- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, University of California, Irvine, CA, United States
- 2R. S. Dow Neurobiology Laboratories, Legacy Research Institute, Portland, OR, United States
A corrigendum on
Adenosine Kinase Inhibition Protects against Cranial Radiation-Induced Cognitive Dysfunction
by Acharya, M. M., Baulch, J. E., Lusardi, T. A., Allen, B. D., Chmielewski, N. N., Baddour, A. D., et al. (2016). Front. Mol. Neurosci. 9:42. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2016.00042
In the original article, in Figure 2 the fourth column (IRR + 5-ITU group) accidentally had incorrect photomicrographs inserted for each channel shown (Merged, ADK, and GFAP). The corrected Figure 2 appears below.
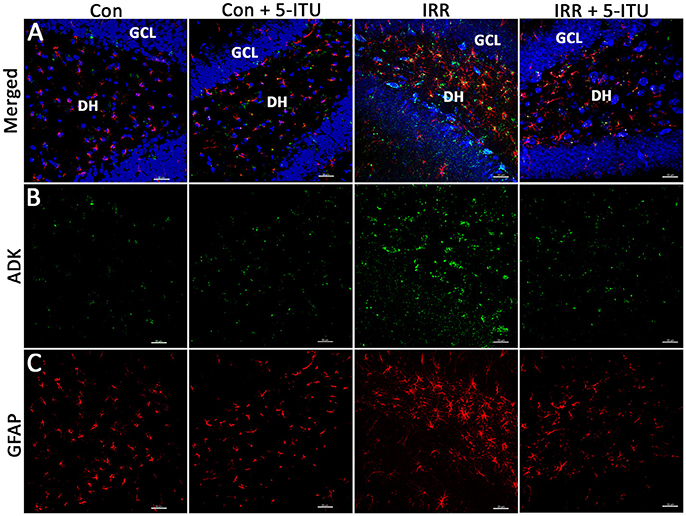
Figure 2. Cranial irradiation elevates adenosine kinase (ADK) immunoreactivity and astrogliosis. Immunofluorescence analysis demonstrates that at 1 month post-treatment, compared to controls (Con and Con + 5-ITU), exposure to cranial irradiation (10 Gy) leads to elevated ADK immunoreactivity (A,B; IRR group; ADK, green; DAPI nuclear counterstain, blue) that is reduced to control levels in irradiated animals treated with 5-ITU (IRR + 5-ITU). Representative confocal micrographs show the presence reactive astrocytic cell bodies (A,C; glial fibrillary acidic protein; GFAP, red) in the hippocampal dentate hilus (DH), sub-granular zone and granule cell layer (GCL) indicating astrogliosis. IRR + 5-ITU animals showed reduced ADK and GFAP immunoreactivity compared to IRR animals. Scale bar: 30 μm.
Similarly, the reference for Osman, A. M. et al. (2014; doi: 10.3727/096368913X674648) has been incorrectly cited. It should be disregarded. The authors apologize for these errors and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Keywords: adenosine, adenosine kinase, astrogliosis, radiation, cancer therapy, cognition, neuroprotection
Citation: Acharya MM, Baulch JE, Lusardi TA, Allen BD, Chmielewski NN, Baddour AAD, Limoli CL and Boison D (2017) Corrigendum: Adenosine Kinase Inhibition Protects against Cranial Radiation-Induced Cognitive Dysfunction. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 10:218. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00218
Received: 02 June 2017; Accepted: 23 June 2017;
Published: 10 July 2017.
Edited and reviewed by: Marina Guizzetti, Oregon Health and Science University, United States
Copyright © 2017 Acharya, Baulch, Lusardi, Allen, Chmielewski, Baddour, Limoli and Boison. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Munjal M. Acharya, bWFjaGFyeWFAdWNpLmVkdQ==
 Munjal M. Acharya
Munjal M. Acharya Janet E. Baulch
Janet E. Baulch Theresa A. Lusardi
Theresa A. Lusardi Barrett D. Allen
Barrett D. Allen Nicole N. Chmielewski
Nicole N. Chmielewski Al Anoud D. Baddour
Al Anoud D. Baddour Charles L. Limoli
Charles L. Limoli Detlev Boison
Detlev Boison