- Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, IBBC, CNR, Monterotondo, Rome, Italy
Kefir, fermented milk rich in probiotics, has attracted growing attention for its potential anti-aging effects. Yet, studies specifically addressing kefir in the context of aging remain limited and scattered across diverse biological fields. To overcome this fragmentation, we applied an integrative approach that combines a cutting-edge AI-assisted algorithm for evidence screening with a Python-based semantic clustering pipeline. This allowed us to systematically map and classify the existing literature into four functional domains of aging: changes in body composition, energy balance, homeostatic signaling networks, and neurodegeneration. The resulting evidence map revealed a marked thematic imbalance, with most studies concentrated in mechanistic pathways such as inflammation and oxidative stress, and far fewer addressing neurocognitive or metabolic outcomes. This asymmetry suggests a structural bias in current research priorities and highlights the need to expand kefir-related studies toward more clinically relevant aging endpoints. By merging AI with domain-specific linguistic tools, our study provides a reproducible and data-driven strategy to uncover thematic blind spots and guide future investigations into kefir’s anti-aging potential.
Introduction
Aging is a complex biological process involving the progressive decline of tissue function, resilience, and homeostatic regulation. While its hallmarks include genomic instability, mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammation, and altered energy metabolism (López-Otín et al., 2013; Franceschi and Campisi, 2014), increasing attention has turned to the role of the gut microbiota in modulating systemic aging mechanisms (Cryan et al., 2019; Bourrie et al., 2016; Farnworth, 2005). Fermented foods—particularly those containing diverse probiotic communities—have been proposed as dietary modulators of host-microbiota interactions (Marsh et al., 2013). Among them, milk kefir, a traditional fermented beverage produced by inoculating milk with complex microbial consortia (kefir grains), has long been regarded as a functional food with broad health potential (Marsh et al., 2013). First proposed by 1908 Medicine Nobel price E. Metchnikoff as a factor in human longevity (Metchnikoff, 1908), kefir is now being re-examined in the light of modern microbiome science (Vinderola et al., 2019).
Yet, despite its widespread use and probiotic richness, kefir remains underrepresented in targeted aging research. While several studies suggest beneficial effects on oxidative stress, immune function, metabolic regulation, and gut integrity (Kairey et al., 2022; Vinderola et al., 2019), the literature is scattered and lacks a unified framework aligned with contemporary models of aging.
In this Perspective, we apply AI-assisted evidence mapping to systematically classify the current scientific literature on kefir and aging according to four functional domains described by Colloca et al. (2020): changes in body composition, neurodegeneration, energy balance, and signaling networks for homeostasis. Rather than exhaustively cataloguing findings, our goal is to identify thematic imbalances and underexplored domains, offering a conceptual map to guide future research into kefir’s anti-aging potential. This strategy was specifically chosen to overcome the scarcity of direct studies explicitly linking kefir consumption with aging outcomes. By adopting a domain-based clustering framework, we were able to capture biologically relevant connections that may not be immediately apparent through traditional keyword-based searches, thus broadening the scope of evidence mapping and maximizing the translational relevance of the identified research gaps.
State of the art by aging domains
To address the heterogeneity of biological mechanisms involved in aging, we adopted the functional classification proposed by Colloca et al., which distinguishes four interconnected domains: changes in body composition, energy balance, homeostasis signaling networks, and neurodegeneration. This taxonomy provides a conceptual framework that reflects both the physiological impact of aging and its clinical manifestations. Mapping the effects of kefir within these domains allows for a more structured interpretation of the literature, highlights neglected outcomes, and supports alignment with scientific priorities.
Changes in body composition
Alterations in body composition—such as reduced muscle mass, increased fat accumulation, and bone mineral density loss—are central to aging and frailty. Osteoporosis, a quintessential example, leads to fragility fractures and accounts for significant global morbidity and healthcare costs (Cruz-Jentoft et al., 2019; Burge et al., 2007). Aging exacerbates these changes via hormonal dysregulation, impaired calcium absorption, and chronic inflammation. Kefir, rich in calcium and often fortified with vitamin D, has been explored for its potential in mitigating bone loss and sarcopenia. In clinical trials, kefir has been associated with improved bone turnover markers and increases in bone mineral density (BMD), especially in postmenopausal women (Curciarello et al., 2021). In murine models, probiotics like Lactobacillus reuteri and Lactobacillus kefiri, found in kefir, significantly improved femoral BMD and suppressed inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6 (Collins et al., 2016; Li et al., 2016; Iraporda et al., 2014). Mechanistically, kefir may support musculoskeletal health during aging by enhancing calcium absorption, modulating parathyroid hormone (PTH) activity, and promoting osteoblast differentiation (Collins et al., 2016; Li et al., 2016). These effects are often accompanied by suppression of pro-resorptive cytokines such as TNF-α, supporting the preservation of bone mineral density under inflammatory conditions (Curciarello et al., 2021).
Energy balance
The balance between energy intake and expenditure becomes increasingly fragile with age, influencing both longevity and metabolic resilience. Several studies have reported that kefir improves glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity in aging models, possibly through microbiota modulation and zonulin downregulation (Ton et al., 2020; Praznikar et al., 2020); while in another study increase Apo1 protein, exerting anti-inflammatory properties (Bellikci-Koyu et al., 2022). In cancer survivors and elderly patients, kefir improved lean mass, reduced fatigue, and decreased Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) levels (Brasiel et al., 2022). Also, modulation of adipokines and cytokines in obesity links kefir to delayed metabolic syndrome (Ouchi et al., 2011). In particular, Apo1 protein is considered an anti-inflammatory mediator that may contribute to these beneficial effects. Despite these findings, energy balance remains underrepresented in kefir and aging research. Underlying these metabolic outcomes, kefir has been shown to activate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and potentially suppress mTOR signaling (El Sayed et al., 2022). These molecular events coincide with improved insulin sensitivity and beneficial modulation of adipokines, such as adiponectin and leptin (Ton et al., 2020; Praznikar et al., 2020; Ouchi et al., 2011), contributing to the restoration of metabolic flexibility in aging models.
Homeostasis signaling networks
Homeostatic signaling is the most explored in the context of kefir. Homeostasis is the capability of a system to regulate its internal surroundings through maintaining a stable, relatively regular set of properties such as temperature and ph. This includes oxidative stress responses, immune function, and inflammation—all central to inflammaging (Franceschi and Campisi, 2014; Ouchi et al., 2011). Kefir and its microbes enhance antioxidant defenses (e.g., superoxide dismutase [SOD], catalase [CAT]), reduce reactive oxygen species (ROS), and modulate cytokines (Fulop et al., 2018). These effects appear across models, from cell lines to humans. Telomere attrition, mitochondrial dysfunction, and senescence are also impacted. Kefir modulates the gut–immune axis and redox balance, suggesting a systemic benefit (Ahmed et al., 2021; Rosa et al., 2020).
Neurodegeneration
Despite compelling hypotheses, kefir’s role in neurodegeneration is underexplored, and relies mostly on reviews. Alzheimer’s disease (AD) involves inflammation, microglial activation, and ROS, all microbiota-sensitive (Heneka et al., 2015; Sharon et al., 2016). One study reported that kefir improved the global cognitive status of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Although the sample size was limited, the intervention resulted in cognitive improvement in 28% of the participants, but no neuroimaging or biomarker-based validation was included (Ton et al., 2020). Animal models confirm neuroprotection, showing improved memory and reduced anxiety-like behavior (Ribeiro et al., 2018). Yet, human trials are lacking, making this the most neglected kefir-aging interface. Emerging preclinical evidence suggests that kefir may exert neuroprotective effects through upregulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and modulation of microglial activation (Rosa et al., 2020; Heneka et al., 2015). These effects are likely mediated, at least in part, via the gut–brain axis, as kefir-derived probiotics influence microbial metabolites and neuroinflammatory signaling. While epigenetic mechanisms, such as telomere attrition, have been proposed in aging-related neurodegeneration, they remain unexplored in the context of kefir. This may contribute to attenuation of cognitive decline, as observed in early-phase clinical studies (Sharon et al., 2016).
Results as evidence map
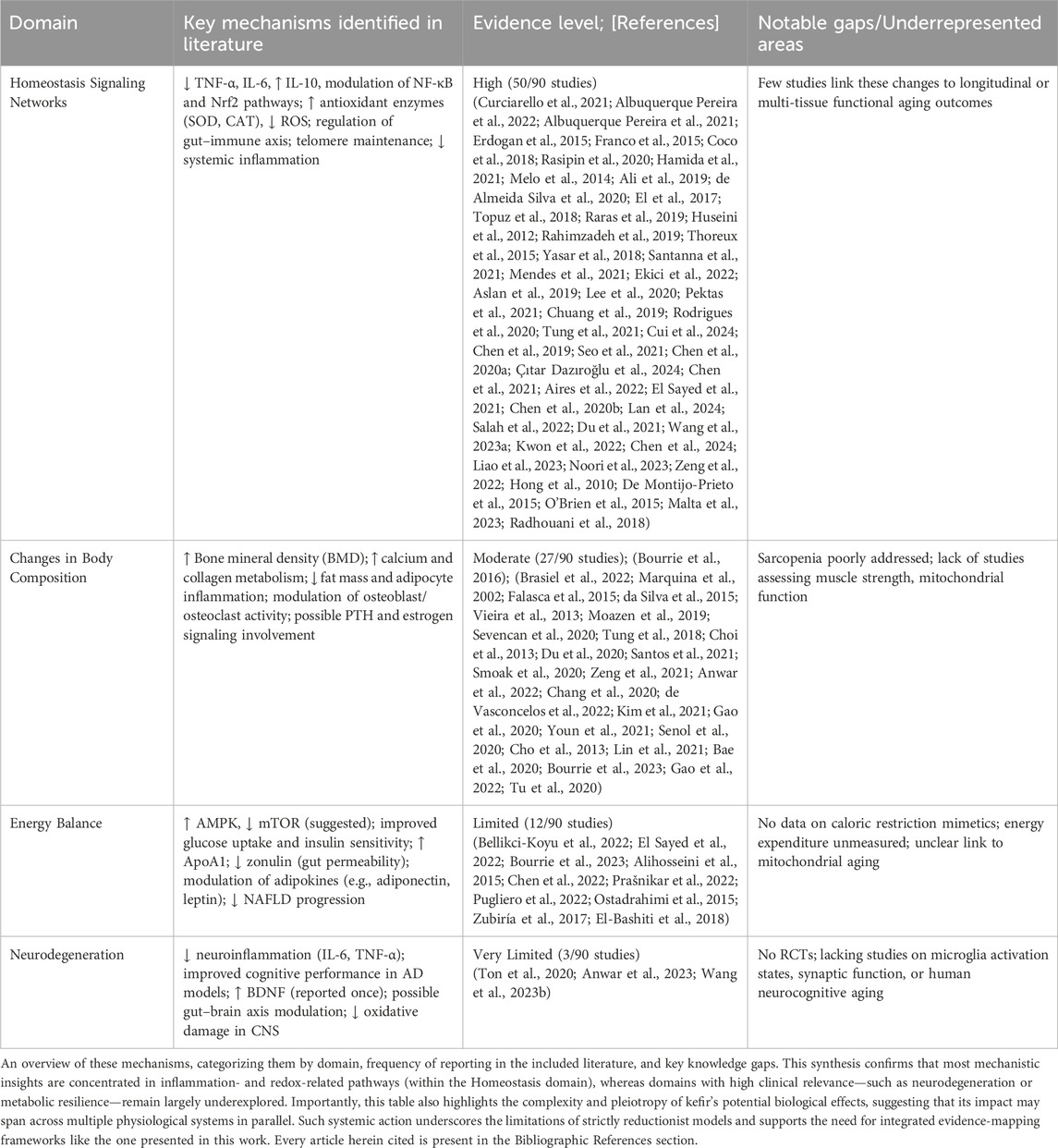
To conceptually frame the biological relevance of kefir in aging, we first present an integrative schematic (Figure 1a) illustrating its potential multisystemic effects across the four functional domains used in this review.
Figure 1. Conceptual and methodological framework of kefir-aging literature mapping. (a) Schematic of kefir’s effects across aging domains. Visual representation of the proposed multisystemic actions of kefir across four functional domains—Homeostasis Signaling Networks, Changes in Body Composition, Energy Balance, and Neurodegeneration—based on evidence extracted from the selected literature. Key pathways include modulation of inflammation (↓ IL-6, TNF-α; ↑ IL-10), redox balance (↑ SOD, CAT; ↓ ROS), metabolic signaling (↑ AMPK, insulin sensitivity; ↓ mTOR, zonulin), bone regulation (↑ BMD, osteoblast activity), and neuroprotection (↑ BDNF; gut–brain axis modulation; ↓ neuroinflammation). (b) PRISMA flow diagram. Summary of the AI-assisted literature screening process, including database retrieval, deduplication, inclusion via ASReview algorithm, and final full-text selection, resulting in 90 studies classified into the four aging domains.
The literature selection process is then summarized in the PRISMA (Page et al., 2021) flow diagram (Figure 1b), detailing database retrieval, deduplication, AI-assisted inclusion (via ASReview), and full-text evaluation steps, which resulted in 90 articles selected for thematic classification. A total of 1,184 records were retrieved from three major databases: PubMed (n = 225), ISI Web of Science (n = 417), and Scopus (n = 542). The search strings are declared in Supplementary data 1 (SD1). After deduplication, 768 unique articles remained. Five additional records were manually added. Screening was conducted using a AI-assisted algorithm “ASReview” (van de Schoot et al., 2021) (SD2), resulting in 93 records selected for inclusion, of which 90 met the criteria after full-text assessment (SD3: complete database). In addition to studies conducted in vertebrate models using traditional grain-derived kefir, this systematic review also included investigations focusing on the primary chemical constituents of kefir, as well as studies evaluating individual microbial strains commonly isolated from kefir. These strains included Candida kefyr, Kluyveromyces marxianus subsp. marxianus, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus, Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens, Lacticaseibacillus paracasei, Lactiplantibacillus plantarum, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and Saccharomyces unisporus (Prado et al., 2015).
The 90 included studies were thematically classified into four domains of aging according to the framework of Colloca et al. This classification was based on a Python-based Python-based semantic analysis pipeline that identified domain-specific keywords within abstracts and titles, as provided in Supplementary Data 4 (SD4: Python script - Jupyter Notebook version). To complement the AI-assisted screening process, the thematic mapping of the selected studies was conducted using a keyword-based semantic clustering strategy. Predefined vocabularies corresponding to the four aging domains proposed by Colloca et al. were applied to the titles and abstracts of the included articles. This rule-based semantic approach does not rely on machine learning algorithms, but provides a structured, reproducible framework to map the current literature landscape and identify thematic biases. We acknowledge that this strategy does not assess the methodological quality of the studies, nor does it replace expert-driven critical synthesis. However, it enables the identification of evidence gaps and research imbalances that merit further exploration. The distribution of articles across the four domains is illustrated in Figures 2a,b.
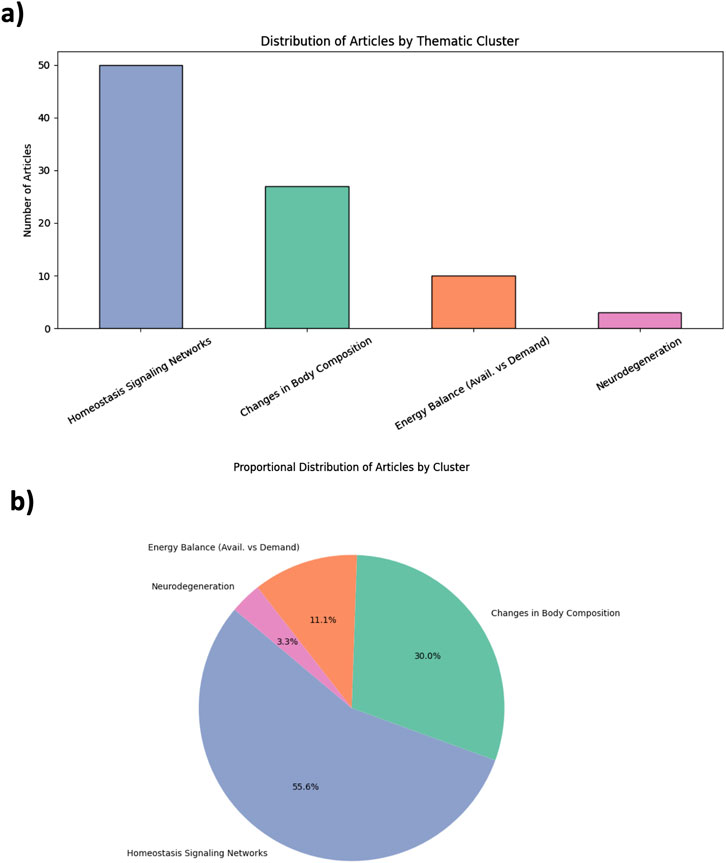
Figure 2. Thematic distribution of kefir and aging studies based on AI-guided evidence mapping. (a) Bar plot showing the number of studies mapped to each aging domain: Homeostasis Signaling Networks, Changes in Body Composition, Energy Balance, and Neurodegeneration. (b) Pie chart illustrating proportional representation across the four domains. The classification is based on semantic keyword clustering applied to abstracts. Each study was assigned to a single domain based on semantic proximity to predefined vocabularies (see Supplementary Table S2). This strategy prioritizes thematic clarity over mechanistic overlap.
A predominant share of studies clustered under the domain of Homeostasis Signaling Networks (n = 50; 55.6%), with a strong focus on inflammation, oxidative stress, and immune pathways. These studies often evaluated cytokine profiles (e.g., Interleukine 6 [IL-6], tumor necrosis factor alpha [TNF-α]), redox balance, and anti-inflammatory properties of kefir or its microbial components. Changes in Body Composition accounted for 27 studies (30%), including research on sarcopenia, bone mineral density, and muscle mass preservation. Energy Balance was explored in 12 studies (11.1%), mostly through metabolic parameters such as insulin sensitivity or lipid metabolism. Only three studies (3.3%) addressed the domain of Neurodegeneration, highlighting the major underrepresentation of neurological outcomes in kefir-related aging research. This pronounced thematic asymmetry reflects a mechanistic bias, favoring inflammation-related molecular pathways while overlooking integrative physiological and cognitive domains. The complete list of included articles, along with titles, keywords, and cluster assignments, is provided as Supplementary Table S2 (ST1), while the vocabulary for classification is defined in the same supplementary file as (ST2).
Discussion
Thematic clustering of 90 studies, spanning publications from 1993 to early 2025, revealed a sensible imbalance in the literature exploring kefir’s relationship with aging. Over half of the studies were concentrated in the domain of homeostasis signaling networks, focusing predominantly on inflammation, oxidative stress, and immune modulation. These are indeed central pathways in aging biology (López-Otín et al., 2013; Franceschi and Campisi, 2014), but their overrepresentation likely reflects a mechanistic bias in the current research paradigm. While molecular mechanisms are important, the relative under representation of domains such as energy balance (11.1%) and neurodegeneration (3.3%) indicates a structural limitation in scope. Notably, domains with direct clinical implications—such as cognitive decline or metabolic flexibility—remain underexplored, despite growing evidence of kefir’s potential to influence gut–brain signaling and metabolic regulation (Cryan et al., 2019; Bourrie et al., 2016; Farnworth, 2005). Neurodegeneration was the least represented domain. This likely reflects both the difficulty in modeling cognitive aging and the underuse of neuroimaging or validated biomarkers in kefir research. Moreover, most studies in this domain were either preclinical or observational, limiting causal inference and clinical applicability.
We propose that future studies integrate longitudinal designs, assess neurocognitive endpoints, and explore inter-domain interactions—such as those between inflammation and sarcopenia, or along the gut–brain and gut–metabolism axes—which may mediate kefir’s multisystemic effects.
Moreover, efforts should be made to standardize kefir preparations, as variations between traditional and industrial formulations may confound biological outcomes (Bourrie et al., 2023).
This Perspective does not aim to provide final answers, but rather to offer a map—constructed with AI support—that reveals where the literature is concentrated and, more importantly, where it remains silent.
To better contextualize this thematic asymmetry, we summarized the domain-specific mechanistic pathways emerging from the included studies in Table 1. This overview highlights both well-characterized molecular actions—especially in the domain of homeostasis—and the relative scarcity of mechanistic insights in domains like energy regulation and neurodegeneration.
Our evidence mapping of kefir and aging literature reveals a pronounced thematic concentration on homeostasis-related signaling, to the detriment of domains like neurodegeneration and energy regulation. By applying a structured clustering model based on the aging domains proposed by Colloca et al. , we highlight the need for a broader and more clinically integrative research agenda. This includes not only exploring kefir’s molecular properties, but also assessing its translational relevance across multiple aging systems.
The approach presented here demonstrates how AI and semantic clustering can support literature synthesis and strategic research planning, offering a reproducible framework to identify gaps and reorient scientific focus in emerging health domains. The herein applied integrative pipeline, indeed, combining AI-assisted screening and semantic clustering, represents a transferable strategy that could be adapted to other functional foods or emerging research domains, maximizing discovery and guiding translational innovation. Finally, we acknowledge that the AI-assisted screening process, while efficient and reproducible, may still be susceptible to latent biases inherent in the literature, including publication bias and preferential keyword usage. These limitations reinforce the importance of expert validation and transparent classification criteria in thematic mapping studies.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
FC: Software, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Validation, Supervision, Writing – review and editing, Resources, Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Visualization, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Methodology.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. English pro-freading and python assisted scripting.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fragi.2025.1628474/full#supplementary-material
References
Ahmed, Z., Wang, Y., Ahmad, A., Khan, S. T., Nisa, M., Ahmad, H., et al. (2021). Biological role of kefir in intestinal health and immunomodulation. Front. Nutr. 8, 709752. doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.709752
Aires, R., Gobbi Amorim, F., Côco, L. Z., da Conceição, A. P., Zanardo, T. É. C., Taufner, G. H., et al. (2022). Use of kefir peptide (Kef-1) as an emerging approach for the treatment of oxidative stress and inflammation in 2K1C mice. Food Funct. 13 (2), 1965–1974. doi:10.1039/D1FO01798E
Albuquerque Pereira, M. F., Morais de Ávila, L. G., Dos Santos Cruz, B. C., Campos, S. B., Licursi de Oliveira, L., Vilela Gonçalves, R., et al. (2021). The role of IL-10 in regulating inflammation and gut microbiome in mice consuming milk kefir and orally challenged with S. typhimurium. Front. Immunol. 12, 703. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.650548
Albuquerque Pereira, M. F., Morais de Ávila, L. G., Dos Santos Cruz, B. C., Almeida, L. F., Macedo Simões, J., Campos Silva, B., et al. (2022). Daily intake of household-produced milk kefir on Salmonella typhimurium infection in C57BL/6 mice: mortality, microbiota modulation, and immunological implications. Food Res. Int. 159, 111648. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111648
Ali, O. S. M., Amin, N. E., Abdel Fattah, S. M., and Abd, E.-R. O. (2019). Ameliorative effect of kefir against γ-irradiation-induced liver injury in Male rats: impact on oxidative stress and inflammation. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 38 (4), 457–467. doi:10.1177/0960327118782454
Alihosseini, N., Moahboob, S. A., Farrin, N., Mobasseri, M., Taghizadeh, A., and Ostadrahimi, A. R. (2015). Effect of probiotic fermented milk (kefir) on serum level of insulin and homocysteine in type 2 diabetes patients. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 85 (3-4), 156–162. doi:10.1024/0300-9831/a000235
Anwar, M. M., Boseila, A. A., Mabrouk, A. A., Abdelkhalek, A. A., and Amin, A. (2022). Impact of lyophilized milk kefir-based self-nanoemulsifying system on cognitive enhancement via the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Nutr. Neurosci. 25 (10), 1986–1998. doi:10.1080/1028415X.2021.1957857
Anwar, M. M., Ali, O. S. M., Ahmed, R. L., Badawi, A. M., and Eltablawy, N. A. (2023). The effect of using kefir grains and mesenchymal stem cells in LPS-induced alzheimer's disease neuroinflammatory model. J. Appl. Biomed. 21 (3), 116–125. doi:10.32725/jab.2023.011
Aslan, E., Sadi, G., Guzel, H., Karaca, C., Korkmaz, O. A., Pektas, M. K., et al. (2019). Kefir prevents adipose tissue growth through the induction of apoptotic elements in high-fructose corn syrup-fed rats. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 8345157. doi:10.1155/2019/8345157
Bae, D., Kim, D. H., Chon, J. W., Song, K. Y., and Seo, K. H. (2020). Synergistic effects of the early administration of Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens DN1 and Kluyveromyces marxianus KU140723-05 on the inhibition of salmonella enteritidis colonization in young chickens. Poult. Sci. 99 (10), 5999–6006. doi:10.1016/j.psj.2020.07.032
Bellikci-Koyu, E., Sarer-Yurekli, B. P., Karagozlu, C., Aydin-Kose, F., Gokhan Ozgen, A., and Buyuktuncer, Z. (2022). Probiotic kefir consumption improves serum apolipoprotein A1 levels in metabolic syndrome patients: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Nutr. Res. 102, 59–70. doi:10.1016/j.nutres.2022.02.006
Bourrie, B. T., Willing, B. P., and Cotter, P. D. (2016). The microbiota and health-promoting characteristics of the fermented beverage kefir. Front. Microbiol. 7, 647. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2016.00647
Bourrie, B. C. T., Forgie, A. J., Makarowski, A., Cotter, P. D., Richard, C., and Willing, B. P. (2023). Consumption of kefir made with traditional microorganisms resulted in greater improvements in LDL cholesterol and plasma markers of inflammation in males when compared to a commercial kefir: a randomized pilot study. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 48 (9), 668–677. doi:10.1139/apnm-2022-0463
Brasiel, P. G. A., Luquetti, SCPD, Medeiros, J. D., Corrêa, J. O. A., Machado, A. B. F., Moreira, A. P. B., et al. (2022). Kefir modulates gut microbiota and reduces DMH-Associated colorectal cancer via regulation of intestinal inflammation in adulthood offsprings programmed by neonatal overfeeding. Food Res. Int. 152, 110708. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110708
Burge, R., Dawson-Hughes, B., Solomon, D. H., Wong, J. B., King, A., and Tosteson, A. (2007). Incidence and economic burden of osteoporosis-related fractures in the United States, 2005–2025. J. Bone Min. Res. 22 (3), 465–475. doi:10.1359/jbmr.061113
Chang, G. R., Cheng, W. Y., Fan, H. C., Chen, H. L., Lan, Y. W., Chen, M. S., et al. (2020). Structural insights into the mechanism of a nanobody that stabilizes PAI-1 and modulates its activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21 (16), 5859. doi:10.3390/ijms21165859
Chen, H. L., Hung, K. F., Yen, C. C., Laio, C. H., Wang, J. L., Lan, Y. W., et al. (2019). Kefir peptides alleviate particulate matter <4 μm (PM4.0)-induced pulmonary inflammation by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway using luciferase transgenic mice. Sci. Rep. 9, 11529. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-47872-4
Chen, M. Y., Wu, H. T., Chen, F. F., Wang, Y. T., Chou, D. L., Wang, G. H., et al. (2020a). Characterization of Tibetan kefir grain-fermented milk whey and its suppression of melanin synthesis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 68 (36), 9792–9800. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.0c06346
Chen, Y. H., Chen, H. L., Fan, H. C., Tung, Y. T., Kuo, C. W., Tu, M. Y., et al. (2020b). Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antifibrotic effects of kefir peptides on salt-induced renal vascular damage and dysfunction in aged stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Antioxidants (Basel) 9 (9), 790. doi:10.3390/antiox9090790
Chen, C. F., Li, H. P., Chao, Y. H., Tu, M. Y., Yen, C. C., Lan, Y. W., et al. (2021). Suppression of dendritic cell maturation by kefir peptides alleviates collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 721594. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.721594
Chen, H. L., Tsai, T. C., Tsai, Y. C., Liao, J. W., Yen, C. C., and Chen, C. M. (2022). Alcohol, drinking pattern, and chronic disease. Nutrients 14 (9), 1954. doi:10.3390/nu14091954
Chen, W., Wang, J., Du, L., Chen, J., Zheng, Q., Li, P., et al. (2024). Kefir microbiota and metabolites stimulate intestinal mucosal immunity and its early development. Microbiol. Spectr. 12 (1), e02456–23. doi:10.1128/spectrum.02456-23
Cho, J. H., Zhang, Z. F., and Kim, I. H. (2013). Effects of single or combined dietary supplementation of β-glucan and kefir on growth performance, blood characteristics and meat quality in broilers. Livest. Sci. 152 (2-3), 216–221. doi:10.1080/00071668.2013.777691
Choi, J. W., Kang, H. W., Lim, W. C., Kim, M. K., Lee, I. Y., and Cho, H. Y. (2013). Kefir prevented excess fat accumulation in diet-induced obese mice. J. Med. Food 16 (3), 147–154. doi:10.1089/jmf.2011.0208
Chuang, K. C., Lai, Y. W., Ko, C. H., Yen, C. C., Chen, H. L., Lan, Y. W., et al. (2019). Therapeutic effects of kefir peptides on adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats through anti-inflammation and downregulation of matrix metalloproteinases. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 63 (21), e1900606. doi:10.1002/mnfr.201900606
Çıtar Dazıroğlu, M. E., Tek, N. A., Akdulum, M. F. C., Yılmaz, C., Yalınay, A. M., Kıran, G., et al. (2024). Effects of kefir consumption on gut microbiota and health outcomes in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Nutrients 16 (7), 1345. doi:10.3390/nu16071345
Coco, L. Z., Aires, R., Carvalho, G. R., Belisário, E. D., Yap, M. K. K., Amorim, F. G., et al. (2018). Unravelling the gastroprotective potential of kefir: exploring antioxidant effects in preventing gastric ulcers. Phytother. Res. 32 (10), 1982–1990. doi:10.1002/ptr.6131
Collins, F. L., Irwin, R., Bierhalter, H., Schepper, J., Britton, R. A., Parameswaran, N., et al. (2016). Lactobacillus reuteri 6475 increases bone density in intact females only under an inflammatory setting. PLoS One 11 (4), e0153180. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0153180
Colloca, G., Di Capua, B., Bellieni, A., Fusco, D., Ciciarello, F., Tagliaferri, L., et al. (2020). Biological and functional biomarkers of aging: definition, characteristics, and how they can impact everyday cancer treatment. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 22 (11), 115. doi:10.1007/s11912-020-00977-w
Cruz-Jentoft, A. J., Bahat, G., Bauer, J., Boirie, Y., Bruyère, O., Cederholm, T., et al. (2019). Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 48 (1), 16–31. doi:10.1093/ageing/afy169
Cryan, J. F., O'Riordan, K. J., Cowan, C. S. M., Sandhu, K. V., Bastiaanssen, T. F. S., Boehme, M., et al. (2019). The microbiota–gut–brain axis. Physiol. Rev. 99 (4), 1877–2013. doi:10.1152/physrev.00018.2018
Cui, Y. Y., Jing, C., Yue, Y., Ning, M. G., Chen, H., Yuan, Y. H., et al. (2024). Kefir ameliorates alcohol-induced liver injury through modulating gut microbiota and fecal bile acid profile in mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 68 (3), e2300301. doi:10.1002/mnfr.202300301
Curciarello, R., Canziani, K. E., Salto, I., Barbiera Romero, E., Rocca, A., Doldan, I., et al. (2021). Probiotic lactobacilli isolated from Kefir promote down-regulation of inflammatory Lamina propria T cells from patients with active IBD. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 658026. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.658026
da Silva, K. N., Fávero, A. G., Ribeiro, W., Ferreira, C. M., Sartorelli, P., Cardili, L., et al. (2015). Effects of kefir fermented milk beverage on sodium dextran sulfate (DSS)-induced colitis in rats. Food Funct. 6 (5), 1710–1717. doi:10.1039/C5FO00217D
de Almeida Silva, M., Mowry, F. E., Peaden, S. C., Andrade, T. U., and Biancardi, V. C. (2020). Kefir ameliorates hypertension via gut-brain mechanisms in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 64 (10), e2000209. doi:10.1002/mnfr.202000209
De Montijo-Prieto, S., Moreno, E., Bergillos-Meca, T., Lasserrot, A., Ruiz-López, M. D., Ruiz-Bravo, A., et al. (2015). A Lactobacillus plantarum strain isolated from kefir protects against intestinal infection with Yersinia enterocolitica O9 and modulates immunity in mice. J. Dairy Sci. 98 (10), 6301–6312. doi:10.3168/jds.2015-9420
de Vasconcelos, R. F., Costa, V., Araujo, B., Maia, T. A. C., Dias, R., Vasconcelos, L., et al. (2022). Predictive glycaemic response of pasta enriched with juice, puree, and pomace from red cabbage and spinach. Nutrients 14 (21), 4575. doi:10.3390/nu14214575
Du, G. A., Guo, Q., Yan, X. H., Chen, H., Yuan, Y. H., and Yue, T. L. (2020). Role of autophagy in alcohol and drug-induced liver injury. Food Chem. Toxicol. 136, 111075. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2019.111075
Du, G., Chang, S., Guo, Q., Yan, X., Chen, H., Shi, K., et al. (2021). Shining a light on Colibactin biology. Toxins 13 (5), 346. doi:10.3390/toxins13050346
Ekici, Ö., Aslan, E., Aladağ, T., Güzel, H., Korkmaz, Ö. A., Bostancı, A., et al. (2022). Masseter muscle and gingival tissue inflammatory response following treatment with high-fructose corn syrup in rats: anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of kefir. J. Food Biochem. 46 (3), e13732. doi:10.1111/jfbc.13732
El, G.-B. E., Timoumi, R., Annaibi, E., Mokni, M., Omezzine, A., Bacha, H., et al. (2017). Protective effects of kefir against deltamethrin-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 55, 9–16. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2017.01.005
El Sayed, N. S., Kandil, E. A., and Ghoneum, M. H. (2021). Probiotics fermentation technology, a novel kefir product, ameliorates cognitive impairment in streptozotocin-induced sporadic alzheimer’s disease in mice. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 5525306. doi:10.1155/2021/5525306
El Sayed, N. S., Kandil, E. A., and Ghoneum, M. H. (2022). Enhancement of insulin/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and modulation of gut microbiome by probiotics fermentation technology, a kefir grain product, in sporadic alzheimer's disease model in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 147, 112660. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112660
El-Bashiti, T. A., Zabut, B. M., and Abu Safia, F. F. (2018). Effect of probiotic fermented milk (Kefir) on some blood biochemical parameters among newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic adult males in Gaza governorate. J. Al Azhar Univ. Gaza Nat. Sci. 20 (2), 21–38. doi:10.12944/CRNFSJ.7.2.25
Erdogan, F. S., Ozarslan, S., Guzel-Seydim, Z. B., and Kok Tas, T. (2015). The effect of kefir produced from natural kefir grains on the intestinal microbial populations and antioxidant capacities of BALB/c mice. J. Dairy Sci. 98 (3), 1457–1465. doi:10.3168/jds.2014-8111
Falasca, K., Vecchiet, J., Ucciferri, C., Di Nicola, M., D'Angelo, C., and Reale, M. (2015). Effect of probiotic supplement on cytokine levels in HIV-infected individuals: a preliminary study. Nutrients 7 (4), 8335–8347. doi:10.3390/nu7105396
Farnworth, E. R. (2005). Kefir – a complex probiotic. Food Sci. Technol. Bull. Funct. Foods 2 (1), 1–17. doi:10.1616/1476-2137.13938
Franceschi, C., and Campisi, J. (2014). Chronic inflammation (inflammaging) and its potential contribution to age-associated diseases. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 69 (Suppl. 1), S4–S9. doi:10.1093/gerona/glu057
Franco, M. C., Golowczyc, M. A., De Antoni, G. L., Pérez, P. F., Humen, M., and Serradell, M. L. A. (2015). Administration of kefir-fermented milk protects mice against Giardia intestinalis infection. J. Nutr. 145 (11), 2194–2200. doi:10.3945/jn.115.219550
Fulop, T., Larbi, A., Dupuis, G., Pawelec, G., Cohen, A. A., Khalil, A., et al. (2018). Immunosenescence and inflamm-aging: two sides of the same coin: friends or foes? Front. Immunol. 8, 1960. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2017.01960
Gao, X., Wang, F., Zhao, P., Zhang, R., and Zeng, Q. (2020). Effect of heat-killed Streptococcus thermophilus on type 2 diabetes rats. J. Dairy Sci. 103 (10), 8754–8763. doi:10.3168/jds.2020-18324
Gao, J., Ding, G., Li, Q., Gong, L., Huang, J., and Sang, Y. (2022). Tibet kefir milk decreases fat deposition by regulating the gut microbiota and gene expression of lpl and Angptl4 in high fat diet-fed rats. J. Dairy Sci. 105 (10), 8026–8037. doi:10.3168/jds.2022-21732
Hamida, R. S., Shami, A., Ali, M. A., Almohawes, Z. N., Mohammed, A. E., Bin-Meferij, M. M., et al. (2021). Kefir: a protective dietary supplementation against viral infection. J. Food Biochem. 45 (8), e13757. doi:10.1111/jfbc.13757
Heneka, M. T., Carson, M. J., El Khoury, J., Landreth, G. E., Brosseron, F., Feinstein, D. L., et al. (2015). Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 14 (4), 388–405. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(15)70016-5
Hong, W. S., Chen, Y. P., Dai, T. Y., Huang, I. N., and Chen, M. J. (2010). Effect of heat-inactivated kefir-isolated Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens M1 on preventing an allergic airway response in mice. J. Sci. Food Agric. 90 (12), 2088–2094. doi:10.1002/jsfa.4042
Huseini, H. F., Rahimzadeh, G., Fazeli, M. R., Mehrazma, M., and Salehi, M. (2012). Evaluation of wound healing activities of kefir products. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 19 (2), 626–634. doi:10.1016/j.burns.2011.12.005
Iraporda, C., Romanin, D. E., Rumbo, M., Garrote, G. L., and Abraham, A. G. (2014). The role of lactate on the immunomodulatory properties of the nonbacterial fraction of kefir. Food Res. Int. 62, 247–253. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2014.03.003
Kairey, L., Leech, B., El-Assaad, F., Bugarcic, A., Dawson, D., and Lauche, R. (2022). The effects of kefir consumption on human health: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Rev. 80 (8), 267–286. doi:10.1093/nutrit/nuac054
Kim, E., Lee, H. G., Han, S., Seo, K. H., Kim, H., Thiel, A., et al. (2021). Identification of sarcopenic obesity in German nursing home residents-the role of body composition and malnutrition in the BaSAlt cohort-study. Nutrients 13 (11), 3791. doi:10.3390/nu13113791
Kwon, O. K., Ahn, K. S., Lee, M. Y., Kim, S. Y., Park, B. Y., Kim, M. K., et al. (2022). Inhibitory effect of kefiran on ovalbumin-induced lung inflammation in a murine model of asthma. J. Agric. Food Chem. 70 (24), 7451–7459. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.2c02147
Lan, Y. W., Chen, Y. C., Yen, C. C., Chen, H. L., Tung, M. C., Fan, H. C., et al. (2024). Kefir peptides mitigate bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice through modulating oxidative stress, inflammation and gut microbiota. Food Chem. Toxicol. 168, 114151. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2024.114151
Lee, M. Y., Ahn, K. S., Kwon, O. K., Kim, M. J., Kim, M. K., Lee, I. Y., et al. (2020). Anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic effects of kefir in a mouse asthma model. J. Med. Food 23 (5), 485–493. doi:10.1089/jmf.2019.0229
Li, J. Y., Chassaing, B., Tyagi, A. M., Vaccaro, C., Luo, T., Adams, J., et al. (2016). Sex steroid deficiency-associated bone loss is microbiota dependent and prevented by probiotics. J. Clin. Invest 126 (6), 2049–2063. doi:10.1172/JCI86062
Liao, C. H., Yen, C. C., Chen, H. L., Liu, Y. H., Chen, Y. H., Lan, Y. W., et al. (2023). Novel kefir exopolysaccharides (KEPS) mitigate lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced systemic inflammation in luciferase transgenic mice through inhibition of the NF-κB pathway. Food Funct. 14 (5), 3042–3052. doi:10.1039/D2FO03750J
Lin, Y. C., Chen, Y. T., Li, K. Y., and Chen, M. J. (2021). Investigating the mechanistic differences of obesity-inducing Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens M1 and anti-obesity Lactobacillus Mali APS1 by microbolomics and metabolomics. Food Funct. 12 (18), 8325–8338. doi:10.1039/D1FO01091H
López-Otín, C., Blasco, M. A., Partridge, L., Serrano, M., and Kroemer, G. (2013). The hallmarks of aging. Cell 153 (6), 1194–1217. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.039
Malta, S. M., Batista, L. L., Guerra Silva, H. C., Franco, R. R., Silva, M. H., Rodrigues, T. S., et al. (2023). Identification of bioactive peptides from a Brazilian kefir sample, and their anti-alzheimer potential in Drosophila melanogaster. Food Funct. 14 (10), 4794–4807. doi:10.1039/D2FO03267C
Marquina, D., Santos, A., Corpas, I., Muñoz, J., Zazo, J., and Peinado, J. M. (2002). Dietary influence of kefir on microbial activities in the mouse bowel. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 35 (2), 136–140. doi:10.1046/j.1472-765X.2002.01155.x
Marsh, A. J., O’Sullivan, O., Hill, C., Ross, R. P., and Cotter, P. D. (2013). Sequencing-based analysis of the bacterial and fungal composition of kefir grains and milks from multiple sources. PLoS One 8 (7), e69371. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0069371
Melo, A. F. D., Mendonça, M. C. P., and Rosa-Castro, R. D. (2014). The protective effects of fermented kefir milk on azoxymethane-induced aberrant crypt formation in mice colon. Nutrition 30 (2), 169–176. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2013.05.017
Mendes, E., Casaro, M. B., Fukumori, C., Ribeiro, W. R., Dos Santos, A. L., Sartorelli, P., et al. (2021). Preventive oral kefir supplementation protects mice from ovariectomy-induced exacerbated allergic airway inflammation. Benef. Microbes 12 (2), 187–197. doi:10.3920/BM2020.0112
Moazen, M., Mazloom, Z., Tanideh, N., Dabbaghmanesh, M. H., Rahmdel, S., Azarpira, N., et al. (2019). Osteoprotective effects of kefir fortified with omega-3 and vitamin C in ovariectomized rats. Phytother. Res. 33 (3), 678–686. doi:10.1002/ptr.6260
Noori, M., Shateri, Z., Babajafari, S., Eskandari, M. H., Parastouei, K., Ghasemi, M., et al. (2023). The effect of probiotic-fortified kefir on depression, appetite, oxidative stress, and inflammatory parameters in Iranian overweight and obese elderly: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Nutr. Neurosci. 26 (8), 1059–1069. doi:10.1080/1028415X.2022.2032956
O'Brien, K. V., Stewart, L. K., Forney, L. A., Aryana, K. J., Prinyawiwatkul, W., and Boeneke, C. A. (2015). The effects of postexercise consumption of a kefir beverage on performance and recovery during intensive endurance training. J. Dairy Sci. 98 (12), 7446–7449. doi:10.3168/jds.2015-9392
Ostadrahimi, A., Taghizadeh, A., Mobasseri, M., Farrin, N., Payahoo, L., Gheshlaghi, Z. B., et al. (2015). Effect of probiotic fermented milk (kefir) on glycemic control and lipid profile in type 2 diabetic patients: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. Iran. J. Public Health 44 (2), 228–237.
Ouchi, N., Parker, J. L., Lugus, J. J., and Walsh, K. (2011). Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 11, 85–97. doi:10.1038/nri2921
Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., et al. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 372, n71. doi:10.1136/bmj.n71
Pektas, M. B., Aslan, E., Guzel, H., Korkmaz, O. A., Celegen, K., Pektas, A., et al. (2021). Kefir protects the liver against high fructose corn syrup–induced phosphodiesterase hyperactivity. Food Funct. 12 (14), 6207–6216. doi:10.1039/d1fo00622j
Prado, M. R., Blandón, L. M., Vandenberghe, L. P., Rodrigues, C., Castro, G. R., Thomaz-Soccol, V., et al. (2015). Milk kefir: composition, microbial cultures, biological activities, and related products. Front. Microbiol. 6, 1177. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2015.01177
Prašnikar, Z. J., Kenig, S., Vardjan, T., Bizjak, M., and Petelin, A. (2022). Effects of kefir or milk supplementation on zonulin in overweight subjects. Eur. J. Nutr. 61 (7), 3457–3467. doi:10.1007/s00394-022-02834-z
Praznikar, Z. J., Kenig, S., Vardjan, T., Bizjak, M. Č., and Petelin, A. (2020). Effects of kefir or milk supplementation on zonulin in overweight subjects. J. Dairy Sci. 103 (5), 3961–3970. doi:10.3168/jds.2019-17696
Pugliero, S., Lima, D. Y., Rodrigues, A. M., Bogsan, C. S. B., Rogero, M. M., Punaro, G. R., et al. (2022). Kefir reduces nitrosative stress and upregulates Nrf2 in the kidney of diabetic rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 108, 109064. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2022.109064
Radhouani, H., Gonçalves, C., Maia, F. R., Oliveira, J. M., and Reis, R. L. (2018). Biological performance of a promising kefiran-biopolymer with potential in regenerative medicine applications: a comparative study with hyaluronic acid. J. Biomed. Mater Res. B Appl. Biomater. 106 (4), 1618–1627. doi:10.1002/jbm.b.33973
Rahimzadeh, G., Fazeli, M. R., Mozafari, N. A., and Mesbahi, M. (2019). Evaluation of anti-microbial activity and wound healing of kefir. Arch. Iran. Med. 22 (10), 582–588.
Raras, T. Y. M., Hidayati, N., and Wardhani, S. O. (2019). High doses of kefir accelerate lung-injury progression in bleomycin-induced pneumonitis in rats. Respir. Toxicol. 68, 22–28. doi:10.1016/j.resp.2019.05.004
Rasipin, E., Dharmana, E., and Hadisaputro, S. (2020). Suhartono. The effects of kefir on the inflammatory status and thyroid function (experimental study on wistar rats after exposure to chlorpyrifos). Indones. J. Pharm. 31 (3), 137–144. doi:10.22146/ijp.53025
Ribeiro, L. F., da Silva, T. A., Osório, F. L., Freinko, R. M., Brito, M. J., Magalhães, R., et al. (2018). Kefir prevents anxiety-like behavior in rats under stress. J. Med. Food. 21 (6), 599–605. doi:10.1089/jmf.2017.4167
Rodrigues, K. L., Carvalho, J. C. T., and Schneedorf, J. M. (2020). Anti-inflammatory properties of kefir and its polysaccharide extract. J. Med. Food 23 (2), 218–227. doi:10.1089/jmf.2019.0189
Rosa, D. D., Dias, M. M. S., Grześkowiak, L. M., Reis, S. A., Conceição, L. L., and Peluzio, MDCG (2020). Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of kefir in aging: findings from preclinical studies. Nutr. Res. Rev. 33 (1), 1–10. doi:10.1017/S0954422419000201
Salah, N., Eissa, S., Mansour, A., El Magd, N. M. A., Hasanin, A. H., El Mahdy, M. M., et al. (2022). Evaluation of the role of kefir in management of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis rat model via modulation of NASH-linked mRNA-miRNA panel. Food Funct. 13 (6), 236–2899. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-27353-x
Santanna, A. F., Filete, P. F., Lima, E. M., Porto, M. L., Meyrelles, S. S., Vasquez, E. C., et al. (2021). Gum Arabic in renal disease (GARDS study): clinical evidence of dietary supplementation impact on progression of renal dysfunction. J. Funct. Foods. 82, 104515. doi:10.1016/j.jff.2021.104515
Santos, F. R. D., Ribeiro, G. H. M., Monteiro-Junior, R. S., Barcala-Jorge, A. S., Guimarães, A. L. S., de Paula, A. M. B., et al. (2021). High-intensity ultrasound-assisted recovery of anthocyanins from jabuticaba by-products using green solvents: effects of ultrasound intensity and solvent composition on the extraction of phenolic compounds. Food Res. Int. 140, 110048. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2020.110048
Senol, A., Isler, M., Sutcu, R., Akin, M., Cakir, E., Ceyhan, B. M., et al. (2020). Kefir treatment ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in rats. J. Med. Food 23 (2), 134–141. doi:10.1089/jmf.2019.4535
Seo, M. K., Park, E. J., Ko, S. Y., Choi, E. W., and Kim, S. (2021). Therapeutic effects of kefir grain lactobacillus-derived extracellular vesicles in mice with TNBS-induced inflammatory bowel disease. J. Dairy Sci. 104 (12), 13421–13430. doi:10.3168/jds.2021-20787
Sevencan, N. O., Isler, M., Kapucuoglu, F. N., Senol, A., Kayhan, B., Kiztanir, S., et al. (2020). Antimicrobial activity and biofilm inhibition of riparins I, II and III and ultrastructural changes in multidrug-resistant bacteria of medical importance. Microb. Pathog. 149, 104529. doi:10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104529
Sharon, G., Sampson, T. R., Geschwind, D. H., and Mazmanian, S. K. (2016). The central nervous system and the gut microbiome. Cell 167 (4), 915–932. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2016.10.027
Smoak, P., Harman, N., Flores, V., Kisiolek, J., Pullen, N. A., Lisano, J., et al. (2020). Kefir is a viable exercise recovery beverage for cancer survivors enrolled in a structured exercise program. Integr. Cancer Ther. 19, 1534735420918934. doi:10.1177/1534735420918934
Thoreux, K., Schmucker, D. L., Fimland, M. S., Mosti, M. P., and Wang, E. (2015). Strength training-induced responses in older adults: attenuation of descending neural drive with age. Age (Dordr). 37 (3), 9784. doi:10.1007/s11357-015-9784-y
Ton, A. M. M., Campagnaro, B. P., Alves, G. A., Aires, R., Côco, L. Z., Arpini, C. M., et al. (2020). Oxidative stress and dementia in alzheimer’s patients: effects of synbiotic supplementation. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2638703–2638714. doi:10.1155/2020/2638703
Topuz, E., Derin, D., Can, G., Kürklü, E., Cinar, S., Aykan, F., et al. (2018). Effect of oral administration of kefir on serum proinflammatory cytokines in 5-FU–induced oral mucositis in patients with colorectal cancer. Support Care Cancer 26 (10), 3467–3474. doi:10.1007/s00520-018-4225-5
Tu, M. Y., Chen, H. L., Tung, Y. T., Kao, C. C., Hu, F. C., Chen, C. M., et al. (2020). Protective effects of (E)-β-Caryophyllene (BCP) in chronic inflammation. Nutrients 12 (11), 3273. doi:10.3390/nu12113273
Tung, Y. T., Chen, H. L., Wu, H. S., Ho, M. H., Chong, K. Y., and Chen, C. M. (2018). Kefir peptides prevent hyperlipidemia and obesity in high-fat-diet-induced obese rats via modulation of lipid metabolism. Sci. Rep. 8, 3935. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-22238-0
Tung, M. C., Lan, Y. W., Li, H. H., Chen, H. L., Chen, S. Y., Chen, Y. H., et al. (2021). Kefir peptides alleviate high-fat diet–induced atherosclerosis by attenuating macrophage accumulation and oxidative stress in ApoE-knockout mice. Front. Immunol. 12, 687129. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.687129
van de Schoot, R., de Bruin, J., Schram, R., Zahedi, P., de Boer, J., Weijdema, F., et al. (2021). ASReview: open source software for efficient and transparent active learning for systematic reviews. Nat. Mach. Intell. 3 (2), 125–133. doi:10.1038/s42256-020-00287-7
Vieira, L. V., de Sousa, L. M., Maia, T. A. C., Gusmão, JNFM, Goes, P., Pereira, K. M. A., et al. (2013). Milk kefir therapy reduces inflammation and alveolar bone loss in a rat model of periodontitis. J. Periodontol. 84 (10), 1427–1436. doi:10.1902/jop.2013.130174
Vinderola, G. (2019). Probiotic and immunomodulatory properties of kefir: a review. J. Dairy Sci. 102 (4), 3721–3735. doi:10.3168/jds.2018-15015
Wang, S. Y., Huang, R. F., Ng, K. S., Chen, Y. P., Shiu, J. S., and Chen, M. J. (2023a). Cross-linked alginate edible coatings incorporated with hexyl acetate: film characteristics and its application on fresh-cut rose apple. Food Biosci. 52, 102410. doi:10.1016/j.fbio.2023.102410
Wang, Y., Wang, D., Lv, H., Dong, Q., Li, J., Geng, W., et al. (2023b). Modulation of the gut microbiota and glycometabolism by a probiotic to alleviate amyloid accumulation and cognitive impairments in AD rats. Food Funct. 14 (10), 5009–5023. doi:10.1039/D3FO00590C
Yasar, M., Taskin, A. K., Kaya, B., Aydin, M., Ozaydin, I., Iskender, A., et al. (2018). The early anti-inflammatory effect of kefir in experimental corrosive esophagitis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 818, 407–414. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.11.030
Youn, H. Y., Kim, H. J., Kim, H., and Seo, K. H. (2021). A comparative evaluation of the kefir yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus A4 and sulfasalazine in ulcerative colitis: anti-inflammatory impact and gut microbiota modulation. Microb. Pathog. 159, 105118. doi:10.1016/j.micpath.2021.105118
Zeng, X., Jia, H., Zhang, X., Wang, X., Wang, Z., Gao, Z., et al. (2021). Supplementation of kefir ameliorates azoxymethane/dextran sulfate sodium-induced colorectal cancer by modulating the gut microbiota. Food Funct. 12 (18), 11641–11655. doi:10.1039/d1fo01729b
Zeng, X., Li, J., Wang, X., Liu, L., Shen, S., Li, N., et al. (2022). Regulation of gut microbiota and microbial metabolome of kefir supernatant against Fusobacterium nucleatum and DSS-co-induced colitis. Front. Microbiol. 13, 847551. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2022.847551
Keywords: kefir, probiotcs, aging, systematic evidence mapping, microbiota, gut-brain axes, multisystem health effects, systematic review
Citation: Chiani F (2025) Kefir and healthy aging: revealing thematic gaps through AI-assisted screening and semantic evidence mapping. Front. Aging 6:1628474. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2025.1628474
Received: 14 May 2025; Accepted: 19 September 2025;
Published: 02 October 2025.
Edited by:
Filipe Cabreiro, University of Cologne, GermanyReviewed by:
Kamran Hosseini, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, IranAnkit Aryal, Louisiana State University, United States
Copyright © 2025 Chiani. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Francesco Chiani, ZnJhbmNlc2NvLmNoaWFuaUBjbnIuaXQ=
 Francesco Chiani
Francesco Chiani