- 1Department of Biological Sciences, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC, United States
- 2Toxicology Graduate Program, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC, United States
- 3Center for Human Health and the Environment, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC, United States
The epidermis is routinely subjected to DNA damage induced by ultraviolet B (UVB) solar radiation. In addition to activating canonical DNA damage responses such as cycle cell checkpoints and DNA repair, UVB-induced DNA damage can also activate additional signaling pathways including inflammatory responses. The pathways activated downstream of UVB-induced DNA damage have a critical role in determining cellular survival to UVB radiation. Here we report that loss of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β (C/EBPβ) in mouse keratinocytes results in enhanced UVB-induced apoptosis through activation of extrinsic apoptosis genes cleaved caspase-8 and truncated BH3 interacting-domain death agonist (tBid). RNAseq and Ingenuity Pathway Analysis of UVB-treated C/EBPβ−/− primary keratinocytes revealed an enrichment of inflammatory signaling pathways, including the type I interferon (IFN-I) pathway as the most enriched pathway. Numerous IFN-I stimulated genes were up-regulated in UVB-treated C/EBPβ−/− keratinocytes, including genes that regulate extrinsic apoptosis. Inhibition of the interferon-α/β receptor or the associated kinase Tyk2 greatly reduced cell death in UVB-exposed C/EBPβ deficient keratinocytes, demonstrating the dependence of IFN signaling in C/EBPβ regulated apoptosis. The apoptosis inducing cytokine tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) was identified as one of the most significant upstream regulators activated in UVB-exposed C/EBPβ−/− keratinocytes compared to UVB exposed wild type control. UVB-exposed C/EBPβ−/− keratinocytes displayed increased expression of TNF-α and the enhanced apoptosis in C/EBPβ−/− keratinocytes was suppressed by a TNF-α neutralizing antibody. Our results indicate that loss of C/EBPβ enhances activation of a non-canonical UVB DNA damage response pathway involving interferon and TNF signaling to induce keratinocyte cell death.
Introduction
As the first line of defense to environmental DNA damage, epidermal keratinocytes experience numerous genotoxic insults daily (Stamatas et al., 2013; Chow and Tron, 2005). As a result, keratinocytes have developed sophisticated DNA damage response signaling networks to maintain genomic integrity. These networks consist of DNA damage sensors, mediators, transducers, and effectors that halt cell cycle progression to enable DNA repair (Giglia-Mari et al., 2011). In addition, when the extent of DNA damage is too severe or cannot be repaired, these networks neutralize the damaged cells by activating cellular senescence or programmed cell death (Chow and Tron, 2005; Giglia-Mari et al., 2011).
Ultraviolet B (UVB) solar radiation is a ubiquitous environmental carcinogen that damages DNA, causes mutations, and leads to harmful consequences such as carcinogenesis (Brash, 1997; Ziegler et al., 1994). In addition to activation of canonical DNA damage responses, including cell cycle checkpoints and DNA repair, UVB-induced DNA damage can also result in cellular inflammation (Li and Chen, 2018; Nakad and Schumacher, 2016; Brzostek-Racine et al., 2011). DNA damage can be sensed as danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) and activate the innate immune response. UVB solar radiation can induce keratinocyte expression and secretion of interferons (IFNs), including IFNβ and IFNκ, and numerous pro-inflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1α (IL-1α), IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10 (Brink et al., 2000; Takashima and Bergstresser, 1996; Yarosh et al., 2000; Klein and Gunther, 2021). Both IFNs and TNF-α have demonstrated potent pro-apoptotic activities in a number of established cell lines and primary tumors (van Loo and Bertrand, 2023; Vanpouille-Box et al., 2018). Numerous studies have also shown that these inflammatory signaling pathways can synergize and amplify the UVB-induced DNA damage response leading to enhanced cell death (Bashir et al., 2009; Tsuru et al., 2001; Cantaert et al., 2010; Karki et al., 2021). Increasing our understanding of the pathways that regulate cell death decisions in response to cellular stress is critical as misregulated cell death is linked to numerous diseases including cancer, infectious diseases, and autoimmune diseases (Vanpouille-Box et al., 2018; Sarkar et al., 2018).
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β (C/EBPβ), a basic leucine zipper transcription factor, has important roles in fundamental cellular processes including differentiation, inflammation, energy metabolism and cell survival (House et al., 2010; Ramji and Foka, 2002; Tsukada et al., 2011; Farmer, 2006; Nerlov, 2007; Sebastian and Johnson, 2006). C/EBPβ has been shown to regulate cell survival in response to DNA damage, toxicants, or oncogenic stress, and knockdown of C/EBPβ in certain cancer cells results in cell apoptosis (Buck et al., 2001; Wessells et al., 2004; Zhu et al., 2002). C/EBPβ is abundantly expressed in epidermal keratinocytes, and our previous work demonstrated that the conditional deletion of C/EBPβ from mouse epidermis (CKOβ mice) resulted in increased levels of UVB-induced apoptosis in mouse skin and upregulation of the type I interferon (IFN-I) response (Tam et al., 2019). However, the mechanism by which C/EBPβ regulates keratinocyte cell death in response to UVB-induced DNA damage is unknown. Our current study shows that the UVB exposure of C/EBPβ deficient keratinocytes results in an enhanced IFN-I and TNF inflammatory signaling response that drives activation of extrinsic apoptosis.
Methods
Mice
Wild Type and C/EBPβ knockout (C/EBPβ−/−) C57BL/6N:129V (B6N:129) hybrid mice were generated by crossing C57BL/6N C/EBPβ+/− and 129/SV C/EBPβ+/− mice as previously described (Sterneck et al., 1997). All animal care and experimentation described in this study was conducted according to National Institute of Health (NIH) guidelines and were approved by the North Carolina State University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
Cell lines and cell culture
BALB/MK2 mouse keratinocytes (gifted from B. E. Weissman) were cultured in calcium-free Eagle’s minimum essential medium (EMEM) (06–174 G, Lonza), 8% Chelex 100-treated fetal bovine serum (FBS) (F2442, Sigma–Aldrich), 4 ng/mL human epidermal growth factor (hEGF) (PHG0311, Life Technologies) and 0.05 mM CaCl2 (Weissman and Aaronson, 1983).
Mouse primary epidermis was isolated from 1–2 day old wild type and C/EBPβ knockout B6N:129 hybrid mouse skin by flotation in Hanks’ Balanced Salt Solution (H9394, Sigma-Aldrich) and 0.25% trypsin (15090-046, Life Technologies) (Sterneck et al., 1997; Hennings et al., 1980). Isolated keratinocytes were plated at 1 × 106 cells per 35 mm cell culture dish in calcium-free EMEM (06-174 G, Lonza), 10% Chelex 100-treated FBS (F2442, Sigma-Aldrich), 10 ng/mL human EGF (PHG0311, Life Technologies), 1% antibiotic/antimycotic (15240, Life Technologies), and 0.05 mM CaCl2 for 24 h. Cells were then washed in PBS and cultured in Keratinocyte serum free medium (SFM, 10725-018, Life Technologies) containing 5 ng/mL human EGF and 50 ng/mL bovine pituitary extract (37000-015, Life Technologies), 10 mg/mL gentamycin (15710-064, Life Technologies), and 0.05 mM CaCl2. Media was replaced every other day; treatment began 5 days post-plating.
Small interfering RNA
BALB/MK2 mouse keratinocytes were transfected with small interfering RNA (siRNA) targeting mouse C/EBPβ (5′-GAAAAGA GGCGUAUGUAUAUUdTdT-3′, Sigma-Aldrich), Bid (ON-TARGETplus J-058612-05-0010, Dharmacon Horizon Discovery), IFNAR1 (ON-TARGETplus SMARTPool L-043696-01-0010, Dharmacon Horizon Discovery), Tyk2 (ON-TARGETplus J-050349-05-0010, Dharmacon Horizon Discovery), or GFP (negative control) (5′-GGCUACGUCCAGGA GCGCACCdTdT-3′, Sigma-Aldrich) at a final concentration of 25 nM (IFNAR1) or 50 nM (C/EBPβ, Bid, Tyk2, GFP). Transfections were performed using TransIT-X2 (MIR 6000, Mirus) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Cells were exposed to treatment 48 h post-siRNA transfection.
UVB treatment
Cells were exposed to UVB using an EB 280C 312 nm UVB lamp (Spectronics). The light intensity was measured with the IL-1700 Research Radiometer (International Light) equipped with an SED 240 sensor. The UVB lamp was positioned above the cells, cell culture medium was removed, cells were washed in PBS, and cells were irradiated in PBS for the amount of time corresponding to the indicated UVB dose (Tam et al., 2019).
Flow cytometry
Cells were detached from culture plates with trypsin and pelleted along with detached, apoptotic cells already found in the supernatant. Pelleted cells were washed twice with PBS and resuspended in 100 μL Annexin V binding buffer (V13246, ThermoFisher Scientific) at a concentration of 1 × 106 cells/mL. Samples received 5 μL Annexin V Pacific Blue (A35122, ThermoFisher Scientific) and 50 mg/mL propidium iodide (PI) (P3566, ThermoFisher Scientific) and were incubated for 15 min at room temperature and protected from light. Samples were diluted to a final volume of 1 mL using Annexin V binding buffer. Samples were analyzed on an Attune NxT Flow Cytometer (A24862, ThermoFisher Scientific) using a 405-nm laser with 450/50 bandpass filter for Annexin V Pacific Blue and a 488-nm laser with 574/26 bandpass filter for PI. Compensation was performed using unstained and single stained controls and data were analyzed using Attune NxT Cytometric Software (A25554, Invitrogen).
ELISA
Secretion of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) in the supernatant of wild type and C/EBPβ knockout primary keratinocytes was measured using mouse TNF-α DuoSet ELISA (DY410) and mouse TRAIL/TNFSF10 DuoSet ELISA (DY1121) in conjunction with the DuoSet ELISA ancillary reagent kit 2 (DY008B) as per manufacturer protocol. Absorbance values were measured at 450 nm and 540 nm using a Multiskan EX microplate spectrophotometer (ThermoFisher Scientific). As specified by the manufacturer, 540 nm absorbance readings were subtracted from 450 nm absorbance readings to correct for signal produced by optical imperfections in the plate and providing a more accurate measurement. Using provided standards sigmoidal four parameter logistic analysis was used to derive standard curves to calculate TNF-α and TRAIL concentration values.
RNA isolation and RT-qPCR
Total RNA was isolated from wild type and B6N:129 primary keratinocytes collected in QIAzol lysis reagent (79306, Qiagen). Following chloroform extraction, the RNA Clean and Concentrator-25 kit (R1018, Zymo Research) was used following the manufacturer’s protocol for total RNA clean-up, DNase I treatment (E1010, Zymo Research) was performed during clean-up. Complimentary DNA was prepared from RNA using ImProm-II Reverse Transcriptase System (A3800, Promega). Reverse transcriptase quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) was performed using TaqMan Fast Advanced Master Mix (4444554, Applied Biosystems) and the following TaqMan gene expression assays: Tnfa (Mm00443258_m1), Isg15 (Mm01705338_s1), Xaf1 (Mm01245815_m1), Irf1 (Mm01288580_m1), Irf7 (Mm00516793_g1), Cebpb (Mm07294206_s1), and Gapdh (Mm99999915_g1). Gene expression was determined using the comparative ΔΔCT method normalized to GAPDH.
Inhibitors
The following pharmacological inhibitors were reconstituted in DMSO: BI-6C9 (17265, Cayman Chemical), BMS986165 (33524, Cayman Chemical), and Z-VAD (OMe)-FMK (14463, Cayman Chemical). Mouse TNF-α neutralizing (D2H4) rabbit mAb (11969, Cell Signaling Technology) was reconstituted in sterile 10 mM HEPES. Mouse keratinocytes were treated with 10 μM or 50 μM BI-6C9 for 30 min, with 25 μM BMS 986165 for 1 h, with 20 μM Z-VAD (OMe)-FMK for 30 min, or with 1 or 10 μg/mL TNF-α neutralizing (D2H4) rabbit mAb for 30 min before UVB treatment. Post-UVB treatment media containing inhibitor/antibody was returned to cells until collection.
Preparation of protein lysates and immunoblot analysis
Cell lysates were collected by scraping into RIPA buffer (PBS, 1% IGEPAL CA-630 (I3021, Sigma), 0.5% sodium deoxycholate (D6750, Sigma-Aldrich), 0.1% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) (BP166, ThermoFisher Scientific)) containing 1 mM AEBSF (328110500, ThermoFisher Scientific), 1 x protease inhibitor cocktail (11836153001, Roche) and 1x Halt phosphatase inhibitor cocktail (78420, ThermoFisher Scientific). To ensure collection of detached cells floating in cell culture media cell culture media was saved and centrifuged 250 x g, the resulting pellet was washed in PBS and then added to cells scraped in RIPA buffer. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunoblot analysis was conducted using the following antibodies: C/EBPβ (ab32358, Abcam), cleaved caspase-3 (9,664, Cell Signaling Technology), cleaved caspase-8 (8,592, Cell Signaling Technology), Bid (2003, Cell Signaling Technology), and β-actin (sc-8432, Santa Cruz Biotechnology). Antibodies were diluted in 1% BSA and 0.1% Tween20 Tris-buffered saline. Membranes were imaged after incubation with Amersham ECL Prime Western Blotting Detection Reagent (RPN2232, Cytiva) using an Amersham Imager 680 RGB (Cytiva).
RNA sequencing
Total RNA was extracted as described above from UVB-exposed wild type and C/EBPβ −/− primary mouse keratinocytes (n = 3 per group). Total RNA samples were submitted to the North Carolina State University Genomic Sciences Laboratory for Illumina RNA library construction and sequencing using Illumina NovaSeq generating 100 M 150 bp paired end reads per sample. Data analysis was performed in consultation with the Bioinformatics Core at NC State’s Center for Human Health and the Environment. The quality of the sequenced data was evaluated using the fastqc application and 12 poor quality bases were trimmed from the 5′-end. The remaining good quality reads were aligned to the Mouse reference genome (mm39) downloaded from the Ensembl database using the STAR aligner (Dobin et al., 2013). Per-gene counts of uniquely mapped reads for each replicate were calculated using the htseq count script from the HTSeq Python package (Putri et al., 2022). The count matrix was imported to the R statistical computing environment for further analysis. Initially, genes that had no count in most replicate samples were discarded. The remaining count data were normalized for sequencing depth and distortion, and the dispersion was estimated using the DESeq2 Bioconductor package in the R statistical computing environment (Love et al., 2014). We fitted a leaner model using treatment levels, and differentially expressed genes were identified after applying multiple testing corrections using the Benjamini–Hochberg procedure (Reiner et al., 2003). The final significant genes were generated using an adj. p-value <0.05. RNAseq data from wild type and C/EBPβ −/− primary keratinocytes were analyzed through the use of ingenuity pathway analysis (QIAGEN, https://digitalinsights.qiagen.com/IPA) to identify canonical pathways, upstream regulators, and associated functions related to the deletion of C/EBPβ in mouse keratinocytes. Data were filtered by FDR <0.05 and an absolute z-score of 2. The RNAseq data has been deposited with GEO accession GSE305019.
Results
C/EBPβ deficient keratinocytes are sensitized to apoptotic cell death after UVB exposure
Our previous work demonstrated that deletion of the C/EBPβ transcription factor from mouse epidermis resulted in increased cell death following exposure to UVB solar radiation (Tam et al., 2019). To begin to understand the mechanisms and pathways responsible for the enhanced cell death in C/EPBβ deficient keratinocytes we utilized siRNA knockdown in BALB/MK2 mouse keratinocytes. Three isoforms of C/EPBβ are expressed due to alternative translational start sites (LAP*, LAP, and LIP), and all three were all effectively silenced with siRNA (Figure 1A). To measure cell death, we used flow cytometry and defined cells likely to be apoptotic as staining positive for Annexin V (AV+) and staining negative for propidium iodide (PI-). Consistent with our previous studies in mouse epidermis, we observed that C/EBPβ knockdown keratinocytes display enhanced cell death as measured by Annexin V and PI staining (Figure 1B). UVB exposure of C/EBPβ deficient keratinocytes resulted in a > 2-fold significant increase in cell death at numerous time points compared to similarly treated controls. In addition to measuring enhanced apoptosis by flow cytometry we observed that C/EBPβ knockdown keratinocytes exposed to UVB display enhanced activation (cleavage) of caspase-3 (Figure 1C). Interestingly, the knockdown of C/EBPβ sensitized keratinocytes to UVB-induced activation of caspase-3 in a dose dependent manner, with caspase-3 activation occurring in C/EBPβ knockdown keratinocytes at much lower UVB doses compared to control (Figure 1D). Caspase activation is critical in the enhanced cell death observed in C/EBPβ deficient keratinocytes as treatment with the pan caspase inhibitor Z-VAD (OMe)-FMK abolishes UVB-induced apoptosis (Figure 1E; Supplementary Figure S1). These results demonstrate that loss of C/EBPβ sensitizes keratinocytes to enhanced caspase-3-mediated apoptosis following UVB exposure.
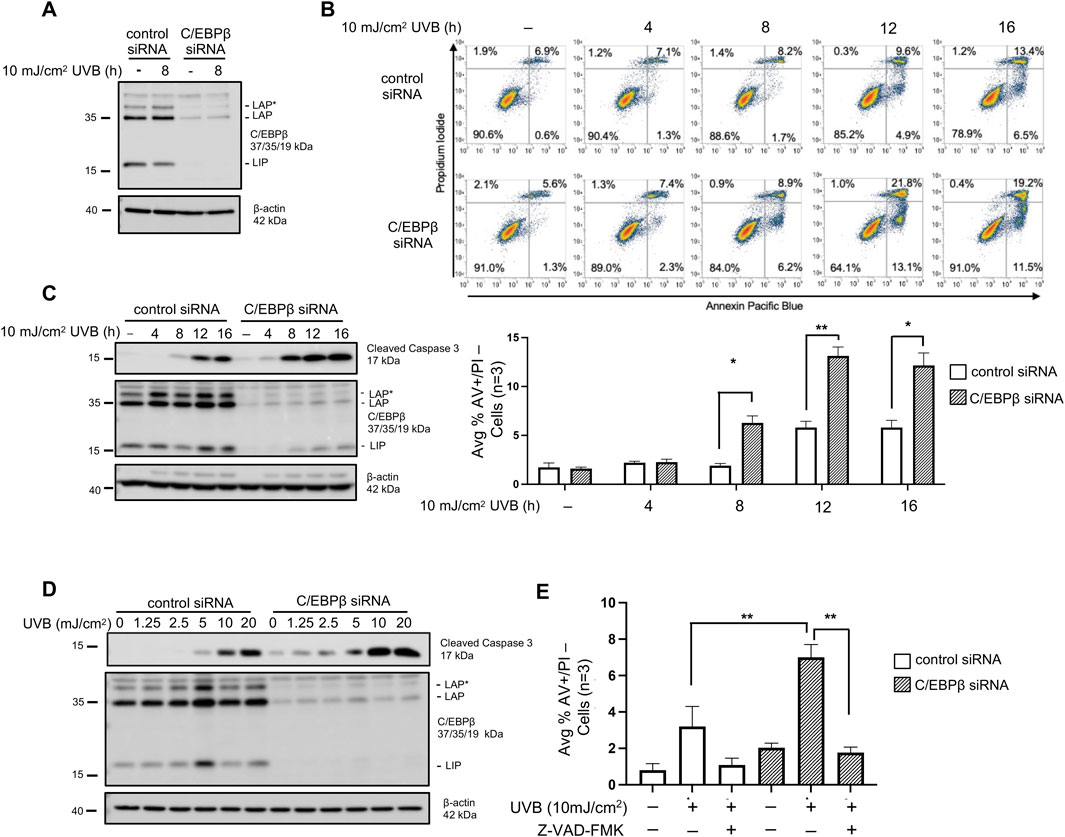
Figure 1. C/EBPβ deficient keratinocytes are sensitized to apoptotic cell death after UVB exposure. (A) BALB/MK2 mouse keratinocytes were transfected with control or C/EBPβ targeting siRNA. 48 h after siRNA transfection cells were treated with 10 mJ/cm2 UVB and were collected 8 h post-UVB. Immunoblot analysis for C/EBPβ and β-actin was conducted. (B) BALB/MK2 keratinocytes were transfected with control or C/EBPβ targeting siRNA. 48 h after siRNA transfection cells were treated with 10 mJ/cm2 UVB and collected 4, 8, 12, and 16 h post-UVB. Collected cells were stained with Annexin V Pacific Blue and propidium iodide (PI) and subjected to flow cytometric analysis. Dots plots are representative images from an n = 3 experiment. Plotted data are mean percentage of cells staining Annexin V+/PI-, ±SD n = 3. (C) BALB/MK2 mouse keratinocytes were transfected with control or C/EBPβ targeting siRNA. 48 h after siRNA transfection cells were treated with 10 mJ/cm2 UVB and were collected 4, 8, 12, and 16 h post-UVB. Immunoblot analysis for cleaved Caspase-3, C/EBPβ, and β-actin was conducted. (D) BALB/MK2 mouse keratinocytes were transfected with control or C/EBPβ targeting siRNA. 48 h after siRNA transfection cells were treated with 0, 1.25, 2.5, 5, 10, or 20 mJ/cm2 UVB. Cells were collected 8 h post-UVB. Immunoblot analysis for cleaved Caspase-3, C/EBPβ, and β-actin was conducted. (E) BALB/MK2 keratinocytes were transfected with control or C/EBPβ targeting siRNA. 48 h after siRNA transfection cells were treated with 20 μM Z-VAD (OMe)-FMK for 30 min prior to exposure to 10 mJ/cm2 UVB. Cells were collected 16 h post-UVB and stained with Annexin V and PI and subjected to flow cytometric analysis. Plotted data are mean percentage of cells staining Annexin V+/PI-, ±SD n = 3. Statistical analysis was done using Student’s t-test for paired data with the significance level set to p < 0.05. * denotes p-value <0.05, ** denotes p-value <0.01.
C/EBPβ deficient keratinocytes activate extrinsic apoptotic pathways following UVB exposure
Caspase-3 serves as the executioner caspase in both extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic pathways (Galluzzi et al., 2018). Caspase-8 is critical in numerous cell death pathways including extrinsic apoptosis and is activated by cleavage (Tummers and Green, 2017). Two active caspase-8 pools can be generated: membrane associated cleaved caspase-8 (p43) and cytosolic cleaved caspase-8 (p18) (Kallenberger et al., 2014). Interestingly, UVB-treated C/EBPβ deficient keratinocytes display early activation of caspase-8 and substantially more cleaved caspase-8 compared to the controls. Furthermore, we were only able to detect the fully activated p18 subunit of caspase-8 in C/EBPβ deficient keratinocytes (Figure 2A). Once activated, caspase-8 can induce apoptosis by directly activating caspase-3, or cleaved caspase-8 can lead to apoptosis via the activation of the BH3 interacting-domain death agonist (Bid) (Kantari and Walczak, 2011). Cleavage of full length Bid by cleaved caspase-8 forms truncated Bid (tBid), which facilitates mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP), leading to caspase-3 activation and apoptosis. Strikingly, UVB-exposed C/EBPβ deficient keratinocytes display a significant reduction in total (uncleaved) Bid (Figure 2B). To determine if activation of Bid is required for the enhanced apoptosis in C/EBPβ deficient keratinocytes we conducted double knockdown experiments of Bid and C/EBPβ in BALB/MK2 keratinocytes. We observed that knocking down Bid in C/EBPβ-depleted keratinocytes greatly diminished the UVB-induced increased activation of caspase-3 seen in C/EBPβ knockdown alone (Figure 2B). The role of Bid in the enhanced apoptosis in C/EBPβ deficient keratinocytes was further confirmed using BI-6C9, a small molecule inhibitor which inhibits the ability of tBid to induce MOMP required for apoptosis (Becattini et al., 2004). Pre-treatment with BI-6C9 prevented cleavage of caspase-3 in C/EBPβ deficient keratinocytes in a similar manner to Bid knockdown (Figure 2C). Together, these results suggest that C/EBPβ regulates an extrinsic apoptotic response mediated by caspase-8 and Bid.
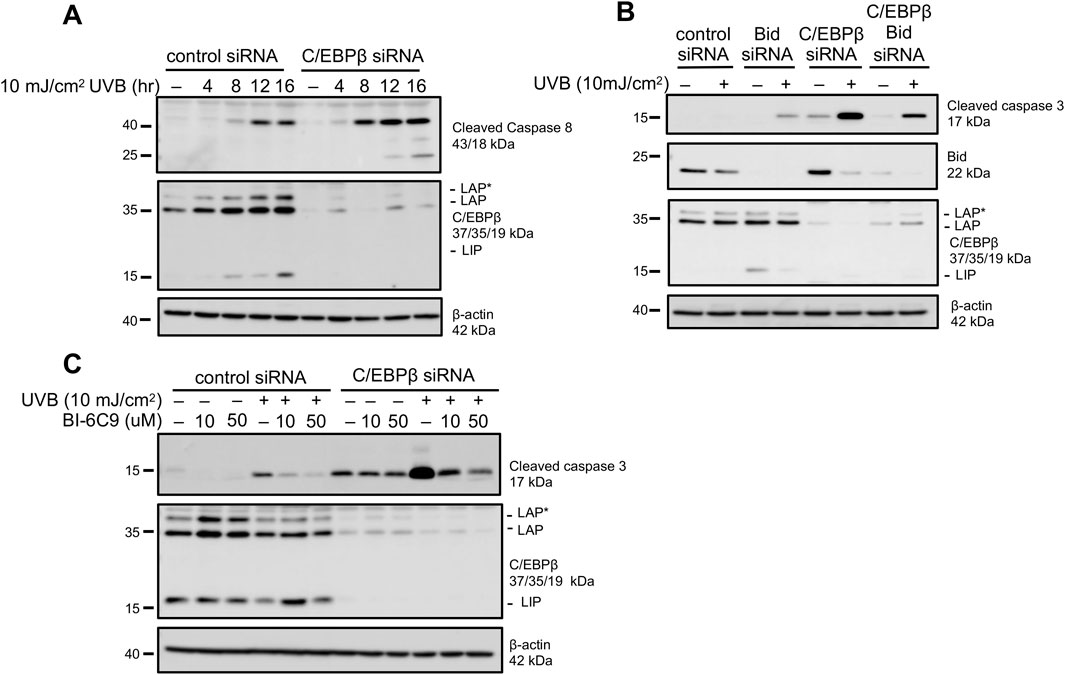
Figure 2. C/EBPβ deficient keratinocytes activate extrinsic apoptotic pathways following UVB exposure. (A) BALB/MK2 keratinocytes were transfected with control or C/EBPβ targeting siRNA. 48 h post-transfection cells were treated with 10 mJ/cm2 UVB. Cells were collected 4, 8, 12, and 16 h post-UVB. Immunoblot analysis for cleaved Caspase-8, C/EBPβ, and β-actin was conducted. (B) BALB/MK2 keratinocytes were transfected with control, Bid, or C/EBPβ targeting siRNA. 48 h post-transfection cells were treated with 10 mJ/cm2 UVB. Cells were collected 8 h post-UVB. Immunoblot analysis for cleaved Caspase-3, Bid, C/EBPβ, and β-actin was conducted. (C) BALB/MK2 keratinocytes were transfected with control or C/EBPβ targeting siRNA. 48 h post-transfection cells were pre-treated with 10 or 50 μM BI-6C9 for 30 min. BALB/MK2 mouse keratinocytes were then treated with 10 mJ/cm2 UVB and were collected 8 h post-UVB. Immunoblot analysis for cleaved Caspase-3, C/EBPβ, and β-actin was conducted.
UVB-exposed C/EBPβ deficient keratinocytes display an enriched type I interferon response
Extrinsic apoptosis is typically initiated by extracellular stress signals, so to further investigate the mechanism(s) responsible for the increased apoptosis in UVB-treated C/EBPβ deficient keratinocytes, we conducted RNAseq analysis on RNA isolated from UVB-treated C/EBPβ−/− and wild type mouse primary keratinocytes. The deletion of C/EBPβ in primary keratinocytes had significant impacts on gene expression. We found 1,732 differentially expressed genes (an absolute log2FC > 1.0 and adj. p-value <0.05) with 986 genes being downregulated and 746 genes being upregulated (Supplementary Table S1). Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) revealed the Hallmark Interferon Alpha response and Hallmark Interferon Gamma response being the top two most positively enriched pathways (Figure 3A). These results confirm previous findings which showed that UVB-exposed C/EBPβ knockout epidermis displayed enrichment of the IFN response (Tam et al., 2019). Numerous interferon stimulated genes (ISGs) were upregulated in UVB-exposed C/EBPβ knockout mouse primary keratinocytes, including pro-apoptotic ISGs such as Xaf1, which significantly increases cellular sensitivity to pro-apoptotic signals (Straszewski-Chavez et al., 2007) (Figure 3B; Supplementary Table S1). To determine whether apoptosis in C/EBPβ deficient keratinocytes is dependent on IFN-I signaling, we conducted a double siRNA knockdown of C/EBPβ and the interferon-α/β receptor 1 (IFNAR1) followed by measurement of apoptosis by flow cytometry. We observed that knocking down IFNAR1 in C/EBPβ-depleted keratinocytes greatly diminished the UVB-induced apoptosis seen in C/EBPβ knockdown alone (Figure 3C; Supplementary Figure S2A). To confirm the involvement of IFN signaling we used the pharmacological inhibitor BMS986165 to inhibit the activity of tyrosine kinase 2 (Tyk2), a member of the Janus kinase (JAK) family known to be required for IFN signaling (Prchal-Murphy et al., 2012). Pretreatment of C/EBPβ knockout primary keratinocytes with the Tyk2 inhibitor significantly reduced ISG expression (Figure 3D) and blocked the induction of apoptosis in C/EBPβ knockout primary keratinocytes as measured by flow cytometry (Figure 3E; Supplementary Figure S2B). These results indicate that the loss of C/EBPβ enhances activation of a UVB-induced DNA damage response pathway involving the IFN-I response that sensitizes keratinocytes UVB-induced cell death.

Figure 3. UVB-exposed C/EBPβ deficient keratinocytes display an enriched type I interferon response. (A) Wild type and C/EBPβ −/− primary keratinocytes were treated with 10 mJ/cm2 UVB. 8 h post-UVB total RNA was isolated and subjected to RNA sequencing. Gene set enrichment analysis with statistically significant (adj. p-value <0.05) positively enriched pathways is shown. (B) TaqMAN Real-Time PCR analysis for various ISGs. Data are expressed as the mean normalized to Gapdh ±SD n = 3. (C) BALB/MK2 keratinocytes were transfected with control, IFNAR1, or C/EBPβ targeting siRNA. 48 h post-transfection cells were treated with 10 mJ/cm2 UVB. 16 h post-UVB cells were stained with Annexin V and PI and subjected to flow cytometric analysis. Plotted data are mean percentage of cells staining Annexin V+/PI-, ±SD n = 3. Knockdown was confirmed by TaqMAN Real-Time PCR. (D) Wild type and C/EBPβ −/− primary keratinocytes were pre-treated with 25 μM BMS986165 for 1 h, then treated with 10 mJ/cm2 UVB. 8 h post-UVB cells were collected and TaqMAN Real-Time PCR analysis for Xaf1 and Isg15 was conducted. Data are expressed as the mean normalized to Gapdh ±SD n = 3. (E) Wild type and C/EBPβ −/− primary keratinocytes were pre-treated with 25 μM BMS986165 for 1 h prior to exposure to 10 mJ/cm2 UVB. 16 h post-UVB cells were stained with Annexin V and PI and subjected to flow cytometric analysis. Plotted data are mean percentage of cells staining Annexin V+/PI-, ±SD n = 3. Statistical analysis was done using Student’s t-test for paired data with the significance level set to p < 0.05. * denotes p-value <0.05, ** denotes p-value <0.01.
C/EBPβ deficient keratinocytes utilize TNF-α mediated signaling to activate UVB-induced apoptosis
We conducted Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) of the RNAseq data set (Supplementary Table S1, adj. p-value ≤0.05) from RNA isolated from UVB-treated C/EBPβ −/− and wild type mouse primary keratinocytes. IPA’s Upstream Regulator Analysis identified numerous IFN-I response genes amongst the top 10 predicted activated upstream regulators with the highest z-score (Figure 4A). Interestingly, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) was also identified in the list of top 10 upstream regulators activated and was the most significant upstream regulator identified (Figure 4A). Additionally, Hallmark TNFA Signaling was one of the top 15 most enriched pathways in our RNAseq dataset (Figure 3A). TNF-α is a central cytokine that drives inflammatory responses, induces inflammatory gene expression and induces cell death (van Loo and Bertrand, 2023). We found that UVB-treated C/EBPβ−/− primary keratinocytes display ∼ 3-fold increase in Tnfa transcript levels compared to UVB-treated wild type mouse primary keratinocytes (Figure 4B). Conducting ELISAs on media from UVB-treated C/EBPβ−/− primary keratinocytes revealed approximately a 2.5-fold increase in secreted TNF-α protein levels compared to UVB-treated wild type mouse primary keratinocytes (Figure 4C). To test the involvement of TNF-α signaling in the C/EBPβ−/− primary keratinocyte apoptotic response, we utilized a TNF-α neutralizing antibody. Pretreatment with a TNF-α neutralizing antibody significantly suppressed apoptosis in UVB-exposed C/EBPβ−/− primary keratinocytes (Figure 4D; Supplementary Figure S3). Taken together, these results demonstrate that the loss of C/EBPβ enhances UVB-induced production of pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-α and that TNF-α has an essential role in mediating the enhanced extrinsic apoptosis observed in UVB-treated C/EBPβ knockout primary keratinocytes. Pretreatment of C/EBPβ−/− primary keratinocytes with the Tyk2 inhibitor BMS986165 greatly reduced TNF-α transcript levels following UVB exposure (Figure 4E). Tyk2 signaling might directly affect TNF-α genes, and its inhibition could suppress TNF-α production. This finding highlight the synergy between IFN-I signaling and TNF-α to induce cell death in UVB-exposed C/EBPβ−/− primary keratinocytes.
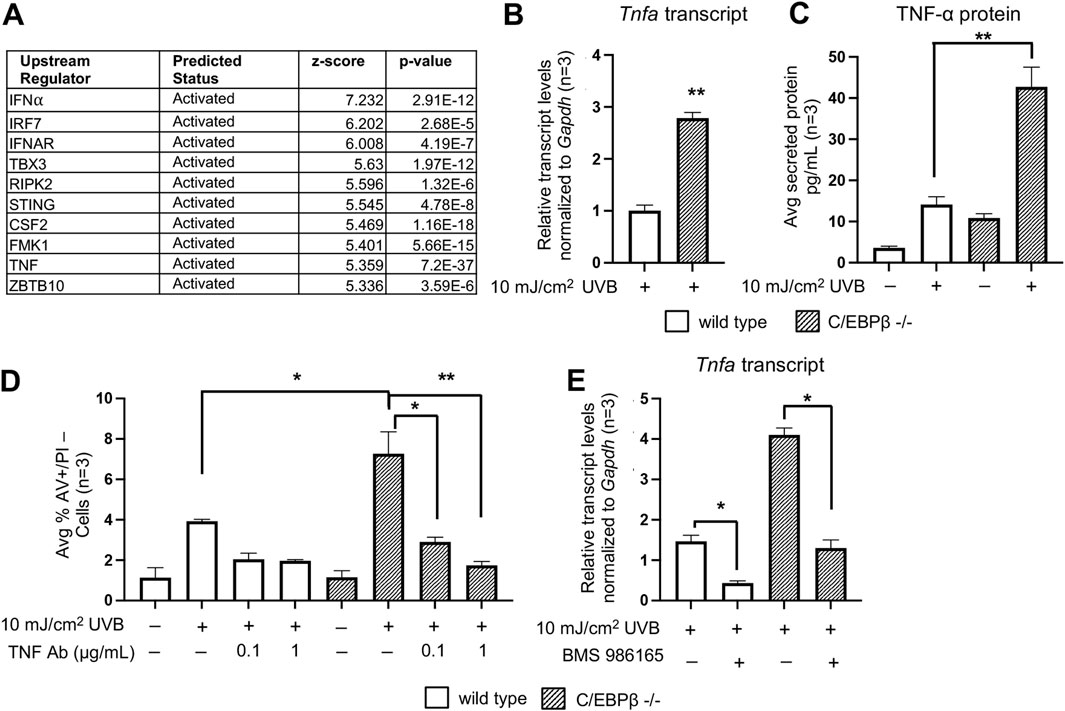
Figure 4. C/EBPβ deficient keratinocytes utilize TNF-α mediated signaling to activated UVB-induced apoptosis. (A) Ingenuity Pathway Analysis’ Upstream Regulator Analysis of RNAseq data reveals top upstream transcription regulators in UVB exposed C/EBPβ −/− primary keratinocytes compared to UVB exposed wild type mice. (B) Wild type and C/EBPβ −/− primary keratinocytes were treated with 10 mJ/cm2 UVB. Cells were collected 8 h post-UVB. TaqMAN Real-Time PCR analysis for Tnfa. Data are expressed as the mean normalized to Gapdh ±SD n = 3. (C) Wild type and C/EBPβ knockout primary mouse keratinocytes were treated with 10 mJ/cm2 UVB. Growth media from cultured cells was collected 8 h post-UVB. Secreted TNF-α protein levels were measured by ELISA. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD n = 3. (D) Wild type and C/EBPβ −/− primary keratinocytes were pre-treated with 0.1 or 1 μg/mL TNF-α neutralizing antibody for 1 h prior to exposure to 10 mJ/cm2 UVB. Cells were collected 16 h post-UVB and stained with Annexin V and PI and subjected to flow cytometric analysis. Plotted data are mean percentage of cells staining Annexin V+/PI-, ±SD n = 3. (E) Wild type and C/EBPβ−/− primary keratinocytes were pre-treated with 25 μM BMS986165 for 1 h, cells were then treated with 10 mJ/cm2 UVB. 8 h post-UVB. TaqMAN Real-Time PCR analysis for Tnfa. Data are expressed as the mean normalized to Gapdh ±SD n = 3. Statistical analysis was done using Student’s t-test for paired data with the significance level set to p < 0.05. * denotes p-value <0.05, ** denotes p-value <0.01.
Discussion
UVB radiation can cause skin damage by inducing DNA damage, oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis of epidermal keratinocytes. Following UVB exposure that results in DNA damage that is too severe or cannot be repaired, keratinocytes can utilize both intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis (Chow and Tron, 2005). We report that silencing of the C/EBPβ transcription factor in epidermal keratinocytes results in the sensitization of keratinocytes to UVB-induced extrinsic apoptosis mediated by the activation of caspase-8 and pro-apoptotic protein Bid. We found that deletion of C/EBPβ in keratinocytes results in the up-regulation of IFN-I signaling pathways, and we found the enhanced activation of apoptosis in C/EBPβ deficient keratinocytes is dependent on the interferon-α/β receptor and the associated kinase Tyk2. Furthermore, the deletion of C/EBPβ resulted in the increased expression of numerous ISGs and TNF-α, with TNF-α being identified as one of the most significant upstream regulators activated in UVB exposed C/EBPβ knockout primary keratinocytes. Additionally, pretreatment with a TNF-α neutralizing antibody suppressed the enhanced UVB-induced apoptosis in C/EBPβ knockout primary keratinocytes. Collectively, our results indicate that loss of C/EBPβ enhances activation of a non-canonical UVB DNA damage response pathway involving inflammatory pathway signaling to induce keratinocyte extrinsic apoptotic cell death.
C/EBPβ (also known as nuclear factor induced by IL-6 (NF-IL-6)) has been shown to regulate numerous cell stress response pathways mediated by IL-6, TNF-α, and IFNs (Tam et al., 2019; Li et al., 2007; Ren et al., 2023). Our previous studies showed that the deletion of C/EBPβ increased ISG expression in UVB-treated mouse epidermis, in regressing skin tumors, and in response to direct activators of the IFN-I response (Tam et al., 2019; House et al., 2023; Messenger et al., 2018). However, in this study we directly link the upregulation of IFN-I signaling to the induction of apoptosis, and identify that in response to UVB-induced DNA damage C/EBPβ −/− primary keratinocytes induce extrinsic apoptosis mediated by TNF-α. We hypothesize that the basal up-regulation of the IFN-I response in C/EBPβ −/− primary keratinocytes primes the cell and results in increased sensitivity to UVB-induced apoptosis. While the IFN-I response is widely appreciated for its ability to sense viral and pathogen-associated RNA and DNA, the IFN-I response can also be activated by DNA fragments which are released from the nucleus and mitochondria into the cytoplasm of the cell after UVB radiation (Li and Chen, 2018; Dunphy et al., 2018; Li et al., 2021). In keratinocytes, UVB radiation has been shown to induce IFN production and secretion (Li et al., 2021; Skopelja-Gardner et al., 2020). It has also been demonstrated that activation of the IFN-I response amplifies UVB-induced keratinocyte apoptosis through a mechanism dependent on caspase-8 (Li et al., 2021). Activation of the IFN-I response can result in the increased expression of ISGs with apoptotic functions that activate extrinsic caspase-8 mediated apoptosis. The deletion of C/EBPβ in mouse keratinocytes resulted in increased expression of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis-associated factor 1 (Xaf1) a pro-apoptotic ISGS that has a role in mediating TNF-induced extrinsic apoptosis (Straszewski-Chavez et al., 2007; Lin et al., 2016; Xia et al., 2006). While a short burst of IFNs is protective against UVB-induced skin inflammation, chronic expression of IFNs present in autoimmune diseases such as cutaneous lupus (CLE) results in exacerbation of the disease through enhanced pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion and hypersensitivity to UVB-induced cell death (Sarkar et al., 2018; Meller et al., 2005; Sontheimer et al., 2017; Stannard et al., 2017). Additional research is necessary to determine the mechanism by which C/EBPβ regulates the IFN-I response following UVB exposure and to explore how C/EBPβ′s function in regulating the IFN-I response could factor in photosensitivity experienced by individuals with inflammatory skin diseases such as CLE.
TNF-α is a multi-effect cytokine in keratinocytes and is a major driver of inflammation and cell death (van Loo and Bertrand, 2023; Bashir et al., 2009). UVB light induces the release of TNF-α from keratinocytes, and TNF-α has a critical role in mediating the UVB-induced apoptosis response in keratinocytes (Yarosh et al., 2000; Kock et al., 1990; Schwarz et al., 1995; Zhuang et al., 1999). Activation of TNFR1/death receptors and caspase-8 is a key keratinocyte pathway for UVB-induced apoptosis (Schwarz et al., 1995; Zhuang et al., 1999). Additionally, the combination of low UVB and exogenous TNF-α has been shown to amplify the keratinocyte apoptotic response (Tsuru et al., 2001). Our findings reported here are consistent with this previous study, as we observed that C/EBPβ −/− primary keratinocytes express higher levels of TNF-α and are sensitized to UVB-induced activation of caspase-3 at UVB doses much lower than UVB-exposed control keratinocytes. Our study further demonstrates the pro-survival function of C/EBPβ in response to a wide range of stress signals including response to DNA damage, toxicants, oncogenic stress, and now inflammatory/innate immune pathway activation (Buck et al., 2001; Wessells et al., 2004; Zhu et al., 2002).
We report that C/EBPβ−/− primary keratinocytes displayed enhanced activation of IFN-I and TNF signaling pathways. IFN-I and TNF-α are key effectors of the innate immune response and are involved in the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus (Banchereau and Pascual, 2006; McInnes and Schett, 2007). Synergistic actions of IFNs and TNF have been described in the host response to viral infection (Karki et al., 2021; Benedict, 2003). TNF-α can activate transcription factors NF-κB and IRF1 to induce expression of IFNβ, and IFN-I signaling enhances TNF-α expression in LPS-activated monocytes and in macrophages (Honda et al., 2006; Molnarfi et al., 2004; Yarilina et al., 2008). IFN-I signaling boost the responsiveness towards other cytokines including TNF-α, resulting in cross priming (Cantaert et al., 2010). We observed that the enhanced apoptosis in C/EBPβ−/− primary keratinocytes is dependent on both IFN-I signaling and TNF-α. Our finding that inhibition of IFNAR1 signaling reduced TNF-α transcript levels is consistent with findings that IFNα antibody treatment downregulates TNF-α expression in skin lesions of SLE patients (Yao et al., 2009). In many cell types, low and constitutive activation of IFN-I signaling boost the responsiveness towards other cytokines including TNF-α, resulting in cross priming.
Collectively, our studies reveal that C/EBPβ promoted keratinocyte survival following UVB exposure through regulation of the IFN-I and TNF inflammatory signaling responses and extrinsic apoptosis. The C/EBPβ-mediated regulation of these pathways could have important roles in UVB-induced skin tumorigenesis, immunity, and systemic inflammatory conditions. Chronic or inappropriate activation of the IFN-I pathway is linked to inflammatory and autoimmune diseases such as lupus erythematosus (LE). Cutaneous LE display increased sensitivity to UVB-induced DNA damage with UVB exposure inducing systemic flares of the disease (Sarkar et al., 2018; Tsoi et al., 2019; Hile et al., 2020). We have demonstrated in vivo, that mice with an epidermal specific deletion of C/EBPβ treated with UVB radiation display upregulation of the IFN-I response, increased apoptosis, and are resistant to UVB-induced skin tumorigenesis. Approaches aimed at non-infectious activation of IFN-I response through activation of the cGAS-STING pathway are being tested as a cancer treatment, with the goal of inducing regulated cell death (Bai et al., 2020). Our lab was part of a recent study that showed deletion of C/EBPβ from pre-existing mouse skin tumors results in the upregulation of the IFN-I response, increased apoptosis, and skin tumor regression (Messenger et al., 2018). Future studies are needed to determine based on the condition, if increasing/decreasing C/EBPβ levels/activity to suppress or enhance an IFN-I response could yield positive therapeutic outcomes to restore proper regulation of cell death.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are publicly available. The authors have submitted the RNAseq datasets for submission to GEO (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/) under GEO accession GSE305019.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by NC State University’s Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
ET: Methodology, Data curation, Visualization, Investigation, Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis. AS: Data curation, Writing – review and editing, Investigation. SK: Writing – review and editing, Data curation, Investigation. DJ: Software, Writing – review and editing, Formal Analysis, Visualization, Methodology. SG: Writing – review and editing, Investigation. JH: Writing – review and editing, Methodology, Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Visualization, Formal Analysis.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was funded in part by a grant from the National Institute of Arthritis, Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (R01AR081974) awarded to J.R.H. and NC State University intramural startup funds awarded to J.R.H. Additional support for this research was provided by the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (P30ES025128) through the NC State University Center for Human Health and the Environment (CHHE) and its Bioinformatics and Genomics Cores. E.E.T was funded in part by a training grant from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (T32ES007046).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fceld.2025.1658598/full#supplementary-material
References
Bai, L., Li, W., Zheng, W., Xu, D., Chen, N., and Cui, J. (2020). Promising targets based on pattern recognition receptors for cancer immunotherapy. Pharmacol. Res. 159, 105017. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105017
Banchereau, J., and Pascual, V. (2006). Type I interferon in systemic lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune diseases. Immunity 25 (3), 383–392. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2006.08.010
Bashir, M. M., Sharma, M. R., and Werth, V. P. (2009). UVB and proinflammatory cytokines synergistically activate TNF-alpha production in keratinocytes through enhanced gene transcription. J. Invest. Dermatol 129 (4), 994–1001. doi:10.1038/jid.2008.332
Becattini, B., Sareth, S., Zhai, D., Crowell, K. J., Leone, M., Reed, J. C., et al. (2004). Targeting apoptosis via chemical design: inhibition of bid-induced cell death by small organic molecules. Chem. Biol. 11 (8), 1107–1117. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2004.05.022
Benedict, C. A. (2003). Viruses and the TNF-related cytokines, an evolving battle. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 14 (3-4), 349–357. doi:10.1016/s1359-6101(03)00030-3
Brash, D. E. (1997). Sunlight and the onset of skin cancer. Trends Genet. 13 (10), 410–414. doi:10.1016/s0168-9525(97)01246-8
Brink, N., Szamel, M., Young, A. R., Wittern, K. P., and Bergemann, J. (2000). Comparative quantification of IL-1beta, IL-10, IL-10r, TNFalpha and IL-7 mRNA levels in UV-irradiated human skin in vivo. Inflamm. Res. 49 (6), 290–296. doi:10.1007/PL00000209
Brzostek-Racine, S., Gordon, C., Van Scoy, S., and Reich, N. C. (2011). The DNA damage response induces IFN. J. Immunol. 187 (10), 5336–5345. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1100040
Buck, M., Poli, V., Hunter, T., and Chojkier, M. (2001). C/EBPbeta phosphorylation by RSK creates a functional XEXD caspase inhibitory box critical for cell survival. Mol. Cell. 8 (4), 807–816. doi:10.1016/s1097-2765(01)00374-4
Cantaert, T., Baeten, D., Tak, P. P., and van Baarsen, L. G. (2010). Type I IFN and TNFα cross-regulation in immune-mediated inflammatory disease: basic concepts and clinical relevance. Arthritis Res. Ther. 12 (5), 219. doi:10.1186/ar3150
Chow, J., and Tron, V. A. (2005). Molecular aspects of ultraviolet radiation-induced apoptosis in the skin. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 9 (6), 289–295. doi:10.1007/s10227-005-0109-0
Dobin, A., Davis, C. A., Schlesinger, F., Drenkow, J., Zaleski, C., Jha, S., et al. (2013). STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 29 (1), 15–21. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/bts635
Dunphy, G., Flannery, S. M., Almine, J. F., Connolly, D. J., Paulus, C., Jonsson, K. L., et al. (2018). Non-canonical activation of the DNA sensing adaptor STING by ATM and IFI16 mediates NF-kappaB signaling after nuclear DNA damage. Mol. Cell. 71 (5), 745–60 e5. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2018.07.034
Farmer, S. R. (2006). Transcriptional control of adipocyte formation. Cell. Metab. 4 (4), 263–273. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2006.07.001
Galluzzi, L., Vitale, I., Aaronson, S. A., Abrams, J. M., Adam, D., Agostinis, P., et al. (2018). Molecular mechanisms of cell death: recommendations of the nomenclature committee on cell death 2018. Cell. Death Differ. 25 (3), 486–541. doi:10.1038/s41418-017-0012-4
Giglia-Mari, G., Zotter, A., and Vermeulen, W. (2011). DNA damage response. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 3 (1), a000745. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a000745
Hennings, H., Michael, D., Cheng, C., Steinert, P., Holbrook, K., and Yuspa, S. H. (1980). Calcium regulation of growth and differentiation of mouse epidermal cells in culture. Cell. 19 (1), 245–254. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(80)90406-7
Hile, G. A., Gudjonsson, J. E., and Kahlenberg, J. M. (2020). The influence of interferon on healthy and diseased skin. Cytokine 132, 154605. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2018.11.022
Honda, K., Takaoka, A., and Taniguchi, T. (2006). Type I interferon [corrected] gene induction by the interferon regulatory factor family of transcription factors. Immunity 25 (3), 349–360. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2006.08.009
House, J. S., Zhu, S., Ranjan, R., Linder, K., and Smart, R. C. (2010). C/EBPalpha and C/EBPbeta are required for Sebocyte differentiation and stratified squamous differentiation in adult mouse skin. PLoS One 5 (3), e9837. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0009837
House, J. S., Gray, S., Owen, J. R., Jima, D. D., Smart, R. C., and Hall, J. R. (2023). C/EBPβ deficiency enhances the keratinocyte innate immune response to direct activators of cytosolic pattern recognition receptors. Innate Immun. 29 (1-2), 14–24. doi:10.1177/17534259231162192
Kallenberger, S. M., Beaudouin, J., Claus, J., Fischer, C., Sorger, P. K., Legewie, S., et al. (2014). Intra- and interdimeric caspase-8 self-cleavage controls strength and timing of CD95-induced apoptosis. Sci. Signal 7 (316), ra23. doi:10.1126/scisignal.2004738
Kantari, C., and Walczak, H. (2011). Caspase-8 and bid: caught in the act between death receptors and mitochondria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1813 (4), 558–563. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.01.026
Karki, R., Sharma, B. R., Tuladhar, S., Williams, E. P., Zalduondo, L., Samir, P., et al. (2021). Synergism of TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma triggers inflammatory cell death, tissue damage, and mortality in SARS-CoV-2 infection and cytokine shock syndromes. Cell. 184 (1), 149–168.e17. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.11.025
Klein, B., and Gunther, C. (2021). Type I interferon induction in cutaneous DNA damage syndromes. Front. Immunol. 12, 715723. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.715723
Kock, A., Schwarz, T., Kirnbauer, R., Urbanski, A., Perry, P., Ansel, J. C., et al. (1990). Human keratinocytes are a source for tumor necrosis factor alpha: evidence for synthesis and release upon stimulation with endotoxin or ultraviolet light. J. Exp. Med. 172 (6), 1609–1614. doi:10.1084/jem.172.6.1609
Li, T., and Chen, Z. J. (2018). The cGAS-cGAMP-STING pathway connects DNA damage to inflammation, senescence, and cancer. J. Exp. Med. 215 (5), 1287–1299. doi:10.1084/jem.20180139
Li, H., Gade, P., Xiao, W., and Kalvakolanu, D. V. (2007). The interferon signaling network and transcription factor C/EBP-beta. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 4 (6), 407–418.
Li, C., Liu, W., Wang, F., Hayashi, T., Mizuno, K., Hattori, S., et al. (2021). DNA damage-triggered activation of cGAS-STING pathway induces apoptosis in human keratinocyte HaCaT cells. Mol. Immunol. 131, 180–190. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2020.12.037
Lin, B., Xu, D., and Leaman, D. W. (2016). X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis-associated factor 1 regulates TNF receptor 1 complex stability. FEBS Lett. 590 (23), 4381–4392. doi:10.1002/1873-3468.12467
Love, M. I., Huber, W., and Anders, S. (2014). Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15 (12), 550. doi:10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8
McInnes, I. B., and Schett, G. (2007). Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 7 (6), 429–442. doi:10.1038/nri2094
Meller, S., Winterberg, F., Gilliet, M., Muller, A., Lauceviciute, I., Rieker, J., et al. (2005). Ultraviolet radiation-induced injury, chemokines, and leukocyte recruitment: an amplification cycle triggering cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 52 (5), 1504–1516. doi:10.1002/art.21034
Messenger, Z. J., Hall, J. R., Jima, D. D., House, J. S., Tam, H. W., Tokarz, D. A., et al. (2018). C/EBPβ deletion in oncogenic Ras skin tumors is a synthetic lethal event. Cell. Death Dis. 9 (11), 1054. doi:10.1038/s41419-018-1103-y
Molnarfi, N., Gruaz, L., Dayer, J. M., and Burger, D. (2004). Opposite effects of IFN beta on cytokine homeostasis in LPS- and T cell contact-activated human monocytes. J. Neuroimmunol. 146 (1-2), 76–83. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2003.10.035
Nakad, R., and Schumacher, B. (2016). DNA damage response and immune defense: links and mechanisms. Front. Genet. 7, 147. doi:10.3389/fgene.2016.00147
Nerlov, C. (2007). The C/EBP family of transcription factors: a paradigm for interaction between gene expression and proliferation control. Trends Cell. Biol. 17 (7), 318–324. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2007.07.004
Prchal-Murphy, M., Semper, C., Lassnig, C., Wallner, B., Gausterer, C., Teppner-Klymiuk, I., et al. (2012). TYK2 kinase activity is required for functional type I interferon responses in vivo. PLoS One 7 (6), e39141. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0039141
Putri, G. H., Anders, S., Pyl, P. T., Pimanda, J. E., and Zanini, F. (2022). Analysing high-throughput sequencing data in Python with HTSeq 2.0. Bioinformatics 38 (10), 2943–2945. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btac166
Ramji, D. P., and Foka, P. (2002). CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins: structure, function and regulation. Biochem. J. 365 (Pt 3), 561–575. doi:10.1042/BJ20020508
Reiner, A., Yekutieli, D., and Benjamini, Y. (2003). Identifying differentially expressed genes using false discovery rate controlling procedures. Bioinformatics 19 (3), 368–375. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btf877
Ren, Q., Liu, Z., Wu, L., Yin, G., Xie, X., Kong, W., et al. (2023). C/EBPβ: the structure, regulation, and its roles in inflammation-related diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 169, 115938. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115938
Sarkar, M. K., Hile, G. A., Tsoi, L. C., Xing, X., Liu, J., Liang, Y., et al. (2018). Photosensitivity and type I IFN responses in cutaneous lupus are driven by epidermal-derived interferon kappa. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 77 (11), 1653–1664. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-213197
Schwarz, A., Bhardwaj, R., Aragane, Y., Mahnke, K., Riemann, H., Metze, D., et al. (1995). Ultraviolet-B-induced apoptosis of keratinocytes: evidence for partial involvement of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the formation of sunburn cells. J. Invest. Dermatol 104 (6), 922–927. doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12606202
Sebastian, T., and Johnson, P. F. (2006). Stop and go: anti-proliferative and mitogenic functions of the transcription factor C/EBPbeta. Cell. Cycle 5 (9), 953–957. doi:10.4161/cc.5.9.2733
Skopelja-Gardner, S., An, J., Tai, J., Tanaka, L., Sun, X., Hermanson, P., et al. (2020). The early local and systemic Type I interferon responses to ultraviolet B light exposure are cGAS dependent. Sci. Rep. 10 (1), 7908. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-64865-w
Sontheimer, C., Liggitt, D., and Elkon, K. B. (2017). Ultraviolet B irradiation causes stimulator of interferon genes-dependent production of protective type I interferon in mouse skin by recruited inflammatory monocytes. Arthritis Rheumatol. 69 (4), 826–836. doi:10.1002/art.39987
Stamatas, G. N., Morello, A. P., and Mays, D. A. (2013). Early inflammatory processes in the skin. Curr. Mol. Med. 13 (8), 1250–1269. doi:10.2174/15665240113139990047
Stannard, J. N., Reed, T. J., Myers, E., Lowe, L., Sarkar, M. K., Xing, X., et al. (2017). Lupus skin is primed for IL-6 inflammatory responses through a keratinocyte-mediated autocrine type I interferon loop. J. Invest. Dermatol. 137 (1), 115–122. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2016.09.008
Sterneck, E., Tessarollo, L., and Johnson, P. F. (1997). An essential role for C/EBPbeta in female reproduction. Genes Dev. 11 (17), 2153–2162. doi:10.1101/gad.11.17.2153
Straszewski-Chavez, S. L., Visintin, I. P., Karassina, N., Los, G., Liston, P., Halaban, R., et al. (2007). XAF1 mediates tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced apoptosis and X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis cleavage by acting through the mitochondrial pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 282 (17), 13059–13072. doi:10.1074/jbc.M609038200
Takashima, A., and Bergstresser, P. R. (1996). Impact of UVB radiation on the epidermal cytokine network. Photochem Photobiol. 63 (4), 397–400. doi:10.1111/j.1751-1097.1996.tb03054.x
Tam, H. W., Hall, J. R., Messenger, Z. J., Jima, D. D., House, J. S., Linder, K., et al. (2019). C/EBPβ suppresses keratinocyte autonomous type 1 IFN response and p53 to increase cell survival and susceptibility to UVB-induced skin cancer. Carcinogenesis 40, 1099–1109. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgz012
Tsoi, L. C., Hile, G. A., Berthier, C. C., Sarkar, M. K., Reed, T. J., Liu, J., et al. (2019). Hypersensitive IFN responses in lupus keratinocytes reveal key mechanistic determinants in cutaneous lupus. J. Immunol. 202 (7), 2121–2130. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1800650
Tsukada, J., Yoshida, Y., Kominato, Y., and Auron, P. E. (2011). The CCAAT/enhancer (C/EBP) family of basic-leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factors is a multifaceted highly-regulated system for gene regulation. Cytokine 54 (1), 6–19. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2010.12.019
Tsuru, K., Horikawa, T., Budiyanto, A., Hikita, I., Ueda, M., and Ichihashi, M. (2001). Low-dose ultraviolet B radiation synergizes with TNF-alpha to induce apoptosis of keratinocytes. J. Dermatol Sci. 26 (3), 209–216. doi:10.1016/s0923-1811(01)00090-1
Tummers, B., and Green, D. R. (2017). Caspase-8: regulating life and death. Immunol. Rev. 277 (1), 76–89. doi:10.1111/imr.12541
van Loo, G., and Bertrand, M. J. M. (2023). Death by TNF: a road to inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 23 (5), 289–303. doi:10.1038/s41577-022-00792-3
Vanpouille-Box, C., Demaria, S., Formenti, S. C., and Galluzzi, L. (2018). Cytosolic DNA sensing in organismal tumor control. Cancer Cell. 34 (3), 361–378. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2018.05.013
Weissman, B. E., and Aaronson, S. A. (1983). BALB and Kirsten murine sarcoma viruses alter growth and differentiation of EGF-dependent balb/c mouse epidermal keratinocyte lines. Cell. 32 (2), 599–606. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(83)90479-8
Wessells, J., Yakar, S., and Johnson, P. F. (2004). Critical prosurvival roles for C/EBP beta and insulin-like growth factor I in macrophage tumor cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 24 (8), 3238–3250. doi:10.1128/mcb.24.8.3238-3250.2004
Xia, Y., Novak, R., Lewis, J., Duckett, C. S., and Phillips, A. C. (2006). Xaf1 can cooperate with TNFalpha in the induction of apoptosis, independently of interaction with XIAP. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 286 (1-2), 67–76. doi:10.1007/s11010-005-9094-2
Yao, Y., Richman, L., Higgs, B. W., Morehouse, C. A., de los Reyes, M., Brohawn, P., et al. (2009). Neutralization of interferon-alpha/beta-inducible genes and downstream effect in a phase I trial of an anti-interferon-alpha monoclonal antibody in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 60 (6), 1785–1796. doi:10.1002/art.24557
Yarilina, A., Park-Min, K. H., Antoniv, T., Hu, X., and Ivashkiv, L. B. (2008). TNF activates an IRF1-dependent autocrine loop leading to sustained expression of chemokines and STAT1-dependent type I interferon-response genes. Nat. Immunol. 9 (4), 378–387. doi:10.1038/ni1576
Yarosh, D., Both, D., Kibitel, J., Anderson, C., Elmets, C., Brash, D., et al. (2000). Regulation of TNFalpha production and release in human and mouse keratinocytes and mouse skin after UV-B irradiation. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 16 (6), 263–270. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0781.2000.160606.x
Zhu, S., Yoon, K., Sterneck, E., Johnson, P. F., and Smart, R. C. (2002). CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-beta is a mediator of keratinocyte survival and skin tumorigenesis involving oncogenic Ras signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 99 (1), 207–212. doi:10.1073/pnas.012437299
Zhuang, L., Wang, B., Shinder, G. A., Shivji, G. M., Mak, T. W., and Sauder, D. N. (1999). TNF receptor p55 plays a pivotal role in murine keratinocyte apoptosis induced by ultraviolet B irradiation. J. Immunol. 162 (3), 1440–1447. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.162.3.1440
Keywords: keratinocytes, CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta, TNF, UVB, apopotosis, inteferon
Citation: Tobin EE, Sharma A, Kros ST, Jima DD, Gray SC and Hall JR (2025) C/EBPβ deficiency enhances keratinocyte apoptosis after UVB-induced DNA damage via regulation of the type I IFN and TNF responses. Front. Cell Death 4:1658598. doi: 10.3389/fceld.2025.1658598
Received: 04 July 2025; Accepted: 20 August 2025;
Published: 03 September 2025.
Edited by:
Eleni Mavrogonatou, National Centre of Scientific Research Demokritos, GreeceReviewed by:
Prasanna Babu Araveti, Boston University, United StatesShivangi Srivastava, Bristol Myers Squibb, United States
Copyright © 2025 Tobin, Sharma, Kros, Jima, Gray and Hall. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jonathan R. Hall, anJoYWxsQG5jc3UuZWR1
 Emma E. Tobin
Emma E. Tobin Ayushma Sharma1
Ayushma Sharma1 Dereje D. Jima
Dereje D. Jima Jonathan R. Hall
Jonathan R. Hall