- 1Nephrology Department, Deyang People’s Hospital, Deyang, China
- 2Department of Nursing, Aobaoka Hospital, Osakasayama, Japan
Background: The pooled prevalence of frailty in maintenance hemodialysis patients is increasing, and research on the effects of intradialytic exercise to improve frailty remains limited.
Objectives: To analyze the effects of intradialytic exercise on frailty in maintenance hemodialysis patients through randomized clinical trials and quasi-experimental studies.
Methods: We performed a comprehensive literature search in PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library, and English-language publications were indexed from January 2010 to August 2024. Statistical analyses were performed using Review Manager V.5.3 and STATA 15.0. Statistical heterogeneity among studies was quantified using the Chi-square and I-square tests, and publication bias was evaluated using Egger’s test and funnel plots.
Results: 31 studies involving 1,365 maintenance hemodialysis patients were included. The data from the meta-analysis showed that intradialytic exercise significantly reduced frailty score (MD = −0.98, 95%CI: 1.90 to −0.06, p = 0.04) and fatigue (SMD = −0.47, 95%CI: 0.72 to −0.23, p = 0.0001). Also, intradialytic exercise significantly increased grip strength (MD = 2.42, 95%CI:0.78 to 4.06, p = 0.004), 6-min walking distance (MD = 36.65, 95%CI:24.90 to 48.39, p < 0.0001), and step counts (SMD = 0.32, 95%CI:0.04 to 0.60, p = 0.03). However, no significant effects were found in body weight (MD = 0.71, 95%CI: 1.28 to 2.69, p = 0.48).
Conclusion: Intradialytic exercise can significantly improve overall frailty and frailty indicators such as grip strength, 6-min walking distance, step counts, and fatigue. Thus, intradialytic exercises might be a viable strategy for frailty in maintenance hemodialysis patients.
Systematic Review registration: CRD42024576582.
1 Introduction
Frailty is a nonspecific clinical state characterized by decreased physiological reserves, increased vulnerability, and diminished stress resistance (Fried et al., 2001), accompanied by an increase in adverse events, including falls, delirium, disability, hospitalization, and death (Buckinx et al., 2015; Kojima et al., 2019). The assessment of overall frailty primarily employs standardized scales. The most commonly used frailty assessment tool is Fried’s Frailty Phenotype (Fried et al., 2001), which includes five indicators of weakness (grip strength), slow walking speed, low physical activity, self-reported exhaustion, and unintentional weight loss. It is considered frail if at least three of these five indicators are present. Frailty is highly prevalent in patients with chronic diseases and has become a hot topic among kidney disease researchers in recent years.
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a clinical syndrome of progressive and irreversible decline in kidney function. The global prevalence of CKD is 9.1% (GBD Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration, 2020). Maintenance hemodialysis (MHD) is the primary renal replacement therapy for treating end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients. MHD patients undergoing long-term hemodialysis are more prone to frailty due to continuous loss of nutrients, decreased muscle strength, and low physical activity. The pooled prevalence of frailty in MHD patients is 46% (Lee and Son et al., 2021), which is 3–10 times higher than in community-dwelling older adults (Nitta et al., 2018). Frailty is an independent predictor of hospitalization and death in MHD patients (McAdams-DeMarco et al., 2013). However, the frailty state is dynamically reversible, and if it can be recognized and intervened promptly, the condition can be delayed or even reversed, and the prognosis can be improved.
The International Conference of Frailty and Sarcopenia Research (ICFSR) published clinical practice guidelines. It recommended that first-line therapy for managing frailty should include a multi-component physical activity program (Dent et al., 2019). Physical activity is the most feasible way to prevent and treat frailty, and it may be ideally suited for ESRD patients on dialysis (Harhay et al., 2020). However, there is insufficient evidence to determine the optimal frequency, intensity, duration, and type of physical activity necessary to manage frailty and the optimal combination of aerobic and resistance exercise.
Five systematic reviews summarized the effects of exercise interventions on MHD patients (Yoo et al., 2022; Li et al., 2024; Neto et al., 2018; Young et al., 2018; Wahida and Rumahorbo, 2022; Yoo et al., 2022 reported 13 studies of home-based exercise that included aerobic exercise, resistance exercise, and behavioral components that significantly improved strength, walking speed, and physical activity, and home-based exercise may be effective in improving specific frailty indicators. However, home-based exercise for dialysis patients has low exercise compliance and lacks adequate supervision. Li et al., 2024 reported 9 studies that showed that intradialytic exercise significantly improved grip strength and 6-min walking distance (6MWD). Neto et al., 2018 reported that 24 meta-analysis studies showed that intradialytic exercise significantly improved 6MWD. Young et al., 2018 reported 8 studies that showed that intradialytic exercise significantly improved 6MWD. Wahida and Rumahorbo, 2022 reported that 15 studies showed that intradialytic exercise significantly improved fatigue. The above four studies of intradialytic exercise included aerobic exercise, resistance exercise, and combined exercise, which could improve the physical function of MHD patients. However, no studies of frailty score were reported, nor were studies of all five frailty indicators reported.
Because the evidence for the effect of intradialytic exercise on frailty in MHD patients remains uncertain, this study conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to provide strong evidence that intradialytic exercise improves frailty and to summarize prescriptions for intradialytic exercise to better guide clinical practice.
2 Methods
2.1 Design
This study was completed using the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines (Page et al., 2021). It has been registered in the International Prospective Register of Systematic Review (PROSPERO): CRD42024576582.
2.2 Eligibility criteria
According to PICOS ((Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes, and Study design) principles (Liberati et al., 2009), we determine the following inclusion criteria: (1) The population were adult patients on MHD for at least 3 months; (2) Intervention group receiving intradialytic exercise (including aerobic exercise or/and resistance exercise); (3) Control group receiving usual care (no exercise or simple stretch); (4) The outcome measures were frailty score or represented at least one frailty indicator (e.g., grip strength, walking speed, physical activity, fatigue, and body weight); (5) randomized clinical trials (RCTs) and quasi-experimental studies. exclusion criteria: (1) without available full text; (2) review; (3) case report; (4) conference or letter; (5) not published in English Language.
2.3 Search strategy
We searched the literature in four databases, including PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library; all the English-language publications were indexed from January 2010 to August 2024. We also reviewed the reference lists of the cited literature to identify other relevant studies. Combinations of controlled vocabulary using Medical Subject Heading (MeSH) terms and free-text terms. The search terms included renal dialysis, hemodialysis, hemodialyses, haemodialysis, hemodiafiltration, haemodiafiltration, exercise, training, intradialytic exercise, intradialytic training, aerobic exercise, aerobic training, resistance exercise, resistance training, frailty, frailties, frailness, debility, debilities, hand strength, grip strength, walking speed, gait speed, walking pace, activities of daily living, daily living activity, physical activity, fatigue, exhaustion, lassitude, body weight, body mass. Boolean operators “OR, AND” were used for the search (Supplementary File 1).
2.4 Study selection and data extraction
Two researchers independently performed the literature search, screening titles and abstracts, full-text reviews, study quality assessment, and data extraction. Any disagreement between two researchers was resolved by discussion until a consensus was reached or by consulting a third researcher. The extracted data included the first author, publication year, country, sample size, exercise modality, exercise frequency, trial duration, exercise protocol, and outcomes.
2.5 Quality assessment of the study
Two researchers used version 2 of the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool for RCTs (ROB 2) and Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) adapted quasi-experimental study evaluation tool to assess the quality of the included studies (Sterne et al., 2019; Barker et al., 2024). The ROB 2 included the randomization process; deviation from the intended intervention; missing outcome data; outcome measures; selection of the reported result; and overall, each indicator contains three levels: low-risk, unclear, and high-risk. The JBI adapted quasi-experimental study evaluation tool included temporal procedure bias; selection and allocation bias; confounding factors bias; administration of intervention/exposure bias; outcome assessment, detection and measurement bias; and participant retention bias, each question can be scored as yes, no, unclear, or not applicable. Any disagreement was resolved by consensus or third-party adjudication.
2.6 Data synthesis and analysis
The treatment effect was measured as the mean and standard deviation (SD) change between the pre-and post-intervention measurements. Continuous data were pooled as the mean differences (MD) and 95% confidence intervals (95%CI) if the outcome measuring methods and units were identical among studies; otherwise, the standardized mean differences (SMD) were used. Statistical heterogeneity among studies was quantified using the Chi-square and I-square (I2) tests. If p < 0.10 or I2>50%, there was significant heterogeneity among studies; the random-effects model was used to combine the data. Otherwise, a fixed-effects model was used. We used the visual assessment of funnel plots and Egger’s test to evaluate publication bias (Egger et al., 1997). We used sensitivity analysis to investigate the robustness of the meta-analysis models. Statistical analyses were performed using Review Manager V.5.3 and STATA 15.0.
3 Results
3.1 Search outcome
A total of 2,537 studies were identified from four databases: PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and the Cochrane Library, and 811 duplicate studies were removed using NoteExpress 3.5 software. After screening the titles and abstracts, 93 studies were selected for full-text screening, and 62 studies were excluded according to the inclusion criteria. Finally, 31 studies were included in the systematic review and meta-analysis. The flow diagram of search and selection is shown in Figure 1.
3.2 Study characteristics
A total of 31 studies involving 1365 MHD patients were included in this study. Among these, 27 studies were RCTs, and 4 studies were quasi-experimental studies. 11 studies were conducted in Europe, 6 studies were conducted in South America, 13 studies were conducted in Asia, and 1 studies were conducted in Oceania. All patients had been receiving hemodialysis for at least 3 months; 669 patients were in the intervention group receiving intradialytic exercise (aerobic exercise or/and resistance exercise), and 696 patients were in the control group receiving usual care. 17 studies included only aerobic exercise by cycle ergometer, 8 studies included resistance exercise by elastic bands, elastic balls, dumbbells, or body weight, and 6 studies included aerobic exercise and resistance exercise. The intervention details among the studies are as follows: the exercise duration ranged from 6 to 48 weeks, the exercise frequency was either 2 or 3 times per week, most of the exercise time was 30–60 min, and most of the exercise was completed between the first and second hours of the hemodialysis session. The exercise intensity is appropriate for low to moderate-intensity exercise at 60–70% of maximal heart rate or 12-16 on the Borg Perceived Exertion Scale. The basic characteristics of the included studies are shown in Table 1.
3.3 Risk of bias
We used the ROB 2 tool to assess the risk of bias for 27 studies. 4 studies were considered to have a low risk of bias, 11 studies were at some risk of bias, and 12 studies were at a high risk of bias. Of these, 20 studies reported detailed randomization methods, and 13 described the allocation concealment process. Due to the nature of the intervention, we found that only 3 studies used the blinding method of participants or intervenors, 12 studies described the blinding of outcome assessors, and 15 studies had trial registration protocols. The results of the risk of bias are detailed in Figures 2A,B. We also used the JBI adapted quasi-experimental study evaluation tool to assess the risk of bias for 4 studies, of these, in the domain of ''participant retention bias'', Mihaescu et al., 2013; Sánchez-Tocino et al., 2022 were answered as no, other risks of bias domains were answered as yes. All risk of bias domains in Desai et al., 2019; Devagourou et al., 2021 were answered as yes.
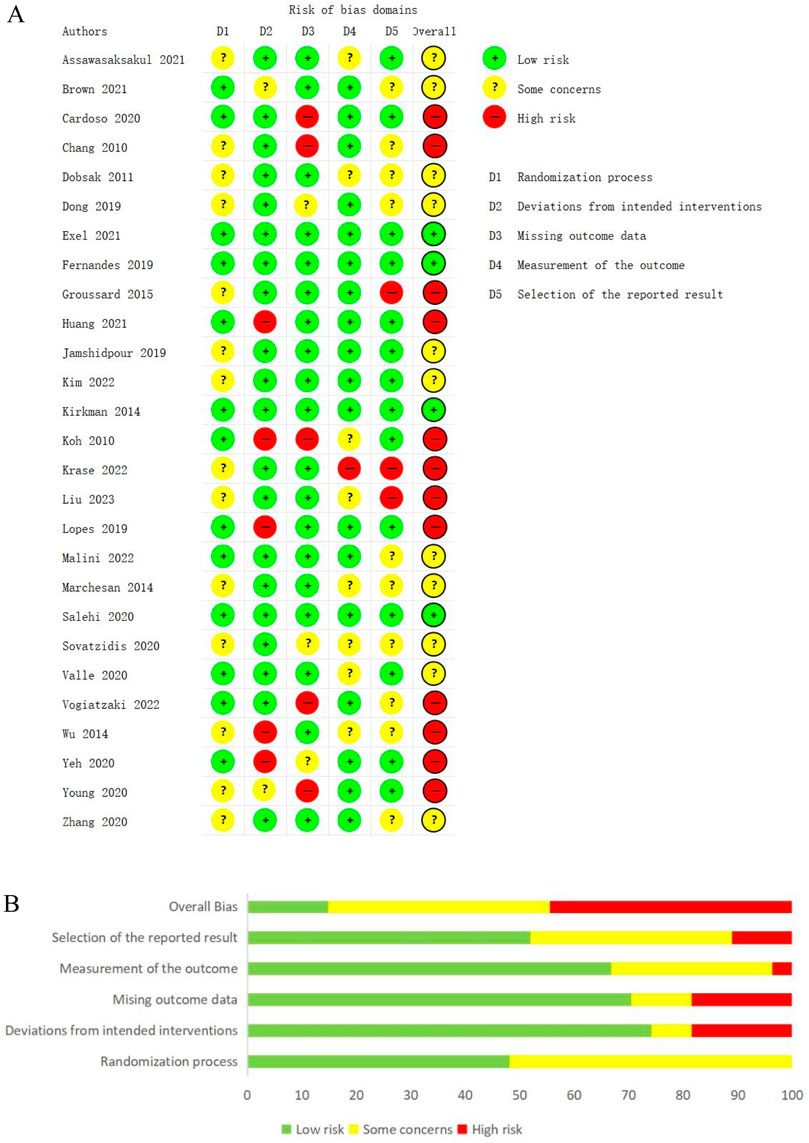
Figure 2. (A) Assessments of risk of bias for the included studies. (B) A summary of the risk of bias assessments for the included studies.
3.4 Frailty indicators and effect sizes
3.4.1 Frailty score
Only 3 studies (Desai et al., 2019; Kim et al., 2022; Sánchez-Tocino et al., 2022) reported frailty scores using Fried’s Frailty Phenotype, involving 124 participants (49 in the experimental groups and 75 in the control groups). Statistical heterogeneity existed between the studies (I2 = 79%, p = 0.008), and after careful checking of the literature, heterogeneity could not be excluded, so the random effects model was chosen. The results showed that intradialytic exercise could reduce frailty score (MD = −0.98, 95%CI: 1.90 to −0.06, p = 0.04; Figure 3). Egger’s test was non-significant (t = 0.34, p = 0.792).
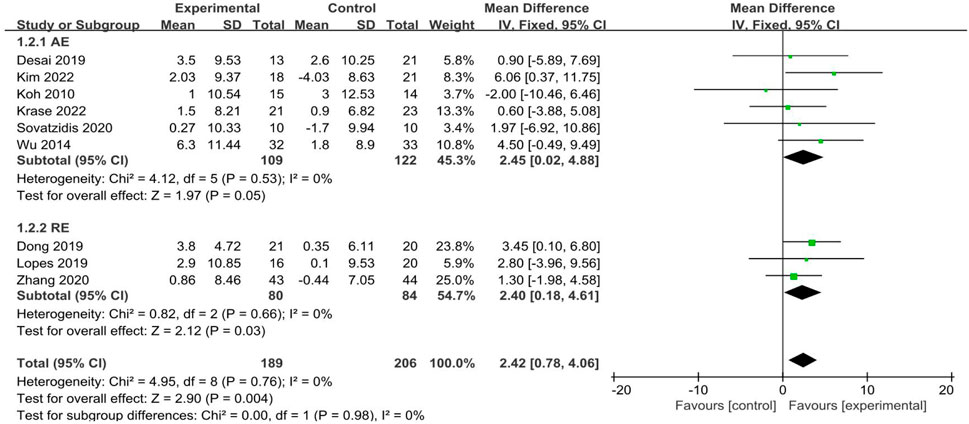
3.4.2 Grip strength
A total of 9 studies (Desai et al., 2019; Dong et al., 2019; Kim et al., 2022; Koh et al., 2010; Krase et al., 2022; Lopes et al., 2019; Sovatzidis et al., 2020; Wu et al., 2014; Zhang et al., 2020) reported grip strength, involving 395 participants (189 in the experimental groups and 206 in the control groups). The analysis of data in the fixed effect model showed that intradialytic exercise could increase grip strength (MD = 2.42, 95%CI:0.78 to 4.06, p = 0.004; Figure 4), with a low level of heterogeneity (I2 = 0%, p = 0.76). Egger’s test was non-significant (t = −0.30, p = 0.773). We also used subgroup analyses to assess the effects of different exercise types and showed that aerobic exercise and resistance exercise both increased grip strength.
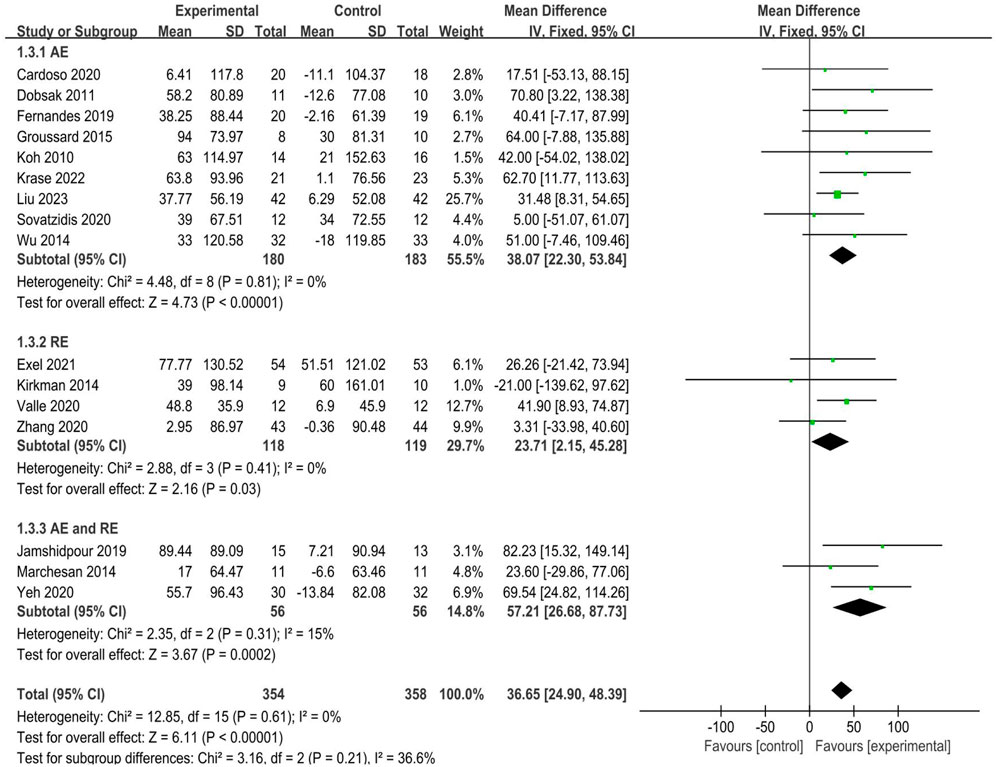
3.4.3 Walking speed
A total of 16 studies (Cardoso et al., 2020; Dobsak et al., 2012; Exel et al., 2021; Fernandes et al., 2019; Groussard et al., 2015; Jamshidpour et al., 2020; Kirkman et al., 2014; Koh et al., 2010; Krase et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2023; Marchesan et al., 2014; Valle et al., 2020; Vogiatzaki et al., 2022; Wu et al., 2014; Yeh et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2020) reported walking speed, as determined by 6MWD, involving 712 participants (354 in the experimental groups and 358 in the control groups). The analysis of data in the fixed effect model showed that intradialytic exercise could increase 6MWD (MD = 36.65, 95%CI:24.90 to 48.39, p < 0.0001; Figure 5), with a low level of heterogeneity (I2 = 0%, p = 0.61). Egger’s test was non-significant (t = 0.62, p = 0.548). We also used subgroup analyses to assess the effects of different exercise types and showed that aerobic exercise, resistance exercise, and combined exercise all increased 6MWD, of these, studies of combined aerobic exercise and resistance exercise appeared to convey a higher improvement (MD = 57.21, 95%CI:26.68 to 87.73, p < 0.001; Figure 5).
3.4.4 Physical activity
A total of 5 studies (Assawasaksakul et al., 2021; Brown et al., 2021; Krase et al., 2022; Mihaescu et al., 2013; Young et al., 2020) reported physical activity, as determined by step counts, involving 204 participants (106 in the experimental groups and 98 in the control groups). The analysis of data in the fixed effect model showed that intradialytic exercise could increase step counts (SMD = 0.32, 95%CI:0.04 to 0.60, p = 0.03; Figure 6A), with a low level of heterogeneity (I2 = 0%, p = 0.61). Egger’s test was non-significant (t = 1.86, p = 0.160).
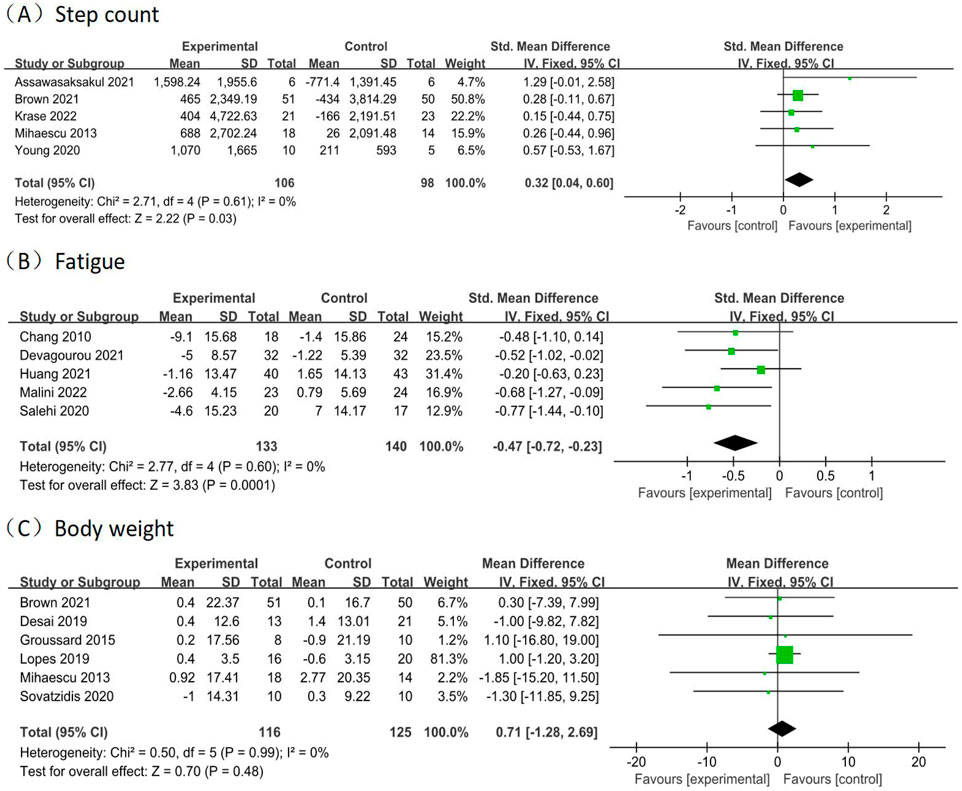
Figure 6. Forest plots of outcomes in step count, fatigue, and body weight. Forest plots of outcomes (A) step count; (B) fatigue; (C) body weight.
3.4.5 Fatigue
A total of 5 studies (Chang et al., 2010; Devagourou et al., 2021; Huang et al., 2021; Malini et al., 2022; Salehi et al., 2020) reported fatigue, involving 273 participants (133 in the experimental groups and 140 in the control groups). The analysis of data in the fixed effect model showed that intradialytic exercise could reduce fatigue (SMD = −0.47, 95%CI: 0.72 to −0.23, p = 0.0001; Figure 6B), with a low level of heterogeneity (I2 = 0%, p = 0.60). Egger’s test was non-significant (t = −3.00, p = 0.058).
3.4.6 Body weight
A total of 6 studies (Brown et al., 2021; Desai et al., 2019; Groussard et al., 2015; Lopes et al., 2019; Mihaescu et al., 2013; Sovatzidis et al., 2020) reported body weight, involving 241 participants (116 in the experimental groups and 125 in the control groups). The analysis of data in the fixed effect model showed no significant effects in the body weight (MD = 0.71, 95%CI: 1.28 to 2.69, p = 0.48; Figure 6C), with a low level of heterogeneity (I2 = 0%, p = 0.99). Egger’s test was non-significant (t = −2.73, p = 0.053).
3.5 Publication bias
Funnel plots of grip strength, 6MWD, step count, fatigue, and body weight checked the possibility of publication bias, showed that the symmetry of the funnel plots is all better, and all Egger’s tests were non-significant (p > 0.05). suggests that there may be a low risk of publication bias. The results of funnel plots are detailed in Figure 7.
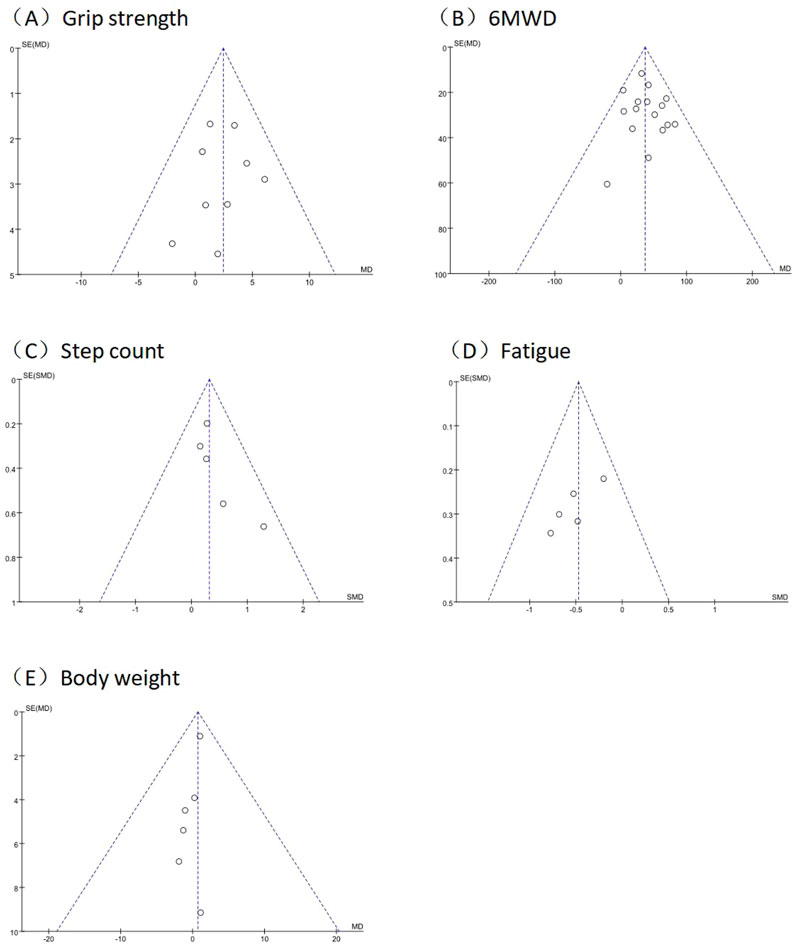
Figure 7. Funnel plot of outcomes in grip strength, 6MWD, step count, fatigue, and body weight. Funnel plots of (A) grip strength; (B) 6MWD; (C) step count; (D) fatigue; (E) body weight.
3.6 Sensitive analysis
Sensitivity analyses were conducted by sequentially excluding studies based on outcome indicators, and using the random-effects model or fixed-effects model to re-perform the analysis. The results showed that the statistical conclusions did not show any change. Hence, the meta-analysis results are stable.
4 Discussion
The prevalence of frailty is high in MHD patients, necessitating the establishment of systematic strategies for frailty identification and intervention. Exercise interventions can improve frailty by enhancing muscle strength and increasing physical activity levels. MHD patients receive an average of 12 h of hemodialysis treatment per week. Intradialysis exercise during this time is more adherence and safer when professionally guided and supervised by healthcare professionals. The United Kingdom Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hemodialysis (Ashby et al., 2019) recommend that “all MHD patients without contraindications in hemodialysis centers should engage in intradialytic exercise as a therapeutic approach to increase physical function and quality of life”. This systematic review and meta-analysis included 31 studies covering aerobic exercise, resistance exercise, and combined exercise, the results confirmed that intradialysis exercise can significantly improve frailty in MHD patients.
The overall frailty status in clinical practice is primarily assessed using standardized scales, and commonly used tools include Fried’s Frailty Phenotype, Frail Scale, Clinical Frailty Scale, and Edmonton Frailty Scale. Among them, Fried’s Frailty Phenotype has a precise objective index and high operability and is most commonly used in clinical practice. Our study found 3 studies reported that intradialytic exercise could reduce frailty score (MD = −0.98, 95%CI: 1.90 to −0.06, p = 0.04). In addition, this conclusion was further supported by a study (Yabe et al., 2022), whose data demonstrated that intradialytic exercise reduced the proportion of frailty patients. In clinical practice, we can develop stratified exercise programs based on the severity of frailty assessed through the frailty phenotype, enabling more personalized interventions. This approach aims to enhance patients’ physical activity capacity and quality of life while reducing healthcare utilization. However, there is still a lack of high-quality studies on improving overall frailty in MHD patients through intradialytic exercise. Large-sample, multicenter RCTs are needed to validate this conclusion in the future.
Grip strength is a simple, rapid, and noninvasive standardized indicator for assessing muscle strength and is an independent predictor of all-cause mortality in MHD patients (Vogt et al., 2016). Grip strength is primarily measured using a grip strength meter, which can reflect the patient’s weakness status. Our study found that intradialytic exercise could increase grip strength in MHD patients (MD = 2.42, 95%CI:0.78 to 4.06, p = 0.004), which is consistent with the results of the Meta-analysis by (Li et al., 2024). The reason may be that exercise can promote muscle protein anabolism, increase muscle fiber cross-sectional area and muscle volume, reduce fat accumulation, and then improve muscle mass and strength, thus increasing grip strength (Wang and Johansen, 2019). Subgroup analyses found that aerobic exercise, and resistance exercise all increased grip strength, patients may choose their preferred exercise type.
The 6MWD is a commonly used indicator to assess muscle function, which reflects exercise tolerance. Its test results are significantly and positively correlated with hemodialysis patients’ survival quality. Epidemiological data show that each 100-m increase in walking distance reduces the risk of all-cause mortality by 5.3% (Noguchi et al., 2022). Our study found that intradialytic exercise could increase the 6MWD in MHD patients (MD = 36.65, 95%CI:24.90 to 48.39, p < 0.0001), which is consistent with the results of the Meta-analysis by (Araujo et al., 2024). The reason may be that exercise induces endocrine changes in skeletal muscle, promotes arterial vasodilatation, stimulates oxygen utilization, and then improves muscle function, reduces muscle atrophy, and improves muscular coordination and endurance, thus increasing the 6MWD (Rhee et al., 2019; Rivera-Brown and Frontera, 2012). Subgroup analyses found that aerobic exercise, resistance exercise, and combined exercise all increased 6MWD, we can guide patients to choose the appropriate exercise type according to their actual situation in clinical practice.
Step counts are an objective indicator to assess physical activity levels, characterized by easy operation and accurate monitoring. Daily physical activity is monitored directly by wearing a pedometer. Our study found that intradialytic exercise could increase step counts in MHD patients (SMD = 0.32, 95%CI:0.04 to 0.60, p = 0.03), which is consistent with the results of the Meta-analysis by (Lock et al., 2021). The reason may be that exercise improves muscle strength and endurance, improves the patient’s exercise capacity, and reduces sedentary behavior, thus increasing step counts (Young et al., 2020).
Fatigue is a highly prevalent symptom in MHD patients, with a combined incidence of 61% (Dou et al., 2023). It is an independent predictor of cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality in MHD patients (Bossola et al., 2015). Our study found that intradialytic exercise could reduce fatigue in MHD patients (SMD = −0.47, 95%CI: 0.72 to −0.23, p = 0.0001), which is consistent with the results of the Meta-analysis by (Wahida and Rumahorbo, 2022). The reason may be that exercise improves muscle oxidative phosphorylation and muscle mitochondrial structure, promotes myocardin heavy chain synthesis, and then increases metabolism and improves systemic blood circulation, thus reducing fatigue (Bossola et al., 2015). The literature included in our study was assessed using the dedicated Fatigue Scale for MHD patients rather than alternative indicators such as conventional depression scales or vitality dimensions. Therefore, a limited number of studies that met the criteria were included.
Body weight is a commonly used indicator to assess health status, and MHD patients often experience weight loss in a chronically frailty state. Our study found no significant effect of intradialysis exercise on improving body weight in MHD patients (MD = 0.71, 95%CI: 1.28 to 2.69, p = 0.48). The reason may be that the exercise intervention duration included in the study was short and has not yet had a significant effect on body weight. In addition, body weight may be affected by a combination of dietary, metabolic, psychological, and disease factors. Longer-period, high-quality RCTs are needed to explore the potential effects of intradialysis exercise on body weight in MHD patients in the future.
Our study has several limitations. Firstly, given the specificity of the exercise intervention in the included studies, it was challenging to implement blinding of participants and researchers. Some studies did not elaborate on the methods used to generate the random sequence and conceal the allocation, which may cause selective bias. Secondly, this study included only published literature, did not search for grey literature, and excluded non-English literature, which may lead to incomplete inclusion. The literature included in this study varied due to differences in the type, frequency, intensity, and duration of the exercise, which may have affected the results of the pooled analyses. Lastly, most of the pooled outcomes in this study assessed indicators of physical frailty, excluding cognitive, psychological, or social domains. The study conclusions cannot fully replace overall frailty.
In conclusion, our study found that intradialytic exercise can significantly improve overall frailty and frailty indicators such as grip strength, 6MWD, step counts, and fatigue in MHD patients, which helps prevent and delay the progression of frailty. In clinical practice, we can tailor exercise programs according to different frailty problems of patients, thereby achieving personalized rehabilitation through improvement in corresponding frailty indicators. Therefore, all MHD patients without contraindications should engage in intradialytic exercise and develop personalized exercise programs according to the patient’s physical condition. More high-quality studies are needed in the future to assess the effect of intradialytic exercise on overall frailty and may further compare the effects of different types of intradialytic exercise on frailty in MHD patients.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
ZZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. JZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. ZY: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. XC: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – review and editing. WQ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphys.2025.1600219/full#supplementary-material
References
Araujo A. M., Orcy R. B., Feter N., Weymar M. K., Cardoso R. K., Bohlke M., et al. (2024). Effects of intradialytic exercise on functional capacity in patients with end-stage chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Res. Sports Med. 32 (1), 28–48. doi:10.1080/15438627.2022.2079983
Ashby D., Borman N., Burton J., Corbett R., Davenport A., Farrington K., et al. (2019). Renal association clinical practice guideline on haemodialysis. BMC Nephrol. 20 (1), 379. doi:10.1186/s12882-019-1527-3
Assawasaksakul N., Sirichana W., Joosri W., Kulaputana O., Eksakulkla S., Ketanun C., et al. (2021). Effects of intradialytic cycling exercise on daily physical activity, physical fitness, body composition, and clinical parameters in high-volume online hemodiafiltration patients: a pilot randomized-controlled trial. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 53 (2), 359–371. doi:10.1007/s11255-020-02677-7
Barker T. H., Habibi N., Aromataris E., Stone J. C., Leonardi-Bee J., Sears K., et al. (2024). The revised JBI critical appraisal tool for the assessment of risk of bias for quasi-experimental studies. JBI Evid. Synth. 22 (3), 378–388. doi:10.11124/JBIES-23-00268
Bossola M., Di Stasio E., Antocicco M., Panico L., Pepe G., Tazza L. (2015). Fatigue is associated with increased risk of mortality in patients on chronic hemodialysis. Nephron 130 (2), 113–118. doi:10.1159/000430827
Brown M. P. M. G., March D. S., Young R., Highton P. J., Young H. M. L., Churchward D. R., et al. (2021). A randomized controlled trial to investigate the effects of intra-dialytic cycling on left ventricular mass. Kidney Int. 99 (6), 1478–1486. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2021.02.027
Buckinx F., Rolland Y., Reginster J. Y., Ricour C., Petermans J., Bruyère O. (2015). Burden of frailty in the elderly population: perspectives for a public health challenge. Arch. Public Health 73 (1), 19. doi:10.1186/s13690-015-0068-x
Cardoso R. K., Araujo A. M., Del Vechio F. B., Bohlke M., Barcellos F. C., Oses J. P., et al. (2020). Intradialytic exercise with blood flow restriction is more effective than conventional exercise in improving walking endurance in hemodialysis patients: a randomized controlled trial. Clin. Rehabil. 34 (1), 91–98. doi:10.1177/0269215519880235
Chang Y., Cheng S. Y., Lin M., Gau F. Y., Chao Y. F. (2010). The effectiveness of intradialytic leg ergometry exercise for improving sedentary life style and fatigue among patients with chronic kidney disease: a randomized clinical trial. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 47 (11), 1383–1388. doi:10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2010.05.002
Dent E., Morley J. E., Cruz-Jentoft A. J., Woodhouse L., Rodríguez-Mañas L., Fried L. P., et al. (2019). Physical frailty: ICFSR international Clinical Practice guidelines for identification and management. J. Nutr. Health Aging 23 (9), 771–787. doi:10.1007/s12603-019-1273-z
Desai M., Mohamed A., Davenport A. (2019). A pilot study investigating the effect of pedalling exercise during dialysis on 6-min walking test and hand grip and pinch strength. Int. J. Artif. Organs 42 (4), 161–166. doi:10.1177/0391398818823761
Devagourou A., Sharma K. K., Yadav R. K., Gupta V. P., Kalaivani M. (2021). An experimental study to evaluate the effect of low-intensity intradialytic exercises on serum urea, creatinine, and fatigue of chronic kidney disease patients undergoing hemodialysis. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transpl. 32 (5), 1253–1259. doi:10.4103/1319-2442.344744
Dobsak P., Homolka P., Svojanovsky J., Reichertova A., Soucek M., Novakova M., et al. (2012). Intra-dialytic electrostimulation of leg extensors may improve exercise tolerance and quality of life in hemodialyzed patients. Artif. Organs 36 (1), 71–78. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1594.2011.01302.x
Dong Z. J., Zhang H. L., Yin L. X. (2019). Effects of intradialytic resistance exercise on systemic inflammation in maintenance hemodialysis patients with sarcopenia: a randomized controlled trial. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 51 (8), 1415–1424. doi:10.1007/s11255-019-02200-7
Dou J., Liu H., Ma Y., Wu Y. Y., Tao X. B. (2023). Prevalence of post-dialysis fatigue: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 13 (6), e064174. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2022-064174
Egger M., Davey Smith G., Schneider M., Minder C. (1997). Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315 (7109), 629–634. doi:10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629
Exel A. L., Lima P. S., Urtado C. B., Dibai-Filho A. V., Vilanova C. L., Sabino E. F. P., et al. (2021). Effectiveness of a resistance exercise program for lower limbs in chronic renal patients on hemodialysis: a randomized controlled trial. Hemodial. Int. 25, 372–379. doi:10.1111/hdi.12918
Fernandes A. O., Sens Y. A. D. S., Xavier V. B., Miorin L. A., Alves V. L. D. S. (2019). Functional and respiratory capacity of patients with chronic kidney disease undergoing cycle ergometer training during hemodialysis sessions: a randomized clinical trial. Int. J. Nephrol. 2019, 7857824. doi:10.1155/2019/7857824
Fried L. P., Tangen C. M., Walston J., Newman A. B., Hirsch C., Gottdiener J., et al. (2001). Frailty in older adults: evidence for a phenotype. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 56 (3), 146–156. doi:10.1093/gerona/56.3.m146
GBD Chronic Kidney Disease Collaboration (2020). Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the global Burden of disease study 2017. Lancet 395 (10225), 709–733. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30045-3
Groussard C., Rouchon-Isnard M., Coutard C., Romain F., Malardé L., Lemoine-Morel S., et al. (2015). Beneficial effects of an intradialytic cycling training program in patients with end-stage kidney disease. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 40 (6), 550–556. doi:10.1139/apnm-2014-0357
Harhay M. N., Rao M. K., Woodside K. J., Johansen K. L., Lentine K. L., Tullius S. G., et al. (2020). An overview of frailty in kidney transplantation: measurement, management and future considerations. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 35 (7), 1099–1112. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfaa016
Huang H. Y., Hung K. S., Yeh M. L., Chou H. L., Yeh A. L., Liao T. Y. (2021). Breathing-based leg exercises during hemodialysis improve quality of life: a randomized controlled trial. Clin. Rehabil. 35 (8), 1175–1184. doi:10.1177/02692155211000738
Jamshidpour B., Bahrpeyma F., Khatami M. R. (2020). The effect of aerobic and resistance exercise training on the health related quality of life, physical function, and muscle strength among hemodialysis patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 24 (2), 98–103. doi:10.1016/j.jbmt.2019.10.003
Kim S., Park H. J., Yang D. H. (2022). An intradialytic aerobic exercise program ameliorates frailty and improves dialysis adequacy and quality of life among hemodialysis patients: a randomized controlled trial. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 41 (4), 462–472. doi:10.23876/j.krcp.21.284
Kirkman D. L., Mullins P., Junglee N. A., Kumwenda M., Jibani M. M., Macdonald J. H. (2014). Anabolic exercise in haemodialysis patients: a randomised controlled pilot study. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 5 (3), 199–207. doi:10.1007/s13539-014-0140-3
Koh K. P., Fassett R. G., Sharman J. E., Coombes J. S., Williams A. D. (2010). Effect of intradialytic versus home-based aerobic exercise training on physical function and vascular parameters in hemodialysis patients: a randomized pilot study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 55 (1), 88–99. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2009.09.025
Kojima G., Liljas A. E. M., Iliffe S. (2019). Frailty syndrome: implications and challenges for health care policy. Risk Manag. Healthc. Policy 12, 23–30. doi:10.2147/RMHP.S168750
Krase A. A., Terzis G., Giannaki C. D., Stasinaki A. N., Wilkinson T. J., Smith A. C., et al. (2022). Seven months of aerobic intradialytic exercise training can prevent muscle loss in haemodialysis patients: an ultrasonography study. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 54 (2), 447–456. doi:10.1007/s11255-021-02931-6
Lee H. J., Son Y. J. (2021). Prevalence and associated factors of frailty and mortality in patients with end-stage renal disease undergoing hemodialysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18 (7), 3471. doi:10.3390/ijerph18073471
Li L., Ma X., Xie C., Li Y. (2024). Resistance exercise interventions for sarcopenia and nutritional status of maintenance hemodialysis patients: a meta-analysis. PeerJ 12, e16909. doi:10.7717/peerj.16909
Liberati A., Altman D. G., Tetzlaff J., Mulrow C., Gotzsche P. C., Ioannidis J. P., et al. (2009). The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ 339, b2700. doi:10.1136/bmj.b2700
Liu H., Zheng F., Yao W., Zhu J., Du X., Shi H., et al. (2023). The impact of aerobic exercise on health-related quality of life among patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis. Med. Baltim. 102 (45), e35990. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000035990
Lock M., Post D., Dollman J., Parfitt G. (2021). Efficacy of theory-informed workplace physical activity interventions: a systematic literature review with meta-analyses. Health Psychol. Rev. 15 (4), 483–507. doi:10.1080/17437199.2020.1718528
Lopes L. C. C., Mota J. F., Prestes J., Schincaglia R. M., Silva D. M., Queiroz N. P., et al. (2019). Intradialytic resistance training improves functional capacity and lean mass gain in individuals on hemodialysis: a randomized pilot trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 100 (11), 2151–2158. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2019.06.006
Malini H., Forwaty E., Cleary M., Visentin D., Oktarina E., Lenggogeni D. P. (2022). The effect of intradialytic range of motion exercise on dialysis adequacy and fatigue in hemodialysis patients. J. Nurs. Res. 30 (4), e221. doi:10.1097/jnr.0000000000000506
Marchesan M., Nunes V. G. S., Rombaldi A. J. (2014). Treinamento físico melhora a aptidão física e a qualidade de vida de pacientes em hemodiálise. Rev. Bras. Cineantropom Desempenho Hum. 16 (3), 334–344. doi:10.5007/1980-0037.2014v16n3p334
McAdams-DeMarco M. A., Law A., Salter M. L., Boyarsky B., Gimenez L., Jaar B. G., et al. (2013). Frailty as a novel predictor of mortality and hospitalization in individuals of all ages undergoing hemodialysis. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 61 (6), 896–901. doi:10.1111/jgs.12266
Mihaescu A., Avram C., Bob F., Gaita D., Schiller O., Schiller A. (2013). Benefits of exercise training during hemodialysis sessions: a prospective cohort study. Nephron Clin. Pract. 124 (1-2), 72–78. doi:10.1159/000355856
Neto M. G., de Lacerda F. F. R., Lopes A. A., Martinez B. P., Saquetto M. B. (2018). Intradialytic exercise training modalities on physical functioning and health-related quality of life in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Rehabil. 32 (9), 1189–1202. doi:10.1177/0269215518760380
Nitta K., Hanafusa N., Tsuchiya K. (2018). Role of frailty on outcomes of dialysis patients. Contrib. Nephrol. 195, 102–109. doi:10.1159/000486940
Noguchi M., Youhira Y., Tanaka M., Kaneko S., Odaira M., Anabata M., et al. (2022). Effects of an additional resistance training intervention in hemodialysis patients performing long-term ergometer exercise during dialysis. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 34 (2), 110–114. doi:10.1589/jpts.34.110
Page M. J., McKenzie J. E., Bossuyt P. M., Boutron I., Hoffmann T. C., Mulrow C. D., et al. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guide line for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 372, n71. doi:10.1136/bmj.n71
Rhee S. Y., Song J. K., Hong S. C., Choi J. W., Jeon H. J., Shin D. H., et al. (2019). Intradialytic exercise improves physical function and reduces intradialytic hypotension and depression in hemodialysis patients. Korean J. Intern Med. 34 (3), 588–598. doi:10.3904/kjim.2017.020
Rivera-Brown A. M., Frontera W. R. (2012). Principles of exercise physiology: responses to acute exercise and long-term adaptations to training. PMR 4 (11), 797–804. doi:10.1016/j.pmrj.2012.10.007
Salehi F., Dehghan M., Mangolian Shahrbabaki P., Ebadzadeh M. R. (2020). Effectiveness of exercise on fatigue in hemodialysis patients: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 12, 19. doi:10.1186/s13102-020-00165-0
Sánchez-Tocino M. L., González-Parra E., Miranda Serrano B., Gracia-Iguacel C., de-Alba-Peñaranda A. M., López-González A., et al. (2022). Evaluation of the impact of an intradialytic exercise programme on sarcopaenia in very elderly haemodialysis patients. Clin. Kidney J. 15 (8), 1514–1523. doi:10.1093/ckj/sfac046
Sovatzidis A., Chatzinikolaou A., Fatouros I. G., Panagoutsos S., Draganidis D., Nikolaidou E., et al. (2020). Intradialytic cardiovascular exercise training alters redox status, reduces inflammation and improves physical performance in patients with chronic kidney disease. Antioxidants (Basel) 9 (9), 868. doi:10.3390/antiox9090868
Sterne J. A. C., Savović J., Page M. J., Elbers R. G., Blencowe N. S., Boutron I., et al. (2019). RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 366, l4898. doi:10.1136/bmj.l4898
Valle F. M. D., Pinheiro B. V., Barros A. A. A., Mendonça W. F., Oliveira A. C., Werneck G. O., et al. (2020). Effects of intradialytic resistance training on physical activity in daily life, muscle strength, physical capacity and quality of life in hemodialysis patients: a randomized clinical trial. Disabil. Rehabil. 42 (25), 3638–3644. doi:10.1080/09638288.2019.1606857
Vogiatzaki E., Michou V., Liakopoulos V., Roumeliotis A., Roumeliotis S., Kouidi E., et al. (2022). The effect of a 6-month intradialytic exercise program on hemodialysis adequacy and body composition: a randomized controlled trial. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 54 (11), 2983–2993. doi:10.1007/s11255-022-03238-w
Vogt B. P., Borges M. C. C., Goés C. R., Caramori J. C. T. (2016). Handgrip strength is an independent predictor of all-cause mortality in maintenance dialysis patients. Clin. Nutr. 35 (6), 1429–1433. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2016.03.020
Wahida A. Z., Rumahorbo H., Murtiningsih M. (2022). The effectiveness of intradialytic exercise in ameliorating fatigue symptoms in patients with chronic kidney failure undergoing hemodialysis: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. J. Taibah Univ. Med. Sci. 18 (3), 512–525. doi:10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.11.004
Wang C. J., Johansen K. L. (2019). Are dialysis patients too frail to exercise? Semin. Dial. 32 (4), 291–296. doi:10.1111/sdi.12786
Wu Y., He Q., Yin X., He Q., Cao S., Ying G. (2014). Effect of individualized exercise during maintenance haemodialysis on exercise capacity and health-related quality of life in patients with uraemia. J. Int. Med. Res. 42 (3), 718–727. doi:10.1177/0300060513509037
Yabe H., Kono K., Yamaguchi T., Yamada N., Ishikawa Y., Yamaguchi Y., et al. (2022). Effect of intradialytic exercise on geriatric issues in older patients undergoing hemodialysis: a single-center non-randomized controlled study. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 54 (11), 2939–2948. doi:10.1007/s11255-022-03205-5
Yeh M. L., Wang M. H., Hsu C. C., Liu Y. M. (2020). Twelve-week intradialytic cycling exercise improves physical functional performance with gain in muscle strength and endurance: a randomized controlled trial. Clin. Rehabil. 34 (7), 916–926. doi:10.1177/0269215520921923
Yoo J., Ruppar T., Wilbur J., Miller A., Westrick J. C. (2022). Effects of home-based exercise on frailty in patients with end-stage renal disease: systematic review. Biol. Res. Nurs. 24 (1), 48–63. doi:10.1177/10998004211033031
Young H. M. L., March D. S., Graham-Brown M. P. M., Jones A. W., Curtis F., Grantham C. S., et al. (2018). Effects of intradialytic cycling exercise on exercise capacity, quality of life, physical function and cardiovascular measures in adult haemodialysis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 33 (8), 1436–1445. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfy045
Young H. M. L., March D. S., Highton P. J., Graham-Brown M. P. M., Churchward D. C., Grantham C., et al. (2020). Exercise for people living with frailty and receiving haemodialysis: a mixed-methods randomised controlled feasibility study. BMJ Open 10 (11), e041227. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-041227
Keywords: intradialytic exercise, hemodialysis, frailty, effects, meta-analysis
Citation: Zou ZH, Zhang JQ, Yi ZH, Chen X and Qing W (2025) Effects of intradialytic exercise on frailty in maintenance hemodialysis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis . Front. Physiol. 16:1600219. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1600219
Received: 27 March 2025; Accepted: 21 October 2025;
Published: 06 November 2025.
Edited by:
Giuseppe D'Antona, University of Pavia, ItalyReviewed by:
Alessandro Capitanini, SOC Nefrologia Pistoia, ItalyKatsumori Takamatsu, Jyoban Hospital, Japan
Copyright © 2025 Zou, Zhang, Yi, Chen and Qing. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wei Qing, MTU4MTQwMTc2MkBxcS5jb20=
 Zhao Hua Zou
Zhao Hua Zou Ji Quan Zhang1
Ji Quan Zhang1
![Forest plot showing mean differences and confidence intervals for three studies: Desai 2019, Kim 2022, and Sánchez-Tocino 2022. The plot compares experimental and control groups, with weights ranging from 29.3% to 35.7%. Pooled mean difference is -0.98 with 95% CI [-1.90, -0.06]. Heterogeneity indicated by Tau²=0.52, Chi²=9.75, and I²=79%. Overall effect test shows Z=2.08, P=0.04.](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/1600219/fphys-16-1600219-HTML/image_m/fphys-16-1600219-g003.jpg)