- 1Department of Thoracic Surgery, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, China
- 2Department of General Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, China
Introduction: The Oxidative Balance Score (OBS) serves as a means to evaluate the systemic oxidative stress status, where the higher OBS score indicates a greater exposure to antioxidants. Few studies have delved into the connection between the systemic oxidative stress status and gallstone.
Methods: A total of 4,376 from the NHANES participants were included in this cross-sectional analysis using 2017–2020 survey cycles. Gallstone was diagnosed by the Patient Health Questionnaire. OBS was scored by 16 dietary factors and 4 lifestyle factors. Logistic regression, subgroup analysis and restricted cubic splines (RCS) were used to assess the association between OBS and gallstone.
Results: In a sample comprising 4,376 individuals, logistic regression illuminated a negative association between OBS and gallstone [OR = 0.96 (0.94, 0.98), p < 0.001]. Compared to the lowest quartile of OBS, the fully adjusted ORs for the highest quartile of total OBS and gallstone were 0.65 (0.45, 0.95), p=0.025. Robust associations were also discerned between gallstone and both dietary and lifestyle OBS. The results of the subgroup analysis showed significant differences in the association between lifestyle OBS and gallstone with respect to age and marital status. RCS analysis indicated a significant linear relationship between OBS and gallstone.
Discussion: Our study exhibited a reverse relationship between OBS and the prevalence of gallstone among American adults, which provided a theoretical foundation for designing personalized dietary regimens and lifestyle modifications to mitigate gallstone formation.
1 Introduction
Gallstones are one of the most common and costly of all the gastrointestinal diseases (Marschall and Einarsson, 2007) and >20% of people with gallstones will develop symptoms in their lifetime (including biliary colic or infections), usually in adulthood (Lammert et al., 2016). Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is considered the most cost-effective management strategy in the treatment of symptomatic gallstones (Bellows et al., 2005). They give rise to substantial health and economic burden. The pathogenesis of gallstones arises from multiple contributors, encompassing dynamic interactions among gender-related predispositions, heritable factor, modifiable behavioral patterns, and disease-mediated metabolic alterations (Shabanzadeh, 2018). Oxidative stress is regarded as one of the primary risk factors contributing to gallstone formation (Koppisetti et al., 2008). Therefore, investigating the role of oxidative stress in the formation and progression of gallstones is crucial for understanding the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms and developing effective preventive strategies.
Oxidative stress is defined as an imbalance between production of free radicals and reactive metabolites, so-called oxidants or reactive oxygen species (ROS), and their elimination by protective mechanisms, referred to as antioxidants (Reuter et al., 2010). This imbalance cause damage to cellular macromolecules such as DNA, lipids and proteins, eventually leading to necrosis and apoptotic cell death (Senoner and Dichtl, 2019). The process can be influenced by various modifiable factors, such as diet, smoking, or medicines (Poljsak et al., 2013). So, the level of oxidative stress in the body is complex. We believe that exposure to a single factor or solely dietary factors may not fully reflect the body’s role in maintaining overall oxidative balance, and a comprehensive evaluation of multiple factor combinations may be more meaningful. OBS has a significant advantage in combining various oxidants and antioxidants in diet and lifestyle, and may be a more accurate overall indicator of oxidative stress (Hernández-Ruiz et al., 2022).
There has been a series of literature to explore the relationship between OBS and depression (Liu et al., 2023), kidney stone (Ke et al., 2023), diabetes (Wu et al., 2023) and other diseases (Xu et al., 2024; Qu, 2023; Hu et al., 2024), but there is no article to discuss the link between gallstones and OBS. Therefore, this study aimed to assess the association between OBS and gallstone among adults in the United States, using NHANES data, for aiding the development of new preventive behavior for the diseases.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study population
This study was a cross-sectional study and the data were primarily obtained from NHANES, a program that is widely used by researchers to assess the health and nutrition status of adults and children in the United States (Xu et al., 2024). Each participant completed questionnaires and examinations at the Mobile Examination Centers (MECs) and written informed consent was obtained from participants.
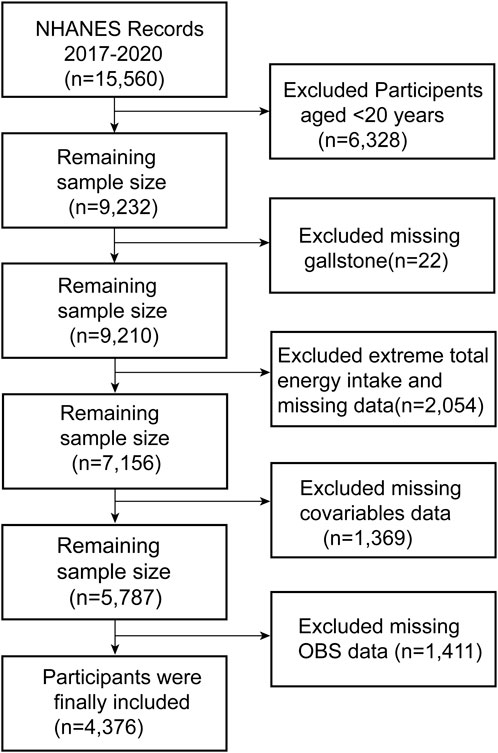
The year 2017–2020,which included a total of 15,560 participants was used for the study data because the questionnaire for gallstones was only available during that time period. Since the questionnaire was only administered to adults aged 20 years and older, we removed participants under the age of 20 years, and based on the purpose of our study, we screened the study population, with detailed inclusion and exclusion criteria provided in Figure 1. To be specific, participants with missing gallstone index data (n = 22), extreme energy intake (total energy intakes below 800 or above 4,200 kcal/day for males and below 500 or above 3,500 kcal/day for females (Hou et al., 2022)) (n = 2,054), missing covariates (n = 1,369) and incomplete OBS data (n = 1,411) were omitted. As a consequence, only 4,376 participants were eligible for complete case analysis.
2.2 Outcome variable
Gallstone cases were identified using the inquiry “Has DR ever said you have gallstones”. Participants who responded affirmatively were classified as having gallstones.
2.3 Exposure variable
OBS was determined by integrating 16 dietary factors and 4 lifestyle components, comprising 5 pro-oxidants and 15 antioxidants (Hernández-Ruiz et al., 2019). Dietary OBS, including dietary fiber, total fat, total folate, vitamins (B6, B12, C and E), niacin, carotene, riboflavin, calcium, iron, selenium, copper, magnesium, and zinc, which were collected from the first dietary recalls.
The lifestyle OBS is composed of four components: smoking, alcohol consumption, physical activity, and body mass index (BMI). Serum cotinine levels were used to quantify the smoking factor, which reflects both direct smoking and exposure to second-hand smoking (Tian et al., 2022). Alcohol consumption was categorized into three groups based on different gender: heavy drinkers (≥15 g/d for women and ≥ 30 g/d for men), non-heavy drinkers (0–15 g/d for women and 0–30 g/d for men), and non-drinkers, who were assigned 0, 1, and 2 points, respectively (Zhang et al., 2022). Total physical activity was quantified as the metabolic equivalent of task (MET), calculated based on the accumulated time of transportation and moderate and vigorous activities per week. MET scores = weekly frequency of each physical activity * duration of each physical activity* each physical activity suggested MET Scores (Tian et al., 2022). Except for alcohol consumption, the other OBS components were categorized by gender and divided into tertiles. Scores were assigned to antioxidants in tertiles 1 to 3 as 0, 1, and 2, respectively, while scores were assigned to pro-oxidants in the opposite order (Supplementary Table S1). A higher OBS score indicates a more substantial antioxidant effect. In cases where OBS components were missing, the corresponding component was assigned a score of 0, regardless of its antioxidant or pro-oxidant nature.
2.4 Covariates
Potential covariates that could confound the association between OBS and gallstones were summarized in the multivariable-adjusted model. Covariates in our study included sex (male, female), age (<40, 40–60, ≥60), ethnicity (Hispanic, non-Hispanic white, non-Hispanic black and other races), education level (below high school, high school, above high school), poverty income ratio (PIR, <1.3, 1.3–3.5, or ≥ 3.5), marital status (married or living with a partner, widowed/divorced/separated, never married), hypertension, diabetes, asthma, coronary heart disease (CHD). The definition of the comorbidities was collected in Supplementary Table S2. In addition, we incorporated total cholesterol (TC; mg/dL) and total energy intake (kcal). More details on variable collection methods can be found in the NHANES Survey Methods and Analysis Guide.
2.5 Statistical analyses
Statistical analyses were conducted utilizing appropriate NHANES sampling weights according to NHANES recommendations and guidelines, accounting for the complicated multistage entire cohort survey. Continuous variables were expressed as mean ± standard error, while categorical variables were displayed as unweighted counts and weighted proportions. ANOVA tests were used for comparing continuous variables, and chi-square tests were employed to examine statistical differences in categorical variables between groups. Then, we investigated the association between OBS and gallstones in 3 different models using multivariate logistic regression models: model 1 was a crude model without adjusting covariates, model 2 was adjusted for age, gender, and race, and model 3 was adjusted for all variables. Identical analyses were conducted for dietary OBS and lifestyle OBS with gallstone. We further assessed the heterogeneity between OBS and gallstones by subgroup analysis, including the following variables: age, gender, race, marital status, PIR, education level, diabetes, hypertension, asthma and CHD. Interaction tests were used to examine the consistency of the relationships between the different subgroups. Sensitivity analysis was performed by systematically eliminating each factor from the adjusted model 3. Finally, a restricted cubic spline (RCS) curve was performed to investigate the potentially nonlinear association between exposure and outcome.
Statistical analyses were two-sided, and p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. All analyses were performed utilizing R (version 4.2.0) and EmpowerStats software (http://www.empowerstats.com).
3 Results
3.1 Baseline characteristics
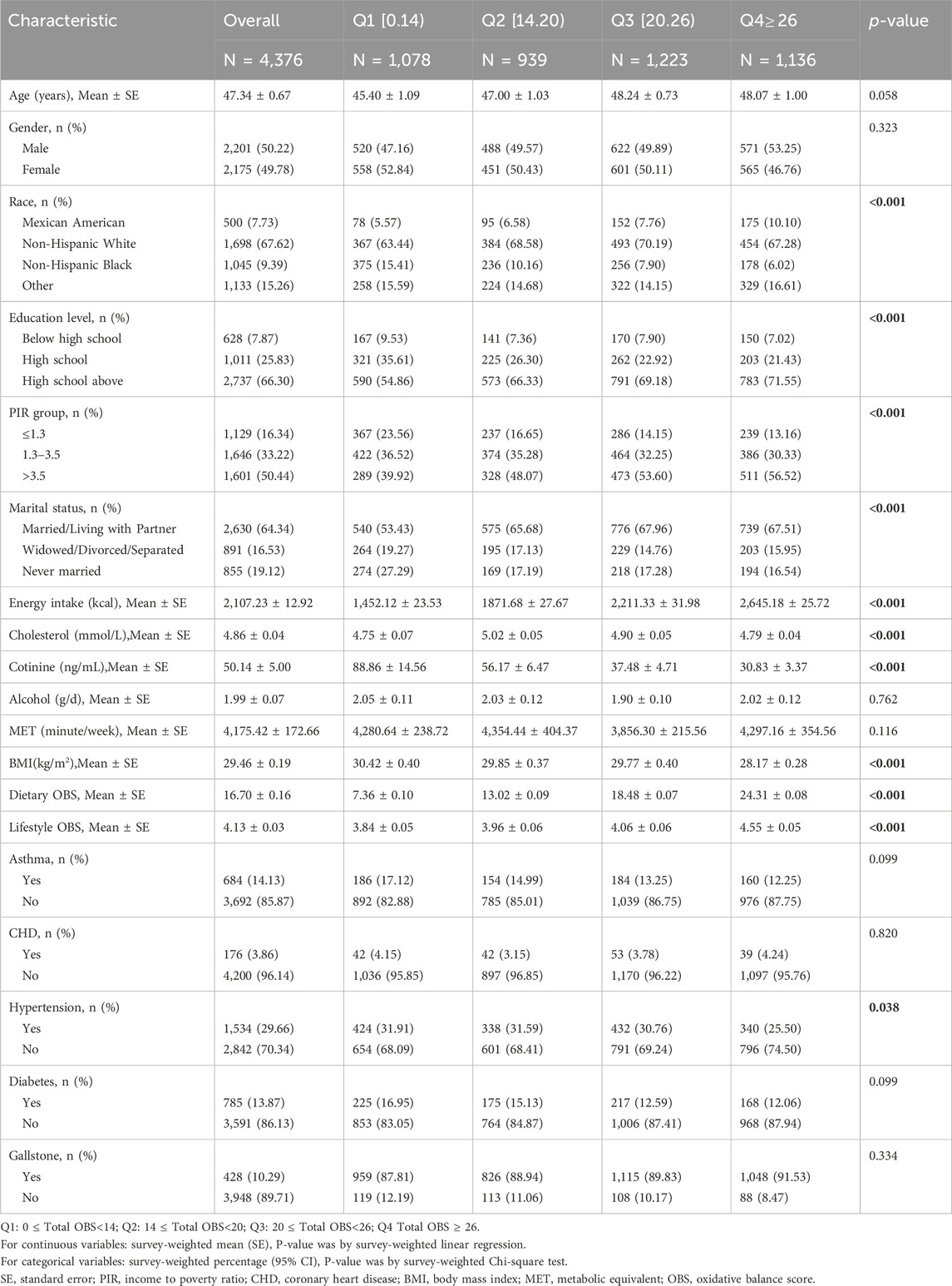
A total of 4,376 subjects with complete information were included in the study after combining covariates. Table 1 presents the baseline characteristics of the participants, stratified by quartiles of total OBS. Among them, 428 had gallstones, accounting for a prevalence rate of 10.29%. The mean age of the subjects was 47.34 ± 0.67 years, with 49.78% being female and the majority being non-Hispanic whites (67.62%). In the higher quartile, we also observed an increase in the consumption of energy, along with higher levels of education, wealth among individuals and those who married or living with partner (all p < 0.001). However, the differences in gender, asthma, CHD and diabetes were not statistically significant. Supplementary Table S3 presents additional baseline characteristic according to the absence or presence of gallstone. Individuals with gallstone tended to be older, predominantly female and had lower OBS scores. The gallstone group also have a higher BMI and exhibited a more significant burden of comorbidities. The educational level showed no significant difference between the two groups.
3.2 Relationship between total OBS and gallstone
To explore the relationship between total OBS and gallstone, we performed the logistic regression analyses. As shown in Table 2, when OBS was treated as a continuous variable, we observed that it was significantly associated with a lower incidence of developing gallstone in both crude model (OR = 0.97 (0.96, 0.99), p < 0.001) and fully adjusted model (OR = 0.96 (0.94, 0.98), p < 0.001). When considering OBS as a categorical variable, in the fully adjusted Model 3, the highest quartile of OBS was more negatively associated with the risk of gallstone than the lowest quartile of OBS (OR = 0.65 (0.45, 0.95), p = 0.025), and maintained relative stability across models. When compared to the reference category of the first OBS quartile, the OR (95% CI) for the third OBS quartile was 0.72 (0.52.0.99), p = 0.045. The observed trend was highly significant (p = 0.006). To sum up, this study revealed a significant inverse correlation between total OBS and gallstone, with individuals in the highest OBS quartile exhibiting a 35% lower risk compared to those in the lowest quartile. In sensitivity analyses, excluding any of the OBS components had no significant effect on the gallstone, indicating the robustness of our finding (Supplementary Table S4).
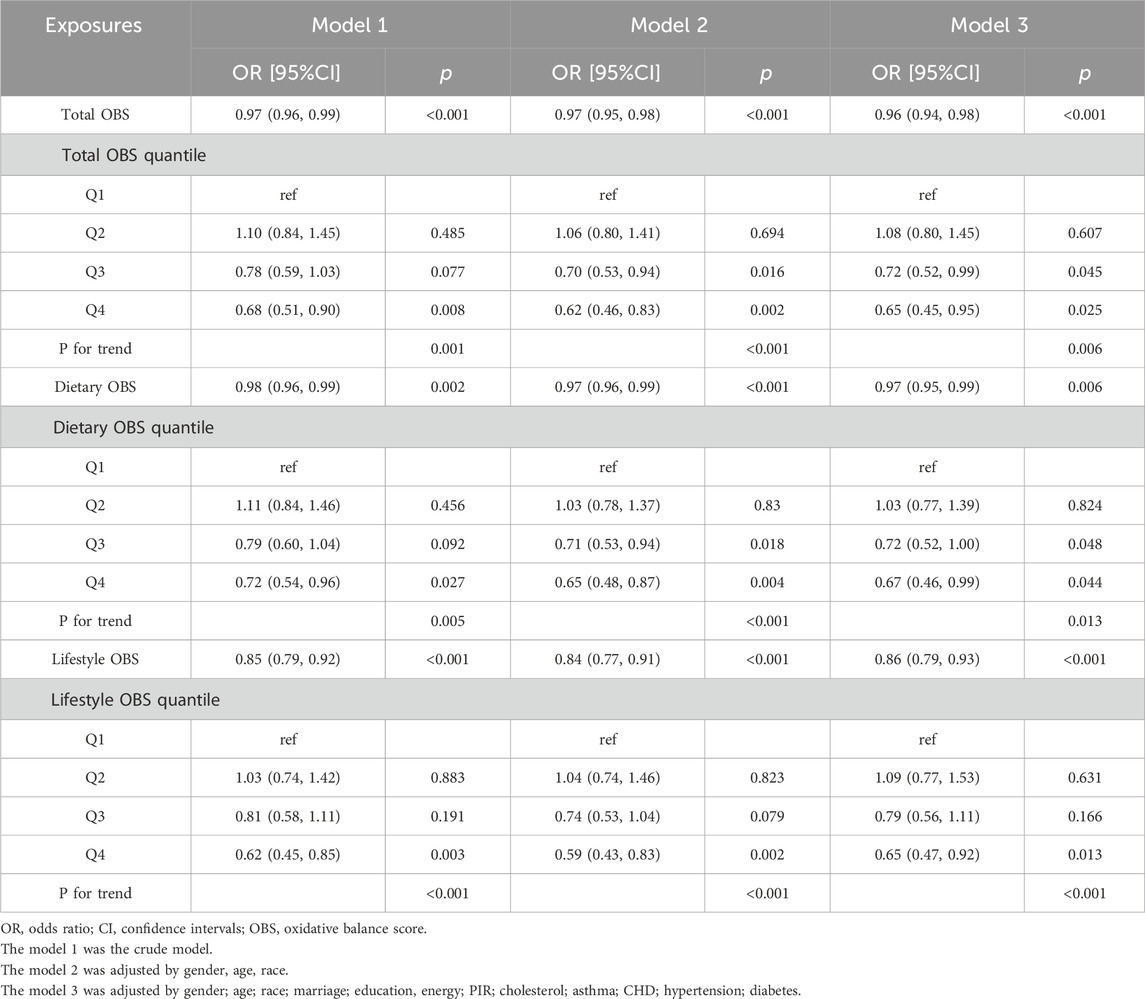
Table 2. Association between the OBS and gallstone prevalence based on logistic regression analysis.
3.3 Association of dietary OBS and lifestyle OBS with gallstone
To investigate the potential differential contributions of lifestyle OBS and dietary OBS to gallstone pathogenesis, we conducted logistic regression analyses parallel to the total OBS evaluation, as presented in Table 2. Both dietary and lifestyle OBS subtypes exhibited statistically significant negative associations with gallstone. Higher levels of continuous dietary and lifestyle OBS consistently showed correlations with a reduced incidence of gallstone (p < 0.05). In the fully adjusted Model 3, the fourth quartile of dietary OBS significantly impacted gallstone (OR = 0.67 (0.46, 0.99), p = 0.044). Similarly, lifestyle OBS also demonstrated a persistent effect, with the fourth quartile indicating a negative correlation with gallstone (OR = 0.65 (0.47, 0.92), p = 0.013). The trend test indicated that the downward trend was statistically significant (p for trend <0.001).
3.4 Subgroup analysis
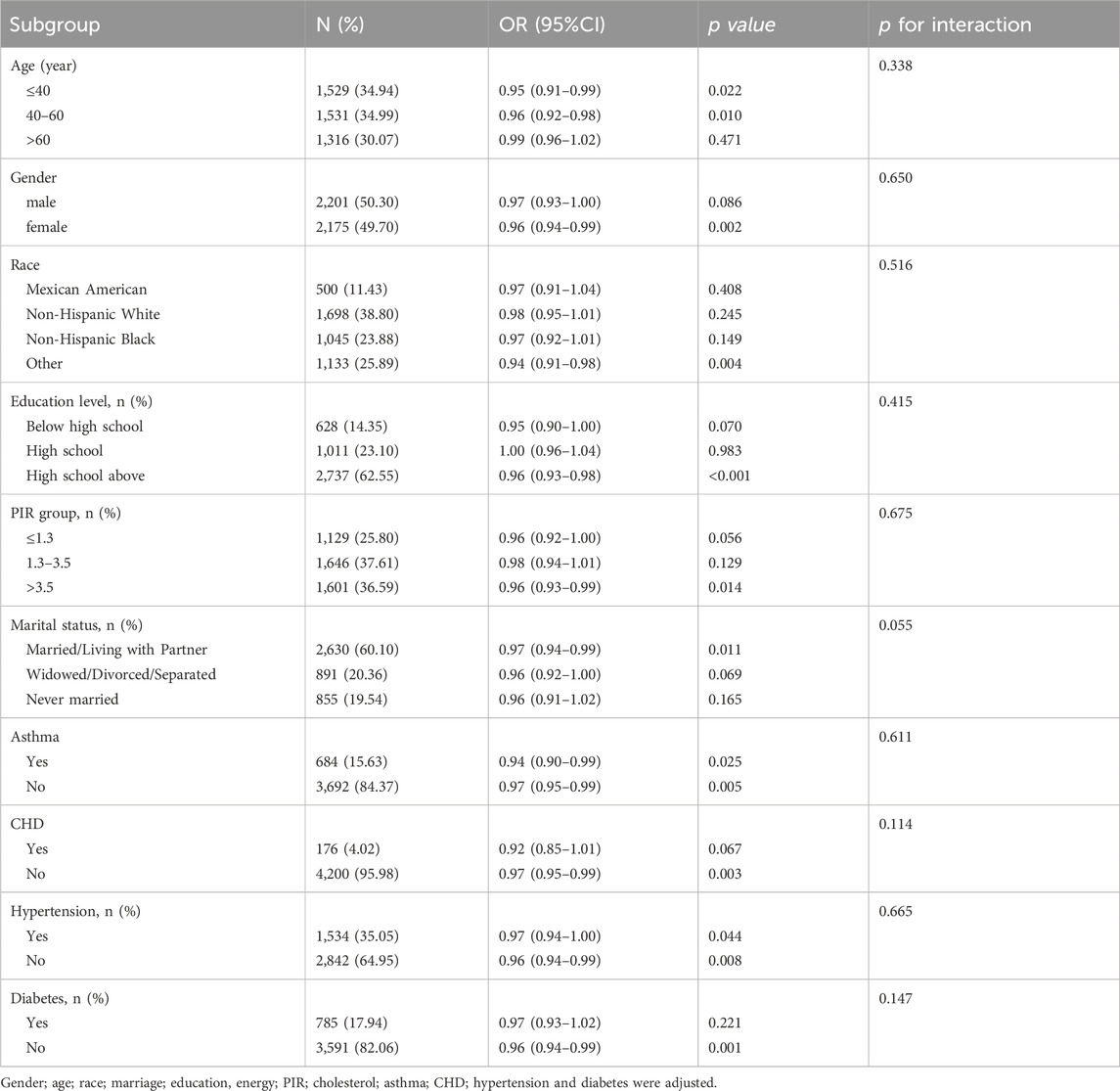
Further, to understand the association between total OBS and gallstone in different populations, we performed the subgroup analyses by fully adjusted multivariate logistic regression analyses stratified by age, race, gender, education levels, PIR, and comorbidities including asthma, CHD, diabetes and hypertension. As showed in Table3, the interaction term was no evidence of effect modification. A significant inverse association was observed in younger age groups (p = 0.022), other race (p = 0.004) and individuals with education below high school (p = 0.070). While point estimates suggested a stronger association in females (OR = 0.96) versus males (OR = 0.97), the interaction term for gender was non-significant (p for interaction = 0.650), indicating no statistical evidence of differential effects by sex.
To further explore potential effect modifiers, we conducted subgroup analyses between lifestyle OBS (Table 4) or dietary OBS (Table 5) and gallstone. A significant interaction by age (p for interaction<0.001) and marital status (p for interaction = 0.013) were observed in the relationship between lifestyle OBS and gallstone. The protective effect of lifestyle OBS was strongest in younger group (OR = 0.75 (0.62.0.91), p = 0.003), which is consistent with total OBS. The inverse association was markedly stronger in individuals with asthma (OR = 0.69 (0.57.0.84), p < 0.001) compared to those without asthma (p for interaction<0.001). Except age, marital status and asthma, our results showed that p-value for interaction was >0.05 among other subgroups, indicating consistency in our findings.
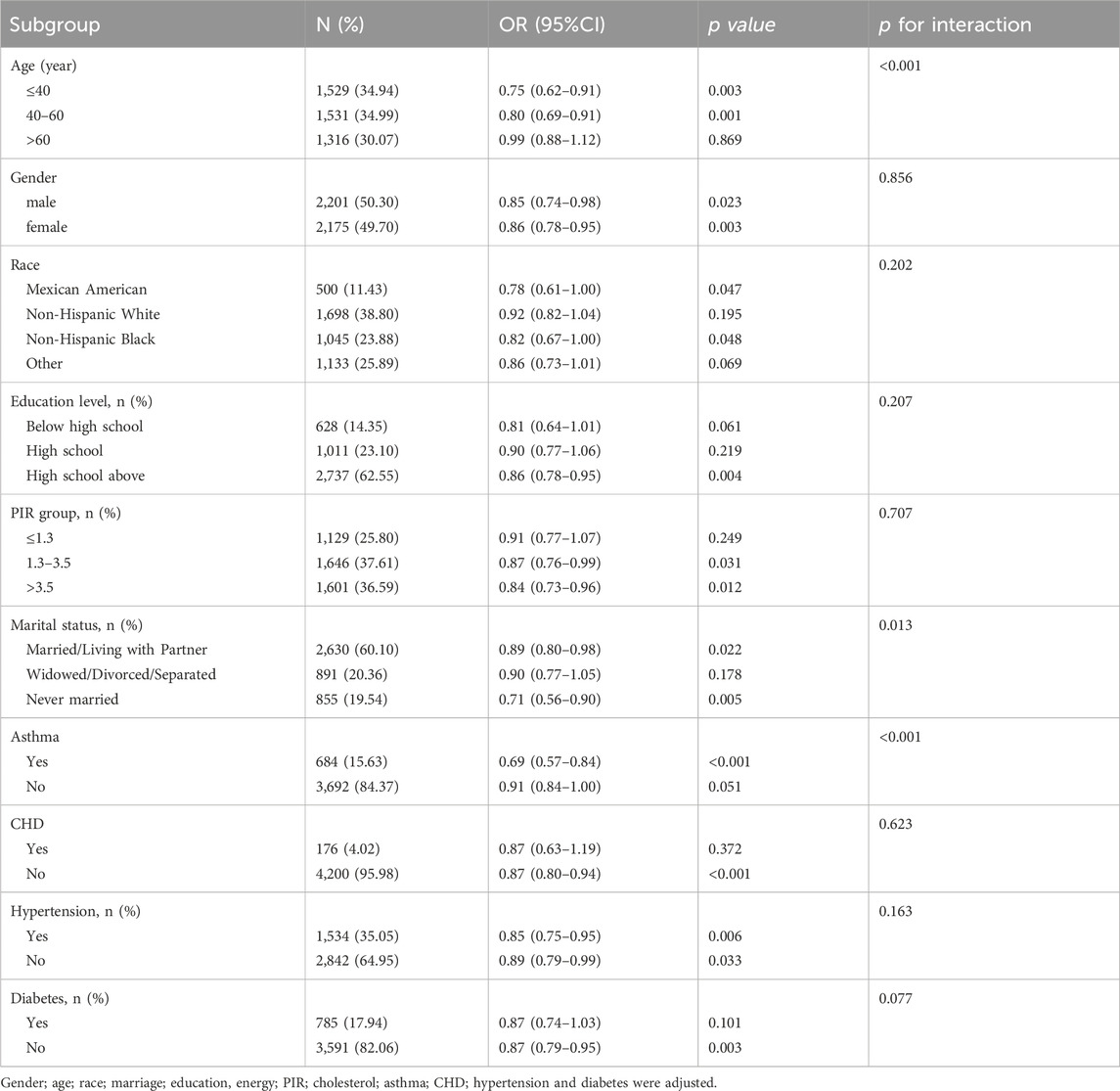
Table 4. Subgroup analysis of the association between lifestyle oxidative balance score and gallstone.
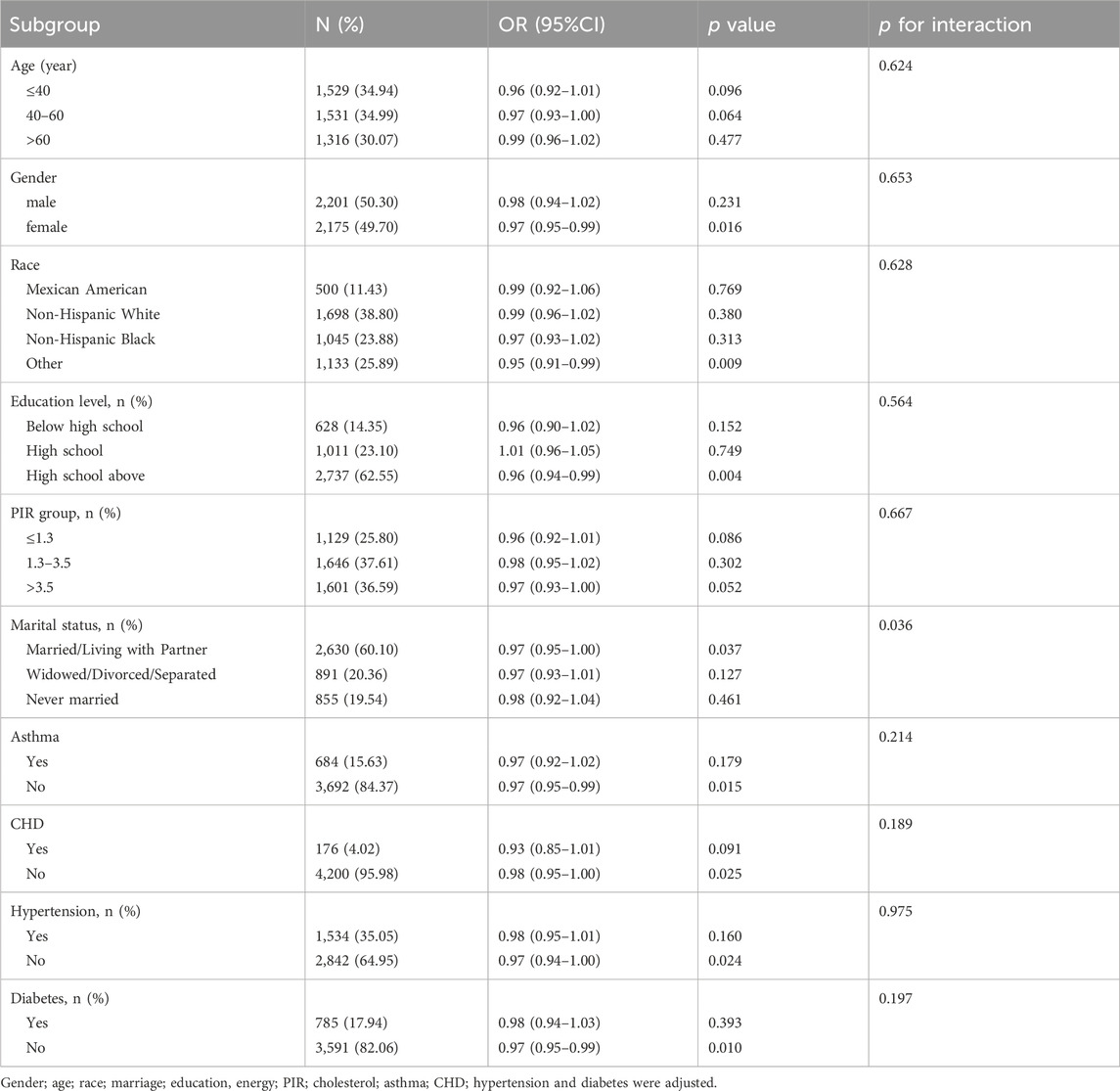
Table 5. Subgroup analysis of the association between dietary oxidative balance score and gallstone.
3.5 RCS analysis
To investigate potential nonlinear associations of gallstone risk with overall OBS and its two subcomponents (dietary OBS and lifestyle OBS), RCS analyses were implemented adjusting for all relevant covariates. As showed in Figure 2, the overall association between total OBS (Figure 2A) and gallstone risk (p for overall = 0.004, p for nonlinear = 0.729) was statistically significant. Interestingly, both diet OBS (Figure 2B) and lifestyle OBS (Figure 2C) exhibit the same trend. However, the non-linear component did not improve the model fit, suggesting a linear dose-response relationship.
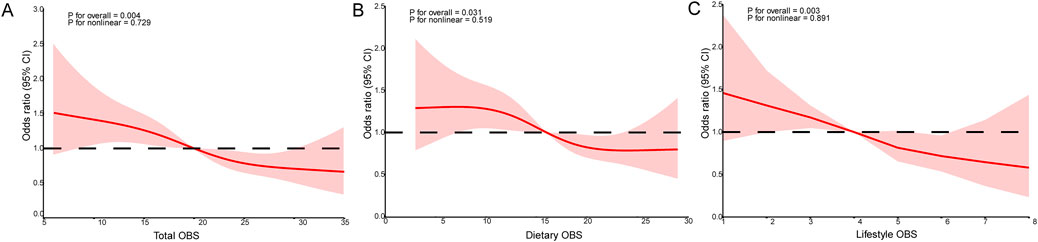
Figure 2. RCS analysis revealed the potential non-linear relationship between OBS and gallstones and it was adjusted by gender, age, race, marriage, education, energy, PIR, cholesterol, asthma, CHD, hypertension and diabetes. (A) The RCS curves of the association between total OBS and gallstone. (B) The RCS curves of the association between dietary OBS and gallstone. (C) The RCS curves of the association between lifestyle OBS and gallstone. RCS, restricted cubic spline, OBS, oxidative balance score; OR, odds ratio; 95% CI, 95% confidence interval; PIR, income to poverty ratio; CHD, coronary heart disease.
4 Discussion
To investigate the relationship between OBS and gallstones, we analyzed data from the NHANES 2017–2020 comprising 4,376 participants, which is a nationally representative survey population in the United States. Our findings revealed a robust negative association between OBS and gallstones even after adjusting for sociodemographic variables and covariates for comorbidities, which is consistent with recently published studies (Zhu et al., 2025; Xiong et al., 2025). However, our study implemented stricter exclusion criteria compared to prior analyses (e.g., n = 6,196 in reference studies), removing participants with implausible energy intake to mitigate confounding from aberrant dietary reporting. This methodological refinement likely enhances internal validity by excluding metabolically extreme populations whose oxidative balance profiles may non-representatively skew OBS-gallstone associations. Moreover, our subgroup analyses generated hypotheses about potentially stronger effects in younger individuals and females. However, the lack of statistically significant interactions precludes definitive claims about effect modification by these factors. In conclusion, a higher OBS is associated with a lower risk of developing gallstones, which highlights the significance of diet and lifestyle in preventing the onset of gallstones.
Numerous studies have demonstrated that oxidative stress represents a substantial risk factor for a variety of diseases including tumors (Cheng et al., 2016), cerebrovascular diseases (Marlatt et al., 2008), diabetes (Zhang et al., 2020), as well as neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s disease (Liu et al., 2012). The most common cellular targets for ROS include cell membrane lipids, proteins, and DNA which causes lipid peroxidation, enzymatic dysfunction, and DNA damage, respectively (Fang et al., 2002; Darley-Usmar and Halliwell, 1996; Floyd, 1990). In this study, the inverse association between OBS and gallstone risk aligns with a studies using ESR spectrum method demonstrating that oxidative stress promotes cholesterol supersaturation in bile, a critical step in gallstone pathogenesis (Liu and Hu, 2002). The research by Tranum Kuar and others in North Indian Population has shown that levels of catalase, SOD, and glutathione-related enzymes were decreased in patients with gallstones in comparison to patients without gallstones, which can be attributed to increase oxidative stress (Kaur and Kaur, 2010). Oxidative stress plays a causative role in the bile duct ligation-induced pigment gallstone formation (Shiesh et al., 2000). A study involving North-East Indian population showed that 8-OH-dG, which is an oxidative stress marker, was significantly higher in the gallstone patients at the plasma and DNA level (Singh et al., 2019). The above-mentioned studies all illustrate the inseparable relationship between oxidative stress and gallstones. A study showed that damage to the gallbladder epithelium mediated by free radicals makes the development of both gallbladder inflammation and gallstone formation more likely (Koppisetti et al., 2008). The mechanism of toxicity by oxygen-derived free radicals is via peroxidation of phospholipids; these are major components of the cell membrane which cause cell death due to loss of cell wall integrity (Weiss, 1989). Phospholipids are also major components of the bile required for cholesterol solubilization (Carey and Small, 1978). Peroxidation of biliary phospholipids is, therefore, the likely mechanism of ROS-induced pronucleating activity. There are also studies indicating that bilirubin oxidation is crucial in the formation of gallstones (Sanikidze and Chikvaidze, 2016). Further studies are needed to clarify the mechanisms of gallstone formation.
Our stratified analyses revealed novel modifiers: the inverse association was markedly stronger in individuals with asthma (OR = 0.69 (0.57–0.84), p < 0.001, p for interaction<0.001). This may imply that oxidative balance modulation exerts amplified protective effects in pro-inflammatory states, warranting mechanistic studies on glutathione pathways in gallstone formation and underscores a potential shared pathophysiology between oxidative stress, chronic inflammation, and gallstone development, as discussed in a review (Reuter et al., 2010). The stronger protective associations of OBS and lifestyle OBS in younger populations (≤60 years) may reflect age-related differences in oxidative stress metabolism. The potential mechanisms may involve age-dependent cellular damage (Genova and Lenaz, 2015; López-Lluch et al., 2015) mediated through dysregulated ROS signaling pathways, compounded by the cumulative impact of multiple comorbidities commonly present in older adult populations. While the overall OBS association did not significantly differ by gender, the numerically stronger effect size in females hypothetically aligns with estrogen’s antioxidant properties (Kim, 2022) that estrogen is a powerful antioxidant, which modulates oxidative stress pathways and gallstone formation through both direct scavenging and stimulating increased expression of antioxidant enzymes (Strehlow et al., 2003). However, non-significant interaction terms (e.g., for gender, education) must be interpreted cautiously. Apparent subgroup differences may reflect type II error due to limited power rather than true biological effect modification. Future studies with larger samples are needed to conclusively examine these associations. A meta-analysis of 10 cohort studies showed an overall 56% increased risk of gallstones among diabetes patients compared with individuals without diabetes (Aune and Vatten, 2016). Several possible mechanisms may explain the association between type 2 diabetes and gallstone disease. For example, hepatic insulin resistance has been shown to directly promote the formation of cholesterol gallstones (Biddinger et al., 2008). Gallbladder hypomotility in diabetes might be an additional predisposing factor for cholesterol gallstone formation (Portincasa et al., 2006).
The robustness of OBS as a composite biomarker derives from its incorporation of both dietary and lifestyle antioxidants with established redox-modulating properties. Fiber may have protective effects against gallstones by reducing the intestinal transit time and reducing the production of bile acids (Marcus and Heaton, 1986). Schwesinger et al. (1999) have shown the protective effect of dietary soluble fiber against cholesterol gallstone formation. Beta-carotene has been shown to suppress lipid peroxidation in mouse models (Iyama et al., 1996). Many vitamins inhibit NO production by iNOS and also directly scavenge ROS and upregulate the activities of antioxidant enzymes (Wu and Meininger, 2002). Vitamin E inhibits ROS-induced generation of lipid peroxyl radicals, thereby protecting cells from peroxidation of PUFA in membrane phospholipids, from oxidative damage of plasma very low-density lipoprotein, cellular proteins, DNA, and from membrane degeneration (Topinka et al., 1989). Magnesium is a cofactor for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, two pentose-cycle enzymes catalyzing the production of NADPH from NADP+. Thus, a deficiency of dietary magnesium reduces glutathione reductase activity and results in radical-induced protein oxidation and marked lesions in tissues (Rock et al., 1995; Stafford et al., 1993). The essential role of selenium in the removal of free radicals and the maintenance of normal human health is epitomized by the etiology of Keshen disease in China (Yang et al., 1983). Lifestyle factors as OBS component also critically modulate gallstone pathogenesis. A case-control study by McMichael et al. demonstrated a significant association between cigarette smoking and gallbladder disease, particularly emphasizing early exposure effects (McMichael et al., 1992). Smoking may promote gallstone pathogenesis through toxic chemical exposure and insulin resistance—a shared pathway linking smoking to both gallstone and type 2 diabetes (Willi et al., 2007), which is a risk factor for gallbladder disease (Shebl et al., 2010). Exercise or physical activity may contribute to ameliorate insulin resistance by improving insulin action and increasing nitric oxide bioavailability as well as by increasing ROS-detoxification and decreasing ROS generation (Ahmadi et al., 2011; Bjork et al., 2012; Belotto et al., 2010). Currently, obesity is a challenging issue worldwide. A study discovered that the expression of antioxidant enzymes is lower in obese individuals (Le Lay et al., 2014). Collectively, the OBS highlights the multifactorial nature of gallstone prevention, emphasizing that combined dietary and lifestyle interventions rather than isolated factors are essential to mitigate the incidence of gallstone.
Clinically, integrating OBS into risk prediction models could enhance early identification of high-risk population such as obese or diabetic individuals particularly. Public health interventions targeting modifiable OBS components for example physical activity and smoking cessation could offer dual benefits for gallstone prevention and cardiometabolic health. Future studies should integrate multi-omics approaches to dissect OBS subcomponents and explore mechanistic links to biliary pathophysiology. However, this study is not without its limitations. Firstly, one shortcoming of the current study is the inability to differentiate between cholesterol gallstones and pigment gallstones, given that these two types have distinct etiologies. However, it's important to note that in the Western world, the overwhelming majority of gallstones are of the cholesterol type. Secondly, the data on diet, physical activity were derived from patient self-reports, potentially introducing recall bias. Thirdly, it is difficult to establish a causal relationship between OBS and gallstone because of the inescapable disadvantage of cross-sectional study. Consequently, it needs more prospectively designed studies to demonstrate the effectiveness of OBS. Fourthly, we fully acknowledge that complete-case analysis may introduce selection bias if data are not missing completely at random. Sensitivity analyses indicate our findings are robust to data variations at some extent. However, we acknowledge that multiple imputation methods might further enhance precision and will be prioritized in future studies.
5 Conclusion
In summary, results from NHANES suggested that OBS was strongly negatively associated with gallstone, stressing the importance of dietary and lifestyle factors in daily life.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes.
Author contributions
XC: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. XH: Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. CY: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – review and editing. ZX: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft. ZC: Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. SL: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was funded by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Serial Number: 82303811), the Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi (Grant serial number: 2023-JC-QN-0840) and the Key Research and Development Projects of Shaanxi Province (Grant serial numbers: 2023-YBSF-359).
Acknowledgments
The authors express gratitude to all participants and investigators of the NHANES.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fragi.2025.1621107/full#supplementary-material
References
Ahmadi, N., Eshaghian, S., Huizenga, R., Sosnin, K., Ebrahimi, R., and Siegel, R. (2011). Effects of intense exercise and moderate caloric restriction on cardiovascular risk factors and inflammation. Am. J. Med. 124 (10), 978–982. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2011.02.032
Aune, D., and Vatten, L. J. (2016). Diabetes mellitus and the risk of gallbladder disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. J. Diabetes. Complications. 30(2):368–373. doi:10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2015.11.012
Bellows, C. F., Berger, D. H., and Crass, R. A. (2005). Management of gallstones. Am. Fam. Physician 72 (4), 637–642.
Belotto, M. F., Magdalon, J., Rodrigues, H. G., Vinolo, M. A. R., Curi, R., Pithon-Curi, T. C., et al. (2010). Moderate exercise improves leucocyte function and decreases inflammation in diabetes. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 162 (2), 237–243. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04240.x
Biddinger, S. B., Haas, J. T., Yu, B. B., Bezy, O., Jing, E., Zhang, W., et al. (2008). Hepatic insulin resistance directly promotes formation of cholesterol gallstones. Nat. Med. 14 (7), 778–782. doi:10.1038/nm1785
Bjork, L., Jenkins, N. T., Witkowski, S., and Hagberg, J. M. (2012). Nitro-oxidative stress biomarkers in active and inactive men. Int. J. Sports Med. 33 (4), 279–284. doi:10.1055/s-0032-1301891
Carey, M. C., and Small, D. M. (1978). The physical chemistry of cholesterol solubility in bile. Relationship to gallstone formation and dissolution in man. J. Clin. Invest. 61 (4), 998–1026. doi:10.1172/JCI109025
Cheng, Y.-T., Yang, C.-C., and Shyur, L.-F. (2016). Phytomedicine-Modulating oxidative stress and the tumor microenvironment for cancer therapy. Pharmacol. Res. 114, 128–143. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2016.10.022
Darley-Usmar, V., and Halliwell, B. (1996). Blood radicals: reactive nitrogen species, reactive oxygen species, transition metal ions, and the vascular system. Pharm. Res. 13 (5), 649–662. doi:10.1023/a:1016079012214
Fang, Y.-Z., Yang, S., and Wu, G. (2002). Free radicals, antioxidants, and nutrition. Nutrition 18 (10), 872–879. doi:10.1016/s0899-9007(02)00916-4
Floyd, R. A. (1990). Role of oxygen free radicals in carcinogenesis and brain ischemia. FASEB J. 4 (9), 2587–2597. doi:10.1096/fasebj.4.9.2189775
Genova, M. L., and Lenaz, G. (2015). The interplay between respiratory supercomplexes and ROS in aging. Antioxid. Redox Signal 23 (3), 208–238. doi:10.1089/ars.2014.6214
Hernández-Ruiz, Á., García-Villanova, B., Guerra-Hernández, E., Amiano, P., Ruiz-Canela, M., and Molina-Montes, E. (2019). A review of a priori defined oxidative balance scores relative to their components and impact on health outcomes. Nutrients 11 (4), 774. doi:10.3390/nu11040774
Hernández-Ruiz, Á., García-Villanova, B., Guerra-Hernández, E. J., Carrión-García, C. J., Amiano, P., Sánchez, M.-J., et al. (2022). Oxidative balance scores (OBSs) integrating nutrient, food and lifestyle dimensions: development of the NutrientL-OBS and FoodL-OBS. Antioxidants (Basel) 11 (2), 300. doi:10.3390/antiox11020300
Hou, W., Han, T., Sun, X., Chen, Y., Xu, J., Wang, Y., et al. (2022). Relationship between carbohydrate intake (quantity, quality, and time eaten) and mortality (total, cardiovascular, and diabetes): assessment of 2003-2014 national health and nutrition examination survey participants. Diabetes Care 45 (12), 3024–3031. doi:10.2337/dc22-0462
Hu, J., Zou, H., Qiao, X., Wang, Y., Lv, M., Zhang, K., et al. (2024). The relationship between oxidative balance scores and chronic diarrhea and constipation: a population-based study. BMC Public Health 24 (1), 1366. doi:10.1186/s12889-024-18683-8
Iyama, T., Takasuga, A., and Azuma, M. (1996). beta-Carotene accumulation in mouse tissues and a protective role against lipid peroxidation. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 66 (4), 301–305.
Kaur, T., and Kaur, S. (2010). Pathophysiological conditions in cholelithiasis formation in North Indian population: spectroscopic, biophysical, and biochemical study. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 138 (1-3), 79–89. doi:10.1007/s12011-010-8618-0
Ke, R., He, Y., and Chen, C. (2023). Association between oxidative balance score and kidney stone in United States adults: analysis from NHANES 2007-2018. Front. Physiol. 14, 1275750. doi:10.3389/fphys.2023.1275750
Kim, S. Y. (2022). Oxidative stress and gender disparity in cancer. Free Radic. Res. 56 (1), 90–105. doi:10.1080/10715762.2022.2038789
Koppisetti, S., Jenigiri, B., Terron, M. P., Tengattini, S., Tamura, H., Flores, L. J., et al. (2008). Reactive oxygen species and the hypomotility of the gall bladder as targets for the treatment of gallstones with melatonin: a review. Dig. Dis. Sci. 53 (10), 2592–2603. doi:10.1007/s10620-007-0195-5
Lammert, F., Gurusamy, K., Ko, C. W., Miquel, J.-F., Méndez-Sánchez, N., Portincasa, P., et al. (2016). Gallstones. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2, 16024. doi:10.1038/nrdp.2016.24
Le Lay, S., Simard, G., Martinez, M. C., and Andriantsitohaina, R. (2014). Oxidative stress and metabolic pathologies: from an adipocentric point of view. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 908539. doi:10.1155/2014/908539
Liu, X., Liu, X., Wang, Y., Zeng, B., Zhu, B., and Dai, F. (2023). Association between depression and oxidative balance score: national health and nutrition examination survey (NHANES) 2005-2018. J. Affect Disord. 337, 57–65. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2023.05.071
Liu, X.-J., Yang, W., and Qi, J.-S. (2012). Oxidative stress and Alzheimer's disease. Sheng Li Xue Bao 64 (1), 87–95.
Liu, X.-T., and Hu, J. (2002). Relationship between bilirubin free radical and formation of pigment gallstone. World J. Gastroenterol. 8 (3), 413–417. doi:10.3748/wjg.v8.i3.413
López-Lluch, G., Santos-Ocaña, C., Sánchez-Alcázar, J. A., Fernández-Ayala, D. J. M., Asencio-Salcedo, C., Rodríguez-Aguilera, J. C., et al. (2015). Mitochondrial responsibility in ageing process: innocent, suspect or guilty. Biogerontology 16 (5), 599–620. doi:10.1007/s10522-015-9585-9
Marcus, S. N., and Heaton, K. W. (1986). Effects of a new, concentrated wheat fibre preparation on intestinal transit, deoxycholic acid metabolism and the composition of bile. Gut 27 (8), 893–900. doi:10.1136/gut.27.8.893
Marlatt, M. W., Lucassen, P. J., Perry, G., Smith, M. A., and Zhu, X. (2008). Alzheimer's disease: cerebrovascular dysfunction, oxidative stress, and advanced clinical therapies. J. Alzheimers Dis. 15 (2), 199–210. doi:10.3233/jad-2008-15206
Marschall, H. U., and Einarsson, C. (2007). Gallstone disease. J. Intern Med. 261 (6), 529–542. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2796.2007.01783.x
McMichael, A. J., Baghurst, P. A., and Scragg, R. K. (1992). A case-control study of smoking and gallbladder disease: importance of examining time relations. Epidemiology 3 (6), 519–522. doi:10.1097/00001648-199211000-00010
Poljsak, B., Šuput, D., and Milisav, I. (2013). Achieving the balance between ROS and antioxidants: when to use the synthetic antioxidants. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 956792. doi:10.1155/2013/956792
Portincasa, P., Moschetta, A., and Palasciano, G. (2006). Cholesterol gallstone disease. Lancet 368 (9531), 230–239. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69044-2
Qu, H. (2023). The association between oxidative balance score and periodontitis in adults: a population-based study. Front. Nutr. 10, 1138488. doi:10.3389/fnut.2023.1138488
Reuter, S., Gupta, S. C., Chaturvedi, M. M., and Aggarwal, B. B. (2010). Oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer: how are they linked? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 49 (11), 1603–1616. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.09.006
Rock, E., Astier, C., Lab, C., Vignon, X., Gueux, E., Motta, C., et al. (1995). Dietary magnesium deficiency in rats enhances free radical production in skeletal muscle. J. Nutr. 125 (5), 1205–1210. doi:10.1093/jn/125.5.1205
Sanikidze, T., and Chikvaidze, E. (2016). Role of the free radicals in mechanisms of gallstone formation: an EPR study. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 172 (1-3), 317–324. doi:10.1093/rpd/ncw237
Schwesinger, W. H., Kurtin, W. E., Page, C. P., Stewart, R. M., and Johnson, R. (1999). Soluble dietary fiber protects against cholesterol gallstone formation. Am. J. Surg. 177 (4), 307–310. doi:10.1016/s0002-9610(99)00047-1
Senoner, T., and Dichtl, W. (2019). Oxidative stress in cardiovascular diseases: still a therapeutic target? Nutrients 11 (9), 2090. doi:10.3390/nu11092090
Shabanzadeh, D. M. (2018). Incidence of gallstone disease and complications. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 34 (2), 81–89. doi:10.1097/MOG.0000000000000418
Shebl, F. M., Andreotti, G., Rashid, A., Gao, Y. T., Yu, K., Shen, M. C., et al. (2010). Diabetes in relation to biliary tract cancer and stones: a population-based study in Shanghai, China. Br. J. Cancer 103 (1), 115–119. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6605706
Shiesh, S. C., Chen, C. Y., Lin, X. Z., Liu, Z. A., and Tsao, H. C. (2000). Melatonin prevents pigment gallstone formation induced by bile duct ligation in Guinea pigs. Hepatology 32 (3), 455–460. doi:10.1053/jhep.2000.16332
Singh, N., Kazim, S. N., Sultana, R., Tiwari, D., Borkotoky, R., Kakati, S., et al. (2019). Oxidative stress and deregulations in base excision repair pathway as contributors to gallbladder anomalies and carcinoma - a study involving North-East Indian population. Free Radic. Res. 53 (5), 473–485. doi:10.1080/10715762.2019.1606423
Stafford, R. E., Mak, I. T., Kramer, J. H., and Weglicki, W. B. (1993). Protein oxidation in magnesium deficient rat brains and kidneys. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 196 (2), 596–600. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1993.2291
Strehlow, K., Rotter, S., Wassmann, S., Adam, O., Grohé, C., Laufs, K., et al. (2003). Modulation of antioxidant enzyme expression and function by estrogen. Circ. Res. 93 (2), 170–177. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000082334.17947.11
Tian, X., Xue, B., Wang, B., Lei, R., Shan, X., Niu, J., et al. (2022). Physical activity reduces the role of blood cadmium on depression: a cross-sectional analysis with NHANES data. Environ. Pollut. 304, 119211. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119211
Topinka, J., Binkova, B., Sram, R. J., and Erin, A. N. (1989). The influence of alpha-tocopherol and pyritinol on oxidative DNA damage and lipid peroxidation in human lymphocytes. Mutat. Res. 225 (3), 131–136. doi:10.1016/0165-7992(89)90130-9
Weiss, S. J. (1989). Tissue destruction by neutrophils. N. Engl. J. Med. 320 (6), 365–376. doi:10.1056/NEJM198902093200606
Willi, C., Bodenmann, P., Ghali, W. A., Faris, P. D., and Cornuz, J. (2007). Active smoking and the risk of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 298 (22), 2654–2664. doi:10.1001/jama.298.22.2654
Wu, C., Ren, C., Song, Y., Gao, H., Pang, X., and Zhang, L. (2023). Gender-specific effects of oxidative balance score on the prevalence of diabetes in the US population from NHANES. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 14, 1148417. doi:10.3389/fendo.2023.1148417
Wu, G., and Meininger, C. J. (2002). Regulation of nitric oxide synthesis by dietary factors. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 22, 61–86. doi:10.1146/annurev.nutr.22.110901.145329
Xiong, T., Chen, Z., Yi, J., Yu, T., and Wang, K. (2025). Higher levels of oxidative balance score linked to lower risk of gallstones: findings from the 2017-2020 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Front. Nutr. 12, 1521882. doi:10.3389/fnut.2025.1521882
Xu, W., Mu, D., Wang, Y., Wang, Y., Wang, C., and Zhang, X. (2024). Association between oxidative balance score and sarcopenia in US adults: NHANES 2011-2018. Front. Nutr. 11, 1342113. doi:10.3389/fnut.2024.1342113
Yang, G. Q., Wang, S. Z., Zhou, R. H., and Sun, S. Z. (1983). Endemic selenium intoxication of humans in China. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 37 (5), 872–881. doi:10.1093/ajcn/37.5.872
Zhang, P., Li, T., Wu, X., Nice, E. C., Huang, C., and Zhang, Y. (2020). Oxidative stress and diabetes: antioxidative strategies. Front. Med. 14 (5), 583–600. doi:10.1007/s11684-019-0729-1
Zhang, W., Peng, S.-F., Chen, L., Chen, H.-M., Cheng, X.-E., and Tang, Y.-H. (2022). Association between the oxidative balance score and telomere length from the national health and nutrition examination survey 1999-2002. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 1345071. doi:10.1155/2022/1345071
Keywords: oxidative balance score, gallstone, NHANES, dietary, lifestyle
Citation: Chen X, Huo X, Ye C, Xu Z, Chen Z and Liu S (2025) Association between oxidative balance score and gallstone in US adults: a cross-sectional study. Front. Aging 6:1621107. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2025.1621107
Received: 08 May 2025; Accepted: 27 June 2025;
Published: 15 July 2025.
Edited by:
Christa J. Nehs, Harvard Medical School, United StatesReviewed by:
Adnan Lakdawala, George Washington University, United StatesAndreas Antzoulas, General University Hospital of Patras, Greece
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Huo, Ye, Xu, Chen and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zilu Chen, bHVjeWNoZW56ekBzdHUueGp0dS5lZHUuY24=; Shiyuan Liu, bGl1c2hpeXVhbkB4anR1LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Xiaoya Chen
Xiaoya Chen Xiongwei Huo2†
Xiongwei Huo2† Changchun Ye
Changchun Ye Zhengshui Xu
Zhengshui Xu