- 1Rehabilitation and Exercise Science Laboratory (RESlab), Department of Business Economics, Health and Social Care (DEASS), University of Applied Sciences and Arts of Southern Switzerland (SUPSI), Landquart, Switzerland
- 2Departement of Neurosurgery, Cantonal Hospital Graubuenden, Chur, Switzerland
- 3Departement of Physiotherapy, International University of Applied Sciences THIM, Landquart, Switzerland
- 4Departement of Neurosciences and Movement Science, University of Fribourg, Fribourg, Switzerland
- 5Departement of Movement and Sport Sciences, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Brussels, Belgium
- 6Department of Business Economics, Health and Social Care (DEASS), University of Applied Sciences and Arts of Southern Switzerland (SUPSI), Manno, Ticino, Switzerland
- 7Departement of Health, Bern University of Applied Sciences, Berne, Switzerland
Introduction: Evidence regarding the diagnostic accuracy of physical assessments and patient-reported outcome measures in lumbar disc herniation with radiculopathy remains inconclusive. This study aimed to evaluate whether selected patient-reported outcome measures and physical assessments accurately reflect treatment progress, regardless of whether the treatment was conservative only or combined with surgery.
Methods: Mobility, isometric strength, pain, numbness, paresthesia, Oswestry Disability Index, International Physical Activity Questionnaire, straight-leg raising test, and the Short Form-36 Health Survey physical and mental components were recorded at baseline, after six weeks, and at six months.
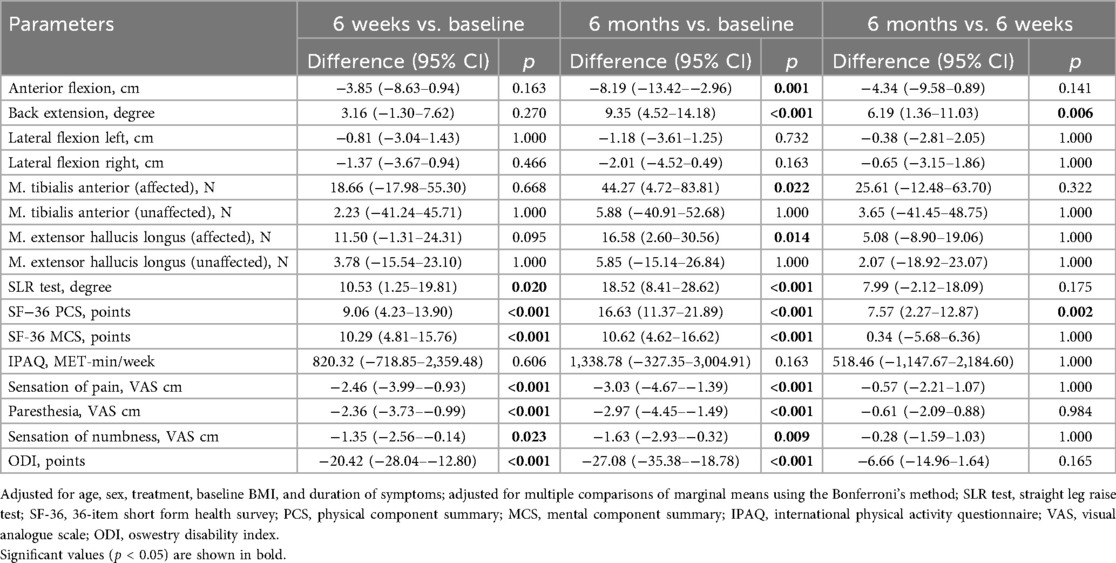
Results: At six weeks (n = 19), significant improvements were observed in the straight-leg raising test (mean difference: 10.53, 95% CI: 1.25–19.81, p = 0.02), the Short Form-36 Health Survey physical component score (9.06, 95% CI: 4.23–13.90, p < 0.001), and the mental component score (10.29, 95% CI: 4.81–15.76, p < 0.001), pain sensation (−2.46, 95% CI: −3.99–−0.93, p < 0.001), paresthesia (−2.36, 95% CI: −3.73–−0.99, p < 0.001), numbness (−1.35, 95% CI: −2.56–−0.14, p = 0.023), and in the Oswestry Disability Index score (−20.42, 95% CI: −28.04–−12.80, p < 0.001). At six months (n = 15), significant benefits were noted in anterior flexion (−8.19, 95% CI: −13.42–−2.96, p = 0.001), back extension (9.35, 95% CI: 4.52–14.18, p < 0.001), and muscle strength in the affected leg (tibialis anterior muscle: 44.27, 95% CI: 4.72–83.81, p = 0.024; extensor hallucis longus muscle: 16.58, 95% CI: 2.60–30.56, p = 0.02). No significant changes occurred in lateral flexion left or right, strength in the unaffected leg, or the International Physical Activity Questionnaire.
Conclusion: The exploratory findings of this study indicate that subjective outcomes improve earlier than objective measures. These findings emphasize the value of combining subjective and objective methods to monitor treatment outcomes and assess progress effectively. Larger studies with more participants, frequent evaluations, and longer follow-up are needed to clarify recovery patterns, determine the most sensitive outcome measures, and define minimal clinically important differences for patients with lumbar disc herniation with radiculopathy.
1 Introduction
Low back pain (LBP) is a major global public health concern, affecting an estimated 619 million people across all age groups in 2020 (1, 2). Despite recovery from an initial episode, approximately one in three individuals experience a recurrence within one year (3). Lumbar radiculopathy (LR) represents one of the most frequent clinical presentations in spine surgery. Its annual incidence has been estimated at 4.9 cases per 1,000 person-years, with a lifetime risk of 3%–5% in the general population (4). The most common cause of LR and radicular pain is lumbar disc herniation (LDH), particularly at the L4–S1 level (5, 6). Diagnosis is typically established through a combination of symptoms and signs indicative of compression or irritation of the lumbar spinal nerve root, such as radicular pain with signs of nerve root tension, neurological deficits, and imaging results that align with the clinical syndrome (7, 8). This is crucial because imaging alone is insufficient, as degenerative findings on MRI are common in asymptomatic or those with atypical symptoms (9). This underscores the need for reliable clinical outcome measures to correlate with the patient's clinical picture. However, the overall diagnostic accuracy of most physical tests for detecting lumbar disc herniation associated with radiculopathy (LDHR) is limited, particularly when applied in isolation (8, 10). Equally important, the patient's perspective is essential for evaluating disease burden and treatment outcomes (11). However, most outcome measures have been developed or extensively validated in surgical and chronic LBP populations, limiting their applicability to specific conditions such as LDHR and conservative treatment (12, 13). In spine surgery, over 200 unique patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) have been described, yet there is no standardization or guideline regarding which instruments should be used for specific spinal conditions or treatments (13). Treatment of LDHR includes both non-surgical and surgical interventions, and in clinical practice, it is often initially unclear which approach a patient will ultimately receive (14–17). Therefore, it is essential to define outcome measures that can be consistently applied across various treatment modalities. Such measures allow consistent monitoring of patient progress, facilitate communication among healthcare providers and patients, and support treatment decision-making. The first step in this process is to evaluate which commonly used outcome measures effectively capture changes over time in patients with LDHR. Observational studies provide an important foundation for this by identifying which outcome measures are sensitive to change, highlighting potential limitations, and generating hypotheses for future research. Accordingly, this observational study focused on evaluating which outcome measures change significantly over time, independent of whether patients received conservative care alone or a combination of conservative and surgical treatment. The objective of this study was to monitor changes of commonly used physical assessments and well-accepted PROMs in patients with LDHR over six months of treatment.
2 Methods
2.1 Design and selection criteria
We prospectively recruited patients with LDHR with or without radicular pain diagnosed by a neurosurgeon during consultations at the Cantonal Hospital of Graubuenden between October 2018 and December 2019 for this observational study. Physical assessment was done to diagnose LR; an MRI was performed to confirm the presence of an LDH, the direction of displacement, and the corresponding lesion level. All patients included in this study received physiotherapy at the Cantonal Hospital Graubünden, regardless of whether they had undergone surgery beforehand. Physiotherapists were instructed to apply standard physiotherapy methods such as manual therapy, mobilization, and exercise therapy. A treatment protocol was completed by the physiotherapists; however, individual treatment sessions were not further analyzed in this study, as the primary aim was to investigate the progression of outcome measures independent of the specific treatment provided. Patients who did not understand or speak German were excluded from the study. Participation in the study did not interfere with the patient's regular physiotherapeutic and medical treatment. The study was approved by the local ethics committee of Zurich, Switzerland (BASEC no.: 2018-00637). All participants signed a written study information and informed consent form.
2.2 Procedure
Demographic information and baseline data were collected one week before surgery for surgical patients and shortly after the first neurosurgical consultation for conservatively treated patients. The two follow-up measurements were taken six weeks and six months after surgery or baseline. All tests were conducted by experienced physiotherapists specifically trained for this project. Self-report questionnaires were administered by the researcher and completed by the patient on the three assessment dates.
2.3 Observed parameters
2.3.1 Demographics
Age, sex, type of treatment, and duration of pain were recorded. Body height (cm) was measured in an upright position with the back against a wall using an inelastic tape measure (Prym, Stolberg, Germany); body weight (kg) was recorded using a body scale (Tanita TBF-611, Tanita Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). Body mass index (BMI) was calculated using the formula: body weight (kg)/height (m)2.
2.3.2 Mobility
The fingertip-to-floor (FTF) test (cm) was used to assess the lumbar maximal anterior and lateral flexion. The FTF is simple to assess and has high responsiveness, validity, and reliability for forward bending (total lumbo-pelvic range) in patients with LBP (18). Extension (°) was measured using a baseline bubble inclinometer (Fabrication Enterprises, Inc., White Plains, NY). Patients performed maximal extension, flexion, and lateral flexion up to the pain threshold, keeping the elbows, fingers, and knees straight and the heels together. The contralateral hip remained in contact with the treatment table during lateral flexion.
2.3.3 Maximal isometric strength
The hand-held dynamometer (HHD) test is a reliable and valid tool for assessing muscle strength and is convenient in a clinical setting due to its ease of use, low cost, and compact size (19). Maximal isometric strength was tested using the NOD HHD (NOD, OT Bioelettronica s.r.l., Turin, Piedmont, Italy). An active strength test of the primary innervated muscle [L3: M. quadriceps femoris; L4: M. quadriceps femoris; M. tibialis anterior (TA); L5: M. TA; M. extensor hallucis longus (EHL); S1: M. gastrocnemius; M. triceps surae] was performed for 3 s using a standardized procedure adapted from Mentiplay et al. (20). The mean of the two closest of three values (N) was used for further analysis.
2.3.4 Neurodynamic
Nerve tension of the affected spinal nerve root was assessed using the straight leg raise (SLR) pain provocation test (21). The SLR demonstrates high sensitivity in surgical studies of patients with LDH (22), but its specificity is considered low, and findings from non-surgical cohorts do not confirm the same level of sensitivity (8, 23, 24). Nevertheless, as the SLR is recommended for diagnosing LDHR, it was included in our study (7, 25). A baseline bubble inclinometer was placed directly above the patella to measure the angle (°) between the examination table and the elevated limb.
2.3.5 Sensory deficits
Patients reported their current intensity of pain, paresthesia, and numbness using a unidimensional 10 cm visual analogue scale (VAS) (26). The VAS ranged from one endpoint with a happy face, indicating “no pain”, to the other endpoint with a sad face, indicating “worst possible pain”. Patients were asked to place a slider on the 10 cm line corresponding to the intensity of pain they were experiencing. The distance in centimeters from the low end of the VAS to the patient's mark was used as a numerical measure of pain severity. This procedure was repeated separately for paresthesia and numbness. Despite evidence suggesting that the measurement properties of VAS and other unidimensional pain rating scales have limitations in capturing the complexity of LBP (27), they remain the most widely recommended and practical tool for tracking pain intensity in clinical and research settings (28).
2.3.6 Disability
Disability was assessed using the German version of the Oswestry Disability Index (ODI), a reliable and valid questionnaire based on the English version 2.1 (29). In accordance with the scoring system recommended by Fairbank et al. (2000), if more than one item was marked, the highest score was used (30).
2.3.7 Health-related quality of life (HRQOL)
General health was evaluated using the German version 2.0 of the 36-item Short Form Health Survey (SF-36). The SF-36 questionnaire has been shown to provide the best balance between length, reliability, validity, responsiveness, and experience in patients with LBP (31).
2.3.8 Physical activity
Physical activity was assessed using the self-administered short German version of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) with a “last 7 days recall”. The IPAQ demonstrates acceptable measurement properties in terms of repeatability, validity, and reliability (32). Data were processed and analyzed according to the official IPAQ scoring protocol [in metabolic equivalents of task (MET)] and reported in MET minutes per week (33).
2.4 Data analysis
Continuous variables are reported as means and standard deviations (SDs), and categorical variables as frequencies and proportions. To assess changes in outcome measures over time, linear mixed-effects models (LMMs) were fitted using restricted maximum likelihood (REML) estimation. A random intercept for participants was included to account for repeated measurements within individuals. Time was treated as the main fixed effect, with age, sex, treatment type, baseline BMI, and symptom duration included as additional fixed effects to control for their potential influence on outcomes. Following the LMM analysis, pairwise comparisons (6 weeks vs. baseline, 6 months vs. baseline, and 6 months vs. 6 weeks) were conducted to further explore time effects. Bonferroni correction was applied to adjust for multiple comparisons. To measure the magnitude of the difference between time points, we reported Cohen's d effect size, which has been added as supplementary material (Supplementary Table S1). A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
All data were recorded in Microsoft Excel (version 16.75.2, Microsoft Corp., Redmond, WA), and statistical analyzes were performed using Stata (Stata Statistical Software: Release 18.0, College Station, TX: StataCorp LP).
3 Results
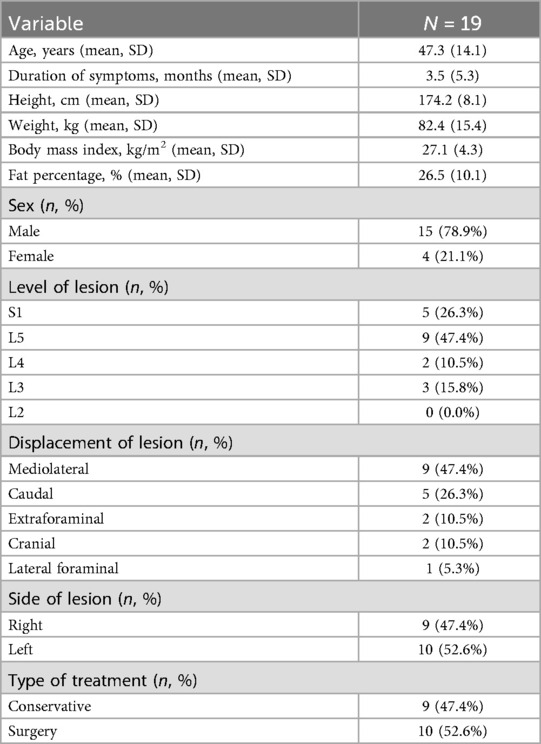
Nineteen patients aged 20–80 met the inclusion criteria, four patients missed the six-month follow-up. One participant failed to answer questions 4b–d of the SF-36 questionnaire at the six-week follow-up and questions 5b–c at both follow-ups, leading to missing values in the two summary scales physical (PCS) and mental component summary (MCS). One baseline value for M. tibialis anterior was missing. Due to the small subgroups (L3: n = 3, S1: n = 4), the maximal isometric strengths of the quadriceps femoris muscle and triceps surae muscle were excluded from the analysis.
The demographic characteristics of the patients are presented in Table 1, while the summary estimates (mean ± SD) of all outcome parameters at each time point are shown in Table 2. LMM analysis revealed significant improvements after six weeks in the SLR test (mean difference: 10.53°, 95% CI: 1.25–19.81; Cohen's d: 0.88, 95% CI: 0.19–1.57), SF-36 PCS (9.06 points, 95% CI: 4.23–13.90; Cohen's d: 1.49, 95% CI: 0.73–2.24), SF-36 MCS (10.29 points, 95% CI: 4.81–15.76; Cohen's d: 1.49, 95% CI: 0.74–2.25), sensation of pain (−2.46 cm, 95% CI: −3.99–−0.93; Cohen's d: −1.25, 95% CI: −1.97–−0.54), paresthesia (−2.36 cm, 95% CI: −3.73–−0.99; Cohen's d: −1.34, 95% CI: −2.06–−0.62), numbness (−1.35 cm, 95% CI: −2.56–−0.14; Cohen's d: −0.87, 95% CI: −1.55–−0.18), and ODI scores (−20.42 points, 95% CI: −28.04–−12.80; Cohen's d: −2.08, 95% CI: −2.88–−1.28) (Table 3 and Supplementary Table S1). While most variables showed slight additional improvement up to 6 months, only the SF-36 PCS demonstrated a statistically significant further increase between the six-week and six-month assessments (7.57 points, 95% CI: 2.27–12.87; Cohen's d: 1.24, 95% CI: 0.45–2.03). Additionally, at the six-month follow-up, anterior flexion (−8.19 cm, 95% CI: −13.42–−2.96; Cohen's d: −1.33, 95% CI: −2.11–−0.55), back extension (9.35°, 95% CI: 4.52–14.18; Cohen's d: 1.63, 95% CI: 0.83–2.43), and muscle strength in the affected leg for TA (44.27 N, 95% CI: 4.72–83.81; Cohen's d: 1.28, 95% CI: 0.18–2.37) and EHL (16.58 N, 95% CI: 2.60–30.56; Cohen's d: 1.46, 95% CI: 0.21–2.71) demonstrated significant improvement. No significant changes were observed over the treatment period for left lateral flexion (LLF) and right lateral flexion (RLF), muscle strength in the unaffected leg (TA and EHL), or physical activity (IPAQ).
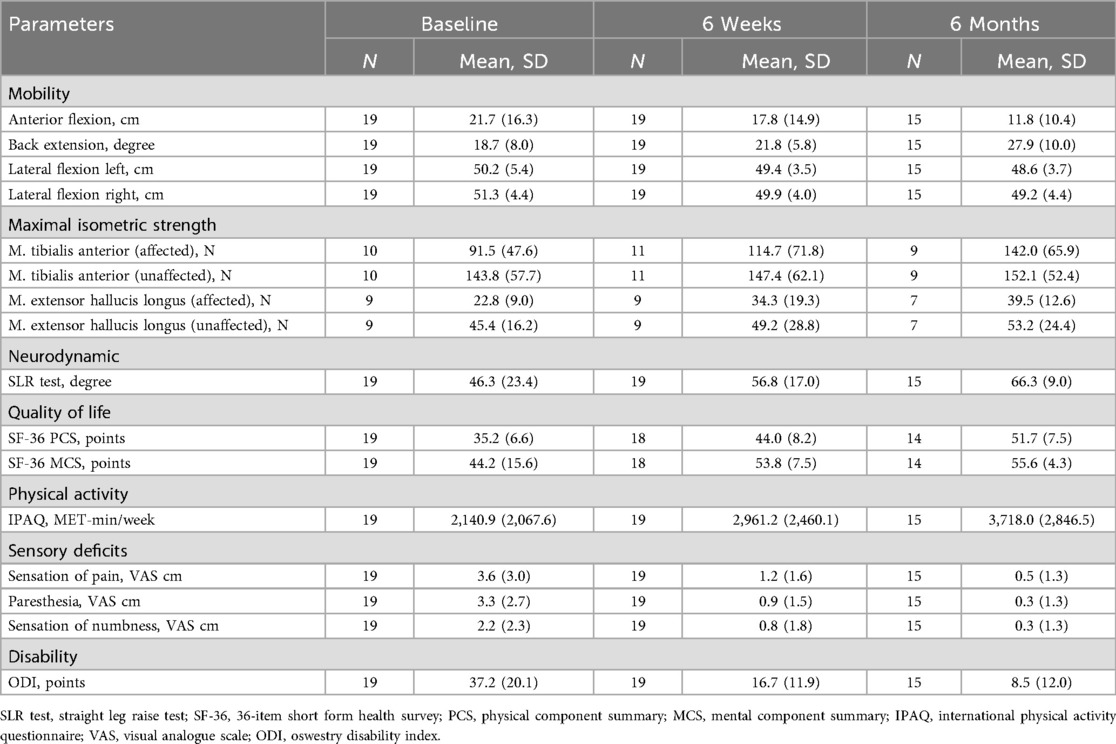
Table 2. Descriptive statistics (mean ± SD) of the mobility, maximal isometric strength, neurodynamic, quality of life, physical activity, sensory deficits, and disability by time points (baseline, 6 weeks, and 6 months).
4 Discussion
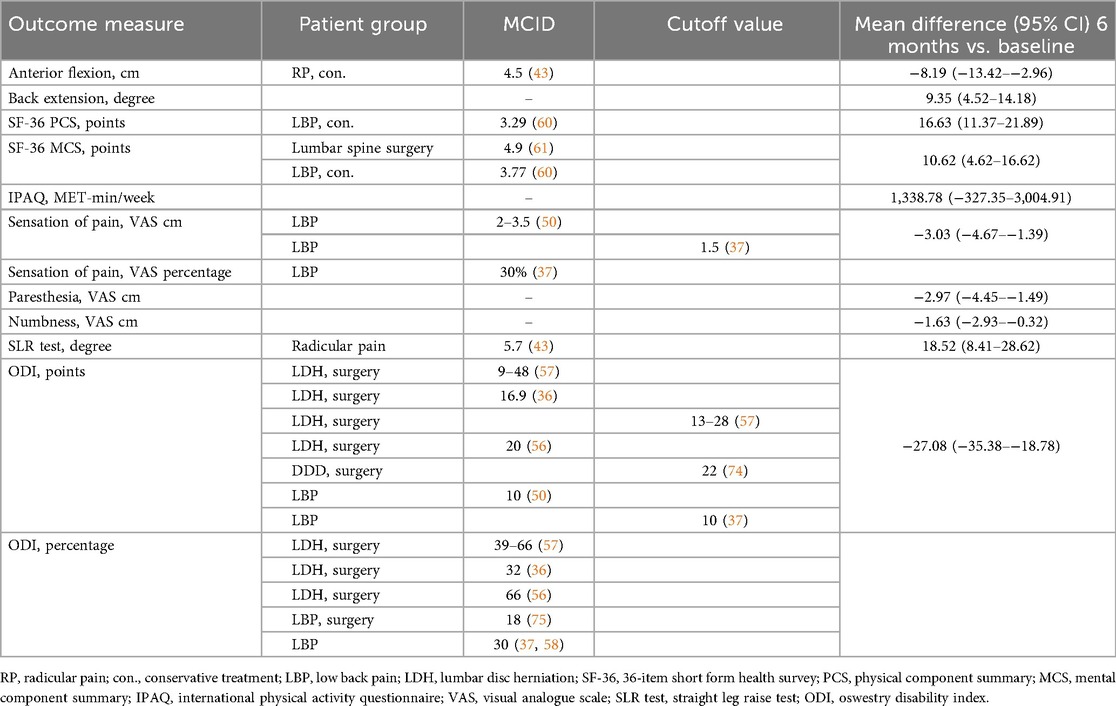
All subjective PROMs investigated in this study, showed significant improvement as early as six weeks after treatment initiation, with the exception of the IPAQ. In contrast, most objective physical assessment parameters demonstrated notable improvements only after six months of treatment. No improvements were observed in lateral flexion. However, more important than statistical significance is the clinical relevance of the treatment-related improvement (34). In this study, the observed effect sizes were notably large, particularly for the ODI and SF-36 PCS, indicating a potentially clinically meaningful benefit. To interpret the clinical relevance of these changes, the minimum clinically important differences (MCIDs) reported in previous studies can serve as a useful benchmark. However, MCIDs can vary depending on the methodology used for their calculation, the timing of follow-up assessments, and the characteristics of the study population (35). Therefore, applying generic MCIDs across different pathologies is not recommended (36). Nevertheless, MCIDs specific to LDHR, particularly in conservatively treated patients, are lacking. In such cases, insights can be drawn from studies involving surgically treated LDH patients or broader low back pain populations (Table 4). A consensus group of experts has proposed MCID for pain and functional status in patients with low back pain, offering guidance in interpreting the mean differences observed in this study (37).
4.1 Mobility
Not only did forward flexion improve significantly throughout the treatment [−8.19 cm (95% CI: −13.42–−2.96)], but back extension also demonstrated significant improvement [9.35° (95% CI: 4.52–14.18)], suggesting that both were restricted at baseline. Many clinical practice guidelines for LBP recommend assessing ROM as a routine diagnostic tool (25, 38). However, the diagnostic performance is equivocal, and its use remains controversial within the spine research community (7, 8, 39, 40). Studies evaluating ROM specifically in patients with LDHR are scarce. Typically, forward flexion is restricted, whereas back extension largely remains unaffected in patients with LBP and those diagnosed with LDH (39, 41, 42). However, in our study, improvements were observed not only in flexion but also in back extension. Ekedahl et al. (2012) established a MCID of 4.5 cm for the FTF test in patients presenting with radicular pain (43). In the present study, the mean improvement of 8.19 cm over the six-month treatment period exceeded this threshold, indicating a clinically meaningful change in trunk flexion among the LDHR cohort. LLF and RLF showed no significant change over the observed period, which contrasts with findings of Weitz (1981), who reported a significantly impaired lateral mobility to one side or the other in LDH patients (44). The results of this study emphasize that ROM measurements, particularly the FTF test, can capture statistically significant and clinically relevant changes and are useful for monitoring treatment progress in LDHR patients.
4.2 Maximal isometric strength
Muscle strength in the TA and EHL of the affected leg improved significantly over the six months of treatment [TA: 44.27 N (95 5 CI: 4.72–83.81); EHL: 16.58 N (95% CI 2.60–30.56)], while the same muscles in the unaffected leg remained unchanged. No studies to date have defined an MCID for muscle strength in patients with LDHR or comparable pathologies. Motor examination has shown a low accuracy in diagnosing LR (45) attributed to LDH (8), regardless of the test used or the LDH level (10). Weakness reported using the Sciatica Bothersomeness Index was found to be 2.4 times more prevalent than clinically observed weakness in the same individuals with sciatica (46). The lack of motor deficits, even in cases of severe LR, may be explained by the fact that spinal nerve damage often affects only a portion of the nerve fibers, while most muscles receive innervation from multiple spinal nerves (47). Furthermore, isometric tests are insufficient for evaluating muscle endurance or fatigue, which patients might perceive and report as weakness (46). However, PROMs primarily focus on pain and often fail to accurately quantify motor deficits (48). While the presence of motor deficits can aid in diagnosing LR and determining the affected level, their absence does not rule out the condition. Muscle strength may not be an ideal primary outcome measure for LDHR because motor examinations generally have low diagnostic accuracy, and the absence of established MCIDs makes it difficult to interpret the clinical relevance of observed changes.
4.3 Neurodynamic
Neurodynamic testing was the only physical examination parameter in our study that demonstrated significant improvement within the first six weeks of treatment with a mean change of 18.52° over the study period (95% CI 8.41–28.62). The sensitivity of the SLR test at baseline among the 17 patients reporting pain (two patients reported no pain) was moderate at 76% (13 positive tests). When restricted to patients with LDH at the L4-S1 level (n = 15), sensitivity remained unchanged at 73% (11 positive tests). The sensitivity of the SLR test in non-surgical LDH patients has demonstrated substantial heterogeneity across studies, ranging from 0.35–0.97 (8, 23, 24). The absence of consistently high sensitivity observed in surgically treated patients may reflect greater nerve root damage in this group, leading to increased responsiveness to nerve tension. This discrepancy may be explained by the fact that radicular pain arises not only from mechanical compression but also from inflammatory processes (49). Consequently, a positive SLR test may serve as a more sensitive indicator of the underlying inflammatory state than high-grade nerve compression alone (24). Other studies on the SLR indicate that its diagnostic utility may be overstated, and it may be more suitable for differential diagnosis or for detecting larger herniations that require surgical management (23). Our findings confirm the limited diagnostic accuracy of the SLR for LDHR, but they also demonstrate statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements over time, supporting its potential value as an outcome measure.
4.4 Sensory deficits
All three symptoms, leg pain (with or without accompanying back pain), paresthesia, and numbness, showed significant reductions throughout the course of treatment [pain: −3.03 cm (95% CI: −4.67–−1.39), paresthesia: −2.97 cm (95% CI: −4.45–−1.49), numbness: −1.63 cm (95% CI: −2.93–−0.32)], with improvements becoming evident as early as six weeks after therapy initiation. Ostelo et al. (2005) identified an MCID of 20 mm on a 0–100 mm VAS for patients with subacute or chronic low back pain, and 35 mm for acute cases (50). Additionally, a consensus group of experts proposed an absolute threshold of 1.5 cm on the VAS or a 30% improvement from baseline as clinically relevant for patients with back pain (37). These results are consistent with the findings of this study. The impact and progression of paresthesia and numbness are rarely reported (51), and no studies to date have specifically examined these symptoms in LDHR patients receiving conservative treatment. In surgical studies with LDH patients, leg pain is reported to be more bothersome than paresthesia or weakness (52), or numbness (53) and is considered a more reliable preoperative predictor of surgical outcomes compared to numbness and weakness (54). Following decompression surgery, leg pain has improved more rapidly (51, 55) and to a greater extent than numbness and paresthesia (51). Consistent with our findings, patients reported a substantial improvement in pain as early as six weeks after treatment. Paresthesia demonstrated gradual improvement, stabilizing at six months, whereas numbness improved more slowly and continued to progress one year after surgery (55). However, numbness and tingling are also reported as highly bothersome by a substantial portion of the population and may represent an underestimated burden (53). Leg pain is the most sensitive and reliable indicator of symptom relief, while paresthesia and numbness, though improving more gradually, remain clinically relevant and should be monitored as part of a comprehensive outcome assessment.
4.5 Disability
Disability, as measured by the ODI score, improved significantly within the first six weeks of treatment and the mean change over the entire treatment period was −27.08 points (95% CI: −35.38–−18.78). Studies involving surgically treated patients with LDH have reported absolute MCID values ranging from 9–48 points one year after surgery (36, 56, 57). The MCID has been shown to be influenced by baseline ODI scores, with higher initial disability associated with greater improvements (57). As a result, percentage changes are generally considered more appropriate than absolute changes when evaluating clinical relevance (36). In surgical studies involving patients with LDH, MCID values ranging from 32%–66% have been reported (36, 56, 57). Additionally, Asher et al. (2020) demonstrated that a 30% reduction in ODI scores, as also recommended by the consensus group of experts, more accurately predicts patient satisfaction one year after lumbar spine surgery than absolute changes (37, 58). The absolute and relative improvements observed in this study fall within the range of values reported in the surgical studies on LDH. Disability is regarded as a reliable clinical indicator of severity in low back disorders (59). The findings of this study suggest that the ODI is a relevant and reliable outcome measure for LDHR, capturing both statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements in disability over the course of treatment.
4.6 Health-related quality of life (HRQOL)
The two summary scales of the SF-36 questionnaire, mental health (MCS) and physical function (PCS), changed significantly as early as six weeks into the treatment. Over the entire treatment period, MCS increased by 10.62 points (4.62–16.62) and PCS by 16.63 points (11.37–21.89). Compared to normative values of the German population in 1994, baseline mean values for both sum scales in our study were lower than those of healthy individuals [PCS: 50.06 (10.33), MCS: 51.44 (8.24)] and aligned with values in patients with lumbar back pain [PCS: 35.22 (9.92), MCS: 47.81 (11.15)] (31). In conservatively treated LBP patients, MCIDs have been defined as improvements of 3.77 points for the MCS and 3.29 points for the PCS after one year of treatment (60), whereas a lumbar spinal surgery study reported a PCS improvement of 4.9 points at one year (61). The patients in this study exhibited substantially greater improvements. At six-month follow-up, mean values improved to levels comparable to those of healthy participants. The ability to compare PCS and MCS scores with normative data and MCIDs makes these two measures a reliable tool for assessing baseline limitations and monitoring progress in LDHR patients.
4.7 Physical activity
The IPAQ score did not demonstrate significant improvement over the six-month treatment period (mean difference: 1,338.78 MET-min/week (−327.35–3,004.91). Its sensitivity to detecting changes in physical activity depends on various factors, including the characteristics of the population studied (62). The validity and reliability of the IPAQ have not been evaluated in individuals with LDHR. In patients with chronic low back pain, the IPAQ long version has shown poor reliability compared to accelerometer data and tended to overestimate physical activity levels, suggesting limited validity (63). Consistent with these findings, the lack of significant change in our cohort may be attributed to multiple contributing factors. Although pain and other subjective outcomes may improve relatively early, actual physical activity is influenced by residual neurological deficits, muscle strength, endurance, and patient confidence in movement. Six months may not be sufficient for substantial changes in daily activity, as persistent restrictions and entrenched sedentary or avoidance behaviors can limit activity increases despite symptom improvement. Additionally, rehabilitation programs often focus on pain relief, range of motion, and functional capacity rather than overall daily activity, and unless exercise adherence outside the clinic is specifically encouraged, total activity levels may not rise significantly. In this study, the IPAQ showed limited sensitivity for detecting changes in physical activity in LDHR patients over six months, likely due to its uncertain reliability and the multifactorial determinants of daily activity. It remains unclear whether significant improvements would be observed over a longer period, potentially supporting its use as a long-term outcome measure.
4.8 General
The primary goals of (surgical) interventions for degenerative spine diseases are to alleviate pain and improve function and HRQOL (64). Various PROMs have been developed to evaluate these variables, each targeting specific aspects such as pain intensity, disability, and HRQOL (12, 13). These tools aim to provide insights into the patient's subjective experience of their condition and the effectiveness of treatments. However, their interpretation can vary across individuals, contributing to their inherent limitations. PROMs have been criticized for their subjective nature, which can lead to issues with interrater and intra-rater reliability due to potential misinterpretation of scales or restricted comparability (64). However, the patient's perception of their disability can be affected by several negative psychological attributes, which are relevant in assessing the severity or outcome of treatment (65, 66). Nevertheless, there is a growing need for objective assessments to be integrated into clinical research and practice for patients with lumbar degenerative disc disease (64, 67). When evaluating spinal function, assessment of impairment primarily relies on comparisons with normative data. This contrasts with extremity evaluation, where impairment can more readily be determined by comparison with the unaffected contralateral side. In this study, we aimed not to compare objective and subjective outcome measures but to identify which outcome measures are effective for monitoring treatment progress in patients with LDHR independent of the treatment received. However, our findings indicated that significant changes were primarily observed in subjective PROMs after six weeks of treatment. In contrast, objective physical examination outcomes only showed significant improvement after a six-month follow-up. The SLR test was the only objective parameter that showed a statistically significant improvement as early as six weeks into the treatment. This finding should be considered when comparing subjective and objective parameters in future research. Since we have only conducted assessments at two time points, we cannot determine the exact time at which significant changes occur, or whether different variables require varying durations to exhibit measurable improvements. Moreover, the question arises as to whether traditional physical examinations are effective outcome measures for patients with LDHR, or if objective functional tests, such as the Timed Up and Go (TUG) or the Five-Repetition Sit-To-Stand test (5R-STS) (64, 68, 69), would provide better information. Today, there is no “gold standard” for objective functional testing for patients with lumbar degenerative disc disease (DDD) (68). Stienen et al. (2019) suggest that a combination of the TUG test, which is particularly sensitive in patients with predominant lumbar radicular pain, and 5R-STS, which is responsive in those experiencing LBP, might be a reasonable approach for patients with DDD. However, the authors emphasize that while objective measures can contribute to evaluating treatment outcomes, they cannot fully replace PROMs (68). This study confirms this.
This study had some limitations. Calculating traditional effect sizes in the context of mixed-effects models presents substantial challenges due to the presence of random effects. These random effects partition the variance across multiple levels (e.g., within-subject and between-subject variance), which complicates the computation and interpretation of standardized effect size statistics such as Cohen's d. Traditional effect size metrics assume a single, pooled standard deviation, but in multilevel models, variance is not uniform, making it difficult to determine whether an effect is “large” at the participant level, the measurement level, or both. As a result, Cohen's d and similar standardized effect sizes may not fully capture the complexity of the underlying data structure (70, 71).
With only 19 patients, the sample size of this study was small, which limits statistical power to detect small or moderate effects. Consequently, the study might not reach statistical significance even when improvements in outcome measures are present (72, 73). Furthermore, the limited sample may not be representative of the broader LDHR population, particularly given heterogeneity in age, symptom severity, and comorbidities. In small samples, individual outliers can disproportionately influence results, potentially affecting both means and variance estimates. Analyses of subgroup effects, such as lesion level or displacement direction, cannot be reliably performed in this context. Therefore, the findings of this study should be considered exploratory and interpreted with caution. Emphasis is placed on observed trends, and confirmation in larger, more diverse cohorts is warranted. We measured at only two time points: after six weeks and after six months. While these assessments capture overall changes, they do not allow precise characterization of the time course of improvements. Intermediate changes, fluctuations, or temporary regressions in symptoms or function could not be detected. Consequently, we cannot determine when the most substantial improvements occur or whether changes follow a linear or non-linear trajectory. Extending the study period to one year with additional intermediate measurements would provide a more complete understanding of improvements beyond the six-month observation window. Furthermore, sparse measurement points limit the statistical modeling of longitudinal trends and reduce the ability to evaluate the rate of improvement or the time required to reach clinically meaningful thresholds. Moreover, it remains uncertain which subjective PROMs and objective assessments are the most reliable and effective outcome measures for evaluating treatment success, or whether alternative physical examinations may offer better insights. Despite these limitations, the observed trends provide valuable preliminary evidence, allowing some conclusions to be drawn from the results and offering essential information for planning subsequent cohort studies or randomized controlled trials, particularly those aimed at evaluating treatment effectiveness and optimizing outcome measurement in this patient population. Future research should focus on identifying the most effective subjective PROMs and objective assessments for evaluating treatment success in patients with LDHR, regardless of the treatment procedure. Additionally, MCIDs should be established for the relevant outcomes in this patient group. Studies incorporating more frequent measurement intervals could provide deeper insight into the temporal progression of the outcomes. Furthermore, it is essential to evaluate whether current examination methods are adequate or if alternative tests, such as the TUG or Motorized Treadmill Test, provide a more accurate reflection of improvements (68, 69).
This investigation demonstrated that many well-established PROMs and physical assessments in clinical spine treatment effectively capture treatment success in patients diagnosed with LDHR, regardless of whether they undergo conservative management or surgery. Subjective PROMs investigated in this study showed significant improvement as early as six weeks after initiation, while in contrast, most of the objective examination parameters demonstrated notable improvements only after six months of treatment.
5 Conclusion
The exploratory findings of this observational study indicate that subjective outcome parameters tend to show significant changes earlier than objective measures. These findings underscore the complementary role of subjective and objective evaluation methods in monitoring treatment outcomes, highlighting the importance of combining both approaches to effectively assess treatment progress. Future investigations with larger cohorts, more frequent assessments, and extended follow-up periods are warranted to better characterize the trajectory of recovery, identify the most reliable and sensitive outcome measures, and establish minimal clinically important differences (MCIDs) for patients with LDHR.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The study involving humans was approved by Ethics committee of Zurich, Switzerland. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
GB: Data curation, Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CZ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Supervision. EH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Validation. JARS: Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis. RC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Thim van der Laan Foundation for their support and Rahel Stoop as well as Carlina Deflorin for their practical assistance in the data assessment.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. AI-assisted technology (ChatGPT, May 2025 version) was employed to assist with ensuring the linguistic accuracy of the English language.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmscd.2025.1672539/full#supplementary-material
References
1. GBD 2021 Low Back Pain C. Global, regional, and national burden of low back pain, 1990–2020, its attributable risk factors, and projections to 2050: a systematic analysis of the global burden of disease study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. (2023) 5(6):e316–e29. doi: 10.1016/s2665-9913(23)00098-x
2. Hoy D, Bain C, Williams G, March L, Brooks P, Blyth F, et al. A systematic review of the global prevalence of low back pain. Arthritis Rheum. (2012) 64(6):2028–37. doi: 10.1002/art.34347
3. da Silva T, Mills K, Brown BT, Herbert RD, Maher CG, Hancock MJ. Risk of recurrence of low back pain: a systematic review. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. (2017) 47(5):305–13. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2017.7415
4. Berry JA, Elia C, Saini HS, Miulli DE. A review of lumbar radiculopathy, diagnosis, and treatment. Cureus. (2019) 11(10):e5934. doi: 10.7759/cureus.5934
5. Bogduk N. On the definitions and physiology of back pain, referred pain, and radicular pain. Pain. (2009) 147(1-3):17–9. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2009.08.020
6. Tarulli AW, Raynor EM. Lumbosacral radiculopathy. Neurol Clin. (2007) 25(2):387–405. doi: 10.1016/j.ncl.2007.01.008
7. Kreiner DS, Hwang SW, Easa JE, Resnick DK, Baisden JL, Bess S, et al. An evidence-based clinical guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation with radiculopathy. Spine J. (2014) 14(1):180–91. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2013.08.003
8. van der Windt DA, Simons E, Riphagen II, Ammendolia C, Verhagen AP, Laslett M, et al. Physical examination for lumbar radiculopathy due to disc herniation in patients with low-back pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2010) (2):Cd007431. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007431.pub2
9. Brinjikji W, Luetmer PH, Comstock B, Bresnahan BW, Chen LE, Deyo RA, et al. Systematic literature review of imaging features of spinal degeneration in asymptomatic populations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. (2015) 36(4):811–6. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4173
10. Al Nezari NH, Schneiders AG, Hendrick PA. Neurological examination of the peripheral nervous system to diagnose lumbar spinal disc herniation with suspected radiculopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine J. (2013) 13(6):657–74. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2013.02.007
11. Weldring T, Smith SM. Patient-Reported outcomes (PROs) and patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs). Health Serv Insights. (2013) 6:61–8. doi: 10.4137/hsi.S11093
12. Kowalski KL, Mistry J, Beilin A, Goodman M, Lukacs MJ, Rushton A. Physical functioning in the lumbar spinal surgery population: a systematic review and narrative synthesis of outcome measures and measurement properties of the physical measures. PLoS One. (2024) 19(8):e0307004. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307004
13. Guzman JZ, Cutler HS, Connolly J, Skovrlj B, Mroz TE, Riew KD, et al. Patient-reported outcome instruments in spine surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). (2016) 41(5):429–37. doi: 10.1097/brs.0000000000001211
14. Hahne AJ, Ford JJ, McMeeken JM. Conservative management of lumbar disc herniation with associated radiculopathy: a systematic review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). (2010) 35(11):E488–504. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181cc3f56
15. El Melhat AM, Youssef ASA, Zebdawi MR, Hafez MA, Khalil LH, Harrison DE. Non-surgical approaches to the management of lumbar disc herniation associated with radiculopathy: a narrative review. J Clin Med. (2024) 13(4):974. doi: 10.3390/jcm13040974
16. Awadalla AM, Aljulayfi AS, Alrowaili AR, Souror H, Alowid F, Mahdi AMM, et al. Management of lumbar disc herniation: a systematic review. Cureus. (2023) 15(10):e47908. doi: 10.7759/cureus.47908
17. Zaina F, Côté P, Cancelliere C, Di Felice F, Donzelli S, Rauch A, et al. A systematic review of clinical practice guidelines for persons with non-specific low back pain with and without radiculopathy: identification of best evidence for rehabilitation to develop the WHO’s package of interventions for rehabilitation. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. (2023) 104(11):1913–27. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2023.02.022
18. Perret C, Poiraudeau S, Fermanian J, Colau MM, Benhamou MA, Revel M. Validity, reliability, and responsiveness of the fingertip-to-floor test. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. (2001) 82(11):1566–70. doi: 10.1053/apmr.2001.26064
19. Stark T, Walker B, Phillips JK, Fejer R, Beck R. Hand-held dynamometry correlation with the gold standard isokinetic dynamometry: a systematic review. PMR. (2011) 3(5):472–9. doi: 10.1016/j.pmrj.2010.10.025
20. Mentiplay BF, Perraton LG, Bower KJ, Adair B, Pua YH, Williams GP, et al. Assessment of lower limb muscle strength and power using hand-held and fixed dynamometry: a reliability and validity study. PLoS One. (2015) 10(10):e0140822. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140822
21. Forst JJ. Contribution to the clinical study of sciatica. Arch Neurol. (1969) 21(2):220–1. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1969.00480140120016
22. Devillé WL, van der Windt DA, Dzaferagić A, Bezemer PD, Bouter LM. The test of Lasègue: systematic review of the accuracy in diagnosing herniated discs. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). (2000) 25(9):1140–7. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200005010-00016
23. Majlesi J, Togay H, Unalan H, Toprak S. The sensitivity and specificity of the slump and the straight leg raising tests in patients with lumbar disc herniation. J Clin Rheumatol. (2008) 14(2):87–91. doi: 10.1097/RHU.0b013e31816b2f99
24. Ekedahl H, Jönsson B, Annertz M, Frobell RB. Accuracy of clinical tests in detecting disk herniation and nerve root compression in subjects with lumbar radicular symptoms. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. (2018) 99(4):726–35. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2017.11.006
25. Phillips FM, Reider B, Mehta V. Lumbar spine. In: Reider B, editor. The Orthopaedic Physical Examination. 2 ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders (2005). p. 335–61.
26. Huskisson EC. Measurement of pain. Lancet. (1974) 2(7889):1127–31. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90884-8
27. Chiarotto A, Maxwell LJ, Ostelo RW, Boers M, Tugwell P, Terwee CB. Measurement properties of visual analogue scale, numeric rating scale, and pain severity subscale of the brief pain inventory in patients with low back pain: a systematic review. J Pain. (2019) 20(3):245–63. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2018.07.009
28. Chiarotto A, Boers M, Deyo RA, Buchbinder R, Corbin TP, Costa LOP, et al. Core outcome measurement instruments for clinical trials in nonspecific low back pain. Pain. (2018) 159(3):481–95. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001117
29. Mannion AF, Junge A, Fairbank JC, Dvorak J, Grob D. Development of a German version of the oswestry disability index. Part 1: cross-cultural adaptation, reliability, and validity. Eur Spine J. (2006) 15(1):55–65. doi: 10.1007/s00586-004-0815-0
30. Fairbank JC, Pynsent PB. The oswestry disability Index. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). (2000) 25(22):2940–52. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200011150-00017
31. Morfeld M, Kirchberger I, Bullinger M. SF-36 Fragebogen zum Gesundheitszustand: Deutsche Version des Short Form-36 Health Survey. 2nd ed Goettingen: Hogrefe (2011).
32. Craig CL, Marshall AL, Sjöström M, Bauman AE, Booth ML, Ainsworth BE, et al. International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Med Sci Sports Exerc. (2003) 35(8):1381–95. doi: 10.1249/01.Mss.0000078924.61453.Fb
33. Sjostrom M, Ainsworth B, Bauman A, Bull F, Hamilton-Craig C, Sallis J. Guidelines for Data Processing and Analysis of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ)—short and long forms (2005). Available online at: https://sites.google.com/view/ipaq/home (Accessed May 6, 2025).
34. Copay AG, Subach BR, Glassman SD, Polly DW Jr., Schuler TC. Understanding the minimum clinically important difference: a review of concepts and methods. Spine J. (2007) 7(5):541–6. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2007.01.008
35. Solomito MJ, Kia C, Makanji H. The minimal clinically important difference for the oswestry disability Index substantially varies based on calculation method: implications to value-based care. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). (2025) 50(10):707–12. doi: 10.1097/brs.0000000000005074
36. Power JD, Perruccio AV, Canizares M, McIntosh G, Abraham E, Attabib N, et al. Determining minimal clinically important difference estimates following surgery for degenerative conditions of the lumbar spine: analysis of the Canadian spine outcomes and research network (CSORN) registry. Spine J. (2023) 23(9):1323–33. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2023.05.001
37. Ostelo RWJG, Deyo RA, Stratford P, Waddell G, Croft P, Von Korff M, et al. Interpreting change scores for pain and functional status in low back pain: towards international consensus regarding minimal important change. Spine. (2008) 33(1):90–4. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e31815e3a10
38. Oliveira CB, Maher CG, Pinto RZ, Traeger AC, Lin CC, Chenot JF, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of non-specific low back pain in primary care: an updated overview. Eur Spine J. (2018) 27(11):2791–803. doi: 10.1007/s00586-018-5673-2
39. Mannion AF, Dvorak J, Müntener M, Grob D. A prospective study of the interrelationship between subjective and objective measures of disability before and 2 months after lumbar decompression surgery for disc herniation. Eur Spine J. (2005) 14(5):454–65. doi: 10.1007/s00586-004-0787-0
40. Katz RT. Impairment and disability rating in low back pain. Clin Occup Environ Med. (2006) 5(3):719–40. doi: 10.1016/j.coem.2006.03.001
41. Tibrewal SB, Pearcy MJ, Portek I, Spivey J. A prospective study of lumbar spinal movements before and after discectomy using biplanar radiography. Correlation of clinical and radiographic findings. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). (1985) 10(5):455–60. doi: 10.1097/00007632-198506000-00010
42. Zheng Z, Wang Y, Wang T, Wu Y, Li Y. A systematic review and meta-analysis on comparative kinematics in the lumbopelvic region in the patients suffering from spinal pain. J Healthc Eng. (2022) 2022:7369242. doi: 10.1155/2022/7369242
43. Ekedahl H, Jönsson B, Frobell RB. Fingertip-to-floor test and straight leg raising test: validity, responsiveness, and predictive value in patients with acute/subacute low back pain. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. (2012) 93(12):2210–5. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2012.04.020
44. Weitz EM. The lateral bending sign. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). (1981) 6(4):388–97. doi: 10.1097/00007632-198107000-00010
45. Tawa N, Rhoda A, Diener I. Accuracy of clinical neurological examination in diagnosing lumbo-sacral radiculopathy: a systematic literature review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. (2017) 18(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s12891-016-1383-2
46. Dove L, Baskozos G, Kelly T, Buchanan E, Schmid AB. Prevalence of weakness and factors mediating discrepancy between reported and observed leg weakness in people with sciatica. Eur Spine J. (2024) 33(11):4229–34. doi: 10.1007/s00586-024-08330-6
47. De Luigi AJ, Fitzpatrick KF. Physical examination in radiculopathy. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. (2011) 22(1):7–40. doi: 10.1016/j.pmr.2010.10.003
48. Stienen MN, Maldaner N, Sosnova M, Joswig H, Corniola MV, Regli L, et al. Lower extremity motor deficits are underappreciated in patient-reported outcome measures: added value of objective outcome measures. Neurospine. (2020) 17(1):270–80. doi: 10.14245/ns.1938368.184
49. Samuelly-Leichtag G, Eisenberg E, Zohar Y, Andraous M, Eran A, Sviri GE, et al. Mechanism underlying painful radiculopathy in patients with lumbar disc herniation. Eur J Pain. (2022) 26(6):1269–81. doi: 10.1002/ejp.1947
50. Ostelo RW, de Vet HC. Clinically important outcomes in low back pain. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. (2005) 19(4):593–607. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2005.03.003
51. Huang P, Sengupta DK. How fast pain, numbness, and paresthesia resolves after lumbar nerve root decompression: a retrospective study of patient’s self-reported computerized pain drawing. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). (2014) 39(8):E529–36. doi: 10.1097/brs.0000000000000240
52. Grøvle L, Haugen AJ, Keller A, Natvig B, Brox JI, Grotle M. The bothersomeness of sciatica: patients’ self-report of paresthesia, weakness and leg pain. Eur Spine J. (2010) 19(2):263–9. doi: 10.1007/s00586-009-1042-5
53. Hasvik E, Haugen AJ, Grøvle L. Symptom descriptors and patterns in lumbar radicular pain caused by disc herniation: a 1-year longitudinal cohort study. BMJ Open. (2022) 12(12):e065500. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-065500
54. Wang Y, Gao F, Zou H. Numbness and weakness recovered at a less extent in patients with lumbar disc herniation after percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy. Pain Res Manag. (2019) 2019:4642701. doi: 10.1155/2019/4642701
55. Sengupta DK. When does pain, paresthesia and numbness resolve following nerve root decompression in cervical and lumbar radiculopathy? A prospective study with Patients’ self-reported data. Spine J. (2013) 13(9):S160. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2013.07.405
56. Solberg T, Johnsen LG, Nygaard ØP, Grotle M. Can we define success criteria for lumbar disc surgery?: estimates for a substantial amount of improvement in core outcome measures. Acta Orthop. (2013) 84(2):196–201. doi: 10.3109/17453674.2013.786634
57. Werner DAT, Grotle M, Gulati S, Austevoll IM, Madsbu MA, Lønne G, et al. Can a successful outcome after surgery for lumbar disc herniation be defined by the oswestry disability Index raw score? Global Spine J. (2020) 10(1):47–54. doi: 10.1177/2192568219851480
58. Asher AM, Oleisky ER, Pennings JS, Khan I, Sivaganesan A, Devin CJ, et al. Measuring clinically relevant improvement after lumbar spine surgery: is it time for something new? Spine J. (2020) 20(6):847–56. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2020.01.010
60. Díaz-Arribas MJ, Fernández-Serrano M, Royuela A, Kovacs FM, Gallego-Izquierdo T, Ramos-Sánchez M, et al. Minimal clinically important difference in quality of life for patients with low back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). (2017) 42(24):1908–16. doi: 10.1097/brs.0000000000002298
61. Copay AG, Glassman SD, Subach BR, Berven S, Schuler TC, Carreon LY. Minimum clinically important difference in lumbar spine surgery patients: a choice of methods using the oswestry disability index, medical outcomes study questionnaire short form 36, and pain scales. Spine J. (2008) 8(6):968–74. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2007.11.006
62. Lee PH, Macfarlane DJ, Lam TH, Stewart SM. Validity of the international physical activity questionnaire short form (IPAQ-SF): a systematic review. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. (2011) 8(1):115. doi: 10.1186/1479-5868-8-115
63. Carvalho FA, Morelhão PK, Franco MR, Maher CG, Smeets R, Oliveira CB, et al. Reliability and validity of two multidimensional self-reported physical activity questionnaires in people with chronic low back pain. Musculoskelet Sci Pract. (2017) 27:65–70. doi: 10.1016/j.msksp.2016.12.014
64. Gautschi OP, Corniola MV, Schaller K, Smoll NR, Stienen MN. The need for an objective outcome measurement in spine surgery–the timed-up-and-go test. Spine J. (2014) 14(10):2521–2. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2014.05.004
65. Turner JA, Jensen MP, Romano JM. Do beliefs, coping, and catastrophizing independently predict functioning in patients with chronic pain? Pain. (2000) 85(1-2):115–25. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3959(99)00259-6
66. Mannion AF, Junge A, Taimela S, Müntener M, Lorenzo K, Dvorak J. Active therapy for chronic low back pain: part 3. Factors influencing self-rated disability and its change following therapy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). (2001) 26(8):920–9. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200104150-00015
67. Joswig H, Stienen MN, Smoll NR, Gautschi OP. Objective functional testing in patients with lumbar degenerative disc disease. Global Spine J. (2017) 7(4):384. doi: 10.1177/2192568217716153
68. Stienen MN, Ho AL, Staartjes VE, Maldaner N, Veeravagu A, Desai A, et al. Objective measures of functional impairment for degenerative diseases of the lumbar spine: a systematic review of the literature. Spine J. (2019) 19(7):1276–93. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2019.02.014
69. Klukowska AM, Schröder ML, Stienen MN, Staartjes VE. Objective functional impairment in lumbar degenerative disease: concurrent validity of the baseline severity stratification for the five-repetition sit-to-stand test. J Neurosurg Spine. (2020) 33(1):4–11. doi: 10.3171/2019.12.Spine191124
70. Lorah J. Effect size measures for multilevel models: definition, interpretation, and TIMSS example. Large-scale Assess Educ. (2018) 6(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s40536-018-0061-2
71. Groß J, Möller A. Effect size estimation in linear mixed models. METRON. (2025). doi: 10.1007/s40300-025-00295-w [Published online ahead of print].
72. Faber J, Fonseca LM. How sample size influences research outcomes. Dental Press J Orthod. (2014) 19(4):27–9. doi: 10.1590/2176-9451.19.4.027-029.ebo
73. Serdar CC, Cihan M, Yücel D, Serdar MA. Sample size, power and effect size revisited: simplified and practical approaches in pre-clinical, clinical and laboratory studies. Biochem Med (Zagreb). (2021) 31(1):010502. doi: 10.11613/bm.2021.010502
74. van Hooff ML, Mannion AF, Staub LP, Ostelo RW, Fairbank JC. Determination of the oswestry disability index score equivalent to a “satisfactory symptom state” in patients undergoing surgery for degenerative disorders of the lumbar spine-a spine Tango registry-based study. Spine J. (2016) 16(10):1221–30. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2016.06.010
Keywords: intervertebral disc displacement, physical examination, patient reported outcome measures, low back pain, lumbosacral region
Citation: Bianchi G, Zweifel C, Hohenauer E, Santos JAR and Clijsen R (2025) Reliable outcome parameters in patients with lumbar radiculopathy attributed to disc herniation: an observational study. Front. Musculoskelet. Disord. 3:1672539. doi: 10.3389/fmscd.2025.1672539
Received: 24 July 2025; Accepted: 7 October 2025;
Published: 21 October 2025.
Edited by:
Maruti Gudavalli, Keiser University, United StatesReviewed by:
Eric Chu, EC Healthcare, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaAhmed M. El Melhat, Cairo University, Egypt
Elvis Mahmutovic, State University of Novi Pazar, Serbia
Copyright: © 2025 Bianchi, Zweifel, Hohenauer, Santos and Clijsen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Giannina Bianchi, Z2lhbm5pbmEuZGlhc0BzdXBzaS5jaA==
 Giannina Bianchi
Giannina Bianchi Christian Zweifel
Christian Zweifel Erich Hohenauer
Erich Hohenauer Joseph Alvin Ramos Santos6
Joseph Alvin Ramos Santos6 Ron Clijsen
Ron Clijsen