- 1 Centre for Smart Modern Construction, Western Sydney University, Kingswood, NSW, Australia
- 2 Commnia Pty Ltd., Sydney, NSW, Australia
The rapid advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the integration of digital technologies present transformative opportunities to improve productivity, safety, and efficiency in construction project management. This study is based on the Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis extension for Scoping Review (PRISMA-ScR), and 144 research articles were reviewed. The application of deep learning (DL)-enabled visual computing (VC) in construction is investigated, and a comprehensive analysis of the technological application and the DL models is conducted. While prior reviews surveyed computer vision in construction broadly, this study’s systematic review focused exclusively on deep learning-enabled VC and its integration with eight digital technologies through a comprehensive mapping of algorithm trends, application domains, and real-world integration challenges. The systematic analysis reveals five primary application domains: Object Detection (33%), Construction Safety (28%), Damage Detection (22%), Construction Quality (9%), and Productivity Analysis (8%). Additionally, the integration of DL-enabled VC with emerging digital technologies such as Automatic Construction Robotics, Unmanned Ground Vehicles, Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, LiDAR, Building Information Modelling, Blockchain, Intelligent Internet of Things, and Digital Twin in construction applications is reviewed extensively. An in-depth analysis of the DL algorithms and models deployed for applications revealed annual trends while illustrating the prominence of Convolutional Neural Networks and their derivatives, such as YOLO, R-CNN, Mask R-CNN, Faster R-CNN, SSD, U-Net, VGG, etc. Finally, the research identified gaps in existing research, proposing directions for prospective investigations of research gaps in areas such as real-world scalability, data quality, and ethical considerations, focusing on future work in explainable AI, edge computing, and privacy-preserving VC.
1 Introduction
The construction sector is vital for any nation to support the development of infrastructure, which results in overall economic development while contributing 13% of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) (Hoedemaekers, 2024; Nisa and Khalid, 2024). Further, it is contributing 7% to job creation and the development of infrastructure (Opoku et al., 2021; Rodrigo et al., 2024). The widespread adoption of modern construction processes served as a catalyst for the development of the modern construction industry, facilitating extensive projects in housing, industry, transport, and city development (Kaya and Dikmen, 2024). However, the construction industry is plagued with multiple challenges, such as poor project performance, quality-related issues, safety concerns, project delays, and cost overruns (Yap et al., 2019). The isolation of processes, complicated stakeholders and the temporary nature of construction projects have increased the level of issues, resulting in delivering large construction projects being challenging (Wuni et al., 2024).
In recent years, there has been a notable surge in the utilisation of technology for construction. Digital transformation has promised a revolution in construction (Perera S. et al., 2023; Begić et al., 2022; Hewavitharana et al., 2025). Importantly, the stakeholders and policymakers have considered digitalisation as an important solution for the challenges in the construction industry, resulting in a strong interest in supporting digitalisation within the industry (Pal et al., 2024; Kaya and Dikmen, 2024). Digital technologies such as Building Information Modelling (BIM), Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), Extended Reality (XR), Blockchain, Internet of Things (IoT), Digital Twins, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Big Data (BD), Cloud Computing (CC), Geographic Information System (GIS), Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV), Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGV), Terrestrial Laser Scanning (TLS) and Robotics can be integrated to create robust solutions for the construction industry by enhancing productivity, sustainability, efficiency, and safety (Baduge et al., 2022; Perera et al., 2020; Mohammadi et al., 2023; Pan and Zhang, 2021; Sánchez et al., 2024; Musarat et al., 2024). The use of Blockchain in construction for enhanced trust and transparency is discussed by multiple scholars (Hewavitharana et al., 2023; Perera et al., 2020; Nanayakkara et al., 2021). Ali et al. (2022) and Sompolgrunk et al. (2023) had presented the integration of multiple digital technologies with BIM. BIM is implemented in modern construction projects to achieve integration and efficiency (Greenwood et al., 2010; Cepa et al., 2023; Zhu et al., 2023; Corrado et al., 2023).
Bahoo et al. (2023) defined AI as the ability of a software system to interpret data and influence hardware to improve decision-making, problem-solving, innovativeness, and adaptation. The layered architecture of Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) simulates the feature extraction and classification capability of the human brain (Pouyanfar et al., 2018; Akinosho et al., 2020; Janiesch et al., 2021). The application of Artificial Intelligence in construction was worth 429.2 million USD in 2018, and the projection for 2026 is to be 4.51 billion USD. 63% of the total market share comprised Machine Learning (ML) and DL algorithms/models (Reports and Data, 2019). While automation and digitalisation offer undeniable benefits to the construction industry, including enhanced performance and efficiency, this technological revolution concurrently creates novel challenges and risks (Salami Pargoo and Ilbeigi, 2023; Hewavitharana et al., 2021).
The utilisation of digital technologies applies to the entire life-cycle of construction processes and has generated a substantial amount of multidimensional data, which necessitates analysis through big data analytics (Nanayakkara et al., 2015; Lu et al., 2025). Moreover, the availability of refined data volumes has facilitated the implementation of data-driven AI applications within the construction industry (Li et al., 2023). Similarly Jan et al. (2023) and Das et al. (2023) highlighted the emergence of AI in conjunction with the vast amount of data acquired through modern digital technologies, which have emerged as crucial components of the cyberphysical systems that form the foundation of the fourth industrial revolution (I4.0). Adaptation of AI techniques possesses the potential to surpass conventional digital technologies in delivering enhanced technical solutions for complex construction industry challenges, thereby contributing to the achievement of desired sustainability goals (Collins et al., 2021; Moragane et al., 2022; Perera et al., 2025a). Establishing similar arguments, a report from Ernst and Young (2021) had presented AI as the new Frontier of digitalisation in the construction industry. Kor et al. (2022), Mondal and Chen (2022) and Nyokum and Tamut (2025) had strengthened the argument by stating that AI and related technologies are best suited for the resolution of uncertainties in the construction industry. AI embedded systems are widely available and have a high usage among users, and explainable AI technologies are making such systems trustworthy (Perera et al., 2025b). However, despite the promising capabilities of AI, the construction industry has yet to fully leverage its transformative potential, hindered by various existing challenges, including data silos and quality issues, workforce skills shortages, interoperability and standardisation gaps, high implementation costs, and stakeholder resistance, which continue to hinder the transformative potential of AI in construction. (Abioye et al., 2021; Elghaish et al., 2022b).
This systematic review aims to analyse the application of DL-driven VC technologies in the construction industry. It is important to evaluate the impact on construction project management systematically by analysing the trends, gaps, and challenges. In the evaluation of the impact of DL-driven VC in the construction sector, key performance indicators (KPIs), namely, efficiency enhancement, safety enhancement, quality enhancement, and productivity enhancement, were identified, and the application categorisation was developed accordingly. While the importance of visual computing in construction is increasingly recognised, existing review literature often surveys traditional computer vision techniques or focuses on specific, isolated applications. Therefore, conducting this systematic review is essential to provide insights into the current state and future directions of DL-driven VC in the construction sector. Furthermore, it systematically maps the evolving landscape of DL algorithms used in VC for construction, highlighting prominent models and annual trends, by identifying the specific integration points of DL-enabled VC with various digital technologies.
The objectives of the review study are to investigate the current applications of deep learning–enabled visual computing in construction, to examine these applications integrated with digital technologies, and lastly to explore gaps that remain for future research and industry adoption. The paper is structured to provide a comprehensive outline of the results presented. A comprehensive literature review follows the introduction. The methodology section of the paper outlines the method used to conduct the systematised review, including the search strategy. The results section visualises the extracted findings and analysis. The discussion section systematically presents the findings, focusing on the opportunities, trends, gaps, and challenges in the application of DL-driven VC in the construction industry.
2 Deep learning enabled visual computing
Computer Vision (CV) and Image Processing (IP) a segments of technology achieving rapid growth of innovation in multiple disciplines such as medical applications, smart device applications, industrial applications, video monitoring, intelligent transportation, remote sensing, military applications, etc (Lepcha et al., 2023). Visual Computing (VC) comprises CV and IP techniques; that is, VC is the broad field of extracting information from visual data. Within VC, CV focuses on interpreting image and video content, while IP enhances and manipulates raw images to support analysis. (Xu et al., 2021). VC applications are based on extracting information from the input images or videos for meaningful interpretation using AI (Ji et al., 2023; Xiong and Tang, 2021). Theoretically, VC is an interdisciplinary technology related to the automated extraction of suitable information from visual input data for understanding or representing the physical world, either qualitatively or quantitatively (Spencer et al., 2019; Perera P. et al., 2023).
Visual data capturing in construction projects for a variety of purposes has resulted in image datasets consisting of 400,000 images per large-scale project (Paneru and Jeelani, 2021). The high availability of visual data, coupled with advancements in AI technologies, has significantly enhanced the feasibility of computer vision-based applications, leading to a projected enhancement in the accuracy of potential deployments (Ekanayake et al., 2021; Khallaf and Khallaf, 2021; Hamledari et al., 2017). DL-driven VC is transforming the technological landscape with their layered architecture of extracting features of visuals (Fan, 2023; O’Mahony et al., 2020; Delhi et al., 2020).
The performance related to accuracy, robustness, and scalability of DL algorithms and models in various computer vision tasks, such as image classification, object detection, image retrieval and semantic segmentation, is higher compared to the traditional CV techniques (Chai et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2021; Nomura et al., 2022). The affordable computing power and the availability of related hardware have made the use of DL for VC a possibility. Specific hardware devices, such as GPUs with parallel multicore systems, have facilitated the resource-intensive computer vision application as a possibility (Afif et al., 2020; Inazumi et al., 2020).
Goswami (2018), Chen S. et al. (2023), Elghaish et al. (2022c) and Elghaish et al. (2022a) had identified the wide use of VC in the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) industry while Zhao et al. (2024) highlighted the capability to deliver advanced solutions when compared to sensor-based technologies. However, Pal and Hsieh (2021), Ekanayake et al. (2022) and Hamledari et al. (2017) had identified a few limitations of DL-driven VC, such as changing viewpoints, highly cluttered spaces, obstructions, and varied illumination conditions. Further achromatic characteristics of objects, such as studs and electrical outlets, can result in poor detection, while the small size of some items has increased this complexity (Mohammed Abdelkader, 2022).
The following methodology section of the study highlights the systematised approach applied to the comprehensive review of the application of DL-driven VC.
3 Methodology
The study adopts an approach that follows a systematic literature review (SLR) to provide a comprehensive understanding of the use of DL-driven VC applications in the construction industry. Further, it has adopted the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) to conduct a transparent and replicable SLR in order to extrapolate the findings of the study (Das et al., 2023).
A systematic review presents a summary of previous studies in the specific field of search and enables the identification of knowledge gaps in the published papers (Watson and Webster, 2020; Mishra and Mishra, 2023). Eriqat et al. (2024) have stated that a systematic literature review should follow an explicit methodology detailing the procedure used to be reproducible and methodical, which heavily relies on the exploitation of prominent research databases, namely, Web of Science and Scopus. Further, this systematic review adheres to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines, (Hijriyah et al., 2024). PRISMA guidelines will ensure the reproducibility of the analysis and the results while ensuring transparent reporting of the study (Mishra and Mishra, 2023).
The quality assessment of the articles filtered through the systematic review is essential to ensure transparency, methodological rigour, completeness of technical detail, and reproducibility (Mushtaha et al., 2025). The methodical process was based on analysing the technological significance driven by AI and DL to resolve the challenges faced by the construction industry is a key purpose of the study. DL-driven technologies have made specific algorithms and models to support more efficient and accurate computer vision and image processing applications, offering unprecedented capabilities for analysing and interpreting visual data in novel solutions. Hence, the analysis of the significant DL algorithms and models is performed. The final analysis would encompass the analysis of the integration of multiple digital technologies with DL-driven visual computing.
3.1 Stage 1: literature search
The process consists of a three-stage search and filtration process of academic journal papers based on specific search criteria. The specifically developed search criterion aimed to assess and examine the specific academic content, based on the keywords related to the objectives and the research questions (Ogunmakinde et al., 2024).
The literature search was performed in April 2024 on the two leading publication databases, Scopus and Web of Science. These databases were selected because of the high level of accuracy and the broad coverage of publications related to the construction industry, and the comprehensive coverage and indexing quality (Das et al., 2023; Yadav et al., 2023). Moreover, Web of Science and Scopus stand as two leading and opposing citation databases (Pranckutė, 2021). In recent times, there has been a notable surge in scholarly publications within this field, indexed by the Web of Science and Scopus citation databases (Zhu and Liu, 2020).
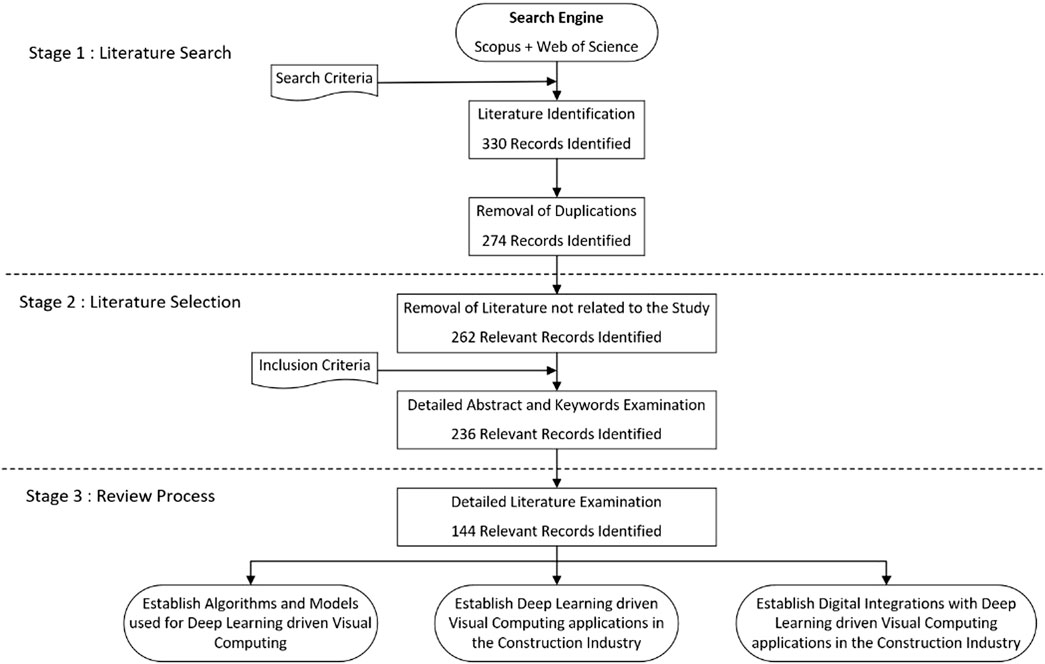
A Boolean search string was developed by considering the specific search requirement of the Boolean searching string, while the keywords were selected through pilot searches, cross-checked against terms used in recent systematic reviews, as follows. Further, the complete research process is illustrated in Figure 1.
(((“construction” OR “building”) AND (“industry” OR “site” OR “infrastructure”)) OR (“built environment”)) AND ((“deep learning” OR “artificial intelligence”) AND (“visual computing” OR “image processing” OR “computer vision”))
A comprehensive search was performed on the two databases under the “article title/abstract/keyword” fields using the Boolean searching string. The exclusion criteria were developed to refine the outcome through the final search operation. A specific exclusion process was performed by considering only the last 5 years of research articles (2020-2024) in order to ensure the review reflects the most current and relevant research in DL-enabled VC. This approach also allows us to avoid including outdated pre-DL techniques that are less representative of contemporary practice (Palmatier et al., 2018; Paul and Criado, 2020). Further, review articles were excluded to ensure inclusion of only primary research with full methodological detail, preventing duplication of findings. The category of research was selected to be Engineering, Construction and Building-related content. The language of the articles was limited to English.
Although there may be some overlap among the keywords in sets, including them ensures a larger number of papers for analysis compared to similar reviews. The objective was to make the keywords collectively exhaustive, even if they were not entirely mutually exclusive (Jacobsen and Teizer, 2022).
Searching for articles in the two databases resulted in 330 publications. The duplicated articles were removed after creating a single record of articles. Once the duplications were removed, the resulting record was composed of 274 articles. A primary screening was performed to confirm the relevance of the complete set of articles.
3.2 Stage 2: literature selection
The second phase of the filtering process was initiated with a comprehensive examination of the abstract and the keywords of the articles. This filtering involved examining the abstracts of the publications to identify topics that fell outside the scope of the review and the removal of review articles. The process of screening involved the assessment of technological adherence to visual computing technologies and applications, namely, image and video processing, computer vision, and computer graphics. The review of keywords and abstracts was performed by two independent reviewers. Applications related to visualisation, VR, and AR were also selected due to the relevance of computer graphics for virtualisation.
3.3 Stage 3: review process
Stage 3 consists of a detailed analysis of the research articles. During the final screening, only the studies with a VC application were considered, and it was examined whether the article had been completed and reported the detailed technical application, including the algorithms used for the application. The final screening had incorporated a methodical bias elimination tool adapted from Mushtaha et al. (2024b). Furthermore, a quality assessment was performed on the final set of included articles to evaluate their methodological rigour and potential for bias. The final screening resulted in 144 articles for the detailed analysis.
4 Results
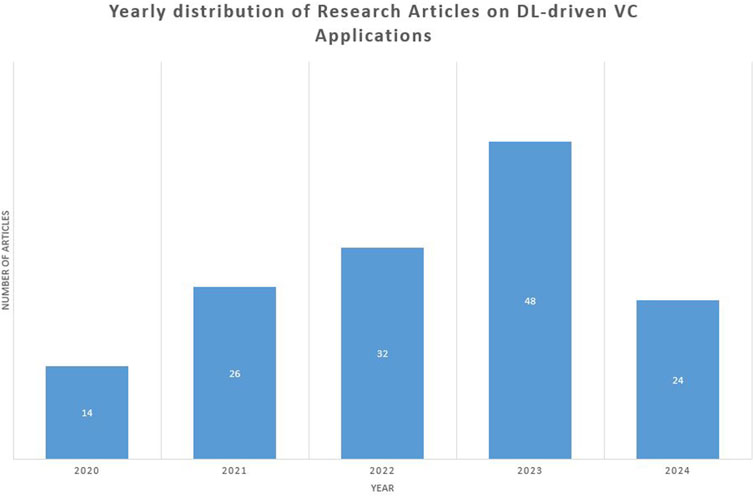
The number of annual publications in DL-based VC applications could be used as an indicator of possible technical applications and their technical feasibility. Mushtaha et al. (2024a) had highlighted the importance of analysing statistics to derive outcomes of a review study, hence a comprehensive analysis in performed. The transformation from traditional computer vision techniques to DL-based techniques illustrates a notable upsurge in the visualisation of Figure 2. Figure 2 illustrates the annual distribution of research articles and highlights significant growth and increasing research interest in this domain. This exponential growth is attributed to several factors, including the increasing accessibility and computational power of Graphics Processing Units (GPUs), the maturation and open sourcing of powerful DL frameworks and the growing recognition of DL’s potential to address complex visual challenges in dynamic construction environments. This trend highlights the rapid shift from traditional computer vision to DL-driven approaches within the sector.
Subsequently, a final set of literature articles was investigated for two crucial parameters: the specific type of deep neural network employed by the authors and the application purpose. The determination of these parameters involved an extensive analysis of the metadata presented in the articles, along with a thorough examination of both the abstracts and full papers. Recurring themes and common objectives of the DL applications were identified and grouped. The robustness of these categories was further validated through keyword co-occurrence analysis (as depicted in Figure 3), which confirmed the strong associations between the identified themes and the research focus of the articles within each category.
It was identified that the DL-based VC applications can be separated into six main subcategories after a thorough investigation. The identified major categories are as follows.
1. Construction Quality
2. Construction Safety
3. Damage Detection
4. Object Detection
5. Productivity Analysis
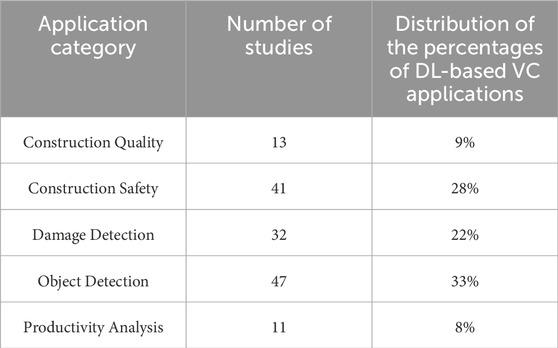
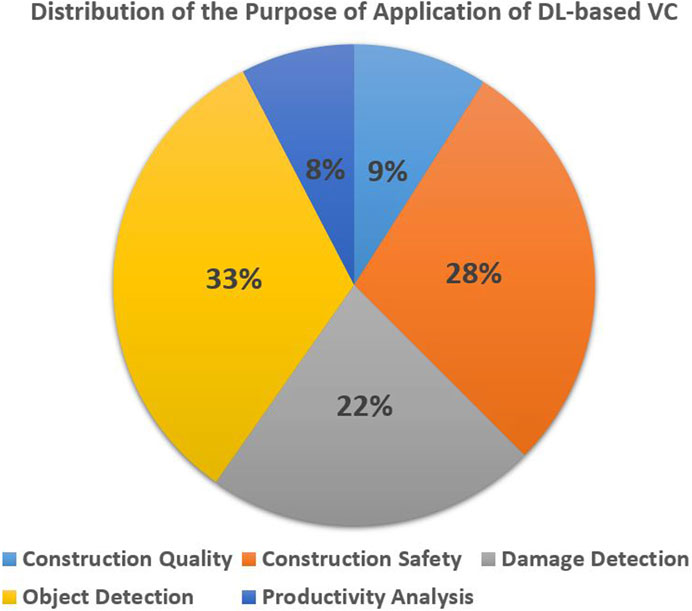
The distribution of application purposes is shown in Table 1, the percentages of applications are presented against the DL-based VC application category.
Figure 4, illustrates the same information by visualisations to interpret trends in application focus. Subsequently, an annual breakdown is provided to conduct a detailed analysis of trends across various application domains.
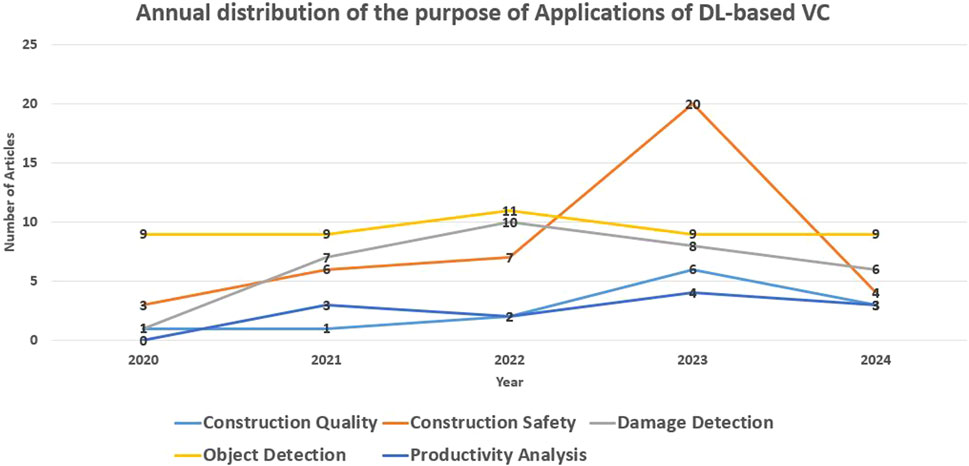
Figure 5 showcases the annual progression of DL-based VC application categories. By examining Figures 4, 5, it becomes evident that Object Detection Applications and Construction Safety-focused Applications exhibit notable prominence with a notable surge.
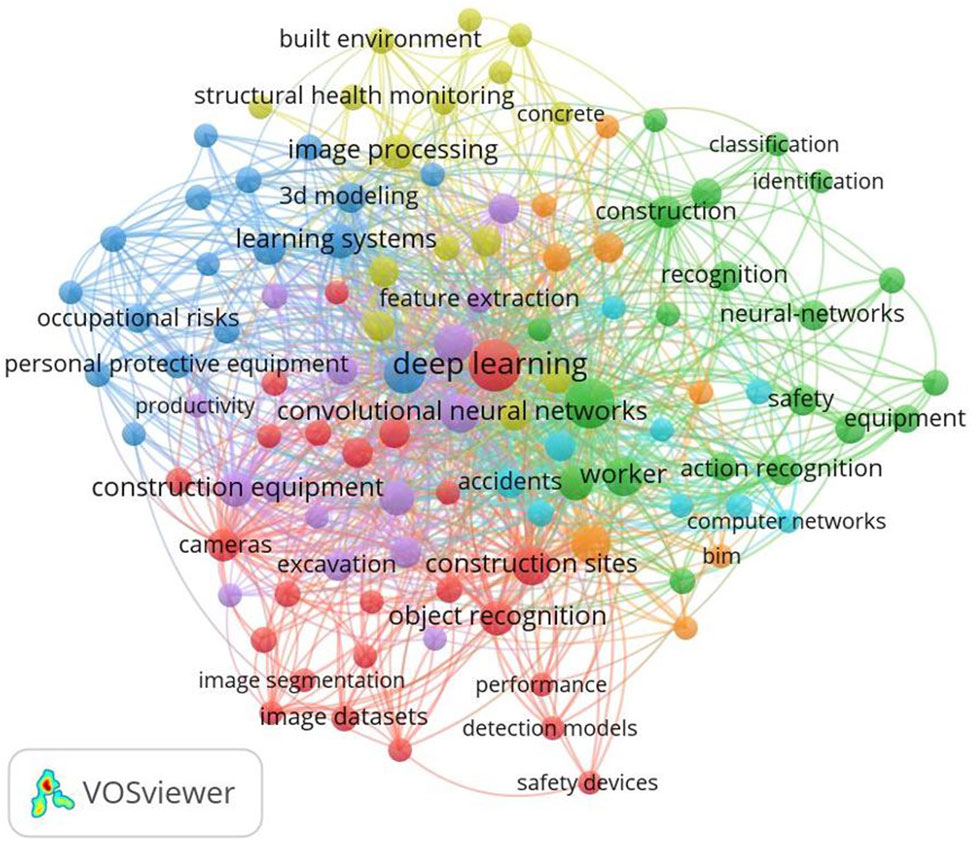
Keywords co-occurrence networks were constructed as part of the scientometric inquiry. Keywords serve to encapsulate the thematic essence of research articles while aiding in their indexing. By mapping all keywords, a comprehensive overview of domain-specific knowledge is obtained (Bukar et al., 2023). The selection of the VOSviewer® software tool was predicated on its proficiency in generating, visualising, and leveraging bibliometric networks (Waltman, 2023). Figure 3 illustrates the keywords co-occurrence network of the Research Articles in a graphical format.
Through keyword analysis, it becomes apparent that numerous terms contribute to comprehending the technological and application landscape of DL-driven VC in the construction industry. Examination of application types reveals the prominence of construction safety applications, as evidenced by keywords such as “personal protective equipment,” “accidents,” “safety,” “worker,” and “occupational risks.” Additionally, object detection emerges as a crucial aspect in VC applications, demonstrated by keywords like “object recognition,” “construction equipment,” “classification,” “identification,” “detection models,” “feature extraction,” “image segmentation,” and “recognition.” Moreover, damage detection garners attention through keywords such as “structural health monitoring” and “concrete.” DL-based analysis of construction productivity is delineated by keywords like “performance” and “productivity” alongside “excavation.” Other noteworthy keywords, such as “convolutional neural networks,” “BIM”, “cameras,” “neural networks,” and “detection models,” emphasise the technological integration of DL and VC. Notably, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) assume a pivotal role in driving VC based on DL, while BIM exhibits clear integration with DL-driven VC applications.
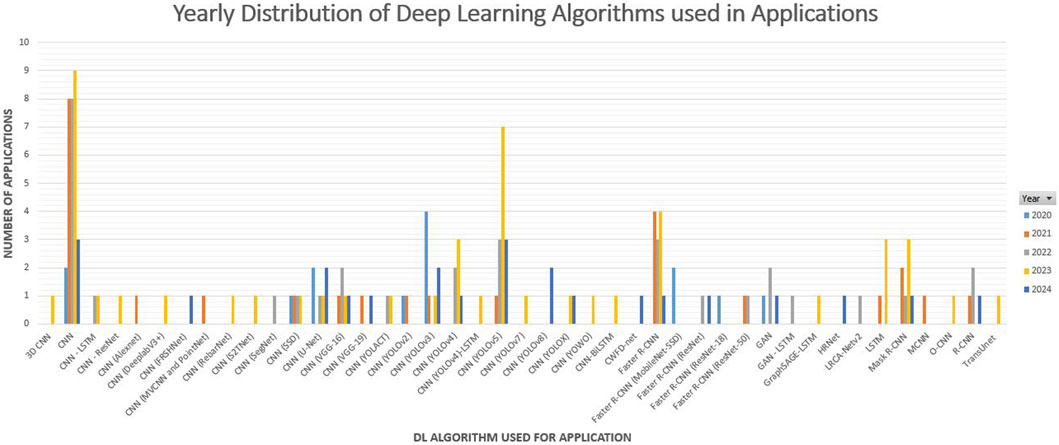
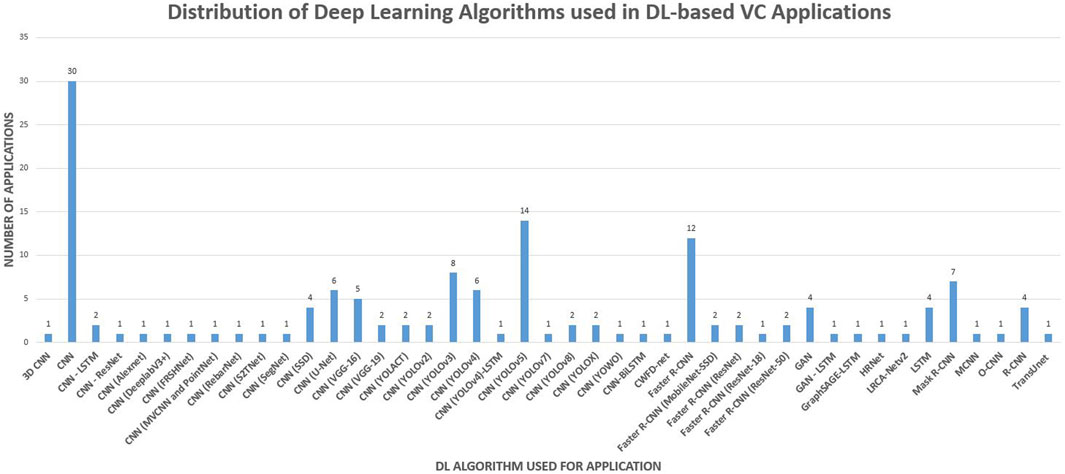
Analysis of keywords revealed the dominance of CNN models for VC applications. A thorough examination of selected articles was conducted to identify the specific DL algorithms and models employed. Certain articles consist of ensembled DL algorithms to devise DL models incorporating diverse DL algorithms to be used for specific applications. CNN is the most utilised and optimised DL model based on the application type and the characteristics of the dataset. The possibility of adjusting the Kernel, Convolutional layers and Pooling layers has resulted in a vast amount of DL algorithms for optimised applications (Alzubaidi et al., 2021). The following Figures 6, 7 were generated to illustrate and analyse the range of CNN algorithms and their frequency of applications. Figure 6 was generated by integrating multiple dimensions, including the year of publication and the DL model utilised, facilitating a focused exploration of DL model trends and particulars. A further analysis was conducted on the prominence of various DL algorithms used for the VC applications. Figure 7 consists of the total number of articles with different DL models and algorithms.
CNNs are a type of feedforward neural network that are designed specifically to process data in the form of pixels. This architecture is well-suited for grid-like data, such as time series and image data. The primary feature that distinguishes CNNs from other types of artificial neural networks (ANNs) is the presence of convolution layers, which gives them their name (Han et al., 2022). Overall, CNNs offer a powerful and flexible tool for visual data processing and analysis, which can outperform traditional ANNs in many applications (Al-Shboul et al., 2023; Thangarajan and Chokkalingam, 2021).
Figure 6 illustrates the Deep Learning algorithms used for the applications per year. A summarised visualisation is presented in Figure 7 below.
Figures 6, 7 provide a key insight by illustrating the emergence of single-stage detector CNN algorithms such as YOLO and SSD. Further double-stage detector CNN algorithms are also being utilised and improved. CNN double-stage detector algorithms, such as R-CNN models, are improved further to create fast R-CNN and faster R-CNN models. In-depth analysis illustrates that the creation of application-specific CNN models, such as “Point-Net” and “Alex-Net”, by modifying the layers of the CNN model. Further, these two visual illustrations depict the diverse algorithms developed for specific tasks and applications.
5 Findings and discussion
The primary focus of this study revolves around the utilisation of VC applications facilitated by DL algorithms/models in the construction industry. The application types of visual computing-based applications were isolated for in-depth analysis, as depicted in Figure 4. The impact on multiple construction processes was assessed in detail, encompassing aspects like efficiency, safety, quality, productivity, and sustainability. Figure 4 highlights the prevalence of construction safety, damage detection, and object detection as the predominant types of VC applications based on DL within the construction industry. Despite consistent enforcement of worksite safety protocols, the construction industry remains plagued by a disproportionately high rate of accidents and casualties, earning its infamous label as one of the world’s most hazardous sectors (Rahnamayiezekavat et al., 2024). Hence, the impact of DL-based VC applications would play a vital role in resolving key issues faced by the construction industry.
When considering the publication year of each study, as depicted in Figure 2, it becomes evident that the utilisation of DL-powered VC in the construction industry is experiencing a notable upsurge. Over the past 5 years, there has been a substantial increase in research and development, and this is attributed to advancements in relevant hardware, which have made the practical implementation of high-tech VC applications feasible. The rise in computing power, the availability of high-precision image and video-capturing cameras, and the significant refinement of DL algorithms have collectively opened new avenues for extensive research and development in this field.
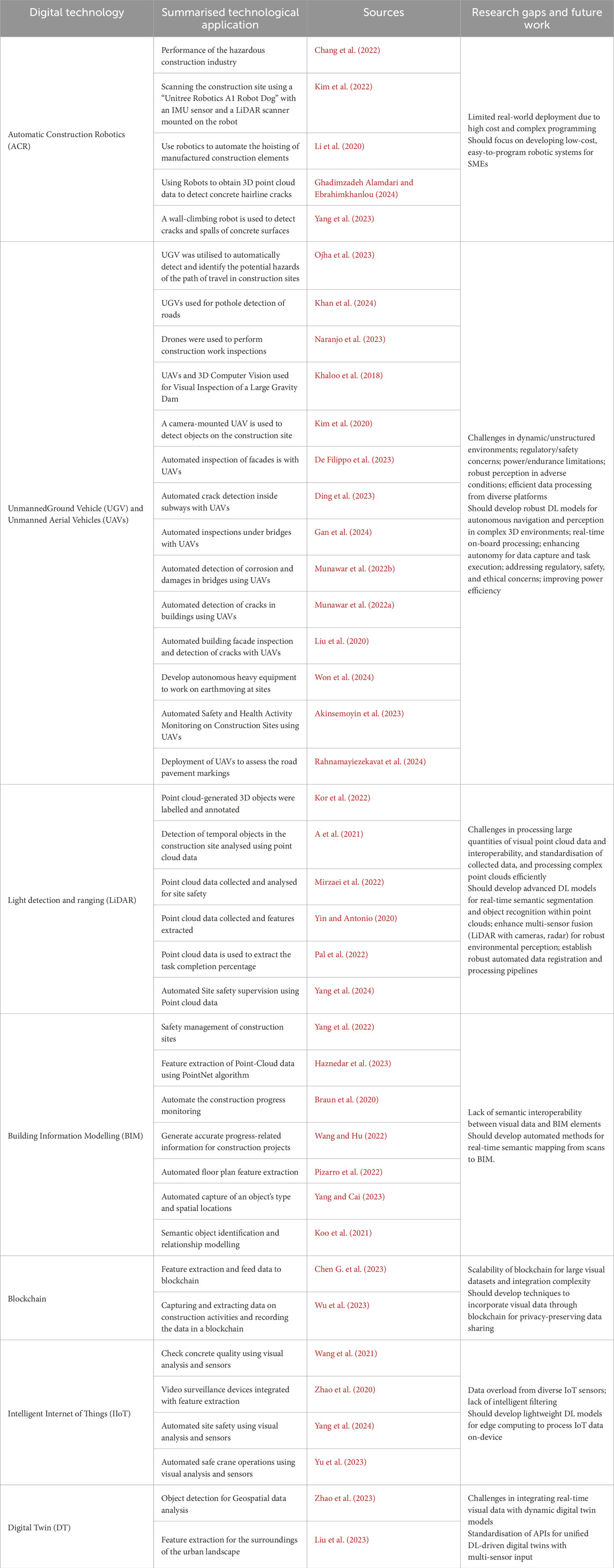
The findings of the study primarily centred on the algorithms and applications related to deep learning in visual computing. It became evident that most visual computing applications employing deep learning techniques were characterised by technological integrations. Notably, research conducted by Pal et al. (2022), Wang and Hu (2022), Pizarro et al. (2022), and Yang and Cai (2023) emphasised the integration of visual computing technologies with BIM, DT, IoT, AR and Robotics.
A detailed analysis was performed on the integration of digital technologies with DL-driven VC applications. A tabular presentation is prepared as Table 2 to illustrate the depth and breadth of the feasible technological integrations.
The upward trajectory of DL-driven VC is evident, as it increasingly addresses challenges encountered in the construction industry through multiple digital technology integrations. Above Table 1 is crucial for understanding the multidisciplinary nature of DL-enabled VC in construction. Industry practitioners can leverage DL-VC for proactive safety monitoring, automated defect detection, and progress tracking. Policymakers can integrate these insights into regulatory frameworks for improved compliance and safety enforcement. The analysis illustrates integration points with key digital technologies and VC. Further, it identifies the corresponding research gaps that impede their full potential and suggests future work directions for each, thereby directly addressing the complexities of real-world implementation and guiding future research efforts. However, it is important to identify the Challenges that remain in scaling DL-VC due to high computing demands, lack of standardised datasets, and interoperability barriers, while workforce readiness is one of the major challenges. Addressing these is critical for real-world adoption. Furthermore, this systematic review provides a comprehensive comprehension of DL-enabled VC within the construction sector, facilitating informed decision-making and industry progress.
6 Research gaps and future directions
The review study delivers empirical evidence portraying the expansion and progression of artificial intelligence (AI)-based applications custom-tailored for the construction sector. The initiation of the DL-based VC has guided substantial opportunities in research and development, resulting in innovative solutions across diverse construction-related domains. This notable advancement can be credited to significant strides in related hardware technologies, which have facilitated the practical implementation of sophisticated VC applications. The augmentation in computational ability, alongside the availability of high-definition image and video-capturing devices, coupled with the extensive refinement of DL algorithms, collectively broadens the horizons for extensive research and development in this domain.
Subsequent research endeavours should be focused on key areas such as construction efficiency enhancement, enhancement of safety, ensuring construction quality, enhancement of productivity of construction methods, and the innovative and adaptive techniques to integrate digital technologies with DL-driven VC. Further, challenges are associated with integrating DL-enabled VC into construction practices and exploring potential avenues for further research and development. It is important to explore the most suitable DL algorithms and models for VC applications. A complementary area of investigation could centre on optimising application performance by fine-tuning DL algorithms through parameter and hyperparameter adjustments to strengthen overall model efficiency. Furthermore, the potential of ensemble learning, wherein two DL algorithms are amalgamated to harness the best attributes of each, holds promise for advancing the accuracy of VC applications.
Conversely, several challenges associated with the application of VC techniques are prominent in the construction sector. Several immediate challenges could be identified, lack of benchmark datasets tailored to construction environments could be identified, which limits the DL model validation. In DL-based applications, the significance of high-quality data plays a pivotal role in enhancing the performance of DL models for visual applications. Fortunately, the construction industry has witnessed extensive digitalisation, resulting in the generation of significant amounts of visual datasets. The inherent complexity of construction sites distorts visual input data. Particularly, lighting conditions and disturbances have rendered capturing quality visual inputs challenging for training and testing DL-driven VC models.
To mitigate these challenges, several approaches could be adopted in DL-driven VC for construction. Data augmentation and synthetic data generation enhance the diversity of training datasets, although they may not fully replicate the complexity of real-world construction environments. High Dynamic Range (HDR) imaging and illumination-invariant feature extraction help address variability in lighting conditions, though they often require additional hardware and preprocessing effort. Domain adaptation and transfer learning enable models trained on large generic datasets to adapt effectively to construction-specific contexts, though risks of bias transfer remain.
Further, the testing and deployment of developed DL-VC models could be highlighted due to the hardware limitations and optimisation challenges. The willingness of the construction industry to invest substantial resources in enhancing computing infrastructure to implement DL-driven VC is a concern. Being among the least digitalised industries, its perspective on embracing this technological shift will be pivotal in determining the use of these novel applications. Development of lightweight DL models optimised for edge devices could be considered as an immediate solution, although such models may sacrifice some accuracy compared to full-scale architectures. Limited integration between DL-VC solutions and existing digital platforms such as BIM, IoT systems, and digital twins could be identified as a key immediate challenge. The development of other digital technologies has provided multi-dimensional integrations for innovative solutions in areas most challenging in the construction industry. Addressing these gaps is critical for enabling practical, on-site implementation in the near term.
Based on the comprehensive analysis of the current landscape of DL-driven VC in construction, several critical research gaps and promising avenues for future exploration have been identified. These concerns and directions are beyond the immediate challenges. The long-term research directions should be focused on the development and adaptation of explainable AI and ethical frameworks to govern data usage, algorithmic fairness, and accountability. Fostering broad industry adoption requires a human-centric approach, developing explainable AI interfaces and intuitive tools that enhance transparent insights into model decisions, thereby improving trust among the stakeholders.
Long-term research and development should be focused on enabling real-time, on-site analytics. Research must prioritise the development of lightweight and efficient Convolutional Neural Network models specifically optimised for deployment on edge devices. These advanced model compression techniques and hardware-aware architectures are critical to optimise the current processing limitations and reduce latency. Further, addressing significant data silos necessitates dedicated efforts towards cross-technology interoperability and data integration. This involves establishing standardised Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), Common Data Environments (CDEs), and unified frameworks to create a more cohesive digital ecosystem that seamlessly integrates with existing visual computing systems.
Further, future research should explore the development of comprehensive guidelines and best practices for ethical AI deployment within the construction industry is essential. Privacy-preserving visual computing approaches, such as federated learning and secure data-sharing mechanisms, will be vital to protect sensitive construction data while supporting large-scale adoption. Finally, the challenge of data scarcity and generalisation for robust deep learning model training demands innovative solutions. Future studies should focus on advanced data augmentation techniques, transfer learning from diverse datasets, and the creation of large-scale, publicly accessible benchmark datasets tailored to construction environments. Additionally, research into synthetic data generation utilising advanced generative models could effectively mitigate data limitations and enhance model generalisation capabilities. Addressing these areas is essential for the transition of DL-driven VC from research prototypes to widespread, impactful industry adoption.
It was noted that the adoption of DL-VC technologies demonstrates considerable variability across regions. Developed economies are making significant investments in robotics, BIM integration, and digital twin technologies, enabling advanced DL-VC applications to be integrated. In contrast, developing regions often face barriers such as inadequate digital infrastructure, limited financial resources, and insufficient training of construction professionals. These disparities highlight the importance of tailoring DL-VC research and deployment strategies to regional contexts, ensuring equitable global diffusion of technological benefits in applications of DL-VC technologies.
In conclusion, the integration of AI-based applications is increasingly shaping the technological transformation of human lives. It is crucial to realise the significance of DL-based visual computing applications in the future of digitalisation within the construction sector for future transformations.
Author contributions
PP: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. SP: Conceptualization, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. XJ: Supervision, Writing – review and editing. MR: Supervision, Writing – review and editing. SN: Supervision, Writing – review and editing. GY: Resources, Writing – review and editing. AY: Resources, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The publication fee was provided by the School of Engineering, Design and Built Environment, Western Sydney University.
Conflict of interest
Authors GY and AY were employed by Commnia Pty Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. Generative AI was used solely to assist with language editing, improving clarity, and refining the structure of the text. All intellectual content, research insights, and interpretations are original and solely the work of the author(s).
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
A, V. T. M., Alexander, B., Florian, N., André, B., Heiko, B., and Denis, W. (2021). Recognition of temporary vertical objects in large point clouds of construction sites. Proc. Institution Civ. Eng. - Smart Infrastructure Constr. 174, 134–149. doi:10.1680/jsmic.21.00033
Abioye, S. O., Oyedele, L. O., Akanbi, L., Ajayi, A., Davila Delgado, J. M., Bilal, M., et al. (2021). Artificial intelligence in the construction industry: a review of present status, opportunities and future challenges. J. Build. Eng. 44, 103299. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2021.103299
Afif, M., Said, Y., and Atri, M. (2020). Computer vision algorithms acceleration using graphic processors NVIDIA CUDA. Clust. Comput. 23, 3335–3347. doi:10.1007/s10586-020-03090-6
Akinosho, T. D., Oyedele, L. O., Bilal, M., Ajayi, A. O., Delgado, M. D., Akinade, O. O., et al. (2020). Deep learning in the construction industry: a review of present status and future innovations. J. Build. Eng. 32, 101827. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2020.101827
Akinsemoyin, A., Awolusi, I., Chakraborty, D., Al-Bayati, A. J., and Akanmu, A. (2023). Unmanned aerial systems and deep learning for safety and health activity monitoring on construction sites. Sensors 23, 6690. doi:10.3390/s23156690
Al-Shboul, A., Gharibeh, M., Najadat, H., Ali, M., and El-Heis, M. (2023). Overview of convolutional neural networks architectures for brain tumor segmentation. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 13, 4594–4604. doi:10.11591/ijece.v13i4.pp4594-4604
Ali, K. N., Alhajlah, H. H., and Kassem, M. A. (2022). Collaboration and risk in building information modelling (BIM): a systematic literature review. Build. [Online] 12, 571. doi:10.3390/buildings12050571
Alzubaidi, L., Zhang, J., Humaidi, A. J., Al-Dujaili, A., Duan, Y., Al-Shamma, O., et al. (2021). Review of deep learning: concepts, CNN architectures, challenges, applications, future directions. J. Big Data 8, 53. doi:10.1186/s40537-021-00444-8
Baduge, S. K., Thilakarathna, S., Perera, J. S., Arashpour, M., Sharafi, P., Teodosio, B., et al. (2022). Artificial intelligence and smart vision for building and construction 4.0: machine and deep learning methods and applications. Automation Constr. 141, 104440. doi:10.1016/j.autcon.2022.104440
Bahoo, S., Cucculelli, M., and Qamar, D. (2023). Artificial intelligence and corporate innovation: a review and research agenda. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 188, 122264. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2022.122264
Begić, H., Galić, M., and Dolacek-Alduk, Z. (2022). Digitalization and automation in construction project’s life-cycle: a review. J. Inf. Technol. Constr. 27, 441–460. doi:10.36680/j.itcon.2022.021
Braun, A., Tuttas, S., Borrmann, A., and Stilla, U. (2020). Improving progress monitoring by fusing point clouds, semantic data and computer vision. Automation Constr. 116, 103210. doi:10.1016/j.autcon.2020.103210
Bukar, U. A., Sayeed, M. S., Razak, S. F. A., Yogarayan, S., Amodu, O. A., and Mahmood, R. A. R. (2023). A method for analyzing text using VOSviewer. MethodsX 11, 102339. doi:10.1016/j.mex.2023.102339
Cepa, J. J., Pavón, R. M., Alberti, M. G., Ciccone, A., and Asprone, D. (2023). A review on the implementation of the BIM methodology in the operation maintenance and transport infrastructure. Appl. Sci. Switz. 13. doi:10.3390/app13053176
Chai, J., Zeng, H., Li, A., and Ngai, E. W. T. (2021). Deep learning in computer vision: a critical review of emerging techniques and application scenarios. Mach. Learn. Appl. 6, 100134. doi:10.1016/j.mlwa.2021.100134
Chang, S., Francis Siu, M.-F., Li, H., and Luo, X. (2022). Evolution pathways of robotic technologies and applications in construction. Adv. Eng. Inf. 51, 101529. doi:10.1016/j.aei.2022.101529
Chen, G., Liu, M., Zhang, Y., Wang, Z., Hsiang, S. M., and He, C. (2023). Using images to detect, plan, analyze, and coordinate a smart contract in construction. J. Manag. Eng. 39, 04023002. doi:10.1061/jmenea.meeng-5121
Chen, S., Dong, F., and Demachi, K. (2023). Hybrid visual information analysis for on-site occupational hazards identification: a case study on stairway safety. Saf. Sci. 159, 106043. doi:10.1016/j.ssci.2022.106043
Collins, C., Dennehy, D., Conboy, K., and Mikalef, P. (2021). Artificial intelligence in information systems research: a systematic literature review and research agenda. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 60, 102383. doi:10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2021.102383
Corrado, R., Soy, M., and Heang, V. (2023). BIM and IFC: awareness and self-assessed knowledge from the perspective of Cambodian university students. Ain Shams Eng. J. 14, 101851. doi:10.1016/j.asej.2022.101851
Das, P., Perera, S., Senaratne, S., and Osei-Kyei, R. (2023). A smart modern construction enterprise maturity model for business scenarios leading to industry 4.0. Smart Sustain. Built Environ. 14, 23–49. doi:10.1108/sasbe-09-2022-0205
De Filippo, M., Asadiabadi, S., Kuang, J. S., Mishra, D. K., and Sun, H. (2023). Ai-powered inspections of facades in reinforced concrete buildings. HKIE Trans. Hong Kong Institution Eng. 30, 1–14. doi:10.33430/v30n1thie-2020-0023
Delhi, V. S. K., Sankarlal, R., and Thomas, A. (2020). Detection of personal protective equipment (PPE) compliance on construction site using computer vision based deep learning techniques. Front. Built Environ. 6, 136. doi:10.3389/fbuil.2020.00136
Ding, Z., Luo, L., Wang, X., Liu, Y., Zhang, W., and Wu, H. (2023). An artificial intelligence-based method for crack detection in engineering facilities around subways. Appl. Sci. 13, 11002. doi:10.3390/app131911002
Ekanayake, B., Wong, J. K.-W., Fini, A. A. F., and Smith, P. (2021). Computer vision-based interior construction progress monitoring: a literature review and future research directions. Automation Constr. 127, 103705. doi:10.1016/j.autcon.2021.103705
Ekanayake, B., Ahmadian Fard Fini, A., Wong, J. K. W., and Smith, P. (2022). A deep learning-based approach to facilitate the as-built state recognition of indoor construction works. Constr. Innov. 24, 933–949. doi:10.1108/ci-05-2022-0121
Elghaish, F., Matarneh, S. T., and Alhusban, M. (2022a). The application of “deep learning” in construction site management: scientometric, thematic and critical analysis. Constr. Innov. 22, 580–603. doi:10.1108/ci-10-2021-0195
Elghaish, F., Matarneh, S. T., Talebi, S., Abu-Samra, S., Salimi, G., and Rausch, C. (2022b). Deep learning for detecting distresses in buildings and pavements: a critical gap analysis. Constr. Innov. 22, 554–579. doi:10.1108/ci-09-2021-0171
Elghaish, F., Talebi, S., Abdellatef, E., Matarneh, S. T., Hosseini, M. R., Wu, S., et al. (2022c). Developing a new deep learning CNN model to detect and classify highway cracks. J. Eng. Des. Technol. 20, 993–1014. doi:10.1108/jedt-04-2021-0192
Eriqat, M. O., Sweis, R. J., and Sweis, G. J. (2024). The challenges of adopting emerging technologies in the AEC industry a literature review and bibliometric analysis. Constr. Innov. doi:10.1108/ci-08-2023-0186
Ernst and Young (2021). AI: construction’s new frontier of digital enablement. Ernst and Young. Available online at: https://www.ey.com/content/dam/ey-unified-site/ey-com/en-us/insights/real-estate-hospitality-construction/documents/ey-ai-construction-s-new-frontier-of-digital-enablement-210114-cover-rev-n.pdf.
Fan, C.-L. (2023). Using convolutional neural networks to identify illegal roofs from unmanned aerial vehicle images. Archit. Eng. Des. Manag. 20, 390–410. doi:10.1080/17452007.2023.2244949
Gan, L., Liu, H., Yan, Y., and Chen, A. (2024). Bridge bottom crack detection and modeling based on faster R-CNN and BIM. IET Image Process. 18, 664–677. doi:10.1049/ipr2.12976
Ghadimzadeh Alamdari, A., and Ebrahimkhanlou, A. (2024). A multi-scale robotic approach for precise crack measurement in concrete structures. Automation Constr. 158, 105215. doi:10.1016/j.autcon.2023.105215
Goswami, T. (2018). “Impact of deep learning in image processing and computer vision,” in Microelectronics, electromagnetics and telecommunications, 2018//2018. Editors J. ANGUERA, S. C. SATAPATHY, V. BHATEJA, and K. V. N. SUNITHA (Singapore: Springer), 475–485.
Greenwood, D., Lockley, S., Malsane, S., and Matthews, J. (2010). “Automated compliance checking using building information models,” in Cobra 2010 - construction, building and real estate research conference of the royal institution of chartered surveyors.
Hamledari, H., Mccabe, B., and Davari, S. (2017). Automated computer vision-based detection of components of under-construction indoor partitions. Automation Constr. 74, 78–94. doi:10.1016/j.autcon.2016.11.009
Han, S., Zhang, S., Li, Y., and Chen, L. (2022). The multilabel fault diagnosis model of bearing based on integrated convolutional neural network and gated recurrent unit. Int. J. Intelligent Comput. Cybern. 15, 401–413. doi:10.1108/ijicc-08-2021-0153
Haznedar, B., Bayraktar, R., Ozturk, A. E., and Arayici, Y. (2023). Implementing PointNet for point cloud segmentation in the heritage context. Herit. Sci. 11, 2. doi:10.1186/s40494-022-00844-w
Hewavitharana, T., Nanayakkara, S., Perera, A., and Perera, P. (2021). “Modifying the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology (UTAUT) model for the digital transformation of the construction industry from the user perspective. Informatics, 8 (4), 81. doi:10.3390/informatics8040081
Hewavitharana, S., Perera, S., Jin, X., Seneviratne, K., and Bamdad, K. (2023). An introduction to blockchain in building services: a literature review. 135–148. doi:10.31705/wcs.2023.12
Hewavitharana, S., Perera, A., Perera, S., Perera, P., and Nanayakkara, S. (2025). Framework for systematic adoption of ERP systems in the Sri Lankan construction industry. Built Environ. Proj. Asset Manag. 15, 629–646. doi:10.1108/bepam-12-2023-0226
Hijriyah, L., Alias, A., and Mohd Sahabuddin, M. F. (2024). Exploring walkability research trends based on systematic literature review (SLR) by applying PRISMA. Open House Int. 49, 63–121. doi:10.1108/ohi-02-2023-0031
Hoedemaekers, C. (2024). The role of infrastructure development in driving economic growth: a study on the United States economy and the oil and gas sector.
Inazumi, S., Intui, S., Jotisankasa, A., Chaiprakaikeow, S., and Kojima, K. (2020). Artificial intelligence system for supporting soil classification. Results Eng. 8, 100188. doi:10.1016/j.rineng.2020.100188
Jacobsen, E. L., and Teizer, J. (2022). Deep learning in construction: review of applications and potential avenues. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 36, 03121001. doi:10.1061/(asce)cp.1943-5487.0001010
Jan, Z., Ahamed, F., Mayer, W., Patel, N., Grossmann, G., Stumptner, M., et al. (2023). Artificial intelligence for industry 4.0: systematic review of applications, challenges, and opportunities. Expert Syst. Appl. 216, 119456. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2022.119456
Janiesch, C., Zschech, P., and Heinrich, K. (2021). Machine learning and deep learning. Electron. Mark. 31, 685–695. doi:10.1007/s12525-021-00475-2
Ji, A., Xue, X., Zhang, L., Luo, X., and Man, Q. (2023). A transformer-based deep learning method for automatic pixel-level crack detection and feature quantification. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 32, 2455–2486. doi:10.1108/ecam-06-2023-0613
Kaya, H. D., and Dikmen, I. (2024). Using system dynamics to support strategic digitalization decisions. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 150, 04024009. doi:10.1061/jcemd4.coeng-14112
Khallaf, R., and Khallaf, M. (2021). Classification and analysis of deep learning applications in construction: a systematic literature review. Automation Constr. 129, 103760. doi:10.1016/j.autcon.2021.103760
Khaloo, A., Lattanzi, D., Jachimowicz, A., and Devaney, C. (2018). Utilizing UAV and 3D computer vision for visual inspection of a large gravity dam. Front. Built Environ., 4–2018. doi:10.3389/fbuil.2018.00031
Khan, M., Raza, M. A., Abbas, G., Othmen, S., Yousef, A., and Jumani, T. A. (2024). Pothole detection for autonomous vehicles using deep learning: a robust and efficient solution. Front. Built Environ. 9, 1323792. doi:10.3389/fbuil.2023.1323792
Kim, D., Lee, S., and Kamat, V. R. (2020). Proximity prediction of Mobile objects to prevent contact-driven accidents in Co-Robotic construction. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 34, 04020022. doi:10.1061/(asce)cp.1943-5487.0000899
Kim, J., Chung, D., Kim, Y., and Kim, H. (2022). Deep learning-based 3D reconstruction of scaffolds using a robot dog. Automation Constr. 134, 104092. doi:10.1016/j.autcon.2021.104092
Koo, B., Jung, R., and Yu, Y. (2021). Automatic classification of wall and door BIM element subtypes using 3D geometric deep neural networks. Adv. Eng. Inf. 47, 101200. doi:10.1016/j.aei.2020.101200
Kor, M., Yitmen, I., and Alizadehsalehi, S. (2022). An investigation for integration of deep learning and digital twins towards construction 4.0. Smart Sustain. Built Environ. 12, 461–487. doi:10.1108/sasbe-08-2021-0148
Lepcha, D. C., Goyal, B., Dogra, A., Sharma, K. P., and Gupta, D. N. (2023). A deep journey into image enhancement: a survey of current and emerging trends. Inf. Fusion 93, 36–76. doi:10.1016/j.inffus.2022.12.012
Li, H., Luo, X., and Skitmore, M. (2020). Intelligent hoisting with car-like Mobile robots. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 146, 04020136. doi:10.1061/(asce)co.1943-7862.0001931
Li, F., Laili, Y., Chen, X., Lou, Y., Wang, C., Yang, H., et al. (2023). Towards big data driven construction industry. J. Industrial Inf. Integration 35, 100483. doi:10.1016/j.jii.2023.100483
Liu, Y., Yeoh, J. K. W., and Chua, D. K. H. (2020). Deep learning–based enhancement of motion blurred UAV concrete crack images. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 34, 04020028. doi:10.1061/(asce)cp.1943-5487.0000907
Liu, C., Sepasgozar, M. E., Shirowzhan, S., and Mohammadi, G. (2021). Applications of object detection in modular construction based on a comparative evaluation of deep learning algorithms. Constr. Innov. 22, 141–159. doi:10.1108/ci-02-2020-0017
Liu, P., Zhao, T., Luo, J., Lei, B., Frei, M., Miller, C., et al. (2023). Towards human-centric digital twins: leveraging computer vision and graph models to predict outdoor comfort. Sustain. Cities Soc. 93, 104480. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2023.104480
Lu, S., Zhou, S., Ding, Y., Kim, M. K., Yang, B., Tian, Z., et al. (2025). Exploring the comprehensive integration of artificial intelligence in optimizing HVAC system operations: a review and future outlook. Results Eng. 25, 103765. doi:10.1016/j.rineng.2024.103765
Mirzaei, K., Arashpour, M., Asadi, E., Masoumi, H., Bai, Y., and Behnood, A. (2022). 3D point cloud data processing with machine learning for construction and infrastructure applications: a comprehensive review. Adv. Eng. Inf. 51, 101501. doi:10.1016/j.aei.2021.101501
Mishra, V., and Mishra, M. P. (2023). “PRISMA for review of management literature – Method, merits, and limitations – an academic review,” in Advancing methodologies of conducting literature review in management domain. Editors S. RANA, J. SINGH, and S. KATHURIA (Emerald Publishing Limited). doi:10.1108/S2754-586520230000002007
Mohammadi, M., Rashidi, M., Yu, Y., and Samali, B. (2023). Integration of TLS-Derived bridge information modeling (BrIM) with a decision support system (DSS) for digital twinning and asset management of bridge infrastructures. Comput. Industry 147, 103881. doi:10.1016/j.compind.2023.103881
Mohammed Abdelkader, E. (2022). On the hybridization of pre-trained deep learning and differential evolution algorithms for semantic crack detection and recognition in ensemble of infrastructures. Smart Sustain. Built Environ. 11, 740–764. doi:10.1108/sasbe-01-2021-0010
Mondal, T. G., and Chen, G. (2022). Artificial intelligence in civil infrastructure health monitoring—Historical perspectives, current trends, and future visions. Front. Built Environ. 8, 1007886. doi:10.3389/fbuil.2022.1007886
Moragane, H. P. M. N. L. B., Perera, B. A. K. S., Palihakkara, A. D., and Ekanayake, B. (2022). Application of computer vision for construction progress monitoring: a qualitative investigation. Constr. Innov. 24, 446–469. doi:10.1108/ci-05-2022-0130
Munawar, H. S., Ullah, F., Heravi, A., Thaheem, M. J., and Maqsoom, A. (2022a). Inspecting buildings using drones and computer vision: a machine learning approach to detect cracks and damages. Drones 6, 5. doi:10.3390/drones6010005
Munawar, H. S., Ullah, F., Shahzad, D., Heravi, A., Qayyum, S., and Akram, J. (2022b). Civil infrastructure damage and corrosion detection: an application of machine learning. Buildings 12, 156. doi:10.3390/buildings12020156
Musarat, M. A., Khan, A. M., Alaloul, W. S., Blas, N., and Ayub, S. (2024). Automated monitoring innovations for efficient and safe construction practices. Results Eng. 22, 102057. doi:10.1016/j.rineng.2024.102057
Mushtaha, A. W., Alaloul, W. S., Baarimah, A. O., Rabah, F. K., Yousafzai, A. K., and Alakhali, A. K. (2024a). “Sustainability assessment of reverse osmosis desalination plants in Gaza city: multi-criteria analysis,” in 2024 ASU international conference in emerging technologies for sustainability and intelligent systems (ICETSIS), 836–841.
Mushtaha, A. W., Alaloul, W. S., Musarat, M. A., Baarimah, A. O., Rabah, F. K., and Alawag, A. M. (2024b). “BIM-GIS integration for infrastructure management in post-disaster stage,” in 2024 ASU international conference in emerging technologies for sustainability and intelligent systems (ICETSIS), 856–861.
Mushtaha, A. W., Alaloul, W. S., Baarimah, A. O., Musarat, M. A., Alzubi, K. M., and Khan, A. M. (2025). A decision-making framework for prioritizing reconstruction projects in post-disaster recovery. Results Eng. 25, 103693. doi:10.1016/j.rineng.2024.103693
Nanayakkara, S., Perera, P., and Perera, A. (2015). Factors incompatibility of selection and implementation of ERP systems for construction organizations. Thailand: The Third International Congress of Interdisciplinary Research and Development.
Nanayakkara, S., Perera, S., Senaratne, S., Weerasuriya, G. T., and Bandara, H. M. N. D. (2021). Blockchain and smart contracts: a solution for payment issues in construction supply chains. Informatics 8, 36. doi:10.3390/informatics8020036
Naranjo, M., Fuentes, D., Muelas, E., Díez, E., Ciruelo, L., Alonso, C., et al. (2023). Object detection-based system for traffic signs on drone-captured images. Drones 7, 112. doi:10.3390/drones7020112
Nisa, M.-U., and Khalid, F. (2024). Impact of infrastructure on economic growth: a comparative analysis of developed and developing countries. J. Asian Dev. Stud. 13, 1161–1173. doi:10.62345/jads.2024.13.1.95
Nomura, Y., Inoue, M., and Furuta, H. (2022). Evaluation of crack propagation in concrete bridges from vehicle-mounted camera images using deep learning and image processing. Front. Built Environ., 8–2022. doi:10.3389/fbuil.2022.972796
Nyokum, T., and Tamut, Y. (2025). Artificial intelligence in civil engineering: emerging applications and opportunities. Front. Built Environ. 11, 1622873. doi:10.3389/fbuil.2025.1622873
Ogunmakinde, O. E., Egbelakin, T., Sher, W., Omotayo, T., and Ogunnusi, M. (2024). Establishing the limitations of sustainable construction in developing countries: a systematic literature review using PRISMA. Smart Sustain. Built Environ. 13, 609–624. doi:10.1108/sasbe-10-2022-0223
Ojha, A., Liu, Y., Shayesteh, S., Jebelli, H., and Sitzabee, W. E. (2023). Affordable multiagent robotic system for same-level fall hazard detection in indoor construction environments. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 37, 04022042. doi:10.1061/(asce)cp.1943-5487.0001052
Opoku, D.-G. J., Perera, S., Osei-Kyei, R., and Rashidi, M. (2021). Digital twin application in the construction industry: a literature review. J. Build. Eng. 40, 102726. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2021.102726
O’Mahony, N., Campbell, S., Carvalho, A., Harapanahalli, S., Hernandez, G. V., Krpalkova, L., et al. (2020). “Deep learning vs. traditional computer vision,” in Advances in computer vision, 2020//2020. Editors K. ARAI, and S. KAPOOR (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 128–144.
Pal, A., and Hsieh, S.-H. (2021). Deep-learning-based visual data analytics for smart construction management. Automation Constr. 131, 103892. doi:10.1016/j.autcon.2021.103892
Pal, A., Lin, J. J., and Hsieh, S. H. (2022). “Automated construction progress monitoring of partially completed building elements leveraging geometry modeling and appearance detection with deep learning,” in Construction research congress 2022: computer applications, automation, and data analytics - selected papers from construction research congress 2022, 708–718.
Pal, A., Lin, J. J., Hsieh, S.-H., and Golparvar-Fard, M. (2024). Activity-level construction progress monitoring through semantic segmentation of 3D-informed orthographic images. Automation Constr. 157, 105157. doi:10.1016/j.autcon.2023.105157
Palmatier, R. W., Houston, M. B., and Hulland, J. (2018). Review articles: purpose, process, and structure. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 46, 1–5. doi:10.1007/s11747-017-0563-4
Pan, Y., and Zhang, L. (2021). Roles of artificial intelligence in construction engineering and management: a critical review and future trends. Automation Constr. 122, 103517. doi:10.1016/j.autcon.2020.103517
Paneru, S., and Jeelani, I. (2021). Computer vision applications in construction: current state, opportunities and challenges. Automation Constr. 132, 103940. doi:10.1016/j.autcon.2021.103940
Paul, J., and Criado, A. R. (2020). The art of writing literature review: what do we know and what do we need to know? Int. Bus. Rev. 29, 101717. doi:10.1016/j.ibusrev.2020.101717
Perera, S., Nanayakkara, S., Rodrigo, M. N. N., Senaratne, S., and Weinand, R. (2020). Blockchain technology: is it hype or real in the construction industry? J. Industrial Inf. Integration 17, 100125. doi:10.1016/j.jii.2020.100125
Perera, P., Perera, S., Xiaohua, J., Rashidi, M., Yazbek, G., Yazbek, A., et al. (2023). Application of visual computing and deep learning in the construction industry. AUBEA.
Perera, S., Jin, X., Das, P., Gunasekara, K., and Samaratunga, M. (2023). A strategic framework for digital maturity of design and construction through a systematic review and application. J. Industrial Inf. Integration 31, 100413. doi:10.1016/j.jii.2022.100413
Perera, P., Perera, S., Jin, X., Rashidi, M., Nanayakkara, S., Yazbek, G., et al. (2025a). An innovative software development methodology for deep learning-driven visual computing in built environment applications. ITcon 30 (Special issue Construction 5.0), 1017–1040. doi:10.36680/j.itcon.2025.041
Perera, P., Perera, S., Jin, X., Rashidi, M., Nanayakkara, S., Yazbek, G., et al. (2025b). Impact of explainable artificial intelligence for sustainable built environment. CIB Conferences 1, 347. doi:10.7771/3067-4883.1668
Pizarro, P. N., Hitschfeld, N., Sipiran, I., and Saavedra, J. M. (2022). Automatic floor plan analysis and recognition. Automation Constr. 140, 104348. doi:10.1016/j.autcon.2022.104348
Pouyanfar, S., Sadiq, S., Yan, Y., Tian, H., Tao, Y., Presa-Reyes, M. E., et al. (2018). A survey on deep learning. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 51, 1–36. doi:10.1145/3234150
Pranckutė, R. (2021). Web of science (WoS) and scopus: the titans of bibliographic information in today’s, 9. Academic World. Publications, 12.
Rahnamayiezekavat, P., Wang, D., Chai, J., Moon, S., Rashidi, M., and Wang, X. (2024). Automated pavement marking integrity assessment using a UAV platform – a test case of public parking. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 24, 1594–1605. doi:10.1080/13467581.2024.2329358
Reports and data (2019). Artificial intelligence (AI) in construction market by technology (machine learning and deep learning, natural language processing), by component, by phase, by deployment type, by applications, by organization size, by end-use, and segment forecasts. Rep. Data. Available online at: https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2019/07/23/1886563/0/en/Artificial-Intelligence-AI-in-Construction-Market-to-Reach-USD-4-51-Billion-By-2026-Reports-And-Data.html.
Rodrigo, N., Omrany, H., Chang, R., and Zuo, J. (2024). Leveraging digital technologies for circular economy in construction industry: a way forward. Smart Sustain. Built Environ. 13, 85–116. doi:10.1108/sasbe-05-2023-0111
Salami Pargoo, N., and Ilbeigi, M. (2023). A scoping review for cybersecurity in the construction industry. J. Manag. Eng. 39, 03122003. doi:10.1061/jmenea.meeng-5034
Sánchez, O., Castañeda, K., Vidal-Méndez, S., Carrasco-Beltrán, D., and Lozano-Ramírez, N. E. (2024). Exploring the influence of linear infrastructure projects 4.0 technologies to promote sustainable development in smart cities. Results Eng. 23, 102824. doi:10.1016/j.rineng.2024.102824
Sompolgrunk, A., Banihashemi, S., and Mohandes, S. R. (2023). Building information modelling (BIM) and the return on investment: a systematic analysis. Constr. Innov. 23, 129–154. doi:10.1108/ci-06-2021-0119
Spencer, B. F., Hoskere, V., and Narazaki, Y. (2019). Advances in computer vision-based civil infrastructure inspection and monitoring. Engineering 5, 199–222. doi:10.1016/j.eng.2018.11.030
Thangarajan, S. K., and Chokkalingam, A. (2021). Integration of optimized neural network and convolutional neural network for automated brain tumor detection. Sens. Rev. 41, 16–34. doi:10.1108/sr-02-2020-0039
Waltman, N. J. V. E. A. L. (2023). VOSviewer manual. Manual for VOSviewer version 1.6.19 . Universiteit Leiden.
Wang, H., and Hu, Y. (2022). Artificial intelligence technology based on deep learning in building construction management system modeling. Adv. Multimedia 2022, 1–9. doi:10.1155/2022/5602842
Wang, D., Ren, B., Cui, B., Wang, J., Wang, X., and Guan, T. (2021). Real-time monitoring for vibration quality of fresh concrete using convolutional neural networks and IoT technology. Automation Constr. 123, 103510. doi:10.1016/j.autcon.2020.103510
Watson, R. T., and Webster, J. (2020). Analysing the past to prepare for the future: writing a literature review a roadmap for release 2.0. J. Decis. Syst. 29, 129–147. doi:10.1080/12460125.2020.1798591
Won, D., Chi, S., and Choi, J. O. (2024). UAV imagery-based automatic classification of ground surface types for earthworks. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 28, 2121–2131. doi:10.1007/s12205-024-1643-x
Wu, H., Li, H., Luo, X., and Jiang, S. (2023). Blockchain-based onsite activity management for smart construction process quality traceability. IEEE Internet Things J. 10, 21554–21565. doi:10.1109/jiot.2023.3300076
Wuni, I. Y., Abankwa, D. A., Koc, K., Adukpo, S. E., and Antwi-Afari, M. F. (2024). Critical barriers to the adoption of integrated digital delivery in the construction industry. J. Build. Eng. 83, 108474. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2024.108474
Xiong, R., and Tang, P. (2021). Machine learning using synthetic images for detecting dust emissions on construction sites. Smart Sustain. Built Environ. 10, 487–503. doi:10.1108/sasbe-04-2021-0066
Xu, S., Wang, J., Shou, W., Ngo, T., Sadick, A.-M., and Wang, X. (2021). Computer vision techniques in construction: a critical review. Archives Comput. Methods Eng. 28, 3383–3397. doi:10.1007/s11831-020-09504-3
Yadav, S., Prakash, A., Arora, M., and Mittal, A. (2023). Digital transformation: exploring cornerstones for construction industry. Kybernetes 53, 5378–5401. doi:10.1108/k-05-2023-0895
Yang, L., and Cai, H. (2023). Cost-efficient image semantic segmentation for indoor scene understanding using weakly supervised learning and BIM. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 37, 04022062. doi:10.1061/jccee5.cpeng-5065
Yang, B., Zhang, B., Zhang, Q., Wang, Z., Dong, M., and Fang, T. (2022). Automatic detection of falling hazard from surveillance videos based on computer vision and building information modeling. Struct. Infrastructure Eng. 18, 1049–1063. doi:10.1080/15732479.2022.2039217
Yang, L., Li, B., Feng, J., Yang, G., Chang, Y., Jiang, B., et al. (2023). Automated wall-climbing robot for concrete construction inspection. J. Field Robotics 40, 110–129. doi:10.1002/rob.22119
Yang, S., Wang, Y., Guo, S., and Feng, S. (2024). An operation site security detection method based on point cloud data and improved YOLO algorithm under the architecture of the power internet of things. J. Eng. 2024, e12344. doi:10.1049/tje2.12344
Yap, J. B. H., Chow, I. N., and Shavarebi, K. (2019). Criticality of construction industry problems in developing countries: analyzing Malaysian projects. J. Manag. Eng. 35, 04019020. doi:10.1061/(asce)me.1943-5479.0000709
Yin, Y., and Antonio, J. (2020). Application of 3D laser scanning technology for image data processing in the protection of ancient building sites through deep learning. Image Vis. Comput. 102, 103969. doi:10.1016/j.imavis.2020.103969
Yu, W.-D., Liao, H.-C., Li, J.-W., Lim, Z.-Y., and Hsiao, W.-T. (2023). Application of AIoT image sensor for lifting operation safety monitoring of Mobile crane. Eng. Proc. 55, 52. doi:10.3390/engproc2023055052
Zhao, Y., Yin, Y., and Gui, G. (2020). Lightweight deep learning based intelligent edge surveillance techniques. IEEE Trans. Cognitive Commun. Netw. 6, 1146–1154. doi:10.1109/tccn.2020.2999479
Zhao, T., Liang, X., Tu, W., Huang, Z., and Biljecki, F. (2023). Sensing urban soundscapes from street view imagery. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 99, 101915. doi:10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2022.101915
Zhao, J., Cao, Y., and Xiang, Y. (2024). Pose estimation method for construction machine based on improved AlphaPose model. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 31, 976–996. doi:10.1108/ecam-05-2022-0476
Zhu, J., and Liu, W. (2020). A tale of two databases: the use of web of science and scopus in academic papers. Scientometrics 123, 321–335. doi:10.1007/s11192-020-03387-8
Keywords: artificial intelligence, construction project management, construction digitalisation, deep learning, digital technologies, visual computing, Construction 4.0, technology in built environment
Citation: Perera P, Perera S, Jin X, Rashidi M, Nanayakkara S, Yazbek G and Yazbek A (2025) Deep learning – enabled visual computing in construction: application and digital technology integration. Front. Built Environ. 11:1655847. doi: 10.3389/fbuil.2025.1655847
Received: 28 June 2025; Accepted: 07 August 2025;
Published: 01 September 2025.
Edited by:
Xianbo Zhao, Central Queensland University, AustraliaReviewed by:
Ahmed Mushtaha, University of Technology Petronas, MalaysiaXin Li, The University of Adelaide, Australia
Copyright © 2025 Perera, Perera, Jin, Rashidi, Nanayakkara, Yazbek and Yazbek. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Prasad Perera, MjIwNDgyOTFAc3R1ZGVudC53ZXN0ZXJuc3lkbmV5LmVkdS5hdQ==
 Prasad Perera
Prasad Perera Srinath Perera
Srinath Perera Xiaohua Jin
Xiaohua Jin Maria Rashidi
Maria Rashidi Samudaya Nanayakkara
Samudaya Nanayakkara Gina Yazbek2
Gina Yazbek2