- Department of Nephrology, Shenzhen Second People’s Hospital, The First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, China
Brucellosis is known to impact multiple organ systems in humans, including the urogenital system; however, the occurrence of glomerular diseases is relatively uncommon. In this study, we present the case of a 45-year-old man with no prior history of renal disease who developed gross hematuria, proteinuria, acute kidney injury, anemia, hypoproteinemia, pleural effusion, arthralgia, and lymphadenopathy following an acute Brucella infection. Renal biopsy revealed mesangial proliferative immunoglobulin A (IgA) nephropathy with partial crescents, classified as M1E0S0T0C2 according to the Oxford classification, in conjunction with Brucella spondylitis. The patient achieved complete remission after 4 months of anti-brucellosis therapy with doxycycline, levofloxacin, and rifampicin. In this paper, we present a case study of IgA nephropathy complicated by cellular crescent lesions resulting from acute Brucella infection, which completely resolved following anti-Brucella therapy. In addition, we review previously documented cases of Brucella-associated glomerular disease confirmed through renal biopsy, aiming to offer a reference for clinical diagnosis and treatment.
Introduction
Brucellosis represents the most widespread zoonotic disease globally, with its endemic regions progressively expanding, thereby constituting a major public health concern worldwide (1, 2). The highest incidence of human brucellosis is observed in Asia, particularly in China and Mongolia, which bear the greatest disease burden (3).
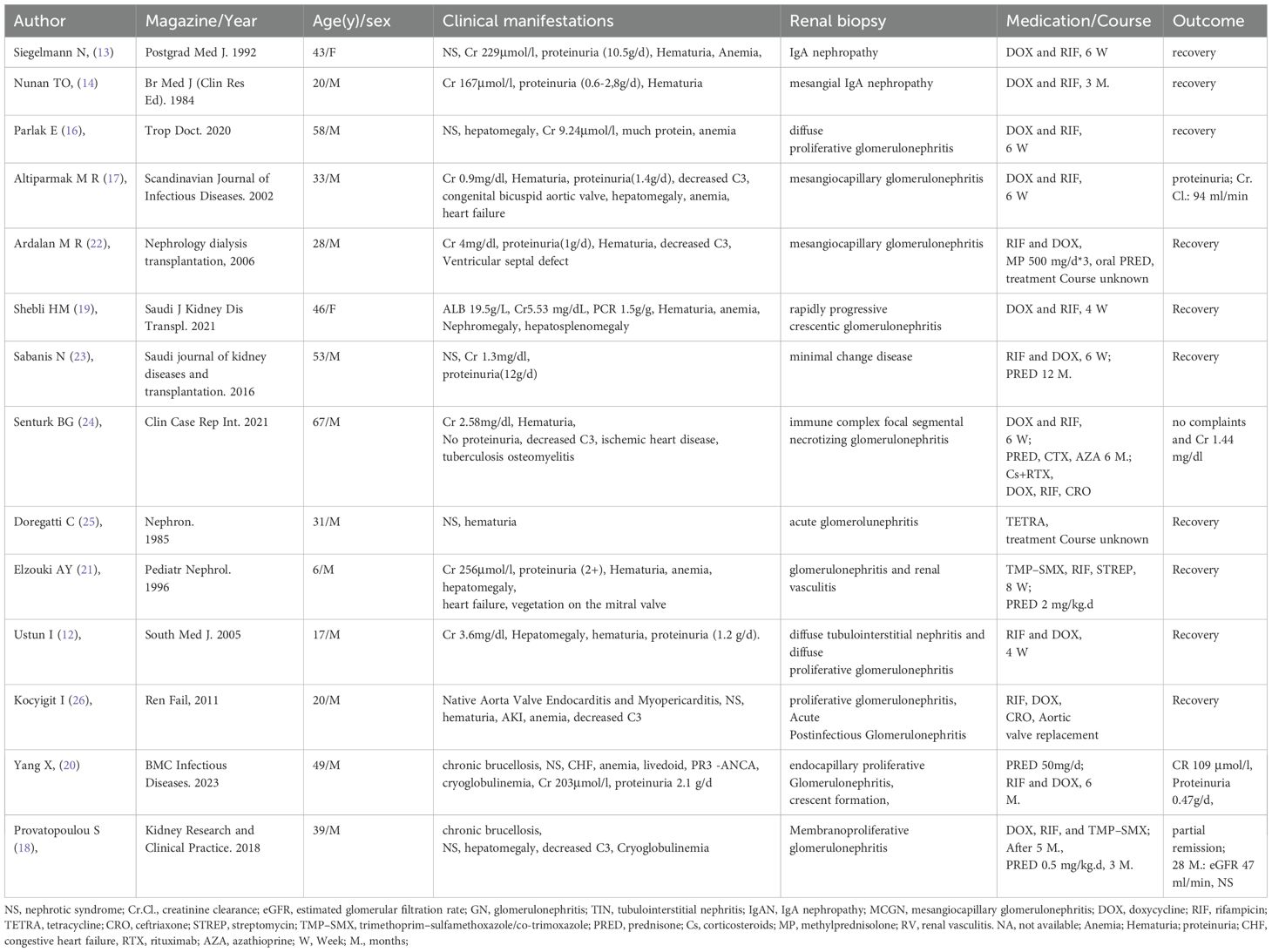
Brucella, a Gram-negative bacterium characterized as facultative intracellular, is the etiological agent responsible for brucellosis. Its primary virulence attribute lies in its ability to persist and replicate within host cells over extended periods, thereby evading detection and response by the host immune system. This capability is fundamental to sustaining its chronic infection (1, 2, 4). Humans can contract the disease through various transmission routes, including contact with infected animals and their secretions, consumption of contaminated food, and occupational exposure, among others (5, 6). The disease is often challenging to accurately diagnose and is prone to misdiagnosis (7). Human brucellosis manifests with nonspecific clinical symptoms and is a systemic disease that can affect multiple organs and systems (4, 8–10), with the bones and joints being the most commonly involved (8). The urogenital system is also frequently affected, with orchitis being a common clinical presentation (9). In addition, the disease can manifest as pyelonephritis, acute interstitial nephritis, and acute kidney injury (9–12). However, glomerular diseases are relatively rare and are primarily documented in case reports within the clinical literature. Renal pathology with renal biopsy may present as immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) (13, 14), as well as diffuse proliferative, mesangiocapillary, membranoproliferative, and crescentic glomerulonephritis (15–20), each with different clinical presentations. Both acute and chronic Brucella infections can result in glomerular lesions. In this paper, we report the first case of IgAN with cellular crescentic lesions secondary to acute Brucella infection in our center.
Case report
A 45-year-old man, who worked as a teacher with no past kidney medical history, was hospitalized on September 13, 2023, at the Department of Nephrology, Shenzhen Second People’s Hospital. On September 1, 2023, 12 days prior to admission, the patient presented with a high fever exceeding 39°C, accompanied by chills, generalized myalgia, arthralgia, hyperhidrosis, nausea, and vomiting. Approximately 20 years ago, the patient experienced an abrupt onset of left-sided deafness. Furthermore, he has a 3-year history of untreated hypertension, with systolic blood pressure readings consistently around 140 mmHg.
Upon admission, a physical examination was conducted, which revealed the following vital signs: blood pressure at 145/90 mmHg, pulse rate at 83 bpm, and body temperature at 38.9°C. Clinical examination indicated the absence of edema and no abnormal findings. Laboratory analyses demonstrated a white blood cell count of 20.5 × 109/L, hemoglobin level of 130 g/L, serum albumin concentration of 31.1 g/L, and blood creatinine levels ranging from 220 to 330 μmol/L. The hypersensitivity C-reactive protein (CRP) was measured at 97.3 mg/L, and procalcitonin (PCT) was 1.06 ng/ml. Urinalysis revealed proteinuria at 2+ mg/dl and red blood cells at 2+ per high-power field (HPF), with a 24-h urinary protein excretion of 1.51 g. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate was 35 mm/h. Tests for Plasmodium sanguinis, dengue antigen/antibody, urine bacterial culture, and tuberculosis infection T cells were all within normal limits. In addition, tests for anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA), anti-glomerular basement membrane (GBM) antibody, anti-double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), and antinuclear antibody (ANA) were negative. Complement C3 was 0.92 g/L and C4 was 0.22 g/L. The patient was negative for hepatitis B, hepatitis C, syphilis, and HIV.A monoclonal protein fraction was not detected in the serum protein electrophoresis. The virology assays for cytomegalovirus, hepatitis viruses, Epstein–Barr virus, and herpes simplex virus returned negative results. Ultrasonographic evaluation of the kidneys indicated normal morphology and size. The cardiac ultrasound findings revealed an enlargement of the left atrium, while the morphology and structure of the cardiac valves appeared normal. Computed tomography (CT) of the lungs showed no evidence of infection or effusion. The patient was administered piperacillin/tazobactam for anti-infective therapy over the course of 1 week. However, symptoms of fever, nausea, vomiting, and arthralgia recurred. The patient presented with a body temperature of 38.3°C and reported symptoms of urinary urgency, frequency, gross hematuria, and a cough without expectoration.
Meropenem was given as anti-infective treatment. A subsequent physical examination revealed no tenderness at the ureteral points, no percussion pain in the renal area, and no edema in the extremities. Repeat laboratory analyses indicated a white blood cell count of 14.73 × 109/L, hemoglobin level of 96.0 g/L, and blood creatinine concentration of 150.5 μmol/L. Urinalysis demonstrated proteinuria at 2+ mg/dl, red blood cells at 3+ per HPF, and negative urine white blood cells. The blood and bone marrow cultures showed no bacterial growth. The patient was also negative for influenza A/B virus and novel coronavirus.
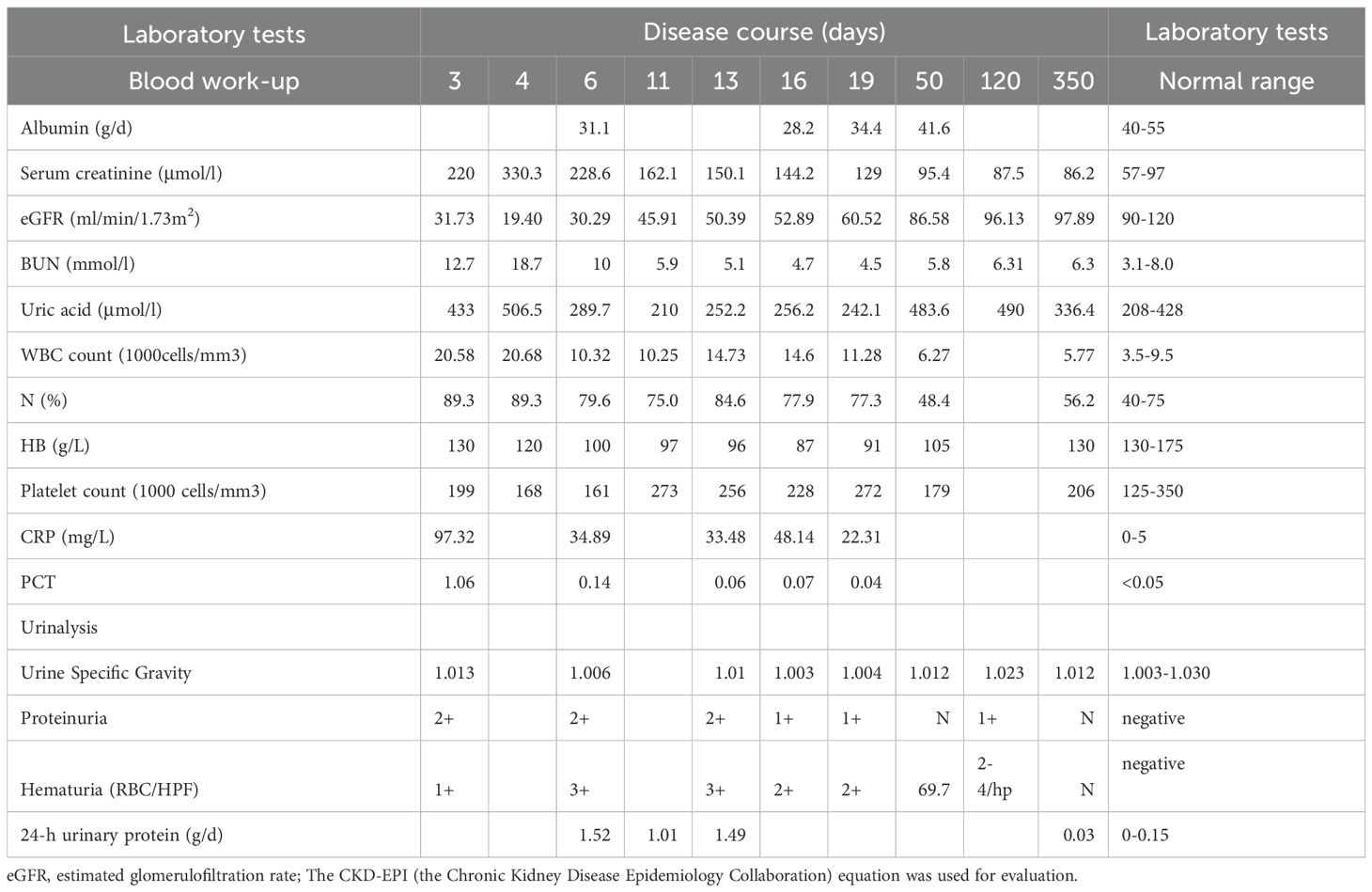
An abdominal ultrasound revealed enlarged kidneys, with the left kidney measuring 130 mm × 61 mm and the right kidney measuring 132 mm × 57 mm. Enlarged lymph nodes were identified in the right axillary region and the bilateral groin area. A cardiac ultrasound showed no valvular vegetation. CT of the lungs indicated inflammation in both lungs and a small amount of effusion. Abdominal CT demonstrated exudative changes around both kidneys, likely due to inflammation. A bone marrow biopsy revealed markedly active hyperplasia in the granulocyte and megakaryocyte lineages, with decreased erythroid hyperplasia; scattered and clustered platelets were readily observed. The renal biopsy pathology indicated mesangial proliferative IgAN with some glomerular crescent formation, classified as M1E0S0T0C2 according to the Oxford classification. Immunofluorescence analysis showed IgG negativity, IgA (++), IgM (+), C3 (+), and C1q negativity, deposited in the mesangial region. Examination under a light microscope revealed 11 glomeruli, with no evidence of glomerular sclerosis or stage sclerosis.
The glomeruli exhibited variability in size, accompanied by a mild proliferation of glomerular mesangial cells and matrix and deposition of fuchsinophilic material in the mesangial area, without evident endothelial cell proliferation. There was fibroid necrosis in segmental capillary vessels observed in two glomeruli, as well as the presence of five small cellular crescents. Vacuolar degeneration of renal tubular epithelial cells was observed. The renal interstitium demonstrated pronounced inflammation, along with mild fibrosis and a slight thickening of the arteriolar walls. Electron microscopy revealed no significant thickening of the glomerular basement membrane, segmental fusion of foot processes, and a small quantity of electron-dense material in select mesangial regions. There were no obvious subepithelial electron-dense deposits (see Figure 1).
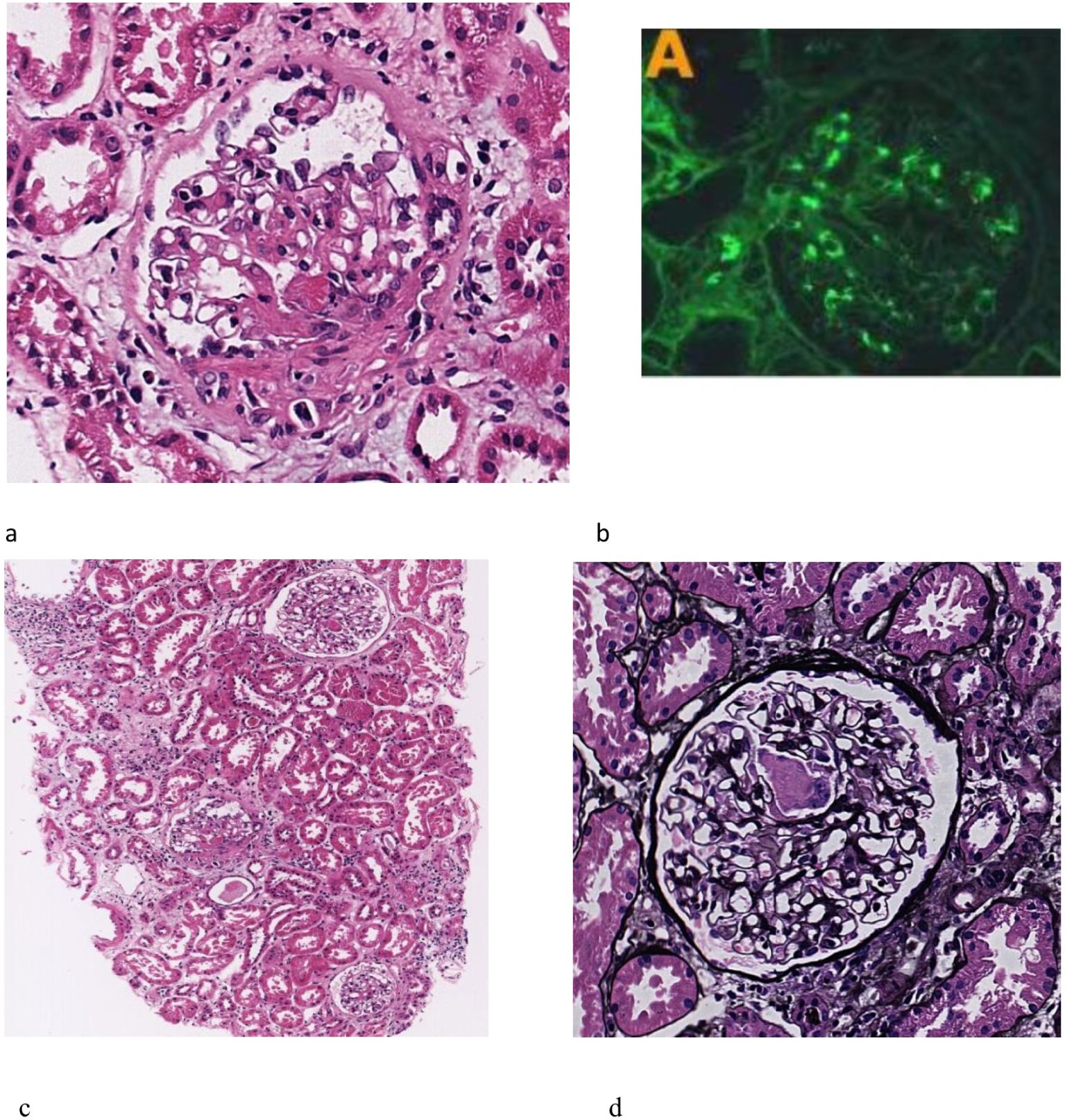
Figure 1. Renal biopsy findings. (a) mild proliferation of mesangial cells and matrix (HE stain, 100×). (b) fibroid necrosis of segmental capillary vessels (PAS stain, 400×). (c) small cell crescents were seen. (HE stain, 400×). (d) Immunofluorescence showed Immunoglobulin A (IgA) is deposited in the mesangial region, exhibiting a comma-like distribution pattern, with a deposition intensity of (++). The renal biopsy pathology revealed mesangial proliferative IgA nephropathy with some glomerular crescent formation, Oxford classification was M1E0S0T0C2, combined with brucellary spondylitis. 11 glomeruli were seen under light microscope, but no glomerular sclerosis and stage sclerosis were observed. The glomeruli were of varying size and size, mild proliferation of mesangial cells and matrix, no obvious endothelial cell proliferation, fuchsinophilic material deposition in the mesangial area, fibroid necrosis of segmental capillary vessels in 2 glomeruli, and 5 small cell crescents were seen. The renal interstitial focus is strong, inflammation and vacuolar degeneration, with mild fibrosis and slight thickening of the arteriole wall. Electron microscope show no obvious thickening of the glomerular basement membrane, segmental fusion of the foot processes, and a small amount of electron-dense material can be seen in a few mesangial areas.
Upon reviewing the patient’s medical history, it was noted that the patient had been in contact with raw mutton 2 weeks prior to disease onset, had sustained damage to the skin on his hands, and had consumed cooked mutton. Further diagnostic tests indicated a positive result (+++) for the Rose Bengal test (RBT) and a positive result (1:200+++) for the standard agglutination test (SAT). Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed scattered patchy, nodular, proton density (PD) fat-suppressed hyperintense signals in the thoracic vertebrae (T4, T5, T7, T9, and T11) and the first lumbar vertebra (L1), with significant lesions observed in L1, which were considered to be infectious in nature, leading to a diagnosis of Brucella spondylitis. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis showed no significant abnormalities. The results of the laboratory tests are presented in Table 1.
The patient was diagnosed with brucellosis, Brucella spondylitis, and brucellosis-related renal impairment. The decision was made to prioritize the treatment of brucellosis, with subsequent treatment plans to be determined based on the efficacy of the initial intervention. A therapeutic regimen consisting of rifampicin (600 mg/day), doxycycline (200 mg/day), and levofloxacin (500 mg/day) was administered, with treatment duration of 4 months. Remarkably, after 7 days of treatment, the patient’s clinical symptoms, including the fever and musculoskeletal pain, were alleviated, although significant sweating persisted. After 1 month, the patient’s sweating had also improved, and the kidney function tests returned to normal. Repeat laboratory analyses revealed a hemoglobin level of 105 g/L, blood albumin of 41.6 g/L, and creatinine at 95.4 μmol/L. Urinalysis indicated negative proteinuria, 69 red blood cells per HPF, and negative urine white blood cells. After 3 months, the creatinine levels decreased to 87.5 μmol/L, and urinalysis showed positive proteinuria, two to four red blood cells per HPF, and a specific gravity of 1.023. The Brucella antibody tube agglutination test was negative. At 11 months of follow-up, the patient’s blood creatinine was 86 μmol/L, and urinalysis indicated resolution of the proteinuria and red blood cells.
Discussion
In this report, we present the case of a 45-year-old male teacher with no prior history of renal disease. The patient reported exposure to raw mutton 2 weeks prior to the onset of symptoms, during which time the skin on his hands was compromised. It is hypothesized that the patient contracted an infection through direct contact with Brucella-contaminated raw mutton. Subsequently, the patient developed glomerulonephritis following acute Brucella infection, which affected multiple organ systems. Renal biopsy revealed mesangial proliferative IgAN with some glomerular crescent formation, classified as M1E0S0T0C2 according to the Oxford classification, in conjunction with Brucella spondylitis. Following a 4-month regimen of anti-brucellosis therapy, which included doxycycline, levofloxacin, and rifampicin, the patient achieved complete remission. Post-treatment, both the urinalysis abnormalities and the renal function were fully restored. We hypothesize that the patient’s IgAN with cellular crescent formation was induced by the Brucella infection.
Brucella infection affects multiple organ systems, with patients often presenting with nonspecific symptoms such as fever, fatigue, night sweats, vomiting, arthralgia, myalgia, hepatomegaly, and lymphadenopathy (4). The literature indicates that both acute and chronic Brucella infections can lead to Brucella nephropathy, which is characterized by a wide range of clinical manifestations, predominantly resulting in acute kidney injury (16–20). The clinical presentations may include gross hematuria and significant proteinuria, with some patients developing nephrotic syndrome, potentially accompanied by anemia, hypocomplementemia, pleural effusion, and cardiac valve vegetations (21). In addition, two cases of chronic Brucella infection have been associated with cryoglobulinemia and ANCA positivity (20). In our case, the patient exhibited renal manifestations alongside anemia, pleural effusion, and, notably, Brucella spondylitis, without evidence of hypocomplementemia or valvular heart disease. These findings suggest that, in patients with Brucella nephropathy, it is crucial to consider and exclude the possibility of Brucella spondylitis and endocarditis.
Prior studies have demonstrated that the renal biopsy pathology results show that, in addition to IgAN, the renal pathology associated with Brucella nephropathy may encompass minimal lesions, diffuse, mesangial, and membranous proliferative glomerulonephritis, and crescentic glomerulonephritis, among others (see Table 2).
In our case, the condition manifested following an acute Brucella infection. The renal biopsy pathology revealed mesangial proliferative IgAN, which was characterized by two instances of glomerular segmental capillary fibrinoid necrosis, five small cell crescents, and a focal area of strong interstitial inflammation. Previous literature has documented two instances of IgAN attributed to acute Brucella infection (13, 14). Compared with these earlier cases, our patient exhibited more pronounced renal pathological changes. Notably, repeated renal biopsies in patients with Brucella-induced IgAN, even after treatment-induced remission, have demonstrated persistent proliferation in the glomerular mesangial region and continued IgA deposition (14).
In our case, the renal pathology also indicated crescentic lesions. Previous studies have reported that acute Brucella infection can lead to rapidly progressive crescentic glomerulonephritis (19), accompanied by acute inflammatory cell infiltration. Previous studies have documented that chronic brucellosis infection is associated with the development of cryoglobulinemia and ANCA-associated vasculitis (20). The renal biopsy of the patient revealed intracapillary proliferative glomerulonephritis with a limited presence of crescents. This finding indicates that Brucella infection may induce alterations in glomerular crescent formation.
Currently, there are no established guidelines or recommendations for the treatment of Brucella nephropathy, with the existing literature limited to case reports. In our case study, the patient received a combination therapy of doxycycline, levofloxacin, and rifampicin over a 4-month period due to complications from Brucella spondylitis and IgAN. The clinical symptoms of the patient showed improvement within 1 week of initiating treatment. After 1 month, the renal function normalized, the proteinuria resolved, and microscopic hematuria decreased. By the end of the 4-month treatment, the hematuria had also resolved. In two previously documented cases of IgAN following Brucella infection, the renal impairment fully resolved after anti-Brucella therapy, with treatment durations of 6 weeks and 3 months, respectively (13, 14). Our observations indicate that while the renal function and proteinuria improved rapidly following anti-Brucella treatment, the hematuria resolved more gradually. This slower resolution of the hematuria may be attributed to the persistent deposition of IgA immune complexes in the mesangial region.
The treatment outcomes for renal glomerular disease secondary to acute brucellosis indicate that the majority of patients achieve complete remission following anti-brucellosis therapy, typically over a period of 6 weeks to 3 months (12, 16, 25). Nonetheless, some patients continue to exhibit persistent proteinuria despite antibacterial treatment alone (17). A subset of these patients has been successfully treated with a combination of corticosteroids and anti-brucellosis agents, leading to full resolution of the glomerular lesions (22, 23). In cases where patients present with concurrent aortic valve endocarditis and pericarditis due to Brucella infection, treatment regimens involving rifampicin, doxycycline, and ceftriaxone (26), or a combination of anti-brucellosis therapy and hormonal therapy (21), have resulted in complete clinical remission. Furthermore, for Brucella-associated rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis, a therapeutic strategy incorporating anti-Brucella agents and immunosuppressive therapies, such as corticosteroids, cyclophosphamide, and azathioprine, has been employed. In certain cases, additional interventions, including rituximab and plasma exchange, have also been utilized (24, 27). These strategies yielded favorable outcomes, with the patients demonstrating good prognosis.
Currently, there are two documented cases of glomerular disease attributed to chronic Brucella infection (18, 20). The clinical manifestations in these patients included nephrotic syndrome, significant renal function impairment, and the presence of cryoglobulinemia. In one case, the renal pathology revealed membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (18). The patient was treated with doxycycline, rifampicin, and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole. After 5 months, the patient’s urinary protein level was 14 g/day, prompting the administration of a reduced dose of corticosteroids, which resulted in partial remission of the proteinuria. The second patient exhibited coexisting cryoglobulinemia and ANCA-associated vasculitis (20) and received treatment with prednisone, doxycycline, and rifampicin for 6 months, leading to the rapid alleviation of all symptoms.
The current therapeutic strategies for Brucella nephropathy primarily target various renal pathological types and associated complications. Different treatment modalities are employed, and most yield favorable prognoses. Nevertheless, there is presently no standardized treatment protocol for Brucella nephropathy (28–30). The glomerular disease induced by Brucella infection is believed to be associated with the production of circulating immune complexes and antibodies (31). The underlying mechanism remains unclear, necessitating further clinical investigation to elucidate both the pathogenesis and the optimal treatment approaches.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Shenzhen Second People’s Hospital (ethical approval document number: 2025-053-01PJ). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
DQ: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. RY: Formal analysis, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. QW: Formal analysis, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. YX: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Shenzhen Key Medical Discipline Construction Fund (Grant No. SZXK009) and the Sanming Project of Medicine in Shenzhen (Grant No. SZSM202211013).
Acknowledgments
We would thank so much to Jinyu Institution for the assistance in analyzing the histological slides.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Qureshi KA, Parvez A, Fahmy NA, Abdel Hady BH, Kumar S, Ganguly A, et al. Brucellosis: epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment-a comprehensive review. Ann Med. (2023) 55:2295398. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2023.2295398
2. Pappas G, Papadimitriou P, Akritidis N, Christou L, and Tsianos EV. The new global map of human brucellosis. Lancet Infect Dis. (2006) 2):6. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(06)70382-6
3. Liu Z, Gao L, Wang M, Yuan M, and Li Z. Long ignored but making a comeback: a worldwide epidemiological evolution of human brucellosis. Emerg Microbes Infect. (2024) 13:2290839. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2023.2290839
4. Pappas G, Akritidis N, Bosilkovski M, and Tsianos E. Brucellosis. N Engl J Med. (2005) 352:2325–36. doi: 10.1056/nejmra050570
5. Kenne C, Mophou Gisèle, Dorville René, and Zongo P. A model for brucellosis disease incorporating age of infection and waning immunity. Mathematics. (2022) 10:1–19. doi: 10.3390/math10040670
6. An CH, Liu ZG, Nie SM, Sun YX, Fan SP, Luo BY, et al. Changes in the epidemiological characteristics of human brucellosis in Shaanxi Province from 2008 to 2020. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:17367. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-96774-x
7. Avijgan M, Rostamnezhad M, and Jahanbani-Ardakani H. Clinical and serological approach to patients with brucellosis: a common diagnostic dilemma and a worldwide perspective. Microb Pathog. (2019) 129:125–30. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.02.011
8. Esmaeilnejad-Ganji SM and Esmaeilnejad-Ganji SMR. Osteoarticular manifestations of human brucellosis: A review. World J Orthop. (2019) 10:54–62. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v10.i2.54
9. Celik M, Akgul F, Alkan S, Altındag D, Esmer F, Sahin A, et al. Testicular involvement of Brucellosis: A 10-year, multicentre study. J Infect Dev Ctries. (2023) 17:1285–91. doi: 10.3855/jidc.18084
10. Gozdas HT and Bal T. Brucellar epididymo-orchitis: a retrospective study of 25 cases. Aging Male. (2020) 23:29–32. doi: 10.1080/13685538.2019.1573892
11. Shoja MM, Khosroshahi HT, Tubbs RS, Varshochi M, and Fervenza FC. Brucellosis mimicking vasculitis in a patient with renal failure and peripheral neuropathy. Am J Med Sci. (2008) 336:285–7. doi: 10.1097/maj.0b013e31815ae3fc
12. Venyo KG. Brucellosis associated with kidney injury and any form of nephropathy a review of the literature. Hamdan Med J. (2016) 9:251–64. doi: 10.7707/hmj.447
13. Siegelmann N, Abraham AS, Rudensky B, and Shemesh O. Brucellosis with nephrotic syndrome, nephritis and IgA nephropathy. Postgrad Med J. (1992) 68:834–6. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.68.804.834
14. Nunan TO, Eykyn SJ, and Jones NF. Brucellosis with mesangial IgA nephropathy: successful treatment with doxycycline and rifampicin. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). (1984) 288:1802. doi: 10.1136/bmj.288.6433.1802
15. Ustun I, Ozcakar L, Arda N, Duranay M, Bayrak E, Duman K, et al. Brucella glomerulonephritis: case report and review of the literature. South Med J. (2005) 98:1216–7. doi: 10.1097/01.SMJ.0000163307.87372.38
16. Parlak E. A case of glomerulonephritis caused by brucellosis. Trop Doct. (2020) 50:360–1. doi: 10.1177/0049475520929505
17. Altiparmak MR, Pamuk GülsümE, Pamuk N, and Tabak F. Brucella glomerulonephritis: review of the literature and report on the first patient with brucellosis and mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis. Scandinavian J Infect Dis. (2002) 34:477–80. doi: 10.1080/003655402320170354
18. Provatopoulou S, Papasotiriou M, Papachristou E, Gakiopoulou H, Marangos M, and Goumenos DS. Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis in a patient with chronic brucellosis. Kidney Res Clin Pract. (2018) 37:298–303. doi: 10.23876/j.krcp.2018.37.3.298
19. Shebli HM, Al-Shayyab SM, Hadadd A, Hjazzat M, Smadi F, Alqudah A, et al. Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis in human brucellosis. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. (2021) 32:1171–5. doi: 10.4103/1319-2442.338294
20. Yang X, Jiao C, Liu X, Zhang Y, Zhou H, and Wang Y. Coexistence of cryoglobulinemia and ANCA-associated vasculitis in a chronic brucellosis patient -a case report and literature review. BMC Infect Dis. (2023) 23:1–9. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08232-w
21. Elzouki AY, Akthar M, and Mirza K. Brucella endocarditis associated with glomerulonephritis and renal vasculitis. Pediatr Nephrol. (1996) 10:748–51. doi: 10.1007/s004670050208
22. Ardalan MR and Shoja AMM. Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis in a patient with brucellosis. Nephrol Dialysis Transplant. (2006) 21:1743. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfk060
23. Sabanis N, Gavriilaki E, Paschou E, Tsotsiou E, Kalaitzoglou A, Kavlakoudis C, et al. Renal manifestations of human brucellosis: First report of minimal change disease. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transplant. (2016) 27:590. doi: 10.4103/1319-2442.182413
24. Senturk BG, Dagel T, Copur S, and Tekin S. Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis associated with brucellosis: A case report. Clin Case Rep Int. (2021) 5:1218.
25. Doregatti C, Volpi A, Tarelli LT, Brognoli M, Giordano F, Meroni M, et al. Acute glomerulonephritisin human Brucellosis. Nephron. (1985) 41:365–6.
26. Kocyigit I, Celik A, Tokgoz B, Ozdogru I, Akgun H, Doganay M, et al. Acute postinfectious glomerulonephritis with native aorta valve endocarditis and myopericarditis due to brucellosis. Ren Fail. (2011) 33:367–70. doi: 10.3109/0886022X.2011.559676
27. Turgay M. Brucellosis with p-ANCA-associated renal failure, leukocytoclastic vasculitis and endocarditis: Case report. J Microbiol Infect Dis. (2011) 1:31–4. doi: 10.5799/ahinjs.02.2011.01.0008
28. Bosilkovski M, Keramat F, and Arapović J. The current therapeutical strategies in human brucellosis. Infection. (2021) 49:823–32. doi: 10.1007/s15010-021-01586-w
29. Li X and Qu J. Diagnosis and treatment scheme for brucellosis (2023 edition). Chin J Infect control. (2024) 23:755–63. doi: 10.12138/j.jssn.1671-9638.20245429
30. Tuon FF, Cerchiari N, Cequinel JC, Droppa EEH, Moreira SDR, Costa TP, et al. Guidelines for the management of human brucellosis in the State of Paraná, Brazil. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. (2017) 50:458–64. doi: 10.1590/0037-8682-0319-2016
Keywords: glomerulonephritis, IgA nephropathy, brucellosis, acute kidney injury, renal biopsy pathology, Brucella-associated glomerular disease
Citation: Qi D, Yu R, Wan Q and Xu Y (2025) IgA nephropathy with crescent cell lesions in a human brucellosis patient: a case report. Front. Nephrol. 5:1594639. doi: 10.3389/fneph.2025.1594639
Received: 16 March 2025; Accepted: 28 June 2025;
Published: 26 August 2025.
Edited by:
Gert Mayer, Innsbruck Medical University, AustriaReviewed by:
Patrick Cunningham, The University of Chicago, United StatesRachel Maurie Gerstein, University of Massachusetts Medical School, United States
Copyright © 2025 Qi, Yu, Wan and Xu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yi Xu, eHV5aTIwMDAxMjM0QDE2My5jb20=
 Dongli Qi
Dongli Qi Ricong Yu
Ricong Yu