- 1Department of Neurology, National Taiwan University Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan
- 2Division of Neurology, Department of Internal Medicine, Lo-Hsu Medical Foundation, Lotung Poh-Ai Hospital, Yilan County, Taiwan
- 3College of Medicine, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan
- 4National Institute of Infectious Diseases and Vaccinology, National Health Research Institutes, Miaoli County, Taiwan
- 5Graduate Institute of Physiology, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan
- 6Department of Medical Research, National Taiwan University Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is known as a mitochondrial disease. Some even regarded it specifically as a disorder of the complex I of the electron transport chain (ETC). The ETC is fundamental for mitochondrial energy production which is essential for neuronal health. In the past two decades, more than 20 PD-associated genes have been identified. Some are directly involved in mitochondrial functions, such as PRKN, PINK1, and DJ-1. While other PD-associate genes, such as LRRK2, SNCA, and GBA1, regulate lysosomal functions, lipid metabolism, or protein aggregation, some have been shown to indirectly affect the electron transport chain. The recent identification of CHCHD2 and UQCRC1 that are critical for functions of complex IV and complex III, respectively, provide direct evidence that PD is more than just a complex I disorder. Like UQCRC1 in preventing cytochrome c from release, functions of ETC proteins beyond oxidative phosphorylation might also contribute to the pathogenesis of PD.
Introduction
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disease worldwide with 6.1 million patients globally in 2016 (GBD 2016 Parkinson’s Disease Collaborators, 2018), and up to 12.9 million people estimated to be affected by 2040 (Dorsey and Bloem, 2018). PD is clinically characterized by slowly progressive, levodopa-responsive bradykinesia with either rigidity or resting tremor (Postuma et al., 2015). Dopaminergic neuronal loss and Lewy body formation in the substantia nigra pars compacta are the hallmarks of most PD pathology.
Etiologies of PD are complex. Most individuals with PD are idiopathic. Only 10% of them showed a clear Mendelian inheritance (Hardy et al., 2009), and environmental factors such as pesticides, heavy metals, illicit substances, and diets also contribute (Ball et al., 2019). In 1983 four cases of levodopa-responsive parkinsonism were described after intravenous injection of synthetic heroin containing 1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) (Langston et al., 1983). The neurotoxicity of MPTP results from its oxidized metabolite, 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridine (MPP+) (Levitt et al., 1982; Glover et al., 1986), which damages oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) by inhibiting the electron transport chain (ETC) of mitochondria (Nicklas et al., 1985). The keystone discovery initiated an era of mitochondrial pathology in PD. Nowadays, a plethora of evidence from electrophysiological and anatomical perspectives has shown that mitochondrial health is essential in the integrity of dopaminergic neurons, especially those in SNc (Bolam and Pissadaki, 2012; Müller et al., 2018). Therefore, to disentangle the complex pathophysiology of PD, mitochondria is undoubtedly one of the key players that should not be missed.
In this review, we will briefly introduce current knowledge about ETC and OXPHOS and their relationships with PD. We will then summarize some of the well-known and newly identified PD-associated genes and their direct or indirect influences on ETC. Finally, we discuss the OXPHOS-independent functions of ETC proteins and their possible implications in PD pathogenesis.
Electron Transport Chain and Parkinson’s Disease
Mitochondria are the powerhouses of eukaryotic cells. This double membrane-bound organelle generates most adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through OXPHOS, processed by ETC embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM). ETC is composed of transmembrane complexes I (cI) to V (cV) and two electron carriers, the ubiquinone (i.e., CoQ) and the cytochrome c (cyt c). For ATP production, electrons are transferred from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen via the transport chain, coupled with the generation of a proton gradient across IMM (Zhao et al., 2019; Figure 1).
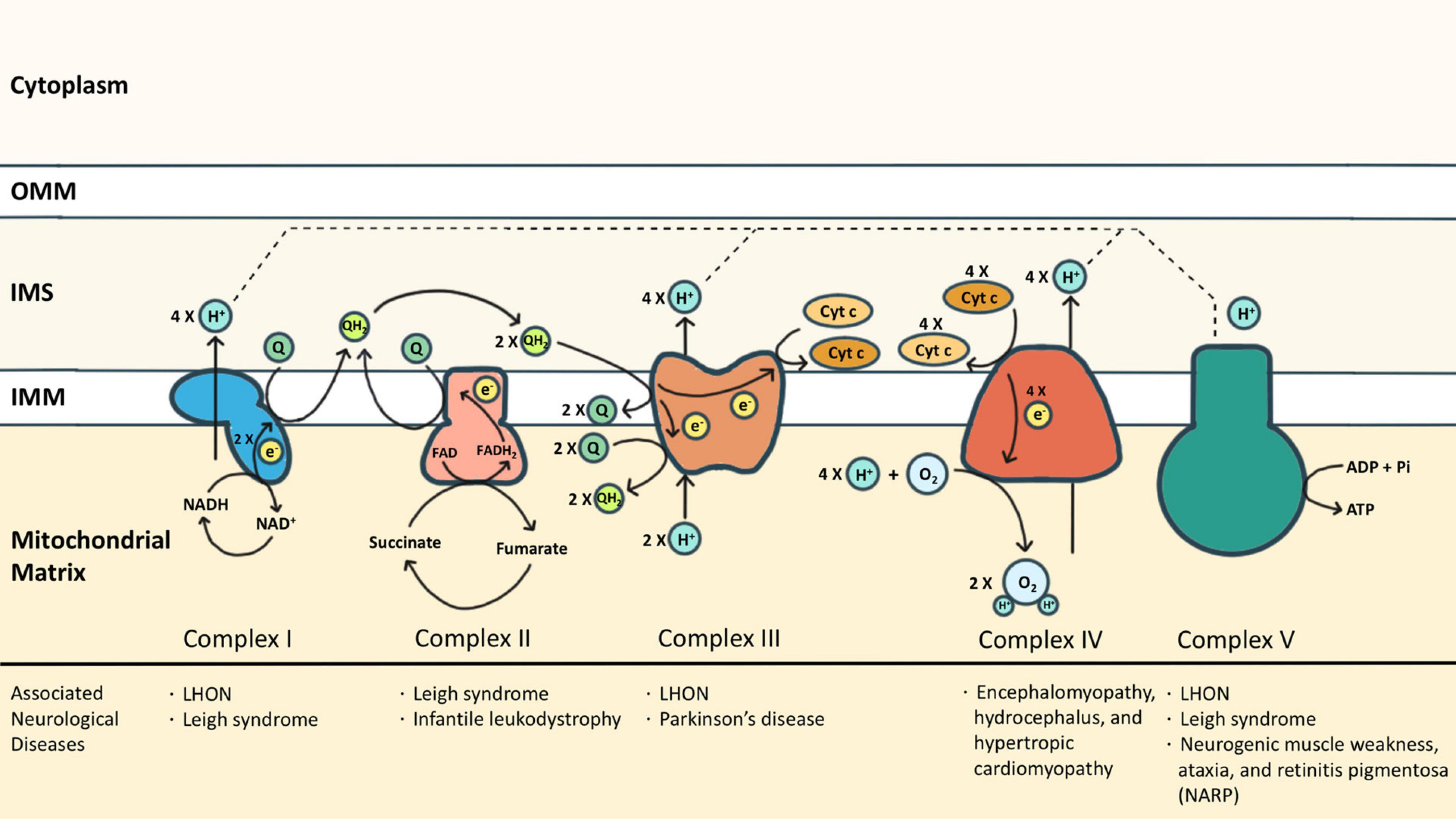
Figure 1. The electron transport chain (ETC) consists of complexes I (cI) to V (cV), as well as two free electron carriers, CoQ and cyt c. NADH and FADH2 donated electrons to cI and cII, respectively, causing reduction of CoQ into CoQH2. The CoQH2 is in turn oxidized by cIII where the electrons are delivered to cyt c. The reduced cyt c was then oxidized by cIV where the oxygen molecule was reduced as the terminal electron acceptor. Protons accumulated in the intermembrane space during oxidative phosphorylation via cI, cIII, and cIV, and are essential for cV to drive ATP synthesis. Some neurological diseases associated with mutations of cI-cV are listed.
Complex I (cI) is an NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase that pumps four protons into the intermembrane space (IMS) upon each NADH oxidation. cI consists of three modules: the N, Q, and P modules. NADH generated from the tricarboxylic acid cycle delivers its electron to the N module. The electron was then passed to the Q module where the CoQ is reduced to ubiquinol (CoQH2) and induces conformational changes of the P module to allow proton translocation (Giachin et al., 2016). Similarly, cII also transfers electrons to CoQ, but by dehydrogenizing succinate to fumarate, which is a part of the tricarboxylic acid cycle. cII is composed of two subunits: the enzymatic subunit (SDHA-SDHB) in the matrix and the anchoring subunit (SDHC-SDHD) across the IMM. The enzymatic subunit exploits two electrons from succinate and passes them through a series of FeS clusters to the anchoring subunit where CoQ is reduced to CoQH2. Different from cI, no proton is translocated for the reactions that occur in cII (Rutter et al., 2010). Electrons from both cI and cII are carried by CoQH2 to enter the Q cycle processed by cIII. The catalytic activity of cIII depends on three redox-active subunits: cytochrome b (MT-CYB), the Rieske iron-sulfur [Fe2-S2] protein (UQCRFS1), and cytochrome c1 (CYC1) (Yang and Trumpower, 1986). Electrons donated by CoQH2 were transduced to cyt c via these three subunits sequentially. Each Q cycle generates two reduced cyt c and transports two protons (Crofts, 2004). The reduced cyt c then shuttles electrons to cIV, namely the cyt c oxidase (COX), whose catalytic core includes subunits 1, 2, and 3. Electrons are exploited from reduced cyt c at subunit 2 and reduce molecular oxygen to water at subunit 1. One proton is simultaneously translocated to IMS via subunit 3 upon each cyt c oxidization (Wilson and Prochaska, 1990). The oxidized cyt c then returns to its pool. In addition to working as an electron carrier, the oxidized cyt c also serves as a scavenger of reactive oxygen species (ROS) (Wang et al., 2003), a cardiolipin peroxidase (Kagan et al., 2005), and an apoptosis activator once released to the cytosol (Ow et al., 2008). The functions of cyt c beyond OXPHOS are discussed in the latter part of this review.
As the final step of OXPHOS, the proton gradient established by cI, cIII, and cIV drives cV to generate ATP. cV consists of two functional domains: F1 and F0. Protons passing through the F0 domain across the IMM to the matrix release the energy provided by the proton electrochemical gradient. The F1 domain at the matrix then uses the energy to charge cells by phosphorylating ADP to ATP (Jonckheere et al., 2012). Each ATP synthesis requires the translocation of 3 or 4 protons (Van Walraven et al., 1996; Guerra et al., 2002).
Dysfunction of ETC has been associated with various neurological diseases from infantile-onset neurodevelopmental regression (such as Leigh syndrome) to adult-onset optic neuropathy or peripheral neuropathy (such as Leber hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) in cI deficiency, and neurogenic muscle weakness, ataxia, and retinitis pigmentosa (NARP) in cV deficiency) (Gorman et al., 2016). Neurodegeneration diseases, especially PD, are also associated with ETC dysfunction. PD has been branded as a “cI disease” because of the discovery of MPP+ (the metabolites of MPTP) which is a cI inhibitor (Nicklas et al., 1985; Ramsay et al., 1986). Rotenone, another commonly reported PD risk factor, is also a cI inhibitor (Betarbet et al., 2000). In post-mortem studies of PD patients, cI functional deficiency is found in substantia nigra or frontal cortex (Schapira et al., 1990; Parker et al., 2008). Similar cI deficiency is also found in non-brain tissues including platelets, skeletal muscles, or fibroblasts, indicating it is a systematic phenomenon (Parker et al., 1989; Wiedemann et al., 1999). Also, reports of cIII and cIV function in PD have been inconsistent (Mizuno et al., 1990; Wiedemann et al., 1999). Impairment of ETC causes excessive ROS, disruption of the electrochemical potential of the proton gradient, insufficient ATP production, and even cell death. Although it is widely observed that ETC functions are compromised in PD, genetic mutations of ETC proteins (either nuclear-encoded or mitochondrial-encoded) are rarely linked to PD. The discrepancy might suggest that the ETC dysfunction is secondary to other mechanisms that closely regulate mitochondria. In other words, ETC represents a hub where different PD-causing patho-mechanisms converge.
PD-Associated Genes and the ETC
To date, over 20 PD-related genes have been discovered. Although these familial PD cases are not common, and some may even have atypical features such as early onset (<50 years of age at onset) or early cognitive or psychiatric involvement, they provide great insights into the pathogenesis of PD. Many of the PD-causing genes affecting quality control systems of mitochondria, lysosomal regulation, or lipid/protein homeostasis, thus directly or indirectly influence ETC functions. In the following section, we will discuss the best-known genes and some newly identified ones with a focus on their influences on ETC (Figure 2 and Tables 1, 2).
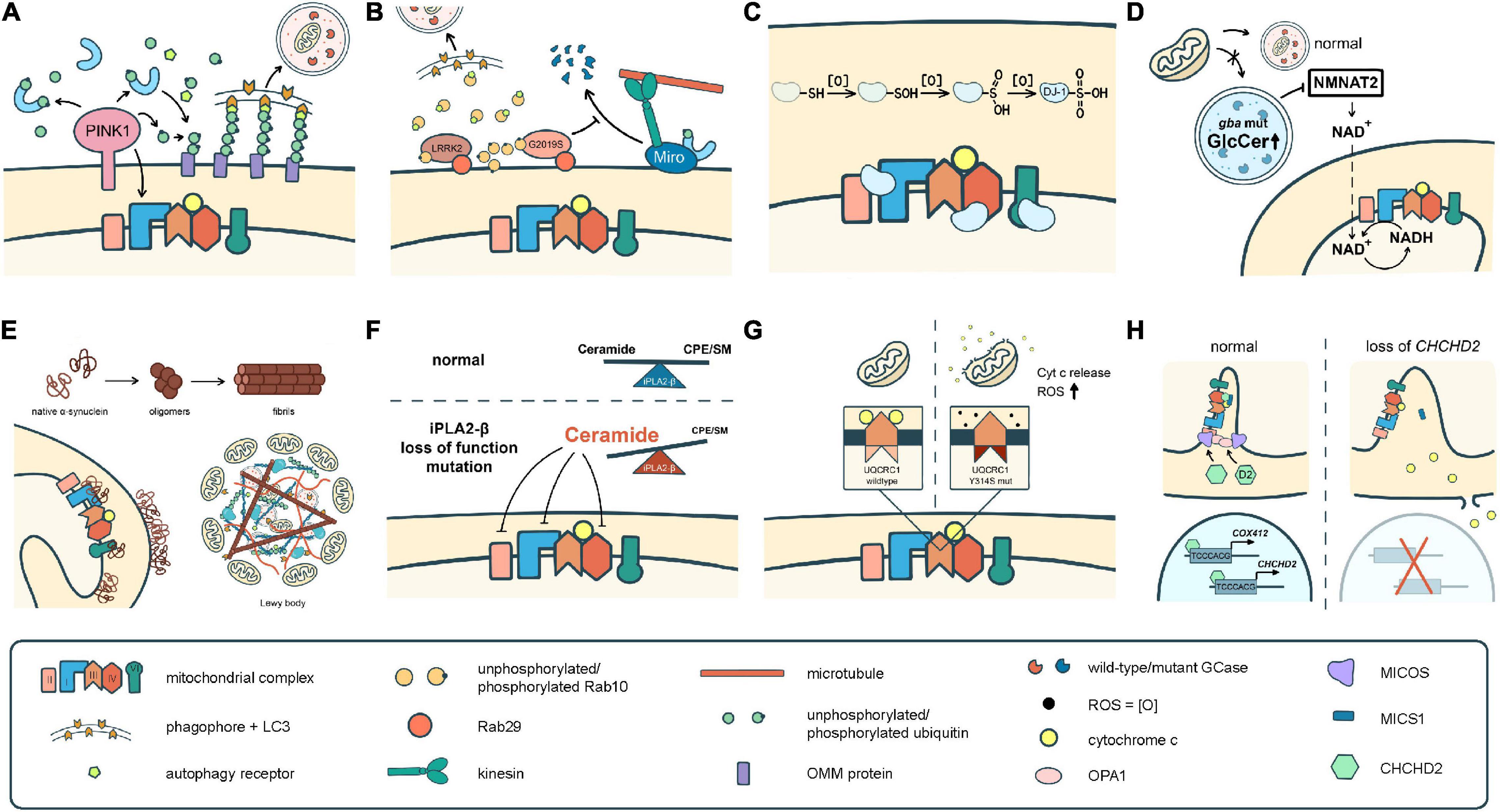
Figure 2. Different pathomechanisms converge on mitochondria in Parkinson’s disease. (A) PINK1 and parkin mediate mitochondrial quality control processes such as mitophagy. PINK1 is also required for phosphorylation of Ndufa10 to facilitate the reduction of ubiquinone by complex I. (B) Mutations in LRRK2 block mitophagy by preventing the degradation of Miro or by trapping Rab10 whose interaction with OPTN is pivotal for autophagy/mitophagy. (C) DJ-1 scavenges ROS through sequential oxidation at Cys106. The oxidized DJ-1 acts as a chaperone to facilitate the assembly and activities of cI, cIV, and cV. (D) Accumulation of GlcCer and other lipids in GCase mutants impairs lysosomal functions. Mutations in GCase reduces the expression of NMNAT2, resulting in a significant reduction of NAD + /NADH. (E) α-Syn monomers or oligomers interrupt the activities of cI and cV. The fibrilized α-Syn triggers Lewy body formation which sequestrates abundant mitochondria. (F) Deficits in iPLA2-β cause lipid imbalance that may interrupt ETC functions. (G) UQCRC1 is critical in cIII assembly and functions, and also prevents cyt c release. (H) CHCHD2 is a chaperone of cIV, activates COX4I2 and its own expression, complexes with MICS to prevent cyt c release, and regulates the cristae structure by stabilizing OPA1 and MICOS complex.
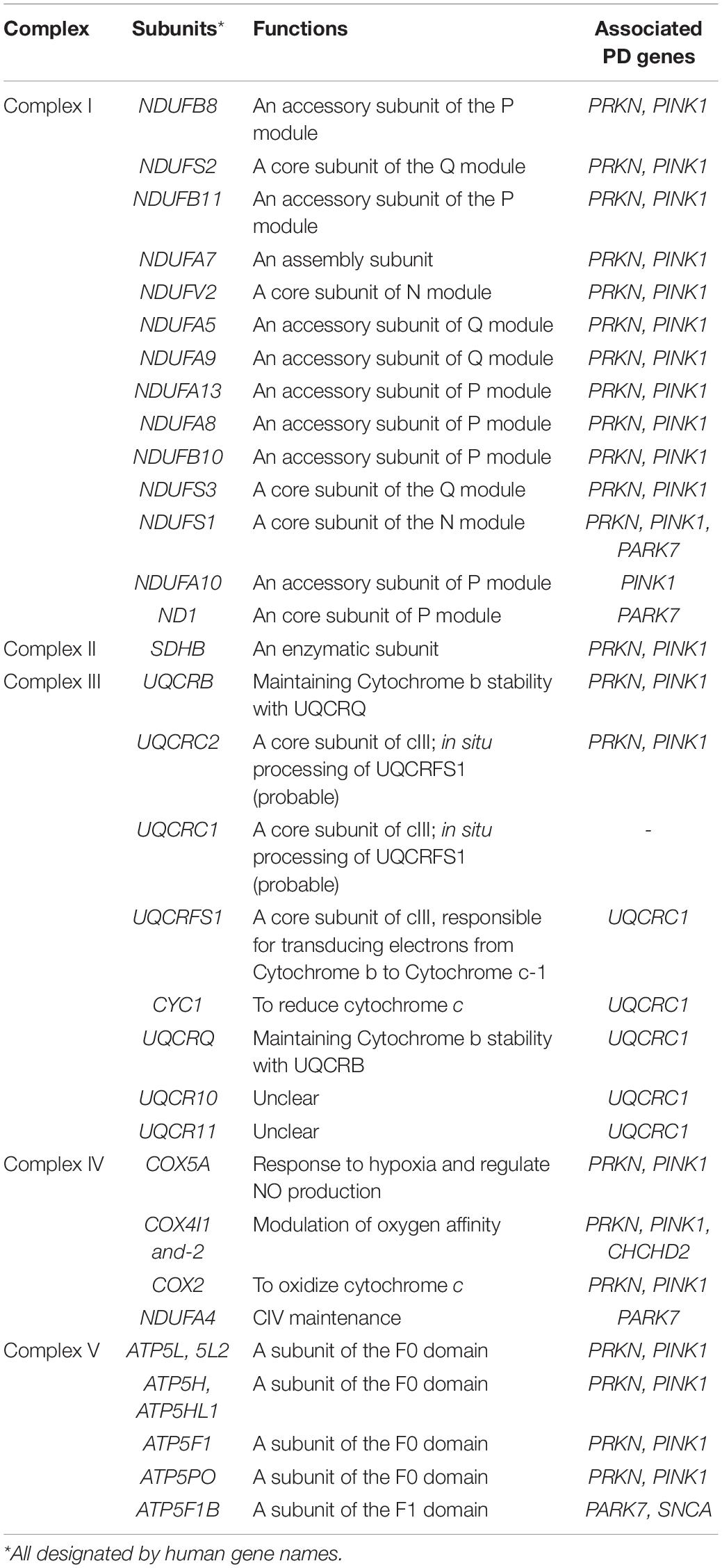
Table 2. Canonical OXPHOS functions of the mitochondrial complex subunits affected by PD-associated genes in Table 1.
PINK1 and PRKN: Key Players of Mitochondria Quality Control
Mutations in PRKN (previously known as PARK2, which encodes parkin) and PINK1 are the most common causes of early onset PD. PRKN mutants on 6q25.2-27 were found in 1998 (Kitada et al., 1998), and PINK1 mutants on 1p35-1p36 were identified in 2001–2002 (Valente et al., 2001, 2002, 2004). Mutations in the two genes have since been reported worldwide (Kilarski et al., 2012). Early onset PD associated with either gene showed similar clinical features, including slow disease progression, good levodopa response, lower limb dystonia, early psychiatric symptoms, and a higher likelihood of motor complications than idiopathic PD (Koros et al., 2017). Pathologically, Lewy bodies can be absent in patients with either PRKN or PINK1 mutations (Poulopoulos et al., 2012; Takanashi et al., 2016). These similarities reflect their common mechanism in PD pathogenesis.
It is now known that parkin, along with PINK1, is critical for mitochondria quality control through various pathways including mitophagy, formation of mitochondrial-derived vesicles, mitochondrial fission, and facilitation of mitochondrial biogenesis (Ge et al., 2020). When mitochondria are jeopardized, PINK1 is recruited to and stabilized on the OMM. The stabilized PINK1 then recruits and activates parkin, an E3 ligase that assembles ubiquitin chains on its substrates including OMM proteins which subsequently recruits ubiquitin-binding autophagy receptors and ultimately leads to autophagosome formation and lysosomal degradation. Other substrates of parkin include Mitofusin-1 and -2, whose proteolysis divert mitochondria from fusion into fission (Tanaka et al., 2010; Ziviani et al., 2010); parkin interacting substrate (PARIS, also known as ZNF746), whose degradation stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis (Shin et al., 2011; Lee et al., 2017); and also hnRNP F, a translation repressor that regulates the localized synthesis of nuclear-encoded mitochondrial proteins (including some ETC components) (Lee et al., 2017). In addition to PINK1-dependent phosphorylation, other post-translational modifications of parkin, such as S-nitrosylation, are also critical for the E3 ligase activity and solubility of parkin and have been comprehensively reviewed elsewhere (Chakraborty et al., 2017).
The integrity of ETC is highly correlated with the PINK1-Parkin-mediated quality control mechanisms. Fibroblasts or leukocytes with parkin loss-of-function mutations showed impaired cI activities (Müftüoglu et al., 2004; Mortiboys et al., 2008), and human fibroblasts or mouse embryonic fibroblasts of PINK1 mutants also showed cI dysfunction (Morais et al., 2009; Amo et al., 2014). The turnover rates of mitochondrial proteins could be an indicator of mitochondrial quality control. A study using fly heads showed that ETC mitochondrial proteins had a greater dependence on parkin or Pink1 than other non-ETC mitochondrial proteins. Nineteen of the ETC proteins had longer half-lives in parkin mutants than in autophagy-impaired Atg7 mutants, suggesting the turnover of these proteins may be achieved via an a selective manner. More than half belong to cI (10/19), while proteins from the other complexes are also affected (1 in cII, 2 in cIII, 3 in cIV, and 3 in cV) (Vincow et al., 2013). The predominance of cI proteins likely explains why cI dysfunction is invariably reported in PRKN or PINK1 mutants.
Activities of cI could also be regulated by PINK1 independent of parkin. An accessory subunit of cI, Ndufa10, is pivotal for the ubiquinone-reducing capacity of cI, and the phosphorylation of Ndufa10 requires PINK1 (Morais et al., 2014). Overexpression of Ndufa10 or expression of its phosphomimetics could reverse the defects in pinkB9-null mutant Drosophila, but not parkin mutants (Morais et al., 2014; Pogson et al., 2014). Ndufa10 phosphorylation also rescued the ROS-induced apoptosis in PINK1 knockout mouse fibroblasts (Morais et al., 2014), suggesting that PINK1 is anti-apoptotic. The anti-apoptotic effects of PINK1 are also attributed to the phosphorylation of the mitochondrial chaperone TRAP1 (also known as Hsp75) which prevents cyt c release from mitochondria (Pridgeon et al., 2007). In tumor cells, TRAP1, phosphorylated by ERK1/2 and Src, prohibited the generation of ROS by inhibiting cII and cIV, respectively (Masgras et al., 2017). Whether the phosphorylation of TRAP1 by PINK1 has any influence on ETC functions awaits further investigation.
DJ-1: A Prominent Chaperone in Mitochondria
DJ-1 (also known as PARK7) mutations cause autosomal recessive, early onset PD. It was initially reported in 2003 from two genetically isolated consanguineous families (Bonifati et al., 2003), and has a frequency of about 0.4% in early onset PD, much lower than that of PRKN and PINK1 (Kilarski et al., 2012).
DJ-1 is ubiquitously expressed (Mita et al., 2018) and serves a dual role as an oxidative sensor and also an antioxidant protein. Immunostaining of oxidized DJ-1 (oxDJ-1) revealed reactivity in SNc, striatum, and inferior olivary nucleus in postmortem brain of elders with Lewy body pathology. Co-localization of oxDJ-1 and α-synuclein (α-Syn) was also reported (Saito et al., 2014). The cysteine residue (C106) in its active site could be sequentially oxidized into the sulfenylated form (-SOH), sulfinated form (-SO2H), and sulfonic form (-SO3H) (Kinumi et al., 2004). The sulfinated form is the active form that not only prevents α-Syn fibrillation (Zhou et al., 2006) but also plays protective roles in promoting mitochondria fission and cell viability to rotenone (Blackinton et al., 2009). These results suggested that DJ-1 is an oxidative stress-dependent chaperone.
Since mitochondria are the major site of intracellular ROS production, it is intuitive that DJ-1 plays an important role in mitochondria physiology. The subcellular and submitochondrial fractionation of mouse brains shows that abundant endogenous DJ-1 is localized in mitochondria (Zhang et al., 2005). Depletion of DJ-1 significantly reduced the oxygen consumption rate, ATP production (Heo et al., 2012), and cI activity (Hayashi et al., 2009). Proteomics assays revealed improper cI assembly in DJ-1-deficient neuronal cells related to loss of CI-75kD (encoded by Ndufs1) (Heo et al., 2012). Direct interactions of DJ-1 with ND1 and with NDUFA4 were also reported (Hayashi et al., 2009). Of note, NDUFA4 is a subunit of cIV, rather than within cI as initially considered (Balsa et al., 2012). Whether cIV activities are influenced by DJ-1 remains unknown.
Recently, Chen et al. (2019) showed DJ-1 binds to the F1FO ATP synthase β subunit. ATPase β subunit is crucial for maintaining the mitochondrial membrane potential through inhibition of proton leakage from the pores formed by the c-subunit of cV, thereby enhancing the ATP synthesis (Alavian et al., 2014). The ATPase β subunit was decreased in DJ-1 knockout mice, thus the ATP production, mitochondrial membrane potential, and neurite outgrowth of dopaminergic neurons were all compromised (Chen et al., 2019). The interactions of DJ-1 and ATP synthase β subunit again demonstrate its role as a mitochondrial chaperone.
PLA2G6: ETC Dysfunction and Lipid Imbalance
PLA2G6-associated neurodegeneration (PLAN) consists of a series of rare diseases: infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy (INAD), atypical neuroaxonal dystrophy (ANAD), dystonia-parkinsonism (DP), and autosomal recessive early onset parkinsonism (AREP). Among them, DP and AREP are both characterized by adult-onset as well as levodopa-responsiveness, and are not reported until 2009 and 2011, respectively (Paisan-Ruiz et al., 2009; Shi et al., 2011). Though previously under-reported, recent studies showed that PLA2G6 might contribute to early onset PD as frequently as 0.54–1.3%, more common than DJ-1 (Kumar et al., 2020; Zhao et al., 2020).
PLA2G6 encodes a group VIA calcium-independent phospholipase A2β enzyme (iPLA2β), which is responsible for the selective hydrolysis of glycerophospholipids to generate fatty acids and lysophospholipids (Jenkins et al., 2006). In PLA2G6-knockout mice, granules containing collapsed mitochondria were observed in axons (Beck et al., 2011). In iPLA2-VIA (the homolog of PLA2G6) null Drosophila, aberrant mitochondria with reduced respiratory chain activities of cI and cII or ATP production were demonstrated (Kinghorn et al., 2015; Lin et al., 2018). These changes, however, are unlikely associated with changes in cardiolipin composition (Kinghorn et al., 2015), which is the main component of mitochondria inner membrane. Lin et al. showed that none of the glycerophospholipids significantly changed in iPLA2-VIA null Drosophila. Rather, they showed a decrease in ceramide phosphoethanolamines, and an increase in ceramides, dihydroceramides, and other sphingolipid intermediates (Lin et al., 2018). Some ceramides are associated with compromised respiratory chain activities, increased ROS production, impaired mitochondria membrane potential, mitophagy, and apoptosis (Kogot-Levin and Saada, 2014). By using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), it was revealed that subunit 2 of cIV might have allosteric interactions with C6-ceramide (Kota et al., 2012). Reduced cIV activities were found in the liver of ceramide synthase 2 deficient mice where very long acyl chain (C22-C24) ceramides were barely detectable while C16-ceramide was accumulated (Zigdon et al., 2013). In cells that have excessive levels of dihydroceramide and dihydrosphingolipids due to the lack of dihydroceramide desaturase 1, the activities of cI and cIV (especially the latter) were inhibited (Gudz et al., 1997). In these animal models, it is still not clear whether cIV activity is affected by PLA2G6/iPLA2-VIA and how the imbalance of lipids influences cI and cII.
GBA1: Lysosomal Dysfunction Linking to ETC Impairment
GBA1 is not a traditional PARK-designated gene. Its biallelic mutations cause Gaucher’s disease, which is a lysosomal storage disease. However, increasing reports have identified GBA1 variants as common risk factors of PD (Lwin et al., 2004; Iwaki et al., 2019). The combined odds ratio of any GBA1 mutant in PD patients versus controls was as high as 5.43 (95% CI, 3.89 to 7.57) according to an international multi-center study, with the most common variants being N370S and L444P (Sidransky et al., 2009). PD patients with GBA1 variants have a more aggressive motor deterioration and accelerated course of dementia than other PD patients (Stoker et al., 2020).
GBA1 encodes β-glucocerebrosidase (GCase), a lysosomal enzyme hydrolyzing glucosylceramide (GlcCer) into glucose and ceramide. The enzyme activity of GCase decreases in mutation carriers and elder individuals (Rocha et al., 2015; Hallett et al., 2018). In contrast to the PLA2G6 mutants that cause accumulation of ceramide, GCase deficiency results in the accumulation of GlcCer, as well as alterations of glucosylsphingosine (GlcSph), sphingosine (Sph), sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) in different brain regions (Muñoz et al., 2021). GCase deficiency impaired lysosomal recycling (Magalhaes et al., 2016) and lysosomes enriched with GlcCer accelerates and stabilizes soluble α-Syn oligomers, which eventually become amyloid fibrils (Mazzulli et al., 2011). GCase deficiency also causes significant mitochondrial morphological changes, decreased oxygen consumption rate, and reduced respiratory chain complex activities (Osellame et al., 2013; Schöndorf et al., 2018).
The mechanism of how a lysosomal enzyme such as GCase influences ETC is elusive. In gba knockout mice inhibited activities of cI and cII-III, but not cIV, were observed. Reduced co-localization of mitochondrial marker with LC3 and parkin recruitment suggested impaired mitophagy which might explain the compromised ETC activities (Osellame et al., 2013). However, the mitophagy theory unlikely explains the discrepancy between cIV and other complexes (Gegg and Schapira, 2016). CoQ, which transfers electrons from cI and cII to cIII, has been shown beneficial for mitochondrial function in fibroblasts from patients of Gaucher disease (de la Mata et al., 2015), but definite evidence showing deficits of CoQ in GCase depleted cells is lacking.
The ETC dysfunction can also result from alterations of mitochondrial metabolism. In iPSC neurons derived from PD patients carrying GBA1 variants, cI perishment with decreased expression of nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferases2 (NMNAT2) was found. Supplementation of NAD+ precursor nicotinamide riboside rescued mitochondrial defects and autophagy. The lipidomic analysis of mitochondria showed no accumulation of GlcCer in mitochondria except for C16-GlcCer (Schöndorf et al., 2018). Where do the C16-GlcCer exactly locate and whether it regulates ETC functions are still unanswered.
LRRK2: A Master Kinase Regulating the Mitochondrial Quality Control System
Mutations in LRRK2, which encodes the leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2), are the most prevalent causes of autosomal dominant PD worldwide. LRRK2-associated PD (LRRK2-PD) are characterized by late-onset (>60 years), with clinical features and treatment response resembling idiopathic PD (Tan et al., 2019; Lesage et al., 2020; Zhao et al., 2020). G2019S is the most common variant in Europe and North America, accounting for 4% of familial PD and 1% of sporadic PD (Healy et al., 2008), while in Asia this variant is rare but prominent allelic heterogeneity was observed (Foo et al., 2017, 2020). One of the main features of LRRK2-PD is its incomplete penetrance which varies among each variant and even different ethnicities (Trinh et al., 2014). A polygenic risk score has been developed to predict the vulnerability of G2019S carriers, and genes involving the vacuolar functions, lysosomal functions, and endocytic pathways were included (Nalls et al., 2019). Recent studies suggested that mitochondrial DNA damage is also a potential biomarker in LRRK2-PD (Gonzalez-Hunt et al., 2020). Reduced cI activities and increased mitochondria DNA copy number were observed in fibroblasts derived from G2019S PD patients than from carriers (Delcambre et al., 2020), implying mitochondria in association with the incomplete penetrance of the G2019S variant.
LRRK2 is an enzyme with both kinase and GTPase activities (Berwick et al., 2019). The kinase activity of LRRK2 is responsible for phosphorylation of a subset of Rab small GTPase (Steger et al., 2016), which are important for exocytosis of synaptic vesicles, and endolysosomal and Golgi apparatus protein sorting (Bae and Lee, 2020). Most PD-associated LRRK2 mutations represent gain-of-function alleles: the G2019S and I2020T in the kinase domain cause hyper-phosphorylation of Rabs (West et al., 2005; Gloeckner et al., 2006), and R1441C/G/H in the Roc-COR domain increase kinase activities through disruption of the GTP hydrolysis activity (Weiss, 2008). Hyperphosphorylation of the Rabs disrupts their interaction with GTP/GDP exchange factors (GEFs), and Rab GDP dissociation inhibitors (GDIs), resulting in their inactivation and membrane-cytosol redistribution (Steger et al., 2016).
Accumulating evidence has shown the impairment of mitochondria in LRRK2 mutants. Fibroblasts from LRRK2-PD patients exhibited defects including reduced mitochondria membrane potential, decreased ATP production, and decreased activities of complexes I, II, and IV than healthy controls. Elongation of mitochondria and increased interconnectivity of mitochondria were also observed in LRRK2-PD fibroblasts (Mortiboys et al., 2010). LRRK2 is recruited to the mitochondrial outer membrane by mitochondria-anchored Rab29 (also called Rab7L1) (Gomez et al., 2019). RAB29 is also a risk gene of PD identified in PARK16 loci from several GWASs (Satake et al., 2009), and in addition to mitochondria Rab29 is also distributed at trans-Golgi network, lysosomes, and autophagic vesicles to regulate membrane trafficking, lysosome homeostasis, and axonal transport of autophagosomes with LRRK2 (Eguchi et al., 2018; Liu et al., 2018; Boecker et al., 2021). When gain-of-function LRRK2 mutants are anchored to mitochondria, it phosphorylates and traps Rab10 nearby (Gomez et al., 2019), causing decreased interaction of Rab10 with OPTN (optineurin), which is an autophagy receptor, therefore impairing mitophagy (Wauters et al., 2020). LRRK2 also regulates mitophagy through interaction with Miro, which anchors mitochondria to microtubules in mitochondria axonal transport (Hsieh et al., 2016). In mitophagy, PINK1/parkin-dependent phosphorylated Miro is targeted to proteasome degradation, thus “quarantining” damaged mitochondria from further transport (Wang et al., 2011). Upon CCCP treatment, Miro interacting with wild-type LRRK2 was degraded with time, while in the LRRK2 G2019S mutant, Miro showed decreased interaction with the mutant as well as resistance to degradation, delaying mitochondrial arrest and clearance in iPSC-derived neurons (Hsieh et al., 2016). In addition to mitophagy, LRRK2 is also involved in other mitochondrial quality control pathways like fusion and fission and its cytoskeleton dynamics and trafficking (Singh et al., 2019). Although evidence showing direct regulation of ETC by LRRK2 is limited, these quality control systems mentioned earlier do have profound impacts on ETCs. A recent in vitro study showed that PINK1-dependent phosphorylation of Ser111 of Rab8A antagonistically regulates the phosphorylation of Thr72 of Rab8A by LRRK2 (Vieweg et al., 2020), suggesting that there might be even closer crosstalk between the two master kinase.
SNCA: A Vicious Cycle of Proteinopathy and Mitochondriopathy
SNCA is the first identified gene associated with PD in 1997 (Polymeropoulos et al., 1997). While α-synuclein (α-Syn), which is encoded by SNCA, is one of the fundamental components in the Lewy body, patients with SNCA mutants (A30P, E46K, H50Q, G51D, A53E, and A53T) or multiplications are really rare, characterized by autosomal dominant inheritance, widely distributed age of onset (from 19 to 81 years), and more rapid cognitive impairment (Rosborough et al., 2017). Physiologically α-Syn is soluble in the cytosol, mainly located at presynaptic terminals to regulate the genesis, maintenance, and release of presynaptic vesicles (Kahle et al., 2000; Cabin et al., 2002; Burré et al., 2010). The α-synucleinopathy results from the imbalance among synthesis, aggregation, and clearance of α-Syn. As a result, aggregation of α-Syn takes place in the cytosol or around membranes. The conformations of the aggregates include oligomers, protofibrils, and fibrils (Lashuel et al., 2013). Accelerated oligomerization is the common trait among different disease mutants (Conway et al., 2000), and a higher propensity of fibrilization might correlate to the earlier onset age in A53T than A30P or E46K (Conway et al., 1998; de Oliveira and Silva, 2019). Post-translational modifications like phosphorylation at Ser129 and truncation at the carboxyl terminal are also pathogenic (Sato et al., 2011; Sorrentino and Giasson, 2020), while Ser87 is protective (Oueslati et al., 2012).
Both oligomers and fibrils (especially the amyloid fibrils) are toxic to mitochondria (Lashuel et al., 2013). Overexpression of α-Syn, cytosolic acidification, and Ser129 phosphorylated pathogenic α-Syn could all induce translocation of α-Syn to mitochondria (Cole et al., 2008; Shavali et al., 2008; Wang et al., 2019). By using a split-GFP tool, the translocated α-Syn was found distributed at the OMM and IMS but not in the matrix. Mutants (A30P and A53T) were more likely translocated to the IMS than the wild-type, and more α-Syn would be translocated to IMS upon oxidative stress or cI inhibition (Vicario et al., 2019). In turn, α-Syn inhibits cI activities in either monomer or oligomerized form (Chinta et al., 2010; Reeve et al., 2015; Ludtmann et al., 2018). Oligomeric α-Syn also selectively oxidized the ATP synthase β subunit and caused mitochondrial lipid peroxidation and increased mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening (Ludtmann et al., 2018). These suggest a vicious feed-forward loop between α-Syn aggregation and mitochondrial dysfunction.
Synergistic with oligomers, α-Syn fibrils impairs mitochondria by sequestering mitochondria and other organelles into Lewy bodies. Mahul-Mellier et al. (2020) added preformed fibrils (PFF) of α-Syn exogenously to the cultured neurons and found that at day 14 inclusions composed of loose fibrils start to interact with organelles, and at day 21 high enrichment of proteins from the mitochondria (including complexes I, II, and V), the endoplasmic reticulum, and the Golgi were detected in the Lewy body-like inclusions, corresponding to the reduction of the maximum OXPHOS capacity and maximum electron transport capacity at day 21. The important discovery links the two competitive but not conflicting theories of proteinopathy and mitochondriopathy in PD pathogenesis.
UQCRC1 and CHCHD2: Two Recently Found PD-Causing Genes Implicating Apoptotic Neuronal Death
The association between CHCHD2 and autosomal dominant late-onset PD was discovered in four independent families through genome-wide linkage analysis (Funayama et al., 2015). CHCHD2 is a member of the coiled-coil-helix-coiled-coil-helix (CHCH) domain-containing protein family known to participate in mitochondrial respiration, redox regulation, membrane ultrastructure, and dynamics in the IMS (Modjtahedi et al., 2016). CHCHD2 binds with cIV and regulates its activity. Under hypoxia, CHCHD2 activates the transcription of itself and COX4I2, which encodes cIV subunit-4 isoform 2 (COX IV-2) (Aras et al., 2015). The findings are compatible with the clinical data showing that fibroblasts derived from a patient with homozygous A71P mutant in CHCHD2 show reduced cIV activity in addition to cI deficiency (Lee et al., 2018). CHCHD2 is also important in maintaining the cristae structure and preventing apoptosis. Cristae are the home of ETC complexes and changes in the structure would alter the distribution of mitochondrial complexes, thus influencing the efficiency of OXPHOS (Gilkerson et al., 2003; Wilkens et al., 2013). In the flight muscles of CHCHD2 null Drosophila, the mitochondrial cristae structure was disorganized (Meng et al., 2017). Cristae integrity is regulated by OPA1 and the MICOS complex (Baker et al., 2019). In cells carrying PD-linked CHCHD2 mutations, the expression level of MICOS components, such as Mitofilin, MINOS1, CHCHD3, CHCHD6, were all reduced (Zhou et al., 2019). In Drosophila, Chchd2 knockout increases the degradation of OPA1 by peptidase YME1L (Liu W. et al., 2020). Similarly, OPA1 degradation is also observed in CHCHD2 and CHCHD10 double-knockout mice (Liu Y. T. et al., 2020). Mass spectrometry analysis reveals that CHCHD2 interacts with MICS1 (Meng et al., 2017), which is involved in cristae organization and cyt c stabilization, thereby prohibiting cells from apoptosis (Oka et al., 2008).
UQCRC1 is a newly identified PD-causing gene that is clinically characterized by autosomal dominant late-onset parkinsonism with polyneuropathy (Lin et al., 2019, 2020). UQCRC1 encodes the mitochondrial ubiquinol-cyt c reductase core protein 1 (UQCRC1), which is a core subunit of cIII. UQCRC1 complexes with UQCRC2 and interacts with UQCRFS1, CYC1, and other cIII subunits to regulate cIII activity (Sunitha et al., 2016; Unni et al., 2019). UQCRC1 and UQCRC2 are homologs to the mitochondrial-processing peptidase subunits and are predicted to process UQCRFS1 in situ during cIII assembly (Fernandez-Vizarra and Zeviani, 2018). However, in vivo experimental validation is required.
To date, only three UQCRC1 human mutations have been identified and functionally validated: Y314S, I311L, and p.Ala25Glyfs*27. All three mutants show reduced maximal oxygen consumption rate, decreased ATP production, and increased ROS in SH-SY5Y cell lines. Drosophila and mice with the Y314S variant both showed degeneration of dopaminergic neurons and locomotor defects (Lin et al., 2020), providing direct evidence for the involvement of cIII in PD pathogenesis.
In addition to regulating cIII activities, UQCRC1 is also anti-apoptotic. In cardiac cells, UQCRC1 prevents ischemia/reperfusion injury by activating the PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β pathway, upregulating the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2, and downregulating the pro-apoptotic protein Bax (Yi et al., 2020). In Drosophila, our recent data reveal that uqcr-c1 associates with cyt c in mitochondria to gate its release (Hung et al., 2021). Previous reports have shown that complex I and II mediate signals for apoptosis (Lemarie and Grimm, 2011). Together, these findings suggest that the respiratory chain complexes are important regulators of apoptosis.
The Many Faces of ETC Proteins: Functions Beyond Bioenergetics and Possible Implications in Neurodegeneration
Abundant studies have focused on mitochondrial quality control, lysosomal functions, apoptosis, and α-Syn aggregation in PD pathogenesis and their influences on ETC functions. In contrast, whether ETC proteins have any direct involvement in these pathways other than bioenergetics remains unclear in neurodegenerative diseases.
The roles of ETC proteins in apoptosis have been extensively studied in cancer cell biology. Both cI and cII are implicated as apoptotic sensors via different mechanisms. In cI, cleavage of NDUFS1 by caspase-3 inhibits cI activities, causing ROS production and collapse of mitochondria membrane potential. The cleavage-resistant mutant NDUFS1 D255A decreases ROS formation and delays the loss of plasma membrane integrity (Ricci et al., 2004), suggesting cI inhibition as an accelerator of apoptosis. A similar mechanism is found in granzyme A-induced apoptosis, in which NDUFS3 was cleaved (Martinvalet et al., 2005). For cII, the acidification of matrix in response to mitochondrial stress causes the disintegration of cII by dissociating the anchoring subunit SDHC-SDHD from the enzyme subunit SDHA-SDHB. As the SDHA-SDHB subunit is still enzymatically active, it produces excessive ROS and causes apoptosis. cII, therefore, is a pH sensor of the matrix in programmed cell death.
The roles of complexes III and IV in apoptosis are less clear, but the electron carrier between the two complexes, cyt c, has been known as a key player by activating apoptosis protease activating factor-1 (Apaf-1) when released to the cytosol. Post-translational modifications, especially phosphorylation, of cyt c have regulatory roles in both electron transport and apoptosis (Kalpage et al., 2019a). Tissue-specific phosphorylation of cyt c at Ser47 and Tyr97 that are enriched in porcine brain tissues and insulin-treated porcine tissues, respectively (Sanderson et al., 2013; Kalpage et al., 2019b), are both anti-apoptotic not only by inhibiting caspase-3 activities (Kalpage et al., 2019b) but also by reducing the cyt c-COX interactions to lower the COX reaction rate and ROS generation (Lee et al., 2006; Guerra-Castellano et al., 2018; Kalpage et al., 2019b). It is not known whether the post-translational modifications of cyt c alter any interactions with cIII. From the lessons of UQCRC1, we now know that cIII can keep cyt c from being released from mitochondria.
Emerging evidence disclosed that there are other moonlight functions of cyt c. Abundant cyt c was shown to translocate to the nucleus prior to caspase activation in the cytosol during the early phase of apoptosis (Nolin et al., 2016). The translocated cyt c hijacks histone chaperones such as suppressor of variegation, enhancer of zeste and trithorax (SET)/template-activating factor (TAF)-Iβ, inhibiting the nucleosome assembly/disassembly activity and DNA repairing (González-Arzola et al., 2015; Díaz-Moreno et al., 2018). DNA damage is common in many neurodegenerative disorders, including PD (Ainslie et al., 2021). Cyt c has also been identified as one of the components of brainstem Lewy bodies (Wakabayashi et al., 2007) and might play as a trigger in α-Syn aggregation (Hashimoto et al., 1999). α-Syn fibrils rather than mutant oligomers or monomers specifically interact with cyt c according to an in vitro study (Leitão et al., 2021). Whether similar aggregations could be replicated in vivo and whether post-translational modifications of cyt c as mentioned earlier have any effects on these moonlight functions are still unknown.
Some evidence showed that ETC proteins are also involved in mitophagy or autophagy. For example, autophagy is inhibited by the cIII inhibitors Antimycin A or myxothiazol (Ma et al., 2011). Another example is ECSIT (evolutionarily conserved signaling intermediate in Toll pathways), which is essential in cI formation (Vogel et al., 2007), found as a parkin substrate and co-localized with LC3B in CCCP-treated macrophages (Carneiro et al., 2018). Upon loss of ECSIT, parkin still accumulates on the mitochondria, but the recruitment of LC3BII to mitochondria is compromised. This suggested that parkin-induced ECSIT ubiquitination is upstream of LC3BII recruitment for the initiation of mitophagy (Carneiro et al., 2018), It is not clear whether ECSIT participates in receptor-mediated mitophagy like other mitochondrial outer membrane proteins such as FUNDC1, NIX, and BNIP3. Further investigation is needed to elucidate whether ECSIT mediates mitochondria clearance via a similar mechanism in the nervous system.
Discussion
In this review, we focus on the central role of ETC in PD pathogenesis. We have discussed that ATP production by mitochondria is directly or indirectly affected by reduced turnover and altered post-translational modifications of ETC proteins, impaired assembly or instability of mitochondrial complexes, abnormal protein aggregation, and dysregulated lipid metabolism. While mutations of ETC proteins are rarely linked as a direct cause of PD (except for UQCRC1), impaired ETC proteins may not only lead to excessive ROS production, but also cause impeded mitophagy, α-Syn aggregation, and apoptosis in PD pathogenesis.
It might be argued that for the long time scale of PD progression, apoptosis is an acute cellular event that on the surface does not perfectly explain the development of PD, but when patients start to have detectable parkinsonism symptoms, there is usually at least 40–60% dopaminergic neuronal loss in the substantia nigra (Giguère et al., 2018), suggesting progressive accumulation of neuronal loss. At the organismal level, apoptosis of dopaminergic neurons occurs over time, responding to stress such as aggregated proteins or ETC dysfunction. At the cellular level, it takes time for a cell to reach the threshold that breaks the balance between pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic pathways. For example, ROS accumulation, alterations of mitochondrial outer membrane permeability, and the attenuation of antiapoptotic signals may fluctuate, and mutant cells with the propensity of releasing cyt c do not mean that it releases cyt c and activate caspases immediately. This concept of ‘apoptotic threshold’ has been well illustrated by a beautiful mathematical model (Rehm et al., 2006). In fact, apoptosis has been implicated in many neurodegenerative diseases, including PD (Moujalled et al., 2021). Although it remains unclear whether loss of ETC function leads to protein aggregation in vivo, apoptosis represents an important pathogenic mechanism that warrants our attention.
In terms of mitochondrial dysfunction, the examples of UQCRC1 and CHCHD2 have suggested that PD is not just a cI disorder. Various genetic models of PD have now shown deficits in cII to cV. The conventional belief of PD as a cI disorder might be the result of publication bias or study limitations in earlier studies. It has been shown that even in cI, the significance of the deficiency could be influenced by the purity of the samples and the assays we use (Parker et al., 2008). By using high-resolution quantitative fluorescence immunohistochemistry, Reeve et al. found that both cI and cIV were deficient in the remaining dopaminergic synapses of idiopathic PD (Reeve et al., 2018). By using imaging mass cytometry, a recent study revealed that there is even more widespread deficiency from complexes I to V in the postmortem human midbrain (Chen et al., 2021), contrary to the findings of earlier studies that were based on the measurements of biochemical activities only.
Mitochondrial therapies have been proposed as a potential treatment of PD (Thomas and Beal, 2010); however, many attempts have failed. The anti-diabetic drugs glitazones which improves mitochondrial functions (such as activities of cI and cIV) and biogenesis (Bogacka et al., 2005; Ghosh et al., 2007) did lower the incidence of PD in retrospective cohort studies (Brauer et al., 2015; Brakedal et al., 2017), but failed to show benefits in modifying disease progression of early PD (NINDS Exploratory Trials in Parkinson Disease (NET-PD) FS-ZONE Investigators, 2015). The randomized clinical trial of high dose CoQ did not slow disease progression (Beal et al., 2014). The limited bioavailability of CoQ has been considered as one of the main reasons for its failure (Bhagavan and Chopra, 2007). Longer follow-up or earlier administration of the drugs at prodromal stages may be necessary to reveal the potential benefits. Idebenone, a synthetic short-chain analog of CoQ with improved lipophilicity and bioavailability (Becker et al., 2010), having been approved as an orphan drug in treating LHON by European Medicines Agency (EMA) (European Medicines Agency [EMA], 2021) and Duchenne muscular dystrophy by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Pharmaceuticals, 2015), is tested in two PD clinical trials: (1) Idebenone Treatment of Early Parkinson’s Disease symptoms (ITEP) (NCT03727295), and (2) A Study of Efficacy and Safety of Idebenone vs. Placebo in Prodromal Parkinson Disease (SEASEiPPD) (NCT04152655). The recruitment status of the former is due to end in May 2021, while the latter is still recruiting and is scheduled to complete by January 2023.
In conclusion, ETC dysfunction is a common feature in PD, secondary to various pathomechanisms. Increasing evidence has shown that cI is not the only affected ETC complex. Other complexes, such as cIII and cIV, are also involved. ETC dysfunction not only reduces ATP production but also induces apoptosis or impaired mitophagy that undermines neuronal viability in PD. So far there is still no silver bullet to prevent or to ameliorate PD progression. Non-etheless, new compounds or existing drugs await testing as potential therapeutic strategies for PD via improving ETC functions (Singh et al., 2021).
Author Contributions
J-LL, T-YL, and C-CC: conceptualization. J-LL and T-YL: writing – original draft. C-CC: funding acquisition and supervision. All authors writing – review and editing.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan (MOST) (108-2311-B-002-011-MY3 and 110-2314-B-002-202) to C-CC.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
We thank the members of Chan Lab for critical comments on this manuscript.
References
Ainslie, A., Huiting, W., Barazzuol, L., and Bergink, S. (2021). Genome instability and loss of protein homeostasis: converging paths to neurodegeneration? Open Biol. 11:200296. doi: 10.1098/rsob.200296
Alavian, K. N., Beutner, G., Lazrove, E., Sacchetti, S., Park, H. A., Licznerski, P., et al. (2014). An uncoupling channel within the c-subunit ring of the F1FO ATP synthase is the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 111, 10580–10585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1401591111
Amo, T., Saiki, S., Sawayama, T., Sato, S., and Hattori, N. (2014). Detailed analysis of mitochondrial respiratory chain defects caused by loss of PINK1. Neurosci. Lett. 580, 37–40. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2014.07.045
Aras, S., Bai, M., Lee, I., Springett, R., Hüttemann, M., and Grossman, L. I. (2015). MNRR1 (formerly CHCHD2) is a bi-organellar regulator of mitochondrial metabolism. Mitochondrion 20, 43–51. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2014.10.003
Bae, E. J., and Lee, S. J. (2020). The LRRK2-RAB axis in regulation of vesicle trafficking and α-synuclein propagation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 1866:165632. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.165632
Baker, N., Patel, J., and Khacho, M. (2019). Linking mitochondrial dynamics, cristae remodeling and supercomplex formation: how mitochondrial structure can regulate bioenergetics. Mitochondrion 49, 259–268. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2019.06.003
Ball, N., Teo, W. P., Chandra, S., and Chapman, J. (2019). Parkinson’s disease and the environment. Front. Neurol. 10:218. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00218
Balsa, E., Marco, R., Perales-Clemente, E., Szklarczyk, R., Calvo, E., Landázuri, M. O., et al. (2012). NDUFA4 is a subunit of complex IV of the mammalian electron transport chain. Cell Metab. 16, 378–386. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.07.015
Beal, M. F., Oakes, D., Shoulson, I., Henchcliffe, C., Galpern, W. R., Haas, R., et al. (2014). A randomized clinical trial of high-dosage coenzyme Q10 in early Parkinson disease: no evidence of benefit. JAMA Neurol. 71, 543–552. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2014.131
Beck, G., Sugiura, Y., Shinzawa, K., Kato, S., Setou, M., Tsujimoto, Y., et al. (2011). Neuroaxonal dystrophy in calcium-independent phospholipase A2β deficiency results from insufficient remodeling and degeneration of mitochondrial and presynaptic membranes. J. Neurosci. 31, 11411–11420. doi: 10.1523/jneurosci.0345-11.2011
Becker, C., Bray-French, K., and Drewe, J. (2010). Pharmacokinetic evaluation of idebenone. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 6, 1437–1444. doi: 10.1517/17425255.2010.530656
Berwick, D. C., Heaton, G. R., Azeggagh, S., and Harvey, K. (2019). LRRK2 Biology from structure to dysfunction: research progresses, but the themes remain the same. Mol. Neurodegener. 14:49. doi: 10.1186/s13024-019-0344-2
Betarbet, R., Sherer, T. B., MacKenzie, G., Garcia-Osuna, M., Panov, A. V., and Greenamyre, J. T. (2000). Chronic systemic pesticide exposure reproduces features of Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 1301–1306. doi: 10.1038/81834
Bhagavan, H. N., and Chopra, R. K. (2007). Plasma coenzyme Q10 response to oral ingestion of coenzyme Q10 formulations. Mitochondrion 7(Suppl.), S78–S88. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2007.03.003
Blackinton, J., Lakshminarasimhan, M., Thomas, K. J., Ahmad, R., Greggio, E., Raza, A. S., et al. (2009). Formation of a stabilized cysteine sulfinic acid is critical for the mitochondrial function of the parkinsonism protein DJ-1. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 6476–6485. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M806599200
Boecker, C. A., Goldsmith, J., Dou, D., Cajka, G. G., and Holzbaur, E. L. F. (2021). Increased LRRK2 kinase activity alters neuronal autophagy by disrupting the axonal transport of autophagosomes. Curr. Biol. 31, 2140.e2146–2154.e2146. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2021.02.061
Bogacka, I., Xie, H., Bray, G. A., and Smith, S. R. (2005). Pioglitazone induces mitochondrial biogenesis in human subcutaneous adipose tissue in vivo. Diabetes 54, 1392–1399. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.54.5.1392
Bolam, J. P., and Pissadaki, E. K. (2012). Living on the edge with too many mouths to feed: why dopamine neurons die. Mov. Disord. 27, 1478–1483. doi: 10.1002/mds.25135
Bonifati, V., Rizzu, P., van Baren, M. J., Schaap, O., Breedveld, G. J., Krieger, E., et al. (2003). Mutations in the DJ-1 gene associated with autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism. Science 299, 256–259. doi: 10.1126/science.1077209
Brakedal, B., Flønes, I., Reiter, S. F., Torkildsen, O., Dolle, C., Assmus, J., et al. (2017). Glitazone use associated with reduced risk of Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 32, 1594–1599. doi: 10.1002/mds.27128
Brauer, R., Bhaskaran, K., Chaturvedi, N., Dexter, D. T., Smeeth, L., and Douglas, I. (2015). Glitazone treatment and incidence of Parkinson’s disease among people with diabetes: a retrospective cohort study. PLoS Med. 12:e1001854. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001854
Burré, J., Sharma, M., Tsetsenis, T., Buchman, V., Etherton, M. R., and Südhof, T. C. (2010). Alpha-synuclein promotes SNARE-complex assembly in vivo and in vitro. Science 329, 1663–1667. doi: 10.1126/science.1195227
Cabin, D. E., Shimazu, K., Murphy, D., Cole, N. B., Gottschalk, W., McIlwain, K. L., et al. (2002). Synaptic vesicle depletion correlates with attenuated synaptic responses to prolonged repetitive stimulation in mice lacking alpha-synuclein. J. Neurosci. 22, 8797–8807. doi: 10.1523/jneurosci.22-20-08797.2002
Carneiro, F. R. G., Lepelley, A., Seeley, J. J., Hayden, M. S., and Ghosh, S. (2018). An essential role for ECSIT in mitochondrial complex I assembly and mitophagy in macrophages. Cell Rep. 22, 2654–2666. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.02.051
Chakraborty, J., Basso, V., and Ziviani, E. (2017). Post translational modification of Parkin. Biol. Direct. 12:6. doi: 10.1186/s13062-017-0176-3
Chen, C., McDonald, D., Blain, A., Sachdeva, A., Bone, L., Smith, A. L. M., et al. (2021). Imaging mass cytometry reveals generalised deficiency in OXPHOS complexes in Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 7:39. doi: 10.1038/s41531-021-00182-x
Chen, R., Park, H. A., Mnatsakanyan, N., Niu, Y., Licznerski, P., Wu, J., et al. (2019). Parkinson’s disease protein DJ-1 regulates ATP synthase protein components to increase neuronal process outgrowth. Cell Death Dis. 10:469. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1679-x
Chinta, S. J., Mallajosyula, J. K., Rane, A., and Andersen, J. K. (2010). Mitochondrial α-synuclein accumulation impairs complex I function in dopaminergic neurons and results in increased mitophagy in vivo. Neurosci. Lett. 486, 235–239. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.09.061
Cole, N. B., Dieuliis, D., Leo, P., Mitchell, D. C., and Nussbaum, R. L. (2008). Mitochondrial translocation of alpha-synuclein is promoted by intracellular acidification. Exp. Cell Res. 314, 2076–2089. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2008.03.012
Conway, K. A., Harper, J. D., and Lansbury, P. T. (1998). Accelerated in vitro fibril formation by a mutant alpha-synuclein linked to early-onset Parkinson disease. Nat. Med. 4, 1318–1320. doi: 10.1038/3311
Conway, K. A., Lee, S. J., Rochet, J. C., Ding, T. T., Williamson, R. E., and Lansbury, P. T. Jr., (2000). Acceleration of oligomerization, not fibrillization, is a shared property of both alpha-synuclein mutations linked to early-onset Parkinson’s disease: implications for pathogenesis and therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97, 571–576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.2.571
Crofts, A. R. (2004). The cytochrome bc1 complex: function in the context of structure. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 66, 689–733. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.66.032102.150251
de la Mata, M., Cotán, D., Oropesa-Ávila, M., Garrido-Maraver, J., Cordero, M. D., Villanueva Paz, M., et al. (2015). Pharmacological chaperones and coenzyme Q10 treatment improves mutant β-Glucocerebrosidase activity and mitochondrial function in neuronopathic forms of gaucher disease. Sci. Rep. 5:10903. doi: 10.1038/srep10903
de Oliveira, G. A. P., and Silva, J. L. (2019). Alpha-synuclein stepwise aggregation reveals features of an early onset mutation in Parkinson’s disease. Commun. Biol. 2:374. doi: 10.1038/s42003-019-0598-9
Delcambre, S., Ghelfi, J., Ouzren, N., Grandmougin, L., Delbrouck, C., Seibler, P., et al. (2020). Mitochondrial mechanisms of LRRK2 G2019S penetrance. Front. Neurol. 11:881. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00881
Díaz-Moreno, I., Velázquez-Cruz, A., Curran-French, S., Díaz-Quintana, A., and De la Rosa, M. A. (2018). Nuclear cytochrome c - a mitochondrial visitor regulating damaged chromatin dynamics. FEBS Lett. 592, 172–178. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12959
Dorsey, E. R., and Bloem, B. R. (2018). The Parkinson Pandemic-A call to action. JAMA Neurol. 75, 9–10. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2017.3299
Eguchi, T., Kuwahara, T., Sakurai, M., Komori, T., Fujimoto, T., Ito, G., et al. (2018). LRRK2 and its substrate Rab GTPases are sequentially targeted onto stressed lysosomes and maintain their homeostasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 115, E9115–E9124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1812196115
European Medicines Agency [EMA] (2021). EMEA/H/C/003834 - Summary of the European Public Assessment Report (EPAR) for Raxone. Available online at: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/raxone (accessed Septemebr 6, 2021).
Fernandez-Vizarra, E., and Zeviani, M. (2018). Mitochondrial complex III Rieske Fe-S protein processing and assembly. Cell Cycle 17, 681–687. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2017.1417707
Foo, J. N., Chew, E. G. Y., Chung, S. J., Peng, R., Blauwendraat, C., Nalls, M. A., et al. (2020). Identification of risk loci for Parkinson disease in Asians and comparison of risk between Asians and Europeans: a genome-wide association study. JAMA Neurol. 77, 746–754. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.0428
Foo, J. N., Tan, L. C., Irwan, I. D., Au, W. L., Low, H. Q., Prakash, K. M., et al. (2017). Genome-wide association study of Parkinson’s disease in East Asians. Hum. Mol. Genet. 26, 226–232. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddw379
Funayama, M., Ohe, K., Amo, T., Furuya, N., Yamaguchi, J., Saiki, S., et al. (2015). CHCHD2 mutations in autosomal dominant late-onset Parkinson’s disease: a genome-wide linkage and sequencing study. Lancet Neurol. 14, 274–282. doi: 10.1016/s1474-4422(14)70266-2
GBD 2016 Parkinson’s Disease Collaborators (2018). Global, regional, and national burden of Parkinson’s disease, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 17, 939–953. doi: 10.1016/s1474-4422(18)30295-3
Ge, P., Dawson, V. L., and Dawson, T. M. (2020). PINK1 and Parkin mitochondrial quality control: a source of regional vulnerability in Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 15:20. doi: 10.1186/s13024-020-00367-7
Gegg, M. E., and Schapira, A. H. (2016). Mitochondrial dysfunction associated with glucocerebrosidase deficiency. Neurobiol. Dis. 90, 43–50. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2015.09.006
Gehrke, S., Wu, Z., Klinkenberg, M., Sun, Y., Auburger, G., Guo, S., et al. (2015). PINK1 and Parkin control localized translation of respiratory chain component mRNAs on mitochondria outer membrane. Cell Metab. 21, 95–108. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.12.007
Ghosh, S., Patel, N., Rahn, D., McAllister, J., Sadeghi, S., Horwitz, G., et al. (2007). The thiazolidinedione pioglitazone alters mitochondrial function in human neuron-like cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 71, 1695–1702. doi: 10.1124/mol.106.033845
Giachin, G., Bouverot, R., Acajjaoui, S., Pantalone, S., and Soler-López, M. (2016). Dynamics of human mitochondrial complex I assembly: implications for neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Mol. Biosci. 3:43. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2016.00043
Giguère, N., Burke Nanni, S., and Trudeau, L. E. (2018). On cell loss and selective vulnerability of neuronal populations in Parkinson’s disease. Front. Neurol. 9:455. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00455
Gilkerson, R. W., Selker, J. M., and Capaldi, R. A. (2003). The cristal membrane of mitochondria is the principal site of oxidative phosphorylation. FEBS Lett. 546, 355–358. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(03)00633-1
Gloeckner, C. J., Kinkl, N., Schumacher, A., Braun, R. J., O’Neill, E., Meitinger, T., et al. (2006). The Parkinson disease causing LRRK2 mutation I2020T is associated with increased kinase activity. Hum. Mol. Genet. 15, 223–232. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddi439
Glover, V., Gibb, C., and Sandler, M. (1986). The role of MAO in MPTP toxicity–a review. J. Neural. Transm. Suppl. 20, 65–76.
Gomez, R. C., Wawro, P., Lis, P., Alessi, D. R., and Pfeffer, S. R. (2019). Membrane association but not identity is required for LRRK2 activation and phosphorylation of Rab GTPases. J. Cell Biol. 218, 4157–4170. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201902184
González-Arzola, K., Díaz-Moreno, I., Cano-González, A., Díaz-Quintana, A., Velázquez-Campoy, A., Moreno-Beltrán, B., et al. (2015). Structural basis for inhibition of the histone chaperone activity of SET/TAF-Iβ by cytochrome c. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 112, 9908–9913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1508040112
Gonzalez-Hunt, C. P., Thacker, E. A., Toste, C. M., Boularand, S., Deprets, S., Dubois, L., et al. (2020). Mitochondrial DNA damage as a potential biomarker of LRRK2 kinase activity in LRRK2 Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Rep. 10:17293. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-74195-6
Gorman, G. S., Chinnery, P. F., DiMauro, S., Hirano, M., Koga, Y., McFarland, R., et al. (2016). Mitochondrial diseases. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2:16080. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2016.80
Gudz, T. I., Tserng, K. Y., and Hoppel, C. L. (1997). Direct inhibition of mitochondrial respiratory chain complex III by cell-permeable ceramide. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 24154–24158. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.39.24154
Guerra, G., Martínez, F., and Pardo, J. P. (2002). On the H+/2e– stoichiometry of the respiratory chain *. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ. 30, 363–367. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2002.494030060133
Guerra-Castellano, A., Díaz-Quintana, A., Pérez-Mejías, G., Elena-Real, C. A., González-Arzola, K., García-Mauriño, S. M., et al. (2018). Oxidative stress is tightly regulated by cytochrome c phosphorylation and respirasome factors in mitochondria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 115, 7955–7960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1806833115
Hallett, P. J., Huebecker, M., Brekk, O. R., Moloney, E. B., Rocha, E. M., Priestman, D. A., et al. (2018). Glycosphingolipid levels and glucocerebrosidase activity are altered in normal aging of the mouse brain. Neurobiol. Aging 67, 189–200. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2018.02.028
Hardy, J., Lewis, P., Revesz, T., Lees, A., and Paisan-Ruiz, C. (2009). The genetics of Parkinson’s syndromes: a critical review. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 19, 254–265. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2009.03.008
Hashimoto, M., Takeda, A., Hsu, L. J., Takenouchi, T., and Masliah, E. (1999). Role of cytochrome c as a stimulator of alpha-synuclein aggregation in Lewy body disease. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 28849–28852. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.41.28849
Hayashi, T., Ishimori, C., Takahashi-Niki, K., Taira, T., Kim, Y. C., Maita, H., et al. (2009). DJ-1 binds to mitochondrial complex I and maintains its activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 390, 667–672. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.10.025
Healy, D. G., Falchi, M., O’Sullivan, S. S., Bonifati, V., Durr, A., Bressman, S., et al. (2008). Phenotype, genotype, and worldwide genetic penetrance of LRRK2-associated Parkinson’s disease: a case-control study. Lancet Neurol. 7, 583–590. doi: 10.1016/s1474-4422(08)70117-0
Heo, J. Y., Park, J. H., Kim, S. J., Seo, K. S., Han, J. S., Lee, S. H., et al. (2012). DJ-1 null dopaminergic neuronal cells exhibit defects in mitochondrial function and structure: involvement of mitochondrial complex I assembly. PLoS One 7:e32629. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032629
Hsieh, C. H., Shaltouki, A., Gonzalez, A. E., Bettencourt da Cruz, A., Burbulla, L. F., St Lawrence, E., et al. (2016). Functional impairment in miro degradation and mitophagy is a shared feature in familial and sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Cell Stem Cell 19, 709–724. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2016.08.002
Hung, Y. C., Huang, K. L., Chen, P. L., Li, J. L., Lu, S. H., Chang, J. C., et al. (2021). UQCRC1 engages cytochrome c for neuronal apoptotic cell death. Cell Rep. 36:109729. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109729
Iwaki, H., Blauwendraat, C., Leonard, H. L., Liu, G., Maple-Grødem, J., Corvol, J. C., et al. (2019). Genetic risk of Parkinson disease and progression:: an analysis of 13 longitudinal cohorts. Neurol. Genet. 5:e348. doi: 10.1212/nxg.0000000000000348
Jenkins, C. M., Yan, W., Mancuso, D. J., and Gross, R. W. (2006). Highly selective hydrolysis of fatty acyl-CoAs by calcium-independent phospholipase A2beta. Enzyme autoacylation and acyl-CoA-mediated reversal of calmodulin inhibition of phospholipase A2 activity. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 15615–15624. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M511623200
Jonckheere, A. I., Smeitink, J. A., and Rodenburg, R. J. (2012). Mitochondrial ATP synthase: architecture, function and pathology. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 35, 211–225. doi: 10.1007/s10545-011-9382-9
Kagan, V. E., Tyurin, V. A., Jiang, J., Tyurina, Y. Y., Ritov, V. B., Amoscato, A. A., et al. (2005). Cytochrome c acts as a cardiolipin oxygenase required for release of proapoptotic factors. Nat. Chem. Biol. 1, 223–232. doi: 10.1038/nchembio727
Kahle, P. J., Neumann, M., Ozmen, L., Muller, V., Jacobsen, H., Schindzielorz, A., et al. (2000). Subcellular localization of wild-type and Parkinson’s disease-associated mutant alpha -synuclein in human and transgenic mouse brain. J. Neurosci. 20, 6365–6373. doi: 10.1523/jneurosci.20-17-06365.2000
Kalpage, H. A., Bazylianska, V., Recanati, M. A., Fite, A., Liu, J., Wan, J., et al. (2019a). Tissue-specific regulation of cytochrome c by post-translational modifications: respiration, the mitochondrial membrane potential. ROS, and apoptosis. FASEB J. 33, 1540–1553. doi: 10.1096/fj.201801417R
Kalpage, H. A., Vaishnav, A., Liu, J., Varughese, A., Wan, J., Turner, A. A., et al. (2019b). Serine-47 phosphorylation of cytochrome c in the mammalian brain regulates cytochrome c oxidase and caspase-3 activity. FASEB J. 33, 13503–13514. doi: 10.1096/fj.201901120R
Kilarski, L. L., Pearson, J. P., Newsway, V., Majounie, E., Knipe, M. D., Misbahuddin, A., et al. (2012). Systematic review and UK-based study of PARK2 (parkin), PINK1, PARK7 (DJ-1) and LRRK2 in early-onset Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 27, 1522–1529. doi: 10.1002/mds.25132
Kinghorn, K. J., Castillo-Quan, J. I., Bartolome, F., Angelova, P. R., Li, L., Pope, S., et al. (2015). Loss of PLA2G6 leads to elevated mitochondrial lipid peroxidation and mitochondrial dysfunction. Brain 138(Pt 7), 1801–1816. doi: 10.1093/brain/awv132
Kinumi, T., Kimata, J., Taira, T., Ariga, H., and Niki, E. (2004). Cysteine-106 of DJ-1 is the most sensitive cysteine residue to hydrogen peroxide-mediated oxidation in vivo in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 317, 722–728. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.03.110
Kitada, T., Asakawa, S., Hattori, N., Matsumine, H., Yamamura, Y., Minoshima, S., et al. (1998). Mutations in the parkin gene cause autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism. Nature 392, 605–608. doi: 10.1038/33416
Kogot-Levin, A., and Saada, A. (2014). Ceramide and the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Biochimie 100, 88–94. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2013.07.027
Koros, C., Simitsi, A., and Stefanis, L. (2017). Genetics of Parkinson’s disease: genotype-phenotype correlations. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 132, 197–231. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2017.01.009
Kota, V., Szulc, Z. M., and Hama, H. (2012). Identification of C(6) -ceramide-interacting proteins in D6P2T Schwannoma cells. Proteomics 12, 2179–2184. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201100527
Kumar, S., Yadav, N., Pandey, S., Muthane, U. B., Govindappa, S. T., Abbas, M. M., et al. (2020). Novel and reported variants in Parkinson’s disease genes confer high disease burden among Indians. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 78, 46–52. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2020.07.014
Langston, J. W., Ballard, P., Tetrud, J. W., and Irwin, I. (1983). Chronic Parkinsonism in humans due to a product of meperidine-analog synthesis. Science 219, 979–980. doi: 10.1126/science.6823561
Lashuel, H. A., Overk, C. R., Oueslati, A., and Masliah, E. (2013). The many faces of α-synuclein: from structure and toxicity to therapeutic target. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 14, 38–48. doi: 10.1038/nrn3406
Lee, I., Salomon, A. R., Yu, K., Doan, J. W., Grossman, L. I., and Hüttemann, M. (2006). New prospects for an old enzyme: mammalian cytochrome c is tyrosine-phosphorylated in vivo. Biochemistry 45, 9121–9128. doi: 10.1021/bi060585v
Lee, R. G., Sedghi, M., Salari, M., Shearwood, A. J., Stentenbach, M., Kariminejad, A., et al. (2018). Early-onset Parkinson disease caused by a mutation in CHCHD2 and mitochondrial dysfunction. Neurol. Genet. 4:e276. doi: 10.1212/nxg.0000000000000276
Lee, Y., Stevens, D. A., Kang, S. U., Jiang, H., Lee, Y. I., Ko, H. S., et al. (2017). PINK1 primes parkin-mediated ubiquitination of PARIS in dopaminergic neuronal survival. Cell Rep. 18, 918–932. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.12.090
Leitão, A. D. G., Rudolffi-Soto, P., Chappard, A., Bhumkar, A., Lau, D., Hunter, D. J. B., et al. (2021). Selectivity of Lewy body protein interactions along the aggregation pathway of α-synuclein. Commun. Biol. 4:1124. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02624-x
Lemarie, A., and Grimm, S. (2011). Mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes: apoptosis sensors mutated in cancer? Oncogene 30, 3985–4003. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.167
Lesage, S., Houot, M., Mangone, G., Tesson, C., Bertrand, H., Forlani, S., et al. (2020). Genetic and phenotypic basis of autosomal dominant Parkinson’s disease in a large multi-center cohort. Front. Neurol. 11:682. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00682
Levitt, P., Pintar, J. E., and Breakefield, X. O. (1982). Immunocytochemical demonstration of monoamine oxidase B in brain astrocytes and serotonergic neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 6385–6389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6385
Lin, C. H., Chen, P. L., Tai, C. H., Lin, H. I., Chen, C. S., Chen, M. L., et al. (2019). A clinical and genetic study of early-onset and familial parkinsonism in taiwan: an integrated approach combining gene dosage analysis and next-generation sequencing. Mov. Disord. 34, 506–515. doi: 10.1002/mds.27633
Lin, C. H., Tsai, P. I., Lin, H. Y., Hattori, N., Funayama, M., Jeon, B., et al. (2020). Mitochondrial UQCRC1 mutations cause autosomal dominant parkinsonism with polyneuropathy. Brain 143, 3352–3373. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaa279
Lin, G., Lee, P. T., Chen, K., Mao, D., Tan, K. L., Zuo, Z., et al. (2018). Phospholipase PLA2G6, a Parkinsonism-associated gene, affects Vps26 and Vps35, retromer function, and ceramide levels, similar to α-Synuclein gain. Cell Metab. 28, 605.e606–618.e606. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.05.019
Liu, W., Duan, X., Xu, L., Shang, W., Zhao, J., Wang, L., et al. (2020). Chchd2 regulates mitochondrial morphology by modulating the levels of Opa1. Cell Death Differ. 27, 2014–2029. doi: 10.1038/s41418-019-0482-7
Liu, Y. T., Huang, X., Nguyen, D., Shammas, M. K., Wu, B. P., Dombi, E., et al. (2020). Loss of CHCHD2 and CHCHD10 activates OMA1 peptidase to disrupt mitochondrial cristae phenocopying patient mutations. Hum. Mol. Genet. 29, 1547–1567. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddaa077
Liu, Z., Bryant, N., Kumaran, R., Beilina, A., Abeliovich, A., Cookson, M. R., et al. (2018). LRRK2 phosphorylates membrane-bound Rabs and is activated by GTP-bound Rab7L1 to promote recruitment to the trans-Golgi network. Hum. Mol. Genet. 27, 385–395. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx410
Ludtmann, M. H. R., Angelova, P. R., Horrocks, M. H., Choi, M. L., Rodrigues, M., Baev, A. Y., et al. (2018). α-synuclein oligomers interact with ATP synthase and open the permeability transition pore in Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Commun. 9:2293. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04422-2
Lwin, A., Orvisky, E., Goker-Alpan, O., LaMarca, M. E., and Sidransky, E. (2004). Glucocerebrosidase mutations in subjects with parkinsonism. Mol. Genet. Metab. 81, 70–73. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2003.11.004
Ma, X., Jin, M., Cai, Y., Xia, H., Long, K., Liu, J., et al. (2011). Mitochondrial electron transport chain complex III is required for antimycin A to inhibit autophagy. Chem. Biol. 18, 1474–1481. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2011.08.009
Magalhaes, J., Gegg, M. E., Migdalska-Richards, A., Doherty, M. K., Whitfield, P. D., and Schapira, A. H. (2016). Autophagic lysosome reformation dysfunction in glucocerebrosidase deficient cells: relevance to Parkinson disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 25, 3432–3445. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddw185
Mahul-Mellier, A. L., Burtscher, J., Maharjan, N., Weerens, L., Croisier, M., Kuttler, F., et al. (2020). The process of Lewy body formation, rather than simply α-synuclein fibrillization, is one of the major drivers of neurodegeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 117, 4971–4982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1913904117
Martinvalet, D., Zhu, P., and Lieberman, J. (2005). Granzyme A induces caspase-independent mitochondrial damage, a required first step for apoptosis. Immunity 22, 355–370. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2005.02.004
Masgras, I., Sanchez-Martin, C., Colombo, G., and Rasola, A. (2017). The chaperone TRAP1 as a modulator of the mitochondrial adaptations in cancer cells. Front. Oncol. 7:58. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00058
Mazzulli, J. R., Xu, Y. H., Sun, Y., Knight, A. L., McLean, P. J., Caldwell, G. A., et al. (2011). Gaucher disease glucocerebrosidase and α-synuclein form a bidirectional pathogenic loop in synucleinopathies. Cell 146, 37–52. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.001
Meng, H., Yamashita, C., Shiba-Fukushima, K., Inoshita, T., Funayama, M., Sato, S., et al. (2017). Loss of Parkinson’s disease-associated protein CHCHD2 affects mitochondrial crista structure and destabilizes cytochrome c. Nat. Commun. 8:15500. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15500
Mita, Y., Kataoka, Y., Saito, Y., Kashi, T., Hayashi, K., Iwasaki, A., et al. (2018). Distribution of oxidized DJ-1 in Parkinson’s disease-related sites in the brain and in the peripheral tissues: effects of aging and a neurotoxin. Sci. Rep. 8:12056. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-30561-z
Mizuno, Y., Suzuki, K., and Ohta, S. (1990). Postmortem changes in mitochondrial respiratory enzymes in brain and a preliminary observation in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 96, 49–57. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(90)90056-s
Modjtahedi, N., Tokatlidis, K., Dessen, P., and Kroemer, G. (2016). Mitochondrial proteins containing coiled-coil-helix-coiled-coil-helix (CHCH) domains in health and disease. Trends Biochem. Sci. 41, 245–260. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2015.12.004
Morais, V. A., Haddad, D., Craessaerts, K., De Bock, P. J., Swerts, J., Vilain, S., et al. (2014). PINK1 loss-of-function mutations affect mitochondrial complex I activity via NdufA10 ubiquinone uncoupling. Science 344, 203–207. doi: 10.1126/science.1249161
Morais, V. A., Verstreken, P., Roethig, A., Smet, J., Snellinx, A., Vanbrabant, M., et al. (2009). Parkinson’s disease mutations in PINK1 result in decreased Complex I activity and deficient synaptic function. EMBO Mol. Med. 1, 99–111. doi: 10.1002/emmm.200900006
Mortiboys, H., Johansen, K. K., Aasly, J. O., and Bandmann, O. (2010). Mitochondrial impairment in patients with Parkinson disease with the G2019S mutation in LRRK2. Neurology 75, 2017–2020. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181ff9685
Mortiboys, H., Thomas, K. J., Koopman, W. J., Klaffke, S., Abou-Sleiman, P., Olpin, S., et al. (2008). Mitochondrial function and morphology are impaired in parkin-mutant fibroblasts. Ann. Neurol. 64, 555–565. doi: 10.1002/ana.21492
Moujalled, D., Strasser, A., and Liddell, J. R. (2021). Molecular mechanisms of cell death in neurological diseases. Cell Death Differ. 28, 2029–2044. doi: 10.1038/s41418-021-00814-y
Müftüoglu, M., Elibol, B., Dalmizrak, O., Ercan, A., Kulaksiz, G., Ogüs, H., et al. (2004). Mitochondrial complex I and IV activities in leukocytes from patients with parkin mutations. Mov. Disord. 19, 544–548. doi: 10.1002/mds.10695
Müller, M., Ahumada-Castro, U., Sanhueza, M., Gonzalez-Billault, C., Court, F. A., and Cárdenas, C. (2018). Mitochondria and calcium regulation as basis of neurodegeneration associated with aging. Front. Neurosci. 12:470. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00470
Muñoz, S. S., Petersen, D., Marlet, F. R., Kücükköse, E., and Galvagnion, C. (2021). The interplay between Glucocerebrosidase, α-synuclein and lipids in human models of Parkinson’s disease. Biophys. Chem. 273:106534. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2020.106534
Nalls, M. A., Blauwendraat, C., Vallerga, C. L., Heilbron, K., Bandres-Ciga, S., Chang, D., et al. (2019). Identification of novel risk loci, causal insights, and heritable risk for Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Lancet Neurol. 18, 1091–1102. doi: 10.1016/s1474-4422(19)30320-5
Nicklas, W. J., Vyas, I., and Heikkila, R. E. (1985). Inhibition of NADH-linked oxidation in brain mitochondria by 1-methyl-4-phenyl-pyridine, a metabolite of the neurotoxin, 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine. Life Sci. 36, 2503–2508. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(85)90146-8
NINDS Exploratory Trials in Parkinson Disease (NET-PD) FS-ZONE Investigators (2015). Pioglitazone in early Parkinson’s disease: a phase 2, multicentre, double-blind, randomised trial. Lancet Neurol. 14, 795–803. doi: 10.1016/s1474-4422(15)00144-1
Nolin, F., Michel, J., Wortham, L., Tchelidze, P., Banchet, V., Lalun, N., et al. (2016). Stage-Specific changes in the water, Na+, Cl- and K+ contents of organelles during apoptosis, demonstrated by a targeted cryo correlative analytical approach. PLoS One 11:e0148727. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148727
Oka, T., Sayano, T., Tamai, S., Yokota, S., Kato, H., Fujii, G., et al. (2008). Identification of a novel protein MICS1 that is involved in maintenance of mitochondrial morphology and apoptotic release of cytochrome c. Mol. Biol. Cell 19, 2597–2608. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-12-1205
Osellame, L. D., Rahim, A. A., Hargreaves, I. P., Gegg, M. E., Richard-Londt, A., Brandner, S., et al. (2013). Mitochondria and quality control defects in a mouse model of Gaucher disease–links to Parkinson’s disease. Cell Metab. 17, 941–953. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2013.04.014
Oueslati, A., Paleologou, K. E., Schneider, B. L., Aebischer, P., and Lashuel, H. A. (2012). Mimicking phosphorylation at serine 87 inhibits the aggregation of human α-synuclein and protects against its toxicity in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurosci. 32, 1536–1544. doi: 10.1523/jneurosci.3784-11.2012
Ow, Y. P., Green, D. R., Hao, Z., and Mak, T. W. (2008). Cytochrome c: functions beyond respiration. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9, 532–542. doi: 10.1038/nrm2434
Paisan-Ruiz, C., Bhatia, K. P., Li, A., Hernandez, D., Davis, M., Wood, N. W., et al. (2009). Characterization of PLA2G6 as a locus for dystonia-parkinsonism. Ann. Neurol. 65, 19–23. doi: 10.1002/ana.21415
Parker, W. D. Jr., Boyson, S. J., and Parks, J. K. (1989). Abnormalities of the electron transport chain in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 26, 719–723. doi: 10.1002/ana.410260606
Parker, W. D. Jr., Parks, J. K., and Swerdlow, R. H. (2008). Complex I deficiency in Parkinson’s disease frontal cortex. Brain Res. 1189, 215–218. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.10.061
Pharmaceuticals, S. (2015). Santhera receives FDA Fast Track Designation for Raxone® /Catena® (idebenone) for the Treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD). Available online at: http://www.santhera.com/assets/files/press-releases/680846_apr_9_2015.pdf (accessed Septemebr 6, 2021).
Pogson, J. H., Ivatt, R. M., Sanchez-Martinez, A., Tufi, R., Wilson, E., Mortiboys, H., et al. (2014). The complex I subunit NDUFA10 selectively rescues Drosophila pink1 mutants through a mechanism independent of mitophagy. PLoS Genet. 10:e1004815. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004815
Polymeropoulos, M. H., Lavedan, C., Leroy, E., Ide, S. E., Dehejia, A., Dutra, A., et al. (1997). Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science 276, 2045–2047. doi: 10.1126/science.276.5321.2045
Postuma, R. B., Berg, D., Stern, M., Poewe, W., Olanow, C. W., Oertel, W., et al. (2015). MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 30, 1591–1601. doi: 10.1002/mds.26424
Poulopoulos, M., Levy, O. A., and Alcalay, R. N. (2012). The neuropathology of genetic Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 27, 831–842. doi: 10.1002/mds.24962
Pridgeon, J. W., Olzmann, J. A., Chin, L. S., and Li, L. (2007). PINK1 protects against oxidative stress by phosphorylating mitochondrial chaperone TRAP1. PLoS Biol. 5:e172. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0050172
Ramsay, R. R., Salach, J. I., Dadgar, J., and Singer, T. P. (1986). Inhibition of mitochondrial NADH dehydrogenase by pyridine derivatives and its possible relation to experimental and idiopathic parkinsonism. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 135, 269–275. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90972-1
Reeve, A. K., Grady, J. P., Cosgrave, E. M., Bennison, E., Chen, C., Hepplewhite, P. D., et al. (2018). Mitochondrial dysfunction within the synapses of substantia nigra neurons in Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 4:9. doi: 10.1038/s41531-018-0044-6
Reeve, A. K., Ludtmann, M. H., Angelova, P. R., Simcox, E. M., Horrocks, M. H., Klenerman, D., et al. (2015). Aggregated α-synuclein and complex I deficiency: exploration of their relationship in differentiated neurons. Cell Death Dis. 6:e1820. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.166
Rehm, M., Huber, H. J., Dussmann, H., and Prehn, J. H. (2006). Systems analysis of effector caspase activation and its control by X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein. Embo J. 25, 4338–4349. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601295
Ricci, J. E., Muñoz-Pinedo, C., Fitzgerald, P., Bailly-Maitre, B., Perkins, G. A., Yadava, N., et al. (2004). Disruption of mitochondrial function during apoptosis is mediated by caspase cleavage of the p75 subunit of complex I of the electron transport chain. Cell 117, 773–786. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.05.008
Rocha, E. M., Smith, G. A., Park, E., Cao, H., Brown, E., Hallett, P., et al. (2015). Progressive decline of glucocerebrosidase in aging and Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2, 433–438. doi: 10.1002/acn3.177
Rosborough, K., Patel, N., and Kalia, L. V. (2017). α-Synuclein and Parkinsonism: updates and future perspectives. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 17:31. doi: 10.1007/s11910-017-0737-y
Rutter, J., Winge, D. R., and Schiffman, J. D. (2010). Succinate dehydrogenase - Assembly, regulation and role in human disease. Mitochondrion 10, 393–401. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2010.03.001
Saito, Y., Miyasaka, T., Hatsuta, H., Takahashi-Niki, K., Hayashi, K., Mita, Y., et al. (2014). Immunostaining of oxidized DJ-1 in human and mouse brains. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 73, 714–728. doi: 10.1097/nen.0000000000000087
Sanderson, T. H., Mahapatra, G., Pecina, P., Ji, Q., Yu, K., Sinkler, C., et al. (2013). Cytochrome C is tyrosine 97 phosphorylated by neuroprotective insulin treatment. PLoS One 8:e78627. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078627
Satake, W., Nakabayashi, Y., Mizuta, I., Hirota, Y., Ito, C., Kubo, M., et al. (2009). Genome-wide association study identifies common variants at four loci as genetic risk factors for Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Genet. 41, 1303–1307. doi: 10.1038/ng.485
Sato, H., Arawaka, S., Hara, S., Fukushima, S., Koga, K., Koyama, S., et al. (2011). Authentically phosphorylated α-synuclein at Ser129 accelerates neurodegeneration in a rat model of familial Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurosci. 31, 16884–16894. doi: 10.1523/jneurosci.3967-11.2011
Schapira, A. H., Cooper, J. M., Dexter, D., Clark, J. B., Jenner, P., and Marsden, C. D. (1990). Mitochondrial complex I deficiency in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurochem. 54, 823–827. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb02325.x
Schöndorf, D. C., Ivanyuk, D., Baden, P., Sanchez-Martinez, A., De Cicco, S., Yu, C., et al. (2018). The NAD+ precursor nicotinamide riboside rescues mitochondrial defects and neuronal loss in iPSC and fly models of Parkinson’s disease. Cell Rep. 23, 2976–2988. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.05.009
Shavali, S., Brown-Borg, H. M., Ebadi, M., and Porter, J. (2008). Mitochondrial localization of alpha-synuclein protein in alpha-synuclein overexpressing cells. Neurosci. Lett. 439, 125–128. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2008.05.005
Shi, C. H., Tang, B. S., Wang, L., Lv, Z. Y., Wang, J., Luo, L. Z., et al. (2011). PLA2G6 gene mutation in autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism in a Chinese cohort. Neurology 77, 75–81. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e318221acd3
Shin, J. H., Ko, H. S., Kang, H., Lee, Y., Lee, Y. I., Pletinkova, O., et al. (2011). PARIS (ZNF746) repression of PGC-1α contributes to neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Cell 144, 689–702. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.010
Sidransky, E., Nalls, M. A., Aasly, J. O., Aharon-Peretz, J., Annesi, G., Barbosa, E. R., et al. (2009). Multicenter analysis of glucocerebrosidase mutations in Parkinson’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 361, 1651–1661. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0901281
Singh, A., Faccenda, D., and Campanella, M. (2021). Pharmacological advances in mitochondrial therapy. EBioMedicine 65:103244. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103244
Singh, A., Zhi, L., and Zhang, H. (2019). LRRK2 and mitochondria: recent advances and current views. Brain Res. 1702, 96–104. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.06.010
Sorrentino, Z. A., and Giasson, B. I. (2020). The emerging role of α-synuclein truncation in aggregation and disease. J. Biol. Chem. 295, 10224–10244. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV120.011743
Steger, M., Tonelli, F., Ito, G., Davies, P., Trost, M., Vetter, M., et al. (2016). Phosphoproteomics reveals that Parkinson’s disease kinase LRRK2 regulates a subset of Rab GTPases. Elife 5:e12813. doi: 10.7554/eLife.12813
Stoker, T. B., Camacho, M., Winder-Rhodes, S., Liu, G., Scherzer, C. R., Foltynie, T., et al. (2020). Impact of GBA1 variants on long-term clinical progression and mortality in incident Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 91, 695–702. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2020-322857
Sunitha, B., Gayathri, N., Kumar, M., Keshava Prasad, T. S., Nalini, A., Padmanabhan, B., et al. (2016). Muscle biopsies from human muscle diseases with myopathic pathology reveal common alterations in mitochondrial function. J. Neurochem. 138, 174–191. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13626
Takanashi, M., Li, Y., and Hattori, N. (2016). Absence of Lewy pathology associated with PINK1 homozygous mutation. Neurology 86, 2212–2213. doi: 10.1212/wnl.0000000000002744
Tan, M. M. X., Malek, N., Lawton, M. A., Hubbard, L., Pittman, A. M., Joseph, T., et al. (2019). Genetic analysis of Mendelian mutations in a large UK population-based Parkinson’s disease study. Brain 142, 2828–2844. doi: 10.1093/brain/awz191
Tanaka, A., Cleland, M. M., Xu, S., Narendra, D. P., Suen, D. F., Karbowski, M., et al. (2010). Proteasome and p97 mediate mitophagy and degradation of mitofusins induced by Parkin. J. Cell Biol. 191, 1367–1380. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201007013
Thomas, B., and Beal, M. F. (2010). Mitochondrial therapies for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 25(Suppl. 1), S155–S160. doi: 10.1002/mds.22781
Trinh, J., Guella, I., and Farrer, M. J. (2014). Disease penetrance of late-onset parkinsonism: a meta-analysis. JAMA Neurol. 71, 1535–1539. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2014.1909
Unni, S., Thiyagarajan, S., Srinivas Bharath, M. M., and Padmanabhan, B. (2019). Tryptophan oxidation in the UQCRC1 subunit of mitochondrial complex III (Ubiquinol-Cytochrome C Reductase) in a mouse model of myodegeneration causes large structural changes in the complex: a molecular dynamics simulation study. Sci. Rep. 9:10694. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-47018-6
Valente, E. M., Abou-Sleiman, P. M., Caputo, V., Muqit, M. M., Harvey, K., Gispert, S., et al. (2004). Hereditary early-onset Parkinson’s disease caused by mutations in PINK1. Science 304, 1158–1160. doi: 10.1126/science.1096284
Valente, E. M., Bentivoglio, A. R., Dixon, P. H., Ferraris, A., Ialongo, T., Frontali, M., et al. (2001). Localization of a novel locus for autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism, PARK6, on human chromosome 1p35-p36. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 68, 895–900. doi: 10.1086/319522
Valente, E. M., Brancati, F., Ferraris, A., Graham, E. A., Davis, M. B., Breteler, M. M., et al. (2002). PARK6-linked parkinsonism occurs in several European families. Ann. Neurol. 51, 14–18.
Van Walraven, H. S., Strotmann, H., Schwarz, O., and Rumberg, B. (1996). The H+/ATP coupling ratio of the ATP synthase from thiol-modulated chloroplasts and two cyanobacterial strains is four. FEBS Lett. 379, 309–313. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)01536-1
Vicario, M., Cieri, D., Vallese, F., Catoni, C., Barazzuol, L., Berto, P., et al. (2019). A split-GFP tool reveals differences in the sub-mitochondrial distribution of wt and mutant alpha-synuclein. Cell Death Dis. 10:857. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-2092-1
Vieweg, S., Mulholland, K., Bräuning, B., Kachariya, N., Lai, Y. C., Toth, R., et al. (2020). PINK1-dependent phosphorylation of Serine111 within the SF3 motif of Rab GTPases impairs effector interactions and LRRK2-mediated phosphorylation at Threonine72. Biochem. J. 477, 1651–1668. doi: 10.1042/bcj20190664
Vincow, E. S., Merrihew, G., Thomas, R. E., Shulman, N. J., Beyer, R. P., MacCoss, M. J., et al. (2013). The PINK1-Parkin pathway promotes both mitophagy and selective respiratory chain turnover in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110, 6400–6405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1221132110
Vogel, R. O., Janssen, R. J., van den Brand, M. A., Dieteren, C. E., Verkaart, S., Koopman, W. J., et al. (2007). Cytosolic signaling protein Ecsit also localizes to mitochondria where it interacts with chaperone NDUFAF1 and functions in complex I assembly. Genes Dev. 21, 615–624. doi: 10.1101/gad.408407
Wakabayashi, K., Tanji, K., Mori, F., and Takahashi, H. (2007). The Lewy body in Parkinson’s disease: molecules implicated in the formation and degradation of alpha-synuclein aggregates. Neuropathology 27, 494–506. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1789.2007.00803.x
Wang, X., Becker, K., Levine, N., Zhang, M., Lieberman, A. P., Moore, D. J., et al. (2019). Pathogenic alpha-synuclein aggregates preferentially bind to mitochondria and affect cellular respiration. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 7:41. doi: 10.1186/s40478-019-0696-4
Wang, X., Winter, D., Ashrafi, G., Schlehe, J., Wong, Y. L., Selkoe, D., et al. (2011). PINK1 and Parkin target Miro for phosphorylation and degradation to arrest mitochondrial motility. Cell 147, 893–906. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.10.018
Wang, Z. B., Li, M., Zhao, Y., and Xu, J. X. (2003). Cytochrome C is a hydrogen peroxide scavenger in mitochondria. Protein Pept. Lett. 10, 247–253. doi: 10.2174/0929866033479013
Wauters, F., Cornelissen, T., Imberechts, D., Martin, S., Koentjoro, B., Sue, C., et al. (2020). LRRK2 mutations impair depolarization-induced mitophagy through inhibition of mitochondrial accumulation of RAB10. Autophagy 16, 203–222. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1603548
Weiss, B. (2008). ROCO kinase activity is controlled by internal GTPase function. Sci. Signal. 1:e27. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.123pe27
West, A. B., Moore, D. J., Biskup, S., Bugayenko, A., Smith, W. W., Ross, C. A., et al. (2005). Parkinson’s disease-associated mutations in leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 augment kinase activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102, 16842–16847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0507360102
Wiedemann, F. R., Winkler, K., Lins, H., Wallesch, C. W., and Kunz, W. S. (1999). Detection of respiratory chain defects in cultivated skin fibroblasts and skeletal muscle of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 893, 426–429. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb07870.x
Wilkens, V., Kohl, W., and Busch, K. (2013). Restricted diffusion of OXPHOS complexes in dynamic mitochondria delays their exchange between cristae and engenders a transitory mosaic distribution. J. Cell Sci. 126(Pt 1), 103–116. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108852
Wilson, K. S., and Prochaska, L. J. (1990). Phospholipid vesicles containing bovine heart mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase and subunit III-deficient enzyme: analysis of respiratory control and proton translocating activities. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 282, 413–420. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90137-n
Yang, X. H., and Trumpower, B. L. (1986). Purification of a three-subunit ubiquinol-cytochrome c oxidoreductase complex from Paracoccus denitrificans. J. Biol. Chem. 261, 12282–12289.
Yi, T., Wu, X., and Li, H. (2020). Ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase core protein 1 overexpression protects H9c2 cardiac cells against mimic ischemia/reperfusion injury through PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 529, 904–909. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.06.089
Zhang, L., Shimoji, M., Thomas, B., Moore, D. J., Yu, S. W., Marupudi, N. I., et al. (2005). Mitochondrial localization of the Parkinson’s disease related protein DJ-1: implications for pathogenesis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 14, 2063–2073. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddi211
Zhao, R. Z., Jiang, S., Zhang, L., and Yu, Z. B. (2019). Mitochondrial electron transport chain, ROS generation and uncoupling (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 44, 3–15. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4188
Zhao, Y., Qin, L., Pan, H., Liu, Z., Jiang, L., He, Y., et al. (2020). The role of genetics in Parkinson’s disease: a large cohort study in Chinese mainland population. Brain 143, 2220–2234. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaa167
Zhou, W., Ma, D., Sun, A. X., Tran, H. D., Ma, D. L., Singh, B. K., et al. (2019). PD-linked CHCHD2 mutations impair CHCHD10 and MICOS complex leading to mitochondria dysfunction. Hum. Mol. Genet. 28, 1100–1116. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddy413
Zhou, W., Zhu, M., Wilson, M. A., Petsko, G. A., and Fink, A. L. (2006). The oxidation state of DJ-1 regulates its chaperone activity toward alpha-synuclein. J. Mol. Biol. 356, 1036–1048. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2005.12.030
Zigdon, H., Kogot-Levin, A., Park, J. W., Goldschmidt, R., Kelly, S., and Merrill, A. H. Jr., et al. (2013). Ablation of ceramide synthase 2 causes chronic oxidative stress due to disruption of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 4947–4956. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.402719
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease, electron transport chain, mitochondria quality control, mitophagy, apoptosis
Citation: Li J-L, Lin T-Y, Chen P-L, Guo T-N, Huang S-Y, Chen C-H, Lin C-H and Chan C-C (2021) Mitochondrial Function and Parkinson’s Disease: From the Perspective of the Electron Transport Chain. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 14:797833. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.797833
Received: 19 October 2021; Accepted: 18 November 2021;
Published: 09 December 2021.
Edited by:
Chuang-Rung Chang, National Tsing Hua University, TaiwanReviewed by:
Shigeru Yanagi, Gakushuin University, JapanKostas Tokatlidis, University of Glasgow, United Kingdom
Kuen-Jer Tsai, National Cheng Kung University, Taiwan
Copyright © 2021 Li, Lin, Chen, Guo, Huang, Chen, Lin and Chan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chih-Chiang Chan, Y2hhbmNjMUBudHUuZWR1LnR3
 Jeng-Lin Li
Jeng-Lin Li Tai-Yi Lin
Tai-Yi Lin Po-Lin Chen
Po-Lin Chen Ting-Ni Guo
Ting-Ni Guo Shu-Yi Huang
Shu-Yi Huang Chun-Hong Chen
Chun-Hong Chen Chin-Hsien Lin
Chin-Hsien Lin Chih-Chiang Chan
Chih-Chiang Chan