- 1Jiangxi Provincial Key Laboratory of Highway Bridge and Tunnel Engineering & Jiangxi Communications Investment Maintenance Technology Group Co., Ltd, Nanchang, China
- 2Jiangxi Communications Investment Group Co., Ltd, Nanchang, China
- 3Engineering Research Centre of Diagnosis Technology of Hydro-Construction, Chongqing Jiaotong University, Chongqing, China
The analysis of crack morphology have important influences on the study of rock mechanical properties and crack propagation behavior. A series of uniaxial compression tests and acoustic emission (AE) tests were conducted on different crack forms of red sand stone (intact rock specimens and single cracked and double cracked specimens). The results show that: 1) Intact rock specimens exhibit higher peak stress, peak strain, and elastic modulus than cracked specimens. Peak stress and elastic modulus are significantly affected by crack configuration, while peak strain differences are relatively minor. Single cracked specimens demonstrate higher peak stress and elastic modulus compared to double crack specimens. 2) During the yield stage and post-peak failure stage, both single and double cracked specimens exhibited distinct AE ringing count and cumulative ringing count surges with increasing fracture inclination angle. The AE ringing counts show a “step-like” growth pattern, while the proportion of cumulative ringing counts increases logarithmically with the inclination angle. 3) Analysis of the failure modes reveals that, with increasing crack inclination angles, single cracked specimens predominantly undergo shear–tensile mixed failure, whereas double cracked specimens progressively evolve from shear tensile mixed failure to tensile failure. These findings provide experimental evidence for assessing crack rock mass stability and predicting failure mechanisms.
1 Introduction
Rock, as a naturally occurring heterogeneous medium, inherently contains defects such as cracks, pores, and joints, which critically influence its mechanical properties (Meng et al., 2018) In mining, slope excavation, and related rock engineering, complex stress conditions and rapid energy release induce new cracks within the rock mass, which subsequently propagate and coalesce, ultimately causing rock mass instability and failure (Zhao et al., 2020). The size, geometry, and spatial distribution of cracks play a crucial role in controlling the overall stability and failure mechanisms of rock masses (Liu et al., 2014; Liu et al., 2021; Xiao et al., 2015). Therefore, investigating the mechanical properties and failure mechanisms of cracked rock masses is essential for guiding underground engineering, deep resource extraction, and rock engineering (Gao et al., 2024).
In recent years, the initiation and propagation patterns of cracks in rocks containing prefabricated cracks have attracted widespread attention from researchers. Zhou et al. (2014) and Zhao et al. (2013) investigated prefabricated cracks in gypsum and cement specimens, showing that crack density, geometry, closure state, and inclination significantly affect the failure strength of rock-like materials. Huang et al. (2024) conducted conventional triaxial compression and confining pressure unloading tests on sandstone specimens with vertical and inclined cracks, and analyzed their stress–strain curves, strength characteristics, and deformation parameters. Jin et al. (2017) carried out uniaxial compression tests on cubic specimens with different crack geometries and found that two discontinuous prefabricated cracks significantly influence crack initiation, failure modes, deformation fields, and energy mechanisms in rock-like materials. Zhang et al. (2023) used discrete element simulations to characterize crack evolution and crack behavior of granite considering inherent microcracks.
Acoustic emission (AE) refers to the physical phenomenon in which rocks release stored strain energy as transient elastic waves during deformation or crack. Since Goodman (1963) demonstrated the Kaiser effect in rock materials, AE technology has evolved into a key nondestructive testing technique and has been extensively applied in investigations of rock mechanical behavior. Miao et al. (2021) employed AE technology to monitor the damage evolution and crack propagation of rocks under high static stress conditions during coupled static–dynamic loading tests. Hao et al. (2022) investigated the transitional behavior and gradual evolution of the acoustic emission count rate and energy release rate during rock crack under different induced stress conditions. Du et al. (2024) performed uniaxial compression and Brazilian tests on different rocks, analyzed AE signals and stress–strain curves to divide the failure process into five stages, and proposed a novel RA–AF based crack classification criterion, concluding that AE parameters at the unstable crack growth stage can accurately predict rock failure modes. Shiotani et al. (2001) employed acoustic emission (AE) characteristics to evaluate the effects of displacement, strain, and temperature measurements on rocks, and proposed a classification criterion for rock crack states. Du et al. (2020) investigated the AE characteristics of rocks under different loading modes and found that tensile cracks are associated with low RA–high AF signals, while shear cracks correspond to high RA–low AF signals, confirming the effectiveness of AF–RA criteria in crack mode identification.
Although previous studies have provided important insights into rock deformation and failure through acoustic emission analysis, most investigations have concentrated on intact rocks or those containing a single type of crack. Systematic comparative studies employing AE to elucidate the relationship between microcrack evolution and failure mechanisms in rocks with different crack geometries remain insufficient and require further research.
This study focuses on different crack forms of red sand stone as the research objects. Uniaxial compression tests combined with acoustic emission monitoring are conducted to investigate the mechanical properties, AE evolution, and failure mechanisms under compressive loading. It also analyzes the differences in rock failure mechanisms using the RA-AF classification method. The results provide important implications for support design in cracked sandstone strata and for the assessment of rock mass stability in engineering practice.
2 Materials and experimental methods
2.1 Specimen preparation
The red sandstone specimens employed in this experiment are taken from Luzhou, Sichuan Province, China. The uniaxial compressive strength of the rock is 28.96 MPa, and its primary mineral constituents are quartz, calcite, albite, and dolomite. According to the test standards of the International Society for Rock Mechanics (ISRM), the specimens are processed into rectangular blocks with dimensions of 100 mm × 50 mm × 50 mm. The precast cracks were through-going parallel cracks generated by wire-cutting at the geometric center of the sandstone blocks, with a length of 10 mm and a width of 1 mm. The crack forms of the specimens include single crack and double cracks. For clarity, a combined alphanumeric notation is adopted for specimen labeling. For example, SF15° and DF15°, where SF/DF represent single cracked/double cracked red sandstone; Respectively, 15 represents the crack dip angle α, where α is the angle between the crack and the horizontal direction. The crack inclination angles were set at 15°, 30°, 45°, 60°, and 75°, each crack type corresponded to five inclination angles, forming a total of ten crack types. The test specimens included in this study comprised the ten cracked-rock specimen types described above and the intact rock (IR) specimens, as shown in Figure 1. Each specimen type comprised three parallel specimens.

Figure 1. Cracked red sandstone rock specimens. (a) Schematic diagram of a single-crack red sandstone specimen. (b) Schematic diagram of double-cracks red sandstone specimen.
2.2 Experimental equipment and setup
The primary equipment used in this experiment includes a rock mechanics testing system and an acoustic emission (AE) system, as shown in Figure 2. Uniaxial compression tests were conducted using an RMT-150C rock mechanics testing system, which has a maximum load capacity of 1,000 kN and an adjustable strain rate ranging from 10−4 to 1.0 mm/s. The test process employed load control mode, with a loading rate of 0.05 kN/s, until specimen failure occured. A total of 33 test groups were conducted, and the failure modes were documented and the stress–strain curves during loading were recorded.
The acoustic emission system used a PCI-2 acoustic emission system with an operating frequency range of 200 kHz to 5 MHz. The threshold for signal acquisition was set to 40 dB. Two miniature piezoelectric sensors were fixed in parallel at both ends of the specimen. To ensure good contact between the sensors and the specimen surface, vacuum silicone grease was used as a coupling agent, and the sensors were fixed in place with insulating tape.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Mechanical characteristics
3.1.1 Stress–strain curve
The uniaxial compression stress–strain curves of specimens with different crack configurations are shown in Figure 3. It can be observed that the stress–strain behavior of intact rock specimens, single cracked and double cracked specimens exhibit similarities, with the axial strain at failure being less than 2.5% for all cases. All specimens undergo four stages: initial compaction, elastic deformation, yield, and post-peak failure.

Figure 3. Stress–strain curves of red sandstone with different crack forms. (a) Single cracked. (b) Double cracked.
Specifically, during the initial compaction stage, the stress–strain curve exhibits significant nonlinearity, as microcracks and pores within the specimen beginning to consolidate. As the stress-strain curve approaches linearity, the elastic stage is entered. In the subsequent yielding stage, microcracks undergo localized crack and propagation, resulting in localized stress drops before the stress reaches its peak. In the final failure stage, the stress–strain curve drops sharply, indicating a sudden failure process, and the specimens exhibit distinct brittle characteristics.
3.1.2 Peak strength, peak strain, and elastic modulus
As shown in Figures 4a–c, the intact rock specimen exhibits higher peak stress, peak strain, and elastic modulus compared to the single cracked and double cracked specimens. The peak stress of the intact rock specimen reaches 32.13 MPa. With an increase in the number of cracks, the peak stress decreased by 14.23%–47.11%; peak strain decreased by 9.35%–21.42%, and elastic modulus decreased by 9.65%–47.12%. Under the same inclination angle, the peak stress and elastic modulus of single cracked specimens are generally higher than those of double cracked specimens. This is attributed to stress concentration induced by the presence of cracks. As the number of cracks increases, more stress concentration zones develop, leading to failure under lower stress levels and a reduction in elastic modulus.

Figure 4. Comparison of mechanical parameters of red sandstone with different crack forms under uniaxial compression. (a) Peak stress. (b) Peak strain-vs. (c) Elastic modulus-E.
Overall, the presence of cracks enhances rock brittleness and different fracture patterns exhibit significant differences in the mechanical properties of red sandstone specimens. Single cracked specimens consistently demonstrate higher peak stress and elastic modulus compared to double cracked specimens. In addition, the same crack type exhibits significant differences under various inclination angles. The peak strength and elastic modulus of both single and double cracked specimens are sensitive to changes in fracture inclination angle, whereas the peak strain is relatively less affected.
3.2 AE characteristics
3.2.1 AE ring count
AE parameters mainly include AE events, AE ring counts, AE energy and AE amplitude. This study focuses on the analysis of AE ring counts and AE cumulative ring counts to investigate the AE response characteristics associated with the failure process of red sandstone with different crack forms under uniaxial compression at different crack inclination angles.
Figures 5, 6 illustrate the variations of stress, AE ring counts, and cumulative ring counts with loading time during uniaxial compression of different cracked red sandstone specimens. Because the constant loading rate (kN/s) is applied, the stress–time curve of the specimens exhibit an approximately linear trend before reaching the peak strength. Therefore, the failure evolution process of double cracked red sandstone under uniaxial compression is analyzed based on the temporal characteristics of AE parameters in conjunction with the stress–strain curve.
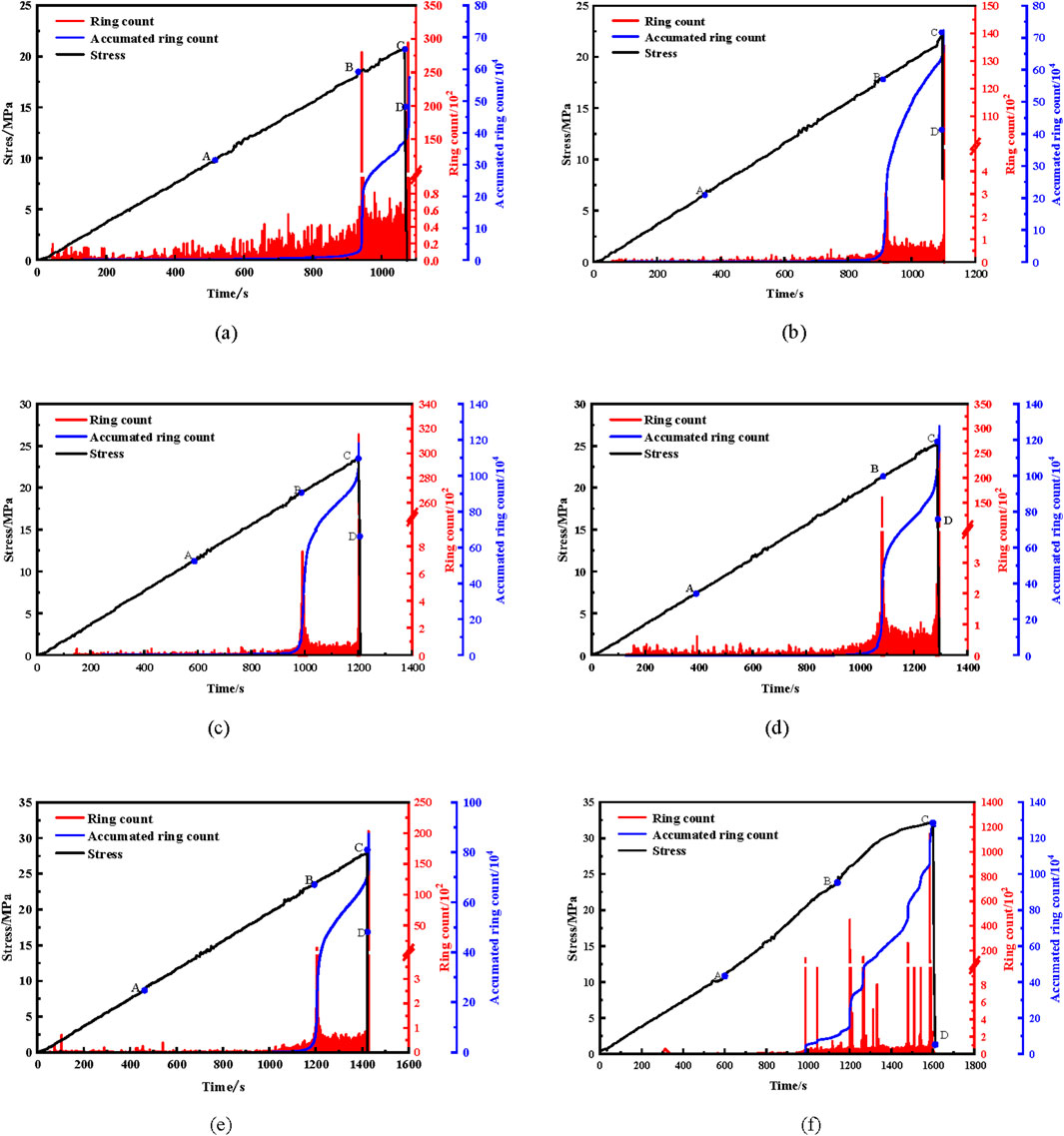
Figure 5. AE ring counts of single cracked rock samples under uniaxial compression. (a) α = 15°. (b) α = 30°. (c) α = 45°. (d) α = 60°. (e) α = 75°. (f) IR.

Figure 6. AE ring counts of double cracked rock samples under uniaxial compression. (a) α = 15°. (b) α = 30°. (c) α = 45°. (d) α = 60°. (e) α = 75°. (f) IR.
Regardless of whether the specimens are intact or cracked, and irrespective of the crack inclination angle, the AE ringing count evolution exhibits a consistent pattern across all red sandstone specimens. During the initial compaction stage (OA) and the elastic deformation stage (AB), axial stress increased slowly, the AE ring counts remain at a low level, with AE cumulative ring counts increasing at an extremely slow rate. This is primarily attributed to the presence of original microcracks and pores within the specimens. In the early loading stage, deformation is dominated by compaction, where microcracks progressively closed but not expanding. Upon entering the elastic deformation stage, the stress–time curve become approximately linear and stress continue to increase. Although stress is concentrated in the closed regions, crack closure has not triggered new cracks, AE activity remains weak, with no significant energy release triggered.
With further increases in axial stress, the test entered the yielding stage (BC). In this stage, some of the original cracks undergo stable propagation, while new cracks form in stress concentration zones, creating secondary cracks. Correspondingly, AE ring counts increase significantly, AE cumulative ring counts rise sharply, and step-like increments appear in regions of local stress drop. Upon entering the post-peak failure stage (CD), the internal crack density approaches saturation, the main crack rapidly propagates from the crack tips and achieves full penetration, leading to overall instability and failure of the specimen. During this process, the strain energy stores within the rock reach its limit and is released instantaneously, causing AE ring counts to remain at a high value accompanied by the largest single AE event response. Meanwhile, the slope of AE cumulative ring counts increased markedly, showing a sharp surge nearly parallel to the time axis.
To clearly illustrate the evolution of AE ring counts across different loading stages, Figures 7, 8 show the relationship between the proportion of AE cumulative ring counts and fracture inclination angle for specimens with different pre-fabricated cracks. It can be observed that, regardless of fracture number, the stage BD consistently exhibits the highest proportion of cumulative AE ring counts. For the intact rock specimen, the proportion of AE cumulative ring counts during the stage BD is 90.54%. As the fracture inclination angle increases, AE cumulative ring count proportions during the stage BD for single cracked specimens are 92.23%, 95.04%, 95.67%, 97.06%, and 98.07%, respectively. While for double cracked specimens are 94.15%, 95.68%, 96.76%, 97.34%, and 98.51%, respectively.

Figure 7. Proportion of AE cumulative ring counts at different loading stages in single cracked red sandstone. (a) Stage Initial compaction. (b) Stage elastic deformation. (c) Stage yield and post-peak failure.

Figure 8. Proportion of AE cumulative ring counts at different loading stages in double cracked red sandstone. (a) Stage Initial compaction. (b) Stage elastic deformation. (c) Stage yield and post-peak failure.
Overall, the proportions of AE cumulative ring counts in stages OA and AB exhibit a logarithmic decrease with increasing fracture inclination, while the stage BD shows a logarithmic increase. This evolutionary pattern provides a good explanation for the stepwise growth characteristics observed in Figures 5, 6.
3.2.2 RA and AF values
During uniaxial loading, the microcracks generated in the specimens are mainly of two types: shear cracks and tensile cracks. By analyzing the RA and AF values of AE signals, the failure mechanisms of cracked red sandstone with different pre-fabricated cracks could be evaluated. Specifically, RA is defined as the ratio of rise time to amplitude, whereas AF is defined as the ratio of ring count to duration.
Tensile cracks are characterized by low RA values and high AF values, whereas shear cracks are characterized by high RA values and low AF values, as illustrated in Figure 9. Zhang and Deng (2020) proposed that the optimal value of the AF:RA separation line can be determined using acoustic emission dominant frequency characteristics, and found that the separation line K (AF/RA) for brittle rocks under compression conditions should be within the range of 100–500.
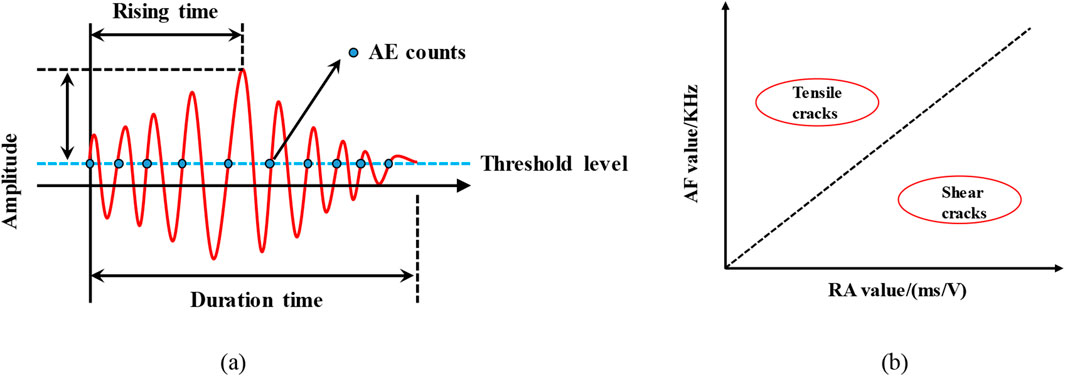
Figure 9. AE monitoring of cracked red sandstone. (a) AE signal characteristic parameters. (b) Classification criteria.
As shown in Figures 10, 11, point density maps of RA–AF distributions are plotted for different crack patterns of res sandstone, where red denotes high-density regions and purple denotes low-density regions. A separation line of K = 200 is defined to classify crack types.

Figure 10. RA–AF scatter plots of single cracked red sandstone. (a) α = 15°. (b) α = 30°. (c) α = 45°. (d) α = 60°. (e) α = 75°. (f) IR.

Figure 11. RA–AF scatter plots of double cracked red sandstone. (a) α = 15°. (b) α = 30°. (c) α = 45°. (d) α = 60°. (e) α = 75°. (f) IR.
Figures 10a–f show scatter plots of intact rock specimens and single cracked specimens under different crack inclination angles. The RA values for the intact red sandstone specimens range from 0 to 10 ms/V, while those for the single cracked specimens extend from 0 to 80 ms/V. Both specimen types exhibit AF values within the range of 0–500 kHz, reflecting a typical high AF and low RA distribution pattern. In the tensile crack-dominated region, AE data points are densely clustered, whereas in the shear crack-dominated region, they are more scattered. This indicates that the microcrack evolution during the uniaxial failure of both intact and single cracked red sandstone specimens is primarily governed by tensile cracking. With increasing crack inclination angle, the RA–AF distribution of double cracked red sandstone exhibit no significant changes. The proportion of tensile cracks increase gradually but only slightly, from 62.4% to 68.1%.
Figures 11a–f show scatter plots of double cracked specimens under different crack inclination angles. It can be observed that RA values range from 0 to 90 ms/V and AF values range from 0 to 550 kHz, indicating that the microcrack evolution in double cracked red sandstone is similar to that in single cracked specimens, being predominantly tensile. However, with increasing crack inclination angle, the RA-AF distribution of double cracked red sandstone change significantly.
Specifically, at low inclination angles from 15° to 30°, AF is mainly distributed within 0∼550 kHz, and RA ranged from 0 to 90 ms/V. In the tensile crack-dominated region, the data points clustered along the AF axis, forming high density “red–yellow zones”, with tensile crack proportions of 58.68% and 69.75%, respectively. When the crack inclination angle increases from 45° to 75°, the RA values drop to the range of 0–4 ms/V, the proportion of shear cracks decrease sharply, and the proportion of tensile cracks rise markedly to 84.54%, 87.06%, and 87.58%, respectively. Compared with 15°, the proportion of tensile cracks at 75° increased by 29.9%.
Therefore, the relationship between the proportion of tensile cracks and the crack angle is fitted using the least squares method for single cracked and double cracked specimens, as shown in Figure 12. The results indicate that both single cracked and double cracked red sandstone exhibit a logarithmic growth evolution characteristic of the proportion of tensile cracks increasing with the crack angle. However, there are significant differences between the two in terms of the magnitude and trend of changes in the proportion of tensile cracks.

Figure 12. Proportion of tensile cracks versus crack inclination angle. (a) Single cracked. (b) Double cracked.
For single cracked specimens, although the proportion of tensile cracks increase gradually with crack inclination, the growth is extremely slow and never exceed 70%. Consequently, the failure mode remains shear tensile mixed failure. Although the certain trend is evident, with crack propagation gradually shifting toward tensile dominance, this transition had not fully realized. For double cracked specimens, the proportion of tensile cracks increases rapidly with angle when the crack inclination angle is small, but the growth slows down after exceeding the critical angle of 45°, exhibiting a logarithmic evolution characteristic of “rapid growth followed by slow growth.”
This trend indicates that the transition of failure mechanisms exhibits both critical and saturation characteristics. As the crack inclination angle increases, the crack propagation pattern gradually shifts from shear tensile mixed failure to tensile failure. The primary reason lies in the absence of crack interaction in single cracked specimens. Stress concentration along the crack plane is mainly governed by crack geometry, leading to a relatively simple crack propagation path that remains dominated by shear–tensile mixed failure. Although tensile stress increases with greater inclination angles, the geometric simplicity of a single cracked limits the expansion space for tensile cracks. Therefore, the growth of tensile cracks was relatively minor, and the failure mode never fully transitioned to tensile failure.
In contrast, the interaction between cracks in double cracked specimens result in more complex crack propagation paths and a more heterogeneous stress field. With increasing inclination angle, the stress concentration effect between the two cracks intensifies, causing crack propagation to occur not only along a single cracked plane but also under the influence of crack interaction. The interaction between cracks in a double-crack system causes stress to be redistributed between the two cracks, and stress transfer between cracks makes it easier for tensile cracks to form. Particularly when the inclination angle increases to 45° or higher, the interaction between cracks become more pronounced, promoting tensile crack propagation. Tensile failure is thereby significantly enhanced and gradually become the dominant mechanism.
4 Conclusion
In this study, uniaxial compression and AE tests are conducted on different crack forms of red sand stone (intact rock specimens and single cracked and double cracked specimens). By comparing and analyzing the effects of crack types on the mechanical properties and microcrack evolution of red sandstone, the main conclusions which may be drawn from the results obtained herein are as follows.
1. The results of uniaxial compression tests show that the stress–strain curves of different crack forms exhibit similar overall trends, but their effects on the mechanical properties of red sandstone differ. The intact specimens show higher peak stress, peak strain, and elastic modulus compared to cracked specimens. Among these parameters, peak stress and elastic modulus are more significantly affected by crack configuration, while peak strain show relatively minor variations. In addition, single cracked specimens generally exhibit higher peak stress and elastic modulus than double cracked, indicating that increased crack density further degrades the mechanical properties of red sandstone.
2. AE signals effectively capture the damage evolution process of the rock. During the initial compaction and elastic deformation stages of loading, the AE ring counts remain low, and the proportion of AE cumulative ring counts exhibit a logarithmic decrease with increasing fracture inclination. Upon entering the yielding and post-peak failure stages, both single cracked and double cracked specimens show a pronounced surge in AE ring counts as the crack inclination angle increases, accompanied by a rapid rise in AE cumulative ring counts. The ring count exhibits a “step-like” increase pattern, while the cumulative ring count ratio shows a logarithmic upward trend with increasing crack inclination angle.
3. Based on the AE parameters AF and RA, tensile cracks are found to dominate microcrack evolution in both single cracked and double cracked specimens. With increasing crack inclination, the proportion of tensile cracks followed a logarithmic growth. However, single cracked specimens showed only a slight increase and remained in a shear–tensile mixed failure mode, whereas double cracked specimens exhibited a rapid increase that slowed after a critical angle, with the failure mode gradually shifting to tensile failure.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
RY: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. LJ: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. PX: Software, Writing – original draft. SY: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. WK: Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The authors declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The authors acknowledge the financial support provided by the Training Program for Academic and Technical Leaders in Key Disciplines in Jiangxi Province, China - Leading Talent Project (20225BCJ22014), Science and Technology Project of Jiangxi Provincial Department of Transportation (2023C0005).
Conflict of interest
Authors RY, SY were employed by Jiangxi Communications Investment Maintenance Technology Group Co., Ltd. Author LJ was employed by Jiangxi Communications Investment Group Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Du, K., Li, X., Tao, M., and Wang, S. (2020). Experimental study on acoustic emission (AE) characteristics and crack classification during rock fracture in several basic lab tests. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 133, 104411. doi:10.1016/j.ijrmms.2020.104411
Du, K., Luo, X., Liu, M., Liu, X., and Zhou, J. (2024). Understanding the evolution mechanism and classification criteria of tensile -shear cracks in rock failure process from acoustic emission (AE) characteristics. Eng. Fract. Mech. 296, 109864. doi:10.1016/j.engfracmech.2024.109864
Gao, H., Xie, H., Zhang, Z., Lu, J., Zhang, D., Zhang, R., et al. (2024). True triaxial energy evolution characteristics and failure mechanism of deep rock subjected to mining-induced stress. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 176, 105724. doi:10.1016/j.ijrmms.2024.105724
Goodman, R. E. (1963). Subaudible noise during compression of rocks. GSA Bull. 74, 487–490. doi:10.1130/0016-7606(1963)74[487:sndcor]2.0.co;2
Hao, J., Zhang, Y., Qiao, L., Deng, N., Li, Q., and Zhang, Q. (2022). Study on gradual fracture of rock and key precursor information before peak stress based on AE monitoring under true triaxial loading. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 34, 04021396. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0004029
Huang, Y.-H., Wu, S.-Y., and Yang, C. (2024). Experimental study on the failure behaviors of sandstone specimens with two fissures under triaxial loading and unloading conditions. Eng. Fract. Mech. 298, 109933. doi:10.1016/j.engfracmech.2024.109933
Jin, J., Cao, P., Chen, Y., Pu, C., Mao, D., and Fan, X. (2017). Influence of single flaw on the failure process and energy mechanics of rock-like material. Comput. Geotechnics 86, 150–162. doi:10.1016/j.compgeo.2017.01.011
Liu, T., Cao, P., and Lin, H. (2014). Damage and fracture evolution of hydraulic fracturing in compression-shear rock cracks. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 74, 55–63. doi:10.1016/j.tafmec.2014.06.013
Liu, Z., Ma, C., Wei, X., and Xie, W. (2021). Experimental study on mechanical properties and failure modes of pre-existing cracks in sandstone during uniaxial tension/compression testing. Eng. Fract. Mech. 255, 107966. doi:10.1016/j.engfracmech.2021.107966
Meng, Q., Zhang, M., Han, L., Pu, H., and Chen, Y. (2018). Acoustic emission characteristics of red sandstone specimens under uniaxial cyclic loading and unloading compression. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 51, 969–988. doi:10.1007/s00603-017-1389-6
Miao, S., Pan, P.-Z., Konicek, P., Yu, P., and Liu, K. (2021). Rock damage and fracturing induced by high static stress and slightly dynamic disturbance with acoustic emission and digital image correlation techniques. J. Rock Mech. Geotechnical Eng. 13, 1002–1019. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2021.05.001
Shiotani, T., Ohtsu, M., and Ikeda, K. (2001). Detection and evaluation of AE waves due to rock deformation. Constr. Build. Mater. 15, 235–246. doi:10.1016/S0950-0618(00)00073-8
Xiao, T., Li, X., and Jia, S. (2015). Failure characteristics of rock with two pre-existing transfixion cracks under triaxial compression. Yanshilixue Yu Gongcheng Xuebao/Chinese J. Rock Mech. Eng. 34, 2455–2462. doi:10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2014.1443
Zhang, Z.-H., and Deng, J.-H. (2020). A new method for determining the crack classification criterion in acoustic emission parameter analysis. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 130, 104323. doi:10.1016/j.ijrmms.2020.104323
Zhang, R., Zhao, C., Xing, J., Niu, J., Chen, H., and Qian, Y. (2023). Macro and micro investigation of fracture behavior and crack evolution considering inherent microcrack in prefabricated flawed granite. Eng. Fract. Mech. 284, 109264. doi:10.1016/j.engfracmech.2023.109264
Zhao, Y.-L., Wan, W., Wang, W.-J., Wang, M., and Peng, Q.-Y. (2013). Fracture experiments on ordered multi-crack body in rock-like materials under uniaxial compression and numerical simulation of wing cracks. Yantu Gongcheng Xuebao/Chinese J. Geotechnical Eng. 35, 2097–2109.
Zhao, K., Yang, D., Gong, C., Zhuo, Y., Wang, X., and Zhong, W. (2020). Evaluation of internal microcrack evolution in red sandstone based on time–frequency domain characteristics of acoustic emission signals. Constr. Build. Mater. 260, 120435. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120435
Keywords: rock mechanics, acoustic emission, fracture classification, RA-AF analysis, uniaxial compression
Citation: Yao R, Jinzhi L, Xianjie P, Yang S and Kui W (2025) Mechanical behavior and acoustic emission evolution of cracked red sandstone under uniaxial compression. Front. Built Environ. 11:1712842. doi: 10.3389/fbuil.2025.1712842
Received: 25 September 2025; Accepted: 18 November 2025;
Published: 18 December 2025.
Edited by:
Xueyu Geng, University of Warwick, United KingdomReviewed by:
Jinyu Dong, North China University of Water Conservancy and Electric Power, ChinaBaoyu Li, Shandong University of Technology, China
Copyright © 2025 Yao, Jinzhi, Xianjie, Yang and Kui. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Liu Jinzhi, anhqdF9saXVqaW56aGlAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Rong Yao1
Rong Yao1 Liu Jinzhi
Liu Jinzhi Sun Yang
Sun Yang Wang Kui
Wang Kui