- 1Canada Excellence Research Chair in Migration and Integration, Toronto Metropolitan University, Toronto, ON, Canada
- 2Department of Political Science, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
- 3Harney Program, Munk School of Global Affairs and Public Policy, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
- 4Policy Studies, Toronto Metropolitan University, Toronto, ON, Canada
The use of technology in migration management has increased in recent years. As such, practitioners and scholars are increasingly interested in the real and potential use of advanced technologies in migration management. This paper offers an early review of academic and gray literature on the use of advanced digital technologies (ADTs) in migration management processes. The primary focus of this review is literature that discusses migration management technologies—ADTs used by institutional actors (governments, NGOs, transnational institutions). This paper is divided into four thematic areas, aimed at providing a summary of major trends in the literature, including research methodologies, types of technologies, purpose of technologies and the migrants impacted by the technologies explored. Based on the literature reviewed, we identify common themes and areas that merit further exploration and research. To close, we offer an early view into the current uses of advanced digital technologies that we have identified in our Migration Tech Tracker, an interactive tool that consolidates the information found in the literature review of the paper including the various uses of technology by the diverse range of actors in the migration sector. The paper leverages the information from the Tracker to both indicate where and how emerging technologies are being used to govern migrants and simultaneously to identify ADTs that are being analyzed, reported on and researched and those that remain underexplored.
1. Introduction
The proliferation of technological solutions is offering new ways to view migration-related challenges and opportunities. Advanced digital technologies (ADTs) have become more commonplace in migration management processes. Scholars and practitioners alike have taken an interest in the potential and real uses of technologies like artificial intelligence in migration management processes. We define ADTs as emerging technologies that engage the latest digitization and digitalization efforts—where digitization refers to the conversion of existing objects into a digital format that can be processed by a computer, and digitalization refers to the improvement or enablement of processes through digital technologies and digitized data (see Table 1 for a full scope of the technologies included in our working definition of ADTs). We have included artificial intelligence in this definition as it is an emerging technology: artificial capabilities are continuing to evolve. ADTs offer alluring solutions for state and non-state actors to explore in the context of migration management because of the ways in which they can increase efficiency, reduce siloes and streamline processes. The implementation of these technologies presents a variety of concerns for migrant rights, including the right to privacy.
We conducted a structured review of literature focused on ADTs used in migration management. This review aims to fill a gap in understandings of the real and potential uses of advanced digital technologies in the migration ecosystem, as well as identify gaps in how these technologies have been studied and discussed in academic scholarship. The use of ADTs in all aspects of life continues to grow, including in migration management. As such, it is important to consider the emerging questions, concerns, and ideas surrounding the use of ADTs in relation to migration management. Implicit in our definition of ADTs is their emerging nature. New research, questions, and lessons will emerge as these technologies are developed and implemented. This review of the literature better positions scholars and practitioners alike to take a proactive approach to prepare for and understand the context within which these technologies can support and/or hinder migrants and other relevant actors in the migration ecosystem.
As such, the aim of this literature review is three-fold. First, we identify and explore what has been written about the use of ADTs in migration management to date. Second, we determine the contribution of this literature to the dialogue around the use of ADTs in migration management. Finally, this review identifies further research questions that need to be asked when exploring the nexus between advanced digital technologies and migration management.
This review complements our effort to map advanced digital technologies in use in the migration ecosystem. We have identified 183 ADT use cases across 116 countries using secondary data sources. These sources were gathered through online search of gray literature including press releases and publicly accessible reports from state immigration institutions, international organizations, and digital technology firms. Our efforts focused on providing an inventory of ADTs as they are, without interrogating or questioning the use of these technologies. This Migration Tech Tracker brings together information from diverse sources to be utilized by researchers, practitioners, and community organizations.
Our literature review is organized into four thematic areas: research methodologies, types of technologies, the purpose of technologies, and migrants impacted. Section 2.1 discusses the different approaches to research on ADTs used for migration management. Section 2.2 reviews major categories for ADTs and how they are discussed or understudied in the literature. Section 2.3 looks at the uses for different kinds of ADTs as they concern migration management. Finally, Section 2.4 discusses the kinds of migrants that are the focus of research into ADTs in migration management, in particular refugees/asylum seekers and illegalized migrants. We use the terms illegalized migrant and illegalized migration to focus attention on the political and institutional processes, including the uses of ADTs, that render people illegal (Bauder, 2014). In some instances, there is overlap in the analysis of these four thematic areas as well as in the research cited and discussed in each section. For example, research that discusses technologies used in migration control and border surveillance (purpose of technologies) is also discussed in the context of illegalized migrants (migrants impacted). We acknowledge this overlap in our discussion as a necessary consequence of identifying trends and implications from relevant studies across the four thematic areas. A brief discussion of the purpose of the study and our scope of research precedes the thematic discussion section. The conclusion highlights some key themes and suggests areas for future exploration.
This literature review includes literature published between 2010 and 2022. We chose this time frame to align with the definition of emerging ADTs. The literature reviewed includes gray literature (i.e., government, non-profit organization, and think tank reports) and academic literature (i.e., journal articles and book chapters). Together, we have reviewed over 171 data sources identified through snowball sampling. Previous work by one of the co-authors (Nalbandian, 2022a) served as the basis for the snowball sampling approach including familiarity with authors and organizations conducting emerging research at the intersection of migration management and technology. Through articles reviewed for related projects, we identified additional sources in the citations and bibliography.
Nedelcu and Soysüren (2022) distinguish between two subfields of study at the intersection of technology and migration: digital migration studies, which focuses on the agency of migrants enacted through technologies (information and communication technologies in particular), and border and surveillance/security studies, which is concerned with the securitization practices of state and supranational entities. Our literature review extends this latter category to focus on ADTs in migration management. This scope includes technologies used for securitization and other uses, including supporting migrants, by state and supranational entities. While we briefly engage literature on digital migration studies in Section 2.3, under Section 2.3.4., we leave a more comprehensive review and analysis of this literature for a future paper.
2. Literature review: thematic discussions
2.1. Research methodologies
Our literature review revealed many resources use multiple methods. The research methods we encountered included (in order of prominence): descriptive (22 sources), case studies (13), qualitative and ethnographic methodologies (12), an examination of legal or policy-related decisions or documents (7) and experiments (5).
2.1.1. Descriptive
Much of the literature uses a descriptive research method, wherein the authors observe and then identify characteristics, trends, and relationships in ADTs in migration management. Some of this literature follows a similar approach in that the author(s) first describes a single or multiple existing ADTs and then frames the use of that technology. For example, Singler (2021) argues that the International Organization for Migration's Migration Information and Data Analysis System or MIDAS—a border management information system developed to provide a low-cost and user-friendly system to collect and analyze traveler and migrant information and which has been deployed in at least 20 countries located in Sub-Saharan Africa, Latin America, Southeast Asia and Oceania—positions migration as a governable problem amenable to techno-solutionist interventions. Similarly, Csernatoni (2018) uses a descriptive approach to examine the European Union's strategy for prioritizing research and implementation of aerial surveillance technologies, including drones, as a key part of its border management policy. By laying this foundation, the author goes on to frame research and development approaches as technical solutions that fail to address the root causes of migration. In another example, Taylor and Meissner (2020) explore migration to and across Europe and argue that, despite increasing interests from tech and data analytics firms, a migrant-focused framing is necessary to ensure that firms developing ADTs view and treat migrants as agents that cannot be stripped of their rights.
2.1.2. Case studies
Case studies are another common research methodology. Some literature draws on individual, in-depth case studies while others take a comparative approach, examining various jurisdictional uses of ADTs to manage migration. Of the former, Gesellschaft für Freiheitsrechte (2020) provides a technical evaluation of the Federal German Migration Office's evaluations of asylum seeker mobile phones through a focus on legislation and policy. Franco (2020) also takes a descriptive case study approach to examine the use of ADTs to track illegalized migrants by Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) in the United States. McCarroll (2020) takes a similar approach to Franco but provides a more holistic image of ICE capabilities to manage migration and illegalized border crossings. Chambers et al. (2021) analyze how the use of a specific surveillance tool at the border between the United States-Mexico has created a funnel effect—shifting illegalized migrant movement to more remote and dangerous pathways.
Of the case studies reviewed, many, in some way, examine Europe and the United States' use of ADTs to manage illegalized migration. The focus on the United States is likely a result of the public availability of information on ADTs deployed at its borders, as well as a reflection of the privileging of the Global North in migration governance research generally (Triandafyllidou, 2022). Madon and Schoemaker (2021) use a case study approach to examine the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) Population Registration and Identity Management Ecosystem (PRIMES) and its ability to engage both refugees and the organizations engaged in service delivery in the Bidi Bidi refugee camp in Uganda. PRIMES amalgamates all the UNHCR's digital registration, identity management and case management tools into one internally connected and interoperable ecosystem. PRIMES includes several repositories of personal data, both biographic and biometric, and enables identity management and documentation, case management and assistance (both cash and in-kind). In another single case study example, Donko et al. (2022) examine the use of the IOM's MIDAS, to manage migration by studying the Burkina Faso-Niger border.
In contrast, other research examines two cases in their article. For example, Bansak et al. (2018) develop a machine learning algorithm to predict the expected success of new refugees to settle in a particular jurisdiction—either the United States or Switzerland. While taking a case study approach, the authors do not provide an in-depth comparison of the factors that contribute to varying results from the machine learning algorithm in the case of the United States and Switzerland—a discussion that would have otherwise offered insight into ways in which ADTs can be applied to varying contexts. Notably, the implementation of ADTs for migration management in the Global South appears to be largely driven by intergovernmental organizations. Many of these articles frame ADTs positively, which yields many questions, one of which is namely, how intergovernmental organizations make decisions about what technology providers and off-the-shelf systems are appropriate to deploy in vulnerable contexts that exist beyond their borders. Of the case studies reviewed, the lack of technical analysis of technologies is noteworthy, save for Gesellschaft für Freiheitsrechte (2020) and Madon and Schoemaker (2021), the latter of which examines the Federal German Migration Office's extraction of personal information from smartphones and other data carriers of asylum seekers.
Molnar and Gill (2018), McCarroll (2020), and Ziebarth and Bither (2021) utilize a user journey methodology in their case studies. Instead of a jurisdictional focus, these articles are structured in a way that centers each step of the migrant journey as a case study. For Ziebarth and Bither (2021), this approach is paired with examples of the different ADTs deployed in the migrant journey, including pre-arrival, border crossing and settlement.
2.1.3. Experiments
Experimental studies are a subfield of the literature that is limited to date. We define experimental studies as literature which explores or tests the use of ADTs in migration management. Bansak et al. (2018) develop a machine learning algorithm to predict the expected success of new refugees settling in a particular jurisdiction. Azizi and Yektansani (2020) conduct an experiment, where the ADT developed—an AI for modeling and forecasting—can predict whether an individual from Mexico will overstay their visa in the United States based on the application of a variety of predictors. These predictors include labor force information; U.S. migration experience among the family; union/marital history; family composition (i.e., number of children); and property, land, and business. Finally, Hoffmann Pham and Luengo-Oroz (2022) and Molina et al. (2022) also engage machine learning models to forecast migration decision-making in relationship with other factors, including weather. This forecasting approach is worthy of further exploration as it can be of great use to migrants and states alike—however, the authors caution about the risks of using ADTs and big data to determine individual decision-making such as the decision to overstay their visa. When it comes to leveraging advanced digital technologies with prediction capabilities to model and forecast human migration and predict movement across borders, it is imperative that these experiments be viewed as merely that—hypothetical instances of prediction. We caution the deployment of ADTs with predictive capabilities to pre-evaluate the potential of migrants to engage in criminalized behavior. These endeavors may generalize across individuals, contexts and situations which can yield harmful or inaccurate results with implications for migrants.
2.1.4. Qualitative and ethnographic
There is a notable body of literature using qualitative or ethnographic research methodologies. Awad and Tossell (2021) conducted in-depth interviews with 10 Syrian men living in the Netherlands to identify empirical faults in the utilitarian narrative surrounding smartphones in the refugee literature. Bock et al. (2020) conducted interviews with displaced people to better understand the usefulness of various information communication technologies. Kaurin (2019) interviews 11 asylum seekers and refugees in Greece, Spain, Germany and Italy to capture their experiences of the asylum process in the European Union and to record attitudes toward and beliefs about the collection of personal information and biometric data. Molnar (2022) conducted interviews with communities in Belgium and Greece exploring how technological experiments on refugees are often discriminatory, breach privacy, and endanger lives. In the US context, Goldstein and Alonso-Bejarano (2017) use interviews with researchers, illegalized workers, and their advocates to learn more about how the workplace has been rendered a site for immigration enforcement. Donko et al. (2022) studied the impacts of MIDAS at one specific location on the Burkina Faso-Niger border using an ethnographic approach that included observation, informal conversations, and structured interviews with a wide variety of actors affected by the introduction of the new system. Madon and Schoemaker (2021) interviewed individuals in the UNHCR, organizational stakeholders and refugees in the world's largest refugee camp in Northern Uganda to learn more about the UNHCR's strategy toward platform openness.
2.2. Type of technologies
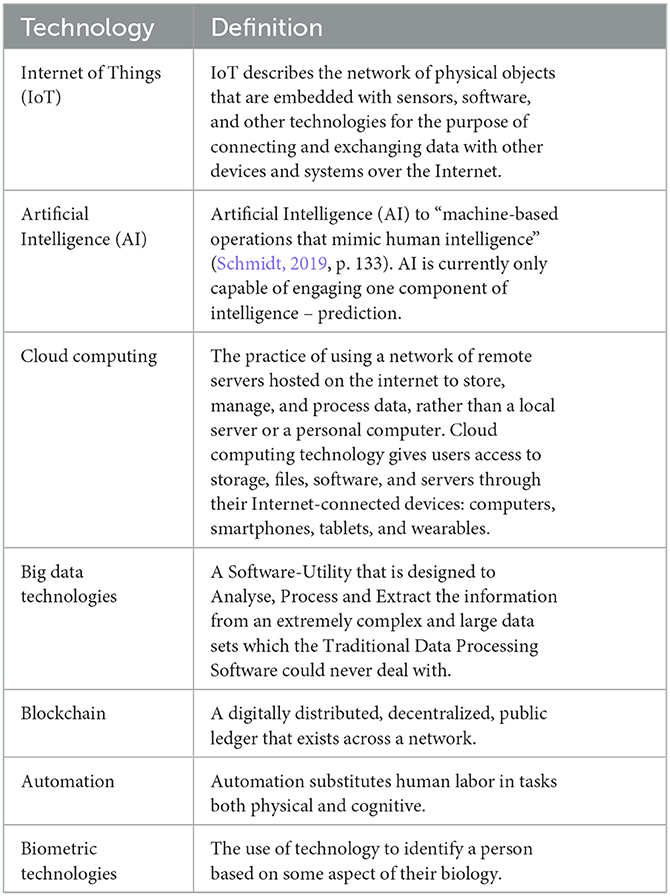
The scope of this literature review focuses on six categories of ADTs: Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, big data technologies, blockchain, automation and biometric technologies (see Table 1 for full definitions and examples). IoT describes the network of physical objects that are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies to connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the Internet. Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to “machine-based operations that mimic human intelligence” (Schmidt, 2019, p. 133). Cloud computing is the practice of using a network of remote servers hosted on the internet to store, manage, and process data, rather than a local server or a personal computer. Cloud computing technology gives users access to storage, files, software, and servers through their Internet-connected devices: computers, smartphones, tablets, and wearables. Big data technologies are software-utility that are designed to analyze, process, and extract the information from extremely complex and large data sets that the traditional data processing software could never deal with. Blockchain is a digitally distributed, decentralized, public ledger that exists across a network. Automation refers to the substitution of human labor in tasks both physical and cognitive. Finally, biometrics refers to the technologies used to identify a person based on some aspect of their biology.
Our research reveals that most of the literature does not distinguish between particular ADTs, but instead reviews a network or ecosystem of technologies as a whole—the use of technology to manage migration. What is noteworthy about this practice is the emphasis on migration and the generic ways in which technologies are discussed—a choice that limits and at the same time generalizes the perspective from which an argument is viewed. Of the articles reviewed, 18 referred to IoTs, 15 to biometric technologies, 12 to AI, seven to big data technologies, five to cloud computing, three to automation and one to blockchain. Articles could have included a reference or focused on more than one category of ADTs. Notably, the lack of emphasis or detail surrounding ADTs in much of the literature raises questions about the migration scholars' knowledge and understanding of the technical aspects of ADTs. For example, some authors refer to biometric technologies as a broader category of AI, which is problematic as not all biometric technology engages AI.
2.2.1. Internet of things
Literature concerned with IoTs largely focused on mobile phones. Gesellschaft für Freiheitsrechte (2020) focused on how “data carriers”—in most contexts, smartphones—can be used to control vulnerable migrants, such as refugees or asylum seekers, who do not have access to their official documentation to prove their identities. The report documents the German government's process for collecting personal data including telephone numbers, contact information, text messages from SMS, WhatsApp, and similar messaging platforms, as well as emails and photos. This report highlights that this practice has been occurring in Germany since 2015 but is also crossing borders as other European states pick up similar policies and practices, including the Netherlands, Estonia, Italy, Lithuania, Norway, Croatia, Austria, Denmark, and Belgium. The authors note how there is a severe lack of transparency into the German practice of using data carriers in place of migrants' official documentation and a distinct need for an evaluation of how “the BAMF (the German Federal Office of Migration and Refugees) deeply violates refugees' privacy in a moment in which they are particularly vulnerable” (Gesellschaft für Freiheitsrechte, 2020, p. 49).
While not within the focused scope for this literature review, Awad and Tossell (2021) challenge the utilitarian perspective of smartphone use. Similarly, Bock et al. (2020) develop a comprehensive list of technologies that support migrants, offering an analysis of the strengths and shortcomings of each tool and the services they provide and, importantly, the role of end users in the design and development of the tools. In doing so, the authors frame successful Internet of Things technologies as those which are oriented to the needs of refugees and migrants and their host societies that effectively facilitate the integration process while helping individuals pursue their respective goals and ambitions. This study is helpful for programmers and engineers to consider the unique characteristics of IoT technologies used by migrants. Taylor (2016) examines the use of mobile phone data to track human mobility and raises questions about function creep and whether states would restrain from using the data acquired for other purposes.
In contrast to the literature on mobile phone use, Csernatoni (2018) examines drones as part of the IoT category, particularly the European Union's strategy for prioritizing research and implementation of aerial surveillance technologies as a key part of its border management policy. The author argues that while these solutions exist, they are ineffective as they do not address the root causes of migration. Petridi (2021), Koca (2022), and Molnar (2022) each examine a wide range of IoT technologies as they address themes of examining how a broad ecosystem of tools being tested on migrants, the importance of centring the migrant in developing technologies to manage and support migrants and how IoTs are contributing to the criminalization of migrants.
2.2.2. Artificial intelligence
Of the literature reviewed, only a handful engage in a deep exploration of the AI tools used. Much of the literature makes brief mention of an AI tool used to manage migrants and lacks a technical exploration of these technologies. Literature that descriptively refers to AI does not offer a sufficiently compelling case for inclusion or assessment here (see Cholakian, 2018; Petridi, 2021; Molnar, 2022—all of whom discuss AI very generally, making mention of it as one of many tools in an ecosystem of ADTs that can or are being used to manage migration). What is interesting, however, is the prevalence of literature that engages an experimental methodology and how it is focused specifically on AI. For example, Bansak et al. (2018) develop an algorithm that engages supervised machine learning to model and predict where migrants might best settle and integrate into their host country. Azizi and Yektansani (2020) use predictive modeling to examine whether an individual from Mexico will live in the United States with or without papers. Interestingly, literature that focuses on AI as an ADT and is experimental, though minimal, is produced by individuals who do not necessarily specialize in ADT or technical research on migration, per-se. For example, in the latter example, Bansak is a political scientist with research interests in research methodology and asylum seekers. As another example, Azizi and Yektansani are both economists. We identify this fact, not to diminish or alter the contribution of this scholars, but rather, to show that the intersection of technology and migration management merits further exploration. This intersection of research can greatly benefit from contributions from interdisciplinary project teams of researchers and practitioners from multiple subject areas.
Other authors take a descriptive approach to the use of AI for managing migrants. Cameron et al. (2022) argue that if international law recognized the obligation to resolve doubt in favor of refugee claimants (i.e., taking the refugee claimant's position as true), AI could build confidence in refugee decision-making by identifying reasons within a claim that suggests to the decision-maker to reduce confidence in their conclusions. For example, a refugee claimant alleges that if they return to their home country, they will be persecuted for their religious beliefs. An AI system could be trained to identify the likelihood that an individual in the described scenario would be persecuted. In the scenario described by Cameron et al. (2022), there would be sufficient and clean enough data for the AI system to assess the likelihood of this outcome and inform the decision-maker of the probability of the refugee claimant's assessment. While a valuable hypothetical, Cameron et al. (2022) explain that this application of AI is unlikely as it requires addressing many competing challenges, including issues with black box AI and how international law resolves doubt. These authors take a foresight-based approach, examining the potential of AI to manage migrants. Carammia and Dumont (2018) focus on the use of ADTs, including AI, to predict migration trends, proposing that by analyzing information and data such as social media posts or the news, it can be possible to determine periods of heightened emigration: “before people even start to move—or maybe even before they start thinking of packing their bags” (p. 2). Cameron et al. (2022) focus on how machine learning can be used to provide a measure of uncertainty to immigration decision-makers—in other words, how much doubt the decisionmaker should have in the facts of a case and therefore, the decision they are leaning toward. These two articles offer a compelling and optimistic view of technology's potential for migration management, and while Cameron et al. (2022) caution about the negative impact ADTs can have on migrant populations, Carammia and Dumont (2018) do not specifically acknowledge that better predicting migrant flows offers states the ability to circumvent migrants arriving at their borders.
2.2.3. Cloud computing
Our research did not yield literature at the intersection of cloud computing and migration management.
2.2.4. Big data technologies
In the literature reviewed, big data is generally referenced passively, without discussion of technical specifics of the technologies developed or deployed. However, Beduschi (2018) tangles with questions around privacy, security, and freedom, offering a perspective that big data technologies may pave the road to protect and support those who request assistance. The author positions international human rights law as a legal framework for states to protect the rights of vulnerable migrants. Under international human rights law, states have a de jure responsibility (a “positive obligation”) to protect and use the latest available technologies (including big data analysis) in this protection effort. Conversely, Franco (2020) outlines the details of migration management in the United States and examines how Palantir Technologies offers data mining and data software technologies which have been used by the Department of Homeland Security to create profiles and track migrants and their families. Franco examines how Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) in the United States has weaponized individuals' personal data—an approach that aligns with Goldstein and Alonso-Bejarano (2017) who argue that the Department of Homeland Security, which includes ICE, is tasked with both combating international terrorism and enforcing national immigration law.
2.2.5. Blockchain
Our research did not yield significant literature at the intersection of blockchain and migration management. An area that merits further exploration is Accenture and Microsoft's development of blockchain technologies to support the UNHCR in providing aid to refugees. Much of the information that currently exists is available through the UNHCR, Accenture, and Microsoft, which offer a positive view of this blockchain technology. Our efforts to uncover additional information about this particular use case have not yielded a response to date.
2.2.6. Automation
While automation does appear in the literature reviewed, it remains unclear as to whether many of the researchers have framed automation as AI. Beduschi (2018) and McCarroll (2020) examine automation broadly, as a part of an ecosystem of technologies—including AI—that exist and go beyond the process of making things work more efficiently.
2.2.7. Biometric technologies
Several authors point to power asymmetries that exist because of the use of biometrics in migration management. Singler (2021) argues that the use of MIDAS can be performative in that it allows Global South countries to affirm their membership with biometrically capable states, while Kaurin (2019) argues that migrants (and refugees in particular) are often forced to give up their digital agency when they share or relinquish biographical data or biometrics. Madianou (2019) argues that the biometric assemblage accentuates asymmetries between refugees and humanitarian agencies and ultimately entrenches inequalities in a global context. Israel (2020) also identifies concerns with the right to privacy and ethics when biometric technologies are introduced in border management systems. Jacobsen and Sandvik (2018) offer an interesting argument from their perspective evaluating the practices of international organizations like the UNHCR which continue to overlook problems like protecting refugees' biometric data and instead focus on biometrics as an accountability mechanism to prevent fraud or aid making its way to terrorists.
Goldstein and Alonso-Bejarano (2017) argue that the United States—using the biometric verification tool eVerify—has rendered the workplace a site for immigration enforcement and has shifted the power dynamic toward employers who leverage this technology to identify and report illegalized migrants. In earlier research on this subject, Papademetriou and Collett (2011) showcase how states increasingly gain control of their ability to manage migrants using biometrics, which offers the ability to verify the identities of migrants before their arrival. In contrast, Farraj (2011) framing of biometric technologies is different in that it strikes a balance between biometrics as a benefit and a risk for migrants.
2.3. Purpose of technology
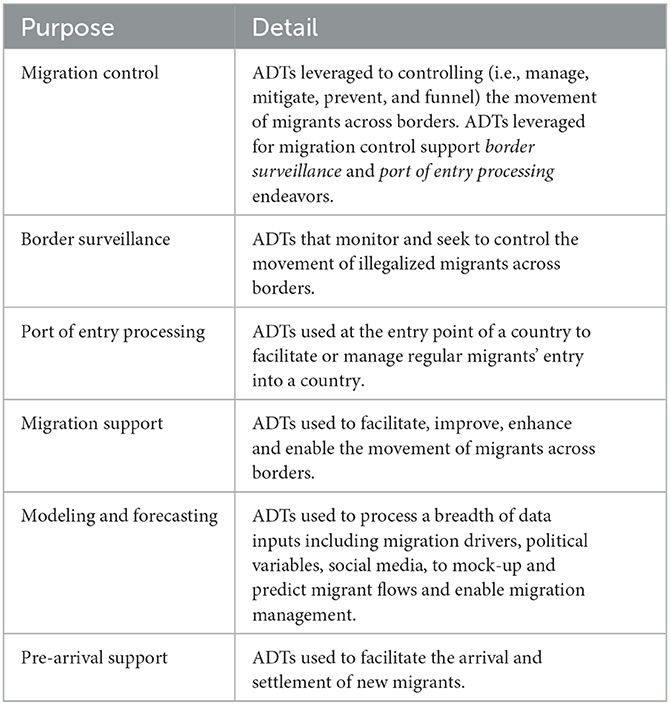
Our literature review considered the purposes of ADTs used in migration management as discussed in the literature. The academic and gray literature discussion of ADTs use for migration management can be sorted into two broad categories: migration control and migration support (see Table 2 for full descriptions of these categories and related sub-segments). The majority of the literature reviewed (34 sources) is concerned with some aspect of controlling the movement of migrants. This literature can be further segmented into border surveillance technologies—those primarily concerned with controlling and surveilling illegalized migrants—and port-of-entry processing, which are focused on processing regular migrants. Research into ADTs for supporting migrants is a smaller subset of the literature and is primarily concerned with service provision for refugees and asylum seekers. We also identified a small segment of literature that covered the use of advanced technologies for other functions related to migration, including modeling and forecasting, pre-arrival processing of migrants, and technologies that migrants themselves utilize as a form of agency. As previously noted, while reviewed in brief, the latter category is outside the scope of our current study on migration management technologies.
2.3.1. Migration control
The role of ADTs that is most prominent in recent literature is migration control. Migration control as a purpose for ADT use is tied closely with narratives of “migration as criminality” and “migration as risk”. Through narratives of “migration as criminality”, the irregular movement of migrants across borders are framed as criminal acts, thus rendering migrants as illegalized (Bauder, 2014). These narratives of criminality and illegality can also be deployed to link migrants to other kinds of crime (Engbersen and van der Leun, 2001). The relationship between risk and migration has been approached from various theoretical perspectives. Migration can be informed by, generate, or ameliorate risk and uncertainty (Williams and BaláŽ, 2012). Within the literature on ADTs for migration management, “migration as risk” most directly concerns the capacity of migration to generate risk for destination states. This prevalence of “migration as risk” thinking reflects a broader discourse in which risk is a central operating principle in economic, political, and social spheres relating to migration governance (Amoore, 2013). In this context, dominant narratives position ADTs for migration control within a system that interprets all migrants as risk bodies in relation to the state; that is, the state is at risk due to migration. Csernatoni (2018) examines the European Union's strategy for prioritizing research and implementation of aerial surveillance technologies including drones as a key part of its border management policy. Through this discussion, the author addresses the transformation of the European Union into a “technological fortress”, linking themes of border militarization and surveillance with migration as criminality and risk. Migration as risk is also used as a narrative framework in critical data studies (Taylor and Meissner, 2020) and the IOM's MIDAS biometric border management system (Singler, 2021).
In our analysis, migration control is further divided into ADTs for border surveillance and port of entry processing. The following two subsections discuss these categories.
2.3.2. Border surveillance
Border surveillance refers to ADTs that monitor and seek to control the movement of illegalized migrants across borders. Literature on border surveillance focuses primarily on illegalized migrants, although a subset of this literature discusses migrants identified as asylum seekers and refugees—the distinctions between these two populations in the literature will be discussed in more detail in Section 2.4.
The literature on border technologies for surveillance involves many of the ADTs discussed in the previous section: Internet of Things (IoT); biometric technologies; big data technologies; and artificial intelligence. The ways these technologies are used have implications for the concept of border surveillance as we define it. Chambers et al. (2021) consider one example of IoT technology in their experimental study of “prevention through deterrence” on the United States-Mexico border. The authors use a geospatial modeling method to predict the effects of the implementation of SBInet integrated fixed towers developed by Boeing to monitor the border. Their findings suggest this IoT technology produces a “funnel effect”, in which the implementation of these surveillance tools has been ineffective in preventing migration and instead has shifted migrant movement to more remote and more dangerous pathways. The deployment of IoTs as border surveillance technology is also prominent in the literature that considers aspects of the European Union's aerial surveillance program as a key part of border management (Jumbert, 2016; Marin and Krajčíková, 2016; Csernatoni, 2018).
In the studies above, the border is a geographically limited space, the demarcated boundary between two states. The literature on ADTs as tools of border surveillance also highlights the role of technology to push borders outward—referred to in this literature as border externalization—as well as inward. Koca (2022) draws on critical border studies and the Foucauldian concept of biopolitics to interpret the implementation of advanced surveillance and IoT technologies along with physical infrastructure along Turkey's borders with Syria and Greece. Through an analysis of government, NGO, media, and academic sources, the author identifies how European Union pressure and discourses of illegality that highlight risks of illegal border crossing, smuggling and terrorism provide key reasons for the implementation of added border security technologies and contrast a concurrent humanitarian discourse.
Singler (2021) and Donko et al. (2022) highlight the IOM's MIDAS program, as another tool in the European Union's externalization of borders. Donko et al. (2022) present the results of ethnographic fieldwork at the site of one MIDAS border post at the Burkina Faso-Niger border to highlight the ways new technologies have changed border relations in the region, including limiting the freedom of movement across borders, introducing economic hardship throughout borderlands communities, and contributing to violent conflict including the destruction of the border facility and accompanying biometric equipment. Singler (2021) examines the performative elements of MIDAS program implementation, including its deployment and training sessions, that help to frame the IOM as a neutral, technical expert on migration management. The author argues that this performative framing of MIDAS obscures how it contributes to new domains of political intervention, specifically of the IOM and European Union (a funder of MIDAS) into Global South migration governance.
ADTs have also been adopted for surveillance purposes to identify and track illegalized migrants living in host countries. As Franco (2020) describes in one case study from the United States, Palantir Technologies offers data mining technologies which have been used by the U.S. Department of Homeland Security to create profiles and track migrants and their families. The tool scrapes data from state and federal entities and supplies agents with information including immigrant history, family relationships, addresses, phone numbers, and biometric data. Through ethnographic research with illegalized migrants in Belgium, Molnar (2022) provides a European case of migration management technologies' role to “track, identify, and control those crossing borders” and its extension geographically and temporarily distant from demarcated borders. The effect of these surveillance programs is to push the border inward, making the liminal experience of border crossing a permanent state for illegalized migrants in surveillance states.
2.3.3. Port of entry processing
A smaller segment of the literature on migration control focuses on port-of-entry processing. ADTs for port-of-entry processing refers to technologies used at the entry point to facilitate or manage regular migrants' entry into a country. Some literature is concerned with the implementation of biometric data collection for all migrants through the IOM's MIDAS (Singler, 2021; Donko et al., 2022) and refugees and asylum seekers in Global North countries (Farraj, 2011). In the case of Farraj (2011), the author speculates on the possible future of biometric usage for refugee and asylum seekers through an analysis of legal precedent in the European Union, United Kingdom, and United States.
Majcher (2022) documents the mechanics of the EU Returns Directive, a Schengen-wide entry ban that prevents anyone expelled from a Schengen country from returning to the region for a period of 5-year. This ban has been facilitated by the Schengen Information System, the cross-European system for tracking irregular and deported migrants. The author finds that data protection and privacy rules for illegalized migrants in these cases are narrower than the right to privacy under European Union convention. Gesellschaft für Freiheitsrechte (2020), a German human rights NGO, provides a technical evaluation of the Federal German Migration Office's evaluations of asylum seekers' smartphones. Under German law, migration officers can claim and download personal data from all “data carriers” (in most contexts this refers to smartphones, but also laptops and other portal electronic devices) for asylum seekers who cannot produce a valid passport or replacement document. The report's authors indicate there are significant technical inefficacies in the technology used by German migration authorities and describe the evaluation as “deep infringements of privacy right” and “experimental use of surveillance technology on the most vulnerable group of society” (Gesellschaft für Freiheitsrechte, 2020, p. 1 and p. 4).
2.3.4. Migration support
Another central purpose of the discussion on technology and migration is a focus on the role of advanced digital technologies to support the migrant experience, although this theme is less developed than conversations around migrant control.
Taylor and Meissner (2020) highlight the potential of big data analytics technologies to support migrants but suggest realizing this outcome requires a narrative reframing of migration as a risk to the migrant rather than the dominant conceptual framing of migrants posing a risk to the destination state. According to the authors, the shaping of migration narratives in post-2015 Europe represents a market opportunity for technology and data analytics firms. By pushing for a narrative reframing that sees migrants as agents and their migration journeys as risk, these firms, benevolent states, and non-profit actors can facilitate the implementation of big data analytics for migrant support. Beduschi (2018) uses a similar risk to migrants' framework in suggesting that big data and other ADTs can act as tools to protect and support vulnerable migrants. Citing examples of crossing the Mediterranean to Europe and human trafficking, the author references international human rights law as the basis for a legal argument in which states have a legal responsibility (a “positive obligation”) to protect vulnerable migrants and to use the latest available technologies (including big data analysis) in these protection efforts. Similarly, Beduschi and McAuliffe (2022) explore the various stages of the immigration process and how AI can potentially be or is already used.
The relationship between technologies used for migrant support and the risk-of-migration framework discussed above is also evident in the strong correlation between the literature on migration support and that concerning refugees and asylum seekers. Articles that analyze or discuss the potential of ADTs to support migrants most often discuss technologies specific to the refugee experience or case studies of ADTs used for refugee services. Several authors argue that biometric technologies can support refugees and asylum seekers by speeding up the identification and registration processes as well as improving service provision by governments and humanitarian organizations (Farraj, 2011; Jacobsen and Sandvik, 2018; Madon and Schoemaker, 2021). Other technologies have been highlighted for their ability to facilitate the settlement and integration of refugees (Ziebarth and Bither, 2021). Bansak et al. (2018) develop a data-driven approach to refugee resettlement that considers geographical context, personal characteristics and synergies between geography and personal characteristics to place refugees in communities where they are most likely to succeed. Ziebarth and Bither (2021) discuss pilot programs from the United States and Switzerland that have already been implemented to improve employment outcomes for refugees based on their placement.
As noted earlier in our discussion, the primary focus of this review is literature that discusses migration management technologies—ADTs used by institutional actors (governments, NGOs, transnational institutions). The scope of this paper is limited in reviewing the body of literature that Nedelcu and Soysüren (2022) refer to as “digital migration studies”.
Based on a limited review of digital migration studies literature, some key themes emerge: (1) the use of ADTs as tools for migrants to gather information and resources, (2) the role of ADTs in bringing visibility to and amplifying the experiences of migrants, and (3) the use of ADTs by non-migrant populations to support migrants. When it comes to the use of ADTs as tools migrants leverage to gather information, Şanlıer Yüksel (2022) examines how asylum seekers, transit, and temporary protected migrants from Syria, Afghanistan, Iran, Iraq and Congo use ICTs in their journey. Ennaji and Bignami (2019) advance this position further, by showcasing how global positioning apps, digital maps and platforms that act as communication channels are leveraged by migrants to navigate the changing (and often hostile) social, political, and economic conditions to which they are exposed. Noori (2022) furthers the discussion on the use of ADTs by migrants to gather information by reflecting on how precarious migrants often rely on smartphones to enhance the overall safety and security of their journey. In contrast, much of the literature we reviewed concerns how ADTs are used by migrants to make themselves visible and to communicate their experiences. Syrett and Keles (2019) discuss how refugee diasporas rely on ICTs to become informed on relevant matters and identify and locate resources that effectively position them to mobilize in various forms, including protest. Kissau and Hunger (2008, p. 6) discuss how ADTs enable migrants to engage in the political sphere, where political participation can be scarce, which allows the otherwise minority migrant group to have a collective voice (Mitra, 2005; Nedelcu, 2018). Georgiou (2018) offers an alternative perspective to migrants' participation in the digital sphere, arguing that these tools grant access to a digital space that is highly hierarchized. Our review has revealed that researchers are examining the ways in which non-migrant populations leverage ADTs to support migrants, often through online activities, like hackathons (Irani, 2015; Madianou, 2019).
Many of these studies focus on how vulnerable migrants utilize smartphones and other information and communication technologies (ICTs) for self-empowerment. In this space, some scholars have problematized the conception of migrant technology use as necessarily empowering or emancipatory. Awad and Tossell (2021) suggest that a utilitarian narrative of smartphone use by refugees leads to the tendency to other or dehumanize migrants. As their interview participants reveal, refugees negotiate paradoxes of connectivity—connectedness through technology as enhancing and limiting freedom or as empowering and burdening. In their critique, the authors suggest that the academic literature assumes the general utility of smartphones for refugees and their work seeks to challenge this premise. We argue that a similar tendency can be found in discussions of migration management technologies. Critical literature tends to focus on the ethics of these technologies (e.g., questions of privacy); however, a gap exists in research toward the general utility or efficacy of ADTs and the data they collect toward solving the problems of refugees or nation-states.
2.3.5. Modeling and forecasting
A third subset of the literature looks at technologies for modeling or forecasting migration projections. These articles focus on artificial intelligence (AI), automation, and big data technologies to process a breadth of data inputs including migration drivers, political variables, social media, etc. Several articles frame these technologies as part of humanitarian and mobility and displacement response programs (Beduschi, 2018; Carammia and Dumont, 2018; Ziebarth and Bither, 2021). Ziebarth and Bither (2021) discuss the Foresight Software developed by the Danish Refugee Council and IBM Research. This machine learning software analyzes historical data from 120 sources and a variety of political, economic, crisis and climate-related variables to predict forced displacement to support humanitarian planning.
Most of the studies concerned with modeling/forecasting migration focus on predicting macro-level migration trends with concern toward humanitarian response and migration management. Azizi and Yektansani (2020) use artificial intelligence to consider the decision-making of individual migrants. The authors are interested in predicting whether an individual from Mexico will live in the United States with or without proper documentation. They conclude that their model would allow a visa application to be approved if, alongside other conditions, they predict the visa applicant will not overstay his or her visa. The AI tested in this paper was claimed to correctly predict 90% of illegalized migration to the United States based on pre-immigration variables alone. The authors note that this study has implications in the context of the United States' implementation of new policies that require additional digital identifying information of all visa applicants including social media and email addresses. It is worth noting that it is unclear the measure or methods used to confirm that the AI correctly predicted with 90% accuracy illegalized migration. Finally, Hoffmann Pham and Luengo-Oroz (2022) examine how machine learning is used to help predict refugee flows while Molina et al. (2022) show how machine learning can be used to study how weather conditions drive migration decisions. Specifically, using supervised machine-learning, the authors discover that weather is related to individual choices about migration.
The focus of research on this theme is primarily speculative and concerned with potential future uses for ADTs. Studies bring up questions of governance, oversight of AI processes, and privacy concerning the data collected (see Ziebarth and Bither, 2021).
2.3.6. Other
Research into technologies that engage with regular migrants before they arrive in the destination country is less prominent in the literature. These technologies include pre-arrival documentation processing and pre-arrival migration support. Technologies for pre-arrival documentation are designed to support the work of immigration authorities to process immigrant documentation and support decision-making. Nalbandian (2022b) evaluates one example of these technologies through an analysis of automated decision-making tools used by Canada's Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada (IRCC) to aid in processing applications through the Temporary Resident Visa stream. Similar automated decision-making technologies have been adopted in the United Kingdom and the European Union (Ziebarth and Bither, 2021). Papademetriou and Collett (2011) provide an earlier discussion of pre-arrival technologies in the context of practices of border externalization.
Technologies for pre-arrival support of migrants often refer to those tools used by various non-profit and government actors to facilitate the arrival and settlement of new migrants. Examples of these technologies include Annie MOORE (Matching and Outcome Optimization for Refugee Empowerment) system that has been piloted in 2018 in the United States, and GeoMatch Algorithm, which was piloted in 2020 in both the United States and Switzerland. These ADTs are developed specifically to facilitate the placement of refugees in communities where they are most likely to find employment (Ziebarth and Bither, 2021). Chatbots are another AI-based technology that are being implemented on immigration websites and visa application portals across Europe (European Migration Network, 2022). Despite the growing usage of various forms of ADT for both pre-arrival support and pre-arrival documentation of migrants, these technologies remain largely undiscussed in migration studies literature.
2.4. Migrants impacted
Our literature review also considered the categories of migrants discussed in the literature. Academic and gray literature has a strong focus on refugees/asylum seekers and illegalized migrants. In contrast, discussion of migrants as a broad category and other categories of migrants (e.g., economic migrant, family sponsorship, and student) were not specifically discussed in many articles.
2.4.1. Refugees/asylum seekers
Literature concerning refugees and asylum seekers was the largest segment of literature focused on specific migrant populations in our review. This literature reflects the geographic scope of the literature, which is primarily focused on Europe and technologies that relate to the refugees and asylum seekers making their way to this region. This focus is also seen as part of the reframing away from migration as risk to the destination country and toward migration as risk to migrants. Conversely, this focus may facilitate the differentiation and privilege of some migrants over others. The literature focused on refugees and asylum seekers is diverse in its focus and concerns various types of ADTs, technology purposes, and the use of different methodologies.
The use of biometric technologies to collect data on refugees and asylum seekers is discussed from different perspectives in the literature. Farraj (2011) and Jacobsen and Sandvik (2018) suggest that these technologies can be beneficial in facilitating access to resources and services. Kaurin (2019) and Molnar (2022) highlight how the requirement of supplying biometric data to receive services is an invasion of privacy and strips these migrants of their agency. Other scholars examine integrated systems that utilize artificial intelligence, big data analysis, cloud computing, and internet of things technologies to coordinate the distribution of services to refugees and asylum seekers (Bansak et al., 2018; Beduschi, 2018; Bock et al., 2020; Bircan and Korkmaz, 2021). These integrated systems address the experiences of refugees in camps, as in the case of the evaluation of the platformization of UNHCR's PRIMES in the Bidi Bidi refugee camp in northern Uganda (see Madon and Schoemaker, 2021), and the optimization of settlement placement of refugees in countries including the United States and Switzerland (see Bansak et al., 2018; Ziebarth and Bither, 2021).
Discussions of ADT use in relation to refugees and asylum seekers frame conversations around both the support and control of these migrants, as well as the other purposes highlighted in the previous section. These conflicting framings reflect the larger discourse around these migrant populations, particularly in Europe. As suggested in the previous section, literature that highlights the support of migrants largely focuses on the facilitation of service provision for these populations, while the migrant control discussion focuses on the asymmetries in power that limit migrant agency. Some of these concerns are elaborated by Madianou (2019), who articulates the concept of technocolonialism to describe how digital innovation and data practices reproduce power asymmetries of humanitarianism through the extraction of value from the data of refugees and other vulnerable people to the benefits of stakeholders. Elsewhere, technologies that focus on modeling or forecasting migration trends are being utilized by humanitarian actors who respond to the needs of these migrants (Ziebarth and Bither, 2021). The subfield of digital migration studies, while outside the scope of our research, also focuses on how refugees and asylum seekers use ADTs for their own agency (Nedelcu and Soysüren, 2022).
2.4.2. Illegalized migrants
Illegalized migrants are another often discussed population in the context of the ADT literature. Unlike refugees and asylum seekers, these migrants are discussed only in the context of migration control and the subtheme of border surveillance, suggesting that while refugees and asylum seekers are migrants deemed worthy of support through the use of ADTs, illegalized migrants are not. However, several articles do not make clear distinctions between these categories of migrants (Molnar, 2022; Soysüren and Nedelcu, 2022), a reference to the complex overlapping nature of these categories, especially in Europe.
Advanced digital technologies that target illegalized migrants cover a range of technology types, but there is a strong association between internet of things (IoT) technologies and the border surveillance of illegalized migrants. Literature at this intersection focuses on drone technology (Csernatoni, 2018) and other surveillance technologies (Chambers et al., 2021). Biometric technologies and integrated systems are also discussed in the literature on illegalized migrants, relationships that bring up similar concerns of agency and privacy to those expressed in the previous section on refugees and asylum seekers.
2.4.3. All migrant groups
A subset of the literature discusses ADTs as they relate to migrants broadly. Much of this literature is descriptive in methodology. These articles describe the nature of ADTs in migration policy rather than reviewing specific empirical research. Authors frame normative arguments about the use of ADTs in migration management (Beduschi, 2018; Molnar, 2022) or speculate on future directions for these1 technologies and scholarship (Carammia and Dumont, 2018).
3. Advanced digital technologies in the migration ecosystem
While technology is being used to support research endeavors into the study of migration, migrants and refugees, our research shows that ADTs are increasingly being implemented to manage migrants and enhance migration processes. To better understand this emerging trend in migration management, we developed an interactive map that situates state and non-state actors' use of ADTs to tackle complex migration challenges—the Migration Tech Tracker (Nalbandian et al., 2022). The Migration Tech Tracker draws on secondary data sources to identify ADTs These sources were gathered through online search of gray literature including press releases and publically accessible reports from state immigration institutions, international organizations, and digital technology firms. The Migration Tech Tracker employs the same scope and taxonomy developed in this paper: AI, automation, big data technologies, biometric technologies, blockchain, cloud computing, and Internet of Things tools. The Migration Tech Tracker captures technologies used for the migration control, border surveillance, port of entry processing, migration support, and modeling and forecasting.
While the focus of this paper is not a complete analysis of the Migration Tech Tracker, a few themes are worth briefly noting. First, the ADTs documented in the Tracker only scratch the surface of actual usage for migration management. Our research process unearthed various vague or incomplete references to ADTs for migration management that were insufficient to include in the tracker. Second, currently a blurry line exists between ADTs for migration management and travel. ADTs used for port-of-entry processing, such as biometrics collection by the US Customs and Border Patrol, collect information from both migrants and short-term travelers. The Migration Tech Tracker focuses on technologies that focus on migrants. Third, transparency on implementation and usage of these technologies is scarce. Most easily accessible information on these ADTs is in the form of press releases documenting the initial launch of these programs and technologies. Finally, research for the Migration Tech Tracker highlights the need for more research into the role of intergovernmental organizations in facilitating the transfer and dissemination of ADTs throughout the Global South.
The data captured in the Tracker reflects the proliferation and use of advanced digital technologies in the migration ecosystem and underpins the importance and value of the research and literature captured in this paper. As reflected in the Tracker as well as this paper—specifically the Sections “2.2” and “2.4”—we have endeavored to strategically “categorize” our assessment of the literature to enable a review that reflects how both technologies and migrants are often categorized by both scholarly and non-scholarly (i.e., government) bodies. The introduction and use of ADTs in the migration ecosystem does not show signs of stopping and therefore, necessitates deep interrogation, analysis, and continued monitoring.
4. Conclusion
This paper provides a summary of recent academic and gray literature on advanced digital technologies (ADTs) used in migration management. We have reviewed literature published between 2010 and 2022 to maintain alignment with the emerging nature of ADTs. The scope of the literature review focuses on Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, big data technologies, blockchain, automation, and biometric technologies. In addition, our literature review, we also briefly highlight a related project, the Migration Tech Tracker, which maps implementation of ADTs for migration management worldwide based on publicly available data.
Much of the literature we reviewed uses a descriptive research method, wherein authors observe and identify characteristics, trends, and relationships in ADTs in migration management. Case studies are also a frequently employed research methodology. Most case studies examine a single case, and the majority of literature, in some way, examines the United States and Europe—likely a result of the large amount of publicly available data on ADT use to manage migration in these regions, and a reflection of the privileging of Global North research in migration studies generally (Triandafyllidou, 2022). Articles focused on migration management in the Global South suggest the use there is largely driven by intergovernmental organizations—many of which frame ADTs positively—raising questions about how intergovernmental organizations make decisions about what technology providers and off-the-shelf systems are appropriate to deploy in vulnerable contexts. Of the literature reviewed, the lack of deep technical analysis of ADTs is noteworthy. A common approach explores ADTs in migration management by engaging a user journey that maps the migrant's journey and interactions with relevant organizations across pre-arrival, border crossing and settlement and integration stages.
While literature engaging experimental methodologies was minimal, it raises questions about whether this will become a bourgeoning area of research as many AI technologies—machine learning, deep learning, predictive technologies, and neural networks—engage big data, and the migration sector is a data-rich space to test and develop experimental technologies. We suggest that further research be conducted to understand the extent and breadth of research on experimental technologies as well as to cloud computing and blockchain—two ADTs for which our research has not yielded significant results. Much of the literature that focuses on biometric technologies does so by examining the ways in which they cause imbalances in power asymmetries between migrants, states, and intergovernmental or non-governmental organizations. There is also great value in analyzing and developing a view of what type of ADTs are used throughout each phase of the migration cycle, as this enables a deeper analysis of areas of priority for state and non-state actors involved in migration governance and offers early insights into what type of tasks technological advancements are geared toward in the migration ecosystem. An example of this view is captured by McAuliffe et al. (2021), which details how AI is used in the migration cycle.
Of the literature reviewed, the majority focused on the use of ADTs to control migrants, often framing migration as criminality or risk. A particularly noteworthy category of migration control is that border surveillance—an area at the intersection of migration management and national security. In contrast, the theme of migrant support is generally less developed in the literature, though, as literature identified and published by states, intergovernmental organizations, or private sector organizations on the use of ADTs for the purpose of migration management is often framed in a positive perspective.
Most of the literature focuses on two populations of migrants: illegalized migrants and refugees/asylum seekers. Some literature discusses migration as a general concept. In considering the categories of migrants impacted by ADTs, little has been written about specific classes of regular migrants, including economic migrants, family sponsorship migrants, and student migrants. Empirical research, including experimental and ethnographic research, on specific categories of regular migrants is understudied in the literature. Nalbandian (2021) provides one example of research into an ADT specifically targeting economic migrants. A descriptive case study, this paper looks at the role of AI and machine learning in Canada's Temporary Resident Visa Application process.
In addition to those mentioned in the preceding paragraphs, we identify several gaps in the literature. The involvement of actors and their relationship to ADTs and migration management could be further explored. As an example, micro-level analysis of the use of ADTs by policymakers and street-level bureaucrats is absent from the literature. Additional empirical qualitative and ethnographic research should be conducted to see how these technologies are engaged with and understood by these actors. More research should also focus on specific categories of regular migrants impacted by ADTs. Following Taylor and Meissner's (2020) suggestion that the use of ADTs for migration management represents a market opportunity, more research should empirically explore the introduction of new corporate actors (i.e., technology companies) in migration governance.
There is a lack of technical depth to the research on ADTs. More interdisciplinary work including collaboration between information scientists and engineers with social scientists and policy experts should be prioritized to gain a deeper understanding of the technical specifications and impacts of these technologies on varied fronts.
The critical literature generally has a negative perception of the uses of ADTs for migration management. Critical work should also engage in speculative uses of ADTs for migration management that are positive, support migrants through their journey while striking the appropriate balance for privacy and security and explore the preconditions of these uses. Our literature review did not incorporate literature on the agency of migrants enacted through information and communication technologies, literature that Nedelcu and Soysüren (2022) refer to as digital migration studies. We leave review and analysis of this literature for a future paper. In addition, we suggest a deeper theoretical exploration of the literature with a focus on asymmetries of power in the implementation of these technologies and the use of Foucauldian concepts of biopower and biopolitics, both of which are recurring themes in the literature we reviewed. Awad and Tossell (2021) suggest that academic literature assumes the general utility of smartphones for refugees and their work seeks to challenge this premise. Similarly, in a discussion of migration management technologies, the focus of this literature review, critical literature tends to focus on the ethics of these technologies (questions of privacy, etc.); however, a gap exists in research on the general utility or efficacy of these ADTs and the data they collect toward solving the problems of migrants or nation-states.
The use of ADTs for migration management is a rapidly growing and evolving space, and research into this field is emergent. Researchers from various disciplines can engage in this space and there is significant potential and need for interdisciplinary collaboration. Additionally, there is a need for informed policymaking to understand the implications and potential of the use of ADTs on the efficacy of migration management as well as the human rights and privacy of migrants. This working paper has presented the current state of the field as well as gaps toward which researchers and policymakers should focus their attention.
Author contributions
The authors contributed equally to this work and the order in which they are presented is to delineate the first point of contact for inquiries related to this paper.
Acknowledgments
This paper develops previous research published in a working paper as part of the Working Papers Series produced jointly by the Toronto Metropolitan Center for Immigration and Settlement (TMCIS) and the CERC in Migration and Integration at Toronto Metropolitan University. Working Papers present scholarly research of all disciplines on issues related to immigration and settlement. The purpose is to stimulate discussion and collect feedback. For further information, visit www.torontomu.ca/centre-for-immigration-and-settlement and www.torontomu.ca/cerc-migration. The Migration Tech Tracker referenced in this paper is an interactive tool developed by Amasia Nalbandian for the CERC in Migration and Integration at Toronto Metropolitan University. The research reflected in the Migration Tech Tracker was collected and synthesized by the authors. The details of the cases captured in the Tech Tracker are subject to change, as the tool itself is intended to be a live and regularly updated inventory of emerging and ever-changing cases of advanced digital technology use cases in the migration ecosystem. This work was supported by the Canada Excellence Research Chair for Migration and Integration, Toronto Metropolitan University, ON, Canada.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Author disclaimer
The views expressed by the authors do not necessarily reflect those of TMCIS or CERC Migration and Integration.
Footnotes
1. ^Migration Tech Tracker: https://www.torontomu.ca/cerc-migration/research/data-and-methods-lab/migration-tech-tracker/.
References
Amoore, L. (2013). The Politics of Possibility: Risk and Security Beyond Probability. Durham, NC: Duke University Press.
Awad, I., and Tossell, J. (2021). Is the smartphone always a smart choice? Against the utilitarian view of the ‘connected migrant.' Inform. Commun. Soc. 24, 611–626. doi: 10.1080/1369118X.2019.1668456
Azizi, S., and Yektansani, K. (2020). Artificial intelligence and predicting illegal immigration to the USA. Int. Migr. 58, 183–193. doi: 10.1111/imig.12695
Bansak, K., Ferwerda, J., Hainmueller, J., Dillon, A., Hangartner, D., Lawrence, D., et al. (2018). Improving refugee integration through data-driven algorithmic assignment. Science 359, 325–329. doi: 10.1126/science.aao4408
Bauder, H. (2014). Why we should use the term ‘illegalized' refugee or immigrant: a commentary. Int. J. Refugee Law 26, 327–332. doi: 10.1093/ijrl/eeu032
Beduschi, A. (2018). The big data of international migration: opportunities and challenges for states under international human rights law. Big Data 49, 37.
Beduschi, A., and McAuliffe, M. (2022). 11 Artificial intelligence, migration and mobility: implications for policy and practice. World Migr. Rep. 2022, 32. doi: 10.1002/wom3.32
Bircan, T., and Korkmaz, E. E. (2021). Big data for whose sake? Governing migration through artificial intelligence. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 8, 1–5. doi: 10.1057/s41599-021-00910-x
Bock, J. G., Haque, Z., and McMahon, K. A. (2020). Displaced and dismayed: how ICTs are helping refugees and migrants, and how we can do better. Inform. Technol. Dev. 26, 670–691. doi: 10.1080/02681102.2020.1727827
Cameron, H. E., Goldfarb, A., and Morris, L. (2022). Artificial intelligence for a reduction of false denials in refugee claims. J. Refugee Stud. 35, 493–510. doi: 10.1093/jrs/feab054
Carammia, M., and Dumont, J. (2018). Can We Anticipate Future Migration Flows? (No. 16), OECD Migration Policy Debates. Paris: OECD.
Chambers, S. N., Boyce, G. A., Launius, S., and Dinsmore, A. (2021). Mortality, surveillance and the tertiary “funnel effect” on the U.S.-Mexico border: a geospatial modeling of the geography of deterrence. J. Borderl. Stud. 36, 443–468. doi: 10.1080/08865655.2019.1570861
Cholakian, H. (2018). Computers over concrete: how technology will revamp immigration and security systems. Harvard Int. Rev. 39, 26–29.
Csernatoni, R. (2018). Constructing the EU's high-tech borders: FRONTEX and dual-use drones for border management. Eur. Secur. 27, 175–200. doi: 10.1080/09662839.2018.1481396
Donko, K., Doevenspeck, M., and Beisel, U. (2022). Migration control, the local economy and violence in the Burkina Faso and Niger Borderland. J. Borderl. Stud. 37, 235–251. doi: 10.1080/08865655.2021.1997629
Engbersen, G., and van der Leun, J. (2001). The social construction of illegality and criminality. Eur. J. Crim. Policy Res. 9, 51–70. doi: 10.1023/A:1011259422222
Ennaji, M., and Bignami, F. (2019). Logistical tools for refugees and undocumented migrants: smartphones and social media in the city of Fès. Work Organ. Labour Glob. 13, 62–78. doi: 10.13169/workorgalaboglob.13.1.0062
European Migration Network (2022). The Use of Digitalisation and Artificial Intelligence in Migration Management [ENM-OECD Inform]. European Commission.
Farraj, A. (2011). Refugees and the biometric future: the impact of biometrics on refugees and asylum seekers [Data set]. Columb. Hum. Rights Law Rev. 42, 891–942.
Franco, T. (2020). The war on immigration in the age of big data and artificial intelligence. Harvard J. Hispanic Policy 32, 77–84.
Georgiou, M. (2018). Does the subaltern speak? Migrant voices in digital Europe. Popular Commun. 16, 45–57. doi: 10.1080/15405702.2017.1412440
Gesellschaft für Freiheitsrechte (2020). Race, Borders, and Digital Technology: Submission to the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights on the Reinforcing, Reproductive and Compounding Effects of the Deployment of Digital Technologies in the Context of Border Enforcement and Administration. United Nations Office of the High Commissioner of Human Rights. Available online at: https://www.ohchr.org/sites/default/files/Documents/Issues/Racism/SR/RaceBordersDigitalTechnologies/Gesellschaft_fur_Freiheitsrechte.pdf (accessed November 1, 2023).
Goldstein, D. M., and Alonso-Bejarano, C. (2017). E-Terrify: securitized immigration and biometric surveillance in the workplace. Hum. Org. 76, 1–14. doi: 10.17730/0018-7259.76.1.1
Hoffmann Pham, K., and Luengo-Oroz, M. (2022). Predictive modelling of movements of refugees and internally displaced people: towards a computational framework. J. Ethnic Migr. Stud. 49, 408–444. doi: 10.1080/1369183X.2022.2100546
Irani, L. (2015). Hackathons and the making of entrepreneurial citizenship. Sci. Technol. Human Values 40, 799–824. doi: 10.1177/0162243915578486
Israel, T. (2020). Facial Recognition at a Crossroads: Transformation at our Borders and Beyond. Samuelson-Glushko Canadian Internet Policy & Public Interest Clinic (CIPPIC), Ottawa, ON, Canada.
Jacobsen, K. L., and Sandvik, K. B. (2018). UNHCR and the pursuit of international protection: accountability through technology? Third World Quart. 39, 1508–1524. doi: 10.1080/01436597.2018.1432346
Jumbert, M. G. (2016). “Creating the EU drone control, sorting, and search and rescue at sea,” in The Good Drone Emerging Technologies, Ethics and International Affairs, eds K. B. Sandvik and M. G. Jumbert (London: Routledge), 89–109.
Kaurin, D. (2019). Data Protection and Digital Agency for Refugees (No. 12), World Refugee Council Research Paper. Centre for International Governance Innovation, Waterloo, ON, Canada.
Kissau, K., and Hunger, U. (2008). Political online-participation of migrants in Germany. Ger. Policy Stud. 4, 5–31.
Koca, B. T. (2022). Bordering processes through the use of technology: the Turkish case. J. Ethnic Migr. Stud. 48, 1909–1926. doi: 10.1080/1369183X.2020.1796272
Madianou, M. (2019). Technocolonialism: digital innovation and data practices in the humanitarian response to refugee crises. Soc. Media Society 5, 146. doi: 10.1177/2056305119863146
Madon, S., and Schoemaker, E. (2021). Digital identity as a platform for improving refugee management. Inform. Syst. J. 31, 929–953. doi: 10.1111/isj.12353
Majcher, I. (2022). The Schengen-wide entry ban: How are non-citizens' personal data protected? J. Ethnic Migr. Stud. 48, 1944–1960. doi: 10.1080/1369183X.2020.1796279
Marin, L., and Krajčíková, K. (2016). “Deploying drones in policing southern European borders: constraints and challenges for data protection and human rights,” in Drones and Unmanned Aerial Systems, eds A. Završnik (Springer International Publishing), 101–127.
McAuliffe, M., Blower, J., and Beduschi, A. (2021). Digitalization and artificial intelligence in migration and mobility: transnational implications of the COVID-19 pandemic. Societies 11, 135–148. doi: 10.3390/soc11040135
McCarroll, E. (2020). Weapons of mass deportation: big data and automated decision-making systems in immigration law. Georgetown Immigr. Law J. 34, 705–731.
Mitra, A. (2005). Creating immigrant identities in cybernetic space: examples from a non-resident Indian website. Media Cult. Soc. 27, 371–390. doi: 10.1177/0163443705051749
Molina, M., Rodewald, A. D., and Garip, F. (2022). How to model the weather-migration link: a machine-learning approach to variable selection in the Mexico-U.S. context. J. Ethnic Migr. Stud. 49, 1–27. doi: 10.1080/1369183X.2022.2100549
Molnar, P. (2022). “Territorial and digital borders and migrant vulnerability under a pandemic crisis,” in Migration and Pandemics: Spaces of Solidarity and Spaces of Exception, eds A. Triandafyllidou (Springer International Publishing), 45–64.
Molnar, P., and Gill, L. (2018). Bots at the Gate: A Human Rights Analysis of Automated Decision-Making in Canada's Immigration and Refugee System. University of Toronto's International Human Rights Program (IHRP) at the Faculty of Law and the Citizen Lab at the Munk School of Global Affairs and Public Policy, Toronto, ON.
Nalbandian, L. (2021). Using Machine-Learning to Triage Canada's Temporary Resident Visa Applications. TMCIS-CERC Working Paper Series, TMCIS-CERC Working Paper Series 2021, 20.
Nalbandian, L. (2022a). An eye for an ‘I:' a critical assessment of artificial intelligence tools in migration and asylum management. CMS 10, 32. doi: 10.1186/s40878-022-00305-0
Nalbandian, L. (2022b). Increasing the accountability of automated decision-making systems: an assessment of the automated decision-making system introduced in Canada's temporary resident visa immigration stream. J. Respons. Technol. 10, 100023. doi: 10.1016/j.jrt.2021.100023
Nalbandian, L., Dreher, N., and Nalbandian, A. (2022). Migration Tech Tracker. Toronto Metropolitan University. Available online at: https://www.torontomu.ca/cerc-migration/data-and-methods-lab/migration-tech-tracker (accessed November 1, 2023).
Nedelcu, M. (2018). “Digital diasporas,” in Handbook of Diaspora Studies, eds C. Fischer and R. Cohen (London: Routledge), 241–250.
Nedelcu, M., and Soysüren, I. (2022). Precarious migrants, migration regimes and digital technologies: the empowerment-control nexus. J. Ethnic Migr. Stud. 48, 1821–1837. doi: 10.1080/1369183X.2020.1796263
Noori, S. (2022). Navigating the Aegean Sea: smartphones, transnational activism and viapolitical in(ter)ventions in contested maritime borderzones. J. Ethn. Migr. Stud. 48, 1856–1872. doi: 10.1080/1369183X.2020.1796265
Papademetriou, D. G., and Collett, E. (2011). A New Architecture for Border Management. Migration Policy Institute.
Petridi, C. (2021). Greek Camps for Asylum Seekers to Introduce Partly Automated Surveillance Systems. AlgorithmWatch. Available online at: https://algorithmwatch.org/en/greek-camps-surveillance/ (accessed November 1, 2023).
Şanlıer Yüksel, I. (2022). Empowering experiences of digitally mediated flows of information for connected migrants on the move. J. Ethn. Migr. Stud. 48, 1838–1855. doi: 10.1080/1369183X.2020.1796264
Schmidt, N, and Stephens, B. (2019). An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence and Solutions to the Problems of Algorithmic Discrimination. Cornell University: Computers and Society, 130–144.
Singler, S. (2021). Biometric statehood, transnational solutionism and security devices: the performative dimensions of the IOM's MIDAS. Theoret. Criminol. 25, 454–473. doi: 10.1177/13624806211031245
Soysüren, I., and Nedelcu, M. (2022). European instruments for the deportation of foreigners and their uses by France and Switzerland: the application of the Dublin III Regulation and Eurodac. J. Ethn. Migr. Stud. 48, 1927–1943. doi: 10.1080/1369183X.2020.1796278
Syrett, S., and Keles, J. Y. (2019). Diasporas, agency and enterprise in settlement and homeland contexts: Politicised entrepreneurship in the Kurdish diaspora. Political Geogr. 73, 60–69. doi: 10.1016/j.polgeo.2019.05.008
Taylor, L. (2016). No place to hide? The ethics and analytics of tracking mobility using mobile phone data. Environ. Plann. D Soc. Space 34, 319–336. doi: 10.1177/0263775815608851
Taylor, L., and Meissner, F. (2020). A crisis of opportunity: market-making, big data, and the consolidation of migration as risk. Antipode 52, 270–290. doi: 10.1111/anti.12583
Triandafyllidou, A. (2022). Decentering the study of migration governance: a radical view. Geopolitics 27, 811–825. doi: 10.1080/14650045.2020.1839052
Williams, A.M., and BaláŽ, V. (2012). Migration, risk, and uncertainty: theoretical perspectives. Popul. Space Place 18, 167–180. doi: 10.1002/psp.663
Keywords: migration management, advanced digital technology, migration control, migration support, migrants, refugees, mobility, technology
Citation: Nalbandian L and Dreher N (2023) Current methodological approaches in studying the use of advanced digital technologies in migration management. Front. Hum. Dyn. 5:1238605. doi: 10.3389/fhumd.2023.1238605
Received: 12 June 2023; Accepted: 24 October 2023;
Published: 14 November 2023.
Edited by:
Haodong Qi, Malmö University, SwedenReviewed by:
Liliana Lyra Jubilut, Universidade Católica de Santos, BrazilSyeda Naushin, University of Malaya, Malaysia
Copyright © 2023 Nalbandian and Dreher. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lucia Nalbandian, bC5uYWxiYW5kaWFuQG1haWwudXRvcm9udG8uY2E=
 Lucia Nalbandian
Lucia Nalbandian Nick Dreher
Nick Dreher