- 1Civil Engineering Department, K.N. Toosi University of Technology, Tehran, Iran
- 2Geography and Urban Sustainability Department, College of Humanities & Social Sciences, UAE University, Al Ain, United Arab Emirates
- 3Department of Buildings and Construction Techniques Engineering, College of Engineering, Al-Mustaqbal University, Hilla, Iraq
Introduction: Identifying optimal locations for constructing emergency water reservoirs for Fire Following Earthquake (FFE) suppression is recognized as a key factor in reducing financial and human losses within FFE crisis management strategies; however, previous studies have not provided a comprehensive model for this purpose.
Methods: This study proposes a method that integrates potential post-earthquake damages, accessibility conditions, and economic considerations to identify the most suitable initial locations for these reservoirs. Based on operational needs in post-earthquake scenarios and relevant literature, the main influential criteria and distance classes were determined. These criteria and distance classes were then weighted and integrated using the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) and Geographic Information System (GIS) methods to generate an optimal location map.
Results: Implementation of the proposed method in Tehran resulted in an optimal location map for FFE-specific emergency water reservoirs. Results indicated that locating reservoirs within 4,000 m of major routes, fire stations, and commercial, industrial, and therapeutic centers simultaneously ensures fire engine access within 10 mins even under worst-case conditions.
Discussion: Furthermore, optimally siting reservoirs within 800 m of demand points reduces access time to below 2 mins.
1 Introduction
Water resource management is recognized as a fundamental cornerstone in addressing natural disasters, playing a vital role in reducing their harmful impacts. Earthquakes can inflict a range of structural damages (Sadeghi-Movahhed et al., 2025; Sadeghi-Movahhed et al., 2024; Majdi et al., 2023; Sadeghi Movahhed et al., 2023; Daniell et al., 2017). Fires Following Earthquakes (FFE) regarded as the most damaging secondary consequence of earthquakes, has caused billions of dollars in losses for various societies in the past (Trifunac and Todorovska, 1998; Mousavi et al., 2008; Butcher et al., 1988; Salazar and McNutt, 2011; The Japan Times, 2024; Lee et al., 2008). In some cases, the damages caused by FFE have far surpassed those of the initial earthquake (Elhami Khorasani and Garlock, 2017). This phenomenon has frequently and extensively occurred in past incidents, presenting serious challenges to urban crisis management infrastructures (Scawthorn, 2009; MaCaffrey, 1983).
The impact of severe earthquakes on urban infrastructures, particularly energy lines and water supply networks, has always been a major concern in disaster management and urban planning (Matsumura et al., 2015; Jiang et al., 2013; Liu et al., 2020; Guo et al., 2011; Alavi et al., 2024; Butler et al., 2017; Ansari et al., 2025). Historically, during severe earthquakes, energy lines and water supply networks in cities have frequently suffered significant damage (Butler et al., 2017; Shuang et al., 2019; Li et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2021; Leig et al., 2019; Uma et al., 2021; Qian et al., 2023). The 1971 San Fernando earthquake resulted in 116 ignitions, causing extensive damage to urban pipelines and water reservoirs. Ultimately, firefighters successfully prevented the spread of the fires by utilizing pools as water sources (Jennings and Wood, 1973; Scawthorn et al., 2005). The 1994 Northridge earthquake resulted in 110 ignitions, over 1,000 leaks in the water system, and damage to pump stations and storage tanks, which caused a reduction in water pressure. Ultimately, the fires were suppressed by firefighters using alternative water sources before they could spread further (Scawthorn et al., 1998).
In the past, reduced water pressure and pipeline ruptures following earthquakes have caused serious disruptions in water distribution across cities (Choi et al., 2018; Shojaeian et al., 2021). Research has shown that the reconstruction of water supply networks after earthquakes is complex and time-consuming, requiring comprehensive modeling of hydraulic conditions and vulnerability assessments (Shuang et al., 2019; Choi et al., 2018). As a result, the provision of alternative water sources is considered one of the most critical challenges in suppressing FFF in urban areas. Some advanced cities, such as San Francisco, have attempted to reduce reliance on the primary water supply network and increase resilience against FFF by establishing alternative water sources. Therefore, the construction of emergency water reservoirs is among the most essential factors for the effective suppression of FFF and minimizing damages. Unlike sources such as wells, the use of reservoirs also minimizes risks associated with power grid fluctuations and pumping disruptions.
Given past incidents, a significant amount of water resources is required for the suppression of FFF. In this regard, it is essential to allocate emergency water reservoirs specifically for suppressing FFF, ensuring they are not simultaneously used for other critical situations. For example, during the Kobe earthquake, water authority officials prohibited firefighters from using certain urban water sources for up to 12 h after the occurrence of FFF due to concerns about drinking water shortages (Scawthorn, 1996). The need for emergency drinking water after an earthquake is one of the primary critical conditions that can arise simultaneously (Santa-Cruz et al., 2024). Given that the volume of water required for drinking and suppression in post-earthquake conditions within a city can be substantial, separate reservoirs must be allocated for each purpose. This approach has been implemented in cities like San Francisco, informed by their experiences in dealing with the FFE phenomenon (Van Dyke, 1996; Scawthorn, 2011). The presence of dedicated emergency water reservoirs can be highly effective in significantly reducing operational time.
On the other hand, today we are faced with megacities that are becoming increasingly crowded and larger. These cities are typically characterized by features such as increased population and building density, severe traffic congestion, and inadequate access networks. Additionally, there are challenges in the proper utilization of resources. Due to the interplay of these characteristics, the formation of vulnerable structures in various parts of cities becomes more likely in post-earthquake conditions and the resulting fires. Therefore, identifying the optimal locations for emergency water reservoirs to suppress FFF is essential for enhancing efficiency and ensuring proper utilization of these reservoirs. According to the literature, no studies have been conducted specifically on the optimal location of emergency water reservoirs for FFE suppression. However, a broader review of the literature reveals that studies have been carried out on optimal location planning for earthquake and post-earthquake conditions, focusing on objectives such as determining the placement of shelters and facilities (Hsu et al., 2022; Toma-Danila et al., 2022). Therefore, since the discussed location planning is directly related to earthquake and post-earthquake conditions, the literature is reviewed by examining studies in these fields.
Multi-Criteria Decision-Making (MCDM) approaches provide a robust framework for analyzing complex problems that involve multiple, and often conflicting, criteria (Sahoo and Goswami, 2023; Goswami et al., 2025). These methods are widely applied in urban planning, risk assessment, and disaster management, where decision-making requires balancing technical, environmental, and social factors (Gaievskyi et al., 2025; Khosravian et al., 2024; Cajot et al., 2017; Halder et al., 2025). Among various MCDM techniques—such as TOPSIS, PROMETHEE, and ELECTRE—the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) is one of the most widely used due to its transparent structure, pairwise comparison mechanism, and ability to incorporate expert judgment (Jalal-ud-Din et al., 2025; Susmaga et al., 2024). The choice of AHP is also supported by previous studies in disaster management and spatial decision-making, where it has demonstrated effectiveness in integrating expert judgment with geospatial data (Morales and de Vries, 2021; Wang et al., 2025). This study employs AHP not only for its methodological advantages but also for its strong compatibility with GIS-based spatial analysis, enabling the integration of expert-based weights with spatial layers to identify optimal locations for emergency water reservoirs (Tanoumand et al., 2025).
Since its introduction by Saaty, AHP has been the subject of extensive theoretical and methodological development (Saaty, 2013). Comprehensive surveys have cataloged its applications across engineering, environmental management, and public policy domains, highlighting both its intuitive pairwise comparison framework and rigorous consistency checks (Ishizaka and Labib, 2011; Vaidya and Kumar, 2006). Subsequent research has extended AHP to handle uncertainty via fuzzy and interval-valued adaptations and to support group decision-making through consensus-building techniques (Escobar and Moreno-jiménez, 2007; Xu and Liao, 2014). Comparative studies further underscore AHP’s robustness relative to alternative MCDM methods, particularly in contexts requiring transparent, expert-driven weighting of criteria (Gebre et al., 2021). These advances reinforce the method’s scientific rigor and justify its application in GIS-based reservoir siting under emergency scenarios.
Research indicates that the use of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) (Environmental Systems Research Institute ESRI, 2020) and MCDM models can significantly enhance the location planning process by integrating risk assessments and stakeholder inputs (Grzeda et al., 2014; Bakhshi Lomer et al., 2023; Hosseini et al., 2022; Sisay et al., 2025). Shao et al. in their study, emphasized that the application of the AHP (Vaidya and Kumar, 2006) for determining the optimal locations of drinking water reservoirs in general emergency situations can significantly expedite access to water resources during critical conditions (Shao et al., 2018). Abdolazimi et al. conducted a study on the optimal placement of emergency drinking water reservoirs using the AHP for post-earthquake scenarios in Shiraz, Iran. In this research, proximity to criteria such as deteriorated urban areas, population density, and adequate accessibility were identified as the most critical factors (Abdolazimi et al., 2022).
The study by Chou et al. on determining the capacity of emergency shelters revealed that evaluating locations based on geographic and demographic criteria can lead to better decision-making in critical situations. They specifically emphasized the importance of proximity to densely populated areas and rapid access to main roads (Chou et al., 2013). Lomer et al. proposed a decision-support system aimed at identifying the most suitable locations for emergency shelters, emphasizing the significance of local context in the decision-making process (Bakhshi Lomer et al., 2023). Additionally, Chen et al. highlighted the necessity of excluding high-risk areas, such as locations near chemical storage facilities, to ensure the safety and effectiveness of emergency shelters (Chen et al., 2018). This approach not only facilitates timely disaster response but also strengthens community resilience (Perrucci and Baroud, 2020; Zhong and Lu, 2018; Sood et al., 2016).
GIS and AHP have also been utilized in identifying optimal locations and prioritizing them for the placement of water reservoirs under normal conditions (Ajitha and Viji, 2023; Bakhtyar Ali Ahmad et al., 2015; Huang et al., 2018; Yi and Tu, 2018; Li et al., 2016). In these studies, factors such as pipelines, elevation, land use, road networks, water supply networks, and slope have been considered as determining criteria for selecting suitable locations for this category of reservoirs. Overall, as highlighted in the literature, one of the prominent approaches in the field of emergency infrastructure location planning is the integration of AHP and GIS. This combination serves as a powerful tool for selection, evaluation, decision-making, and visual representation. The AHP enables a comprehensive evaluation of multiple diverse criteria, leveraging its strength in analyzing complex problems. It allows decision-makers to systematically compare various criteria and select the best option (Saaty, 1987). GIS also facilitates the analysis and integration of criteria within a graphical environment, based on the actual dimensions of geographic information with high precision (Environmental Systems Research Institute ESRI, 2020).
This paper presents a MCDM method that combines AHP and GIS for the optimal location planning of emergency water reservoirs to suppress FFF. In fact, the proposed framework is presented with the aim of addressing existing gaps in studies related to water resource management and identifying their optimal locations for the efficient suppression of FFF. In this method, initial locations for the study area are selected based on post-earthquake damage conditions, accessibility, and economic factors. In the next step, the initially identified locations are scored based on influential criteria and distance classes, which are weighted using the AHP methodology. The weighted criteria and distance classes are converted into spatial layers within ArcGIS. These layers are then combined and analyzed to identify the optimal locations. To demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method, the process has been implemented in the city of Tehran. Ultimately, the study provides a comprehensive map in which the optimal locations for the placement of emergency water reservoirs in the city of Tehran are scored. Hereafter in this paper, the term emergency water reservoirs will be used instead of emergency water reservoirs for suppressing FFF.
2 The proposed framework
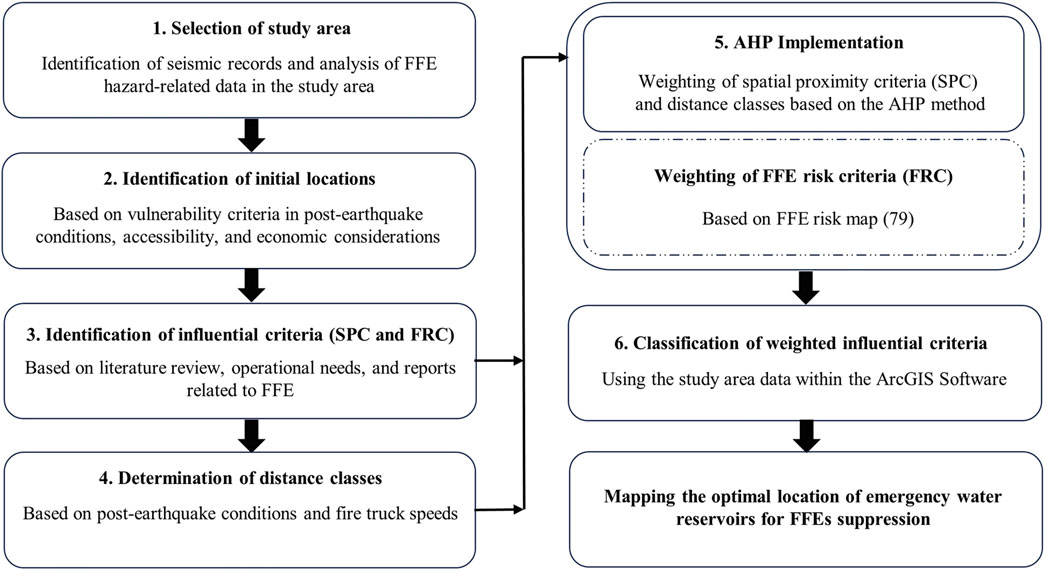
In metropolises facing the risk of FFF, the design and implementation of effective strategies to suppress this phenomenon, as well as enhancing their efficiency through crisis management planning, play a significant role in reducing economic, social, and human losses. In this study, a comprehensive approach is proposed for the optimal location planning of emergency water reservoirs, specifically tailored to the unique conditions of FFF. This framework is illustrated in Figure 1. This framework consists of six main stages and is designed to enhance the accuracy and effectiveness of the location planning process by considering various dimensions of decision-making.
This process begins with selecting the study area, where the geographical and environmental characteristics of the region are examined to determine the significance of suppressing FFE hazards. In the second stage, potential initial locations for the establishment of emergency water reservoirs are identified based on criteria such as vulnerability, accessibility, and economic considerations. Then, through a literature review and analysis of operational needs, influential criteria for location planning are identified to establish a reliable model. In the next stage, appropriate distance classes are determined by considering post-earthquake conditions and the speed of firefighting vehicles to ensure optimal response times. The criteria and distance classes are weighted using the AHP method and then converted into spatial layers within the ArcGIS software. Finally, these layers are combined, and the optimal locations for establishing emergency reservoirs are ranked based on their scores, culminating in the presentation of a comprehensive map.
2.1 Selection of the study area
At this stage, the geographical boundaries of the study area are precisely defined, and the region’s seismic history is analyzed. Additionally, data related to FFE hazards, including seismicity maps, statistics on fire incidents following earthquakes, and infrastructural information, are reviewed. This process aids in identifying the necessity and significance of conducting FFE mitigation studies within the selected area.
2.2 Identification of initial locations
At this stage, a set of potential locations for the establishment of emergency water reservoirs is identified, considering the vulnerability of urban land uses in post-earthquake conditions, accessibility, and economic considerations. This ensures that the selected sites align with both safety priorities and practical implementation criteria. This process specifically focuses on selecting suitable areas within urban communities, particularly in metropolises, due to the varying levels of vulnerability across different locations. It represents a crucial step toward optimizing the location planning of emergency water reservoirs.
The process of selecting initial locations for the placement of emergency water reservoirs is examined, with a focus on the advantages of urban open spaces as primary candidates for these reservoirs. Parks, compared to other land uses, are an optimal choice for the placement of emergency water reservoirs due to their specific characteristics, which will be elaborated upon in the following discussion.
2.2.1 Damage conditions
In the aftermath of severe earthquakes, there is a high likelihood of significant damage to conventional urban structures (Liu et al., 2019; Alizadeh et al., 2021). Consequently, if emergency water reservoirs are located inside or near such structures, structural failures could lead to damage or reduced efficiency of the reservoirs. Therefore, these reservoirs should be situated in open spaces.
2.2.2 Accessibility conditions
Following severe earthquakes, there is a high probability of route blockages caused by damage to buildings and transportation infrastructure (Yu and Gardoni, 2022; Lo et al., 2020). Therefore, emergency water reservoirs should be located in areas with access to the main urban routes, such as highways, to remain outside the zones obstructed by structural collapses during crises. Parks are often situated adjacent to major urban roads.
2.2.3 Economic conditions
Selecting parks as initial locations for the placement of emergency water reservoirs offers significant advantages in terms of economic optimization. These areas are publicly owned lands, allowing their use without the need for land acquisition costs. Establishing reservoirs in parks reduces maintenance and management expenses, as these spaces are under municipal jurisdiction and provide better accessibility to reservoir details for decision-making authorities.
2.3 Identification of influential criteria
At this stage, the most critical influential criteria for the placement of emergency water reservoirs are determined, based on previous studies, operational needs, and reports related to FFE incidents (Tanomand and Mashayekhi, 2025; Rohr et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2021; Sarreshtehdari and Elhami Khorasani, 2021; Sezer et al., 2023; Garg and Garg, 2024). The precise and appropriate selection of these criteria plays a pivotal role in determining the location of emergency water reservoirs and is vital for developing a reliable and efficient decision-making model.
The occurrence of an earthquake, depending on factors such as distance and environmental conditions, results in varying levels of peak ground acceleration (PGA) across different parts of a city. The impact of FFE can differ from the level of PGA across various urban areas, depending on the characteristics of urban land uses (Tanomand and Mashayekhi, 2025). This means that factors related to the type of land use and the configuration of urban spaces can significantly affect the likelihood and intensity of FFF, even in areas where the PGA is below the critical threshold (Tanomand and Mashayekhi, 2025).
In this context, all factors affecting FFE and influential land-use types have been identified and analyzed as key criteria for optimizing the location of emergency water reservoirs. The following sections present the evaluation of each criterion along with the rationale for its selection.
2.3.1 FFE risk criteria (FRC)
In previous research (Tanomand and Mashayekhi, 2025), investigators developed a comprehensive framework for assessing urban FFE risk by considering all influential variables, defining weighted base factors, and incorporating stochastic components. This framework enables the identification of urban areas with the highest FFE probability. The resulting risk map provides precise spatial visualization of FFE risk distribution across urban zones (Tanomand and Mashayekhi, 2025), serving as an effective decision-support tool for optimizing emergency water reservoir locations. Figure 2 illustrates the interaction mechanisms between Influencing factors and weighted basic parameters (Tanomand and Mashayekhi, 2025). The regional risk level is calculated through a weighted combination of these basic factors.
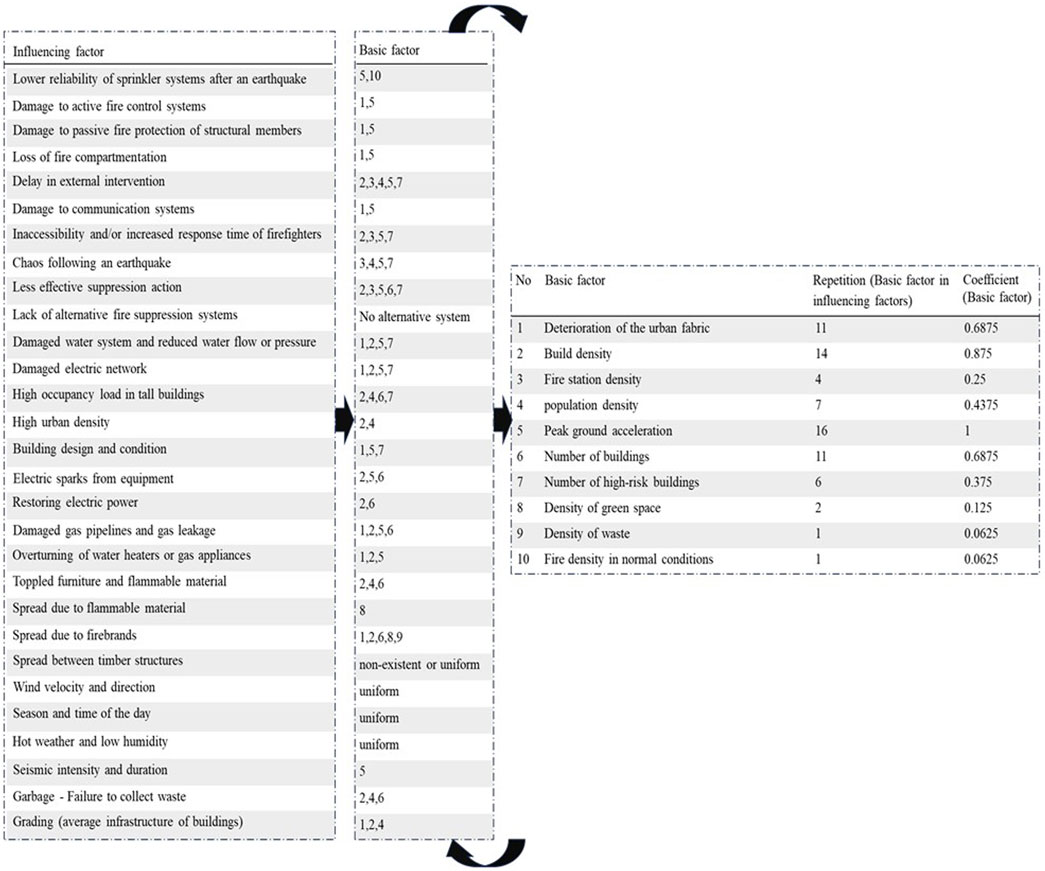
Figure 2. Influencing factors, basic factors, and their coefficients (Tanomand and Mashayekhi, 2025).
The location of emergency resources is significantly influenced by FFE risk and depends on multiple influencing factors, including PGA, building density and characteristics, population density, and fire station distribution density. In low-risk areas, standard-capacity fire stations sufficiently meet existing needs without requiring additional emergency resources. In contrast, high-risk areas face increasing demand for emergency water supply due to critical risk factors and the complex structure of influencing factors, along with the potential for rapid FFE spread and limitations in emergency service delivery, necessitating an optimized strategic approach to emergency reservoir location. Therefore, integrating FFE risk coefficients into the resource location process is not only a technical necessity but also a crucial measure for enhancing crisis management system efficiency and reducing FFE-induced damages.
By incorporating FFE risk as a weighted criteria in the location selection process, urban areas with higher risk levels will receive higher priority in emergency water resource location. Accordingly, each initial location j is assigned a specific weight based on its geographical position within urban zones, proportional to the FFE risk level of that zone. This weight, which serves as a key factor in the location selection process, is calculated using Equation 1.
where
2.3.2 Spatial proximity criteria (SPC)
This study identifies and analyzes five influential land-use types as spatial proximity criteria for optimal emergency water reservoir location selection. The rationale for each criterion is examined below.
2.3.2.1 Major routes (highways, expressways, main streets)
Major routes in cities play a critical role in the transport of emergency response teams and equipment, particularly in emergency situations (Rohr et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2021). One of the most critical factors during an FFE crisis, considering issues such as multiple blockages in the transportation network, traffic, and crowd congestion, is the rapid access of fire stations to emergency water reservoirs. This significantly helps reduce response times and improve the efficiency of suppression operations. Achieving rapid access is directly dependent on the proximity of reservoirs to major routes, as these routes typically have larger widths and are less likely to experience complete blockages during a crisis.
2.3.2.2 Fire stations
The primary mission of fire stations is to control and extinguish fires as quickly as possible. In post-earthquake conditions, fire stations will have an urgent need for water resources to swiftly respond to potential large-scale fires (Sarreshtehdari and Elhami Khorasani, 2021). Emergency water reservoirs should be placed at appropriate distances from fire stations to ensure quick and effective access to water. Proximity to fire stations reduces the response time of firefighting teams and significantly enhances the efficiency of their operations.
2.3.2.3 Commercial land uses
Commercial areas such as markets and shopping centers are significant due to the value, variety, and density of materials and resources they encompass. Additionally, in the event of FFE, the spread rate in commercial land uses is significantly high. Past FFE incidents in commercial centers have also resulted in substantial damages. In the 2024 Wajima earthquake, a FFE broke out in a historic market. This fire lasted approximately 24 h and caused damages amounting to one billion dollars (The Japan Times, 2024).
2.3.2.4 Industrial and workshop land uses
Industrial and workshop areas often contain large facilities and flammable chemicals, which make them highly susceptible to fire hazards. In post-earthquake conditions, these areas are prone to large-scale and widespread fires. Such land uses are significant due to their potential for economic losses and, in some cases, environmental impacts. In the event of FFE, the rate of spread, burning duration, and resulting damages in these areas are extremely high. Therefore, rapid access to water resources in such zones is crucial to prevent environmental and economic catastrophes. For example, during the 2023 Iskenderun Port earthquake, an FFE occurred at the port. This fire lasted for approximately 3 days and caused damages estimated at around 700 million dollars (Sezer et al., 2023).
2.3.2.5 Therapeutic land uses
Therapeutic areas hold significant importance due to their obligation to provide uninterrupted services during crises. In the event of an FFE crisis within these types of land uses, a swift response is crucial. On the other hand, medical facilities, especially hospitals, are structurally designed with special considerations to comply with all suppression precautions (Garg and Garg, 2024), making the likelihood of large-scale fires in these areas relatively low. This factor has been accounted for in the weighting of the criteria.
In this study, residential land uses have not been considered as an influential criterion, despite their role in causing various FFF in past incidents.
1. Residential land uses are uniformly distributed throughout the city and have been considered as a constant factor across the urban area.
2. The distribution of fire stations, commercial land uses, and therapeutic land uses across a city is based on the ratio of population and building density in urban areas. Consequently, the criterion of residential land use has been indirectly considered in this context.
3. In the most recent FFE incidents, the majority of ignitions have occurred in non-residential land uses, specifically in industrial and commercial areas (The Japan Times, 2024; Sezer et al., 2023).
2.3.3 Integration of criteria
In conclusion, a two-component framework has been established for optimal emergency water reservoir location, in which the FFE risk criteria (
2.4 Determination of distance classes
At this stage, distance classifications are determined by considering post-earthquake conditions and the average speed of firefighting vehicles. The primary objective of optimally location emergency water reservoirs is to minimize the response time for firefighting vehicles to access these reservoirs. This step plays a critical role in ensuring appropriate access times to emergency water reservoirs and constitutes one of the key pillars of the proposed framework.
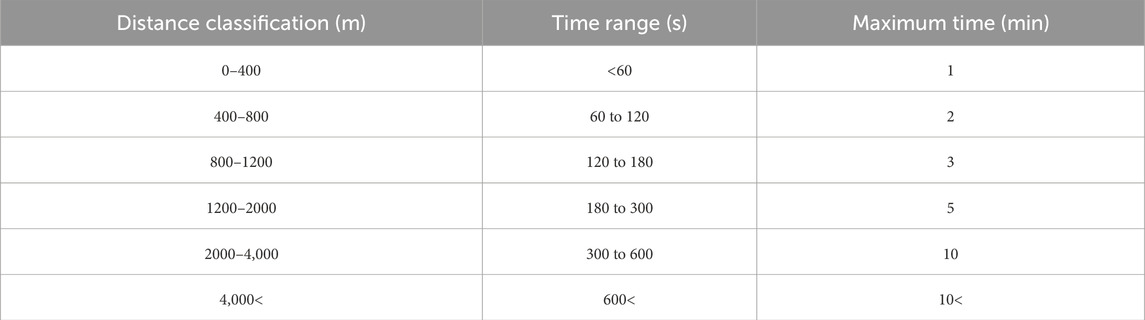
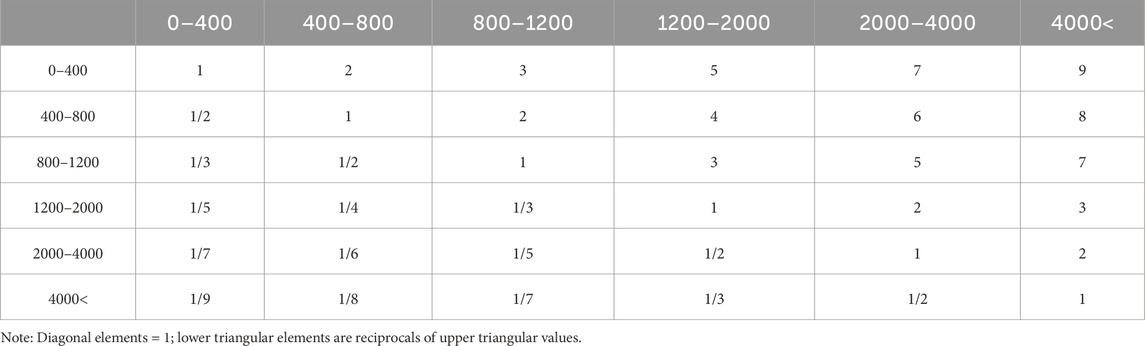
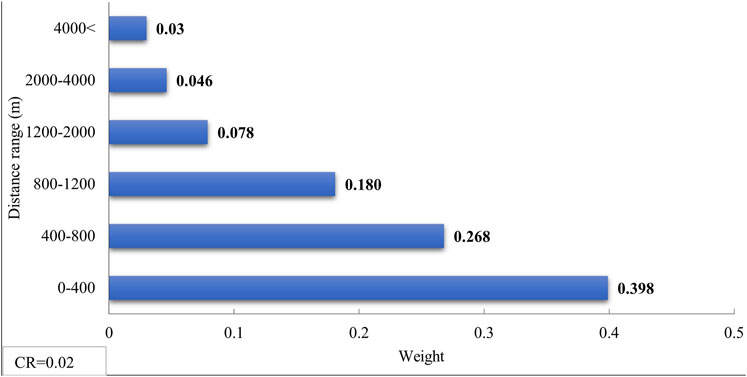
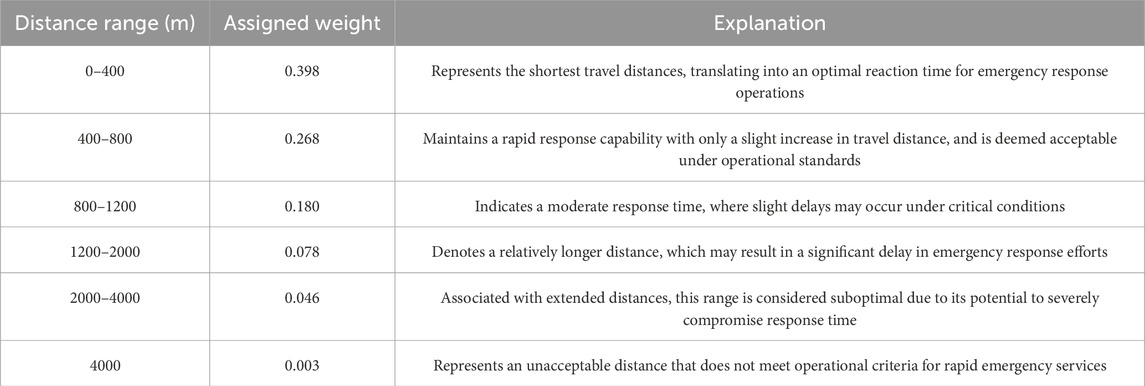
The average speed of firefighting vehicles under non-earthquake conditions is approximately 48 km per hour (13.4 m per second) (FEM Agency, 2022; FEMA, 2014). Considering post-earthquake conditions, factors such as damage to road networks, debris on streets caused by collapsed utility poles or damaged structures, traffic, and similar issues can reduce the speed of firefighting vehicles by up to 50% (FEMA, 2014). Therefore, for post-earthquake conditions, a speed range of 24–48 km per hour is considered. Accordingly, distance classifications are defined based on the speed of firefighting vehicles as presented in Table 1.
The reason for selecting distance classifications with short time intervals is related to the specific conditions that arise following an earthquake and the resulting fires. These conditions necessitate precise and rapid responses to minimize the impact of such events. Under such conditions, firefighting vehicles are initially dispatched directly to the incident site to commence fire suppression operations. If the suppression operations are not successfully completed and the water in the vehicle’s tank is exhausted, the vehicles will inevitably need to return to emergency water reservoirs to refill their tanks. This approach results in the creation of a back-and-forth route between the FFE site and the emergency water reservoirs for firefighting vehicles, which directly affects the response time and the efficiency of the suppression operations. It is worth mentioning that in cases where an FFE spreads on a large scale, this back-and-forth route may need to be repeated multiple times. This repetition can further impact response time and the overall efficiency of the suppression operations.
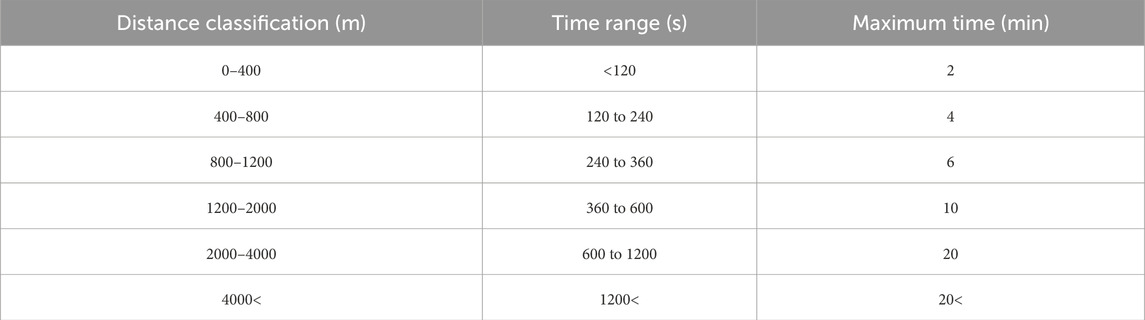
Therefore, considering the creation of a back-and-forth route between the FFE site and the emergency water reservoirs for firefighting vehicles, the time values presented in Table 1 are doubled. The adjusted time values are shown in Table 2 to more accurately reflect the realities of post-earthquake conditions and their impact on suppression operations.
2.5 AHP implementation
This section details the theoretical foundations and computational procedures of the AHP for spatial decision-making in emergency water reservoir location. Developed by Saaty, AHP is a MCDM technique that hierarchically structures complex problems, transforms qualitative judgments into quantitative weights through pairwise comparisons, and rigorously verifies judgment consistency (Saaty, 1987).
In this study, the AHP was used to evaluate and rank spatial criteria for location emergency water reservoirs. Expert opinions were organized into a structured three-tier hierarchy—goal, criteria, and alternatives—and translated into measurable priority weights through pairwise comparisons and consistency checks. These weights were then integrated into GIS to generate suitability maps that identify the most optimal reservoir sites.
2.5.1 Hierarchy construction
The hierarchy included:
(1) Objective: Optimal reservoir site identification,
(2) Evaluation criteria: FFE risk potential, Proximity to fire stations, major routes, commercial land uses, Industrial and workshop land uses, therapeutic land uses,
(3) Decision alternatives: Distance-based zoning classifications.
2.5.2 Judgment integration
Specialized opinions from individual domain experts may result in incomplete or potentially inaccurate evaluations, primarily due to the complexity and multidimensional nature of the decision-making system. To address this, the study relied exclusively on the integrated technical judgment of the authors, whose collective expertise spans structural engineering, urban emergency management, and firefighting operations under post-earthquake FFE conditions.
2.5.3 Pairwise comparison matrices
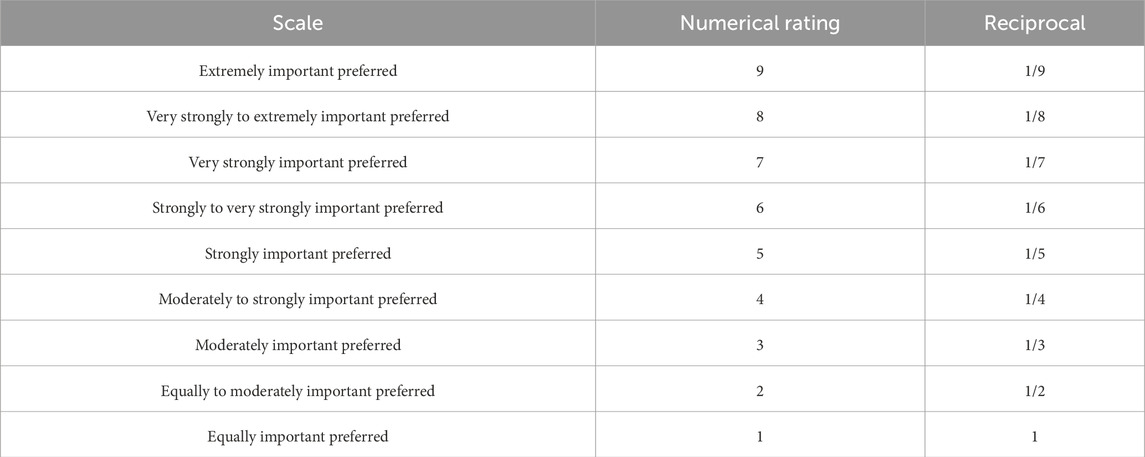
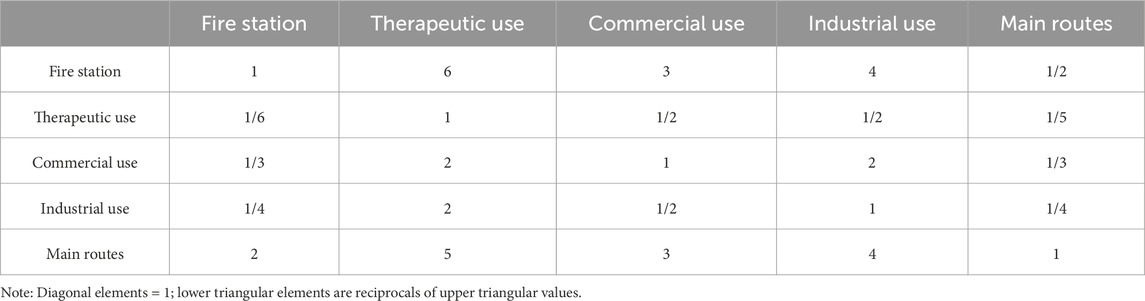
Subject-matter experts (i.e., the authors) participated using structured questionnaires based on Saaty’s 1–9 scale, enabling the quantification of relative importance among evaluation criteria as shown in Table 3 (Çoban, 2023). This collaborative approach ensured that the weighting process reflected a comprehensive and interdisciplinary perspective.
Pairwise comparisons based on Saaty’s 1–9 ratio scale systematically quantify qualitative judgments, thereby enhancing decision robustness (Çoban, 2023). Table 4, 5 present the pairwise comparison matrices for impact criteria and distance classifications (Saaty, 1987). The pairwise comparison matrices follow Saaty’s AHP methodology where all diagonal elements equal 1 (self-comparisons) and lower triangular elements are reciprocals of their corresponding upper triangular values (
2.5.4 Pairwise comparison matrices aggregation
Pairwise comparison judgments from each expert
2.5.5 Priority vector extraction
The final priority vector (
where
2.5.6 Consistency verification and criteria weighting
To ensure judgment consistency, the consistency index (
where
2.6 Classification of influential criteria (FRC and SPC)
In the final stage, using analytical tools in ArcGIS software (Environmental Systems Research Institute ESRI, 2020), weighted SPCs are classified as weighted layers and integrated with the FFE risk criteria (FRCs). This process calculates the optimality score for each candidate location by applying weights determined through the AHP method and using weighted overlay analysis (Equation 2). The final results are presented as maps identifying optimal locations (highest scores) for emergency water reservoir placement.
The system outputs include prioritized maps and informational layers that can be directly utilized in urban planning. The proposed approach, which simultaneously considers safety aspects (FFE risk) and rapid accessibility (proximity criteria), provides a comprehensive solution for reducing damages caused by FFF.
3 Case study
3.1 Study area: Tehran City
FFE have struck numerous seismically active urban centers worldwide—most notably the 1906 San Francisco quake (Mw 7.9), the 1995 Kobe event in Japan (Mw 6.9), and Turkey’s 1999 Izmit disaster (Mw 7.6)—where ruptured gas mains, downed power lines, and structural collapses ignited widespread fires (Elhami Khorasani and Garlock, 2017; Grossi et al., 2011; Mizuno, 1978). These cases reveal how high-magnitude shaking, dense built environments, and intertwined lifeline systems create fertile conditions for post-quake conflagrations. Iran, lying astride the Alpine–Himalayan belt, experiences similarly frequent Mw ≥ 7 earthquakes and hosts major metropolitan areas dependent on aging gas and electrical networks (Environmental Systems Research Institute ESRI, 2020; Şengör et al., 1988). Although documented FFE incidents in Iranian cities remain scarce, the shared tectonic drivers and urban vulnerabilities underscore Iran’s significant potential for cascading fire hazards following a major earthquake (Elhami Khorasani and Garlock, 2017; Mizuno, 1978).
The study area of this article is the metropolis of Tehran, the capital of Iran. This city is located on the southern slopes of the Alborz Mountain range and is surrounded by several active faults (Environmental Systems Research Institute ESRI, 2020; Şengör et al., 1988). Tehran is at risk of severe earthquakes with magnitudes of up to Mw7.5 (Kamranzad et al., 2020; Hashemi et al., 2013). Historical data indicates that the city has experienced significant earthquakes in the past, leading to considerable damage and loss of life (Enferadi et al., 2021).
Although historical earthquakes in Tehran have not resulted in documented FFE incidents, the magnitude and characteristics of several past events suggest a significant potential for such cascading hazards under present urban conditions. Table 7 presents representative historical earthquakes from Tehran and international case studies where FFE did occur, allowing a comparative understanding based on seismic magnitude and contextual vulnerability (Elhami Khorasani and Garlock, 2017; Grossi et al., 2011; Mizuno, 1978). Notable examples from Tehran include the 1665 Damavand earthquake (Ms 6.5) and the 1830 Damavand–Shemiranat event (estimated Ms 7.1), both of which caused considerable damage and exhibit magnitudes comparable to FFE-triggering earthquakes observed in other parts of the world (Kamranzad et al., 2020; Hashemi et al., 2013).
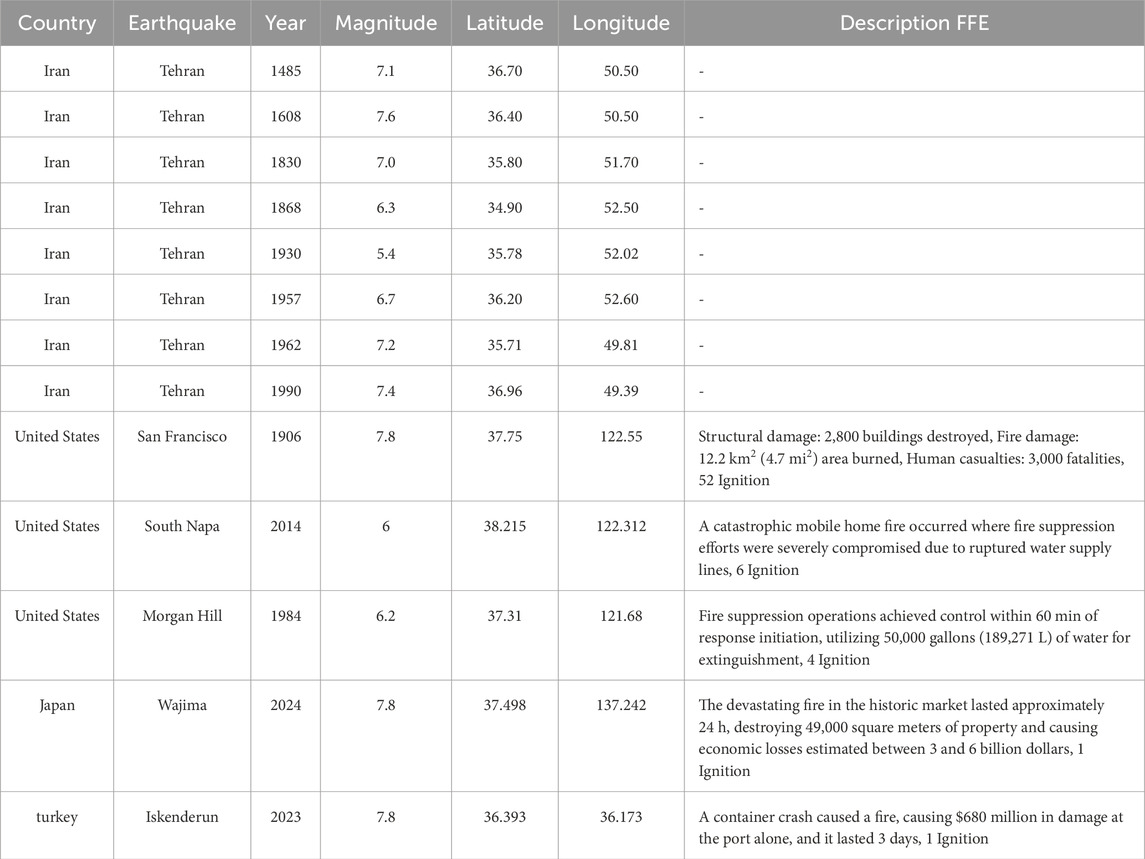
Table 7. Notable historical earthquakes in Tehran and selected international case studies where FFE were documented (Elhami Khorasani and Garlock, 2017; Grossi et al., 2011; Mizuno, 1978).
Figure 5 illustrates the geographical location of Tehran’s districts and regions. The uncoordinated and unbalanced development across different districts of the city has caused the factors influencing FFE to have varying impacts in each district (Tanomand and Mashayekhi, 2025). In addition, the presence of extensive infrastructure, including high-pressure gas networks and high-voltage power lines, has made emergency management more challenging and increased the risk of FFE occurrences.
However, studies related to crisis management indicate that adequate measures to suppress FFE caused by severe earthquakes have not been fully implemented in this city (Hatami and Amani, 2023; Ibrion et al., 2015; F. N., 2000; Heidari et al., 2020). Therefore, considering all these factors, selecting optimal locations for emergency water reservoirs to suppress FFF in Tehran is of great importance. Such an initiative can significantly contribute to reducing the damages caused by FFE.
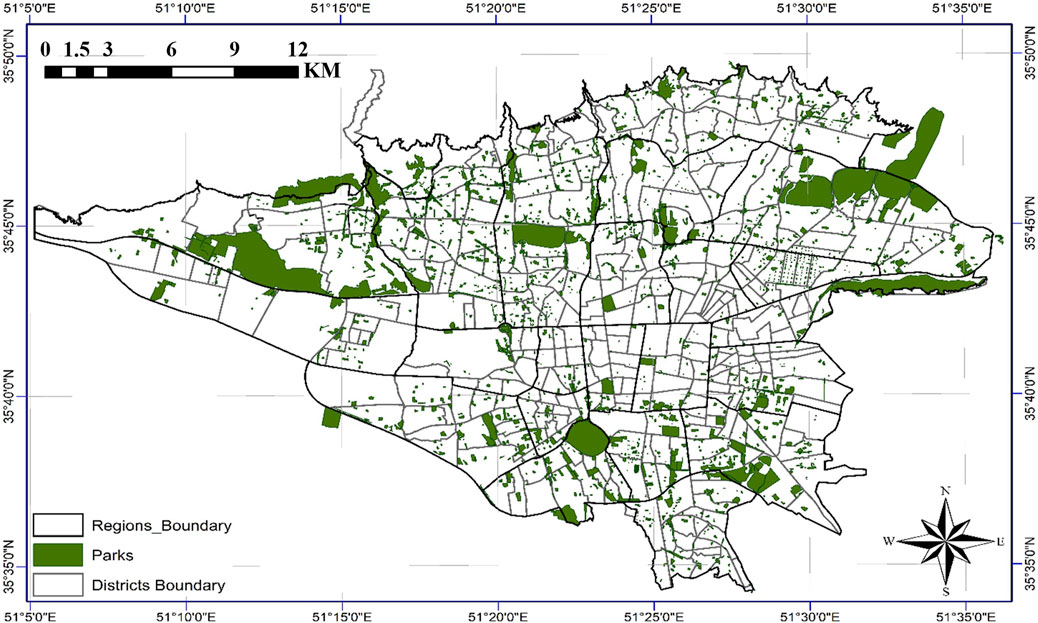
3.2 Initial locations
The city of Tehran has 3,047 parks, which have been considered as the initial locations for the placement of emergency water reservoirs (Figure 6). Tehran, in most of its regions, is influenced by active faults and high urban traffic density. In the event of an earthquake, there is a significant likelihood of widespread blockages in access routes, especially secondary roads, due to debris from collapsed buildings and severe traffic congestion. Therefore, parks, as open spaces with proper accessibility and the potential for developing essential infrastructure, are particularly suitable options for this purpose, in line with the criteria outlined in Section 2.2.
3.3 Classification of FRC
The prior study (Tanomand and Mashayekhi, 2025) computationally derived FFE risk values for Tehran’s districts, presenting them as a classified risk map (Figure 7). Given the alignment of seismic scenarios between (Tanomand and Mashayekhi, 2025) and the current research, these pre-calculated risk values were directly adopted without reanalysis. The map visualizes neighborhood-scale FFE risk levels through a color-gradient classification scheme (low to high risk), maintaining methodological consistency with the original study’s parameters (Tanomand and Mashayekhi, 2025).
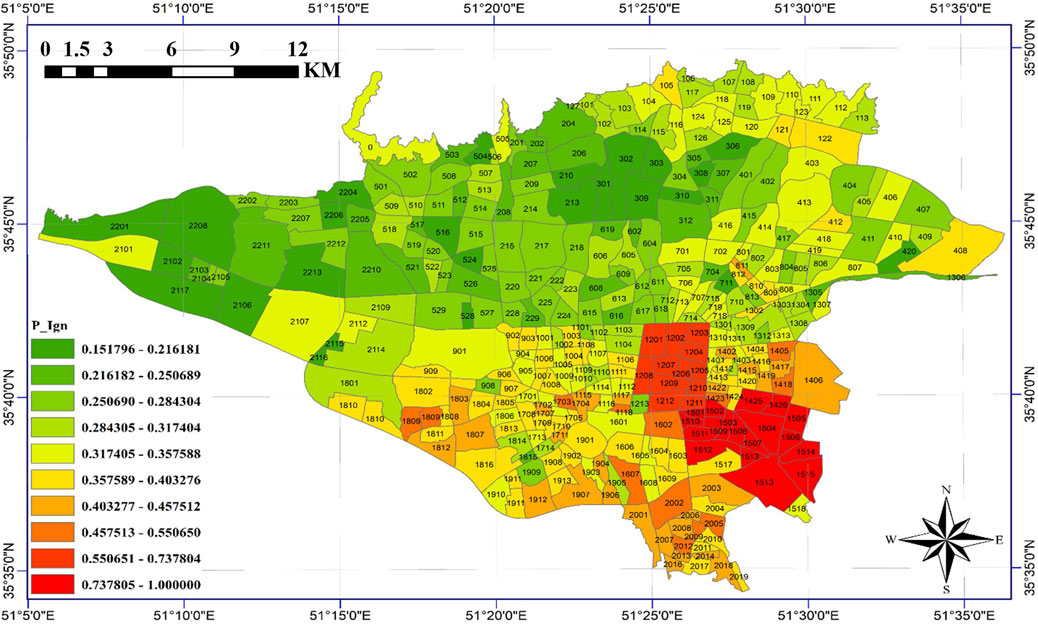
Figure 7. Classification of FRC in Tehran (Tanomand and Mashayekhi, 2025).
3.4 Classification of SPC
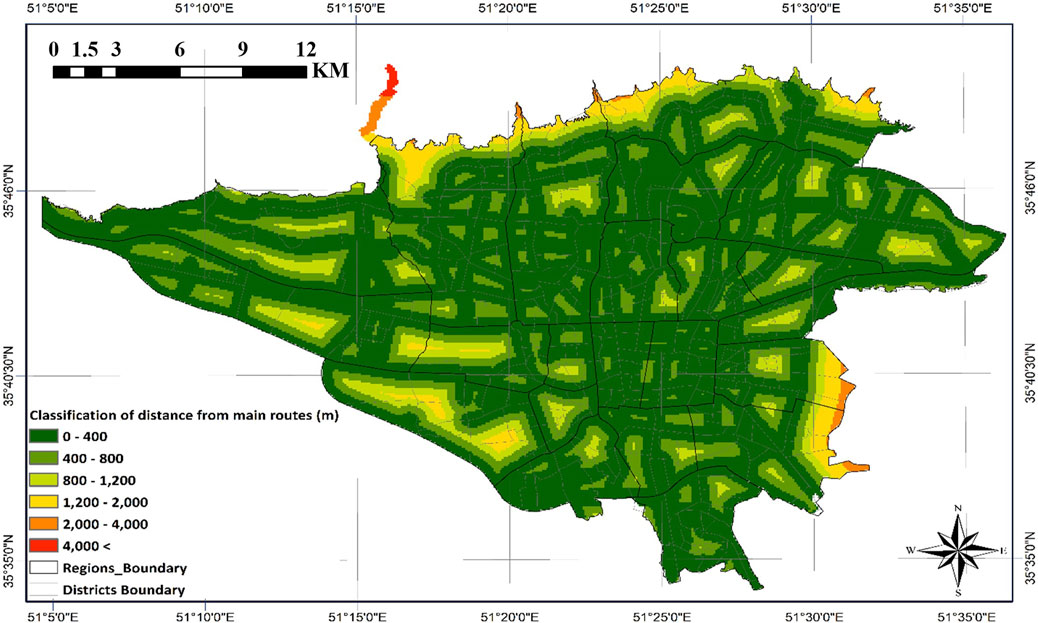
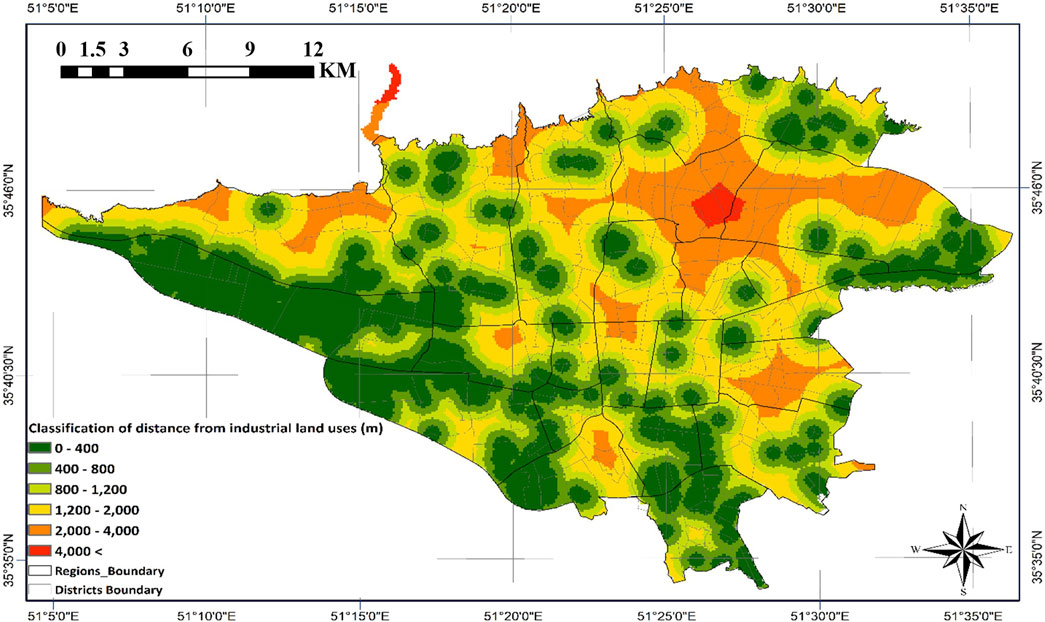
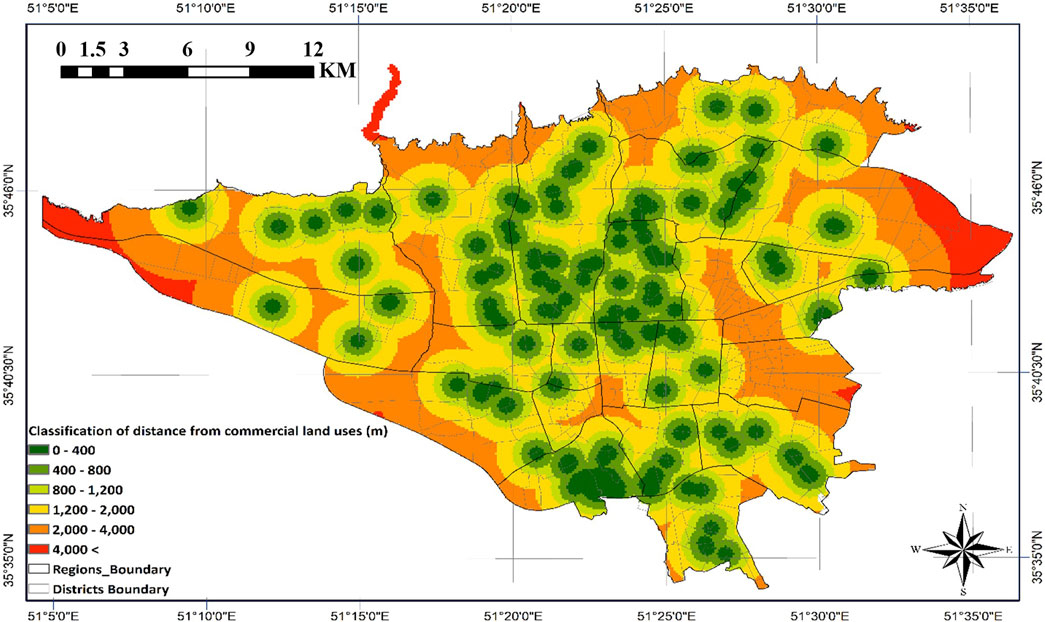
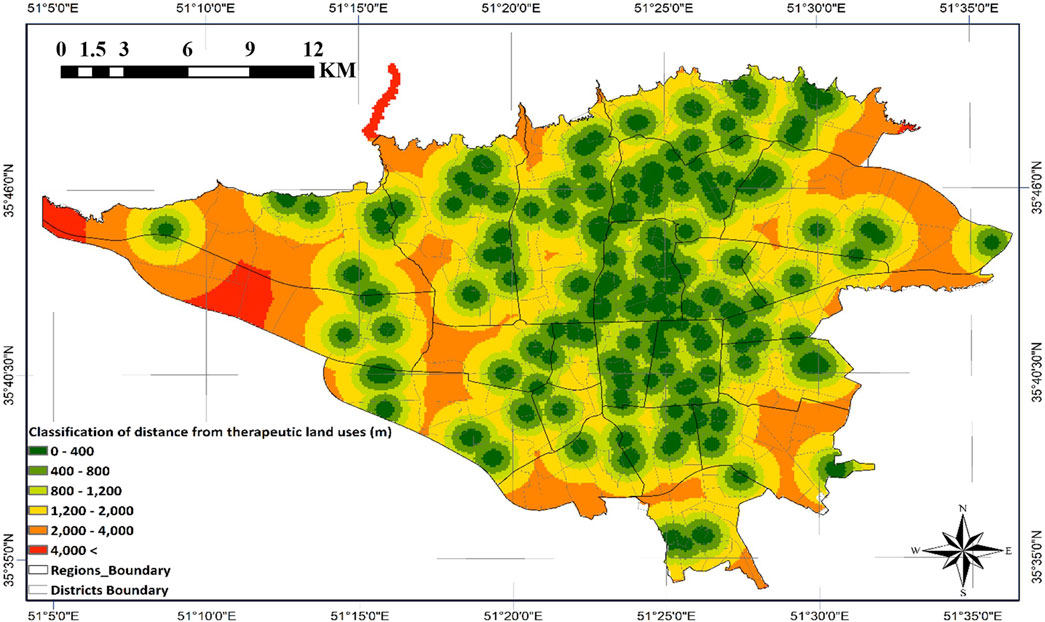
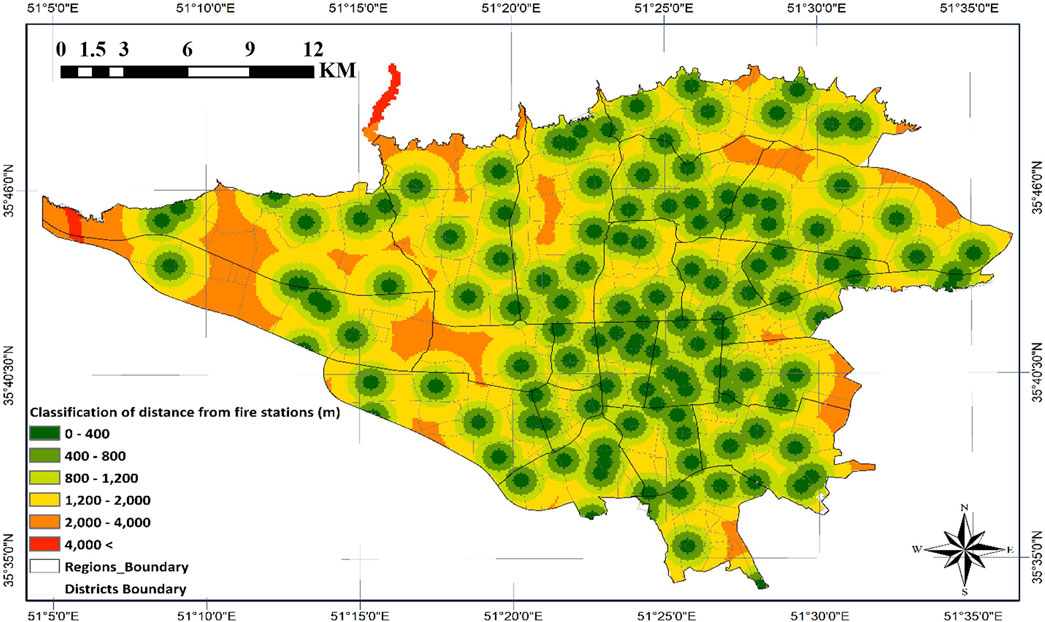
This phase employed ArcGIS software and weighted distance classifications to establish meaningful relationships between influential land uses and potential emergency water reservoir locations in Tehran. As detailed in Section 2, the spatial proximity Criteria maps for reservoir siting were developed and analyzed using weighted distance classifications (Figures 8–12). The classification process was designed such that each criterion was assigned to specific distance thresholds based on its relative importance and operational impact during emergency scenarios.
Figure 8 demonstrates that central and northern urban areas benefit from superior accessibility due to their dense arterial road networks. Areas within 400-m proximity are predominantly clustered along major transportation corridors, indicating their exceptional suitability for emergency reservoir placement. Conversely, southern districts and select central zones experience access constraints due to aging urban fabric and narrow thoroughfares.
Figure 9 reveals elevated fire risk concentrations in southern and southwestern sectors, attributable to industrial land use density. Proximity zones near these industrial areas demand priority consideration given their combustible material storage, with findings strongly supporting high-capacity reservoir deployment in these vulnerable locations.
Figure 10 illustrates the pronounced concentration of commercial activities in central urban cores and select northern nodes. Immediate vicinities surrounding these commercial hubs demonstrate heightened sensitivity due to intensive human activity and economic operations, necessitating strategic reservoir distribution within commercial centers.
Figure 11 indicates relatively equitable spatial distribution of therapeutic land uses citywide. Nevertheless, central and northern zones require focused reservoir placement strategies due to their concentration of specialized medical infrastructure.
Figure 12 highlights significant spatial disparities in fire station coverage. While central areas maintain adequate service provision, peripheral regions exhibit critical access deficiencies, emphasizing the operational imperative for minimal-distance reservoir placement relative to fire service locations.
4 Results
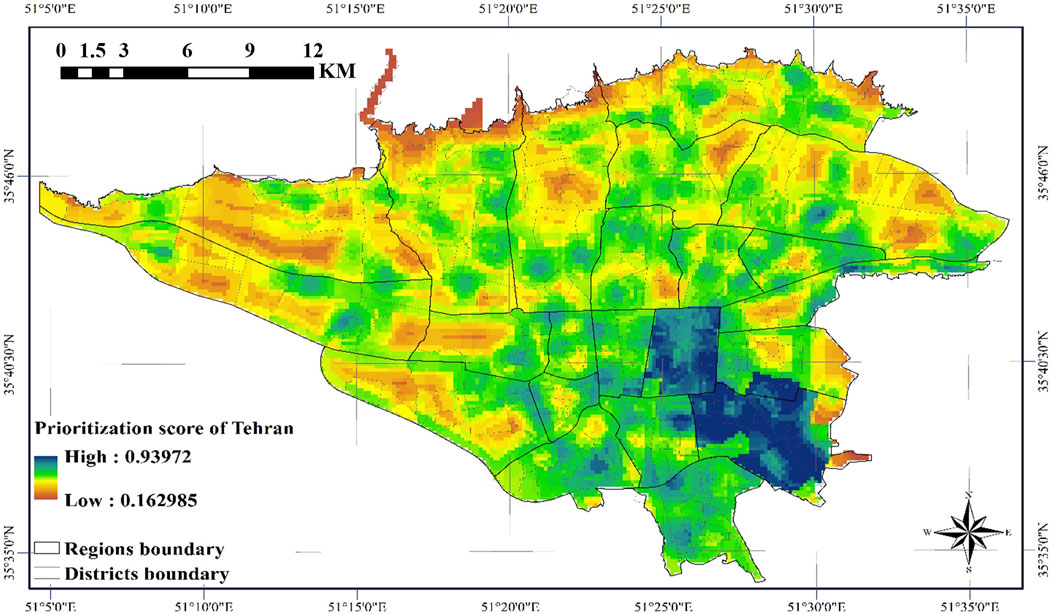
This study presents a novel methodology for identifying optimal locations of emergency water reservoirs to suppress FFE incidents, with specific application to Tehran. The analysis results, presented in Figure 13, demonstrate a comprehensive evaluation framework that integrates (Sadeghi-Movahhed et al., 2025): SPCs classified through AHP-weighted distance classification, and (Sadeghi-Movahhed et al., 2024) FRCs derived from all critical variables influencing FFE occurrence and spread potential. The combined application of these weighted criteria enables precise identification of optimal reservoir locations that effectively balance accessibility for fire suppression teams with high-risk zone coverage. Additionally, in Figure 14, the entire city of Tehran is presented based on the weighting method applied in this study. This can serve as a guideline for other open spaces in case constructing reservoirs in parks encounters limitations.
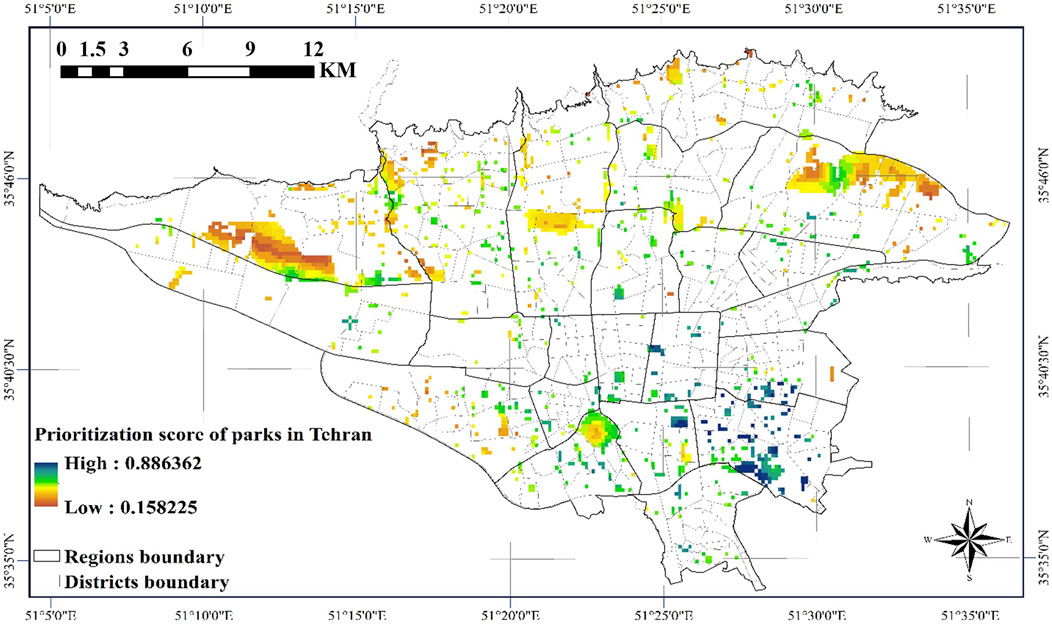
Figure 13. Optimal location map of emergency water reservoirs for FFF suppression in the parks of Tehran city.
Both FRC and SPC play equally vital yet distinct roles in optimal reservoir siting: FRC stratifies urban areas based on FFE occurrence and spread risks, while SPC classifies zones according to land uses affecting both FFE probability and emergency response access. Given their complementary but equally critical nature in emergency planning, each criterion group was assigned an equal 0.5 weighting coefficient in the final suitability assessment, ensuring balanced consideration of both risk mitigation and operational efficiency in the siting process.
The optimal location of emergency water reservoirs has been determined considering post-earthquake conditions. In this regard, parks have been selected as suitable options for the placement of these reservoirs among other locations, as these spaces provide greater reliability in terms of vulnerability, accessibility, and economic considerations. In particular, the absence of heavy structures in these spaces significantly reduces the impact of intense ground shaking and helps maintain the stability of systems associated with emergency water supply. Additionally, in critical post-earthquake conditions, selecting parks as key points enables the rapid activation of support systems and helps mitigate earthquake-induced damages.
The critical importance of optimal location for emergency water reservoirs is particularly emphasized in densely populated urban areas with high vulnerability, where risks of widespread fires, severe traffic congestion, and route blockages are elevated. Accordingly, the site selection process has been conducted by incorporating an FFE risk map based on established FRCs. Optimal siting in such areas can significantly reduce response time, improve accessibility, minimize vulnerability risks for emergency water reservoirs, and ultimately enhance fire suppression performance while reducing both human casualties and economic losses.
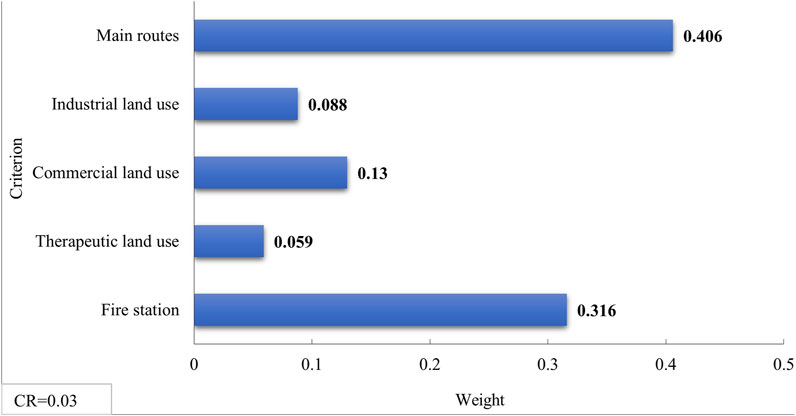
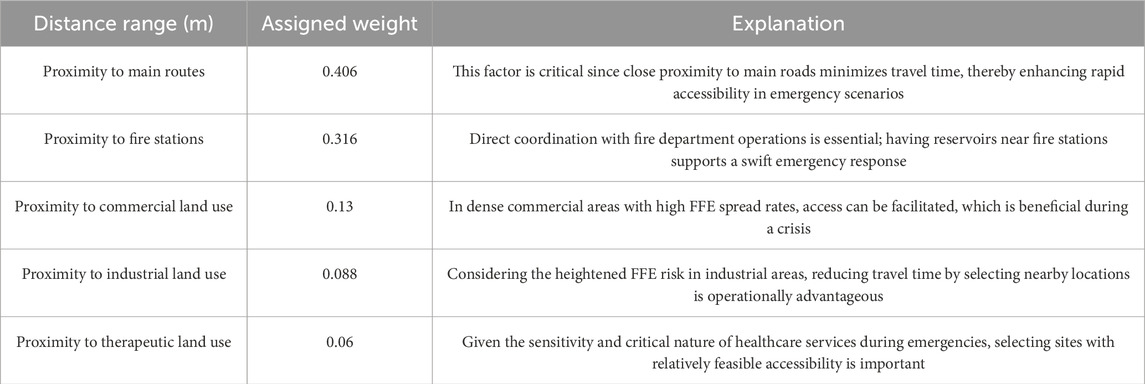
Subsequently, the process of identifying influential criteria for optimal site selection was conducted. Specifically, all factors affecting FFE were considered as FFE risk criteria. Additionally, influential land uses - including proximity to major roads, fire stations, commercial zones, industrial/workshop areas, and therapeutic facilities - were identified and weighted as spatial proximity criteria based on historical FFE experiences and operational requirements. The detailed description and weighting of each criterion are comprehensively presented in Table 8.
The results of the spatial proximity criteria weighting revealed that proximity to main routes and fire stations has the greatest impact on scoring the placement of emergency water reservoirs. These findings highlight the importance of quick access to emergency water reservoirs and proper spatial coordination between reservoirs and fire stations in post-earthquake crisis conditions. In such scenarios, reducing distances can accelerate firefighting responses and improve access to emergency water resources, which is crucial for mitigating damages and losses caused by FFF.
For better analysis, the distance classifications have been divided into six groups based on access time ranges, average speed, and the round-trip paths of firefighting vehicles between FFE locations and emergency water reservoirs (Table 9). The distance classifications were weighted based on the expert opinions of the authors to achieve more accurate analyses during the final decision-making process.
Results indicated that Location reservoirs at distances of less than 4,000 m simultaneously from rom major routes, fire stations, and commercial, industrial, and therapeutic centers ensures that fire engines can access the reservoirs in under 10 min even under worst-case conditions. Moreover, placing the tanks at optimally chosen Locations (within 800 m) reduces the access time to below 2 min Therefore, distances of less than 800 m hold particular significance. These shorter distances are especially important due to the reduced travel times for fire trucks on round trips to emergency water reservoirs. In post-earthquake conditions, where firefighting teams need to frequently refill their water tanks and make repeated trips, shorter distances can play a crucial role in minimizing response times and ensuring the optimal use of emergency water reservoirs.
In the proposed framework process, each park is weighted locally and independently, meaning the weighting of each park is determined based on its proximity to the surrounding influential criteria. This approach enables regional analyses in various urban areas, allowing the optimal locations for the placement of emergency water reservoirs to be identified independently within each urban zone at a local scale.
5 Conclusion
Multiple fires that may occur following an earthquake pose a significant threat to earthquake-prone communities. To address this, various models have been developed for simulating FFF and estimating the amount of water required for their suppression. In this context, the location of emergency water resources for suppression is considered one of the key factors in crisis management strategies. Optimal location of emergency water reservoirs to reduce response time and ensure better access for firefighting vehicles can significantly limit fire spread and consequently play a crucial role in reducing financial and human losses. In this study, a framework for the optimal location of emergency water reservoirs for FFE suppression has been proposed. This method focuses on reducing response times, improving accessibility, and minimizing the vulnerability risks of emergency water reservoirs in post-earthquake conditions. Initially, by considering potential post-earthquake damages, accessibility, and economic considerations, the most suitable areas are selected as primary locations for reservoir placement. Subsequently, based on weighted influential criteria and distance classifications using the AHP method and ArcGIS, a map of optimal locations for emergency water reservoir location is provided. Using the proposed framework, the optimal location of emergency water reservoirs for the city of Tehran was conducted. Finally, the following results can also be inferred from the observations and evaluations:
• Parks were identified as the most suitable urban land use for the initial placement of emergency water reservoirs, considering post-earthquake damage conditions, accessibility, and economic considerations.
• The influential criteria were identified as two equally weighted groups (FRCs and SPCs), encompassing all urban factors and land uses affecting FFE occurrence, risk, and spread, as well as operational requirements and rapid access needs.
• Considering the selection of parks, which are recognized as the most significant open urban spaces, the optimal location process was conducted without taking into account the impacts caused by earthquake intensity.
• The most influential spatial proximity criteria for emergency water reservoir siting were identified, in order of priority, as: as proximity to main routes, fire stations, commercial land uses, industrial and workshop land uses, and therapeutic land uses.
• Time ranges based on the average speed of firefighting vehicles, considering post-earthquake conditions, were identified as the sole criterion for determining distance classifications.
The proposed approach in this article can be effective for all urban communities, including metropolises, that require the establishment of water resources to address the FFE phenomenon. In this study, the initial candidates considered for the placement of emergency water reservoirs are based on expert opinions tailored to the conditions of Tehran. Therefore, for application in other communities with different conditions, further research in this area is required for improvement and greater advancement.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
AT: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. MM: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. MS: Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. AM: Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdolazimi, H., Shahinifar, H., Noroozi, H., and Emtehani, M. (2022). Site selection of emergency drinking water supply tanks in post-earthquake conditions, a case study of shiraz. J. Nat. Environ. Hazards. Univ. Sistan Baluchestan 11 (32), 129–148. doi:10.22111/jneh.2022.37402.1762
Ajitha, T. T., and Viji, R. (2023). “Site suitability analysis of water tank in athivilai village of India using an analytical hierarchy process and a geographical information system.”Water Supply. London, United Kingdom: IWA Publishing, 23 9. 3805–3818. doi:10.2166/ws.2023.222
Alavi, S. H., Mashayekhi, M., and Zolfaghari, M. (2024). Incorporating seismic risk assessment into the determination of the optimal route for gas pipelines. Sustain Resilient Infrastruct. Taylor and Francis 9 (4), 328–348. doi:10.1080/23789689.2024.2319503
Alizadeh, M., Zabihi, H., Rezaie, F., Asadzadeh, A., Wolf, I. D., Langat, P. K., et al. (2021). Earthquake vulnerability assessment for urban areas using an ANN and hybrid SWOT-QSPM model. Remote Sens. (Basel). MDPI 13 (22), 4519. doi:10.3390/rs13224519
Ansari, A., Mandhaniya, P., Malik, B. A., and Ouyang, Z. (2025). Editorial: disaster risk and resilience assessment of multi-utility transportation infrastructure and urban projects. Front. Built Environ. 11. doi:10.3389/fbuil.2025.1619407
Bakhshi Lomer, A. R., Rezaeian, M., Rezaei, H., Lorestani, A., Mijani, N., Mahdad, M., et al. (2023). Optimizing emergency shelter selection in earthquakes using a risk-driven large group decision-making support system. MDPI 15 (5), 4019. doi:10.3390/su15054019
Bakhtyar Ali Ahmad, B. A. A., Himan Shahabi, H. S., and Baharin Ahmad, B. A. (2015). Application of GIS based multi-criteria analysis in site selection of water reservoirs. case study Batu Pahat, Malays. doi:10.19026/rjaset.9.2593
Butcher, G., Hopkins, D., Jury, R., Massey, W., McKay, G., and McVerry, G. (1988). The September 1985 Mexico earthquakes. Bull. N. Z. Soc. Earthq. Eng. 21 (1), 3–96. doi:10.5459/bnzsee.21.1.3-96
Butler, D., Ward, S., Sweetapple, C., Astaraie-Imani, M., Diao, K., Farmani, R., et al. (2017). Reliable, resilient and sustainable water management: the safe and SuRe approach. Glob. Challenges 1. 63–77. doi:10.1002/gch2.1010
Cajot, S., Mirakyan, A., Koch, A., and Maréchal, F. (2017). Multicriteria decisions in urban energy system planning: a review. Front. Energy Res. 5. doi:10.3389/fenrg.2017.00010
Chen, W., Zhai, G., Ren, C., Shi, Y., and Zhang, J. (2018). Urban resources selection and allocation for emergency shelters: in a multi-hazard environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. MDPI 15 (6), 1261. doi:10.3390/ijerph15061261
Choi, J., Yoo, D. G., and Kang, D. (2018). Post-earthquake restoration simulation model for water supply networks. Sustain. MDPI 10 (10), 3618. doi:10.3390/su10103618
Chou, J.-S., Ou, Y.-C., Cheng, M.-Y., Cheng, M.-Y., and Lee, C.-M. (2013). Emergency shelter capacity estimation by earthquake damage analysis. Nat. Hazards 65 3. 2031–2061. doi:10.1007/s11069-012-0461-5
Çoban, V. (2023). Analysis of consistency indices of pairwise comparison methods. Erzincan Üniversitesi Fen Bilim. Enstitüsü Derg. 16 (2), 384–405. doi:10.18185/erzifbed.1241221
Daniell, J. E., Schaefer, A. M., and Wenzel, F. (2017). Losses associated with secondary effects in earthquakes. Front. Built Environ. 3. doi:10.3389/fbuil.2017.00030
Elhami Khorasani, N., and Garlock, M. E. M. (2017). Overview of fire following earthquake: historical events and community responses. Int. J. Disaster Resil. Built Environ. Emerald Publ. Ltd. 8 (02), 158–174. doi:10.1108/IJDRBE-02-2015-0005
Enferadi, S., Shomali, Z. H., and Niksejel, A. (2021). Feasibility study of earthquake early warning in Tehran, Iran. J. Seismol. 25 (4), 1127–1140. doi:10.1007/s10950-021-10014-3
Environmental Systems Research Institute (ESRI) (2020). ArcGIS desktop. Redlands, California: Environmental Systems Research Institute. Available online at: https://www.esri.com.
Escobar, M. T., and Moreno-jiménez, J. M. (2007). Aggregation of individual preference structures in ahp-group decision making. Group Decis. Negot. 16 (4), 287–301. doi:10.1007/s10726-006-9050-x
FEMA (2014). Hazus: MH 2.1 technical manual - FEMA, hazus: MH 2.1 technical manual - Earthquake model, developed by the department of homeland security, federal emergency management agency. Mitigation Division Washington, DC: Federal Emergency Management Agency.
FEM Agency (2022). Hazus earthquake model technical manual. Tech. Rep. Washington, DC: Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA).
F. N. (2000). Disaster mitigation strategies in Tehran, Iran. Disaster prevention and management. An Int. J. 9 (3), 205–212. doi:10.1108/09653560010335194
Forman, E. H., and Gass, S. I. (2001). The analytic hierarchy process—an exposition. Oper. Res. 49 (4), 469–486. doi:10.1287/opre.49.4.469.11231
Gaievskyi, S., Delfrate, N., Ragazzoni, L., and Bahattab, A. (2025). Use of multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) to support decision-making during health emergencies: a scoping review. Front. Public Health 13. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2025.1584026
Garg, A. (2024). “Fire safety,” in Handbook on hospital planning and designing. Editor A. Garg (Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore). doi:10.1007/978-981-99-9001-6_43
Gebre, S. L., Cattrysse, D., and Van Orshoven, J. (2021). Multi-criteria decision-making methods to address water allocation problems: a systematic review. Water (Basel) 13 (2), 125. doi:10.3390/w13020125
Goswami, S. S., Tapankumar, T., Naik, N. C. K., Gowrishankar, J., Bhosle, N., Singh, A., et al. (2025). Multi-model MCDM framework for sustainable renewable energy selection in India: integrating CRITIC-EDAS-CODAS-CoCoSo. Discov. Sustain. 6 (1), 500. doi:10.1007/s43621-025-01069-0
Grossi, P., Williams, C., Cabrera, C., Tabucchi, T., Sarabandi, P., Rodriguez, A., et al. (2011). The 2010 Maule, Chile earthquake: lessons and future challenges. Risk Manag. Solutions (RMS)
Grzeda, S., Mazzuchi, T. A., and Sarkani, S. (2014). “Temporary disaster debris management site identification using binomial cluster analysis and GIS. Disasters38 2. 398–419. doi:10.1111/disa.12040
Guo, E. D., Yang, D., Liu, Z., and Wang, Z. R. (2011). Seismic vulnerability analysis of water pipeline in wenchuan earthquake. Appl. Mech. Mater. 109, 290–295. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.109.290
Halder, S., Saha, S., Sarda, R., and Das, J. (2025). Usage and future path of MCDM for hazard monitoring and risk assessment. 507, 518. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-89246-2_22
Hashemi, M., Alesheikh, A. A., and Zolfaghari, M. R. (2013). A spatio-temporal model for probabilistic seismic hazard zonation of Tehran. Comput. Geosci. Elsevier 58, 8–18. doi:10.1016/j.cageo.2013.04.005
Hatami, H., and Amani, M. (2023). The ability and efficiency of Tehran municipality in managing the possible earthquake crisis in Tehran. J. Crisis Emerg. Manag. 15 (49), 11–26. Available online at: https://www.magiran.com/p2606483
Heidari, M., Heidari, S., and Jafari, H. (2020). The challenges of Iranian health system preparedness before earthquakes based on the world health organization framework. J. Educ. Health Promot 9 (1), 273. doi:10.4103/jehp.jehp_746_19
Hosseini, S. M. A., Ghalambordezfooly, R., and de la Fuente, A. (2022). Sustainability model to select optimal site location for temporary housing units: combining GIS and the MIVES–knapsack model. MDPI 14 (8), 4453. doi:10.3390/su14084453
Hsu, C.-H., Ke, S.-S., and Wu, T.-H. (2022). Development and application of a platform for multidimensional urban earthquake impact simulation. Front. Built Environ. 8. doi:10.3389/fbuil.2022.938747
Huang, L., Wang, L., and Song, J. (2018). Post-disaster business recovery and sustainable development: a study of 2008 wenchuan earthquake. MDPI 10 (3), 651. doi:10.3390/su10030651
Ibrion, M., Mokhtari, M., and Nadim, F. (2015). Earthquake disaster risk reduction in Iran: lessons and “Lessons Learned” from three large earthquake disasters—tabas 1978, rudbar 1990, and bam 2003. Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 6 (4), 415–427. doi:10.1007/s13753-015-0074-1
Ishizaka, A., and Labib, A. (2011). Review of the main developments in the analytic hierarchy process. Expert Syst. Appl. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2011.04.143
Jalal-ud-Din, E.-ul-H., Ahmad, I., and Hussain, A. (2025). Global optimization through PROMETHEE-driven tri-point selection based genetic algorithms. Evol. Intell. 18 (3), 55. doi:10.1007/s12065-025-01039-5
Jennings, P. C., and Wood, J. H. (1973). Engineering features of the san fernando earthquake. Bull. N. Z. Soc. Earthq. Eng. Lower Hutt, New Zealand: New Zealand Society for Earthquake Engineering 6 1. 22–45. doi:10.5459/bnzsee.6.1.22-45
Jiang, J. Q., Yao, X. W., and Lu, Y. T. (2013). Seismic damage assessment of urban water supply pipeline. Appl. Mech. Mater. 316–317, 723–726. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.316-317.723
Kamranzad, F., Memarian, H., and Zare, M. (2020). Earthquake risk assessment for Tehran, Iran. ISPRS Int. J. Geoinf. MDPI 9 (7), 430. doi:10.3390/ijgi9070430
Khosravian, J., Qureshi, S., Rostamzadeh, S., Moradi, B., Derakhshesh, P., Yousefi, S., et al. (2024). Evaluating the feasibility of constructing shopping centers on urban vacant land through a spatial multi-criteria decision-making model. Front. Sustain. Cities 6. doi:10.3389/frsc.2024.1373331
Lee, S., Davidson, R., Ohnishi, N., and Scawthorn, C. (2008). Fire following earthquake—reviewing the state-of-the-art of modeling. SAGE Publ. Sage U. K. 24 4 933–967. doi:10.1193/1.2977493
Leigh, N. G., and Lee, H. (2019). Sustainable and resilient urban water systems: the role of decentralization and planning. MDPI 11 (3), 918. doi:10.3390/su11030918
Li, X., Lam, N., Qiang, Y., Li, K., Yin, L., Liu, S., et al. (2016). Measuring county resilience after the 2008 wenchuan earthquake. Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 7 (4), 393–412. doi:10.1007/s13753-016-0109-2
Li, Z., Zhao, H., Liu, J., Zhang, J., and Shao, Z. (2022). Evaluation and promotion strategy of resilience of urban water supply system under flood and drought disasters. Sci. Rep. Nat. Publ. Group U. K. Lond. 12 (1), 7404. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-11436-w
Liu, C., Li, Y., Yin, H., Zhang, J., and Wang, W. (2020). A stochastic interpolation-based fractal model for vulnerability diagnosis of water supply networks against seismic hazards. Sustain. MDPI 12 (7), 2693. doi:10.3390/su12072693
Liu, J., Shao, Z., and Wang, W. (2021). Resilience assessment and critical point identification for urban water supply systems under uncertain scenarios. Water (Basel). MDPI 13 (20), 2939. doi:10.3390/w13202939
Liu, Y., Li, Z., Wei, B., Li, X., and Fu, B. (2019). “Seismic vulnerability assessment at urban scale using data mining and GIScience technology: application to urumqi (china). Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 10 (1), 958–985. doi:10.1080/19475705.2018.1524400
Lo, I.-T., Lin, C.-Y., Yang, C.-T., Chuang, Y.-J., and Lin, C.-H. (2020). Assessing the blockage risk of disaster-relief road for a large-scale earthquake. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 24 12, 3820–3834. doi:10.1007/s12205-020-0340-7
MaCaffrey, M. A. (1983). Buried pipeline response to reverse faulting during the 1971 san fernando earthquake. ASME, PVP 77, 151–159. doi:10.1016/j.soildyn.2020.106090
Majdi, A., Sadeghi-Movahhed, A., Mashayekhi, M., Zardari, S., Benjeddou, O., and De Domenico, D. (2023). On the influence of unexpected earthquake severity and dampers placement on isolated structures subjected to pounding using the modified endurance time method. Buildings 13 (5), 1278. doi:10.3390/buildings13051278
Matsumura, T., Osaki, S., Kudo, D., Furukawa, H., Nakagawa, A., Abe, Y., et al. (2015). “Water supply facility damage and water resource operation at disaster base hospitals in Miyagi prefecture in the wake of the great east Japan earthquake. Prehosp Disaster Med. 30 2, 193–198. doi:10.1017/S1049023X15000084
Mizuno, H. (1978). On outbreak of fires in earthquakes. Kyoto, Japan: Department of Architecture, Kyoto University Kyoto.
Morales, F. F., and de Vries, W. T. (2021). Establishment of natural hazards mapping criteria using analytic hierarchy process (AHP). Front. Sustain. 2. doi:10.3389/frsus.2021.667105
Mousavi, S., Bagchi, A., and Kodur, V. K. R. (2008). Review of post-earthquake fire hazard to building structures. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 35 (7), 689–698. doi:10.1139/L08-029
Ossadnik, W., Schinke, S., and Kaspar, R. H. (2016). Group aggregation techniques for analytic hierarchy process and analytic network process: a comparative analysis. Group Decis. Negot. 25 (2), 421–457. doi:10.1007/s10726-015-9448-4
Perrucci, D., and Baroud, H. (2020). A review of temporary housing management modeling: trends in design strategies, optimization models, and decision-making methods. MDPI 12 (24), 10388. doi:10.3390/su122410388
Qian, L., Wei, S., Tianlai, Y., Tiancheng, W., and Mohamed, H. (2023). Mathematical methodology in the seismic resilience evaluation of the water supply system. Appl. Math. Nonlinear Sci. 8 (1), 45–54. doi:10.2478/amns.2021.2.00212
Rohr, A., Priesmeier, P., Tzavella, K., and Fekete, A. (2020). System criticality of road network areas for emergency management services—spatial assessment using a tessellation approach. Infrastructures (Basel). MDPI 5 (11), 99. doi:10.3390/infrastructures5110099
Saaty, R. W. (1987). The analytic hierarchy Process—What it is and how it is used. Math. Model. 9 (3–5), 161–176. doi:10.1016/0270-0255(87)90473-8
Saaty, T. L. (2013). “Analytic hierarchy process,” in Encyclopedia of operations research and management science (Boston, MA: Springer US). doi:10.1007/978-1-4419-1153-7_31
Sadeghi-Movahhed, A., De Domenico, D., and Majdi, A. (2024). Structural flexibility impact on pounding severity and seismic performance of adjacent isolated buildings. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 181, 108667. doi:10.1016/j.soildyn.2024.108667
Sadeghi-Movahhed, A., De Domenico, D., Mashayekhi, M., and Majdi, A. (2025). Optimal damping of isolated tall buildings accounting for structural and nonstructural damage. J. Build. Eng. 105, 112497. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2025.112497
Sadeghi Movahhed, A., Shirkhani, A., Zardari, S., Mashayekhi, M., Noroozinejad Farsangi, E., and Majdi, A. (2023). Modified endurance time method for seismic performance assessment of base-isolated structures. J. Build. Eng. 67, 105955. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2023.105955
Sahoo, S. K., and Goswami, S. S. (2023). A comprehensive review of multiple criteria decision-making (MCDM) methods: advancements, applications, and future directions. Decis. Mak. Adv. 1 (1), 25–48. doi:10.31181/dma1120237
Salazar, K., and McNutt, M. (2011). Report on the 2010 Chilean earthquake and tsunami response. Reston, Virginia: US Geological Survey. Available online at: http://pubsdata.usgs.gov/pubs/of/2011/1053/index.html.
Santa-Cruz, S., Fernández de Córdova, G., Vilela, M., Pajuelo, J., Santa-María, M., and Muñoz, K. (2024). Spatial analysis for water supply in seismic emergencies: the Lima-Callao metropolitan area. Front. Built Environ. 10. doi:10.3389/fbuil.2024.1385476
Sarreshtehdari, A., and Elhami Khorasani, N. (2021). Integrating the fire department response within a fire following earthquake framework for application in urban areas. Fire Saf. J. Elsevier 124, 103397. doi:10.1016/j.firesaf.2021.103397
Scawthorn, C. (1996). “Fires following the northridge and kobe earthquakes,” in Thirteenth meeting of the UJNR panel on fire research and safety (Gaithersburg, MD, USA: NIST), 325–334.
Scawthorn, C. (2009). Fire following earthquake. Fire Saf. Sci. 1, 971–979. doi:10.3801/iafss.fss.1-971
Scawthorn, C. (2011). Water supply in regard to fire following earthquake, PEER report 2011-08. Berkeley, CA: Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center, University of California.
Scawthorn, C., Cowell, A. D., and Borden, F. (1998). Fire-related aspects of the northridge earthquake. Gaithersburg, MD: National Institute of Standards and Technology.
Scawthorn, C., Eidinger, J. M., and Schiff, A. (2005). Fire following earthquake, 26. Reston, VA: ASCE Press.
Şengör, A. M. C., Altıner, D., Cin, A., Ustaömer, T., and Hsü, K. J. (1988). Origin and assembly of the tethyside orogenic collage at the expense of gondwana land. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 37 (1), 119–181. doi:10.1144/GSL.SP.1988.037.01.09
Shao, W., Luo, L., Wang, J., Liu, J., Zhou, J., Xiang, C., et al. (2018). The coordination of routine and emergency water resources management: progress in China. Water Int. 43 (7), 943–962. doi:10.1080/02508060.2018.1511201
Shojaeian, A., Farahani, S., Behnam, B., and Mashayekhi, M. (2021). Seismic resilience assessment of tehran’s southern water transmission pipeline using GIS-based analyses. Numer. Methods Civ. Eng. KN Toosi Univ. Technol. 6 (2), 93–106. doi:10.52547/nmce.6.2.93
Shuang, Q., Liu, H. J., and Porse, E. (2019). Review of the quantitative resilience methods in water distribution networks. Water (Basel). MDPI 11 (6), 1189. doi:10.3390/w11061189
Sisay, T., Teku, D., and Abebaw, E. (2025). Solid waste disposal site selection using GIS and the analytic hierarchy process model: a case study conducted in gimba town, northeastern Ethiopia. Front. Sustain. 6. doi:10.3389/frsus.2025.1528851
Sood, R. K., Bocour, A., Kumar, S., Guclu, H., Potter, M., and Shah, T. B. (2016). Impact on primary care access post-disaster: a case study from the rockaway peninsula. Disaster Med. Public Health Prep. 10 3, 492–495. doi:10.1017/dmp.2016.80
Susmaga, R., Szczęch, I., and Brzezinski, D. (2024). Towards explainable TOPSIS: visual insights into the effects of weights and aggregations on rankings. Appl. Soft Comput. 153, 111279. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2024.111279
Tanomand, A., and Mashayekhi, M. (2025). An enhanced method for assigning ignition locations in fire following earthquake modeling.
Tanoumand, A., Mashayekhi, M., Majdi, A., and Farsangi, E. N. (2025). A metaheuristic-based approach for optimizing the allocation of emergency water reservoirs for fire following earthquake suppression. Results Eng. 27, 105925. doi:10.1016/j.rineng.2025.105925
Toma-Danila, D., Tiganescu, A., D’Ayala, D., Armas, I., and Sun, L. (2022). Time-dependent framework for analyzing emergency intervention travel times and risk implications due to earthquakes. Bucharest case study. Front. Earth Sci. (Lausanne). 10. doi:10.3389/feart.2022.834052
Trifunac, M. D., and Todorovska, M. I. (1998). The northridge, California, earthquake of 1994: fire ignition by strong shaking. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 17 3, 165–175. doi:10.1016/S0267-7261(97)00040-7
Uma, S. R., Scheele, F., Abbott, E., and Moratalla, J. (2021). Planning for resilience of water networks under earthquake hazard. Bull. N. Z. Soc. Earthq. Eng. 54 (2), 135–152. doi:10.5459/bnzsee.54.2.135-152
Vaidya, O. S., and Kumar, S. (2006). Analytic hierarchy process: an overview of applications. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 169 (1), 1–29. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2004.04.028
Van Dyke, S. (1996). Firefighting system defies san franciso earthquakes. Opflow 22 (1), 1–5. doi:10.1002/j.1551-8701.1996.tb01282.x
Wang, P., Hu, Y., and Yao, J. (2021). “Refined path planning for emergency rescue vehicles on congested urban arterial roads via reinforcement learning approach,”J. Adv. Transp. Wiley Online Libr. Editors L. Yan, P. Wang, J. Yang, Y. Hu, Y. Han, and J. Yao 1–12. doi:10.1155/2021/8772688
Wang, Y., Liu, W., Chen, C., Li, X., Liu, B., Du, P., et al. (2025). GIS-Based risk assessment of typhoon disasters in coastal provinces of China. Front. Mar. Sci. 12. doi:10.3389/fmars.2025.1548763
Xu, Z., and Liao, H. (2014). Intuitionistic fuzzy analytic hierarchy process. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 22 (4), 749–761. doi:10.1109/TFUZZ.2013.2272585
Yi, F., and Tu, Y. (2018). An evaluation of the paired assistance to disaster-affected areas program in disaster recovery: the case of the wenchuan earthquake. MDPI 10 (12), 4483. doi:10.3390/su10124483
Yu, Y.-C., and Gardoni, P. (2022). Predicting road blockage due to building damage following earthquakes. Reliab Eng. Syst. Saf. Elsevier 219, 108220. doi:10.1016/j.ress.2021.108220
Keywords: fire following earthquake, optimal location, emergency water reservoirs, analytic hierarchy process (AHP), geographic information system (GIS)
Citation: Tanoumand A, Mashayekhi M, S. Ramadan M and Majdi A (2025) Development of a method for optimal location of emergency water reservoirs for FFE suppression using AHP and GIS. Front. Built Environ. 11:1638961. doi: 10.3389/fbuil.2025.1638961
Received: 31 May 2025; Accepted: 24 July 2025;
Published: 08 August 2025.
Edited by:
Dario De Domenico, University of Messina, ItalyReviewed by:
Heri Sutanta, Gadjah Mada University, IndonesiaAdnan Abdulvahitoğlu, Mudanya University, Türkiye
Copyright © 2025 Tanoumand, Mashayekhi, S. Ramadan and Majdi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mona S. Ramadan, bW9uYS5zLnJhbWFkYW5AdWFldS5hYy5hZQ==; Ali Majdi, YWxpLm1hamRpMTk3OEBnbWFpbC5jb20=
 Ali Tanoumand
Ali Tanoumand Mohammadreza Mashayekhi
Mohammadreza Mashayekhi Mona S. Ramadan
Mona S. Ramadan Ali Majdi
Ali Majdi