- 1Department of Rheumatology and Medical Sciences, Clinical Rheumatology Unit, ASST Gaetano Pini-CTO Institute, Milan, Italy
- 2Department of Clinical Sciences & Community Health, Research Center for Adult and Pediatric Rheumatic Diseases, Università Degli Studi di Milano, Milan, Italy
Objective: The hip joint is frequently affected by osteoarthritis (OA) and is a leading cause of disability. This study aims to assess the long-term efficacy of ultrasound-guided intra-articular viscosupplementation for pain relief in patients with hip osteoarthritis secondary to rheumatic diseases compared to primary OA.
Methods: This single-center, retrospective, observational cohort study included patients with hip OA who received intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid (HA) (Hylan G-F 20). Fisher's exact test was applied to evaluate baseline variables, with 95% confidence intervals (CI) calculated for differences in mean outcomes.
Results: A total of 55 patients with primary hip OA (POA) and 16 patients with secondary hip OA (SOA) were included. The mean observation period was 31.3 months (±29.9), with an average of 5 intra-articular injections administered. Both groups showed a positive response to HA injections, with the POA group demonstrating a mean Visual Analog Scale (VAS) pain reduction of 2.97 (95% CI 2.38–3.56), compared to 1.28 (95% CI 0.18–2.37) in the SOA group. At the end of follow-up, pain reduction was less pronounced in the SOA group, which showed higher residual VAS pain scores compared to the POA group (p = 0.029).
Conclusions: This study highlights that HA injections significantly reduce pain in both primary and secondary hip osteoarthritis. However, patients with primary OA experienced greater pain relief, as evidenced by a more substantial reduction in VAS scores compared to those with secondary OA.
1 Introduction
Osteoarthritis (OA) is one of the most disabling chronic conditions and poses a significant public health challenge, with its prevalence rising due to aging populations in developed countries (1). The hip joint, the second-largest weight-bearing joint after the knee, is frequently affected by OA (2). The estimated lifetime risk of developing symptomatic hip OA is 18.5% in men and 28.6% in women by age 85, with nearly 10% of individuals eventually requiring total hip replacement due to end-stage OA (3–6). Effective management of OA is essential to reduce its burden on individuals and healthcare systems.
Chronic systemic inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthritis, and psoriatic arthritis, are characterized by multi-organ and joint involvement, including hip synovitis. Despite advances in treatment over recent decades, these conditions still cause considerable impairment, with many patients developing secondary hip OA. These patients often require long-term medical therapy to manage both the underlying inflammatory disease and the secondary osteoarthritic changes. Notably, up to 8 out of 1,000 patients with rheumatoid arthritis will require total joint replacement, with postoperative complication rates (e.g., infections, fractures, dislocations) reaching 5.3% (7, 8).
Total hip arthroplasty is the primary treatment for end-stage symptomatic OA. Medical management typically involves physical and pharmacological approaches, but these are often insufficient to control pain or prevent disability (9).
Data on the medical management of OA secondary to rheumatic diseases is sparse in the literature. One potential therapeutic option is intra-articular viscosupplementation via hyaluronic acid (HA) injections into the affected joint. The rationale for using viscosupplementation in patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases is supported by findings from several in vitro and in vivo models. HA provides various therapeutic effects, including mechanical improvement of synovial fluid by increasing its viscosity and elasticity, as well as analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects through the inhibition of prostaglandin production (10). By increasing the local concentration of synovial polysaccharides, injected HA displaces degraded HA from its receptors, inhibiting the NF-kB pathway and preventing cartilage degradation (11).
As a result, HA injections are recommended for moderate symptomatic OA, although not for acute flares of inflammatory arthritis. However, the clinical efficacy of viscosupplementation in rheumatic inflammatory conditions remains unclear, with evidence suggesting that synovitis is associated with poorer outcomes following HA injections (12).
Due to its anatomical depth, the hip joint is challenging to access for injections. Therefore, ultrasound (US) guidance is commonly employed, and high-molecular-weight (MW) HA formulations are preferred as they require fewer injections (13).
This study aims to evaluate the effects of HA injections in patients with primary OA (POA) and those with OA secondary to inflammatory rheumatic diseases (SOA).
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study design and population
This retrospective observational cohort study included patients who received intra-articular HA injections in the hip joint at the Rheumatology Unit, ASST-Pini-CTO (Milan, Italy) between 2013 and 2021. The study was approved by the local Ethics Committee (Comitato Etico Milano Area B, protocol no. 125_2017) and included all patients diagnosed with OA who underwent intra-articular HA injections. The objective was to assess the long-term effectiveness of viscosupplementation and compare outcomes between two cohorts: patients with primary hip OA (POA) and those with secondary hip OA due to inflammatory arthritis (SOA).
2.2 Selection criteria
Eligible patients had symptomatic hip OA with a minimum of six months of hip pain, in accordance with the American College of Rheumatology criteria. OA severity was classified according to the Kellgren-Lawrence grading system (grades I–IV), based on standard hip x-rays taken within six months of study enrollment and reviewed by a single evaluator (14–16). Patients in the secondary OA group were also diagnosed with chronic inflammatory conditions according to established international classification criteria, including: the 2010 ACR/EULAR criteria for rheumatoid arthritis (17), the CASPAR criteria for psoriatic arthritis (18), the ASAS classification criteria for axial and peripheral spondyloarthritis (19), the ILAR criteria for juvenile idiopathic arthritis (20), and the ACR/EULAR provisional criteria for polymyalgia rheumatica (21). Patients without available radiographs indicating the Kellgren-Lawrence grade or those lost to follow-up within six months of treatment were excluded.
Both groups underwent US-guided viscosupplementation using the same HA product, and they were followed either until the study's conclusion or their last visit.
2.3 Injection procedure
All patients received 2 ml of intra-articular Hylan G-F 20 (Synvisc®, Sanofi, Paris, France), a sterile, non-pyrogenic solution of chemically cross-linked hyaluronans with a molecular weight of 6,000 kDa (high MW). The solution contains hylan A (soluble) and hylan B (insoluble gel).
The procedure was repeated monthly for three consecutive months (induction phase), followed by maintenance injections every six months if symptomatic relief persisted. Injections were performed using US guidance with a standardized technique, employing a 6–18 MHz linear transducer (Esaote MyLab 70) for visualization. A sterile guide was used for an antero-inferior approach, and an 18-gauge, 15 cm needle was inserted. The correct site of injection was confirmed via real-time US before administering HA.
2.4 Data collection
Baseline demographic and clinical data were collected, including age, gender, height, weight, BMI, and occupation. Clinical features included Kellgren-Lawrence grading, presence and type of femoroacetabular impingement (FAI), history of other joint replacements in the lower limbs, duration of hip pain, and time to arthroplasty. Pain was assessed using a visual analog scale (VAS) with a range of 0–100 mm; for analysis and presentation in tables, figures, and the results section, these scores were converted to a 0–10 scale by dividing by 10. Information on adverse reactions to injections and the need for additional steroid injections was also recorded.
For the SOA group, further clinical data were collected, including joint involvement patterns, disease activity (e.g., SDAI/CDAI for rheumatoid arthritis, DAPSA/cDAPSA for psoriatic arthritis, ASDAS for spondyloarthritis), and pharmacological treatments.
2.5 Statistical analysis
Descriptive statistics were used to summarize demographic and clinical data. For continuous variables (e.g., age, treatment duration, number of HA injections, baseline and follow-up VAS pain scores), comparisons between the POA and SOA groups were performed using Student's t-test. For categorical variables (e.g., sex, Kellgren–Lawrence grade distribution, history of contralateral hip replacement, adverse reactions, completion of induction treatment, and proportion of patients undergoing arthroplasty), Fisher's exact test was applied. We calculated 95% confidence intervals (CI) for differences in mean outcomes. All tests were two-tailed, and a p-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Baseline characteristics of the study population
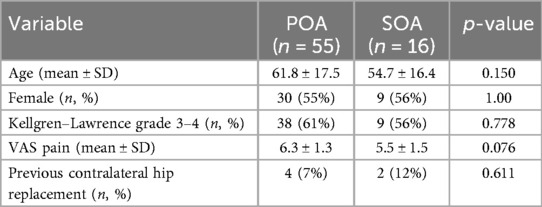
A total of 71 patients (32 males, 39 females) with symptomatic hip OA met the inclusion criteria, with 55 patients diagnosed with primary OA (POA) and 16 with secondary OA (SOA). Sixty-four patients underwent unilateral hip viscosupplementation, while seven (all from the POA group) received bilateral treatment, bringing the total number of hips treated to 78. The main characteristics of the patients are summarized in Table 1. Four patients had a history of developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH), and seven had femoroacetabular impingement (FAI), with two cases of pincer type and five of cam type. At baseline, five patients had previously undergone contralateral hip replacement (including two from the SOA group).
Within the SOA group, the underlying inflammatory diagnoses included juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) in five patients, peripheral spondyloarthritis (SpA) in five, polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) in two, axial SpA in one, psoriatic arthritis (PsA) in one, seronegative rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in one, and anti-citrullinated protein antibody (ACPA)-positive RA in one. Disease activity at baseline was evaluated using specific clinimetric tools (SDAI for RA and JIA; DAPSA for PsA; ASDAS for SpA; clinical evaluation and CRP for PMR) and categorized into remission, low disease activity (LDA), moderate disease activity (MDA), or high disease activity (HDA). At the initiation of viscosupplementation, all SOA patients were in remission (9 patients) or LDA (7 patients). Seven SOA patients were treated with conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (cDMARDs), and seven with biologic DMARDs (bDMARDs).
3.2 Follow-up results
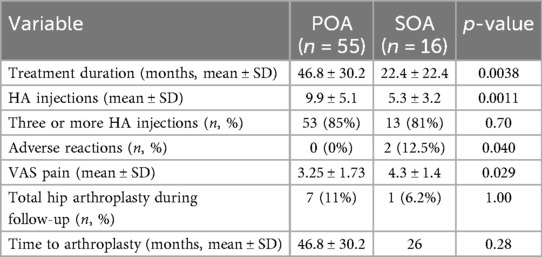
The mean follow-up duration was 31.3 (±29.9) months, with an average of 5 (±4.5) intra-articular injections administered. Induction treatment was completed in 66 hip joints, with 12 patients discontinuing before the end of the three-injection induction phase. Two patients from the SOA group reported injection site pain lasting 7–10 days, which was recorded as an adverse event. No adverse events were reported in the POA group (Table 2). During the follow-up period, eight patients underwent total hip replacement, with an average time to surgery of 32 months after viscosupplementation initiation. Only one SOA patient required surgery.
3.3 Comparison between the Two cohorts
In both groups, a reduction in VAS pain was observed at the end of follow-up. The POA group experienced a mean pain reduction of 2.97 (95% CI 2.38–3.56), compared to 1.28 (95% CI 0.18–2.37) in the SOA group. By the end of the study, the SOA group had higher pain scores and a higher final VAS score compared to the POA group (POA: 3.25 ± 1.73, SOA: 4.3 ± 1.4; p = 0.029) (Figure 1). Additionally, the SOA group had a significantly higher prevalence of adverse reactions (p = 0.04), which consisted in all cases of transient post-injection pain lasting 7–10 days.
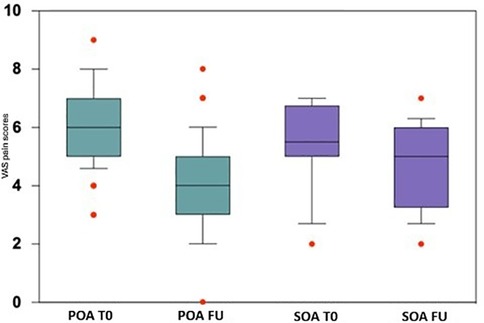
Figure 1. Box plots of VAS pain scores at baseline (T0) and follow-up (FU) for primary (POA) and secondary (SOA) hip osteoarthritis. Boxes represent the median and interquartile range (IQR); whiskers extend to values within 1.5 × IQR; individual points indicate outliers. POA, primary osteoarthritis; SOA, secondary osteoarthritis; T0, baseline; FU, follow-up.
Patients with POA underwent a longer treatment duration and received a greater number of HA injections. However, the proportion of patients completing the induction treatment (three or more injections) did not differ significantly between the two groups (85% in POA vs. 81% in SOA). There were no differences in rheumatic disease activity at baseline or at the end of follow-up, with nine patients in remission and seven in LDA throughout the study.
4 Discussion
Our research group has a particular interest in understanding how hyaluronic acid (HA) can play a pivotal role in improving the quality of life for individuals suffering from this specific subset of hip osteoarthritis (OA). A review of the literature on HA use in secondary OA revealed that most studies are outdated, heterogeneous, and often lack a control group (22, 23). In a previous study, we compared the outcomes of HA injections in primary OA and OA secondary to juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA). The results showed similar benefits in terms of Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) and Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Arthritis Index (WOMAC) scores for both groups during the first year, but after that, the secondary OA group experienced a decline in benefits (23). This new study supports the better outcome of HA injections in the primary OA group compared to the secondary OA group, extending the findings across a broader range of rheumatic diseases. It is worth considering that a more frequent HA injection regimen might further improve pain reduction in the secondary OA group.
An additional consideration is the marked difference in treatment duration and number of injections received between the two groups, with SOA patients discontinuing therapy earlier and receiving significantly fewer HA administrations. This discrepancy may have contributed to the less substantial pain reduction observed in SOA, as a shorter cumulative exposure to HA could limit sustained analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. However, it is equally plausible that the reduced treatment duration reflects lower perceived benefit among SOA patients, leading to earlier discontinuation of therapy. In this context, the higher final VAS scores in SOA may not only indicate a need for regimen optimization but also highlight challenges in long-term adherence when treatment efficacy is perceived as limited. From a clinical standpoint, this underlines the importance of monitoring patient-reported outcomes and considering early predictors of response to identify which patients are likely to maintain long-term benefit from viscosupplementation.
Our study found that hip OA secondary to rheumatic diseases was most commonly associated with JIA and spondyloarthritis, which aligns with the established epidemiology of hip involvement in these conditions (24, 25). Moreover, the VAS pain standard deviation was much higher in the secondary OA group than in the primary OA group, reflecting the variable nature of pain and response to HA injections in the secondary group. The pain reduction observed in the primary OA group after HA injection is consistent with findings already reported in the literature (26).
The observed variability in clinical responses to HA hip injections between primary and secondary OA supports the idea that different OA phenotypes may respond differently to treatments. Several studies have proposed distinct OA phenotypes based on clinical, radiological, and genetic factors. Coutinho de Almeida et al. identified two distinct OA patient profiles through the integration of whole-transcriptome and clinical data (27). One subtype exhibited upregulation of immune response-related genes, which may be relevant to our secondary OA group, while the other was characterized by upregulation of cellular membrane components. In a related study, Snelling et al. found the presence of IL-17 in the synovial fluid of patients with an inflammatory form of primary hip OA (28). These findings underscore the significant role of the synovial environment in determining OA phenotype and suggest that stratifying patients based on cytokine profiles may open new avenues for targeted therapeutic interventions. Cytokines, which sensitize peripheral nerve endings, may contribute substantially to the pain experienced in inflammatory OA, as observed in the secondary OA group (29). The development of more effective, disease-modifying treatments for OA may greatly benefit from a deeper understanding of OA phenotyping.
Although hip joint infiltrations are increasingly recognized for their therapeutic potential, they are not without risks. Post-infiltration pain is the most common adverse event associated with HA injections in hip OA, although it is usually mild and transient, with serious adverse events being rare (30, 31). In our study, the secondary OA group exhibited a higher incidence of post-injection pain than the primary OA group. This might be explained by the fact that the synovial membrane in patients with secondary OA may be more susceptible to inflammation and, consequently, to pain generation.
The significantly higher prevalence of post-injection pain in the SOA group represents an important novel finding, further distinguishing the two phenotypes. This observation supports the concept of an inflammatory OA phenotype, in which the synovial membrane is inherently more reactive and less tolerant to intra-articular procedures, even when systemic disease activity is controlled (remission or LDA). Consequently, the differential efficacy between POA and SOA is compounded by a differential safety profile, suggesting that the overall risk/benefit ratio of viscosupplementation is less favorable in SOA. From a clinical perspective, these findings emphasize the importance of tailoring viscosupplementation strategies to OA phenotype. While both POA and SOA patients experienced pain reduction, the more modest improvement and higher incidence of post-injection pain in SOA underline the need for careful patient selection and counseling. In practice, viscosupplementation may be most effective in primary OA or in secondary OA patients with well-controlled systemic disease activity, but expectations regarding the degree of pain relief should be realistic. For SOA, HA injections may serve as a temporizing measure to delay arthroplasty, but they should be integrated into a multimodal management plan rather than used in isolation, with close monitoring for adverse reactions and a cautious approach to repeated treatments.
This study has several limitations. First, the data were collected retrospectively. Second, the sample size was relatively small, limited by the number of eligible patients referred to our institution. Nevertheless, the population was homogeneous, as all patients were treated with the same HA product and therapeutic protocol. Larger studies are needed to investigate the time to total hip arthroplasty, as our results in this area were inconclusive. Third, defining primary vs. secondary OA relies on identifying hip synovitis. In our study, secondary OA was defined by the presence of radiographic evidence of OA in patients with a history of rheumatic disease. Lastly, the follow-up period was not standardized and varied across patients.
To our knowledge, this is the first study comparing the long-term effects of HA therapy in patients with primary and secondary hip OA.
5 Conclusions
In conclusion, our study demonstrated that HA injections significantly reduce pain in both primary and secondary hip osteoarthritis, although primary OA patients experienced greater pain relief. From a clinical perspective, viscosupplementation appears to be a valuable option for patients with primary OA, while its use in secondary OA should be more carefully individualized. In particular, SOA patients may still benefit, but clinicians should set realistic expectations, integrate HA injections within a multimodal treatment plan, and monitor closely for adverse reactions. Future research should focus on identifying the optimal therapeutic regimen for different OA subgroups and evaluating the effectiveness of HA injections in larger patient populations.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The study was approved by the local Ethics Committee (Comitato Etico Milano Area B. no. 125_2017). Written informed consent to participate in this study was not required from the participants or the participants' legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements due to the retrospective nature of this study. Written informed consent was not obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article as there is no identifiable data.
Author contributions
OL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CA: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. EC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. GT: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. MS: Writing – review & editing. MF: Writing – review & editing. MP: Writing – review & editing. LI: Writing – review & editing. AA: Writing – review & editing. AM: Writing – review & editing. RC: Writing – review & editing, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Wittenauer R, Smith L, Aden K. Priority Medicines for Europe and the World “A Public Health Approach to Innovation” Update on 2004 Background Paper Background Paper 6. 12 Osteoarthritis. Geneva: World Health Organization (2013). p. 1–31. Available online at: http://www.who.int/medicines/areas/priority_medicines/BP6_12Osteo.pdf
2. Zhang Y, Jordan JM. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Clin Geriatr Med. (2010) 26(3):355–69. doi: 10.1016/j.cger.2010.03.001
3. Culliford DJ, Maskell J, Kiran A, Judge A, Javaid MK, Cooper C, et al. The lifetime risk of total hip and knee arthroplasty: results from the UK general practice research database. Osteoarthr Cartil. (2012) 20(6):519–24. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2012.02.636
4. Murphy NJ, Eyles JP, Hunter DJ. Hip osteoarthritis: etiopathogenesis and implications for management. Adv Ther. (2016) 33(11):1921–46. doi: 10.1007/s12325-016-0409-3
5. Murphy LB, Helmick CG, Schwartz TA, Renner JB, Tudor G, Koch GG, et al. One in four people may develop symptomatic hip osteoarthritis in his or her lifetime. Osteoarthr Cartil. (2010) 18(11):1372–9. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2010.08.005
6. Sandell LJ. Etiology of osteoarthritis: genetics and synovial joint development. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2012) 8(2):77–89. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2011.199
7. Chong RWW, Chong CS, Lai CH. Total hip arthroplasty in patients with chronic autoimmune inflammatory arthroplasties. Int J Rheum Dis. (2010) 13(3):235–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1756-185X.2010.01477.x
8. Taylor-Williams O, Nossent J, Inderjeeth CA. Incidence and complication rates for total hip arthroplasty in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis across four decades. Rheumatol Ther. (2020) 7(4):685–702. doi: 10.1007/s40744-020-00238-z
9. Fernandes L, Hagen KB, Bijlsma JWJ, Andreassen O, Christensen P, Conaghan PG, et al. EULAR recommendations for the non-pharmacological core management of hip and knee osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. (2013) 72(7):1125–35. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202745
10. Abatangelo G, Vindigni V, Avruscio G, Pandis L, Brun P. Hyaluronic acid: redefining its role. Cells. (2020) 9(7):1–19. doi: 10.3390/cells9071743
11. Avenoso A, D’Ascola A, Scuruchi M, Mandraffino G, Calatroni A, Saitta A, et al. Hyaluronan in experimental injured/inflamed cartilage: in vivo studies. Life Sci. (2018) 193:132–40. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2017.11.006
12. Wang CC, Wang CT, Tsai KL, Chou CL, Chao JK, Huang HY, et al. Effect of ultrasound-detected synovitis on therapeutic efficacy of hyaluronic acid injection for symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. Rheumatol (United Kingdom). (2021) 60(10):4486–94. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab020
13. De Lucia O, Pierannunzii LM, Pregnolato F, Verduci E, Crotti C, Valcamonica E, et al. Effectiveness and tolerability of repeated courses of viscosupplementation in symptomatic hip osteoarthritis: a retrospective observational cohort study of high molecular weight vs. medium molecular weight hyaluronic acid vs. no viscosupplementation. Front Pharmacol. (2019) 10:1–10. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01007
14. Altman R, Alarcón G, Appelrouth D, Bloch D, Borenstein D, Brandt K, et al. The American college of rheumatology criteria for the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis of the hip. Arthritis Rheum. (1991) 34(5):505–14. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340502
15. Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS. Radiological assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis. (1957) 16(4):494–502. doi: 10.1136/ard.16.4.494
16. Kohn MD, Sassoon AA, Fernando ND. Classifications in brief: Kellgren-Lawrence classification of osteoarthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. (2016) 474(8):1886–93. doi: 10.1007/s11999-016-4732-4
17. Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Naden RL, Felson DT, Aggarwal R, et al. 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American college of rheumatology/European league against rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. (2010) 62(9):2569–81. doi: 10.1002/art.27584
18. Taylor W, Gladman D, Helliwell P, Marchesoni A, Mease P, Mielants H, et al. Classification criteria for psoriatic arthritis: development of new criteria from a large international study. Arthritis Rheum. (2006) 54(8):2665–73. doi: 10.1002/art.21972
19. Dubreuil M, Rahman P, Inman RD. Special article: axial spondyloarthritis classification criteria. J Rheumatol. (2017) 44(6):755–8. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.161196
20. Petty RE, Southwood TR, Manners P, Baum J, Glass DN, Goldenberg J, et al. International league of associations for rheumatology classification of juvenile idiopathic arthritis: second revision, Edmonton, 2001. J Rheumatol. (2004) 31(2):390–2.14760812
21. Dasgupta B, Cimmino MA, Maradit-Kremers H, Schmidt WA, Schirmer M, Salvarani C, et al. 2012 provisional classification criteria for polymyalgia rheumatica. Ann Rheum Dis. (2012) 71(4):484–91. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200329
22. De Lucia O, Murgo A, Pregnolato F, Pontikaki I, De Souza M, Sinelli A, et al. Hyaluronic acid injections in the treatment of osteoarthritis secondary to primary inflammatory rheumatic diseases: a systematic review and qualitative synthesis. Adv Ther. (2020) 37(4):1347–59. doi: 10.1007/s12325-020-01256-7
23. De Lucia O, Luppino AF, Pregnolato F, Murgo A, Pontikaki I, Gattinara M, et al. Hyaluronic acid therapy in hip OA does not perform equally in osteoarthritis secondary to juvenile idiopathic arthritis when compared to primary osteoarthritis: a 2-year preliminary evaluation. Adv Ther. (2022) 39(3):1267–78. doi: 10.1007/s12325-021-02020-1
24. Rania BA, Hanene F, Mariam M, Dorra BN, Wafa T, Kaouther M, et al. Predictive factors of hip involvement in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Rheumatology. (2022) 61(Supplement_2):keac496.019. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keac496.019
25. Boutry N, Khalil C, Jaspart M, Marie-Hélène V, Demondion X, Cotten A. Imaging of the hip in patients with rheumatic disorders. Eur J Radiol. (2007) 63(1):49–58. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2007.03.021
26. Migliore A, Martin LSM, Alimonti A, Valente C, Tormenta S. Efficacy and safety of viscosupplementation by ultrasound-guided intra-articular injection in osteoarthritis of the hip. Osteoarthr Cartil. (2003) 11(4):305–6. doi: 10.1016/S1063-4584(03)00008-6
27. Coutinho De Almeida R, Mahfouz A, Mei H, Houtman E, den Hollander W, Soul J, et al. Identification and characterization of two consistent osteoarthritis subtypes by transcriptome and clinical data integration. Rheumatology (Oxford). (2021) 60(3):1166–75. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa391
28. Snelling SJB, Bas S, Puskas GJ, Dakin SG, Suva D, Finckh A, et al. Presence of IL-17 in synovial fluid identifies a potential inflammatory osteoarthritic phenotype. PLoS One. (2017) 12(4):1–13. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175109
29. Schaible HG. Nociceptive neurons detect cytokines in arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. (2014) 16(1):1–9. doi: 10.1186/s13075-014-0470-8
30. Long DM, Fitzpatrick J. Safety and efficacy of a single intra-articular injection of hyaluronic acid in osteoarthritis of the hip: a case series of 87 patients. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. (2021) 22(1):1–7. doi: 10.1186/s12891-021-04672-0
Keywords: hip osteoarthritis, hyaluronic acid, rheumatic diseases, rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthritis, polymyalgia reumática, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, psoriatic arthritis
Citation: De Lucia O, Artusi C, Cumbo E, Trignani G, Sette M, Ferrito M, Perino M, Ingrao L, Amati A, Murgo A and Caporali R (2025) Hyaluronic acid therapy in hip osteoarthritis: differential efficacy in secondary osteoarthritis due to inflammatory rheumatic diseases vs. primary osteoarthritis—a step toward phenotyping osteoarthritis. Front. Musculoskelet. Disord. 3:1668235. doi: 10.3389/fmscd.2025.1668235
Received: 22 July 2025; Accepted: 6 October 2025;
Published: 24 October 2025.
Edited by:
Emanuele Bizzi, Vita-Salute San Raffaele University, ItalyReviewed by:
Angela Mauro, ASST Fatebenefratelli-Sacco, ItalyMartina Sandini, University of Milan, Italy
Copyright: © 2025 De Lucia, Artusi, Cumbo, Trignani, Sette, Ferrito, Perino, Ingrao, Amati, Murgo and Caporali. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Orazio De Lucia, b3JhemlvLmRlbHVjaWFAYXNzdC1waW5pLWN0by5pdA==
 Orazio De Lucia
Orazio De Lucia Carolina Artusi1
Carolina Artusi1 Matteo Ferrito
Matteo Ferrito Roberto Caporali
Roberto Caporali