- 1Department of Hepatobiliary Pancreatic and Vascular Surgery, First People’s Hospital of Kunming, The Affiliated Calmette Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming, China
- 2Department of Minimally Invasive Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery, Lincang People's Hospital, Lincang, China
- 3Department of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, First People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province, Affiliated Hospital of Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming, China
- 4Department of Oncology, Third People’s Hospital of Honghe Prefecture, Gejiu, China
Introduction: Neurodegenerative diseases (NDs) are progressive disorders with an increasing global health impact. Neural injury biomarkers have emerged as potential tools for early diagnosis and disease monitoring.
Methods: To map research trends in this field, we conducted a comprehensive bibliometric analysis of 1,228 peer-reviewed articles published from 1991 to 2024 using CiteSpace and the Bibliometrix R package.
Results: Our analysis revealed steady publication growth, particularly accelerating after 2015. The United States, United Kingdom, and China produced the highest volume of publications and citations, with institutions such as the University of California System and Harvard University serving as key collaboration hubs. Early research prioritized tau, amyloid-beta (Aβ), cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and mild cognitive impairment (MCI). Since 2020, the focus has expanded to blood-based biomarkers, exosomal microRNAs, and inflammation-related markers such as glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and translocator protein (TSPO). Through citation and clustering analyses, we identified three developmental phases: (1) CSF-based amyloid/tau validation, (2) multimodal and genetic biomarker integration, and (3) the emergence of plasma and neuroinflammatory markers.
Discussion: These trends reflect a paradigm shift toward minimally invasive and multifactorial diagnostic approaches. Our findings underscore evolving priorities in NDs biomarker research and highlight the importance of multi-omics, artificial intelligence (AI), and interdisciplinary collaboration for translational discovery and clinical application.
1 Introduction
Neurodegenerative diseases (NDs), including Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease (PD), and frontotemporal dementia (FTD), are defined by progressive neuronal degeneration, frequently accompanied by cognitive decline and motor dysfunction (Dugger and Dickson, 2017). With aging populations worldwide, the number of individuals with dementia is projected to reach 152.8 million by 2050 (Collaborators, 2022), of which AD accounts for approximately 70% of cases (Reitz and Mayeux, 2014). This escalation poses substantial societal and economic burdens globally. While advancements in genetics and neuroimaging have enhanced our understanding of NDs pathophysiology, the lack of definitive, non-invasive diagnostic tools remains a critical barrier to early detection and disease-modifying therapies.
A key challenge in managing NDs is the absence of reliable biomarkers for early diagnosis (Logroscino et al., 2022). Emerging evidence highlights neural injury biomarkers—encompassing proteins (Raghunathan et al., 2022), lipids (Wei et al., 2023), biofluids (Alcolea et al., 2023), and imaging markers (Dilliott et al., 2023)—as pivotal indicators of neuroinflammation, oxidative stress (OS), and neurodegeneration. Despite their promise, gaps persist in translating these biomarkers into clinical practice (Cheslow et al., 2024). Major hurdles include standardizing protocols for sample collection, improving assay reproducibility, and establishing population-specific cutoff thresholds. Additionally, limited disease specificity restricts the clinical utility of many biomarkers. Addressing these challenges is essential to bridge the gap between discovery and clinical implementation.
Bibliometric analysis has proven effective for mapping research trends, identifying key contributors, and forecasting emerging topics (Hicks et al., 2015; Wei et al., 2022). Although prior studies have broadly examined NDs, few focus specifically on neural injury biomarkers. This study aims to provide a comprehensive bibliometric analysis of research trends, key contributors, and future directions in the application of neural injury biomarkers for NDs.
2 Data and methods
2.1 Retrieval strategy and data collection
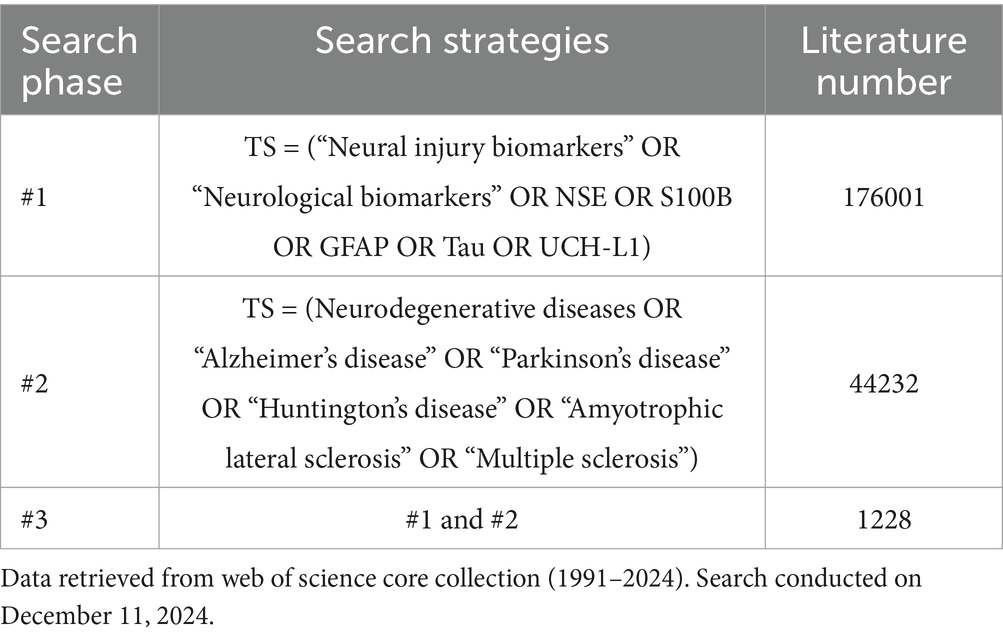
We extracted data from the Web of Science (WOS) Core Collection database, selected for its coverage of over 12,000 academic journals and frequent use in prior bibliometric studies (Ege et al., 2023; Jiang et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2024). Our search strategy targeted studies on neural injury biomarkers in NDs, filtering for “Article” and “Review” document types in English (1991–2024; search date: December 11, 2024). Data were exported in plain text format. The search strategy is detailed in Table 1. A topic search (TS) was conducted, encompassing titles, abstracts, and keywords. The search query combined terms via Boolean operators: TS = (“Neural injury biomarkers” OR “Neurological biomarkers” OR NSE OR S100B OR GFAP OR Tau OR UCH-L1) AND (Neurodegenerative diseases OR “Alzheimer’s disease” OR “Parkinson’s disease” OR “Huntington’s disease” OR “Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis” OR “Multiple sclerosis”). A total of 1,228 articles were retrieved for analysis.
2.2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria: studies categorized as “Article” or “Review” in the WOS database and addressing the application of neural injury biomarkers in NDs.
Exclusion criteria: articles excluded from the analysis included: (1) conference papers, newspapers, books, and other non-peer-reviewed sources; (2) duplicate records; (3) articles with incomplete bibliographic information.
2.3 Data analysis
Bibliometric analysis was performed using CiteSpace v.6.2. R4 (64-bit) and the “Bibliometrix” R package. CiteSpace is a software tool for visualizing and analyzing scientific literature (Chen, 2004). It enables exploration of citation networks, keyword co-occurrence, author collaboration patterns, and the identification of highly-cited references and keywords experiencing citation bursts over specific periods. These features assist in understanding research trends, hotspots, and the evolution of scientific fields. Bibliometrix is an open-source, free-to-use tool written in R (Aria and Cuccurullo, 2017). The Bibliometrix R package was used to extract core bibliometric elements, including titles, abstracts, authors, references, institutions, countries, and keywords. It also generates graphical representations that facilitate the comprehensive analysis of the literature’s knowledge structure.
To ensure reproducibility and comparability, all analyses were conducted using default settings. In CiteSpace, the g-index algorithm was applied with a scaling factor of k = 25. CiteSpace used spectral clustering combined with modularity optimization (resolution parameter γ = 1.0, default) to identify network communities. Clusters were labeled using the log-likelihood ratio (LLR) algorithm, which prioritizes statistically significant and distinctive terms.
3 Results
3.1 Overview of main information
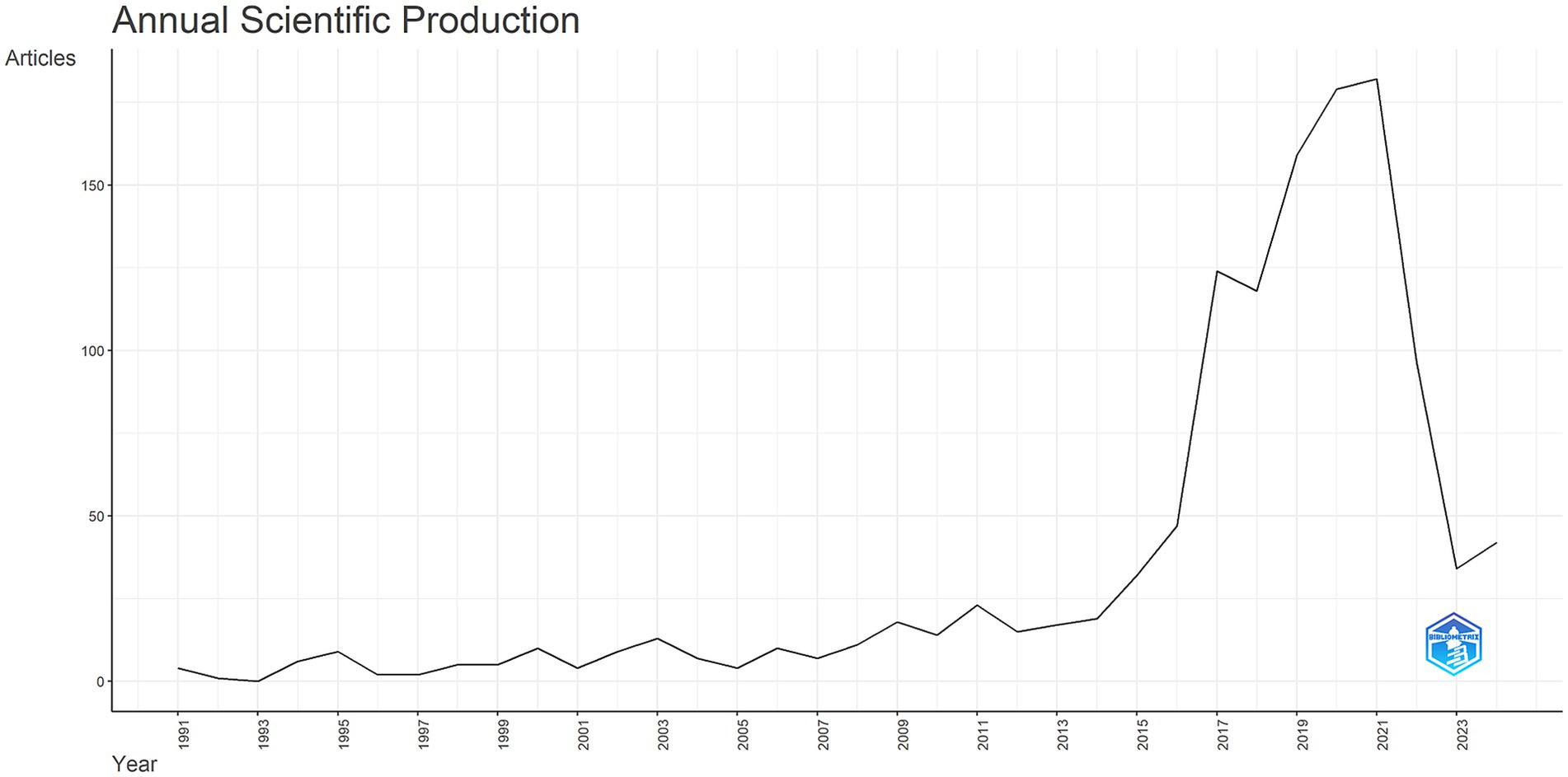
Analysis of the WOS Core Collection data (Figure 1) revealed 1,228 articles published between 1991 and 2024 across 397 journals. Among these, 834 (67.92%) were original research articles, while 394 (32.08%) were reviews. The field exhibited an average annual growth rate of 7.39%, with contributions from 6,844 authors and international collaboration in 30.05% of publications. The total citation count reached 79,916, yielding an average of 48.64 citations/article.
3.2 Publication output trends
The trends in publication output reveal notable shifts in research focus over time (Figure 2). Between 1991 and 2015, publications on neural injury biomarkers remained stable. However, a marked increase in the volume of publications was observed from 2015 onward, with a peak of 188 articles published in 2020. This surge correlated with the advent of high-sensitivity assays such as single-molecule array (SIMOA) and increased funding for translational research following failed anti-amyloid drug trials. These trends underscore growing global interest in biomarkers for NDs diagnosis and prognosis.
3.3 Analysis of countries, institutions, and authors
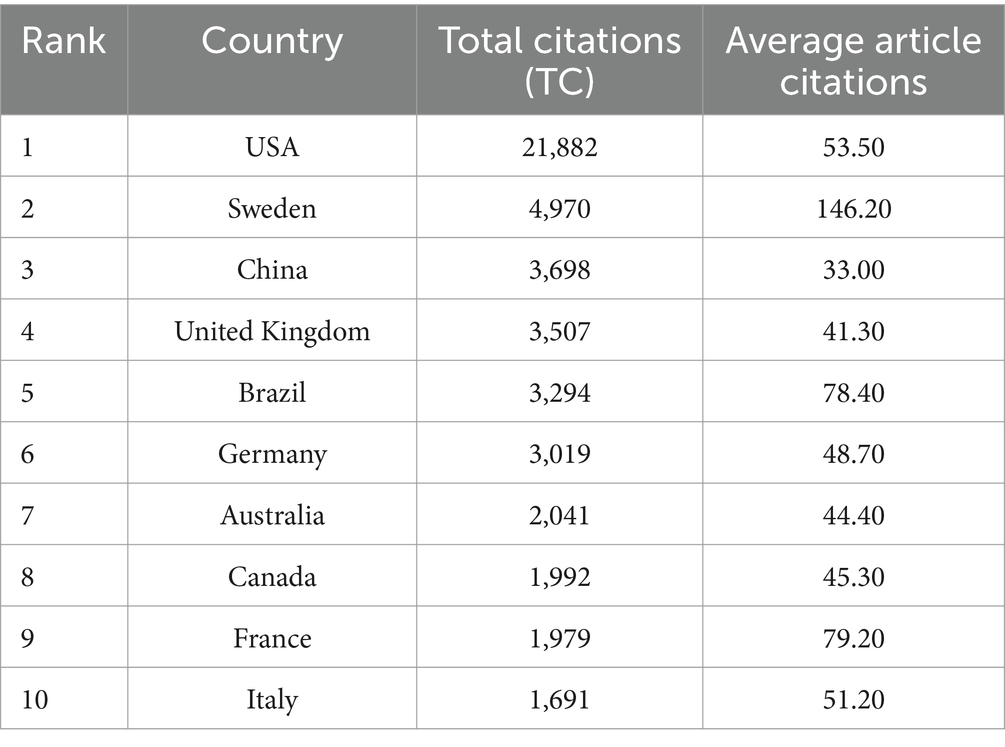
As shown in Figures 3A,B, the United States contributed the largest number of publications (514 articles, 41.86%), followed by the United Kingdom (136 articles, 11.07%), China (113 articles, 9.20%), Germany (108 articles, 8.79%), and Sweden (93 articles, 7.57%). These findings are further supported by Table 2, which shows the United States, Sweden, and China as the leading countries in terms of citation counts. This suggests that these countries are major drivers of research in the field of neural injury biomarkers for NDs.
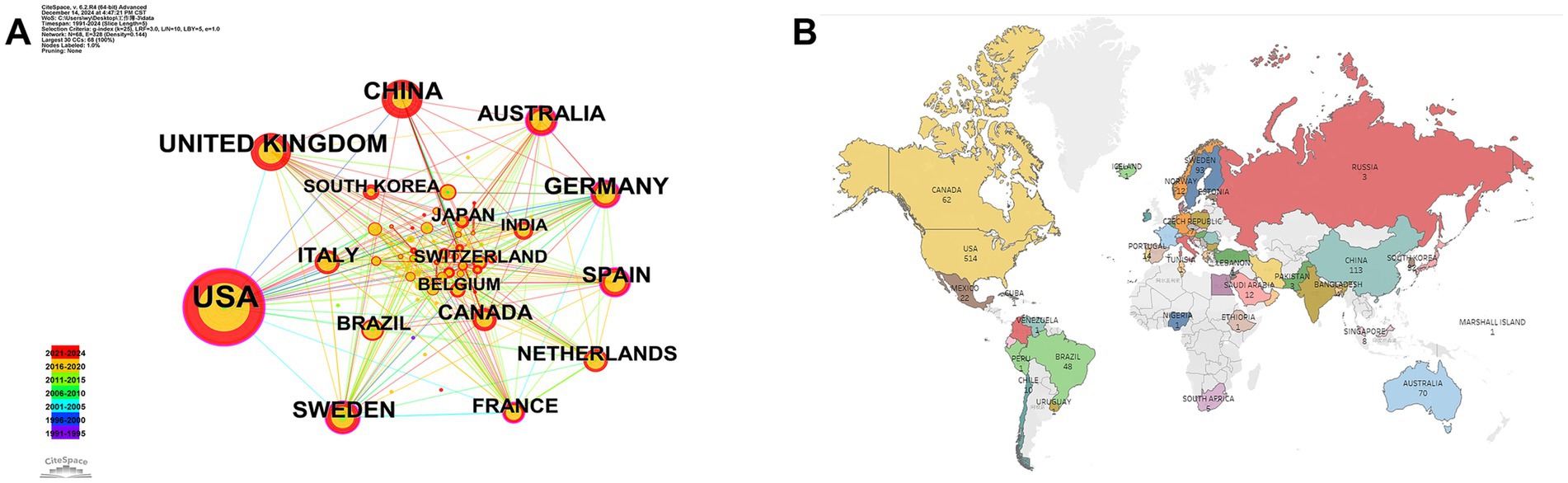
Figure 3. Geographic distribution and international collaboration in neurodegenerative disease biomarker research. (A) Country collaboration network. (B) Global publication distribution by country.
The leading institutions in this area of research include the University of California System (187 articles), Harvard University (180 articles), University of London (145 articles), Washington University (134 articles), and University College London (112 articles) (Figures 4A,B). These institutions have made significant contributions to the field, reflecting their role as key research hubs for neural injury biomarkers.

Figure 4. Institutional contributions. (A) Co-authorship network among institutions. (B) Top contributing institutions by number of publications.
These institutions have made significant contributions to the field, underscoring their role as central research hubs for neural injury biomarkers. The analysis of corresponding authors’ countries (Table 3) reveals that the United States leads with the highest percentage of single-country publications (78.7%), while Germany stands out for its higher proportion of multi-country publications (46.8%). This highlights the strong international collaborative nature of research in this domain. Figure 5A demonstrates that Blennow K and Zetterberg H are two of the most active authors in this field, consistently contributing to the literature over time. Their substantial output reflects their critical role in advancing the understanding of NDs. Figure 5B further emphasizes the geographic distribution of research activity, with the United States, China, and the United Kingdom leading in terms of research output. Notably, Germany and Sweden exhibit a high degree of international collaboration, with over 40% of their publications resulting from multi-country partnerships, reflecting the global interconnectedness of research efforts. As shown in Figure 5C, the production of these prominent authors has remained consistent over the years, with annual publications continuing to reflect their sustained influence and contributions to the field.
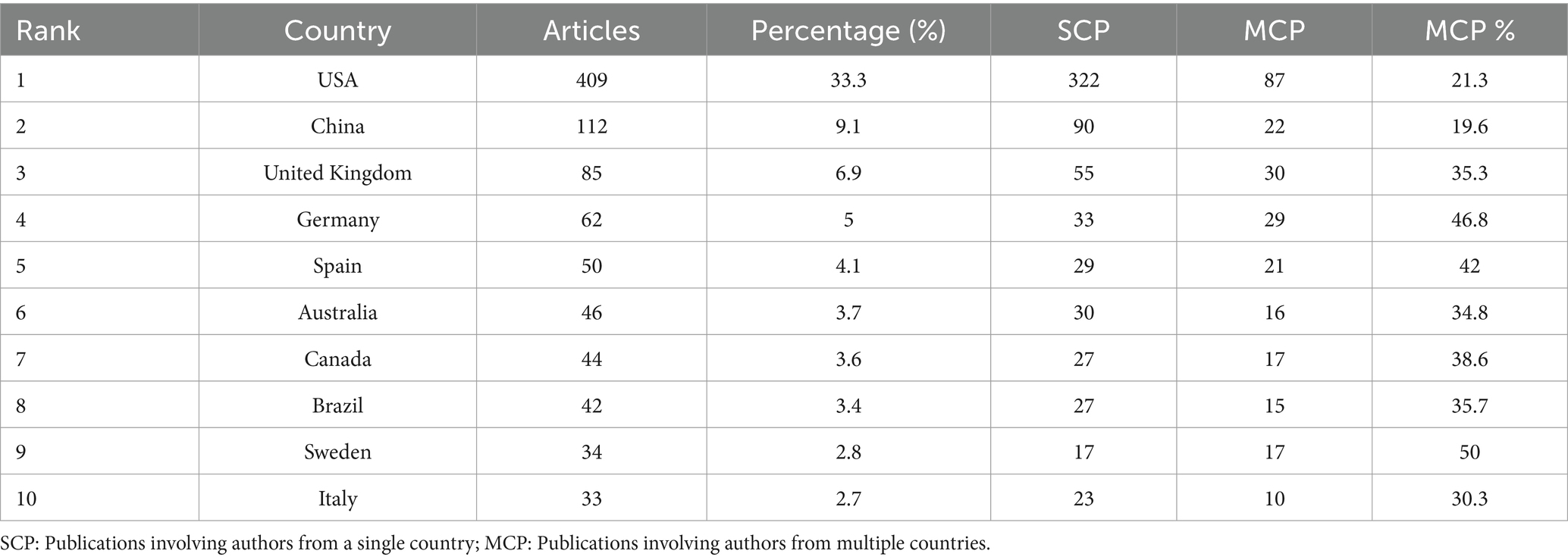
Table 3. Country composition of corresponding authors in neurodegenerative disease biomarker research.
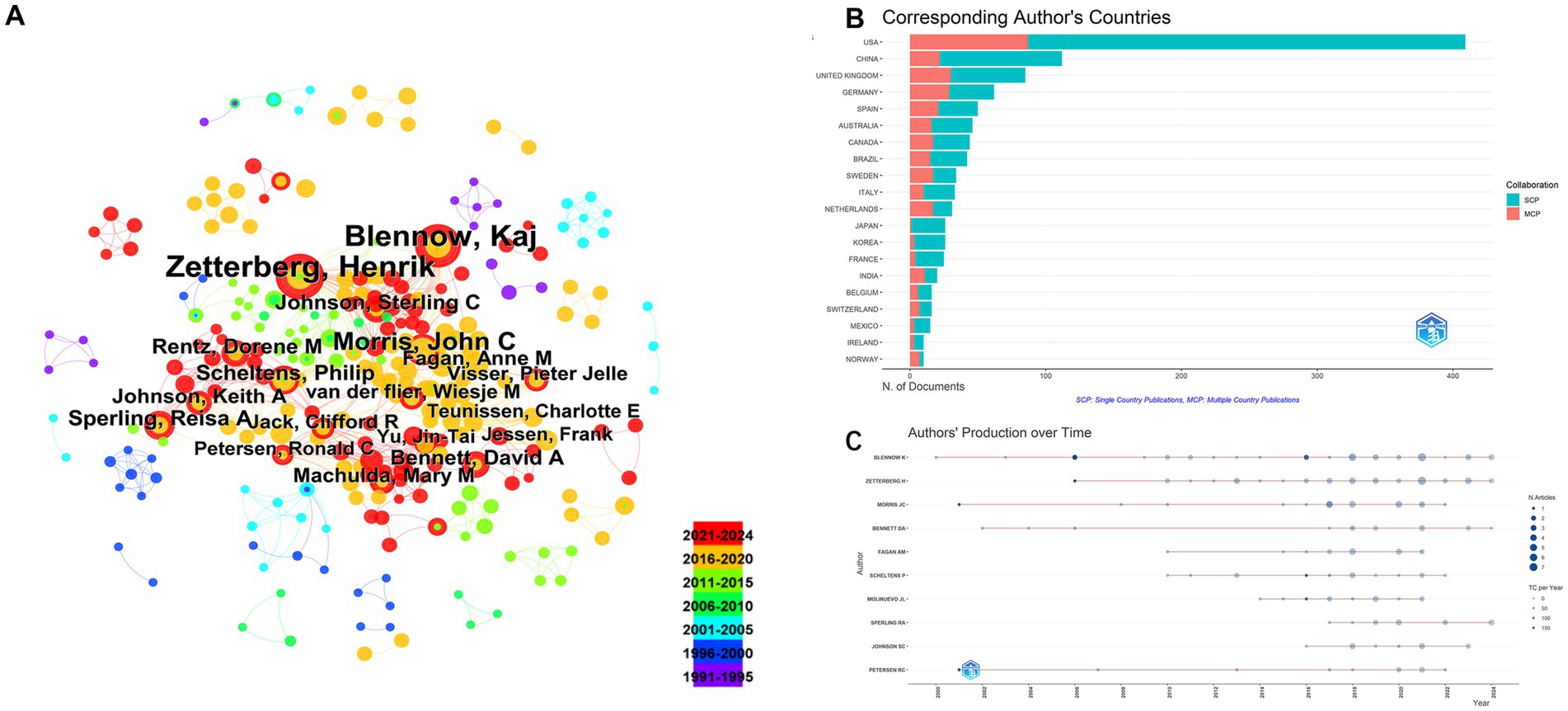
Figure 5. Author-level collaboration and productivity analysis. (A) Co-authorship network among authors. (B) Distribution of corresponding authors’ countries. (C) Temporal distribution of author productivity.
3.4 Core journals
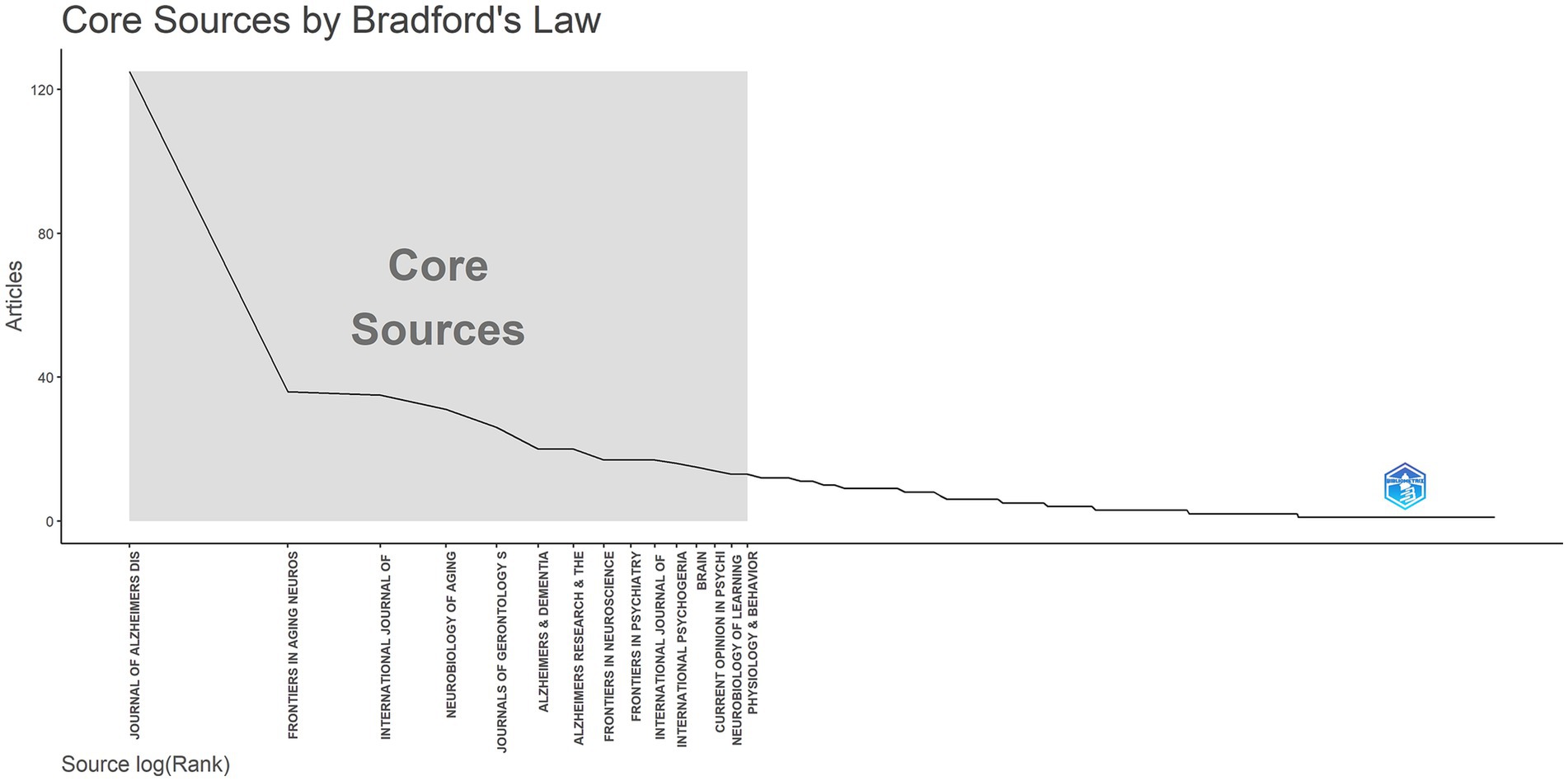
Based on Bradford’s Law, 15 core journals were identified in this field (Figure 6 and Table 4). The top five journals contributing the most to this research area were the Journal of AD, Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, Neurobiology of Aging, and Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences. These journals have become crucial platforms for publishing groundbreaking studies in the field.
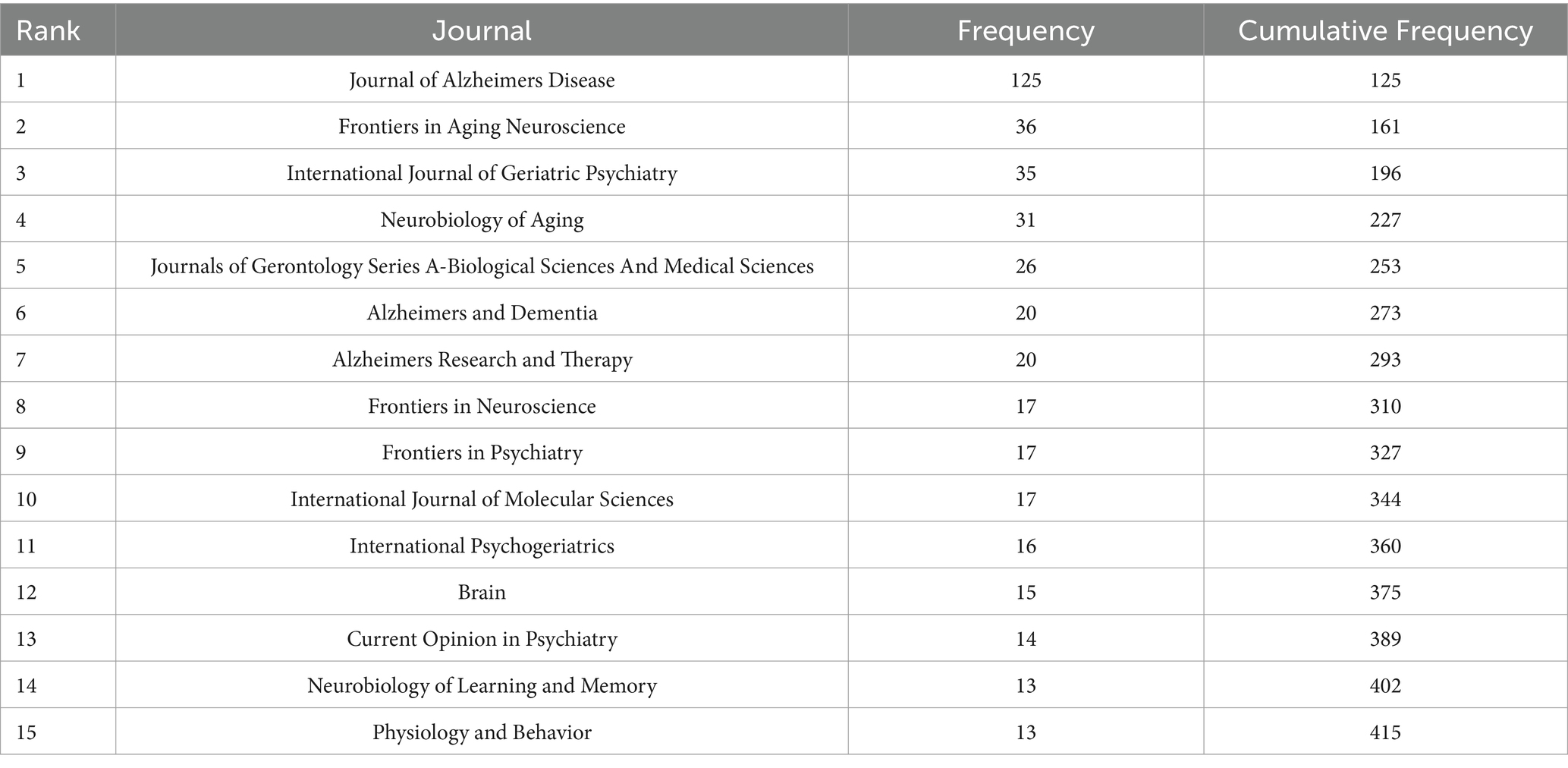
Table 4. Core journals identified in neurodegenerative disease biomarker research according to Bradford’s Law.
3.5 Keyword frequency and research hotspots
The frequency of keywords was analyzed to identify research hotspots. The co-occurrence network (Figure 7A) highlighted prominent topics such as AD, mild cognitive impairment (MCI), dementia, amyloid beta (Aβ), cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), tau, and the National Institute. Figure 7B displays the top 25 keywords with the strongest citation bursts, with neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) exhibiting the highest burst strength (10.42). Prior to 2015, research focused on senile dementia, FTD, and multiple sclerosis (MS), with an emphasis on randomized controlled trials, transgenic mouse studies, tau protein, amyloid precursor protein (APP), and apolipoprotein E (APOE) genotype. However, after 2015, there was a shift toward PD, frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD), and CSF biomarkers. From 2021 to 2024, the keyword “tau” remained a focal point. Figure 7C illustrates the nine most representative clusters, with a Modularity Q value of 0.44, indicating strong clustering, and a Weighted Mean Silhouette S value of 0.71, signifying a compelling cluster structure. These clusters included MCI, OS, NFTs, positron emission tomography (PET), MS, cortical thickness, FTD, randomized controlled trials, and AD. Figure 7D illustrates the development and transformation of keywords in each cluster. It allows us to better recognize changes in a particular topic in a research field over time and to quickly understand the development and frontiers of the field.
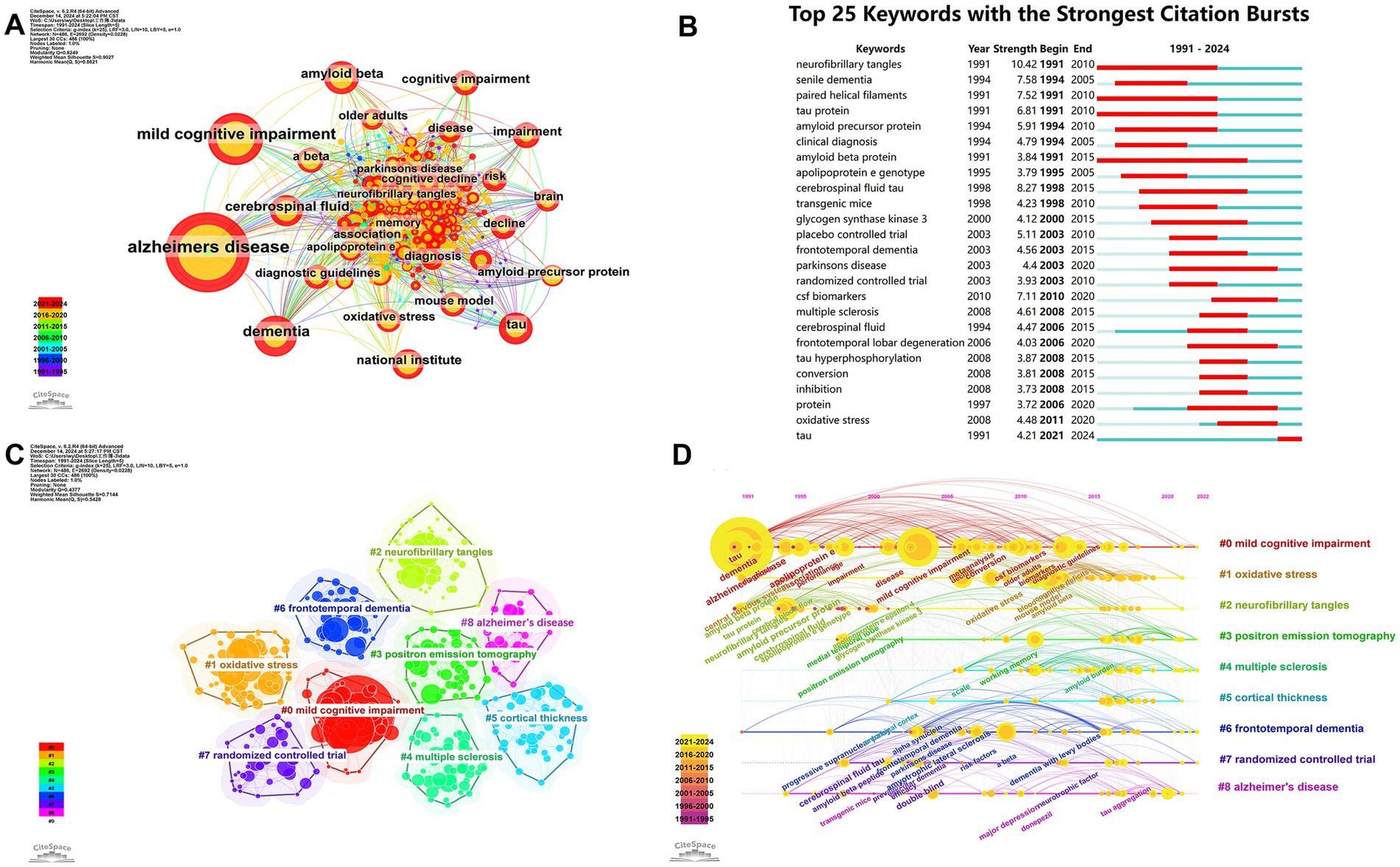
Figure 7. Evolution of research hotspots and thematic trends in neurodegenerative disease biomarker research. (A) Keyword co-occurrence network. (B) Top 25 keywords with the strongest citation bursts. (C) Keyword clusters based on log-likelihood ratio (LLR) analysis. (D) Timeline visualization of keyword cluster development (1991–2024).
Additionally, Figure 8 shows the link between keywords (left), authors’ nationalities (center) and institutions (right). The area of the rectangle is proportional to the number of publications and shows that AD major researchers are from the United States and that multiple institutions are involved in the field.
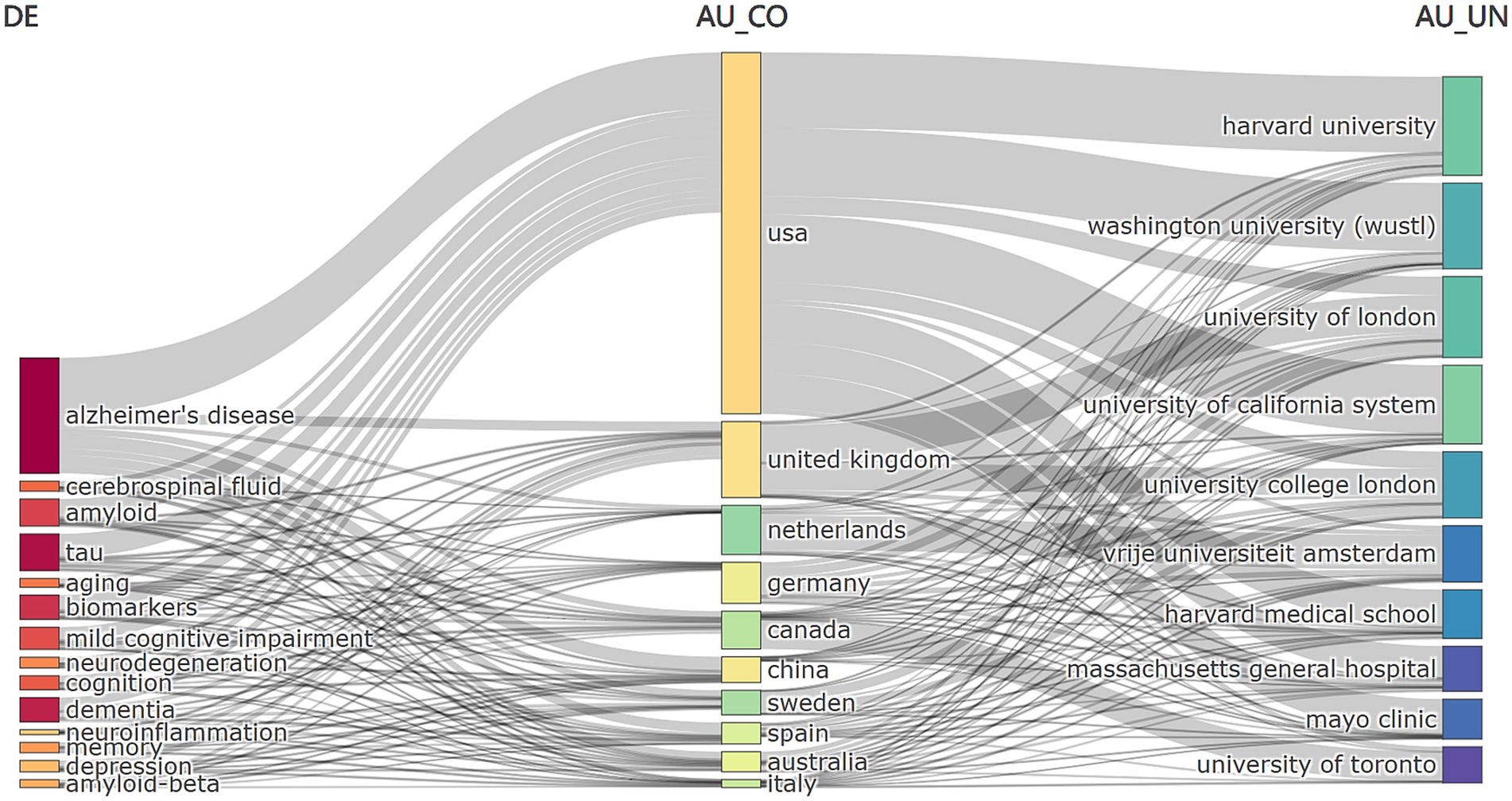
Figure 8. Interlinkages among keywords, author countries, and institutions in neurodegenerative disease biomarker research.
3.6 Co-cited authors and literature
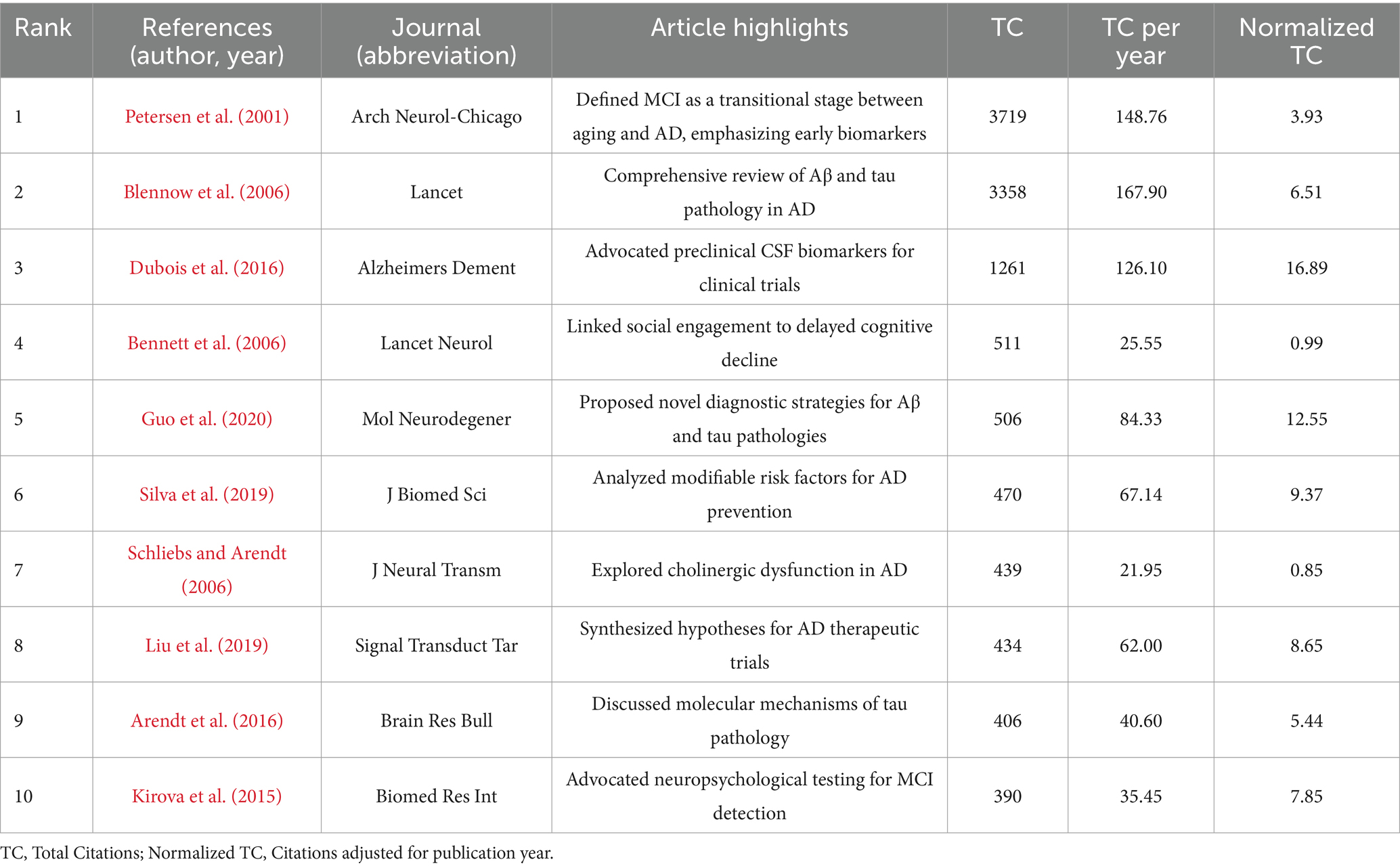
Table 5 lists the top 10 most co-cited articles. Among the most co-cited authors, Petersen et al. (2001) (Mayo Clinic Rochester, USA) had the highest co-citation count (3,719), establishing it as the most influential study in this field. Other highly co-cited works include those by Blennow et al. (2006) (Sahlgren’s University Hospital, Sweden; citation count: 3,358) and Dubois et al. (2016) (Sorbonne Universities, France; citation count: 1,261). These studies have made seminal contributions to understanding neural injury biomarkers in NDs.
4 Discussion
This study presents the comprehensive bibliometric analysis focused specifically on neural injury biomarkers in NDs. It identifies evolving research priorities from CSF-based biomarkers to minimally invasive blood-derived markers, especially post-2020. Notably, the study highlights emerging interest in neuroinflammation and OS as integral pathological components. Furthermore, it delineates three distinct developmental stages of the field, offering a temporal framework that may guide future research and clinical translation.
4.1 Overview of development in the field
The publication volume has increased steadily over the past three decades, with a pronounced surge post-2015. This growth aligns with rising global interest in biomarkers for neurodegeneration and their potential to improve diagnostic and prognostic accuracy. The United States, United Kingdom, and China emerged as leading contributors in both publication output and citation impact.
The most frequently studied biomarkers included tau protein, Aβ, CSF biomarkers, and NFTs. These results corroborate established knowledge linking tau (Scheltens et al., 2021; Ossenkoppele et al., 2022) and Aβ (Soderberg et al., 2023; Jia et al., 2024) to AD pathophysiology. However, our analysis revealed a paradigm shift toward OS-and neuroinflammation-related biomarkers post-2015. Although OS and neuroinflammation represent distinct pathological processes, they exhibit bidirectional interactions: OS triggers reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, leading to lipid peroxidation, protein misfolding, and DNA damage, while chronic neuroinflammation exacerbates neuronal injury via microglial activation (Islam, 2017; Singh et al., 2019; Teleanu et al., 2022). This shift underscores the multifactorial nature of NDs and the need for biomarkers capturing broader pathological spectra.
4.2 Analysis of countries, institutions, and journals
From the perspective of international cooperation and research teams, scientific research institutions in the United States, the United Kingdom, China, Germany and other countries dominate the field, forming several research teams with international influence. The relatively close cooperation network among these teams has contributed to the rapid development of research in this field. However, we also note that despite the significant increase in research results in this field, there are still many challenges in the clinical translational application of biomarkers, such as the specificity, sensitivity, and standardization of biomarkers, which still need to be further researched and solved. Future research should emphasize multidisciplinary integration and foster tighter connections between basic and clinical research to enhance the real-world utility of neural injury biomarkers. Research in this area comes from the University of California System, Harvard University, University of London, Washington University, and University College London.
Moreover, our analysis identified key journals such as Journal of AD and Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience as central to the dissemination of research on neural injury biomarkers. These journals have become crucial platforms for publishing groundbreaking studies and significantly contributing to the field’s development.
4.3 Research hotspots and trends
Keyword co-occurrence analysis identified nine core clusters with AD MCI and Aβ/tau pathology forming recent investigative axes. MCI affects 20–50% of older adults and represents a prodromal stage where early intervention may delay dementia progression (Chaudhary et al., 2020; Tabeeva, 2019). The Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) demonstrates 89% sensitivity and 75% specificity outperforming traditional tools (Tan and Tan, 2021).
Plasma homocysteine (Hcy) and APOE ε4 are associated with the risk of NDs, especially in patients with AD and MCI, with patients with non-carrier genotypes showing more pronounced changes in the neurodegenerative marker (phosphorylated tau 217) (Lin et al., 2025). In addition, retinal imaging, a non-invasive modality, has also shown promise in detecting early microvascular and structural alterations linked to MCI (Christinaki et al., 2022).
OS and neuroinflammation, as intertwined mechanisms, drive lipid peroxidation, protein aggregation, and DNA damage, culminating in neuronal apoptosis (Maciejczyk et al., 2020). Elevated OS markers such as 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) correlate with cognitive decline in AD (Graille et al., 2020; Ghezzi and Mooradian, 2021), while ROS overproduction activates pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, TNF-α), amplifying neuroinflammation via microglial activation (Dhapola et al., 2021; Leng and Edison, 2021). These findings support antioxidant and anti-inflammatory therapies for disease mitigation.
NFTs, beyond influencing neuronal survival, correlate with pathological progression. Hippocampal NFTs density inversely correlates with cognitive impairment in AD (Iliyasu et al., 2023), while tauopathy-specific NFTs distribution aids differential diagnosis (Richardson et al., 2024). Tau-specific PET radiotracers (e.g., 18F-THK5351, 18F-MK-6240) enable in vivo NFTs quantification with 85–90% accuracy (Ishibashi et al., 2024), and transcriptomics link NFTs formation to neuronal stress responses (Otero-Garcia et al., 2022). While PET achieves 90% amyloid detection accuracy, its accessibility remains limited (Doruyter et al., 2021). Conversely, blood-based biomarkers [e.g., plasma neurofilament light chain (NfL) (Quiroz et al., 2020), p-tau217 (Ashton et al., 2022)] revolutionize scalable screening. Emerging frontiers include FTD-specific TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) biomarkers (Chatterjee et al., 2024) and randomized controlled trial (RCT) designs for anti-amyloid therapy evaluation (Hoilund-Carlsen et al., 2024; Logroscino et al., 2025).
This study delineates three transformative phases in neural injury biomarker research, each demarcated by pivotal external events that reshaped the trajectory of biomarker development: (1) 1991–2015: Amyloid/tau hypothesis validation; (2) 2015–2020: Multimodal biomarker integration; (3) 2020–2024: Emergence of blood-based biomarkers and neuroinflammation focus.
4.3.1 Phase I (1991–2015): amyloid and tau hypothesis validation
Foundational work validated the amyloid cascade hypothesis, focusing on CSF Aβ42 and tau detection. Hardy and Higgins established Aβ’s role in AD progression (Hardy and Higgins, 1992), while Blennow et al. (2006) demonstrated diagnostic utility of CSF p-tau/Aβ42 ratios. Despite APP/PS1 transgenic models linking amyloid pathology to cognitive deficits (Jankowsky et al., 2003), clinical translation faced challenges due to CSF invasiveness and poor early-stage correlation (Jack, 2012). Growing skepticism toward amyloid-centric therapies emerged as clinical benefits remained elusive.
4.3.2 Phase II (2015–2020): multimodal biomarker integration, prompted by trial failures
The failure of bapineuzumab Phase 3 trials (Salloway et al., 2014) prompted a paradigm shift toward multimodal integration. MTBR-tau243 in CSF correlated strongly with tau-PET (r = 0.83), surpassing conventional p-tau markers (Horie et al., 2023). Genetic risk factors (APOE ε4, TREM2) gained traction as prognostic indicators (Yeh et al., 2017; Jia et al., 2020). The SIMOA platform achieved 0.62 pg./mL sensitivity, exceeding ELISA and electrochemiluminescence (ECL) assays (Kuhle et al., 2016).
4.3.3 Phase III (2020–2024): rise of blood biomarkers and focus on neuroinflammation
Recent advancements emphasize blood-based biomarkers and neuroinflammation. Plasma p-tau181 reduces tau-PET screening failures by ~50% (Moscoso et al., 2022), while plasma glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) mediates Aβ-PET effects on tau-PET burden and cognitive decline (Pereira et al., 2021). Blood exosomes reflect amyloid and NFTs pathology (Liu et al., 2022), and translocator protein (TSPO) PET maps neuroinflammation in vivo (De Picker et al., 2023). While PET radio-ligands provide regional specificity, integrating fluid-based biomarkers—such as CSF cytokines or plasma GFAP—with neuroimaging endophenotypes offers unprecedented insights into the spatiotemporal interplay between neuroinflammation and AD pathophysiology (Hampel et al., 2020). The ATI(N) framework incorporates inflammation into the amyloid/tau/neurodegeneration (ATN) scheme (Lista et al., 2024), enabling multidimensional assessment via PET, blood biomarkers, and machine learning.
4.4 Future directions
Integrating neuroinflammation and OS into biomarker panels is critical. Plasma GFAP and soluble TREM2 reflect astrocytic and microglial activity, respectively, while 8-OHdG and F2-isoprostanes are emerging peripheral neuronal injury markers. Composite panels (e.g., ATI[N]) capturing amyloid, tau, synaptic loss, and inflammation better reflect disease complexity. Multi-omics integration—including genomics, proteomics, and single-nucleus RNA sequencing (snRNA-seq)—reveals glial subpopulations linked to inflammatory profiles (Sadick et al., 2022) and connects CSF proteomes to GWAS-identified risk variants (Kaiser et al., 2023; Tao et al., 2024). Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) handle high-dimensional datasets effectively. Deep learning (DL) models (e.g., InceptionV3 on 18F-FDG PET) achieve 0.98 AUC for early AD diagnosis (Jimenez-Mesa et al., 2023). ML identifies PD progression subtypes with 0.87–0.95 AUCs using serum NfL as a rapid progression marker (Dadu et al., 2022). Predictive models combining polygenic risk scores, plasma p-tau, and GFAP may stratify patients for targeted therapies. Liquid biopsies (e.g., plasma neuron-derived exosomes) and single-cell spatial transcriptomics promise novel, minimally invasive biomarkers.
4.5 Limitations
While this bibliometric analysis provides valuable insights into the trends in this field, several limitations should be acknowledged. As a bibliometric analysis, our findings are preliminary and hypothesis-generating rather than confirmatory. Further validation through clinical and experimental studies is warranted. First, our study relied exclusively on data from the WOS Core Collection, which, although comprehensive, may not capture all relevant research, particularly studies published in non-English languages or indexed in other databases like Scopus or PubMed. Second, our analysis focused solely on “Articles” and “Reviews,” potentially overlooking other important types of publications, such as conference papers or book chapters. Moreover, bibliometric results do not account for study quality, and citation metrics may be biased by factors such as journal visibility or open access status. Lastly, bibliometric analysis does not directly assess the quality of individual studies, and high citation counts may not necessarily reflect the scientific rigor or validity of the findings.
5 Conclusion
This bibliometric analysis has elucidated the research trends, hotspots, and future directions in the application of neural injury biomarkers for NDs. The findings highlight the increasing role of OS, NFTs, and neuroimaging technologies, particularly PET, in understanding disease mechanisms and advancing early diagnosis. Moving forward, researchers should prioritize multi-omics approaches and the validation of biomarkers to enhance clinical applicability and enable personalized treatment strategies in NDs.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
CP: Writing – original draft, Visualization, Data curation, Software. SS: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Visualization. YD: Visualization, Software, Writing – original draft. MW: Data curation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Alcolea, D., Beeri, M. S., Rojas, J. C., Gardner, R. C., and Lleo, A. (2023). Blood biomarkers in neurodegenerative diseases: implications for the clinical neurologist. Neurology 101, 172–180. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000207193
Arendt, T., Stieler, J. T., and Holzer, M. (2016). Tau and tauopathies. Brain Res. Bull. 126, 238–292. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2016.08.018
Aria, M., and Cuccurullo, C. (2017). Bibliometrix: an R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J. Informetr. 11, 959–975. doi: 10.1016/j.joi.2017.08.007
Ashton, N. J., Janelidze, S., Mattsson-Carlgren, N., Binette, A. P., Strandberg, O., Brum, W. S., et al. (2022). Differential roles of Aβ42/40, p-tau231 and p-tau217 for Alzheimer’s trial selection and disease monitoring. Nat. Med. 28, 2555–2562. doi: 10.1038/s41591-022-02074-w
Bennett, D. A., Schneider, J. A., Tang, Y., Arnold, S. E., and Wilson, R. S. (2006). The effect of social networks on the relation between Alzheimer's disease pathology and level of cognitive function in old people: a longitudinal cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 5, 406–412. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(06)70417-3
Blennow, K., de Leon, M. J., and Zetterberg, H. (2006). Alzheimer's disease. Lancet 368, 387–403. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69113-7
Chatterjee, M., Ozdemir, S., Fritz, C., Mobius, W., Kleineidam, L., Mandelkow, E., et al. (2024). Plasma extracellular vesicle tau and TDP-43 as diagnostic biomarkers in FTD and ALS. Nat. Med. 30, 1771–1783. doi: 10.1038/s41591-024-02937-4
Chaudhary, S., Kumaran, S. S., Kaloiya, G. S., Goyal, V., Sagar, R., Kalaivani, M., et al. (2020). Domain specific cognitive impairment in Parkinson's patients with mild cognitive impairment. J. Clin. Neurosci. 75, 99–105. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2020.03.015
Chen, C. (2004). Searching for intellectual turning points: progressive knowledge domain visualization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101 Suppl 1, 5303–5310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307513100
Cheslow, L., Snook, A. E., and Waldman, S. A. (2024). Biomarkers for managing neurodegenerative diseases. Biomol. Ther. 14:398. doi: 10.3390/biom14040398
Christinaki, E., Kulenovic, H., Hadoux, X., Baldassini, N., Van Eijgen, J., De Groef, L., et al. (2022). Retinal imaging biomarkers of neurodegenerative diseases. Clin. Exp. Optom. 105, 194–204. doi: 10.1080/08164622.2021.1984179
Collaborators (2022). Estimation of the global prevalence of dementia in 2019 and forecasted prevalence in 2050: an analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. Lancet Public Health 7, e105–e125. doi: 10.1016/S2468-2667(21)00249-8
Dadu, A., Satone, V., Kaur, R., Hashemi, S. H., Leonard, H., Iwaki, H., et al. (2022). Identification and prediction of Parkinson's disease subtypes and progression using machine learning in two cohorts. NPJ Parkinsons Dis 8:172. doi: 10.1038/s41531-022-00439-z
De Picker, L. J., Morrens, M., Branchi, I., Haarman, B. C. M., Terada, T., Kang, M. S., et al. (2023). TSPO PET brain inflammation imaging: a transdiagnostic systematic review and meta-analysis of 156 case-control studies. Brain Behav. Immun. 113, 415–431. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2023.07.023
Dhapola, R., Hota, S. S., Sarma, P., Bhattacharyya, A., Medhi, B., and Reddy, D. H. (2021). Recent advances in molecular pathways and therapeutic implications targeting neuroinflammation for Alzheimer's disease. Inflammopharmacology 29, 1669–1681. doi: 10.1007/s10787-021-00889-6
Dilliott, A. A., Berberian, S. A., Sunderland, K. M., Binns, M. A., Zimmer, J., Ozzoude, M., et al. (2023). Rare neurovascular genetic and imaging markers across neurodegenerative diseases. Alzheimers Dement. 19, 5583–5595. doi: 10.1002/alz.13316
Doruyter, A. G. G., Parkes, J., Carr, J., and Warwick, J. M. (2021). PET-CT in brain disorders: the south African context. SA J Radiol 25:2201. doi: 10.4102/sajr.v25i1.2201
Dubois, B., Hampel, H., Feldman, H. H., Scheltens, P., Aisen, P., Andrieu, S., et al. (2016). Preclinical Alzheimer's disease: definition, natural history, and diagnostic criteria. Alzheimers Dement. 12, 292–323. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2016.02.002
Dugger, B. N., and Dickson, D. W. (2017). Pathology of neurodegenerative diseases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 9:35. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a028035
Ege, E., Olevson, C., D'Souza, R. S., Moeschler, S. M., Lamer, T., and Hagedorn, J. M. (2023). A bibliometric analysis of top-cited journal articles related to neuromodulation for chronic pain. Neuromodulation 26, 1510–1517. doi: 10.1016/j.neurom.2022.08.452
Ghezzi, P., and Mooradian, A. D. (2021). Demystifying oxidative stress. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 264, 3–26. doi: 10.1007/164_2020_379
Graille, M., Wild, P., Sauvain, J. J., Hemmendinger, M., Guseva Canu, I., and Hopf, N. B. (2020). Urinary 8-OHdG as a biomarker for oxidative stress: a systematic literature review and Meta-analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21:7483. doi: 10.3390/ijms21113743
Guo, T., Zhang, D., Zeng, Y., Huang, T. Y., Xu, H., and Zhao, Y. (2020). Molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 15:40. doi: 10.1186/s13024-020-00391-7
Hampel, H., Caraci, F., Cuello, A. C., Caruso, G., Nistico, R., Corbo, M., et al. (2020). A path toward precision medicine for Neuroinflammatory mechanisms in Alzheimer's disease. Front. Immunol. 11:456. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00456
Hardy, J. A., and Higgins, G. A. (1992). Alzheimer's disease: the amyloid cascade hypothesis. Science 256, 184–185. doi: 10.1126/science.1566067
Hicks, D., Wouters, P., Waltman, L., de Rijcke, S., and Rafols, I. (2015). Bibliometrics: the Leiden manifesto for research metrics. Nature 520, 429–431. doi: 10.1038/520429a
Hoilund-Carlsen, P. F., Alavi, A., Castellani, R. J., Neve, R. L., Perry, G., Revheim, M. E., et al. (2024). Alzheimer's amyloid hypothesis and antibody therapy: melting glaciers? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25:892. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073892
Horie, K., Salvado, G., Barthelemy, N. R., Janelidze, S., Li, Y., He, Y., et al. (2023). CSF MTBR-tau243 is a specific biomarker of tau tangle pathology in Alzheimer's disease. Nat. Med. 29, 1954–1963. doi: 10.1038/s41591-023-02443-z
Iliyasu, M. O., Musa, S. A., Oladele, S. B., and Iliya, A. I. (2023). Amyloid-beta aggregation implicates multiple pathways in Alzheimer's disease: understanding the mechanisms. Front. Neurosci. 17:1081938. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1081938
Ishibashi, K., Tago, T., Kameyama, M., Toyohara, J., and Ishii, K. (2024). 18F-THK5351 uptake may not estimate neurofibrillary tangles in in vivo images: a comparison with 18F-MK-6240 uptake. Clin. Nucl. Med. 49, 754–756. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000005316
Islam, M. T. (2017). Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction-linked neurodegenerative disorders. Neurol. Res. 39, 73–82. doi: 10.1080/01616412.2016.1251711
Jack, C. R. Jr. (2012). Alzheimer disease: new concepts on its neurobiology and the clinical role imaging will play. Radiology 263, 344–361. doi: 10.1148/radiol.12110433
Jankowsky, J. L., Xu, G., Fromholt, D., Gonzales, V., and Borchelt, D. R. (2003). Environmental enrichment exacerbates amyloid plaque formation in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 62, 1220–1227. doi: 10.1093/jnen/62.12.1220
Jia, J., Ning, Y., Chen, M., Wang, S., Yang, H., Li, F., et al. (2024). Biomarker changes during 20 years preceding Alzheimer's disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 390, 712–722. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2310168
Jia, L., Xu, H., Chen, S., Wang, X., Yang, J., Gong, M., et al. (2020). The APOE epsilon4 exerts differential effects on familial and other subtypes of Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 16, 1613–1623. doi: 10.1002/alz.12153
Jiang, S., Liu, Y., Zheng, H., Zhang, L., Zhao, H., Sang, X., et al. (2023). Evolutionary patterns and research frontiers in neoadjuvant immunotherapy: a bibliometric analysis. Int. J. Surg. 109, 2774–2783. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000000492
Jimenez-Mesa, C., Arco, J. E., Martinez-Murcia, F. J., Suckling, J., Ramirez, J., and Gorriz, J. M. (2023). Applications of machine learning and deep learning in SPECT and PET imaging: general overview, challenges and future prospects. Pharmacol. Res. 197:106984. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2023.106984
Kaiser, S., Zhang, L., Mollenhauer, B., Jacob, J., Longerich, S., Del-Aguila, J., et al. (2023). A proteogenomic view of Parkinson's disease causality and heterogeneity. NPJ Parkinsons Dis 9:24. doi: 10.1038/s41531-023-00461-9
Kirova, A. M., Bays, R. B., and Lagalwar, S. (2015). Working memory and executive function decline across normal aging, mild cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer's disease. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015:748212. doi: 10.1155/2015/748212
Kuhle, J., Barro, C., Andreasson, U., Derfuss, T., Lindberg, R., Sandelius, A., et al. (2016). Comparison of three analytical platforms for quantification of the neurofilament light chain in blood samples: ELISA, electrochemiluminescence immunoassay and Simoa. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 54, 1655–1661. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2015-1195
Leng, F., and Edison, P. (2021). Neuroinflammation and microglial activation in Alzheimer disease: where do we go from here? Nat. Rev. Neurol. 17, 157–172. doi: 10.1038/s41582-020-00435-y
Lin, W. Z., Yu, D., Xiong, L. Y., Zebarth, J., Wang, R., Fischer, C. E., et al. (2025). Homocysteine, neurodegenerative biomarkers, and APOE epsilon4 in neurodegenerative diseases. Alzheimers Dement. 21:e14376. doi: 10.1002/alz.14376
Lista, S., Imbimbo, B. P., Grasso, M., Fidilio, A., Emanuele, E., Minoretti, P., et al. (2024). Tracking neuroinflammatory biomarkers in Alzheimer's disease: a strategy for individualized therapeutic approaches? J. Neuroinflammation 21:187. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03163-y
Liu, W. L., Lin, H. W., Lin, M. R., Yu, Y., Liu, H. H., Dai, Y. L., et al. (2022). Emerging blood exosome-based biomarkers for preclinical and clinical Alzheimer's disease: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Neural Regen. Res. 17, 2381–2390. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.335832
Liu, P. P., Xie, Y., Meng, X. Y., and Kang, J. S. (2019). History and progress of hypotheses and clinical trials for Alzheimer's disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 4:29. doi: 10.1038/s41392-019-0063-8
Logroscino, G., Urso, D., Gnoni, V., Giugno, A., Vilella, D., Castri, A., et al. (2025). Mild cognitive impairment and early Alzheimer's disease eligibility for disease modification therapies in a tertiary Centre for cognitive disorders: a simultaneous real-word study on aducanumab and lecanemab. Eur. J. Neurol. 32:e16534. doi: 10.1111/ene.16534
Logroscino, G., Urso, D., and Savica, R. (2022). Descriptive epidemiology of neurodegenerative diseases: what are the critical questions? Neuroepidemiology 56, 309–318. doi: 10.1159/000525639
Maciejczyk, M., Zalewska, A., and Gerreth, A. K. (2020). Salivary redox biomarkers in selected neurodegenerative diseases. J. Clin. Med. 9:491. doi: 10.3390/jcm9020497
Moscoso, A., Karikari, T. K., Grothe, M. J., Ashton, N. J., Lantero-Rodriguez, J., Snellman, A., et al. (2022). CSF biomarkers and plasma p-tau 181 as predictors of longitudinal tau accumulation: implications for clinical trial design. Alzheimers Dement. 18, 2614–2626. doi: 10.1002/alz.12570
Ossenkoppele, R., van der Kant, R., and Hansson, O. (2022). Tau biomarkers in Alzheimer's disease: towards implementation in clinical practice and trials. Lancet Neurol. 21, 726–734. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(22)00168-5
Otero-Garcia, M., Mahajani, S. U., Wakhloo, D., Tang, W., Xue, Y. Q., Morabito, S., et al. (2022). Molecular signatures underlying neurofibrillary tangle susceptibility in Alzheimer's disease. Neuron 110, 2929–2948.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.06.021
Pereira, J. B., Janelidze, S., Smith, R., Mattsson-Carlgren, N., Palmqvist, S., Teunissen, C. E., et al. (2021). Plasma GFAP is an early marker of amyloid-beta but not tau pathology in Alzheimer's disease. Brain 144, 3505–3516. doi: 10.1093/brain/awab223
Petersen, R. C., Doody, R., Kurz, A., Mohs, R. C., Morris, J. C., Rabins, P. V., et al. (2001). Current concepts in mild cognitive impairment. Arch. Neurol. 58, 1985–1992. doi: 10.1001/archneur.58.12.1985
Quiroz, Y. T., Zetterberg, H., Reiman, E. M., Chen, Y., Su, Y., Fox-Fuller, J. T., et al. (2020). Plasma neurofilament light chain in the presenilin 1 E280A autosomal dominant Alzheimer's disease kindred: a cross-sectional and longitudinal cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 19, 513–521. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30137-X
Raghunathan, R., Turajane, K., and Wong, L. C. (2022). Biomarkers in neurodegenerative diseases: proteomics spotlight on ALS and Parkinson's disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23:299. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169299
Reitz, C., and Mayeux, R. (2014). Alzheimer disease: epidemiology, diagnostic criteria, risk factors and biomarkers. Biochem. Pharmacol. 88, 640–651. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.12.024
Richardson, T. E., Orr, M. E., Orr, T. C., Rohde, S. K., Ehrenberg, A. J., Thorn, E. L., et al. (2024). Spatial proteomic differences in chronic traumatic encephalopathy, Alzheimer's disease, and primary age-related tauopathy hippocampi. Alzheimers Dement. 21:14487. doi: 10.1002/alz.14487
Sadick, J. S., O'Dea, M. R., Hasel, P., Dykstra, T., Faustin, A., and Liddelow, S. A. (2022). Astrocytes and oligodendrocytes undergo subtype-specific transcriptional changes in Alzheimer's disease. Neuron 110:e1710, 1788–1805. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.03.008
Salloway, S., Sperling, R., Fox, N. C., Blennow, K., Klunk, W., Raskind, M., et al. (2014). Two phase 3 trials of bapineuzumab in mild-to-moderate Alzheimer's disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 370, 322–333. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1304839
Scheltens, P., De Strooper, B., Kivipelto, M., Holstege, H., Chetelat, G., Teunissen, C. E., et al. (2021). Alzheimer's disease. Lancet 397, 1577–1590. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32205-4
Schliebs, R., and Arendt, T. (2006). The significance of the cholinergic system in the brain during aging and in Alzheimer's disease. J. Neural Transm. (Vienna) 113, 1625–1644. doi: 10.1007/s00702-006-0579-2
Silva, M. V. F., Loures, C. M. G., Alves, L. C. V., de Souza, L. C., Borges, K. B. G., and Carvalho, M. D. G. (2019). Alzheimer's disease: risk factors and potentially protective measures. J. Biomed. Sci. 26:33. doi: 10.1186/s12929-019-0524-y
Singh, A., Kukreti, R., Saso, L., and Kukreti, S. (2019). Oxidative stress: a key modulator in neurodegenerative diseases. Molecules 24:1583. doi: 10.3390/molecules24081583
Soderberg, L., Johannesson, M., Nygren, P., Laudon, H., Eriksson, F., Osswald, G., et al. (2023). Lecanemab, Aducanumab, and Gantenerumab-binding profiles to different forms of amyloid-Beta might explain efficacy and side effects in clinical trials for Alzheimer's disease. Neurotherapeutics 20, 195–206. doi: 10.1007/s13311-022-01308-6
Tabeeva, G. R. (2019). Mild cognitive impairment: what's next? Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiatr. Im. S S Korsakova 119, 103–110. doi: 10.17116/jnevro2019119101103
Tan, S. N., and Tan, C. (2021). Vortioxetine improves cognition in mild cognitive impairment. Int. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 36, 279–287. doi: 10.1097/YIC.0000000000000376
Tao, Q. Q., Cai, X., Xue, Y. Y., Ge, W., Yue, L., Li, X. Y., et al. (2024). Alzheimer's disease early diagnostic and staging biomarkers revealed by large-scale cerebrospinal fluid and serum proteomic profiling. Innovation 5:100544. doi: 10.1016/j.xinn.2023.100544
Teleanu, D. M., Niculescu, A. G., Lungu, I. I., Radu, C. I., Vladacenco, O., Roza, E., et al. (2022). An overview of oxidative stress, Neuroinflammation, and neurodegenerative diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23:5938. doi: 10.3390/ijms23115938
Wang, J., Wang, S., Zhang, Y., and Zhang, W. (2024). Bibliometric analysis of evolutionary trajectory and prospective directions of LAG-3 in cancer. Front. Immunol. 15:1329775. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1329775
Wei, J., Wong, L. C., and Boland, S. (2023). Lipids as emerging biomarkers in neurodegenerative diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25:131. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010131
Wei, N., Xu, Y., Li, Y., Shi, J., Zhang, X., You, Y., et al. (2022). A bibliometric analysis of T cell and atherosclerosis. Front. Immunol. 13:948314. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.948314
Keywords: neural injury biomarkers, neurodegenerative diseases, multimodal biomarkers, citation analysis, bibliometric analysis
Citation: Pa C, Shen S, Dai Y and Wu M (2025) Bibliometric analysis of neural injury biomarkers in neurodegenerative diseases: research trends and future perspectives. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 19:1614132. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2025.1614132
Edited by:
Zinovia Maria Kefalopoulou, University of Patras, GreeceReviewed by:
Angelo Bellinvia, Santa Maria Nascente, Fondazione Don Carlo Gnocchi Onlus (IRCCS), ItalyNagendra Kumar Rai, Cleveland Clinic, United States
Copyright © 2025 Pa, Shen, Dai and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Min Wu, d205MjExOTIyNjFAMTI2LmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Chengzhou Pa
Chengzhou Pa Shijun Shen
Shijun Shen Yunrui Dai3
Yunrui Dai3