- Department of Architecture, Covenant University, Ota, Nigeria
Innovation hubs foster collaboration, creativity, and economic growth. However, the inclusivity of these spaces remains a critical factor in ensuring equal access and participation by diverse users. This study examined the impact of inclusive architectural design strategies on social inclusion in selected innovation hubs in Nigeria. This study focuses on how these strategies create accessible, collaborative, and equitable spaces. This research identifies the inclusive architectural strategies applicable in innovation hubs and examines the impact of inclusive architectural strategies on improving social inclusion characteristics in innovation hubs. The study used a quantitative method based on structured questionnaires, which reached 170 participants distributed across five innovation hubs in Southwest, Nigeria. The researchers used descriptive and inferential statistical analysis combined with frequency counts and percentages for data evaluation that produced graphical representations. Findings reveal that inclusive architectural elements, such as accessibility compliance, spatial flexibility, and user-centred design, significantly influence social interactions, knowledge exchange, and engagement within innovation hubs. However, barriers such as inadequate planning, lack of policy enforcement, and financial constraints hinder the full implementation of inclusive design principles. The study concludes that integrating inclusive architectural strategies from the initial planning stages can enhance accessibility and foster greater social participation in innovation hubs. By prioritising universal design principles, these spaces can bridge socio-economic gaps, promote innovation, and support diverse user needs. The findings provide valuable insights for architects, policymakers, and stakeholders in developing more inclusive and sustainable innovation environments.
1 Introduction
The development of inclusive architecture has transformed significantly in recent decades, making it a fundamental aspect of modern architectural dialogue (Howe and Martel, 2024). Universal design emerged during the 20th century, particularly in the last period, because people increasingly recognised the necessity of accessible environments (Shkliar and Shushliakova, 2023). Architectural practices developed this new approach because they failed to serve disabled populations, older adults, and other disadvantaged groups. Universal design emerged from the work of architect Ronald Mace when he defined the term in the 1980s. Building design with products and environments represents a system that makes structures completely accessible to people with various abilities and ages (Irene, 2023). Universal design principles, including equitable use, flexibility, and simple, intuitive operation, were widely adopted and expanded to develop modern inclusive architectural design strategies. Such strategies exceed basic accessibility standards to construct physical areas that serve people from all backgrounds while being supportive and inviting to all visitors. Universal design focuses on space creation that offers use for every person to maximum levels with no need for special design or adaptations. International mandates and conventions are the main catalysts for worldwide progress toward inclusive design strategies. Globally, there has been a growing recognition of the need for inclusive design in developed and developing countries. In developed countries, inclusive architectural strategies have been integrated into building codes and standards, leading to the widespread adoption of accessibility features in public and private buildings. For instance, in the United States, the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) of 1990 established comprehensive accessibility requirements for public accommodations, transportation, and telecommunications, serving as a model for other countries (Imrie, R. 2014).
The concept of inclusive architecture is currently being developed in Nigeria, although multiple obstacles and several advantages are directing its growth. The national architectural design method consists of a dual practice of contemporary and classical approaches that depends on economic limitations and local cultural conditions. Implementing inclusive design strategies continues to be irregular despite the positive steps from 2018 when the Disability Rights Law was enacted for accessibility requirements in public buildings and facilities (Mbanugo, 2019). Nigeria’s cities, Abuja and Lagos, adopt inclusive design frameworks for their current development projects through improvements to accessible services along public transport, residential areas, and public spaces and facilities. Adegoke and Mohamed Khaidzir (2024) claim that the lack of sustainable and fair housing in Nigeria is partially due to the limited implementation of architectural design interventions, highlighting that many professionals, including architects and legislators, lack sufficient knowledge of inclusive and universal design principles necessary for accessible development.
Accessibility remains neglected throughout building designs of urban locations since they fail to address navigation barriers, which make it hard for disabled individuals to move around (Chen, 2024). Despite financial and structural challenges, Nigeria’s rapid urbanisation offers a unique opportunity to embed inclusive architectural strategies into emerging infrastructure projects (Obianyo et al., 2021). Inclusive urban design can foster cultural preservation, sustainability, and quality of life through heritage mapping, community engagement, and culturally aligned infrastructure like festival routes, as demonstrated in a case study of Owerri (Agoha, 2023).
Inclusive architecture aligns with key Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by promoting accessibility, equity, and sustainability. It supports SDG 10 (Reduced Inequalities) by eliminating barriers for marginalised groups, SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities and Communities) by fostering inclusive and resilient urban spaces, SDG 4 (Quality Education) by ensuring accessible learning environments, and SDG 9 (Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure) by advocating for universally designed infrastructure. Together, these goals highlight the importance of inclusive architecture in creating a more equitable and sustainable built environment.
The word innovation comes from the Latin innovare, meaning “to renew,” while a hub refers to a central point of activity. An innovation hub is a physical or virtual space designed to bring people together to solve problems, share ideas, and build new ventures (Agarwal et al., 2022; Nam and Kim, 2024). These hubs typically offer access to co-working areas, digital tools, mentorship, and sometimes funding, serving a mix of startups, students, creatives, and professionals (Chowdhury et al., 2023). Innovation hubs thrive on collaboration. They create environments where sectors such as education, government, and business can work to test ideas and develop real-world solutions. Jiménez and Zheng (2021) state that such hubs are expanding globally due to their potential to spark creativity and foster inclusive participation. Egessa and Mwadzogo (2024) describe how a university-based innovation hub in Mombasa brings together students, researchers, and industry practitioners to co-create impactful projects.
In Nigeria, innovation hubs have emerged as vital platforms for tackling youth unemployment, bridging the digital divide, and supporting entrepreneurship. These spaces do more than provide access to technology; they open up pathways for learning, networking, and economic inclusion (Ayegbeni and Ikpeminohena, 2024; Osuji, 2024). This study focuses on innovation hubs located in Southwest Nigeria, specifically in Oyo, Lagos, and Ogun States, which function as strategic spaces for promoting digital literacy, economic empowerment, and social inclusion. The spatial and architectural design of these hubs plays a crucial role in determining who can access and benefit from them. As such, accessibility remains a central concern in assessing the inclusivity and effectiveness of innovation hubs.
This study aims to examine the impact of inclusive architectural design strategies on social inclusion in selected innovation hubs, focusing on how these strategies create accessible, collaborative, and equitable spaces. The objectives it seeks to achieve: Analyse the inclusive architectural strategies applicable in innovation hubs and examine the impact of inclusive architectural strategies on improving social inclusion in innovation hubs.
2 Literature review
2.1 Inclusive architectural strategies
The implementation of inclusive architectural approaches prioritises accessibility along with usability and adaptation for creating places that serve all users, especially disabled individuals, as well as elderly adults and marginalised communities (Gallouzi, 2024). Beyond standard instructions, it is essential to exceed conventional regulatory requirements by systematically identifying and removing physical, sensory, and cognitive barriers that impede meaningful community engagement (Smith and Dropkin, 2018). According to Skiba and Züger (2020), disability does not naturally exist within individuals because the obstacles found in environments create the disability. Employee engagement deteriorates in innovation centres that lack adaptive elements of the intuitive navigation system and versatile layout design, along with engaging zones. Architectural designers must switch operational approaches by removing previous discrimination techniques to build spaces that welcome everyone (Busciantella-Ricci, 2023). Also fundamental to social fairness, while extending past physical accessibility, is the core requirement of inclusive design to develop feelings of belonging. Circulation routes, diverse seating arrangements, and inclusive planning practices create environments that make all users feel recognised and sustained (Howe and Martel, 2024).
2.2 Inclusive architecture strategies applicable in innovation hub
Innovation hubs serve as collaborative spaces for knowledge-sharing, entrepreneurship, and skill development, making inclusivity essential for fostering broad participation. Designed architectural solutions that address the specific needs of visually impaired, hearing-impaired and mobility-impaired individuals increase their involvement in such spaces (Filer and Spain, 2024). The design must be inclusive in innovation hubs when older adults interact with young people and individuals with disabilities. The design of the innovation hub improves participation and comfort for each characterised audience when the unique needs of these groups are given attention. These demanding needs influence building design significantly, so the inclusive architectural strategies for innovation hubs are organised in categories, which are: Building Exterior: Ensure clear, accessible paths, parking, and visual cues for navigation (Hameed, 2021; Kamani et al., 2023). Interior Layout: Avoid complex window divisions and excessive furniture. Provide wide doors, accessible WC cubicles, and group-related facilities for convenience (Kobylarczyk, 2019). Navigation and Circulation: Provide accessible lifts, handrails, and seating; design safe, open layouts (Natapov et al., 2015). Adaptability of Space: Design flexible spaces that can adapt over time, using open floor plans and movable furniture to accommodate changing needs (Magdziak, 2019). Sensory Considerations: Minimise background noise, provide colour coding for easy navigation, and ensure good lighting and tactile guides for visually impaired individuals (Black et al., 2022). Entry and Access: Ensure multiple entry points, automatic or well-marked doors, and clear, barrier-free entrances (Strug and Ślusarczyk, 2017). Information Accessibility: Incorporate assistive technology, clear signage, and tactile elements like Braille and audio guides to make information accessible (Mosca and Capolongo, 2020). Materials and Colour: Use anti-skid flooring, avoid reflective surfaces, and employ distinct colours and tonal contrasts for navigation. Choose acoustic comfort materials (Uzeyirli and Özçevik Bilen, 2021).
2.3 Impact of inclusive architectural strategies on social inclusion in innovation hubs
Inclusive architectural strategies foster social inclusion within innovation hubs by enhancing accessibility, engagement, and economic empowerment. Research indicates that innovation hubs incorporating inclusive design principles experience higher participation rates and create more equitable environments (Dubost, 2023). Research aligns with public discourse, as Ouf and El-Zafarany (2018) show that inclusive spaces foster social ties and improve mental health by reflecting societal diversity and reducing segregation. Innovation hubs that embrace such inclusivity enhance community relations and user satisfaction. Likewise, Errante (2020) highlights accessibility as a right, stressing that barrier-free, community-driven design boosts social inclusion, an approach well-suited to innovation hubs. Orozco et al. (2024) conducted a systematic review on cultural participation and social inclusion, identifying barriers to engagement and stressing the need for inclusive policies. Their findings indicate that inclusive architectural designs significantly impact social participation by removing systemic barriers and enhancing accessibility. In the context of innovation hubs, this underscores the necessity of clear signage, accessible technology, and participatory governance models that promote cultural and economic inclusion. Similarly, Kusimo et al. (2022) identified key barriers to inclusion in Nigerian primary schools, including poor infrastructure, undertrained personnel, and societal discrimination. These challenges mirror those found in innovation hubs, where limited policy enforcement and planning weaknesses continue to undermine inclusive design efforts. The study by Sewell, Kennett, and Pugh (2022) shows that educational obstacles in the classroom go beyond physical barriers to encompass limitations of cognitive and sensory capabilities. Innovation hubs that adopt Universal Design for Learning principles will develop inclusive skill development programs which allow many more participants to engage in educational and entrepreneurial activities. Taiye and Olabode (2022) researched Universal Design (UD) strategies applied to vocational centres in southwestern Nigeria to correlate with accessible facilities that assist young adults with disabilities. According to the study results, building professionals understand UD principles, but inconsistent implementation impedes failed inclusion. Through their research, they apply case studies and questionnaires to demonstrate the mismatch between understanding Universal Design principles and their implementation, requiring stakeholders’ involvement to enhance complete accessibility. The research on vocational schools reflects the necessity of inclusive design elements for educational and innovation hubs, which enhance equal participation despite their restricted general application. Innovation hubs become inclusive platforms that support user groups in terms of economic participation, physical accessibility, and user-centred design to advance social and professional development.
3 Research Methodology
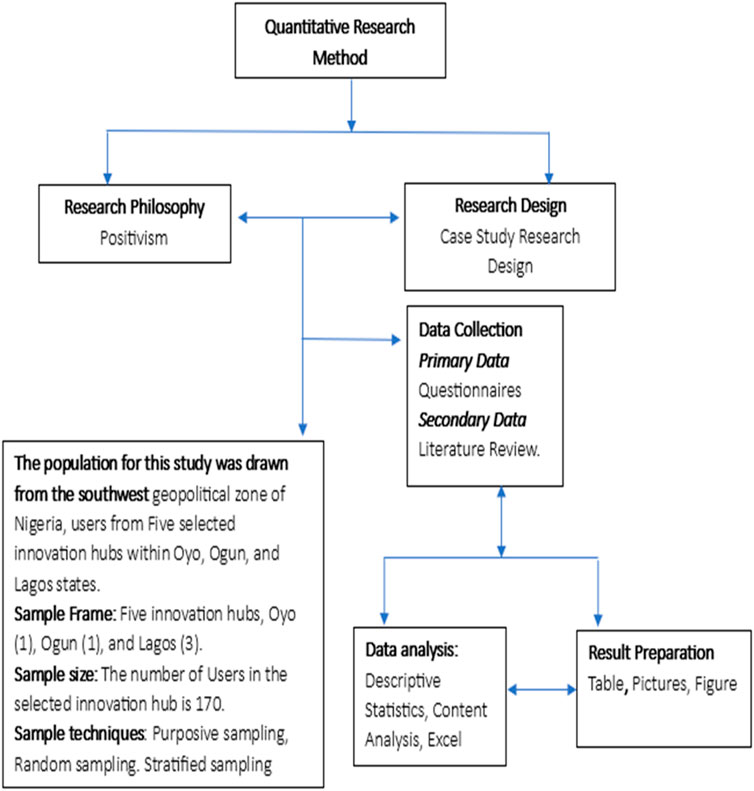
This study adopted a quantitative method for data collection; the study employed a structured questionnaire, and 170 were administered to users and staff of selected innovation hubs as shown in Figure 1. The inclusive architectural strategies were expressed in the question form to elicit information on the subject. The questionnaire was written in English and described in simple sentences to ensure the possibility of giving clarity of intention. The data collected for this study were analysed using both descriptive and inferential statistics. The treatment presented descriptive data using tables, frequency counts, percentages, mean and charts. This approach aligns with established methods of questionnaire-based data analysis (Zlokovich et al., 2023).
3.1 Data collection
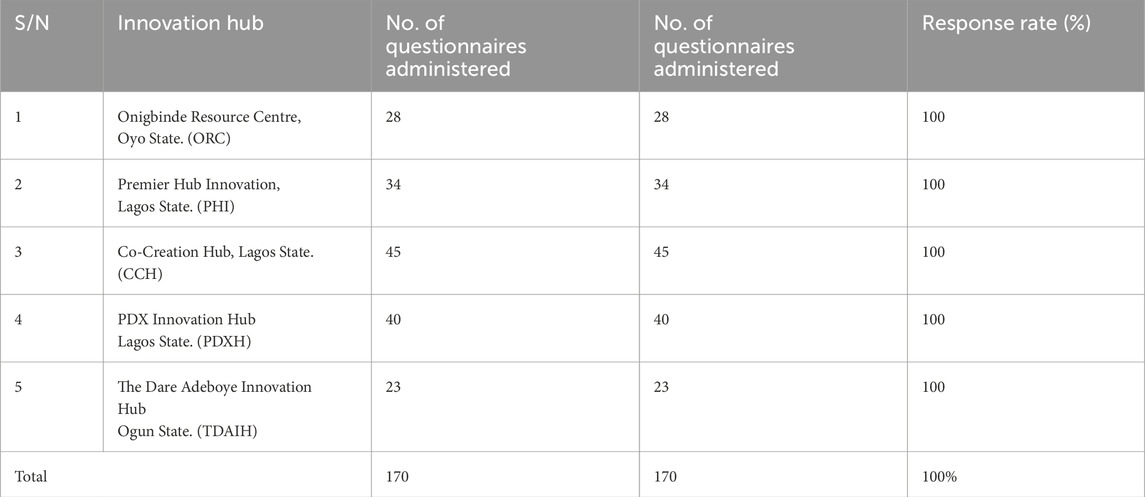
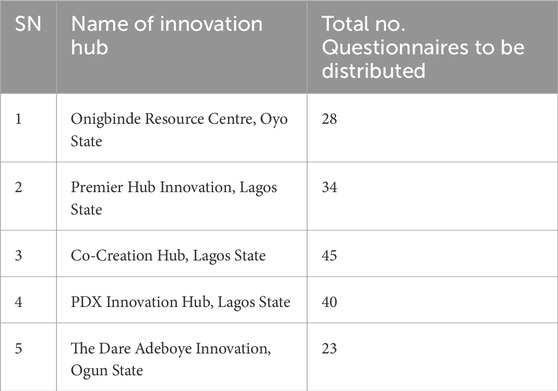
The authors gathered data from both primary and secondary sources. Primary data was collected through structured survey questionnaires distributed to users of five innovation hubs listed in Table 1.
A total of 170 questionnaires were administered, and all were successfully retrieved. The questionnaires were designed to capture user feedback on the adequacy of inclusive architectural elements within the selected facilities. The sampling process requires researchers to pick a portion of the population representing the complete group (Ajithakumari, 2024). The research design used stratified purposive sampling methods for data collection. To achieve proper geographic distribution, the researcher divided the population between Oyo State, Ogun State, and Lagos State. The research adopted purposive sampling as its selection method to choose these particular states because they had research-friendly locations and thriving innovation hubs. The researchers selected five out of ten identified hubs within these states because of time and resource limitations.
3.2 Size of sample
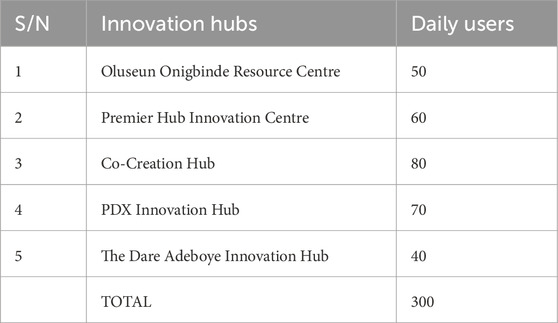
The sample size corresponds to the selected participants from the complete user population. Establishing an exact user count in these buildings was difficult because their purpose changes frequently. The study conducted finite population sample size estimation using Andrew’s (2022) method by determining a total daily user population of 300 across the five innovation hubs listed in Table 2. The equation is represented as:
Where,
By substituting the values into the equation, we get:
The sample size for the survey is approximately 170 see Table 3.
3.3 Unit of data collection
The Proportional Allocation Formula assists researchers in fairly splitting a specific number of questionnaires among different population groups during stratified sampling. The formula allocates resources such as questionnaires according to group size and importance, thus making the sampling process efficient and representative (Aziz et al., 2024). The formula generally takes the form:
Where,
The data gathering took place over 7 weeks, during the morning and afternoon, and on weekdays (Wednesday to Friday). Questionnaire administration began on 15 December 2024, and concluded on 7 February 2025. Secondary data sources included a literature review of relevant studies on inclusive architecture, innovation hubs, and social inclusion strategies. The collected data provided insights into the extent of adoption and effectiveness of inclusive design principles in innovation hubs.
3.3.1 Socio-demographic analysis
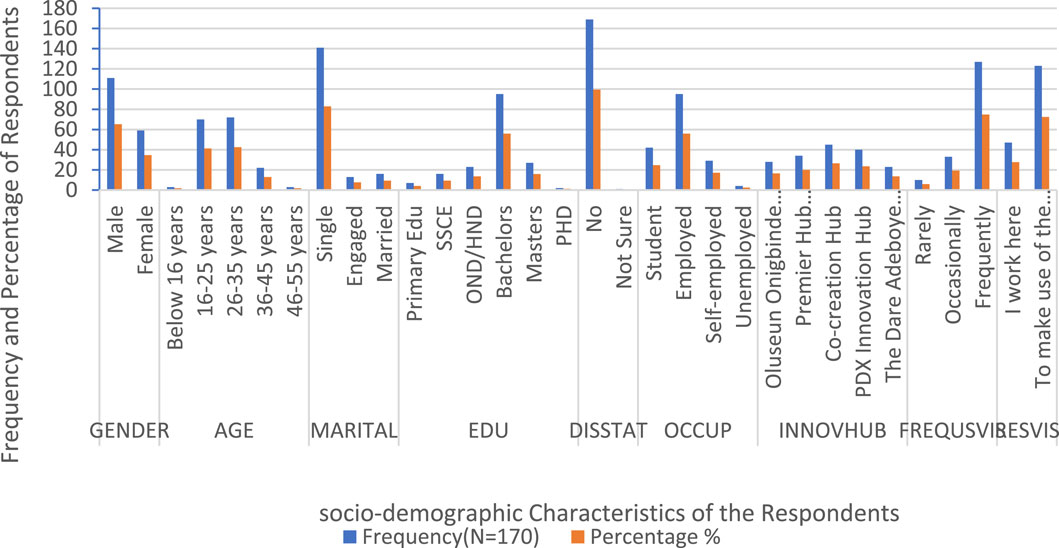
Figure 2 shows the socio-demographic analysis of the respondents, based on a total sample size of 170, which provides a detailed insight into their characteristics. Regarding gender distribution, male respondents constitute a higher proportion, over 55%, while female respondents account for approximately 45%. It indicates a slight gender imbalance in participation, with males being more represented. The age distribution reveals that the largest group of respondents falls within the 16–35 years range, highlighting a youth-dominated sample. Specifically, those aged 16–25 comprise around 35%, while the 26–35 years group comprises about 30%. The below 16 years category has minimal representation (under 5%), whereas those aged 36–45 years represent about 15%, and the 46–55 years group accounts for approximately 10%. It suggests that most respondents are young adults, likely in academic or early career stages. Regarding marital status, most respondents (about 60%) are single, aligning with the dominant youth demographic. Meanwhile, engaged and married respondents comprise around 25%, while the remaining 15% are divorced or widowed. It suggests that most respondents are still in the pre-family life stages. Educational qualification data indicates that most respondents (over 80%) possess higher education degrees. Among them, PhD holders account for the most essential proportion (nearly 35%), followed by Master’s degree holders (about 25%). Bachelor’s degree holders make up approximately 20%, while OND/HND holders make up about 15%. Respondents with only secondary school education (SSCE) or lower comprise less than 10%, with primary education accounting for the smallest share (below 5%). It demonstrates that the respondents are predominantly well-educated.
In terms of disability status (DISSTAT), a vast majority (over 85%) indicated they do not have a disability. In comparison, around 10% were unsure, and only a small fraction (below 5%) reported having a disability. Examining occupational status, students comprise the most significant proportion at approximately 40%, followed closely by employed individuals at around 30%. Self-employed respondents constitute about 15%, while unemployed participants form the smallest group at roughly 10%. It suggests that the respondents are a mix of students, professionals, and entrepreneurs, with a relatively low unemployment rate. The analysis also captures respondents’ involvement with innovation hubs, with engagement spread across multiple centres, including the Oluseun Onigbinde Innovation Hub, Premier Hub Innovation, Co-creation Hub, PDX Innovation Hub, and The Dare Adeboye Innovation Hub. Each hub attracts between 10% and 20% of respondents, indicating a broad interest in technology and innovation-driven environments. When assessing the frequency of visits (FREQUSVIS) to innovation hubs, frequent visitors comprise the largest group at approximately 35%, followed by occasional visitors at around 25%, while those who rarely visit account for about 15%.
Additionally, 10% of respondents work at the hub, emphasising its importance in supporting their activities. The primary reason for visiting the hub (RESVIS) is to use the available resources, as approximately 40% of respondents indicated. It highlights the hub’s crucial role in fostering education, research, and professional development. The socio-demographic profile reveals a highly educated, youth-centric, professionally diverse respondent group, with strong engagement in innovation hubs. Most are students and professionals, frequently utilising hubs for educational and work-related purposes. The analysis also suggests a slight gender imbalance, a dominant presence of single individuals, and a high representation of PhD holders, indicating a knowledge-driven community.
3.3.1.1 Demographic analysis by disability status
Respondents with a disability constituted a small portion of the sample, accounting for less than 5%, while approximately 10% indicated they were unsure of their disability status. Despite their limited representation, this subgroup provided important insights into existing accessibility challenges within the innovation hubs. Reported issues included difficulties with physical access, inadequate signage, and navigation barriers within the built environment. These responses significantly highlighted the limitations of current spatial layouts in meeting the needs of users with disabilities.
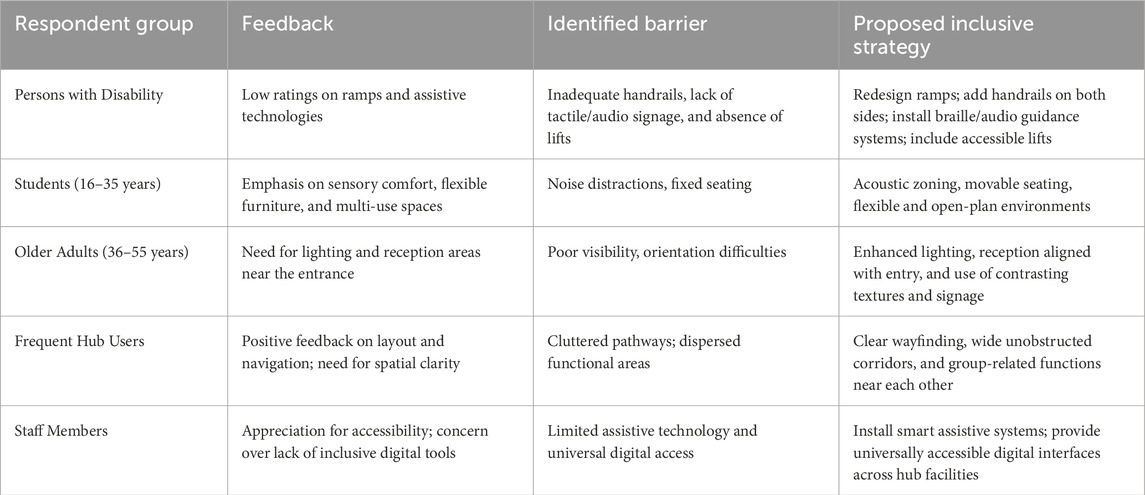
Table 17 highlights how feedback from this group contributed to formulating the inclusive architectural strategies presented in this research. A more detailed analysis of their input, along with the broader implications for inclusive design, is further discussed in the Discussion and Conclusion sections.
3.3.2 Data analysis
The data analysis used a quantitative approach to address the research objectives. Structured questionnaires were distributed among users and staff of five selected innovation hubs in Nigeria as shown in Table 4. The collected data were analysed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS). Descriptive statistical methods, including frequency distributions, were employed to interpret the responses. The findings were presented in tables for clear and concise interpretation.
4 Results
The data analysis is centred on the research objectives outlined in the study. The research objectives include analysing the inclusive architectural strategies applicable in innovation hubs and examining the impact of inclusive architectural strategies on improving social inclusion in innovation hubs. The authors present their findings in a structured sequence that follows the study’s objectives.
4.1 Inclusive architectural strategies in innovation hubs
This section presents the findings from Section B of the questionnaire, where respondents evaluated the adequacy of inclusive architecture strategies in their respective Innovation Hubs. Participants were asked to rate their level of adequacy with statements describing these strategies on a scale of 1–5, with one indicating “Strongly Inadequate,” 2 “Inadequate,” 3 “Neutral,” 4 “Adequate,” and 5 “Strongly Adequate as shown in Figure 3.” Results were then presented based on each category of inclusive architecture strategies.
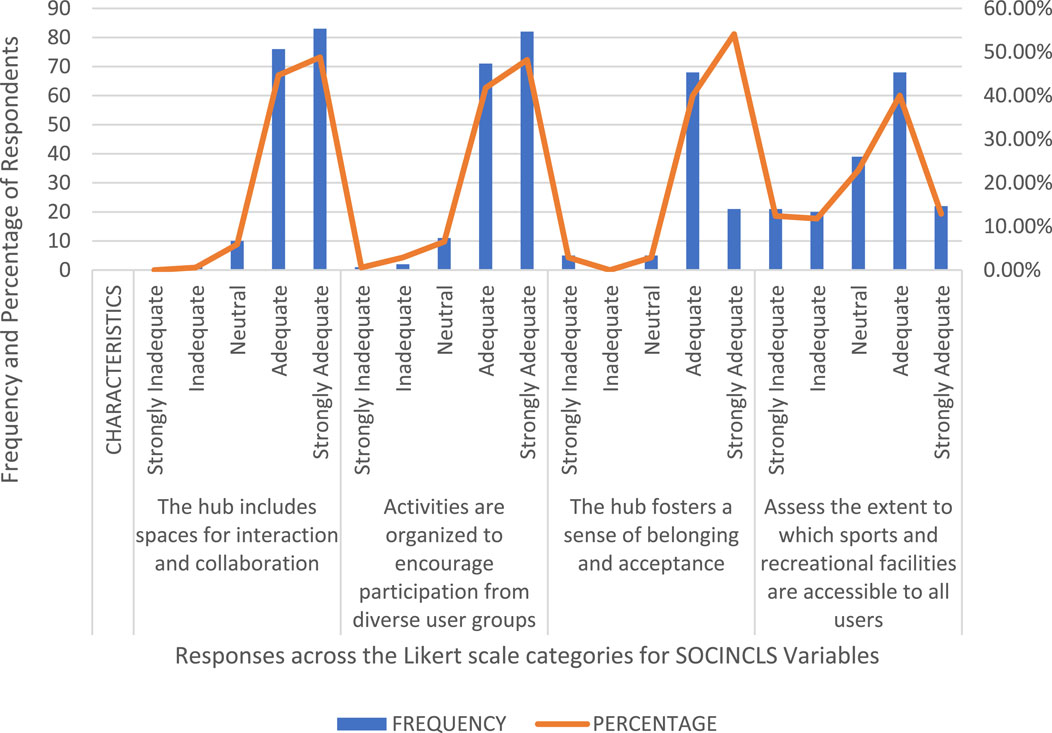
Figure 3. Stacked column chart of respondents’ ratings on social inclusion strategies in innovation hubs.
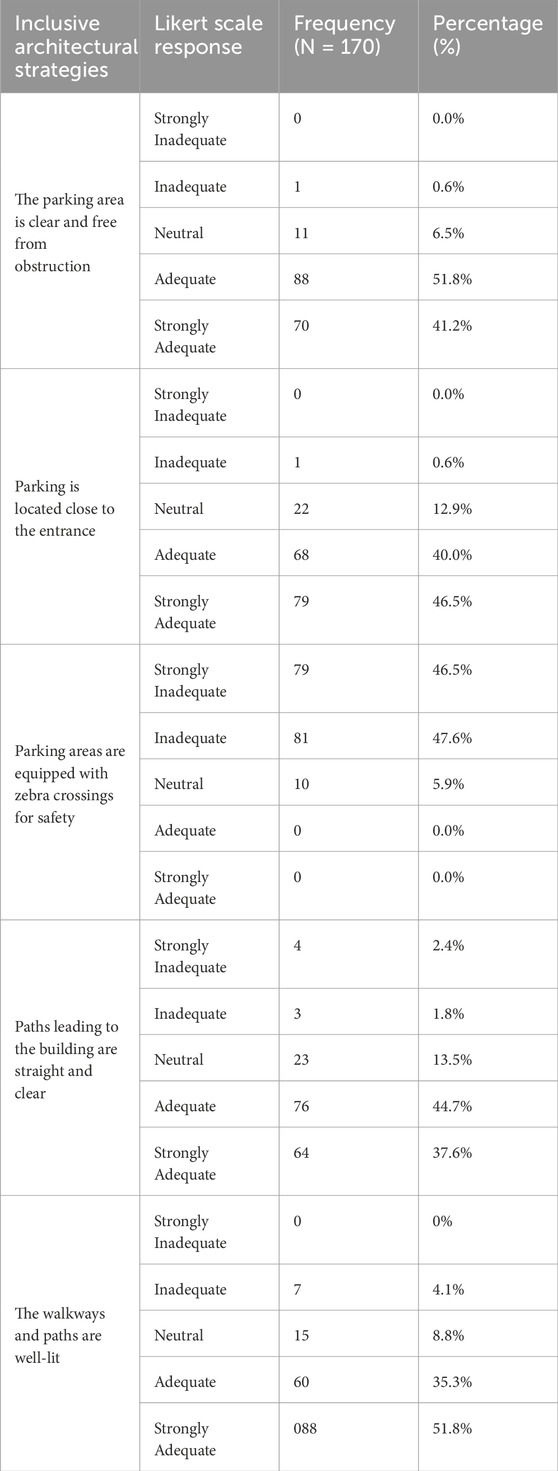
The data from Table 5 survey reveals key insights into the exterior and outdoor areas of the building. Most respondents (93%) agree that the parking area is clear and free from obstructions (The parking area is clear and free from obstructions), indicating that the area is well-maintained and accessible. Additionally, 86.5% of respondents either strongly agree or agree that parking is close to the entrance (Parking is close to the entrance), emphasising good accessibility for users. Most participants, however, strongly disagree (94.1%) that parking areas are equipped with zebra crossings for safety (Parking areas are fitted with zebra crossings for safety), pointing to a critical safety issue that needs addressing.
Regarding the pedestrian pathways, 82.3% of respondents agree or strongly agree that the paths leading to the building are straight and clear (Paths leading to the building are straight and clear), which suggests efficient circulation. Furthermore, 87.1% of respondents feel that the walkways and paths are well-lit (The walkways and paths are well-lit.), reflecting a safe and welcoming environment. Overall, while the parking area and walkways receive mostly positive feedback, there is a notable need for improvement in pedestrian safety within the parking area, notably the addition of zebra crossings.
Several essential elements related to building interior navigation and pathfinding become visible according to Table 6 data. Stairs have handrails on both sides, according to 91.8% of participants, because these handrails extend over the entire path without causing obstacles (Stairs have handrails on both sides). This practice demonstrates proper exterior pathway design. Respondents found paths within the building to be effective positioning due to agreement from 92.9% of participants that they support adequate navigation between areas (The main stairs are centrally located in the building). Most survey participants disagreed about path width limitations because 96.5% expressed concern about inadequate path width (Ramps are equipped with handrails on both sides).
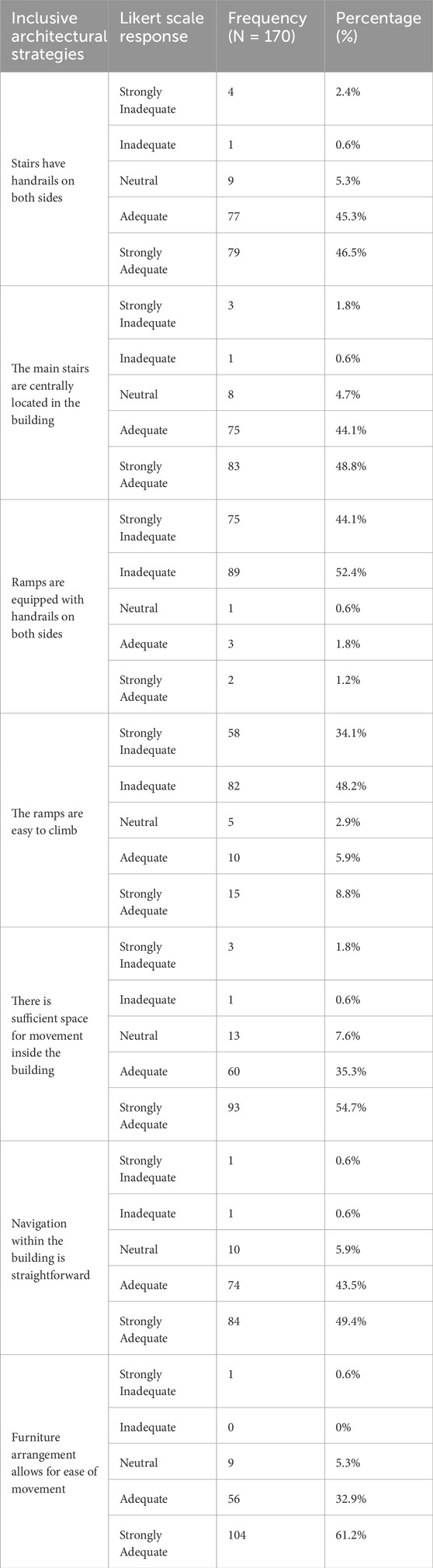
Table 6. Frequency and percentage distribution of responses for categories 2- circulation and wayfinding area.
According to survey results, user comfort appears at risk because the available space remains inadequate. Survey participants gave 90 per cent of positive feedback regarding walking surfaces because they found them easy to navigate during verification (The ramps are easy to climb), and 92.9 per cent of users agreed that path lighting was also adequate (Navigation within the building is straightforward). Survey participants indicated that the 94.1% satisfaction rating about rest facilities proves that the area meets their needs for resting (Furniture arrangement allows for ease of movement). The data shows outstanding accessibility to internal circulation since most users found the building has enough space for movement (Sufficient space for movement inside the building), and routing through the building presents no difficulties (Navigation within the building is straightforward). The furniture placement needs more consideration because its current arrangement restricts movement, which makes circulation less efficient.
The information presented in Table 7 about building interior space accessibility and functionality provides essential details about interior space usability. Most users (94.7%) agree that building doors meet accessibility needs since they offer enough width for simple entry (Doors within the building are wide enough for easy access), according to research findings. Such design features serve as a positive sign that the building promotes inclusivity to everyone. 81.8% of the respondents view all interior spaces of the innovation hub as accessible to everyone. The survey results indicate that accessibility issues remain because 5.8% of respondents express disagreement about access points, mainly related to mobility needs and building design features. The respondents appreciated the building layout (Related functional areas are located near each other) since 73.5% of them adamantly agreed or agreed with this arrangement, which ensures convenient functional area locations. The neutral and disagreeing responses from 26.5% of survey takers point to accessibility problems in some buildings regarding their layout and travel distances. In summary, the building’s interior is primarily seen as accessible, with wide doors and functional areas placed in proximity. There is, however, some room for improvement, particularly in ensuring that all areas are equally accessible to everyone and refining the layout to address any perceived disconnections.
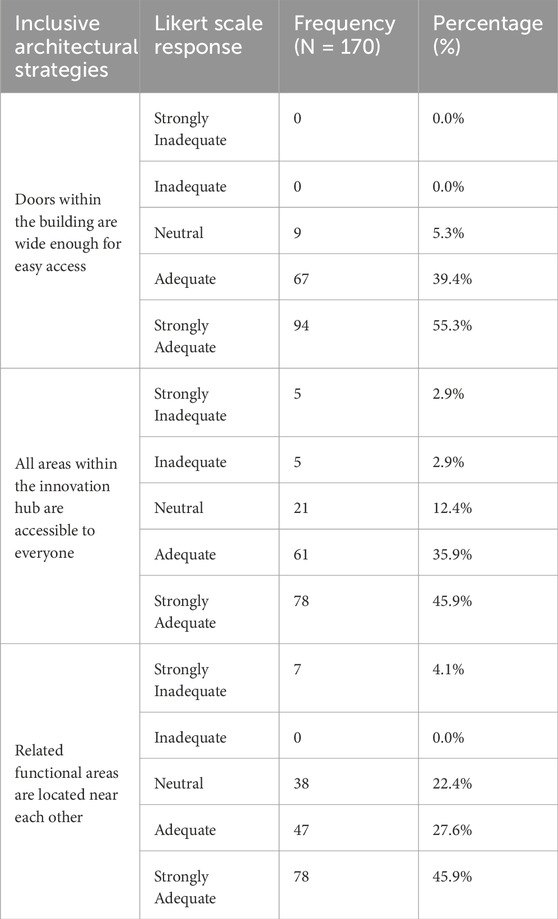
Table 7. Frequency and percentage distribution of responses for categories 3- building interior/interior facilities.
The analysis of the inclusive architectural strategies in Table 8 provides insightful perspectives on user perceptions regarding access arrangements within the building. For (Multiple entry and exit points are available in the building), the responses show a mixed sentiment, with 16.5% strongly disagreeing and 21.2% disagreeing. It indicates that some users feel improvements are necessary. Conversely, 29.4% agreed, and 18.8% strongly agreed, suggesting that many appreciate the flexibility offered by multiple access points.
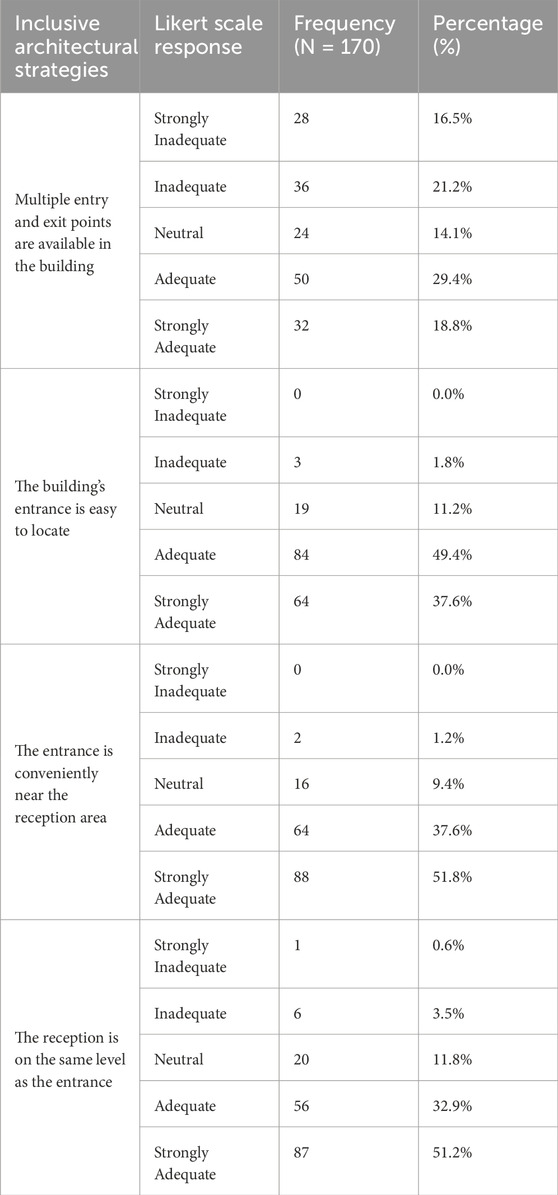
Table 8. Frequency and percentage distribution of responses for categories 4- access arrangements/entrance.
(The building’s entrance is easy to locate.) Focuses on the ease of finding the building’s entrance. A significant majority agreed, with 49.4% agreeing and 37.6% strongly agreeing. It reflects positively on the building’s signage and design, indicating that nearly 87% of respondents find the entrance easy to locate. Responses were similarly favourable for (The entrance is conveniently near the reception area) 37.6% agreed and 51.8% strongly agreed, indicating that approximately 89.4% of users find this arrangement beneficial for accessibility. Lastly, the reception is on the same level as the entrance. The feedback here is also positive, with 32.9% agreeing and 51.2% strongly agreeing. It suggests that around 84% of respondents believe that aligning both facilities vertically is crucial for ensuring ease of access and contributes to a more user-friendly experience. The data indicates a generally positive perception of access arrangements across all inclusive architectural strategies, particularly concerning location and convenience. However, there are still opportunities for improvement in areas such as entry and exit options, as reflected in (Multiple entry and exit points are available in the building). These insights can inform future enhancements to ensure all users have a seamless and accessible experience within the building.
The analysis of Table 9, sensory considerations within the building environment, as reflected in the responses, reveals a largely positive perception among respondents as shown in Table 10. For (The building environment is not noisy,” a significant majority—51.2% strongly agreed and 31.2% agreed—indicating that most users find the noise levels acceptable.
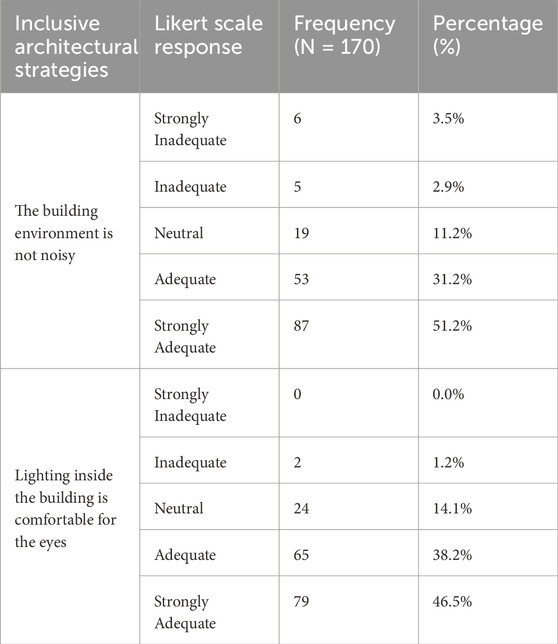
Table 9. Frequency and percentage distribution of responses for categories 5- sensory considerations.
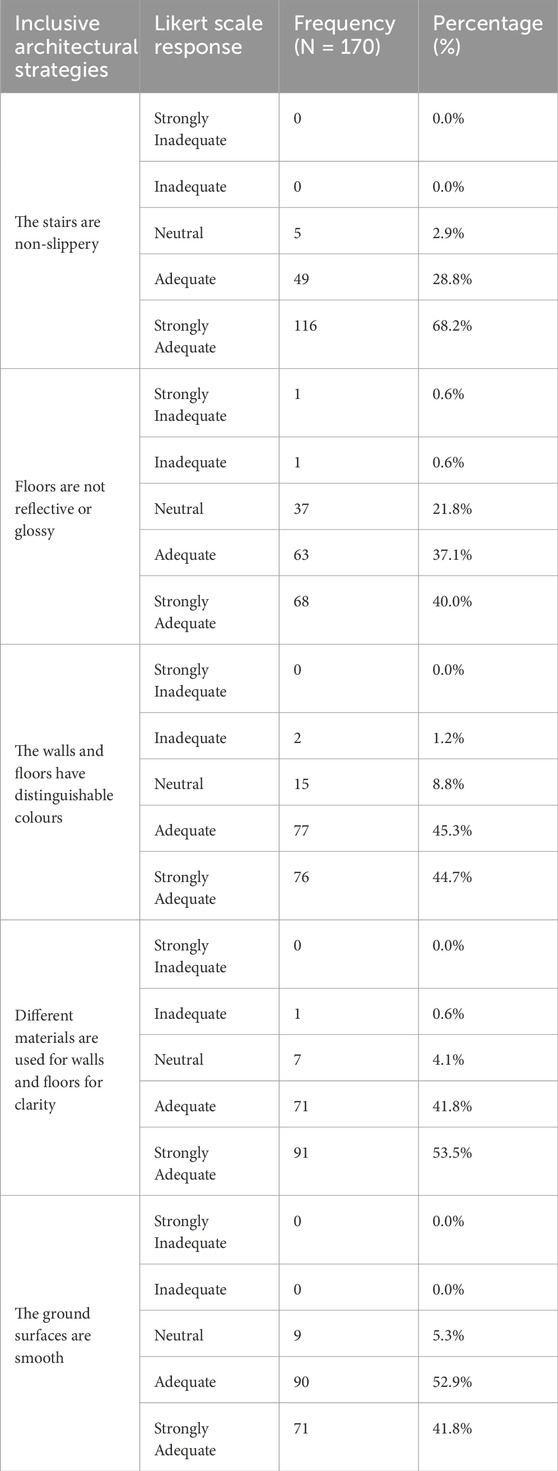
Table 10. Frequency and Percentage Distribution of Responses for Categories 6- Materials and colour.
However, a small portion of respondents expressed concerns, with 3.5% strongly disagreeing and 2.9% disagreeing. Regarding lighting, as evaluated by (Lighting inside the building is comfortable for the eyes), the feedback was similarly favourable; 46.5% strongly agreed and 38.2% agreed that the lighting is comfortable for the eyes, with minimal disagreement noted. Overall, while the findings suggest that the building effectively meets sensory needs regarding noise and lighting, addressing the minor noise-related concerns could further enhance user satisfaction within the space.
The analysis of the materials and colour considerations within the building environment, as reflected in the responses to the MATCOL1-5, reveals a largely positive perception among respondents. For (The stairs are non-slippery), an impressive 68.2% strongly agreed, indicating high confidence in stair safety. Regarding floor reflectivity, addressed by (Floors are not reflective or glossy), 40% strongly agreed and 37.1% agreed that the floors are suitable and non-reflective, suggesting general satisfaction. The feedback for (The walls and floors have distinguishable colours) was similarly favourable, with a combined agreement of approximately 90%. For (Different materials are used for walls and floors for clarity), regarding the use of different materials for clarity, 53.5% strongly agreed, emphasising the importance of material differentiation in enhancing visual clarity. Lastly, concerning the smoothness of ground surfaces assessed by (The ground surfaces are smooth), a majority expressed satisfaction, with 52.9% agreeing and 41.8% strongly agreeing. Overall, these findings suggest that respondents are highly satisfied with the materials and colour choices in the building.
Table 11 above reveals that the analysis of information accessibility within the building, as reflected in the responses to the inclusive architectural strategies, indicates a generally positive perception among respondents. For (Signs within the building are clear and easy to read), a significant majority agreed, with 45.3% agreeing and 45.9% strongly agreeing. It suggests that most users find the signage effectively guides them throughout the space. In contrast, Assistive technologies are available for diverse needs and have received mixed responses. While 40.6% agreed and 20% strongly agreed, there was also notable disagreement, with 10% strongly disagreeing and 14.7% disagreeing. It indicates that while many respondents recognise the presence of assistive technologies, there is room for improvement in ensuring these resources meet the diverse needs of all users. Overall, while signage is perceived positively, enhancing the availability and effectiveness of assistive technologies could further improve information accessibility within the building.
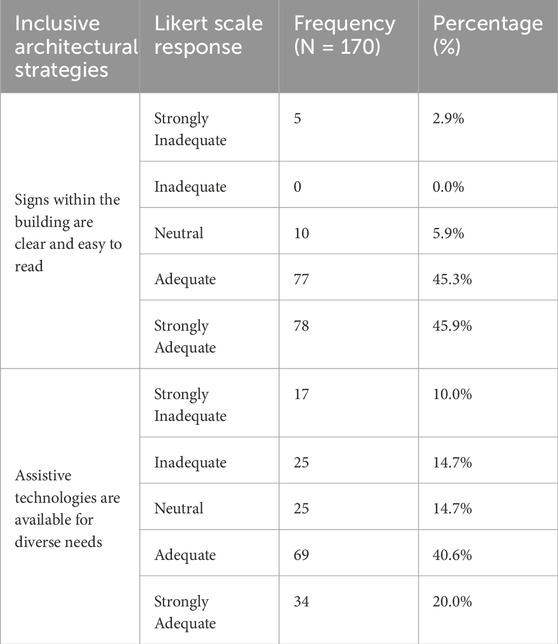
Table 11. Frequency and percentage distribution of responses for categories 7- information accessibility.
Table 12 above shows the analysis of adaptability and flexibility of space within the building, as reflected in the responses, which shows a predominantly positive perception among respondents. For (spaces are designed for multiple functions), an overwhelming majority indicated satisfaction, with 47.1% agreeing and 44.7% strongly agreeing. It suggests that users appreciate the multifunctional design of the spaces available. Similarly, furniture can be rearranged easily for different purposes, and received favourable feedback, with 48.2% agreeing and 41.8% strongly agreeing. The absence of intense disagreement in both inclusive architectural strategies indicates that respondents feel the spaces are adaptable and flexible to meet various needs. These findings highlight that the building effectively accommodates diverse functions and arrangements.
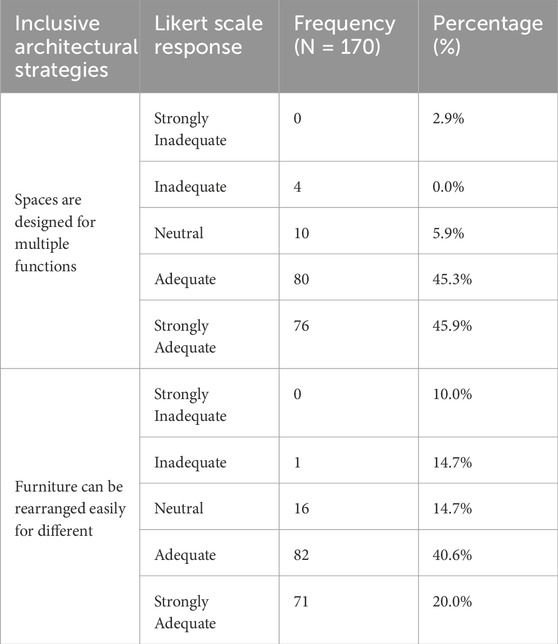
Table 12. Frequency and percentage distribution of responses for categories 8- adaptability and flexibility of space.
4.2 The impact of inclusive architectural strategies on improving social inclusion characteristics in innovation hubs
This section first focuses on the analysis of the findings related to social inclusion characteristics in the context of selected innovation hubs. It also presents the results of the categorical regression analysis, which quantifies categorical data by assigning numerical values to categories, thereby producing an optimal linear regression model for the transformed inclusive architectural strategies. In this study, the dependent variables were the social inclusion characteristics, as outlined in Table 13 and Section C of the questionnaire. The independent variables (predictors) were the inclusive architectural strategies, reflecting the adequacy of inclusive architectural practices (ALLIN) within the selected innovation hubs, as detailed in Section B of the questionnaire. The analysis aimed to examine the impact of inclusive architectural strategies on improving social inclusion within selected innovation hubs.
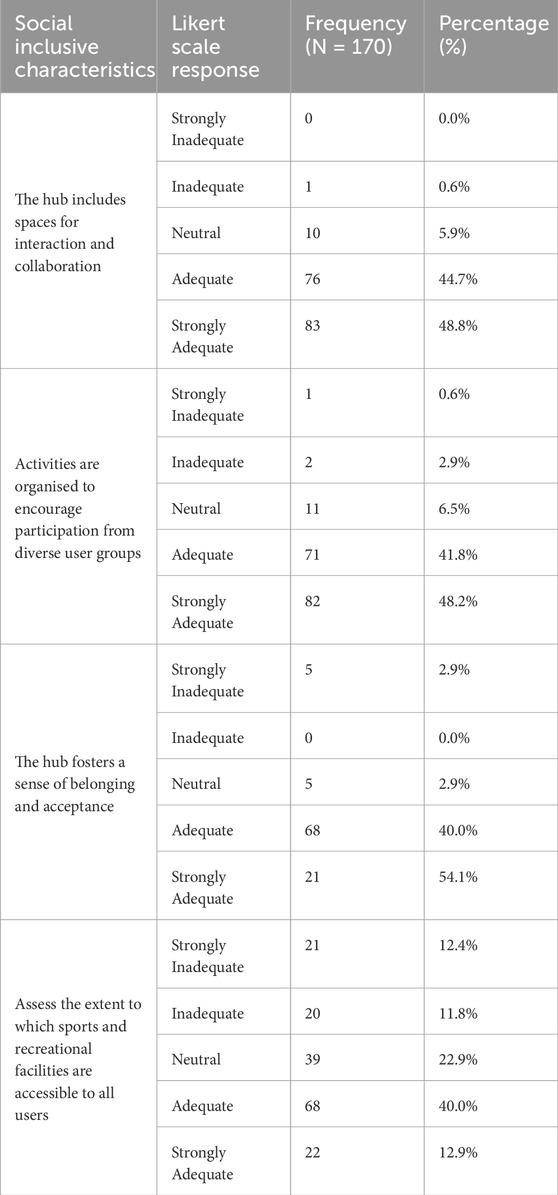
The analysis of social inclusion variables highlights a strong positive perception of social inclusivity in the hub. Interaction spaces (93.5%), diverse participation activities (89%), and a sense of belonging (94.1%) received high approval. However, accessibility to sports and recreational facilities showed mixed responses, with 52.9% agreeing but some expressing concerns. While the hub excels in fostering inclusivity, improvements are needed in recreational accessibility.
4.3 Analysing the impact of social inclusion characteristics in innovation hubs using descriptive and inferential statistics
The process began by computing the variables of social inclusion characteristics, combining all 4 characteristics of social inclusion into a single dependent variable and the inclusive architectural strategies variables as independent variables using IBM SPSS Statistics 27 software. The analysis then commenced with a model fit summary as seen in Table 14, providing the square root of R Square (R), the coefficient of determination (R Square), the adjusted R Square, and the apparent prediction error. Following this, variance analysis (ANOVA) was conducted to determine the statistical significance of the model, yielding the sum of squares, degrees of freedom (df), mean square, the F-value (Mean Square Regression divided by Mean Square Residual (F), and the significance or p-value (Sig) as highlighted in Table 15.
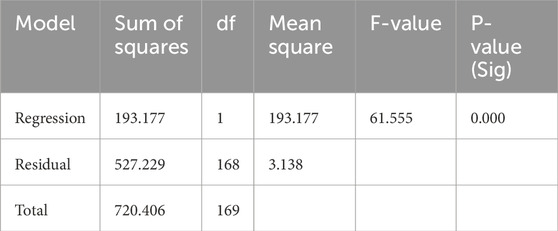
Table 15. Analysis of variance of categorical regression analysis on social inclusion characteristics.
The analysis in Table 16 highlights that inclusive architectural strategies have a substantial and statistically significant positive impact on social inclusion. For every one-unit increase in inclusive strategies, social inclusion increases by 0.639 units. The standardised coefficient (Beta = 0.518) emphasises that this is a substantial relationship. With a t-value of 7.846 and a p-value of <0.001, the effect of inclusive strategies is highly reliable, making them a critical focus for fostering social cohesion. It shows that an inclusive architectural strategy plays a key role in improving social inclusion in innovation hubs.
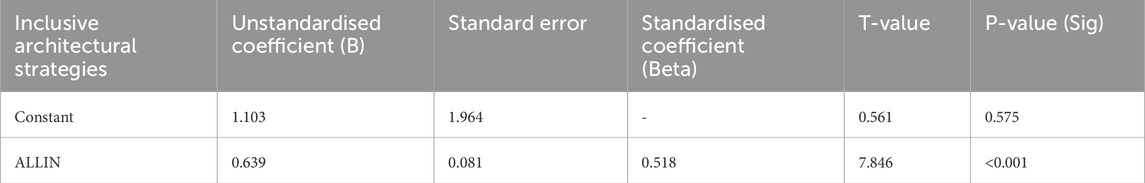
Table 16. Regression coefficients for the impact of inclusive architectural strategies on social inclusion.
4.4 Inclusive architectural strategies informed by respondent group roles and feedback
The interpretation of responses from different categories of respondents provides essential insight into how each user group contributes to the development of inclusive architectural strategies. This section highlights the relationship between user demographics, their perceptions of spatial accessibility, and how their feedback directly informed the recommendations for innovation hub design.
4.4.1 Respondents living with disabilities
Though fewer in number, they offered critical input on physical and sensory accessibility barriers. Their responses revealed dissatisfaction with the usability of ramps and the availability of assistive technologies. While some hubs provided ramps, issues such as inadequate handrails and improper gradients made them difficult to use independently. Additionally, concerns about insufficient signage and assistive tools highlighted the need for inclusive communication measures such as braille, tactile cues, and audio guidance systems. These observations informed recommendations for the redesign of ramps with handrails on both sides, the use of non-slip surfaces, and the integration of assistive communication technologies.
4.4.2 Students
Primarily aged between 16 and 35 years, and accounting for over 40% of respondents, emphasised comfort, adaptability, and functionality in learning and working environments. Many rated features like flexible furniture and multi-functional spaces as “adequate” or “strongly adequate.” However, concerns were raised about noise levels and the rigidity of fixed seating arrangements. These insights support the need for acoustically zoned environments, movable furniture, and open-plan layouts that can accommodate both group collaboration and individual study.
4.4.3 Frequent users of innovation hubs
(Approximately 35% of respondents) generally rated spatial layout and internal navigation features highly. Their feedback emphasised the importance of spatial clarity, well-defined circulation paths, and convenient access to rest and interaction zones. They also noted occasional issues with cluttered corridors and poorly grouped functional areas. This group’s responses informed the strategy to design wide, unobstructed corridors, group-related functions for ease of access, and provide clear directional signage to enhance user orientation.
4.4.4 Older adults
Particularly those aged 36–55 years, highlighted the importance of well-lit walkways and easily identifiable entrances. Several respondents reported challenges related to visibility and spatial orientation, especially in hubs where entrances were not directly connected to reception areas. Their responses informed the recommendation to enhance lighting in transitional zones, align reception areas with entry points, and incorporate contrasting colours and textures to support visual navigation.
4.4.5 Staff members
Many of whom work regularly within the hubs, expressed appreciation for accessible layouts and wide doorways. However, they raised concerns about the limited availability of inclusive digital tools and assistive technologies. Their feedback led to the recommendation for smart assistive systems and the integration of universally accessible digital interfaces to support a wider range of users, including those with sensory or cognitive impairments.
5 Discussion
This study aims to examine the impact of inclusive architectural strategies on social inclusion within selected innovation hubs, focusing on how these strategies create accessible, collaborative, and equitable spaces. The findings suggest that implementing inclusive architectural strategies enhances accessibility, facilitates knowledge exchange, and strengthens social inclusion within innovation hubs.
The role of inclusive architectural design strategies in fostering social inclusion within innovation hubs has gained increasing attention in recent research. Adewale and Odewumi (2024) highlight how barrier-free access, adaptive spatial planning, and user-centred design contribute to more accessible and functional community centres in Lagos Mainland. Their findings emphasise the necessity of policy-driven approaches to ensure equitable access to public spaces. Similarly, Mamuzo et al. (2024) argue that architectural design plays a crucial role in social integration, demonstrating that well-structured community centres featuring open layouts, multifunctional areas, and culturally responsive elements create opportunities for interaction and reduce social exclusion.
Expanding on these perspectives, Sholanke and Eleagu (2024) stress the significance of universal design principles in fostering inclusivity. Their study identifies barrier-free infrastructure, adaptable spaces, and ergonomic features as key elements that enhance accessibility and equity in urban environments. Using the Federal Polytechnic Mubi School of Environmental Science and Technology Building as a case study, Mohammed et al. (2021) assessed the use of inclusive design principles in institutional architecture. The study concluded that just two criteria, flexibility and realism, were followed in the design of the facility using an observational assessment grounded on the seven principles of inclusive design. Fundamental values such as inclusion, adaptation for every user, and responsiveness were especially lacking. The study highlights accessibility gaps for disabled and elderly users and urges early integration of universal design to create inclusive, sustainable spaces (Ugah et al., 2024).
Furthering this discourse, Zallio et al. (2024) explore the integration of Inclusion, Diversity, Equity, and Accessibility (IDEA) principles in the built environment. Their study underscores the importance of incorporating these principles at the early stages of design to ensure that public spaces cater to a broad spectrum of users, including individuals with disabilities and marginalised communities. They emphasise that interdisciplinary collaboration among architects, policymakers, and community members is vital in achieving long-term social and spatial inclusivity. Patrick and McKinnon (2022) complement this by examining the role of co-creation in public space design. Their global case studies reveal that participatory planning, where diverse stakeholders contribute to the design process, leads to more substantial community ownership and increased social cohesion. However, they also acknowledge challenges such as bureaucratic limitations and financial constraints, which often hinder the full realisation of inclusive design.
The findings of this study align with these discussions by demonstrating how inclusive architectural strategies can significantly enhance social inclusion within innovation hubs. The study aimed to examine the impact of inclusive architectural design strategies on social inclusion, particularly how these strategies create accessible, collaborative, and equitable spaces. The first objective sought to identify the inclusive architectural strategies applicable in innovation hubs. Results indicate that key strategies include incorporating universal design principles, flexible spatial arrangements, barrier-free access, and the use of participatory planning approaches. These strategies enhance usability for diverse populations and encourage interaction among various user groups.
The second objective focused on examining the impact of these inclusive strategies on social inclusion within innovation hubs. The results reveal that innovation hubs with accessibility-focused layouts, adaptable workspaces, and cultural sensitivity significantly enhance social interactions and create a sense of belonging among users. Furthermore, participatory design approaches, where stakeholders, including users, designers, and policymakers, collaborate in the design process, were found to contribute to a heightened sense of ownership and engagement within these spaces.
The contribution of respondents was instrumental in shaping the inclusive architectural strategy components proposed in this study. Drawing from the analysed data, feedback from different user groups was systematically integrated into targeted design interventions that addressed their specific spatial and accessibility concerns. As outlined in Table 17, respondents living with disabilities identified challenges such as inadequate ramp design, lack of tactile and auditory navigation aids, and the absence of lifts. These insights informed strategies involving the provision of accessible ramps with appropriate handrails, braille and audio signage, and vertical mobility solutions. Student respondents emphasized the importance of adaptable and sensory-responsive environments, which led to the inclusion of flexible furniture arrangements, acoustic zoning, and multi-functional spaces. The responses of frequent users underscored the need for spatial clarity and efficient circulation, guiding the adoption of open layouts, well-defined circulation paths, and the grouping of related functions. Older adults highlighted visibility and orientation issues, which were addressed through enhanced lighting schemes, entry-reception alignment, and contrast-based wayfinding cues. Finally, staff members stressed the importance of inclusive digital infrastructure, resulting in proposed strategies that incorporated assistive technologies and universally accessible digital systems. These strategy components emerged as a direct response to the empirical findings and reflected a deliberate effort to accommodate user feedback within the architectural design process, thereby advancing the objective of fostering socially inclusive innovation hubs.
However, this study also identifies challenges that align with previous research, particularly those highlighted by Patrick and McKinnon (2022). Financial constraints and bureaucratic inefficiencies often pose significant barriers to fully implementing inclusive design strategies. Many innovation hubs struggle with funding constraints, limiting their ability to integrate comprehensive accessibility measures. Additionally, while policies promoting inclusive design exist, enforcement remains inconsistent, limiting their impact.
6 Conclusion
The study findings emphasise the crucial role of inclusive architectural strategies in fostering social inclusion within selected innovation hubs in southwest Nigeria. Accessible and well-designed spaces significantly enhance collaboration, engagement, and knowledge exchange, creating environments that accommodate diverse user needs. However, architects must critically evaluate how these strategies impact different stakeholders, ensuring that design interventions effectively promote equity and inclusivity. Despite progress in implementing inclusive architectural approaches, challenges persist in addressing the broader social, cultural, and economic dimensions influencing innovation hubs. The need for adaptable, user-centred design solutions that respond to Nigeria’s evolving societal dynamics cannot be overstated. Moving forward, prioritising innovation hubs as catalysts for social equity and sustainable development is essential, reinforcing their role in bridging socio-economic gaps and fostering a more inclusive society.
This study makes a unique contribution by evaluating inclusive architectural strategies within innovation hubs and examining their impact on social inclusion. Drawing on detailed feedback from diverse respondent groups, the research shaped targeted design interventions that respond directly to user needs. Persons with disabilities highlighted challenges related to ramp usability, inadequate signage, and sensory navigation, revealing key accessibility gaps. Students prioritised comfort, adaptability, and the availability of collaborative spaces conducive to learning and innovation. Frequent users underscored the importance of spatial clarity, rest zones, and functional layout to support regular engagement. Older adults expressed concerns about lighting, orientation, and feeling welcome in shared spaces, while staff members identified the absence of inclusive digital tools that could support wider participation. This user feedback aligned closely with broader perceptions of inclusion: over 90% of respondents rated spaces for interaction and collaboration, and participation-focused activities, as either adequate or strongly adequate. Similarly, a strong majority reported that the hub fostered a sense of belonging. However, notable dissatisfaction was expressed regarding the accessibility of recreational facilities, pointing to areas for targeted improvement. These findings were translated into practical architectural responses, including the integration of lifts, tactile signage, flexible layouts, enhanced lighting, and inclusive digital systems. By grounding design strategies in both the lived experiences and measurable perceptions of social inclusion, the study proposes a replicable, user-informed model that links inclusive architecture to equitable and inclusive innovation environments.
6.1 Implications of the findings on the impact of inclusive architectural strategies on social inclusion in innovation hubs in southwest Nigeria
The findings of this study show that inclusive architectural design has a strong and positive effect on social inclusion in innovation hubs. As the effectiveness of inclusive architectural strategies increases, covering areas such as exterior and outdoor access, circulation and wayfinding, building interiors, entrance arrangements, sensory considerations, materials and colours, information accessibility, and adaptable spaces, so does the level of social interaction, participation, and sense of belonging among users. The study clearly shows that well-designed spaces do more than offer physical access; they actively shape users’ experiences, comfort, and engagement. Feedback from people with disabilities revealed major ramps, signage, and navigation challenges, highlighting the need for practical features like tactile floor indicators, handrails, and accessible lifts. Students and younger users emphasised the importance of quiet, flexible, and comfortable environments supporting group collaboration and focused work, suggesting that spatial adaptability directly influences inclusion. Older adults raised concerns about lighting and layout clarity, pointing to the need for clear sightlines and well-aligned entry and reception areas. Staff and regular users noted the value of efficient layouts but also identified gaps in digital accessibility, calling for more inclusive technologies and user-friendly digital interfaces. These perspectives underline that inclusive design must be based on actual user needs and lived experiences, not just technical guidelines. While many hubs show strong progress, the absence of features like recreational accessibility, zebra crossings, and assistive tools shows that inclusion is still uneven, often limited by funding or weak policy enforcement. The findings imply that inclusive architectural strategies are essential tools for promoting equity, especially in shared innovation spaces. When applied thoughtfully and consistently from the planning stage, they can transform innovation hubs into inclusive environments that not only support creativity and learning but also bring people from different backgrounds together in meaningful and equitable ways.
7 Recommendations
Based on the findings of this study, it is essential that inclusive architectural strategies be treated not as optional additions, but as fundamental elements in the planning and development of innovation hubs. These hubs are intended to foster collaboration, creativity, and learning across a wide range of users, including students, researchers, entrepreneurs, and the general public. For them to truly serve this role, they must be designed with inclusion at their core. This begins by incorporating feedback from diverse user groups—especially persons with disabilities, older adults, and students into the design process. The challenges highlighted by respondents in this study, such as difficulty navigating ramps, poor signage for the visually impaired, and the lack of flexible, multi-use spaces, point to clear areas where improvements are needed. Addressing these issues requires a more intentional application of universal design principles, ensuring that everyone can move through, understand, and use the space with ease and dignity.
Beyond design, enforcement also matters. Relevant policies and standards around accessibility should not just exist in written form they must be consistently applied and monitored. Innovation hubs should also prioritise digital accessibility and invest in assistive technologies that allow all users to engage with virtual platforms, shared tools, and learning resources. Just as important is the role of staff and management in maintaining inclusive spaces. Training and awareness programs should be provided so that staff understand the varied needs of users and can provide appropriate support. Inclusion should not only be about removing physical barriers but also about creating a sense of belonging, where people feel safe, seen, and empowered to participate fully.
Finally, these recommendations should not be treated as isolated design suggestions but as part of a wider strategy to promote inclusive and equitable development. Aligning architectural practices with both national priorities and global agendas is essential for long-term impact. Specifically, the inclusive strategies outlined in this study directly support Sustainable Development Goal 10, which addresses the need to reduce inequality within and among populations, and Goal 11, which calls for inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable urban environments. By adopting a more inclusive approach to architectural design and spatial planning, innovation hubs in Southwest Nigeria and across the country can become not just centres of innovation but also models of equity, accessibility, and social progress.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
Ethical review and approval was not required for the study of human participants in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent from the participants or participants’ legal guardian/next of kin was not required to participate in this study in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
Author contributions
EE: Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft. FO: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
Special appreciation is extended to the Covenant University Centre for Research, Innovation, and Discovery (CUCRID) in facilitating the publication of this work. The authors express gratitude for the assistance offered by the innovation hub visited for this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. The author(s) verify and take full responsibility for the use of generative AI in the preparation of this manuscript. Generative AI was used solely for grammar correction and language polishing. All intellectual content, data analysis, and conclusions are the authors’ own work.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fbuil.2025.1632945/full#supplementary-material
References
Adegoke, K. V., and Mohamed Khaidzir, K. A. (2024). Architectural design intervention as a solution to the problem of a lack of sustainable and equitable housing in Nigeria. Quantum J. Soc. Sci. Humanit. 5 (SI1), 186–193. doi:10.55197/qjssh.v5isi1.575
Adewale, B. A., and Odewumi, A. N. (2024). Adoption of inclusive architecture design strategies in selected community centres, Lagos Mainland, Nigeria. Civ. Eng. Archit. 12 (6), 4257–4276. doi:10.13189/cea.2024.120635
Agarwal, R., Green, R., Patterson, E. K., and Pugalia, S. (2022). Encyclopedia of Renewable and sustainable materials. Springer. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-98390-5_237-1
Agoha, B. (2023). “Inclusive sustainable urban design using the Owerri urban village, imo state, Nigeria,” in World congress of architects (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 131–140.
Ajithakumari, G. (2024). Sample size determination and sampling technique. Int. J. Sci. Res. 13 (9), 1432–1440. doi:10.21275/es24924103353
Andrew, V. F. (2022). On the proposed use of a finite-population correction factor in clinical trials. Clin. Trials 19 (6), 697–698. doi:10.1177/17407745221110185
Ayegbeni, A., and Ikpeminohena, V. A. (2024). Innovation and technological entrepreneurship in Nigeria: a catalyst for growth. Econ. Entrepreneursh., 219–221. doi:10.34925/eip.2024.163.2.035
Aziz, H., Li, B., Moulin, H., Wu, X., and Zhu, X. (2024). Almost proportional allocations of indivisible chores: computation, approximation and efficiency. Artif. Intell. 331, 104118. doi:10.1016/j.artint.2024.104118
Black, M. H., McGarry, S., Churchill, L., D’Arcy, E., Dalgleish, J., Nash, I., et al. (2022). Considerations of the built environment for autistic individuals: a review of the literature. Autism 26 (8), 1904–1915. doi:10.1177/13623613221102753
Busciantella-Ricci, D. (2023). “Changing perspective on social inclusion and design: exploring the concept of designing for inclusive attitudes,” in Proceedings of the IASDR 2023 Conference. doi:10.21606/iasdr.2023.527
Chen, H. (2024). Accessibility design research: redesign of the canterbury square. Highlights Sci. Eng. Technol. AGECT 113, 18–23. doi:10.54097/04kgrc97
Chowdhury, E. H., Fjellström, D., Osarenkhoe, A., Hannadige, S. V. S., and Weerasinghe, D. K. C. (2023). The contribution of innovation hubs towards strengthening the regional development in Sweden. Int. J. Innovation Technol. Manag. 20 (02), 2350010. doi:10.1142/S0219877023500104
Dubost, N. (2023). Inclusive innovation and disability: The contributions of social design [Innovation inclusive et handicap: les apports du design social]. Entreprendre and Innover 55 (2), 31–39. doi:10.3917/entin.055.0031
Egessa, M. M., and Mwadzogo, H. A. (2024). Innovation hub as a catalyst for research(er)-led innovation outputs. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 22 (1), 102–108. doi:10.30574/wjarr.2024.22.1.1029
Errante, L. (2020). “Public space: mapping the physical, social, and cultural accessibility for creating urban commons,” in Cultural Commons and Urban Dynamics: A Multidisciplinary Perspective. Editors E. Macrì, V. Morea, and M. Trimarchi (Springer), 113–140. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-54418-8_8
Filer, B., and Spain, A. (2024). Model to design accessible, sensorial, and cognitive spaces: Methodology for healthy and inclusive design. J. Nurs. and Healthc. 9 (2), 1–16. doi:10.33140/jnh.09.02.06
Gallouzi, S. (2024). A pedagogic approach serving inclusive design. Int. J. Archit. Arts Appl. 10 (3), 39–53. doi:10.11648/j.ijaaa.20241003.11
Hameed, A. A. S. (2021). Urban and regional planning strategies to achieve sustainable urban development: (Subject review). International Journal of Advances in Scientific Research and Engineering 7 (3), 22–27. doi:10.31695/IJASRE.2021.33980
Howe, I., and Martel, A. (2024). “Universal design,” in Routledge handbook of high-performance workplaces. Editors C. Candido, I. Durakovic, and S. Marzban (London, United Kingdom: Routledge), 13–25. doi:10.1201/9781003328728-3Booktopia+6
Imrie, R. (2014). “Designing inclusive environments and the significance of universal design,” in Disabling barriers—enabling environments. Editors J. Swain, S. French, C. Barnes, and C. Thomas 3rd ed. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications), 287–296. doi:10.4135/9781473957701
Irene, H.-R. (2023). Universal and ecological design in media accessibility: finding common ground. Univers. Access Inf. Soc. doi:10.1007/s10209-023-01077-9
Jiménez, A., and Zheng, Y. (2021). Unpacking the multiple spaces of innovation hubs. Inf. Soc. 37 (3), 163–176. doi:10.1080/01972243.2021.1897913
Kamani, A. F., Paydar, M., and Gárate, N. V. (2023). Urban park design and pedestrian mobility—case study: temuco, Chile. Sustainability 15 (20), 14804. doi:10.3390/su152014804
Kobylarczyk, J. (2019). Lighting of the urban interior in the residential environment. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 471 (10), 102032. doi:10.1088/1757-899X/471/10/102032
Kusimo, A. O., Duruji, M. M., and Oni, S. (2022). “Barriers to inclusive education in Federal Capital Territory primary schools, Nigeria,” in Paper presented at the 9th International Conference on Education and Education of Social Sciences (Istanbul, Turkey).
Magdziak, M. (2019). “Flexibility and adaptability of the living space to the changing needs of residents,” in IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering (Bristol, United Kingdom: IOP Publishing) 471 7072011. doi:10.1088/1757-899x/471/7/072011
Mamuzo, G. E., Fadairo, J. O., and Obaribirin, A. (2024). Architectural design as a catalyst for social inclusion: exploring the impact of community center architecture on social inclusion in Lagos State. Int. J. Multidiscip. Res. Growth Eval. 5 (4), 1098–1110. doi:10.54660/IJMRGE.2024.5.4.1098-1110
Mbanugo, E. O. (2019). Perspectives and legal implications of inclusive access to the environment for children living with disabilities in Nigeria under the Discrimination against Persons with Disability (Prohibition) Act 2018. J. Law, Policy Glob. 85, 133–142. doi:10.7176/JLPG/85-15
Mohammed, U., Haruna, H., and Lawal, I. M. (2021). Application of inclusive design principles on institutional buildings in Nigeria: a case study of school of environmental science technology building, federal polytechnic, Mubi, Nigeria. Int. J. Sci. and Technoledge 9 (8). doi:10.24940/theijst/2021/v9/i8/ST2108-001
Mosca, E. I., and Capolongo, S. (2020). “Universal design-based framework to assess usability and inclusion of buildings,” in Computational science and its applications – ICCSA 2020: Proceedings, Part V. Editor O. Gervasi (Springer), 316–331. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-58817-5_24
Nam, J.-M., and Kim, G. (2024). A study on the development plan of creative economy innovation center. Korea Creative Econ. Bus. Assoc. J. 8 (3), 211–237. doi:10.48206/kceba.2024.8.3.211
Natapov, A., Kuliga, S., Dalton, R. C., and Hölscher, C. (2015). Building circulation typology and space syntax predictive measures. Proceedings of the 10th International Space Syntax Symposium. London: Space Syntax Laboratory, The Bartlett School of Architecture, University College London, 12 13–17.
Obianyo, I. I., Ihekweme, G. O., Mahamat, A. A., Onyelowe, K. C., Onwualu, A. P., and Soboyejo, A. B. (2021). Overcoming the obstacles to sustainable housing and urban development in Nigeria: the role of research and innovation. Clean. Eng. Technol. 4, 100226. doi:10.1016/j.clet.2021.100226
Orozco, C., Orozco, C. C., and Velasco, S. S. (2024). Social inclusion in cultural participation: a systematic review. Open Access Res. Ser. doi:10.36443/9788418465765
Osuji, C. (2024). The role of incubators and accelerators in nurturing tech talent. J. Technol. Entrepreneursh. Soc. Manag. 3 (3), 1–3. doi:10.61838/kman.jtesm.3.3.1
Ouf, A. S. E. D., and El-Zafarany, N. A. (2018). Diversity and inclusion in the public space as aspects of happiness and well-being. J. Urban Res. 28 (1), 109–129. doi:10.21608/jur.2018.88384
Patrick, M., and McKinnon, I. (2022). Co-creating inclusive public spaces: learnings from four global case studies on inclusive cities. J. Public Space 7 (2), 93–116. doi:10.32891/jps.v7i2.1500
Sewell, A., Kennett, A., and Pugh, V. (2022). Universal design for learning as a theory of inclusive practice for use by educational psychologists. Educ. Psychol. Pract. 38 (4), 364–378. doi:10.1080/02667363.2022.2111677
Shkliar, S., and Shushliakova, O. (2023). Universal Design As The Basis Of Forming An Accessible Architectural Environment Of Modern Cities. Urban Development Spatial Planning. 82 350–363. doi:10.32347/2076-815x.2023.82.350-363
Sholanke, J. C., and Eleagu, A. (2024). Appraisal of universal design strategies for enhancing social inclusion in the development of sporting facilities. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 1342 (1), 012024. doi:10.1088/1755-1315/1342/1/012024
Skiba, I., and Züger, R. (2020). in Basics barrier-free planning. Editor B. Bielefeld Basel, Switzerland and Berlin:Birkhäuser. doi:10.1515/9783035621938
Smith, N., and Dropkin, D. (2018). “Access and inclusion,” in Metric handbook. Editor D. Littlefield 6th ed. London, United Kingdom:Routledge. 41–51.
Strug, B., and Ślusarczyk, G. (2017). Reasoning about accessibility for disabled using building graph models based on BIM/IFC. Vis. Eng. 5 (1), 10–12. doi:10.1186/s40327-017-0048-z
Taiye, A. J. A., and Olabode, O. (2022). Universal design strategies for vocational centers in Nigeria. Int. J. Innovative Sci. Res. Technol. 7 (8), 1387–1395. doi:10.38124/IJISRT22AUG120
Ugah, U. K., Sholanke, A. B., Dimuna, K. O., Akinola, A. O., Ene, V. O., and Nduka-Kalu, I. C. (2024). Universal Design Compliance in South-west Nigeria's Federal Universities' Faculty of Environmental Science Buildings. Civil Engineering and Architecture 12 (6), 4277–4292. doi:10.13189/cea.2024.120636
Uzeyirli, Z., and Özçevik Bilen, A. (2021). A research on acoustical comfort for hearing-impaired individuals in inclusive education places. Build. Acoust. 28 (1), 57–75. doi:10.1177/1351010X20984256
Zallio, M., Chivǎran, C., and Clarkson, P. J. (2024). Exploring inclusion, diversity, equity, and accessibility in the built environment: a case study. Buildings 14 (9), 3018. doi:10.3390/buildings14093018
Zlokovich, M. S., Corts, D. P., and Rogers, M. M. (2023). “Descriptive and inferential statistics,” in The Cambridge handbook of research methods and statistics for the social and behavioral sciences: volume 1: building a program of research. Editors A. L. Nichols, and J. Edlund (Cambridge University Press), 468–493. doi:10.1017/9781009010054.023
Keywords: inclusive architecture, social inclusion, innovation hubs, accessibility, built environment
Citation: Ekhaese EN and Oyelude F (2025) The impact of inclusive architectural strategies on social inclusion characteristics in innovation hubs in Southwest Nigeria. Front. Built Environ. 11:1632945. doi: 10.3389/fbuil.2025.1632945
Received: 27 May 2025; Accepted: 01 July 2025;
Published: 30 July 2025.
Edited by:
Assed N. Haddad, Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, BrazilReviewed by:
Sri Yuliani, Sebelas Maret University, IndonesiaOlubimbola Oladimeji, Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Copyright © 2025 Ekhaese and Oyelude. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Felicia Oyelude, ZmVsaWNpYS5veWVsdWRlcGdzQHN0dS5jdS5lZHUubmc=
†ORCID: Eghosa Noel Ekhaese, orcid.org/0000-0003-3788-7680; Felicia Oyelude, orcid.org/0009-0005-7852-9232
 Eghosa Noel Ekhaese
Eghosa Noel Ekhaese Felicia Oyelude
Felicia Oyelude