- 1Department of Chemistry, College of Natural Science, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI, United States
- 2Institute for Integrative Toxicology, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI, United States
- 3Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, East Leansing, MI, United States
While aging is typically synonymous with the lifespan of an individual, the healthspan, or the total number of years an individual remains healthy and disease-free, is not necessarily related. A current, critical need in society has arisen as current populations are living longer than previous generations, thus increasing the number of people with age-associated diseases. However, the extent of all age mechanisms is not entirely known. Still, studies examining how the exposome, or an individual’s cumulative exposures throughout their life, can influence or modulate aging processes will strengthen our understanding of how to keep individuals healthy and disease-free longer, bridging the gap between lifespan and healthspan. In contrast, previous research has also demonstrated that the exposome impacts aging. One subcategory of the exposome, the specific external, encompasses daily exposures such as diet, lifestyle factors, and occupational and environmental exposures. In this review, we focus on the interactions between factors of the exposome, such as vitamins and minerals, and their effects on aging, cell death, cellular senescence, and unsaturated fatty acid metabolism. We also discuss the interaction between oxidative fatty acid metabolism and aging itself. Overall, understanding how various exposures impact both the oxylipin profile and healthy aging will inform future interventions aimed at improving the healthspan and quality of life for this large aging population.
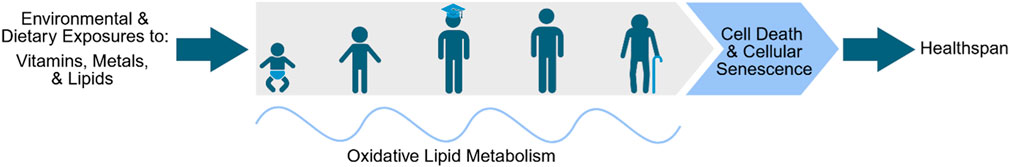
GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT | The goal of this review is to highlight the current understanding of the interactions between the exposome and oxylipin metabolism on healthy aging.
1 Introduction–aging
Aging is a natural, ubiquitous process that refers to the progressive deterioration of functions and regulatory processes, resulting in a reduced ability to maintain homeostasis when challenged by external stresses and increases the interindividual variability in physiological responses (Guo et al., 2022; Mangoni and Jackson, 2004). While the extent of all aging mechanisms is not entirely known, the current understanding of these complex mechanisms involves a combination of genetic, molecular, and environmental factors. Largely, aging is induced by the accumulation of damage due to exposure and response to a variety of stresses (Guo et al., 2022; Mangoni and Jackson, 2004). In the field of aging research, hallmarks of aging have been established including genomic instability, telomere attrition, epigenetic alterations, loss of proteostasis, deregulated nutrient-sensing, mitochondrial dysfunction, cellular senescence, stem cell exhaustion, and altered intracellular communication (López-Otín et al., 2013). As more insights on aging mechanisms have been uncovered, these hallmarks have been expanded upon to include disabled macroautophagy/compromised autophagy, chronic inflammation, and dysbiosis (Guo et al., 2022; López-Otín et al., 2023).
1.1 Increased lifespans in current populations
In the past 70 years alone, the human population has almost tripled, from 2.9 billion (1950) to 7.8 billion (2020) (Garmany et al., 2021). With continued societal and medical progress, the world population is expected to continue this steep increase in the coming decades. This increase in population is partially due to current generations living longer than previous generations with the average life expectancy increasing from 47 to 73 years of age in this same time span (Garmany et al., 2021). However, lifespan and healthspan, which is defined as the total number of years an individual remains healthy and disease-free, are not directly correlated. Decline in the healthspan and quality of life of elderly populations is largely due to age-associated diseases, leading to disability, frailty, and morbidity in these populations. Aging is a major risk factor and driver of a variety of health diseases and conditions affecting elderly populations (Guo et al., 2022; Hodes et al., 2016; Sierra, 2016). Specifically, aging has been shown to be a major risk in chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes (Milanesi et al., 2000), cardiovascular disease (CVD) (Yan et al., 2021), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (Mannino and Buist, 2007; Kukrety et al., 2018), osteoporosis (Chandra and Rajawat, 2021), osteoarthritis (Anderson and Loeser, 2010), Alzheimer’s disease (AD) (Hou et al., 2019; Cortes-Canteli and Iadecola, 2020), and Parkinson’s disease (PD) (Hou et al., 2019; Wood-Kaczmar et al., 2006). Thus, understanding the aging mechanism and how aging impacts healthspan will lead to novel interventions to improve the healthspan and the quality of life of this large aging population. Understanding the implications of perturbations to aging processes by the exposome, defined as an individual’s cumulative exposure throughout their life–can inform intervention methods to keep individuals healthy and disease-free longer, bridging the gap between lifespan and healthspan.
1.2 Current understanding of aging mechanisms, and the influence of the exposome and oxylipin profile on aging
Aging is a complex, multifaceted process that involves the interplay of various mechanisms. Multiple theories explaining the molecular mechanisms of aging have been postulated. Most of these theories can be separated into two main categories: programmed and damage or error theories. Programmed theories suggest that aging is driven by genetically programmed pathways that limit the lifespan based on changes in gene expression for maintenance, repair, and defense response systems (Jin, 2010). Underneath the overarching branch of programmed theories are the programmed longevity, endocrine, and immunological theories. However, damage or error theories suggest that aging is the result of damage accumulation (i.e., ROS, DNA mutations, protein misfolding) in cells and tissues from cumulative environmental exposures over time (Jin, 2010). Aging effects result from the decline in the body’s ability to repair this damage with age, leading to cellular dysfunction. However, one of the main characteristics of aging overall is the accumulation of cellular damage (Vijg and Campisi, 2008). Thus, many of the interactions of the aging hallmarks, cellular damage, and oxidative stress are summarized in Table 1.
Decades of research have demonstrated that aging is impacted by the exposome. Exposome is broadly defined by environmental exposures which people face in everyday life. For example, a recent epidemiological study by Argentieri et al. conducted an exposome-wide analysis of all-cause mortality using the UK Biobank data and identified that 25 specific exposures are associated with proteomic aging (Argentieri et al., 2025). While specific mechanisms on how the exposome impacts aging remain understudied, research has shown that the exposome, including diet, modulates endogenous unsaturated fatty acid metabolism, which generates hundreds, if not thousands, of lipid metabolites (Liu et al., 2017; Rodrigues et al., 2022). These unsaturated fatty acid metabolites are key signaling molecules in many aspects of human physiology. For example, prostaglandins play an important role in inflammation, vascular tone, and pain perception (Innes and Calder, 2018). Recent studies also demonstrated that prostaglandins and the associated metabolic enzymes impact aging (Srour et al., 2024; Palla et al., 2021). However, the effects and associated mechanism of the exposome and unsaturated fatty acids metabolism on aging are underexplored. This review will discuss how senescence and aging pathways can be influenced by specific dietary and environmental exposures of the exposome (vitamins, metals, PUFAs, and oxylipins) and how the exposome can influence oxylipin (oxygenated polyunsaturated fatty acid derivative) metabolism. Overall, the review will examine how these exposures can impact healthy aging.
2 Exposome
The exposome (Figure 1) encapsulates all of the environmental (non-genetic) exposures experienced by an individual from an array of dietary, lifestyle, and demographic factors throughout the lifespan that impact health outcomes (Wild, 2005). Some researchers have broadened the definition of the exposome to include additional factors examining how the body reacts to environmental factors such as biological responses, behavior, and endogenous processes (Miller and Jones, 2014). The exposome includes a network of unique characteristics and exposures of an individual that may result in them being more or less susceptible to particular stressors in their environment (DeBord et al., 2016). Overall, the exposome can be broken into three subcategories: internal, specific external, and general external (DeBord et al., 2016; Wild, 2012). Despite the distinct exposure classifications, these subcategories are considered to be both overlapping and intertwining, and differentiating factors between these categories can be difficult (DeBord et al., 2016). While all three subcategories are vitally important in understanding how the exposome impacts human health and disease, this review will focus on the molecular interactions of specific external factors on aging and oxidative lipid metabolism. Thus, the internal and general external factors are out of scope for this review and have been extensively reviewed elsewhere. Here, we will discuss these briefly below and the corresponding reviews for specific exposomal effects on health have been included.
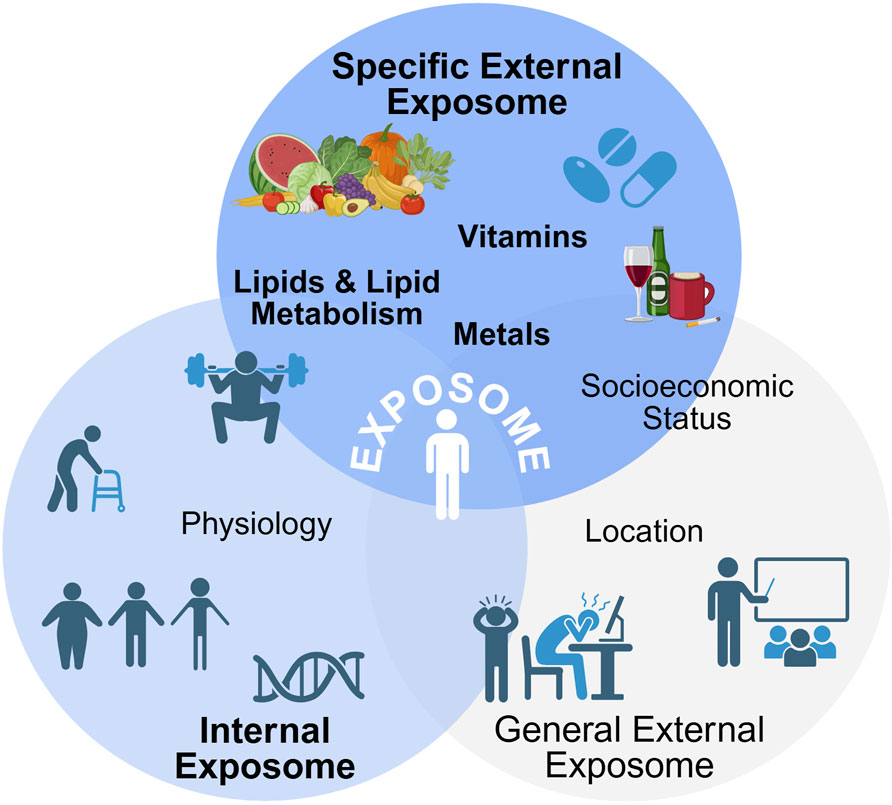
Figure 1. The complete exposome. The exposome can be divided into three subcategories–internal, general external, and specific external, with these subcategories overlapping and intertwining with each other. Overall, the exposome consists of total exposures an individual is exposed to in their lifetime. Created with BioRender.
2.1 Internal
The internal or endogenous factors of the exposome encompass those that are specific to an individual. Specifically, these encompass the internal factors relating to host factors or the impact on cellular environments and processes. Internal factors can include physiology (Jin, 2010; Rappaport, 2011), aging (Guo et al., 2022; Mangoni and Jackson, 2004; Sierra, 2016; Vijg and Campisi, 2008; Fülöp et al., 2009; Fede et al., 2022; Tamburini et al., 2004), body morphology/somatotype (Carter and Heath, 1990; Koleva et al., 2002), physical activity (Thyfault and Bergouignan, 2020; Booth et al., 2012; Gorman et al., 2021; Grundy et al., 2004), and genome (Miller and Jones, 2014; Wild, 2012; Rappaport, 2011). These internal exposures can typically be measured using biomarkers of these endogenous processes.
2.2 General external
Despite overall exposures to the same environmental nuisances, individuals and groups can be impacted differently, and these differences can be partly attributed to the general external exposome. The general external factors are considered the social determinants of health (Friel and Marmot, 2011) as well as the wider effects of social, economic, and physiological status on health and disease (Wild, 2012). General external factors specifically consist of influences from location (Dummer, 2008; Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Guidance for Designing a National Healthcare Disparities Report, 2002; Sogno et al., 2022; Dale et al., 2012), education level (Zajacova and Lawrence, 2018; Kitagawa and Hauser, 2013), socioeconomic status (CDC. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2023; Kivimäki et al., 2020; Rosengren et al., 2019; Havranek et al., 2015; Kivimäki et al., 2018) – including food insecurity (Kopparapu et al., 2020; Campanera et al., 2023; Ma et al., 2024) –, and physiological and mental stress (Miller and Jones, 2014; Wild, 2012; Mariotti, 2015; Smyth et al., 2018; Ng et al., 2020).
2.3 Specific external
Specific external factors include those that have been most extensively studied in epidemiological studies examining exposure and environmental risk factors in disease. These factors include daily exposures attributed to diet, lifestyle factors, medical interventions, occupational and environmental exposures (Wild, 2012). Overall, external factors can be measured using survey instruments and personal sampling (recording). The effect of exposures classified under specific external exposome will be discussed in detail below.
3 Specific external exposome and aging healthspan
The most expansive exposure pathway includes ingestion of exogeneous materials ranging from dietary choices, lifestyle factors (i.e., alcohol, tobacco, caffeine), and medical interventions, namely, pharmaceuticals. Many of these exposures are chronic exposures, potentially leading to serious long-term health effects. Another common source of chronic exposures is external exposure to a host of occupational and environmental agents, including radiation, noise, infectious agents (i.e., pathogens), chemical contaminants, environmental pollutants, and additional occupational exposures (i.e., crystalline silica, diesel exhaust, radon, wood dust) (Wild, 2012). While precautions for environmental and occupational exposure limits are in place, these direct or indirect potential occupational and environmental exposures can result in both short- and long-term health effects, leading to health disparities.
Apart from the abovementioned environmental toxicants, some of the other specific external exposures, specifically dietary choices, can have beneficial effects on health and healthy aging. The association between diet and oxidative stress and inflammatory processes has been widely examined. Plant-based diets consisting of anti-inflammatory and antioxidant-rich foods are associated with decreased levels of oxidative stress and inflammatory biomarkers, which have been extensively reviewed elsewhere (Aleksandrova et al., 2021). However, individual components of these diets (vitamins, polyunsaturated fatty acids) and specific metal exposures on healthy aging have not been extensively reviewed and will be discussed below.
3.1 Micronutrients
There are many crucial nutrients that are required for endogenous functions that must be obtained throughout the diet. Many of these play crucial roles in supporting various bodily functions, reducing oxidative stress, and maintaining cellular integrity. However, the absorption, metabolism, and utilization of these nutrients can decline with aging, resulting in a loss of protection against cellular processes (Doley, 2017). Aging-related changes may also affect dietary intake in older adults due to increased difficulty chewing and swallowing, changes in taste and smell, poor appetite, and self-restriction, all of which may result in deficiencies in obtaining the recommended dietary allowance of nutrients necessary for physiological functions (Doley, 2017). Conversely, some of these nutrients can trigger aging-related mechanisms such as cell death, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction.
3.1.1 Vitamins
Vitamins can be classified as either fat- or water-soluble. Fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) are stored and accumulated in the liver and lipid tissues. Thus, some fat-soluble vitamins can be toxic if taken in excess. Meanwhile water-soluble vitamins (B and C) are not stored in the body as any excess is excreted and these vitamins need to be consumed regularly to prevent deficiencies (Chernoff, 1995). The Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2020–2025 details the daily nutritional goals for the essential vitamins needed at each age range (Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020). However, these guidelines have an upper age of 51+ years and thus do not consider the variability in absorption and utilization that may occur for later aging stages in life. Due to the antioxidant and oxidative stress reducing roles that vitamins play in vivo, more comprehensively understanding their effects in aging is of great interest in current geroscience research.
Several vitamins regulate programmed cell death mechanisms, with consequent implications in aging. While the role of vitamins in cell death, cellular senescence, and aging is not the focus of this review, we summarize the findings of vitamins in cell death/cellular senescence and aging in Tables 2, 3, respectively. The main mechanism of vitamin involvement in these processes is throughout their modulation of oxidative stress and interactions with antioxidant enzymes and vitagenes (i.e., genes that maintain cellular homeostasis during stressful conditions). This may potentially impact lipid oxidation, modulating oxylipin synthesis as vitamins A, B, E, and K have been shown to decrease or prevent lipid peroxidation, thereby inhibiting ferroptosis (Shastak et al., 2023; Jakaria et al., 2023; Shan et al., 2021; Moreira et al., 2011; Hu et al., 2021; Chen et al., 2024; Mishima et al., 2022). Interactions with vitamins A and D also result in the upregulation of antioxidant enzymes to prevent cellular senescence (Sirakawin et al., 2024; Sosa-Díaz et al., 2022), while a vitamin K-dependent protein (VKORC1) limits ROS production, also inhibiting cellular senescence (Chen et al., 2024). Likewise, vitamins A, B, E, and K have been shown to directly protect against cognitive decline and age-associated neurodegenerative diseases (Chernoff, 1995; Gruz-Gibelli et al., 2016; Clarke et al., 2007; Vogiatzoglou et al., 2008; Ochi and Takeda, 2015; Mocchegiani et al., 2014; Popa et al., 2021). In summary, vitamins play a critical role in aging and cell senescence, and various levels of exposure could significantly impact human healthspan (Varesi et al., 2022; Diwan and Sharma, 2022).
The antioxidant capabilities of vitamins have been investigated for their ability to also modulate the lipid profile; thus, influencing aging and age-associated disease risk through this mechanism as well. One study examining variations to lipid classes after multi-micronutrient supplementation (Vitamin A, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12, C, D3, E, calcium, phosphorous, iron, magnesium, and zinc) in children and adolescents found significant reductions in sterol esters (SEs), phosphatidylinositols (PIs), phosphatidylcholines (PCs), and lysophosphatidylcholines (LPCs), and that linoleic, oleic, palmitic, arachidonic, and stearic acid in various lipid classes (SE, PI, PC, LPC, and triacylglycerols) were reduced with supplementation (Chakrabarti et al., 2020). Another study examining long-term antioxidant micronutrient supplementation (Vitamin A, C, E, selenium, and zinc) after 7.5 years identified lower total cancer incidence and all-cause mortality in men but not in women. The authors hypothesize that this sex-based difference may be due to lower baseline antioxidant levels in men (Hercberg et al., 2004). While the interaction between dietary vitamin supplementation and disease prevention has been thoroughly reviewed elsewhere (Rautiainen et al., 2016), current debates state that the benefits of micronutrient supplementation may be lacking among already well-nourished individuals. Two studies, one examining type 2 diabetes and the other examining cognition, also found insignificant benefits with vitamin supplementation (Farvid et al., 2004; Grodstein et al., 2013). Although numerous studies have examined vitamins and aging, the complete involvement of vitamins in maintaining or perturbing healthy aging mechanisms is not entirely understood.
3.2 Metals
Humans also require various minerals and trace elements to sustain vital life processes. The “metallome” describes the entirety of metal and metalloid species (elemental distribution, equilibrium concentrations of free metal ions, and free metal content) in a biological system (cellular compartment, cell, tissue type, or organism) (Szpunar, 2004; Williams, 2001; Lobinski et al., 2010). Metals ions such as calcium, chloride, chromium, cobalt, copper, fluorine, iodine, iron, magnesium, manganese, molybdenum, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, sodium, zinc, and more are necessary for physiological processes. It is estimated that one-third of all proteins require a metal cofactor, and therefore the body also contains mechanisms for regulating these metals from catalyzing cytotoxic reactions (Tainer et al., 1991; Finney and O’Halloran, 2003). Many analytical techniques are used to examine the metallome (Szpunar, 2004) due to both their vital roles (regulatory cofactors, electrolytes, structural function, hormone synthesis, antioxidant activity, cell signaling, energy production, and implication in the prevention of several diseases) and negative consequences (highly toxic, involved in pathophysiology of disease and disease risk) (Doley, 2017; Lobinski et al., 2010). Apart from essential metals needed to sustain physiological processes, humans are exposed to a wide variety of other metals in either environmental or occupational settings, which can have serious health outcomes.
3.2.1 Copper (Cu)
Copper is required by the body for a variety of functions and is required for structural and catalytic properties in many enzymes involved in growth, development, and maintenance (Gaetke and Chow, 2003). Copper is also important for the utilization of iron, synthesis of connective tissue, formation of red blood cells, energy production, and antioxidation (Doley, 2017). The majority (85%–95%) of copper in the body is bound to the multi-copper binding protein ceruloplasmin, but the remaining free copper can react generating ROS (Brewer, 2010). Homeostatic regulation of copper absorption and excretion helps prevent toxicity and deficiency (Turnlund et al., 1998). Despite this regulation, copper deficiency and toxicity can occur in the liver, kidneys, brain, and endocrine system (Gaetke and Chow, 2003; Uriu-Adams and Keen, 2005). Copper deficiency can cause a range of symptoms likely due to a decrease in the activity of ceruloplasmin and subsequent iron accumulation and oxidative stress (Uriu-Adams and Keen, 2005). Copper deficiency can also affect the activity of other copper-containing enzymes, non-copper-containing enzymes within the oxidant defense system, and other ROS scavengers (Uriu-Adams and Keen, 2005). The effect of copper deficiency in decreasing the ability to deal with oxidative stress was demonstrated by increased oxidative damage in a copper-deficient rat model (Saari et al., 1990). Copper toxicity also results in oxidative damage, but this effect is suggested to be more of a direct effect of copper itself interacting to cause oxidative stress throughout the body and perturbing the endocrine system (Gaetke and Chow, 2003; Uriu-Adams and Keen, 2005). Copper toxicity in the pathogenesis of age-related diseases such as neurodegenerative diseases, diabetes, and atherosclerosis has been examined and reviewed extensively elsewhere (Brewer, 2010; Uriu-Adams and Keen, 2005). However, the effect of copper in age-associated diseases is thought to be due to free copper accelerating the production of toxic radicals. For neurodegenerative diseases, one study showed that low amounts of copper in distilled drinking water (0.12 parts per million) dramatically increased Aβ plaques and decreased cognitive performance in a cholesterol-fed rabbit AD model (Sparks and Schreurs, 2003). Further, the amyloid precursor protein has copper-binding domains allowing it to function as a copper chaperone in the brain. Copper can also interact with Aβ peptides to produce H2O2, causing oxidation of Aβ, consequently generating protease-resistant soluble and cross-linked Aβ (Atwood et al., 2000). In humans, those in the highest quintile of total copper intake, combined with a high fat diet, showed an markedly accelerated decline in cognition of at a rate of 19 years over a 6-year period (Morris et al., 2006). A copper-induced cell death (cuproptosis) in which copper exposure results in excessive cellular respiration leading to cell death has recently been described (Chen et al., 2023).
3.2.2 Iron (Fe)
Iron is a vital element for many biological processes including the formation and transport of oxygen in hemoglobin and myoglobin, cellular respiration in the mitochondrial electron transport chain, and DNA synthesis by ribonucleotide reductase (Doley, 2017; Galaris et al., 2019). While excess iron is stored within ferritin in cells, excessive systemic iron can induce hepcidin to sequester iron. Meanwhile, iron deficiency can repress hepcidin expression to regulate the physiological concentrations of iron (Galaris et al., 2019). Iron is tightly controlled at the systemic and cellular levels to prevent iron overload and toxicity, which is associated with liver disease, diabetes, osteoporosis, heart disease, atherosclerosis, and neurodegenerative diseases (Galaris et al., 2019; Puntarulo, 2005). Excess labile iron can result in oxidative stress as iron is a major catalyst in the generation of highly reactive free radicals through the Fenton reactions (Galaris et al., 2019). Increased labile iron and subsequent lipid peroxidation due to ROS production are key features of ferroptosis, an iron-dependent cell death mechanism (Dixon et al., 2012). Age-induced increases in iron due to loss of cellular iron homeostasis mechanisms subsequently increase oxidative stress, contributing to aging-related diseases (James et al., 2015). An iron deficiency can also result in systemic effects, driven by an increase in oxidative stress (Esen Ağar et al., 2021).
3.2.3 Arsenic (As)
Arsenic is a toxic metal and is included in multiple toxic substance and carcinogen lists (Rahman et al., 2018). Arsenic has no known beneficial effects in vivo. Humans can be exposed to arsenic from contaminated water, plants (especially in rice), animal sources, and air and soil sources (Rahman et al., 2018). Prolonged exposure to arsenic causes irreversible damage to the body in a range of organs and systems, including the skin and nervous, respiratory, cardiovascular, immune, hepatic, renal, urinary, and endocrine systems (Rahman et al., 2018). Arsenic has been linked with skin, lung, bladder, liver, and kidney cancer (Rahman et al., 2018). While the mechanism of arsenic toxicity is not entirely defined, lipid peroxidation induced by oxidative stress may be responsible (Xu et al., 2017). One study found that arsenic exposure can lead to a decrease in plasma HDL and an increase in plasma LDL, especially at high arsenic concentrations (Zhao et al., 2021). Another meta-analysis found that arsenic can cause oxidative injury by reducing the anti-oxidative capacity, resulting in increased levels of oxidants and decreased levels of anti-oxidants (Xu et al., 2017). Arsenic may also contribute to multisystem decline through an induced acceleration of physiological aging processes (Sorrentino et al., 2014). In an evaluation of epidemiological data, arsenic exposure was found to accelerate DNA methylation (a measure of biological aging), consequently affecting the risk of age-related morbidity. Specifically, arsenic exposure increased the risk of CVD incidence, CVD mortality, and all-cause mortality (Jiang et al., 2023). Arsenic also triggers nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) by inducing ferroptosis via the Mfn2/IRE1α-ACSL4 pathway, contributing to the lipid metabolism disturbances associated with NASH (Wei et al., 2020).
3.2.4 Cobalt (Co)
Cobalt exposure is typically through food intake, mainly through fish and vegetables, or from inhalation of airborne particles from industrial emissions. Cobalt-contaminated water is very rare (Lang et al., 2009). Chronic exposure to cobalt is associated with cardiac abnormalities, gastrointestinal disturbances, lung disease, and cancer (Lang et al., 2009). A study of data from the NHANES found that cobalt exposure, even within normal range, may be a risk factor for age-related mobility effects (Lang et al., 2009). Cobalt exposure is associated with oxidative stress, as in vivo and in vitro lung samples exposed to cobalt showed an increase in the oxidized form of glutathione (GSSG), decreased reduced form of glutathione (GSH), and increased activity of the pentose phosphate pathway (Lewis et al., 1991). Oxidative stress due to cobalt may also be a mechanism underlying the pathogenesis of PD (Uversky et al., 2002). Cobalt, in the presence of calcium, can also trigger mitochondrial oxidative stress inducing apoptosis (Battaglia et al., 2009).
3.2.5 Cadmium (Cd)
Exposure to the toxic heavy metal cadmium is largely through tobacco smoke, diet, or occupational exposure (Zhang et al., 2023b). Cadmium accumulates in the body and has a biological half-life of 10 years, resulting in chronic endogenous exposure. Therefore, urine cadmium functions as a biomarker of long-term cadmium exposure (García-Esquinas et al., 2015). Cadmium contributes to several age-related diseases such as diabetes, CVD, kidney disease, and bone disease (osteoarthritis, osteoporosis). It also contributes to oxidative stress by stimulating cytokine production, elevating levels of inflammation, and increasing mitochondrial damage (Zhang et al., 2023b; García-Esquinas et al., 2015). An epidemiological study examining NHANES data found that cadmium exposure is associated with increased whole-body phenotypic aging, and smoking (one of the main sources of cadmium exposure) was positively associated with aging (Zhang et al., 2023b). Another study using NHANES data demonstrated that urinary cadmium levels were negatively correlated with telomere length. Telomere shortening is a biomarker of aging and is capable of triggering cellular senescence (Xia et al., 2022). Oxidative stress induced via cadmium may be involved in the mechanisms underlying the development of PD (Uversky et al., 2002). In cancer models, acute cadmium exposure can cause toxic effects. However, chronic exposure can lead to an adaptive reduction in ROS production, at the expense of aberrant gene expression, leading to cadmium-induced carcinogenesis (Liu et al., 2009). Cadmium has also been shown to induce multiple forms of cell death, including apoptosis, necroptosis, autophagy, and pyroptosis (Messner et al., 2015; Zhou et al., 2022).
3.2.6 Selenium (Se)
The trace element selenium is required by the body as it is an element in amino acids and enzymes (selenoproteins) where it contributes to antioxidant defense, immune functions, and metabolic homeostasis (Bjørklund et al., 2022). Selenium is a crucial cofactor for glutathione- and iodine-containing enzymes and is involved in thyroid function (Doley, 2017). However, selenium has a narrow margin of beneficial effects in the body as selenium toxicity can result in pro-oxidant functions and liver, lung, and neurological damage. Selenium deficiency can cause oxidative stress, chronic inflammation, endocrine and immunity dysregulation, reduced life expectancy, acceleration of aging processes, and increased vulnerability to age-related disease (Bjørklund et al., 2022). Selenium deficiency has also been reported to increase in proportion to age and age-related diseases (Savarino et al., 2001). Multiple studies, extensively reviewed elsewhere, examining older adults (largely centenarians) found that those with longer lifespans had either higher serum levels of selenium or much lower percentages of selenium deficiencies, suggesting that inadequate selenium could adversely affect optimal health in aging populations (Bjørklund et al., 2022). Another study found that elderly adults with low levels of selenium experienced significantly higher rates of all-cause mortality than elderly adults with high levels of selenium (Giovannini et al., 2018). It is suggested that the role of selenium in aging may be due to selenoprotein involvement in redox homeostasis and anti-inflammatory activities (Cai et al., 2019). Selenium has also been linked to cellular senescence, as a downregulation in the expression of selenoproteins during selenium deficiency can activate senescence (Legrain et al., 2014) and low levels of selenium can result in shortened telomere length (a hallmark of senescence), which can be rescued by selenium administration (Schoenmakers et al., 2010; Liu et al., 2004). The selenoprotein GPX4 is an essential regulator of ferroptosis and directly prevents uncontrolled phospholipid peroxidation (Ito et al., 2024).
3.2.7 Lead (Pb)
Lead is a well-known toxic element, and exposure to lead can come from a variety of sources such as food, water, paint, air, and occupational settings (Vig and Hu, 2000). Previous lead exposures may alter the aging process as lead can be stored in reservoirs in bones which can protect the body from lead toxicity. However, age-related bone loss can release this stored lead into the bloodstream (Vig and Hu, 2000). A mix of epidemiological, clinical, and autopsy studies demonstrated a trend of increasing lead in the blood or bones with aging, although many results were not statistically significant (Vig and Hu, 2000). Low level lead exposure can result in hypertension, peripheral artery disease, kidney and neurodegenerative diseases, and cognitive impairment (Ahamed and Siddiqui, 2007). Lead may induce oxidative stress in the pathophysiology of these diseases, leading to oxidative damage in the heart, liver, kidney, reproductive organs, and brain (Ahamed and Siddiqui, 2007). A study examining oxidative stress and lead toxicity in lead-exposed workers found that there is a disruption to the oxidant/antioxidant balance in the workers compared to controls (Gurer-Orhan et al., 2004). Additionally, an accumulation of δ-aminolevulinic acid could potentially be a source of ROS in the pathophysiology of lead toxicity (Ahamed and Siddiqui, 2007). Lead binds to the membrane of cells, acting as a stimulant for lipid oxidation which can lead to alterations in the lipid membrane composition. These alterations can affect membrane integrity, permeability, function, and susceptibility to lipid peroxidation (Adonaylo and Oteiza, 1999), suggesting that lipids are highly involved in lead-induced toxicity.
3.2.8 Mercury (Hg)
Mercury is a toxic element that has been used for centuries. Mercury exposure can be due to contact with a variety of sources such as soil, air, water, plants and animals, and can still be found in some older fluorescent lightbulbs, thermometers, and batteries (Kumari et al., 2023). A major issue of mercury is its bioaccumulation and biomagnification properties, as the most hazardous form (methylmercury) is found most frequently due to its quick absorption and slow excretion (Kumari et al., 2023). Mercury poisoning has been associated with many health effects in both male and female reproductive systems, in utero development, and deleterious effects on the central nervous, renal, pulmonary, immune, gastrointestinal, and cardiovascular systems (Kumari et al., 2023; Rice et al., 2014). Mercury can cross the blood brain barrier, causing oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and neuroinflammation, resulting in a wide range of neurological effects (Kumari et al., 2023; Rice et al., 2014; Teixeira et al., 2018). Oxidative stress due to mercury exposure can also induce cell death by cytotoxicity and apoptosis (Teixeira et al., 2018). Mercury can also predispose tissues to aging and one study found that the percentage of people with inorganic mercury in the organs that commonly contain mercury (brain, kidney, thyroid, anterior pituitary, adrenal medulla and pancreas) increased with aging, with the highest levels of mercury in all six organs peaking in the 61–80 years group. Mercury levels slightly decreased in these organs, apart from adrenal medulla, suggesting that those who “aged successfully” likely had lower lifetime mercury exposure giving them an advantage in aging. However, these six organs have also been implicated in the process of accelerated aging; thus, mercury may accelerate aging processes in these organs via a variety of mechanisms. The presence of mercury in multiple organs may also offer an explanation to why certain disorders often occur together (Pamphlett, 2021).
Overall, exposure to metals over the lifespan and accumulation of heavy metals in vivo can result in toxic effects on many of the body’s physiological processes. However, metal exposure, as discussed above, can catalyze cytotoxic reactions and affect oxidative stress, with more severe influential effects on oxidative stress when in combination with aging-related dysregulation of these physiological processes (Szpunar, 2004; Kim Dwon et al., 2022). The consequent oxidative stress resulting from metal exposure can also influence the lipid profile, with previous findings demonstrating that lead, mercury, iron, zinc, and arsenic affect dyslipidemia (measured via cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol) (Kim Dwon et al., 2022; Luo et al., 2022). Meanwhile, other studies have examined changes in the metallome over aging in a variety of tissues (Zhang et al., 2020; Takahashi et al., 2001), with Zhang et al. observing that mice on calorie restriction had shifted but similar trends to aging mice not on calorie restriction, demonstrating that changes in metabolism may slow aging (Zhang et al., 2020). Despite numerous studies examining metals on aging processes, as well as effects of metal deficiency and toxicity on age-related diseases, reviewed elsewhere (Wessels et al., 2015), the extent of metal involvement in oxidative stress, lipid profile modulation, and cell death influencing healthy aging mechanisms are still not entirely understood.
4 Oxidative lipid metabolism and aging healthspan
One of the major macronutrients in the human diet is fats, which are broadly defined as lipids. Lipids encompass cholesterol, saturated fatty acids, mono- and polyunsaturated fatty acids, and trans fats, which can be found as free fatty acids or incorporated into triglycerides and phospholipids. Lipids are key biological molecules responsible for forming cellular membranes, providing cellular energy metabolism, and acting as signaling molecules or affecting membrane fluidity in signal transduction (Mutlu et al., 2021). The subsequent sections will discuss the interactions of the exposome on oxylipin metabolism, including PUFAs, CYPs, EH (specifically sEH), LOX, and COX, followed by exploration of the effects of each section of oxylipin metabolism on aging and senescence.
4.1 Polyunsaturated fatty acids
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are composed of a carboxylic acid head group and a long-chain carbon tail containing at least two carbon-carbon double bonds. These molecules are critical in an extensive list of physiological processes as they can modulate membrane channels and proteins, regulate gene expression via nuclear receptors and transcription factors. PUFA derivatives and glycerophospholipids containing PUFAs can also serve as bioactive signaling molecules and as the building blocks of membrane lipids (Sarparast et al., 2020; Mozaffarian and Wu, 2011; Harayama and Shimizu, 2020). PUFAs are found in all cell membranes and tissues in the body, and are particularly known for their roles in the health, function, and protection of the cardiovascular system, brain, and skin barrier as well as in insulin sensitivity (Mititelu et al., 2025). Specifically, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), an ω-3 PUFA, is an essential membrane component in the brain, retina, and nervous system, comprising around 40%–60% of the membrane fatty acids (Querques et al., 2011; Dyall, 2015). ω-3 PUFA supplements are suggested to be beneficial for cognitive function, vision, and neurological health. Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) supports cardiovascular health and global inflammatory responses through its roles in reducing triglyceride levels, improving endothelial function, and preventing excessive platelet aggregation. Meanwhile, γ-linolenic acid (GLA), an ω-6 PUFA, plays a minor role in the body’s anti-inflammatory processes, and is vital in supporting skin barrier structure and function. Dihomo- γ-linolenic acid (DGLA) functions as a precursor to various anti-inflammatory molecules, while arachidonic acid (AA) and its downstream metabolites are essential in cellular signaling, immune response, and tissue repair (Mititelu et al., 2025). Overall, ω-3 PUFA metabolites tend to be regarded as pro-resolving mediators, while ω-6 PUFA metabolites are generally considered to be pro-inflammatory. However, this consensus is not universally true, as some ω-3 epoxy-PUFA-metabolites promote allergic responses by attenuating mast cell activation while an ω-6 PUFA-metabolite (lipoxin A4) has been shown to be more pro-resolving (Dalli and Serhan, 2019; Shimanaka et al., 2017). The role of PUFAs in the pathology of multiple age-related diseases has been investigated due to their ubiquitous presence, multiple metabolism pathways, and potency despite their low abundance in vivo.
4.1.1 Biosynthesis pathway and dietary intake of PUFAs
Mammals are capable of endogenously synthesizing the respective downstream ω-3 and ω-6 PUFAs from linoleic acid (LA) and α-linolenic acid (ALA); however, LA and ALA must be obtained from the diet (Figure 2). Through elongase and desaturase enzymes, these PUFAs can be produced and thus available for metabolism by cytochrome P450 enzymes, lipoxygenase, and cyclooxygenase (Figure 3), into various oxylipins which will be discussed later in this review. The PUFA biosynthesis pathway is limited. One study found that the conversion of LA to DGLA was between 1.5%–2.1% while the conversion of LA to AA was between 0.3%–0.6% (Demmelmair et al., 1999). Likewise, the conversion of ALA to EPA and DHA was found to be ∼8% and 0%–4% in young men and 21% and 9% in young women, respectively (Burdge et al., 2002; Burdge and Wootton, 2002). Thus, mammals are heavily dependent on the dietary intake of PUFAs. However, the conversion of PUFAs is variable between populations (Mathias et al., 2011). Previous studies found higher levels of circulating long chain-PUFAs (LC-PUFAs) in African Americans than European Americans. As well, African Americans have higher levels of AA over DGLA while European Americans have higher levels of ALA over EPA and ω-3 docosapentaenoic acid (DPA3). Likewise, African American populations were shown to have higher levels of AA and increased AA/DGLA and AA/LA ratios relative to Hispanic American populations. These differences can be partially explained by variations in the frequencies of FADS (fatty acid desaturase) genetic variants between different ancestry populations, with haplotype D (found in African populations) being associated with increased biosynthesis of LC-PUFAs (Mathias et al., 2011; Harris et al., 2019; Lemaitre et al., 2011; Ameur et al., 2012; Yang et al., 2023). Genetic variants in FADS1 and EVOVL2 in a Tunisian population were found to increase levels of AA and the AA/DGLA ratio, increasing the risk for AD in individuals with these genetic variants (Hammouda et al., 2020). Likewise, a recently published review detailed how different genetic variants within the FADS1, FADS2, and EVOVL2 genes can influence atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk differently based on the variant (Liu et al., 2024).
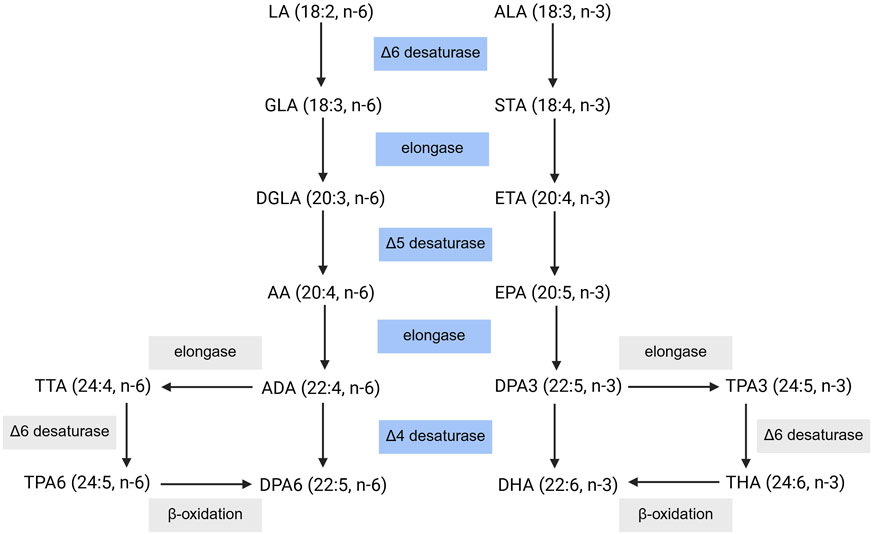
Figure 2. PUFA Biosynthesis Pathway. Dietary intake of LA and ALA can be converted into their respective downstream PUFAs. LA: linoleic acid, GLA: γ-linolenic acid, DGLA: dihomo- γ-linolenic acid, AA: arachidonic acid, ADA: adrenic acid, DPA6: docosapentaenoic acid, TTA: tetracosatetraenoic acid, TPA6, tetracosapentenoic acid (ω-6), ALA: α-linolenic acid, STA: stearidonic acid, ETA: eicosatrienoic acid, EPA: eicosapentaenoic acid, DPA3: docosapentaenoic acid, DHA: docosahexaenoic acid, TPA3: tetracosapentenoic acid (ω-3), THA: tetracosahexaenoic acid. Created with BioRender.com.
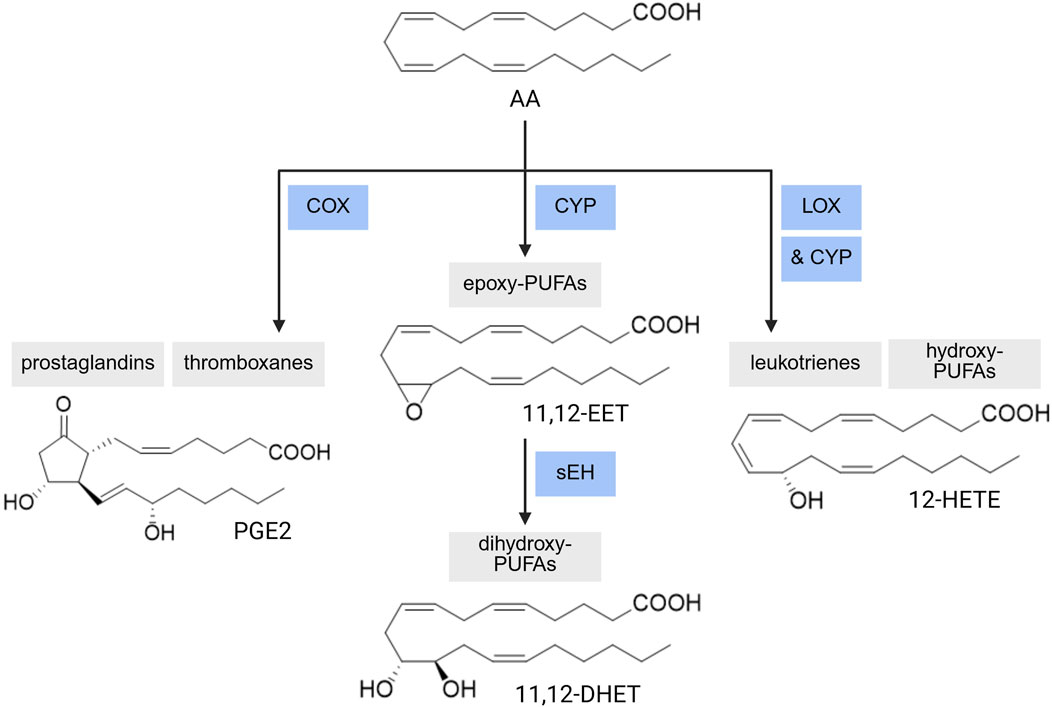
Figure 3. PUFA Enzymatic Metabolism. A range of PUFA metabolites can be produced via CYP-sEH (cytochrome P450-soluble epoxide hydrolase), COX (cyclooxygenase), or LOX (lipoxygenase)-mediated reactions. AA: arachidonic acid, EET: epoxyeicosatrienoic acid, DHET: dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acid, HETE: hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid, PGE2: prostaglandin E2. Created with BioRender.com.
4.1.2 Evidence of the effects of the exposome on PUFAs
External exposomal exposures can directly and indirectly affect the microbiome, leading to dysbiosis, which can affect the functions of the microbiome. The net result is a downstream effect on the internal exposome, which influences human health and disease (Merra et al., 2024; Losol et al., 2023). The effect of the exposome on the microbiome can influence the absorption and biotransformation of PUFAs by gut microbiota, modulating lipid signaling and composition in the body. Some studies also examined the interplay of the exposome and PUFAs, with most studies focusing on the interaction of downstream metabolizing enzymes and their products after external exposures. However, one study examining asthma outcomes with dietary PUFAs showed that higher ω-6 PUFA intake exacerbated asthma severity in response to indoor particulate matter (PM ≤ 2.5) while higher ω-3 PUFA intake alleviated asthma symptoms due to PM (Brigham et al., 2019). Another study found that habitual dietary intake of ω-3 PUFAs has a protective effect against air pollution-induced (PM ≤ 2.5, ozone) cardiovascular effects (Chen et al., 2022). Reviewed elsewhere, increased dietary intake of ω-6 can promote hepatotoxic responses to persistent organic pollutants (i.e., polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB)) including oxidative stress. Meanwhile, changing the ratio of ω-6/ω-3 or increasing ω-3 intake can protect against the PCB-induced inflammation (Hennig et al., 2012).
4.1.3 Evidence of the effects of PUFAs on aging and senescence
Characterizing an association between the dysregulation of lipid metabolism and aging has been a recent focus within the field. A study examining fatty acids in the blood of adults (18–64), older adults (65–89), and long-lived individuals (LLIs, 90–111) found that LLIs and older adults had a reduction in the ω-3 index compared to adults. Interestingly, EPA and DHA levels were similar between adults and LLIs but not older adults, while DPA3 showed a significant decrease with age. However, the authors also note that aging may not modulate ω-3 PUFAs, but instead an increase in ω-3 PUFAs levels may promote longevity. Conversely, for ω-6 PUFAs, higher levels of DGLA were observed in LLIs compared to adults and older adults while LA and AA decreased with age (Ali et al., 2022). An additional study examined the relationship between PUFAs and markers of oxidative stress and inflammation with aging. Blood ω-3 PUFAs and ω-3 index values were associated with increased C-reactive protein levels in male LLIs. ω-3 PUFAs were positively associated with Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity (TEAC) in male LLIs, while the AA/EPA ratio was negatively associated with TEAC values in female LLIs. Increased levels of total ω-3 PUFAs and ω-3 index were also associated with increased MDA concentration in male LLIs, while total ω-6 PUFAs had a significant inverse correlation in female LLIs (Aiello et al., 2024). Furthermore, genetic knockout of Elovl2 (elongase of very long chain fatty acids 2) in mice accelerated aging phenotypes and aging hallmarks, suggesting a role for Elovl2 in aging. Reduction or loss of Elovl2 also results in an increase in fatty acid synthesis, leading to changes in mitochondrial energy metabolism and accumulation of fatty acid precursors for PUFA synthesis in the ER causing ER stress (Li et al., 2022). Other studies in Caenorhabditis elegans demonstrated that changes in dietary PUFAs and oxidative state can modulate the lifespan (Watts, 2016). Understanding the lipid signaling involvement of all fatty acids in aging is also of great interest in the field and has been reviewed elsewhere (Mutlu et al., 2021). Additionally, changes in lipid composition for the various PUFA forms (i.e., triglycerides, phospholipids, etc.) during cellular senescence have been reviewed elsewhere (Hamsanathan and Gurkar, 2022).
4.2 Cytochrome P450s
Cytochrome P450 monooxygenases (CYPs) constitute an extensive family of heme-thiol containing monooxygenases that are responsible for metabolizing xenobiotics such as drugs, pesticides, carcinogens, etc. (Degtyarenko and Archakov, 1993; Bernhardt, 2006; Werck-Reichhart and Feyereisen, 2000). CYPs are also involved in the metabolism of many physiologically important endogenous compounds including steroid hormones, cholesterol, vitamins, and fatty acids (Bernhardt, 2006). Within the body, CYPs are mainly concentrated within the liver due to their role in xenobiotic and endogenous metabolism but are ubiquitously expressed in most tissues including the kidneys, intestines, brain, heart, lung, and skin (Anzenbacher and Anzenbacherová, 2001; Preissner et al., 2013). Within cells, CYPs are predominately membrane-bound on the ER or mitochondria, with the ability to move along the membrane surface as the catalytic domain remains on the cytosolic side but is anchored by the N-terminal transmembrane on the luminal side (Šrejber et al., 2018).
4.2.1 Range of CYP families
Within humans, 57 genes expressing various CYP enzymes have been identified, which can be clustered into 18 families with 43 sub-families (Nelson, 2009). The 57 CYP genes identified from the human genome project gave new insight into the extent of CYP isoforms, with many of these enzymes covering a large range of functions, although the role of some isoforms remains unknown (Ingelmansundberg, 2005). In this review, we will only focus on the CYP isoforms related to PUFA metabolism. Many CYP isoforms have been extensively studied for their role in PUFA metabolism, as CYPs can exert both epoxidation (forming epoxy-PUFAs) and hydroxylation (forming hydroxy-PUFAs) on PUFAs as substrates. The extent of preference for PUFA substrates and the type of reaction have been extensively covered elsewhere (Sarparast et al., 2020).
Overall, CYP2B, 2C (2C8, 9, 18, 19, 23), and 2J (2J2, 3, 5, 9) are the subfamilies that predominately generate epoxy-PUFAs (Sarparast et al., 2020). On the other hand, CYP1A (1A1, 2), 4A (4A1, 11, 12A), and 4F (4F2, 3A, 3B, 8, 12) subfamilies produce mostly hydroxy-PUFAs (Sarparast et al., 2020). However, many of these subfamilies will produce the epoxy- or hydroxy-PUFAs as minor products, respectively. There are some isoforms outside of these subfamilies which are also involved in PUFA oxidative metabolism such as CYP3A4 (mainly epoxidation), CYP2E1 (both reactions), and 2U1 (mainly hydroxylation) (Sarparast et al., 2020). The catalytic cycle of CYP reactions (Denisov et al., 2005; Guengerich, 2018; Meunier et al., 2004) is generally accepted for most P450-catalyzed oxidations; however, specific steps and their respective intermediates within the catalytic cycle have proven difficult to characterize. There are some variations to the cycle for the distribution of charge on the iron atom, the iron-oxo bond, and the porphyrin ring (Guengerich, 2018).
4.2.2 Evidence of the effects of the exposome on CYP
Environmental pollutants have been shown to affect the expression of CYP isoforms. 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) was found to induce CYP1A1 gene expression and enzyme activity. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) can induce the expression of CYP1A1, CYP1A2, and CYP1B1 (Ibrahim et al., 2019; Rao and Kumar, 2015). Long-term exposure to environmental factors can lead to methylation, acetylation or histone modification, affecting CYP gene expression (Jin et al., 2023). Internal exposomal factors, especially stress, can also significantly affect the expression of CYP isoforms. In animal stress models, stress could downregulate the expression of CYP2E1 and CYP2B, while upregulating the expression of CYP1A, CYP2A, CYP2C, CYP2D, and CYP3A isoforms (Konstandi et al., 2014). In rats, some isoforms such as CYP1A2, CYP2B1, and CYP2E1 are expressed at higher levels in young rats while CYP1A1 is only expressed at early stages of development. Similarly, the expression of CYP2C11 and CYP3A2 drastically increased during puberty in rats then declined again with aging (Yun et al., 2010). The stress- and age-related effects on CYP expression could be due to negative effects on and decline in the activity of hormonal systems that are involved in CYP regulation (Konstandi and Johnson, 2023). Human studies have not largely demonstrated significant changes in CYP isoform expression patterns. However, some studies found slight decreases in CYP isoform activity with aging (Konstandi and Johnson, 2023).
Changes to CYP isoform expression result in imbalances in epoxy- and hydroxy-PUFA levels, causing systemic effects due to the range of these metabolites’ activity and contributing to inflammaging. Epoxy-PUFAs are generally considered more anti-inflammatory, while hydroxy-PUFAs are more pro-inflammatory and have been implicated in multiple diseases (Hwang et al., 2017). Environmental exposures that generate ROS can also non-enzymatically react with PUFAs to form hydroxy-PUFAs, further disrupting homeostasis (Zhu et al., 2021).
4.2.3 Evidence of the effects of CYP on aging and senescence
CYP metabolism of unsaturated fatty acids produces bioactive lipid mediators, which impact aging and senescence. Numerous studies have examined CYP-metabolites in age-associated NDs. One study reported increased levels of LA-derived hydroxy-PUFAs (HODEs) in the plasma and erythrocytes of patients with AD, which are positively correlated with clinical severity (Yoshida et al., 2009). Another study examining lipid mediators in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid between AD and healthy individuals, including analysis with strong predictive and discriminant models, identified differences in CYP/sEH and acylethanolamide metabolism that could serve as predictors of AD. Specifically for CYP/sEH metabolism, the partial least squares discriminant analysis performed on the samples found higher levels of 9,10-EpOME and 12,13-EpOME in the cerebrospinal fluid and a decrease in the ratio of 12,13-DiHOME/EpOME in the plasma in the AD group compared to the control group (Borkowski et al., 2021). In postmortem cerebral cortex samples, a positive correlation between various CYP-derived oxylipins and clinical phenotypes of AD were found, including 5-, 9-, and 12-HETE, 12-HEPE, 13-HpODE, 5,6- and 11,12-DHET, and 14,15-DiHETE (Kurano et al., 2022). Meanwhile, levels of oxidized LA metabolites were greatly increased in advanced lesions in postmortem aortas of patients with atherosclerosis (Harland et al., 1971).
CYP-mediated reactions can also produce ROS, leading to oxidative stress. Increased ROS production due to age-related dysregulation of CYPs contributes to DNA damage, protein oxidation, and lipid peroxidation all of which accelerate aging and trigger cellular senescence (Chaudhary et al., 2009). CYP isoforms found within the mitochondria also exacerbates local oxidative stress, both impairing mitochondrial function (a hallmark of aging) and promoting cellular senescence (Hamsanathan and Gurkar, 2022; Chaudhary et al., 2009). The involvement of CYP metabolites in cellular senescence is relatively understudied. However, epoxy-PUFAs generated from CYP enzymes have shown effects similar to the beneficial roles of senescent cells, such as involvement in wound healing, tissue repair, and tumor suppression and reduced proinflammatory factor production (Hamsanathan and Gurkar, 2022). CYP-derived epoxy-PUFAs protect against mitochondrial dysfunction resulting in cellular senescence and suppress pro-inflammatory SASP in cardiac models (Yousef et al., 2024).
One study examining changes between age and CYP levels and activity in the liver found that CYP activity decreased after the age of 40 (Sotaniemi et al., 1997). Serum antipyrine, which is metabolized by at least 10 CYP isoforms, is used to measure in vivo hepatic CYP activity. Clearance of antipyrine declined linearly after age 40, likely due to age-related changes in CYP expression or activity. Meanwhile the half-life of antipyrine increased linearly after age 30, likely due to age-related changes in liver drug distribution and elimination processes (Sotaniemi et al., 1997). Changes in liver CYP metabolizing activity with aging can result in changes to hormone levels, influencing additional age-related changes. In men, testosterone levels are highest in young age and decline throughout the lifespan, while reduced CYP activity in women may lower estrogen levels in postmenopausal women, impacting bone density, cardiovascular, and neurological health (Sotaniemi et al., 1997; Tsuchiya et al., 2005). Age-related increases or decreases of specific CYP isoforms and their activity can result in dysregulated steroid hormone synthesis and metabolism, leading to excessive accumulation or deletion of various hormones as CYP isoforms within the CYP11, CYP17, CYP19, and CYP21 families are involved in steroid biosynthesis. This dysregulation can also result in ROS production, where the ROS can then promote cell death or cellular senescence. The dysregulation of CYP metabolism in endocrine signaling and its impact on human disease has been more deeply reviewed elsewhere by Hossam Abdelmonem et al. (Hossam et al., 2024).
4.3 Epoxide hydrolase(s)
Epoxide hydrolases (EHs) are vastly important in both detoxification, catabolism, and regulatory signaling pathways within the human body (Gautheron and Jéru, 2020; Morisseau and Hammock, 2005). These enzymes metabolize a range of endogenous and exogenous compounds containing an epoxide motif, including pharmaceuticals, toxins, hormones, and epoxy-PUFAs, to their corresponding 1,2-diols (Morisseau and Hammock, 2005; Harris et al., 2008). Within mammals, seven EHs have been identified: microsomal epoxide hydrolase (mEH, encoded by EPHX1), soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH, EPHX2), epoxide hydrolase 3 (EH3, EPHX3), epoxide hydrolase 4 (EH4, EPHX4), hepoxilin hydrolase, leukotriene A4 hydrolase (LTA4H), and cholesterol epoxide hydrolase (Sarparast et al., 2020; Gautheron and Jéru, 2020). To date, no corresponding genes have been identified for hepoxilin hydrolase and cholesterol epoxide hydrolase. However, an α/β-fold hydrolase EH subfamily categorizes mEH, sEH, EH3, and EH4 together from the remaining three EHs (which can be categorized separately based on their catalytic mechanism and substrate preferences) (Decker et al., 2009).
4.3.1 sEH
Overall, mEH and sEH have received significantly more attention than EPHX3/4 and thus, their functions are better understood. mEH, EPHX3, and EPHX4 are out of the scope of this review and have been discussed elsewhere (Sarparast et al., 2020; Decker et al., 2009; Decker et al., 2012). Soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH, EPHX2) can be found in the cytosol and peroxisomes of cells. sEH is a bifunctional enzyme with an N-terminal region responsible for phosphatase activity and a C-terminal region responsible for epoxide hydrolase activity, connected by a proline-rich linker (Harris and Hammock, 2013). sEH is ubiquitously expressed and found at its highest concentrations in the liver and kidney, and sEH regulates important physiological processes in the brain, lungs, and heart (Harris and Hammock, 2013). sEH has specifically been shown to be the main enzyme that degrades epoxy-PUFAs (Bylund et al., 1998), especially at high rates of epoxide formation (Edin et al., 2018). The remaining three EH isoforms are also involved in metabolizing epoxy-fatty acids but at a lower rate. sEH hydrolyzes epoxy-fatty acids and generates trans 1,2-diols with no enantiomeric selectivity. On the other hand, mEH is less active against epoxy-fatty acids (Zeldin et al., 1995), but mEH hydrolyzes these substrates with high enantiomeric selectivity (Zeldin et al., 1993; Summerer et al., 2002).
The mechanism of this catalysis is performed in three steps, along with a contribution from four amino acid residues (Sarparast et al., 2020; Gautheron and Jéru, 2020; Morisseau and Hammock, 2005). Within the substrate binding pocket of sEH, the epoxide substrate is bound through hydrogen bonds with the two tyrosine residues, and the binding of the substrate is further enhanced by the hydrophobic interaction with the protein binding pocket. The epoxide is then activated by the hydrogen bond with the tyrosine residues and opened by a nucleophilic attack of the aspartate (which is orientated and activated by a histidine residue, a second carboxylic acid amino acid, and potentially other amino acids located in the catalytic center) on one of the epoxide carbons forming an enzyme-substrate ester intermediate. Following this, the histidine residue relocates away from the ester, in which a water molecule is then activated by the acid-histidine pair. This activated water then hydrolyzes the ester intermediate resulting in the diol product and original enzyme. The mechanism of mEH conversion of epoxides to diol is highly similar, with differences only including a change in the orientating amino acid and the position of the amino acid in both proteins’ sequence (Morisseau and Hammock, 2005). EH3 and EH4 follow the same mechanism and use the same orientating amino acid as mEH, but likewise have differences in the position of the amino acids involved (Morisseau and Hammock, 2005).
4.3.2 Evidence of the effects of the exposome on sEH
Various environmental factors such as cigarette smoke, PAHs (3-methylcholanthrene, benzo(a)pyrene), and pharmaceuticals (ethinyl estradiol, tamoxifen, raloxifene, isoproterenol) have been examined for effects on sEH expression, with many of these resulting in an upregulation of sEH, shifting the balance toward increased dihydroxy-PUFAs to epoxy-PUFAs ratio (Harris and Hammock, 2013). Exposures to LPS, streptozotocin, and monocrotaline also resulted in downregulation of sEH, which reduces the conversion of epoxy-PUFAs to dihydroxy-PUFAs, preserving the anti-inflammatory properties of epoxy-PUFAs (Harris and Hammock, 2013). External and internal factors that induce oxidative stress can also activate sEH via oxidative intra-disulfide formation. This specific activation not only results in increased specific activity of sEH, but also increases the substrate affinity and catalytic efficiency of sEH (Charles et al., 2021).
4.3.3 Evidence of the effects of sEH on aging and senescence
The precursor metabolites of sEH (epoxy-PUFAs) mediate vasodilation, reduce inflammation, attenuate oxidative stress, and block endoplasmic reticulum stress response. Thus, the conversion of epoxy-to dihydroxy-PUFAs can diminish the beneficial effects of epoxy-PUFAs (Griñán-Ferré et al., 2020). Inhibiting sEH has shown beneficial effects in a variety of age-related diseases such as diabetes (Lee et al., 2020; Anita and Swardfager, 2022), atherosclerosis (Piper and Garelnabi, 2020; Kim SA. et al., 2022), and neurodegenerative diseases (Griñán-Ferré et al., 2020; Ren et al., 2018). sEH directly contributes to aging processes in the colon by enhancing ER stress and cellular senescence (Wang et al., 2023). Finally, genetic knockout of sEH demonstrated beneficial effects following cerebral ischemia in reproductively senescent female mice (Zuloaga et al., 2015).
4.4 Lipoxygenase
Lipoxygenases (LOXs) constitute a family of non-heme iron-containing dioxygenases that catalyze the stereoselective monooxygenation of PUFAs, with their nomenclature typically denoting their positional specificity of oxygen insertion (Kuhn and Thiele, 1999; Czapski et al., 2016). There are five LOXs found in mammals: 5-, 8-, 12-, 15-LOX and LOX-3 in which LOX-3 does not follow the oxygen-insertion trend or nomenclature. While the structures of the various LOX isoforms are similar to each other, differences in substrate cavity, coordination of histidine residues or variations to the non-heme iron in the catalytic center can affect their substrate specificity (Mashima and Okuyama, 2015). Very little is known about the location of most LOX isoforms. However, current understanding suggests that some isoforms can be found in the vasculature, central nervous system, and in endothelial cells. Intracellularly, the LOX isoforms are primarily found in the cytoplasm in their inactive form and upon activation, it will translocate to the nucleus or membrane (plasma, intracellular) (Czapski et al., 2016; Rådmark and Samuelsson, 2009). LOXs are involved in the production of leukotrienes, lipoxins, and hydroxy fatty acids; however, the biological roles for most LOX isoforms are not entirely known (Kuhn and Thiele, 1999). LOXs are capable of peroxidizing membrane lipids resulting in cellular structural changes (Rapoport and Schewe, 1986). The detailed mechanism of LOX is still not entirely known. However, there is a consensus regarding the radical nature of this reaction (Kuhn and Thiele, 1999; Czapski et al., 2016).
4.4.1 Evidence of the effects of the exposome on LOX
Cytokines can regulate the expression of arachidonate lipoxygenase (ALOX) genes, with Th2 cytokines increasing ALOX15 expression (Mashima and Okuyama, 2015). Human patients challenged with aeroallergens (i.e., birch, grass, house dust mite) and diesel exhaust also demonstrated an increase in the expression of ALOX15 in the airway epithelium (Li et al., 2024). External exposures like calcium can regulate the expression of ALOX5, while acrolein, an environmental exposure released from burning tobacco, wood, plastics, gasoline, paraffin wax, and some cooking fats and oils, can increase the expression of 5-LOX via EGFR-dependent activation of the ERK pathway (Kim et al., 2010). Meanwhile zileuton is a pharmaceutically available 5-LOX inhibitor used to control asthma (Mashima and Okuyama, 2015). Phenolic antioxidants (i.e., nordihydroguaiaretic acid and caffeic acid) can also inhibit various LOX isoforms (Mashima and Okuyama, 2015).
4.4.2 Evidence of the effects of LOX on aging and senescence
In general, LOX generates lipid hydroperoxides from PUFAs. These hydroperoxides can interact with metal ions to decompose into other free radicals, resulting in oxidative stress, which accelerates aging via increased cell death and cellular senescence (Mashima and Okuyama, 2015). ALOX12 gene polymorphisms are associated with age-related diseases such as cancers (i.e., esophageal squamous cell, colorectal, and breast), neurological disorders, hypertension, and bone mineral density while ALOXE3 and ALOX12B mutations together are associated with various skin disorders (Mashima and Okuyama, 2015). ALOX5 is negatively associated with neurological disorders, as 5-LOX is upregulated in neuronal tissue during AD. Furthermore, treatment with the 5-LOX inhibitor zileuton in an AD mouse model demonstrated a rescuing effect from AD-like phenotype. Specifically, zileuton improved memory impairment, reduced Aβ plaques via decreased expression of γ-secretase complex, and reduced tau hyperphosphorylation via decreased expression of the binding activators (p35, p25) of the cgk-5 kinase pathway partially responsible for tau hyperphosphorylation (Chu et al., 2013). Meanwhile, an aging mouse model deficient in 12- and 15-LOX found that deficiency in 12/15-LOX leads to increased spleen mass and disruption to spleen microarchitecture, cardiac dysfunction and inflammation, and diminished essential immune cell populations and their phenotypes, overall contributing to age-related inner-organ inflammation (Kain et al., 2021).
The LA-derived 15-LOX metabolite, 13S-hydroperoxyoctadecaenoic acid, has been found to induce apoptosis in colon cancer cells (Shureiqi et al., 2000). In fibroblasts, oncogenic-, stress-, or radiation-induced senescence promoted secretion of leukotrienes and expression of enzymes responsible for leukotriene biosynthesis (Wiley et al., 2019). Following chemotherapy-induced senescence, renal injury was accelerated by cysteinyl leukotrienes (Rubinstein and Dvash, 2017). While leukotrienes are secreted from senescent cells, they appear to function in parallel to SASP factors (Hamsanathan and Gurkar, 2022).
4.5 Cyclooxygenase
Cyclooxygenases (COXs) consists of two isoforms in vertebrates (COX-1 and COX-2) that are responsible for the catalysis of PUFAs to prostaglandins, prostacyclin, thromboxanes, and hydroxy-PUFAs (Rouzer and Marnett, 2009; Rouzer and Marnett, 2003). Both COX isoforms are heterodimers, with each subunit of the dimer containing an epidermal growth domain, membrane-binding domain, and catalytic domain where the cyclooxygenase and peroxidase active sites are found on either side of the heme prosthetic group (Rouzer and Marnett, 2009). COX-1 is continuously expressed and is found in most tissues, while COX-2 expression is inducible (Rouzer and Marnett, 2003). COX-1 and COX-2 are membrane-bound proteins found in the nuclear membrane and in the lumen of the ER (Spencer et al., 1998). A third cyclooxygenase, COX-3, has also been identified as it results from a splice variant of the COX-1 gene. However, this enzyme is not functional in humans (Chandrasekharan et al., 2002). The catalysis of COX occurs in a similar manner to that of nonenzymatic peroxidation. However, COX restricts the location of hydrogen abstraction and will dictate reaction stereochemistry (Rouzer and Marnett, 2009; Rouzer and Marnett, 2003; van der Donk et al., 2002).
4.5.1 Evidence of the effects of the exposome on COX
Both isoforms of COX are inhibited by NSAIDs; but COX-2 can be induced by a variety of environmental factors such as bacterial products, pro-inflammatory cytokines, UV light, cigarette smoke, diet, heavy metals, and xenobiotics (Kim et al., 2016). In endometriosis, upregulation of COX-2 by estrogen, hypoxia, proinflammatory cytokines, environmental pollutants, metabolites and metabolic enzymes, and platelets increases COX-2-derived prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) which can act in a feedback loop for enhanced inflammation (Lai et al., 2019). One study also found that COX-2 and its subsequent metabolite PGE2 are affected during temperature regulation in response to external temperatures (Esh et al., 2021). Dysregulated COX activity due to environmental exposures can contribute to several chronic conditions such as atherosclerosis, arthritis, cancer, diabetes, inflammation, neurodegenerative diseases, and osteoporosis as well as multidrug resistance (Kim et al., 2016; Lai et al., 2019).
4.5.2 Evidence of the effects of COX on aging and senescence
Increased activity of COX-2 is associated with aging, and expression of COX-2 was upregulated in multiple organs in both aged rodent models and humans (Hamsanathan and Gurkar, 2022; Kim et al., 2016). COX-2 expression has also been reported to be increased in many age-related diseases (Kim et al., 2016). A transgenic mouse model with an inducible expression of COX-2 found that this induced expression resulted in several premature aging-related phenotypes and a significantly reduced lifespan, while lung fibroblasts from this model exhibited increased expression of SA-β-gal (Kim et al., 2016). In human lung fibroblasts an upregulation of COX-2 expression and subsequent production of PGE2 was observed in normal and stress-induced senescence, while arachidonic acid supplementation further enhanced this observation and accelerated the incidence of key senescent features (Dagouassat et al., 2013). Senescent cells were shown to produce and accumulate multiple prostaglandin J2 metabolites that can promote senescence arrest and SASP production along with other prostaglandin D2 metabolites (Wiley et al., 2021).
5 Conclusion
There is a current lack of understanding about the intersection of the exposome in geroscience, resulting in many unknowns regarding the mechanisms controlling healthy aging. Previous research has demonstrated epigenetic changes due to environmental exposures (Miller and Jones, 2014), with researchers suggesting that environmental exposures are more impactful than genetic factors in human diseases such as cancer and degenerative diseases (Rappaport, 2011). Some studies have demonstrated that immigrant populations adopt the disease patterns of their host countries (KATO et al., 1973), and that there are regional distinctions in disease rates of the same disease throughout the separate United States populations (KATO et al., 1973). While there is a higher familial risk of certain types of cancer in twin studies, genetics alone is not sufficient to adequately characterize disease risk (Mucci et al., 2016). However, some studies have also examined the specific relationship between environmental exposures and specific mutations in tumors, highlighting the joint contribution of genome and exposome in cancer (Willett, 2002). Due to the large spread of environmental exposures that may contribute to a decline in health and/or involvement in human disease, it is not currently feasible to quantify and examine all these factors. Thus, much of the research in the field of exposure science examines exposures (toxicants) with previously known biologically active roles, such as reactive electrophiles, metabolites, metals, endocrine disruptors, persistent organic compounds, and modulators of immune responses (Rappaport and Smith, 2010). As discussed throughout this review, exposure to many of these substances can affect aging in terms of their involvement in age-related diseases and their contribution to oxidative stress, cell death, and senescence.
5.1 Potential developments in the field
As the exposome encompasses such a large range of exposures and so many of these exposures can interact, a huge knowledge gap remains about how these exposures can co-function in affecting oxylipin metabolism in vivo and in aging-related effects. However, due to the extent of these exposures, it is not feasible to individually test all of these and in combination with each other. Thus, high throughput screening is needed to examine the interaction of the exposome on the oxylipin profile at a large scale, increasing our knowledge of the human relevance of these exposures. Utilizing high throughput screening, additional exposures not detailed within this review should also be examined, such as per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), lifestyle factors (i.e., alcohol, tobacco, caffeine), pharmaceuticals, and other environmental and occupational contaminants for their effects on both oxylipin profile and healthy aging.
Author contributions
JH: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. JA: Writing – review and editing. KL: Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This manuscript is partially supported by R35 MIRA from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (R35 GM146983). JH is partially funded by NIEHS T32 ES007255.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphys.2025.1584195/full#supplementary-material
References
Adonaylo V. N., Oteiza P. I. (1999). Pb2+ promotes lipid oxidation and alterations in membrane physical properties. Toxicology 132 (1), 19–32. doi:10.1016/s0300-483x(98)00134-6
Ahamed M., Siddiqui M. K. J. (2007). Low level lead exposure and oxidative stress: current opinions. Clin. Chim. Acta 383 (1–2), 57–64. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2007.04.024
Aiello A., Medoro A., Accardi G., Calabrò A., Carru C., Cannavo A., et al. (2024). Polyunsaturated fatty acid status and markers of oxidative stress and inflammation across the lifespan: a cross-sectional study in a cohort with long-lived individuals. Exp. Gerontol. 195, 112531. doi:10.1016/j.exger.2024.112531
Aleksandrova K., Koelman L., Rodrigues C. E. (2021). Dietary patterns and biomarkers of oxidative stress and inflammation: a systematic review of observational and intervention studies. Redox Biol. 42, 101869. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2021.101869
Ali S., Aiello A., Zotti T., Accardi G., Cardinale G., Vito P., et al. (2022). Age-associated changes in circulatory fatty acids: new insights on adults and long-lived individuals. GeroScience 45 (2), 781–796. doi:10.1007/s11357-022-00696-z
Ameur A., Enroth S., Johansson Å., Zaboli G., Igl W., Johansson A. C. V., et al. (2012). Genetic adaptation of fatty-acid metabolism: a human-specific haplotype increasing the biosynthesis of long-chain omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 90 (5), 809–820. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.03.014
Anderson A. S., Loeser R. F. (2010). Why is osteoarthritis an age-related disease? Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 24 (1), 15–26. doi:10.1016/j.berh.2009.08.006
Anita N. Z., Swardfager W. (2022). Soluble epoxide hydrolase and diabetes complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (11), 6232. doi:10.3390/ijms23116232
Anzenbacher P., Anzenbacherová E. (2001). Cytochromes P450 and metabolism of xenobiotics. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 58 (5), 737–747. doi:10.1007/pl00000897
Argentieri M. A., Amin N., Nevado-Holgado A. J., Sproviero W., Collister J. A., Keestra S. M., et al. (2025). Integrating the environmental and genetic architectures of aging and mortality. Nat. Med. 31 (3), 1016–1025. doi:10.1038/s41591-024-03483-9
Atwood C. S., Scarpa R. C., Huang X., Moir R. D., Jones W. D., Fairlie D. P., et al. (2000). Characterization of copper interactions with alzheimer amyloid beta peptides: identification of an attomolar-affinity copper binding site on amyloid beta1-42. J. Neurochem. 75 (3), 1219–1233. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.0751219.x
Battaglia V., Compagnone A., Bandino A., Bragadin M., Rossi C. A., Zanetti F., et al. (2009). Cobalt induces oxidative stress in isolated liver mitochondria responsible for permeability transition and intrinsic apoptosis in hepatocyte primary cultures. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 41 (3), 586–594. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2008.07.012
Bernhardt R. (2006). Cytochromes P450 as versatile biocatalysts. J. Biotechnol. 124 (1), 128–145. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2006.01.026
Berridge M. J. (2017). Vitamin D deficiency accelerates ageing and age-related diseases: a novel hypothesis. J. Physiol. 595 (22), 6825–6836.
Bikle D. D. (2014). Vitamin D metabolism, mechanism of action, and clinical applications. Chem. Biol. 21 (3), 319–329.
Birringer M., EyTina J. H., Salvatore B. A., Neuzil J. (2003). Vitamin E analogues as inducers of apoptosis: structure–function relation. Br. J. Cancer. 88 (12), 1948–1955.
Bjørklund G., Shanaida M., Lysiuk R., Antonyak H., Klishch I., Shanaida V., et al. (2022). Selenium: an antioxidant with a critical role in anti-aging. Molecules 27 (19), 6613. doi:10.3390/molecules27196613
Booth F. W., Roberts C. K., Laye M. J. (2012). Lack of exercise is a major cause of chronic diseases. Compr. Physiol. 2 (2), 1143–1211. doi:10.1002/cphy.c110025
Borkowski K., Pedersen T. L., Seyfried N. T., Lah J. J., Levey A. I., Hales C. M., et al. (2021). Association of plasma and CSF cytochrome P450, soluble epoxide hydrolase, and ethanolamide metabolism with Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 13, 149. doi:10.1186/s13195-021-00893-6
Brewer G. J. (2010). Risks of copper and iron toxicity during aging in humans. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 (2), 319–326. doi:10.1021/tx900338d
Brigham E. P., Woo H., McCormack M., Rice J., Koehler K., Vulcain T., et al. (2019). Omega-3 and omega-6 intake modifies asthma severity and response to indoor air pollution in children. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 199 (12), 1478–1486. doi:10.1164/rccm.201808-1474OC
Brunet A., Goodell M. A., Rando T. A. (2023). Ageing and rejuvenation of tissue stem cells and their niches. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 24 (1), 45–62.
Burdge G. C., Jones A. E., Wootton S. A. (2002). Eicosapentaenoic and docosapentaenoic acids are the principal products of α-linolenic acid metabolism in young men. Br. J. Nutr. 88 (4), 355–363. doi:10.1079/BJN2002662
Burdge G. C., Wootton S. A. (2002). Conversion of α-linolenic acid to eicosapentaenoic, docosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids in young women. Br. J. Nutr. 88 (4), 411–420. doi:10.1079/BJN2002689
Bylund J., Kunz T., Valmsen K., Oliw E. H. (1998). Cytochromes P450 with bisallylic hydroxylation activity on arachidonic and linoleic acids studied with human recombinant enzymes and with human and rat liver microsomes. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 284 (1), 51–60. doi:10.1016/s0022-3565(24)37230-1
Cai Z., Zhang J., Li H. (2019). Selenium, aging and aging-related diseases. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 31 (8), 1035–1047. doi:10.1007/s40520-018-1086-7
Campanera M., Gasull M., Gracia-Arnaiz M. (2023). Food security as a social determinant of health: tackling inequalities in primary health care in Spain. Health Hum. Rights 25 (1), 9–21.
Campisi J. (2003). Cellular senescence and apoptosis: how cellular responses might influence aging phenotypes. Exp. Gerontol. 38 (1), 5–11.
Carter J. E. L., Heath B. H. (1990). Somatotyping development and applications. New York, N.Y.: Cambridge University Press.
CDC. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2023). Socioecon. Factors | CDC. Available online at: https://www.cdc.gov/dhdsp/health_equity/socioeconomic.htm.
Červenka J., Tylečková J., Kupcová Skalníková H., Vodičková Kepková K., Poliakh I., Valeková I., et al. (2021). Proteomic characterization of human neural stem cells and their secretome during in vitro differentiation. Front. Cell Neurosci. 14. doi:10.3389/fncel.2020.612560
Chakrabarti A., Eiden M., Morin-Rivron D., Christinat N., Monteiro J. P., Kaput J., et al. (2020). Impact of multi-micronutrient supplementation on lipidemia of children and adolescents. Clin. Nutr. 39 (7), 2211–2219. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2019.09.010
Chakraborty A., Jana N. R. (2017). Vitamin C-Conjugated nanoparticle protects cells from oxidative stress at low doses but induces oxidative stress and cell death at high doses. ACS Appl. Mater Interfaces 9 (48), 41807–41817.
Chandra A., Rajawat J. (2021). Skeletal aging and osteoporosis: mechanisms and therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (7), 3553. doi:10.3390/ijms22073553
Chandrasekharan N. V., Dai H., Roos K. L. T., Evanson N. K., Tomsik J., Elton T. S., et al. (2002). COX-3, a cyclooxygenase-1 variant inhibited by acetaminophen and other analgesic/antipyretic drugs: cloning, structure, and expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 99 (21), 13926–13931. doi:10.1073/pnas.162468699
Chapman J., Fielder E., Passos J. F. (2019). Mitochondrial dysfunction and cell senescence: deciphering a complex relationship. FEBS Lett. 593 (13), 1566–1579.
Charles R. L., Abis G., Fernandez B. F., Guttzeit S., Buccafusca R., Conte M. R., et al. (2021). A thiol redox sensor in soluble epoxide hydrolase enables oxidative activation by intra-protein disulfide bond formation. Redox Biol. 46, 102107. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2021.102107
Chaudhary K. R., Batchu S. N., Seubert J. M. (2009). Cytochrome P450 enzymes and the heart. IUBMB Life. 61 (10), 954–960. doi:10.1002/iub.241
Chen A., Li J., Shen N., Huang H., Hang Q. (2024). Vitamin K: new insights related to senescence and cancer metastasis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA - Rev. Cancer. 1879 (2), 189057. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2023.189057
Chen H., Zhang S., Shen W., Salazar C., Schneider A., Wyatt L. H., et al. (2022). Omega-3 fatty acids attenuate cardiovascular effects of short-term exposure to ambient air pollution. Part Fibre Toxicol. 19, 12. doi:10.1186/s12989-022-00451-4
Chen Z., Li Y. yuan, Liu X. (2023). Copper homeostasis and copper-induced cell death: novel targeting for intervention in the pathogenesis of vascular aging. Biomed. Pharmacother. 169, 115839. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115839
Chernoff R. (1995). Effects of age on nutrient requirements. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 11 (4), 641–652. doi:10.1016/s0749-0690(18)30262-3
Chu J., Li J. G., Praticò D. (2013). Zileuton improves memory deficits, amyloid and tau pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease with plaques and tangles. PLoS ONE 8 (8), e70991. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0070991
Clarke R., Birks J., Nexo E., Ueland P. M., Schneede J., Scott J., et al. (2007). Low vitamin B-12 status and risk of cognitive decline in older adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 86 (5), 1384–1391. doi:10.1093/ajcn/86.5.1384
Corina A., Rangel-Zúñiga O. A., Jiménez-Lucena R., Alcalá-Díaz J. F., Quintana-Navarro G., Yubero-Serrano E. M., et al. (2019). Low intake of vitamin E accelerates cellular aging in patients with established cardiovascular disease: the CORDIOPREV Study. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 74 (6), 770–777.
Cortes-Canteli M., Iadecola C. (2020). Alzheimer's disease and vascular aging: JACC focus seminar. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 75 (8), 942–951. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2019.10.062
Czapski G. A., Czubowicz K., Strosznajder J. B., Strosznajder R. P. (2016). The lipoxygenases: their regulation and implication in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem. Res. 41, 243–257. doi:10.1007/s11064-015-1776-x
Dagouassat M., Gagliolo J. M., Chrusciel S., Bourin M. C., Duprez C., Caramelle P., et al. (2013). The cyclooxygenase-2–prostaglandin E2 pathway maintains senescence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease fibroblasts. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 187 (7), 703–714. doi:10.1164/rccm.201208-1361OC
Dale W. B., Moon S., Armstrong F. (2012). Comprehensive review of ultraviolet radiation and the current status on sunscreens. J. Clin. Aesthetic Dermatol. 5 (9), 18–23.
Dalli J., Serhan C. N. (2019). Identification and structure elucidation of the pro-resolving mediators provides novel leads for resolution pharmacology. Br. J. Pharmacol. 176 (8), 1024–1037. doi:10.1111/bph.14336
DeBord D. G., Carreón T., Lentz T. J., Middendorf P. J., Hoover M. D., Schulte P. A. (2016). Use of the “exposome” in the practice of epidemiology: a primer on -omic technologies. Am. J. Epidemiol. 184 (4), 302–314. doi:10.1093/aje/kwv325
Decker M., Adamska M., Cronin A., Di Giallonardo F., Burgener J., Marowsky A., et al. (2012). EH3 (ABHD9): the first member of a new epoxide hydrolase family with high activity for fatty acid epoxides. J. Lipid Res. 53 (10), 2038–2045. doi:10.1194/jlr.M024448
Decker M., Arand M., Cronin A. (2009). Mammalian epoxide hydrolases in xenobiotic metabolism and signalling. Arch. Toxicol. 83 (4), 297–318. doi:10.1007/s00204-009-0416-0
Degtyarenko K. N., Archakov A. I. (1993). Molecular evolution of P450 superfamily and P450-containing monooxygenase systems. FEBS Lett. 332 (1–2), 1–8. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(93)80470-f
Demmelmair H., Iser B., Rauh-Pfeiffer A., Koletzko K. (1999). Comparison of bolus versus fractionated oral applications of [13C]-linoleic acid in humans. Eur. J. Clin. Invest 29 (7), 603–609. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2362.1999.00477.x
Denisov I. G., Makris T. M., Sligar S. G., Schlichting I. (2005). Structure and chemistry of cytochrome P450. Chem. Rev. 105 (6), 2253–2277. doi:10.1021/cr0307143
Di Micco R., Krizhanovsky V., Baker D., d’Adda Di Fagagna F. (2021). Cellular senescence in ageing: from mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 22 (2), 75–95.
Diwan B., Sharma R. (2022). Nutritional components as mitigators of cellular senescence in organismal aging: a comprehensive review. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 31 (9), 1089–1109. doi:10.1007/s10068-022-01114-y
Dixon S. J., Lemberg K. M., Lamprecht M. R., Skouta R., Zaitsev E. M., Gleason C. E., et al. (2012). Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of non-apoptotic cell death. Cell 149 (5), 1060–1072. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042
Doley J. (2017). “Chapter 14 - vitamins and minerals in older adults: causes, diagnosis, and treatment of deficiency,” in Nutrition and functional foods for healthy aging. Editor R. R. Watson (Academic Press), 125–137. Available online at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128053768000149.
Dummer T. J. B. (2008). Health geography: supporting public health policy and planning. CMAJ Can. Med. Assoc. J. 178 (9), 1177–1180. doi:10.1503/cmaj.071783
Dyall S. C. (2015). Long-chain omega-3 fatty acids and the brain: a review of the independent and shared effects of EPA, DPA and DHA. Front. Aging Neurosci. 7, 52. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2015.00052
Edin M. L., Hamedani B. G., Gruzdev A., Graves J. P., Lih F. B., Arbes S. J., et al. (2018). Epoxide hydrolase 1 (EPHX1) hydrolyzes epoxyeicosanoids and impairs cardiac recovery after ischemia. J. Biol. Chem. 293 (9), 3281–3292. doi:10.1074/jbc.RA117.000298
Esen Ağar B., Akarsu S., Aydin S. (2021). The effect of iron deficiency anemia and different treatment methods on DNA damage: 8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine level. Glob. Pediatr. Health 8, 2333794X211041337. doi:10.1177/2333794X211041337
Esh C. J., Chrismas B. C. R., Mauger A. R., Cherif A., Molphy J., Taylor L. (2021). The influence of environmental and core temperature on cyclooxygenase and PGE2 in healthy humans. Sci. Rep. 11, 6531. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-84563-5
Farvid M. S., Siassi F., Jalali M., Hosseini M., Saadat N. (2004). The impact of vitamin and/or mineral supplementation on lipid profiles in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 65 (1), 21–28. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2003.11.009
Fede C., Fan C., Pirri C., Petrelli L., Biz C., Porzionato A., et al. (2022). The effects of aging on the intramuscular connective tissue. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (19), 11061. doi:10.3390/ijms231911061
Finney L. A., O’Halloran T. V. (2003). Transition metal speciation in the cell: insights from the chemistry of metal ion receptors. Science 300 (5621), 931–936. doi:10.1126/science.1085049
Franceschi C., Bonafè M., Valensin S., Olivieri F., De Luca M., Ottaviani E., et al. (2000). Inflamm-aging: an evolutionary perspective on immunosenescence. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 908 (1), 244–254.
Friel S., Marmot M. G. (2011). Action on the social determinants of health and health inequities goes global. Annu. Rev. Public Health 32 (1), 225–236. doi:10.1146/annurev-publhealth-031210-101220
Fülöp Jr T., Wórum I., Csongor J., Fóris G., Leövey A. (2009). Body composition in elderly people: I. Determination of body composition by multiisotope method and the elimination kinetics of these isotopes in healthy elderly subjects. Gerontology 31 (1), 6–14. doi:10.1159/000212676
Gaetke L., Chow C. K. (2003). Copper toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidant nutrients. Toxicology 189 (1–2), 147–163. doi:10.1016/s0300-483x(03)00159-8
Galaris D., Barbouti A., Pantopoulos K. (2019). Iron homeostasis and oxidative stress: an intimate relationship. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA - Mol. Cell Res. 1866 (12), 118535. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2019.118535
García-Esquinas E., Navas-Acien A., Pérez-Gómez B., Artalejo F. R. (2015). Association of lead and cadmium exposure with frailty in US older adults. Environ. Res. 137, 424–431. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2015.01.013
Garmany A., Yamada S., Terzic A. (2021). Longevity leap: mind the healthspan gap. NPJ Regen. Med. 6, 57. doi:10.1038/s41536-021-00169-5
Gautheron J., Jéru I. (2020). The multifaceted role of epoxide hydrolases in human health and disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (1), 13. doi:10.3390/ijms22010013
Giovannini S., Onder G., Lattanzio F., Bustacchini S., Di Stefano G., Moresi R., et al. (2018). Selenium concentrations and mortality among community-dwelling older adults: results from ilSIRENTE study. J. Nutr. Health Aging 22 (5), 608–612. doi:10.1007/s12603-018-1021-9
Gorman S., Larcombe A. N., Christian H. E. (2021). Exposomes and metabolic health through a physical activity lens: a narrative review. J. Endocrinol. 249, R25–R41. doi:10.1530/JOE-20-0487
Griñán-Ferré C., Codony S., Pujol E., Yang J., Leiva R., Escolano C., et al. (2020). Pharmacological inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase as a new therapy for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurotherapeutics 17 (4), 1825–1835. doi:10.1007/s13311-020-00854-1
Grodstein F., O’Brien J., Kang J. H., Dushkes R., Cook N. R., Okereke O., et al. (2013). Long-term multivitamin supplementation and cognitive function in men: a randomized trial. Ann. Intern Med. 159 (12), 806–814. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-159-12-201312170-00006
Grundy S. M., Brewer H. B., Cleeman J. I., Smith S. C., Lenfant C. (2004). Definition of metabolic syndrome: Report of the national heart, lung, and blood Institute/American heart association conference on scientific issues related to definition. Circulation 109 (3), 433–438. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000111245.75752.C6
Gruz-Gibelli E., Chessel N., Allioux C., Marin P., Piotton F., Leuba G., et al. (2016). The vitamin A derivative all-trans retinoic acid repairs amyloid-β-induced double-strand breaks in neural cells and in the murine neocortex. Neural Plast. 2016, 3707406. doi:10.1155/2016/3707406
Guengerich F. P. (2018). Mechanisms of cytochrome P450-catalyzed oxidations. ACS Catal. 8 (12), 10964–10976. doi:10.1021/acscatal.8b03401
Guo J., Huang X., Dou L., Yan M., Shen T., Tang W., et al. (2022). Aging and aging-related diseases: from molecular mechanisms to interventions and treatments. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 7 (1), 391–440. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-01251-0
Gurer-Orhan H., Sabır H. U., Özgüneş H. (2004). Correlation between clinical indicators of lead poisoning and oxidative stress parameters in controls and lead-exposed workers. Toxicology 195 (2–3), 147–154. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2003.09.009
Hammouda S., Ghzaiel I., Khamlaoui W., Hammami S., Mhenni S. Y., Samet S., et al. (2020). Genetic variants in FADS1 and ELOVL2 increase level of arachidonic acid and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in the Tunisian population. Prostagl. Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 160, 102159. doi:10.1016/j.plefa.2020.102159
Hamsanathan S., Gurkar A. U. (2022). Lipids as regulators of cellular senescence. Front. Physiol. 13, 796850. doi:10.3389/fphys.2022.796850
Harayama T., Shimizu T. (2020). Roles of polyunsaturated fatty acids, from mediators to membranes. J. Lipid Res. 61 (8), 1150–1160. doi:10.1194/jlr.R120000800
Harland W. A., Gilbert J. D., Steel G., Brooks J. W. (1971). Lipids of human atheroma. 5. The occurrence of a new group of polar sterol esters in various stages of human atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 13 (2), 239–246. doi:10.1016/0021-9150(71)90026-8
Harris D. N., Ruczinski I., Yanek L. R., Becker L. C., Becker D. M., Guio H., et al. (2019). Evolution of hominin polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolism: from africa to the new world. Genome Biol. Evol. 11 (5), 1417–1430. doi:10.1093/gbe/evz071
Harris T. R., Aronov P. A., Jones P. D., Tanaka H., Arand M., Hammock B. D. (2008). Identification of two epoxide hydrolases in Caenorhabditis elegans that metabolize mammalian lipid signaling molecules. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 472 (2), 139–149. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2008.01.016
Harris T. R., Hammock B. D. (2013). Soluble epoxide hydrolase: gene structure, expression and deletion. Gene 526 (2), 61–74. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2013.05.008
Havranek E. P., Mujahid M. S., Barr D. A., Blair I. V., Cohen M. S., Cruz-Flores S., et al. (2015). Social determinants of risk and outcomes for cardiovascular disease: a scientific statement from the American heart association. Circulation 132 (9), 873–898. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000228
Hennig B., Ormsbee L., McClain C. J., Watkins B. A., Blumberg B., Bachas L. G., et al. (2012). Nutrition can modulate the toxicity of environmental pollutants: implications in risk assessment and human health. Environ. Health Perspect. 120 (6), 771–774. doi:10.1289/ehp.1104712
Hercberg S., Galan P., Preziosi P., Bertrais S., Mennen L., Malvy D., et al. (2004). The SU.VI.max study: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial of the health effects of antioxidant vitamins and minerals. Arch. Intern Med. 164 (21), 2335–2342. doi:10.1001/archinte.164.21.2335
Hipp M. S., Kasturi P., Hartl F. U. (2019). The proteostasis network and its decline in ageing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 20 (7), 421–435.
Hodes R. J., Sierra F., Austad S. N., Epel E., Neigh G. N., Erlandson K. M., et al. (2016). Disease drivers of aging. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1386 (1), 45–68. doi:10.1111/nyas.13299
Hossam A. B., Abdelaal N. M., Anwer E. K. E., Rashwan A. A., Hussein M. A., Ahmed Y. F., et al. (2024). Decoding the role of CYP450 enzymes in metabolism and disease: a comprehensive review. Biomedicines 12 (7), 1467. doi:10.3390/biomedicines12071467
Hou Y., Dan X., Babbar M., Wei Y., Hasselbalch S. G., Croteau D. L., et al. (2019). Ageing as a risk factor for neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 15 (10), 565–581. doi:10.1038/s41582-019-0244-7
Hu Q., Zhang Y., Lou H., Ou Z., Liu J., Duan W., et al. (2021). GPX4 and vitamin E cooperatively protect hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells from lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis. Cell Death Dis. 12 (7), 706–709. doi:10.1038/s41419-021-04008-9
Hwang S. H., Wagner K., Xu J., Yang J., Li X., Cao Z., et al. (2017). Chemical synthesis and biological evaluation of ω-hydroxy polyunsaturated fatty acids. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 27 (3), 620–625. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.12.002
Ibrahim M., MacFarlane E. M., Matteo G., Hoyeck M. P., Rick K. R. C., Farokhi S., et al. (2019). Functional cytochrome P450 1A enzymes are induced in mouse and human islets following pollutant exposure. Diabetologia 63 (1), 162–178. doi:10.1007/s00125-019-05035-0
Ingelmansundberg M. (2005). The human genome project and novel aspects of cytochrome P450 research. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 207 (2), 52–56. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2005.01.030
Innes J. K., Calder P. C. (2018). Omega-6 fatty acids and inflammation. Prostagl. Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 132, 41–48. doi:10.1016/j.plefa.2018.03.004
Ito J., Nakamura T., Toyama T., Doll S., Suzuki M., Zhang W., et al. (2024). PRDX6 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by directing cellular selenium mobilization. Available online at: http://biorxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2024.06.04.595693.
Jakaria Md, Belaidi A. A., Bush A. I., Ayton S. (2023). Vitamin A metabolites inhibit ferroptosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 164, 114930. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114930
James S. A., Roberts B. R., Hare D. J., Jonge M. D. de, Birchall I. E., Jenkins N. L., et al. (2015). Direct in vivo imaging of ferrous iron dyshomeostasis in ageing Caenorhabditis elegans. Chem. Sci. 6 (5), 2952–2962. doi:10.1039/c5sc00233h
Jeong J. H., Kim M. B., Kim C., Hwang J. K. (2017). Inhibitory effect of vitamin C on intrinsic aging in human dermal fibroblasts and hairless mice. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 27 (2), 555–564.
Jiang E. X., Domingo-Relloso A., Abuawad A., Haack K., Tellez-Plaza M., Fallin M. D., et al. (2023). Arsenic exposure and epigenetic aging: the association with cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality in the strong heart study. Environ. Health Perspect. 131 (12), 127016. doi:10.1289/EHP11981
Jin J., Zhong X. bo (2023). Epigenetic mechanisms contribute to intraindividual variations of drug metabolism mediated by cytochrome P450 enzymes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 51 (6), 672–684. doi:10.1124/dmd.122.001007
Kain V., Mat Y., Halade G. V. (2021). Interaction of aging with lipoxygenase deficiency initiates hypersplenism, cardiac dysfunction, and profound leukocyte directed non-resolving inflammation. GeroScience 44 (3), 1689–1702. doi:10.1007/s11357-021-00496-x
Kato H., Tillotson J., Nichaman M. Z., Rhoads G. G., Hamilton H. B. (1973). Epidemiologic studies of coronary heart disease and stroke in japanese men living in japan, hawall and california: serum lipids and diet. Am. J. Epidemiol. 97 (6), 372–385. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121518
Kim C. E., Lee S. J., Seo K. W., Park H. M., Yun J. W., Bae J. U., et al. (2010). Acrolein increases 5-lipoxygenase expression in murine macrophages through activation of ERK pathway. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 245 (1), 76–82. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2010.02.003
Kim D. won, Ock J., Moon K. W., Park C. H. (2022a). Association between heavy metal exposure and dyslipidemia among Korean adults: from the Korean national environmental health survey, 2015–2017. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19 (6), 3181. doi:10.3390/ijerph19063181
Kim J., Vaish V., Feng M., Field K., Chatzistamou I., Shim M. (2016). Transgenic expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX2) causes premature aging phenotypes in mice. Aging 8 (10), 2392–2406. doi:10.18632/aging.101060
Kim J. E., Jin D. H., Lee S. D., Hong S. W., Shin J. S., Lee S. K., et al. (1998). Vitamin C inhibits p53-induced replicative senescence through suppression of ROS production and p38 MAPK activity. Int. J. Mol. Med. Available from: http://www.spandidos-publications.com/ijmm/article.jsp?article_id=ijmm_22_5_651.
Kim S. A., Lee A. S., Lee H. B., Hur H. J., Lee S. H., Sung M. J. (2022b). Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor, TPPU, attenuates progression of atherosclerotic lesions and vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic switching. Vasc. Pharmacol. 145, 107086. doi:10.1016/j.vph.2022.107086
Kitagawa E. M., Hauser P. M. (2013). Differential mortality in the United States: a study in socioeconomic epidemiology. Harvard University Press. Available online at: https://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.4159/harvard.9780674188471/html?lang=en.
Kivimäki M., Batty G. D., Pentti J., Shipley M. J., Sipilä P. N., Nyberg S. T., et al. (2020). Association between socioeconomic status and the development of mental and physical health conditions in adulthood: a multi-cohort study. Lancet Public Health 5 (3), e140–e149. doi:10.1016/S2468-2667(19)30248-8
Kivimäki M., Vahtera J., Tabák A. G., Halonen J. I., Vineis P., Pentti J., et al. (2018). Neighbourhood socioeconomic disadvantage, risk factors, and diabetes from childhood to middle age in the Young Finns Study: a cohort study. Lancet Public Health 3 (8), e365–e373. doi:10.1016/S2468-2667(18)30111-7
Koleva M., Nacheva A., Boev M. (2002). Somatotype and disease prevalence in adults. Rev. Environ. Health 17 (1), 65–84. doi:10.1515/reveh.2002.17.1.65
Konstandi M., Johnson E. O. (2023). Age-related modifications in CYP-dependent drug metabolism: role of stress. Front. Endocrinol. 14, 1143835. doi:10.3389/fendo.2023.1143835
Konstandi M., Johnson E. O., Lang M. A. (2014). Consequences of psychophysiological stress on cytochrome P450-catalyzed drug metabolism. Neurosci. Biobehav Rev. 45, 149–167. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.05.011
Kopparapu A., Sketas G., Swindle T. (2020). Food insecurity in primary care: patient perception and preferences. Fam. Med. 52 (3), 202–205. doi:10.22454/FamMed.2020.964431
Kuhn H., Thiele B. J. (1999). The diversity of the lipoxygenase family. Many sequence data but little information on biological significance. FEBS Lett. 449 (1), 7–11. doi:10.1016/s0014-5793(99)00396-8
Kukrety S. P., Parekh J. D., Bailey K. L. (2018). Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and the hallmarks of aging. Lung India Off. Organ Indian Chest Soc. 35 (4), 321–327. doi:10.4103/lungindia.lungindia_266_17
Kumari K., Chand G. B. (2023). “Effects of mercury: neurological and cellular perspective,” in Mercury toxicity: challenges and solutions. Editor N. Kumar (Singapore: Springer Nature), 141–162. doi:10.1007/978-981-99-7719-2_5
Kurano M., Saito Y., Uranbileg B., Saigusa D., Kano K., Aoki J., et al. (2022). Modulations of bioactive lipids and their receptors in postmortem Alzheimer’s disease brains. Front. Aging Neurosci. 14, 1066578. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2022.1066578
La Fata G., Seifert N., Weber P., Mohajeri M. H. (2015). Vitamin E supplementation delays cellular senescence in vitro. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 563247.
Lai Z. Z., Yang H. L., Ha S. Y., Chang K. K., Mei J., Zhou W. J., et al. (2019). Cyclooxygenase-2 in endometriosis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 15 (13), 2783–2797. doi:10.7150/ijbs.35128
Lamers Y. (2022). Vitamin B-12 requirements in older adults—increasing evidence substantiates the need to Re-evaluate recommended amounts and dietary sources. J. Nutr. 152 (11), 2317–2318. doi:10.1093/jn/nxac179
Lang I. A., Scarlett A., Guralnik J., Depledge M. H., Melzer D., Galloway T. S. (2009). Age-related impairments of mobility associated with cobalt and other heavy metals: data from NHANES 1999-2004. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 72 (6), 402–409. doi:10.1080/15287390802647336
Lee K. S. S., Ng J. C., Yang J., Hwang S. H., Morisseau C., Wagner K., et al. (2020). Preparation and evaluation of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors with improved physical properties and potencies for treating diabetic neuropathic pain. Bioorg Med. Chem. 28 (22), 115735. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2020.115735
Legrain Y., Touat-Hamici Z., Chavatte L. (2014). Interplay between selenium levels, selenoprotein expression, and replicative senescence in WI-38 human fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 289 (9), 6299–6310. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.526863
Lemaitre R. N., Tanaka T., Tang W., Manichaikul A., Foy M., Kabagambe E. K., et al. (2011). Genetic loci associated with plasma phospholipid n-3 fatty acids: a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies from the charge consortium. PLoS Genet. 7 (7), e1002193. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1002193
Lewis C. P. L., Demedts M., Nemery B. (1991). Indices of oxidative stress in hamster lung following exposure to cobalt(II) ions: in vivo and in vitro studies. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 5 (2), 163–169. doi:10.1165/ajrcmb/5.2.163
Li S., Huff R. D., Rider C. F., Yuen A. C. Y., Carlsten C. (2024). Controlled human exposures to diesel exhaust or particle-depleted diesel exhaust with allergen modulates transcriptomic responses in the lung. Sci. Total Environ. 945, 173688. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.173688
Li X., Wang J., Wang L., Gao Y., Feng G., Li G., et al. (2022). Lipid metabolism dysfunction induced by age-dependent DNA methylation accelerates aging. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 7 (1), 162–212. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-00964-6
Lim J. Y., Kim D., Kim B. R., Jun J. S., Yeom J. S., Park J. S., et al. (2016). Vitamin C induces apoptosis in AGS cells via production of ROS of mitochondria. Oncol. Lett. 12 (5), 4270–4276.
Liu J., Qu W., Kadiiska M. B. (2009). Role of oxidative stress in cadmium toxicity and carcinogenesis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 238 (3), 209–214. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2009.01.029
Liu Q., Liu Z., Wu D., Wang S. (2024). Relationship between polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolism and atherosclerosis. Rev. Cardiovasc Med. 25 (4), 142. doi:10.31083/j.rcm2504142
Liu Q., Wang H., Hu D., Ding C., Xu H., Tao D. (2004). Effects of trace elements on the telomere lengths of hepatocytes L-02 and hepatoma cells SMMC-7721. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 100 (3), 215–227. doi:10.1385/BTER:100:3:215
Liu Q., Wang Q., Xu C., Shao W., Zhang C., Liu H., et al. (2017). Organochloride pesticides impaired mitochondrial function in hepatocytes and aggravated disorders of fatty acid metabolism. Sci. Rep. 7 (1), 46339. doi:10.1038/srep46339
Liu Y. J., McIntyre R. L., Janssens G. E., Houtkooper R. H. (2020). Mitochondrial fission and fusion: a dynamic role in aging and potential target for age-related disease. Mech. Ageing Dev. 186, 111212.
Lobinski R., Becker J. S., Haraguchi H., Sarkar B. (2010). Metallomics: guidelines for terminology and critical evaluation of analytical chemistry approaches (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 82 (2), 493–504. doi:10.1351/pac-rep-09-03-04
López-Otín C., Blasco M. A., Partridge L., Serrano M., Kroemer G. (2013). The hallmarks of aging. Cell 153 (6), 1194–1217. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.039
López-Otín C., Blasco M. A., Partridge L., Serrano M., Kroemer G. (2023). Hallmarks of aging: an expanding universe. Cell. 186 (2), 243–278. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2022.11.001
Losol P., Sokolowska M., Hwang Y. K., Ogulur I., Mitamura Y., Yazici D., et al. (2023). Epithelial barrier theory: the role of exposome, microbiome, and barrier function in allergic diseases. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 15 (6), 705–724. doi:10.4168/aair.2023.15.6.705
Luo T., Chen S., Cai J., Liu Q., Gou R., Mo X., et al. (2022). Association between combined exposure to plasma heavy metals and dyslipidemia in a Chinese population. Lipids Health Dis. 21, 131. doi:10.1186/s12944-022-01743-6
Ma H., Wang X., Li X., Heianza Y., Katzmarzyk P. T., Franco O. H., et al. (2024). Food insecurity and premature mortality and life expectancy in the US. JAMA Intern Med. 184 (3), 301–310. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2023.7968
Mangoni A. A., Jackson S. H. D. (2004). Age-related changes in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics: basic principles and practical applications. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 57 (1), 6–14. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2125.2003.02007.x
Mannino D. M., Buist A. S. (2007). Global burden of COPD: risk factors, prevalence, and future trends. Lancet 370 (9589), 765–773. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61380-4
Mariotti A. (2015). The effects of chronic stress on health: new insights into the molecular mechanisms of brain–body communication. Future Sci. OA 1 (3), FSO23. doi:10.4155/fso.15.21
Mashima R., Okuyama T. (2015). The role of lipoxygenases in pathophysiology; new insights and future perspectives. Redox Biol. 6, 297–310. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2015.08.006
Mathias R. A., Sergeant S., Ruczinski I., Torgerson D. G., Hugenschmidt C. E., Kubala M., et al. (2011). The impact of FADS genetic variants on ω6 polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolism in African Americans. BMC Genet. 12 (1), 50. doi:10.1186/1471-2156-12-50
Mendelsohn A. R., Larrick J. W. (2017). Epigenetic drift is a determinant of Mammalian lifespan. Rejuvenation Res. 20 (5), 430–436.
Merra G., Gualtieri P., La Placa G., Frank G., Della Morte D., De Lorenzo A., et al. (2024). The relationship between exposome and microbiome. Microorganisms 12 (7), 1386. doi:10.3390/microorganisms12071386
Messner B., Türkcan A., Ploner C., Laufer G., Bernhard D. (2015). Cadmium overkill: autophagy, apoptosis and necrosis signalling in endothelial cells exposed to cadmium. Cell Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 73 (8), 1699–1713. doi:10.1007/s00018-015-2094-9
Meunier B., de Visser S. P., Shaik S. (2004). Mechanism of oxidation reactions catalyzed by cytochrome P450 enzymes. Chem. Rev. 104 (9), 3947–3980. doi:10.1021/cr020443g
Meydani S., Ribaya-Mercado J., Russell R., Sahyoun N., Morrow F., Gershoff S. (1991). Vitamin B − 6 deficiency impairs interleukin 2 production and lymphocyte proliferation in elderly adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 53 (5), 1275–1280.
Milanesi A., Weinreb J. E. (2000). “Diabetes in the elderly,” in Endotext Editor K. R. Feingold, B. Anawalt, M. R. Blackman, A. Boyce, G. Chrousos, and E. Corpas, (South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc.). Available online at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279147/.
Miller G. W., Jones D. P. (2014). The nature of nurture: refining the definition of the exposome. Toxicol. Sci. 137 (1), 1–2. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kft251
Mishima E., Ito J., Wu Z., Nakamura T., Wahida A., Doll S., et al. (2022). A non-canonical vitamin K cycle is a potent ferroptosis suppressor. Nature 608 (7924), 778–783. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-05022-3
Mititelu M., Lupuliasa D., Neacşu S. M., Olteanu G., Busnatu Ștefan S., Mihai A., et al. (2025). Polyunsaturated fatty acids and human health: a key to modern nutritional balance in association with polyphenolic compounds from food sources. Foods 14 (1), 46. doi:10.3390/foods14010046
Mocchegiani E., Costarelli L., Giacconi R., Malavolta M., Basso A., Piacenza F., et al. (2014). Vitamin E–gene interactions in aging and inflammatory age-related diseases: implications for treatment. A systematic review. Ageing Res. Rev. 14, 81–101. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2014.01.001
Moreira E. S., Brasch N. E., Yun J. (2011). Vitamin B12 protects against superoxide-induced cell injury in human aortic endothelial cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 51 (4), 876–883. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.05.034
Morisseau C., Hammock B. D. (2005). EPOXIDE HYDROLASES: mechanisms, inhibitor designs, and biological roles. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 45 (1), 311–333. doi:10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.45.120403.095920
Morris M. C., Evans D. A., Tangney C. C., Bienias J. L., Schneider J. A., Wilson R. S., et al. (2006). Dietary copper and high saturated and trans fat intakes associated with cognitive decline. Arch. Neurol. 63 (8), 1085–1088. doi:10.1001/archneur.63.8.1085
Mozaffarian D., Wu J. H. Y. (2011). Omega-3 fatty acids and cardiovascular disease: effects on risk factors, molecular pathways, and clinical events. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 58 (20), 2047–2067. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2011.06.063
Mucci L. A., Hjelmborg J. B., Harris J. R., Czene K., Havelick D. J., Scheike T., et al. (2016). Familial risk and heritability of cancer among twins in nordic countries. JAMA 315 (1), 68–76. doi:10.1001/jama.2015.17703
Mustacich D. J., Bruno R. S., Traber M. G. (2007). Vitamin E in vitamins & hormones. Academic Press 76, 1–21. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0083672907760016.
Mutlu A. S., Duffy J., Wang M. C. (2021). Lipid metabolism and lipid signals in aging and longevity. Dev. Cell 56 (10), 1394–1407. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2021.03.034
Nelson D. R. (2009). The cytochrome P450 homepage. Hum. Genomics 4 (1), 59–65. doi:10.1186/1479-7364-4-1-59
Ng R., Sutradhar R., Yao Z., Wodchis W. P., Rosella L. C. (2020). Smoking, drinking, diet and physical activity—modifiable lifestyle risk factors and their associations with age to first chronic disease. Int. J. Epidemiol. 49 (1), 113–130. doi:10.1093/ije/dyz078
Ochi H., Takeda S. (2015). The two sides of vitamin E supplementation. Gerontology 61 (4), 319–326. doi:10.1159/000366419
Palla A. R., Ravichandran M., Wang Y. X., Alexandrova L., Yang A. V., Kraft P., et al. (2021). Inhibition of prostaglandin-degrading enzyme 15-PGDH rejuvenates aged muscle mass and strength. Science 371 (6528), eabc8059. doi:10.1126/science.abc8059
Pamphlett R. (2021). The prevalence of inorganic mercury in human cells increases during aging but decreases in the very old. Sci. Rep. 11 (1), 16714. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-96359-8
Piper K., Garelnabi M. (2020). Eicosanoids: atherosclerosis and cardiometabolic health. J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol. 19, 100216. doi:10.1016/j.jcte.2020.100216
Popa D. S., Bigman G., Rusu M. E. (2021). The role of vitamin K in humans: implication in aging and age-associated diseases. Antioxidants 10 (4), 566. doi:10.3390/antiox10040566
Preissner S. C., Hoffmann M. F., Preissner R., Dunkel M., Gewiess A., Preissner S. (2013). Polymorphic cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYPs) and their role in personalized therapy. PLoS ONE 8 (12), e82562. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0082562
Puntarulo S. (2005). Iron, oxidative stress and human health. Mol. Asp. Med. 26 (4–5), 299–312. doi:10.1016/j.mam.2005.07.001
Pusceddu I., Herrmann W., Kleber M. E., Scharnagl H., Hoffmann M. M., Winklhofer-Roob B. M., et al. (2020). Subclinical inflammation, telomere shortening, homocysteine, vitamin B6, and mortality: the ludwigshafen risk and cardiovascular health study. Eur. J. Nutr. 59 (4), 1399–1411.
Querques G., Forte R., Souied E. H. (2011). Retina and omega-3. J. Nutr. Metab. 2011, 748361. doi:10.1155/2011/748361
Rådmark O., Samuelsson B. (2009). 5-Lipoxygenase: mechanisms of regulation. J. Lipid Res. 50 (Suppl. l), S40–S45. doi:10.1194/jlr.R800062-JLR200
Rahman M. A., Rahman A., Khan M. Z. K., Renzaho A. M. N. (2018). Human health risks and socio-economic perspectives of arsenic exposure in Bangladesh: a scoping review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 150, 335–343. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.12.032
Rao P. S. S., Kumar S. (2015). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and cytochrome P450 in HIV pathogenesis. Front. Microbiol. 6, 550. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2015.00550
Rapoport S. M., Schewe T. (1986). The maturational breakdown of mitochondria in reticulocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA - Rev. Biomembr. 864 (3–4), 471–495. doi:10.1016/0304-4157(86)90006-7
Rappaport S. M. (2011). Implications of the exposome for exposure science. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 21 (1), 5–9. doi:10.1038/jes.2010.50
Rappaport S. M., Smith M. T. (2010). Epidemiology. Environment and disease risks. Science. 330 (6003), 460–461. doi:10.1126/science.1192603
Rautiainen S., Manson J. E., Lichtenstein A. H., Sesso H. D. (2016). Dietary supplements and disease prevention — a global overview. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 12 (7), 407–420. doi:10.1038/nrendo.2016.54
Raverdeau M., Mills K. H. G. (2014). Modulation of T cell and innate immune responses by retinoic acid. J. Immunol. 192 (7), 2953–2958.
Ren Q., Ma M., Yang J., Nonaka R., Yamaguchi A., Ishikawa K. ichi, et al. (2018). Soluble epoxide hydrolase plays a key role in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 115 (25), E5815-E5823–23. doi:10.1073/pnas.1802179115
Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Guidance for Designing a National Healthcare Disparities Report Swift E. K. (2002). Guidance for the National Healthcare Disparities Report. Washington, DC: National Academies Press US. Geography and Disparities in Health Care 5. Available online at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK221045/.
Ribaya-Mercado J. D., Russell R. M., Sahyoun N., Morrow F. D., Gershoff S. N. (1991). Vitamin B-6 requirements of elderly men and Women1. J. Nutr. 121 (7), 1062–1074.
Rice K. M., Walker E. M., Wu M., Gillette C., Blough E. R. (2014). Environmental mercury and its toxic effects. J. Prev. Med. Pub Health 47 (2), 74–83. doi:10.3961/jpmph.2014.47.2.74
Rodrigues J. A., Narasimhamurthy R. K., Joshi M. B., Dsouza H. S., Mumbrekar K. D. (2022). Pesticides exposure-induced changes in brain metabolome: implications in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disorders. Neurotox. Res. 40 (5), 1539–1552. doi:10.1007/s12640-022-00534-2
Rosengren A., Smyth A., Rangarajan S., Ramasundarahettige C., Bangdiwala S. I., AlHabib K. F., et al. (2019). Socioeconomic status and risk of cardiovascular disease in 20 low-income, middle-income, and high-income countries: the Prospective Urban Rural Epidemiologic (PURE) study. Lancet Glob. Health 7 (6), e748–e760. doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(19)30045-2
Rouzer C. A., Marnett L. J. (2003). Mechanism of free radical oxygenation of polyunsaturated fatty acids by cyclooxygenases. Chem. Rev. 103 (6), 2239–2304. doi:10.1021/cr000068x
Rouzer C. A., Marnett L. J. (2009). Cyclooxygenases: structural and functional insights. J. Lipid Res. 50 (Suppl. l), S29–S34. doi:10.1194/jlr.R800042-JLR200
Rubinstein M., Dvash E. (2017). Leukotrienes and kidney diseases. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 27 (1), 42–48. doi:10.1097/MNH.0000000000000381
Saari J. T., Dickerson F. D., Habib M. P. (1990). Ethane production in copper-deficient rats. Exp. Biol. Med. 195 (1), 30–33. doi:10.3181/00379727-195-43114
Sarparast M., Dattmore D., Alan J., Lee K. S. S. (2020). Cytochrome P450 metabolism of polyunsaturated fatty acids and neurodegeneration. Nutrients 12 (11), 3523. doi:10.3390/nu12113523
Savarino L., Granchi D., Ciapetti G., Cenni E., Ravaglia G., Forti P., et al. (2001). Serum concentrations of zinc and selenium in elderly people: results in healthy nonagenarians/centenarians. Exp. Gerontol. 36 (2), 327–339. doi:10.1016/s0531-5565(00)00218-7
Sayegh S., Fantecelle C. H., Laphanuwat P., Subramanian P., Rustin M. H. A., Gomes D. C. O., et al. (2024). Vitamin D3 inhibits p38 MAPK and senescence-associated inflammatory mediator secretion by senescent fibroblasts that impacts immune responses during ageing. Aging Cell 23 (4), e14093.
Schoenmakers E., Agostini M., Mitchell C., Schoenmakers N., Papp L., Rajanayagam O., et al. (2010). Mutations in the selenocysteine insertion sequence–binding protein 2 gene lead to a multisystem selenoprotein deficiency disorder in humans. J. Clin. Invest 120 (12), 4220–4235. doi:10.1172/JCI43653
Schoenmakers I., Jones K. S. (2024). “Pharmacology and pharmacokinetics of vitamin D,” in Feldman and pike’ s vitamin D (Elsevier), 633–668. Available online at: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/B9780323913867000076.
Sergeev I. N. (2014). Vitamin D-mediated apoptosis in cancer and obesity. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 20 (2), 43–49.
Shan M., Yu X., Li Y., Fu C., Zhang C. (2021). Vitamin B6 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced myocardial injury by ferroptosis and apoptosis regulation. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 766820. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.766820
Shastak Y., Gordillo A., Pelletier W. (2023). The relationship between vitamin A status and oxidative stress in animal production. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 51 (1), 546–553. doi:10.1080/09712119.2023.2239319
Shimanaka Y., Kono N., Taketomi Y., Arita M., Okayama Y., Tanaka Y., et al. (2017). Omega-3 fatty acid epoxides are autocrine mediators that control the magnitude of IgE-mediated mast cell activation. Nat. Med. 23 (11), 1287–1297. doi:10.1038/nm.4417
Shureiqi I., Chen D., Lee J. J., Yang P., Newman R. A., Brenner D. E., et al. (2000). 15-LOX-1: a novel molecular target of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 92 (14), 1136–1142. doi:10.1093/jnci/92.14.1136
Sierra F. (2016). The emergence of geroscience as an interdisciplinary approach to the enhancement of health span and life span. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 6 (4), a025163. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a025163
Simes D. C., Viegas C. S. B., Araújo N., Marreiros C. (2020). Vitamin K as a diet supplement with impact in human health: current evidence in age-related diseases. Nutrients 12 (1), 138.
Sirakawin C., Lin D., Zhou Z., Wang X., Kelleher R., Huang S., et al. (2024). SKN-1/NRF2 upregulation by vitamin A is conserved from nematodes to mammals and is critical for lifespan extension in Caenorhabditis elegans. Aging Cell 23 (3), e14064. doi:10.1111/acel.14064
Smyth J. M., Sliwinski M. J., Zawadzki M. J., Scott S. B., Conroy D. E., Lanza S. T., et al. (2018). Everyday stress response targets in the science of behavior change. Behav. Res. Ther. 101, 20–29. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2017.09.009
Sogno P., Kuenzer C., Bachofer F., Traidl-Hoffmann C. (2022). Earth observation for exposome mapping of Germany: analyzing environmental factors relevant to non-communicable diseases. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinformation 114, 103084. doi:10.1016/j.jag.2022.103084
Sorrentino J. A., Sanoff H. K., Sharpless N. E. (2014). Defining the toxicology of aging. Trends Mol. Med. 20 (7), 375–384. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2014.04.004
Sosa-Díaz E., Hernández-Cruz E. Y., Pedraza-Chaverri J. (2022). The role of vitamin D on redox regulation and cellular senescence. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 193, 253–273. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.10.003
Sotaniemi E. A., Arranto A. J., Pelkonen O., Pasanen M. (1997). Age and cytochrome P450-linked drug metabolism in humans: an analysis of 226 subjects with equal histopathologic conditions. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 61 (3), 331–339. doi:10.1016/S0009-9236(97)90166-1
Sparks D. L., Schreurs B. G. (2003). Trace amounts of copper in water induce β-amyloid plaques and learning deficits in a rabbit model of Alzheimer’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 100 (19), 11065–11069. doi:10.1073/pnas.1832769100
Spencer A. G., Woods J. W., Arakawa T., Singer I. I., Smith W. L. (1998). Subcellular localization of prostaglandin endoperoxide H synthases-1 and -2 by immunoelectron microscopy. J. Biol. Chem. 273 (16), 9886–9893. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.16.9886
Šrejber M., Navrátilová V., Paloncýová M., Bazgier V., Berka K., Anzenbacher P., et al. (2018). Membrane-attached mammalian cytochromes P450: an overview of the membrane’s effects on structure, drug binding, and interactions with redox partners. J. Inorg. Biochem. 183, 117–136. doi:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2018.03.002
Srour E., Martin N., Drullion C., Schutter C. D., Giroud J., Pioger A., et al. (2024). Prostaglandin E2 regulates senescence and post-senescence neoplastic escape in primary human keratinocytes. Aging 16 (21), 13201–13224. doi:10.18632/aging.206149
Summerer S., Hanano A., Utsumi S., Arand M., Schuber F., Blée E. (2002). Stereochemical features of the hydrolysis of 9,10-epoxystearic acid catalysed by plant and mammalian epoxide hydrolases. Biochem. J. 366 (2), 471–480. doi:10.1042/BJ20011778
Szpunar J. (2004). Metallomics: a new frontier in analytical chemistry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 378 (1), 54–56. doi:10.1007/s00216-003-2333-z
Tainer J. A., Roberts V. A., Getzoff E. D. (1991). Metal-binding sites in proteins. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2 (4), 582–591. doi:10.1016/0958-1669(91)90084-i
Takahashi S., Takahashi I., Sato H., Kubota Y., Yoshida S., Muramatsu Y. (2001). Age-related changes in the concentrations of major and trace elements in the brain of rats and mice. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 80 (2), 145–158. doi:10.1385/BTER:80:2:145
Tamburini I., Quartacci M. F., Izzo R., Bergamini E. (2004). Effects of dietary restriction on age-related changes in the phospholipid fatty acid composition of various rat tissues. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 16 (6), 425–431. doi:10.1007/BF03327396
Tanaka T., Biancotto A., Moaddel R., Moore A. Z., Gonzalez-Freire M., Aon M. A., et al. (2018). Plasma proteomic signature of age in healthy humans. Aging Cell 17 (5), e12799.
Teissier T., Boulanger E., Cox L. S. (2022). Interconnections between inflammageing and immunosenescence during ageing. Cells 11 (3), 359.
Teixeira F. B., de Oliveira A. C. A., Leão L. K. R., Fagundes N. C. F., Fernandes R. M., Fernandes L. M. P., et al. (2018). Exposure to inorganic mercury causes oxidative stress, cell death, and functional deficits in the motor cortex. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 11, 125. doi:10.3389/fnmol.2018.00125
Thyfault J. P., Bergouignan A. (2020). Exercise and metabolic health: beyond skeletal muscle. Diabetologia 63 (8), 1464–1474. doi:10.1007/s00125-020-05177-6
Tsuchiya Y., Nakajima M., Yokoi T. (2005). Cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism of estrogens and its regulation in human. Cancer Lett. 227 (2), 115–124. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2004.10.007
Turnlund J., Keyes W., Peiffer G., Scott K. (1998). Copper absorption, excretion, and retention by young men consuming low dietary copper determined by using the stable isotope 65Cu. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 67 (6), 1219–1225. doi:10.1093/ajcn/67.6.1219
Uriu-Adams J. Y., Keen C. L. (2005). Copper, oxidative stress, and human health. Mol. Asp. Med. 26 (4–5), 268–298. doi:10.1016/j.mam.2005.07.015
Uversky V. N., Li J., Bower K., Fink A. L. (2002). Synergistic effects of pesticides and metals on the fibrillation of α-synuclein: implications for Parkinson’s disease. NeuroToxicology 23 (4), 527–536. doi:10.1016/s0161-813x(02)00067-0
van der Donk W. A., Tsai A. L., Kulmacz R. J. (2002). The cyclooxygenase reaction mechanism. Biochemistry 41 (52), 15451–15458. doi:10.1021/bi026938h
Varesi A., Chirumbolo S., Campagnoli L. I. M., Pierella E., Piccini G. B., Carrara A., et al. (2022). The role of antioxidants in the interplay between oxidative stress and senescence. Antioxidants 11 (7), 1224. doi:10.3390/antiox11071224
Vig E. K., Hu H. (2000). Lead toxicity in older adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 48 (11), 1501–1506. doi:10.1111/jgs.2000.48.11.1501
Vijg J., Campisi J. (2008). Puzzles, promises and a cure for ageing. Nature 454 (7208), 1065–1071. doi:10.1038/nature07216
Vogiatzoglou A., Refsum H., Johnston C., Smith S. M., Bradley K. M., De Jager C., et al. (2008). Vitamin B12 status and rate of brain volume loss in community-dwelling elderly. Neurology 71 (11), 826–832. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000325581.26991.f2
Wang B., Han J., Elisseeff J. H., Demaria M. (2024). The senescence-associated secretory phenotype and its physiological and pathological implications. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 25 (12), 958–978.
Wang W., Wagner K. M., Wang Y., Singh N., Yang J., He Q., et al. (2023). Soluble epoxide hydrolase contributes to cell senescence and ER stress in aging mice colon. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (5), 4570. doi:10.3390/ijms24054570
Wang Y., Yuan Q., Xie L. (2018). Histone modifications in aging: the underlying mechanisms and implications. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 13 (2), 125–135.
Watts J. L. (2016). Using Caenorhabditis elegans to uncover conserved functions of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. J. Clin. Med. 5 (2), 19. doi:10.3390/jcm5020019
Wei S., Qiu T., Wang N., Yao X., Jiang L., Jia X., et al. (2020). Ferroptosis mediated by the interaction between Mfn2 and IREα promotes arsenic-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Environ. Res. 188, 109824. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2020.109824
Werck-Reichhart D., Feyereisen R. (2000). Cytochromes P450: a success story. Genome Biol. 1 (6), REVIEWS3003–reviews3003.9. doi:10.1186/gb-2000-1-6-reviews3003
Wessels I. (2015). “Metal homeostasis during development, maturation, and aging: impact on infectious diseases,” in Trace metals and infectious diseases. Editors J. O. Nriagu, and E. P. Skaar (Cambridge (MA): MIT Press). Available online at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK569694/.
Wild C. P. (2005). Complementing the genome with an “exposome”: the outstanding challenge of environmental exposure measurement in molecular epidemiology. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 14 (8), 1847–1850. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-05-0456
Wild C. P. (2012). The exposome: from concept to utility. Int. J. Epidemiol. 41 (1), 24–32. doi:10.1093/ije/dyr236
Wiley C. D., Brumwell A. N., Davis S. S., Jackson J. R., Valdovinos A., Calhoun C., et al. (2019). Secretion of leukotrienes by senescent lung fibroblasts promotes pulmonary fibrosis. JCI Insight 4 (24), e130056. doi:10.1172/jci.insight.130056
Wiley C. D., Sharma R., Davis S. S., Lopez-Dominguez J. A., Mitchell K. P., Wiley S., et al. (2021). Oxylipin biosynthesis reinforces cellular senescence and allows detection of senolysis. Cell Metab. 33 (6), 1124–1136.e5. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2021.03.008
Willett W. C. (2002). Balancing life-style and genomics research for disease prevention. Science 296 (5568), 695–698. doi:10.1126/science.1071055
Williams R. J. P. (2001). Chemical selection of elements by cells. Coord. Chem. Rev. 216–217, 583–595. doi:10.1016/s0010-8545(00)00398-2
Wood-Kaczmar A., Gandhi S., Wood N. W. (2006). Understanding the molecular causes of Parkinson’s disease. Trends Mol. Med. 12 (11), 521–528. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2006.09.007
Xia F., Li Q., Luo X., Wu J. (2022). Association between urinary metals and leukocyte telomere length involving an artificial neural network prediction: findings based on NHANES 1999–2002. Front. Public Health 10, 963138. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2022.963138
Xu M., Rui D., Yan Y., Xu S., Niu Q., Feng G., et al. (2017). Oxidative damage induced by arsenic in mice or rats: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 176 (1), 154–175. doi:10.1007/s12011-016-0810-4
Yan M., Sun S., Xu K., Huang X., Dou L., Pang J., et al. (2021). Cardiac aging: from basic research to therapeutics. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 9570325. doi:10.1155/2021/9570325
Yang C., Veenstra J., Bartz T. M., Pahl M. C., Hallmark B., Chen Y. D. I., et al. (2023). Genome-wide association studies and fine-mapping identify genomic loci for n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids in Hispanic American and African American cohorts. Commun. Biol. 6 (1), 852–915. doi:10.1038/s42003-023-05219-w
Yoshida Y., Yoshikawa A., Kinumi T., Ogawa Y., Saito Y., Ohara K., et al. (2009). Hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid and oxidatively modified peroxiredoxins in the blood of Alzheimer’s disease patients and their potential as biomarkers. Neurobiol. Aging 30 (2), 174–185. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2007.06.012
Yousef A., Fang L., Heidari M., Kranrod J., Seubert J. M. (2024). The role of CYP-sEH derived lipid mediators in regulating mitochondrial biology and cellular senescence: implications for the aging heart. Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1486717. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1486717
Yun K. U., Oh S. J., Oh J. M., Kang K. W., Myung C. S., Song G. Y., et al. (2010). Age-related changes in hepatic expression and activity of cytochrome P450 in male rats. Arch. Toxicol. 84 (12), 939–946. doi:10.1007/s00204-010-0520-1
Zaffarin A. S. M., Ng S. F., Ng M. H., Hassan H., Alias E. (2020). Pharmacology and pharmacokinetics of vitamin E: nanoformulations to enhance bioavailability. Int. J. Nanomedicine. 15, 9961.
Zajacova A., Lawrence E. M. (2018). The relationship between education and health: reducing disparities through a contextual approach. Annu. Rev. Public Health 39, 273–289. doi:10.1146/annurev-publhealth-031816-044628
Zapico S. C., Ubelaker D. H. (2013). mtDNA mutations and their role in aging, diseases and forensic sciences. Aging Dis. 4 (6), 364–380.
Zeldin D. C., Kobayashi J., Falck J. R., Winder B. S., Hammock B. D., Snapper J. R., et al. (1993). Regio- and enantiofacial selectivity of epoxyeicosatrienoic acid hydration by cytosolic epoxide hydrolase. J. Biol. Chem. 268 (9), 6402–6407. doi:10.1016/s0021-9258(18)53266-x
Zeldin D. C., Wei S., Falck J. R., Hammock B. D., Snapper J. R., Capdevila J. H. (1995). Metabolism of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids by cytosolic epoxide hydrolase: substrate structural determinants of asymmetric catalysis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 316 (1), 443–451. doi:10.1006/abbi.1995.1059
Zhang B., Podolskiy D. I., Mariotti M., Seravalli J., Gladyshev V. N. (2020). Systematic age-, organ-, and diet-associated ionome remodeling and the development of ionomic aging clocks. Aging Cell 19 (5), e13119. doi:10.1111/acel.13119
Zhang Y., Chu L., Zhou X., Xu T., Shen Q., Li T., et al. (2023a). Vitamin B12-induced autophagy alleviates high glucose-mediated apoptosis of islet β cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (20), 15217.
Zhang Y., Liu M., Xie R. (2023b). Associations between cadmium exposure and whole-body aging: mediation analysis in the NHANES. BMC Public Health 23 (1), 1675. doi:10.1186/s12889-023-16643-2
Zhao Y., Li M., Tian X., Xie J., Liu P., Ying X., et al. (2021). Effects of arsenic exposure on lipid metabolism: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 31 (3), 188–196. doi:10.1080/15376516.2020.1864537
Zhou J., Zeng L., Zhang Y., Wang M., Li Y., Jia Y., et al. (2022). Cadmium exposure induces pyroptosis in testicular tissue by increasing oxidative stress and activating the AIM2 inflammasome pathway. Sci. Total Environ. 847, 157500. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157500
Zhu K., Browne R. W., Blair R. H., Bonner M. R., Tian M., Niu Z., et al. (2021). Changes in arachidonic acid (AA)- and linoleic acid (LA)-derived hydroxy metabolites and their interplay with inflammatory biomarkers in response to drastic changes in air pollution exposure. Environ. Res. 200, 111401. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2021.111401
Keywords: senescence, molecular mechanism, aging, oxylipin, metabolism, exposome
Citation: Hinman J, Alan JK and Lee KSS (2025) Effects of molecular interactions between the exposome and oxylipin metabolism on healthspan. Front. Physiol. 16:1584195. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1584195
Received: 27 February 2025; Accepted: 21 May 2025;
Published: 01 July 2025.
Edited by:
Walter Swardfager, University of Toronto, CanadaReviewed by:
Andrea Deledda, Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria Cagliari, ItalyNatasha Anita, University of California, San Diego, United States
Copyright © 2025 Hinman, Alan and Lee. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kin Sing Stephen Lee, c2luZ0Btc3UuZWR1
 Jennifer Hinman
Jennifer Hinman Jamie K. Alan
Jamie K. Alan Kin Sing Stephen Lee
Kin Sing Stephen Lee