- 1Health and Social Sciences Cluster, Singapore Institute of Technology, Singapore, Singapore
- 2Public Health and Sport Sciences, University of Exeter, Exeter, England
Editorial on the Research Topic
Insights into falls efficacy and fear of falling
Introduction
Falls efficacy and fear of falling (FOF) are key psychological constructs influencing mobility, independence, and quality of life among older adults (Soh, 2022; Merchant et al., 2020). Although conceptually related, these constructs are distinct: falls efficacy is a cognitive construct referring to the perceived ability to prevent and manage falls (Soh et al., 2024), while FOF relates to vigilance to threats and resultant emotional reponses (Lee and Tak, 2023). Recognising this nuance is essential for clinicians and researchers, who must be equipped to select appropriate measurement tools aligned with the targeted construct and to tailor interventions accordingly. This Research Topic presents five insightful studies that collectively deepen our understanding of falls efficacy and fear of falling, advancing our perspectives on their conceptualisation, measurement, and implications for clinical practice.
Disentangling falls efficacy and FOF
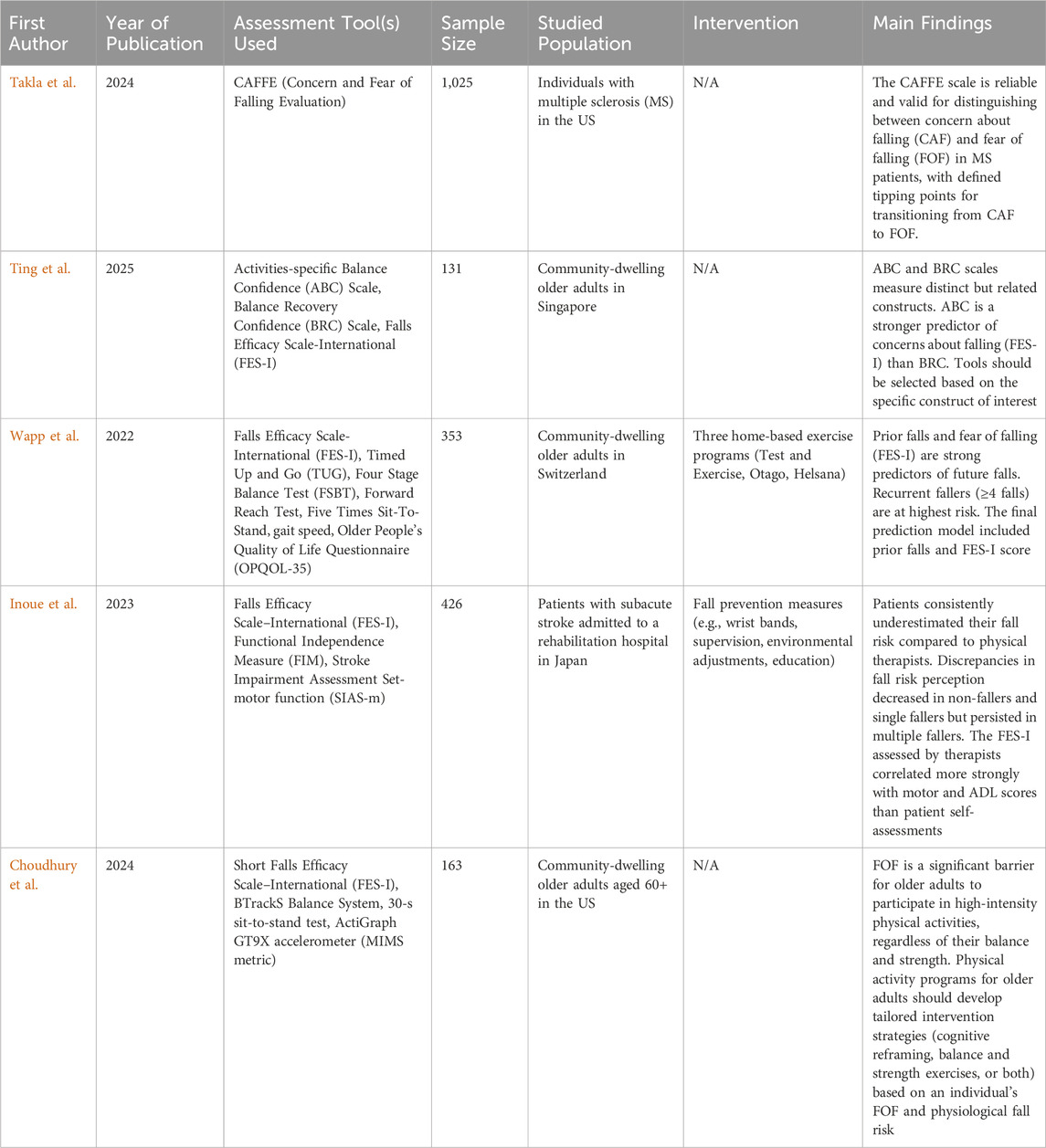
The longstanding conflation of falls efficacy and FOF has posed challenges for clinicians and researchers. Early work by Hadjistavropoulos et al. (Hadjistavropoulos et al., 2011) clarified their distinction through a review of scales such as the Falls Efficacy Scale (FES) (Tinetti et al., 1990), the Activity-specific Balance Confidence (ABC) Scale (Powell and Myers, 1995), and the Survey of Activities and Fear of Falling in the Elderly (SAFE) Scale (Lachman et al., 1998). Falls efficacy was conceptualised as distinct from fear of falling, aligning more closely with balance confidence. Building on this, Ting et al. examined the convergent and predictive validity of the ABC, the Balance Recovery Confidence (BRC), and the Falls Efficacy Scale-International (FES-I) scales among community-dwelling older adults. Their findings revealed moderately strong correlations between ABC and FES-I, with moderate alignment with the BRC. Both ABC and BRC predicted concerns about falling, offering further evidence that these constructs, while related, are not interchangeable. Ting et al.’s work provides a valuable contribution to furthering insights into conceptual boundaries and the need to consider appropriate assessment tools.
Disentangling fear and concerns of falling
Takla et al. offer additional conceptual clarity between FOF and concern about falling (CAF) by introducing the Concern and Fear of Falling Evaluation (CAFFE) Scale. A psychometrically validated instrument that positions CAF and FOF along a continuum adds nuances to how individuals experience fall-related psychological states. The CAFFE provides a promising direction for future research and an assessment tool to evaluate psychologically informed interventions. This aligns with recent commentary by Ellmers and colleagues (Ellmers et al., 2023), who highlighted the importance of differentiating adaptive and maladaptive concerns about falling. While CAF may promote protective behaviours, it can also become maladaptive, manifesting as hypervigilance, activity avoidance, or even denial of risk. This highlights the importance of careful assessment and tailored intervention strategies.
Awareness of potential discrepancies between psychological constructs and other factors
Gaining insight into fall efficacy, FOF, and/or CAF is a useful starting point for crafting person-centred approaches in fall prevention and management practice. Two studies highlighted the potential for discrepancies between psychological constructs and other factors, such as fall risk, warranting greater attention to this aspect. Choudhury et al. explored the interplay between habitual physical activity and the alignment or misalignment of perceived and physiological fall risk in community-dwelling older adults using the Fall Risk Appraisal (FRA) framework. Individuals were categorised into four groups: Low FOF and high physiological fall risk (“Incongruent”); Low FOF and low physiological fall risk (“Rational”); High FOF and high physiological fall risk (“Congruent”); and High FOF and low physiological fall risk (“Irrational”). The study highlighted that FOF is a distinct barrier to activity engagement and underscores the need for tailored interventions.
Inoue et al. examined discrepancies in perceived fall risk between physical therapists and stroke patients in a rehabilitation hospital. The study found that patients consistently underestimated their fall risk, particularly those who went on to experience multiple falls during hospitalisation. Such underestimation advocates the need to enhance tailored patient education and generate greater self-awareness in post-stroke care.
Ultimately, clinicians and researchers are keen to find ways to identify individuals at risk of falling so that prevention strategies can be implemented. Wapp et al. presented a robust fall rate prediction model using prospective fall data from the Swiss CHEF cohort. Through count regression modelling, they identified that the history of falls and FOF were the strongest predictors of future fall rates. Their findings advocate for integrating psychological factors into fall risk assessments to enhance personalised fall prevention strategies. A summary of the five articles is listed in Table 1.
Future directions
Future research needs to incorporate falls efficacy and FOF/CAF into fall prevention and management practice. We anticipate that the levels of these psychological constructs may be different between various clinical populations, including those with neurological, musculoskeletal, and cardiopulmonary conditions, as well as seniors with varying physical abilities residing in hospitals, residential facilities, or those living independently in the community. A robust psychometric evaluation of relevant measurement instruments is necessary to ensure these tools are suitable for the targeted populations. Interventions must be refined based on individual psychological profiles, taking into account contextual influences such as environmental and cultural factors. Longitudinal studies will be essential to understanding how changes in falls efficacy and FOF/CAF could influence long-term mobility, independence, and fall outcomes. A broader integration of psychological metrics into clinical fall risk assessments can help optimise personalised strategies for older adults.
Conclusion
These contributions have deepened our understanding of two critical fall-related psychological dimensions. The topic, “Insights into Falls Efficacy and Fear of Falling,” highlights the importance of nuanced conceptualisation, measurement, and intervention, moving beyond one-size-fits-all approaches toward tailored, person-centred care. With validated tools and emerging theoretical models, the field is well-positioned to address both the cognitive and emotional dimensions of fall risk. We hope this Research Topic catalyses further innovation and collaboration in fall prevention research and practice. We thank all contributing authors, reviewers, and readers for advancing this important field.
Author contributions
SL-HS: Writing – original draft. WY: Writing – review and editing. TX: Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. The text was reviewed for grammar and clarity using generative AI.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ellmers, T. J., Freiberger, E., Hauer, K., Hogan, D. B., McGarrigle, L., Lim, M. L., et al. (2023). Why should clinical practitioners ask about their patients’ concerns about falling? Age Ageing 52 (4), afad057. doi:10.1093/ageing/afad057
Hadjistavropoulos, T., Delbaere, K., and Fitzgerald, T. D. (2011). Reconceptualizing the role of fear of falling and balance confidence in fall risk. J. Aging Health 23 (1), 3–23. doi:10.1177/0898264310378039
Lachman, M. E., Howland, J., Tennstedt, S., Jette, A., Assmann, S., and Peterson, E. W. (1998). Fear of falling and activity restriction: the survey of activities and fear of falling in the elderly (SAFE). J. Gerontology Psychol. Sci. 53B (1), P43–P50. doi:10.1093/geronb/53b.1.p43
Powell, L. E., and Myers, A. M. (1995). The Activities-specific balance confidence (ABC) scale. J. Gerontology Med. Sci. 50A (1), M28–M34. doi:10.1093/gerona/50a.1.m28
Keywords: falls efficacy, fear of falling, concerns about falling, balance confidence, balance recovery confidence, fall prevention and management, measurement instruments, rehabilitation
Citation: Soh SL-H, Young WR and Xu T (2025) Editorial: Insights into falls efficacy and fear of falling. Front. Aging 6:1644435. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2025.1644435
Received: 10 June 2025; Accepted: 29 October 2025;
Published: 13 November 2025.
Edited and reviewed by:
Harshal Mahajan, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Soh, Young and Xu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shawn Leng-Hsien Soh, c2hhd24uc29oQHNpbmdhcG9yZXRlY2guZWR1LnNn
 Shawn Leng-Hsien Soh
Shawn Leng-Hsien Soh William R. Young2
William R. Young2 Tianma Xu
Tianma Xu