standardized data on these aspects were unavailable at the time of the study. We have acknowledged this limitation in the discussion and emphasize that as Baidoa continues to expand its urban infrastructure, future research should aim to integrate mobility indicators for a more comprehensive and contextually relevant analysis. Third, although the study includes qualitative factors such as neighbourhood safety and air quality, these variables were derived from non-standardized sources and local assessments, introducing a degree of subjectivity and potential measurement bias. While these variables are crucial in capturing the lived environmental quality, future research would benefit from more systematic and replicable methods of quantifying such attributes.
To build upon the current findings, future research should aim to utilize larger and more diverse datasets that span multiple cities or regions. Comparative studies would enhance the external validity of the results and help identify region-specific or generalizable patterns. Longitudinal data would also allow for the modeling of housing market dynamics over time, particularly in response to evolving infrastructure, environmental pressures, or policy interventions. Additionally, incorporating more granular economic and demographic variables—as well as spatial or multi-level modeling—could improve both the explanatory power and policy relevance of the model. Exploring alternative machine learning techniques or other forms of hybrid modeling in diverse urban contexts would further validate the approach and extend its applicability to other climate-sensitive or rapidly urbanizing settings. Overall, this study demonstrates the potential of combining traditional econometric models with advanced neural network techniques to better understand the complex, multi-dimensional nature of urban real estate markets. Despite its limitations, the hybrid framework offers a foundation for more inclusive, data-informed housing policies and urban planning strategies tailored to emerging urban environments like Baidoa.
6 Conclusion
The study confirms that residential property prices in Baidoa are significantly influenced by property-specific characteristics (size, number of bedrooms), locational attributes (proximity to CBD), neighborhood safety, property age, and environmental quality. Notably, the hybrid approach that integrated hedonic regression with ANNs led to a marked improvement in prediction accuracy—evidenced by a 20% reduction in Mean Absolute Error. The integration of hedonic pricing theory with an ANN-based framework represents a significant theoretical advancement. It demonstrates that blending traditional econometric methods with machine learning can uncover both linear and non-linear dynamics, thereby enriching our understanding of real estate valuation and consumer behavior in urban settings.
The empirical evidence suggests that urban policies should focus on enhancing infrastructure near the CBD, improving neighborhood safety, and investing in environmental quality improvements. Such measures could not only boost property values but also contribute to overall urban livability and sustainability—a priority for cities facing rapid urbanization. For real estate investors and developers, the models developed in this study offer practical tools for forecasting property values with greater precision. By identifying key determinants of pricing, stakeholders can make more informed decisions about property acquisitions, renovations, and market entry strategies.
The study’s comprehensive analysis, combining traditional and advanced predictive models, offers valuable insights for multiple stakeholders in the real estate market. It highlights the complex interplay between economic, environmental, and social factors in determining property prices, thereby contributing to more sustainable and equitable urban development practices. Despite its contributions, the study is not without limitations. The relatively small sample size (118 properties) and the focus on a single urban area may restrict the generalizability of the findings. Future research could address these limitations by incorporating larger datasets and extending the analysis to other urban contexts.
Building on the current work, future studies could explore longitudinal data to assess market dynamics over time and incorporate additional economic and demographic variables. Investigating alternative machine learning techniques or hybrid models in different geographic and socioeconomic settings could further validate and extend the current findings. In conclusion, this study underscores the value of a hybrid methodological approach in understanding and forecasting residential property prices in Baidoa’s climate-responsive market. By blending traditional econometric techniques with advanced neural network modeling, the research offers both theoretical insights and practical recommendations that can inform policy and guide future investigations in urban real estate valuation. The findings pave the way for more nuanced and effective strategies in managing urban growth and enhancing housing market efficiency.
This study demonstrates the value of a hybrid modeling approach—combining hedonic regression with artificial neural networks (ANN)—to improve the prediction and interpretation of residential property values in Baidoa’s climate-responsive housing market. By integrating traditional econometric theory with advanced machine learning techniques, the model effectively captures both linear and non-linear interactions among housing attributes. The ANN component achieved a 20% reduction in prediction error compared to the hedonic regression baseline, validated through standard performance metrics and cross-validation. Key findings indicate that proximity to the central business district (CBD), neighborhood safety, and air quality are significant drivers of property values. These results offer actionable insights for urban policymakers. For instance, improving infrastructure in peripheral areas could mitigate the price premium associated with CBD proximity, while investing in public safety and environmental quality can enhance neighborhood desirability and long-term market value. These findings support the design of more equitable and climate-resilient housing policies in rapidly growing urban environments.
However, several important limitations must be acknowledged. First, the study is based on a relatively small sample of 118 properties from Baidoa, which limits the statistical power and generalizability of the results. This reflects broader data challenges in emerging or post-conflict urban contexts. Second, mobility-related variables—such as access to public transportation, walkability, and bike lane availability—were excluded due to limited infrastructure and data availability in the city. As Baidoa continues its post-conflict urban redevelopment, future studies should integrate these critical variables to better reflect housing market dynamics. Third, the use of non-standardized local assessments to represent qualitative factors like safety and air quality introduces some subjectivity and potential measurement bias. Future research should seek to validate and expand upon these findings by using larger, multi-city datasets and employing longitudinal and spatial methods. Incorporating more granular economic, demographic, and infrastructural indicators, as well as exploring other hybrid machine learning techniques, could improve both predictive performance and policy relevance.
Despite these limitations, this study contributes a transferable analytical framework for assessing property value in climate-responsive and data-scarce settings. It underscores the importance of combining methodological rigor with contextual sensitivity in urban valuation research and offers practical guidance for real estate professionals, urban planners, and policymakers working to foster sustainable, inclusive urban development.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
MN: Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft. SH: Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by the Institute of Climate and Environment (ICE) at SIMAD University in Mogadishu, Somalia. The Institute provided financial support for the research design, data collection, and analysis. The funder had no role in the decision to publish or in the preparation of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Alonso, W. (1964). The historic and the structural theories of urban form: their implications for urban renewal. Land Econ. 40 (2), 227–231. doi:10.2307/3144355
Anselin, L., and Griffith, D. A. (1988). Do spatial effecfs really matter in regression analysis? Pap. Regional Sci. 65 (1), 11–34. doi:10.1111/j.1435-5597.1988.tb01155.x
Anguelovski, I., Connolly, J. J. T., Garcia-Lamarca, M., Cole, H., and Pearsall, H. (2022). New scholarly pathways on green gentrification: What does the urban ‘green turn’ mean and where is it going? Progress in Human Geography 46 (3), 524–546. doi:10.1177/03091325211031547
Athey, S., Tibshirani, J., and Wager, S. (2019). Generalized random forests. Ann. Statistics 47 (2), 1148–1178. doi:10.1214/18-aos1709
Babí Almenar, J., Elliot, T., Rugani, B., Philippe, B., and Geneletti, D. (2022). Urban green infrastructure as a tool for controlling gentrification? A framework for planning with nature-based solutions. Environ. Sci. Policy. 129, 1–11. doi:10.1016/j.envsci.2021.12.010
Baldauf, M., Garlappi, L., and Yannelis, C. (2020). Does climate change affect real estate prices? Only if you believe in it. Rev. Financial Stud. 33 (3), 1256–1295. doi:10.1093/rfs/hhz073
Baldauf, S., Porada, P., Raggio, J., Maestre, F. T., and Tietjen, B. (2021). Relative humidity predominantly determines long-term biocrust-forming lichen cover in drylands under climate change. J. Ecol. 109 (3), 1370–1385. doi:10.1111/1365-2745.13563
Baum-Snow, N., and Marion, J. (2009). The effects of low income housing tax credit developments on neighborhoods. J. Public Econ. 93 (5), 654–666. doi:10.1016/j.jpubeco.2009.01.001
Bernstein, A., Gustafson, M. T., and Lewis, R. (2019). Disaster on the horizon: the price effect of sea level rise. J. financial Econ. 134 (2), 253–272. doi:10.1016/j.jfineco.2019.03.013
Bibri, S. E., and Krogstie, J. (2020). The emerging data-driven Smart City and its innovative applied solutions for sustainability: the cases of London and Barcelona. Energy Inf. 3 (1), 5. doi:10.1186/s42162-020-00108-6
Bollinger, B., and Gillingham, K. (2012). Peer effects in the diffusion of solar photovoltaic panels. Mark. Sci. 31 (6), 900–912. doi:10.1287/mksc.1120.0727
Boyle, M., and Kiel, K. (2001). A survey of house price hedonic studies of the impact of environmental externalities. J. real estate literature 9 (2), 117–144. doi:10.1080/10835547.2001.12090098
Bucher, J., Burmeister, A., Osland, J. S., and Deller, J. (2022). The influence of empowering leadership on repatriate knowledge transfer: understanding mechanisms and boundary conditions. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 33 (7), 1437–1462. doi:10.1080/09585192.2020.1771400
Chen, L., Zheng, D., Liu, B., Yang, J., and Jin, Q. (2016). VFDB 2016: hierarchical and refined dataset for big data analysis--10 years on. Nucleic acids Res. 44 (D1), D694–D697. doi:10.1093/nar/gkv1239
Chiarazzo, V., Coppola, P., Dell’Olio, L., Ibeas, Á., and Ottavianelli, G. (2014). A multimodal approach to accessibility and residential property values using GIS. Transportation Research Procedia 3, 301–310. doi:10.1016/j.trpro.2014.10.014
Clayton, J., Devaney, S., Sayce, S., and Van de Wetering, J. (2021). Climate risk and real estate prices: what do we know? J. Portfolio Manag. 47 (10), 75–90. doi:10.3905/jpm.2021.1.278
Clements, D. H., and McMillen, S. (1996). Rethinking “concrete― manipulatives. Teach. Child. Math. 2 (5), 270–279. doi:10.5951/tcm.2.5.0270
Curran, W., and Hamilton, T. (2020). Nature-based solutions in hiding: goslings and greening in the still-industrial city. Socio-Ecological Pract. Res. 2, 321–327. doi:10.1007/s42532-020-00064-1
Delventhal, M. J., Fernández-Villaverde, J., and Guner, N. (2021). Demographic transitions across time and space. doi:10.2139/ssrn.3950548.papers.ssrn.com
Diamond, R., McQuade, T., and Qian, F. (2019). The effects of rent control expansion on tenants, landlords, and inequality: evidence from San Francisco. Am. Econ. Rev. 109 (9), 3365–3394. doi:10.1257/aer.20181289
Fotheringham, A. S., Yang, W., and Kang, W. (2017). Multiscale geographically weighted regression (MGWR). Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 107 (6), 1247–1265. doi:10.1080/24694452.2017.1352480
Fuerst, F., McAllister, P., Nanda, A., and Wyatt, P. (2016). Energy performance ratings and house prices in Wales: an empirical study. Energy Policy 92, 20–33. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2016.01.024
Goodman, A. C., and Thibodeau, T. G. (2003). Housing market segmentation and hedonic prediction accuracy. J. Hous. Econ. 12 (3), 181–201. doi:10.1016/s1051-1377(03)00031-7
Guignet, D., Walsh, P., Northcutt, C., and Williams, R. (2019). The impacts of brownfields on property values and the benefits of redevelopment: Evidence from Baltimore, Maryland. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 77, 240–257. doi:10.1016/j.regsciurbeco.2019.06.004
Heok, K. E. (2021). Towards ageing well: planning a future-ready Singapore. Singapore: Centre for Liveable Cities.
Holtan, M. T., Clark, S. S., Conklin, D., Rajkovich, N. B., Habeeb, D., Williams, A., et al. (2024). Extreme heat adaptation planning: a review of evaluation, monitoring, and reporting. J. Environ. Plan. Manag., 1–26. doi:10.1080/09640568.2024.2445832
Kahn, M. E., and Kok, N. (2014). The capitalization of green labels in the California housing market. Regional Sci. Urban Econ. 47, 25–34. doi:10.1016/j.regsciurbeco.2013.07.001
Khoshnoud, M., Sirmans, G. S., and Zietz, E. N. (2023). The evolution of hedonic pricing models. J. real estate literature 31 (1), 1–47. doi:10.1080/09277544.2023.2201020
Kim, H., Kim, H., and Lee, J.-T. (2019). Spatial variation in lag structure in the short-term effects of air pollution on mortality in seven major South Korean cities, 2006-2013. Environ. Int. 125, 595–605. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2018.09.004
Kim, S., Chen, J., Cheng, T., Gindulyte, A., He, J., He, S., et al. (2021). PubChem in 2021: new data content and improved web interfaces. Nucleic acids Res. 49 (D1), D1388–D1395. doi:10.1093/nar/gkaa971
Lundberg, S. (2017). A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. arXiv. doi:10.48550/arXiv.1705.07874
Noonan, D. S., Breznitz, S. M., and Maqbool, S. (2022). Flocking to the crowd: cultural entrepreneur mobility guided by homophily, market size, or amenities? J. Cult. Econ., 59–93. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-18195-5_4
Nor, M. I., Masron, T. A., and Gedi, S. Y. (2019). Modeling of residential property rents in Somalia using two-stage modeling: hedonic regression and artificial neural network. Int. J. Hous. Mark. Analysis 13 (2), 331–356. doi:10.1108/ijhma-04-2019-0042
Nor, M. I., and Raheem, M. M. (2024). Assessing the speculative dynamics and determinants of residential apartment rentals in Mogadishu, Somalia: a hybrid modeling approach. Habitat Int. 144, 102995. doi:10.1016/j.habitatint.2023.102995
Pace, R. K., and Gilley, O. W. (1997). Using the spatial configuration of the data to improve estimation. J. Real Estate Finance Econ. 14, 333–340. doi:10.1023/A:1007762613901
Phillips, S. (2024). Modeling inclusionary zoning’s impact on housing production in los angeles: Tradeoffs and policy implications. Terner Cent. Hous. Innovation. Available online at: https://ternercenter.berkeley.edu.
Pokryshevskaya, E., and Antipov, E. (2020). Robust regression discontinuity estimates of the causal effect of the tripadvisor’s bubble rating on hotel popularity. Higher School of Economics Research Paper No. WP BRP.63.
Redigan, M., Rucker, A., Serowoky, A., and Weber, R. (2023). The equitable land initiative: community land Trusts in detroit's springwells community.
Ribeiro, M. T., Singh, S., and Guestrin, C. (2016). Model-agnostic interpretability of machine learning. arXiv. doi:10.48550/arXiv.1606.05386
Ridker, R. G., and Henning, J. A. (1967). The determinants of residential property values with special reference to air pollution. Rev. Econ. Statistics 49, 246–257. doi:10.2307/1928231
Rosen, S. (1974). Hedonic prices and implicit markets: product differentiation in pure competition. J. political Econ. 82 (1), 34–55. doi:10.1086/260169
Sayce, S. L., Clayton, J., Devaney, S., and van de Wetering, J. (2022). Climate risks and their implications for commercial property valuations. J. Prop. Invest. and Finance 40 (4), 430–443. doi:10.1108/jpif-02-2022-0018
Shellito, J. L., Osland, J. S., Helmer, S. D., and Chang, F. C. (2010). American Board of Surgery examinations: can we identify surgery residency applicants and residents who will pass the examinations on the first attempt? Am. J. Surg. 199 (2), 216–222. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2009.03.006
Soltani, A., and Lee, C. L. (2024). The non-linear dynamics of South Australian regional housing markets: a machine learning approach. Appl. Geogr. 166, 103248. doi:10.1016/j.apgeog.2024.103248
Thomy, B., Morrison, M., Duncan, R., Bark, R. H., Boyle, K. J., and Birtles, P. J. (2024). Investigating revealed preferences for urban waterway conditions: a hedonic property valuation study. Aust. J. Agric. Resour. Econ. 68 (2), 253–269. doi:10.1111/1467-8489.12561
Tnani, M.-A., Subarnaduti, P., and Diepold, K. (2022). Efficient feature learning approach for raw industrial vibration data using two-stage learning framework. Sensors 22 (13), 4813. doi:10.3390/s22134813
Uddin, M. G., Nash, S., Diganta, M. T. M., Rahman, A., and Olbert, A. I. (2022). Robust machine learning algorithms for predicting coastal water quality index. J. Environ. Manag. 321, 115923. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115923
Vandecasteele, I., de Luise, A., Johnson, K., Modvig, P., Karampini, T., Nielsen, H. Ã., et al. (2024). Urban adaptation in Europe: what works? implementing climate action in European cities.
van Binsbergen, J. H., Han, J., Ruan, H., and Xing, R. (2024). A horizon-based decomposition of mutual fund value added using transactions. J. Finance 79 (3), 1831–1882. doi:10.1111/jofi.13331
Wagner, C., Strohmaier, M., Olteanu, A., KäcÄman, E., Contractor, N., and Eliassi-Rad, T. (2021). Measuring algorithmically infused societies. Nature 595 (7866), 197–204. doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03666-1
Wagner, D. L., Grames, E. M., Forister, M. L., Berenbaum, M. R., and Stopak, D. (2021). Insect decline in the Anthropocene: death by a thousand cuts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 118 (2), e2023989118. doi:10.1073/pnas.2023989118
Wei, C., Fu, M., Wang, L., Yang, H., Tang, F., and Xiong, Y. (2022). The research development of hedonic price model-based real estate appraisal in the era of big data. Land 11 (3), 334. doi:10.3390/land11030334
Werner, B. R. (2024). Preliminary analysis of how artificial intelligence will impact affordable housing development. Pratt Institute.
Zevenbergen, C., Fu, D., and Pathirana, A. (2018). Transitioning to sponge cities: challenges and opportunities to address urban water problems in China. Water 10 (9), 1230. doi:10.3390/w10091230
Keywords: residential property prices, hedonic regression, artificial neural networks, urban real estate, hybrid modeling
Citation: Nor MI and Hussein SN (2025) Modeling residential property prices in emerging climate-responsive urban markets: a hybrid modeling framework for Baidoa City-Somalia. Front. Built Environ. 11:1615229. doi: 10.3389/fbuil.2025.1615229
Received: 20 April 2025; Accepted: 23 June 2025;
Published: 11 July 2025.
Edited by:
Wei Lang, Sun Yat-sen University, ChinaReviewed by:
Hasim Altan, Prince Mohammad bin Fahd University, Saudi ArabiaTadeusz Jędrzejczyk, Medical University of Gdansk, Poland
Copyright © 2025 Nor and Hussein. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mohamed Ibrahim Nor, bS5pYnJhaGltQHNpbWFkLmVkdS5zbw==
 Mohamed Ibrahim Nor
Mohamed Ibrahim Nor Shuaib Nour Hussein2
Shuaib Nour Hussein2