- Sustainable Human Settlement and Construction Research Centre (SHSCRC), Department of Construction Management and Quantity Surveying, Faculty of Engineering and Built Environment, University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg, South Africa
Introduction: The traditional procurement system in the construction industry has been plagued by inefficiencies, often serving as a significant obstacle to project delivery. Thus, this study examines the dynamics of adopting smart contracts for project procurement for optimal project success and delivery, with insights and recommendations from the South African Construction Industry.
Method: The study employed a quantitative research approach utilizing descriptive and inferential statistics of Mean Item Score (MIS) and Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA) for data analysis, based on a purposive sampling technique.
Results: The MIS results for the benefit, legal & regulatory constraints, and best practices of smart contracts range between 3.73 - 4.41 values, while the Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) values were higher than the recommended 0.6 value for the EFA and Cronbach's Alpha value of 0.969 across the indicators.
Discussion: The study's findings revealed two categorized benefits of adopting smart contracts: administrative and operational efficiency of project procurement and procurement optimization; two components of legal and regulatory constraints: Transactional and legal encumbrance to smart contract implementation and legal gaps and ambiguity and two best practices: smart contract reliability practices for project procurement and consistent stakeholders’ engagement for smart contract protocol standardization. The study concludes that Smart contracts can transform global project procurement within the construction industry. The study recommends the development of a green paper on smart contract adoption and integrating smart contracts into standard forms of construction contracts.
Highlights
• Smart Contracts can revolutionize the construction industry
• Smart Contracts aid administrative and operational efficiency of project procurement
• There is a need to address Transactional and legal encumbrance to smart contract implementation
• Consistent stakeholders’ engagement ensures smart contract protocol standardization
• Integration of Smart Contracts into Standard Forms of Construction Contracts
1 Introduction
1.1 Background to the study
Achieving economic delivery of projects requires strategic procurement management, as this managerial approach entails the execution of project contracts, management of project suppliers, and optimization of project risk along the entire supply chain. According to Afshari and Bafti (2023), project procurement management is a strategic pillar in construction management, as it entails all stakeholders and agreements involved in a project. Consequently, the complexity in project procurement management evidenced in the need for accountability, streamlining of processes, and minimization or avoidance of delays (Brown and Jones, 2021) has led to the adoption of smart contracts for optimized construction procurement management. The Smart contract is a digital application founded on Blockchain technology that automatically self-executes agreements and ensures the automatic fulfillment of terms and conditions (Clack et al., 2017). Additionally, smart contracts based on blockchain technology set up a reliable and secure system of data by providing secure and tamper-proof transaction records, merging their role, and increasing information management, thereby enhancing the security of construction projects (EY, 2023). According to Ene (2020), the smart contract was created by the Computer Scientist and Cryptographer N. Szabo of which the scientist posited that smart contracts can “utilize protocols and user interfaces to facilitate all steps of the contracting process” Szabo (1997). However, Ene (2020) gave a comprehensive definition of a smart contract as “an electronic code that, upon the occurrence of (a) specified condition(s), is capable of running automatically according to pre-specified functions to execute a transaction between parties, stored and processed on a Blockchain or other distributed network and authenticated by a Digital Signature”. According to Confideal (2017), the smart contract operates on the features of Blockchain Technology, such as reliability, accuracy, immutability, and transparency. Also, the research of He, et al. (2018), as cited in Mao and Chen (2023) opined that smart contract is a decentralized, autonomous, de-trusted, tamper-evident, and self-sufficient system that allows contracting parties to complete transactions in a digital form without any third-party.
Consequently, the advent of smart contracts in the construction industry and specifically within the procurement dynamics of the industry is poised to ensure transparency and accountability of the procurement process, eliminate risks associated with contracts, and aid in the automatic tracking of terms and conditions (Jahani, et al., 2021). Hence, smart contract adoption in the construction industry has become a game-changer for effective and efficient project procurement management. The research of Williams-Elegbe (2018) shows that through smart contracts, corruption in government contracting and the probability of fraud in procurement mechanisms can be reduced. This is also confirmed by the research of RLB Alexander (2023), which states that smart contracts aid in minimizing the complexity of contracts, enhancing the transparency of business transactions in the construction industry, and enhancing surveillance of different activities.
Furthermore, the adoption of smart contracts for project procurement is supported by Rogers’ (2003) Innovation Diffusion Theory (IDT). As discussed by Sahin (2006) and applied by David, et al. (2022), the IDT framework is built around four key elements: the innovation itself, communication channels, time, and the social system. Hence, Smart contracts align well with this framework and reflect Rogers’ (2003), p. 13 definition of technology as “a design for instrumental action that reduces the uncertainty in the cause-effect relationships involved in achieving a desired outcome.” This definition reflects that a smart contract is a technology and innovation that can transform the uncertainties from project procurement throughout the entire lifecycle of a project, thereby facilitating a seamless project delivery. One of the central challenges to technology adoption, as highlighted in IDT and reinforced by Sahin (2006), is the uncertainty surrounding the perceived advantages and disadvantages of the innovation. To address this, the diffusion of innovation requires clear communication channels that encompass knowledge dissemination, persuasion, decision-making, implementation, and confirmation. This research, through its three specific objectives, contributes to this process by outlining the benefits of smart contract adoption in project procurement, identifying the legal and regulatory barriers, and presenting best practices to facilitate its implementation.
1.2 Problem statement
The introduction of smart contracts within the procurement dynamics of the construction industry is timely, given the inefficiency that has marred procurement issues in the industry. According to AIA Contract Document (2023), the traditional mechanism of formulating and executing project contracts has not efficiently addressed payment delays and challenges within the construction industry. This is corroborated by the claims of Levelset (2021) that 76% of Construction Companies encounter payment and financial challenges, including slow payments, no payments, and even payment disputes. Moreover, Peters et al. (2019) research affirmed that many construction companies, especially small and medium-sized companies in developing economies, are plagued with late payments and non-payment of necessary financial and contractual obligations. In a list of 28 causes of these procurement issues, the authors’ research revealed the top six causes: Bureaucratic procedures, poor management of variations, state of the economy, poor process implementation, and acceptability of late payment. This procurement menace is becoming rampant within the industry, leading to poor project delivery, non-compliance with contractual obligations, and poor-quality work (Akaba, et al., 2020). However, introducing smart contracts paves the way for an efficient payment system that honors agreed contractual obligations. According to EY (2023), Smart contracts automatically execute transactions with predefined conditions, thereby increasing transparency in contract management, reducing manual oversight, decreasing conflicts, and improving efficiency. Also, Rathnayake et al. (2022) posited that smart contracts increase trust among contractors, owners, and sub-contractors in managing contracts and reducing susceptibility to conflicts.
Furthermore, in the evaluation of the challenges facing the South African Construction Industry, the research of Khutso et al. (2023), among other issues, revealed that procurement-related issues are a big challenge in the industry, thereby leading to poor quality of construction work, which are based on fraud and corruption of the procurement system, inefficient delivery model, inordinate preferences and the inadequacy of information in choosing professional services and contractors based on standardized quality criteria. Also, according to the Master Dissertation of Bangani (2023), the top five (5) procurement challenges faced by emerging contractors in the South African public sector are late payment by the government, political interference, poorly managed cashflow, too much competition, and lack of understanding of pricing techniques. These challenges narrow down to the terms of contracts and agreements between all the parties, which the blockchain technology of smart contracts can help execute seamlessly.
1.3 Research gap and study objectives
Given the potential of smart contracts in addressing the various issues within the Procurement dynamics in the construction industry, there are few scholarly research on the subject matter. An inquiry into the Scopus database shows that publications on the interoperation of smart contracts and project procurement started in 2018, with just 135 publications as of December 2024 with major subject areas in Engineering and Computer Science. Consequently, from the Scopus database, only two research studies applicable to smart contracts and procurement are from South Africa, signifying low research within the subject matter in the country. Moreover, the two South African research are “Appraising the application of cryptocurrency technologies in the Nigerian built environment: Stakeholders perspectives” in Ebekozien, et al. (2024) and “Harnessing 4IR/5IR technologies for improved procurement and delivery” in Awuzie and Moghayedi (2024). An abstract analysis of this research shows that they are not tailored towards the Republic of South Africa; hence, to the best of the author’s knowledge, there is currently no research on the application of smart contracts within the South African Construction industry. This is a significant geographical research gap that this study bridges and provides more clarity on the interoperation of smart contracts and project procurement management within the South African Construction Industry, with implications for the Southern African Construction industry, emerging markets, and the African economy, in general, considering the economic power of South Africa within the continent.
Therefore, given the transformative potential of smart contracts in project procurement management of the construction industry and the research lacuna of the South African Construction Industry, the cardinal objective of this study is to analyze the adoption of smart contracts in Project Procurement management in the South African Construction Industry. To achieve this objective, this study has formulated three specific objectives, which are:
a. Evaluate the benefits of Smart Contract Adoption in Project Procurement Management;
b. Examine the legal and regulatory constraints for smart contract adoption in Project procurement, and
c. Explore the best practices for adopting smart contracts in project procurement.
1.4 Significance of the study
The adoption of smart contracts within the South African Construction Industry will reposition the existing contract management processes and systems and address project procurement management challenges. By adopting smart contracts for procurement optimization, the industry will internalize the various benefits, thereby becoming a compendium of knowledge for the stakeholders in the industry. Also, according to Xu et al. (2021), smart contracts will ensure accountability within the procurement process and even the scope of procurement, which will simplify contract execution in project procurement and eliminate human errors. According to the author, adopting a smart contract will ensure robust stakeholder communications, simplify the swift interactions between contractors and clients, and remove bureaucratic encumbrance in tendering processes. The research of Weingartner et al. (2018) posited that smart contracts will aid in curbing and fighting corruption in public purchasing. This will reduce the risk for construction industry suppliers, smoothing relationships between contractors, subcontractors, and clients.
Also, according to Migiro and Ambe (2008) and Tshabalala (2024) the procurement dynamics of the Republic of South Africa is guided by certain Acts of the parliament starting from the constitution and Acts such as the Public Finance Management Act 1 of 1999, Municipal Finance Management Act No 56 of 2003, Preferential Procurement Policy Framework Act No 5 of 2000, Broad-based Black Economic Empowerment Act 53 of 2003, Promotion of Administrative Justice Act No 3 of 2000, Promotion of Equality and the prevention of Unfair Discrimination Act No 4 of 2000, Construction Industry Development Board Act No 38 of 2000 and the Prevention and Combating of Corrupt Activities Act No 12 of 2004. Hence, examining the legal and regulatory constraints for smart contract adoption in Project Procurement Management offers research insights into avoidable pitfalls during the adoption process and areas that conflict or align with existing procurement laws and regulations for integration and compliance purposes. Also, identifying best practices for adopting smart contracts will make it easy for construction firms to adopt the technology in managing their various procurement dynamics.
2 Research methodology
This study utilized a quantitative research method to address the adoption of smart contracts in project procurement management within the South African construction industry. Consequently, the study adopted a descriptive quantitative research design, which allowed for the collection of quantitative data through a survey approach to understanding the perceptions and experiences of respondents (Saunders et al., 2019; Creswell, 2014).
2.1 Population, sample size, and sampling technique
Given the geographical research gap of this study, the population for the study consists of professionals within the South African construction industry, which includes project managers, quantity surveyors, procurement officers, and construction project managers. The selection of these professionals follows the recommendation of Fraenkel et al. (2015), that to ensure the reliability of findings, different subgroups need to be included in the research.
However, given the low level of smart contract adoption in the construction industry and low research output, the study utilizes a purposive sampling technique, with sixty (60) built environment professionals targeted. This conformed with Campbell, et al. (2020), who posited that Purposive sampling techniques are used in selecting specific people for research due to their knowledge advantage, and because they may hold important views.
2.2 Data collection and analysis
Given the quantitative research design for this study, a structured questionnaire was used to collect data as the research instrument. According to Dillman et al. (2014), the use of questionnaires enhances the accuracy, anonymity, and validity of data collected. In addition, the structured questionnaire designed in accordance with the research objectives has four sections. The first section addresses the respondents’ demographics, including age, gender, highest educational level, Professions of the respondents, and years of experience. The second section focuses on the benefits of smart contracts, while the third section addresses legal and regulatory constraints, and the fourth section espouses the best practices for adopting smart contracts in project procurement. The indicators in the questionnaire were measured using the Five (5) point Likert scale of 1 – Strongly disagree, 2 - disagree, 3 – Neutral, 4 – Agree, and 5 - strongly agree. Moreover, according to the research of Al Tamimi and Shuib (2009), the Five (5) points Likert scale has different mean levels, which was used in this study: Strongly disagree ranges between 1.00–1.49; Disagree: 1.50–2.49; Neutral: 2.50–3.49; Agree: 3.50–4.49; and strongly agree: 4.50–5.00.
Furthermore, descriptive statistics like frequency and percentage were used to analyze the demographics of the respondents in the analysis of the collected data for the research. Also, given the five-point Likert scale for the rest of the sections of the questionnaire, the Mean Item Score (MIS) was used (Tambwe et al. 2023) as an inferential statistic. The MIS is the average of the responses from the respondents, showing the ranking of the indicators evaluated by the respondents. Also, according to Sykes et al. (2016), MIS is an analysis involving the measurement of central tendency and refers to the average value of a group of numbers by adding up all the figures and dividing them by the number of values. The MIS is accompanied by the standard deviation for each of the indicators ranked by respondents, as the standard deviation measures the spread of data about the mean value (University Center for Teaching and Learning, 2018). In addition, given the nature of this research, in conformance with the research of Martinez and Bartholomew (2017), MIS, which is also an Arithmetic mean can be used for summary statistics, and when optimized with standard deviation, it can be used to draw appropriate inferences.
Furthermore, the various indicators of the section were further subjected to inferential statistics of Principal Component Analysis (PCA), a form of Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA). According to Akinradewo et al. (2022), PCA is a statistical analysis tool that aids in the reduction of large data into clusters based on the theoretical structure of the variables. This method of analysis was confirmed by the research of Surucu et al. (2022) that EFA is a multivariate statistical method that summarizes data and aid in the ease of data interpretation and understanding of relationships and patterns of data variables, which can be achieved using a PCA. Furthermore, according to Surucu et al. (2022), the credibility of EFA is seen through the Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin Measure (KMO) and Bartlett’s Sphericity Test. An EFA analysis with a KMO Value of 0.6 and above and a Bartlett’s Test of Sphericity of P < 0.05 means that the data are suitable for EFA analysis. Moreover, according to the research of Bryant and Yarnold (1995), the EFA is mostly used as an inferential statistic based on the following assumptions of no multicollinearity, the presence of true correlation between variables and component factors, and the inclusion of relevant variables into the analysis.
The research instrument underwent internal reliability validation through expert review by professionals in the construction industry as well as researchers and practitioners within the field of Blockchain technology. Furthermore, all data utilized in the analysis, both for the Mean Item Score (MIS) and the Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA), were assessed for internal consistency using Cronbach’s Alpha. The results revealed a Cronbach’s Alpha value of 0.969 across the 60 items spanning all indicators, which exceeds the acceptable threshold of 0.70 as recommended by Gliem and Gliem (2003) and Nunnally’s (1978) guideline. This is because the closer the alpha value to +1, the greater the internal consistency of items that form the construct. Furthermore, this high-reliability score further corroborates the Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) values reported in Tables 3, 5, 7, all of which were above 0.6, thereby confirming the internal consistency, validity, and reliability of the dataset and the content of the research instrument.
The statistical package for the social science (SPSS) v. 25 and Microsoft Excel software were used to analyze the collected data.
3 Presentation of data and findings
The data for this study was collected using a well-structured questionnaire in an electronic format using Google Forms. However, given the targeted 60 respondents for the study, only 49 responses were retrieved, leading to a response rate of 81.7%. This is an acceptable response rate in conformance with the research of Moser and Kalton (2017), which states that a response rate that is not lower than 30%–40% is considered significant. The analyzed data results are presented in accordance with the specific objectives of this research as stated in Section 1 of the study.
3.1 Demographic analysis of the respondents
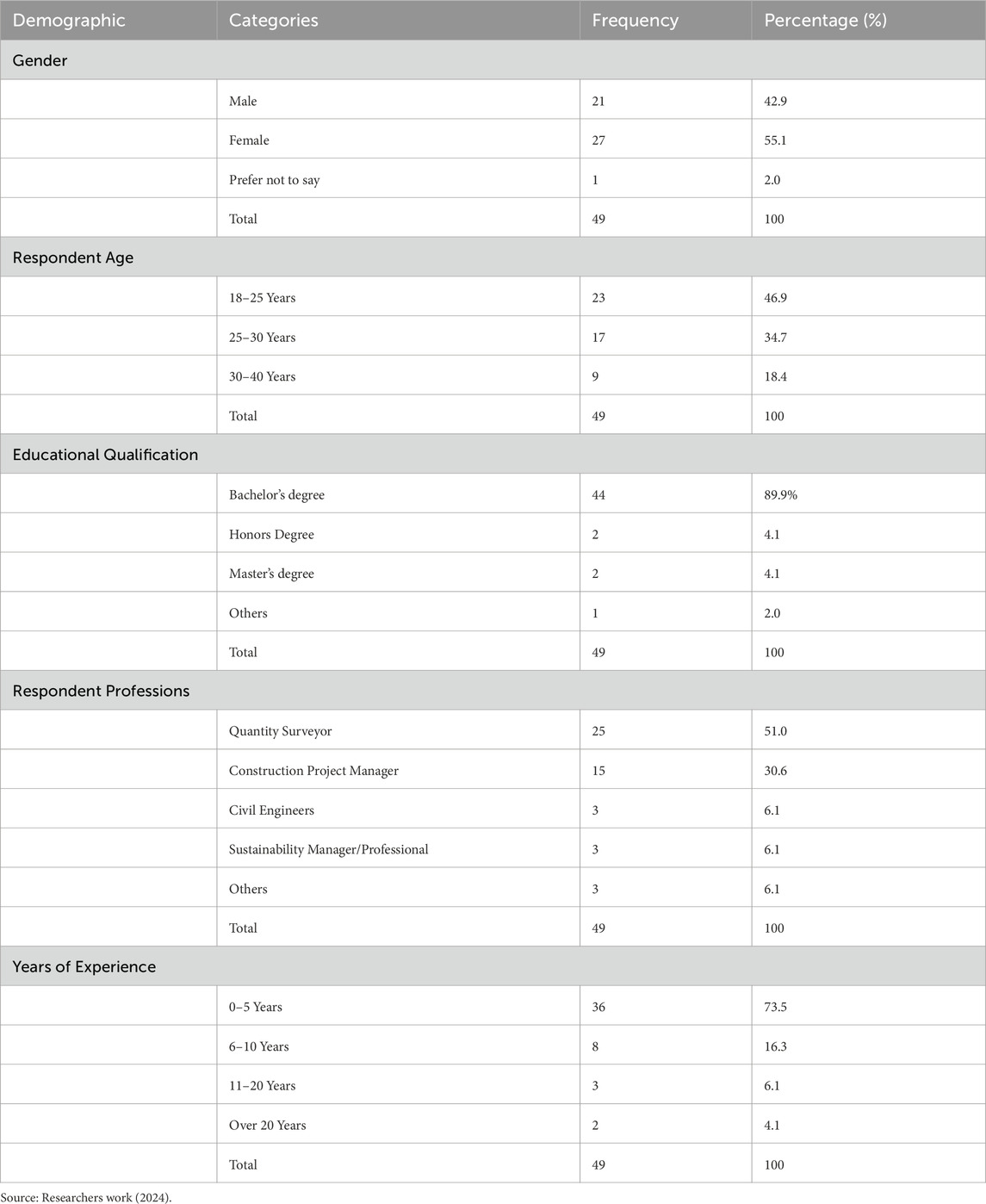
Table 1 shows the demographic analysis of the respondents. According to the Table, there are more females than males, with a representation of 55.1%–42.9%. Also, age distribution shows a younger construction workforce that is very much in tune with the ongoing digitalization of the industry, as more than 70% of the respondents are below 30 years of age. Also, most (89.9%) of the respondents have at least a bachelor’s degree certificate, which further shows their level of understanding regarding the subject matter for the research. Also, most of the respondents are Quantity Surveyors (51%) and Construction Project Managers (30.6%). Furthermore, at least 26.5% of the respondents have 6 years of working experience within the construction industry, and 73.5% of the respondents are very new in the industry and have 0–5 years of experience.
3.2 Benefits of smart contract adoption in project procurement
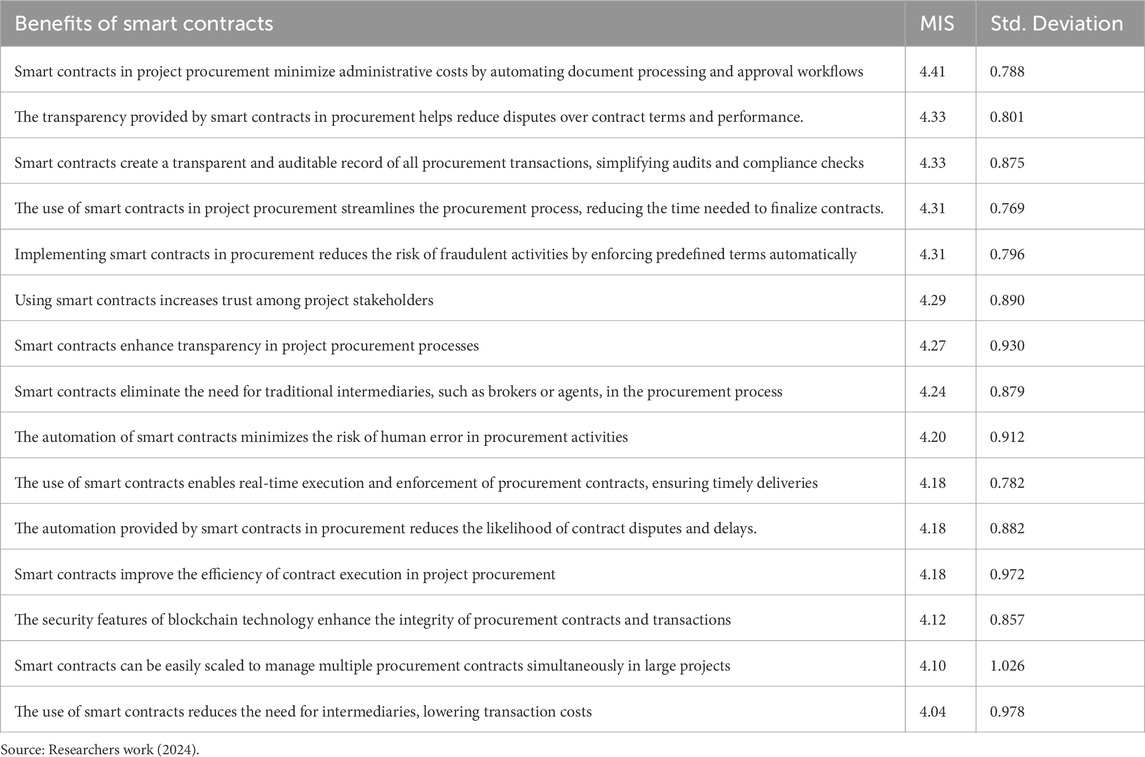
Table 2 shows the respondent ranking of the benefits of the adoption of smart contracts for project procurement within the construction industry. The most rated benefit was that smart contracts reduce administrative costs through automated documentation and approval workflows, with an MIS value of 4.41 and a Standard Deviation (SD) of 0.788. This depicts a strong appreciation for efficiency gains that automation can make possible within the procurement process through smart contracts. The second most ranked benefit refers to transparency, which was highly rated by the respondents because with it comes a clear, auditable record that smart contracts provide, making compliance simpler and enhancing auditability (MIS = 4.33; Standard Deviation = 0.875). Moreover, through this transparency, there will be fewer contract disputes due to the explicit terms encoded in smart contracts, which enable more value in ensuring the reliability of the contract performance. Similarly, preventing fraud was also considered a significant advantage, as the participants viewed the automatic enforcement of the terms in the contract as a way of deterring fraudulent actions. They also favor smart contracts for efficiency in smoothing procurement and reducing time wastage in finalizing contracts. (MIS = 4.31; Standard Deviation = 0.769).
Moreover, while the other benefits, such as removing intermediaries, reducing transaction costs, and minimizing human errors, were appreciated, their ratings were relatively high considering the Likert scale. That would mean although the participants perceive these fields to have value when it comes to looking at the general benefit, automation, transparency, and risk mitigation are rated higher.
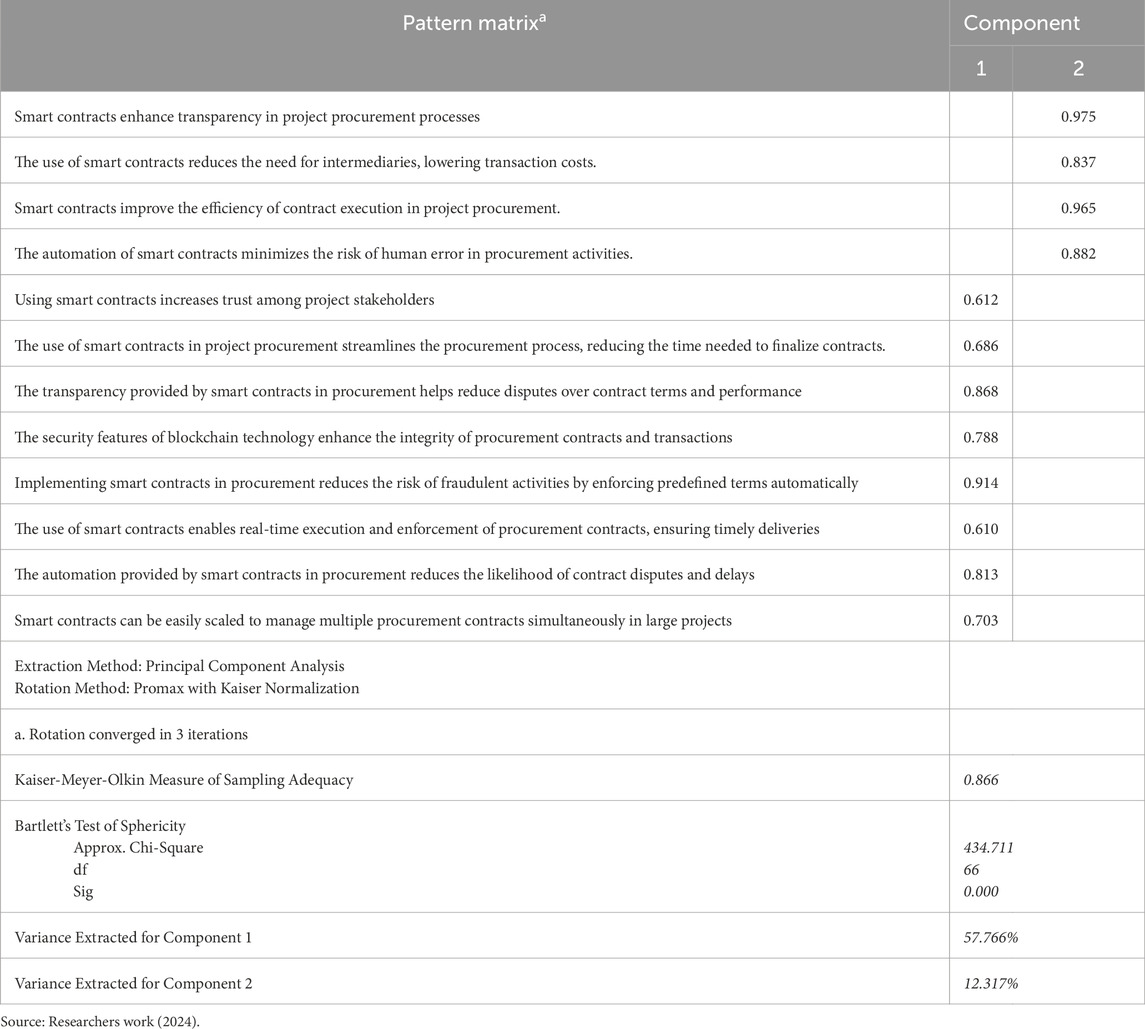
Table 3 presents the Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA) of the Benefits of adopting smart contracts in project procurement. The table contains the pattern matrix, the analysis of the variance, and the KMO. According to the table, the benefits of smart contract adoption in project procurement were reclassified into two components. Also, there is a KMO value of 0.866, which is above the minimum of 0.6 and the Bartlett’s Test of Sphericity is significant at 0.000, less than 0.05; these statistics values are deemed meritorious and acceptable, thereby confirming the authenticity of the two components in line with the research of Surucu et al. (2022) and Field (2009). Furthermore, the two components have a cumulative variance extraction of 70.083%, between the expected 50%–95% extraction level (Surucu et al., 2022).
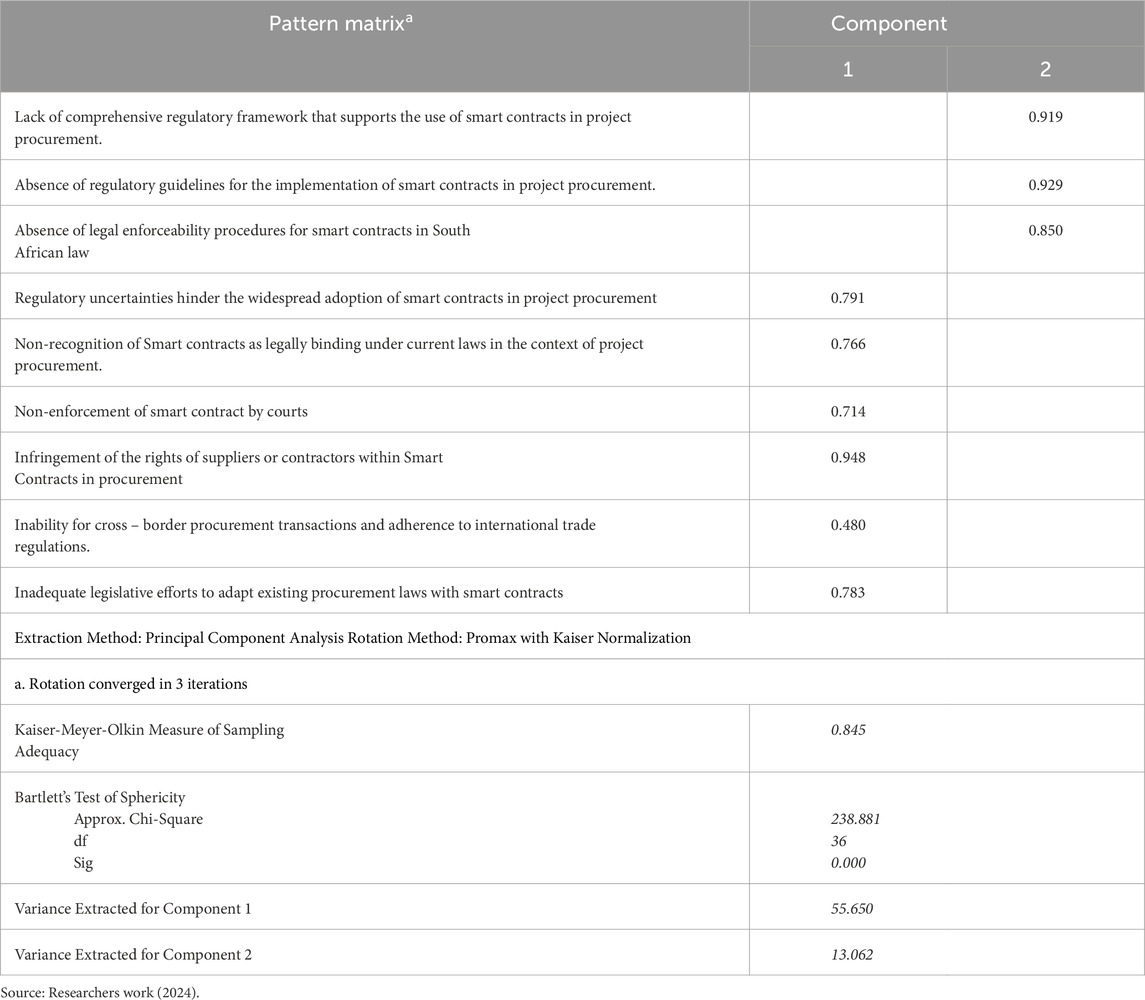
3.3 Legal and regulatory constraints in adopting smart contracts for project procurement
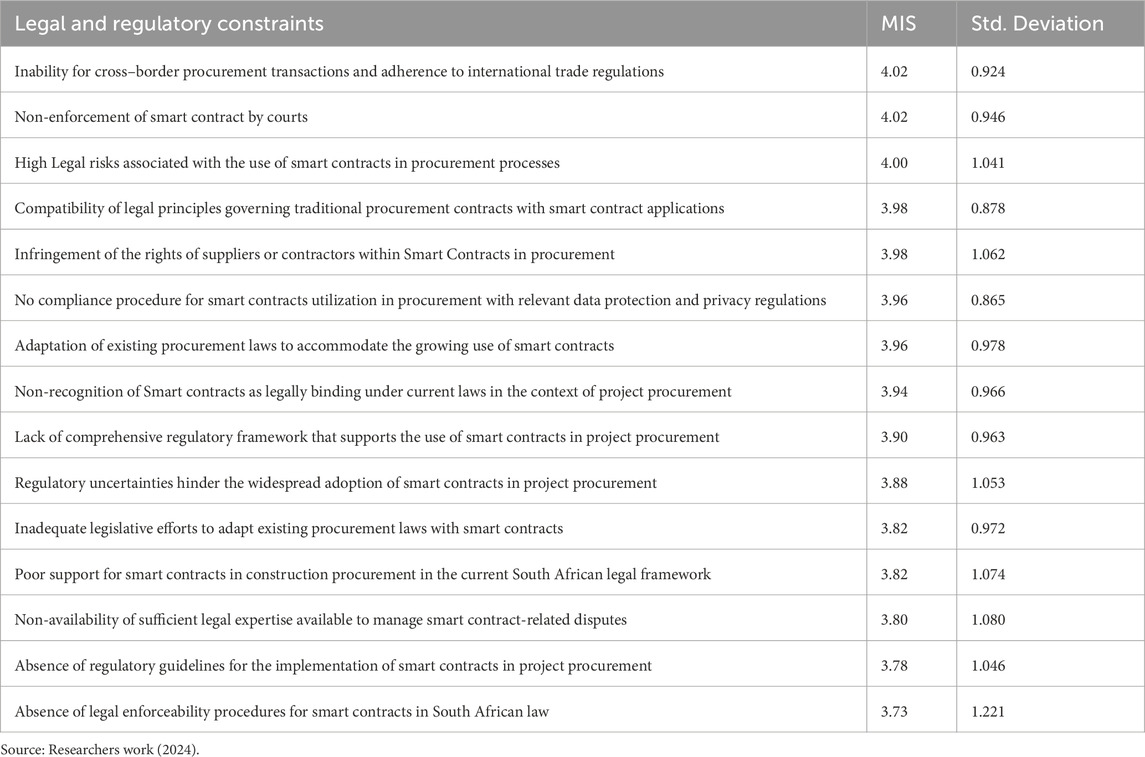
Table 4 presents the legal and regulatory constraints for the adoption of smart contracts for project procurement within the construction industry. According to the table, the respondents established the extent to which legal and regulatory issues affect the adoption of smart contracts in procurement using the five-point Likert scale. The inability to manage cross-border transactions and follow international regulations was rated the highest, with an MIS of 4.02 (Standard Deviation = 0.924). This rating is considered high and indicates that although smart contracts could be adopted for cross-border procurement, regulatory compliance is still a missing gap in the legal environment. Also, of equal importance to the respondents was the possibility of non-enforcement of those smart contracts through the courts, meaning that current traditional legal systems are more recognized in the court of law than smart contracts. Also, high legal risks due to the use of smart contracts were rated as a top constraint, with an MIS of 4.00 and a standard deviation of 1.041, emphasizing the need to address potential liabilities and risks effectively.
Other factors were assessed to be somewhat lower, such as compatibility with traditional procurement laws and compliance with data protection standards. This suggests that, although relevant, these may not necessarily act as the most direct barriers to adoption. Relatively lower ratings regarding the availability of extended regulatory frameworks and legal expertise imply that seamless integration of smart contracts still faces certain challenges, as uncertainties regarding legal regulations and a lack of enough expertise in the management of disputes related to smart contracts pose a significant barrier to wider diffusions and acceptability.
The principal component analysis (PCA) of the exploratory factor analysis of the legal and regulatory constraints for the adoption of smart contracts in project procurement is shown in Table 5. According to the Table, the constraint was classified into two components. Moreover, the KMO value of 0.845 and the high significance level of 0.000 are in line with the recommendations of Field (2009) that the KMO value for exploratory factor analysis should be higher or equal to 0.6 and the significance value of P < 0.05. Also, the cumulative variance extracted for the two components is within the threshold recommendations of various researchers as stated in Surucu et al. (2022).
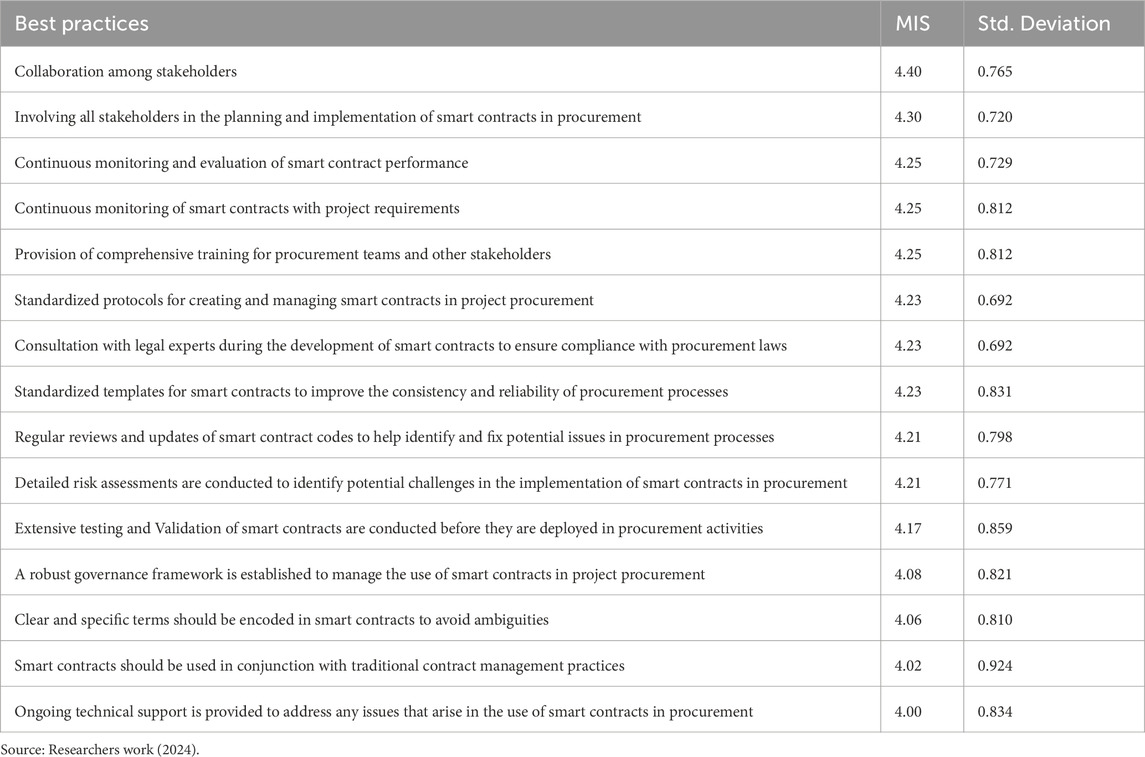
3.4 Best practices for adopting smart contracts in project procurement
Best practices for the effective use of smart contracts in project procurement are rated on collaboration, continuous monitoring, and standardization using a five-point Likert scale, as shown on the MIS and Standard Deviation values of Table 6. The best practice that was of essence was collaboration by stakeholders, recorded with a MIS of 4.40 (Standard Deviation = 0.765). This would therefore translate to a very high rating of the importance of involving all parties concerned in the operation of smart contracts, including suppliers and contractors. Involving stakeholders in the phases of planning and execution of implementation of smart contracts was also ranked high with a MIS of 4.30 and Standard Deviation = 0.720; this means an integrative approach to contract management was valued highly. Also, the continuous monitoring of smart contract performance was considered as one of the most important elements for effective execution, and respondents demonstrated an understanding that ongoing oversight of the project ensures that their requirements are met, with a MIS = 4.25; Standard Deviation = 0.729. Accordingly, a high rating was given by the respondents on the need for standardized protocols for creating and managing smart contracts, reflecting a preference for consistent processes across procurement activities in the South African Construction Industry, with MIS = 4.23; Standard Deviation = 0.692.
Other best practices include consulting legal experts, adopting standardized templates, and periodic reviews of smart contract codes. This shows respondents’ awareness of the complexity of the management of smart contracts. However, the relatively lower scores for ongoing technical support and integration of smart contracts with traditional contract management practices suggest that while collaboration and standardization are recognized, extra technological and organizational support will be required to bridge the gap between digital and traditional procurement practices.
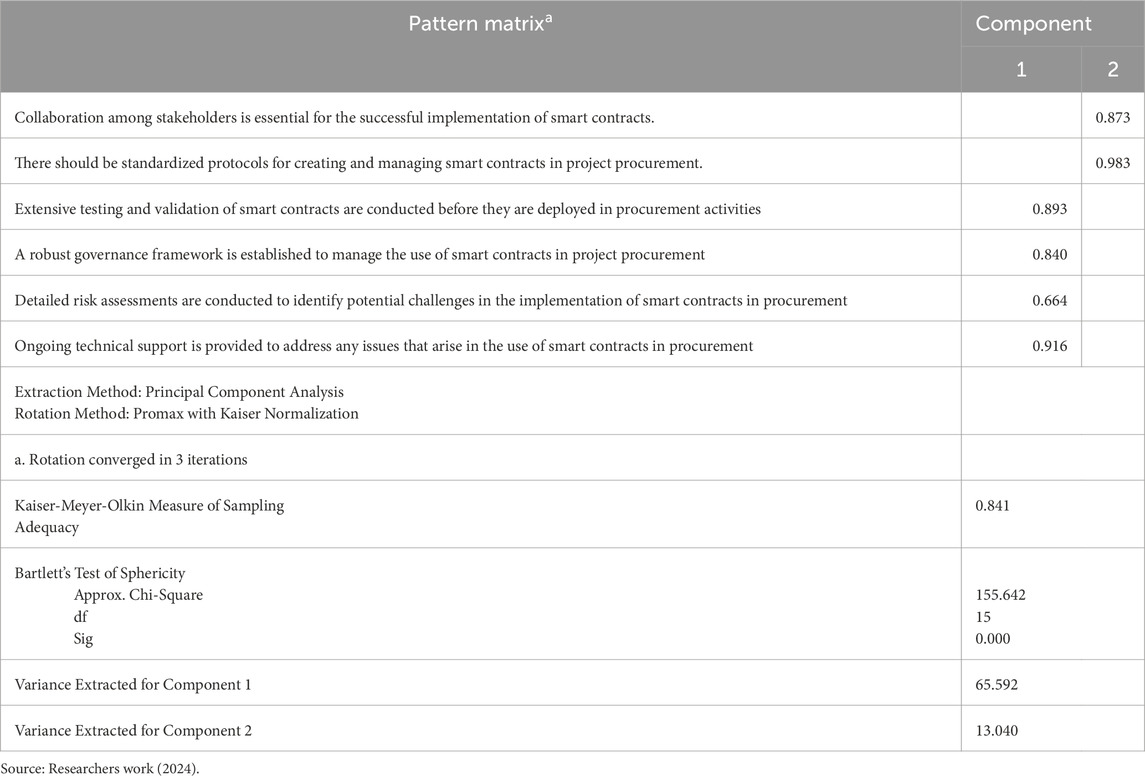
Following the MIS for the best practices for adopting Smart Contracts, the practices were further analyzed using the PCA of Exploratory factor Analysis as presented in Table 7 into two components. Furthermore, the KMO value of O.841 and Bartlett’s Test of Sphericity significance p value of 0.000 are in conformance with the EFA requirements as stated in Field (2009), which were elaborated and confirmed in Surucu et al. (2022).
4 Discussion of findings
This section provides a detailed discussion of the findings presented in Section 3.
4.1 Benefits of smart contract adoption in the project procurement
Table 2 shows the benefits of adopting smart contracts for project procurement. In line with the Likert Scale findings of Al Tamimi and Shuib (2009), the least benefit ranked by the respondents have an MIS of 4.04, depicting that the respondents who are built environment professionals all agree that smart contract adoption for procurement dynamics have huge benefits for the construction industry. The top four benefits from Table 2 are the minimization of administrative costs by automating document processing and approval workflows (MIS = 4.41; SD = 0.788); reduction of disputes over contract terms and performance (MIS = 4.33; SD = 0.801); creation of transparent and auditable record of all procurement transactions, simplifying audits and compliances checks (MIS = 4.33; SD = 0.875); and the fourth benefit is the streamlining of procurement process and reduction in the time to finalize contracts (MIS = 4.31; SD = 0.769). These four top benefits highlight that smart contracts will focus on five categories: Procurement administrative bottlenecks, Procurement Transparency and Accountability; Procurement stakeholders management and engagement; procurement efficiency and ease of contract finalization; and Procurement cost optimization.
Moreover, an in-depth analysis beyond the MIS in Table 2, as stated in Table 3, reveals the pattern matrix of the PCA and that there are two categories of benefits to adopting smart contracts in project procurement. The first component comprises benefits such as an increase in trust among project stakeholders, streamlining of the procurement process for optimal time of finalizing contracts, transparency for the reduction of disputes over contract terms and performance, security features of blockchain for integrity of procurement contracts and transactions, reduction of risk of fraudulent activities leading automatic enforcement of predefined, enablement of real-time execution and enforcement of procurement contracts for timely deliveries, procurement automation in reducing likelihood of contract disputes and delays, and possibility of scaling up of smart contract to manage multiple procurement contracts. This first component of Benefits connotes the Administrative and Operational Efficiency of Project Procurement through smart contract adoption. The second component of benefits entails transparency in project procurement processes, use of smart contracts in reducing the need for intermediaries thereby lowering transaction costs, improvement of efficiency in contract execution in project procurement, and automation of smart contracts to minimize risk of human error in procurement activities. These benefits connote Procurement Optimization through Smart Contracts.
These benefits from the MIS or EFA analysis are evident that adopting smart contracts within the project procurement mechanism will ensure high efficiency and optimization in project procurement management by reducing administrative costs due to automating document processing, reducing manual labor, and gaining time efficiency. Also, the ease in procurement administrative bottleneck will be evident through the auditable and transparent records created by the smart contract, as the records will be recorded in an immutable ledger, which cannot be tampered with or altered (Čeke et al., 2022). Also, given the reduction of disputes over contract clauses and twists in obligations, there will be robust stakeholder engagement before the formation of a contract. This is because, by nature of the smart contract, predefined smart contract terms can be observed to allow for easier enforcement of agreements, which will reduce conflicts and ensure more dialogue.
Moreover, automation is a key distinguishing feature of smart contract applications in project procurement that will lead to administrative and operational efficiency of project procurement as well as procurement optimization. This automation in document processing aligns with Mougayar’s (2016) observations, which highlight how smart contracts simplify administrative tasks and significantly reduce overhead costs. Additionally, the efficiency gained from minimizing manual tasks allows construction firms to redirect resources toward more strategic functions and project areas, especially tasks along the critical path. In addition, the ability of smart contracts to store records transparently and audibly supports the arguments of Wright and De Filippi (2015), emphasizing that transparency enhances accountability and builds trust among stakeholders in digital transactions. This capability is particularly valuable in the construction industry, where the complexity of procurement activities demands openness to foster confidence among project participants and mitigate potential disputes. Also, the study’s findings on the importance of enforceability align with Werbach and Cornell’s (2017) assertion that clear legal interpretations are essential to establish the validity of smart contracts in court. Such enforceability provides a sense of security for businesses adopting digital contracts, as they can rely on legal mechanisms to resolve disputes when they arise.
Furthermore, as stated earlier, Smart contracts offer a significant advantage in reducing disputes by enforcing pre-agreed terms automatically. This highlights smart contracts’ legal reliability and practical utility, as observed by Savelyev (2017). By embedding conditions that self-execute within the contract, compliance is ensured without requiring constant human supervision, thereby minimizing opportunities for manipulation and fraud. Additionally, the inherent security features of blockchain technology, such as immutability and data protection, and enhancement of contract integrity, a benefit also discussed by Tapscott and Tapscott (2016), which further ensures the efficiency and optimization of the various processes in project procurement within the construction industry. The absence of traditional mediators streamlines procurement processes, aligning with Catalini and Gans’ (2018) observations that decentralized systems can drastically reduce transaction costs. This efficiency is particularly beneficial for large-scale construction projects, where speed and cost-effectiveness are critical. Moreover, smart contracts can foster greater trust among project stakeholders leading to procurement optimization. As supported by Risius and Spohrer (2017), the transparency and clarity provided by blockchain technology enhance collaboration, even in challenging project environments, ultimately leading to improved project outcomes.
These findings carry significant implications for the South African construction industry. Companies should intensify their adoption of smart contract technology to automate routine administrative tasks, thereby reducing the time and labor costs associated with manual processes. Smart contracts’ transparency and ability to minimize disputes can enhance accountability among stakeholders, particularly in multi-party projects where trust is critical. Furthermore, smart contracts support compliance and uphold the long-term integrity of procurement processes, reducing fraud and human error risks while strengthening contractor-client relationships and adherence to industry standards. Also, the scalability of smart contracts is especially valuable for large-scale projects, enabling firms to manage numerous contracts without incurring additional administrative burdens. This is particularly advantageous in infrastructure projects, which often involve extensive collaboration, multiple contracts, and tight timelines. By leveraging smart contracts, construction companies can optimize workflows and ensure project efficiency during the procurement process (Özkan et al., 2021). Additionally, the cost savings achieved through the elimination of intermediaries can be reinvested in training and infrastructure development to further facilitate the adoption of digital technologies. Smart contracts integrated into procurement processes have the potential to revolutionize traditional methods, making them more efficient, transparent, and cost-effective. Firms that embrace these innovations will be better positioned to adapt to the digital transformation of the industry and maintain a competitive edge.
4.2 Legal and regulatory constraints for smart contract adoption in project procurement
Table 4 outlines the Legal and Regulatory constraints that might delay or hinder the adoption of smart contracts for project procurement. It is pertinent for stakeholders within the construction industry to take these constraints seriously and avoid the pitfalls. The first four constraints are as follows: cross-border procurement transactions and adherence to international trade regulations (MIS = 4.02; SD = 0.924); Court Enforcement of procurement contracts managed by smart contract (MIS = 4.02; SD = 0.946); Legal Risks associated with the use of smart contracts in procurement are well understood and can be mitigated (MIS = 4.00; SD = 1.041); and Compatibility of legal principles governing traditional procurement contract with smart contract applications (MIS = 3.98; SD = 0.878). The top-ranked constraint by the respondents focuses on the Legality of the adoption of Smart Contracts within the procurement dynamics. This is because most procurement processes within the construction industry follow different procurement laws in bidding/tendering, relationships with suppliers, and contract management. It also highlights the legality of contract management within two different economies in the procurement of materials. However, the introduction of smart contracts does not invalidate existing procurement laws, it aids the efficiency of execution of these laws.
Furthermore, the PCA of the Exploratory Factor Analysis revealed in Table 5 shows that the constraints are classified into two. The first component of constraint focuses on the regulatory uncertainties, non-legal recognition of smart contracts, non - non-enforceability of procurement contracts managed by smart contracts, possible infringement on the right of suppliers or contractors, non - suitability for cross-border procurement transactions, and inadequate legislative efforts to adapt existing procurement laws with smart contracts. This constraint depicts the transactional and legal encumbrances of the implementation of smart contracts. The second component of constraints for the adoption of smart contracts in project procurement encompasses non-support of the current South African Legal framework, unclear regulatory guidelines for the implementation of smart contracts, and the unenforceability of smart contracts in South African Law. These constraints sum up as the Legal gaps and ambiguity within the South African Legal Framework for smart contract implementation. The research of Van Eck and Agbeko (2024) affirmed that there are no legal procedures or recognition for smart contracts within the South African legal frameworks. The authors posit that unlike the United Kingdom through the Data Act to regulate smart contracts, none of such exist within the South African legal landscape.
Consequently, the study highlights from the MIS and EFA posit that the current procurement laws within the Republic of South Africa exhibit low adaptability to smart contracts, given the legal gaps, legal encumbrances, and ambiguity surrounding the procurement system. Savelyev (2017) emphasizes that legal frameworks must evolve in tandem with technological advancements to remain relevant. This flexibility is particularly crucial for South African construction companies aiming to engage in international projects, where compliance with diverse jurisdictions is necessary. Additionally, while respondents highlighted certain constraints, it remains essential to understand and mitigate legal risks associated with the use of smart contracts. This perspective aligns with Risius and Spohrer (2017), who emphasize the critical role of risk assessment in adopting new technologies. By proactively addressing legal challenges, construction companies can seamlessly integrate smart contracts into their operations, thereby fostering both innovation and efficiency.
Moreover, the findings suggest that stakeholders, while cognizant of the various legal encumbrances facing smart contracts within the South African Procurement system and the Construction Industry Contract Management framework should be prepared to tackle them through strategic decisions informed by legal counsel as the Electronic Communications and Transactions Act, 2002 (ECTA) of South Africa may provide legal insights on the way forward for selected procedures within the smart contract. The compatibility of smart contracts with traditional legal concepts underscores the adaptability of existing legal frameworks to evolving technologies. Rather than rendering these frameworks obsolete, smart contracts have the potential to complement and enhance their efficiency and optimization as ranked by the respondents, creating a harmonious integration that preserves legal continuity while embracing innovation. This alignment facilitates the transition for businesses adopting smart contracts and ensures that established legal principles remain relevant and effective in governing digital transactions. Moreover, this alignment fosters a dual advantage: it reduces the barriers to adoption by alleviating concerns about the need for entirely new legal structures and enhances the robustness of the legal system by incorporating advanced technological capabilities with developed countries providing a pathway.
Furthermore, as mentioned by the respondents, smart contracts can streamline processes, improve enforceability, and boost confidence among stakeholders by bridging the gap between traditional and digital paradigms. Also, the study’s findings from the MIS ranking regarding compliance with data protection regulations alleviate concerns raised by De Filippi and Wright (2018), who argued that blockchain-based systems must be designed to respect privacy laws. This aspect is particularly crucial as discussions around digital technologies increasingly prioritize data security and privacy. Ensuring such compliance strengthens trust and facilitates the broader acceptance of smart contracts in the industry and will ease its adaptability with existing procurement law and regulatory framework.
Furthermore, for smart contracts to function effectively within the South African construction industry, it is essential to establish collaboration between industry stakeholders and policymakers to create a supportive legal framework. Reflecting on the emphasis on enforceability in the legal ambiguity and encumbrances, legal professionals must prioritize understanding blockchain technology and smart contracts. This would involve targeted training and workshops for legal experts in the construction sector to equip them with the skills to address court disputes and contract enforcement specific to this digital innovation.
Additionally, data protection and privacy findings underscore the importance of implementing robust data security measures, such as encryption and adherence to relevant data protection laws within the country. This is vital for mitigating the risk of data breaches and maintaining stakeholder trust. Firms should view these measures as compliance requirements and integral components of their digital transformation strategy.
The study’s emphasis on evolving legislation highlights the need for proactive engagement with regulatory bodies. South African construction firms should work closely with industry associations, especially the South African Council for the Project and Construction Management Professions (SACPCMP) to advocate for policies supporting smart contract adoption. By shaping emerging regulations, firms can ensure that new legal frameworks accommodate the unique challenges and opportunities of the construction industry. Thus, creating a stable legal environment that fosters innovation will enable the seamless implementation of smart contracts. At the same time, these frameworks must safeguard the rights of all parties involved, thereby balancing innovation with accountability without any suspicion.
4.3 Best practices for the adoption of smart contracts in project procurement
To maximize the benefits of smart contracts and avoid the legal and regulatory challenges associated with their adoption, the respondents ranked the best practices for ensuring the smooth integration of smart contracts in project procurement in Table 6. The top best practices are as follows: collaboration among stakeholders (MIS = 4.40; SD = 0.765); Involving all stakeholders in the planning and implementation of smart contracts in procurement (MIS = 4.30; SD = 0.720); Continuous monitoring and evaluation of smart contract performance (MIS = 4.25; SD = 0.729); and Continuous monitoring of smart contracts with project requirements (MIS = 4.25; SD = 0.812). Given these best practices and other ranked practices, the respondents focus on stakeholders’ buy-in during the planning and integration of smart contracts within the project procurement and the need to establish smart contract protocols and guidelines. Therefore, this study has statistically established the need for collaboration between the industry, blockchain developers, and academic researchers to formulate a pathway for the adoption of smart contracts in project procurement.
Moreover, the best practices are categorized into two (2) components per the Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA). The first components entail practices such as extensive testing and validation of smart contracts before procurement deployment, robust governance framework for smart contract management, detailed risk assessment, and ready-proof technical support for any issues during smart contract deployment. These practices can be summed up as Smart Contract Reliability Practices for project procurement. The second component focuses on the collaboration among stakeholders and the need for standardized protocols for creating and managing smart contracts in project procurement. These practices connote Consistent stakeholder engagement for Smart Contract Protocol Standardization.
Stakeholder cooperation aligns with Savage et al. (2011), who identified cooperation as a key factor in achieving project success, which is essential for the integration of smart contracts in project procurement. Furthermore, the engagement of stakeholders in the planning process reflects the views of Loosemore et al. (2012), who highlighted the importance of active participation in the management of digital projects. Additionally, continuous monitoring supports the perspective of Risius and Spohrer (2017), who emphasized the need for regular assessments to ensure that smart contracts meet the project’s objectives. Finally, the emphasis on training reinforces the findings of De Filippi and Wright (2018), who stressed the necessity of educating stakeholders about the functionalities of smart contracts.
The findings suggest that construction firms in South Africa need to adopt a collaborative approach for standardized and generally acceptable protocols when implementing smart contracts, ensuring that stakeholders are involved from the planning stages through to execution. Continuous monitoring indicates that firms must establish mechanisms to regularly assess contract performance and adjust when needed. Also, extensive training for all parties is crucial, with investment in educational programs to raise awareness of each party’s role in using smart contracts. Additionally, the need for standardized protocols highlights the importance of developing a set of guidelines to maintain consistency in the application of smart contracts across various projects.
5 Conclusion
The procurement system in the construction industry serves as a cornerstone for successful and efficient project delivery, integrating various construction processes and methods. However, the traditional procurement system reveals significant constraints in the current digital era of the permeating fourth industrial revolution (4IR). These include inefficiencies in procurement operations, delays in planning, material delivery, and site logistics, lack of data integration and optimization for informed decision-making, inadequate management of vendor and supplier relationships, and inefficiencies in contract administration among construction stakeholders. Hence, the introduction of smart contracts as a transformative mechanism offers a revolutionary approach to enhancing procurement efficiency. By addressing these challenges, smart contracts have the potential to modernize and streamline procurement processes, paving the way for more effective and reliable project execution in the construction industry.
Through a Mean Item Score (MIS), the benefits, legal and Regulatory constraints, and best practices for the adoption of smart contracts in project procurement were analyzed, thereby filling a geographical research gap within the South African Construction Industry. Moreover, the indicators were further subjected to Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA) using Principal Component Analysis (PCA). The benefits, constraints, and best practices were analyzed into two components, each summarizing the indicators in line with EFA’s assumptions and KMO and P value validity. The benefits of the adoption of Smart contracts were divided into Component 1: Administrative and Operational Efficiency of Project Procurement; and Component 2: Procurement Optimization. Also, the EFA analysis revealed two categories of legal and regulatory constraints: Component 1: Transactional and Legal Encumbrance of Smart Contract Implementation; and Component 2: Legal Gaps and Ambiguity within the South African Legal Framework. Furthermore, the Best Practices for the adoption of smart contracts within the South African Construction Industry are classified as: Component 1: Smart Contract Reliability Practices for project procurement; and Component 2: Consistent Stakeholders Engagement for Smart Contract Protocol Standardization.
In conclusion, this research has demonstrated that smart contracts have the potential to transform global project procurement within the construction industry by delivering significant improvements in efficiency, transparency, and accountability. However, their widespread adoption remains limited due to persistent regulatory and legal challenges. A phased implementation strategy, emphasizing stakeholder engagement, standardized processes, and continuous monitoring, can help maximize the benefits of this evolving technology. Further research and advocacy efforts are also essential for developing supportive legal frameworks and fostering cross-industry collaboration. These measures will pave the way for the construction sector in South Africa to harness the long-term advantages of smart contracts fully.
Moreover, while this research contributes to the discourse on smart contract adoption for project procurement systems, it has minor limitations. One notable limitation arises from the respondents’ work experience, which predominantly falls within the 0–5 years range. Although the evolving construction management curricula in many South African universities may enhance their understanding of the digitalization of the construction industry, their practical experience in the operationalization of procurement systems may be limited. This could influence the depth of insights provided regarding the real-world application of smart contracts in the construction sector. However, as seen from this study, their perception and ranking have been confirmed with exploratory factor analysis and empirical studies. Additionally, the relatively modest sample size may have influenced the research outcomes. It is possible that a larger sample could yield slightly different results. However, given the conformance to empirical findings as explored in the research, it is reasonable to infer that the conclusions drawn are still valid and might reach the same outcomes, thereby contributing meaningfully to the existing body of knowledge.
Furthermore, although this research aligns with Rogers’ (2003) Innovation Diffusion Theory, further studies are needed to explore the extent and patterns of adoption across the construction industry. Specifically, future research should investigate the distribution of adopters based on Rogers’ categories: innovators (2.5%), early adopters (13.5%), early majority (34%), late majority (34%), and laggards (16%). Such studies would offer deeper insight into which segments of the industry or professional groups are more likely to embrace smart contract technologies for procurement, and at what pace.
6 Practical and theoretical implication
This research has examined the benefits, legal and regulatory challenges, and best practices surrounding the adoption of smart contracts in project procurement within the construction industry. The findings highlight key areas where smart contract integration can significantly enhance and streamline procurement processes across the sector. The following are some practical and theoretical implications that will stimulate the adoption of the research findings.
6.1 Need for training
The findings of this research underscore the critical need to develop a pool of blockchain researchers and practitioners within the construction industry, capable of designing tailored smart contracts that align with the unique procurement frameworks of various construction companies and firms. Additionally, it highlights the importance of training construction firm personnel, especially procurement and tender officers, to build the technical skills and competencies required to understand, write, and implement smart contracts effectively. This capacity-building initiative is essential for driving digital transformation in procurement processes through smart contracts.
6.2 Collaboration between construction stakeholders and lawmakers
The findings of this research underscore the importance of establishing stronger collaboration between construction industry stakeholders and lawmakers. At present, many legislators remain disconnected from the operational realities and advancements within the construction sector, often engaging only during ceremonial or public events. Building meaningful relationships between these two groups is essential for the effective incorporation of smart contracts into procurement frameworks. Such collaboration would allow lawmakers to better understand the value, functionality, and transformative potential of digital technologies like smart contracts. In the context of the Republic of South Africa, this engagement could be initiated through key parliamentary divisions such as the Knowledge and Information Services and the Parliamentary Research Unit. Integrating the heads of these units into academic research initiatives and industry dialogues would provide firsthand exposure to the advantages of smart contracts, thereby laying the groundwork for progressive updates to procurement laws and regulatory frameworks. Additionally, academic and industry collaboration with the Presidential Commission on the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR), established by President Cyril Ramaphosa in his 2018 State of the Nation Address offers another critical platform for bridging this gap. Such engagement would facilitate a smoother policy transition, enabling the construction industry to benefit from digital innovation while ensuring legal alignment and stakeholder buy-in.
6.3 Strategic realignment of the technology acceptance model (TAM)
Another theory underpinning the adoption of smart contracts for project procurement is the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) of Davis (1989), further discussed in Liao et al. (2022) and David et al. (2022), which emphasizes two key dimensions: perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use. However, findings from this research suggest a strategic realignment of this model in the context of the Construction Industry. Specifically, the perceived usefulness of smart contracts appears to play a more pivotal role in driving adoption than perceived ease of use. While ease of use is traditionally a major consideration, in this case, it is tied to technical knowledge requirements particularly blockchain technology applications, which can be addressed through targeted upskilling. Therefore, to promote adoption, stakeholder engagement efforts should focus primarily on communicating the practical benefits and transformative potential of smart contracts in procurement. Simultaneously, procurement professionals should be encouraged to pursue upskilling opportunities, with emphasis on the availability of simplified tools and templates that can ease the learning curve and facilitate a smoother transition into smart contract implementation.
7 Policy recommendations
Given the findings of this study and drawing from Rogers’ (2003) Innovation Diffusion Theory, further corroborated by Sahin’s (2006) research, which emphasizes that the diffusion of innovation occurs through communication channels over time within a social system, the following recommendations are proposed:
7.1 Stakeholder engagement for developing a green paper on smart contract adoption in project procurement
A robust stakeholder engagement process is essential to harness the potential of smart contracts in project procurement and address the legal challenges highlighted in this study. This initiative should bring together key players across the construction industry, supply chain professionals, policymakers, government ministries responsible for public works and infrastructure, blockchain developers, and technology and innovation agencies. This engagement should foster policy dialogues and workshops that explore the opportunities and cross-functional benefits of smart contract adoption in project procurement. These discussions will provide a platform for stakeholders to share insights, perspectives, and recommendations.
Consequently, the outcome of this stakeholder’s engagement should lead to the development of a Green Paper, a foundational document that consolidates stakeholders’ ideas, opinions, and strategies for adopting smart contracts in the construction industry. This Green Paper will serve as a precursor to an action-oriented White Paper, which can provide concrete proposals and a roadmap for implementation. Ultimately, these efforts will guide the formulation of comprehensive regulatory guidelines for the seamless adoption and integration of smart contracts into the project procurement process in the construction industry. This stakeholder engagement that leads to the development of a Green Paper should be led by a trio of the Department of Public Works and Infrastructures, the Council for Built Environment (CBE), and the Construction Industry Development Board (CIDB). This is because these three government bodies and agencies have the necessary authority within the construction industry and built environment to bring about the needed platform and reach for the adoption of smart contracts.
7.2 Integration of smart contracts into standard forms of construction contracts
Globally recognized standard forms of construction contracts, such as the Joint Building Contracts Committee (JBCC), New Engineering Contract (NEC), International Federation of Consulting Engineers (FIDIC), and General Conditions of Contract (GCC), should be adapted to incorporate smart contract processes. These traditional forms, while instrumental in structuring construction agreements, have not fully addressed persistent challenges in procurement, including poor project performance, cost overruns, contract disputes, time delays, and inefficiencies in supply chains. The integration of smart contracts into these frameworks has the potential to revolutionize the procurement mechanisms within the construction industry. By leveraging the automation, transparency, and security features of smart contracts, this adaptation can address the shortcomings of traditional procurement models, enhance project performance, and ensure greater reliability in the execution of contractual obligations.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
LD: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. MK: Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. CA: Project administration, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Afshari, A., and Bafti, F. G. (2023). Construction Project Procurement Management. In: XIII International Symposium Engineering Management and Competitiveness 2023 (EMC 2023). Zrenjanin, Serbia, June 16-17. Available online at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/373947006_CONSTRUCTION_PROJECT_PROCUREMENT_MANAGEMENT.
Akaba, T. I., Norta, A., Udokwu, C., and Draheim, D. (2020). “A framework for the adoption of blockchain-based e-procurement systems in the public sector: a case study of Nigeria,” in Responsible design, implementation, and use of information and communication technology. Editors M. Hattingh, M. Matthee, H. Smuts, I. Pappas, Y. K. Dwivedi, and M. Mäntymäki (Springer), 3–14. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-44999-5_1
Akinradewo, O. I., Aigbavboa, C. O., Edwards, D. J., and Oke, A. E. (2022). A principal component analysis of barriers to the implementation of blockchain technology in the South African built environment. J. Eng. Des. Technol. 20 (4), 914–934. doi:10.1108/JEDT-05-2021-0292
Alexander, A. (2023). Block by block: Smart contracts in South Africa. Perspectives. 2. Available online at: https://www.rlb.com/africa/insight/perspective-2023-vol-2/block-by-block-smart-contracts-in-south-africa/.
Al Tamimi, A., and Shuib, M. (2009). Motivation and attitudes towards learning English: a study of petroleum engineering undergraduates at Hadhramout University of Science and Technology. GEMA Online J. Lang. Stud. 9 (2), 29–55. Available online at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/285838565_Motivation_and_attitudes_towards_learning_English_A_study_of_petroleum_engineering_undergraduates_at_Hadhramout_University_of_Sciences_and_Technology.
Awuzie, B., and Moghayedi, A. (2024). Harnessing 4IR/5IR technologies for improved procurement and delivery. Routledge Handbook of Construction Project Procurement and Delivery. Available online at: https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/10.1201/9781003351269-25/harnessing-4ir-5ir-technologies-improved-procurement-delivery-bankole-awuzie-alireza-moghayedi.
Bangani, S. E. (2023). An appraisal of procurement challenges facing emerging contractors in public sector projects in South Africa (Master’s dissertation, Durban University of Technology). Available online at: https://openscholar.dut.ac.za/bitstream/10321/5458/3/Bangani_SE_2024.pdf.
Brown, A., Jones, B., Kim, J., Ahn, D., and Kang, Y. (2021). Effectiveness of VR crane training with head-mounted display: double mediation of presence and perceived usefulness. Automation Constr. 122, 103506. doi:10.1016/j.autcon.2020.103506
Bryant, F. B., and Yarnold, P. R. (1995). “Principal components analysis and exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis,” in Reading and understanding multivariate statistics. Editors L. G. Grimm, and P. R. Yarnold (American Psychological Association), 99–136.
Campbell, S., Greenwood, M., Prior, S., Shearer, T., Walkem, K., Young, S., et al. (2020). Purposive sampling: complex or simple? Research case examples. J. Res. Nurs. 25 (8), 652–661. doi:10.1177/1744987120927206
Catalini, C., and Gans, J.S. (2018). Initial Coin Offerings and the Value of Crypto Tokens. NBER Working Papers 24418, National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc. Available online at: https://ideas.repec.org/p/nbr/nberwo/24418.html.
Čeke, D., Buzadija, N., and Kunosić, S. (2022). “Enhancing transparency and fairness in public procurement process with the support of blockchain technology: a smart contract-based approach,” in 2022 21st international symposium INFOTEH-JAHORINA (INFOTEH) (IEEE), 1–6. doi:10.1109/INFOTEH53737.2022.9751322
Clack, C. D., Bakshi, V. A., and Braine, L. (2017). Smart contract templates: foundations, design landscape and research directions. Comput. Soc. doi:10.48550/arXiv.1608.00771
Confideal (2017). Smart contracts made simple. NewsBTC. Available online at: https://www.newsbtc.com/2017/10/23/confideal-smart-contracts-made-simple.
Creswell, J. W. (2014). Research design: qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches. 4th ed. London, United Kingdom: Sage Publications.
David, L. O., Nwulu, N. I., Aigbavboa, C. O., and Adepoju, O. O. (2022). Integrating Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR) technologies into the water, energy and food nexus for sustainable security: a bibliometric analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 363, 132522. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132522
Davis, F. D. (1989). Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Q. 13 (3), 319–340. doi:10.2307/249008
De Filippi, P., and Wright, A. (2018). Blockchain and the law: the rule of code. Harvard University Press. doi:10.2307/j.ctv2867sp
Dillman, D. A., Smyth, J. D., and Christian, L. M. (2014). Internet, phone, mail, and mixed-mode surveys: the tailored design method. 4th ed. John Wiley and Sons. doi:10.1002/9781394260645
Ebekozien, A., Aigbavboa, C., Thwala, W. D., Samsurijan, M. S., Ahmed, M. A. H., Aliu, J., et al. (2024). Appraising the application of Cryptocurrency to technologies in the Nigerian Built Environment: Stakeholders Perspectives. Int. J. Build. Pathol. Adapt. 42(7). doi:10.1108/IJBPA-04-2024-0070
Electronic Communication and Transactions Act (2002). Electronic Communication and Transactions Act. Available online at: https://www.gov.za/sites/default/files/gcis_document/201409/a25-02.pdf.
Ene, C. (2020). “Smart contracts – the new form of legal agreements,” in Proceedings of the 14th international conference on business excellence 2020 (Warsaw Poland: Sciendo), 1206–1219. doi:10.2478/picbe-2020-0113
EY (2023). EY Blockchain Analyzer: smart contract and token review. Available online at: https://www.ey.com/en_za/services/blockchain/platforms/smart-contract-token-review.
Fraenkel, J. R., Wallen, N. E., and Hyun, H. H. (2015). How to design and evaluate research in education. 9th ed. McGraw-Hill.
Gliem, J. A., and Gliem, R. R. (2003). “Calculating, interpreting, and reporting Cronbach’s alpha reliability coefficient for Likert-type scales,” in Midwest research-to-practice conference in adult, continuing, and community education. Columbus, OH: The Ohio State University.
He, X., Qin, B., Zhu, Y., Chen, X., and Liu, Y. (2018). “SPESC: a specification language for smart contracts,” IEEE 42nd Annu. Comput. Softw. Appl. Conf. (COMPSAC), 1, 132–137. doi:10.1109/compsac.2018.00025
Jahani, N., Sepehri, A., Vandchali, H. R., and Tirkolaee, E. B. (2021). Application of Industry 4.0 in the procurement processes of supply chains: a systematic literature review. Sustainability 13 (14), 7520. doi:10.3390/su13147520
Khutso, M. L., Nkomo, M. W., and Ramabodu, S. M. (2023). “Investigating challenges facing the performance of South African construction industry: an exploratory study,” in In proceedings of the 8th north American international conference on industrial engineering and operations management (Houston, Texas, USA). Available online at: https://ieomsociety.org/proceedings/2023houston/427.pdf.
Levelset (2021). Construction cash flow and payment report. Available online at: https://www.levelset.com/tools/2021-national-construction-payments-report/.
Liao, Y.-K., Wu, W.-Y., Le, T. Q., and Phung, T. T. T. (2022). The integration of the technology acceptance model and value-based adoption model to study the adoption of e-learning: the moderating role of e-WOM. Sustainability 14 (2), 815. doi:10.3390/su14020815
Loosemore, M., Raftery, J., Reilly, C., and Higgon, D. (2012). Risk management in projects. London: Routledge. doi:10.4324/9780203963708
Mao, T., and Chen, J. (2023). “Smart contract in blockchain,” in Proceedings of the ICBBEM 2022, AHIS. Editor D. Qui 868–875. doi:10.2991/978-94-6463-030-5_86
Martinez, M. N., and Bartholomew, M. J. (2017). What does it “mean”? A review of interpreting and calculating different types of means and standard deviations. Pharmaceutics 9 (14), 14. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics9020014
Migiro, S. O., and Ambe, I. M. (2008). Evaluation of the implementation of public sector supply chain management and challenges: a case study of the central district municipality, North West province, South Africa. Afr. J. Bus. Manag. 2 (12), 230–242. doi:10.5897/AJBM.9000272
Moser, C. A., and Kalton, G. (2017). Survey methods in social investigation. 2nd ed. Basic Books. doi:10.4324/9781315241999
Mougayar, W. (2016). According to fragmentation threatens the promise of blockchain CoinDesk. Available online at: http://www.coindesk.com/fragment-blockchain-identity-market.
Özkan, E., Azizi, N., and Haass, O. (2021). Leveraging smart contract in project procurement through DLT to gain sustainable competitive advantages. Sustainability 13 (23), 13380. doi:10.3390/su132313380
Peters, E., Subar, K., and Martin, H. (2019). Late payment and nonpayment within the construction industry: causes, effects, and solutions. J. Leg. Aff. Dispute Resolut. inEngineering Constr. 11 (3). Available online at: https://ascelibrary.org/doi/epdf/10.1061/(ASCE)LA.1943-4170.0000314.
Rathnayake, I., Wedawatta, G., and Tezel, A. (2022). Smart contracts in the construction industry: a systematic review. Buildings 12 (12), 2082. doi:10.3390/buildings12122082
Risius, M., and Spohrer, K. (2017). A blockchain research framework. Bus. and Inf. Syst. Eng. 59, 385–409. doi:10.1007/s12599-017-0506-0
Sahin, I. (2006). Detailed review of Rogers' diffusion of innovation theory and educational technology-related studies based on Rogers' theory. Turkish Online J. Educ. Technol. 5 (2). Available online at: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED501453.pdf.
Saunders, M. N. K., Lewis, P., and Thornhill, A. (2019). “Research methods for business students,”. 8th ed. New York: Pearson.
Savage, G. T., Bunn, M. D., Gray, B., Xiao, S., Wang, S., Wilson, E. J., et al. (2011). Stakeholder collaboration: implications for stakeholder theory and practice. J. Bus. Ethics 96, 21–26. doi:10.1007/s10551-011-0939-1
Savelyev, A. (2017). Contract law 2.0: ‘Smart’ contracts as the beginning of the end of classic contract law. Inf. and Commun. Technol. Law 26 (2), 116–134. doi:10.1080/13600834.2017.1301036
Surucu, L., Yikilmaz, I., and Maslakci, A. (2022). Exploratory factor analysis (EFA) in quantitative researches and practical consideration. Gumushane Univ. J. Health Sci. 13 (2), 947–965. doi:10.37989/gumussagbil.1183271
Sykes, L. M., Gani, F., and Vally, Z. (2016). Statistical terms part 1: the meaning of the mean and other statistical terms commonly used in medical research. South Afr. Dent. J. 71 (6). Available online at: https://www.scielo.org.za/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0011-85162016000600009.
Szabo, N. (1997). Formalizing and securing relationships on public networks. First Monday 2 (9). doi:10.5210/fm.v2i9.548
Tambwe, O. T., Aigbavboa, C. O., and Akinradewo, O. (2023). Benefits of construction data risks management in the construction industry. J. Eng. Des. Technol. 23, 458–476. doi:10.1108/JEDT-11-2022-0577
Tapscott, D., and Tapscott, A. (2016). Blockchain Revolution: How the Technology behind Bitcoin Is Changing Money, Business, and the World. New York: Penguin. Available online at: https://www.amazon.com/Blockchain-Revolution-Technology
Tshabalala, L. (2024). Gaps and challenges in supply chain management in South African government departments: the role of implementing an integrated financial management system (Master’s thesis, University of the Witwatersrand). Available online at: https://wiredspace.wits.ac.za/server/api/core/bitstreams/15572ccd-e993-4ff2-b3f2-bfeff863893c/content.
University Center for Teaching and Learning (UCTL) (2018). Pittsburgh: Definitions. Available online at: https://teaching.pitt.edu/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/Item-Analysis-Definitions.pdf.
Van Eck, M., and Agbeko, F. D. (2024). The recognition and regulation of smart contracts in South Africa. Potchefstroom Electron. Law J. 27, 1–24. doi:10.17159/1727-3781/2024/v27i0a16383
Weingartner, T., Rao, R., Ettlin, J., Suter, P., and Dublanc, P. (2018). “Smart contracts using Blockly: representing a purchase agreement using a graphical programming language,” in 2018 crypto valley conference on blockchain technology (CVCBT) (IEEE), 55–64. doi:10.1109/CVCBT.2018.00012
Werbach, K., and Cornell, N. (2017). Contracts ex machina. Duke Law J. 67 (2), 313. Available online at: https://scholarship.law.duke.edu/dlj/vol67/iss2/2.
Williams-Elegbe, S. (2018). Public procurement, corruption and blockchain technology: a preliminary (legal) inquiry.
Wright, A., and De Filippi, P. (2015). Decentralized blockchain technology and the rise of lex cryptographia. Soc. Sci. Res. Netw. 34, 41–52. doi:10.2139/ssrn.2580664
Keywords: procurement management, smart contract, blockchain technology, construction projects, project procurement
Citation: David L, Kgomo M and Aigbavboa C (2025) Smart contract in construction procurement: insights and recommendations from South Africa. Front. Built Environ. 11:1620790. doi: 10.3389/fbuil.2025.1620790
Received: 30 April 2025; Accepted: 09 June 2025;
Published: 16 July 2025.
Edited by:
Obuks Ejohwomu, The University of Manchester, United KingdomReviewed by:
Andrew Agapiou, University of Strathclyde, United KingdomJohn Aliu, University of Georgia, United States
Copyright © 2025 David, Kgomo and Aigbavboa. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Love David, bG92ZW9wZXllbWlkQHVqLmFjLnph
 Love David
Love David Marumo Kgomo
Marumo Kgomo