- 1Construction Management and Quantity Surveying, University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg, South Africa
- 2Department of Civil Engineering, College of Engineering and Technology, William V.S. Tubman University, Harper, Liberia
Introduction: The integration of advanced materials and digital technologies into construction is essential for achieving energy efficiency and sustainability, with graphene-zeolite smart flooring offering a multifunctional solution to enhance building performance.
Methods: A mixed-methods approach was employed, combining quantitative data from a survey of 53 construction professionals with a bibliometric analysis of 179 Scopus-indexed publications using VOSviewer.
Results: The survey revealed strong industry support for smart materials and technologies that promote energy savings and address environmental concerns, while the bibliometric review identified research clusters in thermal energy storage, nanomaterials, and digital construction systems. Graphene-zeolite composites were found to improve thermal conductivity, enable passive heat storage and release, and enhance air quality through adsorption, with compatibility for integration with artificial intelligence, Internet of Things, and digital twin technologies to support real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance.
Discussion: Despite these promising attributes, the absence of empirical testing on thermal performance and long-term durability underscores the need for further validation and field studies. These findings contribute to Sustainable Development Goals (SDG 7, SDG 9, and SDG 13) and highlight future research priorities, including scalable manufacturing, lifecycle assessment, and integration across diverse building typologies to fully realise the potential of graphene-zeolite smart flooring in the built environment.
1 Introduction
Today’s construction industry is pressured to meet sustainability and digitalisation goals, driven by rising environmental concerns and stricter global policy frameworks. Modern buildings must now respond to climate change, energy use, and material efficiency, especially in line with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and net-zero carbon targets (Oladunni et al., 2025). Construction contributes significantly to global greenhouse gas emissions, and materials play a significant role in this impact. As global demands for smarter, greener buildings grow, there is a clear need to shift from traditional, resource-heavy practices to solutions that integrate energy efficiency and digital performance (Idowu et al., 2024a; Bolpagni et al., 2022). Though often underestimated, flooring contributes directly to thermal performance, indoor environmental quality, and long-term energy use. According to Mempouo et al. (2010), Floor systems play a crucial role in building energy performance, typically accounting for about 13%–25% of a building’s heat loss or gain, similar to ceilings and roofs, while external walls contribute around 35%–40%. This makes flooring a critical target for material innovation and smart integration. Thus, this study focuses on how advanced materials like graphene and zeolite, with their unique properties, can contribute to sustainable performance and digital transformation in the built environment.
Graphene is a nanomaterial known for its exceptional thermal conductivity around (5000 W m-1 K−1) at room temperature, highest Young’s modulus (∼1,100 GPa), fracture strength (130 GPa), and mobility of charge carriers (200,000 cm2 V−1 s-1) making it suitable for applications in energy storage and thermal regulation (Xin et al., 2015; Saleem et al., 2016; Chaudhary et al., 2024). Zeolite, a naturally occurring microporous mineral, offers adsorption, ion-exchange, and moisture regulation properties, which make it valuable in both environmental filtering and passive indoor climate control (Wang et al., 2020; Othman et al., 2024). When used together in flooring systems, these two materials show synergistic potential. Graphene supports heat flow and smart sensing, while zeolite enhances durability and air quality by trapping pollutants like ammonia and heavy metals. In addition, graphene-zeolite composites have improved compressive and tensile strength, offering long-term resilience against wear and environmental stress (Prudente et al., 2024). These benefits allow the flooring to do more than support foot traffic; it can store and release thermal energy, filter indoor air, and provide input to digital monitoring systems through smart sensors. Combined with Internet of Things (IoTs), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and digital twins (DT), such flooring can actively regulate internal conditions and reduce operational energy costs by an estimated 15%–25%, based on comparable systems (Liu et al., 2023; Das et al., 2025; Stephen S. et al., 2025).
Beyond material performance, this approach aligns with global research and policy trends that promote sustainable construction through advanced manufacturing and smart technologies. Graphene-zeolite smart flooring supports circularity by reducing maintenance needs and extending the building’s lifespan while improving indoor thermal comfort and health outcomes. This study responds directly to these developments, aiming to explore integrating graphene-zeolite materials into floor systems that support digital functions and sustainability. The research has two key goals: first, to identify viable methods for embedding smart flooring in present-day construction; second, to evaluate how such flooring contributes to improved building performance regarding energy, durability, and environmental impact. In doing so, this study contributes to the ongoing shift toward construction methods that are technically advanced, climate-resilient, and digitally responsive.
2 Literature review
2.1 New materials in the construction industry
The construction industry is undergoing rapid transformation, driven by the need for more sustainable, durable, and innovative materials. New materials, such as advanced composites, nanomaterials, and bio-based substances, are reshaping how buildings are designed and constructed (Liu et al., 2023; Chaudhary et al., 2024). According to Abed et al. (2022), these materials offer significant advantages over traditional ones, including improved strength, lighter weight, and environmental benefits. For instance, the development of fibre-reinforced polymers has revolutionised structural applications by providing lightweight yet robust alternatives to steel and concrete. These innovations not only enhance performance but also reduce the carbon footprint of construction projects, aligning with global sustainability goals (Ielo et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2023).
In addition to advanced materials, sustainable construction practices are essential for addressing environmental and economic challenges. Optimisation algorithms are increasingly applied to reduce material consumption, energy use, and emissions in the design phase. For example, Cucuzza et al. (2024a) propose methods to minimise cutting trim losses in steel structures. Olivo et al. (2024) demonstrate how genetic algorithms can improve the retrofitting of RC buildings using steel exoskeletons. These exoskeletons enhance structural resilience and create new external spaces where smart systems like graphene-zeolite flooring could be installed. As discussed by Cucuzza et al. (2024b), constructability-based approaches show how efficient design can align with real-world construction needs. Furthermore, performance-based optimisation of steel exoskeletons (Cucuzza et al., 2025) highlights how such practices promote sustainability beyond individual materials. Integrating these approaches with advanced flooring systems supports the development of innovative and practical buildings. Together, these materials and construction strategies suggest that a combined focus on smart technology and design efficiency is key to advancing sustainable building practices.
A critical focus in recent studies has been the role of nanomaterials, such as graphene, in improving construction material properties. Graphene’s exceptional conductivity, flexibility, and strength make it a game-changer for applications like concrete reinforcement and energy-efficient coatings (Thakur and Kumar, 2024). Additionally, self-healing concrete, which incorporates microcapsules of healing agents, has emerged as a breakthrough innovation (Amran et al., 2022; Rumman et al., 2024). This material can repair cracks automatically, significantly extending the lifespan of structures and reducing maintenance costs. However, despite these advancements, challenges remain. High production costs and limited scalability often hinder the widespread adoption of these materials, highlighting the need for further research into cost-effective manufacturing methods (Sabet, 2024).
In contrast, bio-based materials, such as hempcrete and mycelium, have gained attention for their environmental friendliness and potential to replace conventional materials like bricks and cement (Yadav and Agarwal, 2021). Hempcrete, for example, is a lightweight, insulating material made from hemp fibres and lime. Studies by Yadav and Saini (2022) and Asghari and Memari (2024) have shown that it has excellent thermal and moisture-regulating properties. Similarly, mycelium, derived from fungal networks, is being explored as a sustainable, biodegradable building material. However, questions remain regarding their durability, scalability, and ability to meet regulatory standards (Carcassi et al., 2024). Overall, the literature underscores a growing consensus that while new materials hold great promise, further research is necessary to address their limitations and fully realise their potential in transforming the construction industry.
2.2 Graphene and zeolite in construction
Graphene, a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, has garnered significant attention in the construction industry due to its extraordinary properties (Chaudhary et al., 2024). Nguyen and Nguyen (2016) identified graphene as a versatile material capable of enhancing strength, conductivity, and durability in construction applications. In concrete, for instance, the addition of graphene improves compressive strength and reduces permeability, which enhances its resistance to environmental factors like water and chemicals. These improvements align with the industry’s goals of creating longer-lasting and more sustainable building materials. Graphene’s potential to enhance traditional materials has established it as a cornerstone of innovation in construction (Yu et al., 2017). Furthermore, one of the most promising applications of graphene in construction is its use in energy-efficient technologies. Graphene-based coatings and films have been explored for their exceptional thermal and electrical conductivity (Kumar et al., 2021). These coatings can serve as heat regulators, reducing energy consumption in buildings by improving insulation and enabling smart heating systems. Additionally, graphene-integrated solar panels have been developed to increase energy capture efficiency, allowing buildings to generate renewable energy more effectively (Rumman et al., 2024). While these innovations demonstrate the material’s versatility, their high production cost remains a significant barrier, limiting their widespread adoption in construction projects (Idowu et al., 2024b; Kumar et al., 2021).
Zeolite, a naturally occurring microporous mineral, has gained significant interest in the construction industry due to its unique structural and chemical properties (Chaudhary et al., 2024). Composed of a framework of silica and alumina tetrahedra, zeolite is known for its exceptional absorption capacity, ion exchange capabilities, and thermal stability. In construction, zeolite is often used as an additive in cement and concrete to improve their mechanical and durability properties (Othman et al., 2024). Studies have shown that incorporating zeolite into concrete enhances its resistance to chemical attacks, reduces shrinkage, and improves compressive strength (Markiv et al., 2016; Chen et al., 2024). These properties make zeolite a valuable material for sustainable and high-performance building applications. Furthermore, one of the most notable uses of zeolite in construction is its potential to mitigate environmental impacts. Zeolite’s high ion exchange capacity allows it to capture and store harmful pollutants such as ammonia and heavy metals from the environment (Wang et al., 2020). When used in concrete and other building materials, zeolite can act as a purifier, improving indoor and outdoor air quality. Additionally, its porous structure makes it an effective thermal insulator, contributing to energy-efficient building designs (Tran et al., 2019; Mondal et al., 2021). The use of zeolite as a pozzolanic material in cement also reduces the demand for traditional cement production, which is a significant contributor to carbon emissions. This aligns with global efforts to reduce the environmental footprint of construction (Ibrahim et al., 2022). However, challenges remain in maximising zeolite’s potential in the construction industry. Although zeolite is abundant, its processing and incorporation into construction materials require careful consideration to maintain cost-effectiveness and material compatibility (Mostafaei and Bahmani, 2024; Stephen S. et al., 2025). According to Danish et al. (2022), the variability in zeolite’s natural composition can lead to inconsistencies in performance, necessitating further research into material standardisation. Moreover, large-scale applications of zeolite in construction are still limited due to a lack of comprehensive field studies (Danish et al., 2022; Stephen S. et al., 2025). Despite these challenges, the literature highlights zeolite’s vast potential to enhance sustainability, durability, and functionality in construction, making it a critical focus for future research and development (Wang et al., 2020; Danish et al., 2022; Ibrahim et al., 2022; Stephen S. et al., 2025).
Despite the promising findings in the literature on the use of materials like graphene and zeolite in construction, several gaps remain in their practical application. Most studies focus on the laboratory-level performance of these materials, and there is limited research on how they behave in real-world, large-scale construction projects. Additionally, while both materials show potential for improving the strength, durability, and sustainability of construction materials, there is a lack of detailed studies on the long-term effects and performance of graphene and zeolite in diverse environmental conditions, especially in smart flooring. The high cost of production and challenges with scalability also need more attention. By addressing these issues, the study will contribute valuable insights to the growing body of knowledge on advanced materials in construction, helping to bridge the gap between laboratory findings and real-world applications.
3 Methodology
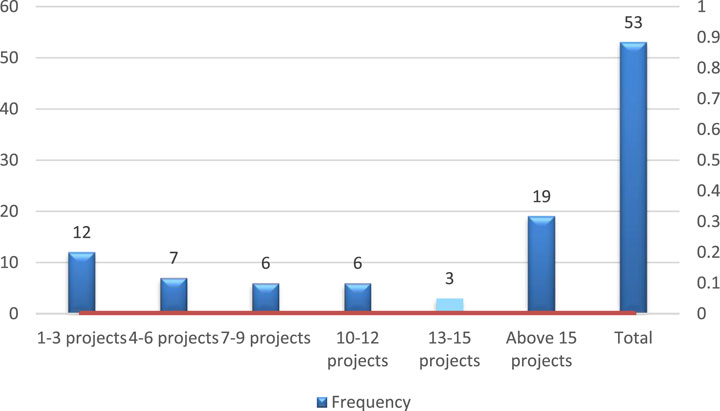
The quantitative data was collected from 53 randomly selected construction professionals using Google Forms. These included Civil Engineers, Architects, Builders, Mechanical Engineers, Construction Managers, Quantity Surveyors, and Electrical Engineers. Most responses came from Quantity Surveyors (43.4%) and Construction Managers (20.8%). The rest were Civil Engineers, Architects, Builders, and Mechanical Engineers. Also, 35.8% of respondents had worked on more than 15 construction projects, while 22.6% had experience on one to three projects, as shown in Figures 2,3. Random sampling was used to reduce bias and ensure fairness, based on Stratton’s (2021) approach. The analysis was done using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS). Tools such as Mean Item Score (MIS), Standard Deviation (SD), and Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA) were used to examine the relationships between the variables.
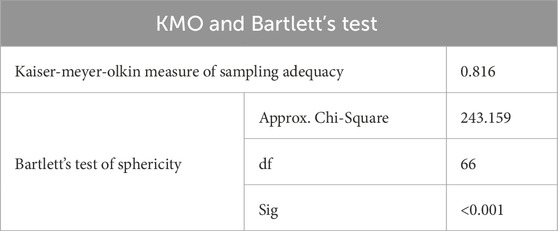
While the sample size was 53, this falls within the acceptable range for exploratory studies. de Winter et al. (2009) recommend a minimum of 50 cases for factor analysis in early-stage research. Furthermore, de Winter et al. (2009) shows that reliable factor analysis results can be achieved with small sample sizes, especially when high communalities (representation) and factors are well-defined. Since this study used EFA in an exploratory context, and not for confirmatory purposes, the chosen sample size was considered appropriate for the goals of this research, especially when it is not popular among scholars in the construction industry. Furthermore, the study’s data was found to be both reliable and valid, with a Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) measure of 0.816 and Bartlett’s test confirming the suitability of the sample. Although larger sample sizes are generally recommended for factor analysis, Williams et al. (2010) show no strict agreement on the exact number needed. While some experts suggest 300 or more cases, others argue that smaller samples are acceptable when certain conditions are met. The study illustrated that high communalities (above 0.60) and strong factor loadings–association between a variable and a factor (above 0.80) can justify using smaller samples. In this study, the Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) value was 0.816, well above the minimum threshold of 0.50, indicating excellent sampling adequacy. Additionally, Bartlett’s Test of Sphericity was highly significant (p < 0.001), confirming that the data had enough correlation to justify factor analysis, as shown in Table 2. These strong test results support the use of a small sample size (n = 53) in this study, as the data were statistically suitable for factor extraction and provided meaningful results that aligned with accepted research standards. In addition, to ensure the survey instrument was valid and reliable, several steps were taken beyond the KMO and Bartlett’s tests. First, the questionnaire items were developed based on a review of relevant literature to ensure content validity. Next, the survey was pre-tested with a small group of construction professionals (n = 6) who were not part of the final sample, as Wang et al. (2022) suggested. Their feedback was used to revise unclear or ambiguous items. This pre-test helped improve the instrument’s clarity, readability, and logical flow. Finally, internal consistency reliability was checked using Cronbach’s alpha for each factor, with values above 0.70 indicating acceptable reliability, as Kennedy (2022) recommended.
The qualitative aspect of the study utilised a bibliometric method to examine research trends and key areas of knowledge, relying on the Scopus database, which has been a comprehensive source covering various scientific fields since 2004 (Baas et al., 2020). Scopus was chosen due to its broad coverage, making it a preferred tool for literature reviews. The search focused on literature related to engineering, material sciences, energy, physics, astronomy, and earth sciences, using terms like “construction,” “floor,” “graphene,” “zeolite,” and “technology.” The search was carried out across all fields, and 206 documents were retrieved. After filtering for relevance (engineering, materials sciences, chemical engineering, energy, and environmental sciences) and English-language articles, 179 were selected, as shown in the study’s framework. The filtration was done to confine the scope of the study within engineering, construction, and related disciplines so as to arrive at the best possible data used without deviating from the study’s aim. To avoid thematic dilution, a careful screening process was applied to remove duplicates, off-topic papers, and articles overlapping with unrelated domains such as medicine or pure physics, which were not directly relevant to construction applications. Each article was assessed for contextual fit, and only those contributing directly to the research scope were retained, as shown in Figure 1. This ensured that the dataset reflected a focused and coherent body of literature aligned with the study’s objectives. The results were then categorised based on keywords, subject areas, country, year, and co-occurrence networks. Using VOSviewer, a bibliometric visualisation tool, keyword networks were mapped to represent the data through distance-based visualisations (Van Eck and Waltman, 2014). The analysis revealed two main clusters, with 22 keywords meeting the threshold of 9 documents per author out of 2,577 keywords generated. This higher threshold was set due to the large volume of final articles and keywords identified.
4 Result and discussion
4.1 Quantitative: objective one
4.1.1 Demographic
Figure 2 shows the distribution of respondents by profession. The majority of respondents are Quantity Surveyors, making up 43.4% of the total sample, with 23 out of 53 respondents. Construction Managers follow closely, representing 20.8% (11 respondents). Civil engineers account for 13.2% of the sample, with 7 respondents, while architects and builders make up 7.5% of the sample, with 4 respondents in each profession. Mechanical Engineers and Electrical Engineers each represent 3.8% of the sample, with 2 respondents from each profession. Overall, the data shows that the sample is heavily weighted towards Quantity Surveyors and Construction Managers, while the other professions are less represented.
Figure 3 presents the distribution of respondents based on the number of projects they have managed. A significant portion of respondents, 35.8% (19 individuals), have managed more than 15 projects. Following that, 22.6% (12 respondents) have managed between 1 and 3 projects, while 13.2% (7 respondents) have overseen 4 to 6 projects. A smaller portion, 11.3% (6 respondents), have managed 7 to 9 projects, and the same percentage (11.3%) is observed for those who have managed 10 to 12 projects. Only 5.7% (3 respondents) have managed between 13 and 15 projects. The data shows a concentration of respondents with more than 15 projects managed, indicating that most participants have significant experience in the field.
4.1.2 Descriptive
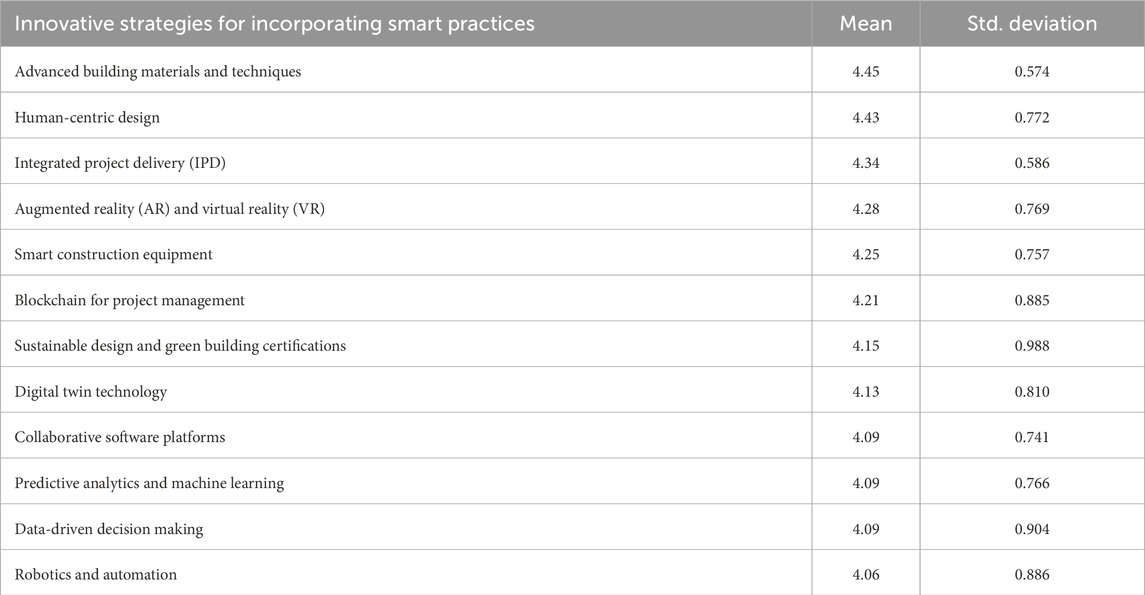
Table 1 presents the means and standard deviations for various innovative strategies in incorporating smart practices in construction. The strategy with the highest mean is “Advanced Building Materials and Techniques,” with a mean of 4.45 and a relatively low standard deviation of 0.574, indicating strong agreement among respondents about its importance. Following closely is “Human-Centric Design” (mean = 4.43, SD = 0.772) and “Integrated Project Delivery (IPD)” (mean = 4.34, SD = 0.586), both of which also received high ratings, showing a strong consensus. “Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)” has a mean of 4.28, suggesting it is also considered an important strategy, though with slightly more variation in responses (SD = 0.769). The strategies with the lowest means are “Robotics and Automation” (mean = 4.06, SD = 0.886), indicating it is viewed as less essential compared to the others, with higher variability in responses. Most strategies have means above 4.0, suggesting that respondents generally view these smart practices as important, but there is some variation in opinions, especially for technologies like blockchain and robotics.
The findings in the table highlight the construction industry’s growing focus on integrating advanced building materials and digital technologies to achieve smarter and more sustainable practices. The high mean score (4.45) for Advanced Building Materials and Techniques directly supports the relevance of Graphene-Zeolite Smart Flooring as a priority innovation. This suggests that stakeholders in the industry increasingly value cutting-edge materials that can enhance building performance, which aligns with the use of graphene for strength and conductivity, and zeolite for environmental and moisture control. Furthermore, the prominence of Human-Centric Design (4.43) and Integrated Project Delivery (IPD) (4.34) points to the importance of designing smart flooring systems that not only improve energy efficiency but also contribute to occupant comfort, health, and usability through real-time sensing and automation. Technologies such as AR/VR, Digital Twin, and Predictive Analytics, all ranking above 4.0, imply that graphene-zeolite flooring systems can be most impactful when integrated into broader digital construction ecosystems, for example, enabling floors to simulate wear patterns, predict failures, or optimise maintenance schedules through digital twins or IoT-based monitoring. These results reinforce that graphene-zeolite smart flooring is not just a material innovation but a strategic enabler of digital transformation, sustainable design, and intelligent infrastructure, placing it firmly at the centre of next-generation construction solutions.
4.1.3 Factor cluster report
Table 2 presents the results of the Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) Measure of Sampling Adequacy and Bartlett’s Test of Sphericity. The KMO value of 0.816 indicates that the sample is adequate for factor analysis, as values above 0.6 are generally considered acceptable. Bartlett’s Test of Sphericity shows a significant result with a chi-square value of 243.159, degrees of freedom (df) of 66, and a p-value of less than 0.001. This suggests that the correlation matrix is not an identity matrix, meaning that the data is suitable for conducting factor analysis. These results confirm that the sample is appropriate and that the data can be further analysed for underlying factors.
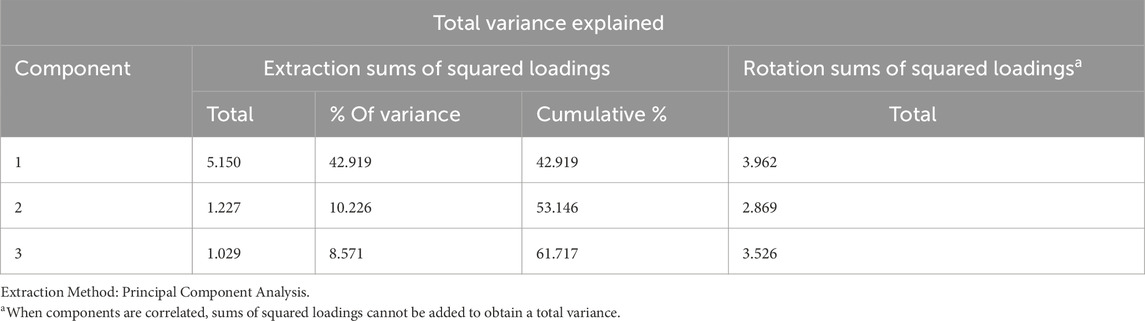
Table 3 presents the total variance explained by each component in the factor analysis. The first component explains 42.92% of the total variance, meaning it is the most significant factor in the data. After rotation, the first component still explains 3.962% of the total variance, but this value is lower because rotation redistributes the variance across the components. The second component explains 10.23% of the variance, bringing the cumulative total to 53.15%. The third component explains 8.57% of the variance, with the cumulative total reaching 61.72%. This shows that the first three components together explain about 62% of the variance in the data, indicating that these components capture a large portion of the information. The extraction method used was Principal Component Analysis, and the note highlights that when components are correlated, the variance from each component cannot be simply added together.
The results from the Principal Component Analysis (PCA) reveal that three main components collectively explain 61.72% of the total variance, indicating a strong and reliable factor structure in the dataset. The first component alone accounts for 42.92% of the variance, which suggests it represents the most influential group of factors related to the integration of smart and sustainable practices in construction. This high explanatory power aligns well with the role of Graphene-Zeolite Smart Flooring, which can serve as a foundational innovation within that dominant component, likely reflecting advanced material use, energy efficiency, and intelligent systems integration. The second and third components, explaining 10.23% and 8.57% respectively, further highlight supporting factors such as digital tools, collaborative processes, and adaptive technologies, all of which are essential for the successful implementation of smart flooring in real-world projects. These components may represent the interplay between technical systems, project delivery models, and user-centred innovation, reinforcing the multidimensional nature of digital transformation in the built environment. Therefore, the PCA findings support the claim that graphene-zeolite smart flooring is not an isolated material advancement but is embedded within a broader matrix of strategies driving sustainable and digital evolution in the construction sector.
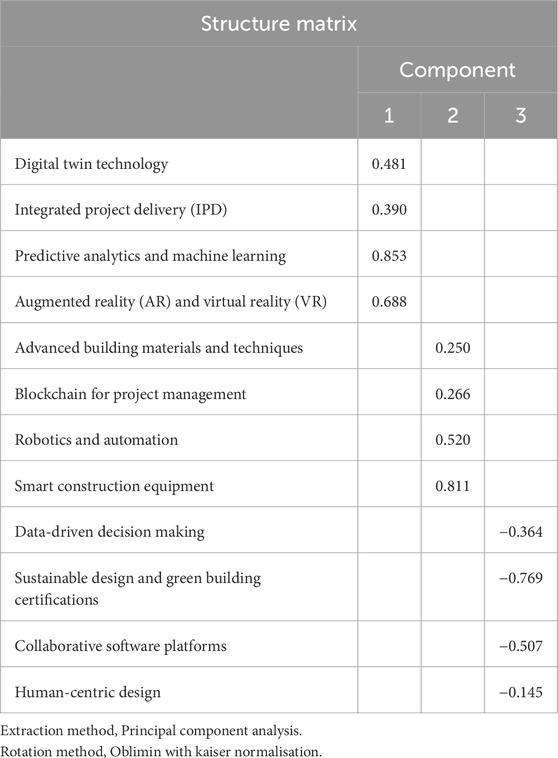
Table 4 presents the structure matrix, which shows the factor loadings for each variable across the three components identified through Principal Component Analysis (PCA) with Oblimin rotation. The loadings show how strongly each variable is associated with each component. For example, “Predictive Analytics and Machine Learning” has a very strong loading of 0.853 on Component 1, indicating that it is highly related to this factor. Similarly, “Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)” have a strong loading of 0.688 on Component 1. In contrast, “Data-driven Decision Making” and “Sustainable Design and Green Building Certifications” have negative loadings on Component 3, suggesting an inverse relationship with this component, with loadings of −0.364 and −0.769, respectively. Variables like “Smart Construction Equipment” and “Robotics and Automation” show strong loadings on Component 2, with values of 0.811 and 0.520, respectively, indicating that they are closely associated with this component. The structure matrix shows that smart digital tools like machine learning, smart equipment, and AR/VR are closely linked to the use of graphene-zeolite smart flooring. These tools help monitor, predict, and improve how the flooring works in buildings. Other factors like robotics and new building materials also support the use of this smart flooring. However, some items like sustainable design and data-driven decision-making show weaker or negative links, which may mean these areas need more focus to support the technology fully. The findings show that using graphene-zeolite smart flooring works best when combined with digital tools and smart construction methods.
The extraction method used was Principal Component Analysis, and the rotation method was Oblimin with Kaiser Normalisation, which allows for correlation between components, as reflected in the varied loadings across different components. This is further grouped into three clusters described below.
The first cluster, associated with Component 1, summarised as Smart Technologies, includes technologies like Predictive Analytics and Machine Learning (85.3%), Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) (68.8%), Digital Twin Technology (48.1%), and Integrated Project Delivery (39.0%). These variables have strong positive loadings, suggesting that they are closely related and form a group that represents advanced digital and analytical technologies in construction. “Integrated Project Delivery (IPD)” (0.390) also belongs to this cluster but with a slightly lower loading. With a cumulative percentage of 42.92%, the overall theme of this cluster revolves around cutting-edge technologies that focus on enhancing the efficiency and decision-making processes in construction projects. Together, these variables represent about 53% of the variance explained by Component 1. Smart technologies like predictive analytics, machine learning, AR, VR, digital twin technology, and integrated project delivery enable the integration of smart practices such as smart flooring by improving efficiency, design precision, and functionality. According to Geyer and Singaravel (2018), predictive analytics and machine learning provide insights into material performance and energy use, allowing for optimised flooring designs. AR and VR enhance planning and visualisation, enabling stakeholders to assess smart flooring systems in virtual environments before installation (Casini, 2022). Digital twin technology creates real-time digital replicas of flooring systems, enabling continuous monitoring and adaptive management (Omrany et al., 2023). Finally, integrated project delivery ensures seamless collaboration among professionals, streamlining the implementation of these advanced systems in construction projects (Dagou et al., 2024). Together, these technologies transform smart flooring into a functional and sustainable innovation in modern buildings.
The second cluster is associated with Component 2, summarised as Construction Innovation, which includes variables like Smart Construction Equipment (81.1%), Robotics and Automation (52.0%), Blockchain for Project Management (26.6%), and Advanced building materials and techniques (25.0%). These variables have a more moderate to high loading on this component, indicating their relevance to each other in transforming construction through automation, equipment, and secure digital management. With a cumulative percentage of 53.15%, the presence of “Blockchain for Project Management” suggests a focus on improving project management practices through new technologies. This cluster represents around 27% of the variance explained by Component 2 and highlights the integration of automation and innovative management practices in construction. Construction innovation, such as smart construction equipment and robotics, speeds up the installation of smart flooring while ensuring high precision and minimal errors (Dörfler et al., 2024). Robotics and automation can also improve the consistency and quality of flooring systems, making them more reliable and adaptable (Bock, 2007). Additionally, advanced building materials and blockchain technology help manage projects more efficiently by tracking resources and improving communication, ensuring the successful integration of smart flooring in modern construction (Zhang et al., 2023).
The third cluster, linked to Component 3, is summarised as Sustainable Practices, which include variables like Data-driven Decision Making (−0.364), Sustainable Design and Green Building Certifications (−0.769), Collaborative Software Platforms (−0.507), and Human-Centric Design (−0.145). These variables have negative loadings, which indicate an inverse relationship with Component 3. With a cumulative percentage of 61.72%, this cluster is centred on sustainability, decision-making, and collaboration, but the negative loadings suggest that these variables are less aligned with the factors represented by Components 1 and 2. This cluster represents the remaining 20% of the variance, focusing on aspects such as environmentally responsible design and the human aspect of construction projects. Sustainable practices like data-driven decision-making help identify the most efficient and eco-friendly smart flooring options by analysing performance data. According to Lin (2021), green building certifications and sustainable design principles ensure that flooring materials are environmentally responsible, aligning with long-term sustainability goals. Also, collaborative software platforms and human-centric design improve communication and user experience, allowing for the seamless integration of smart flooring systems that prioritise both functionality and environmental impact (Brunetti et al., 2022).
4.2 Qualitative: objective two
This section provides a descriptive analysis of publications that reveal research trends and patterns relevant to graphene-zeolite smart flooring as a catalyst for digital and sustainable transformation in construction. It covers publications by year, country, and subject area. These subsections help to identify how interest in smart materials, digital technologies, and sustainable construction practices has evolved over time, which regions and disciplines are leading contributions, and how these insights align with the study’s aim of exploring the integration of advanced materials and smart systems for future-ready construction solutions.
4.2.1 Publication per year
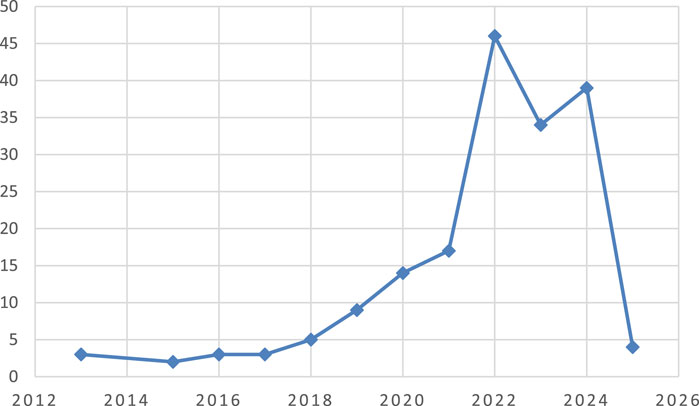
Subjecting the data from 2013 to 2025 due to available publications in the Scopus database, Figure 4 shows the distribution of publications by year, with a noticeable peak in 2022, which recorded 46 publications, the highest in the dataset. Publications have generally decreased since 2022, with 2023 seeing 34 publications and 2024 showing a slight drop to 39. There is a sharp decline in the years 2021 and earlier, with 17 publications in 2021 and progressively fewer in previous years, such as 14 in 2020, 9 in 2019, and 5 in 2018. The years 2017, 2016, 2015, and 2013 have even fewer publications, with only 3 or 2 publications each year. This suggests a significant increase in research activity starting in 2020 and peaking in 2022, followed by a gradual decline in more recent years, possibly due to changes in research trends in relation to when the study was carried out.
4.2.2 Publication per subject area
Figure 5 shows the number of publications across different subject areas, with Engineering leading by a significant margin, having 111 publications. Material Sciences follows closely with 95 publications, indicating strong research activity in this field as well. Chemical Engineering has 44 publications, showing a moderate level of research compared to Engineering and Materials Sciences. Energy and Environmental Sciences have the fewest publications, with 31 and 30, respectively, suggesting these fields may have less research output in this dataset. The data indicates that research is most concentrated in Engineering and Material Sciences, while Energy and Environmental Sciences represent more niche or emerging areas of study.
4.2.3 Publication per country
Table 5 shows the number of publications from different countries. China has the highest number of publications, with 86, indicating a strong research presence in this area. Saudi Arabia follows with 42 publications, showing considerable research activity. India (21 publications) and Iran (19 publications) have a moderate number of publications, while countries like Iraq (18), Egypt (17), and the United States (14) have somewhat fewer publications. Several countries, including Tunisia, Malaysia, Vietnam, and the United Kingdom, have between 6 and 12 publications, showing smaller but still active research contributions. A number of countries, such as Italy, Turkey, Ecuador, Australia, and South Korea, have 6 publications each. Other countries, including Russia, Chile, and Canada, have around 5 publications each, while Spain and Poland have the fewest, with 4 publications each. The category “Undefined” also has 6 publications, which might indicate missing or unclassified data. The data shows that most research is concentrated in China, Saudi Arabia, and a few other countries, while many nations have smaller contributions to the overall publications.
The findings show that research on smart materials and energy-efficient construction, including topics like graphene-zeolite smart flooring, is heavily concentrated in countries like China and Saudi Arabia, which indicates strong global interest and leadership in this field. The presence of moderate contributions from countries such as India, Iran, and Egypt also highlights growing attention in regions with expanding construction markets. However, the relatively low publication numbers from many other countries suggest that there is still limited global adoption and awareness of these innovations. This implies a need for broader international collaboration and knowledge sharing to promote the use of graphene-zeolite flooring as a tool for digital and sustainable transformation in construction worldwide.
4.2.4 Publication per keyword
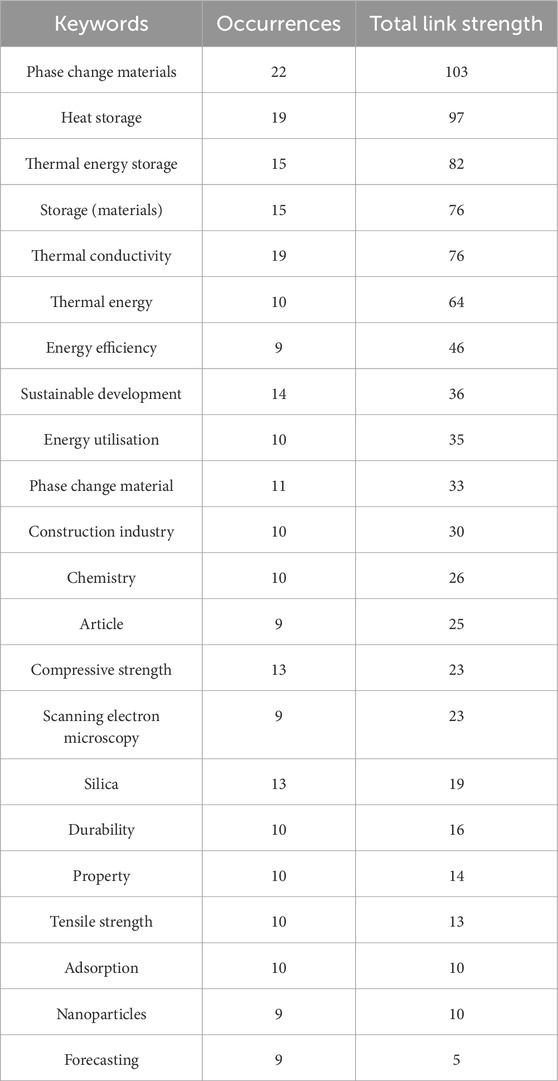
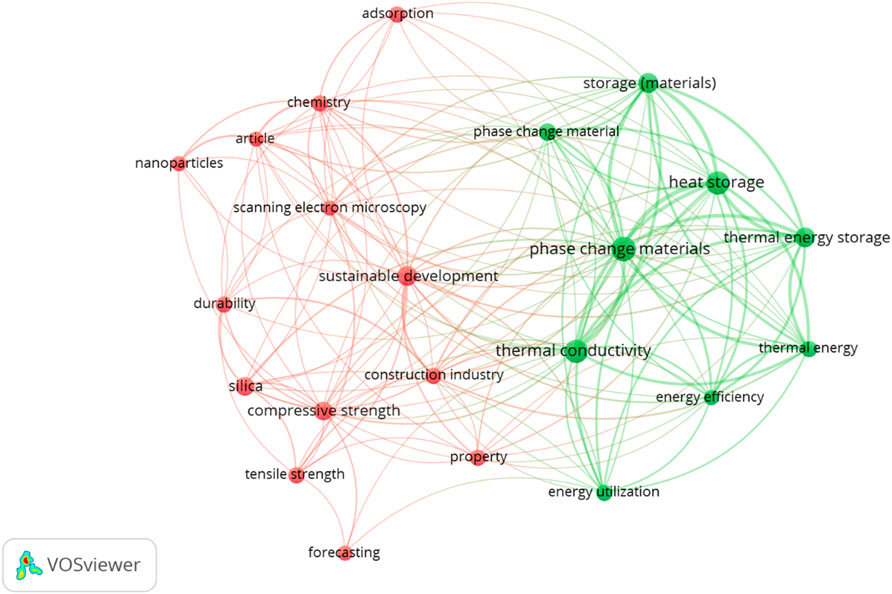
Table 6 shows the occurrences and total link strength of various keywords, which are terms frequently associated with the research data. “Phase change materials” is the most frequently occurring keyword, appearing 22 times with the highest total link strength of 103, suggesting it is a central concept in the studies. Other important keywords include “Heat storage” (19 occurrences, 97 link strength), “Thermal energy storage” (15 occurrences, 82 link strength), and “Storage (materials)” (15 occurrences, 76 link strength), all of which are closely related to energy storage technologies. Keywords such as “Thermal conductivity” (19 occurrences, 76 link strength) and “Energy efficiency” (9 occurrences, 46 link strength) indicate a focus on the performance of materials and systems in energy management. On the other hand, keywords like “Sustainable development” (14 occurrences, 36 link strength) and “Construction industry” (10 occurrences, 30 link strength) highlight the connection of the research to broader environmental and industry contexts. The data also shows several keywords related to material properties, such as “Compressive strength,” “Durability,” and “Tensile strength,” with varying link strengths, reflecting the importance of material performance in the studies.
The keyword analysis reveals that “Phase change materials”, “Heat storage”, and “Thermal energy storage” are among the most frequently occurring and strongly connected terms, indicating a concentrated research interest in energy-efficient and thermally adaptive materials. These themes directly support the application of graphene-zeolite smart flooring, which can be engineered to include thermal regulation properties and improve building energy performance. The frequent mention of “Thermal conductivity” (with 19 occurrences and a link strength of 76) further highlights the relevance of graphene, known for its superior heat conduction, making it ideal for temperature-regulating flooring systems. Likewise, the presence of keywords like “Energy efficiency”, “Sustainable development”, and “Durability” confirms that the current research landscape is aligned with the goals of sustainable and smart construction, which graphene-zeolite flooring directly supports. Terms such as “Compressive strength”, “Silica”, and “Tensile strength” also suggest that mechanical performance and material resilience are key concerns. In these areas, the composite nature of graphene and zeolite can offer superior benefits. The appearance of “Construction industry” among the keywords shows growing attention to applying these innovations in practical settings. Overall, the keyword trends validate that Graphene-Zeolite Smart Flooring is well-positioned within ongoing research priorities that aim to improve thermal management, structural performance, and sustainability in the construction sector.
4.2.5 Occurrence network visualisation
In generating the occurrence map using VOSviewer software, the keywords in Table 6 were limited to 9 occurrences, and 2 clusters were formed from a total of 2,577 keywords, with 22 keywords meeting the set threshold, as seen in Figure 6. Stephen and Aigbavboa (2025) noted that the results of a study depend largely on the keywords used in the search, and researchers should not let this limit the scope of their work. The clusters are described below.
Cluster 1 (13 items), summarised as Construction Materials, includes adsorption, article, chemistry, compressive strength, construction industry, durability, forecasting, nanoparticles, property, scanning electron microscopy, silica, sustainable development, and tensile strength. Graphene-zeolite technology can significantly improve the performance of flooring materials by enhancing various properties such as compressive strength, tensile strength, and durability. When integrated into the flooring system, Prudente et al. (2024) stated that materials like silica and nanoparticles work with graphene to provide additional strength and structural integrity. Combining graphene’s conductivity and zeolite’s adsorption capabilities helps regulate temperature, contributing to energy efficiency by reducing the need for external heating or cooling (Saadat et al., 2024). The study noted that this combination makes the flooring more resilient to wear and tear, ensuring long-term performance and reducing maintenance costs. Also, the use of scanning electron microscopy (SEM) allows for precise analysis of the material’s microstructure, helping to optimise the combination of graphene and zeolite for better thermal conductivity and mechanical properties (Le et al., 2024).
Additionally, the inclusion of sustainable development principles in creatingof these smart flooring systems ensures that the materials are environmentally friendly. Rathore et al. (2022) and Alassaf (2024) stated that by incorporating energy-efficient properties, such as enhanced thermal energy storage and reduced energy consumption, flooring helps lower the carbon footprint of buildings. The adsorption properties of zeolite can also contribute to improving indoor air quality by capturing and neutralising harmful substances. Furthermore, combining advanced materials like nanoparticles and forecasting techniques allows for better performance predictions and material design optimisation (Krzywanski et al., 2024). By integrating smart construction technologies like digital twins, the study continued that technology enables real-time monitoring of the flooring’s performance, optimising energy use and reducing waste. Additionally, augmented reality (AR) can assist in the design and installation process, ensuring that the flooring system is tailored to meet specific building requirements (Pan and Isnaeni, 2024). Blockchain technology can enhance project management by ensuring transparency, traceability, and efficiency in the supply chain (Zhang et al., 2023). At the same time, robotics and automation can streamline the installation process, improving precision and reducing labour costs (Dörfler et al., 2024). Bello S. F. et al. (2024) added that machine learning algorithms can also predict long-term wear and tear, further optimising maintenance schedules. Therefore, by focusing on both the technical and sustainable aspects of construction, graphene-zeolite flooring can offer a balanced solution that meets the needs of modern architecture while promoting eco-friendly practices.
Cluster 2 (8 items), summarised as Energy Storage, includes energy efficiency, energy utilisation, heat storage, phase change material, storage (materials), thermal conductivity, thermal energy, and thermal energy storage. Graphene-zeolite technology can significantly enhance energy storage in flooring systems by improving thermal energy storage and heat storage capabilities (Othman et al., 2024; Chen et al., 2024; Bello J. et al., 2024). The unique combination of graphene’s high thermal conductivity and zeolite’s ability to absorb and release heat makes the flooring system an effective energy storage solution. Phase change materials (PCMs) can be integrated into the flooring, allowing the material to absorb excess heat during the day and release it during cooler hours, thus maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature (Rathore et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2023). The studies continued that this energy storage ability reduces the reliance on external heating or cooling systems, enhancing energy efficiency and reducing energy bills. The improved thermal conductivity ensures that heat is evenly distributed across the floor, helping to maintain a stable environment without temperature fluctuations.
Furthermore, by focusing on energy utilisation and storage, graphene-zeolite technology in flooring can also contribute to sustainability efforts. Storing thermal energy in the material reduces the need for non-renewable energy sources, making buildings more energy efficient (Opeyemi, 2021). Thermal energy storage through these advanced materials allows the floor to act as a passive energy regulator, optimising energy use without additional energy consumption. Additionally, materials with better heat storage and thermal conductivity contribute to a reduction in overall energy consumption, leading to a smaller carbon footprint (Aftab et al., 2021). Farzaneh et al. (2021) added that integrating smart construction technologies like machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) can help predict energy consumption patterns, enabling more precise energy management. AI can further optimise heating and cooling systems based on real-time data, reducing energy waste. Digital twin technology allows for real-time simulations, enabling adjustments in building systems to maximise energy storage and utilisation. Moreover, incorporating augmented reality (AR) in the design phase can improve the precision of energy-efficient features, ensuring that thermal properties are correctly implemented (Kandasamy et al., 2024). Additionally, blockchain technology, automation, and robotics can improve transparency in managing the supply chain of these materials, ensuring sustainability in sourcing and helping install the flooring more efficiently, reducing labour costs and ensuring precise material placement (Khanfar et al., 2021; Dörfler et al., 2024). The combination of these technologies enhances the comfort and performance of indoor spaces and supports the broader goals of energy efficiency and sustainability, making buildings more adaptive to environmental demands.
4.3 Discussions
This review explores the potential of graphene-zeolite smart flooring as a catalyst for sustainable and digital transformation in the construction industry. As the sector seeks to align with global sustainability targets, including the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and net-zero carbon initiatives, there is increasing pressure to adopt materials and technologies that reduce energy consumption, improve environmental performance, and enable smarter infrastructure (Oladunni et al., 2025; Idowu et al., 2024a). Although often overlooked, flooring systems are critical in building energy use and thermal regulation. Studies indicate that floors can contribute significantly to heat loss and gain, especially in multi-storey buildings, underscoring the importance of material innovation in this area (Othman et al., 2024; Kheradmand et al., 2018). Graphene-zeolite composites represent a novel solution to these challenges, offering a multifunctional approach that integrates advanced materials with digital technologies.
4.3.1 Material composition and integration
The graphene-zeolite smart flooring system leverages the unique properties of both materials to deliver superior performance. Graphene, known for its exceptional thermal conductivity around (5,000 W m-1 K−1) at room temperature, highest Young’s modulus (∼1,100 GPa), fracture strength (130 GPa), and mobility of charge carriers (200,000 cm2 V−1 s-1), is ideal for applications requiring efficient heat distribution and energy harvesting (Chaudhary et al., 2024; Nguyen and Nguyen, 2016). Zeolite, a naturally occurring microporous mineral, enhances the composite’s environmental performance with its ability to adsorb moisture, filter pollutants, and provide thermal insulation (Danish et al., 2022; Tran et al., 2019). The integration method described involves dispersing graphene nanosheets with processed zeolite and a polymer binder to form a flexible, layered surface suitable for embedding in modern flooring systems. While the current study version does not detail experimental procedures such as component ratios or curing conditions, these aspects are earmarked for future research to ensure replicability and transparency (Rumman et al., 2024).
4.3.2 Perceptions and industry relevance
Survey responses from construction professionals, including quantity surveyors (43.4%) and construction managers (20.8%), highlighted strong support for innovative building materials that can simultaneously enhance performance and promote sustainability (Stephen S. S. et al., 2025). Respondents stressed the importance of integrating technologies like thermal energy storage, predictive analytics, and advanced construction equipment. Graphene’s ability to improve heat flow and energy storage, combined with zeolite’s moisture control and air purification, positions the composite as a transformative material in construction (Prajapati et al., 2024; Iwuanyanwu et al., 2024). These benefits align with industry needs for energy efficiency and eco-friendly practices, supporting the transition to smarter, greener buildings.
4.3.3 Digital technologies and future integration
Beyond physical material properties, graphene-zeolite smart flooring integrates seamlessly with digital technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), robotics, and blockchain (Kolhe et al., 2023). This integration enables real-time monitoring, adaptive energy management, and predictive maintenance. For instance, embedded sensors using graphene’s conductivity can track temperature, humidity, and occupancy, feeding data into AI systems for optimised heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning (HVAC) operations. Digital twin technology allows for dynamic simulations of floor performance under varying environmental conditions, supporting proactive decision-making during the building lifecycle (Kandasamy et al., 2024).
4.3.4 Research trends and future directions
Keyword analysis from the study revealed an intense research focus on ‘thermal energy storage,’ ‘energy efficiency,’ and ‘phase change materials,’ emphasising global interest in sustainable and smart material development (Rathore et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2023). While the graphene-zeolite composite shows promise in enhancing durability and energy performance, current research primarily focuses on laboratory-scale studies. Real-world trials and lifecycle assessments are needed to validate long-term performance, scalability, and cost-effectiveness (Danish et al., 2022; Bello S. F. et al., 2024). Addressing these gaps is essential to ensure the practical application of graphene-zeolite flooring in large-scale construction projects.
4.4 Comparing graphene-zeolite flooring with existing smart flooring technologies
Smart flooring has taken many forms recently, each developed to meet specific goals like energy efficiency, comfort, safety, or data collection. One example is phase change material (PCM)-embedded concrete, which stores and releases heat to help regulate indoor temperatures (Rashid et al., 2023). It is helpful in places with big temperature swings between day and night. Another common solution is radiant floor heating, which uses pipes or electric coils beneath the floor to provide even, quiet heating. While effective for warmth, these systems can be expensive to install and harder to maintain, especially in retrofitted buildings. Other smart flooring technologies are designed for sensing and interaction. For example, pressure-sensitive floors use piezoelectric or capacitive sensors to detect footsteps and movement (Iskandar et al., 2023). These are often used in smart homes, hospitals, or retail spaces to track activity, improve security, or automate lighting systems. Energy-harvesting floors, such as those using piezoelectric materials, can convert footsteps into small amounts of electrical energy. These have been tested in train stations and schools to power lights or sensors (Li et al., 2022). Another emerging category is touch-responsive floors that react to contact through embedded electronics. These are useful in interactive displays, rehabilitation therapy, and ambient computing environments. Each of these technologies brings value, but usually focuses on a single function: heating, sensing, or energy harvesting.
Beyond material benefits, graphene-zeolite flooring aligns with smart construction trends by enabling real-time monitoring and adaptive control through IoT, AI, and digital twins. Graphene’s conductivity supports embedding pressure and temperature sensors, while zeolite’s environmental properties complement health-focused monitoring systems (Stephen S. et al., 2025). This integration allows flooring to communicate with building management systems, regulate HVAC operations, and enhance energy efficiency. AI and machine learning can further predict usage patterns, optimise thermal energy storage, and reduce operational costs. Digital twin technology adds value by simulating floor performance under varying conditions, supporting predictive maintenance and lifecycle optimisation (Kandasamy et al., 2024).
By comparison, the graphene-zeolite flooring described in the study aims to solve more than just heating or cooling. Graphene brings electrical conductivity and sensing ability, which means the floor can respond to pressure, temperature changes, or other environmental signals. This makes it useful for smart building applications where real-time feedback is essential, such as in energy management or assisted living spaces. Zeolite adds another layer of benefit by improving thermal insulation and contributing to air purification. Its porous structure can trap pollutants like ammonia or heavy metals, which can help improve indoor air quality without needing separate filtration systems. While it may not store heat like PCM or directly warm a space like radiant floors, this dual functionality offers broader benefits, especially in buildings where sustainability and digital integration are priorities.
This suggests a shift from single-purpose flooring to materials that can do multiple things simultaneously. Traditional systems like PCM or radiant heating have clear value in thermal regulation, but they often stop there. The graphene-zeolite floor, on the other hand, combines insulation, air filtering, and smart sensing in a single layer. It’s not necessarily a replacement for other smart flooring technologies, but it represents a step toward flooring systems that contribute more directly to environmental goals and digital transformation. While its full technical performance still needs to be measured, especially in large-scale settings, the approach points to new ways flooring can support smarter, healthier buildings.
4.5 Life cycle assessment (LCA) of graphene-zeolite and other traditional materials
The study highlights the sustainability potential of graphene-zeolite smart flooring. Still, it does not present a complete life cycle assessment (LCA) compared to traditional flooring materials like cement-based concrete or ceramic tiles. A proper LCA would consider raw material extraction, manufacturing, installation, usage, and end-of-life disposal. Traditional concrete, for example, has a high environmental impact due to cement production, which accounts for roughly 8% of global CO2 emissions (Panagoda et al., 2023). In contrast, the graphene-zeolite composite is a more eco-friendly option because it is a naturally abundant mineral with low processing energy, and its porous structure can help regulate indoor air and reduce heating and cooling demands. Integrating phase change materials (PCMs) or smart sensors further supports energy efficiency during the use phase, potentially lowering operational emissions significantly over the floor’s lifetime compared to conventional materials, based on similar studies of thermally active floors (Bera et al., 2025).
However, the sustainability claim of the study becomes more complex when examining graphene production. Most commercially available graphene is produced through energy-intensive methods like chemical vapour deposition (CVD) or chemical exfoliation, which often involve harsh chemicals and significant energy inputs. This high embodied energy can offset some environmental benefits during the use phase. For example, producing the CO2 emitted by producing 1 g of CVD graphene would be above 115 tons equivalent, compared to around 0.9 kg of CO2 per kg of zeolite (Cossutta et al., 2017). If graphene is used in small quantities within the flooring, say, less than 5% by weight, the overall environmental impact may remain favourable, especially if the composite significantly reduces building energy needs. Moreover, newer, greener graphene production methods, such as bio-waste-derived graphene or liquid-phase exfoliation using less hazardous solvents, are being explored to lower the carbon footprint. For a complete sustainability assessment, future versions of the study should include a detailed LCA model quantifying emissions, energy use, and recyclability across the full lifecycle of the graphene-zeolite flooring system.
4.6 Case studies application of graphene-zeolite in improving building perfomance
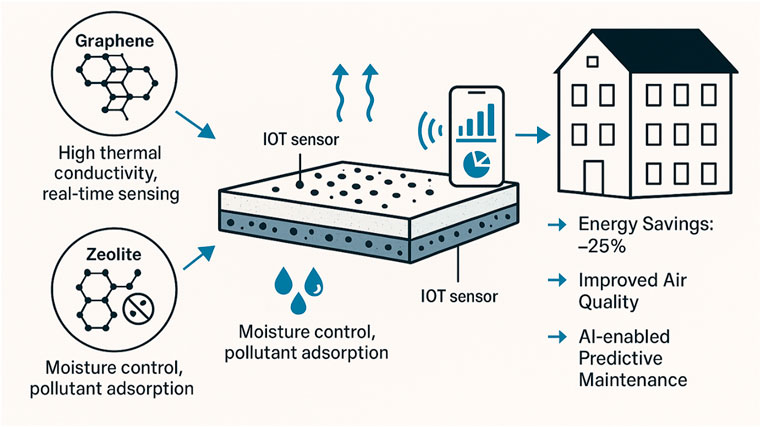
Figure 7 illustrates the conceptual framework of graphene-zeolite smart flooring as explored in the study, emphasising its dual functionality in enhancing thermal and environmental performance within buildings. Graphene’s high thermal conductivity and real-time sensing capability enable efficient heat distribution and integration with IoT systems for continuous monitoring. At the same time, zeolite contributes to moisture regulation and pollutant adsorption, improving indoor air quality. Embedded IoT sensors collect and transmit data to AI-based platforms for predictive maintenance and dynamic energy management. Together, these components support substantial energy savings (approximately 25%) and healthier indoor environments, aligning with the study’s objective of demonstrating how advanced materials can transform conventional flooring into multifunctional systems suitable for sustainable and smart building applications.
In relation to graphene-zeolite as a smart flooring catalyst for digital and sustainable construction, the figure embodies the convergence of advanced material science and intelligent infrastructure, marking a shift toward smarter, greener building systems. By combining graphene’s thermal efficiency with zeolite’s environmental benefits, the flooring system supports passive energy regulation and air purification, directly addressing sustainability goals such as reduced emissions and improved occupant health. Meanwhile, integrating IoT sensors and AI-driven analytics situates this solution within the broader digital transformation of the construction industry, enabling real-time performance tracking, predictive maintenance, and data-informed design decisions. This alignment of material performance with digital intelligence underscores the flooring’s potential as a scalable, future-ready platform that reduces operational energy use and enhances the responsiveness and resilience of built environments.
In northern Portugal, a pilot project integrated graphene-enhanced phase change materials (PCMs) into residential flooring using shape-stabilised composites. This approach enabled significant energy savings by reducing indoor temperature fluctuations by 2 °C–9 °C and cutting HVAC energy consumption by up to 30% during peak cooling and heating seasons (Pereira et al., 2025). The graphene nanoplatelets within the PCM matrix enhanced thermal conductivity by 136%, overcoming the common limitation of poor heat transfer in traditional PCMs. Meanwhile, zeolite’s microporous structure allowed passive humidity regulation and adsorption of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), further improving indoor air quality. Smart IoT sensors embedded in the flooring monitored temperature and occupancy patterns, feeding real-time data to AI-enabled systems for dynamic HVAC adjustment (Liu et al., 2023; Das et al., 2025; Stephen S. et al., 2025). After a year of operation, households reported improved thermal comfort and a measurable decline in energy bills, highlighting the feasibility of graphene-zeolite smart flooring as a sustainable solution for residential applications. In addition, studies across Europe have validated the effectiveness of PCM-integrated floors in different climates. For example, an integrated latent thermal energy storage (ILHTES) system with a PCM-to-air heat exchanger achieved an Energy Saving Ratio (ESR) ranging from 16% in Catania to 44.7% in Stockholm, underscoring the potential for substantial energy savings compared to conventional air conditioning systems (Zhang et al., 2024). Another study in Istanbul and Diyarbakir reported 12% and 9.7% energy load reductions, respectively, demonstrating consistent performance under temperate humid and hot–dry conditions (Murathan and Manioglu, 2024). These findings strengthen the case for graphene-zeolite flooring in residential energy management strategies.
In Tianjin, China, a novel phase change composite flooring system (PFCSS) that integrates microencapsulated PCMs with a solar water heating network to enhance thermal comfort and reduce energy consumption in institutional buildings was developed. Two full-scale buildings, one equipped with the PFCSS and a control building without it, were constructed for comparison. The system demonstrated strong performance using TRNSYS simulation modelling and experimental validation: the model produced a mean relative error of only 0.6%, while consistency analysis yielded a 95.1% agreement between simulated and real-world temperature behaviour (Lu et al., 2017). The flooring system effectively reduced indoor temperature fluctuations and prolonged heating periods during winter, leading to an energy savings of approximately 5.9% compared to the conventional setup while maintaining stable indoor conditions at 20 °C.
The success of this solar-integrated PCM flooring system highlights its potential for deployment in schools, administrative centres, or other low-rise public buildings with significant daytime occupancy and solar exposure. Unlike HVAC-dependent systems, this design leverages passive solar gain stored in the PCM and released during temperature drops, improving comfort without increasing operational complexity. The study also emphasised the system’s ability to shift heating loads, thereby reducing stress on centralised heating systems during peak demand periods. This approach demonstrates how smart flooring materials like graphene-zeolite composites could be adapted to future solar-assisted passive systems in institutional applications.
5 Conclusion
5.1 Summary of key findings
This study has shown that graphene-zeolite smart flooring can play a strong role in improving building performance and supporting sustainable development in construction. By combining graphene’s ability to conduct heat and electricity with zeolite’s thermal insulation and air purification properties, the flooring system offers multiple benefits. These include better energy use, thermal energy storage, indoor air quality improvement, and material strength. In addition, when connected to digital tools such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and digital twins, the flooring can monitor performance, manage energy use, and support predictive maintenance. Survey responses confirmed that industry professionals see value in using advanced materials and digital systems together to make buildings more efficient, durable, and intelligent. The bibliometric analysis also confirmed growing academic interest in key areas such as energy storage and smart materials, which supports the study’s findings.
5.2 Limitations and methodological gaps
While the potential of graphene-zeolite flooring is clear, the study acknowledges that several key aspects were not directly tested. No experiments were conducted to measure thermal energy storage or conductivity using methods like differential scanning calorimetry or hot disk analysis. Similarly, long-term modelling and real-world durability tests are lacking. Though scanning electron microscopy from previous studies helped understand the material’s microstructure, this does not replace actual performance testing. While the composite shows strong theoretical promise, its behaviour in different building types and climates remains unknown. This highlights a clear research gap between material design and full-scale application. Finally, the survey did not provide detailed explanations or definitions for some terminologies in the questionnaire. This might have instigated varying degrees of responses. However, high mean scores obtained for variables like Advanced Building Materials and Techniques and Human-Centric Design suggest that these topics are widely recognised as important, even without detailed technical context.
5.3 Implications for practice and policy
For architects, engineers, and construction managers, the graphene-zeolite floor offers a way to build more energy-efficient and environmentally responsible spaces. Its passive thermal storage capabilities and compatibility with smart monitoring tools suggest that it can reduce energy bills and support better building management. However, given the current stage of development, these materials should first be used in pilot projects or demonstration buildings. Policymakers and industry leaders can support adoption by setting clear performance standards, offering funding for material testing, and encouraging research that bridges the gap between laboratory results and field performance.
5.4 Future research priorities
Future research should focus on testing the flooring under real-world conditions and across different environmental settings. This includes assessing how it performs over time regarding heat storage, air filtration, and mechanical durability. Advanced modelling tools like digital twins can simulate performance and predict energy savings and wear. Researchers should also explore using phase change materials (PCMs) as additives and test how they interact with the graphene-zeolite base. Finally, the study recommends looking into low-impact, scalable methods for graphene production to ensure that the sustainability gains from its use are not offset by manufacturing emissions.
5.5 Contribution to global sustainability goals
The graphene-zeolite smart flooring system supports several global goals for sustainable development. It aligns with SDG 7 by promoting energy efficiency through passive heat regulation. It supports SDG 9 by encouraging innovation in construction materials and integration with digital tools. It also helps advance SDG 13 by lowering building-related emissions and supporting climate-friendly construction practices. While more validation is needed, the approach offers a strong foundation for creating functional, responsive, efficient, and sustainable buildings.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
SS: Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft. CA: Supervision, Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft. AO: Methodology, Data curation, Writing – review and editing, Software, Writing – original draft. AI: Writing – review and editing, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Validation. SA: Writing – review and editing, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Methodology.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. During the preparation of this work, the authors used Quilbot and Grammarly in order to improve the readability and language of the manuscript. After using this tool, the authors reviewed and edited the content as needed and take full responsibility for the content of the published article.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abed, J., Rayburg, S., Rodwell, J., and Neave, M. (2022). A review of the performance and benefits of mass timber as an alternative to concrete and steel for improving the sustainability of structures. Sustainability 14 (9), 5570–24. doi:10.3390/su14095570
Aftab, W., Usman, A., Shi, J., Yuan, K., Qin, M., and Zou, R. (2021). Phase change material-integrated latent heat storage systems for sustainable energy solutions. Energy Environ. Sci. 14 (8), 4268–4291. doi:10.1039/D1EE00527H
Alassaf, Y. (2024). Comprehensive review of the advancements, benefits, challenges, and design integration of energy-efficient materials for sustainable buildings. Buildings 14 (9), 2994–41. doi:10.3390/buildings14092994
Amran, M., Onaizi, A. M., Fediuk, R., Vatin, N. I., Muhammad Rashid, R. S., Abdelgader, H., et al. (2022). Self-healing concrete as a prospective construction material: a review. Materials 15 (9), 3214–3246. doi:10.3390/ma15093214
Asghari, N., and Memari, A. M. (2024). State of the art review of attributes and mechanical properties of hempcrete. Biomass 4 (1), 65–91. doi:10.3390/biomass4010004
Baas, J., Schotten, M., Plume, A., Côté, G., and Karimi, R. (2020). Scopus as a curated, high-quality bibliometric data source for academic research in quantitative science studies. Quant. Sci. Stud. 1 (1), 377–386. doi:10.1162/qss_a_00019
Bello, S. F., Wada, I. U., Ige, O. B., Chianumba, E. C., and Adebayo, S. A. (2024a). AI-driven predictive maintenance and optimization of renewable energy systems for enhanced operational efficiency and longevity. Int. J. Sci. Res. Arch. 13 (1), 1–15. doi:10.30574/ijsra.2024.13.1.1992
Bello, J., Adetoro, P., Mogaji, I., and Stephen, S. (2024b). Exploring the feasibility and benefits of integrating nature-based solutions in stealth construction practices. Intell. Build. Int. 16 (1), 23–36. doi:10.1080/17508975.2024.2378705
Bera, M., Das, S., Garai, S., Dutta, S., Choudhury, M. R., Tripathi, S., et al. (2025). Advancing energy efficiency: innovative technologies and strategic measures for achieving net zero emissions. Carbon Footprints 4 (1), 3–25. doi:10.20517/cf.2024.48
Bolpagni, M., Gavina, R., Ribeiro, D., and Arnal, I. P. (2022). Shaping the future of construction professionals. Industry 4.0 built Environ. Methodol. Technol. Ski. 20, 1–26. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-82430-3_1
Brunetti, D., Gena, C., and Vernero, F. (2022). Smart interactive technologies in the human-centric factory 5.0: a survey. Appl. Sci. 12 (16), 7965–30. doi:10.3390/app12167965
Carcassi, O. B., Salierno, R., Falcinelli, P. A., Paoletti, I. M., and Ben-Alon, L. (2024). Upscaling natural materials in construction: earthen, fast-growing, and living materials. Sustainability 16 (18), 7926–20. doi:10.3390/su16187926
Casini, M. (2022). Extended reality for smart building operation and maintenance: a review. Energies 15 (10), 3785–36. doi:10.3390/en15103785
Chaudhary, V., Gaur, P., and Rustagi, S. (2024). Sustainable materials and technologies. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 40, 1–15. doi:10.1016/j.susmat.2024.e00952
Chen, L., Zhang, Y., Chen, Z., Dong, Y., Jiang, Y., Hua, J., et al. (2024). Biomaterials technology and policies in the building sector: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 22 (2), 715–750. doi:10.1007/s10311-023-01689-w
Cossutta, M., McKechnie, J., and Pickering, S. J. (2017). A comparative LCA of different graphene production routes. Green Chem. 19 (24), 5874–5884. doi:10.1039/C7GC02444D
Cucuzza, R., Rad, M. M., Domaneschi, M., and Marano, G. C. (2024a). Sustainable and cost-effective optimal design of steel structures by minimizing cutting trim losses. Autom. Constr. 167, 105724–20. doi:10.1016/j.autcon.2024.105724
Cucuzza, R., Aloisio, A., Rad, M. M., and Domaneschi, M. (2024b). Constructability-based design approach for steel structures: from truss beams to real-world inspired industrial buildings. Autom. Constr. 166, 105630–17. doi:10.1016/j.autcon.2024.105630
Cucuzza, R., Olivo, J., Bertagnoli, G., Ferro, G. A., and Marano, G. C. (2025). Performance-based optimization of steel exoskeletons: an alternative approach to standard regulations. J. Build. Eng. 104, 112177–20. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2025.112177
Dagou, H., Gürgün, A., Koc, K., and Kunkcu, H. (2024). Navigating the landscape of innovative technologies in construction project management: a comprehensive review. Proc. Eng. Sci. 6 (4), 1621–1632. doi:10.24874/pes06.04.021
Danish, A., Ozbakkaloglu, T., Mosaberpanah, M. A., Salim, M. U., Bayram, M., Yeon, J. H., et al. (2022). Sustainability benefits and commercialization challenges and strategies of geopolymer concrete: a review. J. Build. Eng. 58, 1–25. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2022.105005
Das, S., Mazumdar, H., Khondakar, K. R., and Kaushik, A. (2025). Machine learning integrated graphene oxide-based diagnostics, drug delivery, analytical approaches to empower cancer diagnosis. BMEMat 3 (1), e12117–e12124. doi:10.1002/bmm2.12117
de Winter, J. C., Dodou, D. I., and Wieringa, P. A. (2009). Exploratory factor analysis with small sample sizes. Multivar. Behav. Res. 44 (2), 147–181. doi:10.1080/00273170902794206
Dörfler, K., Dielemans, G., Leutenegger, S., Jenny, S. E., Pankert, J., Sustarevas, J., et al. (2024). Advancing construction in existing contexts: prospects and barriers of 3D printing with Mobile robots for building maintenance and repair. Cem. Concr. Res. 186, 1–14. doi:10.1016/j.cemconres.2024.107656
Farzaneh, H., Malehmirchegini, L., Bejan, A., Afolabi, T., Mulumba, A., and Daka, P. P. (2021). Artificial intelligence evolution in smart buildings for energy efficiency. Appl. Sci. 11 (2), 763–30. doi:10.3390/app11020763
Geyer, P., and Singaravel, S. (2018). Component-based machine learning for performance prediction in building design. Appl. Energy. 228, 1439–1453. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.07.011
Ibrahim, J. E., Tihtih, M., Kurovics, E., Gömze, L. A., and Kocserha, I. (2022). Innovative glass-ceramic foams prepared by alkali activation and reactive sintering of clay containing zeolite (zeolite-poor rock) and sawdust for thermal insulation. J. Build. Eng. 59, 105160–17. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2022.105160
Idowu, A. O., Aigbavboa, C., Oke, A. E., and Aghimien, D. (2024a). Barriers to low carbon retrofitting of higher educational building projects. Proc. Int. Conf. Sci. Eng. Bus. Sustain. Dev. Goals (SEB4SDG), Omu-Aran, Niger., 1–4. doi:10.1109/SEB4SDG60871.2024.10630026
Idowu, A. O., Aigbavboa, C., Oke, A. E., and Ogunbayo, B. F. (2024b). Environmental impact of carbon emission in the South African construction industry. Proc. IEEE 5th Int. Conf. Electro-Comput. Technol. Hum. (NIGERCON), Ado Ekiti, Niger., 1–3. doi:10.1109/NIGERCON62786.2024.10927182
Ielo, I., Giacobello, F., Sfameni, S., Rando, G., Galletta, M., Trovato, V., et al. (2021). Nanostructured surface finishing and coatings: functional properties and applications. Materials 14 (11), 2733–2739. doi:10.3390/ma14112733
Iskandar, A. A. M., Alfonse, M., and El-Horabty, E. S. M. (2023). A comparative study of the different features engineering techniques based on the sensor used in footstep identification and analysis using the floor-based approach. Int. J. Intelligent Comput. Inf. Sci. 23 (4), 66–95. doi:10.21608/ijicis.2023.249378.1307
Iwuanyanwu, O., Gil-Ozoudeh, I., Okwandu, A. C., and Ike, C. S. (2024). The role of green building materials in sustainable architecture: innovations, challenges, and future trends. Int. J. Appl. Res. Soc. Sci. 6 (8), 1935–1950. doi:10.51594/ijarss.v6i8.1476
Kandasamy, P., Veeramani, T. K., Munusamy, V., Sanjth, S., Amurthavalli, S., and Balaji, B. C. (2024). Augmented reality control based energy management system for residence. Recent Adv. Electr. Electron. Eng. 17 (9), 908–917. doi:10.2174/0123520965263887231026071657
Kennedy, I. (2022). Sample size determination in test-retest and Cronbach alpha reliability estimates. Br. J. Contemp. Educ. 2 (1), 17–29. doi:10.52589/BJCE-FY266HK9
Khanfar, A. A., Iranmanesh, M., Ghobakhloo, M., Senali, M. G., and Fathi, M. (2021). Applications of blockchain technology in sustainable manufacturing and supply chain management: a systematic review. Sustainability 13 (14), 7870–20. doi:10.3390/su13147870
Kheradmand, M., Azenha, M., Castro-Gomes, J. P., and De Aguiar, J. L. B. (2018). Energy benefits of cement-based plaster containing hybrid phase-change material. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Constr. Mater. 171, 117–125. doi:10.1680/jcoma.17.00027
Kolhe, N. S., Panicker, A., Mhatre, S., and Vichare, J. (2023). Industry 4.0 and chemical industry: the technology enablers behind strategic growth of chemical companies. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 11 (1), 58–71. doi:10.22214/ijraset.2023.48486
Krzywanski, J., Sosnowski, M., Grabowska, K., Zylka, A., Lasek, L., and Kijo-Kleczkowska, A. (2024). Advanced computational methods for modeling, prediction and optimization—a review. Materials 17 (14), 3521–3529. doi:10.3390/ma17143521
Kumar, S. S., Bashir, S., Ramesh, K., and Ramesh, S. (2021). New perspectives on graphene/graphene oxide based polymer nanocomposites for corrosion applications: the relevance of the graphene/polymer barrier coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 154, 106215–106233. doi:10.1016/j.porgcoat.2021.106215
Le, D. T., Carbonnier, B., Hamadi, S., Grande, D., Fois, M., Naili, S., et al. (2024). Toward the development of graphene/chitosan biocomposite aerogels with enhanced mechanical and thermal insulation performance. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 6 (21), 13132–13146. doi:10.1021/acsapm.4c02301
Li, X., Li, L., Li, N., Bao, M., Bao, Y., Wu, Z., et al. (2022). Sustainable production of engineered bamboo scrimber composites for construction and flooring applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 347, 128615–128619. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.128615
Lin, C. (2021). The role of sustainable building materials in advancing ecological construction. J. Energy Environ. Policy Options. 4 (1), 15–21.
Liu, L., Zhang, Y., Zhang, S., and Tang, B. (2023). Advanced phase change materials from natural perspectives: structural design and functional applications. Adv. Sci. 10 (22), 2207652–13. doi:10.1002/advs.202207652
Lu, S., Zhao, Y., Fang, K., Li, Y., and Sun, P. (2017). Establishment and experimental verification of TRNSYS model for PCM floor coupled with solar water heating system. Energy Build. 140, 245–260. doi:10.1016/j.enbuild.2017.02.018
Markiv, T., Sobol, K., Franus, M., and Franus, W. (2016). Mechanical and durability properties of concretes incorporating natural zeolite. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2, 554–562. doi:10.1016/j.acme.2016.03.013
Mempouo, B., Cooper, E., and Riffat, S. B. (2010). Novel window technologies and the code for sustainable homes in the UK. Int. J. Low-Carbon Technol. 5 (4), 167–174. doi:10.1093/ijlct/ctq013
Mondal, M., Biswas, B., Garai, S., Sarkar, S., Banerjee, H., Brahmachari, K., et al. (2021). Zeolites enhance soil health, crop productivity and environmental safety. Agronomy 11 (3), 448–29. doi:10.3390/agronomy11030448
Mostafaei, H., and Bahmani, H. (2024). Sustainable high-performance concrete using zeolite powder: mechanical and carbon footprint analyses. Buildings 14 (11), 3660–18. doi:10.3390/buildings14113660
Murathan, E. K., and Manioglu, G. (2024). A simulation-based evaluation of using PCMs in buildings for energy efficiency under different climate conditions. J. Energy Storage. 75 (109738), 1–15. doi:10.1016/j.est.2023.109738
Nguyen, B. H., and Nguyen, V. H. (2016). Promising applications of graphene and graphene-based nanostructures. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 7 (2), 023002–023016. doi:10.1088/2043-6262/7/2/023002
Oladunni, O. J., Lee, C. K., Ibrahim, I. D., and Olanrewaju, O. A. (2025). Advances in sustainable additive manufacturing: a systematic review for construction industry to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions. Front. Built Environ. 11 (2025), 1535626–1535642. doi:10.3389/fbuil.2025.1535626
Olivo, J., Cucuzza, R., Bertagnoli, G., and Domaneschi, M. (2024). Optimal design of steel exoskeleton for the retrofitting of RC buildings via genetic algorithm. Comput. Struct. 299, 107396–18. doi:10.1016/j.compstruc.2024.107396
Omrany, H., Al-Obaidi, K. M., Husain, A., and Ghaffarianhoseini, A. (2023). Digital twins in the construction industry: a comprehensive review of current implementations, enabling technologies, and future directions. Sustainability 15 (14), 10908–10926. doi:10.3390/su151410908
Opeyemi, B. M. (2021). Path to sustainable energy consumption: the possibility of substituting renewable energy for non-renewable energy. Energy 228, 1–9. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2021.120519
Othman, F. E., Nordin, N. A., Ismail, N., Zakria, H. S., Junoh, H., and Aziz, M. H. (2024). A review on sustainable graphene production from rice husks: strategies and key considerations. Chem. Eng. J. 497, 154408–154428. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2024.154408
Pan, N. H., and Isnaeni, N. N. (2024). Integration of augmented reality and building information modeling for enhanced construction inspection—a case study. Buildings 14 (3), 612–621. doi:10.3390/buildings14030612
Panagoda, S. S., Ranasinghe, H., Perera, V., Sandunika, I., Tilanka, G., Alwis, S., et al. (2023). Cement manufacturing process and its environmental impact. J. Res. Technol. Eng. 4 (3), 161–168.
Pereira, J., Souza, R., Oliveira, J., and Moita, A. (2025). Phase change materials in residential buildings: challenges, opportunities, and performance. Materials 18 (9), 2063–2079. doi:10.3390/ma18092063
Prajapati, D., Jabborova, D., Saharan, B. S., Singh, N., Patani, A., Singh, S., et al. (2024). Bionanotechnology: a paradigm for advancing environmental sustainability. Indian J. Microbiol. 18, 306–332. doi:10.1007/s12088-024-01389-1
Prudente, I. N., dos Santos, H. C., Fonseca, J. L., de Almeida, Y. A., de Fátima Gimenez, I., and Barreto, L. S. (2024). Graphene family (GFMs), carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and carbon black (CB) on smart materials for civil construction: Self-cleaning, self-sensing and self-heating. J. Build. Eng. 9, 110175–16. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2024.110175
Rashid, F. L., Al-Obaidi, M. A., Dulaimi, A., Bernardo, L. F. A., Eleiwi, M. A., Mahood, H. B., et al. (2023). A review of recent improvements, developments, effects, and challenges on using phase-change materials in concrete for thermal energy storage and release. J. Compos. Sci. 7 (9), 352–34. doi:10.3390/jcs7090352
Rathore, P. K., Gupta, N. K., Yadav, D., Shukla, S. K., and Kaul, S. (2022). Thermal performance of the building envelope integrated with phase change material for thermal energy storage: an updated review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 79, 103690–28. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2022.103690
Rumman, R., Bediwy, A., and Alam, M. S. (2024). Revolutionizing concrete durability: case studies on encapsulation-based chemical (autonomous) self-healing techniques and future directions–A critical review. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 20, e03216–e03232. doi:10.1016/j.cscm.2024.e03216
Saadat, F., Rehman, H. A., Zheng, X., Pan, Q., Wang, B., and Gan, Z. (2024). Progress in zeolite–water adsorption technologies for energy-efficient utilization. Energy 30, 1–30. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2024.133001
Sabet, M. (2024). Exploring biodegradable polymer composites for sustainable packaging: a review on properties, manufacturing techniques, and environmental impacts. Iran. Polym. J. 34, 123–142. doi:10.1007/s13726-024-01365-y
Saleem, H., Edathil, A., Ncube, T., Pokhrel, J., Khoori, S., Abraham, A., et al. (2016). Mechanical and thermal properties of thermoset–graphene nanocomposites. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 301 (3), 231–259. doi:10.1002/mame.201500335
Stephen, S., and Aigbavboa, C. (2025). Enhancing academia–industry partnerships for sustainable building: a change framework for research and innovation integration in Sub-Saharan Africa. Sustainability 17 (9), 3863–35. doi:10.3390/su17093863
Stephen, S. S., Oke, A. E., Aigbavboa, C. O., Akinradewo, O. I., Adetoro, P. E., and Ikuabe, M. (2025a). “Prelims,” in Stealth construction: integrating practices for resilience and sustainability. Leeds: Emerald Publishing Limited. doi:10.1108/978-1-83608-182-120251013
Stephen, S., Aigbavboa, C., and Oke, A. (2025b). Revolutionising green construction: harnessing zeolite and AI-driven initiatives for net-zero and climate-adaptive buildings. Buildings 15 (6), 885–27. doi:10.3390/buildings15060885
Stratton, S. J. (2021). Population research: convenience sampling strategies. Disaster Med. 36 (4), 373–374. doi:10.1017/S1049023X21000649
Thakur, A., and Kumar, A. (2024). “Chemical and physical properties of nano-hybrid smart coatings,” in Nano-hybrid smart coatings: advancements in industrial efficiency and corrosion resistance, 1469, 59–94. doi:10.1021/bk-2024-1469.ch004
Tran, Y. T., Lee, J., Kumar, P., Kim, K. H., and Lee, S. S. (2019). Natural zeolite and its application in concrete composite production. Compos. Part B Eng. 165, 354–364. doi:10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.12.084
Van Eck, N. J., and Waltman, L. (2014). “Visualizing bibliometric networks,” Meas. Sch. Impact Methods Pract. 1 285–320. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-10377-8_13
Wang, Q., Zhang, J., and Ho, J. C. (2020). Zeolite to improve strength-shrinkage performance of high-strength engineered cementitious composite. Constr. Build. Mater. 234, 117335–117339. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117335
Wang, K., Guo, F., Zhang, C., and Schaefer, D. (2022). From industry 4.0 to construction 4.0: barriers to the digital transformation of engineering and construction sectors. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 31 (1), 136–158. doi:10.1108/ECAM-05-2022-0383
Williams, B., Onsman, A., and Brown, T. (2010). Exploratory factor analysis: a five-step guide for novices. Australas. J. Paramed. 8, 1–13. doi:10.33151/ajp.8.3.93
Xin, G., Yao, T., Sun, H., Scott, S. M., Shao, D., Wang, G., et al. (2015). Highly thermally conductive and mechanically strong graphene fibers. Science 349 (6252), 1083–1087. doi:10.1126/science.aaa6502
Yadav, M., and Agarwal, M. (2021). Biobased building materials for sustainable future: an overview. Mater. Today Proc. 43 (5), 2895–2902. doi:10.1016/j.matpr.2021.01.165
Yadav, M., and Saini, A. (2022). Opportunities and challenges of hempcrete as a building material for construction: an overview. Mater. Today Proc. 65, 2021–2028. doi:10.1016/j.matpr.2022.05.576
Yu, X., Cheng, H., Zhang, M., Zhao, Y., Qu, L., and Shi, G. (2017). Graphene-based smart materials. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2 (9), 17046–3. doi:10.1038/natrevmats.2017.46
Zhang, T., Doan, D. T., and Kang, J. (2023). Application of building information modeling-blockchain integration in the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction/Facilities management industry: a review. J. Build. Eng. 12, 107551–17. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2023.107551
Keywords: construction innovation, energy efficiency, graphene, zeolite, smart floor, sustainability
Citation: Stephen S, Aigbavboa C, Oke A, Idowu A and Adekunle S (2025) Graphene-zeolite smart flooring as a catalyst for digital and sustainable transformation in construction: a review. Front. Built Environ. 11:1640950. doi: 10.3389/fbuil.2025.1640950
Received: 04 June 2025; Accepted: 04 August 2025;
Published: 29 August 2025.
Edited by:
Obuks Ejohwomu, The University of Manchester, United KingdomReviewed by:
Raffaele Cucuzza, Polytechnic University of Turin, ItalyOluwole Joseph Oladunni, Durban University of Technology, South Africa
Copyright © 2025 Stephen, Aigbavboa, Oke, Idowu and Adekunle. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Seyi Stephen, c2V5aXN0ZXBoZW4uc3NAZ21haWwuY29t
 Seyi Stephen
Seyi Stephen Clinton Aigbavboa1
Clinton Aigbavboa1 Ayodeji Oke
Ayodeji Oke Ayobami Idowu
Ayobami Idowu