- Department of Rheumatology, Taher Sfar University Hospital, Mahdia, Tunisia
Aseptic spondylodiscitis (SD) is a rare complication of axial spondyloarthritis (AS) that can develop during the course of the disease, often asymptomatically. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the gold standard for diagnosing SD, but due to its rarity, the condition is frequently misdiagnosed. We report the case of a 60-year-old male who presented with back pain and elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels. MRI of the dorsolumbar spine revealed SD from the D6 to D8 vertebrae. An infectious workup was negative. During hospitalization, the patient developed acute abdominal pain, cessation of bowel movements, and gas retention. Abdominal CT revealed ileitis, prompting a colonoscopy, which confirmed Crohn's disease (CD) through histopathological analysis. Pelvic MRI also showed sacroiliitis. The diagnosis of aseptic SD revealing non-radiographic AS associated with CD was made according to the ASAS 2009 criteria, and the patient was treated with sulfasalazine, showing favorable improvement. Only a few cases of SD in patients with AS and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) have been reported. This case underscores that SD can be the initial clinical manifestation of non-radiographic AS associated with CD. Although challenging to recognize, this condition may present with unpredictable and varied clinical symptoms, requiring a comprehensive diagnostic approach.
Introduction
AS is the prototype of the spondyloarthritis group, characterized by predominant involvement of the axial skeleton, and it may also be associated with extra-articular manifestations such as IBD, which occurs in 5%–10% of cases of AS (1). Nevertheless, up to 62% of patients have rheumatic symptoms, which are the most common extra-intestinal manifestation of IBD (2). Aseptic SD in AS, also known as the Andersson lesion, is a rare but well-recognized spinal complication first described by Andersson in 1937 (3). It can develop at any time during AS and may be asymptomatic. Aseptic SD is also a spinal complication of spondylitis in patients with IBD (3). Notably, axial involvement is considerably more prevalent in Crohn's disease (CD), affecting 5%–22% of patients, compared to 2%–6% in ulcerative colitis (4). Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) remains the gold standard for the radiological diagnosis of discovertebral abnormalities associated with this condition (3). However, the rarity and non-specific clinical presentation of aseptic SD contribute to its frequent misdiagnosis, and few studies have thoroughly addressed this entity in the literature. To our knowledge, only a limited number of cases documenting SD in patients with AS associated with IBD have been reported. Here, we present the case of a 60-year-old male who presented with back pain and was ultimately diagnosed with aseptic SD revealing non-radiographic AS in association with CD.
Aim
We report this case to raise clinicians' awareness of aseptic spondylodiscitis in patients with AS who present with acute back pain, including those with AS associated with IBD.
Case report
A 60-year-old man with a history of hypertension presented with a two-month history of progressively worsening back pain, rated 8 on the visual analog scale. He denied any recent infectious symptoms and reported no personal or family history of psoriasis or chronic rheumatic diseases.
On physical examination, no fever was noted. Osteoarticular examination revealed marked tenderness on palpation of the D7 spinous process and back stiffness, with thoracic expansion reduced to 2 cm. The peripheral joint examination revealed no signs of arthritis or synovitis, and both the hip and sacroiliac joints were clinically normal.
Laboratory tests showed a markedly elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) of 110 mm in the first hour (normal <30 mm) and a C-reactive protein (CRP) level of 167 mg/L (normal <6 mg/L). Complete blood count, renal and liver function tests and protein electrophoresis were all within normal limits.
Dorsolumbar (DL) spine x-ray revealed degenerative changes, including disc space narrowing and spondylolisthesis at the L4–L5 level. MRI of the DL spine demonstrated SD at two levels: D6–D7 and D7–D8, with significant inflammatory thickening of the paravertebral soft tissues, but no abscess or epiduritis (Figure 1).
![Three MRI images of the thoracic spine showing abnormalities at three vertebral levels. Panel (a) is a sagittal T1-weighted image revealing reduced signal intensity at the D6-D7 and D7-D8 levels. Panel (b) is a sagittal T2-weighted fat-suppressed image showing increased signal intensity at the same levels. Panel (c) is an axial T2-weighted fat-suppressed sequence demonstrating vertebral hypersignal consistent with bone edema, with extension to the prevertebral soft tissues.]](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/1575740/fmscd-03-1575740-HTML/image_m/fmscd-03-1575740-g001.jpg)
Figure 1. (a–c) magnetic resonance imaging showing signs of intervertebral disc inflammation. Sagittal T1-weighted image (a) reveals reduced signal intensity at the D6–D7 and D7–D8 levels. Sagittal T2-weighted and fat-suppressed images (b) show increased signal intensity at the same levels. Axial T2-weighted and fat-suppressed sequences (c) demonstrate vertebral hypersignal consistent with bone edema, with extension of the signal to the prevertebral soft tissues.
A comprehensive infectious workup was conducted, including transthoracic echocardiography, chest x-ray, urine cytobacteriological examination, blood cultures, Wright serology for brucellosis, and tuberculosis screening. All results were negative.
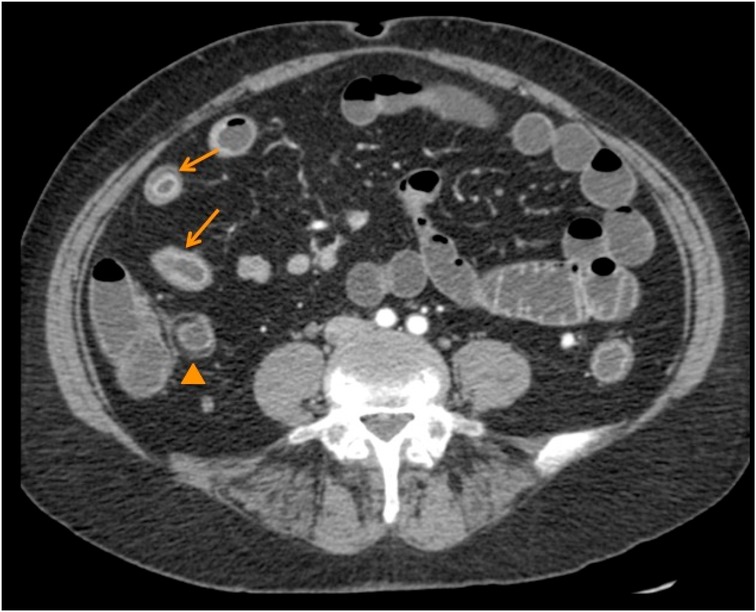
During hospitalization, the patient developed acute abdominal pain, accompanied by cessation of bowel movements, gas retention, and abdominal distension. Abdominal CT revealed signs suggestive of infectious or inflammatory ileitis (Figure 2). Colonoscopy with biopsy showed parietal thickening, lymphoplasmacytic infiltration, and epithelioid granulomas, consistent with CD.
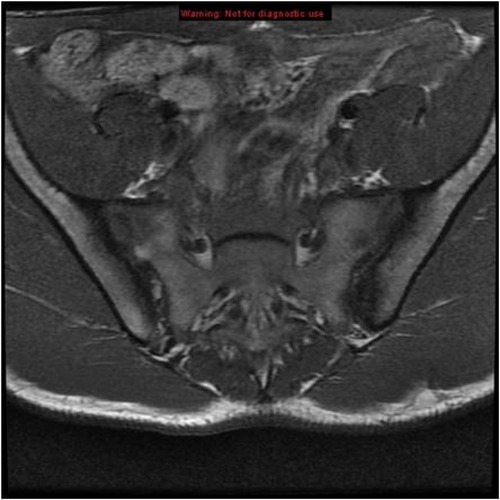
Considering the established diagnosis of Crohn's disease, the absence of fever, and the negative infectious workup, a diagnosis of Andersson lesion within the context of AS was suspected. Pelvic x-ray showed normal sacroiliac joints, but pelvic MRI revealed bilateral sacroiliitis (Figure 3). Based on these findings, a diagnosis of aseptic SD revealing non-radiographic AS associated with Crohn's disease was made, by the ASAS 2009 classification criteria.
The patient was treated with analgesics and sulfasalazine, resulting in significant improvement of both axial and gastrointestinal symptoms, with back pain decreasing to 1 on the visual analog scale.
Discussion
Aseptic SD is a destructive disco vertebral lesion that is uncommon and may easily be overlooked, but it is well-recognized as a complication of ankylosing spondylitis (AS). Its radiological prevalence ranges from 1%–28%, depending on the series (3). Since the first report by Andersson, various mechanisms have been proposed to explain the development of these lesions, including both inflammatory and mechanical (traumatic) etiologies (3).
The inflammatory mechanism is believed to result from hyperpressure of the nucleus pulposus on a cartilaginous plate already weakened by inflammatory infiltration (4). Early erosive forms are thought to have evolved from Romanus lesions (4). Anatomically, the intervertebral disc comprises a peripheral annulus fibrosus, part of the enthesis, and a central nucleus pulposus. The Romanus lesion results from inflammation of the annulus fibrosus, leading to a zone of destruction bounded by osteosclerosis. These can be considered early stages of disco spondylitis and typically evolve into syndesmophytes, although this is not always the case and may progress to classic SD (5). The improvement of pain and imaging features under anti-inflammatory therapy supports this inflammatory hypothesis (5).
Conversely, mechanical factors may also contribute significantly to aseptic SD. The DL junction is highly mobile, and spinal fusion often begins in the lower spine in AS, leading to increased stress at the DL junction. Repetitive mechanical stress on this already compromised region may result in microfractures, explaining the high frequency of aseptic SD in this location (3). Cawley et al. observed that 67% of patients with AS and aseptic SD were engaged in heavy manual labor, though this was not the case for our sedentary patient (6). Aseptic SD has traditionally been considered a late complication of AS, typically arising after 2–30 years of disease evolution (mean duration: 20 years) (6). However, in our case, aseptic SD was the revealing feature of AS associated with CD. The present case is the first to our knowledge to show aseptic SD revealing AS associated with Crohn's disease.
Typically, aseptic SD involves a single level or a few adjacent levels of the spine (4). In our case, two consecutive levels were involved: D6–D7 and D7–D8. Clinical manifestations range from asymptomatic cases to chronic back pain, neurological impairment, and kyphotic deformities (7). Our patient presented with isolated inflammatory back pain and had a normal neurological exam.
The male predominance seen in aseptic SD mirrors that of AS itself (4). Diagnosis is essentially radiological, with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) being the gold standard for detecting early disco vertebral lesions (3). T1-weighted images typically show decreased signal intensity at affected levels, while T2-weighted images reveal hyperintense signals, especially when using contrast-enhanced fat-suppressed sequences (3).
However, the radiological findings of aseptic SD may closely resemble other conditions, notably infectious spondylodiscitis. Both may show bone destruction and narrowing of the disc space. Septic spondylodiscitis often demonstrates discal or epidural abscess formation, paravertebral soft tissue involvement, and systemic signs of infection, whereas inflammatory SD related to AS tends to lack abscesses and systemic symptoms, as seen in our case (8). The absence of fever, negative infectious screening, and typical imaging findings of bilateral sacroiliitis further support an inflammatory origin rather than infection. This observation is consistent with prior studies reporting that biopsies in similar patients with AS and SD fail to yield any positive cultures (9). Therefore, biopsy is not routinely indicated in patients with known AS and SD. Similarly, laboratory findings such as elevated ESR and CRP, while frequently present, lack specificity (4).
Sacroiliitis is found in approximately 20% of patients with IBD, but only one-fifth of them progress to overt axial spondyloarthritis (10). A study by Urlep et al. reported a 3%–6% prevalence of aseptic SD among IBD patients (11), although large-scale studies on this association remain lacking.
Summary
Aseptic SD in AS is not uncommon and is considered one of the inflammatory manifestations of the disease. It is often asymptomatic and likely underestimated, either because it is not routinely screened for or because its symptoms are simply attributed to AS itself. This lesion is predominantly a late complication of AS, with the lumbar or lower thoracic spine more frequently involved. There is currently no consensus on the etiology of aseptic SD; both inflammatory and mechanical factors may contribute.
A crucial aspect of aseptic SD management is avoiding misdiagnosis, particularly confusion with infectious spondylodiscitis, which could result in unnecessary financial and psychological burdens. The prognosis appears favorable with conservative treatment. Our case illustrates how aseptic SD can present as the initial clinical manifestation of non-radiographic AS associated with Crohn's disease. Clinicians should consider the diagnosis of aseptic SD when a patient with AS presents with acute back pain. Although it may be challenging to identify, this condition highlights the broad and sometimes unpredictable clinical spectrum of AS.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
OJ: Writing – original draft. HA: Writing – original draft. MB: Writing – review & editing. ON: Writing – review & editing. MA: Writing – review & editing. RS: Writing – review & editing. MY: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. El Maghraoui A. Extra-articular manifestations of ankylosing spondylitis: prevalence, characteristics and therapeutic implications. Eur J Intern Med. (2011) 22(6):554–60. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2011.06.006
2. Salvarani C, Fries W. Clinical features and epidemiology of spondyloarthritides associated with inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol. (2009) 15(20):2449–55. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.2449
3. Bron JL, de Vries MK, Snieders MN, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE, van Royen BJ. Discovertebral (Andersson) lesions of the spine in ankylosing spondylitis revisited. Clin Rheumatol. (2009) 28(8):883–92. doi: 10.1007/s10067-009-1151-x
4. Langlois S, Cedoz JP, Lohse A, Toussirot E, Wendling D. Aseptic discitis in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a retrospective study of 14 cases. Joint Bone Spine. (2005) 72(3):248–53. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2004.05.015
5. Bouvier M, Tebib J, Colson F. Evolution des spondylodiscopathies de la spondylarthrite ankylosante [development of spondylodiscopathies in ankylosing spondylitis]. Rev Rhum Mal Osteoartic. (1987) 54(3):229–34.3589453
6. Cawley MI, Chalmers TM, Kellgren JH, Ball J. Destructive lesions of vertebral bodies in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. (1972) 31(5):345–58. doi: 10.1136/ard.31.5.345
7. Qin W, Yang P, Zhou F, Mao H, Yang H. Andersson lesion occurring in the lumbosacral segment of a young man: a case report and literature review. World Neurosurg. (2020) 143:419–22. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2020.07.146
8. Salaffi F, Ceccarelli L, Carotti M, Di Carlo M, Polonara G, Facchini G, et al. Differentiation between infectious spondylodiscitis versus inflammatory or degenerative spinal changes: how can magnetic resonance imaging help the clinician? La Radiol Med. (2021) 126(6):843–59. doi: 10.1007/s11547-021-01347-7
9. Nikolaisen C, Nossent H. Early histology in ankylosing spondylitis related spondylodiscitis supports its inflammatory origin. Scand J Rheumatol. (2005) 34(5):396–8. doi: 10.1080/03009740510026625
10. Calin A, Robertson D. Spondylodiscitis and pseudarthrosis in a patient with enteropathic spondyloarthropathy. Ann Rheum Dis. (1991) 50(2):117–9. doi: 10.1136/ard.50.2.117
Keywords: aseptic spondylodiscitis, non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis, back pain, Crohn's disease, Andersson lesion
Citation: Jomaa O, Abid H, Brahem M, Neifar O, Ardhaoui M, Sarraj R and Younes M (2025) Case Report: Aseptic spondylodiscitis revealing non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis associated with Crohn's disease. Front. Musculoskelet. Disord. 3:1575740. doi: 10.3389/fmscd.2025.1575740
Received: 12 February 2025; Accepted: 5 June 2025;
Published: 20 June 2025.
Edited by:
Emanuele Bizzi, Vita-Salute San Raffaele University, ItalyReviewed by:
Crescenzio Scioscia, University of Bari Aldo Moro, ItalyCalogero Velluto, Catholic University of the Sacred Heart, Italy
Copyright: © 2025 Jomaa, Abid, Brahem, Neifar, Ardhaoui, Sarraj and Younes. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Olfa Jomaa, b2xmYWpvbWFhMkBnbWFpbC5jb20=
†ORCID:
Olfa Jomaa
orcid.org/0000-0002-3688-5264
Hayfa Abid
orcid.org/0000-0002-1380-0803
Mouna Brahem
orcid.org/0000-0002-2459-7820
Mahbouba Ardhaoui
orcid.org/0000-0001-5805-7139
Rihab Sarraj
orcid.org/0000-0003-1562-8418
Mohamed Younes
orcid.org/0000-0001-6293-7518
 Olfa Jomaa*†
Olfa Jomaa*† Olfa Neifar
Olfa Neifar