- Department of Speech and Hearing Science, College of Arts and Sciences, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, United States
Adjuvant techniques, or strategies that may be employed alongside language therapy for individuals with aphasia, are increasingly gaining attention for their ability to promote an enhanced brain environment for neuroplasticity. This narrative review describes active ingredients, mechanisms of action, potential modulating factors and evidence for efficacy of non-invasive brain stimulation techniques, such as transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) and transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS); aerobic exercise; intention treatment; and pharmacotherapies, including monoaminergic, cholinergic, glutaminergic, and nootropic medications that have been used in concert with language therapy for aphasia.
Introduction
Chronic language impairments after brain injury, or aphasia, affect approximately a third of the 25.7 million survivors of stroke worldwide (Ali et al., 2021). Therapy for aphasia either targets restoration of function using principles of neuroplasticity or compensation of function using strategies or devices to assist with communicative effectiveness. Restorative treatments for aphasia have leveraged adjuvant techniques that enhance neuroplasticity through various mechanisms. These techniques may help to create a more favorable environment for the brain to adapt and respond to therapy following injury. Adjuvant techniques for aphasia are particularly important, as widely used treatments have a substantial percentage of non-responders (Efstratiadou et al., 2018; Johnson et al., 2019; Pierce et al., 2019), and thus, people with aphasia could benefit from techniques that enhance traditional therapy.
Language processing in the brain involves several key regions, which are often lateralized to the left hemisphere. According to the Wernicke-Lichtheim model (Lichteim, 1885), the left inferior frontal gyrus (i.e., Broca's area—essential for language production) is connected to the posterior portion of the left superior temporal gyrus (i.e., Wernicke's area—essential for language comprehension) by the arcuate fasciculus. Damage to any of the aforementioned substrates may result in impaired communication. For example, an injury to Broca's area often results in impaired speech production (i.e., Broca's aphasia) whereas damage to the arcuate fasciculus often results in impaired repetition, despite intact comprehension (i.e., conduction aphasia; Bernal and Ardila, 2009). The Wernicke-Lichtheim model provides a foundational, simplified understanding of language processing. However, language processing is a highly interconnected function involving a wider-spread network of brain regions and pathways. Additional substrates and networks of the brain critical for language include, but are not limited to, the angular gyrus, supramarginal gyrus, primary auditory cortex, the default mode network, and various subcortical structures, such as the basal ganglia and thalamus (Chen et al., 2021; Fridriksson et al., 2018c; Gordon et al., 2020). Together, the comprehension and production of language are a complex process that integrates various regions and pathways in the brain. Targeting specific brain regions, pathways, and networks alongside language deficits in speech-language therapy is of utmost importance given the connection, though non-linear, between clinical presentation and the site of neurological injury.
Herein, we review adjuvant techniques that have been reported in the aphasia treatment literature, including non-invasive brain stimulation such as transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) and repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS); aerobic exercise such as walking or cycling; intention treatment; and pharmacotherapy in the acute and chronic stages of recovery, including monoaminergic, cholinergic, glutaminergic, and nootrophic medications. Each section will cover the active ingredients of each approach, mechanisms of action, potential modulating factors, and evidence of efficacy.1
Non-invasive brain stimulation
Broadly, the goal of non-invasive brain stimulation (NIBS) in post-stroke language recovery is to enhance behavioral speech-language therapy (SLT) by promoting neuroplasticity. The two most commonly used NIBS techniques are transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) and repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS).
tDCS uses saline-soaked sponge electrodes to deliver a constant current of 1–2 mA to the region of interest (Breining and Sebastian, 2020). The polarity is binary such that there is an anodal and cathodal electrode. It is largely agreed that the anodal electrode excites neural activity in the targeted brain region, whereas the cathodal electrode inhibits activity (Crosson et al., 2015). Researchers typically administer anodal tDCS during SLT to the lesioned area (i.e., the left hemisphere), or cathodal tDCS to the contralesional area (i.e., the right hemisphere; Breining and Sebastian, 2020).
rTMS uses a head coil to deliver a changing magnetic field at a high frequency (> 1, 5, or 10 Hz) to excite the targeted region, or at a low frequency (≤1 Hz) to inhibit the region (Crosson et al., 2015; Yoon T. H. et al., 2015). Thus, rTMS differs from tDCS in that rTMS can elicit motor activity, but tDCS cannot. That is, rTMS can directly cause neurons to fire action potentials, whereas tDCS enhances excitability but does not directly elicit motor activity. Both rTMS and tDCS can be administered with or without simultaneous SLT. Although tDCS and rTMS differ in their applications to aphasia therapy, both achieve the same goal of modulating neuronal activity.
Active ingredients
NIBS consists of two active ingredients. The first is the application of an excitatory or inhibitory signal to the brain. In studies employing tDCS, anodal (i.e., excitatory) tDCS is most often used and applied to the site of lesion (Elsner et al., 2020). Although less common, high frequency rTMS can also be used to excite neuronal activity (Zhang et al., 2017). In right-handed individuals, the site of lesion may be the left inferior frontal gyrus, or the left temporoparietal region, broadly (Elsner et al., 2020; Fridriksson et al., 2018b). Through this technique, surviving neurons in the perilesional tissue are stimulated. Conversely, cathodal (i.e., inhibitory) tDCS or low frequency rTMS may be applied to the contralateral, homologous site of the lesion (e.g., right inferior frontal gyrus, right temporoparietal region; Breining and Sebastian, 2020; da Silva et al., 2018; Spigarelli et al., 2024). The rationale behind this method is that inhibition of the right hemisphere will force activation to shift back to the left hemisphere (Ren et al., 2019).
The second active ingredient is the use of NIBS with or without concurrent speech-language therapy (SLT). The theory underlying excitatory NIBS usage during SLT is that neurotransmission is facilitated through increasing the neuron's resting potential. Proponents of this theory argue that NIBS is task-dependent, meaning the neurons must be attempting to fire for NIBS to have an augmentative effect (Bikson et al., 2018; Kronberg et al., 2017). As such, tDCS is almost always administered during SLT. However, rTMS is sometimes used in the absence of SLT (Spigarelli et al., 2024).
Mechanisms of action
The goal of both tDCS and rTMS is to induce long-lasting changes in cortical excitability to promote language recovery in individuals with post-stroke aphasia. In other words, by increasing long-term potentiation (LTP) or decreasing long-term depression (LTD) in the perilesional tissue, NIBS facilitates more efficient neurotransmission (Kronberg et al., 2017). There are a few leading theories as to how this effect is achieved.
Myelination, a proposed mechanism of LTP, is the process by which the axons of active neurons become surrounded by oligodendroglia cells (Maas and Angulo, 2021). It is dependent upon the release of glutamate onto the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors of the oligodendrocytes. This process increases the speed at which the cell fires and communicates with its synaptic connections (Lundgaard et al., 2013). Increasing neuronal activity via NIBS may promote myelination, potentially explaining why individuals who receive NIBS during SLT can name pictures with increased accuracy and reduced latency. However, more sensitive measures (e.g., diffusion tensor imaging) are needed to measure myelination to draw more definitive conclusions (Maas and Angulo, 2021).
Alternatively, NIBS may rely on NMDA receptors to change neuronal resting potential (Stagg and Nitsche, 2011). In the animal literature, Kronberg et al. (2017) found that direct current stimulation did not modulate neuronal firing when NMDA receptors were blocked in hippocampal brain slices, despite the presence of strong neural activity. The authors concluded that NMDA receptors are critical in modulating neuronal activity via NIBS. Furthermore, when these NMDA receptors are unopposed, NIBS can either increase firing in the perilesional tissue or decrease firing in the contralesional tissue by altering resting potential (Radman et al., 2009; Rahman et al., 2013). These changes may lead to more efficient neurotransmission and potential restoration of function.
As a whole, understanding of the mechanisms underlying NIBS is still developing. While there is consensus that NIBS influences cortical excitability, the precise mechanism in which this change occurs appears multifaceted and nuanced depending on the technique. For instance, TMS is more likely to indirectly activate neurons at the synapse rather than the axon hillock and maintain precision of stimulation site than transcranial electric stimulation (e.g., tDCS), which is more direct and can result in a shifted stimulation site (Kobayashi and Pascual-Leone, 2003). More research examining the physiological basis of NIBS is needed to guide its clinical usage in people with aphasia (PWA).
Potential modulating factors
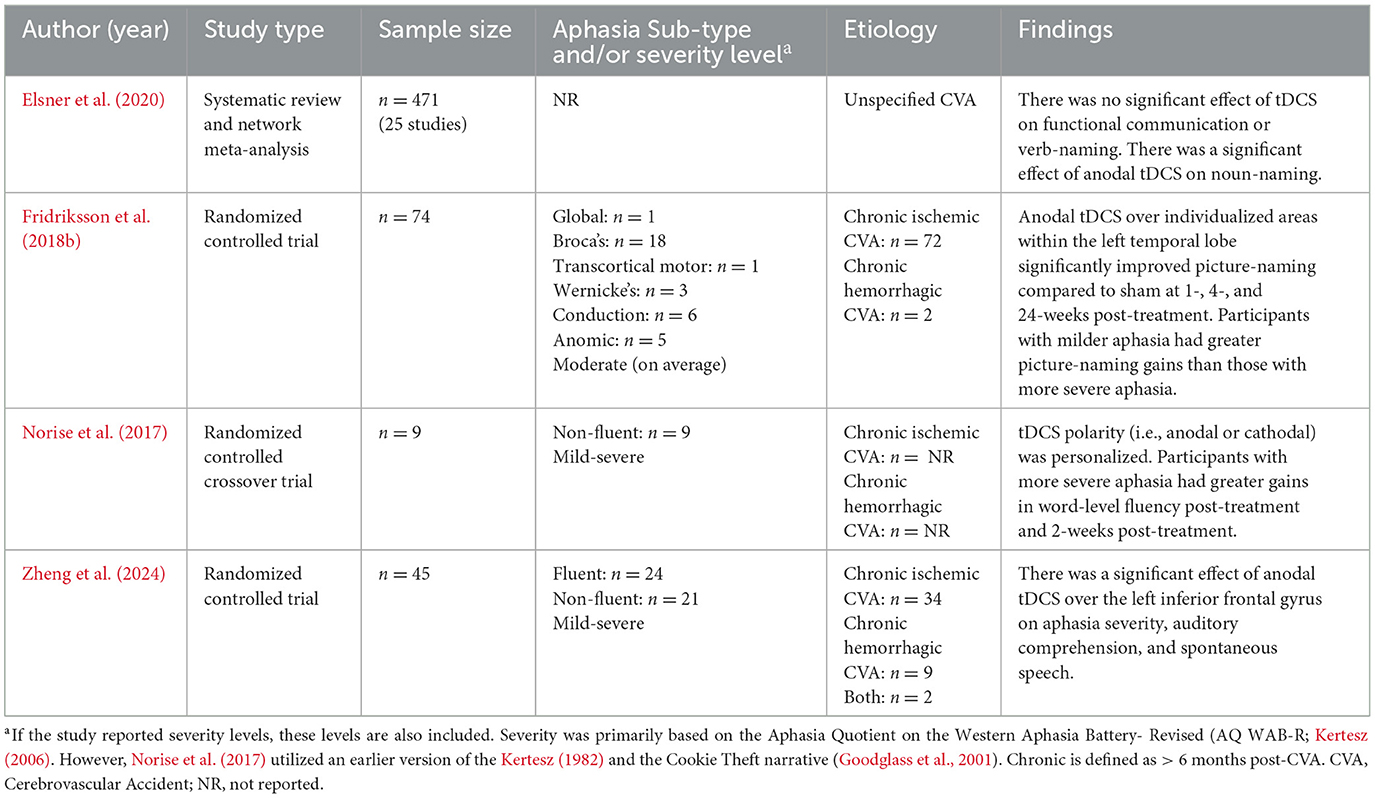
Some factors that influence the response to NIBS include but are not limited to: lesion size and location, stroke stage, aphasia type and severity, protein production, genetics, and the timing of NIBS usage. To begin, larger lesion sizes have been correlated with a greater degree of improvement following tDCS treatment, which may be secondary to the fact that people with large lesions often present with more severe aphasia (Meier et al., 2019; Norise et al., 2017). Lesion size also influences the site of stimulation (Fridriksson et al., 2018a; Hara et al., 2017). Personalizing stimulation sites based on lesion size and location is a promising approach to expedite treatment outcomes (Fridriksson et al., 2018c).
The time since stroke, or stroke stage, may also modulate the effect of NIBS. In the months following stroke, significant changes occur throughout the brain, such as the lateralization of language functions to the right hemisphere during the acute stages of aphasia recovery (Kiran, 2012; Saur et al., 2006). Whereas, this shift is compensatory, it can become maladaptive when it persists into the subacute and chronic stages (Ren et al., 2019; Turkeltaub, 2015; Yao et al., 2020). Consequently, NIBS is most often employed during the subacute or chronic stage to minimize right hemisphere activation and amplify left hemisphere activation (Breining and Sebastian, 2020). It is generally agreed that most language improvement happens naturally within the first 3 months following stroke (Berthier, 2005; Robey, 1998; Stockert et al., 2020). Thus, NIBS usage may be most appropriate later in recovery as a remediating agent.
Aphasia type and severity are also essential to consider. The right hemisphere is more likely to be recruited in those with more severe aphasia, thus, exciting the right hemisphere may be more appropriate for those with severe language impairments than those with mild or moderate impairments (Liu et al., 2024). Norise et al. (2017) found that those with more severe, expressive deficits demonstrated the greatest improvement following a tDCS + SLT treatment protocol. These findings suggest that NIBS may be more effective for those with more severe deficits, possibly because their recovery progresses slower than expected, requiring additional treatment.
It has been proposed that the release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), and therefore the gene that controls BDNF secretion, modulate the effect of NIBS. BDNF is a protein that is released at the synapse during neural activity (Coelho et al., 2013; Lu, 2003). It is critical for neuroplasticity, and thus language recovery, as it modulates LTP and LTD (Dresang et al., 2022). Those with the typical (val/val) BDNF genotype tend to show greater neuroplasticity, including increased response to rehabilitation and increased ipsilesional cortical activation, in comparison to those with the atypical (Met allele carrier) genotype (Kim et al., 2016). This supports the notion that those with the atypical BDNF genotype have a downregulation in BDNF secretion (Dresang et al., 2022). Furthermore, Fritsch et al. (2010) demonstrated that direct current stimulation was dependent upon BDNF release. This explains the correlation between the typical BDNF genotype, and presumably higher levels of BDNF, and neuroplasticity in tDCS (Fridriksson et al., 2018a) and rTMS studies (Dresang et al., 2022; Uhm et al., 2015). In other words, NIBS is more likely to improve language performance through cortical plasticity in post-stroke individuals who carry the typical BDNF genotype because they express higher levels of BDNF.
Lastly, the time at which NIBS is used can influence its effect on the brain. In clinical practice, NIBS tends to be used during SLT, as NIBS is activity-dependent (Fritsch et al., 2010) and task-specific (Bikson et al., 2018; Kronberg et al., 2017). However, the use of NIBS after SLT can disrupt therapeutic gains (Rosenkranz et al., 2000). It is suspected that anodal tDCS may strengthen unintended connections, whereas cathodal tDCS may diminish the training-induced activation if administered after training. Taken together, the implementation of precise NIBS timing in clinical settings is crucial.
Evidence of efficacy
Preliminary evidence has demonstrated that NIBS, specifically tDCS, may support language recovery in PWA. However, there is significant variability in the stimulation parameters used across studies (i.e., variability in the strength of signal, site of stimulation, etc.). As such, this section will focus on the most common protocols used in NIBS research and their efficacy.
There is good evidence to support the use of anodal tDCS on the left cortex when paired with concurrent SLT. The most recent randomized controlled trial (RCT) investigating anodal tDCS to the left inferior frontal gyrus was conducted by Zheng et al. (2024). They performed a double-blind experiment in which 1 mA was delivered during 20 min of SLT to individuals with chronic aphasia across 5 consecutive timepoints. Compared to sham stimulation, participants who received active tDCS demonstrated greater improvement in name and word-finding. These results corroborate previous studies utilizing left cortex stimulation (Elsner et al., 2020; Fridriksson et al., 2018b).
Fewer studies have investigated the duration of the effect of tDCS. For example, Zheng et al. (2024) measured language abilities through the Western Aphasia Battery- Revised (Kertesz, 2006) immediately after treatment, but did not probe for maintenance. Furthermore, Norise et al. (2017) found no impact of tDCS on measures of fluency at 2-months post-treatment. Thus, although anodal tDCS appears to improve word-finding abilities in the short-term, more research is needed to determine the long-term effect of anodal tDCS on naming and other language skills (Table 1).
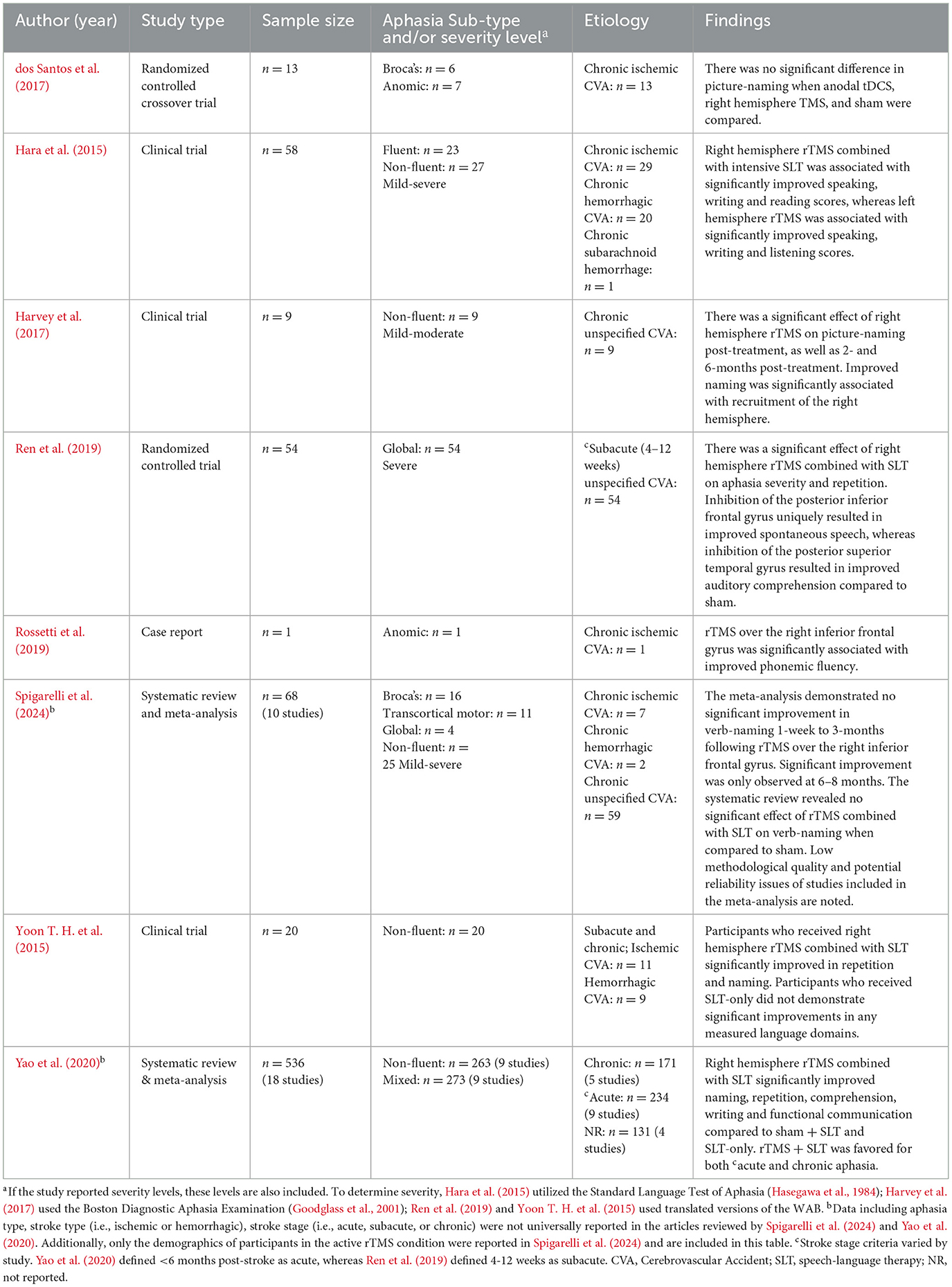
Furthermore, there is mixed evidence supporting the use of low frequency rTMS on the right cortex with or without concurrent SLT. Some studies have demonstrated that this protocol for rTMS can improve language outcomes for people with aphasia (PWA) in the chronic (Hara et al., 2015; Harvey et al., 2017; Rossetti et al., 2019), subacute (Ren et al., 2019; Yoon T. H. et al., 2015), and even acute (Yao et al., 2020) stage of stroke.
First looking at rTMS without SLT, dos Santos et al. (2017) found no difference in picture-naming abilities between TMS and SLT in their RCT involving individuals in the chronic stage of recovery. Furthermore, a meta-analysis by Spigarelli et al. (2024) found that rTMS was only superior to SLT alone for verb-naming at 6–8 months post-treatment in people with chronic stroke.
In studies that have combined rTMS with SLT, the results are also mixed, but more promising. Whereas, Spigarelli et al. (2024) found no significant difference between active and sham rTMS when combined with SLT in their systematic review, a meta-analysis by Yao et al. (2020) found that rTMS + SLT enhanced naming abilities for individuals with acute and chronic stroke more than sham + SLT or SLT alone.
Altogether, rTMS over the right cortex may benefit individuals with acute or subacute stroke when combined with SLT. However, studies should clearly state how they defined stroke stage (i.e., the range of time after stroke) to more clearly investigate this notion. Given the mixed evidence for rTMS in people in the chronic stage, anodal tDCS over the left cortex is favored over low frequency rTMS for this population. More research is needed to determine whether concurrent SLT is a necessary ingredient in rTMS studies, and if rTMS is an effective therapy for language recovery in either condition (Table 2).
Research on NIBS has aimed to determine optimal stimulation parameters, including stimulation site, signal polarity and pattern. For rTMS, there is evidence for high frequency stimulation on the left (Zhang et al., 2017) and right hemispheres (Hara et al., 2017). Additionally, the use of theta burst stimulation, a specific rTMS pulse pattern, has also gained popularity (Breining and Sebastian, 2020), and case studies have offered supporting evidence for its effect on language recovery (Georgiou et al., 2019; Griffis et al., 2016; Vuksanović et al., 2015). For tDCS, the right cerebellum is being considered as a site of stimulation. In two separate studies using anodal and cathodal tDCS, an improvement in language, albeit via different domains, was observed when compared to sham stimulation (Marangolo et al., 2018; Sebastian et al., 2017). Going forward, research on NIBS should directly compare stimulation parameters while also considering that the “optimal configuration” may vary from person-to-person.
Aerobic exercise
Aerobic exercise is a repetitive physical activity that utilizes the body's metabolic system to generate energy (Millstein et al., 2020). Regular participation in aerobic exercise (e.g., walking, running, cycling) improves the capacity of the cardiovascular system to transport oxygen, providing health benefits (Almeida and Araújo, 2003; Kemi and Wisløff, 2010). Aerobic exercise helps prevent chronic disease, supports brain health, lowers cholesterol, and reduces blood pressure (Lautenschlager et al., 2012; Piercy et al., 2018; Warburton et al., 2006).
Moreover, it can have a positive impact on cognitive functioning (Mayer et al., 2021; Mikkelsen et al., 2017; Smith and Merwin, 2021; Yao et al., 2021), such as executive functioning skills (Guiney and Machado, 2013; Rand et al., 2010), speed of information processing (Quaney et al., 2009), memory (Gómez-Pinilla et al., 2007; Vaynman et al., 2004; Yamada et al., 2002), and language (Cumming et al., 2012; El-Tamawy et al., 2014; Gary and Brunn, 2014; Gomez-Pinilla and Hillman, 2013; Mayer et al., 2021)
Active ingredients
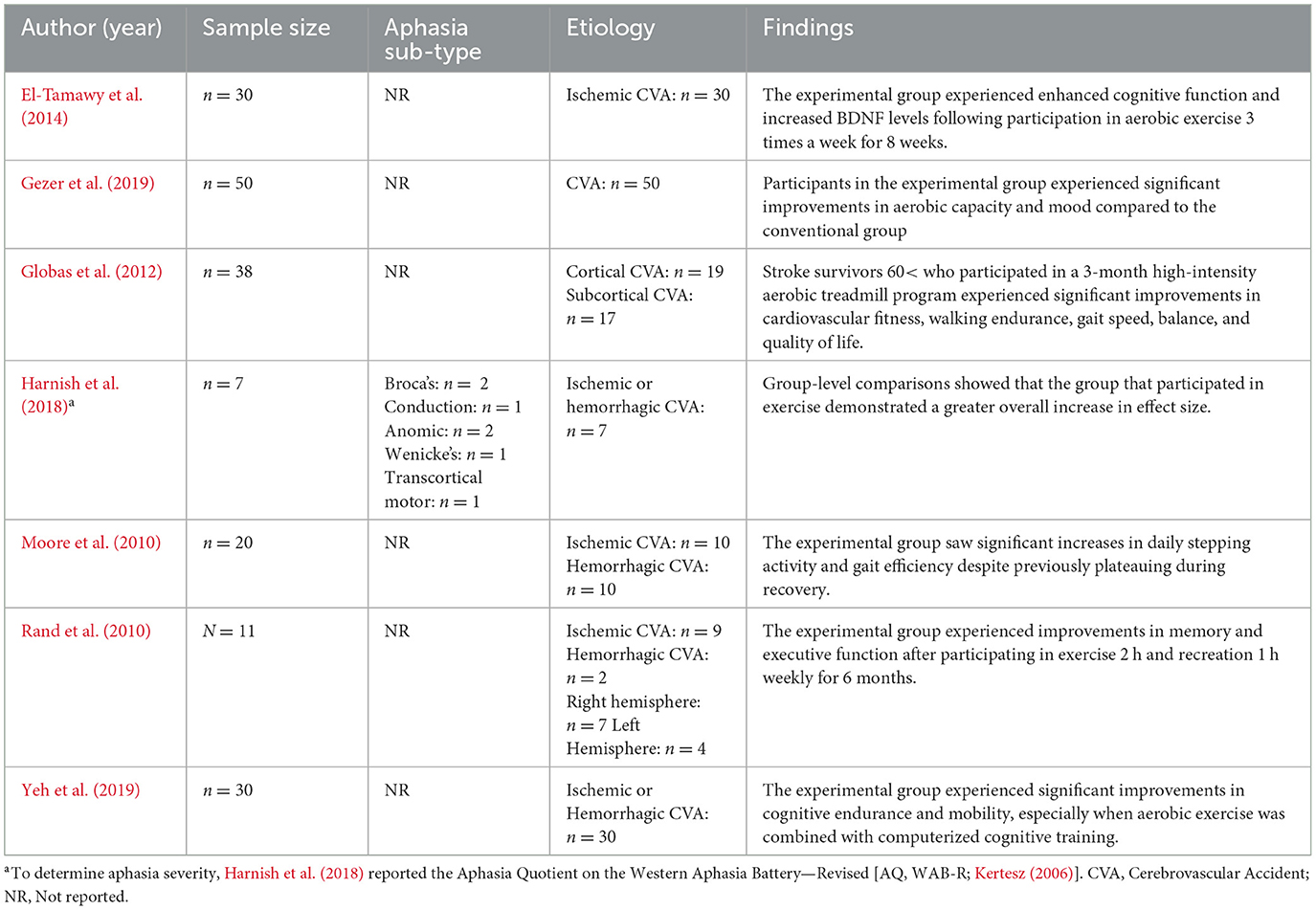
The intensity and duration (i.e., dose) of aerobic exercise serve as key active ingredients. Research suggests that programs lasting at least 4 weeks are effective (Moore et al., 2010; Zheng et al., 2016), but longer durations (e.g., 8 weeks or more) are often recommended for optimal improvement (Gezer et al., 2019; Harnish et al., 2018; Potempa et al., 1995). Tracking aerobic exercise dose amongst stroke survivors can include the addition of wearable technology to monitor exercise progress, providing real-time data on physical activity and outcomes (Patel et al., 2012; Powell et al., 2016). However, the intensity and duration of aerobic exercise should be individualized based on each person's functional capacity. That is, the “dosage” of exercise, defined by frequency, intensity, and duration, needs to be tailored to the unique needs and limitations of each individual (Potempa et al., 1996; Winstein et al., 2016). Doing so is essential for maximizing the benefits of aerobic exercise, particularly for PWA. One caveat is that the optimal dosage of exercise required to enhance neuroplastic changes associated with language recovery is unknown at this time.
Mechanisms of action
Aerobic exercise is increasingly recognized for its potential to facilitate brain recovery following stroke, particularly in the areas of neuroplasticity and mental health (Medeiros et al., 2020; Penna et al., 2021). It has been linked to the upregulation of BDNF, and thus increased neuroplasticity and management of energy metabolism (Allard et al., 2017; Vaynman et al., 2004; Vaynman and Gomez-Pinilla, 2005). In addition to highly plastic brain environment, increased levels of BDNF are positively associated with enhanced cognitive functions, all of which may support the restoration of language functions in PWA (Cunha et al., 2010; Gómez-Pinilla et al., 2007; Huang and Reichardt, 2001; Vaynman et al., 2004; Yamada et al., 2002).
In a study by Harnish et al. (2018), PWA who participated in a 12-week aerobic exercise program and language therapy demonstrated increased levels of BDNF and improved language performance. However, interpretation of these findings is limited by the fact that data were not collected on participants' genotypes. There are genetic variations in the BDNF gene that control the activity-dependent secretion of BDNF (Egan et al., 2003). Thus, individuals with BDNF polymorphisms (e.g., -met allele carriers) may experience less BDNF upregulation as a result of aerobic exercise, highlighting the importance of patient-specific factors, such as genetics, in response to therapeutic techniques.
PWA are more likely to experience post-stroke depression (PSD) than those without aphasia, which can further challenge rehabilitation and recovery (Zanella et al., 2023). PSD is associated with negative outcomes such as higher mortality rates and decreased quality of life (Medeiros et al., 2020; Robinson and Jorge, 2016). Participation in aerobic exercise positively impacts serotonin and dopamine levels, which are key neurotransmitters involved in mood regulation (Duman et al., 2008), and alleviate symptoms of depression in people with aphasia.
By reducing symptoms of depression, aerobic exercise can indirectly benefit language recovery and overall quality of life. Improved mental health boosts motivation and energy, which can improve engagement in language rehabilitation activities. Together, while the direct impact of aerobic exercise on language recovery remains an area to be investigated, its role in improving mental health, specifically by reducing PSD (Wong et al., 2016), suggests that aerobic exercise may enhance overall recovery.
Potential modulating factors
Physical limitations and stroke stage may impact the effectiveness of aerobic exercise. Many stroke survivors face challenges in performing physical exercises due to weakened motor function and fatigue. Appropriate adaptations should come from collaboration with physical and occupational therapists to help meet the unique needs of each individual, enabling them to safely engage in exercise and benefit from its effects (Gaskins et al., 2021; Kwakkel et al., 2004).
Next, the stage of stroke recovery influences the individual's physical capacity, particularly in the early post-stroke period. Peak oxygen consumption is reduced within the first 4 months following a stroke, indicating lower cardiovascular fitness and endurance during this acute stage (Mackay-Lyons et al., 2020; MacKay-Lyons and Hewlett, 2005), likely impacting participation in standard aerobic exercise. As recovery progresses, oxygen consumption typically improves, reflecting the body's gradual adaptation to physical activity. Engagement in a greater frequency and intensity of aerobic exercise may be better suited in more chronic stages post-stroke.
Adaptations to exercise intensity, frequency, and duration must be individualized. Research on stroke rehabilitation shows variability in exercise participation, with frequency ranging from one to five sessions per week (Gezer et al., 2019). Personalized treatment plans that take into account the patient's stage of recovery, physical capabilities, and overall health, will ensure that aerobic exercise remains both effective and safe.
Evidence of efficacy
Preliminary evidence suggests that aerobic exercise offers benefits when combined with traditional SLT (Harnish et al., 2018; Medeiros et al., 2020). For example, Yeh et al. (2019) found that aerobic exercise in stroke patients with mild cognitive impairment in combination with computerized cognitive training led to better cognitive and functional outcomes compared to the control group. Moreover, Harnish et al. (2018) found significant positive effects of aerobic exercise on post-stroke language recovery. These more recent findings build upon earlier studies that also found a relationship between aerobic exercise and language recovery following stroke (Cumming et al., 2012; Rand et al., 2010)
Though, the conclusions of these studies and others similar (Globas et al., 2012), are limited by small sample sizes and reduced insight into long-term effects of aerobic exercise on aphasia recovery, as opposed to more global improvement, such as reduced levels of depression.
Overall, there is modest evidence to support aerobic exercise as an adjuvant to aphasia rehabilitation (Cumming et al., 2012; El-Tamawy et al., 2014; Gary and Brunn, 2014; Gomez-Pinilla and Hillman, 2013; Guiney and Machado, 2013; Harnish et al., 2018; Rand et al., 2010). Larger sample sizes, investigations into the mechanism of action, and further exploration of the optimal dosage and timing of exercise are critical future directions (Table 3).
Intention treatment
Intention is the selection for execution and initiation of a specific action. Crosson et al. (2005) suggest that non-fluent aphasia is a “disorder of intention,” as individuals with non-fluent aphasia present with difficulty initiating verbal language output. This may suggest that the underlying language deficits may be more related to the selection and initiation of words. Intention treatment aims to re-map language production to undamaged brain areas that support intention movements. This approach leverages neural pathways for intention and re-lateralizes language production to the right frontal lobe through behavioral manipulations.
Active Ingredients
Intention treatment relies on two primary active ingredients. The first is initiating a complex left-hand movement within the patient's left hemispace (i.e., the left side of the visual field; Crosson et al., 2005), motivated by research indicating that individuals with lesions perform better on language tasks when their attention is directed toward the patient's ipsilesional space (Coslett, 1999; Dotson et al., 2008). For instance, individuals with left parietal lesions demonstrated improved language performance when the stimuli were placed in their left hemispace. During intention treatment, participants first lift a lid of a box with their left hand to initiate the presentation of a stimulus item (i.e., initiating the treatment). This movement engages ipsilesional pathways and primes intention mechanisms in the right hemisphere. The second active ingredient is pairing a verbal output naming task with the left-hand movements. If participants responded to the stimulus correctly, they moved forward to the next trial with no left-hand movements. If incorrect, they repeated the correct stimulus following a therapist's cue while making circular hand gestures (Crosson et al., 2007). The coordinated movement (i.e., left-hand movement and output naming task) primes the intention mechanisms in the right hemisphere and facilitate the re-lateralization of language functions (Picard and Strick, 1996).
Mechanisms of action
The primary mechanism of action for intention treatment is the re-lateralization, or the shift, of language function from the dominant language hemisphere (i.e., the left) to the nondominant hemisphere (i.e., the right; Crosson, 2008), which is facilitated by the engagement of intentional motor behaviors (i.e., complex left-hand movements). When intentional motor movements are performed, the medial frontal cortex, lateral frontal structures, and basal ganglia are activated (Crosson et al., 2005; Heilman et al., 2003). These substrates play crucial roles in the initiation and execution of motor movements.
The pre-supplementary motor area (pre-SMA) in the medial frontal cortex is involved in motor planning and intention. It is also activated during word generation (Crosson et al., 2001; Picard and Strick, 1996), and damage to this area may help explain a form of non-fluent aphasia (i.e., impaired word generation, intact comprehension/repetition; Beeson and Bayles, 1997). Previous research has suggested a disconnect between the language production processes (e.g., repetition) and the language initiation processes (e.g., word generation; Richards et al., 2002). The complex left-hand movements activate the right pre-SMA, which is near to regions controlling these movements. The proximity suggests that these movements may prime the right hemisphere's intention mechanisms, thereby enhancing word production (Picard and Strick, 1996). The right pre-SMA is intimately linked with the right lateral pre-frontal cortex, an area of the brain responsible for executive functions and cognitive tasks (Matsuzaka et al., 1992; Picard and Strick, 1996). The treatment's effectiveness is based on the assumption that left-hand movements prime the right lateral frontal mechanism, enhancing word generation adults with aphasia (Crosson, 2008).
Potential modulating factors
The individual assessment of lesion characteristics, such as size and location, is necessary to determine the potential benefits of intention treatment. Lesion characteristics may influence the availability of perilesional tissue and the integrity of subcortical structures, such as the basal ganglia, which are essential for neuroplasticity (Demarco et al., 2022; Knopman et al., 1984; Parkinson et al., 2009). In patients with aphasia, larger lesions reduce the amount of perilesional tissue for neuroplastic reorganization, limiting the left hemisphere's capacity to recover language ipsilaterally and increasing the reliance on the right hemisphere (Blank et al., 2003). Patients with larger left-hemisphere lesions may benefit more from intention treatment, as this approach could help re-lateralize language functions to brain regions better suited for neuroplastic recovery (Crosson et al., 2007). Conversely, smaller lesions often result in more healthy, perilesional tissue (Demarco et al., 2022; Kiran and Thompson, 2019), allowing local reorganization in the left hemisphere and reducing the need for the compensatory use of the right hemisphere.
The location of the lesion and extent of subcortical damage can influence the efficacy of intention treatment (Kiran and Thompson, 2019; Payabvash et al., 2010; Stockert et al., 2020). Lesions in the frontal and pre-SMA regions of the left hemisphere may benefit more from engaging the contralateral regions (i.e., intention treatment; Picard and Strick, 1996; Sailor et al., 2003). Lesions sparing the basal ganglia and thalamus have been reported to facilitate the natural re-lateralization of language functions even in the absence of explicit behavioral modifications (Crosson et al., 2005). For example, Crosson et al. (2005) found that one participant showed re-lateralization to the right frontal mechanisms after treatment, while the other participant showed re-lateralization before treatment due to intact basal ganglia and thalamus substrates. It is hypothesized that if these substrates are damaged (i.e., thalamus and basal ganglia), the ability to re-lateralize language function may be impeded (Crosson et al., 2005; Kim et al., 2002).
Importantly, Researchers must consider both the size and location as potential modulating factors. For example, a small lesion of the basal ganglia can impede the shift in language function to the right hemisphere, despite the lesion size being small (Crosson, 2008). Thus, while individuals with larger lesions may benefit more from intention treatment, the extent of subcortical damage can also modulate the effects.
Evidence of efficacy
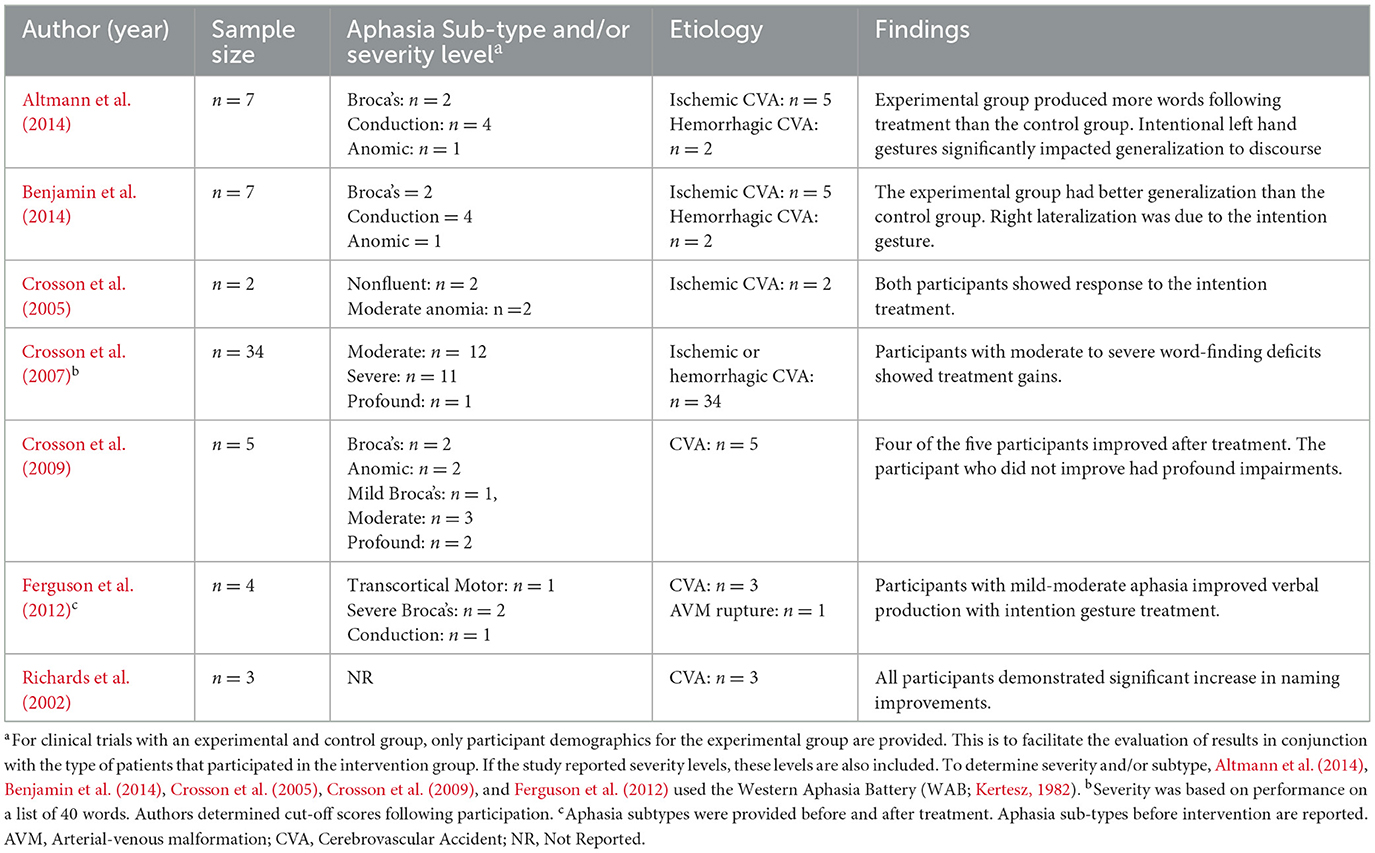
Initial studies show that intention treatment is effective for people with chronic, non-fluent aphasia (Crosson et al., 2007; Richards et al., 2002). Moreover, participants re-learned words at a quicker rate during the intention treatment as opposed to the experimental control, particularly for those with moderate to severe word-finding deficits. However, fewer individuals with profound word-naming deficits demonstrated meaningful improvements. Table 4 presents aphasia sub-types and severity levels for included experimental studies exploring the efficacy of intention treatment. Together, results suggest that individuals with moderate-severe anomia demonstrate the greatest benefits from intention treatment.
Undeniably, the ultimate goal of SLT is not to solely name black-and-white images but to generalize language outcomes from speech therapy to communicate effectively within one's environment (Wright and Shisler, 2005). Mixed results have been presented on the effectiveness of intention techniques in response generalization (i.e., from trained items to untrained items; Crosson et al., 2007, 2009; Ferguson et al., 2012). Notably, Altmann et al. (2014) demonstrated that individuals within an intentional gestures group demonstrated large improvements in discourse tasks, suggesting the presence of stimulus generalization (i.e., from trained tasks to untrained tasks), though this finding has yet to be replicated.
The studies above demonstrate the intention treatment can enhance word production but lack evidence on whether the treatment engages the right lateral frontal mechanisms. As mentioned earlier, Crosson et al. (2005) found that one patient (n = 2) demonstrated re-lateralization to the right frontal mechanisms after the treatment. Later studies with larger sample sizes, greater experimental control, and the completion of imaging with control participants supported the hypothesis of re-lateralization to the right lateral frontal mechanism after the intention treatment (Benjamin et al., 2014; Crosson et al., 2009).
Taken together, there is ample evidence to support intention treatment as an adjuvant to aphasia rehabilitation by enhancing word production and supporting re-lateralization to the right frontal brain mechanisms. However, the foundational studies exploring intention treatment papers are relatively dated. Despite its therapeutic efficacy, it serves better as a theoretical foundation by informing clinical rehabilitation research that laterality can play a vital role in language recovery.
Pharmacotherapy
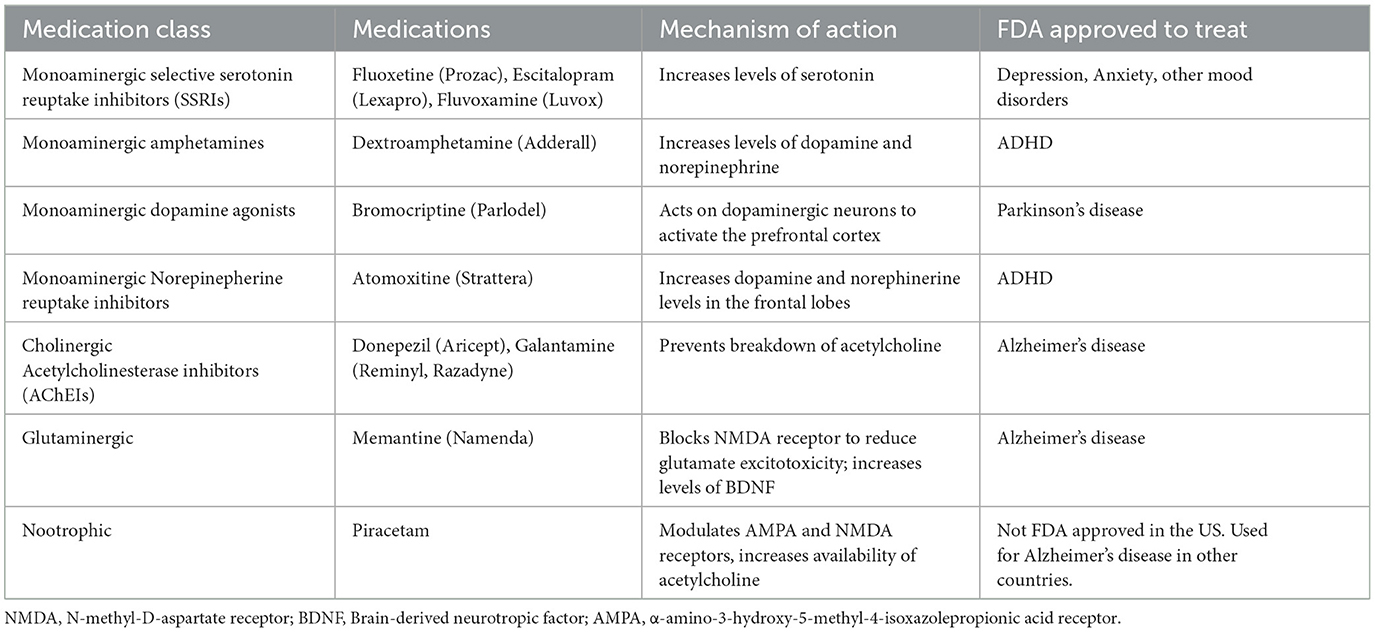
Medications are another adjuvant strategy studied to enhance the effects of aphasia therapy. If the goal of adjuvants is to create a better neural environment for plasticity to subsequently engage through the experience of aphasia therapy, then medications are a logical choice to study. There have been no medications approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of aphasia. Below we outline the active ingredients and mechanisms of action in medications studied during both the acute and chronic phases of aphasia recovery. Since classes of medications have different mechanisms of action, we describe the active ingredients (i.e., medications) and mechanisms of action together for each type of medication.
Acute phase pharmacotherapy
There is limited research to date on pharmacological adjuvants to aphasia treatment in the acute phase of recovery. Table 5 lists medication adjuvants and their mechanisms of action.
Active Ingredients and Mechanisms of Action
Thrombolytic medications
As the standard of care for acute ischemic stroke, thrombolytic medications (e.g., Alteplase and Tenecteplase) are a first-line treatment to reduce the amount and extent of a lesion. Mechanical thrombectomy, also a first-line treatment for acute stroke, is outside the scope of this review.
Monoaminergic medications
Monoaminergic medications target various neurotransmitter systems involved in mood, cognition, and behavior. By increasing levels of serotonin, SSRIs improve the brain environment for experience-dependent neuroplasticity (Stockbridge, 2022). Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), such as fluoxetine (i.e., Prozac), escitalopram (i.e., Lexapro), and fluvoxamine (i.e., Luvox) are commonly prescribed for mood disorders such as depression and anxiety and have been studied for post-stroke aphasia (Hillis et al., 2018); improvements in post-stroke depression could also improve cognitive and language outcomes (Robinson and Jorge, 2016).
Nootrophic medications
Piracetam is broadly categorized as a nootropic medication, or a cognitive enhancer. Its mechanism of action related to aphasia treatment is somewhat unclear. Cichon et al. (2021) state that it is a GABA derivative, which has inhibitory properties, but the primary mechanism of action is thought to be related to modulation of AMPA and NMDA receptors that are important for long-term potentiation, and thus, neuroplasticity. Piracetam has also been associated with the cholinergic system by increasing the availability of acetylcholine in certain brain regions (Kishore and Parle, 2009).
Chronic phase pharmacotherapy
Active ingredients and mechanisms of action
Monoaminergic medications
Monoaminergic medications, including amphetamines, dopamine agonists, and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, work on the neurotransmitter systems associated with serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, and enhance neuroplasticity.
Norepinepherine reuptake inhibitors work by increasing dopamine and norepinephrine levels in the frontal lobe, which improves executive function, attention, and language processing (Park et al., 2022). Atomoxitine (i.e., Strattera) is a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor that is commonly used for treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder but may improve cognitive functions that underly language (Yamada et al., 2016).
Amphetamines (i.e., stimulants) increase the concentration of neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and norepinephrine, at the synapse. There is some evidence from studies in the animal literature that amphetamines can assist with neural sprouting and synaptogenesis after stroke (Feeney et al., 1982; Goldstein and Davis, 1990; Hurwitz et al., 1991)
Bromocriptine is a dopamine agonist. The mechanism of action for dopamine agonists is stimulation of the dorsolateral frontostriatal circuit which leads to activation of the prefrontal cortex, an area important for executive functions and language processing. Bromocriptine is thought to act on dopaminergic neurons that project to the basal ganglia, supplementary motor area, and anterior cingulum (Stockbridge, 2022).
Atomoxetine is a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor that has shown potential in improving comprehension in individuals with cognitive impairment post stroke (Yamada et al., 2016). Norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors increase norepinephrine and dopamine levels to activate the prefrontal cortex (Park et al., 2022).
Cholinergic medications
Cholinergic medications, or Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs), are medications often used in managing Alzheimer's disease (AD). AChEIs, such as donepezil and galantamine inhibit the breakdown of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that is vital for cognitive functions like learning, memory, and attention (Berthier et al., 2006). Language deficits that occur in post-stroke aphasia and other vascular etiologies of cognitive impairment are thought to be impacted by disruptions in the cholinergic system (Dávila et al., 2023). The lateral cholinergic pathway supplies cholinergic innervation to language areas in the brain and is particularly vulnerable to post-stroke lesions. Thus, preventing the breakdown of acetylcholine boosts cholinergic activity which may assist with learning, memory, attention, and language functions (Dávila et al., 2023).
Glutaminergic medications
Glutaminergic medications work to restore balance in the glutaminergic system that is often disrupted post-stroke. Memantine, a glutaminergic medication used in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, works by blocking the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, a type of glutamate receptor. Memantine reduces glutamate excitotoxicity, thereby potentially promoting neuroplasticity (Barbancho et al., 2015; Gawande et al., 2024) and increases levels of BDNF, which contributes to neuronal survival, growth, and synaptic plasticity (Dávila and Berthier, 2024).
Potential modulating factors
The effectiveness of monoaminergic and cholinergic agents in aphasia is likely influenced by individual patient and lesion characteristics, such as age, overall cognitive abilities, co-occurring medical conditions, and lesion size that potentially impact response to treatment. Some medications may be more appropriate for an individual depending on their type of aphasia and/or severity of aphasia. The pairing of a medication with those patients who would most benefit from the medication's mechanism of action needs further investigation; genetics may play a role in the probability of responsiveness (Di Piño et al., 2016). Finally, as an adjuvant, medications that are combined with language therapy depend in part on the language therapy itself. That is, the effectiveness of the pharmacological agent in assisting with aphasia may be modulated in part by the intensity and/or individualization of language therapy to maximize the potential for neuroplastic changes.
Evidence of efficacy
Monoaminergic medications
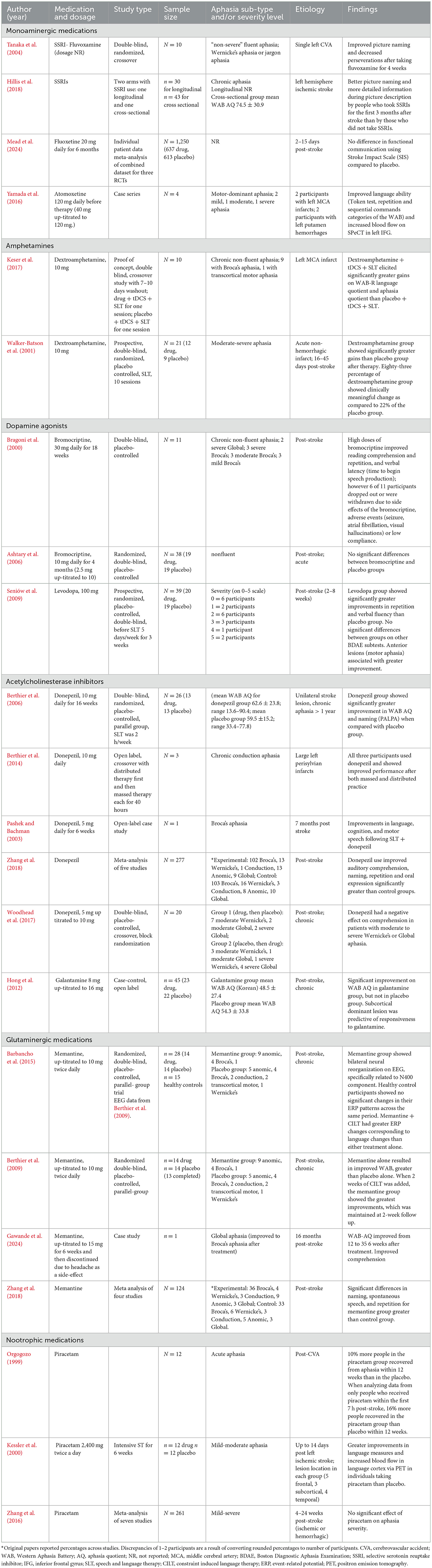
SSRIs. Tanaka et al. (2004) found in a double-blind, randomized, crossover study, that 10 patients with fluent aphasia improved on picture naming and exhibited decreased perseverations after taking fluvoxamine for 4 weeks. Corroborating these findings, a cross-sectional study of individuals with chronic aphasia showed that those who took SSRIs for the first 3 months after stroke demonstrated better picture naming ability and provided more detailed information during picture description than those who did not take SSRIs, but had similar aphasia severity, depressive symptoms, and lesion characteristics (Hillis et al., 2018). However, a meta-analysis of three randomized controlled trials including almost 6000 individuals who were post stroke found that fluoxetine use daily for 6 months did not significantly improve functional communication abilities using the Stroke Impact Scale (SIS) compared to a placebo (Mead et al., 2024). It is important to note that the outcome measures in these trials were functional communication and did not include a thorough language assessment. Thus, there is some data to suggest that SSRI use may be promising in the treatment of post-stroke aphasia, but larger clinical trials with less extensive language testing showed that functional language, using broad measures, did not benefit from SSRI use. Therefore, additional studies with larger sample sizes that include thorough assessment of language abilities are warranted. See Table 6 for a summary of the pharmacological studies reviewed.
SNRIs. There is emerging evidence in a small sample of four individuals with “motor-dominant” aphasia, that atomoxetine (i.e., Strattera) may assist with language recovery post-stroke (Yamada et al., 2016). Atomoxitine combined with intensive speech therapy resulted in improved language ability and increased blood flow on SPECT in the left inferior frontal gyrus. Neuroimaging confirmed that improvements in language were associated with increased cerebral blood flow, pointing to the utility of SNRIs in modulating norepinephrine and dopamine to increase neuroplasticity. Additional research is needed to replicate these preliminary findings.
Amphetamines
Amphetamines have been studied as an aphasia therapy adjuvant with inconsistent findings. Whereas, there is some evidence for benefits of amphetamines (Keser et al., 2017; Walker-Batson et al., 2001), there has been other research that has shown no significant improvement (McNeil et al., 1997).
It should be noted that most of the studies investigating dextroamphetamine as a treatment for post-stroke aphasia are small studies with modest results and lack of replication (Stockbridge, 2022). Although amphetamines have been studied for post-stroke aphasia, they are not commonly prescribed to individuals post-stroke due to the risk of increased blood pressure; however, several studies have found that when administered and monitored appropriately, there may not be a significant risk of hypertension with the use of dextroamphetamine post-stroke (Keser et al., 2017; Walker-Batson et al., 2001)
Dopamine agonists
Dopamine agonists have been studied for aphasia treatment with inconsistent findings. Bromocriptine in high dosages was shown to improve reading comprehension and repetition in 11 individuals with chronic non-fluent aphasia (Bragoni et al., 2000) however, there are multiple studies that found no significant gains with its use in the treatment of aphasia (Ashtary et al., 2006; Gupta et al., 1995; Sabe et al., 1995). Similarly, levodopa has very modest support from one randomized controlled trial (Seniów et al., 2009) which showed significantly greater improvements in repetition and verbal fluency abilities over placebo. Individuals with anterior lesions tended to show greater improvement, which suggests that lesion location may play a role in its efficacy for post-stroke aphasia.
One caveat to the use of dopamine agonists is that there has been some discussion of the role of genetics and the ability to benefit from cortical plasticity vs. subcortical plasticity, which could, in theory, be enhanced by dopamine agonists. Individuals with the atypical variant of BDNF (i.e., -met allele carriers) show less ability to benefit from cortical plasticity induced by tDCS and aphasia therapy (Fridriksson et al., 2018b; Kristinsson et al., 2019). Di Piño et al. (2016) suggest that subcortical plasticity should be investigated in -met carriers, potentially via dopamine agonists, to determine if they are more likely to respond, based on studies of mice (Qin et al., 2011, 2014). That is, individuals with the atypical variant of BDNF may rely more on subcortical plasticity since cortical plasticity is disrupted. This highlights the likely possibility that genetics may modulate best candidacy for medications used to enhance neuroplasticity.
Cholinergic medications
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
In the chronic phase of recovery, donepezil is the most studied AChEi in individuals with post-stroke aphasia and has a good amount of support for its efficacy. Several clinical trials have shown that donepezil may enhance language recovery in chronic post-stroke aphasia, particularly when combined with speech and language therapy (Berthier et al., 2006, 2014; Pashek and Bachman, 2003; Yoon S. Y. et al., 2015). In a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial, Berthier et al. (2006) found a large effect size for improvement in overall language function (WAB AQ) and naming abilities (PALPA) in 13 participants who used donepezil when compared with 13 individuals who received placebo. Aphasia therapy occurred for 2 h per week and was a “syndrome-specific standard approach” (Berthier et al., 2006; p. 1687). Zhang et al. (2018) conducted a meta-analysis of five studies that included a total of 277 patients. Donepezil was found to be beneficial for post-stroke aphasia. However, one study found that donepezil may have worsened comprehension in patients with moderate to severe chronic Wernicke's or global aphasia (Woodhead et al., 2017), indicating there may be an interaction with aphasia severity or type. In sum, donepezil has a good amount of evidence supporting its use as an adjuvant to post-stroke language therapy.
Evidence for galantamine in post-stroke aphasia is less extensive. A review of 96 patients treated with galantamine in the chronic period and 60 in the acute phases showed that use of galantamine or donepezil yielded positive effects in spontaneous speech, repetition, naming, and auditory comprehension (Dávila et al., 2023). Moreover, one case-control study found that galantamine significantly improved language function in patients with chronic post-stroke aphasia as measured by the Western Aphasia Battery (Hong et al., 2012). Thus, there is some evidence for efficacy of AChEi medications in the treatment of aphasia.
Glutaminergic medications
Various studies (Barbancho et al., 2015; Berthier et al., 2009; Cichon et al., 2021; Gawande et al., 2024) suggest that memantine may be a safe and effective adjuvant to aphasia therapy in the chronic stage of recovery. One clinical trial (Berthier et al., 2009) found that treatment with memantine alone resulted in improved aphasia severity scores over placebo. The addition of 2 weeks of constraint-induced language therapy yielded highly significant improvements from both groups, with the memantine + therapy group showing the greatest improvements. Barbancho et al. (2015) analyzed electroencephalography (EEG) data from the same trial and found that individuals in the memantine group demonstrated bilateral neural reorganization, specifically related to the N400 component, which is associated with semantic processing. They also demonstrated that the combination of memantine and constraint-induced language therapy yielded greater ERP changes over memantine or placebo alone.
Nootropic medications
The research on piracetam has yielded mixed results. Some studies show benefits (Stockbridge, 2022), whereas others report no significant advantages (Huber et al., 1997; Zhang et al., 2018). The Piracetam in Acute Stroke Study (PASS) found that for individuals with aphasia, 10 percent more patients in the piracetam group recovered from aphasia within 12 weeks than in the placebo group. When analyzing data from only those individuals who received piracetam in the first 7 h, the difference between groups increased to 16% (Orgogozo, 1999). Corroborating this work, Kessler et al. (2000) found greater improvements in language measures and increased blood flow in language eloquent cortex in individuals taking piracetam over placebo. However, a later meta-analysis on piracetam for post-stroke aphasia found no significant effect of piracetam on aphasia severity (Zhang et al., 2016). Thus, early pilot studies endorsed some advantages to the use of piracetam in this population, but follow-up meta-analyses failed to demonstrate efficacy.
In sum, donepezil and memantine are two medications with the strongest support in the literature for the treatment of aphasia (Cichon et al., 2021). Galantamine also has emerging evidence (Dávila et al., 2023; Hong et al., 2012). The degree to which SSRIs improve language is unclear, but they are commonly used for depression, which is prevalent post-stroke, and thus, could also have an indirect effect on language. There has been little support for dopamine agonists, such as bromocriptine and levodopa in the treatment of post-stroke aphasia; however, future research taking genetics into consideration, specifically BDNF polymorphisms may assist with matching patients who may be more or less responsive. Any potential gains from pharmacological adjuvants should be weighed against medication side effects.
Future research should investigate the best choice of medications based on individual profiles, such as aphasia presentation, cognitive skills, co-morbidities, and biomarkers. Future research should also explore the combination of various monoaminergic medications or the combination of monoaminergic and cholinergic medications as an adjuvant to aphasia therapy. Larger scale randomized controlled trials should be conducted to establish treatment guidelines, including dosing and treatment duration. Finally, the promise of these medications in combination with non-invasive brain stimulation techniques should continue to be investigated.
There are other techniques that have been explored for aphasia treatment that are compensatory in nature (e.g., brain-computer interface, AAC) or may be used for restorative therapy (e.g., virtual reality), but they are not adjuvants as we have defined herein. That is, they may be a vehicle for enhanced communication or a therapeutic technique, but they are not used to create a more neuroplastic brain environment as a canvas for the experience of therapy. We also opted to exclude yoga, even though it is gaining popularity as a therapeutic technique for aphasia, as the mechanism remains unclear. See the following references for more information on brain computer interface (Kleih and Botrel, 2024; Musso et al., 2022), AAC (Dietz et al., 2020), virtual reality (Devane et al., 2023), and yoga (Bislick et al., 2023).
Discussion
Adjuvant techniques offer promising ways to enhance aphasia therapy outcomes by several different mechanisms of action. Non-invasive brain stimulation (NIBS), aerobic exercise, and pharmacological interventions may contribute to a more favorable brain environment that supports neuroplasticity, which is essential for effective language recovery. NIBS techniques, such as TMS and tDCS, can modulate brain activity to improve language processing. For example, improved naming abilities have been observed in studies where rTMS (Yao et al., 2020; Yoon T. H. et al., 2015) and tDCS (Fridriksson et al., 2018b; Zheng et al., 2024) were combined with SLT. Future studies are needed to clarify the duration of effects, the optimal stroke stage for stimulation, and which stimulation technique or parameters are favored depending on patient-specific factors.
Aerobic exercise can increase levels of BDNF, a neurotrophin that promotes neurogenesis and is important for cognitive and language function. BDNF plays a critical role in neuroplasticity and is known to be important for learning and memory. Depression (Pompon et al., 2019, 2022), stress (Jewell and Harnish, 2024), and anxiety are common challenges in post-stroke aphasia rehabilitation. Exercise has the potential to mitigate these effects as well (Harris et al., 2019).
Pharmacotherapies that target neurotransmitter systems can improve cognitive functions and mood, further supporting therapy engagement. For example, memantine, an NMDA receptor antagonist that is considered a glutaminergic medication, has resulted in significant improvements in language function in individuals with chronic post-stroke aphasia, particularly when combined with constraint-induced language therapy (Barbancho et al., 2015; Berthier et al., 2009). Donepezil, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, has also shown promise in some studies when combined with SLT, although there is some evidence of negative effects on comprehension for moderate to severe aphasia (Woodhead et al., 2017). Individualizing pharmacotherapies based on an individual's specific needs is crucial. Future studies are needed to determine the optimal drug and language treatment regimen based on an individual's probability of responsiveness.
The effectiveness of adjuvant techniques likely vary depending on individual factors, such as the type and severity of aphasia (Woodhead et al., 2017), the time since stroke, lesion size and location (Seniów et al., 2009), genetics (Di Piño et al., 2016; Qin et al., 2011, 2014), and overall health status. A comprehensive approach that combines evidence-based aphasia therapy with individualized adjuvant techniques has the best chances of improving outcomes for individuals with aphasia.
Author contributions
SH: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CJ: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. NF: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. GT: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. GA: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The authors on this review article were supported by the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders of the National Institutes of Health under award number R01DC017711 (SH) and F31DC022142 (CJ).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
1. ^Evidence of efficacy sections include a table summarizing the experimental trials reviewed. These tables include the aphasia subtypes reported in each trial to provide a clearer understanding of which individuals may benefit from the adjuvant technique best. Importantly, this paper did not conduct a systematic review. The articles included in this review and corresponding tables are not an exhaustive list of all completed trials for the adjuvant technique.
References
Ali, M., VandenBerg, K., Williams, L. J., Williams, L. R., Abo, M., Becker, F., et al. (2021). Predictors of poststroke aphasia recovery. Stroke 52, 1778–1787. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.031162
Allard, J. S., Ntekim, O., Johnson, S. P., Ngwa, J. S., Bond, V., Pinder, D., et al. (2017). APOEε4 impacts up-regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor after a six-month stretch and aerobic exercise intervention in mild cognitively impaired elderly African Americans: a pilot study. Exp. Gerontol. 87, 129–136. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2016.11.001
Almeida, M. B., and Araújo, C. G. S. (2003). Effects of aerobic training on heart rate. Rev. Bras. Med. Esporte 9, 113–120. doi: 10.1590/S1517-86922003000200006
Altmann, L. J. P., Hazamy, A. A., Carvajal, P. J., Benjamin, M., Rosenbek, J. C., and Crosson, B. (2014). Delayed stimulus-specific improvements in discourse following anomia treatment using an intentional gesture. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 57, 439–454. doi: 10.1044/1092-4388(2013/12-0224)
Ashtary, F., Janghorbani, M., Chitsaz, A., Reisi, M., and Bahrami, A. (2006). A randomized, double-blind trial of bromocriptine efficacy in nonfluent aphasia after stroke. Neurology 66, 914–916. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000203119.91762.0c
Barbancho, M. A., Berthier, M. L., Navas-Sánchez, P., Dávila, G., Green-Heredia, C., García-Alberca, J. M., et al. (2015). Bilateral brain reorganization with memantine and constraint-induced aphasia therapy in chronic post-stroke aphasia: an ERP study. Brain Lang. 145–146, 1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2015.04.003
Beeson, P. M., and Bayles, K. A. (1997). “Aphasia,” in Handbook of Neuropsychology and Aging, ed. P. D. Nussbaum (Springer: New York), 298–314. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4899-1857-4_20
Benjamin, M. L., Towler, S., Garcia, A., Park, H., Sudhyadhom, A., Harnish, S., et al. (2014). A behavioral manipulation engages right frontal cortex during aphasia therapy. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 28, 545–553. doi: 10.1177/1545968313517754
Bernal, B., and Ardila, A. (2009). The role of the arcuate fasciculus in conduction aphasia. Brain 132, 2309–2316. doi: 10.1093/brain/awp206
Berthier, M. L. (2005). Poststroke aphasia: epidemiology, pathophysiology and treatment. Drugs Aging 22, 163–182. doi: 10.2165/00002512-200522020-00006
Berthier, M. L., Dávila, G., Green-Heredia, C., Moreno Torres, I., Juárez y Ruiz de Mier, R., De-Torres, I., et al. (2014). Massed sentence repetition training can augment and speed up recovery of speech production deficits in patients with chronic conduction aphasia receiving donepezil treatment. Aphasiology 28, 188–218. doi: 10.1080/02687038.2013.861057
Berthier, M. L., Green, C., Higueras, C., Fernández, I., Hinojosa, J., and Martín, M. C. (2006). A randomized, placebo-controlled study of donepezil in poststroke aphasia. Neurology 67, 1687–1689. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000242626.69666.e2
Berthier, M. L., Green, C., Lara, J. P., Higueras, C., Barbancho, M. A., Dávila, G., et al. (2009). Memantine and constraint-induced aphasia therapy in chronic poststroke aphasia. Ann. Neurol. 65, 577–585. doi: 10.1002/ana.21597
Bikson, M., Brunoni, A. R., Charvet, L. E., Clark, V. P., Cohen, L. G., Deng, Z., et al. (2018). Rigor and reproducibility in research with transcranial electrical stimulation: an NIMH-sponsored workshop. Brain Stimul. 11, 465–480. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2017.12.008
Bislick, L., Dietz, A., Duncan, E. S., and Cornelius, K. (2023). The feasibility and benefits of a virtual yoga practice for stroke survivors with aphasia. Am. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 32, 1679–1688. doi: 10.1044/2023_AJSLP-22-00269
Blank, S. C., Bird, H., Turkheimer, F., and Wise, R. J. S. (2003). Speech production after stroke: the role of the right pars opercularis. Ann. Neurol. 54, 310–320. doi: 10.1002/ana.10656
Bragoni, M., Altieri, M., Di, V., Padovani, P. A., Mostardini, C., Lenzi, G. L., et al. (2000). Bromocriptine and speech therapy in non-fluent chronic aphasia after stroke. Neurol. Sci. 21, 19–22. doi: 10.1007/s100720070114
Breining, B. L., and Sebastian, R. (2020). Neuromodulation in post-stroke aphasia treatment. Curr. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Rep. 8, 44–56. doi: 10.1007/s40141-020-00257-5
Chen, X., Chen, L., Zheng, S., Wang, H., Dai, Y., Chen, Z., et al. (2021). Disrupted brain connectivity networks in aphasia revealed by resting-state fMRI. Front. Aging Neurosci. 13:666301. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.666301
Cichon, N., Wlodarczyk, L., Saluk-Bijak, J., Bijak, M., Redlicka, J., Gorniak, L., et al. (2021). Novel advances to post-stroke aphasia pharmacology and rehabilitation. J. Clin. Med. 10:3778. doi: 10.3390/jcm10173778
Coelho, F. G. de M., Gobbi, S., Andreatto, C. A. A., Corazza, D. I., Pedroso, R. V., and Santos-Galduróz, R. F. (2013). Physical exercise modulates peripheral levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF): a systematic review of experimental studies in the elderly. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 56, 10–15. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2012.06.003
Coslett, H. B. (1999). Spatial influences on motor and language function. Neuropsychologia 37, 695–706. doi: 10.1016/S0028-3932(98)00116-X
Crosson, B. (2008). An intention manipulation to change lateralization of word production in nonfluent aphasia: current status. Semin. Speech Lang. 29, 188–200. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1082883
Crosson, B., Fabrizio, K. S., Singletary, F., Cato, M. A., Wierenga, C. E., Parkinson, R. B., et al. (2007). Treatment of naming in nonfluent aphasia through manipulation of intention and attention: a phase 1 comparison of two novel treatments. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 13, 582–594. doi: 10.1017/S1355617707070737
Crosson, B., McGregor, K. M., Nocera, J. R., Drucker, J. H., Tran, S. M., and Butler, A. J. (2015). The relevance of aging-related changes in brain function to rehabilitation in aging-related disease. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 9:307. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2015.00307
Crosson, B., Moore, A. B., Gopinath, K., White, K. D., Wierenga, C. E., Gaiefsky, M. E., et al. (2005). Role of the right and left hemispheres in recovery of function during treatment of intention in aphasia. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 17, 392–406. doi: 10.1162/0898929053279487
Crosson, B., Moore, A. B., McGregor, K. M., Chang, Y. L., Benjamin, M., Gopinath, K., et al. (2009). Regional changes in word-production laterality after a naming treatment designed to produce a rightward shift in frontal activity. Brain Lang. 111, 73–85. doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2009.08.001
Crosson, B., Sadek, J. R., Maron, L., Gökçay, D., Mohr, C. M., Auerbach, E. J., et al. (2001). Relative shift in activity from medial to lateral frontal cortex during internally versus externally guided word generation. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 13, 272–283. doi: 10.1162/089892901564225
Cumming, T. B., Tyedin, K., Churilov, L., Morris, M. E., and Bernhardt, J. (2012). The effect of physical activity on cognitive function after stroke: a systematic review. Int. Psychogeriatr. 24, 557–567. doi: 10.1017/S1041610211001980
Cunha, C., Brambilla, R., and Thomas, K. L. (2010). A simple role for BDNF in learning and memory? Front. Mol. Neurosci. 3:2010. doi: 10.3389/neuro.02.001.2010
da Silva, F. R., Mac-Kay, A. P. M. G., Chao, J. C. T., dos Santos, M. D., and Gagliadi, R. J. (2018). Transcranial direct current stimulation: a study on naming performance in aphasic individuals. CODAS 30:e20170242. doi: 10.1590/2317-1782/20182017242
Dávila, G., and Berthier, M. L. (2024). Are pharmacotherapeutics effective for treating aphasia? Expert Rev. Neurother. 24, 267–271. doi: 10.1080/14737175.2024.2313557
Dávila, G., Torres-Prioris, M. J., López-Barroso, D., and Berthier, M. L. (2023). Turning the spotlight to cholinergic pharmacotherapy of the human language system. CNS Drugs 37, 599–637. doi: 10.1007/s40263-023-01017-4
Demarco, A. T., Van Der Stelt, C., Paul, S., Dvorak, E., Lacey, E., Snider, S., et al. (2022). Absence of perilesional neuroplastic recruitment in chronic poststroke aphasia. Neurology 99, e119–e128. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000200382
Devane, N., Behn, N., Marshall, J., Ramachandran, A., Wilson, S., and Hilari, K. (2023). The use of virtual reality in the rehabilitation of aphasia: a systematic review. Disabil. Rehabil. 45, 3803–3822. doi: 10.1080/09638288.2022.2138573
Di Piño, G., Pellegrino, G., Capone, F., Assenza, G., Florio, L. U. C. I. A., Falato, E. M. M. A., et al. (2016). Val66Met BDNF polymorphism implies a different way to recover from stroke rather than a worse overall recoverability. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 30, 3–8. doi: 10.1177/1545968315583721
Dietz, A., Wallace, S., and Weissling, K. (2020). Revisiting the role of augmentative and alternative communication in aphasia rehabilitation. Am. J. Speech-Lang. Pathol. 29, 909–913. doi: 10.1044/2019_AJSLP-19-00041
dos Santos, M. D., Cavenaghi, V. B., Mac-Kay, A. P. M. G., Serafim, V., Venturi, A., Truong, D. Q., et al. (2017). Non-invasive brain stimulation and computational models in post-stroke aphasic patients: Single session of transcranial magnetic stimulation and transcranial direct current stimulation. A randomized clinical trial. Sao Paulo Med. J. 135, 475–480. doi: 10.1590/1516-3180.2016.0194060617
Dotson, V., Singletary, F., Fuller, R., Koehler, S., Moore, A. B., Rothi, L. J. G., et al. (2008). Treatment of word-finding deficits in fluent aphasia through the manipulation of spatial attention: preliminary findings. Aphasiology 22, 103–113. doi: 10.1080/02687030600990983
Dresang, H. C., Harvey, D. Y., Xie, S. X., Shah-Basak, P. P., DeLoretta, L., Wurzman, R., et al. (2022). Genetic and neurophysiological biomarkers of neuroplasticity inform post-stroke language recovery. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 36, 371–380. doi: 10.1177/15459683221096391
Duman, C. H., Schlesinger, L., Russell, D. S., and Duman, R. S. (2008). Voluntary exercise produces antidepressant and anxiolytic behavioral effects in mice. Brain Res. 1199, 148–158. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.12.047
Efstratiadou, E. A., Papathanasiou, I., Holland, R., Archonti, A., and Hilari, K. (2018). A systematic review of semantic feature analysis therapy studies for aphasia. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 61, 1261–1278. doi: 10.1044/2018_JSLHR-L-16-0330
Egan, M., Kojima, M., Callicott, J., Goldberg, T., Kolachana, B., Bertolino, A., et al. (2003). The BDNF val66met polymorphism affects activity-dependent secretion of BDNF and human memory and hippocampal function. Cell 112, 257–269. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00035-7
Elsner, B., Kugler, J., and Mehrholz, J. (2020). Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) for improving aphasia after stroke: A systematic review with network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 17:88. doi: 10.1186/s12984-020-00708-z
El-Tamawy, M. S., Abd-Allah, F., Ahmed, S. M., Darwish, M. H., and Khalifa, H. A. (2014). Aerobic exercises enhance cognitive functions and brain derived neurotrophic factor in ischemic stroke patients. NeuroRehabilitation 34, 209–213. doi: 10.3233/NRE-131020
Feeney, D., Gonzalez, A., and Law, W. (1982). Amphetamine, haloperidol, and experience interact to affect rate of recovery after motor cortex injury. Science 217, 855–857. doi: 10.1126/science.7100929
Ferguson, N., Evans, K., and Raymer, A. (2012). A comparison of intention and pantomime gesture treatment for noun retrieval in people with aphasia. Am. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 21, S126–S139. doi: 10.1044/1058-0360(2012/11-0076)
Fridriksson, J., den Ouden, D.-B., Hillis, A. E., Hickok, G., Rorden, C., Basilakos, A., et al. (2018c). Anatomy of aphasia revisited. Brain 141, 848–862. doi: 10.1093/brain/awx363
Fridriksson, J., Elm, J., Stark, B. C., Basilakos, A., Rorden, C., Sen, S., et al. (2018a). BDNF genotype and tDCS interaction in aphasia treatment. Brain Stimul. 11, 1276–1281. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2018.08.009
Fridriksson, J., Rorden, C., Elm, J., Sen, S., George, M. S., and Bonilha, L. (2018b). Transcranial direct current stimulation vs sham stimulation to treat aphasia after stroke: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Neurol. 75, 1470–1476. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.2287
Fritsch, B., Reis, J., Martinowich, K., Schambra, H. M., Ji, Y., Cohen, L. G., et al. (2010). Direct current stimulation promotes BDNF-dependent synaptic plasticity: potential implications for motor learning. Neuron 66, 198–204. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.03.035
Gary, R. A., and Brunn, K. (2014). Aerobic exercise as an adjunct therapy for improving cognitive function in heart failure. Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2014:157508. doi: 10.1155/2014/157508
Gaskins, N. J., Bray, E., Hill, J. E., Doherty, P. J., Harrison, A., and Connell, L. A. (2021). Factors influencing implementation of aerobic exercise after stroke: a systematic review. Disabil. Rehabil. 43, 2382–2396. doi: 10.1080/09638288.2019.1704075
Gawande, S. R., Joshi, A. D., Jhaveri, R. H., and Acharya, A. (2024). Effect of memantine in chronic poststroke aphasia: a clinical vignette. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 103, E74–E76. doi: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000002438
Georgiou, A., Konstantinou, N., Phinikettos, I., and Kambanaros, M. (2019). Neuronavigated theta burst stimulation for chronic aphasia: two exploratory case studies. Clin. Linguist. Phonetics 33, 532–546. doi: 10.1080/02699206.2018.1562496
Gezer, H., Karaahmet, O. Z., Gurcay, E., Dulgeroglu, D., and Cakci, A. (2019). The effect of aerobic exercise on stroke rehabilitation. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 188, 469–473. doi: 10.1007/s11845-018-1848-4
Globas, C., Becker, C., Cerny, J., Lam, J. M., Lindemann, U., Forrester, L. W., et al. (2012). Chronic stroke survivors benefit from high-intensity aerobic treadmill exercise: a randomized control trial. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 26, 85–95. doi: 10.1177/1545968311418675
Goldstein, L., and Davis, J. (1990). Post-lesion practice and amphetamine-facilitated recofery of beam walking in the rat. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 1, 311–314. doi: 10.3233/RNN-1990-1501
Gomez-Pinilla, F., and Hillman, C. (2013). The influence of exercise on cognitive abilities. Compr. Physiol. 3, 403–428. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c110063
Gómez-Pinilla, F., Huie, J. R., Ying, Z., Ferguson, A. R., Crown, E. D., Baumbauer, K. M., et al. (2007). BDNF and learning: evidence that instrumental training promotes learning within the spinal cord by up-regulating BDNF expression. Neuroscience 148, 893–906. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.05.051
Goodglass, H., Kaplan, E., and Barresi, B. (2001). Boston Diagnostic Aphasia Examination. Boston, MA: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins.
Gordon, E. M., Laumann, T. O., Marek, S., Raut, R. V., Gratton, C., Newbold, D. J., et al. (2020). Default-mode network streams for coupling to language and control systems. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 117, 17308–17319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2005238117
Griffis, J. C., Nenert, R., Allendorfer, J. B., and Szaflarski, J. P. (2016). Interhemispheric plasticity following intermittent theta burst stimulation in chronic poststroke aphasia. Neural Plast. 2016:4796906. doi: 10.1155/2016/4796906
Guiney, H., and Machado, L. (2013). Benefits of regular aerobic exercise for executive functioning in healthy populations. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 20, 73–86. doi: 10.3758/s13423-012-0345-4
Gupta, S. R., Mlcoch, A. G., Scolaro, C., and Moritz, T. (1995). Bromocriptine treatment of nonfluent aphasia. Neurology 45, 2170–2173. doi: 10.1212/WNL.45.12.2170
Hara, T., Abo, M., Kakita, K., Mori, Y., Yoshida, M., and Sasaki, N. (2017). The effect of selective transcranial magnetic stimulation with functional near-infrared spectroscopy and intensive speech therapy on individuals with post-stroke aphasia. Eur. Neurol. 77, 186–194. doi: 10.1159/000457901
Hara, T., Abo, M., Kobayashi, K., Watanabe, M., Kakuda, W., and Senoo, A. (2015). Effects of low-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation combined with intensive speech therapy on cerebral blood flow in post-stroke aphasia. Transl. Stroke Res. 6, 365–374. doi: 10.1007/s12975-015-0417-7
Harnish, S. M., Rodriguez, A. D., Blackett, D. S., Gregory, C., Seeds, L., Boatright, J. H., et al. (2018). Aerobic exercise as an adjuvant to aphasia therapy: theory, preliminary findings, and future directions. Clin. Ther. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2017.12.002
Harris, A., Austin, M., Blake, T. M., and Bird, M. L. (2019). Perceived benefits and barriers to yoga participation after stroke: a focus group approach. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 34, 153–156. doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2018.11.015
Harvey, D. Y., Podell, J., Turkeltaub, P. E., Faseyitan, O., Coslett, H. B., and Hamilton, R. H. (2017). Functional reorganization of right prefrontal cortex underlies sustained naming improvements in chronic aphasia via repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation. Cogn. Behav. Neurol. 30, 133–144. doi: 10.1097/WNN.0000000000000141
Hasegawa, T., Kishi, H., Shigeno, K., Tanemura, J., Kusunoki, T., Kifune, Y., et al. (1984). A study on aphasia rating scale: a method for overall assessment of SLTA results. High. Brain Funct. Res. 4, 638–646.
Heilman, K. M., Watson, R. T., and Valenstein, E. (2003). “Neglect and related disorders,” in Clinical Neuropsychology, 4th ed. (New York, NY: Oxford University Press), 296−346. doi: 10.2496/apr.4.638
Hillis, A. E., Beh, Y. Y., Sebastian, R., Breining, B., Tippett, D. C., Wright, A., et al. (2018). Predicting recovery in acute poststroke aphasia. Ann. Neurol. 83, 612–622. doi: 10.1002/ana.25184
Hong, J. M., Shin, D. H., Lim, T. S., Lee, J. S., and Huh, K. (2012). Galantamine administration in chronic post-stroke aphasia. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 83, 675–680. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2012-302268
Huang, E. J., and Reichardt, L. F. (2001). Neurotrophins: roles in neuronal development and function. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 24, 677–736. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.24.1.677
Huber, W., Willmes, K., Poeck, K., Van Vleymen, B., and Deberdt, W. (1997). Piracetam as an adjuvant to language therapy for aphasia: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled pilot study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 78, 245–250. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9993(97)90028-9
Hurwitz, B. E., Dalton Dietrich, W., McCabe, P. M., Alonso, O., Watson, B. D., Ginsberg, M. D., et al. (1991). Amphetamine promotes recovery from sensory-motor integration deficit after thrombotic infarction of the primary somatosensory rat cortex. Stroke 22, 648–654. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.22.5.648
Jewell, C. C., and Harnish, S. M. (2024). Safety-seeking behaviors and anxiety maintenance in people with aphasia: a viewpoint. Am. J. Speech-Lang. Pathol. 33, 2121–2126. doi: 10.1044/2024_AJSLP-23-00419
Johnson, J. P., Meier, E. L., Pan, Y., and Kiran, S. (2019). Treatment-related changes in neural activation vary according to treatment response and extent of spared tissue in patients with chronic aphasia. Cortex 121, 147–168. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2019.08.016
Kemi, O. J., and Wisløff, U. (2010). High-intensity aerobic exercise training improves the heart in health and disease. J. Cardiopulm. Rehabil. Prev. 30, 2–11. doi: 10.1097/HCR.0b013e3181c56b89
Kertesz, A. (2006). Western Aphasia Battery- Revised (WAB-R). San Antonio, TX: PsychCorp. doi: 10.1037/t15168-000
Keser, Z., Dehgan, M. W., Shadravan, S., Yozbatiran, N., Maher, L. M., and Francisco, G. E. (2017). Combined dextroamphetamine and transcranial direct current stimulation in poststroke aphasia. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 96, S141–S145. doi: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000000780
Kessler, J., Thiel, A., Karbe, H., and Heiss, W. D. (2000). Piracetam improves activated blood flow and facilitates rehabilitation of poststroke aphasic patients. Stroke 31, 2112–2116. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.31.9.2112
Kim, D. Y., Quinlan, E. B., Gramer, R., and Cramer, S. C. (2016). BDNF Val66Met polymorphism is related to motor system function after stroke. Phys. Ther. 96, 533–539. doi: 10.2522/ptj.20150135
Kim, Y. H., Ko, M. H., Parrish, T. B., and Kim, H. G. (2002). Reorganization of cortical language areas in patients with aphasia: a functional MRI study. Yonsei Med. J. 43, 441–445. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2002.43.4.441
Kiran, S. (2012). What is the nature of poststroke language recovery and reorganization? ISRN Neurol. 2012:786872. doi: 10.5402/2012/786872
Kiran, S., and Thompson, C. K. (2019). Neuroplasticity of language networks in aphasia: advances, updates, and future challenges. Front. Neurol. 10:295. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00295
Kishore, S., and Parle, M. (2009). Piracetam: a review of its mechanisms of action and applications. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 93, 311–318.
Kleih, S. C., and Botrel, L. (2024). Post-stroke aphasia rehabilitation using an adapted visual P300 brain-computer interface training: improvement over time, but specificity remains undetermined. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 18:1400336. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2024.1400336
Knopman, D. S., Seines, O. A., Niccum, N., and Rubens, A. B. (1984). Recovery of naming in aphasia: Relationship to fluency, comprehension and CT findings. Neurology 34, 1461–1470. doi: 10.1212/WNL.34.11.1461
Kobayashi, M., and Pascual-Leone, A. (2003). Transcranial magnetic stimulation in neurology. Lancet Neurol. 2, 145–156. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(03)00321-1
Kristinsson, S., Yourganov, G., Xiao, F., Bonilha, L., Stark, B. C., Rorden, C., et al. (2019). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor genotype-specific differences in cortical activation in chronic aphasia. J. Speech Lang. Hear Res. 62, 3923–3936. doi: 10.1044/2019_JSLHR-L-RSNP-19-0021
Kronberg, G., Bridi, M., Abel, T., Bikson, M., and Parra, L. C. (2017). Direct current stimulation modulates LTP and LTD: activity dependence and dendritic effects. Brain Stimul. 10, 51–58. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2016.10.001
Kwakkel, G., Van Peppen, R., Wagenaar, R. C., Dauphinee, S. W., Richards, C., Ashburn, A., et al. (2004). Effects of augmented exercise therapy time after stroke: a meta-analysis. Stroke 35, 2529–2539. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000143153.76460.7d
Lautenschlager, N. T., Cox, K., and Cyarto, E. V. (2012). The influence of exercise on brain aging and dementia. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1822, 474–481. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.07.010
Liu, N., Ye, T. F., and Yu, Q. W. (2024). The role of the right hemisphere homologous language pathways in recovery from post-stroke aphasia: a systematic review. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 343:111866. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2024.111866
Lu, B. (2003). BDNF and activity-dependent synaptic modulation. Learn. Mem.10, 86–98. doi: 10.1101/lm.54603
Lundgaard, I., Luzhynskaya, A., Stockley, J. H., Wang, Z., Evans, K. A., Swire, M., et al. (2013). Neuregulin and BDNF induce a switch to NMDA receptor-dependent myelination by oligodendrocytes. PLoS Biol. 11:1001743. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001743
Maas, D. A., and Angulo, M. C. (2021). Can enhancing neuronal activity improve myelin repair in multiple sclerosis? Front. Cell. Neurosci. 15:645240. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.645240
Mackay-Lyons, M., Billinger, S. A., Eng, J. J., Dromerick, A., Giacomantonio, N., Hafer-Macko, C., et al. (2020). Aerobic exercise recommendations to optimize best practices in care after stroke: AEROBICS 2019 update. Phys. Ther. 100, 149–156. doi: 10.1093/ptj/pzz153
MacKay-Lyons, M. J., and Hewlett, J. (2005). Exercise capacity and cardiovascular adaptations to aerobic training early after stroke. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 12, 31–44. doi: 10.1310/RDQM-JTGL-WHAA-XYBW
Marangolo, P., Fiori, V., Caltagirone, C., Pisano, F., and Priori, A. (2018). Transcranial cerebellar direct current stimulation enhances verb generation but not verb naming in poststroke Aphasia. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 30, 188–199. doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_01201
Matsuzaka, Y., Aizawa, H., and Tanji, J. (1992). A motor area rostral to the supplementary motor area (presupplementary motor area) in the monkey: Neuronal activity during a learned motor task. J. Neurophysiol. 68, 653–662. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.68.3.653
Mayer, J. F., Sandberg, C. W., Mozeiko, J., Madden, E. B., and Murray, L. L. (2021). Cognitive and linguistic benefits of aerobic exercise: a state-of-the-art systematic review of the stroke literature. Front. Rehabil. Sci. 2:785312. doi: 10.3389/fresc.2021.785312
McNeil, M. R., Doyle, P. J., Spencer, K. A., Jackson Goda, A., Flores, D., and Small, S. L. (1997). A double-blind, placebo-controlled study of pharmacological and behavioural treatment of lexical-semantic deficits in aphasia. Aphasiology 11, 385–400. doi: 10.1080/02687039708248479
Mead, G., Graham, C., Lundström, E., Hankey, G. J., Hackett, M. L., Billot, L., et al. (2024). Individual patient data meta-analysis of the effects of fluoxetine on functional outcomes after acute stroke. Int. J. Stroke 19, 798–808. doi: 10.1177/17474930241242628
Medeiros, G. C., Roy, D., Kontos, N., and Beach, S. R. (2020). Post-stroke depression: a 2020 updated review. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 66, 70–80. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2020.06.011
Meier, E. L., Johnson, J. P., Pan, Y., and Kiran, S. (2019). The utility of lesion classification in predicting language and treatment outcomes in chronic stroke-induced aphasia. Brain Imaging Behav. 13, 1510–1525. doi: 10.1007/s11682-019-00118-3
Mikkelsen, K., Stojanovska, L., Polenakovic, M., Bosevski, M., and Apostolopoulos, V. (2017). Exercise and mental health. Maturitas 106, 48–56. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2017.09.003
Millstein, R. A., Huffman, J. C., Thorndike, A. N., Freedman, M., Scheu, C., Kim, S., et al. (2020). How do positive psychological constructs affect physical activity engagement among individuals at high risk for chronic health conditions? a qualitative study. J. Phys. Act. Health 17, 977–986. doi: 10.1123/jpah.2019-0295
Moore, J. L., Roth, E. J., Killian, C., and Hornby, T. G. (2010). Locomotor training improves daily stepping activity and gait efficiency in individuals poststroke who have reached a “plateau” in recovery. Stroke 41, 129–135. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.563247
Musso, M., Hübner, D., Schwarzkopf, S., Bernodusson, M., LeVan, P., Weiller, C., et al. (2022). Aphasia recovery by language training using a brain-computer interface: a proof-of-concept study. Brain Commun. 4:fcac008. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcac008
Norise, C., Sacchetti, D., and Hamilton, R. (2017). Transcranial direct current stimulation in post-stroke chronic aphasia: the impact of baseline severity and task specificity in a pilot sample. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 11:260. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2017.00260
Orgogozo, J.-M. (1999). Piracetam in the treatment of acute stroke. Pharmacopsychiatry 32, 25–32. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-979233
Park, J. M., Choi, S., and Kim, Y. W. (2022). Effectiveness of atomoxetine (Strattera) for the treatment of poststroke aphasia combined with cognitive impairment. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 45, 17–20. doi: 10.1097/WNF.0000000000000495
Parkinson, B. R., Raymer, A., Chang, Y. L., FitzGerald, D. B., and Crosson, B. (2009). Lesion characteristics related to treatment improvement in object and action naming for patients with chronic aphasia. Brain Lang. 110, 61–70. doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2009.05.005
Pashek, G. V., and Bachman, D. L. (2003). Cognitive, linguistic and motor speech effects of donepezil hydrochloride in a patient with stroke-related aphasia and apraxia of speech. Brain Lang. 87, 179–180. doi: 10.1016/S0093-934X(03)00259-1
Patel, S., Park, H., Bonato, P., Chan, L., and Rodgers, M. (2012). A review of wearable sensors and systems with application in rehabilitation. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 9:21. doi: 10.1186/1743-0003-9-21
Payabvash, S., Kamalian, S., Fung, S., Wang, Y., Passanese, J., Kamalian, S., et al. (2010). Predicting language improvement in acute stroke patients presenting with aphasia: a multivariate logistic model using location-weighted atlas-based analysis of admission CT perfusion scans. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 31, 1661–1668. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A2125
Penna, L. G., Pinheiro, J. P., Ramalho, S. H. R., and Ribeiro, C. F. (2021). Effects of aerobic physical exercise on neuroplasticity after stroke: Systematic review. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 79, 832–843. doi: 10.1590/0004-282x-anp-2020-0551
Picard, N., and Strick, P. L. (1996). Motor areas of the medial wall: a review of their location and functional activation. Cereb. Cortex 6, 342–353. doi: 10.1093/cercor/6.3.342
Pierce, J. E., Menahemi-Falkov, M., O'Halloran, R., Togher, L., and Rose, M. L. (2019). Constraint and multimodal approaches to therapy for chronic aphasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuropsychol. Rehabil. 29, 1005–1041. doi: 10.1080/09602011.2017.1365730
Piercy, K. L., Troiano, R. P., Ballard, R. M., Carlson, S. A., Fulton, J. E., Galuska, D. A., et al. (2018). The physical activity guidelines for Americans. JAMA 320, 2020–2028. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.14854
Pompon, R. H., Fassbinder, W., McNeil, M. R., Yoo, H., Kim, H. S., et al. (2022). Associations among depression, demographic variables, and language impairments in chronic post-stroke aphasia. J. Commun. Disord. 100:106266. doi: 10.1016/j.jcomdis.2022.106266
Pompon, R. H., Smith, A. N., Baylor, C., and Kendall, D. (2019). Exploring associations between a biological marker of chronic stress and reported depression and anxiety in people with aphasia. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 62, 4119–4130. doi: 10.1044/2019_JSLHR-L-19-0111
Potempa, K., Braun, L. T., Tinknell, T., and Popovich, J. (1996). Benefits of aerobic exercise after stroke. Sports Med. 21, 337–346. doi: 10.2165/00007256-199621050-00003
Potempa, K., Lopez, M., Braun, L. T., Szidon, J. P., Fogg, L., and Tincknell, T. (1995). Physiological outcomes of aerobic exercise training in hemiparetic stroke patients. Stroke 26, 101–115. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.26.1.101
Powell, L., Parker, J., St-James, M. M., and Mawson, S. (2016). The effectiveness of lower-limb wearable technology for improving activity and participation in adult stroke survivors: a systematic review. J. Med. Internet Res. 18:e259. doi: 10.2196/jmir.5891
Qin, L., Jing, D., Parauda, S., Carmel, J., Ratan, R. R., Lee, F. S., et al. (2014). An adaptive role for BDNF Val66Met polymorphism in motor recovery in chronic stroke. J. Neurosci. 34, 2493–2502. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4140-13.2014
Qin, L., Kim, E., Ratan, R., Lee, F. S., and Cho, S. (2011). Genetic variant of BDNF (Val66Met) polymorphism attenuates stroke-induced angiogenic responses by enhancing anti-angiogenic mediator CD36 expression. J. Neurosci. 31, 775–783. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4547-10.2011
Quaney, B. M., Boyd, L. A., McDowd, J. M., Zahner, L. H., He, J., Mayo, M. S., et al. (2009). Aerobic exercise improves cognition and motor function poststroke. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 23, 879–885. doi: 10.1177/1545968309338193
Radman, T., Ramos, R. L., Brumberg, J. C., and Bikson, M. (2009). Role of cortical cell type and morphology in subthreshold and suprathreshold uniform electric field stimulation in vitro. Brain Stimul. 2, 215–228, doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2009.03.007
Rahman, A., Reato, D., Arlotti, M., Gasca, F., Datta, A., Parra, L. C., et al. (2013). Cellular effects of acute direct current stimulation: Somatic and synaptic terminal effects. J. Physiol. 591, 2563–2578. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.247171
Rand, D., Eng, J. J., Liu-Ambrose, T., and Tawashy, A. E. (2010). Feasibility of a 6-month exercise and recreation program to improve executive functioning and memory in individuals with chronic stroke. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 24, 722–729. doi: 10.1177/1545968310368684
Ren, C., Zhang, G., Xu, X., Hao, J., Fang, H., Chen, P., et al. (2019). The effect of rTMS over the different targets on language recovery in stroke patients with global aphasia: a randomized sham-controlled study. Biomed Res. Int. 2019:4589056. doi: 10.1155/2019/4589056
Richards, K., Singletary, F., Gonzalez Rothi, L. J., Koehler, S., and Crosson, B. (2002). Activation of intentional mechanisms through utilization of nonsymbolic movements in aphasia rehabilitation. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 39, 445–454.
Robey, R. R. (1998). A meta-analysis of clinical outcomes in the treatment of aphasia. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 41, 172–187. doi: 10.1044/jslhr.4101.172
Robinson, R. G., and Jorge, R. E. (2016). Post-stroke depression: a review. Am. J. Psychiatry 173, 221–231. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2015.15030363
Rosenkranz, K., Nitsche, M. A., Tergau, F., and Paulus, W. (2000). Diminution of training-induced transient motor cortex plasticity by weak transcranial direct current stimulation in the human. Neurosci. Lett. 296, 61–63. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3940(00)01621-9
Rossetti, A., Malfitano, C., Malloggi, C., Banco, E., Rota, V., and Tesio, L. (2019). Phonemic fluency improved after inhibitory transcranial magnetic stimulation in a case of chronic aphasia. Int. J. Rehabil. Res. 42, 92–95. doi: 10.1097/MRR.0000000000000322
Sabe, L., Salvarezza, F., Cuerva, A. G., Leiguarda, R., and Starkstein, S. (1995). A randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled study of bromocriptine in nonfluent aphasia. Neurology 45, 2272–2274. doi: 10.1212/WNL.45.12.2272
Sailor, J., Meyerand, M. E., Moritz, C. H., Fine, J., Nelson, L., Badie, B., et al. (2003). Supplementary motor area activation in patients with frontal lobe tumors and arteriovenous malformations. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 24, 1837–1842.
Saur, D., Lange, R., and Baumgaertner, A. (2006). Dynamics of language reorganization after stroke. Brain 129, 1371–1384. doi: 10.1093/brain/awl090
Sebastian, R., Saxena, S., Tsapkini, K., Faria, A. V., Long, C., Wright, A., et al. (2017). Cerebellar tDCS: a novel approach to augment language treatment post-stroke. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 10:695. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2016.00695
Seniów, J., Litwin, M., Litwin, T., Leśniak, M., and Członkowska, A. (2009). New approach to the rehabilitation of post-stroke focal cognitive syndrome: effect of levodopa combined with speech and language therapy on functional recovery from aphasia. J. Neurol. Sci. 283, 214–218. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2009.02.336
Smith, P. J., and Merwin, R. M. (2021). The role of exercise in management of mental health disorders: an integrative review. Annu. Rev. Med. 72, 45–62. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-060619-022943
Spigarelli, M., Lalancette, A., Masse-Alarie, H., and Wilson, M. A. (2024). Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for action naming in aphasia rehabilitation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Sci. 14:665. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14070665
Stagg, C. J., and Nitsche, M. A. (2011). Physiological basis of transcranial direct current stimulation. Neuroscientist 17, 37–53. doi: 10.1177/1073858410386614
Stockbridge, M. D. (2022). Better language through chemistry: augmenting speech-language therapy with pharmacotherapy in the treatment of aphasia. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 185, 261–272. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-823384-9.00013-X
Stockert, A., Wawrzyniak, M., Klingbeil, J., Wrede, K., Kümmerer, D., Hartwigsen, G., et al. (2020). Dynamics of language reorganization after left temporo-parietal and frontal stroke. Brain 143, 844–861. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaa023
Tanaka, Y., Albert, M. L., Aketa, S., Hujita, K., Noda, E., Takashima, M., et al. (2004). Serotonergic therapy for fluent aphasia [Abstract P02.150]. Neurology 62(7 Suppl.):A166.
Turkeltaub, P. E. (2015). Brain stimulation and the role of the right hemisphere in aphasia recovery. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 15:72. doi: 10.1007/s11910-015-0593-6
Uhm, K. E., Kim, Y. H., Yoon, K. J., Hwang, J. M., and Chang, W. H. (2015). BDNF genotype influence the efficacy of rTMS in stroke patients. Neurosci. Lett. 594, 117–121. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2015.03.053
Vaynman, S., and Gomez-Pinilla, F. (2005). License to run: exercise impacts functional plasticity in the intact and injured central nervous system by using neurotrophins. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 19, 283–295. doi: 10.1177/1545968305280753
Vaynman, S., Ying, Z., and Gomez-Pinilla, F. (2004). Hippocampal BDNF mediates the efficacy of exercise on synaptic plasticity and cognition. Eur. J. Neurosci. 20, 2580–2590. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2004.03720.x
Vuksanović, J., Jelić, M. B., Milanović, S. D., Kačar, K., Konstantinović, L., and Filipović, S. R. (2015). Improvement of language functions in a chronic non-fluent post-stroke aphasic patient following bilateral sequential theta burst magnetic stimulation. Neurocase 21, 244–250. doi: 10.1080/13554794.2014.890731
Walker-Batson, D., Curtis, S., Natarajan, R., Ford, J., Dronkers, N., Salmeron, E., et al. (2001). A double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the use of amphetamine in the treatment of aphasia. 32, 2093–2098. doi: 10.1161/hs0901.095720
Warburton, D. E. R., Nicol, C. W., and Bredin, S. S. D. (2006). Prescribing exercise as preventive therapy. CMAJ. 174, 961–974. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.1040750
Winstein, C. J., Stein, J., Arena, R., Bates, B., Cherney, L. R., Cramer, S. C., et al. (2016). Guidelines for adult stroke rehabilitation and recovery: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American heart association/American stroke association. Stroke 47, e98–e169. doi: 10.1161/STR.0000000000000098
Wong, A., Lau, A. Y. L., Lo, E., Tang, M., Wang, Z., Liu, W., et al. (2016). Relations between recent past leisure activities with risks of dementia and cognitive functions after stroke. PLoS ONE 11:159952. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159952
Woodhead, Z. V. J., Crinion, J., Teki, S., Penny, W., Price, C. J., and Leff, A. P. (2017). Auditory training changes temporal lobe connectivity in ‘Wernicke's aphasia': a randomised trial. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 88, 586–594. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2016-314621
Wright, H. H., and Shisler, R. J. (2005). Working memory in aphasia: theory, measures, and clinical implications. Am. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 14, 107–118. doi: 10.1044/1058-0360(2005/012)
Yamada, K., Mizuno, M., and Nabeshima, T. (2002). Role for brain-derived neurotrophic factor in learning and memory. Life Sci. 70, 735–744. doi: 10.1016/S0024-3205(01)01461-8
Yamada, N., Kakuda, W., Yamamoto, K., Momosaki, R., and Abo, M. (2016). Atomoxetine administration combined with intensive speech therapy for post-stroke aphasia: evaluation by a novel SPECT method. Int. J. Neurosci. 126, 829–838. doi: 10.3109/00207454.2015.1074226
Yao, L., Fang, H., Leng, W., Li, J., and Chang, J. (2021). Effect of aerobic exercise on mental health in older adults: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Psychiatry 12:748257. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.748257
Yao, L., Zhao, H., Shen, C., Liu, F., Qiu, L., and Fu, L. (2020). Low-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in patients with poststroke aphasia: systematic review and meta-analysis of its effect upon communication. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 63, 3801–3815. doi: 10.1044/2020_JSLHR-19-00077
Yeh, T.-T., Chang, K-C., and Wu, C. Y. (2019). The active ingredient of cognitive restoration: a multicenter randomized controlled trial of sequential combination of aerobic exercise and computer-based cognitive training in stroke survivors with cognitive decline. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 100, 821–827. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2018.12.020
Yoon, S. Y., Kim, J.-K., An, Y., and Kim, Y. W. (2015). Effect of donepezil on wernicke aphasia after bilateral middle cerebral artery infarction: subtraction analysis of brain F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomographic images. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 38, 147–150. doi: 10.1097/WNF.0000000000000089
Yoon, T. H., Han, S. J., Yoon, T. S., Kim, J. S., and Yi, T. I. (2015). Therapeutic effect of repetitive magnetic stimulation combined with speech and language therapy in post-stroke non-fluent aphasia. NeuroRehabilitation 36, 107–114. doi: 10.3233/NRE-141198
Zanella, C., Laures-Gore, J., Dotson, V. M., and Belagaje, S. R. (2023). Incidence of post-stroke depression symptoms and potential risk factors in adults with aphasia in a comprehensive stroke center. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 30, 448–458. doi: 10.1080/10749357.2022.2070363
Zhang, H., Chen, Y., Hu, R., Yang, L., Wang, M., Zhang, J., et al. (2017). RTMS treatments combined with speech training for a conduction aphasia patient. Medicine 96:e7399. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007399
Zhang, J., Wei, R., Chen, Z., and Luo, B. (2016). Piracetam for aphasia in post-stroke patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. CNS Drugs. 30, 575–587. doi: 10.1007/s40263-016-0348-1
Zhang, X., Shu, B., Zhang, D., Huang, L., Fu, Q., and Du, G. (2018). The efficacy and safety of pharmacological treatments for post-stroke aphasia. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 17, 509–521. doi: 10.2174/1871527317666180706143051
Zheng, G., Zhou, W., Xia, R., Tao, J., and Chen, L. (2016). Aerobic exercises for cognition rehabilitation following stroke: a systematic review. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 25, 2780–2789. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2016.07.035
Zheng, Z. S., Wang, K. X., Millan, H., Lee, S., Howard, M., Rothbart, A., et al. (2024). Transcranial direct stimulation over left inferior frontal gyrus improves language production and comprehension in post-stroke aphasia: a double-blind randomized controlled study. Brain Lang. 257:105459. doi: 10.1016/j.bandl.2024.105459
Keywords: aphasia, adjuvant, treatment, non-invasive brain stimulation (NIBS), aerobic exercise, pharmacotherapy
Citation: Harnish SM, Jewell CC, Freitag NG, Terry GE and Anderson GI (2025) Aphasia rehabilitation: a narrative review of adjuvant techniques. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 19:1554147. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2025.1554147
Received: 01 January 2025; Accepted: 30 June 2025;
Published: 30 July 2025.
Edited by:
Lorie Gage Richards, The University of Utah, United StatesReviewed by:
Zulay R. Lugo, Central University of Venezuela, VenezuelaArun Karumattu Manattu, University of Wisconsin-Madison, United States
Nilton Santos-Junior, University of São Paulo, Brazil
Copyright © 2025 Harnish, Jewell, Freitag, Terry and Anderson. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Stacy M. Harnish, aGFybmlzaC4xOEBvc3UuZWR1
 Stacy M. Harnish
Stacy M. Harnish Courtney C. Jewell
Courtney C. Jewell Natalie G. Freitag
Natalie G. Freitag Grace E. Terry
Grace E. Terry Gillian I. Anderson
Gillian I. Anderson