Abstract
Cerebral ischemia and hypoxia play key roles in the occurrence and development of vascular cognitive impairment (VCI). However, the pathophysiology of VCI remains unclear. Necroptosis is a non-cysteine-dependent form of cell death mediated by serine/threonine kinases receptor-interacting protein kinase-1 and -3 and mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein. A search of PubMed and Web of Science was conducted using terms related to VCI and necroptosis. Necroptosis is important in neuroinflammation, neuronal loss, blood–brain barrier dysfunction, and demyelination. Cerebral ischemia activates the necroptotic pathway, and necroptosis inhibitors have a significant inhibitory effect on brain injury. This review focuses on the pathogenesis of VCI and clarifies the core regulatory mechanism of necroptosis in vascular dementia, which lays a scientific foundation for cognitive impairment prevention and treatment by targeting necroptosis in VCI.
1 Introduction
Research on vascular cognitive impairment (VCI) is mainly focused on the influence of vascular factors on any degree of cognitive function, from mild deficits to prodromal and fully developed dementia (Badji et al., 2023; Chang Wong and Chang Chui, 2022). In 2018, 50 million people are estimated to be affected globally, of which approximately 25% are Chinese (Lu et al., 2020), and this number is expected to triple by 2050 (Liu et al., 2024; Guo et al., 2023). Moreover, patients with VCI have a high mortality rate (Ren and Qu, 2023).
Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion (CCH) and cerebral hypoxia are the key causes of VCI (Rajeev et al., 2023). The molecular and cellular pathogenic mechanisms of VCI are only partially elucidated. Recent studies have shown that necroptosis plays an important role in brain tissue injury caused by cerebral ischemia and hypoxia (Nikseresht et al., 2019). However, despite growing evidence on necroptosis in ischemic brain injury, its precise role in VCI pathology remains unclear.
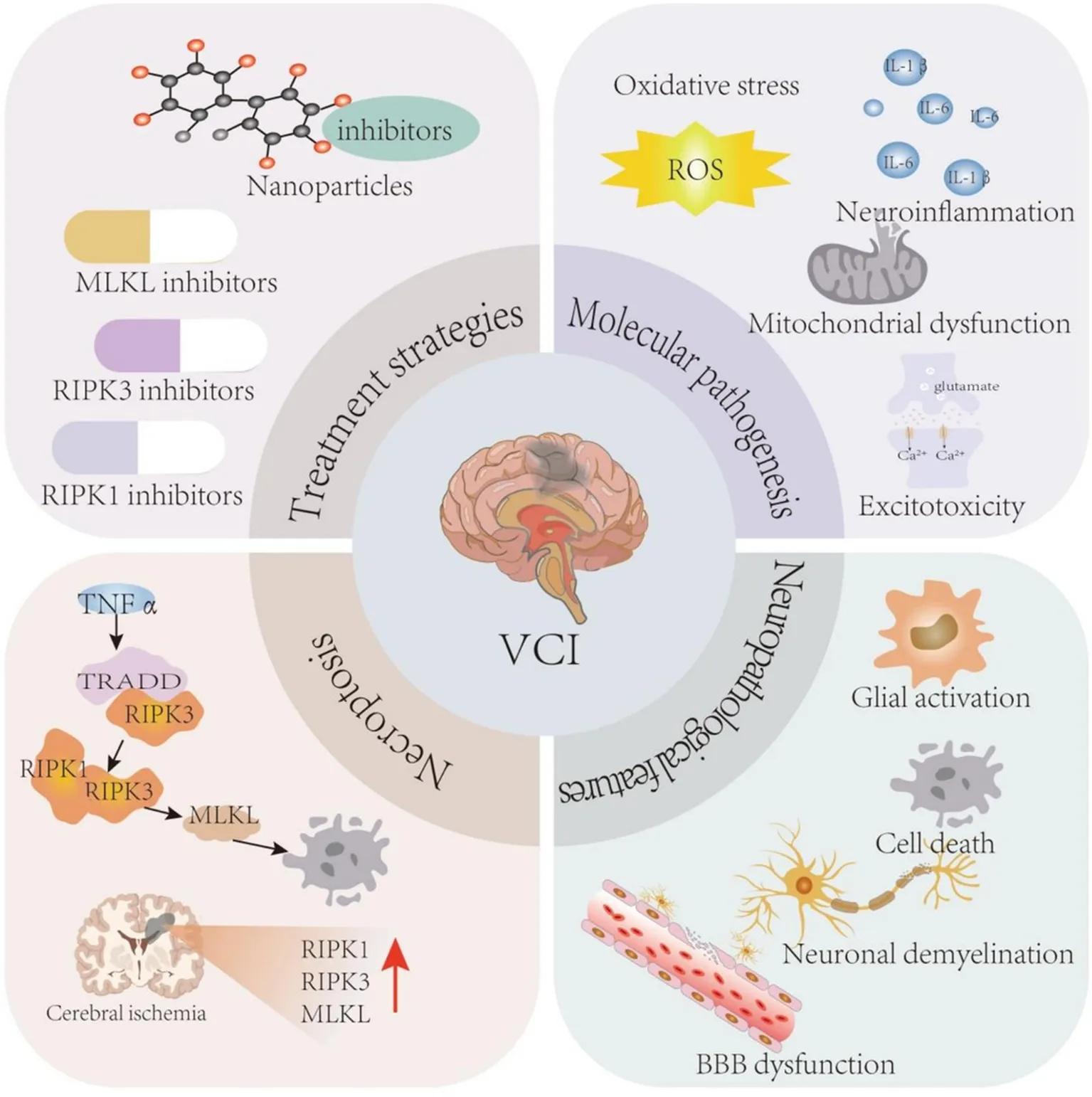
In this review, we summarize the current knowledge of the molecular mechanisms and pathological changes in VCI, describe the role of necroptosis in the pathological changes caused by cerebral ischemia and hypoxia, and discuss the application of necroptosis inhibitors as potential therapeutic interventions for VCI (Figure 1).
Figure 1

Molecular mechanism and pathological changes of VCI. The molecular mechanisms of VCI mainly include oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and mitochondrial dysfunction. The pathological changes of VCI mainly include glial activation, cell death, BBB dysfunction, neuronal demyelination, and white matter lesions. BBB, blood brain barrier; IL, interleukin; ROS, reactive oxygen species; VCI, vascular cognitive impairment.
2 Research status of the pathogenesis of VCI
The concept of VCI was first proposed by Hachinski and Bowler (1993). This concept has gradually replaced vascular dementia to describe cognitive decline caused by cerebrovascular diseases (Hachinski and Bowler, 1993; van der Flier et al., 2018). VCI can be divided into mild and severe forms; the latter includes post-stroke, subcortical ischemic vascular, multi-infarct, and mixed dementias (Skrobot et al., 2018; Masserini et al., 2023). Several mechanisms play a role in VCI progression; however, pathological mechanisms involve reduced cerebral blood flow, neuronal death, glial cell activation, white matter lesions (WMLs), blood–brain barrier (BBB) damage, and endothelial dysfunction. Oxidative stress and inflammation are the two main underlying mechanisms (Kalaria et al., 2024; Fitzgibbon-Collins et al., 2021). However, a thorough understanding of this complex disease is lacking. Therefore, a consensus on the underlying causes of VCI is needed.
Animal models used in VCI research typically mimic cerebral ischemia, including CCH, to simulate the underlying pathology of VCI. The whole brain is placed in a state of ischemia and hypoxia, resulting in progressive and persistent brain damage, such as energy metabolism imbalance, neuroinflammation, and white matter demyelination (He et al., 2023; Zheng et al., 2023). Cerebral blood flow reduction is also observed in VCI patients, causing neural and vascular changes such as the activation of glial cells, BBB dysfunction, demyelination, and endothelial cell (EC) damage (Zhang et al., 2023; Cheng et al., 2024). Cerebral ischemia is linked to known mechanisms of VCI, including neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, neuronal death, and energy imbalance (Rajeev et al., 2023; Zhao et al., 2023). In the following section, we review the pathogenesis of VCI caused by cerebral ischemia in detail.
2.1 Molecular pathogenesis of VCI
2.1.1 Oxidative stress
Oxidative stress results in accumulation of numerous oxidative intermediates, such as reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen radicals, leading to tissue damage and cell death (Martemucci et al., 2023; Maiese, 2023). Cerebral ischemia and hypoxia in VCI increases ROS levels in cerebrovascular ECs (Zeylan et al., 2024) and can cause disruption of Ca2+ homeostasis in the brain, impairing the function of the mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC) in ECs. Activation of ROS enzymes, such as nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase (Nox), xanthine oxidase, and nitric oxide synthase (NOS), causes the production of excess ROS to further promote the occurrence of oxidative stress (Wang et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2023). In rodent models of CCH, Nox2 levels in the brain and in hippocampal neurons are increased and associated with cognitive impairment (Alfieri et al., 2022; Choi et al., 2014). Oxygen generates other ROS, such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and hydroxyl free radicals, through a series of disproportionation reactions. In vitro experiments using cells exposed to H2O2 to simulate an oxidative stress injury have been performed (Song et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2021). Antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase, and catalase are decreased in the peripheral blood of VCI patients, whereas the oxidative stress markers malondialdehyde (MDA), reactive ROS, and lactate dehydrogenase are increased (Krishnan and Rani, 2014; Xue et al., 2017). Oxidative stress is the basic pathological process of VCI; however, the mechanism has not been fully elucidated, and further in-depth study is needed.
2.1.2 Neuroinflammation
Neuroinflammation is an immune cascade mediated by microglia and astrocytes in the central nervous system (CNS) (Sanz et al., 2024; Villa-Gonzalez et al., 2024), which is caused by pathological injuries such as infection, ischemia, and hypoxia (Titisari et al., 2024; Thiankhaw et al., 2024). Neuroinflammation triggered by cerebral ischemia and hypoxia in a VCI mouse model causes WMLs, cognitive dysfunction, and learning and memory deficits. In addition, various proinflammatory factors, such as interleukin beta 1 (IL-1β) and IL-6, are significantly increased in brain tissue and serum (Gao et al., 2024; Tang et al., 2024). Neuroinflammation induces neuronal dysfunction and death, leading to cognitive dysfunction (Villa-Gonzalez et al., 2024; Huang et al., 2024). Continuous damage to the vascular system results in the destruction of the BBB, further promoting the inflammatory response and eventually leading to more severe cognitive dysfunction and even dementia (Tang et al., 2024; Nyul-Toth et al., 2024). Additionally, the complement system can also cause neuroinflammation. In the early stages of VCI, complement components (C1q and C3) facilitate phagocytosis and clearance of amyloid fibrils; however, in late stages, C5 activates the membrane attack complex to induce neuroinflammation and neuronal damage (Batista et al., 2024; Wen et al., 2024). In summary, the entire inflammatory process promotes astrogliosis, endothelial dysfunction, BBB disruption, and complement system disorders, leading to neuronal damage.
2.1.3 Mitochondrial dysfunction
Mitochondria, known as the “powerhouse” organelles of the cell, provide 95% of cellular energy and play an important role many cell biological processes (Spinelli and Haigis, 2018; Hu et al., 2024). Ischemia and hypoxia reduces the synthesis of ATP in nerve cells, the Na+/K+ pump on the cell membrane is inactivated, and excitatory amino acid (mainly glutamate) levels increase, which activates the formation of mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP). This leads to Ca2 + overload and disrupts the mitochondrial membrane potential (Wang et al., 2023; Rahi and Kaundal, 2024). The open mPTP also allows other metabolites to enter the mitochondrial matrix space and uncouples the mitochondrial ETC from ATP synthase activity, leading to a reduction in ATP, cessation of oxidative phosphorylation, and finally, production of excessive ROS (Beg et al., 2024; He et al., 2022). ROS destroy the activities of complexes I to IV and impairs mitochondrial respiratory function, resulting in mitochondrial outer membrane damage. Cytochrome C and apoptosis-inducing factor in mitochondria are released into the cytoplasm and promote neuronal apoptosis (Okoye et al., 2023). Additionally, prolonged hypoxia, mitochondrial Ca2+ overload, and excessive ROS accumulation may completely inhibit or over-activate mitophagy, leading to mitochondrial homeostasis imbalance and further aggravating cerebral ischemic injury and cognitive impairment (Wang et al., 2024). Therefore, mitochondrial dysfunction is among the fundamental causes of nerve damage and cognitive impairment in VCI.
2.1.4 Excitotoxicity
Excitotoxicity is one of the earliest discovered and widely recognized molecular mechanisms of injury after ischemic stroke (Burch et al., 2024). Due to disordered metabolism in the ischemic area in VCI, excessive release of the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate in the synaptic cleft increases activation of the N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA), α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid, and kainic acid receptors, causing increased Ca2+ influx. The dramatic increase in intracellular Ca2+ activates neutral proteases, endonucleases, and phospholipases, resulting in the destruction of DNA and the neuronal cytoskeleton, simultaneously producing various free radicals and apoptotic bodies and eventually causing neuronal apoptosis (Rajeev et al., 2023; Deng et al., 2019). Moreover excitability toxicity and excessive NMDA receptor activation triggers the JNK/c-Jun/AP-1 signal transduction pathway, further expanding ischemic cell death (Nuzzo et al., 2019). Furthermore, NMDA activation stimulates NOS to produce a high concentration of NO, which further promotes neuronal damage (Wang et al., 2024; de Sousa Maciel et al., 2022). In summary, excitotoxicity is an important neurobiological phenomenon that plays a key role in various neurological diseases and injuries.
2.2 Neuropathological features of VCI
2.2.1 Glial activation
Glial activation, particularly microglial activation, results in polarization towards proinflammatory M1 and anti-inflammatory M2 phenotypes (Ye et al., 2024; Lokesh et al., 2024). M1 microglia secrete a variety of proinflammatory cytokines, whereas M2 microglia secrete a series of anti-inflammatory cytokines that promote endocytosis and eventually reduce neuronal damage (Mo et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2024). Microglial cells in the brain of VCI patients multiply, especially in the white matter, and quickly activate, causing morphological changes (Zhao et al., 2024) that mainly promote the polarization of microglia cells to the proinflammatory M1 phenotype. Secreted proinflammatory factors aggravate brain tissue damage after ischemia (Pang et al., 2023). In vitro experiments showed that 2,3,5,6-tetramethylpyrazine had an anti-inflammatory effect, restraining the inactivation of the NF-κB signaling pathway to inhibit the polarization of M1 microglia and reducing the expression of inducible NO synthase and CD86 M1 markers and proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-6, thereby reducing lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced neuroinflammation (Chen et al., 2023). Another study showed that paeoniflorin inhibited activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway, thereby blocking the polarization of M1 microglia in the hippocampal CA1 region of VCI rats and reducing the expression of inflammatory mediators IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and NO. Furthermore, paeoniflorin can upregulate the expression of anti-inflammatory factors IL-10 and TGF-β1 in M2 microglia, thereby reducing neuroinflammation in the hippocampal CA1 region (Luo et al., 2018). In conclusion, microglia can promote neuroinflammation in chronic cerebral ischemia by activating the NF-κB signaling pathway (Chen et al., 2024).
2.2.2 Cell death
Programmed cell death is a regulatory mechanism mediated by signal transduction pathways. Abnormal regulation of programmed cell death is associated with neurodegenerative diseases and cancer (Yang et al., 2022). In CCH animal models, as ischemic time was prolonged, apoptosis of hippocampal neurons and Bax expression increased, while expression of the anti-apoptotic factor Bcl-2 decreased (Niu et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2021). Expression of the autophagy markers P62 and LC3-II/LC3-I increased (Xu et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2023), whereas ferroptosis-related proteins such as solute carrier family 7 member 11 and GPX4 were downregulated (Fan et al., 2024; Lou et al., 2024). Additionally, expression of pyroptotic proteins caspase-3, nod-like receptor pyrin domain-containing protein 3 (NLRP3), GSDMD-N, caspase-1 p20 (its active form), and ASC were increased (Zhu et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2023). Necroptosis plays an important role in hippocampal neuron loss and white matter damage after chronic cerebral ischemia (Nikseresht et al., 2019; Chen et al., 2018). Various cell death modes mediate VCI cell loss; however, necroptosis plays a particularly prominent role and is a potential target for regulating VCI neuron loss.
2.2.3 BBB dysfunction
The BBB is an important physiological barrier between the CNS and peripheral blood circulation. It selectively transports nutrients, expels toxic substances and metabolites (Zhang et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2024), and maintains the dynamic stability of the internal environment of the CNS (Shang et al., 2024; Bai and Ge, 2024).
The mechanism of BBB dysfunction in VCI is not fully understood; however, oxidative stress, excitotoxicity, and neuroinflammation promote dysregulation of EC apical tight junction proteins, leading to increased BBB permeability. This promotes the entry of cytokines, immunoglobulins, and self-secreted serum factors into the brain, resulting in collagen deposition around the corpus callosum. Subsequently, WMLs are formed, resulting in cognitive decline (Rajeev et al., 2022; Rajeev et al., 2022). Additionally, increased endothelial transendocytosis after CCH leads to BBB dysfunction (Shang et al., 2024). In cerebral ischemia, excitatory toxicity from increased Ca2+ concentration in the EC cytoplasm induces metabolic disorders, mitochondrial dysfunction, protease activity, and the activation of phospholipase and ROS generation. These common factors cause EC membrane injury and vascular cell death, damaging the integrity of the BBB (Shah et al., 2024; Zhao et al., 2022). Animal experiments have shown that CCH-induced cognitive impairment can be improved by alleviating neuroinflammation and protecting the BBB (Wang et al., 2023; Li et al., 2022).
2.2.4 Neuronal demyelination and WMLs
WMLs are predominantly involved in brain structure changes, and the main pathological features are demyelination, gliosis, loss of nerve fibers and oligodendrocytes, and microglial activation (Lin et al., 2024; Xiao et al., 2023). WMLs are associated with a 73% increased risk of VCI (Hu et al., 2021). CCH induces oxidative stress, inflammation, oligodendrocyte apoptosis, and microglial activation, promotes demyelination, decreases nerve fiber microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2) levels, and increases myelin basic protein levels, leading to impaired cognitive function and further aggravating WMLs (Jiang et al., 2024; Guo et al., 2022). Therefore, extensive cerebral ischemia-induced WMLs are now considered the key drivers and most important pathological features of VCI and dementia and are an important cause of cognitive deficits.
Pathophysiological studies on cerebral ischemia suggest that glial cell activation, cell death pathways, BBB function, and therapeutic interventions for WMLs may inhibit the pathological progression of VCI.
3 Necroptosis
Necroptosis is a form of programmed cell death that differs from apoptosis and does not depend on caspase activity. Necroptosis is characterized by the activation of receptor-interacting protein kinase (RIPKs), followed by phosphorylation and activation of mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein (MLKL), resulting in plasma membrane rupture and the release of cellular contents. Eventually, the cytoplasm and nucleus disassemble, and the cell dies (Ai et al., 2024; Guo et al., 2024).
3.1 Molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways of necroptosis
Necroptosis relies mainly on death receptor activation, including TNF receptor 1 (TNFR1), Fas/CD95, and TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptors (Wu et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2024).
3.1.1 Classical pathway
In the classical necroptotic pathway, TNF-α binds to its receptor TNFR1 and then combines with TNF receptor-associated death domain protein (TRADD), RIPK1, TNF receptor-associated factor family proteins (TRAFs), and inhibitor of apoptosis protein cIAP1/2 and linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex (LUBAC) to form complex I (Wu et al., 2024; Wendlocha et al., 2024). In response to deubiquitinating enzymes such as cylindromatosis (CYLD), RIPK1 dissociates from complex I and recruits Fas-associated death domain protein (FADD), which then binds to pro-caspase-8 to generate complex IIa. When caspase-8 is inhibited, RIPK1 is autophosphorylated at Ser166 and binds to RIPK3 via the RIPK homotypic interaction motif to form complex IIb, and RIP3 is phosphorylated at Ser227 to promote MLKL phosphorylation. Phosphorylated MLKL (p-MLKL) oligomerizes and translocates to the cell membrane, leading to the disruption of cell and organelle membranes and eventually to necrosis (Ranjan and Pathak, 2024; Tran et al., 2024) (Figure 2).
Figure 2

Necroptotic pathways. In the classical necroptosis pathway, TNF-α binds to its receptor TNFR1 and then to TRADD, RIPK1, TRAF family proteins, cIAP1/2, and LUBAC to form complex I, which is critical for cell survival. In most cases, TRADD in complex I acts as an adaptor molecule that, once activated, recruits RIPK1 to TNFR1, cIAP1/2, and TRAF2/5 to promote complex I stabilization. TGF-β-activated kinase 1 is then activated to recruit IKK complexes. This leads to the activation of the NF-κB pathway, which promotes the production of inflammatory factors and cell survival. CYLD is recruited to complex I through its adaptor protein spermatogenesis-associated 2, which in turn binds to LUBAC. The proximity of CYLD to its substrate depends on the ubiquitin-binding protein A20. Once CYLD mediates the deubiquitination of RIPK1, the stability of complex I decreases. RIPK1 dissociates from complex I on the plasma membrane and recruits Fas-associated death domain protein (FADD), which then binds to pro-caspase-8 to form complex IIa. In complex IIa, the caspase-8 complex activates the caspase signaling pathway to induce apoptosis, thereby triggering cell death. When caspase-8 is inhibited, RIPK1 is autophosphorylated and binds to RIPK3 via the RIPK homotypic interaction motif to form complex IIb, and RIPK3 phosphorylation promotes MLKL phosphorylation. p-MLKL oligomerizes and translocates to the cell membrane, leading to the disruption of cell and organelle membranes and eventually to necrosis. The non-classical necroptotic pathway is complex and diverse. Double-stranded RNA molecules recognize and bind TLR3 and LPS recognizes and binds TLR4 and recruits phosphorylated RIPK1 and RIPK3 by binding TRIF, leading to programmed necrosis. ZBP1 recognizes and binds to Z-form RNA molecules released by virus-released nucleic acids in the cytoplasm, and simultaneously activates and phosphorylates RIPK3, which acquires kinase activity. Activated RIPK3 phosphorylates MLKL and induces necroptosis.
3.1.2 Non-classical pathway
Necroptosis involves several non-classical pathways. Although the activation pathways are not identical, RIPK and MLKL are activated. For example, Z-DNA binding protein 1(ZBP1) activates RIPK3-dependent cell death upon binding to Z-form nucleic acids, including Z-RNA produced by certain viral or endogenous retroviral elements (Yang et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2023). Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) recognizes and binds to double-stranded RNA molecules in the cytoplasm and recruits and phosphorylates RIPK1 and RIPK3 via the bound toll-like receptor linker molecule 1 (TRIF). TLR4 is a membrane receptor that combines with LPS signaling molecules and relies on TRIF recruitment of RIPK1 and RIPK3 (Muendlein et al., 2022; Chen et al., 2022). Type I/II interferon can activate double-stranded RNA-dependent kinase, which binds RIPK1 and RIPK3 (Rosenberg and Sibley, 2021). TRAIL can convert apoptosis into an RIPK1-dependent necrosis pathway in an acidic environment (Park et al., 2020). TNFR lacking the death domain can initiate necrosis via the RIPK1-FADD-caspase-8 complex (Abd El-Aal et al., 2022; Pham et al., 2019). In some cases, MLKL can be directly activated independently of RIPK3 activation.
4 Necroptosis in VCI
Clinical research on VCI is usually based on animal models of cerebral hypoperfusion and ischemia. In 2005, Degterev et al. (2005) first demonstrated the existence of necroptosis via a mechanism different from that of apoptosis in a mouse model of ischemic brain injury. Subsequently, an increasing number of studies have shown that necroptosis plays an important role in the pathogenesis of cerebral ischemic lesions (Deng et al., 2019; Fan et al., 2024). Increased expression of necroptosis markers such as TNF-α, RIPK3, and MLKL is observed in animal models (Chevin et al., 2022). Increased expression of RIPK1 and RIPK3 has been observed in oxygen and glucose deprivation (OGD)-induced cell injury models in vitro (Ni et al., 2018; Zhu et al., 2021). Therefore, necroptosis can be used as a new therapeutic target in VCI. Below, we review necroptosis in VCI pathological changes.
4.1 Necroptosis and neuroinflammation
The essence of classical necroptotic pathway is that TNF-α triggers a “programmed” proinflammatory form of cell necrosis by binding to its receptor TNFRI (He et al., 2024). During VCI cerebral ischemia, MLKL is phosphorylated and translocates to the plasma membrane, leading to an influx of Ca2+ and Na+ ions, which immediately opens the mPTP. Inflammatory cell damage-associated molecular patterns such as mitochondrial DNA, high mobility group box1 (HMGB1), and IL-1 are released (Prasad Panda et al., 2023). HMGB1is released from the nucleus to the cytoplasm and binds directly to TLR4 to activates NF-κB, thereby promoting the production of various proinflammatory mediators (Albaqami et al., 2024). HMGB1 inhibition in the brain tissue of cerebral ischemia mice models and in vitro studies increases TBK1 and IFNβ encephalitis markers and decreases NF-κB (Saeedan et al., 2023; Li et al., 2023). Additionally, NLRP3 or caspase-8 can activate inflammasome formation in response to RIPK3. Activation of the TLR4 signaling pathway promotes NF-κB to activate IL-1β, IL-18, and other precursors (Jiang et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2024). Researchers have focused on neuronal necroptosis in VCI. Targeting RIPK1/RIPK3 and MLKL may help overcome therapeutic barriers in the treatment of neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases and in preventing neuronal necroptosis.
4.2 Necroptosis and neuronal cell death
The expression of necroptosis kinases, including MLKL/p-MLKL, RIPK3/p-RIPK3, and RIPK1/p-RIPK1, was significantly increased in the brain tissue of an OGD-induced neuronal injury model and the brain tissue of cerebral ischemia animal models (Fan et al., 2024; Yan et al., 2022). Moreover, the levels of neuronal necrotizing factors and colocalization of NeuN and MLKL were also increased in middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) mice (Huang et al., 2023), indicating that necroptosis is involved in neuronal death in cerebral ischemia. Vieira et al. (2014) explored the mechanism of OGD-induced necroptosis in hippocampal neurons in vitro and observed that the upregulation of RIPK1 and RIPK3 protein levels induced by ischemic injury was positively correlated with the death of hippocampal neurons. RIP1 kinase blockade showed a significant neuroprotective effect, resulting in a 66% survival rate in the “ischemic” group, compared to an 83% survival rate in animals given the RIPK inhibitor necrostatin (Mitroshina et al., 2022). Necroptosis may play an important role in cell death and neuronal damage caused by cerebral ischemia.
4.3 Necroptosis and BBB
The BBB is a unique microvascular system, and ECs of the brain microvascular system constitute a key component of the BBB (Sweeney et al., 2019; Bellut et al., 2021). As mentioned previously, cerebral ischemic injury leads to disruption of BBB function and a significant increase in its permeability. Levels of the necroptosis biomarkers pRIPK1, pRIPK3, and p-MLKL increase in brain tissues, and they colocalize with the cerebral microvascular EC marker CD31 (Li et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2021). After administration of RIPK1 inhibitor, necrostatin 1, endothelial necroptosis and BBB leakage were significantly decreased (Chen et al., 2019; Chen et al., 2019). Furthermore, in a mouse RIPK1 and MLKL double knockout stroke model, the permeability of the BBB is significantly reduced (Lule et al., 2021). This indicates that brain ischemic injury activates programmed cell death of vascular ECs, leading to dysfunction of the BBB.
4.4 Necroptosis and demyelination
Oligodendrocytes form myelin to accelerate axon impulse conduction. In OGD-induced cells and permanent MCAO models, the number of neurons and astrocytes expressing RIP1K, RIP3K, and RIP1K-RIP3K complexes is increased, and MAP2 and GFAP levels are decreased. RIP1K knockdown or necrosis inhibition-1 (Nec) treatment reduces the necroptosis of neurons and astrocytes, thereby inducing demyelination (Ni et al., 2018). Demyelination has been observed in other neuropathies such as multiple sclerosis (MS) and spinal cord injury (SCI). TNFα levels are increased in the serum, brain, and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with MS, and RIPK1 is activated in mature oligodendrocytes and neurons in animal models and patients with MS (Picon et al., 2021; Zelic et al., 2021). RIPK1 and the oligodendrocyte marker IBA1 are colocalized in brain tissue (Ma et al., 2022). Administration of RIPK1 inhibitors protected mature oligodendrocytes from death and alleviated symptoms of nerve injury in a mouse model of MS, suggesting that inhibition of RIPK1 activity inhibits demyelination (Yoshikawa et al., 2018; Fan et al., 2019). RIPK3/MLKL-mediated necroptosis causes oligodendrocyte death and demyelination in SCI (Fiani et al., 2021; Song et al., 2024). Therefore, necroptosis may play an important role in nerve demyelination in VCI.
Few studies have investigated necroptosis in VCI. However, an increasing number of researchers have focused on the importance of necroptosis in cranial nerve injury. Therefore, targeting necroptosis pathway proteins for VCI therapy is feasible, and several necroptosis pathway inhibitors have been developed for experimental treatments.
5 Necroptosis is the target of VCI treatment
Existing small-molecule inhibitors targeting key proteins in the necroptotic pathway have shown promising therapeutic effects. In recent years, the application of nanotechnology with functional materials and biomedical science fusion technology to induce or inhibit necroptosis has provided great opportunities for the treatment of diseases and may be a potential therapeutic strategy.
5.1 Necroptosis inhibitors
RIPK3, RIPK1, and MLKL play important roles in neuronal necroptosis in VCI. Therefore, targeted inhibition of these kinases can improve neuronal necroptosis and thus improve cognitive impairment in VCI.
5.1.1 RIPK1 inhibitors
RIPK1 has a unique hydrophobic pocket that modulates its kinase activity through structural changes. All RIPK1 inhibitors reported to date bind to this pocket (Xie et al., 2013). Nec-1 was first discovered by screening necroptotic inhibitors (Chevin et al., 2022). Nec-1 significantly reduces ischemia-induced RIPK1 and increases the number of neurons in a rat MCAO cerebral ischemia model, thus showing a protective effect on brain injury (Deng et al., 2019). In an LPS-induced neuritis mouse model, Necs can inhibit microglia activation by inhibiting RIPK1 phosphorylation, thereby inhibiting neuroinflammation (Kim et al., 2023). GSK481, GSK772, GSK963, and GSK547 are also RIPK1 inhibitors (Mifflin et al., 2020). RIPK1 inhibitors such as SAR443820, SIR2446M, GFH312 have been tested in phase I clinical trials in healthy subjects, It has a good safety, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profile (Hincelin-Mery et al., 2024; Sun et al., 2024; Lickliter et al., 2023). RIPK1 inhibitors showed various neural inflammatory disease treatment effects but did not specifically inhibit necroptosis because they can also inhibit apoptosis.
5.1.2 RIPK3 inhibitors
Unlike RIPK1, RIPK3 does not affect apoptosis, and targeted inhibition of RIPK3 more specifically controls necroptosis (Prasad Panda et al., 2023). Therefore, specific RIPK3 inhibitors are important for necroptosis-related drug research and development. Classical RIPK3 small-molecule inhibitors include GSK840, GSK84, GSK872, and GW39B (Sun et al., 2024; Xu et al., 2023). GSK872 administration decreased RIPK3, p-JNK, and IL-6 expression and neuronal death and improved neurobehavior in rats (Hu et al., 2020). Moreover, GSK872 inhibited neuronal necroptosis in intracerebral hemorrhage mice through the death domain-associated protein signaling pathway (Bai et al., 2024). Many RIPK3 inhibitors, such as AZD5423, Compound-42, and Zharp-99, have been developed to inhibit necrotizing apoptosis in mouse inflammatory models and acute kidney injury, thereby alleviating kidney injury and systemic inflammation (He et al., 2023; Xu et al., 2022). Therefore, RIPK3 inhibitors could also have a neuroprotective effect in VCI.
5.1.3 MLKL inhibitors
MLKL, which comprises a four-helix bundle (4HB) and pseudokinase (psK) domains, acts as an executor of necroptosis and is an important drug target, and many inhibitors have been tested in previous studies. These include covalent inhibitors, ATP competitive inhibitors, and noncovalent inhibitors (Tang and Zhuang, 2024; Martinez-Osorio et al., 2023). As irreversible covalent inhibitors, necrosulfonamide and compound TC13172 both bind to Cys86 of human MLKL to protect cells from necroptosis; however, they do not affect necroptosis in mouse cells (Ji et al., 2021). GW806742X was the first molecule discovered that protects the cell from necroptosis by competing with ATP binding at the psK domain of MLKL (Pierotti et al., 2020). Another noncovalent inhibitor binds to the 4HB domain of MLKL, thereby inhibiting its action (Cui et al., 2022). However, the current molecular regulators of MLKL are in the early drug development stage and still have some limitations, so they are mainly applied in research.
5.2 Nanotechnology targets necroptosis
Nanotechnology can overcome the traditional drug delivery problem and has attracted much attention in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases (Zhang et al., 2019; Zang et al., 2022). The surface of nanoparticles can carry various therapeutic small-molecule drugs, proteins, peptides and proteins, small interfering RNA, microRNA, and DNA, which can recognize and bind to target cells (Zhang et al., 2019). The main limitation of VCI-targeted therapy is that drugs cannot cross the BBB easily, limiting their delivery to the target site. Nanotechnology can solve these problems by improving the pharmacokinetics of drugs and obtaining better neurovascular access (Amani et al., 2019). Few studies have been conducted on nanotechnology targeting necroptosis for treating VCI. However, loaded nanoparticles have a significant neuroprotective effect in a cerebral ischemia model, and targeting necroptosis in tumors has a significant effect.
The oxidative stress products ROS and MDA increase during cerebral ischemia, and their inhibition can improve brain tissue damage. Baicalin loaded onto cyclodextrin and polyethylene glycol–polylactic acid-co-glycolic acid (PEG-PLGA) to form polyethylene PEG-PLGA nanoparticles (PEG-PLGA RNP) significantly reduced the levels of MDA and ROS in the brain tissue of MCAO rats (Li et al., 2022). ROS-responsive chitosan-bilirubin nanoparticles loaded with Statin (ChiBil-Statin) reduced ROS production in an OGD-induced cell model by approximately 5.6-fold (Raveena et al., 2024). Inhibition of HMGB1 can reduce brain damage caused by neuroinflammation. 8β-glycyrrhetinic acid is a potent intracellular HMGB1 inhibitor. ROS-responsive polymer-drug conjugate nanoparticles (diglycolic acid) designed to prevent the translocation of HMGB1 inhibited the polarization of microglia to the M1 phenotype both in vitro and in vivo (Jin et al., 2023). Direct administration of neutrophil-mediated nanoparticles to the cerebral ischemic area can significantly reduce the infarct volume in MCAO mice, thereby improving cognitive impairment (Zhang et al., 2017). In conclusion, nanotechnology can reduce neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in cerebral ischemia and plays a key role in neuroprotection.
Targeting cancer cells with nanoparticles to induce necroptosis is widely used in cancer therapy. Liang et al. (2024) developed a MUC1 aptamer-targeting nanocomposite (MUC1@Chi-Ag@CPB@SHK, MUC1@ACS) for delivering shikonin and chitosan silver nanoparticles. The accumulation of MUC1@ACS nanoparticles at the tumor site increased by 6.02 times. Upregulation of RIPK3, p-RIPK3, and tetramer MLKL expression synergistically induces tumor cell necroptosis. Iron-palladium nanozyme and shikonin-encapsulated functional lipid nanoparticles increase ROS production in tumor cells and promote programmed cell death, thereby inhibiting tumor cell growth in vitro (Xie et al., 2024).
Nanotechnology targeting necroptosis in the treatment of VCI has not been reported; however, it has shown good neuroprotective effects against cerebral ischemic injury and a significant tumor-inhibitory effect. Therefore, we reasoned that nanotechnology targeting necroptosis in VCI treatment should be neuroprotective.
6 Conclusion and future prospects
This review elaborates on the potential pathophysiological mechanisms of VCI. Any one of these pathological mechanisms can trigger a vicious cycle of accelerated brain damage. However, these mechanisms have not been fully elucidated.
Necroptosis is mainly induced by extracellular factors (TNFα) and participates in pathophysiological processes in various diseases, such as neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, and autoimmune diseases. The intersection of necroptosis and apoptosis regulation increases the complexity of related pathways, such as caspase-8, FADD, and RIPK1, which are programmed in the cell apoptosis and necroptosis pathways in complex relationships. Additionally, necroptosis varies among tissues and is closely associated with VCI occurrence. Studies have shown that involvement of neuroinflammation and necroptosis in the hippocampus during vascular dementia in post-mortem brain examinations, However, research on necroptosis in VCI is limited, and the degree of its effect remains unclear.
Several necroptosis inhibitors targeting necroptosis pathway proteins have been developed as experimental treatments. Blockade of necroptosis by RIPK1-, RIPK3-, or MLKL-targeting therapy can effectively reduce oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and neuronal death caused by ischemic brain injuries. Nanotechnology has also demonstrated good neuroprotective effects against cerebral ischemic injury. Therefore, nanotechnology targeting necrotizing ptosis may be a potential neuroprotective strategy to alleviate VCI brain damage. However, the extent of necroptosis compared to other pathways of death remains to be clarified. Second, although new necroptosis inhibitors with neuroprotective potential have been studied in phase 1 clinical trials, research is still in its early stages and the cytotoxicity of these inhibitors remains to be elucidated. Finally, necroptosis in the ischemic core and peri-infarct areas of the brain in stroke patients is most convincing; However, it is limited by the small sample size.
In conclusion, necroptosis is involved in the formation and progression of VCI, and interventions targeting necroptosis may effectively control neural injury after cerebral ischemia. Therefore, necroptosis inhibition may be a new target for the prevention and treatment of ischemic stroke.
Statements
Author contributions
SW: Writing – original draft. LC: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. CS: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. ZL: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. JT: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LW: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. XZ: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The Science and Technology Project funded by the Education Department of Jiangxi Province (GJJ211813 to LC, GJJ2201928 to LW), the Provincial Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (20224BAB206040 to XZ), Foundation of Students’ Platform for Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program: 202411843024 to XZ and S202411843050 to CS, and the Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of Jiangxi Province (2022B1010 to LC).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Abd El-Aal S. A. El-Abhar H. S. Abulfadl Y. S. (2022). Morin offsets PTZ-induced neuronal degeneration and cognitive decrements in rats: the modulation of TNF-alpha/TNFR-1/RIPK1,3/MLKL/PGAM5/Drp-1, IL-6/JAK2/STAT3/GFAP and Keap-1/Nrf-2/HO-1 trajectories. Eur. J. Pharmacol.931:175213. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.175213
2
Ai Y. Meng Y. Yan B. Zhou Q. Wang X. (2024). The biochemical pathways of apoptotic, necroptotic, pyroptotic, and ferroptotic cell death. Mol. Cell84, 170–179. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.11.040
3
Albaqami F. F. Abdel-Rahman R. F. Althurwi H. N. Alharthy K. M. Soliman G. A. Aljarba T. M. et al . (2024). Targeting inflammation and oxidative stress for protection against ischemic brain injury in rats using cupressuflavone. Saudi Pharm. J.32:101933. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2023.101933
4
Alfieri A. Koudelka J. Li M. Scheffer S. Duncombe J. Caporali A. et al . (2022). Nox2 underpins microvascular inflammation and vascular contributions to cognitive decline. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab.42, 1176–1191. doi: 10.1177/0271678X221077766
5
Amani H. Mostafavi E. Alebouyeh M. R. Arzaghi H. Akbarzadeh A. Pazoki-Toroudi H. et al . (2019). Would colloidal gold Nanocarriers present An effective diagnosis or treatment for ischemic stroke?Int. J. Nanomedicine14, 8013–8031. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S210035
6
Badji A. Youwakim J. Cooper A. Westman E. Marseglia A. (2023). Vascular cognitive impairment – past, present, and future challenges. Ageing Res. Rev.90:102042. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2023.102042
7
Bai R. Ge X. (2024). Blood-brain barrier disruption following brain injury: implications for clinical practice. Histol. Histopathol.39, 1435–1441. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-740
8
Bai Q. Wang S. Rao D. Zhou Z. Wang J. Wang Q. et al . (2024). RIPK3 activation promotes DAXX-dependent neuronal necroptosis after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. CNS Neurosci. Ther.30:e14397. doi: 10.1111/cns.14397
9
Batista A. F. Khan K. A. Papavergi M. T. Lemere C. A. (2024). The importance of complement-mediated immune signaling in Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci.25:817. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020817
10
Beg M. A. Huang M. Vick L. Rao K. N. S. Zhang J. Chen Y. (2024). Targeting mitochondrial dynamics and redox regulation in cardiovascular diseases. Trends Pharmacol. Sci.45, 290–303. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2024.02.001
11
Bellut M. Papp L. Bieber M. Kraft P. Stoll G. Schuhmann M. K. (2021). NLPR3 inflammasome inhibition alleviates hypoxic endothelial cell death in vitro and protects blood-brain barrier integrity in murine stroke. Cell Death Dis.13:20. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04379-z
12
Burch A. M. Garcia J. D. O'Leary H. Haas A. Orfila J. E. Tiemeier E. et al . (2024). TRPM2 and CaMKII signaling drives excessive GABAergic synaptic inhibition following ischemia. J. Neurosci.44:e1762232024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1762-23.2024
13
Chang Wong E. Chang Chui H. (2022). Vascular cognitive impairment and dementia. Continuum (Minneap. Minn.)28, 750–780. doi: 10.1212/CON.0000000000001124
14
Chen Y. S. Chuang W. C. Kung H. N. Cheng C. Y. Huang D. Y. Sekar P. et al . (2022). Pan-caspase inhibitor zVAD induces Necroptotic and Autophagic cell death in TLR3/4-stimulated macrophages. Mol. Cells45, 257–272. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2021.0193
15
Chen A. Q. Fang Z. Chen X. L. Yang S. Zhou Y. F. Mao L. et al . (2019). Microglia-derived TNF-alpha mediates endothelial necroptosis aggravating blood brain-barrier disruption after ischemic stroke. Cell Death Dis.10:487. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1716-9
16
Chen J. Jin H. Xu H. Peng Y. Jie L. Xu D. et al . (2019). The neuroprotective effects of Necrostatin-1 on subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats are possibly mediated by preventing blood-brain barrier disruption and RIP3-mediated necroptosis. Cell Transplant.28, 1358–1372. doi: 10.1177/0963689719867285
17
Chen C. A. Li C. X. Zhang Z. H. Xu W. X. Liu S. L. Ni W. C. et al . (2024). Qinzhizhudan formula dampens inflammation in microglia polarization of vascular dementia rats by blocking MyD88/NF-kappaB signaling pathway: through integrating network pharmacology and experimental validation. J. Ethnopharmacol.318:116769. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116769
18
Chen Y. Peng F. Yang C. Hou H. Xing Z. Chen J. et al . (2023). SIRT1 activation by 2,3,5,6-tetramethylpyrazine alleviates neuroinflammation via inhibiting M1 microglia polarization. Front. Immunol.14:1206513. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1206513
19
Chen Y. Zhang L. Yu H. Song K. Shi J. Chen L. et al . (2018). Necrostatin-1 improves long-term functional recovery through protecting oligodendrocyte precursor cells after transient focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Neuroscience371, 229–241. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.12.007
20
Cheng Y. Liu Y. Wu R. Xu Y. Sun M. Wang F. et al . (2024). Identification of candidate genes associated with development of vascular cognitive impairment by integrated bioinformatics analysis combined with biological experiments. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci.79:glad267. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glad267
21
Chevin M. Chabrier S. Allard M. J. Sebire G. (2022). Necroptosis blockade potentiates the neuroprotective effect of hypothermia in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Biomedicines10. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10112913
22
Choi D. H. Lee K. H. Kim J. H. Seo J. H. Kim H. Y. Shin C. Y. et al . (2014). NADPH oxidase 1, a novel molecular source of ROS in hippocampal neuronal death in vascular dementia. Antioxid. Redox Signal.21, 533–550. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.5129
23
Cui B. Yan B. Wang K. Li L. Chen S. Zhang Z. (2022). Discovery of a new class of uracil derivatives as potential mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein (MLKL) inhibitors. J. Med. Chem.65, 12747–12780. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00548
24
de Sousa Maciel I. Sales A. J. Casarotto P. C. Castren E. Biojone C. Joca S. R. L. (2022). Nitric oxide synthase inhibition counteracts the stress-induced DNA methyltransferase 3b expression in the hippocampus of rats. Eur. J. Neurosci.55, 2421–2434. doi: 10.1111/ejn.15042
25
Degterev A. Huang Z. Boyce M. Li Y. Jagtap P. Mizushima N. et al . (2005). Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic potential for ischemic brain injury. Nat. Chem. Biol.1, 112–119. doi: 10.1038/nchembio711
26
Deng M. Chen S. R. Chen H. Luo Y. Dong Y. Pan H. L. (2019). Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling mediates opioid-induced presynaptic NMDA receptor activation and analgesic tolerance. J. Neurochem.148, 275–290. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14628
27
Deng X. X. Li S. S. Sun F. Y. (2019). Necrostatin-1 prevents necroptosis in brains after ischemic stroke via inhibition of RIPK1-mediated RIPK3/MLKL signaling. Aging Dis.10, 807–817. doi: 10.14336/AD.2018.0728
28
Fan X. Lin F. Chen Y. Dou Y. Li T. Jin X. et al . (2024). Luteolin-7-O-beta-d-glucuronide ameliorates cerebral ischemic injury: involvement of RIP3/MLKL signaling pathway. Molecules29:1665. doi: 10.3390/molecules29071665
29
Fan H. Tang H. B. Shan L. Q. Liu S. C. Huang D. G. Chen X. et al . (2019). Quercetin prevents necroptosis of oligodendrocytes by inhibiting macrophages/microglia polarization to M1 phenotype after spinal cord injury in rats. J. Neuroinflammation16:206. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1613-2
30
Fan B. Zhang Y. Luo Q. Hao C. Liao W. (2024). Physical and social environmental enrichment alleviate ferroptosis and inflammation with inhibition of TLR4/MyD88/p38MAPK pathway in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rats. Brain Res. Bull.208:110897. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2024.110897
31
Fiani B. Kondilis A. Soula M. Tao A. Alvi M. A. (2021). Novel methods of necroptosis inhibition for spinal cord injury using translational research to limit secondary injury and enhance endogenous repair and regeneration. Neurospine18, 261–270. doi: 10.14245/ns.2040722.361
32
Fitzgibbon-Collins L. K. Heckman G. A. Bains I. Noguchi M. McIlroy W. E. Hughson R. L. (2021). Older adults' drop in cerebral oxygenation on standing correlates with postural instability and may improve with sitting prior to standing. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci.76, 1124–1133. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glaa194
33
Gao X. Chen J. Yin G. Liu Y. Gu Z. Sun R. et al . (2024). Hyperforin ameliorates neuroinflammation and white matter lesions by regulating microglial VEGFR(2) /SRC pathway in vascular cognitive impairment mice. CNS Neurosci. Ther.30:e14666. doi: 10.1111/cns.14666
34
Guo J. Dove A. Wang J. Laukka E. J. Ekström I. Dunk M. M. et al . (2023). Trajectories of olfactory identification preceding incident mild cognitive impairment and dementia: a longitudinal study. EBioMedicine98:104862. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104862
35
Guo Y. S. Yuan M. Han Y. Shen X. Y. Gao Z. K. Bi X. (2022). Effects of enriched environment on microglia and functional white matter recovery in rats with post stroke cognitive impairment. Neurochem. Int.154:105295. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2022.105295
36
Guo Y. Zhou J. Wang Y. Wu X. Mou Y. Song X. (2024). Cell type-specific molecular mechanisms and implications of necroptosis in inflammatory respiratory diseases. Immunol. Rev.321, 52–70. doi: 10.1111/imr.13282
37
Hachinski V. C. Bowler J. V. (1993). Vascular dementia. Neurology43, 2159–2160. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.10.2159-a
38
He Y. Chen X. Wu M. Hou X. Zhou Z. (2023). What type of cell death occurs in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion? A review focusing on pyroptosis and its potential therapeutic implications. Front. Cell. Neurosci.17:1073511. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1073511
39
He X. Liu J. Zang W. J. (2022). Mitochondrial homeostasis and redox status in cardiovascular diseases: protective role of the vagal system. Free Radic. Biol. Med.178, 369–379. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.12.255
40
He X. Y. Wang F. Suo X. G. Gu M. Z. Wang J. N. Xu C. H. et al . (2023). Compound-42 alleviates acute kidney injury by targeting RIPK3-mediated necroptosis. Br. J. Pharmacol.180, 2641–2660. doi: 10.1111/bph.16152
41
He Y. Yang T. Li J. Li K. Zhuang C. Zhang M. et al . (2024). Identification of a marine-derived sesquiterpenoid, Compound-8, that inhibits tumour necrosis factor-induced cell death by blocking complex II assembly. Br. J. Pharmacol.181, 2443–2458. doi: 10.1111/bph.16364
42
Hincelin-Mery A. Nicolas X. Cantalloube C. Pomponio R. Lewanczyk P. Benamor M. et al . (2024). Safety, pharmacokinetics, and target engagement of a brain penetrant RIPK1 inhibitor, SAR443820 (DNL788), in healthy adult participants. Clin. Transl. Sci.17:e13690. doi: 10.1111/cts.13690
43
Hu H. Y. Ou Y. N. Shen X. N. Qu Y. Ma Y. H. Wang Z. T. et al . (2021). White matter hyperintensities and risks of cognitive impairment and dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 36 prospective studies. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev.120, 16–27. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2020.11.007
44
Hu C. Shi Z. Liu X. Sun C. (2024). The research progress of mitochondrial transplantation in the treatment of mitochondrial defective diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci.25:1175. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021175
45
Hu W. Wu X. Yu D. Zhao L. Zhu X. Li X. et al . (2020). Regulation of JNK signaling pathway and RIPK3/AIF in necroptosis-mediated global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Exp. Neurol.331:113374. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2020.113374
46
Huang S. Hou D. Zhang L. Pei C. Liang J. Li J. et al . (2023). LncRNA MALAT1 promoted neuronal necroptosis in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion mice by stabilizing HSP90. Neurochem. Res.48, 3457–3471. doi: 10.1007/s11064-023-03991-z
47
Huang X. Tan J. Ji Y. Luo J. Zhao Y. Zhao J. (2024). BRCC3 mediates inflammation and pyroptosis in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by activating the NLRP6 inflammasome. CNS Neurosci. Ther.30:e14697. doi: 10.1111/cns.14697
48
Ji Y. Ward L. A. Hawkins C. J. (2021). Reconstitution of human Necrosome interactions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biomol. Ther.11:153. doi: 10.3390/biom11020153
49
Jiang Q. Ding Y. Li F. Fayyaz A. I. Duan H. Geng X. (2024). Modulation of NLRP3 inflammasome-related-inflammation via RIPK1/RIPK3-DRP1 or HIF-1alpha signaling by phenothiazine in hypothermic and normothermic neuroprotection after acute ischemic stroke. Redox Biol.73:103169. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103169
50
Jiang W. R. Zhou Y. M. Wu W. Yang L. J. Wu Y. Zhang X. Y. et al . (2024). A circRNA ceRNA network involved in cognitive dysfunction after chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Aging (Albany NY)16, 1161–1181. doi: 10.18632/aging.205387
51
Jin L. Zhu Z. Hong L. Qian Z. Wang F. Mao Z. (2023). ROS-responsive 18beta-glycyrrhetic acid-conjugated polymeric nanoparticles mediate neuroprotection in ischemic stroke through HMGB1 inhibition and microglia polarization regulation. Bioact. Mater.19, 38–49. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.03.040
52
Kalaria R. N. Akinyemi R. O. Paddick S. M. Ihara M. (2024). Current perspectives on prevention of vascular cognitive impairment and promotion of vascular brain health. Expert. Rev. Neurother.24, 25–44. doi: 10.1080/14737175.2023.2273393
53
Kim D. Y. Leem Y. H. Park J. S. Park J. E. Park J. M. Kang J. L. et al . (2023). RIPK1 regulates microglial activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation and MPTP-induced Parkinson's disease mouse models. Cells12:417. doi: 10.3390/cells12030417
54
Krishnan S. Rani P. (2014). Evaluation of selenium, redox status and their association with plasma amyloid/tau in Alzheimer's disease. Biol. Trace Elem. Res.158, 158–165. doi: 10.1007/s12011-014-9930-x
55
Li X. Li S. Ma C. Li T. Yang L. (2022). Preparation of baicalin-loaded ligand-modified nanoparticles for nose-to-brain delivery for neuroprotection in cerebral ischemia. Drug Deliv.29, 1282–1298. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2064564
56
Li X. Yang X. Lu H. Wang W. Cai L. Chen J. et al . (2023). Calycosin attenuates the inflammatory damage of microglia induced by oxygen and glucose deprivation through the HMGB1/TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin.55, 1415–1424. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2023125
57
Li T. Zheng J. Wang Z. Xu L. Sun D. Song H. et al . (2022). Maresin 1 improves cognitive decline and ameliorates inflammation and blood-brain barrier damage in rats with chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Brain Res.1788:147936. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2022.147936
58
Li Y. Zou C. Chen C. Li S. Zhu Z. Fan Q. et al . (2023). Myeloid-derived MIF drives RIPK1-mediated cerebromicrovascular endothelial cell death to exacerbate ischemic brain injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA120:e2219091120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2219091120
59
Liang J. Tian X. Zhou M. Yan F. Fan J. Qin Y. et al . (2024). Shikonin and chitosan-silver nanoparticles synergize against triple-negative breast cancer through RIPK3-triggered necroptotic immunogenic cell death. Biomaterials309:122608. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2024.122608
60
Lickliter J. Wang S. Zhang W. Zhu H. Wang J. Zhao C. et al . (2023). A phase I randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled study assessing the safety and pharmacokinetics of RIPK1 inhibitor GFH312 in healthy subjects. Clin. Transl. Sci.16, 1691–1703. doi: 10.1111/cts.13580
61
Lin S. Landon B. Zhang H. Jin K. (2024). Pericyte dysfunction contributes to vascular cognitive impairment induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats. Aging Dis.15, 1357–1372. doi: 10.14336/AD.2023.0821-1
62
Liu Z. Garcia Reino E. J. Harschnitz O. Guo H. Chan Y. H. Khobrekar N. V. et al . (2023). Encephalitis and poor neuronal death-mediated control of herpes simplex virus in human inherited RIPK3 deficiency. Sci. Immunol.8:eade2860. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.ade2860
63
Liu Y. Tan Y. Zhang Z. Yi M. Zhu L. Peng W. (2024). The interaction between ageing and Alzheimer's disease: insights from the hallmarks of ageing. Transl. Neurodegener.13:7. doi: 10.1186/s40035-024-00397-x
64
Lokesh M. Bandaru L. J. M. Rajanna A. Dhayal V. S. Challa S. (2024). M1 polarization induction by lead and amyloid peptides in microglial cells: implications for neurodegeneration process. Environ. Toxicol.39, 4267–4277. doi: 10.1002/tox.24305
65
Lou T. Wu H. Feng M. Liu L. Yang X. Pan M. et al . (2024). Integration of metabolomics and transcriptomics reveals that Da chuanxiong formula improves vascular cognitive impairment via ACSL4/GPX4 mediated ferroptosis. J. Ethnopharmacol.325:117868. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.117868
66
Lu H. Zhang J. Liang Y. Qiao Y. Yang C. He X. et al . (2020). Network topology and machine learning analyses reveal microstructural white matter changes underlying Chinese medicine Dengzhan Shengmai treatment on patients with vascular cognitive impairment. Pharmacol. Res.156:104773. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104773
67
Lule S. Wu L. Sarro-Schwartz A. Edmiston W. J. III Izzy S. Songtachalert T. et al . (2021). Cell-specific activation of RIPK1 and MLKL after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab.41, 1623–1633. doi: 10.1177/0271678X20973609
68
Luo X. Q. Li A. Yang X. Xiao X. Hu R. Wang T. W. et al . (2018). Paeoniflorin exerts neuroprotective effects by modulating the M1/M2 subset polarization of microglia/macrophages in the hippocampal CA1 region of vascular dementia rats via cannabinoid receptor 2. Chin. Med.13:14. doi: 10.1186/s13020-018-0173-1
69
Ma X. R. Yang S. Y. Zheng S. S. Yan H. H. Gu H. M. Wang F. et al . (2022). Inhibition of RIPK1 by ZJU-37 promotes oligodendrocyte progenitor proliferation and remyelination via NF-kappaB pathway. Cell Death Discov.8:147. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-00929-2
70
Maiese K. (2023). The impact of aging and oxidative stress in metabolic and nervous system disorders: programmed cell death and molecular signal transduction crosstalk. Front. Immunol.14:1273570. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1273570
71
Martemucci G. Fracchiolla G. Muraglia M. Tardugno R. Dibenedetto R. S. D'Alessandro A. G. (2023). Metabolic syndrome: a narrative review from the oxidative stress to the management of related diseases. Antioxidants (Basel)12:2091. doi: 10.3390/antiox12122091
72
Martinez-Osorio V. Abdelwahab Y. Ros U. (2023). The many faces of MLKL, the executor of necroptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci.24:10108. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210108
73
Masserini F. Baso G. Gendarini C. Pantoni L. (2023). Therapeutic strategies in vascular cognitive impairment: a systematic review of population, intervention, comparators, and outcomes. Alzheimers Dement.19, 5795–5804. doi: 10.1002/alz.13409
74
Mifflin L. Ofengeim D. Yuan J. (2020). Receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 (RIPK1) as a therapeutic target. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov.19, 553–571. doi: 10.1038/s41573-020-0071-y
75
Mitroshina E. V. Loginova M. M. Yarkov R. S. Urazov M. D. Novozhilova M. O. Krivonosov M. I. et al . (2022). Inhibition of neuronal necroptosis mediated by RIPK1 provides neuroprotective effects on hypoxia and ischemia in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci.23:735. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020735
76
Mo Y. Xu W. Fu K. Chen H. Wen J. Huang Q. et al . (2022). The dual function of microglial polarization and its treatment targets in ischemic stroke. Front. Neurol.13:921705. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.921705
77
Muendlein H. I. Connolly W. M. Magri Z. Jetton D. Smirnova I. Degterev A. et al . (2022). ZBP1 promotes inflammatory responses downstream of TLR3/TLR4 via timely delivery of RIPK1 to TRIF. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA119:e2113872119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2113872119
78
Ni Y. Gu W. W. Liu Z. H. Zhu Y. M. Rong J. G. Kent T. A. et al . (2018). RIP1K contributes to neuronal and astrocytic cell death in ischemic stroke via activating Autophagic-lysosomal pathway. Neuroscience371, 60–74. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.10.038
79
Nikseresht S. Khodagholi F. Ahmadiani A. (2019). Protective effects of ex-527 on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through necroptosis signaling pathway attenuation. J. Cell. Physiol.234, 1816–1826. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27055
80
Niu Y. Wan C. Zhang J. Zhang S. Zhao Z. Zhu L. et al . (2021). Aerobic exercise improves VCI through circRIMS2/miR-186/BDNF-mediated neuronal apoptosis. Mol. Med.27:4. doi: 10.1186/s10020-020-00258-z
81
Nuzzo T. Feligioni M. Cristino L. Pagano I. Marcelli S. Iannuzzi F. et al . (2019). Free d-aspartate triggers NMDA receptor-dependent cell death in primary cortical neurons and perturbs JNK activation, tau phosphorylation, and protein SUMOylation in the cerebral cortex of mice lacking d-aspartate oxidase activity. Exp. Neurol.317, 51–65. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2019.02.014
82
Nyul-Toth A. Patai R. Csiszar A. Ungvari A. Gulej R. Mukli P. et al . (2024). Linking peripheral atherosclerosis to blood-brain barrier disruption: elucidating its role as a manifestation of cerebral small vessel disease in vascular cognitive impairment. Geroscience46, 6511–6536. doi: 10.1007/s11357-024-01194-0
83
Okoye C. N. Koren S. A. Wojtovich A. P. (2023). Mitochondrial complex I ROS production and redox signaling in hypoxia. Redox Biol.67:102926. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102926
84
Pang X. W. Mei C. Qiu W. Wu L. J. Tian D. S. (2023). Editorial: immune mechanisms in white matter lesions: clinical and pathophysiological implications. Front. Immunol.14:1149625. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1149625
85
Park S. Y. Park H. H. Park S. Y. Hong S. M. Yoon S. Morgan M. J. et al . (2020). Reduction in MLKL-mediated endosomal trafficking enhances the TRAIL-DR4/5 signal to increase cancer cell death. Cell Death Dis.11:744. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02941-9
86
Pham C. L. Shanmugam N. Strange M. O'Carroll A. Brown J. W. Sierecki E. et al . (2019). Viral M45 and necroptosis-associated proteins form heteromeric amyloid assemblies. EMBO Rep.20:e46518. doi: 10.15252/embr.201846518
87
Picon C. Jayaraman A. James R. Beck C. Gallego P. Witte M. E. et al . (2021). Neuron-specific activation of necroptosis signaling in multiple sclerosis cortical grey matter. Acta Neuropathol.141, 585–604. doi: 10.1007/s00401-021-02274-7
88
Pierotti C. L. Tanzer M. C. Jacobsen A. V. Hildebrand J. M. Garnier J. M. Sharma P. et al . (2020). Potent inhibition of necroptosis by simultaneously targeting multiple effectors of the pathway. ACS Chem. Biol.15, 2702–2713. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.0c00482
89
Prasad Panda S. Kesharwani A. Prasanna Mallick S. Prasanth D. Kumar Pasala P. Bharadwaj Tatipamula V. (2023). Viral-induced neuronal necroptosis: detrimental to brain function and regulation by necroptosis inhibitors. Biochem. Pharmacol.213:115591. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115591
90
Rahi V. Kaundal R. K. (2024). Exploring the intricacies of calcium dysregulation in ischemic stroke: insights into neuronal cell death and therapeutic strategies. Life Sci.347:122651. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.122651
91
Rajeev V. Chai Y. L. Poh L. Selvaraji S. Fann D. Y. Jo D. G. et al . (2023). Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion: a critical feature in unravelling the etiology of vascular cognitive impairment. Acta Neuropathol. Commun.11:93. doi: 10.1186/s40478-023-01590-1
92
Rajeev V. Fann D. Y. Dinh Q. N. Kim H. A. de Silva T. M. Jo D. G. et al . (2022). Intermittent fasting attenuates Hallmark vascular and neuronal pathologies in a mouse model of vascular cognitive impairment. Int. J. Biol. Sci.18, 6052–6067. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.75188
93
Rajeev V. Fann D. Y. Dinh Q. N. Kim H. A. de Silva T. M. Lai M. K. P. et al . (2022). Pathophysiology of blood brain barrier dysfunction during chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in vascular cognitive impairment. Theranostics12, 1639–1658. doi: 10.7150/thno.68304
94
Ranjan K. Pathak C. (2024). Cellular dynamics of Fas-associated death domain in the regulation of Cancer and inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci.25:3228. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063228
95
Raveena N. Kim J. H. Kim J. H. Thomas R. G. Choi K. H. Jeong Y. Y. (2024). Reactive oxygen species-responsive chitosan-bilirubin nanoparticles loaded with statin for treatment of cerebral ischemia. Biomater. Res.28:0097. doi: 10.34133/bmr.0097
96
Ren Y. Qu S. (2023). Constituent isoflavones of Puerariae radix as a potential neuroprotector in cognitive impairment: evidence from preclinical studies. Ageing Res. Rev.90:102040. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2023.102040
97
Rosenberg A. Sibley L. D. (2021). Toxoplasma gondii secreted effectors co-opt host repressor complexes to inhibit necroptosis. Cell Host Microbe29, 1186–1198.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2021.04.016
98
Saeedan A. S. Abdel-Rahman R. F. Soliman G. A. Ogaly H. A. Abdel-Kader M. S. (2023). Amentoflavone attenuates oxidative stress and neuroinflammation induced by cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in rats by targeting HMGB1-mediated TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Saudi Pharm. J.31:101798. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2023.101798
99
Sanz P. Rubio T. Garcia-Gimeno M. A. (2024). Neuroinflammation and epilepsy: from pathophysiology to therapies based on repurposing drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci.25:4161. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084161
100
Shah H. Paul G. Yadav A. K. (2024). Surface-tailored Nanoplatform for the diagnosis and Management of Stroke: current strategies and future outlook. Mol. Neurobiol.61, 1383–1403. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03635-x
101
Shang J. Li W. Zhang H. Wang W. Liu N. Gao D. et al . (2024). C-kit controls blood-brain barrier permeability by regulating caveolae-mediated transcytosis after chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Biomed. Pharmacother.170:115778. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115778
102
Skrobot O. A. Black S. E. Chen C. DeCarli C. Erkinjuntti T. Ford G. A. et al . (2018). Progress toward standardized diagnosis of vascular cognitive impairment: guidelines from the vascular impairment of cognition classification consensus study. Alzheimers Dement.14, 280–292. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2017.09.007
103
Song M. Kang K. Wang S. Zhang C. Zhao X. Song F. (2024). Elevated intracellular ca(2+) functions downstream of mitodysfunction to induce Wallerian-like degeneration and necroptosis in organophosphorus-induced delayed neuropathy. Toxicology504:153812. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2024.153812
104
Song Y. Wang L. B. Bei Y. Qin D. X. Ai L. Y. Ma Q. Z. et al . (2020). Carvacryl acetate, a semisynthetic monoterpenic ester obtained from essential oils, provides neuroprotection against cerebral ischemia reperfusion-induced oxidative stress injury via the Nrf2 signalling pathway. Food Funct.11, 1754–1763. doi: 10.1039/c9fo02037c
105
Spinelli J. B. Haigis M. C. (2018). The multifaceted contributions of mitochondria to cellular metabolism. Nat. Cell Biol.20, 745–754. doi: 10.1038/s41556-018-0124-1
106
Sun A. L. A. Gillies J. D. Shen Y. Deng H. Xue F. Ma Y. et al . (2024). A phase I randomized study to evaluate safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of SIR2446M, a selective RIPK1 inhibitor, in healthy participants. Clin. Transl. Sci.17:e13857. doi: 10.1111/cts.13857
107
Sun X. Wu Y. Xu F. Liu C. (2024). Screening of potent RIPK3 inhibitors to attenuate necroptosis and inflammation in mouse traumatic brain injury models. Exp. Neurol.372:114633. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2023.114633
108
Sweeney M. D. Zhao Z. Montagne A. Nelson A. R. Zlokovic B. V. (2019). Blood-brain barrier: from physiology to disease and Back. Physiol. Rev.99, 21–78. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00050.2017
109
Tang L. Xie D. Wang S. Gao C. Pan S. (2024). Piezo1 knockout improves post-stroke cognitive dysfunction by inhibiting the Interleukin-6 (IL-6)/glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) pathway. J. Inflamm. Res.17, 2257–2270. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S448903
110
Tang Y. Zhuang C. (2024). Design, synthesis and anti-necroptosis activity of fused heterocyclic MLKL inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem.102:117659. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2024.117659
111
Thiankhaw K. Chattipakorn N. Chattipakorn S. C. (2024). How calcineurin inhibitors affect cognition. Acta Physiol (Oxf.)240:e14161. doi: 10.1111/apha.14161
112
Titisari N. Fauzi A. Abdul Razak I. S. Mohd Noor M. H. Samsulrizal N. Ahmad H. (2024). Dietary menhaden fish oil supplementation suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment in diabetic rats. Pharm. Biol.62, 447–455. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2024.2351933
113
Tran H. T. Kratina T. Coutansais A. Michalek D. Hogan B. M. Lawlor K. E. et al . (2024). RIPK3 cleavage is dispensable for necroptosis inhibition but restricts NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cell Death Differ.31, 662–671. doi: 10.1038/s41418-024-01281-x
114
van der Flier W. M. Skoog I. Schneider J. A. Pantoni L. Mok V. Chen C. L. H. et al . (2018). Vascular cognitive impairment. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers4:18003. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2018.3
115
Vieira M. Fernandes J. Carreto L. Anuncibay-Soto B. Santos M. Han J. et al . (2014). Ischemic insults induce necroptotic cell death in hippocampal neurons through the up-regulation of endogenous RIP3. Neurobiol. Dis.68, 26–36. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2014.04.002
116
Villa-Gonzalez M. Rubio M. Martin-Lopez G. Mallavibarrena P. R. Vallés-Saiz L. Vivien D. et al . (2024). Pharmacological inhibition of mTORC1 reduces neural death and damage volume after MCAO by modulating microglial reactivity. Biol. Direct19:26. doi: 10.1186/s13062-024-00470-5
117
Wang D. P. Kang K. Hai J. Lv Q. L. Wu Z. B. (2024). Alleviating CB2-dependent ER stress and mitochondrial dysfunction improves chronic cerebral Hypoperfusion-induced cognitive impairment. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol.19:1. doi: 10.1007/s11481-024-10098-x
118
Wang Z. Li T. Du M. Zhang L. Xu L. Song H. et al . (2023). β-hydroxybutyrate improves cognitive impairment caused by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion via amelioration of neuroinflammation and blood-brain barrier damage. Brain Res. Bull.193, 117–130. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2022.12.011
119
Wang H. Liu Y. Guo Z. Cui M. Pang P. Yang J. et al . (2023). Enhancement of oligodendrocyte autophagy alleviates white matter injury and cognitive impairment induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats. Acta Pharm. Sin. B13, 2107–2123. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.03.014
120
Wang H. Luo W. Chen H. Cai Z. Xu G. (2024). Mitochondrial dynamics and mitochondrial autophagy: molecular structure, orchestrating mechanism and related disorders. Mitochondrion75:101847. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2024.101847
121
Wang H. Qi W. Zou C. Xie Z. Zhang M. Naito M. G. et al . (2021). NEK1-mediated retromer trafficking promotes blood-brain barrier integrity by regulating glucose metabolism and RIPK1 activation. Nat. Commun.12:4826. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25157-7
122
Wang H. Y. Takagi H. Stoney P. N. Echeverria A. Kuhn B. Hsu K. S. et al . (2024). Anoxia-induced hippocampal LTP is regeneratively produced by glutamate and nitric oxide from the neuro-glial-endothelial axis. iScience27:109515. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109515
123
Wang Y. Wang Y. Li S. Jin H. Duan J. Lu X. et al . (2023). Insights of Chinese herbal medicine for mitochondrial dysfunction in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion induced cognitive impairment: existed evidences and potential directions. Front. Pharmacol.14:1138566. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1138566
124
Wang X. Zhang S. Lv B. Chen H. Zhang W. Dong L. et al . (2024). Circular RNA PTP4A2 regulates microglial polarization through STAT3 to promote neuroinflammation in ischemic stroke. CNS Neurosci. Ther.30:e14512. doi: 10.1111/cns.14512
125
Wang J. Zhu Y. Yang L. Liu H. Zhou T. Xu F. et al . (2021). Early diagnosis of cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury and revelation of its regional development by a H(3)R receptor-directed probe. ACS Sens.6, 1330–1338. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.0c02667
126
Wen L. Bi D. Shen Y. (2024). Complement-mediated synapse loss in Alzheimer's disease: mechanisms and involvement of risk factors. Trends Neurosci.47, 135–149. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2023.11.010
127
Wendlocha D. Kubina R. Krzykawski K. Mielczarek-Palacz A. (2024). Selected Flavonols targeting cell death pathways in Cancer therapy: the latest achievements in research on apoptosis, autophagy, necroptosis, Pyroptosis, Ferroptosis, and Cuproptosis. Nutrients16:1201. doi: 10.3390/nu16081201
128
Wu X. Nagy L. E. Gautheron J. (2024). Mediators of necroptosis: from cell death to metabolic regulation. EMBO Mol. Med.16, 219–237. doi: 10.1038/s44321-023-00011-z
129
Xiao Y. Guan T. Yang X. Xu J. Zhang J. Qi Q. et al . (2023). Baicalin facilitates remyelination and suppresses neuroinflammation in rats with chronic cerebral hypoperfusion by activating Wnt/beta-catenin and inhibiting NF-kappaB signaling. Behav. Brain Res.442:114301. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2023.114301
130
Xie W. Li Y. Guo Z. Lu J. Li G. Zhang Z. et al . (2024). FePd Nanozyme- and SKN-encapsulated functional lipid nanoparticles for Cancer Nanotherapy via ROS-boosting necroptosis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces16, 18411–18421. doi: 10.1021/acsami.3c18497
131
Xie T. Peng W. Liu Y. Yan C. Maki J. Degterev A. et al . (2013). Structural basis of RIP1 inhibition by necrostatins. Structure21, 493–499. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2013.01.016
132
Xu Y. Liang C. Zhang W. Yu J. Xing C. Liu H. et al . (2023). Profiling of the chemical space on the phenyl group of substituted benzothiazole RIPK3 inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem.131:106339. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.106339
133
Xu L. Qu C. Liu Y. Liu H. (2023). The environmental enrichment ameliorates chronic cerebral hypoperfusion-induced cognitive impairment by activating autophagy signaling pathway and improving synaptic function in hippocampus. Brain Res. Bull.204:110798. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2023.110798
134
Xu C. H. Wang J. N. Suo X. G. Ji M. L. He X. Y. Chen X. et al . (2022). RIPK3 inhibitor-AZD5423 alleviates acute kidney injury by inhibiting necroptosis and inflammation. Int. Immunopharmacol.112:109262. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109262
135
Xue Y. Qu Z. Fu J. Zhen J. Wang W. Cai Y. et al . (2017). The protective effect of astaxanthin on learning and memory deficits and oxidative stress in a mouse model of repeated cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Brain Res. Bull.131, 221–228. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2017.04.019
136
Yan W. T. Yang Y. D. Hu X. M. Ning W. Y. Liao L. S. Lu S. et al . (2022). Do pyroptosis, apoptosis, and necroptosis (PANoptosis) exist in cerebral ischemia? Evidence from cell and rodent studies. Neural Regen. Res.17, 1761–1768. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.331539
137
Yang Y. Wang W. Tian Y. Shi J. (2022). Sirtuin 3 and mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP): a systematic review. Mitochondrion64, 103–111. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2022.03.004
138
Yang T. Wang G. Zhang M. Hu X. Li Q. Yun F. et al . (2023). Triggering endogenous Z-RNA sensing for anti-tumor therapy through ZBP1-dependent necroptosis. Cell Rep.42:113377. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113377
139
Ye D. Liu J. Lin L. Hou P. Feng T. Wang S. (2024). The Ang-(1-7)/MasR axis ameliorates neuroinflammation in hypothermic traumatic brain injury in mice by modulating phenotypic transformation of microglia. PLoS One19:e0303150. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0303150
140
Yoshikawa M. Saitoh M. Katoh T. Seki T. Bigi S. V. Shimizu Y. et al . (2018). Discovery of 7-Oxo-2,4,5,7-tetrahydro-6 H-pyrazolo[3,4- c]pyridine derivatives as potent, orally available, and brain-penetrating receptor interacting protein 1 (RIP1) kinase inhibitors: analysis of structure-kinetic relationships. J. Med. Chem.61, 2384–2409. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b01647
141
Zang X. Song J. Li Y. Han Y. (2022). Targeting necroptosis as an alternative strategy in tumor treatment: from drugs to nanoparticles. J. Control. Release349, 213–226. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.06.060
142
Zelic M. Pontarelli F. Woodworth L. Zhu C. Mahan A. Ren Y. et al . (2021). RIPK1 activation mediates neuroinflammation and disease progression in multiple sclerosis. Cell Rep.35:109112. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109112
143
Zeylan M. E. Senyuz S. Picon-Pages P. García-Elías A. Tajes M. Muñoz F. J. et al . (2024). Shared proteins and pathways of cardiovascular and cognitive diseases: relation to vascular cognitive impairment. J. Proteome Res.23, 560–573. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.3c00289
144
Zhang Y. Li M. Gao X. Chen Y. Liu T. (2019). Nanotechnology in cancer diagnosis: progress, challenges and opportunities. J. Hematol. Oncol.12:137. doi: 10.1186/s13045-019-0833-3
145
Zhang C. Ling C. L. Pang L. Wang Q. Liu J. X. Wang B. S. et al . (2017). Direct macromolecular drug delivery to cerebral ischemia area using neutrophil-mediated nanoparticles. Theranostics7, 3260–3275. doi: 10.7150/thno.19979
146
Zhang Q. Liu X. Gao S. Yan S. Li A. Wei Z. et al . (2023). Multimodal magnetic resonance imaging on brain structure and function changes in vascular cognitive impairment without dementia. Front. Aging Neurosci.15:1278390. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1278390
147
Zhang H. Shang J. Li W. Gao D. Zhang J. (2024). Increased expression of VCAM1 on brain endothelial cells drives blood-brain barrier impairment following chronic cerebral Hypoperfusion. ACS Chem. Neurosci.15, 2028–2041. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.4c00039
148
Zhang X. Shi X. Wang J. Xu Z. He J. (2021). Enriched environment remedies cognitive dysfunctions and synaptic plasticity through NMDAR-ca(2+)-Activin a circuit in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rats. Aging (Albany NY)13, 20748–20761. doi: 10.18632/aging.203462
149
Zhang Y. Zhang E. Hou L. Lu H. Guo T. Wang R. et al . (2024). Assessing and mitigating foodborne acetochlor exposure induced ileum toxicity in broiler chicks: the role of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids supplementation and molecular pathways analysis. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol.199:105761. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2023.105761
150
Zhang Y. Zhang J. Zhao Y. Zhang Y. Liu L. Xu X. et al . (2023). ChemR23 activation attenuates cognitive impairment in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-induced neuronal pyroptosis. Cell Death Dis.14:721. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06237-6
151
Zhao A. Liu N. Yao M. Zhang Y. Yao Z. Feng Y. et al . (2022). A review of neuroprotective effects and mechanisms of Ginsenosides from Panax Ginseng in treating ischemic stroke. Front. Pharmacol.13:946752. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.946752
152
Zhao S. Xu Z. Niu X. Cao C. Gu Y. Wang H. et al . (2024). The role of SUMO specific peptidase 3 in secondary inflammation of ischemic stroke in mice. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. basis Dis.1870:167104. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2024.167104
153
Zhao F. Zhong L. Wang Y. Wang R. Yang Z. Luo Y. et al . (2023). Untargeted metabolomics uncovering neuroprotective effect of Dl-3-n-butylphthalide on improving cognitive impairment induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats. Int. Immunopharmacol.119:110271. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110271
154
Zheng J. Peng S. Cui L. Liu X. Li T. Zhao Z. et al . (2023). Enriched environment attenuates hippocampal theta and gamma rhythms dysfunction in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion via improving imbalanced neural afferent levels. Front. Cell. Neurosci.17:985246. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.985246
155
Zhou A. L. Swaminathan S. K. Salian V. S. Wang L. Curran G. L. Min H. K. et al . (2024). Insulin signaling differentially regulates the trafficking of insulin and amyloid Beta peptides at the blood-brain barrier. Mol. Pharm.21, 2176–2186. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.3c00784
156
Zhou Y. Xiang Y. Liu S. Li C. Dong J. Kong X. et al . (2024). RIPK3 signaling and its role in regulated cell death and diseases. Cell Death Discov.10:200. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-01957-w
157
Zhu J. Du J. Kou W. Liu C. Fan J. Zhu Z. et al . (2024). Probucol protects against brain damage caused by intra-neural pyroptosis in rats with vascular dementia through inhibition of the Syk/Ros pathway. Aging (Albany NY)16, 4363–4377. doi: 10.18632/aging.205593
158
Zhu Y. M. Lin L. Wei C. Guo Y. Qin Y. Li Z. S. et al . (2021). The key regulator of necroptosis, RIP1 kinase, contributes to the formation of Astrogliosis and glial scar in ischemic stroke. Transl. Stroke Res.12, 991–1017. doi: 10.1007/s12975-021-00888-3
Summary
Keywords
necroptosis, chronic cerebral hypoperfusion, vascular cognitive impairment, cerebral ischemia, neurodegenerative disease
Citation
Wei S, Cheng L, Shen C, Li Z, Teng J, Wang L and Zhang X (2025) Necroptosis in vascular cognitive impairment: mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Front. Aging Neurosci. 17:1599773. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1599773
Received
25 March 2025
Accepted
10 June 2025
Published
25 June 2025
Volume
17 - 2025
Edited by
Jiu Chen, Nanjing University, China
Reviewed by
Leonardo Duarte Santos, Moinhos de Vento Hospital, Brazil
Bin Du, Sichuan University, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Wei, Cheng, Shen, Li, Teng, Wang and Zhang.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaorong Zhang, jjzhangxiaorong@163.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.