- 1Department Anesthesiology, Perioperative and Pain Medicine, Stanford University School of Medicine, Palo Alto, CA, United States
- 2Department of Family, Community and Preventive Medicine, University of Arizona College of Medicine-Phoenix, Phoenix, AZ, United States
- 3Phoenix VA Health Care System, Phoenix, AZ, United States
- 4Division of Primary Care and Population Health, Department of Medicine, Stanford University School of Medicine, Palo Alto, CA, United States
- 5Division of Primary, Preventive, and Community Care, Stanford University School of Medicine, Palo Alto, CA, United States
- 6Phoenix VA Health Care System, Department of Psychiatry, University of Arizona College of Medicine-Phoenix, Phoenix, AZ, United States
- 7Department of Population Health, Section on Tobacco, Alcohol, and Drug Use, New York University School of Medicine, New York, NY, United States
- 8Intermountain Healthcare, Family Medicine, Layton, UT, United States
- 9Friends Research Institute, Baltimore, MD, United States
- 10Private Practitioner, Englewood, CO, United States
Growing concerns about the safety of long-term opioid therapy and its uncertain efficacy for non-cancer pain have led to relatively rapid opioid deprescribing in chronic pain patients who have been taking opioid for years. To date, empirically supported processes for safe and effective opioid tapering are lacking. Opioid tapering programs have shown high rates of dropouts and increases in patient distress and suicidal ideation. Therefore, safe strategies for opioid deprescribing that are more likely to succeed are urgently needed. In response to this demand, the EMPOWER study has been launched to examine the effectiveness of behavioral medicine strategies within the context of patient-centered opioid tapering in outpatient settings (https://empower.stanford.edu/). The EMPOWER protocol requires an efficient process for ensuring that collaborative opioid tapering would be offered to the most appropriate patients while identifying patients who should be offered alternate treatment pathways. As a first step, clinicians need a screening tool to identify patients with Opioid Use Disorder (OUD) and to assess for OUD severity. Because such a tool is not available, the study team composed of eight chronic pain and/or addiction experts has extended a validated screening instrument to develop a brief and novel consensus screening tool to identify OUD and assess for OUD severity for treatment stratification. Our screening tool has the potential to assist busy outpatient clinicians to assess OUD among patients receiving long-term opioid therapy for chronic pain.
Growing concerns about adverse effects and potential harms associated with long-term opioid use combined with lack of effectiveness data (1–3) have led national and state organizations to recommend reducing initiation of opioid medications for chronic pain (4, 5), and in some cases to impose mandated tapering (6, 7). To date, empirically supported processes for effective outpatient opioid tapering are lacking, potentially contributing to high rates of patient attrition (~ 53.3%) (8, 9) and seeking other sources of opioids (10). While the literature remains nascent, a pilot study has demonstrated that prescribing physicians can help patients reduce opioid dose by about 50%, without an increase in pain intensity, by using a slow and individualized tapering method at outpatient settings (11). Intensive interdisciplinary programs (12) may be appropriate to reduce opioid medications for patients who have more medical or psychiatric complexity, although access to these programs is notably limited. Furthermore, clinical practice guidelines recommend that prescribing physicians routinely assess patients on long-term opioid therapy for opioid use disorder (OUD) (4). According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM)-5, OUD is defined as a cluster of cognitive, behavioral, and physiological symptoms indicating that the individual continues using the substance despite significant substance-related problems (13) and exists on a continuum of severity (mild, moderate, and severe) (13). For patients with a diagnosis of OUD, particularly moderate-severe OUD, medication for addiction treatment (MAT) is recommended rather than opioid tapering (14, 15). Therefore, deprescribing approaches need to be tailored to an individual patient to optimize the likelihood of successful reduction.
One challenge in assessing OUD and its severity is that the American Psychiatric Association's DSM has modified various diagnostic terms over the years to define the spectrum of problematic opioid use. Historically, DSM-III (16) and DSM-IV (17) used two distinct diagnostic categories to describe problematic opioid use: abuse and dependence. The DSM-IV diagnostic term of abuse is defined by “a maladaptive pattern of substance use manifested by recurrent and significant adverse consequences related to the repeated use of substances,” and the definition of dependence is the same as that of OUD in DSM-5 (13). In contrast to the diagnoses of abuse and dependence in the DSM-IV, the DSM-5 has adopted a dimensional approach (18) in which OUD is now diagnosed along a continuum of mild, moderate and severe. This change requires clinicians to understand both the current and previous diagnostic classification systems as well as the degree of concordance between the two systems because cumulative data for evidence-based addiction treatment have been derived from the previous systems (19, 20) and new treatment studies and recommendations use the current version of DSM. Studies show that patients with DSM-5 moderate or severe OUD have a high degree of concordance with DSM-IV opioid dependence. Specifically, DSM-5 moderate to severe OUD yields 99% sensitivity and 99% positive predictive value (PPV) for DSM-IV opioid dependence (21). In contrast, only 18% of patients with mild OUD meet criteria for DSM-IV opioid dependence (21). As such, clinicians using a binary diagnostic approach (yes vs. no) for OUD will be limited in offering optimal treatments for diverse patients on long-term opioid therapy. Therefore, accurate and scalable systems to identify OUD and assess for OUD severity are critical for treatment stratification, but no such system or screening tool is currently available (22).
Development of the EMPOWER Study Expert Consensus Protocol for OUD Screening
The EMPOWER study team first searched for a screening tool to identify OUD by severity categories when preparing to launch a study to investigate the effectiveness of behavioral medicine strategies within the context of patient-centered opioid tapering in outpatient settings (23). Our search yielded several self-report instruments that were validated and widely used to assess prescription opioid misuse and aberrant drug-taking behaviors such as the Current Opioid Misuse Measure (24), Pain Medication Questionnaire (25), and Prescription Opioid Misuse Index (26). There are also self-reports to screen for opioid abuse or dependence such as the NIDA-modified ASSIST (27), Drug Abuse Screening Test (28), Prescription Opioid Abuse Checklist (29), Prescription Drug Use Questionnaire (30), Addiction Behavior Checklist (31), and Rapid Opioid Dependence Screen (32). These existing tools intended for use in patients receiving long-term opioid therapy for chronic pain aim to identify opioid aberrant medication-related behavior, misuse, abuse, or dependence and either suffer from intolerably low sensitivity or are too lengthy for practical use in primary care settings with high patient volumes (33, 34). More importantly, these tools do not provide OUD severity for treatment stratification. After determining the lack of existing suitable tools, the EMPOWER study team decided to develop an efficient and scalable tool to assess OUD severity and identify the most appropriate care pathway.
When launching the EMPOWER study, the study team recognized that opioid tapering is not right for everyone. Patients with moderate or severe symptoms of OUD may be ill-suited to outpatient tapering and require different care pathways (14, 15). To identify OUD and assess OUD severity, the study team identified two candidate tools: the Tobacco, Alcohol, Prescription Medication, and Other Substance use (TAPS-1 and 2) (35) and DSM-5 OUD criteria (13). The TAPS-1 and−2 were developed to screen for a problematic use of alcohol, tobacco, and other substances in patients visiting primary care clinics. The TAPS uses a two-step screening process (35). In the first step, the four-item TAPS-1 is administered to all patients and screens for the use of four substance types in the past 12 months. Then, the appropriate items on TAPS-2 assessing the use of each substance in the past 3 months are administered to those who endorse other than “never” response on the TAPS-1 items. The TAPS has acceptable sensitivity (>0.70) and specificity (>0.85) when screening for problematic use of tobacco, alcohol and marijuana, but unacceptably low sensitivity (0.48) when screening for OUD specific to prescription opioid use (35). Alternatively, clinicians may use the 11 criteria for OUD defined by the DSM-5 OUD (13). Yet, the DSM-5 criteria are rarely used to assess OUD (36) because it is not practical to conduct the clinical interview for every patient on long-term opioid therapy in a busy clinic.
The EMPOWER Consensus Protocol for OUD Screening and Treatment Stratification
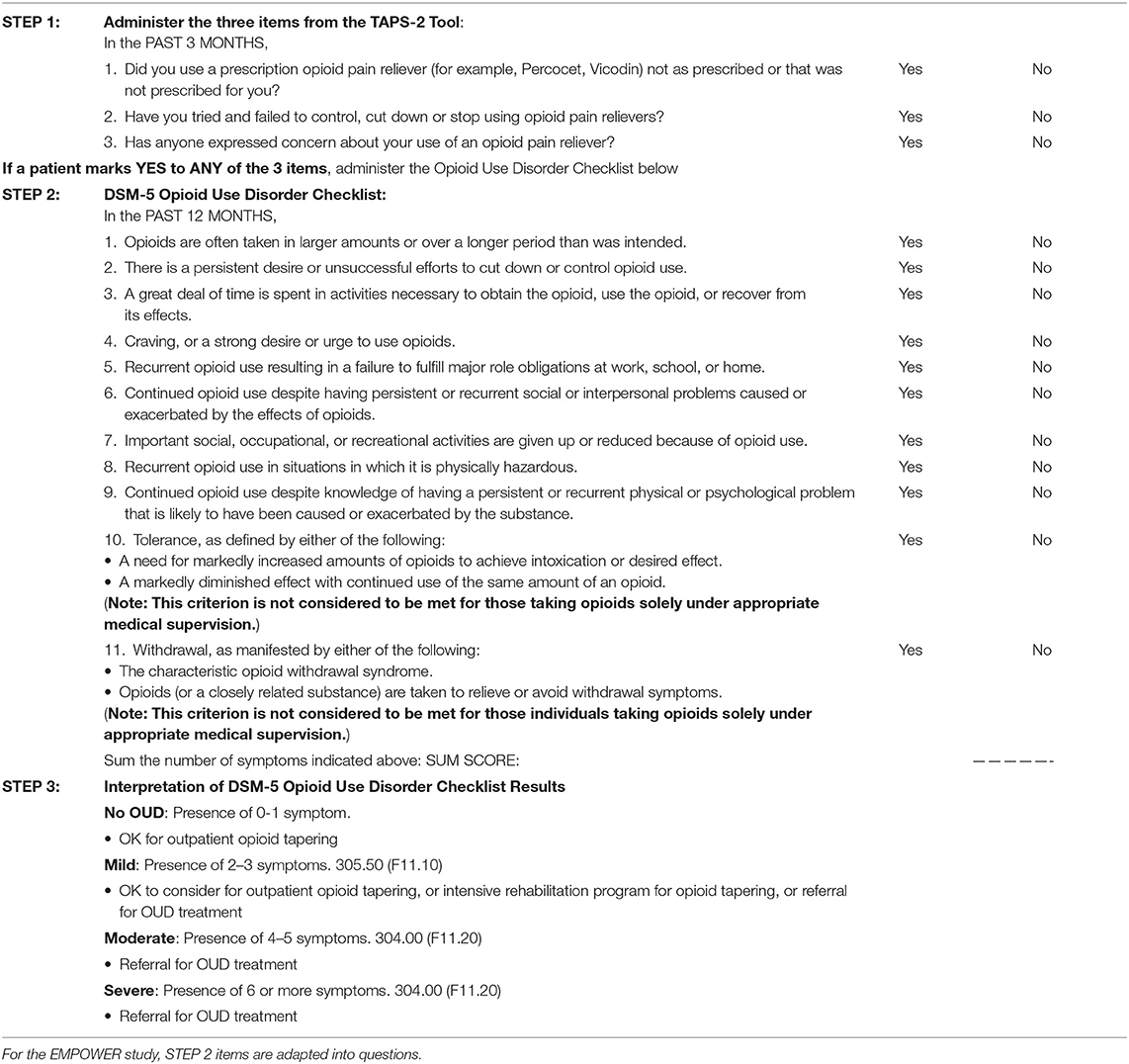
The EMPOWER study team composed of eight chronic pain and/or addiction experts developed a novel consensus protocol to identify OUD and assess for OUD severity in patients taking long-term prescription opioids for chronic pain. The study team modified the two-step process used in the TAPS. To increase sensitivity, the team, in collaboration with the authors of TAPS (35), decided to use all three opioid items in the TAPS-2 as initial screening items, instead of using the TAPS-1. Next, to optimize specificity and assess for OUD severity, the DSM-5 OUD criteria were used in the form of a checklist. Therefore, the EMPOWER consensus protocol for screening and distinguishing severity of OUD includes (Table 1): (Step 1) all three opioid items from the TAPS-2 and (Step 2) the DSM-5 Criteria Checklist for OUD to (Step 3) stratify the severity of OUD. Step 1 can be self-administered in a paper format to all patients on opioid therapy. Based on patients' responses on Step 1, a clinician completes the checklist during the in-person clinical interview only with those endorsing any of the 3 screening items (Step 2).
The opioid-prescribing clinician has historical knowledge of the opioid and other drug taking behavior of their patients; this, combined with the medical record and prescription drug monitoring databases, can serve as collateral information in determining a diagnosis and its corresponding severity. Clinicians are reminded of the caveat for tolerance and withdrawal symptoms in Table 1, Step 2. These two underlined items are not considered criteria for OUD when opioids are taken as prescribed; rather, tolerance and withdrawal symptoms are indices of expected normal physiologic adaptation to persistent opioid use, which is distinct from addiction or opioid use disorder.
Strength and Limitations of the EMPOWER Study Expert Consensus Protocol
In the absence of existing validated methods, we provide our consensus screening protocol in response to the urgent societal need for such tools so that (a) clinicians may offer appropriate treatments to a heterogeneous patient population receiving long-term opioid therapy for chronic pain (Table 1, Step 3), and (b) researchers can study characteristics and treatment outcomes of patients with appropriate opioid use and across the spectrum of OUD severity. Our screening protocol can also facilitate efficient evaluation of eligibility for our multi-site pragmatic study of patient-centered opioid tapering (23). We are currently investigating the validity and reliability of administrating our protocol in an electronic format using an open-source learning healthcare system (https://choir.stanford.edu/). Additionally, we will examine data for patients who are screened as having no or mild OUD severity using our two-step protocol and will characterize their opioid taper and pain reduction outcomes.
Achieving optimal results for prescription opioid tapering requires careful assessment of patients and their opioid-taking behaviors because such assessment ensures that effective individualized opioid tapering or opioid addiction treatments are delivered to patients according to their individual needs. The EMPOWER study team found a gap in existing approaches for practical, individualized opioid deprescribing due to the lack of a brief tool to identify OUD and stratify severity for patients with chronic pain receiving long-term opioid therapy. Our study team has developed a streamlined consensus protocol to identify OUD and assess for OUD severity for clinical and research use.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Author Contributions
DY: conceptualization, writing—original draft, review, and editing. AM: conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft, and review and editing. BD: conceptualization, methodology, writing—review and editing, and project administration. C-YC, KD, PF, AK, JM, JP, RPS, and RLS: conceptualization, methodology, writing—review and editing. M-CK: conceptualization and methodology. SM: conceptualization, methodology, writing—review and editing, project administration, and supervision. All authors: contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
This work was supported through a Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) Award (OPD-1610-37007) (PI, BD). All statements in this report are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the views of the PCORI, its Board of Governors or Methodology Committee. DY (K23 DA048972) and SM (K24DA029262) received funding from the National Institute on Drug Abuse. SM also received Redlich Pain Endowment.
Conflict of Interest
RPS reports serving as a consultant to Verily Life Sciences, Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
1. Glanz JM, Binswanger IA, Shetterly SM, Narwaney KJ, Xu S. Association between opioid dose variability and opioid overdose among adults prescribed long-term opioid therapy. JAMA Netw Open. (2019) 2:e192613. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.2613
2. Chou R, Turner JA, Devine EB, Hansen RN, Sullivan SD, Blazina I, et al. The effectiveness and risks of long-term opioid therapy for chronic pain: a systematic review for a National Institutes of Health Pathways to Prevention Workshop. Ann Intern Med. (2015) 162:276–86. doi: 10.7326/M14-2559
3. Hoffman EM, Watson JC, St Sauver J, Staff NP, Klein CJ. Association of long-term opioid therapy with functional status, adverse outcomes, and mortality among patients with polyneuropathy. JAMA Neurol. (2017) 74:773–9. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2017.0486
4. Dowell D, Haegerich TM, Chou R. CDC guideline for prescribing opioids for chronic pain -United States, 2016. JAMA. (2016) 315:1624–45. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.1464
5. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. HHS guide for clinicians on the appropriate dosage reduction or discontinuation of long-term opioid analgesics. Available online at: https://www.hhs.gov/opioids/sites/default/files/2019-10/Dosage_Reduction_Discontinuation.pdf Published October (2019) (accessed June 25, 2020).
6. Oregon Health Authority. Guideline note 60: opioid prescribing for conditions of the back and spine. prioritized list of health services. Available online at: https://www.oregon.gov/oha/HPA/DSI-HERC/PrioritizedList/7-1-2016_Prioritized_List_of_Health_Services.pdf (accessed June 25, 2020).
7. Kertesz SG, Satel SL, DeMicco J, Dart RC, Alford DP. Opioid discontinuation as an institutional mandate: questions and answers on why we wrote to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Subst Abus. (2019) 40:466–8. doi: 10.1080/08897077.2019.1635973
8. Kurita G, Højsted J, Sjøgren P. Tapering off long-term opioid therapy in chronic non-cancer pain patients: a randomized clinical trial. Eur J Pain. (2018) 22:1528–43. doi: 10.1002/ejp.1241
9. Fiellin DA, Schottenfeld RS, Cutter CJ, Moore BA, Barry DT, O'Connor PG. Primary care–based buprenorphine taper vs maintenance therapy for prescription opioid dependence: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med. (2014) 174:1947–54. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2014.5302
10. Manhapra A, Arias AJ, Ballantyne JC. The conundrum of opioid tapering in long-term opioid therapy for chronic pain: a commentary. Subst Abus. (2018) 39:152–61. doi: 10.1080/08897077.2017.1381663
11. Darnall BD, Ziadni MS, Stieg RL, Mackey IG, Kao M-C, Flood P. Patient-centered prescription opioid tapering in community outpatients with chronic pain. JAMA Intern Med. (2018) 178:707–8. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2017.8709
12. Cunningham JL, Evans MM, King SM, Gehin JM, Loukianova LL. Opioid tapering in fibromyalgia patients: experience from an interdisciplinary pain rehabilitation program. Pain Med. (2016) 17:1676–85. doi: 10.1093/pm/pnv079
13. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Association (2013).
14. Kampman K, Jarvis M. American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM) national practice guideline for the use of medications in the treatment of addiction involving opioid use. J Addict Med. (2015) 9:358–67. doi: 10.1097/ADM.0000000000000166
15. Oesterle TS, Thusius NJ, Rummans TA, Gold MS. Medication-assisted treatment for opioid-use disorder. Mayo Clin Proc. (2019) 94:2072–86. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2019.03.029
16. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 3rd ed. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Association (1980).
17. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association (1994).
18. Narrow WE, Kuhl EA. Dimensional approaches to psychiatric diagnosis in DSM-5. J Ment Health Policy Econ. (2011) 14:197–200.
19. Mattick RP, Breen C, Kimber J, Davoli M. Methadone maintenance therapy versus no opioid replacement therapy for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2009) 3:CD002209. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002209.pub2
20. Mattick RP, Breen C, Kimber J, Davoli M. Buprenorphine maintenance versus placebo or methadone maintenance for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2014) 2:CD002207. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002207.pub4
21. Peer K, Rennert L, Lynch KG, Farrer L, Gelernter J, Kranzler HR. Prevalence of DSM-IV and DSM-5 alcohol, cocaine, opioid, and cannabis use disorders in a largely substance dependent sample. Drug Alcohol Depend. (2013) 127:215–9. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2012.07.009
22. Wakeman SE. Diagnosis and treatment of opioid use disorder in 2020. JAMA. (2020) 323:2082–3. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.4104
23. Darnall BD, Mackey SC, Lorig K, ao M-C, Mardian A, Stieg R, et al. Comparative effectiveness of cognitive behavioral therapy for chronic pain and chronic pain self-management within the context of voluntary patient-centered prescription opioid tapering: the empower study protocol. Pain Med. (2019) 21:1523–31. doi: 10.1093/pm/pnz285
24. Butler SF, Budman SH, Fernandez KC, Houle B, Benoit C, Katz N, et al. Development and validation of the current opioid misuse measure. Pain. (2007) 130:144–56. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2007.01.014
25. Holmes CP, Gatchel RJ, Adams LL, Stowell AW, Hatten A, Noe C, et al. An opioid screening instrument: long-term evaluation of the utility of the pain medication questionnaire. Pain Pract. (2006) 6:74–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1533-2500.2006.00067.x
26. Knisely JS, Wunsch MJ, Cropsey KL, Campbell ED. Prescription Opioid Misuse Index: a brief questionnaire to assess misuse. J Subst Abuse Treat. (2008) 35:380–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat.2008.02.001
27. National Institute on Drug Abuse. NIDA-modified ASSIST V2.0. 2013. The survey is available online at: https://www.drugabuse.gov/sites/default/files/pdf/nmassist.pdf (accessed July 03, 2021).
28. Yudko E, Lozhkina O, Fouts A. A comprehensive review of the psychometric properties of the drug abuse screening test. J Subst Abuse Treat. (2007) 32:189–98. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat.2006.08.002
29. Chabal C, Erjavec MK, Jacobson L, Mariano A, Chaney E. Prescription opiate abuse in chronic pain patients: clinical criteria, incidence, and predictors. Clin J Pain. (1997) 13:150–5. doi: 10.1097/00002508-199706000-00009
30. Compton PA, Wu SM, Schieffer B, Pham Q, Naliboff BD. Introduction of a self-report version of the Prescription Drug Use Questionnaire and relationship to medication agreement noncompliance. J Pain Symptom Manage. (2008) 36:383–95. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2007.11.006
31. Wu SM, Compton P, Bolus R, Schieffer B, Pham Q, Baria A, et al. The addiction behaviors checklist: validation of a new clinician-based measure of inappropriate opioid use in chronic pain. J Pain Symptom Manage. (2006) 32:342–51. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2006.05.010
32. Wickersham JA, Azar MM, Cannon CM, Altice FL, Springer SA. Validation of a brief measure of opioid dependence: the Rapid Opioid Dependence Screen (RODS). J Correctional Health Care. (2015) 21:12–26. doi: 10.1177/1078345814557513
33. Moore TM, Jones T, Browder JH, Daffron S, Passik SD. A comparison of common screening methods for predicting aberrant drug-related behavior among patients receiving opioids for chronic pain management. Pain Med. (2009) 10:1426–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4637.2009.00743.x
34. Jones T, Moore T, Levy JL, Daffron S, Browder JH, Allen L, et al. A comparison of various risk screening methods in predicting discharge from opioid treatment. Clin J Pain. (2012) 28:93–100. doi: 10.1097/AJP.0b013e318225da9e
35. McNeely J, Wu L-T, Subramaniam G, Sharma G, Cathers LA, Svikis D, et al. Performance of the tobacco, alcohol, prescription medication, and other substance use (TAPS) tool for substance use screening in primary care patients. Ann Intern Med. (2016) 165:690–9. doi: 10.7326/M16-0317
Keywords: screening tool, opioid use disorder, long-term opioid use, opioid deprescribing, consensus protocol
Citation: You DS, Mardian AS, Darnall BD, Chen C-YA, De Bruyne K, Flood PD, Kao M-C, Karnik AD, McNeely J, Porter JG, Schwartz RP, Stieg RL and Mackey SC (2021) A Brief Screening Tool for Opioid Use Disorder: EMPOWER Study Expert Consensus Protocol. Front. Med. 8:591201. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.591201
Received: 04 August 2020; Accepted: 23 February 2021;
Published: 31 March 2021.
Edited by:
Rollin Gallagher, University of Ferrara, ItalyReviewed by:
Peggy Compton, University of Pennsylvania, United StatesJoseph W. Frank, VA Eastern Colorado Health Care System, United States
William Becker, Yale University, United States
Copyright © 2021 You, Mardian, Darnall, Chen, De Bruyne, Flood, Kao, Karnik, McNeely, Porter, Schwartz, Stieg and Mackey. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sean C. Mackey, c21hY2tleUBzdGFuZm9yZC5lZHU=
†Deceased
 Dokyoung S. You
Dokyoung S. You Aram S. Mardian
Aram S. Mardian Beth D. Darnall1
Beth D. Darnall1 Anita D. Karnik
Anita D. Karnik Joel G. Porter
Joel G. Porter Robert P. Schwartz
Robert P. Schwartz Sean C. Mackey
Sean C. Mackey