- 1Department of Floriculture & Landscaping, College of Horticulture, (Central Agricultural University, Imphal), Bermiok, India
- 2Division of Fruit Science, Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR)-Indian Agriculture Research Institute (IARI) Regional Station, Kalimpong, West Bengal, India
- 3Central Silk Board (CSB)-Central Sericultural Research & Training Institute (CSR&TI), Ministry of Textiles – Govt. of India, Jammu-Kashmir, India
- 4Department of Horticulture, College of Agriculture (Central Agricultural University, Imphal), Kyrdemkulai, Meghalaya, India
- 5MTTC & VTC, Department of Horticulture, College of Community Science (Central Agricultural University, Imphal), Tura, Meghalaya, India
- 6Department of Horticulture, M. S. Swaminathan School of Agriculture, Centurion University of Technology and Management, Paralakhemundi, India
- 7Department of Garden Management/Horticulture/Landscaping, Kerala State Council for Science, Technology and Environment (KSCSTE)-Malabar Botanical Graden and Institute for Plant Sciences, Kozhikode, Kerala, India
Orchids are one of the most diverse and economically significant plant families, recognized for their ornamental, medicinal, and commercial value in global floriculture. However, the conservation of orchid species faces significant challenges due to habitat destruction, illegal trade, and climate change. In situ and ex situ conservation approaches, including advanced micropropagation technologies, have been pivotal in preserving the genetic diversity of endangered orchids. Cutting-edge modern biotechnological techniques including in vitro propagation, cryopreservation, and seed banking and its integration can be promising in the conservation of orchids. Furthermore, international policies such as Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora have been enacted to regulate the trade of orchids, though illegal harvesting persists. This paper offers a comprehensive overview of both conservation strategies and the commercial aspects of orchids, emphasizing the need for balanced trade and sustainable conservation practices.
1 Introduction
Orchids are the most beautiful ornamental flowering plant across the world due to their attractive appearance with respect to flower shape and colors. Orchid belongs to family Orchidaceae, which is the second largest among flowering plants (Bhatt, 2020). The name orchid is derived from the root tuber which is similar to testicle, and they have diversified habitats in nature, such as epiphytes, lithophytes, terrestrial, and saprophytes (Venkaiah et al., 2020). The Orchidaceae family has 24,500 species, 788 genera, and 10,000 orchid hybrids and cultivars (Sheehan and Sheehan, 1994; Mabberley, 1997; Dressler, 2006). Orchids are present worldwide, mainly in three areas, viz., Tropical America, Indo-Malayan, and Eastern Himalaya, except Antarctica (Bhatt, 2020). South America is also having a vast orchid diversity. The diverse agro-ecological conditions of India favored the occurrence of a rich orchid biodiversity with 135 species from warm coastal regions to the cool Himalayan regions of India, which provided temperate, sub-tropical, and tropical regions (Hegde, 2020). India has two biodiversity hotspots, viz., northeastern region and western ghats (Bhatt, 2020). Orchids occur in both epiphytotic as well as terrestrial form in Eastern Himalayan and Western Ghats and the middle altitude of approximately 1,500–2,500 m in Western Himalayan. The epiphytotic orchid species are abundantly present in tropical forests (72%) (Karthikeyan, 2000). In Sikkim, there are 529 species classified under 132 genera, comprising seven intraspecific taxa (six variations and one subspecies) (Maity et al., 2019).
The orchid flowers have racemose inflorescence with three petals and sepals and show a bilateral symmetry. The flowering stem varied from basal (Cymbodium), apical (Dendrobium, Cattleya), and axillary (Vanda) (Buanong and Uthairatanakij, 2020). The orchid flowers are perishable in nature, which leads to senescence and wilting. This phenomenon has been associated with ethylene sensitivity which varied in different orchid flowers (Buanong and Uthairatanakij, 2020). The orchid plants have many applications in various areas such as food, medicines, ornamentals, flavoring (vanilla), tea, charms, aphrodisiacs, clothing, art, poisons, narcotics, and religious ceremonies (Cuoco and Cronan, 2009; Koopowitz, 2001). Among the orchid species, Vanilla is well known for its edible fruits. It is utilized for the preparation of vanillin, a natural essence (Chugh et al., 2009). The Vanilla species is suitable for plant tissue culture studies as it has been utilized for in vitro multiplication (Kalimuthu et al., 2006), somatic embryogenesis (Janarthanam and Seshadri, 2008), genetic transformation (Malabadi and Nataraja, 2007), and in vitro conservation approach (Divakaran et al., 2006). Bulbophyllum is another important orchid plant that has medicinal value. Bulbophyllum is useful in the treatment of fever, tuberculosis, inflammation, etc (Kumari et al., 2012; Pant, 2013). Some of the Bulbophyllum species such as B. neilgherrense, B. odoratissimum, and B. sterile are also useful in leucoderma and rheumatism (Rajendran et al., 1997; Shanavaskhan et al., 2012).
India is having vast genetic resources of orchids across the northeastern and western ghats. South America is the megadiverse center worldwide for orchid, and Brazil and Colombia both have rich orchid diversity. The conservation of these genetic resources is of utmost priority for orchid breeders. There are several approaches of germplasm conservation which have been used in orchids, i.e., in situ (Qin et al., 2012) and ex-situ (Seaton et al., 2010; Gogoi et al., 2012) approaches, in vitro conservation (Maneerattanarungroj et al., 2007; Martin and Pradeep, 2003; Lopez-Puc, 2013), and cryopreservation (Merritt et al., 2014; Schofield et al., 2018). Through this chapter, an attempt has been made to discuss the different methods used for the conservation of orchids via traditional as well as modern methods.
2 Global orchid status
Orchids are one of the popular plant groups as cut flowers (De, 2015; FloraHolland, 2015) and as potted plants (USDA, 2016) in the global floriculture trade, which accounts for approximately 10% of the global fresh cut flower trade (De, 2015). The global import value of all cut flowers was $8,490 million during 2019, which is a 6.1% decline from the previous year, but there was 3.0% average annual growth for the 5-year period in 2015–2019. The quality traits of orchid which attribute to its superior value as cut flower include the variable unique attractiveness, long shelf life, high productivity, right season of bloom, and ease of packing and transportation. Orchids are also commercially known for other purposes, such as medicinal products and food. Commercially known orchids are generally propagated artificially, raised under protected conditions, and traded as cut flowers.
Orchids are widely distributed all over the world, with over 25,000 species and several hybrids. Many species are classified as endangered due to habitat loss, climate change, and over-collection (Fay and Rankou, 2016). Conservation initiatives by organizations such as the IUCN and CITES attempt to preserve orchid biodiversity. The whole orchid family (Orchidaceae) is offered protection through Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) (UNEP-WCMC, 2017). This is done to ensure that worldwide trade does not pose any threat to wild populations (Dhanda et al., 2022). Over 30,000 orchid species are included on CITES Appendix II, which would imply that the trade of these plants is allowed with some degree of restriction to prevent some forms of unlimited exploitation of these species. There should be strict rules on trading them, especially regarding those specimens which were collected in the wild, and the required CITES permits should be obtained (Dhanda et al., 2022). The list of some of the most endangered orchids includes one that is found in CITES Appendix I, which prohibits the commercial and international trade of wild specimens. They include several separate species, such as Peristeria elata and Cattleya jongheana and also the genera Paphiopedilum and Phragmipedium. Nevertheless, it is possible to trade artificially propagated plants upon obtaining the permits (Dhanda et al., 2022).
Orchid species are routinely evaluated in connection with the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List. Only 3,400–4,000 or 3% to 4% out of the estimated 27,800 or more orchid species are assessed to date, but a substantial number of them, about 56%–59% is threatened (critically endangered, endangered, or vulnerable) (Fay, 2018; Wraith and Pickering, 2018). In its Red List, the IUCN has cited illegal collection, deforestation due to forestry, development and agriculture, and climate change as the key threats to orchids. The issue with threats and level of the risk may be influenced by region and form of growth (terrestrial or epiphytic) (Wraith and Pickering, 2018). Due to the ongoing extinction in the wild, IUCN (Orchid Specialist Group) carries out a global program of orchid assessment, research, and conservation management. It highlights the necessity to protect the habitats together with the ex situ conservation (including botanic gardens) as an issue of the highest priority (Kumar et al., 2024).
2.1 Species contributions in global markets
Global orchid production has been active in tropical and subtropical countries, many of which have automated and efficiently managed large greenhouses. The most important exported potted orchid in the trade at present is Phalaenopsis, which has tremendous breeding and micropropagation technology achievements in several countries, such as Belgium, The Netherlands, Taiwan, and Thailand. Another reason for its popularity is the ease of its controlled flower induction for scheduled and year-around production. Cut orchids such as Cymbidium, Dendrobium, Oncidium, and Vanda are important cut flowers worldwide. Orchids are now quite popular in the global market, partly due to their long shelf-life, diverse colors, and other desirable traits pursued by consumers, depending on the location or culture. European Union (EU) and the United States are the most important countries or areas for marketing of assortments of orchid products. New markets for orchids are increasing annually.
As of the 2000s, Cymbidium was one of the most popular orchids, cultivated commercially for horticultural utilities like cut flowers, potted plants, medicines, etc., and is a valuable genetic resource. These orchids are grown in cooler climates at higher elevation and are originated from tropical and sub-tropical Asia (De et al., 2019). Cymbidiums were rated the highest in European countries, with major international markets at Singapore, Japan, and Dutch. In Singapore markets, Cymbidium orchids imported from The Netherlands were valued at US$11.18 per stem—while those from New Zealand were at US$3.33 per stem in Japan—and fetched the highest value of about 331 Euro cents per stem at a Dutch auction during 2003–2007 (De et al., 2019). Cymbidium has also marked its zone in the favorable hill ecology of Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, and Darjeeling, particularly the northeastern hill states of India. More than 250 Cymbidium hybrids are cultivated commercially in East Sikkim, covering an area of 25 ha and producing 5 lakhs spikes per year. This region has been announced as Agri-Export Zone of Cymbidium orchids in India.
Phalaenopsis orchid holds the largest market share in the global orchid market with value at US$1,293.8 million in 2020 (De et al., 2019). Phalaenopsis is the second most known potted flowering plant and cut flower across the globe, which are commercially cultivated in Japan, The Netherlands, Taiwan, Germany, and the US. These orchids are easy to grow, have varieties of hues, forms, and sizes, have long vase life, and is available throughout the year. Taiwanese Phalaenopsis orchids were valued at US$13 million during 2006 in the US market, having a worldwide turnover value of US$35.4 million.
Dendrobium accounts for the majority of orchid cut flower trade, besides being the second largest genus of Orchidaceae family. Dendrobiums of unique variations are grown throughout the world. Thailand is the major grower and largest exporter of Dendrobium orchids, accounting for 22% of supplies to European nations (De et al., 2019). Other genera grown in Thailand for global trade includes Vanda, Mokana, Oncidium, Cattleya, and Ascocenda.
Recently, Cattleya has taken center stage with high growth rate in the global orchid market and predicted expectancy of 5.6% compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) during the forecast period of 2021–2027. Big showy blooms and ease of growth make Cattleya cultivation incredibly rewarding. The popularity of Cattleya in decorative ornaments has been attributed to boost its growth. The popularity of cattleyas can be estimated from the fact that around two million Cattleya flowers are sold annually in the US market at US$ 4.89 per unit (Pant et al., 2020). Singapore had started with orchid currency way back in 1967, with Cattleya being depicted on $100 currency against a Singapore waterfront (Kirti et al., 2012). In Thailand, around 2.7% of the total orchid export is shared by Cattleya orchids for which Japan and Singapore are the major importers (De et al., 2019). Vanda, grown throughout the Australasia region, is also well known among global traders, collectors, and hobbyists.
2.2 Global import of orchid cut flowers
According to data from International Trade Centre 2020, the import of cut orchids was valued at $214 million in 2019. The cut orchid import value faced an average of 1.4% annual decline over the past 5 years. Japan is known to be the world’s largest importer of cut orchids. In 2019, Japan imported $62.4 million worth of cut orchids, accounting for 29.2% of the global import value. Next to Japan, the United States stands in second place as the largest importer of cut orchids worth $22.9 million, which is 10.7% of the global import value. Other major cut orchid importers are Italy, China, Vietnam, the United Kingdom, France, Germany, Singapore, and Australia, respectively. The Japanese market receives the largest cut orchids worth $28.9 million from Taiwan, which accounts for 46.3% of all Japan imports. Another 32.1% of all Japanese cut orchids import worth $20.0 million came from Thailand, serving as the second largest source. Other major exporters to the Japanese market in 2019 were Vietnam, New Zealand, Malaysia, China, South Korea, Singapore, and Australia. Meanwhile, in the US market, Thailand was the major exporter of cut orchids at $13.0 million, holding a 57.0% share of all US imports. The second largest exporter was The Netherlands with a value at $6.7 million or 29.5% of all US imports, with a 12.3% decline from 2018 to 2019. Other important exporters to the US market were New Zealand, Vietnam, Malaysia, and Taiwan.
The demand for orchid cut flowers is increasing, particularly in regions such as Europe, North America, and Japan. International trade is restricted to prevent the exploitation of wild populations (Hinsley et al., 2017). The largest importing countries are the United States, Germany, and The Netherlands.
2.3 Global export of orchid cut flowers
Orchids are known for the variability of ornamental traits based on geographical location. Hence, export of certain types of orchid in a commercial scale would be from the respective favorable locations to another where it is preferred and is in demand. The Netherlands and New Zealand are well known for their Cymbidium; The Netherlands and Taiwan for Phalaenopsis; Malaysia, Singapore, and Thailand for Dendrobium and Mokara; and Taiwan and Thailand for Oncidium and Vanda. The Netherlands was the world’s largest cut orchid exporter, with an export value of $83.8 million in 2019, a 37.6% share of the total global export value, and a 10.3% decline over 2018. The second largest cut orchid exporter was Thailand, having a value worth $69.9 million, with a 31.3% market share and a 2.5% decline over 2018. Taiwan was the third largest cut orchid exporter at $36.5 million, with a 16.3% market share and a 27.6% growth over 2018. Other exporters were Singapore, New Zealand, Vietnam, China, Malaysia, South Korea, and Belarus. Global trade data shows Thailand to be exporting the largest quantity of cut orchids worldwide at 23,089 tons, while The Netherlands exported 4,328 tons, and Taiwan exported 2,093 tons.
Thailand, The Netherlands, and Taiwan are among the largest exporters of orchid cut flowers. These countries have developed extensive cultivation systems to meet the global demand (Sharma, 2017). Biotechnology has played a crucial role in improving production efficiency and disease resistance.
2.4 Trading of wild orchids
Apart from the commercially popular species, wild orchid trading has also been reported, which are often illegally harvested. This practice dates back to the Victorian era, wherein numerous tropical orchids were collected for export to Europe (Sanders, 2017). There was widespread practice of wild orchid trades to Europe, the USA, and Japan until the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES) was established during the 1970s (Cribb et al., 2003; Koopowitz et al., 2003). Even then, this trade of wild plants continued with the demand from domestic (Flores-Palacios and Valencia-Diaz, 2007), regional (Phelps and Webb, 2015), and professional collectors (Hinsley et al., 2015; Phelps, 2015). Meanwhile, many countries formally document commercial trade in wild plants, like Cambodia (Hinsley, 2011), China (Shepherd et al., 2007; Gale et al., 2014), Indonesia, Vietnam (Hinsley et al., 2016), Thailand, Myanmar, Lao (Schuiteman, 2013; Phelps and Webb, 2015), Nepal (Subedi et al., 2013), Mexico (Flores-Palacios and Valencia-Diaz, 2007), Peru (Cribb, 2005), Costa Rica, Madagascar, and Malaysia.
3 Orchid germplasm collections
Priorities and strategies for the collection followed by their conservation are defined based on the economic value of the cultivated species, distribution of wild species, and its potential use in crop improvement program for sustainable utilization and conservation of the genetic resources. In India, ICAR-NRC for Orchids, Botanical Survey of India, and various state and regional universities and institutes have carried out several explorations to collect and conserve the valuable orchid resources across the country.
3.1 Status of collections
ICAR-NRC for Orchids, Sikkim, carried out several explorations to different parts of the country for the collection and conservation of valuable orchid germplasm since 1996. Structured and well-planned explorations were conducted in the orchid-rich biodiversity hotspots. The germplasm collections were made as plantlets, tubers, capsules fruits, seeds, and floral parts. They were acclimatized and conserved in orchidariums and used in breeding programs. To date, ICAR-NRC for Orchids has collected and preserved the germplasm of ~400 species from across the country. Among the collections, 83 species are rare, endangered, and threatened (RET), and 52 species are of medicinal interest. The RET collections include Dendrobium draconis, D. ruckeri, D. praecinctum, Diplomeris hirsuta, Ornithochilus difformis, Paphiopedilum fairrieanum, P. venustum, P. villosum, P. hirsutissimum, P. spicerianum, Renanthera imscootiana (red vanda), Satyrium nepalense, Taeniophyllum retrospiculatum, Vanda coerulea (blue Vanda), Zeuxine flava, and Z. reflexa. The collected orchid germplasm is being utilized successfully in the breeding program to develop new varieties and hybrids. The other research institutes, universities, and regional research organizations are maintaining their collections in their respective locations. Collection of the precious orchid germplasm will be more focused on rare, endangered, and threatened (RET) species, which could be helpful for the identification of trait-specific germplasm and can be saved/conserve for future needs (Ram Pal et al., 2022).
To counter the mounting dangers to orchids, various conservation projects have been launched at the global, national, and local levels. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List examines orchid conservation status and identifies extinction-risk species (Fay et al., 2015). Many orchids are also protected by the Convention on International Commerce in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES), which governs international commerce to prevent overexploitation (Hinsley et al., 2017).
Protected areas and botanical gardens play an important role in orchid conservation by preserving both in situ and ex situ populations. Orchid restoration initiatives have been successfully implemented in a variety of places (Cribb et al., 2003). Furthermore, breakthroughs in biotechnology, like as micropropagation and cryopreservation, have improved the ability to protect rare and endangered orchid species (Chen et al., 2006).
4 Threats to orchid germplasm
Orchids are vulnerable to environmental change (Gale et al., 2018) due to their unique habitat and growth requirements. Orchids are ecological indicators because of their sensitivity to habitat fragmentation and anthropogenic disturbance (Martín-Forés et al., 2022). Out of 28,000 known species (WCSP, 2010), IUCN Global Red List has assessed about 1641 orchid species as of July 2020, out of which 747 species are tagged as “threatened” and 197 as “critically endangered” (Fay, 2020). There are numerous factors which trigger the drastic reduction of the orchid population. Most impactful threats are illegal orchid trade, habitat destruction, unsustainable or illegal harvesting and collection for horticulture, food, or medicine, and climate change.
Orchids suffer various problems, including habitat destruction, unlawful collection, climate change, and the introduction of exotic species (Vogt-Schilb et al., 2016). The fast conversion of forests into agricultural land and urban projects has resulted in the fragmentation of natural orchid habitats, rendering populations more vulnerable to extinction.
Illegal harvesting for horticultural and therapeutic purposes exacerbates the demise of specific orchid species. Many orchids are gathered from the wild to suit a market demand, frequently without using sustainable procedures. Species with great commercial value, such as Paphiopedilum and Dendrobium, are especially vulnerable.
4.1 Illegal trade and indiscriminate collection of wild orchids
Among the factors stated above, illegal trade may be considered the biggest threat to orchid population (Chaudhary, 2021). This practice encourages local indiscriminate collection due to demand and requirements for food or medicine. Illegal and unsustainable orchid collection is reported to have a significant impact on species like Cattleya, Laelia, Renanthera, and some slipper orchids, while some orchids have been removed from the wild to the point of extinction. However, most of the collections are not necessarily for horticulture commercial purposes and do not impose much threat (Cribb et al., 2003; Fay et al., 2015). In order to control illegal smuggling, all orchids were placed on the appendices of CITES (Cribb et al., 2003). However, the illegal trade across international border continues without permits under CITES (Fay et al., 2015; Hinsley et al., 2018). Cases of non-systematic documentation of orchid trade are reported for traditional medicines in East Asia, food in the eastern Mediterranean and the Middle East (Kreziou et al., 2016; de Boer et al., 2017), and chikanda in South-Eastern Africa (Veldman et al., 2014).
Measures are being taken during the course of time in order to check illegal trade. Proper regulation and documentation of trade dynamics, strengthening legal trade, and raising the profile of orchid trade among policy makers, conservationists, and the public have been suggested (Hinsley et al., 2018). Efforts are likewise being made to check on cases of non-compliance with CITES regulations (Ghorbani et al., 2014; Hinsley et al., 2017). Other measures include the development of DNA-based technology to identify orchid species incorporation in food stuffs, making it feasible for creating records (de Boer et al., 2017). On the contrary, documentation of orchid species unintentionally on CITES has become a limiting factor for the collection of scientific studies and conservation research (Roberts and Solow, 2008).
The illegal trade in wild orchids is a multibillion-dollar business fueled by collectors, traditional medicine practitioners, and horticulture hobbyists (Hinsley et al., 2017). Many orchid species, including rare and endemic types, are illegally transported across borders, breaking CITES and national conservation laws (Phelps et al., 2015).
Unregulated harvesting has a negative impact on wild populations, causing habitat damage and species decrease. Orchids rely on certain mycorrhizal fungus for germination, making it difficult to repopulate once populations have been depleted in their natural environments (Swarts and Dixon, 2009a). This indiscriminate harvest jeopardizes biodiversity and disrupts environmental equilibrium.
Although international conventions like CITES govern orchid commerce, enforcement is challenging because of weak legal frameworks and limited resources (Fay, 2016). Smuggling networks take advantage of regulatory gaps, frequently mislabeling species or laundering wild orchids through legitimate commerce channels (Ghorbani et al., 2014).
4.2 Habitat loss and climate change
Orchids play important roles in ecosystem health and resilience but are deeply impacted by habitat loss and climate change. The rapidly declining number of orchid species in the wild is driven by the continuous habitat loss due to various reasons—most significantly, climate change (Wraith and Pickering, 2018; Wraith et al., 2020; Liu et al., 2010; Seaton et al., 2013). The slipper orchids were reportedly assessed for the Global Red List recently due to habitat destruction and unprecedented collection (Fay and Rankou, 2016; Wang et al., 2021). Other reasons for habitat loss include deforestation, change in land use, reproduction complexity, and relying on other organisms for life cycle (Swarts and Dixon, 2009a; Hinsley et al., 2018). This is triggering latitudinal and altitudinal shifts of species around the globe. Apart from the slipper orchids, nearly 56.5% of orchid species are under threat of extinction, and action should be taken urgently to conserve them. There is a report that two-thirds of habitats of 25 hotspots of biodiversity has been lost, bringing about a higher risk of extinction of many species (Brooks et al., 2002). In a different incidence, drastic change was observed in the species composition of orchids in a Mediterranean island as a result of change in land use (Vogt-Schilb et al., 2016). Habitat loss is also triggering latitudinal and longitudinal shifts of species around the globe.
4.2.1 Orchids and habitat loss
4.2.1.1 Vulnerability to habitat changes
The primary sources of damage to the habitat are the damage of deforestation, agriculture, and urbanization, which are the leading causes of the decline in orchids across the world (Wraith and Pickering, 2018; Kumar et al., 2024). A number of orchid species are especially vulnerable to any alterations in the environment due to their specific ecological requirements, e.g., their special relations with certain fungi and insect pollinators.
4.2.1.2 Population decline and extinction
The population of orchids has reduced drastically due to land destruction and spread of habitat. The number of native orchids has declined by up to half in certain regions (including the UK) (Wraith and Pickering, 2018). Habitat degradation and over-collection to supply the horticulture trade, especially among rare and visually spectacular genera, have even led to species extinction.
4.2.1.3 Conservation efforts
Orchid conservation revolves around ex situ cultivation in botanical gardens, establishment of reserves, conservation of habitats, and legislative measures. Due to the high degree of their reliance on natural habitats and symbiotic species, orchids continue to need in situ conservation.
The habitat of orchids is being translocated to climatically suitable locations (Thammasiri, 2015). The condition is intensified by the complex interactions with other organisms, pollinators, mycorrhizal fungi, and host trees, which impose a higher risk as these biotics are also affected by habitat or climate change. This signifies the vulnerability of orchids in the face of global change.
4.2.2 Orchids and climate change
4.2.2.1 Climate changing sensitive
Orchids are particularly susceptible to alterations in temperature and precipitation because they depend on sensitive microclimates, specific pollinators, and even compatible mycorrhizal fungi in order to survive (Barman and Devadas, 2013). Climate change may have led to less reproductive success due to implications on fungal symbiont survival, pollinator availability and timing, timing of orchid flowering, and seed germination (Barman and Devadas, 2013).
4.2.2.2 Migration and range shifts
Global warming is causing the shifting of many orchids to higher latitudes or altitudes where their natural distribution and weather wellbeing are to be found or sometimes leading to population decline when the orchids’ habitats are no longer available (Barman and Devadas, 2013).
4.2.2.3 Ecosystem roles and indicators
Orchids are an essential component of ecosystems; some, especially epiphytic orchids, which form a substantial percentage (as much as 19%) of canopy plants in tropical forests can assist in the process of water regulation and filtering (Hernández-Mejía et al., 2024). Forces that affect their numbers can be signals to the presence of more dramatic environmental disturbances, and their health and presence are indicators of the health of the ecosystem and climate.
5 Germplasm conservation approaches
Numerous evaluations have been written about orchid conservation; Western Australia hosted the first International Orchid Conservation Congress in 2001 (Dixon et al., 2003). Effective conservation will also depend on maintaining the vital connections with animals, fungi, and other plants that enable them to survive. The improvement in orchid species documentation—including how many species should be recognized, where they occur, and how they are related to one another—provides the background information needed to establish conservation priorities. Given the significance of these relationships, the subject for the 5th International Orchid Conservation Congress, which took place on La Réunion in 2013, was “Making the Links” (Fay et al., 2015; Fay, 2016).
Particularly in tropical locations, many orchid groups remain little understood, and phylogenetic studies will be required to determine the number of species that should be recognized as well as those that are phylogenetically separated and, as a result, of great conservation significance—for instance, Borba et al. (2014) demonstrated that the little-known and uncommon monospecific genus Cotylolabium from Brazil occupies a unique position as a sister to the rest of the subtribe Spiranthinae. As such, it should be given top priority for conservation because it shares the same amount of phylogenetic history (Fay, 2018). Genetic research can be used to determine which populations or regions should be given top priority for conservation at the population level.
5.1 In situ method
The conservation of orchids involves protecting the natural habitat of the species, encouraging orchid biodiversity, and ensuring the survival of the rare species of orchids. Anthropogenic activities and natural calamities, disappearance of habitats, and large-scale illegal trade are the causes that may lead to the risk for the extinction of thousands of rare and endemic species in protected areas and sanctuaries. Hence, in situ conservation should also be supplemented with appropriate ex situ conservation measures. The in situ conservation of species is most desirable for orchids as it ensures their natural growth, proliferation, and perpetuation, which allow the process of evolution to continue as part of the natural ecosystem. The protection of natural habitats by establishing sanctuaries, biosphere reserves, and forest reserves; the salvation of plants from degraded and threatened habitats and their culture in orchidaria, botanical gardens, and other rescue centers; and the propagation of threatened plants through in vivo/in vitro approaches and their re-introduction into well-protected habitats are among other measures suggested for orchid conservation. The most effective approach to the in situ conservation of orchid species takes into account the life history traits of the species and the roles of mycorrhizal fungi and pollinators.
Conservation through in situ comprises the protection of species in its natural habitat. This approach focuses on overall habitat protection and ensures the conservation of species and its associated biota. In India, protected areas (PA) in the form of national parks and sanctuaries are declared under Wildlife (Protection) Act, with a main focus on faunal wealth but may incidentally include orchid habitats also. In situ areas may not entirely serve the purpose of orchid conservation but definitely assist in the process. Establishing orchid sanctuaries is a focused approach. A few have been attempted in the states of Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim. A biosphere belt with trans boundaries is another way of conservation of natural habitat for orchids and epiphytes (Shashidhar, 2013). Biosphere reserves are adaptable protected areas that maintain the globally recognized genetic diversity in the representative environment. Under the “Man and Biosphere” (MAB) initiative, UNESCO first proposed the creation of a biosphere reserve in 1971. In 1979, the world’s first biosphere reserve was created. There are currently 564 biosphere reserves established in 109 nations worldwide (De and Singh, 2019).
India has an intricate protective area network (PAN) comprising 86 national parks and 480 wildlife sanctuaries covering approximately 4.66% of the total geographical area of the country and is expected to further expand in the future (Ram et al., 2011). This PAN protects the species that are present in those forests. Unfortunately, many important and endangered orchid species lie outside the PAN (viz., Paphiopedilum druryi in Aghasthymalai hills of Kerala, Vanda coerulea in Meghalaya, Paphiopedilum wardii and P. spicerianum in Assam, and Renanthera imscootiana in Arunachal Pradesh). At present, the orchids also figure prominently in the Red Data Book prepared by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). The entire family has been included in Appendix-II of Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES), of which the international trade is strictly controlled and monitored (Pant, 2013). There are some species, such as Liparis olivacea, which have already been extinct from the wild (Subedi, 2011). A few state governments like Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Karnataka, and West Bengal have designated the orchid-rich habitats as “orchid sanctuaries” under the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 (amended in 1992). Any attempt to remove orchids from their natural habitat should be considered poaching or smuggling. Liu et al. (2020) found that approximately 52.2% of 1,582 orchid species have been discovered in at least one national nature reserve, and approximately 26% (412 species) have been found in three or more national nature reserves; these estimates are generally in agreement with those of Qin et al. (2012).
5.2 Ex situ method
The ex situ method is the preservation of germplasm outside the natural habitat (De and Pathak, 2018). Some orchid conservation organizations have the principal aim of establishing reserves, one being the Orchid Conservation Alliance (OCA), which states that “preservation of natural orchid habitat preserves the orchids, their pollinators, their genetic diversity, and other fauna, as well as the birds, frogs, insects, reptiles, and mammals in the forests where they live” (OCA, 2017). However, this will not in itself be sufficient, given the pressures that orchids face from habitat destruction, unsustainable harvesting, and climate change. Meeting these challenges will, in many cases, also involve a combination of creating new habitats, transplantation, and ex situ conservation in seedbanks and living collections. The Gran Canaria Declaration II on Climate Change and Plant Conservation in 2006 stated that “ex situ collections have a key role to play in securing the conservation of wild plant species as natural resources, as an insurance policy for the future, as a basis for restoration and reintroduction programs, and as support for adaptation of livelihoods to climate change and shifting climate zones”. The ex situ conservation principle refers to off-site selection and storage of genetically representative seeds and, where applicable, somatic tissues, regeneration of plants from the stored material, continued cultivation of species to produce conservation units (Johansen and Rasmussen, 1992; Seaton and Pritchard, 2003), and storage of ecologically competent orchid mycorrhizas.
5.2.1 Orchid seed bank
Ex situ conservation strategies such as propagation and seed banking are fundamental components in any integrated conservation approach (Cribb et al., 2003), providing long-term security. Millions of seeds are produced in a single capsule of orchids. However, they lack the functional endosperm and require specific mycorrhizal association for germination under natural conditions; consequently, the percentage of germination is low. Many orchids have been germinated through asymbiotic technique where germination is found to be as high as 90%. The seeds of orchids are orthodox in nature (Seaton et al., 2010) and provide a great scope for long-term storage through low temperature.
Orchid seed banking has been shown to be an invaluable tool for conserving the maximum amount of genetic diversity in the minimum space and has the potential to enable the conservation of valuable material for possible re-introduction and habitat restoration programs in the future. The Darwin Initiative project, “Orchid Seed Stores for Sustainable Use” (OSSSU), is currently establishing a global network of orchid seed banks focusing initially on countries with high orchid biodiversity in Asia and Latin America (Seaton et al., 2010). The Orchid Seed Bank Challenge in Western Australia has achieved seed storage and mycorrhizal selection for three quarters of the 408 native terrestrial species in southwestern Australian biodiversity hotspot (Swarts and Dixon, 2009a, b), and the global Darwin Initiative project Orchid Seed Stores for Sustainable Use (OSSSU) has, at the time of writing, already exceeded its initial 3-year target of 240 species by a considerable margin, and a new interim target of 1,000 species has been set. In another case, an orchid cryo-seed bank in Singapore has successfully stored seeds of native species including Cymbidium finlaysonianum, Cymbidium bicolor, Grammatophyllum speciosum, Dendrobium crumenatum, Spathoglottis plicata, Bulbophyllum vaginatum, and Dendrobium anosmun (Yam et al., 2010). They followed the following procedure for storing the seeds: (1) collect fresh seeds from healthy, mature seed capsules, (2) desiccate the seed for several days in a desiccator which contains a saturated solution and calcium chloride, (3) transfer a small quantity of dried seeds to a 2-mL cryogenic vial, and (4) store the vial in a liquid nitrogen freezer. These conserved seeds can be germinated as and when required through and in vitro technique in different germination medium like MS medium (Murashige and Skoog, 1962) and Knudson C medium, depending on the species.
5.2.2 Field gene reserves
Field gene reserves will include botanical gardens, orchidariums, and conservatory centers, wherein germplasm is collected from a natural habitat or from other sources including commercial houses and nurseries and are maintained in the field or protected structures. Plants growing in living collections are an important resource for educational and research purposes in botanical gardens (Villanueva-Almanza, 2021), but cultivation specifically for conservation is demanding and only rarely practiced effectively (Ramsay and Dixon, 2003). A potential problem with living collections that needs to be addressed is the restricted size of the gene pool of most species in cultivation. Botanical gardens tend to have either one specimen or a very small number of clones of any one species. From the perspective of conservation, it would be more useful to grow large populations of at least some species, thereby providing a better representation of the wider gene pool and an insight into within-species diversity as well as the diversity of orchid species. There is an opportunity for botanical gardens to coordinate their activities through organizations such as Botanical Gardens Conservation International (BGCI) and to exchange information about what plants reside in their collections and to exchange pollens of endangered species.
In the UK, Plant Heritage (formerly the National Council for the Conservation of Plants and Gardens) plays an important role in recognizing important plant collections (Oakeley, 2000) to conserve, grow, propagate, document, and make available out of the amazing resources of garden plants that exist in the UK. The United States Botanic Garden houses over 27,000 orchid species which were confiscated in the US under CITES regulations and which are conserved ex situ where the plants are used for research and showcased for educational displays and programming (Villanueva-Almanza, 2021). The National Botanical Garden (NBG) of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine plays the lead role in ex situ conservation and propagation of tropical plants in Ukraine (Cherevchenko et al., 2007) and contains about 4,500 plants representing approximately 170 genera and 450 natural species (not counting the artificial hybrids and cultivars). Most of the species of the collection (more than 70%) are native to Southeast Asia, whereas the remaining 30% are orchids from South America and Central America, with a few genera from Africa (including Madagascar). In China, the ex situ conservation of endangered P. armeniacum is successful aided at the National Orchid Conservation Center of China in Shenzhen (referred to as the Orchid Center) (Wang et al., 2021). In India, Botanical Survey of India (BSI) is maintaining three national orchidaria and experimental gardens, with one each at Tamil Nadu, West Bengal, and Meghalaya, where representative species of the region are being cultivated (De and Pathak, 2018). Similarly, Arunachal Pradesh State Forest Research Institute is maintaining a large number of orchid species at Orchid Research Centres as a measure of the ex situ conservation of orchids. At present, there are 13 botanical gardens in India maintaining a number of orchid species. Moreover, in the field gene banks of TBGRI, Trivandrum, nearly 600 different species and 150 hybrids of orchids are maintained; NRC for Orchids, Pakyong, Sikkim has nearly 90 different genera and a number of hybrids of commercial orchids, and Orchid House at Panjab University, Chandigarh maintains nearly 100 species of orchids and some hybrids of commercial importance (De and Pathak, 2018). Recently, an orchidarium has also been established at IBSD, Shillong, Meghalaya, and the same project has been replicated at COA, Kyrdemkulai, Meghalaya to render awareness and training to the local mass on the importance of orchid conservation (Devi and Behera, 2020).
5.3 In vitro method
Plant tissue culture (PTC) is a viable tool for the conservation and micro-propagation of plant germplasm, particularly for plants like orchids, which require a rapid regeneration of their populations (Chugh et al., 2009; Bhattacharyya et al., 2016, 2018; Sahoo et al., 2018), and the conservation of parental characteristics (Bhattacharyya et al., 2017). Moreover, the establishment of in vitro germplasm banks through PTC can save valuable resources such as materials, space, and labor (Singh et al., 2015; Pacheco et al., 2016), conserving the plant species for an indefinite period of time (Reed et al., 2013; Kendon et al., 2017). However, establishing this conservation strategy requires the development of a system of conservation for each species studied (Offord CA, 2017). Asymbiotic seed germination techniques, applied for the conservation of endangered and threatened taxa, have been reported to be useful in the reintroduction of many orchids (Pedroza-Marique et al., 2005; Stewart and Kane, 2006; Deb and Imchen, 2006). Since the population size of endangered orchid Vanda coerulea is steadily declining, asymbiotic seed germination technique was used to increase the population size because orchid seed germination is a slow process (Roy et al., 2011). In vitro-raised seedlings of these orchid species were acclimatized and reintroduced in natural habitats.
Generally, the in vitro storage of cultured propagules could be achieved through two different methods. Firstly, a plant material was subjected to direct storage, where established cultures of protocorms and somatic embryos were transferred to growth chambers with various low temperature and light intensity. The low-temperature storage of orchid callus also proved to be of considerable importance for the preservation of genetic diversity and specific clones (Sivasubramaniam et al., 1987). Similarly, Na and Knodo (1995) reported on the tissue culture shoot primordium method that holds promise for the long-term conservation of the gene resources of the Yunnan threatened orchid Vanda pumila and can be, furthermore, applied to stable, clonal mass propagation of ornamentally important strains after artificial selection.
In the second method, the plant materials were encapsulated by sodium alginate, using Ca(NO3)2 as the gelling agent to develop synthetic seeds. These synthetic seeds were subsequently stored at various temperatures, with or without growth retardants. The alginate coat protects the micropropagule and thus has practical application for the germplasm conservation of an elite plant species and exchange of axenic plant materials between laboratories (Hung and Trueman, 2011; Ahmad et al., 2012). Alginate-coated, nonembryogenic micropropagules were relatively inexpensive to produce and easy to handle, transport, and plant. Furthermore, they can be used for cryopreservation via encapsulation dehydration and encapsulation vitrification techniques (Wang et al., 2002). During storage, encapsulated propagules require no transfer to fresh medium, thus reducing the cost of maintaining germplasm in vitro (West et al., 2006).
Furthermore, though attempts have been made to propagate orchid species in vitro using various explants (Anuprabha et al., 2017; Arora et al., 2016; Bhatti et al., 2017; Borah et al., 2015; Kaur et al., 2017) so as to develop effective protocols for in vitro propagation, the data is meager in terms of the size of the orchid family. There is a need for studies on genetic stability to avoid the somaclonal variants and slow growth cultures for longer storage duration to avoid frequent transfers.
5.4 Cryobiotechnology
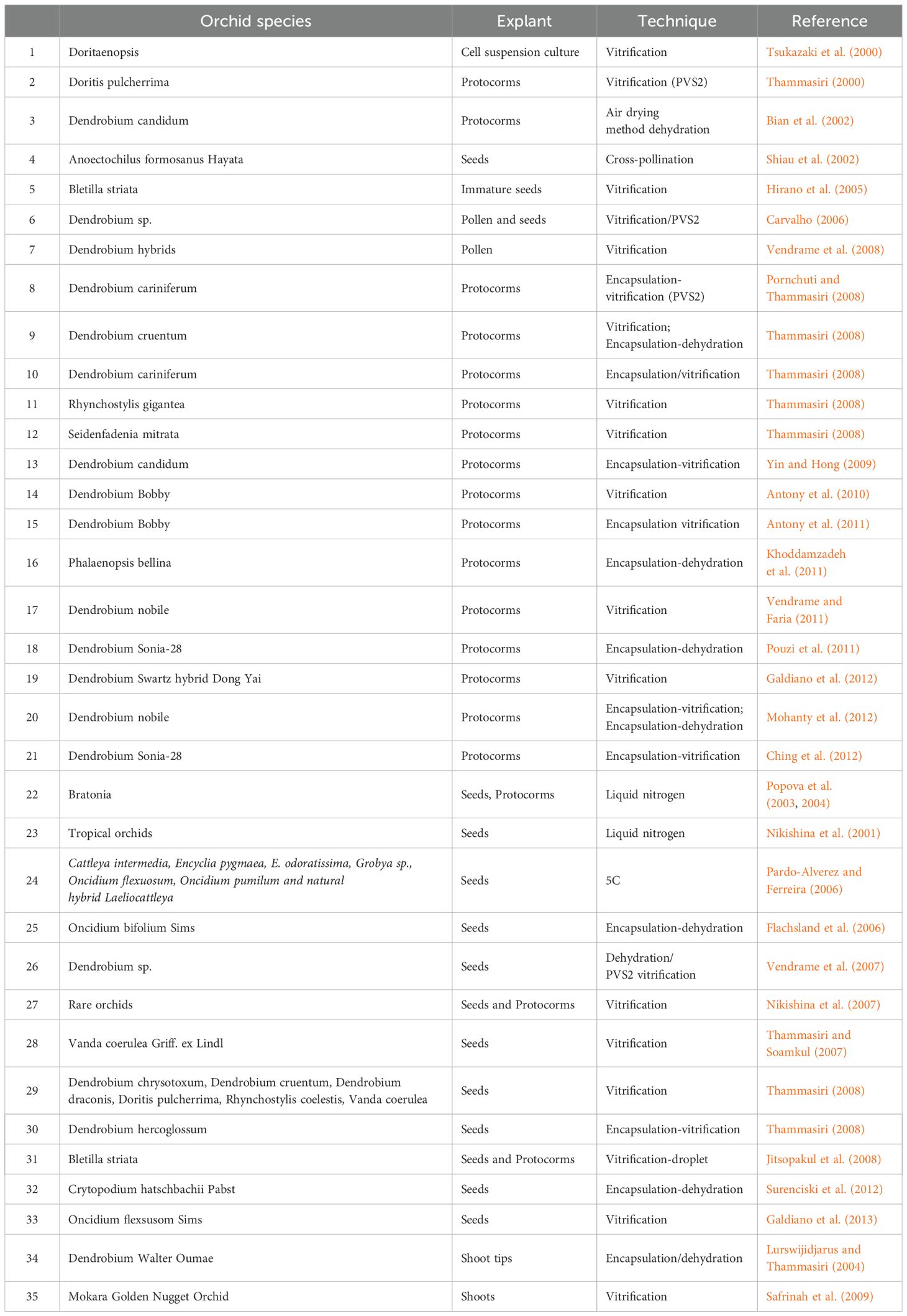
The conservation of plant genetic resources for a long term is the necessity of the time, and it has been achieved through an innovative technique known as cryopreservation. It is helpful in preserving the plant germplasm in its original form and is a valuable method by which a plant species which has been threatened to extinction can be preserved for a longer period. This method is most suitable for perennial plants which have long gestation period such as mulberry, apple, mango, rubber tree, etc. By using this technique, the plant material remained in the non-dividing phase and all of the activities, i.e., biochemical and biophysical, were seized when the material is subjected to -196 °C under liquid nitrogen (Kartha, 1985). The movement of molecules is suspended at very low (negative) temperatures, and the liquid phase settled in cells (Vasco, 2002). Biological reactions like respiration and enzymatic series are also suppressed (Benson et al., 1998). The most important application of cryopreservation is germplasm storage and multiplication in a pathogen-free environment which helps in germplasm exchange. It is a simple and cost-effective approach which allows the storage of germplasm accessions for a longer period, making this method suitable for germplasm conservation of orchids and other crop plants. The different explants such as buds, roots, tubers, apical meristems, pollens, somatic and zygotic embryos, and other parts can be stored efficiently and can be used for the regeneration of genetic resources (Bajaj, 1995). After thawing, the stored explant is capable of producing the whole plants through in vitro propagation methods (Engelmann, 1991). In orchid, Thammasiri (2000) reported on the cryopreservation of Thai wild orchid Doritis pulcherrima using vitrification method. The other methods such as encapsulation–dehydration, encapsulation–vitrification, and droplet–vitrification have also been studied and successfully used in orchid species (Sopalun et al., 2010a, b). A large number of orchid species have been conserved through cryopreservation methods, which have been reviewed nicely by Vendrame et al. (2014) (Table 1). The cryopreserved parts such as protocorms and seeds have the ability to develop into normal seedlings (Thammasiri, 2020). Cryopreservation has resulted in good results in terms of regeneration after cryopreservation as Thammasiri (2002) obtained 99%, 95%, 62%, and 85% germination, respectively, in Thai orchid species. Vanilla is another important orchid species conserved using the vitrification process (Gonzalez-Arnao et al., 2020; Hernández-Ramírez et al., 2014).
5.5 Biotechnological application and trade in orchids
Biotechnological methods are crucial in creating ornamentals with enhanced floral and “high-value” qualities. They are frequently used to change the color, scent, look, disease resistance, and shelf life of flowers, among other things (Tiwari and Jen Tsung, 2023; Tiwari et al., 2023). With the aid of genetic engineering, the desired characteristics of orchids can be chosen, and the flowering time, color, scent, and vase life can all be controlled. Using the mutant ethylene receptor gene, the first attempts at genetic engineering were made to improve growth and vase life in Oncidium and Odontoglossum orchids (Raffeiner et al., 2009). Since they have shorter vase lives than Phalaenopsis, Oncidium and Odontoglossum are less commercially successful orchids. A flower-specific promoter was used by Raffeiner et al. to create the Arabidopsis ethylene receptor mutant gene etr1-1, which decreased the transgenic orchids’ sensitivity to exogenous ethylene and extended their vase life. Similar to this, P. amabilis’ adaptive response to cold stress was successfully produced through genetic engineering in orchids by inserting the rice gene for the cold-inducible lipid transfer protein (LTP). Gene such as the class 1 Knox DOH1 gene added to change growth and morphology. Their overexpression in Dendrobium under in vitro conditions resulted in aberrant numerous shoot developments and decreased cytokinin content (Yu et al., 2001). Modern disease diagnosis techniques made possible by biotechnological developments have allowed for both laboratory and field detection. Through nucleic acid amplification, a sophisticated chip-based integrated microfluidic system has been created for automated, quick virus detection. By purifying pathogen-specific RNA from the diseased sample, this method was used to detect Cymbidium mosaic virus (CMV), the most common orchid virus (Chang et al., 2013). The biotechnologies of orchids have been totally transformed by recent developments in genetic manipulation techniques, which have also created new opportunities for “hybrid” creation with desired traits. With the development of genetic transformation technologies and the production of transgenic mutants with the desired features, the genetic modification of orchids has seen considerable success (Tiwari et al., 2024).
5.6 Application of molecular approaches and its impact in society
Orchid molecular biology research has accelerated our understanding of their genetics, evolution, and special characteristics to a great extent. It has also contributed largely in conservation, horticulture, medicine, and trade. Important orchid characteristics such as flower shape, color, flowering period, fragrance, resistance to disease, and medicinal properties have been found by molecular research such as genome sequencing, transcriptomics, and genetic transformation (Zhang et al., 2022; Li et al., 2022)—for example, scientists have been able to identify flower color and shape-controlling genes through the sequencing of more than a dozen orchid genomes. These characteristics are important for scientific evolutionary research as well as for developing new commercial varieties with desired traits (Zhang et al., 2022; Li et al., 2020).
5.6.1 Societal impact
5.5.1.1 Conservation
Molecular methods have refined population genetics research and have rendered conservation to be more targeted for threatened orchid species. Conservationists can more effectively manage and restore orchid species under threat from habitat loss and over-exploitation through an understanding of genetic diversity and interactions (Zhang et al., 2022).
5.5.1.2 Industrialization and horticulture
Orchids are of utmost value in the international floriculture plant market and hold economic significance. Cultivation is enhanced by creating new varieties with enhanced characteristics, e.g., enhanced shelf life, more beautiful flowers, or stress tolerance, by molecular breeding, marker-assisted selection, and technology like CRISPR-based genome editing (Zhang et al., 2022; Li et al., 2021).
5.5.1.3 Pharmacology and traditional medicine
Investigations of medicinal orchids such as Dendrobium have identified genes that cause the production of healing chemicals. This has added to the scientific evidence of traditional utilization as well as breeding strategies for higher yields (Zhang et al., 2022). The health supplement and drug consumption industries are impacted by this.
5.5.1.4 Vanilla production
Global vanilla flavor and scent commerce depends on breeding for greater quality and yields, fueled by state-of-the-art molecular knowledge of the Vanilla planifolia genome (Zhang et al., 2022).
5.5.1.5 Basic science
Due to their uniqueness and diversity, orchids have been used in the past as model systems to investigate reproductive biology, plant–pollinator interactions, and evolution. These problems are currently being tackled at a mechanistic, gene-function level due to the advances in molecular biology, which bridge evolutionary biology with applied breeding (Li et al., 2022; Hsiao et al., 2011; Tsai et al., 2008). Molecular biology application to orchids has transformed the scientific foundation and practical uses of the plant, with enhanced evolutionary understanding, conservation for specific populations, commercial utilization, and confirmation and improvement of medicinal properties. Genomics, biotechnology, and traditional research have converged to result in unparalleled breakthroughs (Zhang et al., 2022; Li et al., 2022; Hsiao et al., 2011). Most of the significant constraints remain to date, such as the requirement to balance biotechnological progress and preserve wild genetics as well as surmounting the technical barrier of genome editing in most orchid species (Zhang et al., 2022).
6 Conclusion
Climate change, illegal harvesting, and habitat destruction have combined to put orchid conservation at a crucial stage. While biotechnology offers promising solutions through advanced techniques such as tissue culture, cryopreservation, and genetic conservation, the role of international trade cannot be overlooked. As orchids continue to play a significant role in the global economy, particularly in the floriculture market, a more sustainable approach is needed to balance commercial interests with conservation efforts. Regulatory frameworks like CITES have been instrumental in curbing illegal trade, yet challenges remain in ensuring compliance and protecting wild populations. Ultimately, the integration of biotechnological innovations with global trade regulations can ensure the long-term survival of orchid species while fostering economic growth. Collaborative efforts between researchers, policymakers, and commercial entities are essential to achieve this balance, safeguarding one of the most ecologically and economically important plant families.
Author contributions
DS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. NG: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. PS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MD: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. PM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. KP: Resources, Writing – review & editing. CJ: Resources, Writing – review & editing. RB: Resources, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ahmad N., Faisal M., Fatima N., and Anis M. (2012). Encapsulation of micro-cuttings for propagation and short-term preservation in Ruta graveolens L.: a plant with high medicinal value. Acta Physiol. Plant 34, 2303–2310. doi: 10.1007/s11738-012-1031-x
Antony J. J. J., Keng C. L., Rathinam X., Marimuthu S., and Subramaniam S. (2011). Effect of preculture and PVS2 incubation conditions followed by histological analysis in the cryopreserved PLBs of'Dendrobium'Bobby Messina orchid. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 5, pp.1557–1564. doi: 10.1007/s12010-013-0369-x
Antony J. J. J., Keng C. L., Rathinam X., Sinniah U. R., and Subramaniam S. (2010). Preliminary study on cryopreservation of Dendrobium Bobby Messina protocorm-like bodies by vitrification. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 9, pp.7063–7070. doi: 10.5897/AJB10.1060
Anuprabha P. P., Ankush P., and Kumar P. (2017). Regeneration competence of Dendrobium nobile Lindl. through pseudobulb segments: A study in vitro. J. Orchid Soc. India 31, 71–75. doi: 10.24327/ijrsr.2017.0811.1126
Arora S. K., Pathak P., Verma S., Prakash A., Dhiman K., and Mahant K. C. (2016). Mass propagation of Dendrobium amoenum Wall. ex Lindl. through stem nodal explants: A study in vitro. J. Orchid Soc. India 30, 51–55. doi: 10.22244/rheedea.2021.31.03.14
Bajaj Y. P. S. (1995). “Cryopreservation of plant cell, tissue, and organ culture for the conservation of germplasm and biodiversity,” in Cryopreservation of plant germplasm I, vol. 32 . Ed. Bajaj Y. P. S. (Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg), 3–28.
Barman D. and Devadas R. (2013). Climate change on orchid population and conservation strategies: a review. J. Crop Weed 9, 1–12.
Benson E. E., Lynch P. T., and Stacey G. N. (1998). Advances in plant cryopreservation technology: current applications in crop plant biotechnology. Ag Biotech. News Inf 10, 33–141. doi: 10.5772/32860
Bhatt V. P. (2020). “Species diversity and distribution of orchids in Rudraprayag district, Uttarakhand, India,” in Orchid Biology: Recent Trends & Challenges (Springer, Singapore), 139–148.
Bhattacharyya P., Kumar V., and Van Staden J. (2017). Assessment of genetic stability amongst micropropagated Ansellia africana, a vulnerable medicinal orchid species of Africa using SCoT markers. S Afr J. Bot. 108, 294–302. doi: 10.1016/j.sajb.2016.11.007
Bhattacharyya P., Kumaria S., and Tandon P. (2016). High frequency regeneration protocol for Dendrobium nobile: A model tissue culture approach for propagation of medicinally important orchid species. S Afr J. Bot. 104, 232–243. doi: 10.1016/j.sajb.2015.11.013
Bhattacharyya P., Paul P., Kumaria S., and Tandon P. (2018). Transverse thin cell layer (t-TCL)- mediated improvised micropropagation protocol for endangered medicinal orchid Dendrobium aphyllum Roxb: an integrated phytomolecular approach. Acta Physiol. Plant 40, 137. doi: 10.1007/s11738-018-2703-y
Bhatti S. K., Verma J., Jaspreet K. S., and Pathak P. (2017). Symbiotic seed germination of Aerides multiflora Roxb - A study in vitro. J. Orchid Soc. India 31, 85–91. doi: 10.1007/978-981-32-9456-1_7
Bian H. W., Wang J. H., Lin W. Q., Han N., and Zhu M. Y. (2002). Accumulation of soluble sugars, heat-stable proteins and dehydrins in cryopreservation of protocorm-like bodies ofDendrobium candidumby the air-drying method. J. Plant Physiol. 159, 1139–1145. doi: 10.1078/0176-1617-00824
Borba E. L., Salazar G. A., and Mazzoni-Viveiros and Batista S. J. A. (2014). Phylogenetic position and floral morphology of the Brazilian endemic, monospecific genus Cotylolabium: a sister group for the remaining Spiranthinae (Orchidaceae). Bot. J. Linnean Soc. 175 (1), 29–46.
Borah N. J., Chakraborty S., Choudhary S. R., and Dutta B. K. (2015). In vitro propagation of Paphiopedilum spicerianum (Reichb. F.) Pfitz.- A rare and endangered orchid species from NorthEast India. J. Orchid Soc. India 29, 85–90.
Brooks T. M., Mittermeier R. A., Mittermeier C. G., Da Fonseca G. A. B., Rylands A. B., Konstant W. R., et al. (2002). Habitat loss and extinction in the hotspots of biodiversity. Cons Biol. 16, 909–923. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1739.2002.00530.x
Buanong M. and Uthairatanakij A. (2020). “Postharvest Technology of Cut Flowers of Orchids,” in Orchid Biology: Recent Trends & Challenges (Springer, Singapore), 95–117.
Carvalho V. S. (2006). Criopreservação de sementes e pólen de orquídeas (Cryopreservation of orchid seeds and pollen). Universidade Federal de Viçosa, Viçosa, Minas Gerais (MG.
Chang W. H., Yang S. Y., Lin C. L., Wang C.-H., Li P.-C., Chen T.-Y., et al. (2013). Detection of viruses directly from the fresh leaves of a Phalaenopsis orchid using a microfluidic system. Nanomedicine 9, 1274–1282. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2013.05.016
Chaudhary S. (2021). Threats to Nepal’s endangered orchids. Available online at: https://globalvoices.org/2021/07/06/threats-to-Nepals-endangered-orchids/ (Accessed July 6, 2021).
Chen L., Kawai H., Oku T., Takahashi C., and Niimi Y. (2006). Introduction of Odontoglossum ringspot virus coat protein gene into Cymbidium niveo-marginatum mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens to produce transgenic plants. J. Jpn. Soc Hortic. Sci. 75, 249–255. doi: 10.2503/jjshs.75.249
Cherevchenko T. M., Buyun L. I., Kovalska L. A., and Long V. N. (2007). Ex situ conservation of tropical orchids in Ukraine. Lankesteriana 7, 129–133. doi: 10.15517/lank.v7i1-2.18451
Ching L. P., Antony J. J. J., Poobathy R., and Subramaniam S. (2012). Encapsulation-vitrification of Dendrobium sonia-28 supported by histology. Plant Omics 5, 345–350. doi: 10.3316/informit.672695770568546
Chugh S., Guha S., and Rao I. U. (2009). Micropropagation of orchids: a review on the potential of different explants. Sci. Hortic. (Amsterdam) 122, 507–520. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2009.07.016
Cribb P. J. (2005). Phragmipedium kovachii. Curtis’s Botanical Magazine 22, 8–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1355-4905.2005.00454.x
Cribb P. J., Kell S. P., Dixon K. W., and Barrett R. L. (2003). “Orchid conservation: a global perspective,” in Orchid conservation. Eds. Dixon K. W., Kell S. P., Barrett R. L., and Cribb P. J. (Sabah Natural History Publications, Kota Kinabalu), 1–24.
Cuoco L. B. and Cronan J. B. (2009). Orchidaceae: using a globalized commodity to promote conservation and sustainable economic development in Southern Ecuador. J. Sustain For 28, 799–824. doi: 10.1080/10549810902936623
De L. C. (2015). Commercial Orchids (Berlin: De Gruyter Open). Available online at: http://www.degruyter.com/view/product/456245.
De L. C. and Pathak P. (2018). Conservation, management, and utilization of orchid genetic resources. J. Orchid Soc. India 32, 81–91.
De L. C., Pathak P., Rao A. N., and Rajeevan P. K. (2019). 2 Global Orchid Industry In book: Commercial Orchids (Warsaw, Polland: De Gruyter Open). Available online at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/336604199_2_Global_Orchid_Industry/citations.
De L. C. and Singh D. R. (2019). Research paper biodiversity, conservation and bio-piracy in orchids-an overview. J. Global Biosci. 4, 2030–2043.
Deb C. R. and Imchen T. (2006). In vitro propagation of threatened terrestrial orchid Malaxis khasiana Soland ex. Swartz through immature seed culture. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 44, 762–766.
de Boer H. J., Ghorbani A., Manzanilla V., Raclariu A.-C., Kreziou A., Ounjai S., et al. (2017). DNA metabarcoding of orchidderived products reveals widespread illegal orchid trade. Proc. R Soc. B 284, 20171182. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2017.1182
Devi M. P. and Behera U. K. (2020). “Orchid Production: A Rural Bio-entrepreneurship Option in Meghalaya,” in COAK Newsletter Bulletin, vol. 3. , 1–20.
Dhanda S., Bullough L. A., Whitehead D., Grey J., and White K. (2022). A review of the edible orchid trade (Kew, Surrey, U.K: Royal Botanic Gardens).
Divakaran M., Babu K. N., and Peter K. V. (2006). Conservation of Vanilla species in vitro. Sci. Hortic. 110, 175–180. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2006.07.003
Dixon K. W., Kell S. P., Barrett R. L., and Cribb P. J. (Eds.) (2003). Orchid conservation (Kota Kinabalu: Sabah Natural History Publications).
Engelmann F. (1991). In vitro conservation of tropical plant germplasm - a review. Euphytica 57, 227–243. doi: 10.1007/BF00039669
Fay M. F. (2018). Orchid conservation: how can we meet the challenges in the twenty-first century? Bot. Stud. 59, 16. doi: 10.1186/s40529-018-0232-z
Fay M. F., Pailler T., and Dixon K. W. (2015). Orchid conservation: making the links. Ann. Botany. 116 (3), 377–379.
Fay M. and Rankou H. (2016). “Slipper orchids on the IUCN Red List,” in 2015 Annual Report to the Environment Agency—Abu Dhabi (Framework Support for Implementing the Strategic Plan of the IUCN Species Survival Commission), 106–111.
Flachsland E., Terada G., Scocchi A., Rey H., Mroginski L., and Engelmann F. (2006). Cryopreservation of seeds and in vitro-cultured protocorms of Oncidium bifolium Sims.(Orchidaceae) by encapsulation-dehydration. CryoLetters 27, 235–242.
FloraHolland (2015). “Facts and figures,” in FloraHolland facts and figures 2015. Available online at: https://www.royalfloraholland.com/media/5685262/RoyalFloraHolland_Annual_Report_2015_ENG_facts_and_figures.pdf.
Flores-Palacios A. and Valencia-Diaz S. (2007). Local illegal trade reveals unknown diversity and involves a high species richness of wild vascular epiphytes. Biol. Conserv. 137, 372–387. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2006.12.017
Galdiano R. F., Lemos E. G., Faria R. T., and Vendrame W. A. (2012). Cryopreservation of Dendrobium hybrid seeds and protocorms as affected by phloroglucinol and Supercool X1000. Scientia Hortic. 148, 154–160. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2012.09.036
Galdiano Junior R. F., Lemos E.G. de M., and Vendrame W. A. (2013). Cryopreservation, early seedling development, and genetic stability of Oncidium flexuosum Sims. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Culture (PCTOC) 114, 1–10. doi: 10.1007/s11240-013-0304-4
Gale S., Bizid A., Liu K., and Chan K. (2014). A guide to orchids of Hong Kong (Kota Kinabalu: Natural History Publications (Borneo).
Gale S. W., Fischer G. A., Cribb P. J., and Fay M. F. (2018). Orchid conservation: bridging the gap between science and practice. Bot. J. Linn Soc. 186, 425–434. doi: 10.1093/botlinnean/boy003
Ghorbani A., Gravendeel B., Zarre S., and de Boer H. (2014). Illegal wild collection and international trade of CITES-listed terrestrial orchid tubers in Iran. Trafc Bull. 26, 52–58.
Gogoi K., Kumaria S., and Tandon P. (2012). Ex situ conservation of Cymbidium eburneum Lindl.: a threatened and vulnerable orchid, by asymbiotic seed germination. 3 Biotech. 2, 337–343. doi: 10.1007/s13205-012-0062-8
González-Arnao M. T., Hernández-Ramírez F., Dolce N. R., Rascón-Díaz M. P., and Cruz-Cruz C. A. (2020). “Cryobiotechnological studies in Vanilla: The orchid of multi-industrial uses,” in Orchid Biology: Recent Trends & Challenges (Springer, Singapore), 21–35.
Hegde S. N. (2020). “Status of Orchid Industry in India,” in Orchid Biology: Recent Trends & Challenges (Springer, Singapore), 11–20.
Hernández-Mejía J. A., Rosa-Manzano E. D. L., and Delgado-Sánchez P. (2024). Ecosystem services provided by orchids: a global analysis. Botanical Sci. 102, 671–685. doi: 10.17129/botsci.3478
Hernández-Ramírez F., González-Arnao M. T., Cruz-Cruz C., Pastelin-Solano M., and Engelmann F. (2014). Comparison of different preconditioning and loading treatments with vanilla (Vanilla planifolia Jack.) apices cryopreserved using the droplet-vitrification procedure. Acta Hortic. 1039, 173–180. doi: 10.17660/ActaHortic.2014.1039.22
Hinsley A. (2011). Notes on the trade of orchids in the Cardamom Mountains, Pursat and Koh Kong Provinces. Cambodian J. Nat. Hist 1, 11–13.
Hinsley A., de Boer H. J., Fay M. F., Gale S. W., Gardiner L. M., Gunasekara R. S., et al. (2018). A review of the trade in orchids, and its implications for conservation. Bot. J. Linn Soc. 186, 435–455. doi: 10.1093/botlinnean/box083
Hinsley A., Lee T. E., Harrison J. R., and Roberts D. L. (2016). Estimating the extent and structure of trade in horticultural orchids via social media. Conserv. Biol. 30, 1038–1047. doi: 10.1111/cobi.12721
Hinsley A., Nuno A., Ridout M., St John F. A. V., and Roberts D. L. (2017). Estimating the extent of CITES noncompliance among traders and end-consumers; lessons from the global orchid trade. Cons Lett. 10, 602–609. doi: 10.1111/conl.12316
Hinsley A., Verissimo D., and Roberts D. L. (2015). Heterogeneity in consumer preferences for orchids in international trade and the potential for the use of market research methods to study demand for wildlife. Biol. Conserv. 190, 80–86. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2015.05.010
Hirano T., Godo T., Mii M., and Ishikawa K. (2005). Cryopreservation of immature seeds of Bletilla striata by vitrification. Plant Cell Rep. 23, 534–539. doi: 10.1007/s00299-004-0893-9
Hsiao Y.-Y., Pan Z.-J., Hsu C.-C., Yang Y.-P., Hsu Y.-C., Chuang Y.-C., et al. (2011). Research on orchid biology and biotechnology. Plant Cell Physiol. 52, 1467–1486. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcr100
Hung C. D. and Trueman S. J. (2011). Encapsulation technology for short term preservation and germplasm distribution of the African mahonagy Khaya Senegalensis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 107, 397–405. doi: 10.1007/s11240-011-9990-y
Janarthanam B. and Seshadri S. (2008). Plantlet regeneration from leaf derived callus of Vanilla planifolia Andr. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Plant 44, 84–89. doi: 10.1007/s11627-008-9123-4
Jitsopakul N., Thammasiri K., and Ishikawa K. (2008). Cryopreservation of Bletilla striata mature seeds, 3-day germinating seeds and protocorms by droplet-vitrification. CryoLetters 29, 517–526.
Kalimuthu K., Senthilkumar R., and Murugalatha N. (2006). Regeneration and mass multiplication of Vanilla planifolia Andr. A Trop. orchid. Curr. Sci. 91, 1401–1403.
Kartha K. K. (1985). “Meristem culture and germplasm preservation,” in Cryopreservation of plant cells and organs. Ed. Kartha K. K. (CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida), 115–134.
Karthikeyan S. (2000). “A statistical analysis of flowering plants of India,” in Flora of India, Introductory, vol. 2 . Eds. Singh N. P., Singh P. K., Hajra P. K., and Sharma B. D. (New Delhi: BSI Culcutta), xi+469pp.
Kaur S., Pathak P., Prakash A., Anamika, and Sharma A. (2017). Ex situ conservation of floriculturally and medicinally important endangered orchid, Coelogyne cristata Lindl. J. Orchid Soc. India 31, 15–22.
Kendon J. P., Rajaovelona L., Sandford H., Fang R., Bell J., and Sarasan V. (2017). Collecting near mature and immature orchid seeds for ex situ conservation: ‘in vitro collecting’ as a case study. Bot. Stud. 58, 34. doi: 10.1186/s40529-017-0187-5
Khoddamzadeh A. A., Sinniah U. R., Lynch P., Kadir M. A., Kadzimin S. B., and Mahmood M. (2011). Cryopreservation of protocorm-like bodies (PLBs) of Phalaenopsis bellina (Rchb. f.) Christenson by encapsulation-dehydration. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Culture (PCTOC) 107, 471–481. doi: 10.1007/s11240-011-9997-4
Kirti D., Anuprabha, Promila P., and Sagar P. V. (2012). Orchid news the orchid society of India Chandigarh. Newslett. Orchid Soc. India Chandigarh 27-28, 18–20. doi: 10.31838/jcr.07.12.651
Koopowitz H., Lavarack P. S., and Dixon K. W. (2003). “The nature of threats to orchid conservation,” in orchid conservation. Eds. Dixon K. W., Kell S. P., Barrett R. L., and Cribb P. J. (Sabah Natural History Publications, Kota Kinabalu), 25–42.
Kreziou A., de Boer H., and Gravendeel B. (2016). Harvesting of salep orchids in north-western Greece continues to threaten natural populations. Oryx 50, 393–396. doi: 10.1017/S0030605315000265
Kumar J., Katoch D., Thakur A., Pathania A., Anand A., and Choudhary K. (2024). A comprehensive review on threats and conservation status of orchids. J. Appl. Biol. Biotechnol. 12, 43–47. doi: 10.7324/JABB.2024.150084
Kumari H., Pushpan R., and Nishteswar K. (2012). Multi-faceted actions of orchids in ethno-medicine-an appraisal. Int. J. Pharm. Biol. Arch. 3, 996–1002.
Li C., Dong N., Zhao Y., Wu S., Liu Z., and Zhai J. (2021). A review for the breeding of orchids: Current achievements and prospects. Hortic. Plant J. 7, 380–392. doi: 10.1016/j.hpj.2021.02.006
Li Y., Zhang B., and Yu H. (2022). Molecular genetic insights into orchid reproductive development. J. Exp. Bot. 73, 1841–1852. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erac016
Li B. J., Zheng B. Q., Wang J. Y., Tsai W. C., Lu H. C., Zou L. H., et al. (2020). New insight into the molecular mechanism of colour differentiation among floral segments in orchids. Commun. Biol. 3, 89. doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-0821-8
Liu H., Feng C. L., Luo Y. B., Chen B. S., Wang Z. S., and Gu H. Y. (2010). Potential challenges of climate change to orchid conservation in a Wild Orchid Hotspot in South western China. Bot. Rev. 76, 174–192. doi: 10.1007/s12229-010-9044-x
Liu H., Liu Z., Jin X., Gao J., Chen Y., Liu Q., et al. (2020). Assessing conservation efforts against threats to wild orchids in China. Conserv. Biol. 243, 108484. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2020.108484
Lopez-Puc G. (2013). An effective in vitro slow growth protocol for conservation of the orchid Epidendrum chlorocorymbos Schltr. Trop. Subtropical Agroecosystems 16, 61–68. doi: 10.56369/tsaes.1360
Lurswijidjarus W. and Thammasiri K. (2004). Cryopreservation of shoot tips of Dendrobium Walter Oumae by encapsulation/dehydration. Sci. Asia 30, 293–299. doi: 10.2306/scienceasia1513-1874.2004.30.293
Mabberley D. J. (1997). The plant book, a portable dictionary of the vascular plants (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press), 507.
Maity D., Ghosh J., Pradhan A., Mukherjee S. K., and Maiti G. G. (2019). Enumeration of orchids of sikkim. Pleione 13, 355–384. doi: 10.26679/Pleione.13.2.2019.355-384
Malabadi R. B. and Nataraja K. (2007). Genetic transformation of Vanilla planifolia by Agrobacterium tumefaciens using shoot tip sections. Res. J. Bot. 2, 86–94. doi: 10.3923/rjb.2007.86.94
Maneerattanarungroj P., Bunnag S., and Monthatong M. (2007). In vitro conservation of Cleisostoma areitinum (Rchb. f.) Garay, rare Thai orchid species by an encapsulation-dehydration method. Asian J. Plant Sci. 6, 1235–1240.
Martin K. P. and Pradeep A. K. (2003). Simple strategy for the in vitro conservation of Ipsea malabarica an endemic and endangered orchid of the Western Ghats of Kerala, India. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Culture 74, 197–200. doi: 10.1023/A:1023971625994
Martín-Forés I., Bywaters S. L., Sparrow B., and Guerin G. R. (2022). Simultaneous effect of habitat remnancy, exotic species, and anthropogenic disturbance on orchid diversity in South Australia I. Conservation Science and Practice, 4. doi: 10.1111/csp2.12652
Merritt D. J., Hay F. R., Swarts N. D., Sommerville K. D., and Dixon K. W. (2014). Ex situ conservation and cryopreservation of orchid germplasm. Int. J. Plant Sci. 175, 46–58. doi: 10.1086/673370
Mohanty P., Das M. C., Kumaria S., and Tandon P. (2012). High-efficiency cryopreservation of the medicinal orchid Dendrobium nobile Lindl. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Culture (PCTOC) 109, 297–305. doi: 10.1007/s11240-011-0095-4
Murashige T. and Skoog F. (1962). A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiologia plantarum. 15 (3).
Na H. and Knodo K. (1995). Conservation of gene resources in epiphytic Vanda pumila (Orchidaceae) by Tissue-cultured shoots primordia. Plant Tissue Culture Lett. 12, 273–279. doi: 10.5511/plantbiotechnology1984.12.273
Nikishina T. V., Popov A. S., Kolomeitseva G. L., and Golovkin B. N. (2001). Effect of cryoconservation on seed germination of rare tropical orchids. Russian J. Plant Physiol. 48, 810–815. doi: 10.1023/A:1012520927743
Nikishina T. V., Popova E. V., Vakhrameeva M. G., Varlygina T. I., Kolomeitseva G. L., Burov A. V., et al. (2007). Cryopreservation of seeds and protocorms of rare temperate orchids. Russian J. Plant Physiol. 54, 121–127. doi: 10.1134/S1021443707010189
OCA (2017). The orchid conservation alliance. Available online at: https://orchidconservationalliance.org/ (Accessed September 27, 2017).
Offord CA (2017). Germplasm Conservation A2 - Thomas, Brian. Eds. Murray B. G. and Murphy D.J.B.T.-E. (Oxford: Academic Press), 281–288. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394807-6.00046–0
Pacheco G., Simão M., Vianna M., Garcia R., Vieira M., and Mansura E. (2016). In vitro conservation of Passiflora- a review. Scientia Hortic. 211, 305–311. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2016.09.004
Pant B. (2013). Medicinal orchids and their uses: tissue culture a potential alternative for conservation. Afr J. Plant Sci. 7, 448–467. doi: 10.5897/AJPS2013.1031
Pant M., Negi A., Singh A., Gautam A., and Rawat M. (2020). Cattleya orchids: a mini review. J. Crit. Rev. 7, 4592–4598. doi: 10.31838/jcr.07.12
Pardo-Alvarez V. and Ferreira A. G. (2006). Armazenamento de sementes de orquídeas (Orchid seed storage). Rev. Bras. sementes 28, 92–98. doi: 10.1590/S0101-31222006000100013
Pedroza-Marique J., Fernandez-Lizarazo C., and Suarez-Silva A. (2005). Evaluation of the effect of three growth regulators in the germination of Comparettia falcata seeds under in vitro conditions. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biology-Plant 44, 838–843. doi: 10.1079/IVP2005698
Phelps J. (2015). A blooming trade: illegal trade of ornamental orchids in mainland Southeast Asia (Thailand, Lao PDR, Myanmar) (Petaling Jaya: TRAFFIC).
Phelps J. and Webb E. L. (2015). Invisible” wildlife trades: Southeast Asia’s undocumented illegal trade in wild ornamental plants. Biol. Conserv. 186, 296–305. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2015.03.030
Popov A. S., Popova E. V., Nikishina T. V., and Kolomeytseva G. L. (2004). The development of juvenile plants of the hybrid orchid Bratonia after seed cryopreservation. CryoLetters 25, 205–212.
Popova E. V., Nikishina T. V., Kolomeitseva G. L., and Popov A. S. (2003). The effect of seed cryopreservation on the development of protocorms by the hybrid orchid Bratonia. Russian J. Plant Physiol. 50, 672–677. doi: 10.1023/A:1025600526588
Pornchuti W. and Thammasiri K. (2008). Cryopreservation of protocorms of Dendrobium cariniferum Rchb. f. Acta Hortic. 788, 63–68. doi: 10.17660/ActaHortic.2008.788.6
Pouzi N. Z., Rathinam X., Antony J. J. J., Poobathy R., and Subramaniam S. (2011). Early investigation on cryopreservation of Dendrobium sonia-28 using encapsulation-dehydration with modified Evan blue assay. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 10, 3534–3539. doi: 10.5897/AJB10.1128
Qin W., Jiang M., Xu W., and He Z. (2012). Assessment of in situ conservation of 1,334 native orchids in China. Biodiversity Sci. 20, 177–183. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2012.07108
Raffeiner B., Serek M., and Winkelmann T. (2009). Agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated transformation of Oncidium and Odontoglossum orchid species with the ethylene receptor mutant gene etr1-1. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 98, 125–134. doi: 10.1007/s11240-009-9545-7
Rajendran A., Rao R., Ravikumar N. K., and Henry A. N. (1997). Some medicinal orchids of southern India. Anc Sci. Life 17, 1–4.
Ram R. B., Lata R., and Meena M. L. (2011). Conservation of floral biodiversity of Himalayan Mountain regions with special reference to orchids. Asian Agri-History 15, 231–241.
Ramsay M. M. and Dixon K. W. (2003). Propagation science, recovery and translocation of terrestrial orchids. Orchid Conserv. 259–288.
Ram Pal P., Babu K., and Dayamma M. (2022). “Indian Orchid Germplasm: Conservation and Utilization,” in Floriculture and Ornamental Plants, Handbooks of Crop Diversity: Conservation and Use of Plant Genetic Resources. Eds. Datta S. K. and Gupta Y. C. Singapore: Springer Singapore.
Reed B. M., Gupta S., and Uchendu E. E. (2013). “In vitro genebanks for preserving tropical biodiversity,” in Conservation of Orchids the Gems of the Tropics. Eds. Normah M., Chin H., and Reed B. (Springer, New York, NY), 77–106.
Roberts D. L. and Solow A. R. (2008). The efect of the convention on international trade in endangered species on scientifc collections. Proc. R Soc. B 275, 987–989. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2007.1683
Roy A. R., Patel R. S., Patel V. V., Sajeev S., and Deka B. C. (2011). Asymbiotic seed germination, mass propagation and seedling development of Vanda coerulea Griff ex. Lindl. (Blue Vanda): An in vitro protocol for an endangered orchid. Scientia Hortic. 128, 325–331. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2011.01.023
Safrinah R., Xavier R., Uma Rani S., and Sreeramanan S. (2009). Optimisation of cryopreservation technique in Mokara golden nugget orchid using PVS2 vitrification. Int. J. Agric. Res. 4, 218–227. doi: 10.3923/ijar.2009.218.227
Sahoo M. P., Mayengbam P. D., Dasgupta M., Prakash N., and Ngachan S. V. (2018). An efficient protocol for in vitro regeneration and conservation of Shirui lily (Lilium mackliniae Sealy): a lab-to-land approach to save the rare endangered Asiatic lily species. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. - Plant. 54, 701–710. doi: 10.1007/s11627-018-9916-z
Sanders P. (2017). “Historical letters from Sanders’ orchid hunters,” in Sanders Orchids. Available online at: https://www.sandersorchids.com/sanders-orchids/the-orchid-hunters/.
Schofield E., Jones E. P., and Sarasan V. (2018). Cryopreservation without vitrification suitable for large scale cryopreservation of orchid seeds. Botanical Stud. 59, pp.1–pp.9. doi: 10.1186/s40529-018-0229-7
Schuiteman A. (2013). “Orchids of Laos,” in Proceedings of 20th World Orchid Conference Singapore 2011. Eds. Elliott J., Kurzweil H. F., O’Byrne P., Tan K. W., van der Schans A. S., Wong S. M., and Yam T. W. (National Parks Board & Orchid Society of South East Asia, Singapore), 523–533.
Seaton P. T., Hu H., Perner H., and Pritchard H. W. (2010). Ex situ conservation of orchids in a warming world. Bot. Rev. 76, 193–203. doi: 10.1007/s12229-010-9048-6
Seaton P., Kendon J. P., Pritchard H. W., Murti Puspitaningtyas D., and Marks T. R. (2013). Orchid conservation: The next ten years. Lankesteriana 13, 93–101. doi: 10.15517/lank.v0i0.11545
Seaton P. T. and Pritchard H. W. (2003). “Orchid germplasm collection, storage and exchange,” in Orchid conservation. Eds. Dixon K. W., Kell S. P., Barrett R. L., and Cribb P. J. (Natural History Publications, Kota Kinabalu, Sabah), 227–258.
Shanavaskhan A. E., Sivadasan M., Alfarhan A. H., and Thomas J. (2012). Ethno medicinal aspects of angiospermic epiphytes and parasites of Kerala, India. Indian J. Tradit Knowl. 11, 250–258.
Shashidhar K. S. (2013). Orchid conservation – strategies (The Orchid Society of Karnataka). Available online at: http://www.toskar.org/orchid-conservation-strategies/.
Sheehan T. and Sheehan M. (1994). An illustrated survey of orchid genera (Oregon: Timber Press Inc.).
Shepherd C. R., Compton J., and Warne S. (2007). “Transport infrastructure and wildlife trade conduits in the GMS: regulating illegal and unsustainable wildlife trade,” in Biodiversity Conservation Corridors Initiative International Symposium Proceedings (Asia Development Bank, Bangkok), 27–28.
Shiau Y. J., Sagare A. P., Chen U. C., Yang S. R., and Tsay H. S. (2002). Conservation of Anoectochilus formosanus Hayata by artificial cross-pollination and in vitro culture of seeds. Botanical Bull. Academia Sin. 43, 123–130.
Singh H., Kumar S., and Singh B. D. (2015). In vitro conservation of pointed gourd (Trichosanthes dioica) germplasm through slow-growth shoot cultures: Effect of flurprimidol and triiodobenzoic acid. Sci. Hortic. (Amsterdam). 182, 41–46. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2014.11.009
Sivasubramaniam S., Loh C. S., Lee Y. K., and Hew C. S. (1987). Low temperature storage of Dendrobium Multico White callus tissue. Malayan Orchid Rev. (Singapore) 21, 22–26.
Sopalun K., Thammasiri K., and Ishikawa K. (2010a). Micropropagation of the Thai orchid Grammatophyllum speciosum Blume. Plant Cells Tissue Organ Cult 101, 143–150. doi: 10.1007/s11240-010-9671-2
Sopalun K., Thammasiri K., and Ishikawa K. (2010b). Vitrification-based cryopreservation of Grammatophyllum speciosum protocorms. CryoLetters 31, 347–357.
Stewart S. L. and Kane M. K. (2006). Asymbiotic seed germination and in vitro seedling development of Habernaria macroceratitis (Orchidaceae) a rare Florida terrestrial orchid. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 86, 147–158. doi: 10.1007/s11240-006-9098-y
Subedi A. (2011). New species, pollinator interactions and pharmaceutical potential of Himalayan orchids. Leiden University, The Netherlands.
Subedi A., Kunwar B., Choi Y., Dai Y., van Andel T., Chaudhary R. P., et al. (2013). Collection and trade of wild-harvested orchids in Nepal. J. Ethnobiology Ethnomedicine 9, 64. doi: 10.1186/1746-4269-9-64
Surenciski M. R., Flachsland E. A., Terada G., Mroginski L. A., and Rey H. Y. (2012). Cryopreservation of Cyrtopodium hatschbachii Pabst (Orchidaceae) immature seeds by encapsulation-dehydration. Biocell 36, 31–36.
Swarts N. D. and Dixon K. W. (2009a). Perspectives on orchid conservation in botanic gardens. Trends Plant Sci. 14, 590–598. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2009.07.008
Swarts N. D. and Dixon K. W. (2009b). Terrestrial orchid conservation in the age of extinction. Ann. Bot. 104, 543–556. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcp025
Thammasiri K. (2000). Cryopreservation of seeds of a Thai orchid (Doritis pulcherrima lindl.) by vitrification. Cryo Lett. 21, 237–244.
Thammasiri K. (2002). Preservation of seeds of some Thai orchid species by vitrification. In Proceedings of the 16th world orchid conference. Vancouver. Vancouver Orchid Society. 248–251.
Thammasiri K. (2008). Cryopreservation of some thai orchid species. Acta Hort 788, 53–62. Available online at: http://www.actahort.org/books/788/788_5.htm.
Thammasiri K. (2015). Current status of orchid production in Thailand. Acta Hort 1078, 25–33. doi: 10.17660/ActaHortic.2015.1078.2
Thammasiri K. (2020). “Cryopreservation Development of Some Endangered Thai Orchid Species,” in Orchid Biology: Recent Trends & Challenges (Springer, Singapore), 3–10.
Thammasiri K. and Soamkul L. (2007). Cryopreservation of Vanda coerulea Griff. ex Lindl. seeds by vitrification. Sci. Asia 33, 223–227. doi: 10.2306/scienceasia1513-1874.2007.33.223
Tiwari P., Bose S. K., Gautam A., and Chen J.-T. (2023). Emerging insights into the cultivation strategies, ethnomedicinal uses, and socioeconomic attributes of Orchids. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 20, 420–438. doi: 10.1080/14620316.2022.2164524
Tiwari P. and Jen Tsung C. (2023). Advances in Orchid Biology, Biotechnology, and Omics (Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: Springer Publication), ISBN.
Tiwari P., Sharma A., Bose S. K., and Park K. I. (2024). Advances in orchid biology: biotechnological achievements, translational success, and commercial outcomes. Horticulturae 10, 152. doi: 10.3390/horticulturae10020152
Tsai W. C., Hsiao Y. Y., Pan Z. J., Hsu C. C., Yang Y. P., Chen W. H., et al. (2008). Molecular biology of orchid flowers: With emphasis on Phalaenopsis. Adv. Botanical Res. 47, 99–145. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2296(08)00003-7
Tsukazaki H., Mii M., Tokuhara K., and Ishikawa K. (2000). Cryopreservation of Doritaenopsis suspension culture by vitrification. Plant Cell Rep. 19, 1160–1164. doi: 10.1007/s002990000255
UNEP-WCMC (2017). CITES Trade Statistics Derived from the CITES Trade Database (Cambridge: UNEP World Conservation Monitoring Centre). Available online at: https://trade.cites.org.
USDA (2016). Floriculture Crops 2015 Summary (United States Department of Agriculture, National Agricultural Statistics Service). Available online at: http://usda.mannlib.cornell.edu/usda/current/FlorCrop/FlorCrop-04-26-2016.pdf.
Veldman S., Otieno J., van Andel T., Gravendeel B., and de Boer H. (2014). Efforts urged to tackle thriving illegal orchid trade in Tanzania and Zambia for Chikanda production. Trafc Bull. 26, 47–50.
Vendrame W. A., Carvalho V. S., Dias J. M., and Maguire I. (2008). Pollination of Dendrobium hybrids using cryopreserved pollen. HortScience 43, 264–267. doi: 10.21273/HORTSCI.43.1.264
Vendrame W. A., Carvalho V. S., and Dias J. M. M. (2007). In vitro germination and seedling development of cryopreserved Dendrobium hybrid mature seeds. Scientia Hortic. 114, 188–193. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2007.06.006
Vendrame W. A. and Faria R. T. (2011). Phloroglucinol enhances recovery and survival of cryopreserved Dendrobium nobile protocorms. Scientia Hortic. 128, 131–135. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2010.12.018
Vendrame W., Faria R. T. D., Sorace M., and Sahyun S. A. (2014). Orchid cryopreservation. Ciec. e Agrotecnologia 38, 213–229. doi: 10.1590/S1413-70542014000300001
Venkaiah M., Prakasa Rao J., Tarakeswara Naidu M., Prameela R., Janaki Rao P., and Padal S. B. (2020). “Orchid Diversity in the Eastern Ghats of Northern Andhra Pradesh, India,” in Orchid Biology: Recent Trends & Challenges (Springer, Singapore), 189–206.
Villanueva-Almanza L. (2021). Approaches for orchid conservation at the U.S. Botanic Garden by August 14, 2021. doi: 10.13140/RG.2.2.12595.14883
Vogt-Schilb H., Pradel R., Geniez P., Hugot L., Delage A., Richard F., et al. (2016). Responses of orchids to habitat change in Corsica over 27 years. Ann. Bot. 118, 115–123. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcw070
Wang Q., Batuman P., Li M., Bar J., and Gafny R. (2002). A simple and efficient cropreservation of in vitro shoot tips of Troyer citrage (Poncirus trifolia (L.) Raf. 9 Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck) by encapsulation vitrification. Euphytica 128, 135–142. doi: 10.1023/A:1020683305690
Wang M., Li S., Chen L., Li J., Li L., Rao W., et al. (2021). Conservation and reintroduction of the rare and endangered orchid Paphiopedilum Armeniacum. Ecosystem Health Sustainability 7, 1903817. doi: 10.1080/20964129.2021.1903817
WCSP (2010). (World Checklist of Selected Plant Families). Available online at: http://data.kew.org/cgi-bin/vpfg1992/genlist.pl?ORCHIDACEAE.
West T. P., Ravindra M. B., and Preece J. E. (2006). Encapsulation, cold storage and growth of Hibiscus moscheutos nodal segments. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 87, 223–231. doi: 10.1007/s11240-006-9155-6
Wraith J., Norman P., and Pickering C. (2020). Orchid conservation and research: An analysis of gaps and priorities for globally Red Listed species. Ambio 49, 1601–1611. doi: 10.1007/s13280-019-01306-7
Wraith J. and Pickering C. (2018). Quantifying anthropogenic threats to orchids using the IUCN Red List. Ambio 47, 307–317. doi: 10.1007/s13280-017-0964-0
Yam T. W., Tay F., Ang P., and Chua J. (2010). EX SITU ORCHID CONSERVATION - A CASE STUDY FROM THE SINGAPORE BOTANIC GARDENS. Acta Hortic. 878, 21–28. doi: 10.17660/ActaHortic.2010.878.1
Yin M. and Hong S. (2009). Cryopreservation of Dendrobium candidum Wall. ex Lindl. protocorm-like bodies by encapsulation-vitrification. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Culture (PCTOC) 98, 179–185. doi: 10.1007/s11240-009-9550-x
Yu H., Yang S. H., and Goh C. J. (2001). Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of a Dendrobium orchid with the 1 knox gene DOH1. Plant Cell Rep. 20, 301–305. doi: 10.1007/s002990100334
Keywords: orchid conservation, biotechnology, in vitro propagation, cryopreservation, illegal orchid trade, conservation, orchid germplasm, endangered species
Citation: Sarmah D, Gurung N, Saini P, Devi MP, Mohapatra P, Pramanik K, Jena C and B. R (2025) Advances in orchid conservation: biotechnology applications and global trade dynamics. Front. Conserv. Sci. 6:1653827. doi: 10.3389/fcosc.2025.1653827
Received: 27 June 2025; Accepted: 18 August 2025;
Published: 06 November 2025.
Edited by:
Aseesh Pandey, Govind Ballabh Pant National Institute of Himalayan Environment and Sustainable Development, IndiaReviewed by:
K. Chandra Sekar, Govind Ballabh Pant National Institute of Himalayan Environment and Sustainable Development, IndiaNaga Jogayya Kothakota, Centurion University of Technology and Management School of Management, India
Copyright © 2025 Sarmah, Gurung, Saini, Devi, Mohapatra, Pramanik, Jena and B. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dipika Sarmah, ZHNkaXBpa2FzYXJtYWhAZ21haWwuY29t; Nastasha Gurung, bmF0YXNoYWd1cnVuZzIzQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
 Dipika Sarmah
Dipika Sarmah Natasha Gurung
Natasha Gurung Pawan Saini
Pawan Saini Mayengbam Premi Devi
Mayengbam Premi Devi Priyadarshani Mohapatra5
Priyadarshani Mohapatra5