- 1Department of Nursing, North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong, China
- 2Department of Radiology, Chongqing General Hospital, Chongqing University, Chongqing, China
- 3Department of Nursing, Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong, China
- 4Chongqing University FuLing Hospital, Chongqing, China
- 5Army Characteristic Medical Center of PLA, Chongqing, China
Background: Iodinated contrast media-acute adverse reactions (ICM-AARs) are frequent and clinically significant complications associated with radiological imaging. Despite investigation of their risk factors, there is no consensus, and no comprehensive synthesis has been conducted. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to investigate the factors influencing ICM-AARs.
Methods: A systematic search for studies published in Chinese or English up to 22 July 2024 in the PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, Embase, CNKI, WanFang, CQVIP, and SinoMed databases was conducted. Studies on patients undergolng contrast-enhanced CT examinations with nonionic ICM were selected. The primary outcome measures were risk factors associated with ICM-AARs. The studies were analyzed for heterogeneity using the Q-test and I2 statistic, while publication bias was assessed using funnel plots, Egger's test, and Begg's test. Stata 17 software was used for the meta-analysis.
Results: Seventeen studies were included, encompassing 2,576,446 CT-enhanced examinations. Of these, 11,621 acute adverse reactions were reported, with a mean incidence of 0.45% and a quality score of ≥7. The meta-analysis showed that female sex (OR = 1.27, 95% CI = 1.13, 1.41), age <35 years (OR = 1.77, 95% CI = 1.19, 2.64), high body mass index (OR = 1.06, 95% CI = 1.01, 1.10), type of medical visit (outpatient) (OR = 2.23, 95% CI = 1.01, 4.93), history of adverse ICM reactions (OR = 11.03, 95% CI = 2.25, 53.97), history of other allergies (OR = 3.16, 95% CI = 1.27, 7.84), history of asthma (OR = 1.75, 95% CI = 1.19, 2.57), hyperthyroldism (OR = 4.59, 95% CI = 1.65, 12.82), and type of ICM (OR = 2.27, 95% CI = 1.68, 3.06) were risk factors for ICM-AARs. Age >60 years (OR = 0.71, 95% CI = 0.53, 0.95), pre-injection medication (OR = 0.56, 95% CI = 0.39, 0.79), and hypertensive disorders (OR = 0.78, 95% CI = 0.65, 0.94) were identified as protective against ICM-AARs.
Conclusions: The incidence of ICM-AARs is influenced by a variety of clinical and demographic factors. Healthcare professionals may benefit from dynamically assessing patient-specific risk factors and considering targeted preventive measures for high-risk groups, particularly in populations similar to those studied.
Systematic Review Registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/, PROSPERO (CRD42024571470).
1 Introduction
Iodinated contrast media (ICM) is an important auxiliary tool in medical imaging as it can distinguish among different tissues, thereby enhancing diagnostic precision. ICMs include both ionic and non-ionic types, of which non-ionic ICMs are currently the most widely used contrast media in CT enhancement due to their greater safety (1). As of 2017, ICM has been used more than 100 million times per year worldwide (2). Although ICM is well tolerated, 0.4%‒1.3% of the population may still experience ICM-related adverse reactions (3–5), ranging from mild nausea, vomiting, and skin itching to severe anaphylactic shock and death (6, 7). ICM adverse reactions are classified according to the time of appearance into acute adverse reactions (AARs) (≤1 h) and delayed adverse reactions (>1 h) (8–10), with AARs categorized into allergic (hypersensitivity) and non-allergic (physiological) reactions; however, due to the limited data available, the present study does not provide a stratified analysis of these subtypes. AARs include nausea and vomiting, allergic symptoms, and laryngeal edema, among others. Approximately 90% of adverse reactions are AARs (11), with almost all potentially life-threatening adverse reactions occurring within 20 min of ICM injection (12). Therefore, identification of the factors influencing ICM-AARs is crucial. Various influencing factors have reported in recent years, and a comprehensive understanding of them would contribute significantly to the early recognition and treatment of ICM-AARs. Therefore, this meta-analysis aimed to synthesize current evidence on factors influencing the onset of ICM-AARs. The findings would support hypothesis generation and inform clinical strategies for identifying potentially high-risk populations. In addition, the results may help inform patient education in the risks associated with contrast media, optimize risk stratification protocols before contrast administration, and guide institutional policies on the selection of contrast media.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study registration
The research followed the Priority Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) reporting standards (13). The protocol has been registered with the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PROSPERO) [CRD42024571470].
2.2 Literature search
The PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, Embase, CNKI, WanFang Database, CQVIP, and SinoMed databases were comprehensively searched for relevant studies. The search period spanned from database inception to July 2024. Searches utilized both medical subject headings (MeSH) and free-text terms, including “contrast media”, “iodinated contrast media”, “drug-related side effects”, “adverse reactions”, “acute adverse reactions”, and “risk factors”. Details of the search strategies used for the different databases are shown in Supplementary Table S1A.
2.3 Selection criteria
The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) The study type was a cohort study, case-control study, or cross-sectional study; (2) The study population consisted of patients with CT-enhanced non-ionic ICM-AARs; (3) The outcome measure factors affecting ICM-AARs, and the study data could be extracted as odds ratios (ORs), hazard ratios (HRs), risk differences (RDs), and 95% confidence intervals (CIs); (4) The language of the publication was either Chinese or English.
The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) Duplicate studies; (2) Review articles, Conference abstracts, meta-analyses, and animal experiments; (3) Unavailability of full text or incomplete data; (4) Low-quality studies.
2.4 Data extraction
After the literature screening, two researchers (Liu, K and Zhu, YY) independently extracted the information from the articles. The extracted data primarily included the following variables: author, time of publication, country, number of CT examinations, number of AARs, incidence, study design, and influencing factors. In cases of disagreement, discussions were held and resolved with a third investigator (Long, J).
2.5 Risk of bias assessment
Two researchers (Liu, K and Zhu, YY) independently evaluated the quality of the included studies for risk of bias, and any disagreement during the evaluation process was resolved through discussion or consultation with a third researcher (Long, J). Case-control studies and cohort studies were scored using the Newcastle Ottawa Scale (NOS) (14) with a total score of 9, where scores of 0‒3 indicated low quality, 4‒6 indicated moderate quality, and 7‒9 indicated high quality. Cross-sectional studies were evaluated using the quality assessment criteria recommended by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) (15), with a total score of 11, where 0‒3 indicated low quality, 4‒7 represented moderate quality, and ≥8 indicated high quality. Studies with scores ≥6 were classified as high-quality studies. To ensure the quality of the articles, studies with scores <6 were excluded from the analysis.
2.6 Statistical analysis
Stata 17 software was used for data analysis, combining the ORs and 95% CIs from the multifactorial analyses, with a significance level of α = 0.05, giving preference to multifactorial-adjusted data. The ORs were converted into log(OR) and their standard errors (SE). The combined OR estimates were calculated using both fixed and random effects models. Judgments were based on the results of the heterogeneity test (Q-test method) and the I2 statistic (16); values of P > 0.1 and I2 < 50% represented acceptable heterogeneity between studies, and a fixed-effects model was used, while values of P ≤ 0.1 and I2 ≥ 50% indicated significant heterogeneity between the studies. Sources of heterogeneity were explored through subgroup analyses (17). If no source of heterogeneity was identified, a random-effects model was used. Sensitivity analyses were performed using a case-by-case exclusion method. When the number of articles included in a single outcome was ≥10, a funnel plot was drawn (18), and Egger's and Begg's tests were used to assess publication bias.
3 Results
3.1 Study identification
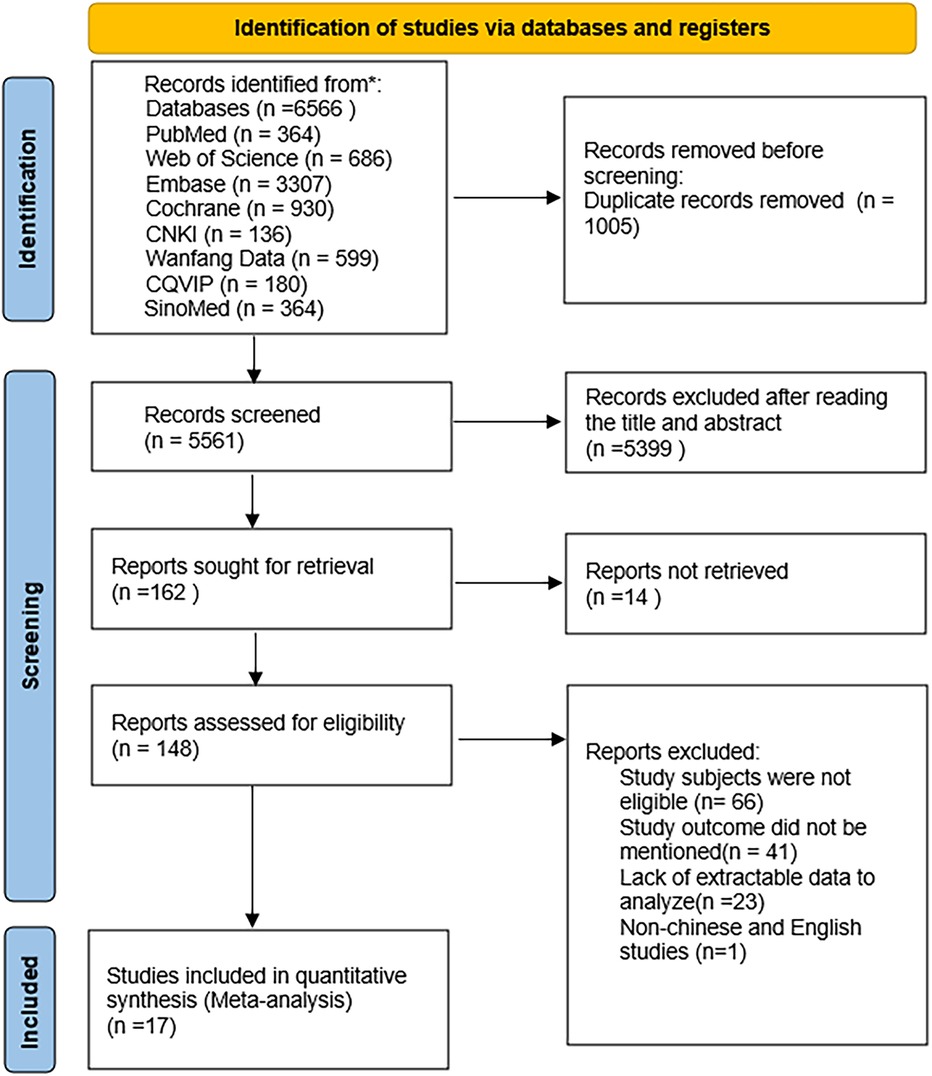
The database search yielded 6,566 potentially eligible articles, including 5,287 in English and 1,279 in Chinese. Duplicate studies totaled 1,005 articles and were excluded. A further 5,399 articles were excluded as their titles and abstracts did not meet the inclusion and exclusion criteria. After reviewing the full texts of 164 articles, 17 were finally included (19–35), with 7 in Chinese (19–25) and 10 in English (26–35). The literature screening process is illustrated in Figure 1.
3.2 Study characteristics and risk of bias assessment
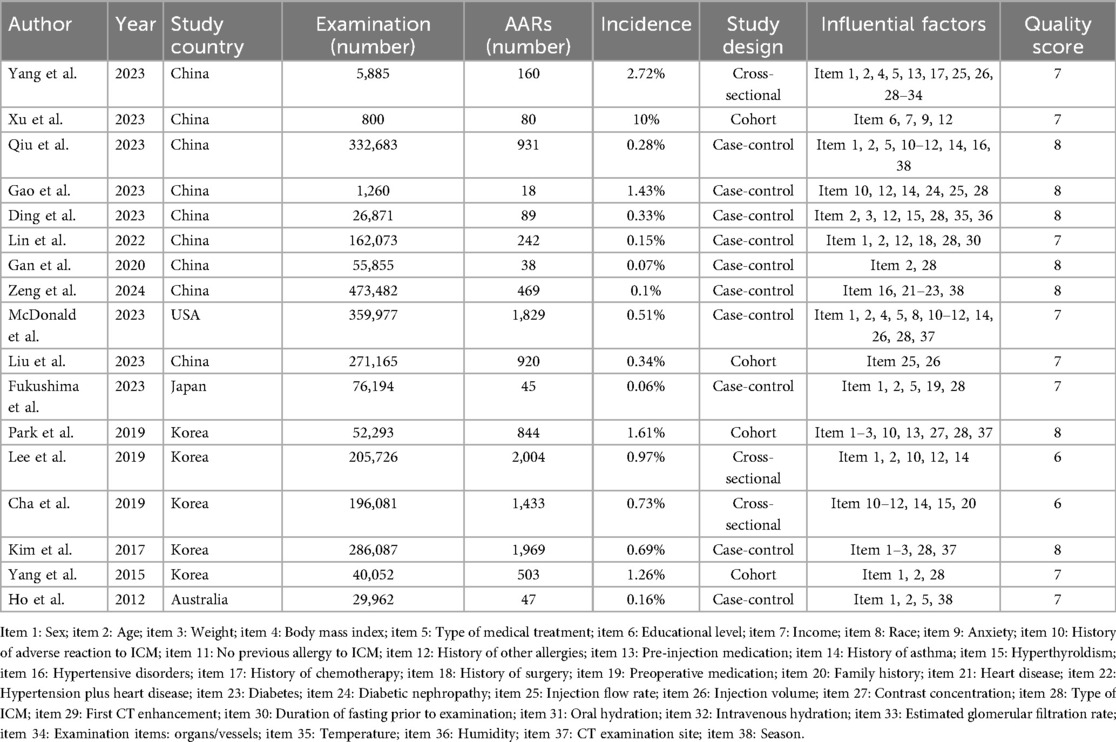
Of the 17 studies ultimately included, 4 were cohort studies, 10 were case-control studies, and 3 were cross-sectional studies. The included studies were from China (n = 8), the USA (n = 1), Japan (n = 1), South Korea (n = 5), and Australia (n = 1). A total of 25,764,46 CT enhancement examinations were described in the studies, among which 11,621 cases of ICM-AARs occurred, with a mean incidence rate of 0.45%. Thirty-eight influencing factors were described. The NOS and AHRQ scores ranged from 6 to 8, indicating a low risk of bias. The fundamental characteristics and quality assessment results are presented in Table 1. The details of the NOS and AHRQ scores are shown in Supplementary Table S1B.
3.3 Results of meta-analysis of factors influencing ICM-AARs
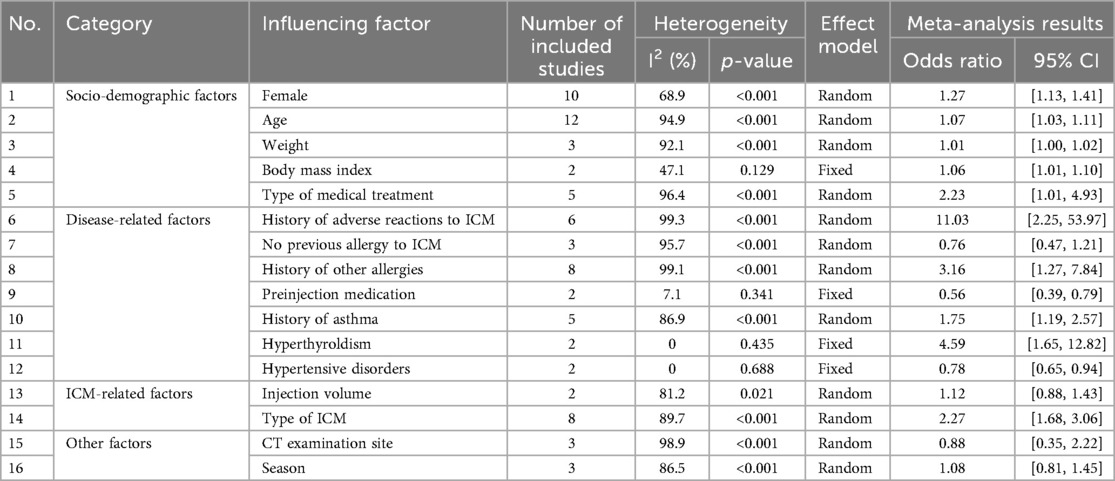
We analyzed the risk factors associated with ICM-AARs by combining the ORs from the multifactorial analyses. Seventeen studies with ≥2 influencing factors were combined, resulting in a total of 16 influencing factors. The results of the meta-analysis showed that female sex, age, high body mass index, type of medical treatment, history of adverse reaction to ICM, history of other allergies, history of asthma, hyperthyroldism, and type of ICM iodine contrast media were risk factors for ICM-AARs. In contrast, pre-injection medication and hypertension were found to be protective against ICM-AARs. There was insufficient evidence to suggest an association between other factors (e.g., body weight, previous ICM allergy-free use, injection dose, site of CT examination, and season) and ICM-AARs. The details are provided in Table 2.
In addition, subgroup analyses based on age and type of contrast agent were conducted. In terms of age, participants were divided into a young group (<35 years), a middle-aged group (35–60 years), and an older group (>60 years). The results suggested a lower reported incidence of ICM-AARs in the older group, although this finding should be interpreted cautiously given the potential influence of clinical and reporting biases (Figure 2).
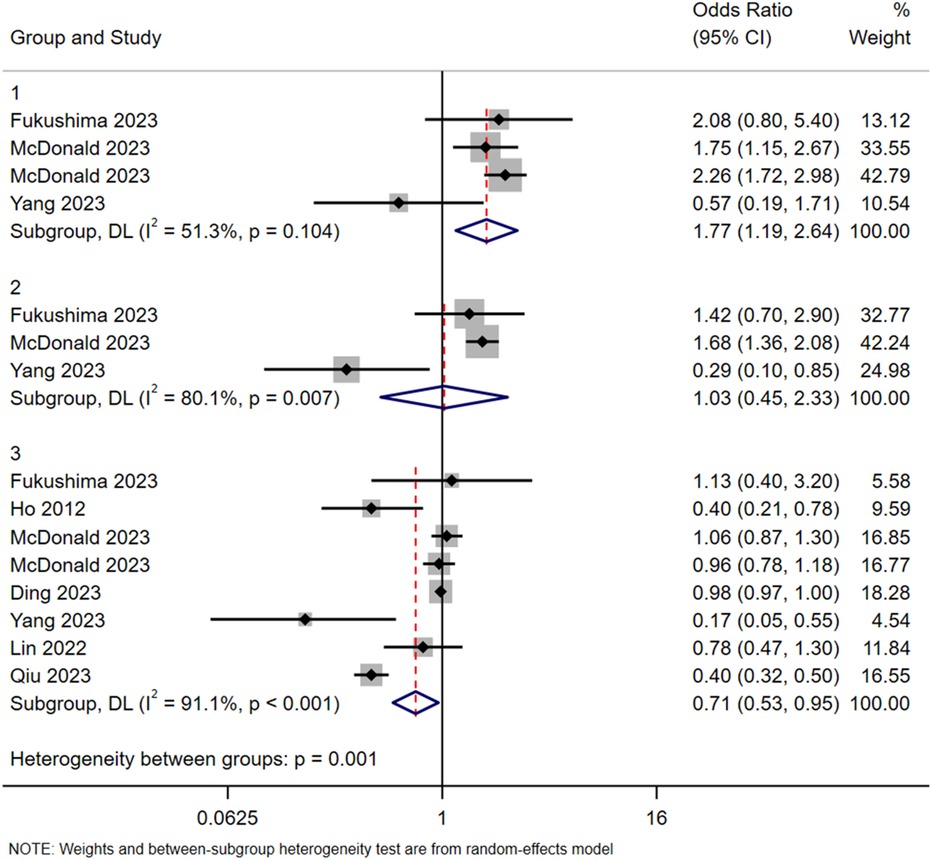
Figure 2. Subgroup analysis in terms of age. Group 1: <35 years old; Group 2: 35–60 years old; Group 3: >60 years old.
Six subgroups were identified according to the type of contrast media (Iohexol as reference): Iodixanol, Iobitridol, Iopamidol, Iomeprol, Iopromide, and Iodephor. Among them, the combined effect size OR and 95% CI of Iodixanol was 1.04 (0.72, 1.51), while the values for Iobitridol were 0.97 (0.49, 1.93), Iopamidol 1.51 (0.94, 2.44), Iomeprol 3.31 (1.58, 6.91), Iopromide 3.71 (1.68, 8.18), and Iodephor 2.36 (1.36, 4.11). The details are shown in Figure 3.
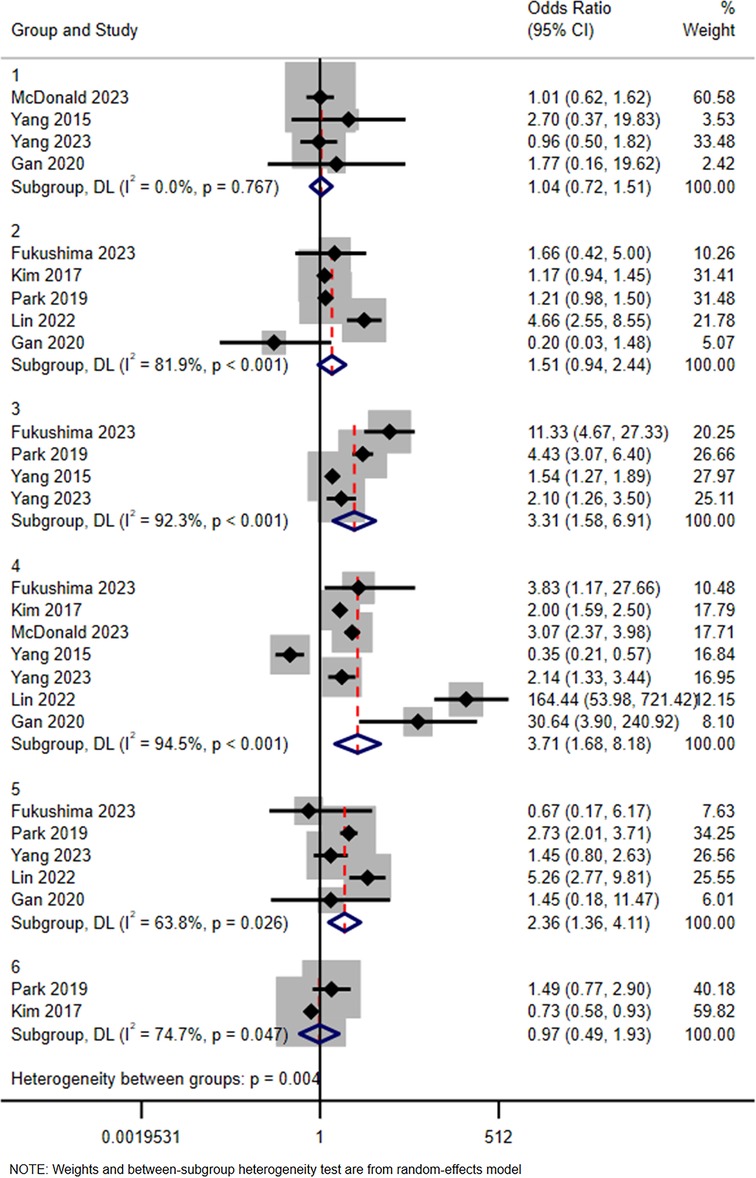
Figure 3. Subgroup analysis in terms of type of iodine contrast media (iohexol represents the reference). Group 1: Iodixanol; Group 2: Iopamidol; Group 3: Iomeprol; Group 4: Iopromide; Group 5: Iodephor; Group 6: Iobitridol.
3.4 Sensitivity analyses
For studies with I2 > 50% and more than two articles among the influencing factors, sensitivity analysis was conducted using the item-by-item exclusion method. After excluding individual studies one-by-one, the results indicated that the composite effect size did not change significantly before and after exclusion, suggesting that the results of the meta-analysis were relatively stable.
3.5 Publication bias
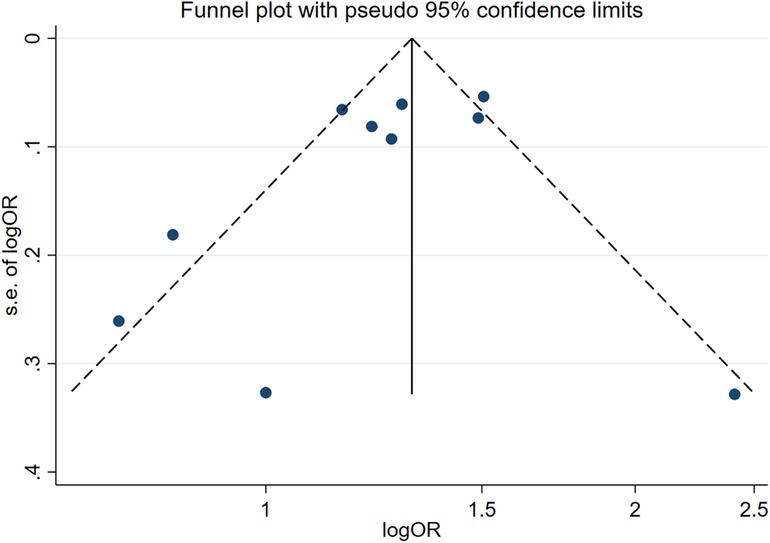
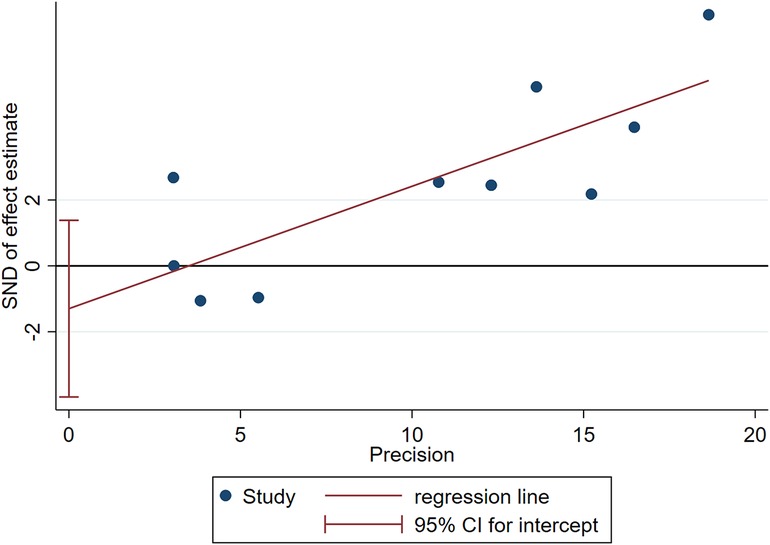
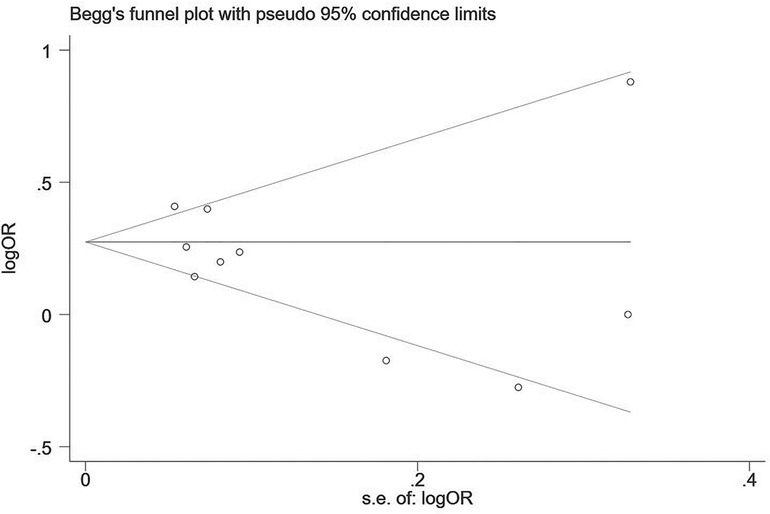
Two influencing factors, sex and age, were described in ≥10 articles. Age, as a continuous variable, was classified in various ways across different studies, which limited direct application of a funnel plot to detect publication bias. Therefore, publication bias was only assessed for sex. The funnel plot showed good symmetry (Figure 4). Egger's test yielded a value of P = 0.297 and Begg's test yielded P = 0.592, indicating an absence of significant publication bias in the meta-analysis and enhancing the reliability of the results. Details are shown in Figures 5, 6.
4 Discussion
4.1 Socio-demographic factors
The findings indicated that female patients had a 27% increased risk of ICM-AARs compared to male patients. This result suggests that females may be more sensitive to ICM, and therefore female patients should exercise greater caution when using ICM. These findings are not consistent with the results of a meta-analysis conducted by Lee et al. (36). This discrepancy may be due to the more defined target population, broader population coverage, and larger sample size in the present study, all of which could have influenced the study results. These findings suggest that differences in sex may be relevant in assessing ICM-AARs risk and warrant further investigation in broader and more diverse populations.
Comparison of the risk of ICM-AARs among different age groups indicated that the risk was lower in the older group (> 60 years) and higher in the younger group (<35 years), relative to the middle-aged group (35‒60 years). This may be attributed to older individuals having reduced sensory perception and relatively higher tolerance (37, 38). Another explanation is that younger patients lack knowledge of the examination process, have relatively weaker psychological tolerance, and experience more anxiety during the examination, thus exacerbating the physiological reaction (20). It is recommended that healthcare professionals pay more attention to young patients, strengthen examination-related education, and alleviate the anxiety of patients.
A correlation was observed between ICM-AARs and body mass index. Higher body mass index values have been linked to stronger immune and histamine responses (39), and consequently, a higher risk of ICM -AARs. Although it was found that the correlation between body weight and ICM-AARs was not significant, this factor should not be ignored in clinical practice.
The study results indicated a higher risk of ICM-AARs in outpatients compared to inpatients, consistent with the findings of Dean et al. (40). Mild reactions in inpatients may be under-recognized due to reduced perception resulting from sedation or altered mental status (27). In contrast, outpatients may more readily perceive contrast-induced discomfort due to extended monitoring and the lack of sedation.
4.2 Disease-related factors
The results showed that the combined effect size OR for patients with a history of adverse reactions to ICM vs. those without a history of adverse reactions to ICM was 11.03 with a 95% CI (2.25, 53.97). A history of ICM-related adverse reactions was defined as the appearance of allergic-like responses (e.g., urticaria) or physiological reactions (e.g., edema) within one hour of ICM administration, or from one hour up to several days after ICM administration. It is hypothesized that previous adverse reactions may have triggered or augmented the immune response in patients, making them more susceptible to adverse reactions when re-exposed to ICM. Therefore, this factor should prioritized as an important risk indicator in clinical practice.
The results suggest that premedication may act as a protective factor against ICM-AARs. Currently, drugs such as antihistamines or steroids can be used prophylactically to reduce the incidence of adverse reactions before ICM injection in patients with a history of mild adverse reactions (41). However, drugs such as sterolds are not effective in preventing adverse reactions in patients with a history of moderate to severe adverse reactions to ICM (42). One study noted that in patients with a prior history of severe adverse reactions to ICM, replacement of the ICM with one having a different side chain to the original ICM helped reduce the incidence of serious adverse reactions (43). However, we acknowledge a key limitation in that the definition and application of this variable were not standardized among the different studies. Future research should aim to clearly define and standardize premedication protocols to better inform clinical risk management and preventive strategies.
The findings indicated that a history of asthma, hyperthyroldism, and other allergies were significant risk factors for ICM-AARs. Asthmatic patients may exhibit stronger allergic reactions to ICM due to airway hyperresponsiveness and specific immune responses (44). Patients with hyperthyroldism may also be at increased risk of adverse reactions due to the iodine content of ICM, potentially leading to further disturbances in thyrold function (2). Furthermore, patients with a history of allergies and previous adverse reactions to ICM may exhibit increased sensitivity to ICM, necessitating special attention to these patients when administering ICM. The present study also observed an interesting phenomenon, specifically, patients with hypertension appeared to be at a lower risk of ICM-AARs. Hypertensive patients may have a reduced risk of ICM-AARs due to the long-term use of antihypertensive medications, potentially increasing their tolerance to these agents. However, few studies have addressed these factors, and further pharmacological studies are necessary to verify these findings.
4.3 Iodine contrast media-related factors
The subgroup analyses of ICM types indicated that Iomeprol, Iopromide, and Iodephor were associated with a higher risk of ICM-AARs compared to Iohexol. The differences between Iodixanol, Iobitridol, Iopamidol, and Iohexol were, however, not statistically significant. A study by Terrenato et al. (45) observed a higher incidence of Iopromide-related adverse reactions compared to Iodixanol, possibly due to the hemodynamic effects of the former, which may lead to transiently increased heart rate and decreased blood pressure (46). Additionally, the American Handbook for the Use of Radiological Contrast Media (47) reported that the overall incidence of Iopromide-related reactions was 0.7%, while the incidence of acute anaphylactic-like reactions for Iohexol and Iodixanol was 0.6%. These statistics are essentially consistent with the results obtained in this study. Based on our findings, in the absence of special circumstances, it is recommended that ICMs associated with a lower risk of adverse reactions be used to ensure patient safety. With the increasing diversity of ICM currently used in clinical practice, future studies should provide more detailed reporting on key physicochemical properties, such as osmolality and iodine concentration, to enable detailed mechanistic analyses and risk stratification. Due to the different descriptors of injection flow rate (19, 22, 28) and injection dose (19, 27, 28), these parameters could not be effectively combined to analyse their effects on ICM-AARs, and more in-depth studies are needed in the future.
Of the 17 studies included in this meta-analysis, the majority were conducted in China and South Korea, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to populations in other regions. Differences in the usage patterns of contrast media, patient physiology, and genetic background between Asian and Western populations could influence the risk patterns associated with ICM-AARs. Therefore, it is suggested that studies from Europe and the USA be included in the future to enhance the universality and external validity of the conclusions.
The present study utilized the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) and the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) checklist to assess the methodological quality of the included studies, considering a score of ≥6 as indicative of high quality. However, we acknowledge that this threshold may be relatively lenient, particularly when synthesizing data with substantial clinical heterogeneity. Although the majority of the included studies demonstrated acceptable quality scores, variations in methodological rigor may still have introduced potential bias in the pooled estimates. To address this, sensitivity analyses were performed to examine the robustness of the results in terms of study quality. Future research may benefit from the application of stricter or tiered quality criteria to enhance the interpretability and credibility of the findings of meta-analyses.
In this meta-analysis, several pooled effects were found to show extremely high statistical heterogeneity, with I2 values generally exceeding 90%, indicating substantial variability among the included studies. Possible sources of this heterogeneity include differences in study design and geographical variations. Although most analyses reached statistical significance, these findings should be interpreted with caution given the extent of heterogeneity.
The study has several limitations. First, all the included studies were observational in nature, which may introduce inherent biases. Second, the age group classifications were determined through discussion based on previous studies, potentially introducing selection bias. Third, in cases where the event incidence was below 10%, certain hazard ratios (HRs) (31) and risk differences (RDs) (28) were approximated as odds ratios (ORs). Although this approximation is unlikely to have substantially affected the overall statistical significance of the results, it may have reduced the interpretability of some pooled effect estimates. Moreover, moderate to high heterogeneity was observed in certain subgroup analyses, which may weaken the strength of some conclusions. While random-effects models were used to account for between-study variability, the heterogeneity may reflect differences in study design, populations, or outcome definitions. Therefore, the results should be interpreted with caution, particularly in subgroups with substantial heterogeneity. Furthermore, to ensure the methodological quality of the included studies, those with quality scores below 6 were excluded. While this approach could enhance the reliability of the pooled estimates, it may also introduce selection bias by the exclusion of potentially relevant studies with lower scores. Finally, this study did not include all possible influencing factors, and future research should continue to explore additional risk factors associated with ICM-AARs.
5 Conclusion
This meta-analysis identified risk factors and protective factors associated with ICM-AARs. Female sex, age <35 years, high body mass index, outpatient status, history of asthma, hyperthyroldism, history of other allergies, history of ICM-AARs, and type of ICM (Iomeprol, Iopromide, Ioversol) were found to be risk factors for ICM-AARs, whereas age >60 years, pre-injection medication, and hypertensive disorders were identified as protective factors. These findings may provide a useful reference for clinical risk assessment, particularly in settings comparable to the populations studied, though further prospective verification is needed.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
This study was based solely on previously published studies and did not involve any direct interaction with human participants or animals. Therefore, ethical approval and informed consent were not required. This aligns with PRISMA and journal expectations for systematic reviews.
Author contributions
KeL: Data curation, Software, Writing – original draft. XC: Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Data curation, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing. JL: Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. CL: Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. LC: Formal analysis, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. KaL: Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. CM: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
I would like to give my heartfelt thanks to all the people who have ever helped me with this paper. First of all, my sincere and hearty thanks and appreciation go firstly to my supervisor, Ms. Mu Changping, whose suggestions and encouragement have given me much insight into these translation studies. It has been a great privilege and joy to study under his guidance and supervision. Secondly, I'am extremely grateful to all my friends and classmates who have kindly provided me assistance in the course of preparing this paper. Finally, I'am grateful to all those who devoted much time to reading this thesis and gave me much advice, which will benefit me in my later studies.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fradi.2025.1656949/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Voltolini S, Cofini V, Murzilli F, Bignardi D, Borro M, Calamari M, et al. Hypersensitivity reactions to iodinate contrast media in Italy: a retrospective study. Characteristics of patients and risk factors. Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol. (2022) 54:60–7. doi: 10.23822/EurAnnACI.1764-1489.225
2. Böhm I, Morelli J, Nairz K, Silva Hasembank Keller P, Heverhagen JT. Myths and misconceptions concerning contrast media-induced anaphylaxis: a narrative review. Postgrad Med. (2017) 129:259–66. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2017.1282296
3. Pradubpongsa P. Adverse reactions to iodinated contrast media: prevalence, risk factors and outcome-the results of a 3-year period. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. (2013) 31:299–306. doi: 10.12932/AP0297.31.4.2013
4. Jang EB, Suh CH, Kim PH, Kim AY, Do K-H, Lee JH, et al. Incidence and severity of nonionic low-osmolar iodinated contrast medium-related adverse drug reactions in the Republic of Korea: comparison by generic. Medicine (Baltimore). (2023) 102:e33717. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000033717
5. Sodagari F, Mozaffary A, Wood CG, Schmitz B, Miller FH, Yaghmai V. Reactions to both nonionic iodinated and gadolinium-based contrast media: incidence and clinical characteristics. Am J Roentgenol. (2018) 210:715–9. doi: 10.2214/AJR.17.18655
6. Lombardo P, Boehm I. Physiological reaction following contrast medium administration: what kind of reaction is this? Eur J Intern Med. (2019) 62:e15. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2019.01.015
7. Brown SGA. Clinical features and severity grading of anaphylaxis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2004) 114:371–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2004.04.029
8. Baerlocher MO, Asch M, Myers A. Allergic-type reactions to radiographic contrast media. CMAJ. (2010) 182:1328. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.090371
9. Brockow K, Romano A, Aberer W, Bircher AJ, Barbaud A, Bonadonna P, et al. Skin testing in patients with hypersensitivity reactions to iodinated contrast media—a European multicenter study. Allergy. (2009) 64:234–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2008.01832.x
10. Working Group on safe use of Contrast Media, Chinese Society of Radiology. Guidelines for the use of iodinated contrast media (2nd edition). Chin Med J. (2014) 94:3363–9. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1005-1201.2013.10.001
11. Jianxun C, Guoli Y, Kangyan Z, Rong W, Gang H, Radiology DO, et al. Adverse reactions induced by non-ionic iodinated contrast agent in 20,418 patients receiving CT examination. Chin J Med Imaging. (2017) 25:876–80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5185.2017.11.021
12. Kodzwa R. ACR manual on contrast Media: 2018 updates. Radiol Technol. (2019) 91:97–100. doi: 10.1007/s00330-024-10605-x
13. Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JPA, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. (2009) 6:e1000100. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000100
14. Ma L-L, Wang Y-Y, Yang Z-H, Huang D, Weng H, Zeng X-T. Methodological quality (risk of bias) assessment tools for primary and secondary medical studies: what are they and which is better? Mil Med Res. (2020) 7:7. doi: 10.1186/s40779-020-00238-8
15. Rostom A, Dube C, Cranney A, Saloojee N, Sy R, Garritty C. Celiac Disease. Evidence Reports/technology Assessments, no. 104. Appendix D. Rockville (MD): Quality Assessment Forms: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality US (2004). Available online at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK35156/
16. Borenstein M, Higgins JPT, Hedges LV, Rothstein HR. Basics of meta-analysis: i2 is not an absolute measure of heterogeneity. Res Synth Methods. (2017) 8:5–18. doi: 10.1002/jrsm.1230
17. Shi-hong Z. Subgroup analysis and sensitive analysis should be set up reasonably in meta-analysis. Chin J Contemp Neurol Neurosurg. (2016) 16:1–2. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6731.2016.01.001
18. Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. Br Med J. (1997) 315:629–34. doi: 10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629
19. Yang Q, Wang H, Li Q, Li Z. Analysis of the current situation and influencing factors of acute adverse reactions of CT-enhanced iodine contrast medium. 护理研究. (2023) 37:2122–9. doi: 10.12102/j.issn.1009-6493.2023.12.008
20. Xu W, Liu Y. To investigate the correlation between acute adverse reactions of iodine contrast agent and anxiety state in enhanced CT examination. J Cent South Univ. (2023) 48:1225–33. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2023.220537
21. Qiu H, Wang L, Li J, Chen L, Li X, Wang LR, et al. Acute adverse reactions and influencing factors of non-ionic iodine contrast in 332,683 patients undergoing contrast-enhanced CT scanning. J Army Med Univ. (2023) 45:257–64. doi: 10.16016/j.2097-0927.202208068
22. Gao W, Li J, Shi B, Zhang L, Dong Q, Mei L. To analyze the risk factors of acute adverse reactions of iodinated contrast media in enhanced CT examination and to construct a prediction model. Huaihai Med. (2023) 41:483–6. doi: 10.14126/j.cnki.1008-7044.2023.05.011
23. Ding M, Yang X. To analyze the causes and risk factors of acute adverse reactions of iodine contrast media. Gen Pract Nurs. (2023) 21:2965–8. doi: 10.12104/j.issn.1674-4748.2023.21.022
24. Lin X, Hong Z, Situ Q, Huang M, Liu X. To construct and evaluate the prediction model of acute adverse reactions of iodinated contrast media in enhanced CT examination in cancer hospital. Mod Clin Nurs. (2022) 21:13–8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8283.2022.09.003
25. Gan M, Liu C, Zhao L, Chong W. Analysis of related factors for acute adverse reactions of CT contrast media. J China Med Univ. (2020) 49:458–62. doi: 10.12007/j.issn.0258-4646.2020.05.016
26. Zeng W, Tang J, Xu X, Zhang Y, Zeng LM, Zhang YT, et al. Safety of non-ionic contrast media in CT examinations for out-patients: retrospective multicenter analysis of 473,482 patients. Eur Radiol. (2024) 34:5450–77. doi: 10.1007/s00330-024-10654-2
27. McDonald JS, Larson NB, Schmitz JJ, Kolbe AB, Hunt CH, Hartman RP, et al. Acute adverse events after iodinated contrast agent administration of 359,977 injections: a single-center retrospective study. Mayo Clin Proc. (2023) 98:1820–30. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2023.02.032
28. Liu H, Qiu H, Liu J, Wang L, Zhao L, Wang Y, et al. Stratified assessment and warning regimen for prevention of acute adverse reactions to iodinated contrast media: results of 150,343 cases in a tertiary hospital. Med Biol Eng Comput. (2023) 61:709–20. doi: 10.1007/s11517-022-02751-5
29. Fukushima Y, Taketomi-Takahashi A, Suto T, Hirasawa H, Tsushima Y. Clinical features and risk factors of iodinated contrast media (ICM)-induced anaphylaxis. Eur J Radiol. (2023) 164:110880. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2023.110880
30. Park HJ, Son JH, Kim T-B, Kang MK, Han K, Kim EH, et al. Relationship between lower dose and injection speed of iodinated contrast material for CT and acute hypersensitivity reactions: an observational study. Radiology. (2019) 293:565–72. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2019190829
31. Lee S, Kang D, Kim J, Yoon S, Choi Y, Lee W, et al. Incidence and risk factors of immediate hypersensitivity reactions associated with low-osmolar iodinated contrast media: a longitudinal study based on a real-time monitoring system. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. (2019) 29:444–50. doi: 10.18176/jiaci.0374
32. Cha MJ, Kang DY, Lee W, Yoon SH, Choi YH, Byun JS, et al. Hypersensitivity reactions to iodinated contrast Media: a multicenter study of 196,081 patients. Radiology. (2019) 293:117–24. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2019190485
33. Kim SR, Lee JH, Park KH, Park HJ, Park JW. Varied incidence of immediate adverse reactions to low-osmolar non-ionic iodide radiocontrast media used in computed tomography. Clin Exp Allergy. (2017) 47:106–12. doi: 10.1111/cea.12803
34. Yang M-S, Choi S-I, Song W-J, Kim S-H, Kang H-R, Park H-W, et al. Impact of an electronic consultant system on hypersensitivity reactions to iodinated radiocontrast media: an observational study. Postgrad Med J. (2015) 91:193–9. doi: 10.1136/postgradmedj-2013-132538
35. Ho J, Kingston RJ, Young N, Katelaris CH, Sindhusake D. Immediate hypersensitivity reactions to IV nonionic iodinated contrast in computed tomography. Asia Pac Allergy. (2012) 2:242–7. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2012.2.4.242
36. Lee H, Song S, Oh Y-K, Kang W, Kim E. Is gender still a predisposing factor in contrast-media associated adverse drug reactions? A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials and observational studies. Eur J Radiol. (2017) 89:81–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2017.01.015
37. Talmon A, Tal Y, Moss J, Hershkowitz I, Shaham D, Sosna J, et al. Clinical impact of allergy and pre-medication in CT studies with low-osmolality intravenous iodinated contrast media. Clin Radiol. (2022) 77:210–5. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2021.12.009
38. Woo S-D, Yoon J, Doo G-E, Park Y, Lee Y, Lee S-H, et al. Common causes and characteristics of adverse drug reactions in older adults: a retrospective study. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. (2020) 21:87. doi: 10.1186/s40360-020-00464-9
39. Suh MJ, Park JA, Ko H, Kang M, Kim J, Lee J, et al. Is body mass Index related to skin reactivity to histamine but not to specific allergens? A 2-year follow-up study on Korean children. Am J Rhinol Allergy. (2022) 36:142–8. doi: 10.1177/19458924211032469
40. Dean KE, Starikov A, Giambrone A, Hentel K, Min R, Loftus M. Adverse reactions to intravenous contrast media: an unexpected discrepancy between inpatient and outpatient cohorts. Clin Imaging. (2015) 39:863–5. doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2015.04.014
41. Motosugi U, Ichikawa T, Sano K, Onishi H. Acute adverse reactions to nonionic iodinated contrast Media for CT: prospective randomized evaluation of the effects of dehydration, oral rehydration, and patient risk factors. AJR Am J Roentgenol. (2016) 207:931–8. doi: 10.2214/AJR.16.16051
42. Park HJ, Park J-W, Yang M-S, Kim M-Y, Kim S-H, Jang GC, et al. Re-exposure to low osmolar iodinated contrast media in patients with prior moderate-to-severe hypersensitivity reactions: a multicentre retrospective cohort study. Eur Radiol. (2017) 27:2886–93. doi: 10.1007/s00330-016-4682-y
43. Sohn K-H, Seo J, Kang D-Y, Lee S-Y, Kang H-R. Finding the optimal alternative for immediate hypersensitivity to low-osmolar iodinated contrast. Invest Radiol. (2021) 56:480–5. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000765
44. Fernandez J. Overview of allergic reactions. Available online at: https://www.msdmanuals.cn/home/immune-disorders/allergic-reactions-and-other-hypersensitivity-disorders/overview-of-allergic-reactions (Accessed October 8, 2024)
45. Terrenato I, Sperati F, Musicco F, Pozzi AF, Di Turi A, Caterino M, et al. Iodixanol versus iopromide in cancer patients: evidence from a randomized clinical trial. J Cell Physiol. (2018) 233:2572–80. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26132
46. An J, Jung H, Kwon OY, Kang Y, Lee J-H, Won H-K, et al. Differences in adverse reactions among iodinated contrast media: analysis of the KAERS database. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. (2019) 7:2205–11. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2019.02.035
47. ACR Manual on Contrast Media. (2024). Available online at: https://www.acr.org/-/media/ACR/Files/Clinical-Resources/Contrast_Media (Accessed September 27, 2024)
Keywords: iodine, contrast media, acute adverse reactions, influencing factors, meta-analysis
Citation: Liu K, Cheng X, Zhu Y, Long J, Li C, Cui L, Li K and Mu C (2025) Predictors of acute adverse reactions to non-ionic iodinated contrast media in CT imaging: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Radiol. 5:1656949. doi: 10.3389/fradi.2025.1656949
Received: 30 June 2025; Accepted: 12 August 2025;
Published: 19 September 2025.
Edited by:
Dominic Gascho, University of Zurich, SwitzerlandReviewed by:
Concetto Sessa, Provincial Health Authority of Ragusa (ASP Ragusa), ItalyIsca Hershkowitz, Hadassah Medical Center, Israel
João José Joaquim, Coimbra School of Health Technology, Portugal
Copyright: © 2025 Liu, Cheng, Zhu, Long, Li, Cui, Li and Mu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Changping Mu, MTM2NTc2MzkwNDJAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Ke Liu1,2
Ke Liu1,2 Kang Li
Kang Li Changping Mu
Changping Mu