- 1School of Health Management, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
- 2School of Basic Medical Sciences, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
- 3Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital (Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences), Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
- 4School of Public Health, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
- 5School of Stomatology, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
- 6School of Public Health, Peking University, Beijing, China
- 7School of Health Management, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
A Corrigendum on
Impact of intermittent fasting on physical activity: a national survey of Chinese residents aged 18–80 years
by He F, Bai S, Xu X, Miao J, Yu H, Qiu J, Wu Y, Fan Y and Shi L (2025). Front. Physiol. 16:1582036. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1582036
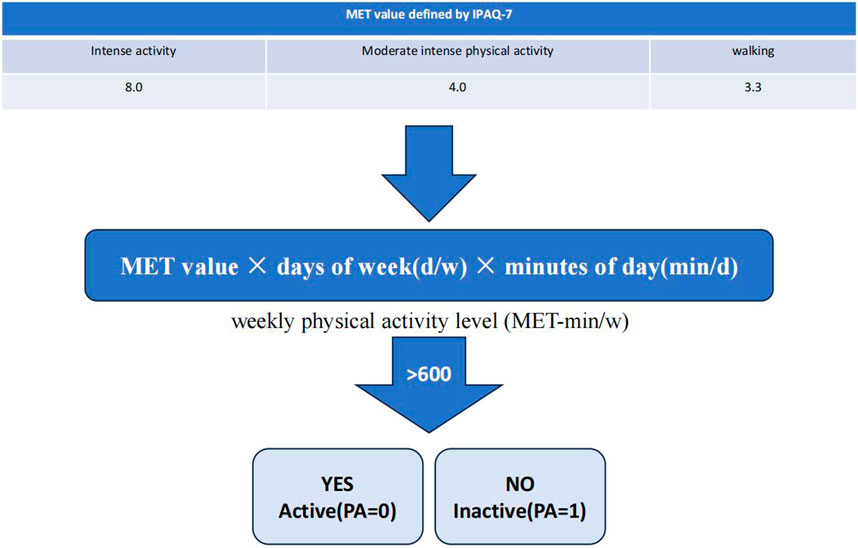
In the published article, there was an error in “Figure 1 Two levels of physical activity” as published. In this figure, there was an error in the box “No,Inactive (PA = 0)”, the correct form should be “No, Inactive (PA = 1).”
The corrected Figure 1 and its caption appear below.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: intermittent fasting, physical activity, multiple logistic regression, health management, China
Citation: He F, Bai S, Xu X, Miao J, Yu H, Qiu J, Wu Y, Fan Y and Shi L (2025) Corrigendum: Impact of intermittent fasting on physical activity: a national survey of Chinese residents aged 18–80 years. Front. Physiol. 16:1628669. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1628669
Received: 14 May 2025; Accepted: 20 May 2025;
Published: 30 May 2025.
Edited and reviewed by:
Yong-Bo Zheng, Peking University Sixth Hospital, ChinaCopyright © 2025 He, Bai, Xu, Miao, Yu, Qiu, Wu, Fan and Shi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lei Shi, aHlkbGVpc2hpQDEyNi5jb20=; Yangdong Fan, ZnlkX2hlQHNpbmEuY29t; Yibo Wu, YmptdXd1eWlib0BvdXRsb29rLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Feiying He
Feiying He Shiyu Bai
Shiyu Bai Xiangchun Xu3†
Xiangchun Xu3† Jingqiao Miao
Jingqiao Miao Jiale Qiu
Jiale Qiu Lei Shi
Lei Shi