- 1Institute for Nanobiotechnology, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, United States
- 2Department of Biomedical Engineering, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, United States
- 3Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, United States
- 4Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, United States
A corrigendum on
The influence of physiological and pathological perturbations on blood-brain barrier function
by Zhao, N., Chung, T. D., Guo, Z., Jamieson, J. J., Liang, L., Linville, R. M., Pessell, A. F., Wang, L., and Searson, P. C. (2023). Front. Neurosci. 17:1289894. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1289894
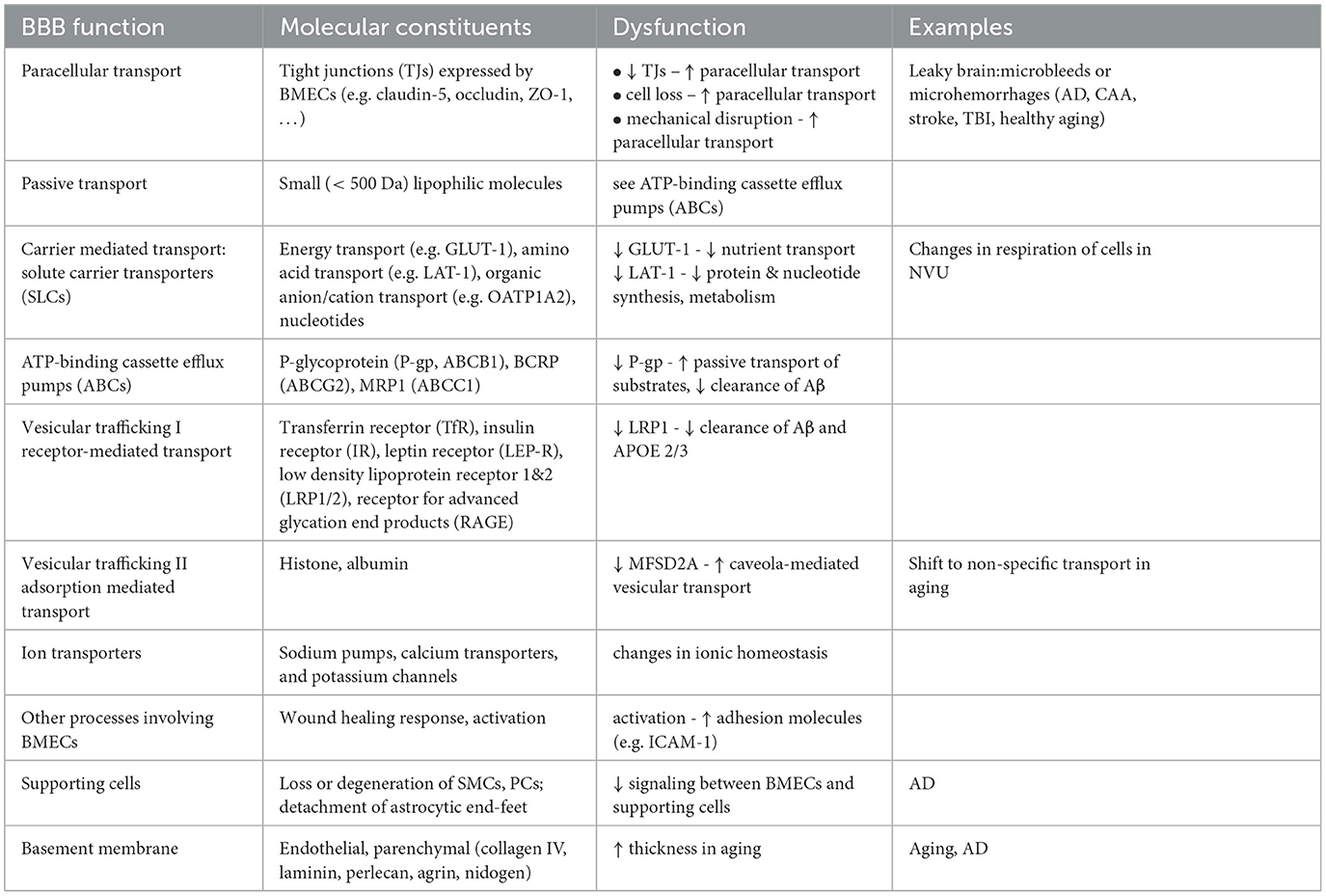
In the published article, there was an error in Table 1 as published. In row 6, column 3, “Ab” should be “Aβ”. In row 5, column 3, “Ab” should be “Aβ”. The corrected Table 1 and its caption Blood-brain barrier (BBB) components and examples of dysfunction appear below.
There was also an error in Section 3. Temperature, paragraph 1, “when CBF is lowest” should be “when CBF is highest”. The corrected paragraph appears below:
The average core body temperature (Tc) of healthy individuals is around 36°C (Mackowiak et al., 1992; Mackowiak and Worden, 1994; Sund-Levander and Grodzinsky, 2009; Protsiv et al., 2020). The average temperature of the brain is typically 1–2°C higher than Tc due to its high metabolic rate (Bain et al., 2015). Recent studies suggest that brain temperature varies with brain region and age, with temperatures as high as 40°C measured in the thalamus of healthy adults (Rzechorzek et al., 2022). The average brain temperature shows diurnal cycles, with the lowest temperature at night when CBF is highest, although these cycles are compromised with aging (Rzechorzek et al., 2022).
The authors apologize for these errors and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: blood-brain barrier, perturbations, dysfunction, brain health, neurovascular unit, brain pathologies
Citation: Zhao N, Chung TD, Guo Z, Jamieson JJ, Liang L, Linville RM, Pessell AF, Wang L and Searson PC (2024) Corrigendum: The influence of physiological and pathological perturbations on blood-brain barrier function. Front. Neurosci. 17:1328902. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1328902
Received: 27 October 2023; Accepted: 20 November 2023;
Published: 21 March 2024.
Edited and reviewed by: Einar M. Sigurdsson, New York University, United States
Copyright © 2024 Zhao, Chung, Guo, Jamieson, Liang, Linville, Pessell, Wang and Searson. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Peter C. Searson, searson@jhu.edu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Nan Zhao1†
Nan Zhao1† Peter C. Searson
Peter C. Searson