- Key Laboratory of Physical Fitness and Exercise Rehabilitation of Hunan Province, College of Physical Education, Hunan Normal University, Changsha, China
Physiological cardiac hypertrophy represents an adaptive response of the heart to chronic physiological stimuli, including sustained exercise, and is characterized by cardiomyocyte enlargement and structural optimization to enhance pumping efficiency. While several studies on cardiac physiological adaptation have been published recently, a systematic integration of information on exercise-regulated hormonal and growth factor networks remains lacking. To address this limitation, toward the systematization of a ‘multi-dimensional mechanism’ model, here we review the molecular mechanisms underlying exercise-induced physiological cardiac hypertrophy, with particular focus on how physical activity regulates hormones and growth factors including insulin-like growth factor-1, vascular endothelial growth factor, neuregulin-1, and norepinephrine. These mediators activate intricate signaling pathway networks that promote protein synthesis in cardiomyocytes, strengthen myocardial contractility, and induce angiogenesis. The highlighted findings not only provide novel insights into the cardioprotective mechanisms of exercise but also identify potential biomarkers that enable the development of precision exercise prescriptions tailored to individuals with cardiovascular diseases.
1 Introduction
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) remain the leading cause of global mortality (Naghavi et al., 2024). Approximately 20.5 million deaths were reported in 2021—accounting for one-third of global mortality—as was a substantial increase of over 6 million cases between 1990 and 2019, as per the 2023 World Heart Federation (Naghavi et al., 2024). Physical inactivity is a key modifiable risk factor contributing to the global burden of CVD. Physiological cardiac hypertrophy is defined as an adaptive myocardial adaptation(physiological) process driven by hemodynamic demands during physiological challenges such as chronic exercise and pregnancy (Weeks and McMullen, 2011). This non-pathological adaptation involves cardiomyocyte enlargement with concomitant increased myofibril density and diameter, resulting in enhanced contractile function and cardiac output. Key features include preserved or mildly elevated ejection fraction and coronary reserve, proportional angiogenesis, increased myoglobin expression, and the absence of pathological markers such as myocardial fibrosis or necrosis (Qiu et al., 2022). Furthermore, it is accompanied by increased mitochondrial biogenesis and enhanced mitochondrial function (Abel and Doenst, 2011). Importantly, this hypertrophic response, with cardioprotective benefits, is reversible (Qiu et al., 2022). Given the critical role of physiological cardiac hypertrophy in cardiovascular adaptation, elucidating its regulatory mechanisms is a research priority.
Exercise, as a non-invasive intervention, is globally recommended for both preventing and managing CVD. In addition to improving myocardial contractility and endurance capacity, chronic exercise promotes structural cardiac adaptation, with physiological hypertrophy serving as its hallmark adaptation. Dynamic fluctuations in circulating hormones and cytokines during acute exercise and recovery phases act as key mediators of exercise-induced cardiac adaptation (Qiu et al., 2022). These bioactive molecules activate signaling pathways that regulate cardiomyocyte proliferation, differentiation, and metabolic adaptation, thereby inducing beneficial hypertrophy (Waring et al., 2014; Chen et al., 2021). Notably, hormonal and growth factor responses exhibit marked sensitivity to exercise type, intensity, and duration, suggesting the existence of a sophisticated molecular regulatory network. Therefore, studying the exercise-mediated regulation of such biomolecules offers dual benefits: advancing our understanding of cardiac adaptation mechanisms and guiding the design of personalized exercise regimens for cardiovascular rehabilitation. Although existing research has predominantly focused on isolated hormonal pathways, critical knowledge gaps persist regarding (1) the dynamic synergistic regulation of exercise-induced hormonal networks; (2) the dose-response relationships of specific exercise modalities in targeted populations (e.g., individuals with diabetes); and (3) the mechanistic interplay between lymphangiogenesis and fibrotic thresholds. In this study, we address these unresolved questions through multi-dimensional mechanistic integration. This encompasses the hierarchical integration of molecular, cellular, and systemic adaptations orchestrated by exercise-regulated hormonal networks, spanning the following four interconnected dimensions: (1) the molecular dimension involving cross-talk between key signaling pathways activated by hormones and growth factors; (2) the cellular dimension coordinating responses across cardiomyocytes, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts; (3) the temporal dimension reflecting dynamic hormone fluctuations during acute exercise versus chronic training; and (4) the systemic dimension integrating endocrine, exercise, and hemodynamic stimuli. These dimensions function synergistically rather than additively, forming an adaptive network that scales with exercise intensity and duration.
2 Exercise-induced myocardial proliferation and growth
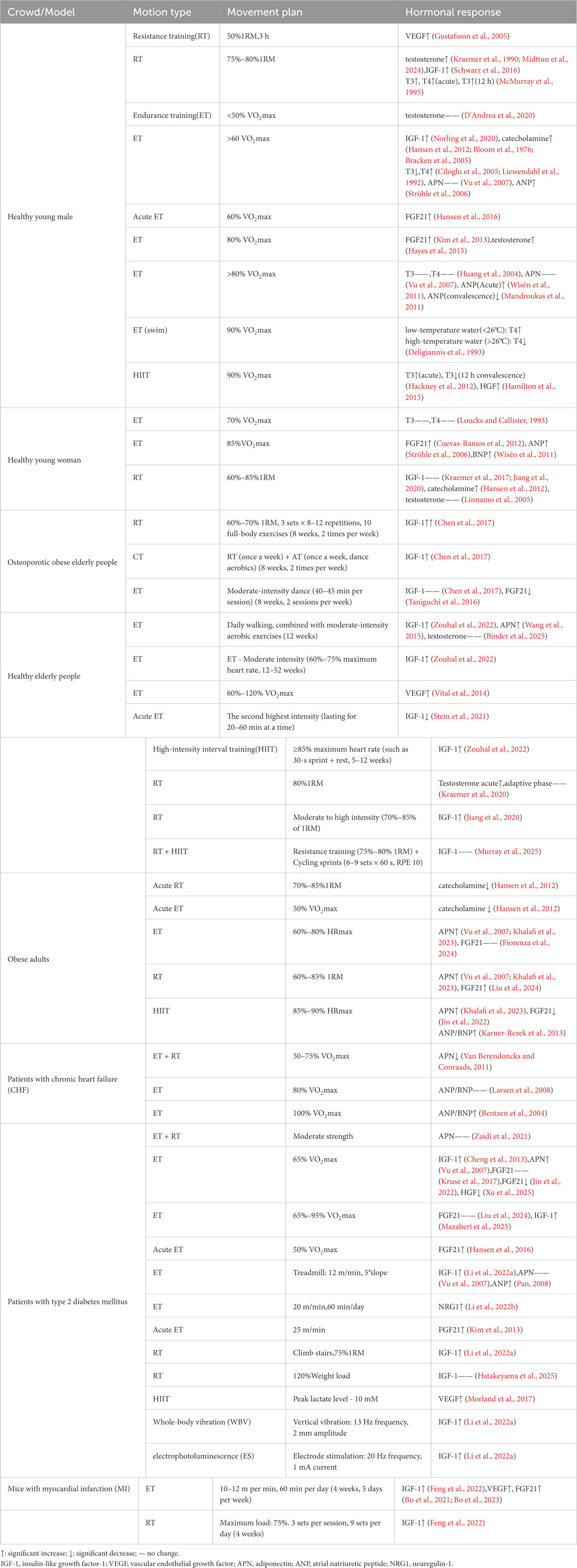
Prolonged exercise training leads to morphologic adaptations typical of the athlete’s heart syndrome, including the progressive volumetric expansion of cardiomyocytes, with increased sarcomeric diameter (Hastings et al., 2024). This adaptation process primarily manifests as left ventricular hypertrophy proportional to the exercise intensity and the duration of cumulative training, within established physiological limits (Kemi et al., 2005). This adaptive transformation involves the coordinated activation of endocrine and paracrine signaling pathways (Figure 1). Specifically, hormonal mediators and growth factors cooperatively regulate the molecular mechanisms that enhance myocardial contractile performance, improve metabolic substrate utilization, and increase cardiac functional reserve. These integrative adaptations collectively enable the cardiovascular system to meet elevated metabolic demands during sustained physical activity while maintaining the hemodynamic equilibrium.
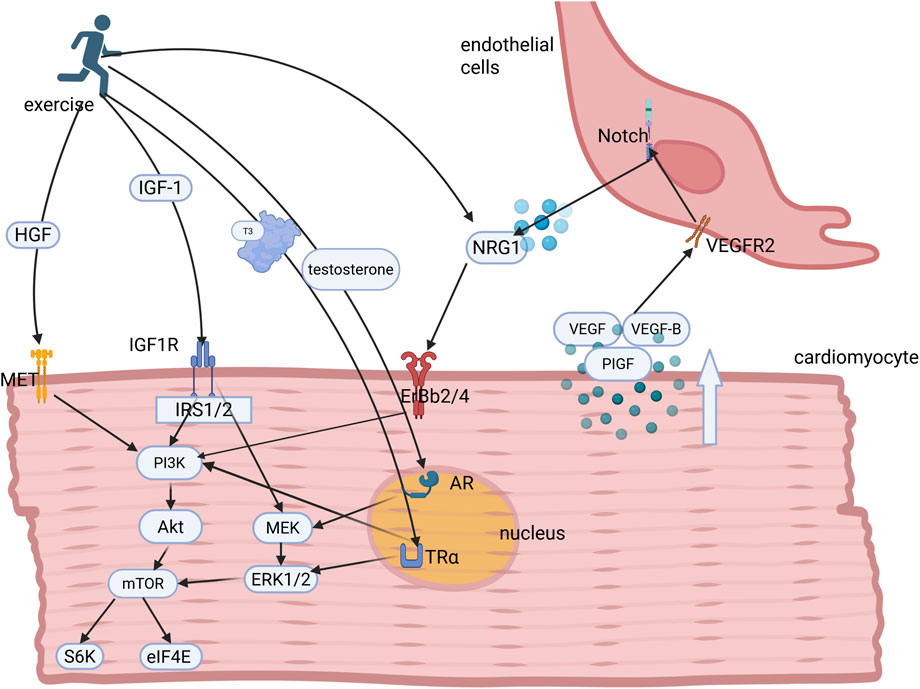
Figure 1. Hormonal and growth factor regulation underlying exercise-induced myocardial proliferation and growth. Exercise stimulates the secretion of key hormones and growth factors, including IGF-1, HGF, testosterone, NRG1, and triiodothyronine (T3), which bind to their cognate receptors to activate downstream PI3K/AKT and MEK/ERK1/2 signaling cascades. These pathways collectively orchestrate cardiomyocyte proliferation and hypertrophic growth. Concomitantly, exercise induces paracrine VEGF secretion from cardiomyocytes, which binds to endothelial cell surface receptors to initiate Notch signaling. This intercellular crosstalk promotes endothelial NRG1 release, which together with circulatory NRG1, amplifies ErbB-mediated signaling in cardiomyocytes, thereby establishing a coordinated microenvironment for adaptive cardiac adaptation. IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor-1; IRS1, insulin receptor substrates 1; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; AKT, protein kinase B; ERKs, extracellular signal-regulated kinases; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; NRG1, neuregulin-1; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.
2.1 Insulin-like growth Factor-1 (IGF-1)
IGF-1, a multifunctional peptide hormone, regulates cardiac metabolic homeostasis, hypertrophic adaptation, cellular senescence, and apoptosis through IGF-1 receptor (IGF1R)-mediated signaling pathways (Troncoso et al., 2014). Previous studies have reported that moderate-intensity aerobic exercise enhances cardiac expression of IGF-1 and IGF1R (Weeks et al., 2017; Cheng et al., 2013). For instance, a 4-week swimming training protocol significantly increased myocardial IGF-1 mRNA levels in zebrafish (Chen et al., 2021). have, murine models with partial IGF-1 deficiency exhibit impaired cardiac function and fibrotic remodeling(pathological) (González-Guerra et al., 2017). Mechanistically, IGF-1 regulates cardiac mass and function via insulin receptor substrates 1 (IRS1) and 2, as genetic knockout of both IRS isoforms abolishes exercise-induced physiological hypertrophy (Riehle et al., 2014). The phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt) axis, a key downstream target of IRS signaling, controls myocardial growth dynamics. Dysregulation of this pathway, characterized by reduced PI3K activation and increased Akt dephosphorylation, significantly compromises cardiac adaptation to exercise (Riehle et al., 2014).
Furthermore, extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs) serve as complementary signaling mediators for IGF-1-induced physiological cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. These mitogen-activated protein kinases play dual roles in physiological and pathological cardiac remodeling (Gallo et al., 2019). Notably, the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MEK)/ERK cascade interacts synergistically with PI3K/Akt signaling to coordinate the transcriptional regulation of cardiomyocyte growth and proliferation, forming an integrated signaling network that modulates hypertrophic responses to hemodynamic stress (Chattergoon et al., 2014; Sundgren et al., 2003).
2.2 Testosterone
Testosterone, a steroid hormone produced in Leydig cells, the ovaries, and the adrenal cortex, has cardioprotective effects by mitigating fibrotic remodeling and oxidative stress (Bianchi, 2018). Acute high-intensity resistance exercise induces rapid testosterone surges, primarily mediated by activating the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, and transient decreases in plasma sex hormone-binding globulin levels during intense physical exertion (Vingren et al., 2010). Androgen signaling enhances cardiac IGF-1 expression, with testosterone supplementation inducing dose-dependent increases in myocardial mass and IGF-1 content in preclinical models (Zebrowska et al., 2017). At the molecular level, testosterone interacts with nuclear androgen receptors (AR) in cardiomyocytes (Jänne et al., 1993), triggering MEK/ERK1/2 signaling, which activates the mTORC1/S6K1 pathway, ultimately driving physiological hypertrophy development (Altamirano et al., 2009).
2.3 Thyroid hormones
Thyroid hormones, which are essential nuclear receptor ligands for cardiac morphogenesis and metabolic regulation, primarily act through the peripheral conversion of thyroxine (T4) to bioactive triiodothyronine (T3), mediated by type 2 deiodinase (Mullur et al., 2014). Acute moderate-to-vigorous aerobic exercise induces transient increases in serum T3, T4, and thyroid-stimulating hormone levels (Hackney and Saeidi, 2019). These hormones bind to cardiac thyroid hormone receptors TRα1 (localized in the nucleus and cytoplasm) and TRβ1 (Mullur et al., 2014). In turn, TRα1 initiates rapid PI3K activation and subsequent Akt-mTOR-S6K pathway stimulation following T3 binding (K et al., 2006). Simultaneously, T3 promotes ERK phosphorylation in cardiomyocytes, establishing a synergistic signaling mechanism that enhances protein synthesis and contractile machinery adaptation, ultimately improving cardiac contractility (Chattergoon et al., 2014).
2.4 Neuregulin-1(NRG1)
NRG1, a key member of the epidermal growth factor family in the cardiovascular system (Falls, 2003), modulates multiple cardiac processes, including myocardial metabolism, cellular proliferation, and regeneration. Chronic exercise training enhances NRG1/ErbB signaling (Cai et al., 2016), since pharmacological inhibition of this pathway abolishes exercise-mediated cardiac repair in rodent models (Cai et al., 2016). Specifically, endothelial-derived NRG1 acts via paracrine signaling, binding to ErbB3/ErbB4 receptors on neighboring cardiomyocytes to initiate ErbB2 heterodimer formation (Odiete et al., 2012). These receptor complexes, particularly ErbB2/ErbB4 heterodimers, are critical for cardiomyocyte proliferation by activating downstream PI3K/Akt signaling, which, in turn, coordinates ventricular myocyte differentiation and hypertrophic growth (Zhao et al., 1998).
2.5 Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)
HGF has multifunctional cardioprotective effects, including th inhibiting apoptosis and autophagy, promoting angiogenesis, suppressing fibrosis and inflammation, regulating immune function, and stimulating cardiomyocyte regeneration (Arechederra et al., 2013; Gallo et al., 2015). Chronic aerobic exercise induces the significant upregulation of myocardial HGF expression (Zhang et al., 2021). Mechanistically, HGF signaling is mediated by c-Met tyrosine kinase receptors. Upon ligand binding, receptor autophosphorylation initiates activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling cascade (Gallo et al., 2015; Gallo et al., 2014). Notably, transgenic HGF overexpression improves post-myocardial infarction recovery in murine models by enhancing angiogenesis, reducing cardiomyocyte apoptosis, and restoring ventricular contractile function (Jayasankar et al., 2005).
Emerging evidence indicates that diverse exercise paradigms elicit distinct endocrine and cardiovascular adjustments across various demographic groups, potentially influencing myocardial proliferation and growth outcomes. Consequently, exercise prescriptions should be personalized according to individual health profiles. In patients recovering from myocardial infarction, low-intensity aerobic training predominantly elevates IGF-1 and NRG1 levels while mitigating exercise-induced cardiovascular risks (Cai et al., 2016; Tan et al., 2023). In normotensive individuals, both acute and chronic aerobic or resistance training foster cardiovascular adaptation, with high-intensity resistance training demonstrating superior efficacy in enhancing anabolic hormone profiles (IGF-1, testosterone) (Grubb et al., 2014; Seo et al., 2018), whereas HGF reaches peak levels following prolonged endurance exercise (Bonsignore et al., 1985). Notably, obese populations experience acute exercise-induced endocrine dysregulation, marked by heightened catecholamine responses and aberrant fluctuations in testosterone, growth hormone, and thyroxine (Hansen et al., 2012). In contrast, systematic exercise training restores endocrine homeostasis, significantly improving hormonal balance and metabolic regulation in this demographic (Hansen et al., 2012).
3 Exercise-induced cardiovasculogenesis and lymphangiogenesis
Physical training enhances coronary vasodilation, improves myocardial perfusion, and stimulates capillary network expansion through neovascularization and collateral vessel formation. Cardiac lymphatic vessels regulate interstitial fluid clearance, directing the subendocardial drainage toward the epicardial collectors, which ultimately drain via mediastinal lymph nodes into the venous system (Liu and Oliver, 2023). Exercise-induced lymphangiogenesis serves as an adaptive mechanism that alleviates inflammatory cell infiltration, suppresses fibrotic remodeling, and reduces myocardial edema (Henri et al., 2016). Furthermore, itprovides therapeutic benefits in ischemic cardiomyopathy (Shimizu et al., 2018).
This coordinated vascular-lymphatic adaptation is regulated by exercise-modulated catecholamines and growth factors such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and HGF (Figure 2).
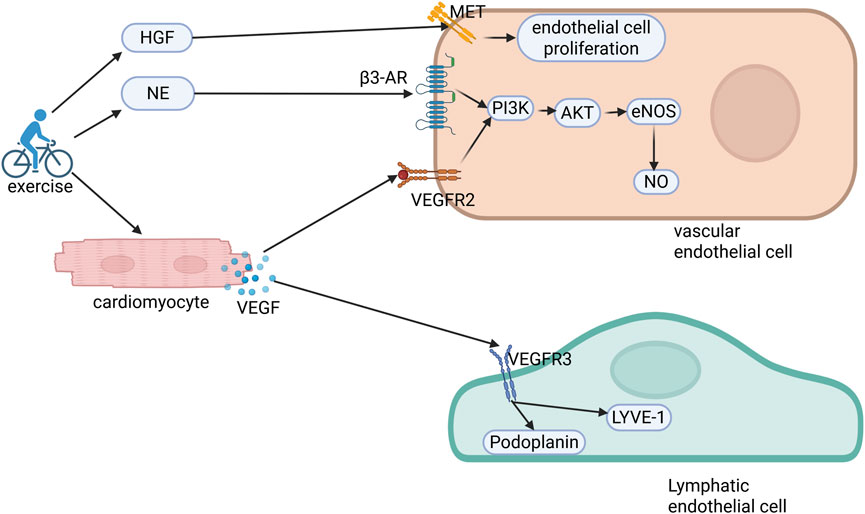
Figure 2. Molecular mechanisms of exercise-induced cardiovascular and lymphatic angiogenesis. Exercise elevates circulating hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and norepinephrine (NE) levels while stimulating cardiomyocyte-derived vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) secretion. HGF binds to c-Met receptors on endothelial cells, facilitating their proliferation and migration. Concurrently, NE and VEGF engage β3-adrenergic receptors (β3-AR) and VEGFR2, respectively, activating the PI3K/AKT/eNOS/NO signaling axis to orchestrate coronary angiogenesis. Furthermore, VEGF interacts with VEGFR3 on lymphatic endothelial cells, upregulating the lymphangiogenic markers LYVE-1 and podoplanin, thereby establishing a dual regulatory network of coordinated vascular and lymphatic adaptation. PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; AKT, protein kinase B; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; NO, nitric oxide.
3.1 VEGF
The VEGF family coordinates vascular and lymphatic development through receptor-specific interactions: VEGF-A, VEGF-B, and placental growth factor (PlGF) bind VEGFR1, whereas VEGF-C and VEGF-D selectively activate VEGFR3 (Ferrara et al., 2003). VEGFR2 serves as the pivotal receptor orchestrating angiogenesis (Kappas et al., 2008). Under VEGFR1 deficiency or elevated VEGF-B/PlGF bioavailability, VEGF exhibits enhanced binding affinity to VEGFR2 leading to a higher activation efficacy and amplified angiogenic processes (Shibuya, 2006). Exercise induces cardiomyocyte-derived VEGF paracrine signaling, which activates endothelial VEGFRs to stimulate the PI3K/Akt and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS)/nitric oxide (NO) pathways (Wilson et al., 2015; Dimmeler et al., 1999). The eNOS/NO axis plays a pivotal role in coronary angiogenesis and cardioprotection (Bernardo et al., 2018), with Akt-dependent eNOS phosphorylation serving as a central regulatory mechanism (Dimmeler et al., 1999). Coronary angiogenesis modulates hypertrophic responses, as evidenced by endothelial VEGFR2/Notch-dependent NRG1 release, promoting physiological hypertrophy (Kivelä et al., 2019).
VEGF-C and VEGF-D are primary mediators of exercise-induced lymphangiogenesis. Recent studies found that LYVE-1 facilitates lymphatic endothelial cell (LEC) migration via integrin α9β1 signaling (Capuano et al., 2019), whereas podoplanin mediates lymphatic lumen formation through CLEC-2 receptor-dependent mechanisms (Suzuki-Inoue et al., 2018). In murine models, swimming and eccentric training upregulate cardiac VEGF-C and VEGF-D expression (Bei et al., 2022), which bind VEGFR3 onLECs to enhance lymphatic density and upregulate the lymphangiogenic markers LYVE-1 and podoplanin. Pharmacological VEGFR3 inhibition blocks exercise-mediated lymphangiogenesis (Bei et al., 2022), while LYVE-1 facilitates endothelial migration (Wu et al., 2014). Podoplanin, a LEC-specific glycoprotein, controls lymphatic morphogenesis, as its deficiency causes lymphatic maldevelopment and nodal edema (Schacht et al., 2003).
3.2 HGF
HGF has pleiotropic effects on cardiovascular homeostasis through its high-affinity receptor, c-Met tyrosine kinase. Mechanistically, HGF stimulates endothelial cell proliferation and migration while suppressing apoptosis via PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK signaling cascades, thereby promoting neovascularization (Bussolino et al., 1992). This pro-angiogenic action is amplified through synergistic interactions with VEGF and angiopoietin-1, which collectively stabilize nascent vessels by recruiting pericytes and enhancing endothelial barrier function (Gallo et al., 2015). In preclinical chronic ischemic models (e.g., porcine myocardial infarction), intramyocardial HGF administration increases capillary density by 30%–40% and improves regional blood flow, as quantified using microsphere perfusion assays. These benefits extend to functional outcomes, with HGF-treated animals exhibiting enhanced left ventricular ejection fraction and reduced infarct size (Yuan et al., 2012). However, HGF’s role is context-dependent: while beneficial in ischemia, HGF exacerbates tumor angiogenesis and atherosclerotic plaque vulnerability by upregulating matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and promoting intraplaque neovascularization (Abounader and Laterra, 2005; Ma et al., 2002).
3.3 Epinephrine and norepinephrine
Exercise-induced catecholamine release mediates sympatho-adrenal activation, enhancing cardiac output through chronotropic and inotropic effects while regulating vascular tone (Motiejunaite et al., 2021). Chronic activation of the endothelial β3-adrenergic receptor (β3-AR) represents a cardioprotective mechanism. β3-AR signaling stimulates eNOS through its phosphorylation at Ser1177 and dephosphorylation at Thr495, amplifying NO production without altering eNOS expression (Calvert et al., 2011). Notably, adrenaline-deficient mice develop pathological left ventricular hypertrophy after 6 weeks of treadmill training, characterized by interstitial fibrosis and impaired diastolic function; this phenotype is rescued by β3-AR agonist treatment (Mendes et al., 2018). These findings highlight β3-AR’s unique role in balancing exercise-induced hemodynamic stress and adaptive vascular growth.
Exercise triggers a complex molecular cascade that regulates coronary and lymphatic vascular development. The VEGF family (VEGF-A/B, PlGF, and VEGF-C/D) and their receptors (VEGFR1-3) coordinate angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis (Ferrara et al., 2003). VEGFR2 is pivotal for angiogenesis, with heightened activity under VEGFR1 suppression or elevated VEGF-B/PlGF signaling (Kappas et al., 2008; Shibuya, 2006). Cardiomyocyte-derived VEGF activates endothelial VEGFRs, initiating PI3K/Akt and eNOS/NO pathways critical for coronary angiogenesis and cardioprotection (Wilson et al., 2015; Dimmeler et al., 1999). VEGF-C/D drive lymphangiogenesis via LYVE-1-mediated endothelial migration and podoplanin-dependent lumen formation (Bei et al., 2022). HGF complements these effects by promoting endothelial proliferation/migration and neovascularization through PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK pathways, synergizing with VEGF and angiopoietin-1 to enhance outcomes (beneficial in ischemia but risk-augmenting in tumors/atherosclerosis) (Gallo et al., 2015; Bussolino et al., 1992). Catecholamines (epinephrine/norepinephrine) released during exercise activate sympatho-adrenal signaling via β3-ARs, boosting cardiac output, modulating vascular tone, and amplifying NO production via eNOS activation, reinforcing cardioprotection (Calvert et al., 2011; Mendes et al., 2018). While exercise improves coronary perfusion, prolonged endurance training may induce maladaptive coronary changes (Lin et al., 2017). Optimizing exercise protocols for coronary disease requires precision medicine—tailoring regimens using dose-response modeling, biomarkers, and psychosocial profiling to maximize therapeutic benefits while mitigating risks.
4 Exercise-mediated mitochondrial adaptation and metabolic reprogramming
Mitochondrial dysfunction is a hallmark of CVD. Importantly, moderate exercise activates mitochondrial adaptation through enhanced respiratory chain activity, and improved quality control (biogenesis, mitophagy, and fusion/fission dynamics), leading to the maintenance of cellular homeostasis (Guan et al., 2019; Campos et al., 2017). For instance, a 3-week endurance training program was shown to normalize the redox balance and restore mitochondrial efficiency in a high-fat diet-induced rodent model (Tocantins et al., 2023). Central to this adaptation is the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1α (PGC-1α), a master transcriptional regulator abundantly expressed in cardiomyocytes. PGC-1α coordinates mitochondrial biogenesis by interacting with nuclear receptors (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α[PPARs] and estrogen-related receptor [ERRs]) and transcription factors (NRF-1/2), thereby promoting the oxidative phosphorylation capacity, fatty acid β-oxidation, and mitochondrial DNA replication (Figure 3) (Finck and Kelly, 2006; Lehman et al., 2000). Furthermore, the synergistic interaction between ERRα and PGC-1α fine-tunes mitochondrial gene networks to ensure metabolic flexibility (Schreiber et al., 2004).
Figure 3. Molecular mechanisms of exercise-induced mitochondrial adaptation and metabolic optimization. Exercise upregulates the cardiac expression of NE, IGF-1, and APN. NE engagesβ3-AR to activate the eNOS/NO signaling axis, subsequently amplifying the expression of PGC-1α. Concurrently, IGF-1 and APN stimulate the activation of PGC-1α through their respective receptors. This transcriptional coactivator orchestrates mitochondrial reprogramming by synergizing with PPARα and ERRs to enhance fatty acid β-oxidation, while also collaborating with NRF-1 and ERRs to upregulate the expression of Tfam. This coordinated regulation drives mitochondrial DNA transcription and biogenesis, and consequently energy substrate optimization and enhanced oxidative capacity.NE, norepinephrine; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor-1; APN, adiponectin; β3-AR, β3-adrenergic receptors; PGC-1α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1α; ERRs, estrogen-related receptors; NRF-1, nuclear respiratory factor-1; Tfam, mitochondrial transcription factor A.
4.1 Epinephrine and norepinephrine
Exercise-induced sympathoadrenal activation elevates circulating catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine) and upregulates cardiacβ3-AR expression. β3-AR signaling enhances the activity of eNOS through two post-translational modifications: the phosphorylation of Ser1177 (activation) and the dephosphorylation of Thr495 (inactivation); these collectively amplify eNOS-derived NO production without altering total eNOS protein levels (Calvert et al., 2011). The resultant NO/cGMP signaling cascade activates PGC-1α, NRF-1, and mitochondrial transcription factor A, driving mitochondrial biogenesis and respiratory chain optimization (Nisoli et al., 2004). This pathway is indispensable for exercise-induced metabolic adaptation, as evidenced by eNOS-knockout mice, which fail to show mitochondrial proliferation or improved oxidative capacity following training (Nisoli et al., 2003; Vettor et al., 2014). The age-associated decline in mitochondrial integrity observed in cardiovascular pathologies may be associated with β3-AR downregulation.
4.2 IGF-1
IGF-1, elevated in response to both acute and chronic exercise, coordinates myocardial energy substrate utilization via IRS-mediated pathways. IRS1/2 are critical adapters linking IGF-1 receptor activation to downstream effectors. Notably, IRS deficiency disrupts the exercise-induced stabilization of PGC-1α at the protein level even if the mRNA levels are unchanged, highlighting the role of IRS in post-transcriptional regulation, such as mTORC1-dependent translation (Riehle et al., 2014). IGF-1 finally enhances fatty acid β-oxidation by upregulating PPARα and carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1B, while simultaneously optimizing glucose metabolism during high-intensity exercise through GLUT4 translocation and hexokinase II activation (Friehs et al., 2001).
4.3 Adiponectin (APN)
APN, an adipocytokine inversely correlated with the body mass index, is robustly elevated by high-intensity exercise, particularly in individuals with obesity or metabolic syndrome (Khalafi and Symonds, 2020). APN stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis through the following two synergistic mechanisms: (1) transcriptional activation of PGC-1α by inhibiting AMP-activated protein kinase-dependent histone deacetylase (HDAC), and (2) post-translational deacetylation of PGC-1α by SIRT1, increasing its transcriptional coactivator function (Lin et al., 2013). In murine models, APN administration rescues doxorubicin-induced mitochondrial fragmentation by restoring the fusion-fission balance via mitofusin-2 and dynamin-related protein 1 regulation; conversely, APN knockout mice exhibit defective oxidative phosphorylation and accelerated cardiac aging (Yan et al., 2013). Clinically, exercise-induced APN elevation correlates with improved insulin sensitivity and reduced intramyocardial lipid deposition in patients with diabetes, suggesting that APN is both a biomarker and mediator of exercise benefits in metabolic heart disease (Lee et al., 2011).
The interplay between exercise-induced hormonal regulators (catecholamines, IGF-1, and APN) and PGC-1α orchestrates mitochondrial adaptation and metabolic reprogramming critical for cardiovascular adaptation. β3-AR-mediated eNOS activation amplifies NO/cGMP signaling, driving PGC-1α-dependent mitochondrial biogenesis and respiratory chain optimization (Nisoli et al., 2004). IGF-1, elevated by exercise, coordinates energy substrate utilization via IRS1/2-dependent pathways, stabilizing PGC-1α protein levels through mTORC1-regulated translation and enhancing fatty acid oxidation and glucose metabolism (Riehle et al., 2014; Friehs et al., 2001; Ren et al., 1999). APN, robustly induced by high-intensity exercise, synergistically activates PGC-1α transcriptionally (via AMPK-HDAC inhibition) and post-translationally (via SIRT1-mediated deacetylation), restoring mitochondrial dynamics and improving oxidative phosphorylation (Lin et al., 2013). Collectively, aerobic and resistance training counteract age-related PGC-1α suppression (Neto et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2024), likely through catecholamine- and APN-driven metabolic reprogramming, establishing a mechanistic framework for precision exercise interventions targeting metabolic and age-related cardiovascular disorders.
5 Exercise-mediated attenuation of cardiac fibrosis
Cardiac fibrosis, defined as the pathological replacement of cardiomyocytes with a collagenous matrix following injury or necrosis (Fan and Kassiri, 2021), represents a terminal pathological process in CVD. Notably, exercise has therapeutic effects against fibrosis induced by diverse etiologies, including hypertension, rheumatoid arthritis, and aging (Hong et al., 2022; Peyronnel et al., 2024; Wright et al., 2014). This cardioprotective action is mediated via testosterone, HGF, and fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) signaling pathways (Figure 4).
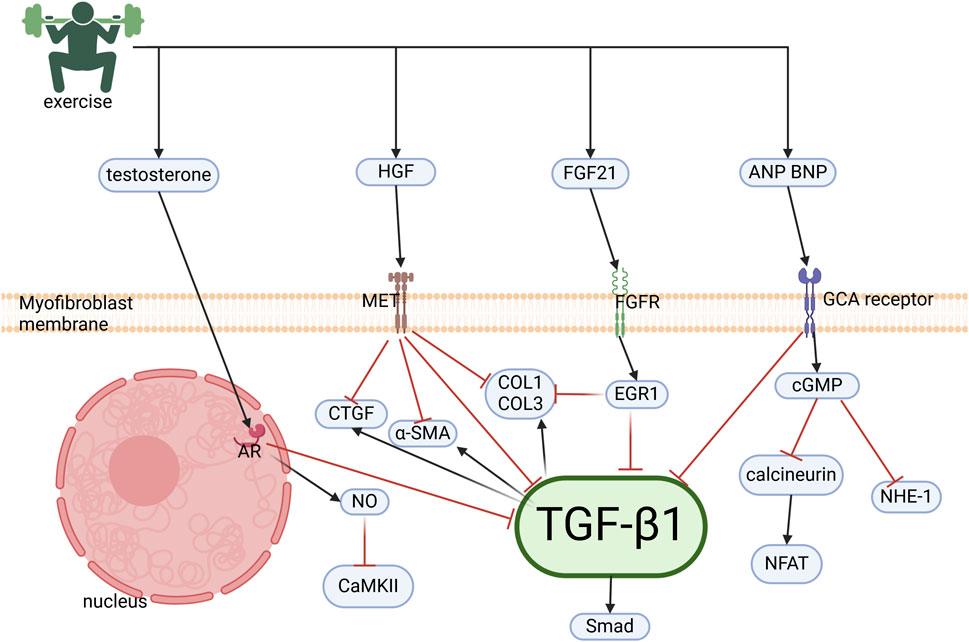
Figure 4. Molecular mechanisms of exercise-induced cardiac anti-fibrotic effects. Exercise induces the cardiac upregulation of testosterone, HGF, FGF21, ANP, and BNP, which collectively suppress fibrogenesis via inhibition of the TGFβ1/Smad pathway in cardiac fibroblasts. Testosterone attenuates collagen synthesis through two mechanisms: (1) Suppression of TGFβ1/Smad signaling and (2) NO-mediated inhibition of Ca2+/CaMKII. HGF antagonizes downstream effectors of TGFβ1, including CTGF, preventing ECM deposition. FGF21 upregulates EGR1, which represses collagen and TGF-β1 expression. ANP/BNP signaling through GCA receptors inhibits calcineurin/NFAT, NHE-1, and TGFβ1/Smad cascades, establishing a multi-targeted anti-fibrotic regulatory network.HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; FGF21, fibroblast growth factor 21; ANP, atrial natriuretic peptide; BNP, B-type natriuretic peptide; TGFβ1,Transforming growth factor-β1; NO, nitric oxide; CaMKII, calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II; CTGF, connective tissue growth factor; ECM, extracellular matrix; EGR1, early growth response protein 1; GCA, guanylyl cyclase-A; NHE-1, sodium-hydrogen exchanger 1
5.1 Testosterone
Transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), a master regulator of fibrogenesis, drives myofibroblast differentiation, extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition (e.g., collagen I/III and fibronectin), and pro-fibrotic gene activation (e.g., α-smooth muscle actin [α-SMA] and connective tissue growth factor [CTGF]) (Fan and Kassiri, 2021). Exercise-induced testosterone elevation counteracts these processes via a dual mechanism. First, testosterone attenuates TGF-β1-mediated phosphorylation of the Akt/mTOR/4EBP1 axis in cardiac fibroblasts, thereby suppressing proliferation, ECM synthesis, and myofibroblast transdifferentiation (Chung et al., 2014). Second, androgenic signaling increases NO production through eNOS activation. NO exerts anti-fibrotic effects by inhibiting Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II, which promotes collagen synthesis via histone deacetylase 4 nuclear translocation (Chung et al., 2021). In fact, preclinical studies reported that rodents with impaired NO synthesis (e.g., eNOS knockout mice) exhibited exacerbated pathological remodeling following exercise, highlighting NO’s critical role in maintaining fibrotic homeostasis (Souza et al., 2007).
5.2 HGF
HGF, upregulated by chronic aerobic exercise, exerts anti-fibrotic effects through multiple molecular pathways mediated by its tyrosine kinase receptor c-MET. First, HGF directly suppresses the transcription of TGF-β1 in cardiac fibroblasts, thereby reducing the bioavailability of TGF-β1 and limiting pro-fibrotic signaling (Nakamura et al., 2005). Second, HGF activates the ERK1/2/MAPK signaling cascade, which induces the expression of decorin, a small leucine-rich proteoglycan that binds and sequesters TGF-β1 within the ECM. This spatial neutralization prevents TGF-β1 from engaging its receptor, effectively blunting the downstream Smad2/3 phosphorylation and subsequent fibrotic gene activation (Kobayashi et al., 2003). Finally, HGF attenuates fibrosis by downregulating key markers of myofibroblast activation, including CTGF, a downstream effector of TGF-β1, and α-SMA, a hallmark of fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transition (Gallo et al., 2015). Collectively, these mechanisms underscore HGF’s pivotal role in mitigating ECM remodeling and preserving myocardial compliance under pathological stress.
5.3 FGF21
FGF21, a secretory protein, has pleiotropic cardioprotective effects, including preserving myocardial tissue, regulating metabolic homeostasis, suppressing fibrosis, and preventing atrial remodeling (Zhao et al., 2023). Aerobic or endurance exercise significantly elevates circulating FGF21 levels (Bo et al., 2021), which may contribute to the modulation of energy metabolism and ultimately to post-exercise recovery. In young females, serum FGF21 concentrations are significantly elevated following a 2-week exercise regimen (Cuevas-Ramos et al., 2012). Mechanistically, FGF21 activates fibroblast growth factor receptors on cell surfaces to induce early growth response protein 1 expression while suppressing fibrotic mediators, including collagen type I, collagen type III, and TGF-β1 (Li et al., 2021). Furthermore, FGF21 modulates TGF-β1/Smad2/3 and NF-κB signaling pathways, downregulating MMP activity to suppress fibrotic remodeling and scar formation (Ma et al., 2021; Pan et al., 2017). Notably, genetic ablation of FGF21 was shown to abolish the inhibitory effects of aerobic exercise on oxidative stress, ER stress, and apoptosis in myocardial infarction models (Bo et al., 2021).
5.4 Natriuretic peptides
Although excessive exercise may induce pressure overload and pathological hypertrophy (Zhou et al., 2020), atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) and B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP), both established biomarkers of pathological hypertrophy, also play critical roles in blood pressure regulation and fluid-electrolyte homeostasis. Their plasma concentrations increase proportionally to the cardiac output during exercise-induced stress (Yoshiga et al., 2019; Wisén et al., 2011). Importantly, by binding to renal and vascular receptors, these peptides promote natriuresis, diuresis, and vasodilation (Baris Feldman et al., 2023). Within the myocardium, ANP and BNP primarily act through guanylyl cyclase-A receptors to inhibit calcineurin/NFAT, NHE-1, and TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathways (Calvieri et al., 2012), thereby reducing fibroblast proliferation, suppressing inflammatory infiltration, and preventing pathological hypertrophy (Bie, 2018; Kapoun et al., 2004).
The anti-fibrotic effects of exercise are intricately linked to a biphasic dose-response relationship, where the intensity and duration of physical activity play pivotal roles in determining its therapeutic outcomes. At moderate levels, exercise exerts potent anti-fibrotic actions by orchestrating a sophisticated hormonal and growth factor-mediated response (Hong et al., 2022). The delicate balance between exercise’s therapeutic benefits and potential risks becomes apparent at excessive intensities. Overexertion may paradoxically induce pressure overload and pathological hypertrophy, potentially exacerbating ischemia-induced fibrosis (Zhou et al., 2020). This underscores the importance of tailoring exercise regimens to individual patient needs, particularly for those with fibrotic cardiomyopathy. Implementing progressive, low-intensity exercise protocols enables the maximization of therapeutic benefits while minimizing the risk of iatrogenic harm. Such an approach ensures that the anti-fibrotic effects of exercise are harnessed effectively, promoting myocardial compliance and reducing ECM accumulation, without triggering adverse pathological responses (Wright et al., 2014). Ultimately, the judicious prescription of exercise, based on a nuanced understanding of its biphasic dose-response relationship, holds promise as a valuable adjunct therapy in managing cardiac fibrosis.
6 Multi-dimensional integration of exercise-induced signaling networks in physiological cardiac hypertrophy
Exercise impacts the heart across four dimensions: molecular, cellular, systemic, and temporal (Figure 5). During the acute phase of exercise, the sympatho-adrenal axis is activated, triggering catecholamine release. Catecholamines inhibit thyroxine deiodination, thereby reducing the conversion of T4 to T3 during high-intensity exercise (Kobayashi et al., 1966; Nauman et al., 1980). Simultaneously, they stimulate insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1) secretion, consequently decreasing free IGF-1 release and promoting blood glucose elevation (Fernqvist-Forbes et al., 1997). Beyond increased cardiac mechanical stress releasing ANP during exercise, epinephrine can directly induce cardiomyocyte secretion of ANP variants (Sejersen et al., 2022; Huang et al., 1992). Furthermore, catecholamines have been shown to modulate VEGF and IL-6 to enhance angiogenesis (Chakroborty et al., 2009). The early (acute phase) catecholamine (NE) surge activates cardiomyocyte β3-AR, promoting mitochondrial workload, and activates PGC-1α via eNOS/NO signaling, augmenting mitochondrial adaptation during the adaptive phase (Yoshida et al., 2023). These adaptations meet the demands for substrate transport and energy metabolism during exercise. In the adaptive phase following exercise, concentrations of hormones, including T3, IGF-1, NRG1, testosterone, FGF21, and APN increase. IGF-1 has been demonstrated to activate VEGF expression in the heart (Li et al., 2017; Puddu et al., 2021). IGF-1 and NRG1 synergistically regulate cardiac development: IGF-1 is suitable for early expansion of cardiomyocyte numbers, while NRG1 promotes metabolic maturation and electromechanical integration in later stages (Rupe et al., 2017). FGF21 enhances APN production, which subsequently acts on cardiomyocytes to promote mitochondrial bioenergetics. APN partially mediates the protective effects of FGF21 against diastolic dysfunction and cardiac injury induced by HF with reduced ejection fraction in mice (Zhang et al., 2025). VEGF potently drives endothelial cell proliferation and migration, initiating new vessel sprouting and extension. HGF is a potent pro-migratory, pro-morphogenic, and pro-angiogenic maturation factor with significant barrier-stabilizing effects. Both VEGF and HGF respond to stimuli and cooperate to promote angiogenesis (Sulpice et al., 2009; Yang et al., 2015). The interplay among the locomotor, circulatory, and endocrine systems; signal transmission and crosstalk among hormones and growth factors; interactions among cardiomyocytes, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts; and the heart’s responses during both the acute and adaptive phases of exercise collectively drive physiological cardiac adaptation across these dimensions.
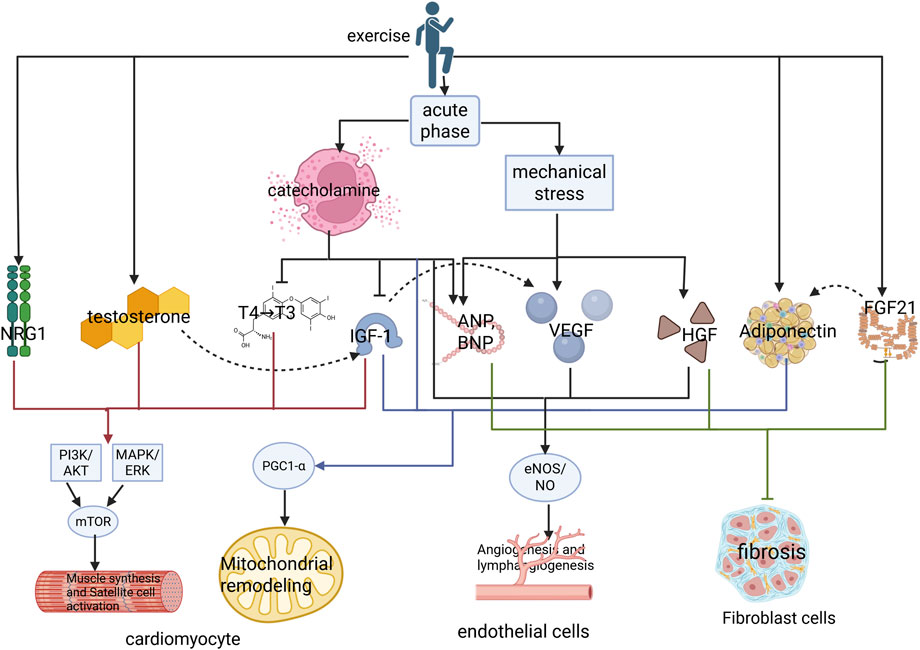
Figure 5. Multidimensional mechanism of exercise induced physiological hypertrophy of the heart. Exercise first promotes the secretion of catecholamines and increases the mechanical stress of the heart through the sympathetic adrenal medullary axis during the acute phase. Catecholamines inhibit the conversion of thyroid hormone T4 to T3 and suppress free IGF-1 by increasing the concentration of IGFBP1. Simultaneously, catecholamines act together with increased mechanical stress to promote the secretion of natriuretic peptides. Catecholamines can also increase mitochondrial energy metabolism and vascular proliferation in the acute phase. During the adaptation period of exercise, the concentration of catecholamines decreases, while concentrations of NRG1, T3, testosterone, IGF-1, VEGF, and FGF21 begin to increase, and FGF21 targets the regulation of adiponectin secretion. IGF-1 may stimulate an increase in VEGF. Finally, NRG1, T3, testosterone, and IGF-1 synergistically activate the PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK signaling pathways in cardiomyocytes, which synergistically activate mTOR signaling to promote the synthesis of myocardial fibers and activation of satellite cells. IGF-1 synergistically activates PGC1- α with adiponectin, increasing mitochondrial biogenesis. HGF and VEGF synergistically activate eNOS/NO signaling to promote angiogenesis. HGF, elevated concentrations of testosterone, natriuretic peptide, and FGF21 can inhibit the transformation of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts, protecting the heart from pathological remodeling. IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor-1; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; AKT, protein kinase B; ERKs, extracellular signal-regulated kinases; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; NRG1, neuregulin-1; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; NO, nitric oxide; PGC-1α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1α; FGF21, fibroblast growth factor 21.
Notably, different exercise modalities and intensities may elicit distinct hormonal responses across diverse populations (Table 1). The dose-response relationship between exercise and cardiac health exhibits a “J-shaped curve”: moderate exercise intensity induces physiological cardiac hypertrophy by activating protective molecular pathways, thereby enhancing cardiac function and metabolic adaptability. However, excessive exercise exceeding an individual’s tolerance threshold triggers pressure overload, leading to aberrant elevations in ANP/BNP, activation of the calcineurin pathway, and mitochondrial dysfunction, consequently promoting pathological remodeling and fibrosis (Carraro and Franceschi, 1997; Bernardo et al., 2010). Optimizing intensity and protocols requires the integration of population baseline status, dynamic biomarkers, and individualized progression principles to achieve a precise balance between cardioprotection and risk mitigation. Due to variations among populations and influences from factors. Including sex, genetics, and environment, no study has identified a universal exercise intensity threshold distinguishing physiological from pathological hypertrophy. Nevertheless, based on the data presented in Table 1, we can tentatively estimate that the approximate aerobic exercise intensity risk threshold for healthy adults lies approximately 80%–85% VO2max, while the resistance training intensity risk threshold is approximately 85% 1RM. Obese populations may exhibit more pronounced acute responses. Supporting this, zebrafish exercised at 80% of maximal critical swimming speed (Ucrit) for 4 weeks developed pathological cardiac hypertrophy (Zhou et al., 2020). Sixteen weeks of high-intensity endurance training (60 cm/s, 60 min/day) resulted in diastolic dysfunction and increased fibrosis in rats (Benito et al., 2011).
Sex and disease-related disparities in exercise-induced hormonal responses significantly influence myocardial adaptation. In males, resistance training (e.g., 75%–80% 1RM) more readily elevates testosterone and IGF-1 levels, promoting cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and suppressing myocardial apoptosis by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway. Conversely, females exhibit greater sensitivity to endurance training-induced increases in FGF21. Under disease states, obesity/diabetes attenuates catecholamine and FGF21 responsiveness; however, endurance training can still improve myocardial mitochondrial function via the IGF-1 pathway. In patients with heart failure (HF) patients, post-exercise elevations in ANP/BNP following high-intensity exercise may exacerbate cardiac loading. Conversely, post-myocardial infarction exercise promotes angiogenesis via IGF-1/VEGF signaling. Notably, individuals with sarcopenic obesity require higher-intensity resistance training to elevate IGF-1 levels.
7 Conclusion and prospect
This study reviews the molecular mechanisms by which exercise induces physiological cardiac hypertrophy, underscoring the central role of the multi-dimensional regulation of hormonal and growth factor networks in cardiovascular protection. Future studies should develop dynamic biomarker panels to personalize exercise dosing in HF, leveraging the biphasic responses of exercise-induced mediators revealed in this review. A stratified framework monitoring safety thresholds (e.g., ANP/BNP and troponin for pressure overload and injury, respectively) and efficacy signals (e.g., VEGF-C/HGF for angiogenesis; FGF21/APN for mitochondrial adaptation, lipid metabolism, and insulin sensitivity; and TGF-β1 suppression for anti-fibrosis) can guide intensity titration. Integrating wearable hemodynamic sensors with serial biomarker profiling (pre-/post-exercise) could enable adaptive algorithms—such as moderate continuous training for patients with HF with reduced ejection fraction who exhibit IGF-1 resistance versus carefully dosed high-intensity interval training for those with obesity who have HF with preserved ejection fraction when APN/FGF21 ratios indicate metabolic responsiveness—thereby balancing cardioprotection while minimizing pathological strain. Multicenter trials validating these panels are essential to translate mechanistic insights into precision exercise prescriptions for HF subpopulations.
Furthermore, circulating biomarker levels may predict athletic ability in patients with HF. As demonstrated in preclinical models, baseline NRG1 deficiency correlates with impaired cardiac repair capacity, while exercise-induced NRG1 elevation (>40% from baseline) enhances ErbB4-mediated cardiomyocyte proliferation and metabolic maturation—key mechanisms for functional recovery. Clinical validation should determine whether pre-intervention NRG1 thresholds can identify patients most likely to benefit from moderate-intensity endurance protocols, particularly those with ischemic cardiomyopathy, where NRG1/ErbB signaling is essential for angiogenesis and fibrosis regression.
The genetic polymorphisms of some important receptors cannot be ignored due to their impact on exercise outcomes and cardiovascular responses. The IGF1R rs1464430 polymorphism exhibits associations with exercise type: the AA genotype appears more favorable for endurance-oriented sports, while the C allele is a distinguishing feature among strength/power athletes (Ben-Zaken et al., 2015). The β2-AR Gln27Glu polymorphism significantly influences the therapeutic response to carvedilol in patients with chronic HF, with Glu27 homozygotes exhibiting significantly greater improvements in systolic/diastolic function and exercise hemodynamics (Metra et al., 2010). β2-AR Arg16Gly homozygosity is associated with enhanced muscle mass and strength gains in athletes (Jenkins et al., 2018). Furthermore, the VEGFR2 His472Gln polymorphism enhances aerobic endurance by increasing VO2max and the proportion of slow-twitch fibers (Ahmetov et al., 2009).
Beyond the mediators discussed above, emerging research highlights novel regulators involved in exercise-induced cardiac adaptation. Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 protects the heart against oxidative stress during exercise, attenuating pressure overload-induced pathological cardiac hypertrophy and dysfunction (Ni et al., 2025). MicroRNA-223-3p and Myostatin have been identified as novel biomarkers indicative of acute exercise and training-induced cardiac adaptation (Fernandez-Vivero et al., 2025; Heineke et al., 2010; Lenk et al., 2012). Irisin mediates multiple cardioprotective effects of exercise, including cardiac angiogenesis, anti-inflammation, energy metabolism optimization, and mitophagy (Guo et al., 2024). Furthermore, IL-6 plays a functional role in mediating exercise-induced improvements in cardiac contractile function (Jønck et al., 2024). These newly identified mediators warrant focused investigation in future research to refine our understanding of the molecular mechanisms underpinning cardiac adaptation to exercise.
Author contributions
SH: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization. ZC: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. HL: Writing – original draft, Visualization. LZ: Writing – original draft, Funding acquisition, Resources. ZZ: Writing – review and editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition. XP: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. CT: Writing – review and editing, Funding acquisition, Resources.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 81801392, 32100919, and 32371182), and the National Students’ Platform for Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program (grant number S202410542008).
Acknowledgments
We thank the Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of physical fitness and exercise rehabilitation for providing core facilities.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
CVDs, cardiovascular diseases; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor-1; IGF1R, insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor; IRS1, insulin receptor substrates 1; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; Akt, protein kinase B; ERKs, extracellular signal-regulated kinases; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; NRG1, neuregulin-1; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; PlGF, placental growth factor; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; NO, nitric oxide; LEC, lymphatic endothelial cell; MMPs, matrix metalloproteinases; β3-AR, β3-adrenergic receptor; PGC-1α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1α; PPARs, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α; ERRs, estrogen-related receptor; APN, adiponectin; HDAC, histone deacetylase; FGF21, fibroblast growth factor 21; TGF-β1, transforming growth factor-β1; ECM, extracellular matrix; α-SMA, α-smooth muscle actin; CTGF, connective tissue growth factor; ANP, atrial natriuretic peptide; BNP, B-type natriuretic peptide; HF, heart failure.
References
Abel E. D., Doenst T. (2011). Mitochondrial adaptations to physiological vs. pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Cardiovasc. Res. 90 (2), 234–242. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvr015
Abounader R., Laterra J. (2005). Scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor in brain tumor growth and angiogenesis. Neuro-oncology 7 (4), 436–451. doi:10.1215/S1152851705000050
Ahmetov I. I., Hakimullina A. M., Popov D. V., Lyubaeva E. V., Missina S. S., Vinogradova O. L., et al. (2009). Association of the VEGFR2 gene His472Gln polymorphism with endurance-related phenotypes. Eur. J. Appl. Physiology 107 (1), 95–103. doi:10.1007/s00421-009-1105-7
Altamirano F., Oyarce C., Silva P., Toyos M., Wilson C., Lavandero S., et al. (2009). Testosterone induces cardiomyocyte hypertrophy through mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 pathway. J. Endocrinol. 202 (2), 299–307. doi:10.1677/JOE-09-0044
Arechederra M., Carmona R., González-Nuñez M., Gutiérrez-Uzquiza A., Bragado P., Cruz-González I., et al. (2013). Met signaling in cardiomyocytes is required for normal cardiac function in adult mice. Biochimica Biophysica Acta 1832 (12), 2204–2215. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.08.008
Baris Feldman H., Chai Gadot C., Zahler D., Mory A., Aviram G., Elhanan E., et al. (2023). Corin and left atrial cardiomyopathy, hypertension, arrhythmia, and fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 389 (18), 1685–1692. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2301908
Bei Y., Huang Z., Feng X., Li L., Wei M., Zhu Y., et al. (2022). Lymphangiogenesis contributes to exercise-induced physiological cardiac growth. J. Sport Health Sci. 11 (4), 466–478. doi:10.1016/j.jshs.2022.02.005
Ben-Zaken S., Meckel Y., Nemet D., Eliakim A. (2015). IGF-I receptor 275124A>C (rs1464430) polymorphism and athletic performance. J. Sci. Med. sport 18 (3), 323–327. doi:10.1016/j.jsams.2014.03.007
Benito B., Gay-Jordi G., Serrano-Mollar A., Guasch E., Shi Y., Tardif J. C., et al. (2011). Cardiac arrhythmogenic remodeling in a rat model of long-term intensive exercise training. Circulation 123 (1), 13–22. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.938282
Bentzen H., Pedersen R. S., Nyvad O., Pedersen E. B. (2004). Effect of exercise on natriuretic peptides in plasma and urine in chronic heart failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 93 (2-3), 121–130. doi:10.1016/S0167-5273(03)00156-6
Bernardo B. C., Weeks K. L., Pretorius L., McMullen J. R. (2010). Molecular distinction between physiological and pathological cardiac hypertrophy: experimental findings and therapeutic strategies. Pharmacol. and Ther. 128 (1), 191–227. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2010.04.005
Bernardo B. C., Ooi J. Y. Y., Weeks K. L., Patterson N. L., McMullen J. R. (2018). Understanding key mechanisms of exercise-induced cardiac protection to mitigate disease: current knowledge and emerging concepts. Physiol. Rev. 98 (1), 419–475. doi:10.1152/physrev.00043.2016
Bianchi V. E. (2018). Testosterone, myocardial function, and mortality. Heart Fail. Rev. 23 (5), 773–788. doi:10.1007/s10741-018-9721-0
Bie P. (2018). Natriuretic peptides and normal body fluid regulation. Compr. Physiol. 8 (3), 1211–1249. doi:10.1002/cphy.c180002
Binder E. F., Bartley J. M., Berry S. D., Doré P. M., Fisher S. R., Fortinsky R. H., et al. (2025). Combining exercise training and testosterone therapy in older women after hip fracture: the STEP-HI randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw. open 8 (5), e2510512. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.10512
Bloom S. R., Johnson R. H., Park D. M., Rennie M. J., Sulaiman W. R. (1976). Differences in the metabolic and hormonal response to exercise between racing cyclists and untrained individuals. J. Physiology 258 (1), 1–18. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011403
Bo W., Ma Y., Xi Y., Liang Q., Cai M., Tian Z. (2021). The roles of FGF21 and ALCAT1 in aerobic exercise-induced cardioprotection of postmyocardial infarction mice. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 8996482. doi:10.1155/2021/8996482
Bo W., Ma Y., Feng L., Yu M., Zhang L., Cai M., et al. (2023). FGF21 promotes myocardial angiogenesis and mediates the cardioprotective effects of exercise in myocardial infarction mice. J. Appl. Physiology Bethesda, Md. 135 (3), 696–705. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00307.2023
Bonsignore M. R., Morici G., Riccioni R., Huertas A., Petrucci E., Veca M., et al. (1985). Hemopoietic and angiogenetic progenitors in healthy athletes: different responses to endurance and maximal exercise. J. Appl. Physiology Bethesda, Md. 109 (1), 60–67. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.01344.2009
Bracken R. M., Linnane D. M., Brooks S. (2005). Alkalosis and the plasma catecholamine response to high-intensity exercise in man. Med. Sci. sports Exerc. 37 (2), 227–233. doi:10.1249/01.mss.0000152704.34531.b6
Bussolino F., Di Renzo M. F., Ziche M., Bocchietto E., Olivero M., Naldini L., et al. (1992). Hepatocyte growth factor is a potent angiogenic factor which stimulates endothelial cell motility and growth. J. Cell Biol. 119 (3), 629–641. doi:10.1083/jcb.119.3.629
Cai M. X., Shi X. C., Chen T., Tan Z. N., Lin Q. Q., Du S. J., et al. (2016). Exercise training activates neuregulin 1/ErbB signaling and promotes cardiac repair in a rat myocardial infarction model. Life Sci. 149, 1–9. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2016.02.055
Calvert J. W., Condit M. E., Aragón J. P., Nicholson C. K., Moody B. F., Hood R. L., et al. (2011). Exercise protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via stimulation of β(3)-adrenergic receptors and increased nitric oxide signaling: role of nitrite and nitrosothiols. Circulation Res. 108 (12), 1448–1458. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.241117
Calvieri C., Rubattu S., Volpe M. (2012). Molecular mechanisms underlying cardiac antihypertrophic and antifibrotic effects of natriuretic peptides. J. Mol. Med. Berlin, Ger. 90 (1), 5–13. doi:10.1007/s00109-011-0801-z
Campos J. C., Queliconi B. B., Bozi L. H. M., Bechara L. R. G., Dourado P. M. M., Andres A. M., et al. (2017). Exercise reestablishes autophagic flux and mitochondrial quality control in heart failure. Autophagy 13 (8), 1304–1317. doi:10.1080/15548627.2017.1325062
Capuano A., Pivetta E., Sartori G., Bosisio G., Favero A., Cover E., et al. (2019). Abrogation of EMILIN1-β1 integrin interaction promotes experimental colitis and colon carcinogenesis. J. Int. Soc. Matrix Biol. 83, 97–115. doi:10.1016/j.matbio.2019.08.006
Carraro U., Franceschi C. (1997). Apoptosis of skeletal and cardiac muscles and physical exercise. Aging (Milan, Italy) 9 (1-2), 19–34. doi:10.1007/BF03340125
Chakroborty D., Sarkar C., Basu B., Dasgupta P. S., Basu S. (2009). Catecholamines regulate tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 69 (9), 3727–3730. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4289
Chattergoon N. N., Louey S., Stork P. J., Giraud G. D., Thornburg K. L. (2014). Unexpected maturation of PI3K and MAPK-ERK signaling in fetal ovine cardiomyocytes. Am. J. physiology. Heart Circulatory Physiology 307 (8), H1216–H1225. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00833.2013
Chen H. T., Chung Y. C., Chen Y. J., Ho S. Y., Wu H. J. (2017). Effects of different types of exercise on body composition, muscle strength, and IGF-1 in the elderly with sarcopenic obesity. J. Am. Geriatrics Soc. 65 (4), 827–832. doi:10.1111/jgs.14722
Chen Z., Zhou Z., Peng X., Sun C., Yang D., Li C., et al. (2021). Cardioprotective responses to aerobic exercise-induced physiological hypertrophy in zebrafish heart. J. Physiological Sci. JPS 71 (1), 33. doi:10.1186/s12576-021-00818-w
Cheng S. M., Ho T. J., Yang A. L., Chen I. J., Kao C. L., Wu F. N., et al. (2013). Exercise training enhances cardiac IGFI-R/PI3K/Akt and Bcl-2 family associated pro-survival pathways in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Int. J. Cardiol. 167 (2), 478–485. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2012.01.031
Chung C. C., Hsu R. C., Kao Y. H., Liou J. P., Lu Y. Y., Chen Y. J. (2014). Androgen attenuates cardiac fibroblasts activations through modulations of transforming growth factor-β and angiotensin II signaling. Int. J. Cardiol. 176 (2), 386–393. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.07.077
Chung C. C., Lin Y. K., Kao Y. H., Lin S. H., Chen Y. J. (2021). Physiological testosterone attenuates profibrotic activities of rat cardiac fibroblasts through modulation of nitric oxide and calcium homeostasis. Endocr. J. 68 (3), 307–315. doi:10.1507/endocrj.EJ20-0344
Ciloglu F., Peker I., Pehlivan A., Karacabey K., Ilhan N., Saygin O., et al. (2005). Exercise intensity and its effects on thyroid hormones. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 26 (6), 830–834. doi:10.1038/ncpendmet0047
Cuevas-Ramos D., Almeda-Valdés P., Meza-Arana C. E., Brito-Córdova G., Gómez-Pérez F. J., Mehta R., et al. (2012). Exercise increases serum fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) levels. PloS one 7 (5), e38022. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0038022
D'Andrea S., Spaggiari G., Barbonetti A., Santi D. (2020). Endogenous transient doping: physical exercise acutely increases testosterone levels-results from a meta-analysis. J. Endocrinol. Investigation 43 (10), 1349–1371. doi:10.1007/s40618-020-01251-3
Deligiannis A., Karamouzis M., Kouidi E., Mougios V., Kallaras C., Plasma T. S. H. (1993). Plasma TSH, T3, T4 and cortisol responses to swimming at varying water temperatures. Br. J. sports Med. 27 (4), 247–250. doi:10.1136/bjsm.27.4.247
Dimmeler S., Fleming I., Fisslthaler B., Hermann C., Busse R., Zeiher A. M. (1999). Activation of nitric oxide synthase in endothelial cells by Akt-dependent phosphorylation. Nature 399 (6736), 601–605. doi:10.1038/21224
Falls D. L. (2003). Neuregulins: functions, forms, and signaling strategies. Exp. cell Res. 284 (1), 14–30. doi:10.1016/s0014-4827(02)00102-7
Fan D., Kassiri Z. (2021). Modulation of cardiac fibrosis in and beyond cells. Front. Mol. Biosci. 8, 750626. doi:10.3389/fmolb.2021.750626
Feng L., Li B., Xi Y., Cai M., Tian Z. (2022). Aerobic exercise and resistance exercise alleviate skeletal muscle atrophy through IGF-1/IGF-1R-PI3K/Akt pathway in mice with myocardial infarction. Am. J. Physiology. Cell Physiology 322 (2), C164–c176. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00344.2021
Fernandez-Vivero D., Terrados N., Pinto-Hernandez P., Noguero-Lopez C., Fernandez-Garcia B., Whitham M., et al. (2025). A multiscale in silico analysis identifies plasma levels of miR-223-3p as an emerging biomarker of cardiac response to acute exercise and training in olympic medallists. Scand. J. Med. and Sci. sports 35 (6), e70092. doi:10.1111/sms.70092
Fernqvist-Forbes E., Hilding A., Ekberg K., Brismar K. (1997). Influence of circulating epinephrine and norepinephrine on insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metabolism 82 (8), 2677–2680. doi:10.1210/jcem.82.8.4167
Ferrara N., Gerber H. P., LeCouter J. (2003). The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat. Med. 9 (6), 669–676. doi:10.1038/nm0603-669
Finck B. N., Kelly D. P. (2006). PGC-1 coactivators: inducible regulators of energy metabolism in health and disease. J. Clin. Investigation 116 (3), 615–622. doi:10.1172/JCI27794
Fiorenza M., Checa A., Sandsdal R. M., Jensen S. B. K., Juhl C. R., Noer M. H., et al. (2024). Weight-loss maintenance is accompanied by interconnected alterations in circulating FGF21-adiponectin-leptin and bioactive sphingolipids. Medicine 5 (7), 101629. doi:10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101629
Friehs I., Stamm C., Cao-Danh H., McGowan F. X., del Nido P. J. (2001). Insulin-like growth factor-1 improves postischemic recovery in hypertrophied hearts. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 72 (5), 1650–1656. doi:10.1016/s0003-4975(01)03098-3
Gallo S., Sala V., Gatti S., Crepaldi T. (2014). HGF/Met Axis in heart function and cardioprotection. Biomedicines 2 (4), 247–262. doi:10.3390/biomedicines2040247
Gallo S., Sala V., Gatti S., Crepaldi T. (2015). Cellular and molecular mechanisms of HGF/Met in the cardiovascular system. Clin. Sci. Lond. Engl. 1979 129 (12), 1173–1193. doi:10.1042/CS20150502
Gallo S., Vitacolonna A., Bonzano A., Comoglio P., Crepaldi T. (2019). ERK: a key player in the pathophysiology of cardiac hypertrophy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20 (9), 2164. doi:10.3390/ijms20092164
González-Guerra J. L., Castilla-Cortazar I., Aguirre G. A., Muñoz Ú., Martín-Estal I., Ávila-Gallego E., et al. (2017). Partial IGF-1 deficiency is sufficient to reduce heart contractibility, angiotensin II sensibility, and alter gene expression of structural and functional cardiac proteins. PloS one 12 (8), e0181760. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0181760
Grubb A., Joanisse S., Moore D. R., Bellamy L. M., Mitchell C. J., Phillips S. M., et al. (2014). IGF-1 colocalizes with muscle satellite cells following acute exercise in humans. Appl. physiology, Nutr. metabolism = Physiologie appliquee, Nutr. metabolisme 39 (4), 514–518. doi:10.1139/apnm-2013-0430
Guan Y., Drake J. C., Yan Z. (2019). Exercise-induced mitophagy in skeletal muscle and heart. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 47 (3), 151–156. doi:10.1249/JES.0000000000000192
Guo W., Peng J., Su J., Xia J., Deng W., Li P., et al. (2024). The role and underlying mechanisms of irisin in exercise-mediated cardiovascular protection. PeerJ 12, e18413. doi:10.7717/peerj.18413
Gustafsson T., Ameln H., Fischer H., Sundberg C. J., Timmons J. A., Jansson E. (2005). VEGF-A splice variants and related receptor expression in human skeletal muscle following submaximal exercise. J. Appl. physiology Bethesda, Md. 98 (6), 2137–2146. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.01402.2004
Hackney A. C., Saeidi A. (2019). The thyroid axis, prolactin, and exercise in humans. Curr. Opin. Endocr. metabolic Res. 9, 45–50. doi:10.1016/j.coemr.2019.06.012
Hackney A. C., Kallman A., Hosick K. P., Rubin D. A., Battaglini C. L. (2012). Thyroid hormonal responses to intensive interval versus steady-state endurance exercise sessions. Horm. (Athens, Greece) 11 (1), 54–60. doi:10.1007/BF03401537
Hamilton B., Tol J. L., Knez W., Chalabi H. (2015). Exercise and the platelet activator calcium chloride both influence the growth factor content of platelet-rich plasma (PRP): overlooked biochemical factors that could influence PRP treatment. Br. J. sports Med. 49 (14), 957–960. doi:10.1136/bjsports-2012-091916
Hansen D., Meeusen R., Mullens A., Dendale P. (2012). Effect of acute endurance and resistance exercise on endocrine hormones directly related to lipolysis and skeletal muscle protein synthesis in adult individuals with obesity. Sports Med. Auckl. N.Z. 42 (5), 415–431. doi:10.2165/11599590-000000000-00000
Hansen J. S., Pedersen B. K., Xu G., Lehmann R., Weigert C., Plomgaard P. (2016). Exercise-induced secretion of FGF21 and follistatin are blocked by pancreatic Clamp and impaired in type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metabolism 101 (7), 2816–2825. doi:10.1210/jc.2016-1681
Hastings M. H., Castro C., Freeman R., Abdul Kadir A., Lerchenmüller C., Li H., et al. (2024). Intrinsic and extrinsic contributors to the cardiac benefits of exercise. Basic Transl. Sci. 9 (4), 535–552. doi:10.1016/j.jacbts.2023.07.011
Hatakeyama J., Inoue S., Jiang H., Yokoi R., Moriyama H. (2025). Exercise-induced interactions between skeletal muscle and bone via myokines and osteokine in mice: role of FNDC5/irisin, IGF-1, and osteocalcin. Bone 190, 117314. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2024.117314
Hayes L. D., Grace F. M., Baker J. S., Sculthorpe N. (2015). Exercise-induced responses in salivary testosterone, cortisol, and their ratios in men: a meta-analysis. Sports Med. Auckl. N.Z. 45 (5), 713–726. doi:10.1007/s40279-015-0306-y
Heineke J., Auger-Messier M., Xu J., Sargent M., York A., Welle S., et al. (2010). Genetic deletion of myostatin from the heart prevents skeletal muscle atrophy in heart failure. Circulation 121 (3), 419–425. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.882068
Henri O., Pouehe C., Houssari M., Galas L., Nicol L., Edwards-Lévy F., et al. (2016). Selective stimulation of cardiac lymphangiogenesis reduces myocardial edema and fibrosis leading to improved cardiac function following myocardial infarction. Circulation 133 (15), 1484–1497. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.020143
Hong Y., Yang A. L., Wong J. K. S., Masodsai K., Lee S. D., Lin Y. Y. (2022). Exercise intervention prevents early aged hypertension-caused cardiac dysfunction through inhibition of cardiac fibrosis. Aging 14 (10), 4390–4401. doi:10.18632/aging.204077
Huang W., Lee D., Yang Z., Copolov D. L., Lim A. T. (1992). Norepinephrine stimulates immunoreactive (ir) atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) secretion and pro-ANP mRNA expression from rat hypothalamic neurons in culture: effects of alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Endocrinology 130 (4), 2426–2428. doi:10.1210/endo.130.4.1312457
Huang W. S., Yu M. D., Lee M. S., Cheng C. Y., Yang S. P., Chin H. M., et al. (2004). Effect of treadmill exercise on circulating thyroid hormone measurements, Medical principles and practice: international journal of the Kuwait University. Health Sci. Centre 13 (1), 15–19. doi:10.1159/000074045
Jänne O. A., Palvimo J. J., Kallio P., Mehto M. (1993). Androgen receptor and mechanism of androgen action. Ann. Med. 25 (1), 83–89. doi:10.3109/07853899309147863
Jayasankar V., Woo Y. J., Pirolli T. J., Bish L. T., Berry M. F., Burdick J., et al. (2005). Induction of angiogenesis and inhibition of apoptosis by hepatocyte growth factor effectively treats postischemic heart failure. J. Cardiac Surg. 20 (1), 93–101. doi:10.1111/j.0886-0440.2005.200373.x
Jenkins N. D. M., Colquhoun R. J., Tomko P. M., Gradnigo T., Magrini M. A., Muddle T. W. D., et al. (2018). Genetic variant in the β(2) -adrenergic receptor (Arg16Gly) influences fat-free mass, muscle strength and motor unit behaviour in young men. Exp. Physiol. 103 (12), 1645–1655. doi:10.1113/EP087145
Jiang Q., Lou K., Hou L., Lu Y., Sun L., Tan S. C., et al. (2020). The effect of resistance training on serum insulin-like growth factor 1(IGF-1): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Complementary Ther. Med. 50, 102360. doi:10.1016/j.ctim.2020.102360
Jin L., Geng L., Ying L., Shu L., Ye K., Yang R., et al. (2022). FGF21-Sirtuin 3 Axis confers the protective effects of exercise against diabetic cardiomyopathy by governing mitochondrial integrity. Circulation 146 (20), 1537–1557. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.122.059631
Jønck S., Løk M., Durrer C., Wedell-Neergaard A. S., Lehrskov L. L., Legaard G. E., et al. (2024). Exercise-induced changes in left ventricular strain are affected by interleukin-6 activity: an exploratory analysis of a randomised-controlled trial in humans with abdominal obesity. Exp. Physiol. 109 (7), 1134–1144. doi:10.1113/EP091800
Kenessey A., Ojamaa K. (2006). Thyroid hormone stimulates protein synthesis in the cardiomyocyte by activating the Akt-mTOR and p70S6K pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 281 (30), 20666–20672. doi:10.1074/jbc.M512671200
Kapoun A. M., Liang F., O'Young G., Damm D. L., Quon D., White R. T., et al. (2004). B-type natriuretic peptide exerts broad functional opposition to transforming growth factor-beta in primary human cardiac fibroblasts: fibrosis, myofibroblast conversion, proliferation, and inflammation. Circulation Res. 94 (4), 453–461. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000117070.86556.9F
Kappas N. C., Zeng G., Chappell J. C., Kearney J. B., Hazarika S., Kallianos K. G., et al. (2008). The VEGF receptor Flt-1 spatially modulates Flk-1 signaling and blood vessel branching. J. cell Biol. 181 (5), 847–858. doi:10.1083/jcb.200709114
Karner-Rezek K., Knechtle B., Fenzl M., Gredig J., Rosemann T. (2013). Does continuous endurance exercise in water elicit a higher release of ANP and BNP and a higher plasma concentration of FFAs in pre-obese and obese men than high intensity intermittent endurance exercise? - study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 14, 328. doi:10.1186/1745-6215-14-328
Kemi O. J., Haram P. M., Loennechen J. P., Osnes J. B., Skomedal T., Wisløff U., et al. (2005). Moderate vs. high exercise intensity: differential effects on aerobic fitness, cardiomyocyte contractility, and endothelial function. Cardiovasc. Res. 67 (1), 161–172. doi:10.1016/j.cardiores.2005.03.010
Khalafi M., Symonds M. E. (2020). The impact of high-intensity interval training on inflammatory markers in metabolic disorders: a meta-analysis. Scand. J. Med. and Sci. sports 30 (11), 2020–2036. doi:10.1111/sms.13754
Khalafi M., Hossein Sakhaei M., Kheradmand S., Symonds M. E., Rosenkranz S. K. (2023). The impact of exercise and dietary interventions on circulating leptin and adiponectin in individuals who are overweight and those with obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Adv. Nutr. (Bethesda, Md.) 14 (1), 128–146. doi:10.1016/j.advnut.2022.10.001
Kim K. H., Kim S. H., Min Y. K., Yang H. M., Lee J. B., Lee M. S. (2013). Acute exercise induces FGF21 expression in mice and in healthy humans. PloS one 8 (5), e63517. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0063517
Kivelä R., Hemanthakumar K. A., Vaparanta K., Robciuc M., Izumiya Y., Kidoya H., et al. (2019). Endothelial cells regulate physiological cardiomyocyte growth via VEGFR2-mediated paracrine signaling. Circulation 139 (22), 2570–2584. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.036099
Kobayashi I., Yamlada T., Shichijo K. (1966). Effects of epinephrine and chemically related compounds on enzymatic deiodination of thyroxine, triiodothyronine, monoiodotyrosine and diiodotyrosine in vitro. Metabolism Clin. Exp. 15 (8), 694–706. doi:10.1016/s0026-0495(66)80005-7
Kobayashi E., Sasamura H., Mifune M., Shimizu-Hirota R., Kuroda M., Hayashi M., et al. (2003). Hepatocyte growth factor regulates proteoglycan synthesis in interstitial fibroblasts. Kidney Int. 64 (4), 1179–1188. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00202.x
Kraemer W. J., Marchitelli L., Gordon S. E., Harman E., Dziados J. E., Mello R., et al. (1990). Hormonal and growth factor responses to heavy resistance exercise protocols. J. Appl. Physiology Bethesda, Md 69 (4), 1442–1450. doi:10.1152/jappl.1990.69.4.1442
Kraemer W. J., Ratamess N. A., Nindl B. C. (2017) “Recovery responses of testosterone, growth hormone, and IGF-1 after resistance exercise,”J. Appl. Physiology (3) 122. 549–558. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00599.2016
Kraemer W. J., Ratamess N. A., Hymer W. C., Nindl B. C., Fragala M. S. (2020). Growth hormone(s), testosterone, insulin-like growth factors, and cortisol: roles and integration for cellular development and growth with exercise. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 11, 33. doi:10.3389/fendo.2020.00033
Kruse R., Vienberg S. G., Vind B. F., Andersen B., Højlund K. (2017). Effects of insulin and exercise training on FGF21, its receptors and target genes in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 60 (10), 2042–2051. doi:10.1007/s00125-017-4373-5
Larsen A. I., Helle K. B., Christensen M., Kvaløy J. T., Aarsland T., Dickstein K. (2008). Effect of exercise training on chromogranin A and relationship to N-ANP and inflammatory cytokines in patients with chronic heart failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 127 (1), 117–120. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2007.04.012
Lee S., Park Y., Dellsperger K. C., Zhang C. (2011). Exercise training improves endothelial function via adiponectin-dependent and independent pathways in type 2 diabetic mice. Am. J. physiology. Heart Circulatory Physiology 301 (2), H306–H314. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.01306.2010
Lehman J. J., Barger P. M., Kovacs A., Saffitz J. E., Medeiros D. M., Kelly D. P. (2000). Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1 promotes cardiac mitochondrial biogenesis. J. Clin. Investigation 106 (7), 847–856. doi:10.1172/JCI10268
Lenk K., Erbs S., Höllriegel R., Beck E., Linke A., Gielen S., et al. (2012). Exercise training leads to a reduction of elevated myostatin levels in patients with chronic heart failure. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 19 (3), 404–411. doi:10.1177/1741826711402735
Li Z., Duan W., Cui C., Liu Y., Li C., Liu Y. (2017). AAV9-IGF1 protects TDP-25 cells from apoptosis and oxidative stress partly via up-regulating the expression of VEGF in vitro. Neurosci. Lett. 640, 123–129. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2017.01.009
Li J., Gong L., Zhang R., Li S., Yu H., Liu Y., et al. (2021). Fibroblast growth factor 21 inhibited inflammation and fibrosis after myocardial infarction via EGR1. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 910, 174470. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174470
Li B., Feng L., Wu X., Cai M., Yu J. J., Tian Z. (2022a). Effects of different modes of exercise on skeletal muscle mass and function and IGF-1 signaling during early aging in mice. J. Exp. Biol. 225 (21), jeb244650. doi:10.1242/jeb.244650
Li S., Wang M., Ma J., Pang X., Yuan J., Pan Y., et al. (2022b). MOTS-C and exercise restore cardiac function by activating of NRG1-ErbB signaling in diabetic rats. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 13, 812032. doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.812032
Liewendahl K., Helenius T., Näveri H., Tikkanen H. (1992). Fatty acid-induced increase in serum dialyzable free thyroxine after physical exercise: implication for nonthyroidal illness. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metabolism 74 (6), 1361–1365. doi:10.1210/jcem.74.6.1592881
Lin H., Lian W. S., Chen H. H., Lai P. F., Cheng C. F. (2013). Adiponectin ameliorates iron-overload cardiomyopathy through the PPARα-PGC-1-dependent signaling pathway. Mol. Pharmacol. 84 (2), 275–285. doi:10.1124/mol.112.083964
Lin J., DeLuca J. R., Lu M. T., Ruehm S. G., Dudum R., Choi B., et al. (2017). Extreme endurance exercise and progressive coronary artery disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 70 (2), 293–295. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2017.05.016
Linnamo V., Pakarinen A., Komi P. V., Kraemer W. J., Häkkinen K. (2005). Acute hormonal responses to submaximal and maximal heavy resistance and explosive exercises in men and women. J. Strength Cond. Res. 19 (3), 566–571. doi:10.1519/R-15404.1
Liu X., Oliver G. (2023). The lymphatic vasculature in cardiac development and ischemic heart disease. Circulation Res. 132 (9), 1246–1253. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.321672
Liu C., Yan X., Zong Y., He Y., Yang G., Xiao Y., et al. (2024). The effects of exercise on FGF21 in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PeerJ 12, e17615. doi:10.7717/peerj.17615
Loucks A. B., Callister R. (1993). Induction and prevention of low-T3 syndrome in exercising women. Am. J. Physiology 264 (5 Pt 2), R924–R930. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.1993.264.5.R924
Ma H., Calderon T. M., Fallon J. T., Berman J. W. (2002). Hepatocyte growth factor is a survival factor for endothelial cells and is expressed in human atherosclerotic plaques. Atherosclerosis 164 (1), 79–87. doi:10.1016/s0021-9150(02)00062-x
Ma Y., Kuang Y., Bo W., Liang Q., Zhu W., Cai M., et al. (2021). Exercise training alleviates cardiac fibrosis through increasing fibroblast growth factor 21 and regulating TGF-β1-smad2/3-MMP2/9 signaling in mice with myocardial infarction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (22), 12341. doi:10.3390/ijms222212341
Mandroukas A., Metaxas T. I., Heller J., Vamvakoudis E., Christoulas K., Riganas C. S., et al. (2011). The effect of different exercise-testing protocols on atrial natriuretic peptide. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 31 (1), 5–10. doi:10.1111/j.1475-097X.2010.00971.x
Mazaheri F., Hoseini R., Gharzi A. (2025). Vitamin D and exercise improve VEGF-B production and IGF-1 levels in diabetic rats: insights the role of miR-1 suppression. Sci. Rep. 15 (1), 1328. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-81230-3
McMurray R. G., Eubank T. K., Hackney A. C. (1995). Nocturnal hormonal responses to resistance exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiology Occup. Physiology 72 (1-2), 121–126. doi:10.1007/BF00964126
Mendes P., Martinho R., Leite S., Maia-Moço L., Leite-Moreira A. F., Lourenço A. P., et al. (2018). Chronic exercise induces pathological left ventricular hypertrophy in adrenaline-deficient mice. Int. J. Cardiol. 253, 113–119. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.10.014
Metra M., Covolo L., Pezzali N., Zacà V., Bugatti S., Lombardi C., et al. (2010). Role of beta-adrenergic receptor gene polymorphisms in the long-term effects of beta-blockade with carvedilol in patients with chronic heart failure. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 24 (1), 49–60. doi:10.1007/s10557-010-6220-5
Midttun M., Overgaard K., Zerahn B., Pedersen M., Rashid A., Østergren P. B., et al. (2024). Beneficial effects of exercise, testosterone, vitamin D, calcium and protein in older men-A randomized clinical trial. J. Cachexia, Sarcopenia Muscle 15 (4), 1451–1462. doi:10.1002/jcsm.13498
Morland C., Andersson K. A., Haugen Ø P., Hadzic A., Kleppa L., Gille A., et al. (2017). Exercise induces cerebral VEGF and angiogenesis via the lactate receptor HCAR1. Nat. Commun. 8, 15557. doi:10.1038/ncomms15557
Motiejunaite J., Amar L., Vidal-Petiot E. (2021). Adrenergic receptors and cardiovascular effects of catecholamines. Ann. d'endocrinologie 82 (3-4), 193–197. doi:10.1016/j.ando.2020.03.012
Mullur R., Liu Y. Y., Brent G. A. (2014). Thyroid hormone regulation of metabolism. Physiol. Rev. 94 (2), 355–382. doi:10.1152/physrev.00030.2013
Murray M., Vlietstra L., Best A. M. D., Sims S. T., Loehr J. A., Rehrer N. J. (2025). Post-exercise whey protein supplementation: effects on IGF-1, strength, and body composition in pre-Menopausal women, a randomised controlled trial. Nutrients 17 (12), 2033. doi:10.3390/nu17122033
Naghavi M., Ong K. L., Aali A., Ababneh H. S., Abate Y. H., Abbafati C., et al. (2024). Global burden of 288 causes of death and life expectancy decomposition in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet London, Engl. 403 (10440), 2100–2132. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(24)00367-2
Nakamura T., Matsumoto K., Mizuno S., Sawa Y., Matsuda H., Nakamura T. (2005). Hepatocyte growth factor prevents tissue fibrosis, remodeling, and dysfunction in cardiomyopathic hamster hearts. Am. J. physiology. Heart Circulatory Physiology 288 (5), H2131–H2139. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.01239.2003
Nauman A., Kamiński T., Herbaczyńska-Cedro K. (1980). In vivo and in vitro effects of adrenaline on conversion of thyroxine to triiodothyronine and to reverse-triiodothyronine in dog liver and heart. Eur. J. Clin. Investigation 10 (3), 189–192. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2362.1980.tb00019.x
Neto I. V. S., Pinto A. P., Muñoz V. R., de Cássia Marqueti R., Pauli J. R., Ropelle E. R., et al. (2023). Pleiotropic and multi-systemic actions of physical exercise on PGC-1α signaling during the aging process. Ageing Res. Rev. 87, 101935. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2023.101935
Ni L., Lu B., Peng G., Ma W., Guo Z., Huang L., et al. (2025). Exercise-preconditioning attenuates TAC-induced cardiac hypertrophy and myocardial injury through activating NRF2. Free Radic. Biol. and Med. 239, 80–90. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2025.07.024
Nisoli E., Clementi E., Paolucci C., Cozzi V., Tonello C., Sciorati C., et al. (2003). Mitochondrial biogenesis in mammals: the role of endogenous nitric oxide. Sci. (New York, N.Y.) 299 (5608), 896–899. doi:10.1126/science.1079368
Nisoli E., Falcone S., Tonello C., Cozzi V., Palomba L., Fiorani M., et al. (2004). Mitochondrial biogenesis by NO yields functionally active mitochondria in mammals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101 (47), 16507–16512. doi:10.1073/pnas.0405432101
Norling A. M., Gerstenecker A. T., Buford T. W., Khan B., Oparil S., Lazar R. M. (2020). The role of exercise in the reversal of IGF-1 deficiencies in microvascular rarefaction and hypertension. GeroScience 42 (1), 141–158. doi:10.1007/s11357-019-00139-2
Odiete O., Hill M. F., Sawyer D. B. (2012). Neuregulin in cardiovascular development and disease. Circulation Res. 111 (10), 1376–1385. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.267286
Pan S. S. (2008). Alterations of atrial natriuretic peptide in cardiomyocytes and plasma of rats after different intensity exercise. Scand. J. Med. and Sci. Sports 18 (3), 346–353. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0838.2007.00684.x
Pan Z. C., Wang S. P., Ou T. T., Liu H., Ma J. W., Wang W. X., et al. (2017). A study on the expression of FGF-21 and NF-κB pathway in the tissues of atherosclerotic mice. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 21 (3 Suppl. l), 102–107. Available online at: https://www.europeanreview.org/wp/wp-content/uploads/102-107-Expression-of-FGF-21-and-NF-%CE%BAB-pathway-in-the-tissues-of-atherosclerotic-mice.pdf.
Peyronnel C., Kessler J., Bobillier-Chaumont Devaux S., Houdayer C., Tournier M., Chouk M., et al. (2024). A treadmill exercise reduced cardiac fibrosis, inflammation and vulnerability to ischemia-reperfusion in rat pristane-induced arthritis. Life Sci. 341, 122503. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2024.122503
Puddu A., Sanguineti R., Maggi D. (2021). Caveolin-1 down-regulation reduces VEGF-A secretion induced by IGF-1 in ARPE-19 cells. Life Basel, Switz. 12 (1), 44. doi:10.3390/life12010044
Qiu Y., Pan X., Chen Y., Xiao J. (2022). Hallmarks of exercised heart. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 164, 126–135. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2021.12.004
Ren J., Samson W. K., Sowers J. R. (1999). Insulin-like growth factor I as a cardiac hormone: physiological and pathophysiological implications in heart disease. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 31 (11), 2049–2061. doi:10.1006/jmcc.1999.1036
Riehle C., Wende A. R., Zhu Y., Oliveira K. J., Pereira R. O., Jaishy B. P., et al. (2014). Insulin receptor substrates are essential for the bioenergetic and hypertrophic response of the heart to exercise training. Mol. Cell. Biol. 34 (18), 3450–3460. doi:10.1128/MCB.00426-14
Rupert C. E., Coulombe K. L. K. (2017). IGF1 and NRG1 enhance proliferation, metabolic maturity, and the force-frequency response in hESC-derived engineered cardiac tissues. Stem cells Int. 2017, 7648409. doi:10.1155/2017/7648409
Schacht V., Ramirez M. I., Hong Y. K., Hirakawa S., Feng D., Harvey N., et al. (2003). T1alpha/podoplanin deficiency disrupts normal lymphatic vasculature formation and causes lymphedema. EMBO J. 22 (14), 3546–3556. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg342
Schreiber S. N., Emter R., Hock M. B., Knutti D., Cardenas J., Podvinec M., et al. (2004). The estrogen-related receptor alpha (ERRalpha) functions in PPARgamma coactivator 1alpha (PGC-1alpha)-induced mitochondrial biogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101 (17), 6472–6477. doi:10.1073/pnas.0308686101
Schwarz N. A., McKinley-Barnard S. K., Spillane M. B., Andre T. L., Gann J. J., Willoughby D. S. (2016). Effect of resistance exercise intensity on the expression of PGC-1α isoforms and the anabolic and catabolic signaling mediators, IGF-1 and myostatin, in human skeletal muscle. Appl. physiology, Nutr. metabolism = Physiologie Appliquee, Nutr. Metabolisme 41 (8), 856–863. doi:10.1139/apnm-2016-0047
Sejersen C., Bjerre-Bastos J. J., Goetze J. P., Nielsen H. B., Bihlet A. R., Secher N. H. (2022). Effect of adrenaline on serum mid-regional pro-atrial natriuretic peptide and central blood volume. Exp. Physiol. 107 (9), 1037–1045. doi:10.1113/EP090516
Seo D. Y., Lee S. R., Kwak H. B., Park H., Seo K. W., Noh Y. H., et al. (2018). Exercise training causes a partial improvement through increasing testosterone and eNOS for erectile function in middle-aged rats. Exp. Gerontol. 108, 131–138. doi:10.1016/j.exger.2018.04.003
Shibuya M. (2006). Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 (VEGFR-1/Flt-1): a dual regulator for angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 9 (4), 225–230. doi:10.1007/s10456-006-9055-8
Shimizu Y., Polavarapu R., Eskla K. L., Pantner Y., Nicholson C. K., Ishii M., et al. (2018). Impact of lymphangiogenesis on cardiac remodeling after ischemia and reperfusion injury. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 7 (19), e009565. doi:10.1161/JAHA.118.009565
Souza H. C., Penteado D. M., Martin-Pinge M. C., Barbosa Neto O., Teixeira Vde P., Blanco J. H., et al. (2007). Nitric oxide synthesis blockade increases hypertrophy and cardiac fibrosis in rats submitted to aerobic training. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 89 (2), 88–93. doi:10.1590/s0066-782x2007001400005
Stein A. M., da Silva T. M. V., Coelho F. G. M., Rueda A. V., Camarini R., Galduróz R. F. S. (2021). Acute exercise increases circulating IGF-1 in Alzheimer's disease patients, but not in older adults without dementia. Behav. brain Res. 396, 112903. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2020.112903
Ströhle A., Feller C., Strasburger C. J., Heinz A., Dimeo F. (2006). Anxiety modulation by the heart? Aerobic exercise and atrial natriuretic peptide. Psychoneuroendocrinology 31 (9), 1127–1130. doi:10.1016/j.psyneuen.2006.08.003
Sulpice E., Ding S., Muscatelli-Groux B., Bergé M., Han Z. C., Plouet J., et al. (2009). Cross-talk between the VEGF-A and HGF signalling pathways in endothelial cells. Biol. Cell 101 (9), 525–539. doi:10.1042/BC20080221
Sundgren N. C., Giraud G. D., Schultz J. M., Lasarev M. R., Stork P. J., Thornburg K. L. (2003). Extracellular signal-regulated kinase and phosphoinositol-3 kinase mediate IGF-1 induced proliferation of fetal sheep cardiomyocytes. Am. J. physiology. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiology 285 (6), R1481–R1489. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00232.2003
Suzuki-Inoue K., Tsukiji N., Shirai T., Osada M., Inoue O., Ozaki Y. (2018). Platelet CLEC-2: roles beyond hemostasis. Seminars Thrombosis Hemostasis 44 (2), 126–134. doi:10.1055/s-0037-1604090
Tan Y., Feng P., Feng L., Shi L., Song Y., Yang J., et al. (2023). Low-dose exercise protects the heart against established myocardial infarction via IGF-1-upregulated CTRP9 in male mice. MedComm 4 (6), e411. doi:10.1002/mco2.411
Taniguchi H., Tanisawa K., Sun X., Kubo T., Higuchi M. (2016). Endurance exercise reduces hepatic fat content and serum fibroblast growth factor 21 levels in elderly men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metabolism 101 (1), 191–198. doi:10.1210/jc.2015-3308
Tocantins C., Martins J. D., Rodrigues Ó M., Grilo L. F., Diniz M. S., Stevanovic-Silva J., et al. (2023). Metabolic mitochondrial alterations prevail in the female rat heart 8 weeks after exercise cessation. Eur. J. Clin. Investigation 53 (11), e14069. doi:10.1111/eci.14069
Troncoso R., Ibarra C., Vicencio J. M., Jaimovich E., Lavandero S. (2014). New insights into IGF-1 signaling in the heart. Trends Endocrinol. Metabolism TEM 25 (3), 128–137. doi:10.1016/j.tem.2013.12.002
Van Berendoncks A. M., Conraads V. M. (2011). Functional adiponectin resistance and exercise intolerance in heart failure. Curr. Heart Fail. Rep. 8 (2), 113–122. doi:10.1007/s11897-011-0056-6
Vettor R., Valerio A., Ragni M., Trevellin E., Granzotto M., Olivieri M., et al. (2014). Exercise training boosts eNOS-dependent mitochondrial biogenesis in mouse heart: role in adaptation of glucose metabolism. Am. J. Physiology. Endocrinol. Metabolism 306 (5), E519–E528. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00617.2013
Vingren J. L., Kraemer W. J., Ratamess N. A., Anderson J. M., Volek J. S., Maresh C. M. (2010). Testosterone physiology in resistance exercise and training: the up-stream regulatory elements. Sports Med. Auckl. N.Z. 40 (12), 1037–1053. doi:10.2165/11536910-000000000-00000
Vital T. M., Stein A. M., de Melo Coelho F. G., Arantes F. J., Teodorov E., Santos-Galduróz R. F. (2014). Physical exercise and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in elderly: a systematic review. Archives Gerontology Geriatrics 59 (2), 234–239. doi:10.1016/j.archger.2014.04.011
Vu V., Riddell M. C., Sweeney G. (2007). Circulating adiponectin and adiponectin receptor expression in skeletal muscle: effects of exercise. Diabetes/metabolism Res. Rev. 23 (8), 600–611. doi:10.1002/dmrr.778
Wang X., You T., Murphy K., Lyles M. F., Nicklas B. J. (2015). Addition of exercise increases plasma adiponectin and release from adipose tissue. Med. Sci. sports Exerc. 47 (11), 2450–2455. doi:10.1249/MSS.0000000000000670
Waring C. D., Vicinanza C., Papalamprou A., Smith A. J., Purushothaman S., Goldspink D. F., et al. (2014). The adult heart responds to increased workload with physiologic hypertrophy, cardiac stem cell activation, and new myocyte formation. Eur. Heart J. 35 (39), 2722–2731. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehs338
Weeks K. L., McMullen J. R. (2011). The athlete's heart vs. the failing heart: can signaling explain the two distinct outcomes? Physiol. Bethesda, Md 26 (2), 97–105. doi:10.1152/physiol.00043.2010
Weeks K. L., Bernardo B. C., Ooi J. Y. Y., Patterson N. L., McMullen J. R. (2017). The IGF1-PI3K-Akt signaling pathway in mediating exercise-induced cardiac hypertrophy and protection. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1000, 187–210. doi:10.1007/978-981-10-4304-8_12
Wilson M. G., Ellison G. M., Cable N. T. (2015). Basic science behind the cardiovascular benefits of exercise. Heart British Card. Soc. 101 (10), 758–765. doi:10.1136/heartjnl-2014-306596
Wisén A. G., Ekberg K., Wohlfart B., Ekman R., Westrin A. (2011). Plasma ANP and BNP during exercise in patients with major depressive disorder and in healthy controls. J. Affect. Disord. 129 (1-3), 371–375. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2010.09.002
Wright K. J., Thomas M. M., Betik A. C., Belke D., Hepple R. T. (2014). Exercise training initiated in late middle age attenuates cardiac fibrosis and advanced glycation end-product accumulation in senescent rats. Exp. Gerontol. 50, 9–18. doi:10.1016/j.exger.2013.11.006
Wu M., Du Y., Liu Y., He Y., Yang C., Wang W., et al. (2014). Low molecular weight hyaluronan induces lymphangiogenesis through LYVE-1-mediated signaling pathways. PloS one 9 (3), e92857. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0092857
Xu D. H., Zhang X. Y., Liu S. Y., Wei J., Zhan J. H., Du J. K., et al. (2025). KLK8/HGF/Met signaling pathway mediates diabetes-associated hippocampal neuroinflammation in male mice. Theranostics 15 (13), 6290–6312. doi:10.7150/thno.109513
Yan W., Zhang H., Liu P., Wang H., Liu J., Gao C., et al. (2013). Impaired mitochondrial biogenesis due to dysfunctional adiponectin-AMPK-PGC-1α signaling contributing to increased vulnerability in diabetic heart. Basic Res. Cardiol. 108 (3), 329. doi:10.1007/s00395-013-0329-1
Yang Y., Chen Q. H., Liu A. R., Xu X. P., Han J. B., Qiu H. B. (2015). Synergism of MSC-secreted HGF and VEGF in stabilising endothelial barrier function upon lipopolysaccharide stimulation via the Rac1 pathway. Stem cell Res. and Ther. 6, 250. doi:10.1186/s13287-015-0257-0
Yoshida T., Fujitani M., Farmer S., Harada A., Shi Z., Lee J. J., et al. (2023). VMHdm/c(SF-1) neuronal circuits regulate skeletal muscle PGC1-α via the sympathoadrenal drive. Mol. Metab. 77, 101792. doi:10.1016/j.molmet.2023.101792
Yoshiga C., Dawson E. A., Volianitis S., Warberg J., Secher N. H. (2019). Cardiac output during exercise is related to plasma atrial natriuretic peptide but not to central venous pressure in humans. Exp. Physiol. 104 (3), 379–384. doi:10.1113/EP087522
Yuan Q. Y., Huang J., Chu B. C., Li X. J., Li X. S., Si L. Y. (2012). A targeted high-efficiency angiogenesis strategy as therapy for myocardial infarction. Life Sci. 90 (17-18), 695–702. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2012.03.003
Zaidi H., Byrkjeland R., Njerve I. U., Åkra S., Solheim S., Arnesen H., et al. (2021). Adiponectin in relation to exercise and physical performance in patients with type 2 diabetes and coronary artery disease. Adipocyte 10 (1), 612–620. doi:10.1080/21623945.2021.1996699
Zebrowska A., Sadowska-Krepa E., Jagsz S., Klapcinska B., Langfort J. (2017). Cardiac hypertrophy and IGF-1 response to testosterone propionate treatment in trained male rats. Open Life Sci. 12 (1), 120–127. doi:10.1515/biol-2017-0014
Zhang G. L., Sun M. L., Zhang X. A. (2021). Exercise-induced adult cardiomyocyte proliferation in mammals. Front. Physiology 12, 729364. doi:10.3389/fphys.2021.729364
Zhang H., Zhang Y., Zhang J., Jia D. (2024). Exercise alleviates cardiovascular diseases by improving mitochondrial homeostasis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 13 (19), e036555. doi:10.1161/JAHA.124.036555
Zhang K., Gan J., Wang B., Lei W., Zhen D., Yang J., et al. (2025). FGF21 protects against HFpEF by improving cardiac mitochondrial bioenergetics in mice. Nat. Commun. 16 (1), 1661. doi:10.1038/s41467-025-56885-9
Zhao Y. Y., Sawyer D. R., Baliga R. R., Opel D. J., Han X., Marchionni M. A., et al. (1998). Neuregulins promote survival and growth of cardiac myocytes. Persistence of ErbB2 and ErbB4 expression in neonatal and adult ventricular myocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 273 (17), 10261–10269. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.17.10261
Zhao Z., Cui X., Liao Z. (2023). Mechanism of fibroblast growth factor 21 in cardiac remodeling. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 10, 1202730. doi:10.3389/fcvm.2023.1202730
Zhou Z., Zheng L., Tang C., Chen Z., Zhu R., Peng X., et al. (2020). Identification of potentially relevant genes for excessive exercise-induced pathological cardiac hypertrophy in zebrafish. Front. Physiology 11, 565307. doi:10.3389/fphys.2020.565307
Keywords: physiological cardiac hypertrophy, exercise, hormones, growth factors, mitochondria
Citation: Huang S, Chen Z, Li H, Zheng L, Zhou Z, Peng X and Tang C (2025) An overview of the multi-dimensional mechanisms of exercise-regulated hormones and growth factors in cardiac physiological adaptation. Front. Physiol. 16:1642389. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1642389
Received: 09 June 2025; Accepted: 29 August 2025;
Published: 10 September 2025.
Edited by:
Thomas William Lowder, Baptist Health Foundation, United StatesReviewed by:
Bing Bo, Henan University, ChinaBauyrzhan Toktarbay, Nazarbayev University School of Medicine (NUSOM), Kazakhstan
Copyright © 2025 Huang, Chen, Li, Zheng, Zhou, Peng and Tang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zuoqiong Zhou, emhvdXp1b3Fpb25nQGh1bm51LmVkdS5jbg==; Xiyang Peng, eGl5YW5ncGVuZ0BodW5udS5lZHUuY24=; Changfa Tang, Y2hhbmdmYXRhbmdAaHVubnUuZWR1LmNu
 Shuaiwang Huang
Shuaiwang Huang Zhanglin Chen
Zhanglin Chen Changfa Tang
Changfa Tang