- School of Civil Engineering, Vellore Institute of Technology (VIT), Vellore campus, Vellore, Tamil Nadu, India
This study investigates advanced Ni–NiO coatings for improving the corrosion protection of mild steel in alkaline concrete environments using an integrated experimental and computational approach. Mild steel samples were coated with Ni–NiO, both as duplex coatings and in combination with epoxy and PVDF binders, and their corrosion resistance was evaluated. Electrochemical methods, such as Tafel analysis and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), were employed to assess the corrosion performance over a 28-day exposure period. COMSOL Multiphysics simulations were conducted by modelling key parameters, including the geometry of the steel-concrete system, the mechanical properties of steel, concrete, and corrosion products, as well as the diffusion coefficients of Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions, corrosion current density, porosity, and coating thicknesses. These simulations accurately replicated the progressive corrosion-induced damage and ion transport phenomena observed experimentally, enabling a direct comparison with experimental results. The Ni–NiO duplex system demonstrated higher corrosion resistance compared to other coated samples, which consistently exhibited the lowest corrosion rates, highest impedance, and most stable corrosion potentials throughout the study period. The enhanced performance of the duplex coatings was attributed to the formation of a dense, chemically stable barrier and the synergistic effects of the oxide layers and zincate pretreatment, as validated by both computational modelling and electrochemical data. This combined experimental and computational investigation demonstrates the significant potential of Ni–NiO duplex coatings for the long-term protection of steel reinforcements in concrete structures.
1 Introduction
In materials science and engineering, preventing steel structures from corroding in extremely alkaline concrete environments is a significant challenge (Van Nguyen et al., 2022). Over time, corrosion can severely impair the strength and longevity of steel reinforcements, ultimately leading to structural failure (Qu et al., 2021; Shi et al., 2020). Therefore, selecting appropriate coating materials and optimising their structures is necessary for effective corrosion mitigation (Zhang et al., 2022). Nickel (Ni)-based coatings have become a promising solution owing to their remarkable mechanical strength, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance. Electrodeposited and binder-based Ni coatings have become increasingly popular because they create stable, corrosion-resistant layers, making them excellent for long-term structural protection (Suhas and Shanmugapriya, 2024; Liu et al., 2020; Suhas and Shanmugapriya, 2025).
Recent developments in Ni-based coatings have significantly enhanced their surface performance by adding nanomaterials such as silicon carbide (SiC), zirconium dioxide (ZrO2), titanium nitride (TiN), cerium dioxide (CeO2), aluminium oxide (Al2O3), and zinc oxide (ZnO) (Suhas and Shanmugapriya, 2024; Liu et al., 2020; Suhas and Shanmugapriya, 2025). Kumar et al. (2019) studied passive (W) tungsten oxide films and found that Ni–W alloy coatings exhibited better corrosion resistance than pure Ni coatings (Kumar et al., 2019). Similarly, research on transition metal oxides, such as nickel oxide (NiO), a p-type semiconductor with a broad bandgap (3.6–4.0 eV), has shown that it is a promising material for corrosion-resistant coatings due to its excellent mechanical and chemical resilience (Sun et al., 2021; Tripathi et al., 2024). Salicio-Paz et al. (2019). Due to their porous nature, NiO thin films enhance barrier protection and reduce the likelihood of metallic substrate degradation, as seen in Ni-P coatings with an optimal phosphorus concentration, which exhibit outstanding anticorrosion performance in chloride-rich environments (Salicio-Paz et al., 2019; Yuan et al., 2020). Xinhao Sun et al. (2021) observed that while nickel oxide exhibits poorer mechanical properties than other oxide ceramics, with higher hardness but lower fracture toughness than metallic Ni, combining NiO with Ni can enhance the coating’s mechanical properties and improve its corrosion resistance (Sun et al., 2021).
Surface coating technologies for corrosion protection primarily include sol-gel, spray, and dip coating methods, with polymer-based modifications and electrolytic deposition being the most prevalent approaches (Suhas and Shanmugapriya, 2025; Chen et al., 2022; Li et al., 2024; Gutierrez et al., 2017). Among these, polymer modification constitutes a substantial portion of coatings; however, the incorporation of water and other additives can introduce challenges such as an increased risk of coating failure compared to other methods. Electrolytic deposition, on the other hand, presents a facile and effective technique for directly applying nanomaterial-based coatings to substrates without the need for complex modifications, thereby enhancing coating performance and durability (Suhas and Shanmugapriya, 2025; Chen et al., 2022; Li et al., 2024).
Duplex nickel coatings, which consist of multiple nickel-based layers, have been extensively investigated due to their enhanced corrosion resistance resulting from a combination of passivation and barrier effects. Various duplex systems, such as Ni-P/Ni-B, Ni-P/Ni-W-P, and Ni-P/Ni-Cu-P, have demonstrated higher corrosion protection compared to monolayer coatings, benefiting from the synergistic interaction of their constituent layers. For example, Chen et al. (2018) reported that Ni-P/Ni-W-P duplex coatings on AZ91D magnesium alloys exhibited significantly enhanced corrosion resistance, attributed to the Ni-W-P layer enhancing passivation and the Ni-P layer serving as a robust chemical barrier.
Despite the improved corrosion resistance of duplex coatings, their adhesion strength has sometimes been reported as lower or sub-optimal compared to other types of coatings. Gutierrez et al. (2017) demonstrated that multistep zincate pretreatment significantly enhanced both the adhesion strength and corrosion resistance of electroless Ni-P coatings on aluminium alloys, underscoring the crucial role of surface pretreatment in achieving durable duplex coatings. Consequently, duplex-coated mild steel substrates that undergo appropriate zincate pretreatment also demonstrate enhanced adhesion and corrosion resistance, reinforcing the importance of pretreatment processes in optimising coating performance (Chen et al., 2022; Li et al., 2024; Gutierrez et al., 2017).
However, real-world applications require a more comprehensive assessment of coating performance under complex and aggressive conditions that are difficult to replicate in the laboratory (Cui et al., 2023). Therefore, integrating cutting-edge computational simulations with experimental research is crucial for a deeper understanding of the protective layer performance, particularly considering the growing complexity of coating failure processes (Korec et al., 2023). Computational modelling enables the predictive analysis of coating behaviour and offers helpful recommendations for structural optimisation and material selection (Prajapati et al., 2022). For instance, COMSOL Multiphysics can be utilised to model stresses and strains in coatings, providing insights into critical parameters such as von Mises stress, eigen strain, and phase-field diagrams. Additionally, simulations can predict crack width and propagation, which are essential for understanding the durability and failure mechanisms of coatings (Cui et al., 2023; Korec et al., 2023; Prajapati et al., 2022).
This study aims to address a critical gap in the understanding of corrosion protection by thoroughly investigating advanced Nickel-Nickel Oxide (Ni-NiO) duplex coatings on mild steel in highly alkaline simulated concrete pore solutions. The limitations associated with corrosion analysis of most duplex coatings stem from their testing in general alkaline solutions, rather than the highly alkaline environments of concrete pore solutions, which have not been thoroughly investigated despite existing evidence that duplex coatings enhance corrosion resistance and zincate pretreatment improves adhesion. Moreover, most of these studies have relied on conventional electrochemical techniques, including open-circuit potential (OCP), Tafel polarisation (TP), and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), which are often conducted in standard salt solutions. A comprehensive assessment under aggressive concrete pore conditions, integrating both experimental and advanced computational analyses, has been lacking. This research combines accelerated weight loss analysis and analytical validation in a concrete pore solution to analyse the corrosion inhibition capability of the sample coated on mild steel. Furthermore, the advanced methodology of using COMSOL for numerical simulations to examine the stress distribution, phase-field evolution, and fracture propagation provides a real-time understanding of the mechanical integrity of the coating structure and long-term endurance. The novelty of this study lies in its integrated, multi-method approach, which not only compares the corrosion resistance of a novel Ni-NiO duplex sample with polymer-modified Ni-NiO coatings (PVDF and epoxy) but also analytically validates the corrosion inhibition capability and examines the real-time mechanical integrity of the coating structure and long-term endurance through numerical simulations. This comprehensive assessment highlights the superior corrosion resistance and durability provided by the Ni-NiO duplex coating, offering valuable insights to enhance the lifespan and safety of reinforced concrete infrastructure.
2 Materials and methods
Mild steel samples were prepared for coating by sequential abrasion using silicon carbide (SiC) abrasive paper with a grit size of 1000, followed by magnetic polishing to enhance the surface smoothness. The samples were then degreased with acetone to remove contaminants. A 1 cm2 area was exposed for coating by encasing the samples with Teflon tape, while the opposite side was left uncovered over an area of 3–5 cm for electrochemical analysis. The coatings used included epoxy resin and hardener from Pidilite Industries Pvt. Ltd. and PVDF from Sigma Aldrich Chemicals Pvt. Ltd. Duplex coatings were also applied to these samples.
A simulated concrete pore solution was prepared by adding 0.1 M sodium hydroxide to a base solution, followed by adding 0.002 M calcium sulphate dihydrate, 0.3 M potassium hydroxide, and 0.03 M calcium hydroxide. The solution was corrosive because of the incorporation of 0.5 M NaCl. ZnO, nickel sulphate, nickel chloride, and boric acid were sourced from Sisco Research Laboratories Pvt. Ltd. Nickel and nickel oxide nanoparticles (average particle size of 50 nm) were obtained from Central Drug House Pvt. Ltd.
2.1 Binder coating preparation
The epoxy coating was formulated using a hardener-to-epoxy resin ratio of 1:5 (0.6 mL hardener and 3 mL epoxy). A resin-to-hardener ratio of 2:5 was used to prepare modified epoxy coatings. Specifically, the Ni-epoxy and NiO–epoxy coatings incorporated 500 mg of nickel (Ni) nanopowder and nickel oxide (NiO) nanopowder, respectively. The Composite Coating was prepared by combining 250 mg of Ni nanopowder and 250 mg of NiO nanopowder, maintaining the same 2:5 hardener-to-resin ratio. A composite of Ni-NiO nanopowder and a PVDF solution (PVDF and N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone) was prepared in an 8:1 (160 g PVDF and 4 mL NMP) volumetric ratio. The formulation was mechanically stirred to ensure its homogeneity.
After meticulous coating preparation, individual samples were coated onto mild steel with an area of 1 cm2 for testing.
2.2 Ni -NiO duplex coating
Before nickel electroplating, mild steel substrates underwent zincate treatment to enhance the adhesion of the deposited coating. The zincate bath was formulated by dissolving 150 g of sodium hydroxide (NaOH), 100 g of zinc oxide (ZnO), 1 g of ferric chloride (FeCl3), and 10 g of potassium sodium tartrate (C4H4KNaO6) in 1 L of deionised water. The substrates were immersed in this solution for 45 s to ensure optimal surface preparation before the subsequent electroplating process.
The nickel electrodeposition process utilised a matte nickel electrolyte formulated with 24 g of nickel sulfate (NiSO4), 2 g of nickel chloride (NiCl2), and 3 g of boric acid (H3BO3) dissolved in 100 mL of deionised water. The bath was operated at a current density of 0.96 A/dm2, maintained at pH 4.0, and a temperature of 55 °C. The deposition occurred over 120 s using a DC power supply, with the cathode (mild steel substrate) and anode (nickel electrode) positioned 20 mm apart in parallel to ensure uniform coating. A reduced current of 0.12 A was applied to the 1 cm2 active surface area for an optimised layer consistency. After the deposition, coating thickness measurements were conducted at five distinct locations using a Digimess TT-210 instrument to verify the process’s reliability.
A Ni/NiO duplex layer was formed by exposing the samples to different temperatures ranging from 350 °C to 550 °C for 30 min in a muffle furnace in the presence of oxygen. The samples were heated at intervals of 50 °C to optimise the amount of NiO produced. Conditions such as temperature and time are critical for controlling the thickness and uniformity of the NiO layer. To ensure consistency, all the samples were placed in the furnace core to minimise the temperature gradients and enhance the homogeneity of the oxidation process.
2.3 Weight loss analysis
Weight loss analysis was used to measure the cumulative material degradation over time. The sample was connected to a DC power source to accelerate corrosion, and the weight loss was analysed over a 60-day sample period, as shown in Equation 1 (Suhas and Shanmugapriya, 2024; Suhas and Shanmugapriya, 2025):
where,
S1 = weight of the Sample without inhibitor.
Sn = weight of the Sample with inhibitor.
2.4 Characterisation of the coatings
The oxidised NiO film was examined using a FEI QUANTA 250 FEG Finite Element Scanning Electron Microscope (FESEM). The corrosion resistance of the samples was assessed using OCP (Open Circuit Potential), EIS (Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy), and Tafel plots. Corrosion studies were conducted using a simulated concrete pore solution, which was considered an electrolyte solution.
Measurements were performed using a Gill AC potentiostat (ACM) instrument in the field with a three-electrode apparatus: a saturated calomel electrode (SCE) as the reference electrode, a platinum wire serving as the counter electrode, and a steel specimen, as shown in Figure 1a. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) is a non-destructive technique that applies low-amplitude alternating current (AC) signals to electrochemical systems, providing insights into their corrosion behaviour by analysing their impedance responses, as outlined in ASTM G3-14 (2019). EIS was performed with an OCP of 10 mV sinusoidal potential perturbation at frequencies between 100 kHz and 10 MHz. The scan rate used to measure the LSV was 10 mV/min. A Bruker D8 Advance X-ray diffractometer with a Cukα radiation source was used to evaluate the composition and generation mechanism of the passive layers. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) scan ranged from 10° to 80°. Figure 1a shows the setup and output models for the Tafel extrapolation.
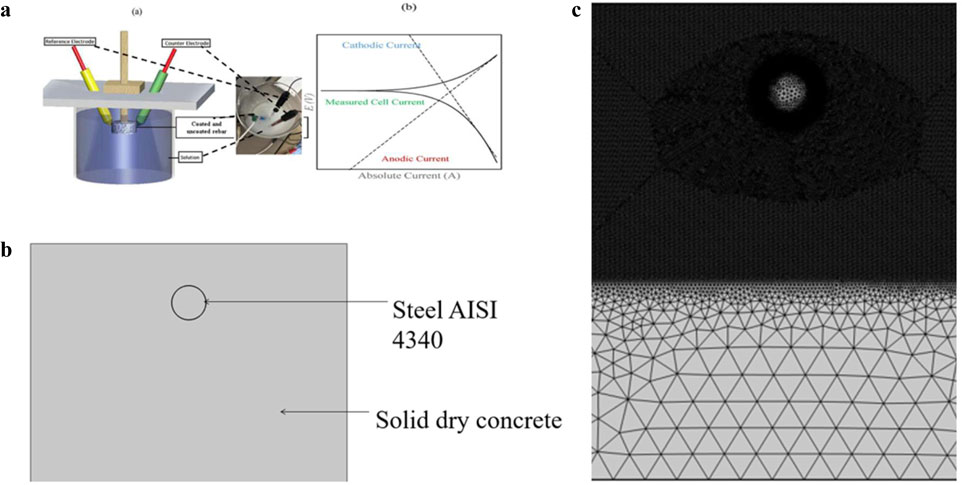
Figure 1. (a) Schematic representation of (a) corrosion test setup and (b) Tafel extrapolation. (b) 2D Concrete rebar interface geometric representation. (c) Schematic representation of meshing.
2.5 Analytical validation
In this study, the corrosion current density (Icorr) was determined using a widely accepted analytical approach based on the mass loss of corrosive materials. The corrosion current density was calculated using Equation 2:
Where,
Icorr is the corrosion current density (A/m2).
n is the number of electrons involved in the corrosion reaction (n = 2 for Fe, Ni, and NiO).
F is Faraday’s constant (96,485 C/mol).
A is the area of the corroded surface (m2).
Δm is the mass loss of the iron (kg).
Δt is the corrosion measurement period (s).
This equation provides the corrosion current density (Icorr) in amperes per square metre (A/m2), which is a key parameter for evaluating the corrosion rate in an electrochemical system. The corrosion rate can be derived and used to assess the severity of corrosion over time by measuring the mass loss of a material, determining its exposure time, and calculating its surface area. This can be used to validate the electrochemical results.
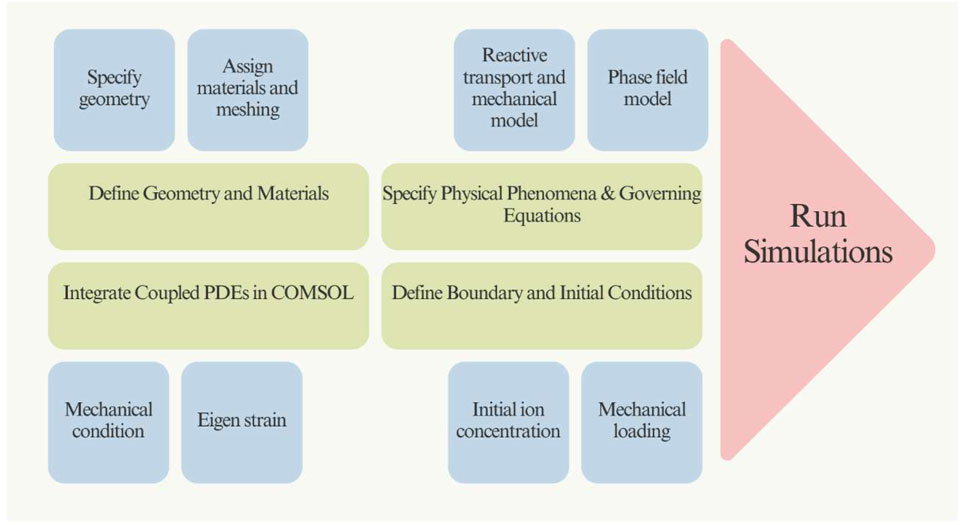
2.6 Simulation
The workflow of the simulation for the coating is illustrated in Figure 2. A 2D asymmetric stationary model of a coated rebar embedded in a concrete environment was developed using COMSOL Multiphysics software (version 6.1). The geometry of the model is detailed in Table 1 and depicted in Figure 1b.
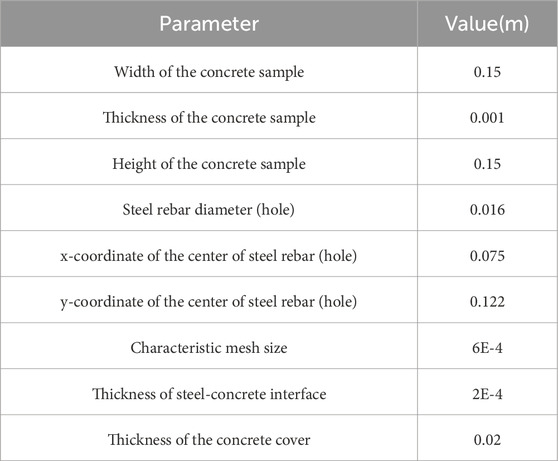
Table 1. Geometry (Korec et al., 2023).
Figure 1c shows the meshing of the material sketched or shown for modelling purposes. The elements are small triangular components that make up the model and do not overlap because of the meshing.
The behaviour of each component within the system is represented by a mathematical function that encapsulates the physical response. However, these functions may initially be undefined or complex, necessitating the use of numerical approximation techniques to obtain their solutions. The accuracy of the overall model depends on the precision with which these component functions are approximated and integrated into a more extensive system. Subsequently, the library content was added, and the system’s required parameters were incorporated. In this case, Steel AISI 4340 and solid dry concrete were added, and then the coating was applied as a stacked sequence of materials. The COMSOL library was the source of all required resources.
2.6.1 1Mechanism of corrosion-induced cracking and its current modelling
Corrosion-induced cracking in reinforced concrete structures begins when water and oxygen infiltrate the concrete, triggering the oxidation of steel rebars and the formation of iron oxides (Korec et al., 2023). These corrosion products expand, generating internal pressure that strains the concrete and initiates cracking (Cui et al., 2023). Over time, crack propagation damages structural integrity, emphasising the need for advanced models that simulate key mechanisms such as corrosion expansion and stress distribution using finite element analysis (FEA) (Suhas and Shanmugapriya, 2024).
The mechanical properties of the materials used in the numerical simulations are presented in Table 2. However, coatings are not entirely impervious to harsh environments and require careful handling during installation to avoid damage. Corrosion-generated Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions diffuse through concrete under electrochemical gradients, as shown in Equations 3,4 and precipitate as iron hydroxides (Fe(OH)2/Fe(OH)3) within the pore network (Korec et al., 2023). The precipitation reactions are as follows.
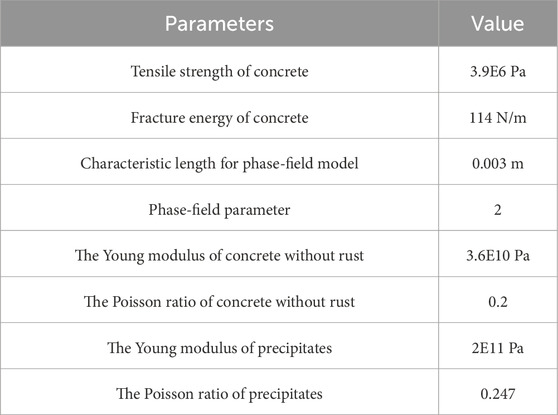
Table 2. Mechanism of materials (Cui et al., 2023).
This precipitation process resulted in significant volumetric expansion within the concrete matrix. The volume of the corrosion products, primarily iron hydroxides (Fe(OH)2 and Fe(OH)3), is substantially more significant than the volume of the original steel rebar. This volume expansion is due to the bulky corrosion products, which occupy a greater volume than the metals they replace.
The expansive pressure from the precipitation of iron hydroxides induces tensile stress in the surrounding concrete matrix, leading to microcracking, as expressed in Equation 5. The stress σ induced by this expansion can be modelled using:
where E is Young’s modulus of concrete, and ϵ is the strain due to the volumetric expansion of precipitates.
The formation and propagation of cracks in concrete due to precipitation increases the permeability, allowing more aggressive species to penetrate the concrete matrix, as expressed in Equation 6. This enhanced transport can be modelled by an increased effective diffusion coefficient Dc, which is dependent on the crack width:
where D is the diffusion coefficient in uncracked concrete and α is a proportionality constant.
These equations model the corrosion current density and associated electrochemical reactions, such as the oxidation of iron and the precipitation of iron hydroxides. Integrating these models with reactive transport simulations can predict the impact of corrosion on structural integrity, including crack propagation and the effects of environmental factors such as chloride ingress and oxygen availability.
2.6.2 Reactive transport model
A reactive transport modelling computer method combines chemical processes, solute transport, and fluid movement in porous media (Prajapati et al., 2022). Reactive transport modelling provides a foundation for simulating the dynamic interaction between physical and chemical processes in porous media. The parameters of the physical and chemical methods are listed in Table 3.
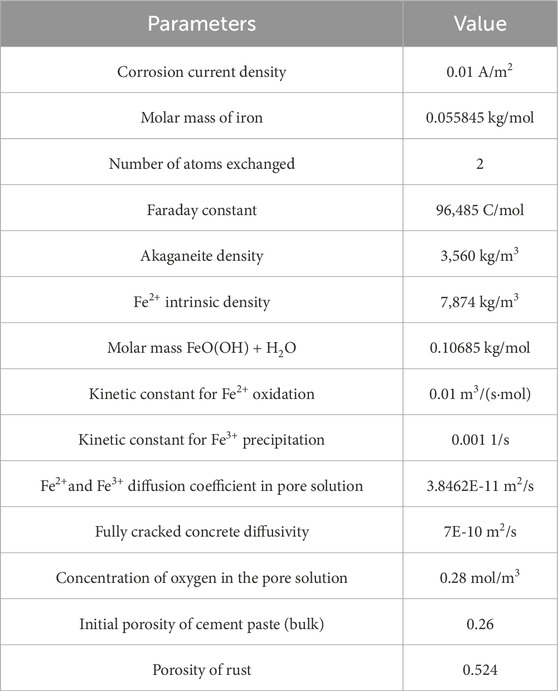
Table 3. Transport Model parameters (Korec et al., 2023).
A Representative Volume Element (RVE) was defined to capture the essential features of the concrete-rebar system. The primary fields within the RVE include the concentrations of Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions, displacement field, and phase field representing cracks (Prajapati et al., 2022).
The reactive transport of Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions in concrete is governed by the coupled partial differential equations (PDEs) as in Equations 7, 8:
where CFe2+and CFe3+are the concentrations of Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions, DFe2+and DFe3+are their respective diffusion coefficients, and RFe2+and RFe3+are reaction terms.
The primary chemical reactions considered included the oxidation of Fe2+ to Fe3+ as in Equation 9:
precipitation of iron hydroxides as represented in Equation 4
The reaction rates were modelled using kinetic rate laws. For the oxidation of Fe2+ as in Equation 10:
where k ox is the oxidation rate constant. For the precipitation of Fe(OH)3 as in Equation 11:
where kprec is the precipitation rate constant.
The eigenstrain due to precipitation-induced volumetric expansion is modelled as given in Equation 12:
where β is the expansion coefficient, and Vprec is the volume fraction of precipitated material.
This approach involves solving coupled partial differential equations that describe the diffusion and reaction of ions such as Fe2+ and Fe3+, which are crucial for understanding corrosion-induced cracking. The mechanism of corrosion-induced cracking involves the oxidation of steel rebars, resulting in the formation of expansive corrosion products that strain the concrete and initiate cracks.
2.6.3 Phase-field description of precipitation-induced cracks
The phase-field method is used to describe the formation and propagation of cracks. The phase-field variable ϕ ranges from 0 (intact material) to 1 (fully cracked material). The evolution of ϕ is governed by the system’s total free energy, which includes contributions from elastic energy, fracture energy, and the phase-field gradient energy (Cui et al., 2023).
For quasi-brittle materials such as concrete, the total free energy Ψ is given in Equation 13:
where ψ e ψ e is the elastic energy density, G c is the critical energy release rate, and ℓ ℓ is the phase-field length scale parameter.
The overall governing equations for the simulation are, The Reactive Transport Equation is the same as Equations 7,8
Mechanical Equilibrium as in Equation 14:
where the stress tensor σ σ is related to the strain tensor ϵ ϵ by as in Equation 15:
Phase-Field Evolution as in Equation 16:
where M is the mobility parameter, and δ Ψ/δ ϕ is the functional derivative of the free energy concerning the phase-field variable. These equations were implemented in COMSOL Multiphysics to simulate the behaviour of rebars coated with a Ni-NiO bilayer, Ni-NiO epoxy single-layer, and Ni-NiO PVDF single-layer coatings embedded in concrete. The simulations provided insights into the phase-field evolution, crack width, eigenstrain, displacement, and Fe2+ and Fe3+ concentrations under different environmental conditions.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Weight loss analysis
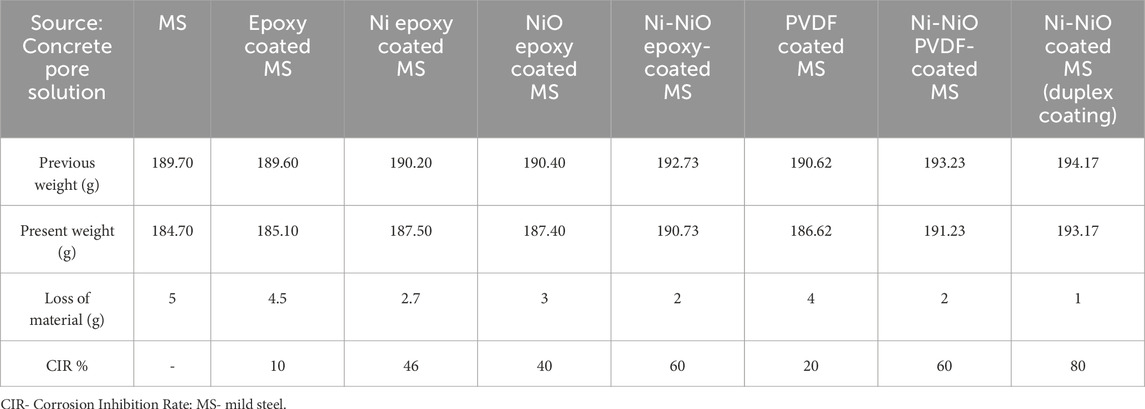
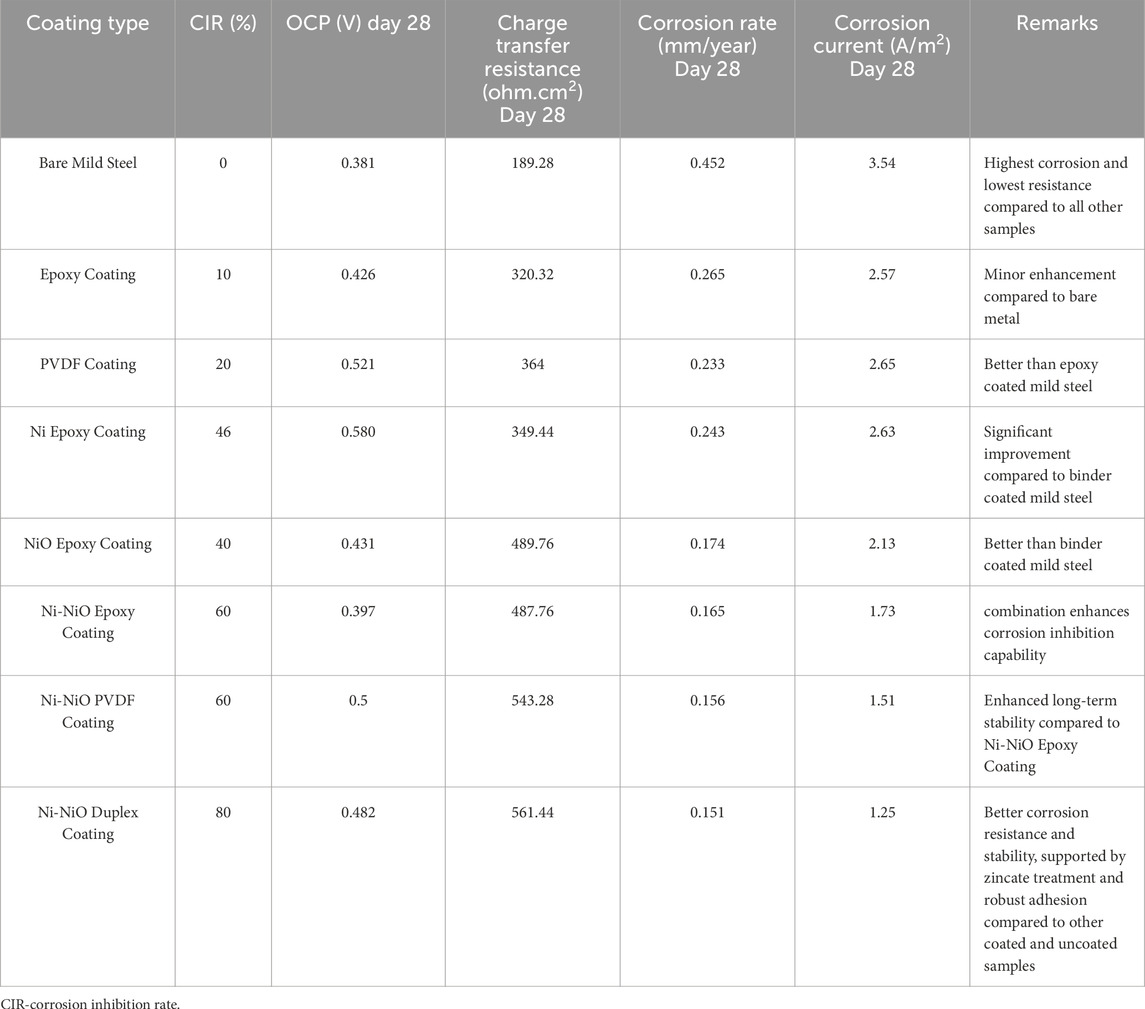
The gravimetric analysis results in Table 4 reveal significant variations in the corrosion resistances of the coated and uncoated mild steel samples. The uncoated mild steel exhibited the highest weight loss, amounting to 5.0 g, which served as a baseline for evaluating the effectiveness of the different coatings in inhibiting corrosion. The epoxy and PVDF coatings demonstrated marginal reductions in weight loss with 10% and 20% inhibition, respectively. However, modifying the epoxy with Ni or NiO coatings significantly enhanced the corrosion inhibition, with the Ni-epoxy and NiO-epoxy coatings achieving 46% and 40% inhibition, respectively. The hybrid Ni-NiO systems further enhanced the corrosion inhibition of both the epoxy and PVDF variants, with each earning 60% inhibition, highlighting the potential benefits of combining Ni and NiO in coating formulations. The Ni-NiO duplex coating demonstrated exceptional corrosion resistance with an impressive corrosion inhibition of 80%.
The higher corrosion inhibition capability of the Ni-NiO duplex coating is most likely due to the zincate process, which improves adhesion by forming a Zn-rich interlayer that acts as a sacrificial anode, thereby delaying substrate corrosion.
3.2 OCP analysis
The open-circuit potential (OCP) was used to analyse the potential difference between the working and reference electrodes when no external potential was applied to the system. Figure 3a presents the OCP values of the coated and uncoated mild steel samples after the initial immersion in the concrete pore solution on the 1st and 28th days. The variation in the OCP of the three Ni-NiO composite coatings was much smaller than that of the uncoated and coated samples.
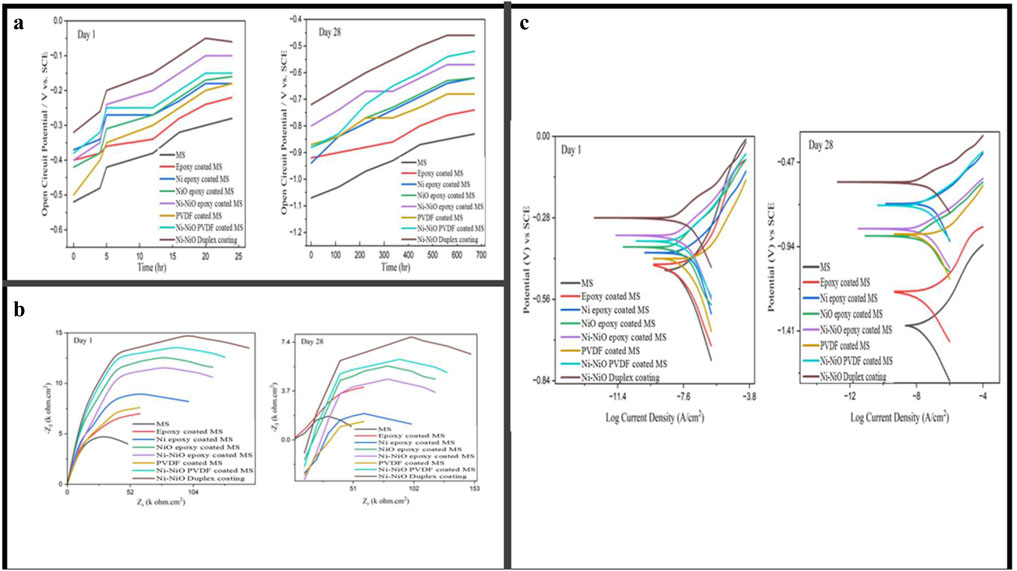
Figure 3. (a) Open-circuit potential for uncoated and coated mild-steel specimens. (b) Nyquist plots for uncoated and coated mild steel specimens. (c) Tafel plot for uncoated and coated mild steel specimens in concrete pore solution.
As illustrated in Figure 3a, the average OCP values of the Ni-NiO duplex coatings were the highest, which is attributed to the synergistic effect of the metallic conductivity of Ni and the passivation of NiO. Furthermore, the increased bandwidth of NiO allows it to function as an inductor, thereby offering protection against steel corrosion, and its metallic properties are enhanced by incorporating Ni (Sun et al., 2021). Among the three Ni-NiO-modified coatings, the second-highest OCP was observed for the Ni-NiO modified by epoxy, demonstrating favourable initial OCP values. However, the polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) coating gradually stabilised, and its OCP value increased owing to the stabilisation of the metal coating system, ultimately surpassing the corrosion inhibition performance of epoxy-modified Ni-NiO by the 28th day. Compared to the Ni-NiO/PVDF- and Ni-NiO/epoxy-coated mild steel samples, the duplex-coated sample exhibited the highest OCP on both the 1st and 28th days, owing to the duplex formation of Ni and NiO and the robust adhesion facilitated by zincate pretreatment.
3.3 EIS analysis
The Nyquist plots depicted in Figure 3b provide a comparative analysis of the impedance behaviour of the coated and uncoated mild steel samples on days 1 and 28. On Day 1, the uncoated MILD STEEL sample exhibited the smallest semicircle diameter, indicating the lowest impedance and minimal corrosion resistance. Among the coated samples, the Ni-NiO duplex coating applied to the rebar exhibited the largest semicircle diameter, indicating higher impedance and corrosion inhibition. Coatings such as Ni-epoxy-coated MILD STEEL and NiO epoxy-coated MILD STEEL exhibit intermediate performances, with semicircle diameters larger than that of the uncoated MILD STEEL but smaller than that of the Ni-NiO duplex coating (Suhas and Shanmugapriya, 2024).
The Ni-NiO/PVDF-coated samples maintained a high impedance after 28th days of exposure, suggesting that PVDF modification enhanced long-term corrosion inhibition. In contrast, the Ni-NiO/epoxy combination decreased the impedance over time, indicating a reduction in its protective qualities, despite initially offering corrosion resistance. The Ni-NiO duplex layer demonstrated significant corrosion resistance, likely due to its more stable and uniform structure, which forms a denser barrier against corrosive agents. Additionally, the zincate process used for surface preparation before Ni-NiO electrodeposition likely enhances the electrode’s performance.
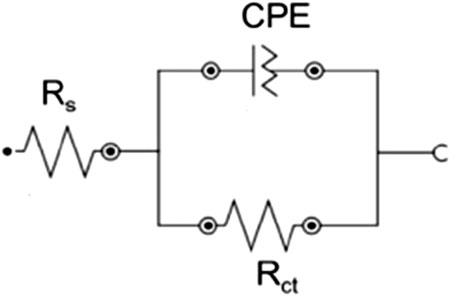
The corrosion inhibition ability of a sample can be derived from an equivalent circuit, as shown in Figure 4, which consists of the solution resistance (Rsol), charge transfer resistance (Rct), and constant phase element (CPE), where CPE replaces the pure capacitance in the model. The impedance of the CPE as a modified capacitor is given by Equation 17 (Suhas and Shanmugapriya, 2024).
In this equation, (Y0+) is the proportional factor, (j) is the imaginary unit, (ω) is the angular frequency, and (n) is the exponent, ranging between −1 and 1, depending on the value of n, reflecting the degree of heterogeneity formed on the surface film.
Two methods were used to calculate the effective capacitance based on the CPE parameters n and Y0. The effective capacitance of the double-layer region (Ceff, dl) is determined using Brug’s formula, which is applied when local inhomogeneities cause time-constant dispersion at the interface using Equation 18 (Suhas and Shanmugapriya, 2024):
When the time-constant dispersion results from variations in the properties perpendicular to the electrode surface, Hsu and Mansfeld’s equation was employed to compute the effective capacitance of the resulting film, as shown in Equation 19:
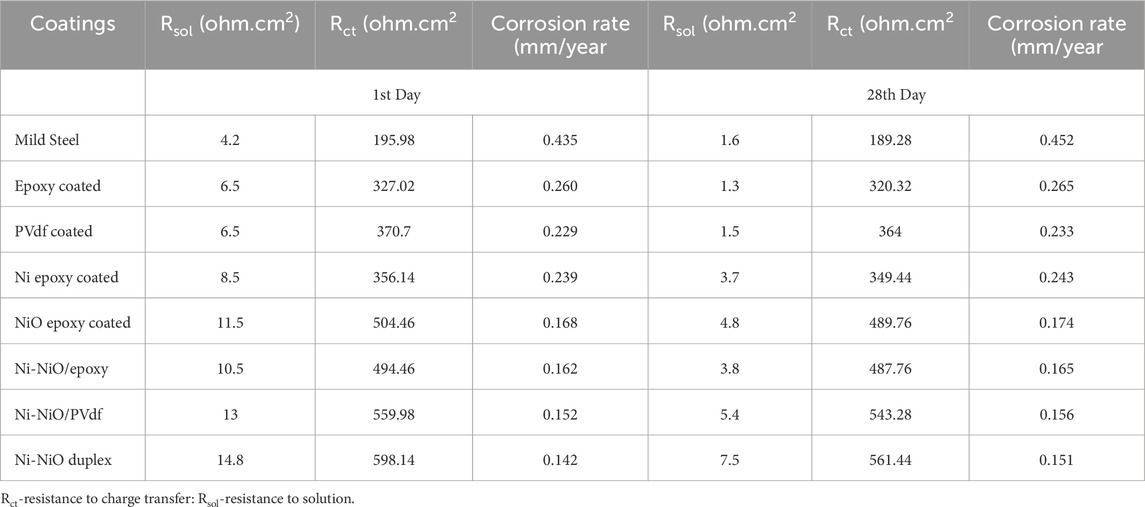
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) was used to investigate the corrosion behaviour of mild steel samples immersed in exposed environments. The Nyquist fit data were derived using an equivalent circuit, as shown in Figure 3b, and are detailed in Table 5, which consists of Rsol, Rct, and CR.
As shown in Table 5, the uncoated mild steel specimen exhibited the highest corrosion rate. In contrast, the samples coated with the binder exhibited a slightly reduced corrosion rate compared to that of the uncoated sample. Notably, the three samples coated with Ni-NiO exhibited the lowest corrosion rates and highest resistance to charge transfer. The Nyquist fit corroborates this pattern among the three Ni-NiO duplex coatings, indicating that the Ni-NiO epoxy had the highest corrosion rate, followed by the Ni-NiO/PVDF and Ni-NiO duplexes on both the 1st and 28th days. Specifically, the Ni-NiO duplex coatings exhibited the lowest corrosion rates of 0.142 mm/y on day 1 and 0.151 mm/y on day 28, with the highest charge-transfer resistance values of 598.14 Ω cm2 on day 1 and 561.44 Ω cm2 on day 28, as illustrated in Table 5. These results surpassed those of other coated and uncoated mild steel samples.
3.4 Tafel plot
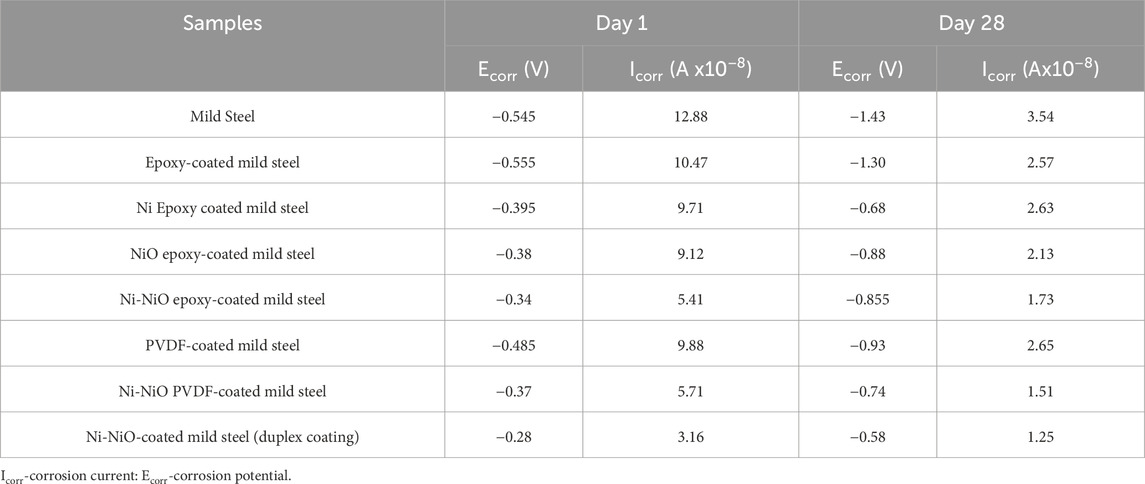
Tafel analysis, shown in Figure 3c, is a widely used electrochemical technique for evaluating the corrosion resistance of materials by determining the corrosion potential (Ecorr) and current (Icorr), as shown in Table 6. This method involves extrapolating Tafel slopes from polarisation curves to assess the kinetic parameters of corrosion reactions. In this study, Tafel analysis was employed to validate the OCP and Nyquist plots and to compare the corrosion performance of various coated and uncoated mild steel samples.
A comparative study of the corrosion of all Ni-NiO-modified coatings provided excellent corrosion inhibition. Among the Ni-NiO samples, the second highest corrosion inhibition was exhibited by the Ni-NiO-modified PVDF coatings, which demonstrated enhanced long-term performance with Icorr of 1.51 × 10−8 A, surpassing that of the Ni-NiO epoxy variants (Icorr = 1.73 × 10−8 A). PVDF’s gradual outperformance in epoxy systems is attributed to its piezoelectric properties and low water absorption, which delay the plasticisation of the coating under cyclic ageing conditions. The Tafel analysis results highlight the higher corrosion resistance of the Ni-NiO-modified coatings on mild steel, which exhibited the highest corrosion inhibition. Compared to all the samples, exceptional performance is attributed to the chemically stable matrix of the Ni-NiO duplex coatings, which initially achieved the highest corrosion potential (Ecorr = −0.28 V) and the lowest corrosion current (Icorr = 3.16 × 10−8 A), outperforming all other systems. By Day 28, the Ni-NiO duplex coatings maintained exceptional stability, with an Ecorr of −0.58 V and an Icorr of 1.25 × 10−8 A, owing to the synergistic effects of the materials, including the protective oxide layer that formed over time. Additionally, zincate pretreatment of the surface enhances adhesion, further improving the durability of these coatings in simulated concrete environments.
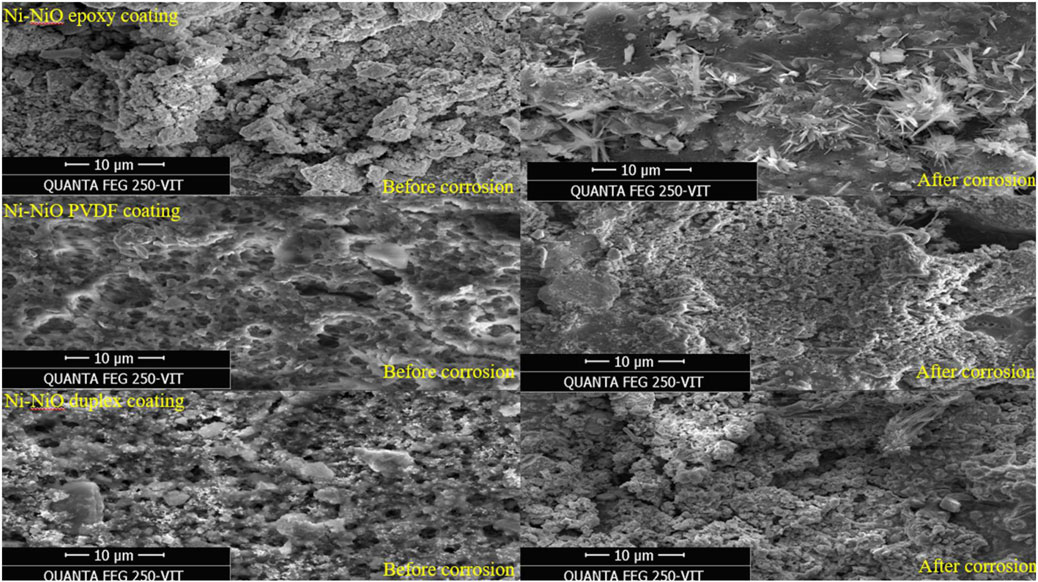
3.5 Surface morphology
The Finite Element Scanning Electron Microscope (FESEM) images in Figure 5 reveal distinct morphological changes on the surfaces of the Ni-NiO/epoxy, Ni-NiO/epoxy, and Ni-NiO duplex coatings before and after corrosion. The surface of the Ni-NiO epoxy-coated mild steel initially exhibited an algal-like sheet structure that transformed into flower-like projections after corrosion. Similarly, the Ni-NiO PVDF-coated sample exhibited small, sheet-like structures before corrosion, which became denser and less uniform after exposure. In contrast, the Ni-NiO duplex coating maintained a thick sheet-like structure before and after corrosion, and an increased density was observed over time.
These results highlight that microscopic defects were visible in the Ni-NiO-modified samples with PVDF and epoxy coatings, before and after corrosion. However, only minute defects occurred in the Ni-NiO duplex coating, which could be attributed to the preparation of the zincate surface of the mild steel plate. This process enhances the chemical stability of steel and ensures better adhesion through electrodeposition.
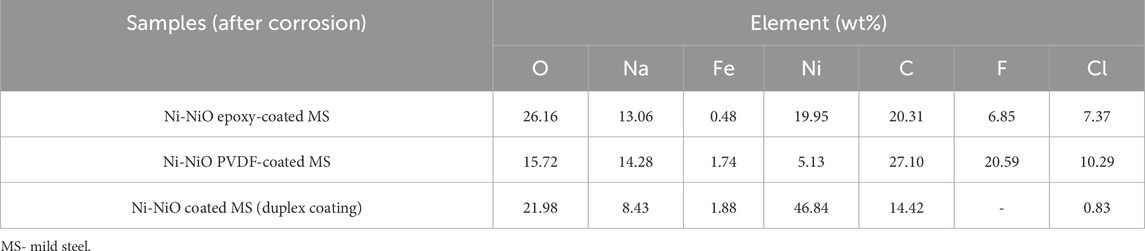
Table 7 provides insight into the Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS) of the coatings, confirming the presence of Ni and NiO in the protective layer. This composition directly influences the corrosion resistance, with a higher Ni content enhancing passivation and NiO, improving stability and adhesion. The interaction of the coating with the concrete pore solution introduced Na+ ions to the surface, particularly in the presence of NaOH, which may have affected the stability of the passive layer. Despite the presence of NaCl, the Ni-NiO duplex coating demonstrated superior performance in maintaining its integrity, indicating its ability to withstand alkaline conditions within the concrete matrix.
The gravimetric analysis results in Table 4 reveal significant variations in the corrosion resistances of the coated and uncoated mild steel samples. The uncoated mild steel exhibited the highest weight loss, amounting to 5.0 g, which served as a baseline for evaluating the effectiveness of the different coatings in inhibiting corrosion. The epoxy and PVDF coatings demonstrated marginal reductions in weight loss with 10% and 20% inhibition, respectively. However, modifying the epoxy with Ni or NiO coatings significantly enhanced the corrosion inhibition, with the Ni-epoxy and NiO-epoxy coatings achieving 46% and 40% inhibition, respectively. The hybrid Ni-NiO systems further enhanced the corrosion inhibition of both the epoxy and PVDF variants, with each earning 60% inhibition, highlighting the potential benefits of combining Ni and NiO in coating formulations. The Ni-NiO duplex coating exhibited exceptional corrosion resistance, with an impressive 80% corrosion inhibition (Suhas and Shanmugapriya, 2024).
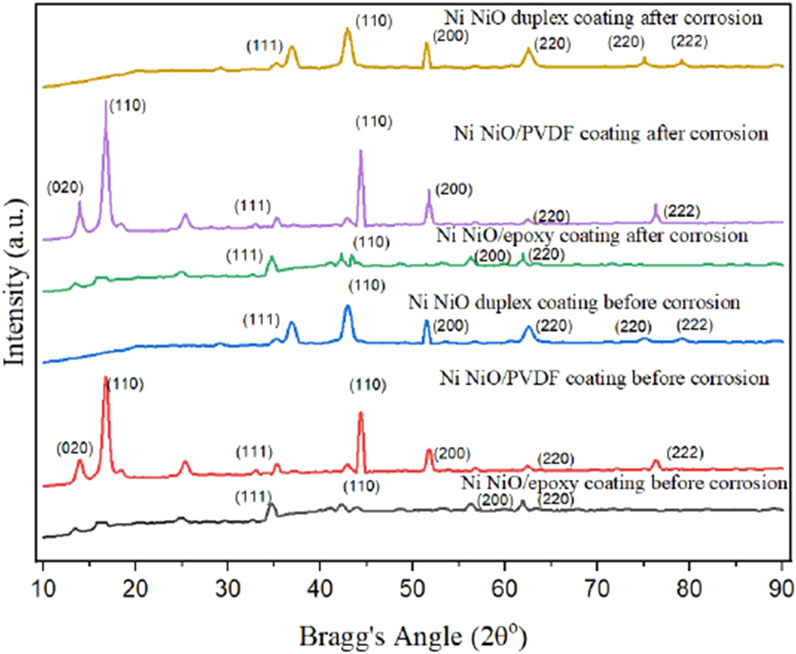
3.6 XRD analysis
The X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis shown in Figure 6 illustrates the structural properties of Ni-NiO duplex, Ni-NiO/PVDF, and Ni-NiO/epoxy coatings on mild steel, both before and after corrosion in concrete pore solutions. Before corrosion, all coatings display sharp diffraction peaks at characteristic Bragg angles, including 44.5° (Ni (111)), 51.8° (Ni (200), and 76.4° (Ni (220)), indicating the presence of well-crystallised nickel and nickel oxide phases. The Ni-NiO duplex coating exhibited the highest peak intensities, particularly at these angles, suggesting a more robust and densely packed crystalline structure than those of the other coatings. This dense, crystalline arrangement is crucial for providing a robust physical barrier against corrosive ions, such as chloride (Cl−), which are commonly present in concrete environments. The Ni-NiO/PVDF and Ni-NiO/epoxy coatings also exhibited similar peaks, although with slightly lower intensities, indicating a lower crystalline stability than that of the duplex system. After corrosion, the Ni-NiO duplex coating retained much of its crystalline structure, with only a minimal reduction in the peak intensities at 44.5°, 51.8°, and 76.4°, indicating excellent corrosion resistance. The Ni-NiO/PVDF coating, while retaining its peaks at these angles, showed a more noticeable decline in intensity, suggesting some degradation in crystallinity, likely due to the limited resistance of the polymeric PVDF to harsh chemical environments. The Ni-NiO/epoxy coating exhibited the most significant reduction in peak intensity, particularly in the Ni (111) and Ni (200) planes, indicating more pronounced structural deterioration and, consequently, less effective corrosion protection than the other coatings. This suggests that, although epoxy-based coatings provide initial corrosion resistance, they are more prone to microcracking and long-term degradation. Among all the coatings, the Ni-NiO duplex system was the most effective in maintaining structural integrity and providing higher corrosion inhibition in aggressive environments, such as those found in concrete pore solutions.
3.7 Analytical validation
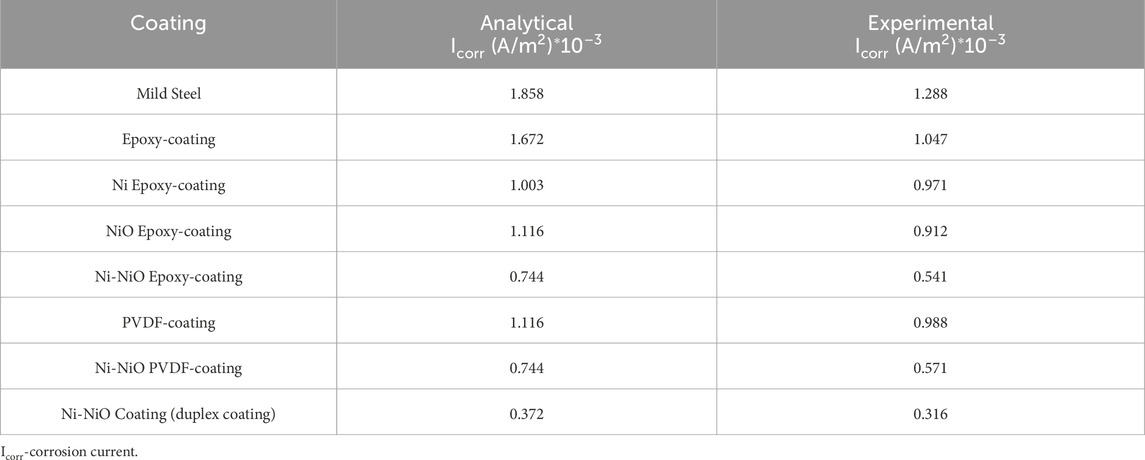
The corrosion current densities of various coated and uncoated mild steels were evaluated using the analytical equation in Equation 2 and the experimental methods, as summarised in Table 8. The results show that uncoated mild steel exhibited the highest analytical corrosion current density (Icorr) of 1.858 × 10−3 A/m2. In contrast, the Ni-NiO duplex coating demonstrated the lowest analytical Icorr at 0.372 × 10−3 A/m2, with an experimental value of 0.316 × 10−3 A/m2.
The incorporation of nickel (Ni) and nickel oxide (NiO) into the coatings significantly enhanced the corrosion resistance of mild steel. The analytical results consistently showed higher Icorr values than the experimental measurements, likely because of the accelerated corrosion conditions simulated by direct current (DC) testing. This discrepancy was more pronounced for the epoxy and PVDF coatings. Overall, this study demonstrates that applying protective coatings, particularly those containing Ni and NiO, can substantially improve the corrosion resistance of mild steel. The Ni-NiO duplex coating was the most effective formulation, highlighting its potential for applications requiring high corrosion protection. The Ni-NiO duplex-coated mild steel showed a lower variation between the analytical and experimental data, indicating its excellent coating stability and adhesion properties compared to the other coated and uncoated samples.
3.8 Simulation
3.8.1 Von Mises stress
The stress distributions around the steel rebar with the Ni-NiO/epoxy, Ni-NiO/PVDF, and Ni-NiO duplex coatings are shown in Figure 7a. The low stress concentration indicates that the duplex coating is excellent for dispersing stress and minimising stress hotspots. The Ni-NiO/PVDF coating exhibited a stress distribution with a Ni-NiO/PVDF-coated rebar monolayer in concrete. The stress concentration was higher than in the Ni-NiO duplex layer, suggesting that the duplex coating may be a more efficient stress reducer than the Ni-NiO/PVDF layer. The stress distribution with a Ni-NiO/epoxy-coated rebar embedded in concrete is shown for Ni-NiO/epoxy coatings. The Ni-NiO/epoxy coating may exacerbate the stress concentration around the rebar due to its significantly more intense stress concentration compared to that in Ni-NiO/PVDF. The elastic modulus of the steel coating affects the increase in stress, which may accelerate the onset and propagation of coating cracks (Korec et al., 2023). In this case, less crack formation occurs in the Ni-NiO duplex coating, indicating that it is the most corrosion-resistant corrosion inhibitor, which provides reassurance regarding its protective properties.
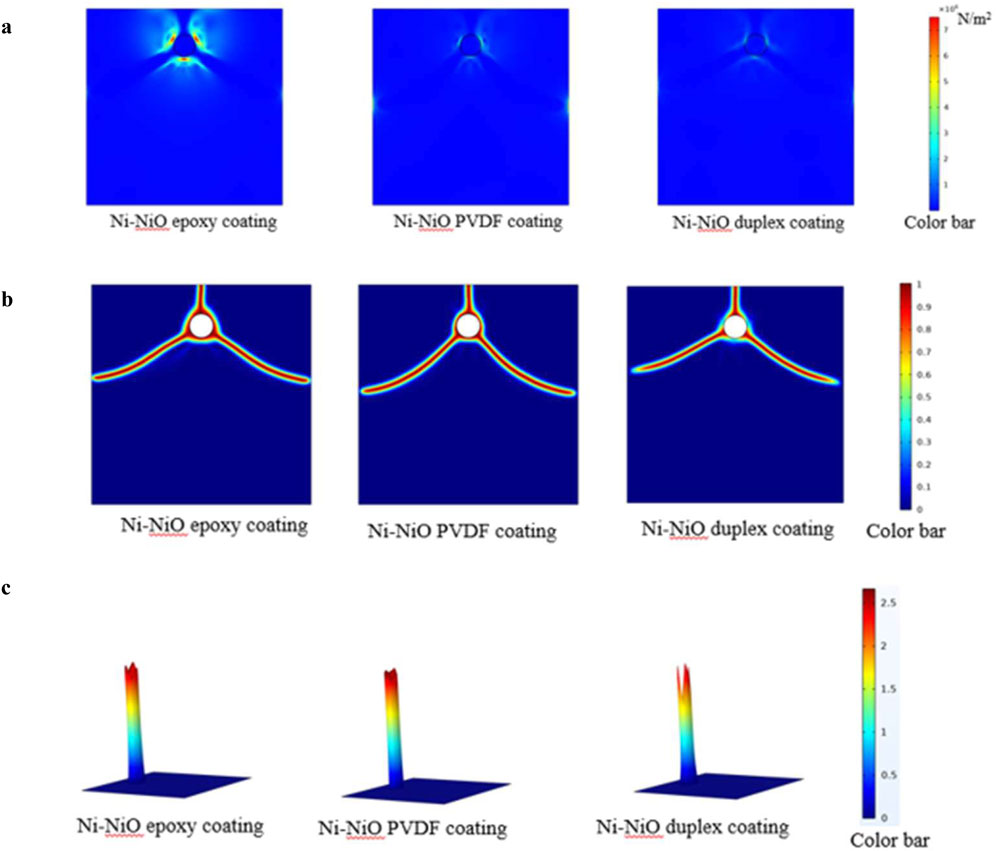
Figure 7. (a) Von Mises stress for different coated rebars embedded in concrete. (b) Phase field diagram for different coated rebars embedded in concrete. (c) Eigenstrain for different coated rebars embedded in concrete.
3.8.2 Phase field diagram
Figure 7b, which captures the development of phases over time, provides a deep understanding of the impact of coatings, such as those made of Ni-NiO/epoxy, Ni-NiO/PVDF, and Ni-NiO duplex coatings, on the durability and structural integrity of rebar in corrosive environments. By offering essential insights, phase-field analysis enhances the understanding of rebar performance and durability in construction, simulating the concrete-rebar system, and predicting crack development, propagation, and overall influence on mechanical qualities.
As shown in Figure 7b, potential corrosion is a complex process that occurs concurrently with microstructural development and solidification. The colour distribution of the Ni-NiO duplex obtained via multilayer coating indicates a localised concentration of a species, which may signify the start of the corrosion process. The circle indicates a flaw or contaminant that serves as the location for corrosion nucleation. Compared with the Ni-NiO duplex coating, the coloured area on the Ni-NiO/PVDF-coated rebar grew, indicating that the corrosion process continued. This growth underscores the potential implications of corrosion. Insights into the corrosion process were obtained from the distribution form. The Ni-NiO/epoxy-coated rebar in concrete exhibited a greater afflicted region and a more noticeable concentration gradient, suggesting that corrosion had advanced further. This indicates the presence of more advanced corrosion phases. It was validated that the Ni-NiO duplex coating had the highest corrosion inhibition compared to the other composites in both experimental and real-time situations.
3.8.3 Eigen strain
The concept of eigenstrain, which refers to the strain a material experiences due to various events, is crucial for understanding the behaviour of coated rebar types buried in concrete. The eigenstrain data depicted in Figure 7c clearly illustrate the internal stresses in these materials. The investigation focused on three different coating types: Ni-NiO/epoxy, Ni-NiO/PVDF, and Ni-NiO duplexes.
The eigenstrain values of the three coatings directly affected their performance. The Ni-NiO duplex coating, with the lowest eigenstrain value, experienced the least internal stress and therefore had the lowest propensity for corrosion. This finding is consistent with previous studies, which have shown that duplex coatings can provide enhanced protection against corrosion by forming a more stable barrier. The Ni-NiO epoxy coating, with an intermediate eigenstrain value, exhibited moderate internal stress and a corresponding risk of corrosion. Epoxy coatings exhibit strong adhesion and resistance to environmental factors, which may increase their efficacy. In contrast, the Ni-NiO/PVDF coating, which had the highest eigenstrain value, exhibited the highest propensity for corrosion and the most significant internal stress. Despite their advantages, PVDF coatings may not be as effective as other coatings in reducing internal stress. The Ni-NiO duplex coating demonstrated the most effective reduction in corrosion-related stress.
3.8.4 Crack width
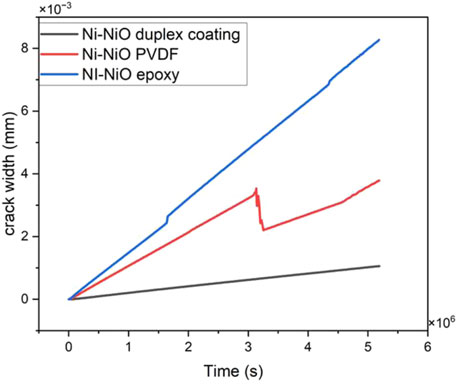
Crack width is a crucial indicator of the structural integrity and longevity of concrete construction, as shown in Figure 8. It gauges the size of the cracks that propagate over time, which may be affected by several variables, such as the coating on the rebar. Rebar corrosion caused by cracks in concrete that allow hostile substances, such as water and chlorides, to seep through may jeopardise the building’s lifespan. The graph shows the crack widths for the three distinct coatings on the rebar—Ni-NiO duplex coating, Ni-NiO/PVDF, and Ni-NiO/epoxy—progress.
The crack width of the Ni-NiO duplex coating showed a minimal increase in crack size over time, remaining comparatively constant. This shows that by slowing the spread of cracks, the Ni-NiO duplex coating effectively preserves the structural integrity of the concrete. For the Ni-NiO/PVDF coating, the crack width initially increased before reaching a plateau. This suggests that while there is an initial increase in the crack size, it eventually stabilises. However, given the initial growth, the coating’s ability to stop crack development may not be as strong as that of the Ni-NiO duplex coating. The crack width of the Ni-NiO/epoxy coating increased more noticeably with time, indicating that it was less successful in stopping crack propagation. As more aggressive substances may enter through wider cracks and reach the rebar, this might result in a greater risk of corrosion. Corrosion Consequences The observed crack widths in the coatings directly correlate with the likelihood of corrosion. Because it effectively stopped the crack propagation, the Ni-NiO duplex coating with the lowest crack width suggested the least possible corrosion. The intermediate crack width of the Ni-NiO/PVDF coating indicates a moderate corrosion risk. As the Ni-NiO/epoxy coating could not effectively stop crack formation, it had the highest corrosion risk. It also exhibited the widest cracks.
3.9 Summary of results
Table 9 highlights that bare mild steel exhibited the highest corrosion rate and poorest resistance, while conventional epoxy and PVDF coatings brought only modest improvements. Nickel-based composite coatings, particularly the Ni-NiO duplex system, offered a marked enhancement in corrosion protection, achieving the highest corrosion inhibition rate (80%) and the lowest corrosion rate (0.151 mm/year). Overall, advanced duplex and composite coatings incorporating both Ni and NiO significantly outperformed other systems, demonstrating the most effective barrier properties and long-term stability under corrosive conditions.
4 Conclusion
This study successfully evaluated the corrosion behaviour of mild steel coated with Ni, NiO, and Ni-NiO nanomaterials, focusing on the performance of duplex coatings in concrete pore solutions. The results demonstrate that Ni-NiO duplex coatings offer higher corrosion resistance compared with epoxy- and PVDF-modified coatings, making them a promising solution for protecting steel-reinforced concrete structures in aggressive environments. The key findings are as follows.
• The corrosion performance of Ni-NiO duplex-coated mild steel pretreated using a zincate process was initially assessed by dipping the coated steel in a concrete pore solution, followed by the application of DC for accelerated corrosion. T80% setup yielded a CIR of 80%, indicating excellent initial corrosion resistance. Subsequent electrochemical tests, including EIS and Tafel polarisation, further confirmed the long-term protective capabilities of the coating. EIS results showed a slight increase in corrosion rate, from 0.142 mm/year to 0.151 mm/year, over 28 days, accompanied by a corresponding decrease in the Rct, from 598.14 Ωcm2 to 561.44 Ωcm2. Tafel polarisation data indicated a shift in the Ecorr from −0.28 V on Day 1 to −0.58 V on Day 28, reflecting a progressive improvement in corrosion protection. The corrosion Icorr also decreased from 3.16 × 10−8 A on Day 1–1.25 × 10−8 A on Day 28, further validating the coating’s effectiveness in preventing corrosion.
• The enhanced crystallinity structure retention, as observed in the XRD analysis, further validates these findings. The FESEM images revealed that the Ni-NiO duplex coating had fewer defects than the other coatings, due to the improved adhesion achieved through zincate treatment and electrodeposition. EDS analysis confirmed that the nick84 %depletion was lower (46.84% remaining in the duplex system) than that in the epoxy and PVDF-modified samples, demonstrating excellent elemental stability.
• These results, the analytical Icorr (calculated from weight loss during DC-connected accelerated corrosion testing), demonstrate the Ni-NiO duplex coating as a highly effective solution for mitigating corrosion in harsh environments. The analytical corrosion current, which showed a slightly higher value of 0.372 (A/m2) × 10–3 compared to the experimental value of 0.316 (A/m2) × 10–3, reflects the more aggressive corrosion conditions applied during accelerated testing. Despite this, both the experimental and analytical results confirmed the robust performance of the coating in preventing corrosion.
• Numerical simulations conducted using COMSOL Multiphysics confirmed the experimental findings, demonstrating that the Ni-NiO duplex coating effectively reduced the von Mises stress, phase-field values, and eigenstrain, thereby mitigating the crack initiation and propagation. The simulations revealed that the Ni-NiO duplex coating had the smallest crack widths, indicating a minimal risk of corrosion and suggesting its potential for enhancing the durability of steel reinforcements in concrete environments. In contrast, the larger crack widths observed in the epoxy-modified coatings indicate a higher susceptibility to corrosion. These results highlight the Ni-NiO duplex coating’s superior performance and applicability in protecting rebars in concrete structures, offering long-term corrosion resistance under practical conditions.
These findings underscore the effectiveness of Ni-NiO duplex coatings in providing robust protection against corrosion, particularly in chloride-laden environments, where concrete pore solutions pose a significant threat to steel reinforcement. By integrating the experimental results with real-time numerical simulations, this study provides a comprehensive understanding of the coating performance, paving the way for its application in large-scale infrastructure protection. The Ni-NiO duplex system is a durable and efficient solution for enhancing the longevity and safety of steel-reinforced concrete structures exposed to harsh chloride-rich marine environments. Additionally, it demonstrates that the Ni–NiO duplex coating exhibits higher suitability and performance compared to conventional epoxy and PVDF coatings, as well as their modified variants, which are commonly used in high-rise construction. Future investigations should focus on validating the performance of the coating under extended cyclic mechanical loading, longer exposure durations, and real-time field conditions to ascertain its effectiveness and longevity in dynamic service environments. Such comprehensive validation is crucial for optimising coating technology and facilitating its successful transition from laboratory research to widespread industrial and infrastructural applications.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
VS: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. TS: Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was financially supported by a seed grant from the Vellore Institute of Technology, Vellore (Seed grant no. SG20230107).
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of the Civil Engineering and Centre for Biomaterials, Cellular and Molecular Theranostics labs at Vellore Institute of Technology, Vellore, for providing facilities to conduct this research.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Chen, J., Wang, Y., Gao, W., Wang, D., Chen, S., and Luan, J. (2022). A newly designed NiP duplex coating on friction stir welding joint of 6061-T6 aluminum. Surf. Coatings Technol. 448, 128940. doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2022.128940
Cui, C., Ma, R., and Martínez-Pañeda, E. (2023). Electro-chmmmmodellinganical phase field modeling of localized corrosion: theory and COMSOL implementation. Eng. Comput. 39 (6), 3877–3894. doi:10.1007/s00366-023-01833-8
Gutierrez, A. G., Pech-Canul, M. A., and Sebastian, P. J. (2017). Zincating effect on corrosion resistance of electroless ni-p coating on aluminum alloy 6061. Fuel Cells 17 (6), 770–777. doi:10.1002/fuce.201600212
Korec, E., Jirásek, M., Wong, H. S., and Martínez-Pañeda, E. (2023). A phase-field chemo-mechanical model for corrosion-induced cracking in reinforced concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 393, 131964. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.131964
Kumar, U. P., Shanmugan, S., Kennady, C. J., and Anticorrosion, A. (2019). Anti-corrosion and microstructural properties of Ni–W alloy coatings: effect of 3, 4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde. Heliyon 5 (3), e01288. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01288
Li, Z., Bi, H., Gunnarsson, S., Weinell, C. E., and Dam-Johansen, K. (2024). Delamination of thermally sprayed ZnAl15/organic duplex coating systems on structural steel for offshore wind applications. Surf. Coatings Technol. 485, 130796. doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2024.130796
Liu, J., Liu, H., Tian, X., Yang, H., and Hao, J. (2020). Microstructural evolution and corrosion properties of Ni-based alloy coatings fabricated by multi-layer laser cladding on cast iron. J. Alloys Compd. 822, 153708. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.153708
Prajapati, V., Kumar, Y., Gupta, D., Kalam, A., and Dubey, M. (2022). Analysis of pitting corrosion of pipelines in a marine corrosive environment using COMSOL multiphysics. J. Bio-and Tribo-Corrosion 8, 21–11. doi:10.1007/s40735-021-00620-6
Qu, L., Wang, Q., Xu, S., Wang, N., and Shi, Z. (2021). Chloride corrosion resistance of double-layer anticorrosive coating in simulated concrete pore solution. Constr. Build. Mater. 295, 123682. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.123682
Salicio-Paz, A., Grande, H., Pellicer, E., Sort, J., Fornell, J., Offoiach, R., et al. (2019). Monolayered versus multilayered electroless NiP coatings: impact of the plating approach on the microstructure, mechanical and corrosion properties of the coatings. Surf. Coatings Technol. 368, 138–146. doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2019.04.013
Shi, J., Ming, J., Wang, D., and Wu, M. (2020). Improved corrosion resistance of a new 6% Cr steel in simulated concrete pore solution contaminated by chlorides. Corros. Sci. 174, 108851. doi:10.1016/j.corsci.2020.108851
Suhas, V. S., and Shanmugapriya, T. (2024). Evaluation of the corrosion inhibition capability of mild steel coated with a ZnO-Ni/PVDF nanocomposite in a simulated concrete pore solution: an electrochemical investigation and numerical simulation. Arabian J. Sci. Eng. 50, 12643–12663. doi:10.1007/s13369-024-09317-7
Suhas, V. S., and Shanmugapriya, T. (2025). Corrosion performance of ZnO-Based hybrid coated mild steel in concrete pore solutions. Mater. Lett. 385, 138163. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2025.138163
Sun, X., Zheng, D., Pan, F., Qin, C., Li, Y., Wang, Z., et al. (2021). 3D nanoporous ni@ NiO/metallic glass sandwich electrodes without corrosion cracks for flexible supercapacitor application. Appl. Surf. Sci. 545, 149043. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.149043
Tripathi, V., Rai, S., and Ji, G. (2024). Coating of ethanolic extract of mint leaves, with and without addition of NiO nanoparticles, on mild steel for its corrosion prevention in saline water. Mater. Today Proc. doi:10.1016/j.matpr.2024.05.133
Van Nguyen, C., Bui, Q. H., and Lambert, P. (2022). Experimental and numerical evaluation of the structural performance of corroded reinforced concrete beams under different corrosion schemes. Structures 45. Elsevier, 2318–2331. doi:10.1016/j.istruc.2022.10.043
Yuan, H., Qi, F., Zhao, N., Wan, P., Zhang, B., Xiong, H., et al. (2020). Graphene oxide decorated with titanium nanoparticles to reinforce the anti-corrosion performance of epoxy coating. Coatings 10 (2), 129. doi:10.3390/coatings10020129
Keywords: coated mild steel, corrosion, analytical corrosion current, electrochemical measurements, COMSOL
Citation: Suhas VS and Shanmugapriya T (2025) Advanced Ni-Nio coatings for enhanced corrosion inhibition of mild steel in alkaline concrete environments: an integrated experimental and computational analysis. Front. Built Environ. 11:1621284. doi: 10.3389/fbuil.2025.1621284
Received: 30 April 2025; Accepted: 07 August 2025;
Published: 03 September 2025.
Edited by:
Hindavi Gavali (Tikate), NICMAR University Pune, IndiaReviewed by:
Carina M. Stolz, Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, BrazilDyana Joseline, NICMAR University Pune, India
Copyright © 2025 Suhas and Shanmugapriya. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: T. Shanmugapriya, c2hhbm11Z2Fwcml5YS50QHZpdC5hYy5pbg==
†ORCID: Shanmugapriya T, orcid.org/0000-0003-1565-152X
 V. S. Suhas
V. S. Suhas T. Shanmugapriya
T. Shanmugapriya